The arms race meant that the US feared war in Vietnam because of potential nuclear attack from the Soviet Union.
|
|
|
- Melanie Lindsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The situation in Vietnam by 1961 Vietnam was a French colony, known as French Indochina. Ho Chi Minh was at war with the French, fighting for Vietnamese independence. He won a decisive victory at Dien Bien Phu in The Geneva Peace Accords (1954) split the country at the 17 th Parallel. North Vietnam became Communist under Ho Chi Minh whilst South Vietnam became a democracy, eventually led by Ngo Dinh Diem. President Eisenhower showed American support for the South. Ngo Dinh Diem was corrupt. Elections were rigged and the culture of the tribal Montagnards came under attack. The ARVN (Army of the Republic of Vietnam) led attacks against Viet Minh forces, which led to insurgency in the South. Ho Chi Minh wanted unity with the South and was supported by China and the Soviet Union who provided military and economic aid. The National Liberation Front for the Liberation of South Vietnam (NFL) was founded in The context of the Cold War The arms race meant that the US feared war in Vietnam because of potential nuclear attack from the Soviet Union. Involvement in the Cold War was based on the policy of containment (keeping Communism within current Communist countries) and the Domino Theory (that if a country fell to Communism then those surrounding it would fall too). These become the main reasons for involvement in Vietnam. There was a Communist revolution in China in Nikita Khrushchev was the leader of the Communist Soviet Union after the death of Stalin in Both countries supported the Communist Ho Chi Minh. The US was also involved in a war in Korea to prevent the Communist takeover of the South. This set a precedent for US involvement in Asia against Communism. The actions and policies of President Kennedy
2 President John F. Kennedy came into office in January 1961 with the same worldview as Eisenhower. He felt the forces of Communism were a threat that had to be met by the US. He became further involved in South Vietnam as the power of the Viet Cong grew. One of Kennedy s first actions was to sponsor an unsuccessful anti-communist invasion of the Bay of Pigs in Cuba in April This failure led to an increased desire for success against Communism in South-East Asia. He needed to prove himself. Kennedy tried to reduce insurgency in South Vietnam through two non-combat methods. Firstly, the Strategic Hamlet Programme placed peasants into armed and protected villages to deny the Viet Cong manpower, food and intelligence. The peasants disliked this because it uprooted them from their ancestral lands. Ho Chi Minh- leader of North Vietnam- was incredibly popular and well liked by the people. Thus, he was able to mobile mass support. Lots of people moved from South to North Vietnam. The significance of the assassinations of President Diem and President Kennedy The Cuban Missile Crisis in 1962, when the Soviet Union began placing missiles in Cuba, was the closest the world ever came to nuclear war. Afterwards, talks between Kennedy and Khrushchev relaxed the tensions between the US and Soviet Union. The leader of South Vietnam (DIEM) was corrupt, brutal and oppressive. He dealt savagely with any Buddhist opposition in the country. The US felt something had to be done as protest and discontent was building. The arrest and assassination of Diem marked the end of a successful CIA-backed coup d'état (the sudden overthrow of a government by a small group). The removal of Diem presented the US with a chance to further their influence in South Vietnam. Kennedy was assassinated on 22 November LBJ became US president with a more aggressive policy towards Vietnam. LBJ: Who was advising Johnson The Working Group Defence department, State department, Central Intelligence Agency (CIA), Joint Chiefs of Staff (JCS). They told him: o An independent, anti-communist South Vietnam was vital to America o That the Domino Theory was a real possibility and danger o That American national prestige, credibility and honour were at stake o Increasing the war was needed as the weak South Vietnamese government were struggling This was all well and good but Johnson needed to convince Congress (US Government) and the US public that there was a need for more intervention in
3 Vietnam. (Remember Johnson cannot raise the money to go to war without Congress approval) USA ATTACKED: On July 28, 1964 the United States ordered the Navy destroyer the USS Maddox to sail to the Gulf of Tonkin. The Maddox was to assist South Vietnamese commandos on raids in North Vietnam. The first couple of days nothing happened and then on August 2 the Maddox was attacked. Three North Vietnamese torpedo boats attacked the destroyer. The Maddox fought back sinking two and sending the other ship away crippled. The people of the United States wanted action for the attack on the Maddox. Then there was report of a second alleged attack, although Captain said he was unsure who had fired. Due to the attacks Congress gave Johnson the power to do additional military action to North Vietnam for the future. The Tokin Gulf Resolution was formed due to this. It was formed to "Take all necessary measures to repel an armed attack against the forces of the United States and to prevent further aggression." Johnson won a landslide victory in the November 1964 presidential election partly because he was seen as the great protector, taking revenge on the North Vietnamese for the Gulf of Tonkin attack.
4
5 USA TACTICS VIETNAM WAR: Tactic What was this? Why was it used? How successful was it? Operation Rolling Thunder Search and destroy Operation Rolling Thunder was an US response to a Vietcong attack on an American base, Pleiku. Nine Americans were killed and nearly 100 wounded. It was the use of helicopters by the Americans. They landed the helicopters close to the Vietcong-controlled villages. Vietcong suspects would be interrogated, usually in a brutal manner. It was designed to destroy roads, railways and Vietcong bases in North Vietnam, especially the Ho Chi Minh Trial. The Americans used search and destroy tactics to try and flush the Vietcong out of the countryside. The heavy bombing did not destroy the Vietcong. The campaign was only supposed to last eight weeks but continued until October 1968 (3 years) T It had little effect on the guerrilla tactics used by the Vietcong. 643,000 tons of bombs were dropped ( 3 times the number dropped in WW2) 900 US aircraft were lost. Estimated damage done to North Vietnam was $300 million. Cost to the US of these raids was estimated at $900 million. Led to increased demand for soldiers. Draft increased in Heavy financial burden- war was costing 17 billion by the end. Civilian casualties were very high. This made the US and South Vietnamese forces even more unpopular. Often led to deaths of innocent civilians including women and children. The missions made ordinary people hate the Americans: as one marine said of a search and destroy mission If they weren t Viet Cong before we got there, they sure as hell were by the time we left. The Viet Cong often helped the villager s re-build their homes and bury their dead (win hearts and minds). US soldiers who took part in search and destroy suffered psychological consequence, became trigger happy, PTSD, addicted to heroin, de sensitized to death. By ,000 men were treated for combat wounds and 20,000 for drug abuse. Between 1966 and 1973 there were 503,000 cases of desertion. Force was inexperienced with little knowledge of guerrilla warfare. Not full combat troops but men who had been drafted in and who had no skill or desire to fight. 70,000 VETERANS SUFFERED PTSD after effects.
6 Agent Orange and napalm My Lai massacre These were chemical weapons used by the Americans: - Agent Orange destroyed forests and crops. Exposure to it could cause cancers and birth defects. - Napalm contained petrol and chemicals which burned skin to the bone. On 16th March, 1968, nine helicopter gunships landed three US platoons near the village of My Lai. Over a two hour period, the Americans killed hundreds of men, women and children - probably 300, but maybe more. Rapes and body mutilation took place. They were used to try and flush the Vietcong out of the jungle. The US troops were on a search and destroy mission and My Lai was believed to be a Vietcong stronghold. These tactics did not work. It turned world opinion against the USA for using inhumane weapons- made USA look brutal and inhumane. The public did not support what they were doing and this hurt the soldiers morale. It alienated even more of the South Vietnamese people who turned to the Vietcong. The truth about the massacre did not come out for eighteen months and publication of graphic photos followed. Pictures of the massacre were shown around the word and people were appalled. It was another reason why many Americans began to turn against the war. Massacre removed any thoughts that amerciasn were fighting a moral good v evil war. US soldiers returning home referred to as baby killers.
