SymbiMUN Model United Nations Conference. Historic Security Council Study Guide. Agenda:
|
|
|
- Magnus Edgar Benson
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SymbiMUN 2017 Model United Nations Conference Historic Security Council Study Guide Agenda: Steps to facilitate an immediate end to the Vietnam Conflict
2 Table of Contents Sr. No. TOPIC 1 Letter from the Executive Board 2 The Vietnam War: An Introduction 3 A Brief Outline 4 Main Parties involved in the Conflict 5 Timeline of the Conflict 7 Questions a Resolution Must Answer (QARMA) 8 References and Further Reading
3 1. Letter from the Executive Board Dear Delegates, It gives me immense pleasure to introduce myself as the Chairperson of the Historic Security Council for Symbiosis MUN Just being a part of it is a big honour for me and I expect the highest level of debate to take place in this conference. In my belief, a Historic Security Council is a wonderful simulation which gives us an opportunity to study the past in the present and then go back into the past and change it. It is a retrospective decision making process which requires unconventional thinking abilities in addition to a good understanding of the actual past scenario. This in my belief is what distinguishes a great MUNner from a good one. As far as the topic area is concerned- The Vietnam Conflict, I believe that there is a lot of loss to life and property that could have been averted if some decisions were taken differently in the period of the war. It is my belief that the delegates will be able to come up with comprehensive resolutions after having discussed the agenda in extensively. As the President of the Historic Security Council, my role is to moderate debate and to ensure that delegates maintain the flow of discussion. I wish all the delegates the best of luck for the conference. I hope that all of you come extremely well prepared for the conference with ample research so that we can have constructive discussion and deliberations over the period of three days. I m looking forward to seeing all of you. Regards, Executive Board, UNHSC, SymbiMUN 2017
4 2. The Vietnam War-An Introduction The Vietnam war is considered as one of the most morally ambiguous, lengthy and futile wars in World history. Practically a proxy war between the United States of America and the erstwhile Soviet Union in the midst of the Cold War, the Vietnam War was one of the most bloody wars too have occurred causing the death of more than 3.5 million people in all. Although, a war that was technically fought between North Vietnam and South Vietnam, it was actually an indirect war between the United Stated States of America and the USSR who supported the South Vietnamese and North Vietnamese respectively. It also included a lightly armed South Vietnamese group called the Viet-kong or the National Liberation Front (NLF) which specialised in guerrilla warfare and were against the United States of America and the allied forces. The United States of America during that period of history during the early 1950s were trying to prevent the spread of communism and were propagating democracy. At the same point in time, the USSR was trying to spread communism across different parts of the world. Both countries were looking towards forming their own powerful blocs and spread their strong influence across the world. Once North Vietnam became a supporter and follower of communism under USSR influence, the United States of America intervened immediately to prevent the further spread of communism across Vietnam and the Middle East. The war lasted from with over 55,000 US soldiers losing their lives, more, 1.1 million dead North Vietnamese soldiers, South Vietnamese soldiers and about half a million people from Vietnam and Laos also lost their lives. Ultimately, the US troops were withdrawn in August, 1973 as result of the US Congress passing the Case-Church amendment. The war ultimately ended in April, 1975 when the Vietnam People s Army captured Saigon. North and South Vietnam were re-unified after this. There were steps that could have been taken differently by the UNSC that could have further prevented such losses.
5 3. The Historic Security Council at Symbiosis MUN 2017-A Brief Outline Dear Delegates, As mentioned earlier, the Historic Security Council is a retrospective decision making process and requires a lot of good research on the decisions and their repercussions. It is quintessential to avoid repetition while at the same time not changing your country policy to such a great extent that it has little or no semblance with the actual situation prevalent during that time in history. Hence, striking the correct balance is of utmost significance. In relation to how we shall be moving forward with reference to the agenda and committee at Symbiosis MUN 2017, I d like to firstly state that quite contrary to the name of the agenda i.e. The Vietnam Conflict, the HSC in this case is not being convened at the time of the full blown Vietnam War. In the present situation, the situation in Vietnam is that of an armed conflict with rising tensions among the different parties involved in it. The HSC is being convened in November, The situation as of the said date might be considered analogues to a situation that might come into existence between North and South Sudan in the future considering the present day issues of the Janjaweed, oil among other things. There have been various act of aggression by the North Vietnamese military, the South Vietnamese military, the United States of America and the Viet Kong which is just beginning to become a more aggressive guerrilla outfit. At this juncture, Operation Rolling Thunder or a similar attack was already very imminent. Furthermore, with the assassination of Diem and his brother, South Vietnam was in complete disarray. The Viet Kong were taking advantage of this to mobilise the masses. The United Nations Security Council is convened in the midst of such rising conflict, imminent war and problems faced by neighbouring countries like Cambodia and Laos.
6 4. Main Parties Involved in the Conflict This is a brief note on the various main parties involved in the conflict at the point in time when the UNSC is being convened: i. United States of America and South Vietnam The United States of America believes that it is of monumental importance that the seeds of communism do not spread across South East Asia. The fact that the Communism wave had reached North Vietnam which was deeply influenced by the Communist ideologies of Ho Chi Min among other was looked upon as a bad precedent. The USA has increased its military presence in South Vietnam where it trains the South Vietnamese groups. There have been sporadic acts of aggression committed by the United States of America against the North Vietnamese military and the Viet Kong. The monumental Gulf of Tonkin resolution has been passed in the U.S of A which provides the extra-constitutional powers to President Lyndon Johnson to take all necessary steps to thwart any further attacks on the US forces in Vietnam. This is after two US Destroyers have been attacked and destroyed by the North Vietnamese forces in August, The corrupt South Vietnamese regime under President Diem lost a lot of support among the people before his assassination. After making an attempt to strike a peace deal with Ho Chi Minh of North Vietnam, Diem had further lost support of the United States of America. ii. North Vietnam and the USSR North Vietnam being a communist regime is supported by the USSR which is also looking at the entire situation as proxy war against democracy and the United States of America. The Politburo continues to provide military aid to the guerrilla forces of the Viet Kong to wage further armed aggression against the South Vietnamese regime of Diem and the United States of America. North Vietnam under Ho Chi Minh has already developed a lot of popular support among the people of the region and unlike South Vietnam is much better mobilised for the imminent war like situation with support from the Viet Kong as well.
7 The North Vietnamese forces had already been quite successful in the armed conflict against the French forces which have completely withdrawn from the region. As a result of greater numbers and stronger leadership, the forces generally make use of the ploy to attack regions if South Vietnam in large numbers. There is also an imminent threat of an imminent aerial attack being carried out by the US forces after various act of aggression by them among which the most significant one is the attack on the US Destroyer by the North Vietnamese patrol boats. iii. Viet Kong (National Liberation Front) The Viet Kong are basically a guerrilla outfit in South Vietnam which basically comprises of South Vietnamese who are totally against the oppressive and corrupt Diem regime and the United States of America for supporting it. A well organised outfit that is taking full advantage of the popular support against the Diem regime, they are able to mobilise section of the South Vietnamese masses against the United States of America and the Diem regime. They are successful in carrying out surprise guerrilla style attacks in various regions of South Vietnam and taking control of them. Receiving support from the forces of North Vietnam and proxy support from the USSR, they are slowly and steadily becoming a major threat to the US of A and the South Vietnamese regime which is also in disarray at the given juncture. iv. Cambodia and Laos Cambodia and Laos are the neighbouring nations that are being affected as a result of the entire conflict in Vietnam. The South Vietnamese forces are penetrating regions of these two countries and there has been loss of life and property as well. It is important for the UNSC to take steps to ensure that these neighbouring nations are not affected by the situation prevalent in Vietnam.
8 5. Timeline of the War (Up to October, 1967) The timeline presented below gives a brief description of the various events that took place during the Vietnam War up to October The Historic Security Council meet is dated to convene on November 2, This is the period after the attack on the two US destroyers by the North Vietnam Army Communist activist Ho Chi Minh secretly returns to Vietnam after 30 years in exile and organizes a nationalist organization known as the Viet Minh (Vietnam Independence League). After Japanese troops occupy Vietnam during World War II, the U.S. military intelligence agency Office of Strategic Services (OSS) allies with Ho Chi Minh and his Viet Minh guerrillas to harass Japanese troops in the jungles and to help rescue downed American pilots Amid rumors of a possible American invasion, Japanese oust the French colonial government which had been operating independently and seize control of Vietnam, installing Bao Dai as their puppet ruler. Ho Chi Minh garners massive support during the famines that strike the region. To disarm the Japanese, the Allies divide the country in half at the 16th parallel. Vietnam, Laos and Cambodia become French colonies again. Ho Chi Minh's guerrillas occupy Hanoi and proclaim a provisional government. He declares independence and also declares himself president of the Democratic Republic of Vietnam and pursues American recognition but is repeatedly ignored by President Harry Truman Ho Chi Minh agrees to permit French troops to return to Hanoi temporarily in exchange for French recognition of his Democratic Republic of Vietnam. Chinese troops then depart. Ho Chi Minh spends 4 months in France trying to negotiate recognition for full independence but fails in his attempts.
