Suggested Study Guide
|
|
|
- Imogene Quinn
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Suggested Study Guide BEFORE SEEING THE PERFORMANCE: 1. Ask the class to brainstorm all they know about Russia and the Russian people. 2. Ask students to locate Russia on a map of the world. How does Russia s large size, geographic location, and climate affect the daily lives of the people there? How has Russia s size, location, and climate affected Russian history? 3. Have students read and discuss the attached information about Russia, Russian daily life, politics, and theatre. 4. Discuss capitalism and socialism as economic systems. Discuss democracy and communism as governmental systems. What are the pros and cons of each system? How would your daily life be different if you did not live in a Western democracy? 5. Consider the daily lives of members of The Moscow Boys Choir in today s more democratic Russia, and in the past, in communist Russia. How do you suppose life would have been better or worse for them under communism? What do you think are the advantages and disadvantages of life for the boys and their families under the current system? 6. Review the attached vocabulary list or have the students provide their own definitions of some of the words on the list, and share them with the class. 7. Possible talking points for music classes: a. What kind of a singing voice do you have? What musical part would you sing in a choral performance? If you could sing any song for your class, what would it be? Encourage your students to sing their favorite songs in class! b. How and why would certain foods affect vocal quality? c. What would be the best foods to eat for dinner if you had to sing that evening? Which would be the worst? d. How can the temperature of the things you eat and drink affect your voice? AFTER SEEING THE PERFORMANCE: 1. The Choir performs traditional folk songs, classical music, and contemporary music in their concerts. Why do you suppose they do this? 2. What effect did the different pieces performed by the Choir have on the audience? What was your favorite selection the Choir performed? Why did you prefer that selection to the others that were performed? 3. If someone asked you about the performance you saw, what would you tell them about? Why would you pick that particular part of the show to share with them? 4. How does music convey emotion, even when you don t understand the words? 5. What does the Conductor do in the choir? How does the Conductor s body language and gestures let the choir know what to do during their performance? 6. Consider the gestures and signs we use every day to communicate with others. What meanings or intentions do the gestures we use convey to others? How has the meaning of certain gestures changed over time? *Please note that this is only a suggested guide. As each group of students differs, instructors may wish to focus on only a few of the proposed topics of discussion or create their own study guide more suited to their particular student group. An original study guide may be derived from the attached background on Russia, the bibliography provided, or by using other sources of choice. The Management hopes that the students enjoy this cultural experience that will deepen their understanding of this unique culture!
2 RUSSIA AND HER PEOPLE A Brief Overview Russia was first inhabited by nomadic Slavic tribes, at one time known as the Atavars, during the 7 th century BC. The name Russia is derived from the Atavar word for north. It is thought that the word Russia was initially used by Norwegian and Swedish explorers to refer to the area occupied by the Atavars as the Vikings discovered trade routes. Viking explorers traded extensively with the Atavars, who were without a formal written language during this time, and the visiting Vikings used the term russeeyans to describe their trading partners. Some of the first towns in what is now known as present-day Russia were built by the Goths, who arrived to the region in the 3rd century AD. Since then, Russia has been home to many different people, not all of them peaceful. The Russians have had a written language since the 9 th century AD when the Christian missionaries, Cyril and Methodius, developed a Greek-based alphabet for the Slavic people in order to translate religious texts. In honor of these missionaries, the Russian alphabet is called Cyrillic and it is still in use today, in a modified form. In 882 AD, the Viking leader Oleg founded the Russian state by combining the main trading centers into a kind of province, governed by the city of Kiev. In 988 AD, the ruler of Kiev, Vladimir I, converted to Christianity. It is believed that he chose Greek Orthodoxy over Roman Catholicism because of the heavy trading Kiev did with Constantinople, the capitol of the Byzantine Empire. The faith was adapted to become the Russian Orthodox Church. At this time, and for many centuries to follow, Russia s economy was based on feudalism. This is an economic and social system in which land worked by serfs was held by vassals or boyars in exchange for military and other services to their kings and princes. There was a vast difference between the quality of life for the upper classes and that of the lower classes. Princes and boyars (or landowners) comprised the upper classes. The boyars were granted land rights by powerful kings and princes and these two groups lived in comparative luxury while the common people lived a difficult and impoverished existence. Ivan IV reigned as the first czar of Russia (pronounced tzar ; also spelled tsar) from about 1550 AD. The term czar is an adaptation from the Roman Empire s title for their supreme leader, Caesar. Ivan IV adopted this title and for many centuries thereafter, the leader of Russia was known as the Czar. Ivan was born in 1530, and is better known as Ivan the Terrible for his fierce temper and habit of torturing and executing those who opposed him, even members of his own family, which is why Ivan had no suitable heir to his throne. Therefore, the lines of succession to the Russian throne were fluid for almost two hundred years after his death. Traditionally, when a Czar died, he was succeeded by the person who held the most power in the government. Czar Paul ( ) brought back the law of primogeniture, in which the inheritance of power or kingship is bestowed upon the eldest son. Czar Alexander II ( ) finally freed the serfs from servitude in Since the serfs could not own land individually, land titles would be held by the commune, or mir, to which the former serfs belonged. By setting up land stewardship in this way, Alexander II unknowingly planted the seeds which later developed into modern-day communism.
3 In January 1905, the working classes rebelled and a battle ensued between the Czar s troops and the people. This battle became known historically as Bloody Sunday, and the people demanded the abdication of Czar Nicholas II. In October 1917, the October Revolution occurred, which overthrew the oligarchy in power at the time, and called into question Czar Nicholas divine right to rule Russia. The divine right of kings is a theory of government that holds that a monarch receives the right to rule directly from a god and not from the people over which that monarch rules. After the revolution, The Czar and his family were exiled to a remote province of Russia for a time, and later, executed by the leaders of the rebellion. The leaders of this rebellion became known as the Bolsheviks. The vast majority of the Russian people went on strike against the Czar and the imperial form of government, and the first Socialist State was formed. These events ushered in the rise of communism in Russia under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin. Over the course of the coming years, adjacent countries also embraced communism, some willingly and some by force. These countries joined with Russia to form the Soviet Union, or the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR). Thus, Russia became a 20 th Century super-power and a major force in the development of socialism and the communist form of government. For much of the 20 th Century, the Soviet Union was based upon the principles of socialism, where a country s means of production and distribution is owned by that society rather than by individuals or private companies. Communism is a governmental form of socialism as interpreted by the political leader Vladimir Lenin and the economic theorist Karl Marx, among others. Communism promotes common ownership of property and goods. Under the communist regime in Russia, the government owned and regulated everything pertaining to the daily life of the people. People were not allowed to speak out against the government, vote, or leave the country without permission from the Communist Party leaders. In 1985, Mikhail Gorbachev became the Soviet leader. Gorbachev wanted to move the Soviet Union into the modern world, and institute a more democratic, open style of government. This new way of thinking became known as glasnost, meaning openness and the Russian government adopted the policy of perestroika, meaning reconstruction or rebuilding. In 1991, amid much political strife and social chaos in Russia, Gorbachev resigned as head of the Communist Party and the Soviet Union officially disbanded. In recent years, the Russian government has in many ways successfully made their transition to democracy and capitalism, the economic system currently in use by the majority of the world s governments. Capitalism is an economic system in which the means of production and distribution of most goods and services is privately owned and operated for profit. After over 70 years of one form of government, it continues to take time for Russia s government, and her economy, to evolve into truly democratic and capitalist entities. Since 1991, Russia has made great inroads towards becoming a more democratic society. Although remnants of the communist system still remain in Russia, the country continues to move toward a more capitalist economy, and a more democratic system of government. Visitors traveling to Russia today will find modern cities, replete with stores filled with goods, people in tune with the latest technologies and culture, as well as a bustling commercial sector. As their long and rich history has proven, the Russian people are innovative, resilient, and determined, and their hopes and dreams for a prosperous and bright future will be realized through their hard work and the vision and willingness of their leaders to allow economic and political freedom for all to flourish.