7 VIETCONG TACTICS Guerrilla Tactics Tactic What was this? Why was it used? How successful was it? They fought a guerrilla war, ambushing US patrols, setting booby traps and landmines, and planting bombs in towns. They mingled in with the peasants, wearing ordinary clothes.they were supplied with rockets and weapons by China and Russia. Their tactic was "hanging onto the belts" of the Americans - staying so close to the Americans so they could not use air or artillery backup without killing their own men. The Americans couldn't identify who the enemy was. They knew the landscape and had the support of the people- used this to their advantage. Incredibly. America, despite their military and economic advantage, could not beat them. It made US soldiers paranoid and seriously harmed their morale as they could not deal or win against these tactics. Led to serious injuries, death, PTSD amongst soldiers. Brought USA into an unwinnable expensive war- 17 billion a year. Meant they needed more and more troops to deal with these tactics. Led to the draft being increased in 1965 which was deeply unpopular. Booby traps are an example of a Viet Cong tactic. Example of Guerilla Tactic. For example, the Viet Cong would place trip wires or dig holes filled with spikes, sometimes coated in human excrement, and then would cover the hole with leaves to deceive the enemy. Markers like broken sticks would be left on the path to warn fellow Viet Cong about the locations. See Above See above Power of VC fighters- Fighting for causes they really believed in e.g. unification and independence. Many welcomed the chance to fight for liberation. They won the support of the peasants who were unhappy with the government and the search and destroy tactics being used against them. Almost unlimited economic resources. They were prepared to accept a very heavy body count and between 500,000 and 900,000 died during the war. They knew the terrain and were skilled in guerrilla and jungle warfare. Did not have good air power or much money.
8 They were supplied by the USSR and China. The USSR provided 8,000 anti-aircraft guns and 200 anti-aircraft missile sites. Total assistance is estimated at $2 billion between 1965 and Their bases were very well hidden and surrounded by booby traps Tunnels These were used by Viet Cong guerrillas as hiding spots during combat, as well as serving as communication and supply routes, hospitals, food and weapon caches and living quarters for numerous guerrilla fighters. They knew the landscape and used this to their advantage. Deeply frustrated the US soldiers who could not locate the tunnels. Impact see above. The Ho Chi Minh Trail This was a network of paths that served as hidden route through the jungle, not only of Vietnam but neighbouring Laos and Cambodia as well, for Viet Cong soldiers and Vietnamese Civilians. The Viet Cong used it to move troops, weapons and other supplies into and around the country without being detected by the Americans. It was essential in allowing the North Vietnamese to beat the Americans. The Americans couldn't attack their supply routes without escalating the war in to Laos and Cambodia Tet Offensive Started on 31st January, It was an attack by the Vietcong on more than 100 cities, towns and military bases throughout South Vietnam, including Saigon during Vietnamese New Year It was totally different to the guerrilla fighting they has used before and was a surprise attack. 15 man suicide squad took over American embassy and held out for 6 hours. Northern town of Hue captured and took 25 days for US to retake it at a loss of 3000 civilians. Tet Offensive could be seen as a huge failure for the North Vietnamese and Vietcong; 47% of the people killed during the Tet Offensive were Vietcong, 24% were NVA and 22% were civilians. Just 5% were South Vietnam Army ARVN and 2% were US troops. This seems to show it was a massive success for the Americans As a result of what they saw as a failure, the North Vietnamese agreed to peace talks soon after the
9 The Communists expected the people to join them, but the uprisings they hoped for did not happen. Tet Offensive ended. VC lost most of its best guerrilla fighters From now on, the NVA did most of the fighting, as the Vietcong never recovered from the setback of Tet. On the other hand, the Tet Offensive was a huge turning point and was a major reason why more and more Americans turned against the war; Before the Tet Offensive, the Americans had been quite confident - maybe complacent - about the way the war was going. The US media had given the Americans back home the impression that the war would soon end. But, when the news of Tet appeared, many Americans felt that they had been deceived by the army. Vietcong troops were shown inside the US embassy in Saigon, which seemed to show that the war could not be won, or at least not for a long time. Most Americans became convinced that the war had to be ended as soon as possible. Tet also played a large part in Johnson's decision to give up hopes of standing as President again. Richard Nixon, the Republican candidate, promised to end the war and was elected as President.
10 REASONS FOR US WITHDRAWAL: The importance of television and the media in influencing public opinion Vietnam was the first television war. It brought the horror of war into people's living rooms and eventually turned many against it. The US administration, unlike most governments at war, made no official attempt to censor the reporting in the Vietnam War. Every night, on colour television, people saw pictures of dead and wounded marines. Walter Cronkite was a powerful and influential broadcaster on Vietnam War.
11 One of the most influential acts during the war was the decision of Life Magazine to fill one edition with photographs of the 242 US soldiers killed in Vietnam during one week of the fighting. Public opinion polls carried out at the time, however, suggested that tax increases to pay for the war, or the death of someone they knew, were far more likely to influence most people's attitude towards the war than the mass media. Growing student protests from 1966 The first march to Washington against the war took place in December, Only 25,000 people took part but it was still the largest anti-war demonstration in American history. The first big protests came in October 1965 when the draft was increased. In February 1965, it had only been 3,000 a month but in October it was increased to 33,000 a month. Those who had the necessary pull had the opportunity to draft-dodge but this was not a luxury open to many poor working class young men. Tearing up or burning your draft paper became a common occurrence and was seen to be the first of the protests against the Vietnam War. The most famous person to do this was the world heavyweight-boxing champion Muhammad Ali. Between 1963 and 1973, 9,118 men were prosecuted for refusing to be drafted into the army. In March 1966, 50,000 anti-war protesters took part in a rally in one of America s most famous cities New York. With a population that ran into millions, it could be argued that they represented a very small minority of the city. In 1967, 100,000 took part in a protest rally in Washington DC. In 1971, 300,000 took part in an anti-war demonstration in the same city. This particular protest involved many veterans from the war. When they publicly threw away their medals and medal ribbons, many in America were shocked In 1967, a group of distinguished academics under the leadership of Bertrand Russell, set up the International War Crimes Tribunal. After interviewing many witnesses, they came to the conclusion that the United States was guilty of using weapons against the Vietnamese that were prohibited by international law. The United States armed forces were also found guilty of torturing captured prisoners and innocent civilians. The Tribunal, and other critics of the war, claimed that the US behaviour in Vietnam was comparable to the atrocities committed by the Nazis in Europe during the Second World War. Many of the anti-war protesters were also hippies, a group of youths who protested against society as a whole. They used drugs and music to rebel against the norm and joined in with mass protest marches against the Vietnam War e.g Kenn State Massacre.