9 In a major affront to Ho Chi Minh, the French high commissioner for Indochina proclaims a separatist French-controlled government for South Vietnam (Republic of Chochinchina). After a series of violent clashes with Viet Minh, French forces bombard Haiphong harbor and occupy Hanoi, forcing Ho Chi Minh and his Viet Minh forces to retreat into the jungle. The Vietminh launch a guerrilla attack against the French The French install Bao Dai as puppet head of state in South Vietnam and establish the (South) Vietnamese National Army The People's Republic of China and the Soviet Union recognize Ho Chi Minh's Democratic Republic of Vietnam. China then begins sending military advisors and modern weapons to the Viet Minh. The United States and Britain recognize Bao Dai's French-controlled South Vietnam government. Viet Minh begin an offensive against French outposts in North Vietnam near the Chinese border. United States military involvement in Vietnam begins as President Harry Truman authorizes $15 million in military aid to the French. The U.S. establishes a Military Assistance Advisory Group (MAAG) in Saigon to aid the French Army The Vietminh under Gen Giap and the French forces under Gen De Lattre continue warfare across regions of Vietnam. France urges the United States of America to offer more military aid. Gen Giap is replaced by Gen Raoul Salian in course of time as he is ailing from cancer. The casualties of the Viet Minh and the French armies continue to rise.
10 1953 The United States of America increase military aid to the French troops in Vietnam. They come up with the famous Domino theory which states that if one nation falls to communism, then the others in the region will also be affected by it one at a time. Hence, they claim it is their duty to the world to prevent this from happening. The Viet Minh and the French troops continue warfare May 7, The French suffer a decisive defeat at the Battle of Dien Bien Phu. July 21, The Geneva Accords creates a cease-fire for the peaceful withdrawal of the French from Vietnam and provides a temporary boundary between North and South Vietnam at the 17th parallel In January, the first direct shipment of U.S. military aid to Saigon arrives. The U.S. also offers to train the fledgling South Vietnam Army. Ho Chi Minh s regime receives and accepts Soviet aid. October 23, Bao Dai is ousted from power, defeated by Prime Minister Diem in a U.S.-backed plebiscite which was rigged. Diem is advised on consolidating power by U.S. Air Force Col. Edward G. Lansdale, who is attached to the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA). October 26, The Republic of South Vietnam is proclaimed with Diem as its first president. In America, President Eisenhower pledges his support for the new government and offers military aid In January 1956, Diem launches a brutal crackdown against Viet Minh suspects in the countryside. Those arrested are denied counsel and hauled before
11 "security committees" with many suspects tortured or executed under the guise of 'shot while attempting escape.' The French withdraw completely from Vietnam The Soviet Union proposes permanent division of Vietnam into North and South, with the two nations admitted separately to the United Nations. The United States of America however, refuses to recognise the communist regime of Ho Chi Minh in North Vietnam The armed revolution begins as Ho Chi Minh declares a People's War to unite all of Vietnam under his leadership. His Politburo now orders a changeover to an all-out military struggle. United Nations Security Council Resolution 132, adopted on September 7, 1959, decides to appoint a sub-committee consisting of Argentina, Italy, Japan and Tunisia, and instructed it to examine statements made before the Council concerning Laos and to receive further statements and documents, and make inquiries and report to the Council as soon as possible. It was the only resolution adopted by the Security Council in July 8, Two U.S. military advisors, Maj. Dale Buis and Sgt. Chester Ovnand, are killed by Viet Minh guerrillas at Bien Hoa, South Vietnam. They are the first American deaths in the region Corruption increases in the President Diem run South Vietnamese regime which is backed by the USA. They begin to become unpopular among the people because of unpopular and unfair trials, torture and executions of people. Thousands who fear arrest flee to North Vietnam. The National Liberation Front is also called the Viet-kong is established in South Vietnam.
12 1961 The Soviet Union further pledges its support to the Ho Chi Minh regime. John F Kennedy becomes President of the United States of America. US Vice President Lyndon B. Johnson visits President Diem in South Vietnam and hails the embattled leader as the 'Winston Churchill of Asia.' The US sends troops to South Vietnam to train Vietnamese soldiers. They are called the Green Berets. By December 1961, the Viet Cong guerrillas control much of the countryside in South Vietnam and frequently ambush South Vietnamese troops February 6, MACV, the U.S. Military Assistance Command for Vietnam, is formed. It replaces MAAG-Vietnam, the Military Assistance Advisory Group which had been established in The Declaration on the Neutrality of Laos signed in Geneva by the U.S. and 13 other nations, prohibits U.S. invasion of portions of the Ho Chi Minh trail inside eastern Laos The Viet Cong are victorious in the Battle of Ap Bac as 350 Viet Cong fighters defeat a large force of American-equipped South Vietnamese troops attempting to seize a radio transmitter. Political pressure mounts on the Kennedy administration to disassociate itself from Diem's repressive, family-run government. Diem responds to the deepening unrest by imposing martial law. US Ambassador Lodge reports a coup is "imminent." South Vietnamese President Ngo Dinh Diem and his brother Nho are executed during a coup. Saigon celebrates the downfall of Diem's regime. Viet Cong use the unstable political situation to increase their hold over the rural population of South Vietnam to nearly 40 percent.
13 President John F. Kennedy is assassinated in Dallas. Lyndon B. Johnson is sworn in as the 36th U.S. President. By year's end, there are 16,300 American military advisors in South Vietnam which received $500 million in U.S. aid during General Minh is ousted from power in a bloodless coup led by General Nguyen Khanh who becomes the new leader of South Vietnam. Secret U.S.-backed bombing raids begin against the Ho Chi Minh trail inside Laos, conducted by mercenaries flying old American fighter planes. The cost to America of maintaining South Vietnam's army and managing the overall conflict in Vietnam now rises to two million dollars per day. The U.S. National Security Council recommends the bombing of North Vietnam. President Johnson approves only the planning phase by the Pentagon. President Johnson's aides begin work on a Congressional resolution supporting the President's war policy in Vietnam. The resolution is shelved temporarily due to lack of support in the Senate, but will later be used as the basis of the Gulf of Tonkin resolution. Summer - As 56,000 Viet Cong spread their successful guerrilla war throughout South Vietnam, they are reinforced by North Vietnamese Army (NVA) regulars pouring in via the Ho Chi Minh trail. Responding to this escalation, President Johnson approves Operation Plan 34A, CIA-run covert operations using South Vietnamese commandos in speed boats to harass radar sites along the coastline of North Vietnam. The raids are supported by U.S. Navy warships in the Gulf of Tonkin including the destroyer U.S.S. Maddox which conducts electronic surveillance to pinpoint the radar locations. General Maxwell D. Taylor, chairman of the Joint Chiefs of Staff, is appointed by President Johnson as the new U.S. ambassador to South Vietnam.