4 A DAY IN THE LIFE OF THE MOSCOW BOYS CHOIR Russian children begin attending primary school at the age of 6 or 7 and stay in school until the age of 16. At age 16, they can choose to enter trade school and attend a technical or professional institute, or, continue their formal education until age 18 where they prepare to take exams for entrance into a University. The Russian school year is the same as the normal school year here in the West, beginning around the first of September, and ending in early June. To become a touring member of the Choir takes a lot of talent and perseverance. The boys are chosen from over 400 students in the Moscow Boys Capella, the school they attend in Moscow. In addition to their vocal training, each boy takes a variety of classes. They study mathematics, geography, science, history, and usually take a foreign language (such as English, German, French, or Chinese). They also learn how to play a musical instrument, such as the piano, the violin, the bassoon, the trumpet, the drums, or other musical instrument, to round out their musical training. The boys begin studying music and voice at about age 5, but are not allowed to perform publicly until they are at least 9 years of age. Boys between the ages of 9 and 14 comprise the bulk of the touring Choir. These young men sing the soprano and alto parts of the songs in the repertoire. When you see THE MOSCOW BOYS CHOIR in performance, you will notice that there are older members in the Choir. These performers are graduates from the Moscow Boys Capella, and they sing the tenor, baritone, and bass parts of the music. When they are not in class, most of the boys live with their parents, or other family members, in Moscow and in the suburbs around Moscow. While at home and on tour, they are always mindful of their voices and, therefore, observe strict bedtimes and dietary restrictions to stay in top vocal form. You will often find the boys sipping warm or room temperature liquids. This is not only because it is Russian custom to drink most beverages warm, but, because it is also relaxing to the throat and aids in the preparation for the evening s performance. They also adhere to a very healthy diet that includes a minimum of dairy products, which can inhibit breathing and adversely affect the vocal chords. This is not to say that they don t enjoy an occasional trip to McDonald s or Pizza Hut, which they do as often as possible! A typical day on tour for them consists of early mornings on the bus to drive to the city where they will perform that evening or the next day. Upon arrival, they go to their hotel and get settled into their rooms. Then, they go to the theatre where they prepare for their performance. After the performance, there may be a reception or brief party where the Choir members meet and greet audience members, as well as chat with students and children their own age. After this, it s back to the hotel, where everyone has a good night s sleep before starting all over again the next day. During their time off, they often organize a quick game of European-style football, which we call soccer. They also play video games, go to the movies, enjoy a swim at their hotel, read a book, or send s and text messages home to their families and friends on their cell phones. In essence, these youngsters are very much like their Western counterparts, only they travel the world sharing their incredible musical gifts!
5 The boys see a great deal of North America while on tour and enjoy meeting people from all walks of life in their travels. When they return home to Moscow, they have a wealth of memories that they eagerly share with their families and friends. Becoming a member of the Moscow Boys Choir means hard work, and being far from home for long periods of time, but it also offers benefits such as travel and fun! Here are only a few of the Choir s many accomplishments over the years: 2012 marked the Choir s Twelfth North American tour. On previous North American tours, they have been invited to perform at Disneyland, Six Flags Over Texas, Dollywood, and the Crystal Cathedral in Southern California. They have recorded many television specials in Russia and in North America, including a high definition TV Special for HDNet Television, and they recorded a performance for National Public Radio s program, Performance Today. They appear regularly on television nationally and internationally performing on such programs as Russia s Steps and Culture TV, CBS Christmas Eve Holiday Special, and Reverend Robert Schuller s Hour of Power. In December of 1999, the boys visited the White House where they sang for and met President Bill Clinton, his wife and our current Secretary of State Hillary Rodham Clinton, and their daughter Chelsea Clinton! The boys have toured extensively in Europe performing for members of the British Royal Family at The Royal Albert Hall in London, and many prestigious venues in their own country such as the Bolshoi Theatre, the Great Hall of the Moscow Conservatory, the Tchaikovsky Concert Hall, the Olympic Hall, and the Kremlin for their Presidents and other dignitaries. They have performed with many famous singers from around the world, including Andrea Bocelli on Red Square in Moscow. They have toured many countries in addition to Russia and the United States including South Korea, Japan, Canada, France, Germany, Italy, Belgium, and Holland. And yet, with all of these incredible accomplishments, members of THE MOSCOW BOYS CHOIR are very much like young people anywhere in the world except they have incredible talents that they share with people everywhere, bringing joy to millions, and the gift of music to the world! The above is provided by tour management to enhance the performance the audience will see by THE MOSCOW BOYS CHOIR. These documents are intended to be used as an introduction to Russian history and daily life. Instructors may wish to use the above information as a foundation for further, more intense study of Russia. Updated June 2013.
6 a capella--to sing without accompaniment. SUGGESTED VOCABULARY LIST accompaniment--a musical term referring to a musical part supporting a vocal part. alto--the lower range of the human voice between tenor and mezzo-soprano. audition--a hearing to try out an actor or singer. baritone--the medium range of a male voice between tenor and bass. bass--the lowest range of a male voice. Bolsheviks--original members of the majority faction that came into power after the Russian Revolution of boyars--landowners controlled by royalty in feudal economies. capitalism--an economic system in which the means of production and distribution are predominantly privately owned and operated for profit. communism--a type of socialism in which the people are ruled by a central government which controls all industry. Cyrillic--the alphabet for the Russian language created by the Christian missionaries Cyril and Methodius in the 9 th century. Divine right of Kings--the right of a sovereign to rule as set forth by the theory of government that holds that a monarch receives the right to rule directly from a god and not from the people. feudalism--economic and social system in medieval Europe, in which land, worked by serfs, was held by vassals in exchange for military and other services to kings and princes. forte--a musical term meaning loud. oligarchy--a government in which power belongs to a few persons. Orthodox Church--the Christian church that is dominant in Eastern Europe, Western Asia, and parts of North Africa. perestroika--russian term for the policy adopted by that government meaning to rebuild or reconstruct. perseverance--to continue a course of action despite difficulty or opposition. primogeniture--a social system in which an inheritance or political power is bestowed upon the first-born son of a ruler or landowner. repertoire--the stock of songs that a singer or troupe is always prepared to perform. socialism--a theory by which a country s means of production and distribution are owned by that society rather than by individuals. soprano--the highest range of the human singing voice, usually in women or boys. tenor--the highest range of the adult male singing voice. czar--(also spelled tsar) the Russian word for ruler or emperor.
7 BIBLIOGRAPHY Sources for this Study Guide This study guide is intended to enhance your student s enjoyment of THE MOSCOW BOYS CHOIR s performance. Information sources are listed below, but there is so much more to know about Russia and her people. For further reading, there are many internet websites with information on Russia, her past and her present. Or, suggest that your students pay a visit to their local public library sometime soon! Agnes, Michael, ed. Webster s New World Dictionary and Thesaurus. Simon & Schuster, Inc., Harvey, Miles. The Fall of the Soviet Union. Children s Press, Inc., Resnick, Abraham. Russia, A History to Regensteiner Publishing Enterprises, Inc., Sallnow, John and Tatyana Saiko. Russia. Steck-Vaughn Company, Website Reference: Updated June 2013.