12 Protests originated in colleges because, at the start of the war, men could avoid the draft by continuing their education. Students used a range of ways to avoid the fighting, including getting braces and claiming insanity. Alongside students, the Civil Rights Movement also had a role in anti-war protest. Black people were fighting for equality in America and they argued that it was unfair that black soldiers were dying in Vietnam for a country that did not recognise them as equals. Martin Luther King encouraged peaceful protest from African Americans. Eldridge Cleaver, a Civil Rights activist pointed out, in many southern states of America, blacks were being denied the right to vote in elections. Therefore, blacks were fighting in Vietnam "for something they don't have for themselves." Johnson and Congress naturally paid great attention to public opinion. It is generally agreed that opposition to the war from the public and in the press was the main reason why Johnson finally decided upon retreat. Supporters of the war, however, continued to put pressure on Johnson to maintain the fighting. COST: 17 Billion a year was an impossible burden for the taxpayer to carry, especially as they questioned the reasons for being in the war in the first place. Vietnamization: By 1969 more than 36,000 members of the US military had been killed in the war. Nixon began the policy of Vietnamization to try to end the war. This meant taking American troops out of Vietnam and leaving the South Vietnamese troops of the ARVN to do the fighting. The USA would still help by giving arms and money and advice to the ARVN. At the same time, Nixon continued peace talks as well as continuing to bomb North Vietnam heavily to try to persuade them to give up. Idea of the Madman theory came about in relation to Nixon. Nixon ordered the invasion of Cambodia in 1970 and then Laos in The aim was to disrupt the Ho Chi Minh Trail and to destroy Vietcong bases in these countries. The invasions also led to more protests against the war back in the USA. It seemed as if Nixon was escalating the war, not trying to bring about peace. Operation Linebacker II:
13 In October 1972, Henry Kissinger, the US Secretary of State, announced that peace was at hand. However, when President Thieu refused to accept the peace terms Nixon escalated the bombing of North Vietnam. The bombing began on the 12 th December and continued for 12 days. This operation was called Operation Linebacker II and was the biggest aerial attack of the war. The aim of the attack was to win concessions from the communists at peace talks in Paris. The bombing was relentless, more than 1600 civilians died and 70 US airmen were killed or captured. The New York Times responded and called the bombing Diplomacy through Terror. In January 1973 the USA and North Vietnam signed a treaty to end the war Agreement: An agreement was reached in October The terms were: North Vietnam dropped its demand that President Thieu be replaced by coalition. Nixon and Kissinger agreed to allow the North Vietnamese army to remain in the areas they controlled. The Vietcong were allowed to participate in the final settlement. A ceasefire agreement was reached and the USA agreed to withdraw all remaining troops. All US prisoners of war would be repatriated. BUT: North Vietnam then invaded the South and, in 1975 Saigon fell to the Communists. The government of North Vietnam united both North and South Vietnam on 2 July 1976 to form the Socialist Republic of Vietnam.
Chapter 19: Going To war in Vietnam
 Heading Towards War Vietnam during WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the. returned to Vietnam
Heading Towards War Vietnam during WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the. returned to Vietnam
The War in Vietnam. Chapter 30
 The War in Vietnam Chapter 30 Vietnam A colony of France until after World War II 1954- War for Independence led by Ho Chi Minh Ho Chi Minh The Geneva Accords The Geneva Accords divided the country into
The War in Vietnam Chapter 30 Vietnam A colony of France until after World War II 1954- War for Independence led by Ho Chi Minh Ho Chi Minh The Geneva Accords The Geneva Accords divided the country into
Ended French rule in Indo-China
 Vietnam Review Dien Bien Phu in 1954 the main French forces were surrounded at this location in the north of Vietnam and forced to surrender. This was a turning point in that it ended the French control
Vietnam Review Dien Bien Phu in 1954 the main French forces were surrounded at this location in the north of Vietnam and forced to surrender. This was a turning point in that it ended the French control
VIETNAM WAR
 VIETNAM WAR 1955-1975 #30 http://www.military.com/video/offduty/movies/classic-forrest-gump-invietnam-war/1069387728001 PRESIDENTS DURING THE VIETNAM WAR Dwight D. Eisenhower. John F. Kennedy. Lyndon B.
VIETNAM WAR 1955-1975 #30 http://www.military.com/video/offduty/movies/classic-forrest-gump-invietnam-war/1069387728001 PRESIDENTS DURING THE VIETNAM WAR Dwight D. Eisenhower. John F. Kennedy. Lyndon B.
Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs. non Communist South Organized by Ho Chi Minh
 1956 Elections are cancelled (1 of Geneva Accords) 1957 The Vietcong attack in South Vietnam Vietcong are South Vietnamese communists Guerrilla fighters Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs.
1956 Elections are cancelled (1 of Geneva Accords) 1957 The Vietcong attack in South Vietnam Vietcong are South Vietnamese communists Guerrilla fighters Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs.
Vietnam Introduction. Answer the following questions on a sticky note...
 Vietnam Introduction Answer the following questions on a sticky note... https://www.youtube.c om/watch?v=epfnsk5l 26U Burning Monk 1. Why was the burning monk event significant? How did people in the U.S.
Vietnam Introduction Answer the following questions on a sticky note... https://www.youtube.c om/watch?v=epfnsk5l 26U Burning Monk 1. Why was the burning monk event significant? How did people in the U.S.
ANSWER KEY..REVIEW FOR Friday s QUIZ #15 Chapter: 29 -Vietnam
 ANSWER KEY..REVIEW FOR Friday s QUIZ #15 Chapter: 29 -Vietnam Ch. 29 sec. 1 - skim and scan pages 908-913 and then answer the questions. French Indochina: French ruled colony made up of Vietnam, Laos,
ANSWER KEY..REVIEW FOR Friday s QUIZ #15 Chapter: 29 -Vietnam Ch. 29 sec. 1 - skim and scan pages 908-913 and then answer the questions. French Indochina: French ruled colony made up of Vietnam, Laos,
VIETNAM WAR
 VIETNAM WAR 1965-1972 FRENCH CONTROL French controlled Vietnam until World War II Vietnam taken by Japan Ho Chi Minh called for an independence of Vietnam Eight Year war between France and Ho Chi Minh
VIETNAM WAR 1965-1972 FRENCH CONTROL French controlled Vietnam until World War II Vietnam taken by Japan Ho Chi Minh called for an independence of Vietnam Eight Year war between France and Ho Chi Minh
VUS.13b. The Vietnam War. U. S. government s anti- Communist strategy of containment in Asia
 VUS.13b The Vietnam War U. S. government s anti- Communist strategy of containment in Asia Help the French and send some advisors- Increase advisors, send some troops- Escalate- we can not lose a war Peace
VUS.13b The Vietnam War U. S. government s anti- Communist strategy of containment in Asia Help the French and send some advisors- Increase advisors, send some troops- Escalate- we can not lose a war Peace
The Vietnam War,
 The Vietnam War, 1954 1975 Who was Ho Chi Minh? Vietnamese Communist who wanted self rule for Vietnam. Why did the United States aid the French? The French returned to Vietnam in 1946. As the Vietminh
The Vietnam War, 1954 1975 Who was Ho Chi Minh? Vietnamese Communist who wanted self rule for Vietnam. Why did the United States aid the French? The French returned to Vietnam in 1946. As the Vietminh
The Vietnam War. Summary
 The Vietnam War Summary The Vietnam War grew out of the American commitment to the containment of communism during the Cold War. For approximately fifteen years, the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (North
The Vietnam War Summary The Vietnam War grew out of the American commitment to the containment of communism during the Cold War. For approximately fifteen years, the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (North
Chapter 30-1 CN I. Early American Involvement in Vietnam (pages ) A. Although little was known about Vietnam in the late 1940s and early
 Chapter 30-1 CN I. Early American Involvement in Vietnam (pages 892 894) A. Although little was known about Vietnam in the late 1940s and early 1950s, American officials felt Vietnam was important in their
Chapter 30-1 CN I. Early American Involvement in Vietnam (pages 892 894) A. Although little was known about Vietnam in the late 1940s and early 1950s, American officials felt Vietnam was important in their
OBJECTIVES. Describe and evaluate the events that led to the war between North Vietnam and South Vietnam.
 OBJECTIVES Describe and evaluate the events that led to the war between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. Identify and explain the foreign policy of the United States at this time, and how it relates to
OBJECTIVES Describe and evaluate the events that led to the war between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. Identify and explain the foreign policy of the United States at this time, and how it relates to
Chapter 19 GOING TO WAR IN VIETNAM
 Chapter 19 GOING TO WAR IN VIETNAM VIETNAM DURING WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the Japanese.