14 President Johnson also appoints Lt. Gen William C. Westmoreland to be the new U.S. military commander in Vietnam. June 4, United Nations Security Council Resolution 189 is adopted unanimously and deplores an incident caused by the penetration of units of the Republic of Vietnam in to Cambodia and requests compensation for the Cambodians. The resolution then requests that all States and authorities recognize and respect Cambodia's neutrality and territorial integrity, deciding to send 3 of its members to the places the most recent incidents had occurred to report back to the Council in 45 days with suggestions. Cambodia had previously complained of acts of aggression and intrusions by South Vietnamese and American troops into its territory. On July 24, 1964, the mission sent by the Council reported that the situation at the frontier remained tense and a solution had yet to be found. July 31, In the Gulf of Tonkin, as part of Operation Plan 34A, South Vietnamese commandos in unmarked speed boats raid two North Vietnamese military bases located on islands just off the coast. In the vicinity is the destroyer U.S.S. Maddox. August 2, Three North Vietnamese patrol boats attack the American destroyer U.S.S. Maddox in the Gulf of Tonkin ten miles off the coast of North Vietnam. They fire three torpedoes and machine-guns, but only a single machine-gun round actually strikes the Maddox with no causalities. U.S. Navy fighters from the carrier Ticonderoga, led by Commander James Stockdale, attack the patrol boats, sinking one and damaging the other two. At the White House, it is Sunday morning (twelve hours behind Vietnam time). President Johnson, reacting cautiously to reports of the incident, decides against retaliation. Instead, he sends a diplomatic message to Hanoi warning of "grave consequences" from any further "unprovoked" attacks. Johnson then orders the Maddox to resume operations in the Gulf of Tonkin in the same vicinity where the attack had occurred. Meanwhile, the Joints Chiefs of Staff put U.S. combat troops on alert and also select targets in North Vietnam for a possible bombing raid, should the need arise. August 3, The Maddox, joined by a second destroyer U.S.S. C. Turner Joy begin a series of vigorous zigzags in the Gulf of Tonkin sailing to within eight miles of North Vietnam's coast, while at the same time, South
15 Vietnamese commandos in speed boats harass North Vietnamese defenses along the coastline. By nightfall, thunderstorms roll in, affecting the accuracy of electronic instruments on the destroyers. Crew members reading their instruments believe they have come under torpedo attack from North Vietnamese patrol boats. Both destroyers open fire on numerous apparent targets but there are no actual sightings of any attacking boats. August 4, Although immediate doubts arise concerning the validity of the second attack, the Joint Chiefs of Staff strongly recommend a retaliatory bombing raid against North Vietnam. At the White House, President Johnson decides to retaliate. Thus, the first bombing of North Vietnam by the United States occurs as oil facilities and naval targets are attacked without warning by 64 U.S. Navy fighter bombers. Two Navy jets are shot down during the bombing raids, resulting in the first American prisoner of war, Lt. Everett Alvarez of San Jose, California, who is taken to an internment center in Hanoi. August 7, In response to the two incidents involving the Maddox and Turner Joy, the U.S. Congress, at the behest of President Johnson, overwhelmingly passes the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution put forward by the White House allowing the President "to take all necessary steps, including the use of armed force" to prevent further attacks against U.S. forces. The Resolution, passed unanimously in the House and 98-2 in the Senate, grants enormous power to President Johnson to wage an undeclared war in Vietnam from the White House. Furthermore, the United States of America threatens to carry out aerial campaigns in the near future. August 21, In Saigon, students and Buddhist militants begin a series of escalating protests against General Khanh's military regime. As a result, Khanh resigns as sole leader in favor of a triumvirate that includes himself, Gen. Minh and Gen. Khiem. The streets of Saigon soon disintegrate into chaos and mob violence amid the government's gross instability. September 2, 1964 The United Nations Security Council is convened in order to discuss the escalating tensions in Vietnam and solutions to solve the conflict which does not only affect Vietnam but also Cambodia and Laos.
16 November 1964: Between the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution and the U.S. presidential election in November 1964, the situation in Vietnam had changed for the worse. In the countryside even the best ARVN units seemed incapable of defeating the main forces of the Viet Cong. The communists were now deliberately targeting U.S. military personnel and bases, beginning with a mortar attack on the U.S. air base at Bien Hoa near Saigon in November. Many of US President Johnson s advisers now began to argue for some sort of retaliation against the North. Air attacks against North Vietnam, they argued, would boost the morale of the shaky South Vietnamese and reassure them of continuing American commitment. February 1965: In mid-february, without public announcement, the United States began a campaign of sustained air strikes against the North that were code-named Rolling Thunder. The bombing campaign followed more frequent attacks. It was closely directed from the White House in order to avoid provoking the Chinese or Soviets through such actions as attacking ports where Soviet ships might be docked or hitting targets near the Chinese border. Yet it was soon apparent that the bombing would have little direct impact on the struggle in South Vietnam, where the communists appeared to be gaining ground inexorably. July 1965: US President Johnson took the final steps that would commit the United States to full-scale war in Vietnam: he authorized the dispatch of 100,000 troops immediately. December 1966: 100,000 more US soldiers were deployed in Vietnam. By the end of 1966, the United States had dropped more bombs on North Vietnam than it had dropped on Japan during World War II and more than it had dropped during the entire Korean War. Yet the bombing seemed to have little impact on the communists ability to carry on the war. North Vietnam was primarily an agricultural country with few industries to destroy. Many of the necessities of Hanoi s war effort came directly from China and the Soviet Union, which competed with each other to demonstrate support for Ho Chi Minh s heroic war against U.S. imperialism. The Soviets provided an estimated 1.8 billion rubles in military and economic aid and sent 3,000 military advisers and technicians along with sophisticated weapons to the North. China spent an estimated two billion dollars in assisting Hanoi; at the height of its effort, it had more than 300,000 engineering, medical, and anti-
17 aircraft artillery troops in the Democratic Republic of Vietnam. Even when bombing knocked out more than 80 percent of the North s petroleum-storage facilities during the summer of 1966, the CIA reported no discernible shortages of petroleum or disruption of transportation. While the air raids continued, North Vietnam progressively strengthened its air defenses with the help of the latest radars, anti-aircraft guns, missiles, and modern jet fighters supplied by the Soviets and Chinese. By the end of 1966 the United States had already lost almost 500 aircraft and hundreds of air crewmen killed or held as prisoners of war. October 1967: By October 1967 growing numbers of Americans were becoming increasingly dissatisfied with the war. Some, especially students, intellectuals, academics, and clergymen, opposed the war on moral grounds, pointing out that large numbers of civilians in both the North and the South were becoming the chief victims of the war and that the United States was in reality supporting a corrupt and oppressive dictatorship in Saigon. In Hanoi the communist leadership was also becoming impatient with the progress of the war. Although pleased with their ability to hold their own against the more-numerous and better-armed Americans and their South Vietnamese allies, they were aware that the United States showed no sign of giving up its hopes of victory and indeed had continued to pour more troops into Vietnam 6. Questions a Resolution Must Answer (QARMA) i. What are the measures that can be taken to strike a peace agreement between the regimes of North and South Vietnam? ii. What are the parameters and measures that must be taken into consideration while chalking out the borders of North and South Vietnam in the outcome that peaceful reconciliation is not possible and the region must be divided? iii. Should the member nations start taking the necessary steps to recognise South Vietnam/North Vietnam as nations of the world and support their membership to the United Nations and other bodies? iv. What are the steps that must be taken to prevent the neighbouring countries from being affected by the armed conflict in Vietnam?
18 v. Should there be any military sanctions/economic sanctions imposed against nations providing military aid and support to the forces in North Vietnam/South Vietnam/Viet Kong? vi. What are the steps that can be taken to ensure that other member nations of the United Nations do not directly intervene in the armed conflict by supporting the North Vietnam/South Vietnam regimes? vii. What are the possibilities of providing financial aid to regions in North and South Vietnam that have suffered a great loss to life and property as a result of the armed conflict? viii. Is there a possibility of establishing a Transitional Federal Government under the auspices of the United Nations to ensure peace while a transitional strategy can be worked out? 7. References and Further Reading i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi.
Ch 29-1 The War Develops
 Ch 29-1 The War Develops The Main Idea Concern about the spread of communism led the United States to become increasingly violent in Vietnam. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze how the Cold war and
Ch 29-1 The War Develops The Main Idea Concern about the spread of communism led the United States to become increasingly violent in Vietnam. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze how the Cold war and
OBJECTIVES. Describe and evaluate the events that led to the war between North Vietnam and South Vietnam.
 OBJECTIVES Describe and evaluate the events that led to the war between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. Identify and explain the foreign policy of the United States at this time, and how it relates to
OBJECTIVES Describe and evaluate the events that led to the war between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. Identify and explain the foreign policy of the United States at this time, and how it relates to
Ended French rule in Indo-China
 Vietnam Review Dien Bien Phu in 1954 the main French forces were surrounded at this location in the north of Vietnam and forced to surrender. This was a turning point in that it ended the French control
Vietnam Review Dien Bien Phu in 1954 the main French forces were surrounded at this location in the north of Vietnam and forced to surrender. This was a turning point in that it ended the French control
VIETNAM WAR
 VIETNAM WAR 1955-1975 #30 http://www.military.com/video/offduty/movies/classic-forrest-gump-invietnam-war/1069387728001 PRESIDENTS DURING THE VIETNAM WAR Dwight D. Eisenhower. John F. Kennedy. Lyndon B.
VIETNAM WAR 1955-1975 #30 http://www.military.com/video/offduty/movies/classic-forrest-gump-invietnam-war/1069387728001 PRESIDENTS DURING THE VIETNAM WAR Dwight D. Eisenhower. John F. Kennedy. Lyndon B.
Chapter 19: Going To war in Vietnam
 Heading Towards War Vietnam during WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the. returned to Vietnam
Heading Towards War Vietnam during WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the. returned to Vietnam
THEMES. 1) EXPANDING DEMOCRACY: America s mission in Vietnam was to halt the spread of communism-a threat to democracy.