Bell Activity. What does it feel like to be in a group where one person insists on always getting his or her own way? How might other members respond?
 History of Russia Objectives Know important events and people from the history of tsarist Russia. Know the reason for the rise and fall of the Soviet Union. Explain the cause and effects of the Russian
History of Russia Objectives Know important events and people from the history of tsarist Russia. Know the reason for the rise and fall of the Soviet Union. Explain the cause and effects of the Russian
Readiness Activity. (An activity to be done before viewing the video)
 KNOWLEDGE UNLIMITED NEWS Matters Russia in Ruins: Can the Nation Survive? Vol. 2 No. 4 About NEWSMatters Russia in Ruins: Can the Nation Survive? is one in a series of NEWSMatters programs. Each 15-20
KNOWLEDGE UNLIMITED NEWS Matters Russia in Ruins: Can the Nation Survive? Vol. 2 No. 4 About NEWSMatters Russia in Ruins: Can the Nation Survive? is one in a series of NEWSMatters programs. Each 15-20
3 Themes in Russian History
 History of Russia 3 Themes in Russian History 1. Expansion east and west From 800 AD to 1900s the land Russia controlled increased greatly because of their powerful leaders 2. Harsh treatment of common
History of Russia 3 Themes in Russian History 1. Expansion east and west From 800 AD to 1900s the land Russia controlled increased greatly because of their powerful leaders 2. Harsh treatment of common
Russian Revolution Workbook
 Russian Revolution Workbook Name: Per. # Unit 2 Russian Revolution Test Date: Unit Overview Score Workbook Score Warm Up Score 1 Revolutions Unit Overview Key Terms 1. Marxism 2. Communism 3. Bloody Sunday
Russian Revolution Workbook Name: Per. # Unit 2 Russian Revolution Test Date: Unit Overview Score Workbook Score Warm Up Score 1 Revolutions Unit Overview Key Terms 1. Marxism 2. Communism 3. Bloody Sunday
RUSSIA S LEADERS. Click map to view Russia overview video.
 RUSSIA S LEADERS Click map to view Russia overview video. CZAR NICHOLAS 1894-1917 Czar Nicholas Romanov II the last of the czars. Made attempts to modernize, not successful Russia defeated in Russo-Japanese
RUSSIA S LEADERS Click map to view Russia overview video. CZAR NICHOLAS 1894-1917 Czar Nicholas Romanov II the last of the czars. Made attempts to modernize, not successful Russia defeated in Russo-Japanese
Unit 7: The Rise of Totalitarianism
 Unit 7: The Rise of Totalitarianism After WWI, many people in nations impacted by the Great War were willing to accept rule by dictators who controlled all aspects of society. In the 1920s and 1930s Russia,
Unit 7: The Rise of Totalitarianism After WWI, many people in nations impacted by the Great War were willing to accept rule by dictators who controlled all aspects of society. In the 1920s and 1930s Russia,
Revolution and Nationalism
 Revolution and Nationalism 1900-1939 Revolutions in Russia Section 1 Long-term social unrest in Russia exploded in revolution, and ushered in the first Communist government. Czars Resist Change Romanov
Revolution and Nationalism 1900-1939 Revolutions in Russia Section 1 Long-term social unrest in Russia exploded in revolution, and ushered in the first Communist government. Czars Resist Change Romanov
(3) parliamentary democracy (2) ethnic rivalries
 1) In the Soviet Union, Joseph Stalin governed by means of secret police, censorship, and purges. This type of government is called (1) democracy (2) totalitarian 2) The Ancient Athenians are credited
1) In the Soviet Union, Joseph Stalin governed by means of secret police, censorship, and purges. This type of government is called (1) democracy (2) totalitarian 2) The Ancient Athenians are credited
Russian History. Lecture #1 Ancient History The Romanov s
 Russian History Lecture #1 Ancient History The Romanov s Outline Russia Lecture #1 Ancient Russia Settlement of Russia Yaroslav the Wise Mongol Invasion of Russia Retaking Russia Ivan the Great Ivan the
Russian History Lecture #1 Ancient History The Romanov s Outline Russia Lecture #1 Ancient Russia Settlement of Russia Yaroslav the Wise Mongol Invasion of Russia Retaking Russia Ivan the Great Ivan the
the Russian Revolution in 1917? Warm Up Question: calling themselves communists gained
 Essential Question: How did Vladimir Lenin & the Bolsheviks transform Russia during the Russian Revolution in 1917? Warm Up Question: Based on what you know about communism, why do you think people calling
Essential Question: How did Vladimir Lenin & the Bolsheviks transform Russia during the Russian Revolution in 1917? Warm Up Question: Based on what you know about communism, why do you think people calling
History Revolutions: Russian Teach Yourself Series Topic 3: Factors that contributed to the revolution
 History Revolutions: Russian Teach Yourself Series Topic 3: Factors that contributed to the revolution A: Level 14, 474 Flinders Street Melbourne VIC 3000 T: 1300 134 518 W: tssm.com.au E: info@tssm.com.au
History Revolutions: Russian Teach Yourself Series Topic 3: Factors that contributed to the revolution A: Level 14, 474 Flinders Street Melbourne VIC 3000 T: 1300 134 518 W: tssm.com.au E: info@tssm.com.au
Date Period. Section 2 pg , Russia Under the Czars and The Beginning of Unrest : Group A
 Name Date Period With a partner, brainstorm three questions you could ask the class that would help them understand the important details of the image, what is happening, and its connection to the Russian
Name Date Period With a partner, brainstorm three questions you could ask the class that would help them understand the important details of the image, what is happening, and its connection to the Russian
Cruel, oppressive rule of the Czars for almost 100 years Social unrest for decades Ruthless treatment of peasants Small revolts amongst students and
 Cruel, oppressive rule of the Czars for almost 100 years Social unrest for decades Ruthless treatment of peasants Small revolts amongst students and soldiers that resulted in secret revolutionary groups
Cruel, oppressive rule of the Czars for almost 100 years Social unrest for decades Ruthless treatment of peasants Small revolts amongst students and soldiers that resulted in secret revolutionary groups
History Revolutions: Russia Teach Yourself Series Topic 3: Trigger factors that contributed to the revolution
 History Revolutions: Russia Teach Yourself Series Topic 3: Trigger factors that contributed to the revolution A: Level 14, 474 Flinders Street Melbourne VIC 3000 T: 1300 134 518 W: tssm.com.au E: info@tssm.com.au
History Revolutions: Russia Teach Yourself Series Topic 3: Trigger factors that contributed to the revolution A: Level 14, 474 Flinders Street Melbourne VIC 3000 T: 1300 134 518 W: tssm.com.au E: info@tssm.com.au
All societies, large and small, develop some form of government.
 The Origins and Evolution of Government (HA) All societies, large and small, develop some form of government. During prehistoric times, when small bands of hunter-gatherers wandered Earth in search of
The Origins and Evolution of Government (HA) All societies, large and small, develop some form of government. During prehistoric times, when small bands of hunter-gatherers wandered Earth in search of
Eastern Absolutism Serfdom In the west peasants gained rights as a labor shortage swept eastern Europe workers became a necessity In eastern Europe
 Eastern Absolutism Serfdom In the west peasants gained rights as a labor shortage swept eastern Europe workers became a necessity In eastern Europe during the seventeenth century the rights of the peasants
Eastern Absolutism Serfdom In the west peasants gained rights as a labor shortage swept eastern Europe workers became a necessity In eastern Europe during the seventeenth century the rights of the peasants
Absolutism Activity 1
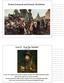
 Absolutism Activity 1 Who is in the painting? What do you think is going on in the painting? Take note of the background. What is the message of the painting? For example, why did the author paint this?