Chapter 19 GOING TO WAR IN VIETNAM VIETNAM DURING WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the Japanese.
Chapter 20. The Vietnam War Era
 Chapter 20 The Vietnam War Era 1954-1975 Ho Chi Minh The most important voice who demanded independence for Vietnam. Communist leader of the Vietminh. Vietminh The term initially used to describe all Vietnamese
Chapter 20 The Vietnam War Era 1954-1975 Ho Chi Minh The most important voice who demanded independence for Vietnam. Communist leader of the Vietminh. Vietminh The term initially used to describe all Vietnamese
Vietnam Before WWII During the early 1900s, nationalism was strong in. As the Vietnamese sought or reform of the colonial government, several
 Name Date Per Vietnam Before WWII During the early 1900s, nationalism was strong in. As the Vietnamese sought or reform of the colonial government, several political parties formed. One of the leaders
Name Date Per Vietnam Before WWII During the early 1900s, nationalism was strong in. As the Vietnamese sought or reform of the colonial government, several political parties formed. One of the leaders
SECTION 1: MOVING TOWARD CONFLICT PAGE 730
 CHAPTER 22 SECTION 1: MOVING TOWARD CONFLICT PAGE 730 Main Idea: America gets involved in Vietnam to stop the spread of communism TERMS AND NAMES: Ho Chi Minh Ngo Dinh Diem Vietcong Vietminh domino theory
CHAPTER 22 SECTION 1: MOVING TOWARD CONFLICT PAGE 730 Main Idea: America gets involved in Vietnam to stop the spread of communism TERMS AND NAMES: Ho Chi Minh Ngo Dinh Diem Vietcong Vietminh domino theory
VIETNAM 04/14/15 ORIGINS OF THE VIETNAM WAR s French establish control over Indochina - Southeast Asia
 VIETNAM Have you seen Charlie? 04/12/15 2 ORIGINS OF THE VIETNAM WAR 1800 s French establish control over Indochina - Southeast Asia Modern countries: Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos Transplanted French laws
VIETNAM Have you seen Charlie? 04/12/15 2 ORIGINS OF THE VIETNAM WAR 1800 s French establish control over Indochina - Southeast Asia Modern countries: Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos Transplanted French laws
THEMES. 1) EXPANDING DEMOCRACY: America s mission in Vietnam was to halt the spread of communism-a threat to democracy.
 THEMES 1) EXPANDING DEMOCRACY: America s mission in Vietnam was to halt the spread of communism-a threat to democracy. 2) CONSTITUTIONAL CONCERNS: Among the constitutional issues of the Vietnam War era
THEMES 1) EXPANDING DEMOCRACY: America s mission in Vietnam was to halt the spread of communism-a threat to democracy. 2) CONSTITUTIONAL CONCERNS: Among the constitutional issues of the Vietnam War era
Standard 8.0- Demonstrate an understanding of social, economic and political issues in contemporary America. Closing: Quiz
 Standard 8.0- Demonstrate an understanding of social, economic and political issues in contemporary America. Opening: Great Society Chart Work Period: Vietnam War Notes Political Cartoon Double Flow Map
Standard 8.0- Demonstrate an understanding of social, economic and political issues in contemporary America. Opening: Great Society Chart Work Period: Vietnam War Notes Political Cartoon Double Flow Map
Notes: LG: Analyze how the 1960s changed America.
 Notes: LG: Analyze how the 1960s changed America. USSR Nikita Khrushchev 1953-1964 1. Cold War Abroad in the 1960s a. 1961, Bay of Pigs Invasion (Cuba) i. President Eisenhower and CIA train Cuban
Notes: LG: Analyze how the 1960s changed America. USSR Nikita Khrushchev 1953-1964 1. Cold War Abroad in the 1960s a. 1961, Bay of Pigs Invasion (Cuba) i. President Eisenhower and CIA train Cuban
Ch 29-1 The War Develops
 Ch 29-1 The War Develops The Main Idea Concern about the spread of communism led the United States to become increasingly violent in Vietnam. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze how the Cold war and
Ch 29-1 The War Develops The Main Idea Concern about the spread of communism led the United States to become increasingly violent in Vietnam. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze how the Cold war and
Conflict U.S. War
 Conflict - 1945-1975 U.S. War 1964-1973 Overview of the Vietnam War Why is Vietnam still a painful war to remember? Longest war in U.S. history and only war we lost It showed Americans that our power is
Conflict - 1945-1975 U.S. War 1964-1973 Overview of the Vietnam War Why is Vietnam still a painful war to remember? Longest war in U.S. history and only war we lost It showed Americans that our power is
Modern American History Unit 8: The 1960s The Vietnam War Notes and Questions
 Modern American History Unit 8: The 1960s The Vietnam War Notes and Questions The Vietnam War A. Vietnam: A Painful War U.S. involvement in conflicts in Vietnam lasted from mid-1940s to 1975 Only war the
Modern American History Unit 8: The 1960s The Vietnam War Notes and Questions The Vietnam War A. Vietnam: A Painful War U.S. involvement in conflicts in Vietnam lasted from mid-1940s to 1975 Only war the
National Nightmare Begins: Origins of Vietnam War
 National Nightmare Begins: Origins of Vietnam War From late 1800 s until WWII (When Japan took over) France ruled Indochina (Vietnam, Laos & Cambodia). French took land from peasants & built large plantations,
National Nightmare Begins: Origins of Vietnam War From late 1800 s until WWII (When Japan took over) France ruled Indochina (Vietnam, Laos & Cambodia). French took land from peasants & built large plantations,
1) Read the article on American involvement in Vietnam
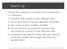 Warm Up 1) Read the article on American involvement in Vietnam 1) Circle in the causes of the Vietnam War 2) Put a star next to the key people/ countries 3) Box in key events, battles, treaties 4) Put
Warm Up 1) Read the article on American involvement in Vietnam 1) Circle in the causes of the Vietnam War 2) Put a star next to the key people/ countries 3) Box in key events, battles, treaties 4) Put
1969 U.S. troops begin their withdrawal from Vietnam
 Vietnam War Years Timeline 1964 LBJ becomes President 1965 First major combat units arrive in Vietnam 1968 M.L.King and Robert Kennedy are assassinated 1969 U.S. troops begin their withdrawal from Vietnam
Vietnam War Years Timeline 1964 LBJ becomes President 1965 First major combat units arrive in Vietnam 1968 M.L.King and Robert Kennedy are assassinated 1969 U.S. troops begin their withdrawal from Vietnam
There will be some disturbing images and footage as we cover this unit, please do your best to act as adults, and learn from this war.