 THEMES 1) EXPANDING DEMOCRACY: America s mission in Vietnam was to halt the spread of communism-a threat to democracy. 2) CONSTITUTIONAL CONCERNS: Among the constitutional issues of the Vietnam War era
THEMES 1) EXPANDING DEMOCRACY: America s mission in Vietnam was to halt the spread of communism-a threat to democracy. 2) CONSTITUTIONAL CONCERNS: Among the constitutional issues of the Vietnam War era
1969 U.S. troops begin their withdrawal from Vietnam
 Vietnam War Years Timeline 1964 LBJ becomes President 1965 First major combat units arrive in Vietnam 1968 M.L.King and Robert Kennedy are assassinated 1969 U.S. troops begin their withdrawal from Vietnam
Vietnam War Years Timeline 1964 LBJ becomes President 1965 First major combat units arrive in Vietnam 1968 M.L.King and Robert Kennedy are assassinated 1969 U.S. troops begin their withdrawal from Vietnam
National Nightmare Begins: Origins of Vietnam War
 National Nightmare Begins: Origins of Vietnam War From late 1800 s until WWII (When Japan took over) France ruled Indochina (Vietnam, Laos & Cambodia). French took land from peasants & built large plantations,
National Nightmare Begins: Origins of Vietnam War From late 1800 s until WWII (When Japan took over) France ruled Indochina (Vietnam, Laos & Cambodia). French took land from peasants & built large plantations,
VIETNAM WAR
 VIETNAM WAR 1965-1972 FRENCH CONTROL French controlled Vietnam until World War II Vietnam taken by Japan Ho Chi Minh called for an independence of Vietnam Eight Year war between France and Ho Chi Minh
VIETNAM WAR 1965-1972 FRENCH CONTROL French controlled Vietnam until World War II Vietnam taken by Japan Ho Chi Minh called for an independence of Vietnam Eight Year war between France and Ho Chi Minh
Chapter 19 GOING TO WAR IN VIETNAM
 Chapter 19 GOING TO WAR IN VIETNAM VIETNAM DURING WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the Japanese.
Chapter 19 GOING TO WAR IN VIETNAM VIETNAM DURING WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the Japanese.
TRUMAN S ROLE IN VIETNAM. = America is busy!!!!!
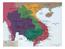 TRUMAN S ROLE IN VIETNAM Saw Vietnam as extension of Cold War - democracy v. communism! France fighting to re-gain Vietnam Truman supported France with money supplies because didn t want Something going
TRUMAN S ROLE IN VIETNAM Saw Vietnam as extension of Cold War - democracy v. communism! France fighting to re-gain Vietnam Truman supported France with money supplies because didn t want Something going
Gulf of Tonkin Resolution Lesson Plan
 Resolution Lesson Plan Central Historical Question: Was the U.S. planning to go to war with North Vietnam before the Resolution? Materials: Powerpoint Timeline Documents A-D Guiding Questions Plan of Instruction:
Resolution Lesson Plan Central Historical Question: Was the U.S. planning to go to war with North Vietnam before the Resolution? Materials: Powerpoint Timeline Documents A-D Guiding Questions Plan of Instruction:
Chapter 30-1 CN I. Early American Involvement in Vietnam (pages ) A. Although little was known about Vietnam in the late 1940s and early
 Chapter 30-1 CN I. Early American Involvement in Vietnam (pages 892 894) A. Although little was known about Vietnam in the late 1940s and early 1950s, American officials felt Vietnam was important in their
Chapter 30-1 CN I. Early American Involvement in Vietnam (pages 892 894) A. Although little was known about Vietnam in the late 1940s and early 1950s, American officials felt Vietnam was important in their
Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs. non Communist South Organized by Ho Chi Minh
 1956 Elections are cancelled (1 of Geneva Accords) 1957 The Vietcong attack in South Vietnam Vietcong are South Vietnamese communists Guerrilla fighters Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs.
1956 Elections are cancelled (1 of Geneva Accords) 1957 The Vietcong attack in South Vietnam Vietcong are South Vietnamese communists Guerrilla fighters Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs.
The War in Vietnam. Chapter 30
 The War in Vietnam Chapter 30 Vietnam A colony of France until after World War II 1954- War for Independence led by Ho Chi Minh Ho Chi Minh The Geneva Accords The Geneva Accords divided the country into
The War in Vietnam Chapter 30 Vietnam A colony of France until after World War II 1954- War for Independence led by Ho Chi Minh Ho Chi Minh The Geneva Accords The Geneva Accords divided the country into
Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs. non Communist South Organized by Ho Chi Minh
 1956 Elections are cancelled (1 of Geneva Accords) 1957 The Vietcong attack in South Vietnam Vietcong are South Vietnamese communists Guerrilla fighters Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs.
1956 Elections are cancelled (1 of Geneva Accords) 1957 The Vietcong attack in South Vietnam Vietcong are South Vietnamese communists Guerrilla fighters Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs.
Ho Declares Independence of Vietnam British Forces Land in Saigon, Return Authority to French First American Dies in Vietnam
 1945 Ho Chi Minh Creates Provisional Government Following the surrender of Japan to Allied forces, Ho Chi Minh and his People's Congress form a provisional government. Japan transfers all power to Ho's
1945 Ho Chi Minh Creates Provisional Government Following the surrender of Japan to Allied forces, Ho Chi Minh and his People's Congress form a provisional government. Japan transfers all power to Ho's
ANSWER KEY..REVIEW FOR Friday s QUIZ #15 Chapter: 29 -Vietnam
 ANSWER KEY..REVIEW FOR Friday s QUIZ #15 Chapter: 29 -Vietnam Ch. 29 sec. 1 - skim and scan pages 908-913 and then answer the questions. French Indochina: French ruled colony made up of Vietnam, Laos,
ANSWER KEY..REVIEW FOR Friday s QUIZ #15 Chapter: 29 -Vietnam Ch. 29 sec. 1 - skim and scan pages 908-913 and then answer the questions. French Indochina: French ruled colony made up of Vietnam, Laos,
1. America slowly involves itself in the war in Vietnam as it seeks to halt the spread of communism.
 The War in Vietnam Indochina was still another Cold War battlefield. France had controlled Vietnam since the middle of the 19th century, only to be supplanted by Japan during the Second World War. Meanwhile,
The War in Vietnam Indochina was still another Cold War battlefield. France had controlled Vietnam since the middle of the 19th century, only to be supplanted by Japan during the Second World War. Meanwhile,
Modern American History Unit 8: The 1960s The Vietnam War Notes and Questions
 Modern American History Unit 8: The 1960s The Vietnam War Notes and Questions The Vietnam War A. Vietnam: A Painful War U.S. involvement in conflicts in Vietnam lasted from mid-1940s to 1975 Only war the
Modern American History Unit 8: The 1960s The Vietnam War Notes and Questions The Vietnam War A. Vietnam: A Painful War U.S. involvement in conflicts in Vietnam lasted from mid-1940s to 1975 Only war the
SECTION 1: MOVING TOWARD CONFLICT PAGE 730
 CHAPTER 22 SECTION 1: MOVING TOWARD CONFLICT PAGE 730 Main Idea: America gets involved in Vietnam to stop the spread of communism TERMS AND NAMES: Ho Chi Minh Ngo Dinh Diem Vietcong Vietminh domino theory
CHAPTER 22 SECTION 1: MOVING TOWARD CONFLICT PAGE 730 Main Idea: America gets involved in Vietnam to stop the spread of communism TERMS AND NAMES: Ho Chi Minh Ngo Dinh Diem Vietcong Vietminh domino theory
Historical Security Council (1967)
 Research Report XXVII Annual Session Historical Security Council (1967) The Vietnam War Research Report Page 1 of 9 Mik Dijkman Maurits de Lint Forum: Historical Security Council (1967) Issue: Student
Research Report XXVII Annual Session Historical Security Council (1967) The Vietnam War Research Report Page 1 of 9 Mik Dijkman Maurits de Lint Forum: Historical Security Council (1967) Issue: Student
VUS.13b. The Vietnam War. U. S. government s anti- Communist strategy of containment in Asia
 VUS.13b The Vietnam War U. S. government s anti- Communist strategy of containment in Asia Help the French and send some advisors- Increase advisors, send some troops- Escalate- we can not lose a war Peace
VUS.13b The Vietnam War U. S. government s anti- Communist strategy of containment in Asia Help the French and send some advisors- Increase advisors, send some troops- Escalate- we can not lose a war Peace
The Vietnam War,
 The Vietnam War, 1954 1975 Who was Ho Chi Minh? Vietnamese Communist who wanted self rule for Vietnam. Why did the United States aid the French? The French returned to Vietnam in 1946. As the Vietminh
The Vietnam War, 1954 1975 Who was Ho Chi Minh? Vietnamese Communist who wanted self rule for Vietnam. Why did the United States aid the French? The French returned to Vietnam in 1946. As the Vietminh
 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 The reason the French did not want to give up Vietnam.
$100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 The reason the French did not want to give up Vietnam.
UNIT Y222 THE COLD WAR IN ASIA
 UNIT Y222 THE COLD WAR IN ASIA 1945-1993 NOTE: BASED ON 2 X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources Western Policies
UNIT Y222 THE COLD WAR IN ASIA 1945-1993 NOTE: BASED ON 2 X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources Western Policies
There will be some disturbing images and footage as we cover this unit, please do your best to act as adults, and learn from this war.
