The Philippines. Map of South East Asia. Map of the Philippines. Quick Facts
|
|
|
- Griffin Byrd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Map of South East Asia The Philippines Course: South East Asia Lecturer: Professor Soong Student: Daleen Baker (U ) Map of the Philippines The Philippines consists of 7,107 islands Luzon and Mindanao account for two-thirds thirds of the land area. Population 84,765,000 Capital Manila; 10,677,000 Area 300,000 square kilometers (115,831 square miles) Language Filipino (based on Tagalog), English, and 8 major dialects Religion Roman Catholic, Protestant, Muslim, Buddhist Currency Philippine peso Life Expectancy 70 GDP per Capita U.S. $4,600 Literacy Percent 96 Quick Facts 1
2 Colonial Period: Spanish to American Rule First Asian nation to expel Western colonial power 1565 Spanish naval forces reach Philippines from New Spain (South America) Islands conceived as a base for the eventual Christianization of Asian peoples capital city Manila (1571( 1571) ) became the western terminus of annual galleon convoys operating from Acapulco in New Spain Western voyages carried mainly military and missionary passengers plus a substantial cargo of Mexican silver The return trip carried valuable Chinese freight, which was brought to Manila in Chinese junks Islander resistance to Spanish control was minimal : no central government existed; much of the task of pacifying the population was accomplished by participating regular missionary orders. Economic development, apart from the Manila trade, slow during the first two centuries of Spanish control Considerable achievement realized educationally as part of the Christianizing program Manila was attacked by Dutch forces in the 1660s and was occupied temporarily by British- Indian troops by Europe s s Seven Year s s War a century later 1760s Mexican silver tapered off Collapse of Spain s s rule in continental America after 1815 raised difficult problems for the Philippines Major changes in economic policy manifested in the last quarter of the 18th century cultivation of cash crops like tobacco, indigo, hemp and sugar was actively encouraged, Manila was opened to foreign shipping 2
3 Result of these changes was:- the rise of a new, prosperous, Filipino, export- oriented, agricultural elite that would have important consequences for the emergence of the nationalist leadership in the second half of the 19th century 1835 introduction of free trade policies : Greater contact between seamen and traders from Europe and the United States and new entrepreneurial class in the Philippines 1869 opening of the Suez Canal gave the Filipino trade with Europe a stimulus as never before Revolts Against Spanish Rule Revolts marked by opposition to : colonial injustice, racial discrimination in appointments to clerical positions and, agrarian exploitation by the friars Bohol Revolt in 1744 and in Pangasinan Ilokos Revolt in the 1760s Revolts served as an inspiration for the nationalist movements of the late 19th century Filipino protests eventually found expression in the novels of Jose Rizal of the 1880s Spanish authorities executed Rizal for treason in 1896 March 1897,, an assembly of the revolutionaries proclaimed the Philippines a republic and elected Emilio Aguinaldo its president Aguinaldo forces reached stalemate with Spanish authorities Peace pact made to break stalemate: Aguinaldo to go into exile in Hong Kong and be paid a sum of money Spanish agreed to reforms such as free press and Filipino representation in bureaucracy BOTH parties broke pact dd 3
4 Waning Spanish Empire Cuba-centred Spanish- American War of 1898 strategic for U.S. to prevent Spanish Pacific fleet from joining Caribbean fleet Commodore George Dewey approached Aguinaldo in Hong Kong 1899 United States annexed the Philippines and restored order to the islands Reasons for U.S. Intervention U.S. historian, Richard Hofstadter, observed: The taking of the Philippine Islands from Spain in 1899 marked a major historical departure for the American people (American expansionism) Basic ideas of Darwin, Fiske and Mahan were in circulation at the beginning of the 1890s. They all contributed to the intellectual climate of the United States and influenced political leaders Economic reasons: depression of 1893; restrictive tariff policies of European countries held for the U.S. businesses the fear and prospect of shrinking markets Henry Cabot Lodge best represented the views of fellow expansionists : Duty and interest alike, duty of the highest kind and interest of the highest and best kind, impose upon us the retention of the Philippines, the development of the islands and the expansion of our Eastern commerce In the early 1930s,, the Democratic Party advocacy of Filipino self-rule found unexpected support during the Great Depression from American producers of sugar, dairy products, cordage fiber and cotton seed. These groups opposed duty-free Philippines imports to the American market Tydings-McDuffie Act of 1934,, under which Filipinos were authorized to prepare their own constitution 4
5 Japan and the Philippines President Quezon after 1936 was fated to be pushed aside by the Japanese invasion of progressive noninvolvement of U.S. in the internal affairs of the Philippines in the late 1930s,, gave Japan opportunity to augment influence World War II, Japanese interest in Philippine lumber, hemp and copra was substantial. Japan had 35% interest in Philippine minerals (iron, manganese, copper) Manuel Quezon either ignored or underestimated the nature of Japanese expansionism Within a few days of the Pearl Harbor attack on December 7, 1941 Japan attacked the Philippines March , MacArthur fled to Australia President Quezon also fled, set up a government in exile in Washington October 1944,, the liberation of the Philippines began with MacArthur s forces retaking Leyte Full independence was granted to the Philippines on July 4, 1946 Independent Philippines: Postwar Developments to Present Philippines functioned as a working democracy for 25 years after independence Two major parties, the Liberals and the Nationalists, dominated the political scene 5
6 The New Constitution Inspiration for the Philippine constitution was American Power was centralized in the office of the President, elected every 4 years Separation of powers among the executive, legislative and judiciary branches The legislature has two houses: a Senate with 24 members, one-third elected every two years for a period of six years, and House of Representatives, the lower chamber with a maximum of 120 members, elected every four years System of courts headed by the Supreme Court reasserted its four-decade decade-old tradition of independence and integrity Bill of Rights Country s s government held sovereignty and jurisdiction over all the islands except the military and naval bases granted to the United States Manuel Roxas and Elpidio Quirino Manuel Roxas became president of the Philippines in April 1946 His anti-communist credentials endeared him to the Filipino landlord class, the church, the civil service and the U.S. army brass, business interests and the State Department Roxas government received considerable moral and material support from the U.S. including more than half a billion for war damage claims Instead of rehabilitating the war-affected, affected, officials rehabilitated their pockets Roxas died in 1948 Elpidio Quirino ( ), introduced land reform and new plans for the country s industrialization in order to improve the common people s s economic conditions. Quirino government received a loan of a quarter billion dollars from U.S., but no benefits accrued to the average person 6