 There will be some disturbing images and footage as we cover this unit, please do your best to act as adults, and learn from this war. Vietnam Intro Before WWII, Vietnam was a colony of the French Japanese
There will be some disturbing images and footage as we cover this unit, please do your best to act as adults, and learn from this war. Vietnam Intro Before WWII, Vietnam was a colony of the French Japanese
UNDERGROUND COMPLEXES
 UNDERGROUND COMPLEXES TET OFFENSIVE Morale among U.S. soldiers remained generally high from 1965-1968. Many battlefield successes. Johnson Admin. reported that the war was all but won. Temporary ceasefire
UNDERGROUND COMPLEXES TET OFFENSIVE Morale among U.S. soldiers remained generally high from 1965-1968. Many battlefield successes. Johnson Admin. reported that the war was all but won. Temporary ceasefire
HISTORY REVISION GUIDE
 Name Paper 2 HISTORY REVISION GUIDE THE USA AND VIETNAM: FAILURE ABROAD AND AT HOME 1964-1975 NOTE: This guide only prepares you for the Paper 2 Section B questions on Vietnam. You must use your other
Name Paper 2 HISTORY REVISION GUIDE THE USA AND VIETNAM: FAILURE ABROAD AND AT HOME 1964-1975 NOTE: This guide only prepares you for the Paper 2 Section B questions on Vietnam. You must use your other
The Vietnam War Era ( ) Lesson 2 America s Role Escalates
 The Vietnam War Era (1954-1975) Lesson 2 America s Role Escalates The Vietnam War Era (1954-1975) Lesson 2 America s Role Escalates Learning Objectives Analyze the major issues and events that caused President
The Vietnam War Era (1954-1975) Lesson 2 America s Role Escalates The Vietnam War Era (1954-1975) Lesson 2 America s Role Escalates Learning Objectives Analyze the major issues and events that caused President
C. Continuing protests Doves wanted an immediate withdrawal that was complete, unconditional, and irreversible.
 I. VIETNAM WAR spread across 5 presidencies and spanned 25 years Direct U.S involvement from 1963-1973 A. France lost control of Vietnam after the battle of Dien Bien Phu in 1954 1. U.S. by 1954 had financed
I. VIETNAM WAR spread across 5 presidencies and spanned 25 years Direct U.S involvement from 1963-1973 A. France lost control of Vietnam after the battle of Dien Bien Phu in 1954 1. U.S. by 1954 had financed
Moving Toward Conflict
 The Vietnam War Years Moving Toward Conflict Terms and Names Ho Chi Minh Leader of North Vietnam Vietminh Communist group led by Ho Chi Minh domino theory Eisenhower s explanation for stopping communism
The Vietnam War Years Moving Toward Conflict Terms and Names Ho Chi Minh Leader of North Vietnam Vietminh Communist group led by Ho Chi Minh domino theory Eisenhower s explanation for stopping communism
Chapter 29. Section 3 and 4
 Chapter 29 Section 3 and 4 The War Divides America Section 3 Objectives Describe the divisions within American society over the Vietnam War. Analyze the Tet Offensive and the American reaction to it. Summarize
Chapter 29 Section 3 and 4 The War Divides America Section 3 Objectives Describe the divisions within American society over the Vietnam War. Analyze the Tet Offensive and the American reaction to it. Summarize
The Cold War Finally Thaws Out. Korean War ( ) Vietnam War ( ) Afghan War ( )
 The Cold War Finally Thaws Out Korean War (1950-1953) Vietnam War (1963-1973) Afghan War (1979-1989) Korean war Split after WWII between US and USSR Temporary gov ts created in images of their major allies
The Cold War Finally Thaws Out Korean War (1950-1953) Vietnam War (1963-1973) Afghan War (1979-1989) Korean war Split after WWII between US and USSR Temporary gov ts created in images of their major allies
netw rks Where in the world? When did it happen? The Vietnam Era Lesson 1 Kennedy s Foreign Policy ESSENTIAL QUESTION Terms to Know GUIDING QUESTIONS
 Lesson 1 Kennedy s Foreign Policy ESSENTIAL QUESTION What motivates people to act? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. Why did President Kennedy seek new ways to deal with the challenges and fears of the Cold War? 2.
Lesson 1 Kennedy s Foreign Policy ESSENTIAL QUESTION What motivates people to act? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. Why did President Kennedy seek new ways to deal with the challenges and fears of the Cold War? 2.
TRUMAN S ROLE IN VIETNAM. = America is busy!!!!!
 TRUMAN S ROLE IN VIETNAM Saw Vietnam as extension of Cold War - democracy v. communism! France fighting to re-gain Vietnam Truman supported France with money supplies because didn t want Something going
TRUMAN S ROLE IN VIETNAM Saw Vietnam as extension of Cold War - democracy v. communism! France fighting to re-gain Vietnam Truman supported France with money supplies because didn t want Something going
War. Ho Chi Minh. domino theory. Dien Bien Phu SEATO. Vietcong Gulf of Tonkin Resolution. the end of WWII? ce? supporting
 Chapter 29 Section 1 Origins of the Vietnam War Ho Chi Minh domino theory Dien Bien Phu SEATO Vietcong Gulf of Tonkin Resolution 1. Witness History: What countries made up French Indochina? 2. What state
Chapter 29 Section 1 Origins of the Vietnam War Ho Chi Minh domino theory Dien Bien Phu SEATO Vietcong Gulf of Tonkin Resolution 1. Witness History: What countries made up French Indochina? 2. What state
History Skill Builder. Perspective Taking
 History Skill Builder Perspective Taking Perspective Taking History is a written by people, with different points of view and biases. Conflicts arise from differences of opinion, competing interests. Compromises
History Skill Builder Perspective Taking Perspective Taking History is a written by people, with different points of view and biases. Conflicts arise from differences of opinion, competing interests. Compromises
PRESIDENT NIXON & THE WITHDRAWAL FROM VIETNAM. L obj: to consider whether the USA lost the war in Vietnam, or whether the Vietcong won it.
 PRESIDENT NIXON & THE WITHDRAWAL FROM VIETNAM L obj: to consider whether the USA lost the war in Vietnam, or whether the Vietcong won it. US Presidents (during Vietnam) Dwight Eisenhower 1953 61 John F
PRESIDENT NIXON & THE WITHDRAWAL FROM VIETNAM L obj: to consider whether the USA lost the war in Vietnam, or whether the Vietcong won it. US Presidents (during Vietnam) Dwight Eisenhower 1953 61 John F
Ch. 16 Sec. 1: Origins of the Vietnam War
 CHAPTER 16 QUESTIONS 5 sections, and Document Based Questions Ch. 16 Sec. 1: Origins of the Vietnam War 1) French Indochina included which three cultures? 2) How many people lived in Indochina by the end
CHAPTER 16 QUESTIONS 5 sections, and Document Based Questions Ch. 16 Sec. 1: Origins of the Vietnam War 1) French Indochina included which three cultures? 2) How many people lived in Indochina by the end
Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs. non Communist South Organized by Ho Chi Minh
 1956 Elections are cancelled (1 of Geneva Accords) 1957 The Vietcong attack in South Vietnam Vietcong are South Vietnamese communists Guerrilla fighters Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs.
1956 Elections are cancelled (1 of Geneva Accords) 1957 The Vietcong attack in South Vietnam Vietcong are South Vietnamese communists Guerrilla fighters Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs.
20 th /Raffel The Vietnam War: Containment Leads to Disaster About this Assignment: The Vietnam war was one of the most controversial wars in
 20 th /Raffel The Vietnam War: Containment Leads to Disaster About this Assignment: The Vietnam war was one of the most controversial wars in American history. In retrospect, there were many missed opportunities
20 th /Raffel The Vietnam War: Containment Leads to Disaster About this Assignment: The Vietnam war was one of the most controversial wars in American history. In retrospect, there were many missed opportunities
UNIT Y222 THE COLD WAR IN ASIA
 UNIT Y222 THE COLD WAR IN ASIA 1945-1993 NOTE: BASED ON 2 X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources Western Policies
UNIT Y222 THE COLD WAR IN ASIA 1945-1993 NOTE: BASED ON 2 X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources Western Policies
The Vietnam War Why does the United States get involved in Vietnam?