 There will be some disturbing images and footage as we cover this unit, please do your best to act as adults, and learn from this war. Vietnam Intro Before WWII, Vietnam was a colony of the French Japanese
There will be some disturbing images and footage as we cover this unit, please do your best to act as adults, and learn from this war. Vietnam Intro Before WWII, Vietnam was a colony of the French Japanese
The Vietnam War: Tragic Conflict in Asia Affected an American Generation
 The Vietnam War: Tragic Conflict in Asia Affected an American Generation By History.com on 05.02.17 Word Count 2,327 Level MAX Hovering U.S. Army helicopters pour machine gun fire into a tree line to cover
The Vietnam War: Tragic Conflict in Asia Affected an American Generation By History.com on 05.02.17 Word Count 2,327 Level MAX Hovering U.S. Army helicopters pour machine gun fire into a tree line to cover
Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos Annotation
 Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos Annotation Name Directions: A. Read the entire article, CIRCLE words you don t know, mark a + in the margin next to paragraphs you understand and a next to paragraphs you don t
Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos Annotation Name Directions: A. Read the entire article, CIRCLE words you don t know, mark a + in the margin next to paragraphs you understand and a next to paragraphs you don t
The Vietnam War Vietnamization and Peace with Honor
 The Vietnam War Vietnamization and Peace with Honor Name: Class: Vietnamization General Creighton Abrams, who replaced General Westmoreland as U.S. Commander in Vietnam in 1968, had very different ideas
The Vietnam War Vietnamization and Peace with Honor Name: Class: Vietnamization General Creighton Abrams, who replaced General Westmoreland as U.S. Commander in Vietnam in 1968, had very different ideas
C. Continuing protests Doves wanted an immediate withdrawal that was complete, unconditional, and irreversible.
 I. VIETNAM WAR spread across 5 presidencies and spanned 25 years Direct U.S involvement from 1963-1973 A. France lost control of Vietnam after the battle of Dien Bien Phu in 1954 1. U.S. by 1954 had financed
I. VIETNAM WAR spread across 5 presidencies and spanned 25 years Direct U.S involvement from 1963-1973 A. France lost control of Vietnam after the battle of Dien Bien Phu in 1954 1. U.S. by 1954 had financed
Chapter 20. The Vietnam War Era
 Chapter 20 The Vietnam War Era 1954-1975 Ho Chi Minh The most important voice who demanded independence for Vietnam. Communist leader of the Vietminh. Vietminh The term initially used to describe all Vietnamese
Chapter 20 The Vietnam War Era 1954-1975 Ho Chi Minh The most important voice who demanded independence for Vietnam. Communist leader of the Vietminh. Vietminh The term initially used to describe all Vietnamese
Standard 8.0- Demonstrate an understanding of social, economic and political issues in contemporary America. Closing: Quiz
 Standard 8.0- Demonstrate an understanding of social, economic and political issues in contemporary America. Opening: Great Society Chart Work Period: Vietnam War Notes Political Cartoon Double Flow Map
Standard 8.0- Demonstrate an understanding of social, economic and political issues in contemporary America. Opening: Great Society Chart Work Period: Vietnam War Notes Political Cartoon Double Flow Map
The Vietnam War Why does the United States get involved in Vietnam?
 Why does the United States get involved in Vietnam? Vietnam had been a French colony since the late 1800s. After World War II, the French began to battle the Viet Minh, who wanted to kick out the French
Why does the United States get involved in Vietnam? Vietnam had been a French colony since the late 1800s. After World War II, the French began to battle the Viet Minh, who wanted to kick out the French
The Vietnam War. Summary
 The Vietnam War Summary The Vietnam War grew out of the American commitment to the containment of communism during the Cold War. For approximately fifteen years, the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (North
The Vietnam War Summary The Vietnam War grew out of the American commitment to the containment of communism during the Cold War. For approximately fifteen years, the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (North
Conflict U.S. War
 Conflict - 1945-1975 U.S. War 1964-1973 Overview of the Vietnam War Why is Vietnam still a painful war to remember? Longest war in U.S. history and only war we lost It showed Americans that our power is
Conflict - 1945-1975 U.S. War 1964-1973 Overview of the Vietnam War Why is Vietnam still a painful war to remember? Longest war in U.S. history and only war we lost It showed Americans that our power is
20 th /Raffel The Vietnam War: Containment Leads to Disaster About this Assignment: The Vietnam war was one of the most controversial wars in
 20 th /Raffel The Vietnam War: Containment Leads to Disaster About this Assignment: The Vietnam war was one of the most controversial wars in American history. In retrospect, there were many missed opportunities
20 th /Raffel The Vietnam War: Containment Leads to Disaster About this Assignment: The Vietnam war was one of the most controversial wars in American history. In retrospect, there were many missed opportunities
The Cold War Finally Thaws Out. Korean War ( ) Vietnam War ( ) Afghan War ( )
 The Cold War Finally Thaws Out Korean War (1950-1953) Vietnam War (1963-1973) Afghan War (1979-1989) Korean war Split after WWII between US and USSR Temporary gov ts created in images of their major allies
The Cold War Finally Thaws Out Korean War (1950-1953) Vietnam War (1963-1973) Afghan War (1979-1989) Korean war Split after WWII between US and USSR Temporary gov ts created in images of their major allies
Vietnam Introduction. Answer the following questions on a sticky note...
 Vietnam Introduction Answer the following questions on a sticky note... https://www.youtube.c om/watch?v=epfnsk5l 26U Burning Monk 1. Why was the burning monk event significant? How did people in the U.S.
Vietnam Introduction Answer the following questions on a sticky note... https://www.youtube.c om/watch?v=epfnsk5l 26U Burning Monk 1. Why was the burning monk event significant? How did people in the U.S.
UNDERGROUND COMPLEXES
 UNDERGROUND COMPLEXES TET OFFENSIVE Morale among U.S. soldiers remained generally high from 1965-1968. Many battlefield successes. Johnson Admin. reported that the war was all but won. Temporary ceasefire
UNDERGROUND COMPLEXES TET OFFENSIVE Morale among U.S. soldiers remained generally high from 1965-1968. Many battlefield successes. Johnson Admin. reported that the war was all but won. Temporary ceasefire
Vietnam Before WWII During the early 1900s, nationalism was strong in. As the Vietnamese sought or reform of the colonial government, several
 Name Date Per Vietnam Before WWII During the early 1900s, nationalism was strong in. As the Vietnamese sought or reform of the colonial government, several political parties formed. One of the leaders
Name Date Per Vietnam Before WWII During the early 1900s, nationalism was strong in. As the Vietnamese sought or reform of the colonial government, several political parties formed. One of the leaders
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Cold War Tensions (Chapter 30 Quiz)
 Cold War Tensions (Chapter 30 Quiz) What were the military and political consequences of the Cold War in the Soviet Union, Europe, and the United States? After World War II ended, the United States and
Cold War Tensions (Chapter 30 Quiz) What were the military and political consequences of the Cold War in the Soviet Union, Europe, and the United States? After World War II ended, the United States and
History Skill Builder. Perspective Taking
 History Skill Builder Perspective Taking Perspective Taking History is a written by people, with different points of view and biases. Conflicts arise from differences of opinion, competing interests. Compromises
History Skill Builder Perspective Taking Perspective Taking History is a written by people, with different points of view and biases. Conflicts arise from differences of opinion, competing interests. Compromises
VIETNAM 04/14/15 ORIGINS OF THE VIETNAM WAR s French establish control over Indochina - Southeast Asia
 VIETNAM Have you seen Charlie? 04/12/15 2 ORIGINS OF THE VIETNAM WAR 1800 s French establish control over Indochina - Southeast Asia Modern countries: Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos Transplanted French laws
VIETNAM Have you seen Charlie? 04/12/15 2 ORIGINS OF THE VIETNAM WAR 1800 s French establish control over Indochina - Southeast Asia Modern countries: Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos Transplanted French laws
World History Flashpoint #2 Vietnam
 World History 3201 Flashpoint #2 Vietnam KEY TERMS: Viet Cong : Communists in South Vietnam who opposed the Diem (Capitalist South Vietnamese Leader) government. Viet Minh : Vietnamese nationalists who
World History 3201 Flashpoint #2 Vietnam KEY TERMS: Viet Cong : Communists in South Vietnam who opposed the Diem (Capitalist South Vietnamese Leader) government. Viet Minh : Vietnamese nationalists who
And The Republicans VIETNAM. BY Leonard P. Liggio. of it.
 VIETNAM And The Republicans The War In Vietnam. The Text of the Controversial Republican White Paper Prepared by the Staff of the Senate Republican Policy Committee, Washington,.D.C., Public Affairs Press.
VIETNAM And The Republicans The War In Vietnam. The Text of the Controversial Republican White Paper Prepared by the Staff of the Senate Republican Policy Committee, Washington,.D.C., Public Affairs Press.