Absolutism Activity 1 Who is in the painting? What do you think is going on in the painting? Take note of the background. What is the message of the painting? For example, why did the author paint this?
Chapter 7: Rejecting Liberalism. Understandings of Communism
 Chapter 7: Rejecting Liberalism Understandings of Communism * in communist ideology, the collective is more important than the individual. Communists also believe that the well-being of individuals is
Chapter 7: Rejecting Liberalism Understandings of Communism * in communist ideology, the collective is more important than the individual. Communists also believe that the well-being of individuals is
INTRODUCTION TO ANIMAL FARM. Buzan, Ballard, Novak, McGlothlin, Millhouse
 INTRODUCTION TO ANIMAL FARM Buzan, Ballard, Novak, McGlothlin, Millhouse Where We ve Been Where We ve Been GOVERNMENT, is the idea that a system can regulate, organize, rule, or control a community or
INTRODUCTION TO ANIMAL FARM Buzan, Ballard, Novak, McGlothlin, Millhouse Where We ve Been Where We ve Been GOVERNMENT, is the idea that a system can regulate, organize, rule, or control a community or
Chapter Russia and Central Europe
 Chapter 17-18 Russia and Central Europe Natural Environments Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus cover 12% of the world s land area. Russia is the world s largest country. The Siberian rivers (Ob, Yenisey, and
Chapter 17-18 Russia and Central Europe Natural Environments Russia, Ukraine, and Belarus cover 12% of the world s land area. Russia is the world s largest country. The Siberian rivers (Ob, Yenisey, and
Eastern European and Russian Absolutism. Ivan IV Ivan the Terrible ( )
 Eastern European and Russian Absolutism Ivan IV Ivan the Terrible (1547-1584) became Tsar at age of 3 and watched rival groups of nobles who sought to control the country when he took charge, he saw treason
Eastern European and Russian Absolutism Ivan IV Ivan the Terrible (1547-1584) became Tsar at age of 3 and watched rival groups of nobles who sought to control the country when he took charge, he saw treason
Standard: SS6H3 Explain conflict and change in Europe.
 Standard: SS6H3 Explain conflict and change in Europe. Element: a. Describe the aftermath of World War I: the rise of communism, the Treaty of Versailles, the rise of Nazism, and worldwide depression.
Standard: SS6H3 Explain conflict and change in Europe. Element: a. Describe the aftermath of World War I: the rise of communism, the Treaty of Versailles, the rise of Nazism, and worldwide depression.
Revolution and Nationalism
 Revolution and Nationalism 1900-1939 Revolutions in Russia Section 1 Long- term social unrest in Russia exploded in revolution, and ushered in the first Communist government. Czars Resist Change Romanov
Revolution and Nationalism 1900-1939 Revolutions in Russia Section 1 Long- term social unrest in Russia exploded in revolution, and ushered in the first Communist government. Czars Resist Change Romanov
Unit 2 Changes and Challenges: Part 1 - The Russian Revolution
 Unit 2 Changes and Challenges: Part 1 - The Russian Revolution Revolution=Radical Change At the beginning of the 20 th Century, Russia was ripe for change Over 95% of the population was rural/ peasantry
Unit 2 Changes and Challenges: Part 1 - The Russian Revolution Revolution=Radical Change At the beginning of the 20 th Century, Russia was ripe for change Over 95% of the population was rural/ peasantry
The Russian Revolution. Adapted from slides by Scott Masters Crestwood College
 The Russian Revolution Adapted from slides by Scott Masters Crestwood College Pre-Revolutionary Russia Only true autocracy left in Europe No type of representative political institutions Nicholas II became
The Russian Revolution Adapted from slides by Scott Masters Crestwood College Pre-Revolutionary Russia Only true autocracy left in Europe No type of representative political institutions Nicholas II became
European History
 European History 101 http://www.ling.gu.se/projekt/sprakfrageladan/images/europe_map.gif Ancient Greece 800BC ~ 200BC Birthplace of Democracy Known for system of government city-states Spread Greek culture
European History 101 http://www.ling.gu.se/projekt/sprakfrageladan/images/europe_map.gif Ancient Greece 800BC ~ 200BC Birthplace of Democracy Known for system of government city-states Spread Greek culture
I. The Russian Empire A. The Russian Empire traces its roots back to the principality of Muscovy, which began to expand in the 1400s. B.
 Unit 8 SG 2 Name Date I. The Russian Empire A. The Russian Empire traces its roots back to the principality of Muscovy, which began to expand in the 1400s. B. Ivan III (the Great) married Zoe Palaeologus,
Unit 8 SG 2 Name Date I. The Russian Empire A. The Russian Empire traces its roots back to the principality of Muscovy, which began to expand in the 1400s. B. Ivan III (the Great) married Zoe Palaeologus,
Factories double from Trans-Siberian Railway finally finished in More and more people work in factories
 World history Factories double from 1863-1900 Trans-Siberian Railway finally finished in 1916 More and more people work in factories o Terrible conditions, child labor, very low pay o Unions were illegal
World history Factories double from 1863-1900 Trans-Siberian Railway finally finished in 1916 More and more people work in factories o Terrible conditions, child labor, very low pay o Unions were illegal
World War I Revolution Totalitarianism
 World War I Revolution Totalitarianism Information Who The Triple Alliance France Britain - Russia The Triple Entente Germany Italy Austria Hungary Mexico Africa Middle East India China Information What
World War I Revolution Totalitarianism Information Who The Triple Alliance France Britain - Russia The Triple Entente Germany Italy Austria Hungary Mexico Africa Middle East India China Information What
Kowtowing to the Chinese Emperor
 Kowtowing to the Chinese Emperor Critical Challenge Critical Question What advice would you give to Britain s ambassador to China in 1816 on the matter of the British trade delegation kowtowing to the
Kowtowing to the Chinese Emperor Critical Challenge Critical Question What advice would you give to Britain s ambassador to China in 1816 on the matter of the British trade delegation kowtowing to the
Nations in Upheaval: Europe
 Nations in Upheaval: Europe 1850-1914 1914 The Rise of the Nation-State Louis Napoleon Bonaparte Modern Germany: The Role of Key Individuals Czarist Russia: Reform and Repression Britain 1867-1894 1894
Nations in Upheaval: Europe 1850-1914 1914 The Rise of the Nation-State Louis Napoleon Bonaparte Modern Germany: The Role of Key Individuals Czarist Russia: Reform and Repression Britain 1867-1894 1894
History Revolutions: Russian Teach Yourself Series Topic 1: Chronology of key events
 History Revolutions: Russian Teach Yourself Series Topic 1: Chronology of key events A: Level 14, 474 Flinders Street Melbourne VIC 3000 T: 1300 134 518 W: tssm.com.au E: info@tssm.com.au TSSM 2015 Page
History Revolutions: Russian Teach Yourself Series Topic 1: Chronology of key events A: Level 14, 474 Flinders Street Melbourne VIC 3000 T: 1300 134 518 W: tssm.com.au E: info@tssm.com.au TSSM 2015 Page
Aspects of the United Kingdom's Government Parliamentary
 Name Class Period UNIT 6 MAIN IDEA PACKET: Comparative Political & Economic Systems AMERICAN GOVERNMENT CHAPTERS: 22 & 23 CHAPTER 22 COMPARATIVE POLITICAL SYSTEMS Chapter 22 Section 1: Great Britain In
Name Class Period UNIT 6 MAIN IDEA PACKET: Comparative Political & Economic Systems AMERICAN GOVERNMENT CHAPTERS: 22 & 23 CHAPTER 22 COMPARATIVE POLITICAL SYSTEMS Chapter 22 Section 1: Great Britain In
The Russian Revolution. Peace, Bread, Land, Almost
 Name: Period: 1 2 5 6 8 The Russian Revolution VI Peace, Bread, Land, Almost Purpose: Could the October Revolution have succeeded without the pragmatism of Lenin and ideology of Trotsky? Part One: Russian
Name: Period: 1 2 5 6 8 The Russian Revolution VI Peace, Bread, Land, Almost Purpose: Could the October Revolution have succeeded without the pragmatism of Lenin and ideology of Trotsky? Part One: Russian
Who wants to be a. Expert on the Cold War?!