 Why does the United States get involved in Vietnam? Vietnam had been a French colony since the late 1800s. After World War II, the French began to battle the Viet Minh, who wanted to kick out the French
Why does the United States get involved in Vietnam? Vietnam had been a French colony since the late 1800s. After World War II, the French began to battle the Viet Minh, who wanted to kick out the French
The Vietnam War Era ( ) Lesson 4 The War s End and Effects
 The Vietnam War Era (1954-1975) Lesson 4 The War s End and Effects The Vietnam War Era (1954-1975) Lesson 4 The War s End and Effects Learning Objectives Assess Nixon s new approach to the war, and explain
The Vietnam War Era (1954-1975) Lesson 4 The War s End and Effects The Vietnam War Era (1954-1975) Lesson 4 The War s End and Effects Learning Objectives Assess Nixon s new approach to the war, and explain
Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos Annotation
 Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos Annotation Name Directions: A. Read the entire article, CIRCLE words you don t know, mark a + in the margin next to paragraphs you understand and a next to paragraphs you don t
Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos Annotation Name Directions: A. Read the entire article, CIRCLE words you don t know, mark a + in the margin next to paragraphs you understand and a next to paragraphs you don t
1. America slowly involves itself in the war in Vietnam as it seeks to halt the spread of communism.
 The War in Vietnam Indochina was still another Cold War battlefield. France had controlled Vietnam since the middle of the 19th century, only to be supplanted by Japan during the Second World War. Meanwhile,
The War in Vietnam Indochina was still another Cold War battlefield. France had controlled Vietnam since the middle of the 19th century, only to be supplanted by Japan during the Second World War. Meanwhile,
VIETNAM: LEAD UP TO WAR
 VIETNAM: LEAD UP TO WAR Southeast Asia s Colonial History France gained control of Vietnam by 1883 despite fierce resistance from the Vietnamese. The French combined Vietnam with Laos and Cambodia to form
VIETNAM: LEAD UP TO WAR Southeast Asia s Colonial History France gained control of Vietnam by 1883 despite fierce resistance from the Vietnamese. The French combined Vietnam with Laos and Cambodia to form
The Sixties and Seventies. The Cold War cools down, Civil Rights get complicated, and the Baby Boomers come of age.
 The Sixties and Seventies The Cold War cools down, Civil Rights get complicated, and the Baby Boomers come of age. Learning Targets Describe the Kennedy years, with specific detail covering: The election
The Sixties and Seventies The Cold War cools down, Civil Rights get complicated, and the Baby Boomers come of age. Learning Targets Describe the Kennedy years, with specific detail covering: The election
Bell Ringer: April 18(19), 2018
 Announcements: 1: Test 5/4! Review is on the Weebly! Bell Ringer: April 18(19), 2018 Materials: 1: Spiral/blank sheet of paper 2: Vietnam War DBQ (PREAP) 1. Set up your Cornell notes 2. Across the top
Announcements: 1: Test 5/4! Review is on the Weebly! Bell Ringer: April 18(19), 2018 Materials: 1: Spiral/blank sheet of paper 2: Vietnam War DBQ (PREAP) 1. Set up your Cornell notes 2. Across the top
Lyndon Johnson and Vietnam. A Case Study
 Lyndon Johnson and Vietnam A Case Study Who was Lyndon B Johnson? Which US President won an election with the largest ever popular majority? Lyndon Baines Johnson, who took 61% of the vote in 1964. He
Lyndon Johnson and Vietnam A Case Study Who was Lyndon B Johnson? Which US President won an election with the largest ever popular majority? Lyndon Baines Johnson, who took 61% of the vote in 1964. He
Ho Declares Independence of Vietnam British Forces Land in Saigon, Return Authority to French First American Dies in Vietnam
 1945 Ho Chi Minh Creates Provisional Government Following the surrender of Japan to Allied forces, Ho Chi Minh and his People's Congress form a provisional government. Japan transfers all power to Ho's
1945 Ho Chi Minh Creates Provisional Government Following the surrender of Japan to Allied forces, Ho Chi Minh and his People's Congress form a provisional government. Japan transfers all power to Ho's
Gulf of Tonkin Resolution Lesson Plan
 Resolution Lesson Plan Central Historical Question: Was the U.S. planning to go to war with North Vietnam before the Resolution? Materials: Powerpoint Timeline Documents A-D Guiding Questions Plan of Instruction:
Resolution Lesson Plan Central Historical Question: Was the U.S. planning to go to war with North Vietnam before the Resolution? Materials: Powerpoint Timeline Documents A-D Guiding Questions Plan of Instruction:
Chapter 22. The Vietnam War Years
 Chapter 22 The Vietnam War Years Chapter 22-1 Moving Toward Conflict French Indochina 3 countries Vietnam Laos Cambodia French colonies late 1800s-WWII French Indochina French took land from native people
Chapter 22 The Vietnam War Years Chapter 22-1 Moving Toward Conflict French Indochina 3 countries Vietnam Laos Cambodia French colonies late 1800s-WWII French Indochina French took land from native people
2) How many cities in South Vietnam and how many U.S. air bases were attacked in the Tet Offensive?
 1) What is the Vietnamese holiday of Tet? 2) How many cities in South Vietnam and how many U.S. air bases were attacked in the Tet Offensive? 3) Why did American support for the Vietnam War change after
1) What is the Vietnamese holiday of Tet? 2) How many cities in South Vietnam and how many U.S. air bases were attacked in the Tet Offensive? 3) Why did American support for the Vietnam War change after
The Vietnam War
 The Vietnam War 1968-1973 LBJ: Grew increasingly unpopular over the course of his term. In 1968, his popularity dropped from 48% to 36%. Getting out of Vietnam As much as Nixon wanted to stop the protests
The Vietnam War 1968-1973 LBJ: Grew increasingly unpopular over the course of his term. In 1968, his popularity dropped from 48% to 36%. Getting out of Vietnam As much as Nixon wanted to stop the protests
The Vietnam War Years. B. Domino theory C. Vietcong D. Tonkin Gulf Resolution E. Napalm F. Credibility gap
 study guide Chapter Name The Vietnam War Years Period Due Directions: Write Definitions on a separate sheet of paper. 1. A. Ho Chi Minh B. Domino theory C. Vietcong D. Tonkin Gulf Resolution E. Napalm
study guide Chapter Name The Vietnam War Years Period Due Directions: Write Definitions on a separate sheet of paper. 1. A. Ho Chi Minh B. Domino theory C. Vietcong D. Tonkin Gulf Resolution E. Napalm
Nixon & Vietnam -Peace with Honor
 Nixon & Vietnam -Peace with Honor Vietnamization withdraw troops over extended period SV can gradually take back war US will give $, weapons, advice Anti-war protests massive Vietnam moratorium in Oct
Nixon & Vietnam -Peace with Honor Vietnamization withdraw troops over extended period SV can gradually take back war US will give $, weapons, advice Anti-war protests massive Vietnam moratorium in Oct
Kennedy & Johnson. Chapters 38 & 39
 Kennedy & Johnson Chapters 38 & 39 Kennedy s Presidency Young, inspirational, refreshing Young Cabinet Sec. of Defense - Robert McNamara Attorney General - Robert Kennedy Wanted to target organized crime
Kennedy & Johnson Chapters 38 & 39 Kennedy s Presidency Young, inspirational, refreshing Young Cabinet Sec. of Defense - Robert McNamara Attorney General - Robert Kennedy Wanted to target organized crime
Conflict in Indochina
 Conflict in Indochina 1954 French defeat at Dien Bien Phu Ba.le took place over 4 stages: 13 March: cut off French supply routes 30 March: start of a 5- day assault 5 April: encroachment; digging trenches
Conflict in Indochina 1954 French defeat at Dien Bien Phu Ba.le took place over 4 stages: 13 March: cut off French supply routes 30 March: start of a 5- day assault 5 April: encroachment; digging trenches
Name Period Date. Civil Rights Movement and Vietnam War Unit Test Review. Test Format- 50 questions 15 matching. 5 map, 3 reading a chart, 27 MC
 Name Period Date Civil Rights Movement and Vietnam War Unit Test Review Test Format- 50 questions 15 matching. 5 map, 3 reading a chart, 27 MC 1. What was LBJ s (President Johnson) program to end poverty
Name Period Date Civil Rights Movement and Vietnam War Unit Test Review Test Format- 50 questions 15 matching. 5 map, 3 reading a chart, 27 MC 1. What was LBJ s (President Johnson) program to end poverty
How Did President Nixon Get the United States Out of Vietnam?