Introduction to East and Southeast Asia. Second World War. The most noticeable group was Vietminh (Viet Nam Doc Lap Dong Minh:
 Introduction In Vietnam, political movements against colonizer emerged significantly before the Second World War. The most noticeable group was Vietminh (Viet Nam Doc Lap Dong Minh: League for Independence
Introduction In Vietnam, political movements against colonizer emerged significantly before the Second World War. The most noticeable group was Vietminh (Viet Nam Doc Lap Dong Minh: League for Independence
Chapter 17 Lesson 1: Two Superpowers Face Off. Essential Question: Why did tension between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R increase after WWII?
 Chapter 17 Lesson 1: Two Superpowers Face Off Essential Question: Why did tension between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R increase after WWII? Post WWII Big Three meet in Yalta Divide Germany into 4 zones (U.S.,
Chapter 17 Lesson 1: Two Superpowers Face Off Essential Question: Why did tension between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R increase after WWII? Post WWII Big Three meet in Yalta Divide Germany into 4 zones (U.S.,
Ch. 16 Sec. 1: Origins of the Vietnam War
 CHAPTER 16 QUESTIONS 5 sections, and Document Based Questions Ch. 16 Sec. 1: Origins of the Vietnam War 1) French Indochina included which three cultures? 2) How many people lived in Indochina by the end
CHAPTER 16 QUESTIONS 5 sections, and Document Based Questions Ch. 16 Sec. 1: Origins of the Vietnam War 1) French Indochina included which three cultures? 2) How many people lived in Indochina by the end
A HISTORY OF THE VIETNAM WAR
 A HISTORY OF THE VIETNAM WAR EXAM INFORMATION This exam was developed to enable schools to award credit to students for knowledge equivalent to that learned by students taking the course. This examination
A HISTORY OF THE VIETNAM WAR EXAM INFORMATION This exam was developed to enable schools to award credit to students for knowledge equivalent to that learned by students taking the course. This examination
The Vietnam War Era ( ) Lesson 4 The War s End and Effects
 The Vietnam War Era (1954-1975) Lesson 4 The War s End and Effects The Vietnam War Era (1954-1975) Lesson 4 The War s End and Effects Learning Objectives Assess Nixon s new approach to the war, and explain
The Vietnam War Era (1954-1975) Lesson 4 The War s End and Effects The Vietnam War Era (1954-1975) Lesson 4 The War s End and Effects Learning Objectives Assess Nixon s new approach to the war, and explain
U.S. wants to withdraw but cannot do so until the ARVN are ready.
 VIETNAMIZATION U.S. wants to withdraw but cannot do so until the ARVN are ready. The ARVN and RVNAF are supplied with modern weapons and aircraft in the hope that they can defend themselves. PACIFICATION-A
VIETNAMIZATION U.S. wants to withdraw but cannot do so until the ARVN are ready. The ARVN and RVNAF are supplied with modern weapons and aircraft in the hope that they can defend themselves. PACIFICATION-A
Chapter 29 Section 4 The War s End and Impact
 Chapter 29 Section 4 The War s End and Impact President Nixon inherited an unpopular war and increasing troubles on the home front. Peace Talks Stall Formal peace talks began in May, 1968 in Paris US wanted
Chapter 29 Section 4 The War s End and Impact President Nixon inherited an unpopular war and increasing troubles on the home front. Peace Talks Stall Formal peace talks began in May, 1968 in Paris US wanted
(i Nha Trang;,:: Cam Ranht
 CWA 4.1- Origins of the Vietnam War (Page 1 of 6) Ck History. Instructions: On each page, first, underline the dates and time markers (for example, "In the same year... ') in the text below. Next, write
CWA 4.1- Origins of the Vietnam War (Page 1 of 6) Ck History. Instructions: On each page, first, underline the dates and time markers (for example, "In the same year... ') in the text below. Next, write
VIETNAM: LEAD UP TO WAR
 VIETNAM: LEAD UP TO WAR Southeast Asia s Colonial History France gained control of Vietnam by 1883 despite fierce resistance from the Vietnamese. The French combined Vietnam with Laos and Cambodia to form
VIETNAM: LEAD UP TO WAR Southeast Asia s Colonial History France gained control of Vietnam by 1883 despite fierce resistance from the Vietnamese. The French combined Vietnam with Laos and Cambodia to form
Communism in the Far East. China
 Communism in the Far East China Terms and Players KMT PLA PRC CCP Sun Yat-Sen Mikhail Borodin Chiang Kai-shek Mao Zedong Shaky Start In 1913 the newly formed Chinese government was faced with the assassination
Communism in the Far East China Terms and Players KMT PLA PRC CCP Sun Yat-Sen Mikhail Borodin Chiang Kai-shek Mao Zedong Shaky Start In 1913 the newly formed Chinese government was faced with the assassination
Moving Toward Conflict
 The Vietnam War Years Moving Toward Conflict Terms and Names Ho Chi Minh Leader of North Vietnam Vietminh Communist group led by Ho Chi Minh domino theory Eisenhower s explanation for stopping communism
The Vietnam War Years Moving Toward Conflict Terms and Names Ho Chi Minh Leader of North Vietnam Vietminh Communist group led by Ho Chi Minh domino theory Eisenhower s explanation for stopping communism
The Invasion of Cambodia and Laos during the Vietnam War
 June 9th. 2014 World Geography 11 The Invasion of Cambodia and Laos during the Vietnam War Daphne Wood! On October 4th, 1965, the United States Air Force begun a secret bombing campaign in Cambodia and
June 9th. 2014 World Geography 11 The Invasion of Cambodia and Laos during the Vietnam War Daphne Wood! On October 4th, 1965, the United States Air Force begun a secret bombing campaign in Cambodia and
1) Read the article on American involvement in Vietnam
 Warm Up 1) Read the article on American involvement in Vietnam 1) Circle in the causes of the Vietnam War 2) Put a star next to the key people/ countries 3) Box in key events, battles, treaties 4) Put
Warm Up 1) Read the article on American involvement in Vietnam 1) Circle in the causes of the Vietnam War 2) Put a star next to the key people/ countries 3) Box in key events, battles, treaties 4) Put
SS7H3e Brain Wrinkles
 SS7H3e End of WWII The United States, Soviet Union, and Great Britain made an agreement on how they would after World War II. Each country was supposed to the lands that were impacted by the war. They
SS7H3e End of WWII The United States, Soviet Union, and Great Britain made an agreement on how they would after World War II. Each country was supposed to the lands that were impacted by the war. They
THE IRON CURTAIN. From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic an iron curtain has descended across the continent. - Winston Churchill
 COLD WAR 1945-1991 1. The Soviet Union drove the Germans back across Eastern Europe. 2. They occupied several countries along it s western border and considered them a necessary buffer or wall of protection
COLD WAR 1945-1991 1. The Soviet Union drove the Germans back across Eastern Europe. 2. They occupied several countries along it s western border and considered them a necessary buffer or wall of protection
Conflict in Indochina
 Conflict in Indochina 1954 French defeat at Dien Bien Phu Ba.le took place over 4 stages: 13 March: cut off French supply routes 30 March: start of a 5- day assault 5 April: encroachment; digging trenches
Conflict in Indochina 1954 French defeat at Dien Bien Phu Ba.le took place over 4 stages: 13 March: cut off French supply routes 30 March: start of a 5- day assault 5 April: encroachment; digging trenches
xvi Chronology 2 Aug North Vietnamese patrol boats attack the Maddox in the Gulf of Tonkin near the North Vietnamese coast. 4 5 Aug Both t
 CHRONOLOGY May 1941 Formation of the Vietminh. 2 Sept. 1945 Ho Chi Minh publicly declares a provisional government and Vietnamese national independence. 23 Nov. 1946 French bombardment of Haiphong. Oct.
CHRONOLOGY May 1941 Formation of the Vietminh. 2 Sept. 1945 Ho Chi Minh publicly declares a provisional government and Vietnamese national independence. 23 Nov. 1946 French bombardment of Haiphong. Oct.
Bell Ringer: April 18(19), 2018
 Announcements: 1: Test 5/4! Review is on the Weebly! Bell Ringer: April 18(19), 2018 Materials: 1: Spiral/blank sheet of paper 2: Vietnam War DBQ (PREAP) 1. Set up your Cornell notes 2. Across the top
Announcements: 1: Test 5/4! Review is on the Weebly! Bell Ringer: April 18(19), 2018 Materials: 1: Spiral/blank sheet of paper 2: Vietnam War DBQ (PREAP) 1. Set up your Cornell notes 2. Across the top
Name Period Date. Civil Rights Movement and Vietnam War Unit Test Review. Test Format- 50 questions 15 matching. 5 map, 3 reading a chart, 27 MC
 Name Period Date Civil Rights Movement and Vietnam War Unit Test Review Test Format- 50 questions 15 matching. 5 map, 3 reading a chart, 27 MC 1. What was LBJ s (President Johnson) program to end poverty
Name Period Date Civil Rights Movement and Vietnam War Unit Test Review Test Format- 50 questions 15 matching. 5 map, 3 reading a chart, 27 MC 1. What was LBJ s (President Johnson) program to end poverty
The 1960s ****** Two young candidates, Senator John F. Kennedy (D) and Vice-President Richard M. Nixon (R), ran for president in 1960.