7 The Magsaysay Revolution Early 1950s, Ramon Magsaysay appointed as country s s new defense minister. Magsaysay promised social welfare legislation, expeditions and better justice and education and general services at the village level. Magsaysay s policy destroyed the Huk movement by 1951 Magsaysay s frequent forays into the rural areas, running an efficient government and success in bringing peace made him very popular Magsaysay died in a plane crash in Cebu in 1957 The Marcos Regime Under both Carlos Garcia (1957( 1960) ) and Diosdado Macapagal ( ), politics assumed primacy and the programs for the peasants and poor initiated by the government went unimplemented Ferdinand Marcos defeated Macapagal to become president in 1965 President of the Liberal Senate under Macapagal Defected to the Nationalist Party to be elected president 7
8 The Marcos Regime (contd.) Campaigned on a platform of land reform and economic development First administration was marked by some improvement in the economy helped by the use of miracle rice (IR-8) Country suddenly became an exporter of rice, though on a modest scale New strain of rice required equipment and heavy economic inputs leaving this new field of prosperity to the larger landowners. Prices soared by more than 50% amid reports of widespread corruption and rumors of vast accumulation of wealth by the Marcos family 1971 the Senate elections were marred by violence and deaths Marcos opponents won six of the eight seats in Senate and his vice-president deserted him for the opposition Liberal Party Benigno Aquino 1972 the report of the constitutional convention proposed a shift to a parliamentary system of government Marcos, however perceived a major threat to his power by the popular, dynamic, brilliant and young Senator Aquino. On September 23, 1972,, Marcos proclaimed martial law Aquino was the son of a former senator, and was thus well-acquainted with politics became senator at the age of 35 most likely to succeed Marcos popular feelings were running high for Aquino 8
9 Martial Law Thousands of Marcos political opponents were imprisoned, including Benigno Aquino Marcos shut down newspapers and established government control over radio and television All individual freedoms were suppressed and strikes banned Significantly Marcos consulted the armed forces in all his acts, thus giving the military a political role for the first time in Filipino history Benigno Aquino Assassination August 21, 1983 the world was shocked to hear that Aquino has been shot to death at Manila Airport Government identified Ronaldo Galman y Dawang,, a Communist, as the assassin. Eyewitness reports witnessed soldiers firing at Aquino s head The People s s Power Historic presidential elections of February 1986 were fought between Ferdinand Marcos and Corazon Aquino (Benigno s widow) Marcos claimed victory in an election widely criticized for deception, fraud on a large scale and chicanery The People s s Power (cont.) Aquino met with ambassadors from 14 European nations and Japan and urged their governments not to recognize the Marcos regime International response of almost unanimously in favor of Aquino 9
10 Corazon Aquino ( ) Turning point came on February 22,, when Defense Minister Juan Enrile and acting Chief of Staff Fidel Ramos quit their posts to protest the rigged election Declared support to Aquino Supported by Roman Catholic Cardinal Jaime Sin on a private radio station, calling people to pour into the streets. Within 24 hours, over a million Filipinos on the streets Within 48 hours, the Marcos regime fell, with Marcos unceremoniously leaving the country with his family and cronies for the U.S. The Ramos, Estrada, and Macapagal-Arroyo Administrations Fidel Ramos, elected president 1992,, continued Aquino policies; country saw new levels of stability and economic improvement Joseph Estrada, elected president 1998 Within 2 years, people demonstrated against the corruption of his regime November 13, 2000 he was impeached Forced to step down on January Gloria Macapagal-Arroyo Succeeded Estrada Daughter of former President Diosdado Macapagal Trained as economist in U.S. Went to Washington in September 2001 to show support for Bush Administration 10
11 Several groups, including Communists, Muslims, angered by her wooing U.S. Her contribution to security and stability of her country is laudable. 11
PHILIPPINE HISTORY Part 2
 PHILIPPINE HISTORY Part 2 AMERICAN COLONIAL GOVERNMENT 1. MILITARY GOVERNMENT April 14, 1898 the day after the fall of Manila Ruled by a MILITARY Governor - His authority lasted as long as the war existed
PHILIPPINE HISTORY Part 2 AMERICAN COLONIAL GOVERNMENT 1. MILITARY GOVERNMENT April 14, 1898 the day after the fall of Manila Ruled by a MILITARY Governor - His authority lasted as long as the war existed
Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War
 Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War 1 Imperialism & Expansion CH 14-1 Imperialism & War Name Reasons why the United States becomes an imperialist nation. 1-New Markets 2-Anglo-Saxonism 3-Modern Navy 4-Into
Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War 1 Imperialism & Expansion CH 14-1 Imperialism & War Name Reasons why the United States becomes an imperialist nation. 1-New Markets 2-Anglo-Saxonism 3-Modern Navy 4-Into
Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea
 Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea In the last half of the 1800s, the United States joined the race for control of overseas territories.
Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea In the last half of the 1800s, the United States joined the race for control of overseas territories.
Changing The Constitution
 part one 3 Changing The Constitution I P E R 4 Introduction Copyright 2004 Published by The Institute for Political and Electoral Reform (IPER) ISBN 971-92681-2-3 part one 5 acidcowart collective sanpablo
part one 3 Changing The Constitution I P E R 4 Introduction Copyright 2004 Published by The Institute for Political and Electoral Reform (IPER) ISBN 971-92681-2-3 part one 5 acidcowart collective sanpablo
Chapter 17, Section 1 I. Building Support for Imperialism (pages ) A. Beginning in the 1880s, Americans wanted the United States to become a
 Chapter 17, Section 1 I. Building Support for Imperialism (pages 520 522) A. Beginning in the 1880s, Americans wanted the United States to become a world power. Their change in attitude was a result of
Chapter 17, Section 1 I. Building Support for Imperialism (pages 520 522) A. Beginning in the 1880s, Americans wanted the United States to become a world power. Their change in attitude was a result of
Empire and Expansion. Chapter 27
 Empire and Expansion Chapter 27 Imperialism Stronger nations attempt to create empires by dominating weaker nations. The late 1800s marked the peak of European imperialism, with much of Africa and Asia
Empire and Expansion Chapter 27 Imperialism Stronger nations attempt to create empires by dominating weaker nations. The late 1800s marked the peak of European imperialism, with much of Africa and Asia
Chapter 12 Section 1 The Imperialist Vision. Click on a hyperlink to view the corresponding slides.