 How Did President Nixon Get the United States Out of Vietnam? LESSON 2 SECTION 33.2 Text pp. 587 591 Read How Did President Nixon Get the United States Out of Vietnam? (pp. 587-591). Study Exercises Write
How Did President Nixon Get the United States Out of Vietnam? LESSON 2 SECTION 33.2 Text pp. 587 591 Read How Did President Nixon Get the United States Out of Vietnam? (pp. 587-591). Study Exercises Write
A Decade of Conflict
 A Decade of Conflict The Vietnam War One of the most traumatic periods of U.S. history. Spanned more than a decade Caused massive destruction both in Southeast Asia and on the American home front. Lives
A Decade of Conflict The Vietnam War One of the most traumatic periods of U.S. history. Spanned more than a decade Caused massive destruction both in Southeast Asia and on the American home front. Lives
The Vietnam War
 The Vietnam War 1968-1973 LBJ: As his term was coming to an end, he cut back on bombing North Vietnam and called for peace talks which failed. Nixon: Claimed in 1968 election that he had a secret plan
The Vietnam War 1968-1973 LBJ: As his term was coming to an end, he cut back on bombing North Vietnam and called for peace talks which failed. Nixon: Claimed in 1968 election that he had a secret plan
The Vietnam War Vietnamization and Peace with Honor
 The Vietnam War Vietnamization and Peace with Honor Name: Class: Vietnamization General Creighton Abrams, who replaced General Westmoreland as U.S. Commander in Vietnam in 1968, had very different ideas
The Vietnam War Vietnamization and Peace with Honor Name: Class: Vietnamization General Creighton Abrams, who replaced General Westmoreland as U.S. Commander in Vietnam in 1968, had very different ideas
The Vietnam War, Finish Vietnam Z Charts Start Vietnam Notes FYI: Vocab Quiz TOMORROW TEST MONDAY
 The Vietnam War, 1954-1975 Finish Vietnam Z Charts Start Vietnam Notes FYI: Vocab Quiz TOMORROW TEST MONDAY Vietnam the Early Years Vietnam was once a French colony, but in 1954 Ho Chi Minh led Vietnamese
The Vietnam War, 1954-1975 Finish Vietnam Z Charts Start Vietnam Notes FYI: Vocab Quiz TOMORROW TEST MONDAY Vietnam the Early Years Vietnam was once a French colony, but in 1954 Ho Chi Minh led Vietnamese
The Stormy Sixties. Chapter 38
 The Stormy Sixties Chapter 38 Kennedy Nixon Debates John F Kennedy and Richard Nixon had first presidential debate on TV Kennedy s New Frontier Spirit JFK elected by small margin over Nixon in 1960 Youngest
The Stormy Sixties Chapter 38 Kennedy Nixon Debates John F Kennedy and Richard Nixon had first presidential debate on TV Kennedy s New Frontier Spirit JFK elected by small margin over Nixon in 1960 Youngest
Historical Security Council (1967)
 Research Report XXVII Annual Session Historical Security Council (1967) The Vietnam War Research Report Page 1 of 9 Mik Dijkman Maurits de Lint Forum: Historical Security Council (1967) Issue: Student
Research Report XXVII Annual Session Historical Security Council (1967) The Vietnam War Research Report Page 1 of 9 Mik Dijkman Maurits de Lint Forum: Historical Security Council (1967) Issue: Student
 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 The reason the French did not want to give up Vietnam.
$100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 The reason the French did not want to give up Vietnam.
Conflict in Asia Homework Work book. Class. Teacher
 Name: Class. Teacher 1 Conflict in Korea The Causes of the Korean War During the 1950s an ARMS Race was developing between USSR and the USA, both superpowers were anxious not to get involved in a head-to-head
Name: Class. Teacher 1 Conflict in Korea The Causes of the Korean War During the 1950s an ARMS Race was developing between USSR and the USA, both superpowers were anxious not to get involved in a head-to-head
Assess Nixon s new approach to the war, and explain why protests continued.
 Objectives Assess Nixon s new approach to the war, and explain why protests continued. Explain what led to the Paris Peace Accords and why South Vietnam eventually fell to the communists. Evaluate the
Objectives Assess Nixon s new approach to the war, and explain why protests continued. Explain what led to the Paris Peace Accords and why South Vietnam eventually fell to the communists. Evaluate the
Chapter 29 Section 4 The War s End and Impact
 Chapter 29 Section 4 The War s End and Impact President Nixon inherited an unpopular war and increasing troubles on the home front. Peace Talks Stall Formal peace talks began in May, 1968 in Paris US wanted
Chapter 29 Section 4 The War s End and Impact President Nixon inherited an unpopular war and increasing troubles on the home front. Peace Talks Stall Formal peace talks began in May, 1968 in Paris US wanted
How does the U.S. get out?
 How does the U.S. get out? When the strongest nation in the world can be tied up for four years in a war in Vietnam with no end in sight, when the richest nation in the world can t manage it s own economy,
How does the U.S. get out? When the strongest nation in the world can be tied up for four years in a war in Vietnam with no end in sight, when the richest nation in the world can t manage it s own economy,
BELL UH-1 HUEY. U.S. pioneered the use of air-mobility. The main workhorse helicopter in Vietnam was the Bell UH-1 Iroquois-better known as the Huey.
 U.S. pioneered the use of air-mobility. The main workhorse helicopter in Vietnam was the Bell UH-1 Iroquois-better known as the Huey. TWO VERSIONS I. Troop Transport II.Gunship BELL UH-1 HUEY BENEFITS:
U.S. pioneered the use of air-mobility. The main workhorse helicopter in Vietnam was the Bell UH-1 Iroquois-better known as the Huey. TWO VERSIONS I. Troop Transport II.Gunship BELL UH-1 HUEY BENEFITS:
Chapter 24 The Vietnam War Section 1 The War Unfolds
 Chapter 24 The Vietnam War 1950-1975 Section 1 The War Unfolds 1 The Vietnam War Memorial in Washington, DC Over 58,000 American soldiers were killed in the Vietnam War. The names of all the soldiers that
Chapter 24 The Vietnam War 1950-1975 Section 1 The War Unfolds 1 The Vietnam War Memorial in Washington, DC Over 58,000 American soldiers were killed in the Vietnam War. The names of all the soldiers that
What post-war issues caused the Western Allies and the Soviet Union to disagree? What did Churchill mean by an iron curtain has descended?
 The Cold War I. Friend and Foe A. During WWII the US and USSR were. B. The could not have been beaten without the Soviets. C. Near the end of the war the allies met to discuss the. II. The A. Roosevelt,
The Cold War I. Friend and Foe A. During WWII the US and USSR were. B. The could not have been beaten without the Soviets. C. Near the end of the war the allies met to discuss the. II. The A. Roosevelt,
Vietnam War. Andrew Rodgers, Jeda Niyomkul, Marcus Johnson, Oliver Gray, Annemarie Rakoski, and Langley McEntyre
 Vietnam War Andrew Rodgers, Jeda Niyomkul, Marcus Johnson, Oliver Gray, Annemarie Rakoski, and Langley McEntyre Before the War The Modern-day countries of Vietnam, Cambodia and Laos known as Indochina
Vietnam War Andrew Rodgers, Jeda Niyomkul, Marcus Johnson, Oliver Gray, Annemarie Rakoski, and Langley McEntyre Before the War The Modern-day countries of Vietnam, Cambodia and Laos known as Indochina
Vietnam & the Limits of Power I. Kennedy & the New Frontier A. Style & Promise 1. John F. Kennedy (JFK) a. wealthy son of Joseph b. c.