 The 1960s A PROMISING TIME? As the 1960s began, many Americans believed they lived in a promising time. The economy was doing well, the country seemed poised for positive changes, and a new generation
The 1960s A PROMISING TIME? As the 1960s began, many Americans believed they lived in a promising time. The economy was doing well, the country seemed poised for positive changes, and a new generation
Chapter 29. Section 3 and 4
 Chapter 29 Section 3 and 4 The War Divides America Section 3 Objectives Describe the divisions within American society over the Vietnam War. Analyze the Tet Offensive and the American reaction to it. Summarize
Chapter 29 Section 3 and 4 The War Divides America Section 3 Objectives Describe the divisions within American society over the Vietnam War. Analyze the Tet Offensive and the American reaction to it. Summarize
Chapter 22. The Vietnam War Years
 Chapter 22 The Vietnam War Years Chapter 22-1 Moving Toward Conflict French Indochina 3 countries Vietnam Laos Cambodia French colonies late 1800s-WWII French Indochina French took land from native people
Chapter 22 The Vietnam War Years Chapter 22-1 Moving Toward Conflict French Indochina 3 countries Vietnam Laos Cambodia French colonies late 1800s-WWII French Indochina French took land from native people
The Vietnam War Years. B. Domino theory C. Vietcong D. Tonkin Gulf Resolution E. Napalm F. Credibility gap
 study guide Chapter Name The Vietnam War Years Period Due Directions: Write Definitions on a separate sheet of paper. 1. A. Ho Chi Minh B. Domino theory C. Vietcong D. Tonkin Gulf Resolution E. Napalm
study guide Chapter Name The Vietnam War Years Period Due Directions: Write Definitions on a separate sheet of paper. 1. A. Ho Chi Minh B. Domino theory C. Vietcong D. Tonkin Gulf Resolution E. Napalm
The arms race meant that the US feared war in Vietnam because of potential nuclear attack from the Soviet Union.
 The situation in Vietnam by 1961 Vietnam was a French colony, known as French Indochina. Ho Chi Minh was at war with the French, fighting for Vietnamese independence. He won a decisive victory at Dien
The situation in Vietnam by 1961 Vietnam was a French colony, known as French Indochina. Ho Chi Minh was at war with the French, fighting for Vietnamese independence. He won a decisive victory at Dien
The Cold War Begins. After WWII
 The Cold War Begins After WWII After WWII the US and the USSR emerged as the world s two. Although allies during WWII distrust between the communist USSR and the democratic US led to the. Cold War tension
The Cold War Begins After WWII After WWII the US and the USSR emerged as the world s two. Although allies during WWII distrust between the communist USSR and the democratic US led to the. Cold War tension
The Vietnam War
 The Vietnam War 1968-1973 LBJ: Grew increasingly unpopular over the course of his term. In 1968, his popularity dropped from 48% to 36%. Getting out of Vietnam As much as Nixon wanted to stop the protests
The Vietnam War 1968-1973 LBJ: Grew increasingly unpopular over the course of his term. In 1968, his popularity dropped from 48% to 36%. Getting out of Vietnam As much as Nixon wanted to stop the protests
The Making of a Stalemate. The Vietnam War
 The Making of a Stalemate The Vietnam War 1965-1967 LBJ s search for advice - Eisenhower WhiteHouseTapes.org Transcript + Audio Clip WhiteHouseTapes.org Transcript + Audio Clip WhiteHouseTapes.org Transcript
The Making of a Stalemate The Vietnam War 1965-1967 LBJ s search for advice - Eisenhower WhiteHouseTapes.org Transcript + Audio Clip WhiteHouseTapes.org Transcript + Audio Clip WhiteHouseTapes.org Transcript
What post-war issues caused the Western Allies and the Soviet Union to disagree? What did Churchill mean by an iron curtain has descended?
 The Cold War I. Friend and Foe A. During WWII the US and USSR were. B. The could not have been beaten without the Soviets. C. Near the end of the war the allies met to discuss the. II. The A. Roosevelt,
The Cold War I. Friend and Foe A. During WWII the US and USSR were. B. The could not have been beaten without the Soviets. C. Near the end of the war the allies met to discuss the. II. The A. Roosevelt,
Unit 7: The Cold War
 Unit 7: The Cold War Standard 7-5 Goal: The student will demonstrate an understanding of international developments during the Cold War era. Vocabulary 7-5.1 OCCUPIED 7-5.2 UNITED NATIONS NORTH ATLANTIC
Unit 7: The Cold War Standard 7-5 Goal: The student will demonstrate an understanding of international developments during the Cold War era. Vocabulary 7-5.1 OCCUPIED 7-5.2 UNITED NATIONS NORTH ATLANTIC
Fascism is a nationalistic political philosophy which is anti-democratic, anticommunist, and anti-liberal. It puts the importance of the nation above
 1939-1945 Fascism is a nationalistic political philosophy which is anti-democratic, anticommunist, and anti-liberal. It puts the importance of the nation above the rights of the individual. The word Fascism
1939-1945 Fascism is a nationalistic political philosophy which is anti-democratic, anticommunist, and anti-liberal. It puts the importance of the nation above the rights of the individual. The word Fascism
Politics of the Cold War
 Politics of the Cold War Standards SSUSH20 The student will analyze the domestic and international impact of the Cold War on the United States. c. Describe the Cuban Revolution, the Bay of Pigs, and the
Politics of the Cold War Standards SSUSH20 The student will analyze the domestic and international impact of the Cold War on the United States. c. Describe the Cuban Revolution, the Bay of Pigs, and the
Lyndon Johnson and Vietnam. A Case Study
 Lyndon Johnson and Vietnam A Case Study Who was Lyndon B Johnson? Which US President won an election with the largest ever popular majority? Lyndon Baines Johnson, who took 61% of the vote in 1964. He
Lyndon Johnson and Vietnam A Case Study Who was Lyndon B Johnson? Which US President won an election with the largest ever popular majority? Lyndon Baines Johnson, who took 61% of the vote in 1964. He
Vietnam War. Andrew Rodgers, Jeda Niyomkul, Marcus Johnson, Oliver Gray, Annemarie Rakoski, and Langley McEntyre
 Vietnam War Andrew Rodgers, Jeda Niyomkul, Marcus Johnson, Oliver Gray, Annemarie Rakoski, and Langley McEntyre Before the War The Modern-day countries of Vietnam, Cambodia and Laos known as Indochina
Vietnam War Andrew Rodgers, Jeda Niyomkul, Marcus Johnson, Oliver Gray, Annemarie Rakoski, and Langley McEntyre Before the War The Modern-day countries of Vietnam, Cambodia and Laos known as Indochina
Is it Justified for the President to expand executive power during war time?
 Paul Bennis Goshen High School, Goshen N.Y. U.S. Military History Is it Justified for the President to expand executive power during war time? Wilson F.D.R. 1. Japanese Internment 2. Schenk v. U.S. J.F.K.
Paul Bennis Goshen High School, Goshen N.Y. U.S. Military History Is it Justified for the President to expand executive power during war time? Wilson F.D.R. 1. Japanese Internment 2. Schenk v. U.S. J.F.K.