 Chapter 12 Section 1 The Imperialist Vision Click on a hyperlink to view the corresponding slides. Click the Speaker button to listen to the audio again. continued on next slide Guide to Reading Main
Chapter 12 Section 1 The Imperialist Vision Click on a hyperlink to view the corresponding slides. Click the Speaker button to listen to the audio again. continued on next slide Guide to Reading Main
In the early 1900's the United States engaged in conflicts with Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines.
 Ch 18-Section 3 - Acquiring New Lands In the early 1900's the United States engaged in conflicts with Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines. Puerto Rico Fearful of losing autonomy that they had won under
Ch 18-Section 3 - Acquiring New Lands In the early 1900's the United States engaged in conflicts with Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines. Puerto Rico Fearful of losing autonomy that they had won under
Functions of the Datu Chief executive Law-giver Chief judge Military head Assisted by a Council of Elders called the maginoo
 PHILIPPINE HISTORY PHILIPPINE HISTORY PRE-SPANISH GOVERNMENT SETTLEMENTS BARANGAY villages that consisted of more or less 100 families DATU ruler of the barangay Functions of the Datu Chief executive Law-giver
PHILIPPINE HISTORY PHILIPPINE HISTORY PRE-SPANISH GOVERNMENT SETTLEMENTS BARANGAY villages that consisted of more or less 100 families DATU ruler of the barangay Functions of the Datu Chief executive Law-giver
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e. Chapter Nineteen: From Crisis to Empire
 Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e The Politics of Equilibrium Electoral Stability High Turnout for Elections Cultural Basis of Party Identification Catholics Tended to Vote Democrat 2 The Politics of
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e The Politics of Equilibrium Electoral Stability High Turnout for Elections Cultural Basis of Party Identification Catholics Tended to Vote Democrat 2 The Politics of
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions.
 SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. Known as the Sun
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. Known as the Sun
Mark Anthony D. Abenir, MCD Department of Social Sciences University of Santo Tomas
 Mark Anthony D. Abenir, MCD Department of Social Sciences University of Santo Tomas EARLY AGITATIONS FOR INDEPENDENCE Independence Missions Failed Agitations for Independence OSROX & Quezon Hare-Hawes-
Mark Anthony D. Abenir, MCD Department of Social Sciences University of Santo Tomas EARLY AGITATIONS FOR INDEPENDENCE Independence Missions Failed Agitations for Independence OSROX & Quezon Hare-Hawes-
18 America Claims an Empire QUIT
 18 America Claims an Empire QUIT CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE SECTION 1 Imperialism and America GRAPH MAP SECTION 2 The Spanish-American War SECTION 3 Acquiring New Lands SECTION 4
18 America Claims an Empire QUIT CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE SECTION 1 Imperialism and America GRAPH MAP SECTION 2 The Spanish-American War SECTION 3 Acquiring New Lands SECTION 4
Functions of the Datu Chief executive Law-giver Chief judge Military head Assisted by a Council of Elders called the maginoo
 PHILIPPINE HISTORY PHILIPPINE HISTORY PRE-SPANISH GOVERNMENT SETTLEMENTS BARANGAY villages that consisted of more or less 100 families DATU ruler of the barangay Functions of the Datu Chief executive Law-giver
PHILIPPINE HISTORY PHILIPPINE HISTORY PRE-SPANISH GOVERNMENT SETTLEMENTS BARANGAY villages that consisted of more or less 100 families DATU ruler of the barangay Functions of the Datu Chief executive Law-giver
Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism
 Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism 1. List the ideas that fueled American Imperialism. 2. How were yellow journalists able to influence Americans opinions on foreign policy? 3. The person who urged
Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism 1. List the ideas that fueled American Imperialism. 2. How were yellow journalists able to influence Americans opinions on foreign policy? 3. The person who urged
Training on Making Governance Gender Responsive
 Organized by: Training on Making Governance Gender Responsive for local governments (city/municipality) and the government bureaucracy political parties, training institutes, human rights and other civil
Organized by: Training on Making Governance Gender Responsive for local governments (city/municipality) and the government bureaucracy political parties, training institutes, human rights and other civil
World History (Survey) Chapter 28: Transformations Around the Globe,
 World History (Survey) Chapter 28: Transformations Around the Globe, 1800 1914 Section 1: China Responds to Pressure from the West In the late 1700s, China was self-sufficient. It had a strong farming
World History (Survey) Chapter 28: Transformations Around the Globe, 1800 1914 Section 1: China Responds to Pressure from the West In the late 1700s, China was self-sufficient. It had a strong farming
Unit 5. US Foreign Policy, Friday, December 9, 11
 Unit 5 US Foreign Policy, 1890-1920 I. American Imperialism A. What is Imperialism? B. Stated motivations (how we were helping others) Helping free countries from foreign domination Spreading Christianity
Unit 5 US Foreign Policy, 1890-1920 I. American Imperialism A. What is Imperialism? B. Stated motivations (how we were helping others) Helping free countries from foreign domination Spreading Christianity
Chapter 19: Republic To Empire
 Chapter 19: Republic To Empire Objectives: o We will examine the policies America implemented in their newly conquered territories after the Spanish American War. o We will examine the various changes
Chapter 19: Republic To Empire Objectives: o We will examine the policies America implemented in their newly conquered territories after the Spanish American War. o We will examine the various changes
America s Path to Empire. APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8
 America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8 1890-1892 Foreign Policy The Influence of Sea Power upon History (1890): Alfred Thayer Mahan Sea power throughout history gives advantages US lies