 Who wants to be a Expert on the Cold War?! Which statement describes the economic history of Japan since World War II? A: Japan has withdrawn from the world economic community and has practices economic
Who wants to be a Expert on the Cold War?! Which statement describes the economic history of Japan since World War II? A: Japan has withdrawn from the world economic community and has practices economic
General Overview of Communism & the Russian Revolution. AP World History Chapter 27b The Rise and Fall of World Communism (1917 Present)
 General Overview of Communism & the Russian Revolution AP World History Chapter 27b The Rise and Fall of World Communism (1917 Present) Communism: A General Overview Socialism = the belief that the economy
General Overview of Communism & the Russian Revolution AP World History Chapter 27b The Rise and Fall of World Communism (1917 Present) Communism: A General Overview Socialism = the belief that the economy
Georgia High School Graduation Test Tutorial. World History from World War I to World War II
 Georgia High School Graduation Test Tutorial World History from World War I to World War II Causes of World War I 1. Balkan Nationalism Causes of World War I 2. Entangled Alliances Causes of World War
Georgia High School Graduation Test Tutorial World History from World War I to World War II Causes of World War I 1. Balkan Nationalism Causes of World War I 2. Entangled Alliances Causes of World War
World Civilizations. The Global Experience. Chapter. The Rise of Russia. AP Seventh Edition
 World Civilizations The Global Experience AP Seventh Edition Chapter 21 The Rise of Russia Figure 21.1 Early Russian tsar Ivan V, 1682 1696. Ivan was actually sickly and ineffective and soon gave way to
World Civilizations The Global Experience AP Seventh Edition Chapter 21 The Rise of Russia Figure 21.1 Early Russian tsar Ivan V, 1682 1696. Ivan was actually sickly and ineffective and soon gave way to
PETERS TOWNSHIP HIGH SCHOOL
 PETERS TOWNSHIP HIGH SCHOOL COURSE SYLLABUS: ACADEMIC HISTORY OF WESTERN CIVILIZATION Course Overview and Essential Skills The purpose of this overview course is to provide students with an understanding
PETERS TOWNSHIP HIGH SCHOOL COURSE SYLLABUS: ACADEMIC HISTORY OF WESTERN CIVILIZATION Course Overview and Essential Skills The purpose of this overview course is to provide students with an understanding
UNIT 10 The Russian Revolution (1917)
 UNIT 10 (1917) o o Background o Tsar Nicholas II o The beginning of the revolution o Lenin's succession o Trotsky o Stalin o The terror and the purges Background In 1900 Russia was a poor country compared
UNIT 10 (1917) o o Background o Tsar Nicholas II o The beginning of the revolution o Lenin's succession o Trotsky o Stalin o The terror and the purges Background In 1900 Russia was a poor country compared
Russia During the Early- Modern Period
 Russia During the Early- Modern Period Review of Russian History Kievan Rus Dominated by Kiev, but various other principalities throughout Ties with Byzantine Empire Adopted Orthodox Christianity in 900
Russia During the Early- Modern Period Review of Russian History Kievan Rus Dominated by Kiev, but various other principalities throughout Ties with Byzantine Empire Adopted Orthodox Christianity in 900
Ancient World Timelines World History Through the Renaissance Middle Ages Timelines Before the Renaissance Empires in Africa such as Ghana, Mali, and
 Ancient World Timelines World History Through the Renaissance Middle Ages Timelines Empires in Africa such as Ghana, Mali, and Songhai came to power. Muhammad was told by the angel Gabriel to be a prophet
Ancient World Timelines World History Through the Renaissance Middle Ages Timelines Empires in Africa such as Ghana, Mali, and Songhai came to power. Muhammad was told by the angel Gabriel to be a prophet
**REVIEW: CHAPTER 10 NATIONALISM**
 10-4: Not breaking Russia apart but conflict that spills over Main Idea **REVIEW: CHAPTER 10 NATIONALISM** In the 1800s, Italian states rebelled against Austria and unified as the Kingdom of Italy. Learning
10-4: Not breaking Russia apart but conflict that spills over Main Idea **REVIEW: CHAPTER 10 NATIONALISM** In the 1800s, Italian states rebelled against Austria and unified as the Kingdom of Italy. Learning
1. This was Russia's first elected assembly
 Russian Revolution Exam Choose the letter of the term or name that matches the description. soviet b. Nicholas II Bloody Sunday b. Duma Bolsheviks Ruso-Japanese War pogrom Mensheviks e. Trans-Siberian
Russian Revolution Exam Choose the letter of the term or name that matches the description. soviet b. Nicholas II Bloody Sunday b. Duma Bolsheviks Ruso-Japanese War pogrom Mensheviks e. Trans-Siberian
Russia. Chapter 20. Chapter 20, Section
 Chapter 20, Section World Geography Chapter 20 Russia Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 20, Section World Geography
Chapter 20, Section World Geography Chapter 20 Russia Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 20, Section World Geography
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 27 Reading Guide. Russia and Japan: Industrialization Outside the West p
 Name: Date: Period: Chapter 27 Reading Guide Russia and Japan: Industrialization Outside the West p.626-644 1. Using p. 630 & 635, locate the following places on the map. a. Japan b. Manchuria c. Russian
Name: Date: Period: Chapter 27 Reading Guide Russia and Japan: Industrialization Outside the West p.626-644 1. Using p. 630 & 635, locate the following places on the map. a. Japan b. Manchuria c. Russian
In Your Notebook-- What do you remember about the causes of the Russian Revolution? What were the revolutionaries trying to achieve?
 In Your Notebook-- What do you remember about the causes of the Russian Revolution? What were the revolutionaries trying to achieve? What were some of the major events of the revolution itself? What results
In Your Notebook-- What do you remember about the causes of the Russian Revolution? What were the revolutionaries trying to achieve? What were some of the major events of the revolution itself? What results
Magruder s American Government
 Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 23 Comparative Economic Systems 200 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 23 Comparative Economic Systems SECTION Capitalism SECTION 2 Socialism
Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 23 Comparative Economic Systems 200 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 23 Comparative Economic Systems SECTION Capitalism SECTION 2 Socialism
Starter Activity Peace, Land, and Bread
 Starter Activity: Vladimir Lenin led a Russian Revolution promising the people Peace, Land, and Bread. Based on this slogan, what problems was Russia facing that would lead to a revolution? (Why were peace,
Starter Activity: Vladimir Lenin led a Russian Revolution promising the people Peace, Land, and Bread. Based on this slogan, what problems was Russia facing that would lead to a revolution? (Why were peace,
The Rise of Russia. AP World History
 The Rise of Russia AP World History A Newly Independent Russia 1380: Battle of Kulikova (alliance of Russian feudal princes) led to Golden Horde defeat Mongol attempts to subjugate Russians continued for
The Rise of Russia AP World History A Newly Independent Russia 1380: Battle of Kulikova (alliance of Russian feudal princes) led to Golden Horde defeat Mongol attempts to subjugate Russians continued for
(Trotsky, Tolstoy, Gorky) 15. A group of thinkers in Russia called... stood for absolute individualism.