China Summit. Situation in Taiwan Vietnam War Chinese Relationship with Soviet Union c. By: Paul Sabharwal and Anjali. Jain
 China Summit Situation in Taiwan Vietnam War Chinese Relationship with Soviet Union c. By: Paul Sabharwal and Anjali Jain I. Introduction In the 1970 s, the United States decided that allying with China
China Summit Situation in Taiwan Vietnam War Chinese Relationship with Soviet Union c. By: Paul Sabharwal and Anjali Jain I. Introduction In the 1970 s, the United States decided that allying with China
War. Ho Chi Minh. domino theory. Dien Bien Phu SEATO. Vietcong Gulf of Tonkin Resolution. the end of WWII? ce? supporting
 Chapter 29 Section 1 Origins of the Vietnam War Ho Chi Minh domino theory Dien Bien Phu SEATO Vietcong Gulf of Tonkin Resolution 1. Witness History: What countries made up French Indochina? 2. What state
Chapter 29 Section 1 Origins of the Vietnam War Ho Chi Minh domino theory Dien Bien Phu SEATO Vietcong Gulf of Tonkin Resolution 1. Witness History: What countries made up French Indochina? 2. What state
The Vietnam War
 The Vietnam War 1968-1973 LBJ: As his term was coming to an end, he cut back on bombing North Vietnam and called for peace talks which failed. Nixon: Claimed in 1968 election that he had a secret plan
The Vietnam War 1968-1973 LBJ: As his term was coming to an end, he cut back on bombing North Vietnam and called for peace talks which failed. Nixon: Claimed in 1968 election that he had a secret plan
CWA 4.1 Origins of the Vietnam War (Page 4 of 6)
 CWA 4.1 Origins of the Vietnam War (Page 4 of 6) Ho Chi Minh, 1946. Cropped version Source: Wikipedia Commons, Vietnamese Public Domain, http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:ho_chi _Minh_1946_and_signature.jpg
CWA 4.1 Origins of the Vietnam War (Page 4 of 6) Ho Chi Minh, 1946. Cropped version Source: Wikipedia Commons, Vietnamese Public Domain, http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:ho_chi _Minh_1946_and_signature.jpg
One war ends, another begins
 One war ends, another begins Communism comes from the word common, meaning to belong equally to more than one individual. The related word, commune is a place where people live together and share property
One war ends, another begins Communism comes from the word common, meaning to belong equally to more than one individual. The related word, commune is a place where people live together and share property
AUSTRALIA S VIETNAM WAR A PERSONAL PERSPECTIVE FORESTVILLE RSL SUB-BRANCH
 AUSTRALIA S VIETNAM WAR A PERSONAL PERSPECTIVE Introduction The aim of our talk is to provide you with: an overview of the Vietnam War from an Australian context, our personal perspectives of the War,
AUSTRALIA S VIETNAM WAR A PERSONAL PERSPECTIVE Introduction The aim of our talk is to provide you with: an overview of the Vietnam War from an Australian context, our personal perspectives of the War,
Notes: LG: Analyze how the 1960s changed America.
 Notes: LG: Analyze how the 1960s changed America. USSR Nikita Khrushchev 1953-1964 1. Cold War Abroad in the 1960s a. 1961, Bay of Pigs Invasion (Cuba) i. President Eisenhower and CIA train Cuban
Notes: LG: Analyze how the 1960s changed America. USSR Nikita Khrushchev 1953-1964 1. Cold War Abroad in the 1960s a. 1961, Bay of Pigs Invasion (Cuba) i. President Eisenhower and CIA train Cuban
Post World War II...The Cold War
 Post World War II...The Cold War Thesis Statement The Post WWII era has been dominated by the Cold War and events today are reflective of Cold War dynamics (propaganda, us vs. them, good vs. evil, UN Security
Post World War II...The Cold War Thesis Statement The Post WWII era has been dominated by the Cold War and events today are reflective of Cold War dynamics (propaganda, us vs. them, good vs. evil, UN Security
INTRODUCTION. Major countries involved
 15.03 17.03 RESEARCH REPORT COMMITTEE : HISTORICAL COUNCIL ISSUE: IMPROVING ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL CONDITIONS IN VIETNAM AND RESTORING PEACEFUL INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS IN EASTERN ASIA CHAIRS : ZOE GAILLOT
15.03 17.03 RESEARCH REPORT COMMITTEE : HISTORICAL COUNCIL ISSUE: IMPROVING ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL CONDITIONS IN VIETNAM AND RESTORING PEACEFUL INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS IN EASTERN ASIA CHAIRS : ZOE GAILLOT
East Asia in the Postwar Settlements
 Chapter 34 " Rebirth and Revolution: Nation-building in East Asia and the Pacific Rim East Asia in the Postwar Settlements Korea was divided between a Russian zone of occupation in the north and an American
Chapter 34 " Rebirth and Revolution: Nation-building in East Asia and the Pacific Rim East Asia in the Postwar Settlements Korea was divided between a Russian zone of occupation in the north and an American
THE EARLY COLD WAR YEARS. US HISTORY Chapter 15 Section 2
 THE EARLY COLD WAR YEARS US HISTORY Chapter 15 Section 2 THE EARLY COLD WAR YEARS CONTAINING COMMUNISM MAIN IDEA The Truman Doctrine offered aid to any nation resisting communism; The Marshal Plan aided
THE EARLY COLD WAR YEARS US HISTORY Chapter 15 Section 2 THE EARLY COLD WAR YEARS CONTAINING COMMUNISM MAIN IDEA The Truman Doctrine offered aid to any nation resisting communism; The Marshal Plan aided
3/2/2017. Dwight Eisenhower & The Cold War. Election of Adlai Stevenson Democratic Candidate. Dwight D. Eisenhower Ike Republican Candidate
 1 2 3 4 Dwight Eisenhower & The Cold War Election of 1952 Adlai Stevenson Democratic Candidate Dwight D. Eisenhower Ike Republican Candidate 5 6 7 1952 Election Results Dwight D. Eisenhower 34 th President
1 2 3 4 Dwight Eisenhower & The Cold War Election of 1952 Adlai Stevenson Democratic Candidate Dwight D. Eisenhower Ike Republican Candidate 5 6 7 1952 Election Results Dwight D. Eisenhower 34 th President
World History Chapter 23 Page Reading Outline
 World History Chapter 23 Page 601-632 Reading Outline The Cold War Era: Iron Curtain: a phrased coined by Winston Churchill at the end of World War I when her foresaw of the impending danger Russia would
World History Chapter 23 Page 601-632 Reading Outline The Cold War Era: Iron Curtain: a phrased coined by Winston Churchill at the end of World War I when her foresaw of the impending danger Russia would
The Sixties and Seventies. The Cold War cools down, Civil Rights get complicated, and the Baby Boomers come of age.
 The Sixties and Seventies The Cold War cools down, Civil Rights get complicated, and the Baby Boomers come of age. Learning Targets Describe the Kennedy years, with specific detail covering: The election
The Sixties and Seventies The Cold War cools down, Civil Rights get complicated, and the Baby Boomers come of age. Learning Targets Describe the Kennedy years, with specific detail covering: The election
netw rks Where in the world? When did it happen? The Vietnam Era Lesson 1 Kennedy s Foreign Policy ESSENTIAL QUESTION Terms to Know GUIDING QUESTIONS
 Lesson 1 Kennedy s Foreign Policy ESSENTIAL QUESTION What motivates people to act? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. Why did President Kennedy seek new ways to deal with the challenges and fears of the Cold War? 2.
Lesson 1 Kennedy s Foreign Policy ESSENTIAL QUESTION What motivates people to act? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. Why did President Kennedy seek new ways to deal with the challenges and fears of the Cold War? 2.
Introduction to World War II By USHistory.org 2017
 Name: Class: Introduction to World War II By USHistory.org 2017 World War II was the second global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. The war involved a majority of the world s countries, and it is considered
Name: Class: Introduction to World War II By USHistory.org 2017 World War II was the second global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. The war involved a majority of the world s countries, and it is considered
World History (Survey) Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present
 World History (Survey) Chapter 33: Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present Section 1: Two Superpowers Face Off The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February
World History (Survey) Chapter 33: Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present Section 1: Two Superpowers Face Off The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February
Kennedy & Johnson. Chapters 38 & 39
 Kennedy & Johnson Chapters 38 & 39 Kennedy s Presidency Young, inspirational, refreshing Young Cabinet Sec. of Defense - Robert McNamara Attorney General - Robert Kennedy Wanted to target organized crime
Kennedy & Johnson Chapters 38 & 39 Kennedy s Presidency Young, inspirational, refreshing Young Cabinet Sec. of Defense - Robert McNamara Attorney General - Robert Kennedy Wanted to target organized crime
PRESIDENT NIXON & THE WITHDRAWAL FROM VIETNAM. L obj: to consider whether the USA lost the war in Vietnam, or whether the Vietcong won it.
 PRESIDENT NIXON & THE WITHDRAWAL FROM VIETNAM L obj: to consider whether the USA lost the war in Vietnam, or whether the Vietcong won it. US Presidents (during Vietnam) Dwight Eisenhower 1953 61 John F
PRESIDENT NIXON & THE WITHDRAWAL FROM VIETNAM L obj: to consider whether the USA lost the war in Vietnam, or whether the Vietcong won it. US Presidents (during Vietnam) Dwight Eisenhower 1953 61 John F
WORLD HISTORY WORLD WAR II
 WORLD HISTORY WORLD WAR II BOARD QUESTIONS 1) WHO WAS THE LEADER OF GERMANY IN THE 1930 S? 2) WHO WAS THE LEADER OF THE SOVIET UNION DURING WWII? 3) LIST THE FIRST THREE STEPS OF HITLER S PLAN TO DOMINATE
WORLD HISTORY WORLD WAR II BOARD QUESTIONS 1) WHO WAS THE LEADER OF GERMANY IN THE 1930 S? 2) WHO WAS THE LEADER OF THE SOVIET UNION DURING WWII? 3) LIST THE FIRST THREE STEPS OF HITLER S PLAN TO DOMINATE