America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8 1890-1892 Foreign Policy The Influence of Sea Power upon History (1890): Alfred Thayer Mahan Sea power throughout history gives advantages US lies
China Resists Outside Influence
 Name CHAPTER 28 Section 1 (pages 805 809) China Resists Outside Influence BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about imperialism in Asia. In this section, you will see how China dealt with foreign
Name CHAPTER 28 Section 1 (pages 805 809) China Resists Outside Influence BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about imperialism in Asia. In this section, you will see how China dealt with foreign
Imperialism. U.S. Foreign Policy. U.S. Foreign Policy 10/30/13. Chapter 10. Monroe Doctrine. Many Spanish colonies revolting
 Imperialism Chapter 10 U.S. Foreign Policy Monroe Doctrine No new colonization by Europe in western hemisphere U.S. stays out of European affairs If Europe attempts to colonize in the west, U.S. would
Imperialism Chapter 10 U.S. Foreign Policy Monroe Doctrine No new colonization by Europe in western hemisphere U.S. stays out of European affairs If Europe attempts to colonize in the west, U.S. would
The United States Lesson 2: History of the United States
 Lesson 2: History of the United States ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is history important? Terms to Know indigenous living or occurring naturally in a particular place nomadic describes a way of life in which
Lesson 2: History of the United States ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is history important? Terms to Know indigenous living or occurring naturally in a particular place nomadic describes a way of life in which
NATIONAL DEFENSE UNIVERSITY NATIONAL WAR COLLEGE INFORMED QUESTIONS PAPER: PHILIPPINE POLITICS
 NATIONAL DEFENSE UNIVERSITY NATIONAL WAR COLLEGE INFORMED QUESTIONS PAPER: PHILIPPINE POLITICS CAPT MICHAEL S. ROGERS, USN 5604 THE GLOBAL SECURITY ARENA SEMINAR D PROFESSOR DR. ALLEN L. KEISWETTER ADVISOR
NATIONAL DEFENSE UNIVERSITY NATIONAL WAR COLLEGE INFORMED QUESTIONS PAPER: PHILIPPINE POLITICS CAPT MICHAEL S. ROGERS, USN 5604 THE GLOBAL SECURITY ARENA SEMINAR D PROFESSOR DR. ALLEN L. KEISWETTER ADVISOR
This is a September 2010 publication of your PCC Mission & Evangelism Committee
 This is a September 2010 publication of your PCC Mission & Evangelism Committee HISTORY OF THE PHILIPPINES Pre-1500- Native people, and Malay migrants, Muslim migrants to Mindanao, Chinese form a merchant
This is a September 2010 publication of your PCC Mission & Evangelism Committee HISTORY OF THE PHILIPPINES Pre-1500- Native people, and Malay migrants, Muslim migrants to Mindanao, Chinese form a merchant
AMERICA AND THE WORLD. Chapter 13 Section 1 US History
 AMERICA AND THE WORLD Chapter 13 Section 1 US History AMERICA AND THE WORLD THE RISE OF DICTATORS MAIN IDEA Dictators took control of the governments of Italy, the Soviet Union, Germany, and Japan End
AMERICA AND THE WORLD Chapter 13 Section 1 US History AMERICA AND THE WORLD THE RISE OF DICTATORS MAIN IDEA Dictators took control of the governments of Italy, the Soviet Union, Germany, and Japan End
BECOMING A WORLD POWER
 BECOMING A WORLD POWER CHAPTER 10 IMPERIALISM THE PRESSURE TO EXPAND Americans had always sought to expand the size of their nation, and throughout the 19th century they extended their control toward the
BECOMING A WORLD POWER CHAPTER 10 IMPERIALISM THE PRESSURE TO EXPAND Americans had always sought to expand the size of their nation, and throughout the 19th century they extended their control toward the
Letter from President Fillmore asking Japan. American ships to stop for supplies safety reasons
 Chapter 19-21 Introduction Japan 1853 Not open to trading with other countries Commodore Matthew Perry went to Japan with a small fleet of warships (Gunboat Diplomacy) Letter from President Fillmore asking
Chapter 19-21 Introduction Japan 1853 Not open to trading with other countries Commodore Matthew Perry went to Japan with a small fleet of warships (Gunboat Diplomacy) Letter from President Fillmore asking
Communism in the Far East. China
 Communism in the Far East China Terms and Players KMT PLA PRC CCP Sun Yat-Sen Mikhail Borodin Chiang Kai-shek Mao Zedong Shaky Start In 1913 the newly formed Chinese government was faced with the assassination
Communism in the Far East China Terms and Players KMT PLA PRC CCP Sun Yat-Sen Mikhail Borodin Chiang Kai-shek Mao Zedong Shaky Start In 1913 the newly formed Chinese government was faced with the assassination
Time: 1 Block period (1:45) National Standards:
 Time: 1 Block period (1:45) National Standards: World History Era 8, Standard 1A: Analyze why European colonial territories and Latin American countries continued to maintain largely agricultural and mining
Time: 1 Block period (1:45) National Standards: World History Era 8, Standard 1A: Analyze why European colonial territories and Latin American countries continued to maintain largely agricultural and mining
Chapter 17. Becoming a World Power ( )
 Chapter 17 Becoming a World Power (1872 1912) 1 Chapter Overview: During this era, economic and military competition from world powers convinced the United States it must be a world power. The United States
Chapter 17 Becoming a World Power (1872 1912) 1 Chapter Overview: During this era, economic and military competition from world powers convinced the United States it must be a world power. The United States
The United States Looks Overseas
 The United States Looks Overseas 1853-1915 Interact with History In 1893, American sugar planters in the Kingdom of Hawaii thought they could make more money if Hawaii were an American state. So they staged
The United States Looks Overseas 1853-1915 Interact with History In 1893, American sugar planters in the Kingdom of Hawaii thought they could make more money if Hawaii were an American state. So they staged
APUSH. U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! EMPIRE & EXPANSION
 APUSH 1890-1909 EMPIRE & EXPANSION U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 27 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 19 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 21 Important Ideas Since the
APUSH 1890-1909 EMPIRE & EXPANSION U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 27 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 19 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 21 Important Ideas Since the
Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of???