 6 RUSSIAN REVOLUTION Q.1. (A) Complete the following statements by choosing appropriate alternatives from those given in the brackets : *1. Karl Marx was a... Philosopher. (Russian, German, Polish) *2.
6 RUSSIAN REVOLUTION Q.1. (A) Complete the following statements by choosing appropriate alternatives from those given in the brackets : *1. Karl Marx was a... Philosopher. (Russian, German, Polish) *2.
The Russian Revolution. 10/5/2018 Bennifield
 The Russian Revolution Bennifield 1 Bennifield 2 STANDARD The student will explain conflict and change in Europe to the 21 st century. Bennifield 3 Essential Question How did the Russian Revolution contribute
The Russian Revolution Bennifield 1 Bennifield 2 STANDARD The student will explain conflict and change in Europe to the 21 st century. Bennifield 3 Essential Question How did the Russian Revolution contribute
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Chapter 16, Section 3 For use with textbook pages 514 519 THE RUSSIAN REVOLUTION KEY TERMS soviets councils in Russia composed of representatives from the workers and soldiers (page 516) war communism
Chapter 16, Section 3 For use with textbook pages 514 519 THE RUSSIAN REVOLUTION KEY TERMS soviets councils in Russia composed of representatives from the workers and soldiers (page 516) war communism
World History Alpha Lenze Final Exam Study Guide. Answer the questions as best you can include Who, What, When, Where, Why, How and So What.
 World History Alpha Lenze 2013-14 Final Exam Study Guide Answer the questions as best you can include Who, What, When, Where, Why, How and So What. 1. What was a result of the Treaty of Verdun in 843?
World History Alpha Lenze 2013-14 Final Exam Study Guide Answer the questions as best you can include Who, What, When, Where, Why, How and So What. 1. What was a result of the Treaty of Verdun in 843?
UNIT 6 THE RUSSIAN REVOLUTION
 UNIT 6 THE RUSSIAN REVOLUTION I; LONG-TERM CAUSES A. AUTOCRACY OF THE CZAR 1. Censorship 2. Religious and ethnic intolerance 3. Political oppression I; LONG-TERM CAUSES B. ECONOMIC PROBLEMS 1. Russia began
UNIT 6 THE RUSSIAN REVOLUTION I; LONG-TERM CAUSES A. AUTOCRACY OF THE CZAR 1. Censorship 2. Religious and ethnic intolerance 3. Political oppression I; LONG-TERM CAUSES B. ECONOMIC PROBLEMS 1. Russia began
Unit 4: Age of isms Rise of European Dominance
 Unit 4: 1450-1750 Age of isms Rise of European Dominance Renaissance the word renaissance means rebirth this is Europe s rebirth of culture and thought begins ~ 1400 in Italy, and spreads northward resurgence
Unit 4: 1450-1750 Age of isms Rise of European Dominance Renaissance the word renaissance means rebirth this is Europe s rebirth of culture and thought begins ~ 1400 in Italy, and spreads northward resurgence
Subverting the Orthodoxy
 Subverting the Orthodoxy Rousseau, Smith and Marx Chau Kwan Yat Jean-Jacques Rousseau, Adam Smith, and Karl Marx each wrote at a different time, yet their works share a common feature: they display a certain
Subverting the Orthodoxy Rousseau, Smith and Marx Chau Kwan Yat Jean-Jacques Rousseau, Adam Smith, and Karl Marx each wrote at a different time, yet their works share a common feature: they display a certain
Name: Global 10 Section. Global Regents Pack #10. Turning Points
 Name: Global 10 Section Global Regents Pack #10 Turning Points Theme : Turning Points Most events in history are turning points! Ancient Greece Athens City-States (because of geography) Democracy Theatre
Name: Global 10 Section Global Regents Pack #10 Turning Points Theme : Turning Points Most events in history are turning points! Ancient Greece Athens City-States (because of geography) Democracy Theatre
Final Review. Global Studies
 Final Review Global Studies Major Belief Systems Judaism Confucianism Christianity Buddhism Hinduism Islam Middle East China Middle East India, China India Middle East Monotheism, 10 Commandments, Torah,
Final Review Global Studies Major Belief Systems Judaism Confucianism Christianity Buddhism Hinduism Islam Middle East China Middle East India, China India Middle East Monotheism, 10 Commandments, Torah,
Karl Marx. Louis Blanc
 Karl Marx Louis Blanc Cooperatives! First cooperative 1844 in Rochdale, England " Formed to fight high food costs " 30 English weavers opened a grocery store with $140 " Bought goods at wholesale " Members
Karl Marx Louis Blanc Cooperatives! First cooperative 1844 in Rochdale, England " Formed to fight high food costs " 30 English weavers opened a grocery store with $140 " Bought goods at wholesale " Members
A Level History. Independent Summer Learning Introductory Assignment
 A Level History Independent Summer Learning Introductory Assignment Introduction During the two year History A Level course you will study two units and complete 1 piece of coursework. The Units will focus
A Level History Independent Summer Learning Introductory Assignment Introduction During the two year History A Level course you will study two units and complete 1 piece of coursework. The Units will focus
History route 2 Higher level and standard level Paper 1 Communism in crisis
 History route 2 Higher level and standard level Paper 1 Communism in crisis 1976 1989 Friday 13 November 2015 (morning) 1 hour Instructions to candidates Do not open this examination paper until instructed
History route 2 Higher level and standard level Paper 1 Communism in crisis 1976 1989 Friday 13 November 2015 (morning) 1 hour Instructions to candidates Do not open this examination paper until instructed
SSWH14: ANALYZE THE AGE OF REVOLUTIONS ELEMENT A: EXAMINE ABSOLUTISM THROUGH A COMPARISON OF THE REIGNS OF LOUIS XIV & TSAR PETER THE GREAT.