 Need to know What was President Roosevelt s Gentlemen s Agreement with Japan? Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of??? imperialism Stronger nations dominating
Need to know What was President Roosevelt s Gentlemen s Agreement with Japan? Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of??? imperialism Stronger nations dominating
Unit 4: Imperialism. Name: Word Definition Analysis
 Name: Unit 4: Imperialism Word Definition Analysis 1. Imperialism (191) Policy by which strong nations Did America practice imperialism? extend their political, military, If so where? and economic control
Name: Unit 4: Imperialism Word Definition Analysis 1. Imperialism (191) Policy by which strong nations Did America practice imperialism? extend their political, military, If so where? and economic control
PROFILE OF THE PHILIPPINES
 Page 1 PROFILE OF THE PHILIPPINES SIZE: 115,831 square miles of land and water, more than 7,000 islands. Total area is slightly larger than Arizona. POPULATION: 91.1 million (CIA 2007), with 12 million
Page 1 PROFILE OF THE PHILIPPINES SIZE: 115,831 square miles of land and water, more than 7,000 islands. Total area is slightly larger than Arizona. POPULATION: 91.1 million (CIA 2007), with 12 million
Imperialism and America
 Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire CHAPTER 10 Section 1 (pages 342-345) Imperialism and America American Expansionism (pages 342-344) Why did Americans support imperialism? In 1893, Queen Liliuokalani
Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire CHAPTER 10 Section 1 (pages 342-345) Imperialism and America American Expansionism (pages 342-344) Why did Americans support imperialism? In 1893, Queen Liliuokalani
Changing Role of Civil Society
 30 Asian Review of Public ASIAN Administration, REVIEW OF Vol. PUBLIC XI, No. 1 ADMINISTRATION (January-June 1999) Changing Role of Civil Society HORACIO R. MORALES, JR., Department of Agrarian Reform
30 Asian Review of Public ASIAN Administration, REVIEW OF Vol. PUBLIC XI, No. 1 ADMINISTRATION (January-June 1999) Changing Role of Civil Society HORACIO R. MORALES, JR., Department of Agrarian Reform
Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power
 Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power Objective: Why did the United States become imperialistic and what were the outcomes? Goal: Students will be able to understand the causes and effects of imperialism
Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power Objective: Why did the United States become imperialistic and what were the outcomes? Goal: Students will be able to understand the causes and effects of imperialism
BELLRINGER. Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies?
 BELLRINGER Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies? U.S. INTERVENTION ABROAD Ms. Luco IB Hist Americas LEARNING
BELLRINGER Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies? U.S. INTERVENTION ABROAD Ms. Luco IB Hist Americas LEARNING
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions.
 SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. EQ: What is characteristics
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. EQ: What is characteristics
Transformations Around the Globe. Ch
 Transformations Around the Globe Ch 28 1800-1914 China + the West China looked down on foreigners China was self-sufficient Strong agricultural economy Extensive mining + industry China wasn t interested
Transformations Around the Globe Ch 28 1800-1914 China + the West China looked down on foreigners China was self-sufficient Strong agricultural economy Extensive mining + industry China wasn t interested
Imperial China Collapses Close Read
 Imperial China Collapses Close Read Standards Alignment Text with Close Read instructions for students Intended to be the initial read in which students annotate the text as they read. Students may want
Imperial China Collapses Close Read Standards Alignment Text with Close Read instructions for students Intended to be the initial read in which students annotate the text as they read. Students may want
Expanding Horizons: Imperialism
 Expanding Horizons: Imperialism In August 1914, World War I broke out in Europe, which drowned out the Progressive Era. Leading up to this, U.S. foreign policy had been drastically changing. IMPERIALISM
Expanding Horizons: Imperialism In August 1914, World War I broke out in Europe, which drowned out the Progressive Era. Leading up to this, U.S. foreign policy had been drastically changing. IMPERIALISM
Bell Work. Describe Truman s plan for. Europe. How will his plan help prevent the spread of communism?
 Bell Work Describe Truman s plan for dealing with post-wwii Europe. How will his plan help prevent the spread of communism? Objectives Explain how Mao Zedong and the communists gained power in China. Describe
Bell Work Describe Truman s plan for dealing with post-wwii Europe. How will his plan help prevent the spread of communism? Objectives Explain how Mao Zedong and the communists gained power in China. Describe
Imperialism and America
 CHAPTER 10 Section 1 ( pages 342 345) Imperialism and America BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about Woodrow Wilson. In this section, you will learn how economic activity led to political
CHAPTER 10 Section 1 ( pages 342 345) Imperialism and America BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about Woodrow Wilson. In this section, you will learn how economic activity led to political
Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power ( )
 Name: Period Page# Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power (1890 1915) Section 1: The Pressure to Expand What factors led to the growth of imperialism around the world? In what ways did the United States begin
Name: Period Page# Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power (1890 1915) Section 1: The Pressure to Expand What factors led to the growth of imperialism around the world? In what ways did the United States begin
American Foreign Policy, : The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly.
 American Foreign Policy, 1880-1920: The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly. Each group will become experts on their assigned country. Create poster showing how U.S. policy toward your respective country was good,
American Foreign Policy, 1880-1920: The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly. Each group will become experts on their assigned country. Create poster showing how U.S. policy toward your respective country was good,
Fascism is a nationalistic political philosophy which is anti-democratic, anticommunist, and anti-liberal. It puts the importance of the nation above
 1939-1945 Fascism is a nationalistic political philosophy which is anti-democratic, anticommunist, and anti-liberal. It puts the importance of the nation above the rights of the individual. The word Fascism
1939-1945 Fascism is a nationalistic political philosophy which is anti-democratic, anticommunist, and anti-liberal. It puts the importance of the nation above the rights of the individual. The word Fascism
Ch 29-1 The War Develops
 Ch 29-1 The War Develops The Main Idea Concern about the spread of communism led the United States to become increasingly violent in Vietnam. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze how the Cold war and
Ch 29-1 The War Develops The Main Idea Concern about the spread of communism led the United States to become increasingly violent in Vietnam. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze how the Cold war and
Filipino Americans: From Indians to Asians in the United States. College of Education 22 June 2018: Sacramento, CA
 Filipino Americans: From Indians to Asians in the United States College of Education 22 June 2018: Sacramento, CA James Sobredo, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Ethnic Studies Sacramento State
Filipino Americans: From Indians to Asians in the United States College of Education 22 June 2018: Sacramento, CA James Sobredo, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Ethnic Studies Sacramento State
Comparative Constitution Drafting Processes in the Philippines, Thailand and Burma:
 C ONSTITUTION DRAFTING PROCESSES B U R M A L A W Y E R S ' C O U N C I L Comparative Constitution Drafting Processes in the Philippines, Thailand and Burma: Drafting Process plays Crucial Role for Contents
C ONSTITUTION DRAFTING PROCESSES B U R M A L A W Y E R S ' C O U N C I L Comparative Constitution Drafting Processes in the Philippines, Thailand and Burma: Drafting Process plays Crucial Role for Contents
4. During the late 1800s, the port of entry for the majority of immigrants was a. Boston b. New York City c. Philadelphia d.
 Chapters 14-18 Presentations Test 1. The cruise of the Great White Fleet showed that a. the Atlantic could be crossed safely. b. Great Britain was a second-rate power. c. the United States was a naval
Chapters 14-18 Presentations Test 1. The cruise of the Great White Fleet showed that a. the Atlantic could be crossed safely. b. Great Britain was a second-rate power. c. the United States was a naval
throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not.
 1. Tell what at least three of the symbols you see on this flag represent. 2. Do you think these three symbols would be recognized throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not. 3. Why would this
1. Tell what at least three of the symbols you see on this flag represent. 2. Do you think these three symbols would be recognized throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not. 3. Why would this
Modern World History
 Modern World History Chapter 19: Struggles for Democracy, 1945 Present Section 1: Patterns of Change: Democracy For democracy to work, there must be free and fair elections. There must be more than one
Modern World History Chapter 19: Struggles for Democracy, 1945 Present Section 1: Patterns of Change: Democracy For democracy to work, there must be free and fair elections. There must be more than one
President William McKinley
 President William McKinley William McKinley was born in Niles, Ohio on January 29, 1843 to a large family where he was the seventh of eight children. His family moved to Poland, Ohio when he was ten years
President William McKinley William McKinley was born in Niles, Ohio on January 29, 1843 to a large family where he was the seventh of eight children. His family moved to Poland, Ohio when he was ten years
American Upon the Global Stage Was America Imperialist? Or Was America Exceptional?
 APUSH Kind American Imperialism American Upon the Global Stage Was America Imperialist? Or Was America Exceptional? History of American Foreign Policy Neutrality & Isolationism Neutrality Proclamation
APUSH Kind American Imperialism American Upon the Global Stage Was America Imperialist? Or Was America Exceptional? History of American Foreign Policy Neutrality & Isolationism Neutrality Proclamation
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 3 The Rise of Napoleon and the Napoleonic Wars ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What causes revolution? How does revolution change society? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary capable having or showing ability
Lesson 3 The Rise of Napoleon and the Napoleonic Wars ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What causes revolution? How does revolution change society? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary capable having or showing ability
Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos Annotation
 Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos Annotation Name Directions: A. Read the entire article, CIRCLE words you don t know, mark a + in the margin next to paragraphs you understand and a next to paragraphs you don t
Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos Annotation Name Directions: A. Read the entire article, CIRCLE words you don t know, mark a + in the margin next to paragraphs you understand and a next to paragraphs you don t
Warm up: We have discussed the Chinese role in constructing the railroads in the west. How do you think that the Chinese were treated by other
 Warm up: We have discussed the Chinese role in constructing the railroads in the west. How do you think that the Chinese were treated by other groups? SSUSH14 Explain America s evolving relationship with
Warm up: We have discussed the Chinese role in constructing the railroads in the west. How do you think that the Chinese were treated by other groups? SSUSH14 Explain America s evolving relationship with
New Global Patterns. Imperialism II
 New Global Patterns Imperialism II 1800-1914 本は近代化 Japan Modernizes Japan isolated itself from the world from 1600-1853 Japan s reaction to western imperialism was to become imperialist herself. Japan
New Global Patterns Imperialism II 1800-1914 本は近代化 Japan Modernizes Japan isolated itself from the world from 1600-1853 Japan s reaction to western imperialism was to become imperialist herself. Japan
gave stock to influential politicians. And the Whiskey Ring in the Grant administration united Republicans officials, tax collectors, and whiskey
 The period between 1870 and 1890 is the only time in American history described in a derogatory way as the Gilded Age, after the title of an 1873 novel co-authored by Mark Twain. Gilded means covered with
The period between 1870 and 1890 is the only time in American history described in a derogatory way as the Gilded Age, after the title of an 1873 novel co-authored by Mark Twain. Gilded means covered with
How Shall We Govern Ourselves?
 How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
Japan s Pacific Campaign Close Read
 Japan s Pacific Campaign Close Read Standards Alignment Text with Close Read instructions for students Intended to be the initial read in which students annotate the text as they read. Students may want
Japan s Pacific Campaign Close Read Standards Alignment Text with Close Read instructions for students Intended to be the initial read in which students annotate the text as they read. Students may want
Unpacking Democratic Transitions: The Case of Philippines
 Unpacking Democratic Transitions 1 Unpacking Democratic Transitions: The Case of Philippines This project was conducted under the guidance of Western University s Leadership and Democracy Lab and is the
Unpacking Democratic Transitions 1 Unpacking Democratic Transitions: The Case of Philippines This project was conducted under the guidance of Western University s Leadership and Democracy Lab and is the
Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power,
 Name: Class Period: Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1865-1917 Amsco Chapter 20 Reading Assignment: Ch. 21 AMSCO Purpose: This guide is intended to provide a space for you to record
Name: Class Period: Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1865-1917 Amsco Chapter 20 Reading Assignment: Ch. 21 AMSCO Purpose: This guide is intended to provide a space for you to record
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 2 China After World War II ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does conflict influence political relationships? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary final the last in a series, process, or progress source a
Lesson 2 China After World War II ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does conflict influence political relationships? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary final the last in a series, process, or progress source a
Growing Pains in the Americas THE EUROPEAN MOMENT ( )
 Growing Pains in the Americas THE EUROPEAN MOMENT (1750 1900) Or we could call today s notes: The history of the Western Hemisphere in the 19 th century as they face problems keeping order and confront
Growing Pains in the Americas THE EUROPEAN MOMENT (1750 1900) Or we could call today s notes: The history of the Western Hemisphere in the 19 th century as they face problems keeping order and confront
The Road to War in the Pacific