 SSWH14: ANALYZE THE AGE OF REVOLUTIONS ELEMENT A: EXAMINE ABSOLUTISM THROUGH A COMPARISON OF THE REIGNS OF LOUIS XIV & TSAR PETER THE GREAT. LOUIS XIV v Medieval European feudalism had placed the majority
SSWH14: ANALYZE THE AGE OF REVOLUTIONS ELEMENT A: EXAMINE ABSOLUTISM THROUGH A COMPARISON OF THE REIGNS OF LOUIS XIV & TSAR PETER THE GREAT. LOUIS XIV v Medieval European feudalism had placed the majority
The Russian Revolution(s)
 The Russian Revolution(s) -1905-1921- Pre-Revolutionary Russia Only true autocracy left in Europe No type of representative political institutions, but did have instruments of oppression (secret police)
The Russian Revolution(s) -1905-1921- Pre-Revolutionary Russia Only true autocracy left in Europe No type of representative political institutions, but did have instruments of oppression (secret police)
How did the basic structure of society in eastern Europe become different from that of western Europe in the early modern period? How and why did the
 How did the basic structure of society in eastern Europe become different from that of western Europe in the early modern period? How and why did the rulers of Austria, Prussia, and Russia manage to build
How did the basic structure of society in eastern Europe become different from that of western Europe in the early modern period? How and why did the rulers of Austria, Prussia, and Russia manage to build
Teachers Name: Nathan Clayton Course: World History Academic Year/Semester: Fall 2012-Spring 2013
 Amory High School Curriculum Map Teachers Name: Nathan Clayton Course: World History Academic Year/Semester: Fall 2012-Spring 2013 Essential Questions First Nine Weeks Second Nine Weeks Third Nine Weeks
Amory High School Curriculum Map Teachers Name: Nathan Clayton Course: World History Academic Year/Semester: Fall 2012-Spring 2013 Essential Questions First Nine Weeks Second Nine Weeks Third Nine Weeks
2008 World History I History and Social Science Standards of Learning STANDARD
 Provider York County School Division Course Title World History I Last Updated 2010-11 Course Syllabus URL http://yorkcountyschools.org/virtuallearning/coursecatalog.aspx Correlation: Content must address
Provider York County School Division Course Title World History I Last Updated 2010-11 Course Syllabus URL http://yorkcountyschools.org/virtuallearning/coursecatalog.aspx Correlation: Content must address
Write 3 words you think of when you hear Cold War? THE COLD WAR ( )
 THE Write 3 words you think of when you hear Cold War? COLD WAR (1948-1989) ORIGINS of the Cold War: (1945-1948) Tension or rivalry but NO FIGHTING between the United States and the Soviet Union This rivalry
THE Write 3 words you think of when you hear Cold War? COLD WAR (1948-1989) ORIGINS of the Cold War: (1945-1948) Tension or rivalry but NO FIGHTING between the United States and the Soviet Union This rivalry
THE RUSSIAN REVOLUTION (1917)
 THE RUSSIAN REVOLUTION (1917) 1. Introduction 2. Background to the revolution 3. The rise of Lenin and the Bolsheviks 4. Civil War 5. Triumph of the communists 6. Lenin s succession 7. The terror and the
THE RUSSIAN REVOLUTION (1917) 1. Introduction 2. Background to the revolution 3. The rise of Lenin and the Bolsheviks 4. Civil War 5. Triumph of the communists 6. Lenin s succession 7. The terror and the
(What would you buy if you won the lottery?) What will move Kings and Queens from Monarchy to Absolute Monarchy?
 Predictions Predict how the Empires in the Americas, Africa and Asia, built by Europeans rulers during the Age of Exploration, will affect Europe s monarchs. Predict what they might do with their increased
Predictions Predict how the Empires in the Americas, Africa and Asia, built by Europeans rulers during the Age of Exploration, will affect Europe s monarchs. Predict what they might do with their increased
Chapter 18 Reading Guide: The Rise of Russia
 CHAPTER SUMMARY The rise of the Russian Empire, unlike Western colonial empires, although altering power balances through Eurasia involved only limited commercial exchange. After freeing themselves from
CHAPTER SUMMARY The rise of the Russian Empire, unlike Western colonial empires, although altering power balances through Eurasia involved only limited commercial exchange. After freeing themselves from
STANDARDS. a. Explain how rising communism and socialism in the United States led to the Red Scare and immigrant restriction.
 AFTER WORLD WAR I STANDARDS SSUSH15 The student will analyze the origins and impact of U.S. involvement in World War I. d. Describe passage of the Eighteenth Amendment, establishing Prohibition, and the
AFTER WORLD WAR I STANDARDS SSUSH15 The student will analyze the origins and impact of U.S. involvement in World War I. d. Describe passage of the Eighteenth Amendment, establishing Prohibition, and the
Chapter 4: The Fall of Tsarism. Revolution
 Chapter 4: The Fall of Tsarism Revolution What is a Revolution? A complete change in the way things are done (Agricultural Revolution, Industrial Revolution, Russian Revolution) Sometimes peaceful Sometimes
Chapter 4: The Fall of Tsarism Revolution What is a Revolution? A complete change in the way things are done (Agricultural Revolution, Industrial Revolution, Russian Revolution) Sometimes peaceful Sometimes
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Age of Napoleon
 The Age of Napoleon Objectives Understand Napoleon s rise to power and why the French strongly supported him. Explain how Napoleon built an empire and what challenges the empire faced. Analyze the events
The Age of Napoleon Objectives Understand Napoleon s rise to power and why the French strongly supported him. Explain how Napoleon built an empire and what challenges the empire faced. Analyze the events
Magruder s American Government
 Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 22 Comparative Political Systems 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 22 Comparative Political Systems SECTION 1 Great Britain SECTION
Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 22 Comparative Political Systems 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 22 Comparative Political Systems SECTION 1 Great Britain SECTION
Magruder s American Government
 Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 22 Comparative Political Systems 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 22 Comparative Political Systems SECTION 1 Great Britain SECTION
Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 22 Comparative Political Systems 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 22 Comparative Political Systems SECTION 1 Great Britain SECTION
Origins of the Cold War. A Chilly Power Point Presentation Brought to You by Ms. Shen
 Origins of the Cold War A Chilly Power Point Presentation Brought to You by Ms. Shen What was the Cold War? The Cold War was a 40+ year long conflict between the U.S. and the Soviet Union that started
Origins of the Cold War A Chilly Power Point Presentation Brought to You by Ms. Shen What was the Cold War? The Cold War was a 40+ year long conflict between the U.S. and the Soviet Union that started
CHAPTER EIGHTEEN The Rise of Russia
 CHAPTER EIGHTEEN The Rise of Russia World Civilizations, The Global Experience AP* Edition, 5th Edition Stearns/Adas/Schwartz/Gilbert *AP and Advanced Placement are registered trademarks of The College
CHAPTER EIGHTEEN The Rise of Russia World Civilizations, The Global Experience AP* Edition, 5th Edition Stearns/Adas/Schwartz/Gilbert *AP and Advanced Placement are registered trademarks of The College
Russia Continued. Competing Revolutions and the Birth of the USSR
 Russia Continued Competing Revolutions and the Birth of the USSR Review: 3 Main Causes of Russian Revolution of 1917 Peasant Poverty Farmers: indebted and barely above subsistence level Outdated agricultural
Russia Continued Competing Revolutions and the Birth of the USSR Review: 3 Main Causes of Russian Revolution of 1917 Peasant Poverty Farmers: indebted and barely above subsistence level Outdated agricultural
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions.
 SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. EQ: What is characteristics
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. EQ: What is characteristics
Paul W. Werth. Review Copy
 Paul W. Werth vi REVOLUTIONS AND CONSTITUTIONS: THE UNITED STATES, THE USSR, AND THE ISLAMIC REPUBLIC OF IRAN Revolutions and constitutions have played a fundamental role in creating the modern society
Paul W. Werth vi REVOLUTIONS AND CONSTITUTIONS: THE UNITED STATES, THE USSR, AND THE ISLAMIC REPUBLIC OF IRAN Revolutions and constitutions have played a fundamental role in creating the modern society
Name Class Date. The French Revolution and Napoleon Section 3
 Name Class Date Section 3 MAIN IDEA Napoleon Bonaparte rose through military ranks to become emperor over France and much of Europe. Key Terms and People Napoleon Bonaparte ambitious military leader who
Name Class Date Section 3 MAIN IDEA Napoleon Bonaparte rose through military ranks to become emperor over France and much of Europe. Key Terms and People Napoleon Bonaparte ambitious military leader who
THE COLD WAR ( )
 THE COLD WAR (1948-1989) ORIGINS of the Cold War: (1945-1948) Tension or rivalry but NO FIGHTING between the United States and the Soviet Union This rivalry divided the world into two teams (capitalism
THE COLD WAR (1948-1989) ORIGINS of the Cold War: (1945-1948) Tension or rivalry but NO FIGHTING between the United States and the Soviet Union This rivalry divided the world into two teams (capitalism
Ch. 6.3 Radical Period of the French Revolution. leader of the Committee of Public Safety; chief architect of the Reign of Terror
 the right to vote Ch. 6.3 Radical Period of the French Revolution leader of the Committee of Public Safety; chief architect of the Reign of Terror period from September 1793 to July 1794 when those who
the right to vote Ch. 6.3 Radical Period of the French Revolution leader of the Committee of Public Safety; chief architect of the Reign of Terror period from September 1793 to July 1794 when those who
Britain vs. France by 1715
 Absolutism Britain vs. France by 1715 English Monarchy Limited monarchy Free trade Strong parliament Stable government down to the present Seeds of American Revolution French Monarchy Absolute monarchy
Absolutism Britain vs. France by 1715 English Monarchy Limited monarchy Free trade Strong parliament Stable government down to the present Seeds of American Revolution French Monarchy Absolute monarchy
Napoleon. Global History and Geography II
 Global History and Geography II Napoleon Name: Date: In 1799, a thirty-year-old general named Napoleon Bonaparte forced the Directory to resign. He took control of the government with the backing of the
Global History and Geography II Napoleon Name: Date: In 1799, a thirty-year-old general named Napoleon Bonaparte forced the Directory to resign. He took control of the government with the backing of the
1. What nineteenth century state was known as the Middle Kingdom to its populace? a. a) China b. b) Japan c. d) Iran d.
 1. What nineteenth century state was known as the Middle Kingdom to its populace? a. a) China b) Japan c. d) Iran d. c) Ottoman Empire 2. Which of the following was a factor in creating China s internal
1. What nineteenth century state was known as the Middle Kingdom to its populace? a. a) China b) Japan c. d) Iran d. c) Ottoman Empire 2. Which of the following was a factor in creating China s internal
Clash of Philosophies: 11/10/2010
 1. Notebook Entry: Nationalism Vocabulary 2. What does nationalism look like? EQ: What role did Nationalism play in 19 th century political development? Common Language, Romanticism, We vs. They, Irrational
1. Notebook Entry: Nationalism Vocabulary 2. What does nationalism look like? EQ: What role did Nationalism play in 19 th century political development? Common Language, Romanticism, We vs. They, Irrational
B.A. IN HISTORY. B.A. in History 1. Topics in European History Electives from history courses 7-11
 B.A. in History 1 B.A. IN HISTORY Code Title Credits Major in History (B.A.) HIS 290 Introduction to History 3 HIS 499 Senior Seminar 4 Choose two from American History courses (with at least one at the
B.A. in History 1 B.A. IN HISTORY Code Title Credits Major in History (B.A.) HIS 290 Introduction to History 3 HIS 499 Senior Seminar 4 Choose two from American History courses (with at least one at the
POLITICAL IDEOLOGY. By the end of this lesson, I will list and explain five political ideologies using specific examples from history.
 POLITICAL IDEOLOGY By the end of this lesson, I will list and explain five political ideologies using specific examples from history. WHAT DOES IDEOLOGY MEAN? Idea ----- Ideology ----- way of thinking
POLITICAL IDEOLOGY By the end of this lesson, I will list and explain five political ideologies using specific examples from history. WHAT DOES IDEOLOGY MEAN? Idea ----- Ideology ----- way of thinking
Characteristics of the Russian Empire in 19 th Century
 Characteristics of the Russian Empire in 19 th Century Geography of Europe Geography of Russia Tsar Alexander I December 23, 1777 December 1, 1825 Alexander succeeded to the throne after his father was
Characteristics of the Russian Empire in 19 th Century Geography of Europe Geography of Russia Tsar Alexander I December 23, 1777 December 1, 1825 Alexander succeeded to the throne after his father was
Social Studies: World History Grades 10 1 st Nine Weeks At a Glance (Week 1-9)
 Social Studies: World History Grades 10 1 st Nine s At a Glance ( 19) 1 1A, A, 15 AB, 16 A C, 17AB, 19A, 0B, 3A, 7A, 9A, FH, 30A : I, 3B and 4D How did nomadic farming life lead to the emergence of civilizations?
Social Studies: World History Grades 10 1 st Nine s At a Glance ( 19) 1 1A, A, 15 AB, 16 A C, 17AB, 19A, 0B, 3A, 7A, 9A, FH, 30A : I, 3B and 4D How did nomadic farming life lead to the emergence of civilizations?
RUSSIA: INDUSTRIALIZATION AND REVOLUTION ( ) AP World History: Chapter 23b
 RUSSIA: INDUSTRIALIZATION AND REVOLUTION (1750-1914) AP World History: Chapter 23b Russia: Transformation from Above In the U.S. = social and economic change has always come from society as people sought
RUSSIA: INDUSTRIALIZATION AND REVOLUTION (1750-1914) AP World History: Chapter 23b Russia: Transformation from Above In the U.S. = social and economic change has always come from society as people sought
WORLD HISTORY: THE INTER-WAR YEARS
 WORLD HISTORY: THE INTER-WAR YEARS Society in the 1920s Russian Revolution Germany and Hitler Italy and Mussolini Miscellaneous 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400
WORLD HISTORY: THE INTER-WAR YEARS Society in the 1920s Russian Revolution Germany and Hitler Italy and Mussolini Miscellaneous 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400
Construct maps that display the location of a variety of Earth's physical features (e.g., plateaus, rivers, deltas
 Subject Grade Level 7 Social Studies G.1.7.1 G.1.7.10 G.1.7.2 G.1.7.3 G.1.7.4 G.1.7.5 G.1.7.6 G.1.7.7 G.1.7.8 G.1.7.9 Description Determine the absolute and relative location of a specific place Construct
Subject Grade Level 7 Social Studies G.1.7.1 G.1.7.10 G.1.7.2 G.1.7.3 G.1.7.4 G.1.7.5 G.1.7.6 G.1.7.7 G.1.7.8 G.1.7.9 Description Determine the absolute and relative location of a specific place Construct
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions.
 SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. Known as the Sun
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. Known as the Sun
World History Unit 12 Lesson 1 The Congress of Vienna
 Unit 12 Lesson 1 The Congress of Vienna After the Napoleonic Wars, Europe faced many problems: 1) Many countries leaders had been replaced by Napoleon. 2) Some countries had been eliminated. 3) The liberalism
Unit 12 Lesson 1 The Congress of Vienna After the Napoleonic Wars, Europe faced many problems: 1) Many countries leaders had been replaced by Napoleon. 2) Some countries had been eliminated. 3) The liberalism
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 4 The Fall of Napoleon and the European Reaction ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What causes revolution? How does revolution change society? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary civil involving the general
Lesson 4 The Fall of Napoleon and the European Reaction ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What causes revolution? How does revolution change society? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary civil involving the general
The red Scare. Background. Background 12/12/2014. Could it happen here!?
 The red Scare Could it happen here!? At the beginning of WWI, Russia was still ruled by Tsar Nicholas II who, like Kaiser Wilhelm in Germany, was an autocrat (like a king, or emperor). If you have ever
The red Scare Could it happen here!? At the beginning of WWI, Russia was still ruled by Tsar Nicholas II who, like Kaiser Wilhelm in Germany, was an autocrat (like a king, or emperor). If you have ever