 The Road to War in the Pacific What is an Expansionist Power? A state that takes over countries & keeps extending territory whenever & wherever it can. Imperialism - the policy of extending the power and
The Road to War in the Pacific What is an Expansionist Power? A state that takes over countries & keeps extending territory whenever & wherever it can. Imperialism - the policy of extending the power and
The New Nation Faces Challenges
 SECTION 2 hat You ill Learn... Main Ideas 1. The United States had difficulties with other nations. 2. Internal economic problems plagued the new nation. 3. Shays s Rebellion pointed out weaknesses in
SECTION 2 hat You ill Learn... Main Ideas 1. The United States had difficulties with other nations. 2. Internal economic problems plagued the new nation. 3. Shays s Rebellion pointed out weaknesses in
STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015
 STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015 AGE OF IMPERIALISM! (1900s- 1914) MILITARY Alfred T. Mahan argued for a strong NAVY in his book Influence of Sea Power Upon History Easier
STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015 AGE OF IMPERIALISM! (1900s- 1914) MILITARY Alfred T. Mahan argued for a strong NAVY in his book Influence of Sea Power Upon History Easier
Today s Topics. Quiz 1 Populism & The Segregated South The U.S. as a World Power
 Today s Topics Quiz 1 Populism & The Segregated South The U.S. as a World Power 1 The Transformation of the West 2 The Transformation of the West Remaking Indian Life Forced assimilation The Dawes Act
Today s Topics Quiz 1 Populism & The Segregated South The U.S. as a World Power 1 The Transformation of the West 2 The Transformation of the West Remaking Indian Life Forced assimilation The Dawes Act
A Place of Three Cultures
 A Place of Three Cultures A Place of Three Cultures A broad square in Mexico City stands as a symbol of the complexity of Mexican culture. The Plaza de lastresculturas The Three Cultures is located on
A Place of Three Cultures A Place of Three Cultures A broad square in Mexico City stands as a symbol of the complexity of Mexican culture. The Plaza de lastresculturas The Three Cultures is located on
19 th Amendment. 16 th Amendment 17 th Amendment 18 TH Amendment established direct election of United States Senators by popular vote
 16 th Amendment 17 th Amendment 18 TH Amendment 1913-gave Congress the power to tax personal income 1913- established direct election of United States Senators by popular vote 1919- banned the sale of
16 th Amendment 17 th Amendment 18 TH Amendment 1913-gave Congress the power to tax personal income 1913- established direct election of United States Senators by popular vote 1919- banned the sale of
Welcome to History 12 Political and Social History of the U.S. II From 1876 to the present Prof. Valadez
 Welcome to History 12 Political and Social History of the U.S. II From 1876 to the present Prof. Valadez 1 Topics The U.S. as a World Power Progressive Era 2 Becoming a World Power The New Imperialism
Welcome to History 12 Political and Social History of the U.S. II From 1876 to the present Prof. Valadez 1 Topics The U.S. as a World Power Progressive Era 2 Becoming a World Power The New Imperialism
Name: Class: Date: Life During the Cold War: Reading Essentials and Study Guide: Lesson 3
 Reading Essentials and Study Guide Life During the Cold War Lesson 3 The Asian Rim ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How does war result in change? What challenges may countries face as a result of war? Reading HELPDESK
Reading Essentials and Study Guide Life During the Cold War Lesson 3 The Asian Rim ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How does war result in change? What challenges may countries face as a result of war? Reading HELPDESK
World History (Survey) Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present
 World History (Survey) Chapter 33: Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present Section 1: Two Superpowers Face Off The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February
World History (Survey) Chapter 33: Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present Section 1: Two Superpowers Face Off The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February
Chapter 18. American Claims an Empire
 Chapter 18 American Claims an Empire Section 1: Imperialism and American Imperialism 1880s U.S. interest in building an Empire builds Imperialism = Stronger : Economic, political, or military control Europeans
Chapter 18 American Claims an Empire Section 1: Imperialism and American Imperialism 1880s U.S. interest in building an Empire builds Imperialism = Stronger : Economic, political, or military control Europeans
WORLD HISTORY WORLD WAR II
 WORLD HISTORY WORLD WAR II BOARD QUESTIONS 1) WHO WAS THE LEADER OF GERMANY IN THE 1930 S? 2) WHO WAS THE LEADER OF THE SOVIET UNION DURING WWII? 3) LIST THE FIRST THREE STEPS OF HITLER S PLAN TO DOMINATE
WORLD HISTORY WORLD WAR II BOARD QUESTIONS 1) WHO WAS THE LEADER OF GERMANY IN THE 1930 S? 2) WHO WAS THE LEADER OF THE SOVIET UNION DURING WWII? 3) LIST THE FIRST THREE STEPS OF HITLER S PLAN TO DOMINATE
The Spanish American-War 4 Causes of the War: Important Events 1/7/2018. Effects of the Spanish American War
 The Spanish American-War 4 Causes of the War: Sugar (Economic) Spanish Cruelties (Humanitarian) The Sinking of the USS Maine (Self-Defense/National Pride) Spanish Brutalities and Yellow Journalism (Political
The Spanish American-War 4 Causes of the War: Sugar (Economic) Spanish Cruelties (Humanitarian) The Sinking of the USS Maine (Self-Defense/National Pride) Spanish Brutalities and Yellow Journalism (Political
Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism ( )
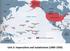 Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism (1890-1930) What is an empire? Is imperialism the same as colonization? Why would the U.S. get involved in this practice? What is the difference between acquiring and
Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism (1890-1930) What is an empire? Is imperialism the same as colonization? Why would the U.S. get involved in this practice? What is the difference between acquiring and
Unit 6 Review Sheets Foreign Policies: Imperialism Isolationism (Spanish-American War Great Depression)
 Speak softly & carry a big stick; you will go far -Theodore Roosevelt Work or fight -National War Labor Board Unit 6 Review Sheets Foreign Policies: Imperialism Isolationism (Spanish-American War Great
Speak softly & carry a big stick; you will go far -Theodore Roosevelt Work or fight -National War Labor Board Unit 6 Review Sheets Foreign Policies: Imperialism Isolationism (Spanish-American War Great
Warm ups *About how much of the Cambodian population was killed by the Khmer Rouge? *How were the Khmer Rouge finally stopped?
 Warm ups 5.10.2017 *About how much of the Cambodian population was killed by the Khmer Rouge? *How were the Khmer Rouge finally stopped? Lesson Objective: *describe how physical geography affects the people
Warm ups 5.10.2017 *About how much of the Cambodian population was killed by the Khmer Rouge? *How were the Khmer Rouge finally stopped? Lesson Objective: *describe how physical geography affects the people
SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR VOCAB
 SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR VOCAB 1. War of 1812 2. Monroe Doctrine 3. Mexican War 4. Yellow journalism 5. USS Maine 6. Rough Riders 7. San Juan Hill 8. Anti-Imperialist League 9. Platt Amendment 10.Diplomacy
SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR VOCAB 1. War of 1812 2. Monroe Doctrine 3. Mexican War 4. Yellow journalism 5. USS Maine 6. Rough Riders 7. San Juan Hill 8. Anti-Imperialist League 9. Platt Amendment 10.Diplomacy
Nation Building and economic transformation in the americas,
 Chapter 23 Nation Building and economic transformation in the americas, 1800-1890 BEFORE YOU BEGIN Most students have significantly more knowledge of U.S. history than other regions in the Americas. This
Chapter 23 Nation Building and economic transformation in the americas, 1800-1890 BEFORE YOU BEGIN Most students have significantly more knowledge of U.S. history than other regions in the Americas. This
Chapter 12: Transformations Around the Globe,
 Chapter 12: Transformations Around the Globe, 1800 1914 China and Japan respond differently to the European powers. The United States influences Latin America, and Mexico undergoes a revolution. Theodore
Chapter 12: Transformations Around the Globe, 1800 1914 China and Japan respond differently to the European powers. The United States influences Latin America, and Mexico undergoes a revolution. Theodore
East Asia in the Postwar Settlements
 Chapter 34 " Rebirth and Revolution: Nation-building in East Asia and the Pacific Rim East Asia in the Postwar Settlements Korea was divided between a Russian zone of occupation in the north and an American
Chapter 34 " Rebirth and Revolution: Nation-building in East Asia and the Pacific Rim East Asia in the Postwar Settlements Korea was divided between a Russian zone of occupation in the north and an American
Name Class Date. The French Revolution and Napoleon Section 3
 Name Class Date Section 3 MAIN IDEA Napoleon Bonaparte rose through military ranks to become emperor over France and much of Europe. Key Terms and People Napoleon Bonaparte ambitious military leader who
Name Class Date Section 3 MAIN IDEA Napoleon Bonaparte rose through military ranks to become emperor over France and much of Europe. Key Terms and People Napoleon Bonaparte ambitious military leader who
Imperialism. Policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker territories
 Imperialism Policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker territories Global Competition European nations had been establishing colonies for years Asia
Imperialism Policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker territories Global Competition European nations had been establishing colonies for years Asia
General Overview of Communism & the Russian Revolution. AP World History Chapter 27b The Rise and Fall of World Communism (1917 Present)
 General Overview of Communism & the Russian Revolution AP World History Chapter 27b The Rise and Fall of World Communism (1917 Present) Communism: A General Overview Socialism = the belief that the economy
General Overview of Communism & the Russian Revolution AP World History Chapter 27b The Rise and Fall of World Communism (1917 Present) Communism: A General Overview Socialism = the belief that the economy
Events Leading to the American Revolution
 Events Leading to the American Revolution Colonization Main Reason was for Mercantilism: Making money for the mother country Joint-stock company: investors share ownership and profits Charters: grants
Events Leading to the American Revolution Colonization Main Reason was for Mercantilism: Making money for the mother country Joint-stock company: investors share ownership and profits Charters: grants
10 year civil war ( ), U.S. concerns owned 20% of the nation s territory. individual rights), and also influenced by the outbreak of WWI
 MEXICAN REVOLUTION 10 year civil war (1910-1920), U.S. concerns owned 20% of the nation s territory. Caused primarily by internal forces (growing nationalist resentment and individual rights), and also
MEXICAN REVOLUTION 10 year civil war (1910-1920), U.S. concerns owned 20% of the nation s territory. Caused primarily by internal forces (growing nationalist resentment and individual rights), and also
Chapter 16: Attempts at Liberty
 Chapter 16: Attempts at Liberty 18 th Century Few people enjoyed such rights as, and the pursuit of ; and absolutism was the order of the day. The desire for personal and political liberty prompted a series
Chapter 16: Attempts at Liberty 18 th Century Few people enjoyed such rights as, and the pursuit of ; and absolutism was the order of the day. The desire for personal and political liberty prompted a series
Unit 7. Historical Background for Southern and Eastern Asia
 Unit 7 Historical Background for Southern and Eastern Asia What You Will Learn Historical events in Southern and Eastern Asia have shaped the governments, nations, economies, and culture through conflict
Unit 7 Historical Background for Southern and Eastern Asia What You Will Learn Historical events in Southern and Eastern Asia have shaped the governments, nations, economies, and culture through conflict
Tragedy of Small Power Politics: Duterte, Philippines & the South China Sea Disputes. Richard J. Heydarian
 Tragedy of Small Power Politics: Duterte, Philippines & the South China Sea Disputes Richard J. Heydarian Outline Anatomy of PH foreign policy-formulation Why PH filed the arbitration case How PH responded
Tragedy of Small Power Politics: Duterte, Philippines & the South China Sea Disputes Richard J. Heydarian Outline Anatomy of PH foreign policy-formulation Why PH filed the arbitration case How PH responded
Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914?
 Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914? From 1890 to 1914, the United States expanded its role in world affairs and gained new overseas colonies Class Activity:
Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914? From 1890 to 1914, the United States expanded its role in world affairs and gained new overseas colonies Class Activity:
Becoming a World Power Chapter 17
 Becoming a World Power 1872-1912 Chapter 17 imperialism Imperialism Why? New Markets Sen. Beverage Anglo-Saxon World Kipling Christianity Josiah Strong The work which the English race began when it
Becoming a World Power 1872-1912 Chapter 17 imperialism Imperialism Why? New Markets Sen. Beverage Anglo-Saxon World Kipling Christianity Josiah Strong The work which the English race began when it
Neutrality under Jefferson and Madison
 Neutrality under Jefferson and Madison Thomas Jefferson had no problem defeating his Federalist opponent in 1804. Obtaining the Louisiana Purchase and accomplishing a reduction of the national debt assured
Neutrality under Jefferson and Madison Thomas Jefferson had no problem defeating his Federalist opponent in 1804. Obtaining the Louisiana Purchase and accomplishing a reduction of the national debt assured
Democratization Introduction and waves
 Democratization Introduction and University College Dublin 18 January 2011 Outline Democracies over time Period Democracy Collapse 1828-1926 33 0 1922-1942 0 22 1943-1962 40 0 1958-1975 0 22 1974-1990
Democratization Introduction and University College Dublin 18 January 2011 Outline Democracies over time Period Democracy Collapse 1828-1926 33 0 1922-1942 0 22 1943-1962 40 0 1958-1975 0 22 1974-1990
Content Statement/Learning Goal:
 Ch 6-3 Questions Content Statement/Learning Goal: Explain how Enlightenment ideas influenced the American Revolution, French Revolution and Latin American wars for Independence. Napoleon Bonaparte Coup
Ch 6-3 Questions Content Statement/Learning Goal: Explain how Enlightenment ideas influenced the American Revolution, French Revolution and Latin American wars for Independence. Napoleon Bonaparte Coup