 Vietnam & the Limits of Power I. Kennedy & the New Frontier A. Style & Promise 1. John F. Kennedy (JFK) a. wealthy son of Joseph b. c. WWII Vet; US ; PT 109 d. good looks 2. elected President 1960 a. overcame
Vietnam & the Limits of Power I. Kennedy & the New Frontier A. Style & Promise 1. John F. Kennedy (JFK) a. wealthy son of Joseph b. c. WWII Vet; US ; PT 109 d. good looks 2. elected President 1960 a. overcame
Ch 29-4 The War Ends
 Ch 29-4 The War Ends The Main Idea President Nixon eventually ended U.S. involvement in Vietnam, but the war had lasting effects on the United States and in Southeast Asia. Content Statement/Learning Goal
Ch 29-4 The War Ends The Main Idea President Nixon eventually ended U.S. involvement in Vietnam, but the war had lasting effects on the United States and in Southeast Asia. Content Statement/Learning Goal
World History Flashpoint #2 Vietnam
 World History 3201 Flashpoint #2 Vietnam KEY TERMS: Viet Cong : Communists in South Vietnam who opposed the Diem (Capitalist South Vietnamese Leader) government. Viet Minh : Vietnamese nationalists who
World History 3201 Flashpoint #2 Vietnam KEY TERMS: Viet Cong : Communists in South Vietnam who opposed the Diem (Capitalist South Vietnamese Leader) government. Viet Minh : Vietnamese nationalists who
World History (Survey) Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present
 World History (Survey) Chapter 33: Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present Section 1: Two Superpowers Face Off The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February
World History (Survey) Chapter 33: Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present Section 1: Two Superpowers Face Off The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February
The Making of a Stalemate. The Vietnam War
 The Making of a Stalemate The Vietnam War 1965-1967 LBJ s search for advice - Eisenhower WhiteHouseTapes.org Transcript + Audio Clip WhiteHouseTapes.org Transcript + Audio Clip WhiteHouseTapes.org Transcript
The Making of a Stalemate The Vietnam War 1965-1967 LBJ s search for advice - Eisenhower WhiteHouseTapes.org Transcript + Audio Clip WhiteHouseTapes.org Transcript + Audio Clip WhiteHouseTapes.org Transcript
The Invasion of Cambodia and Laos during the Vietnam War
 June 9th. 2014 World Geography 11 The Invasion of Cambodia and Laos during the Vietnam War Daphne Wood! On October 4th, 1965, the United States Air Force begun a secret bombing campaign in Cambodia and
June 9th. 2014 World Geography 11 The Invasion of Cambodia and Laos during the Vietnam War Daphne Wood! On October 4th, 1965, the United States Air Force begun a secret bombing campaign in Cambodia and
SWBAT: Explain how Nixon addressed the issues of the Vietnam War. Do Now: The Silent Majority
 SWBAT: Explain how Nixon addressed the issues of the Vietnam War Do Now: The Silent Majority Johnson Decline to Run in 1968 Toward the end of his term as President, Johnson had reduced bombing of North
SWBAT: Explain how Nixon addressed the issues of the Vietnam War Do Now: The Silent Majority Johnson Decline to Run in 1968 Toward the end of his term as President, Johnson had reduced bombing of North
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Cold War Tensions (Chapter 30 Quiz)
 Cold War Tensions (Chapter 30 Quiz) What were the military and political consequences of the Cold War in the Soviet Union, Europe, and the United States? After World War II ended, the United States and
Cold War Tensions (Chapter 30 Quiz) What were the military and political consequences of the Cold War in the Soviet Union, Europe, and the United States? After World War II ended, the United States and
JFK/LBJ/Vietnam Test Review Key
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: April 9, 2015 JFK/LBJ/Vietnam Test Review Key 1. Identify and describe the Vietnam War (US2B) Vietnam War: Vietnam had once been a French colony in Indochina. Vietcong with
Name: Class Period: Due Date: April 9, 2015 JFK/LBJ/Vietnam Test Review Key 1. Identify and describe the Vietnam War (US2B) Vietnam War: Vietnam had once been a French colony in Indochina. Vietcong with
Ruled by foreign powers China, France, Japan Independence led by Ho Chi Minh Educated in France, Russia, and China communist Followers: the Vietminh
 Ruled by foreign powers China, France, Japan Independence led by Ho Chi Minh Educated in France, Russia, and China communist Followers: the Vietminh French back in 1946 Install Bo Dai emperor Ho Chi Minh
Ruled by foreign powers China, France, Japan Independence led by Ho Chi Minh Educated in France, Russia, and China communist Followers: the Vietminh French back in 1946 Install Bo Dai emperor Ho Chi Minh
China (900 AD) Independence (1500) France (to 1941) Japan ( ) Independence led by Ho Chi Minh. Vietnam-U.S. allied in WWII
 China (900 AD) Independence (1500) France (to 1941) Japan (1941-1945) Vietnam-U.S. allied in WWII Independence led by Ho Chi Minh Educated in France, Russia, and China communist Followers: the Vietminh
China (900 AD) Independence (1500) France (to 1941) Japan (1941-1945) Vietnam-U.S. allied in WWII Independence led by Ho Chi Minh Educated in France, Russia, and China communist Followers: the Vietminh
Introduction to East and Southeast Asia. Second World War. The most noticeable group was Vietminh (Viet Nam Doc Lap Dong Minh:
 Introduction In Vietnam, political movements against colonizer emerged significantly before the Second World War. The most noticeable group was Vietminh (Viet Nam Doc Lap Dong Minh: League for Independence
Introduction In Vietnam, political movements against colonizer emerged significantly before the Second World War. The most noticeable group was Vietminh (Viet Nam Doc Lap Dong Minh: League for Independence
INTRODUCTION. Major countries involved
 15.03 17.03 RESEARCH REPORT COMMITTEE : HISTORICAL COUNCIL ISSUE: IMPROVING ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL CONDITIONS IN VIETNAM AND RESTORING PEACEFUL INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS IN EASTERN ASIA CHAIRS : ZOE GAILLOT
15.03 17.03 RESEARCH REPORT COMMITTEE : HISTORICAL COUNCIL ISSUE: IMPROVING ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL CONDITIONS IN VIETNAM AND RESTORING PEACEFUL INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS IN EASTERN ASIA CHAIRS : ZOE GAILLOT
U.S. wants to withdraw but cannot do so until the ARVN are ready.
 VIETNAMIZATION U.S. wants to withdraw but cannot do so until the ARVN are ready. The ARVN and RVNAF are supplied with modern weapons and aircraft in the hope that they can defend themselves. PACIFICATION-A
VIETNAMIZATION U.S. wants to withdraw but cannot do so until the ARVN are ready. The ARVN and RVNAF are supplied with modern weapons and aircraft in the hope that they can defend themselves. PACIFICATION-A
Is it Justified for the President to expand executive power during war time?
 Paul Bennis Goshen High School, Goshen N.Y. U.S. Military History Is it Justified for the President to expand executive power during war time? Wilson F.D.R. 1. Japanese Internment 2. Schenk v. U.S. J.F.K.
Paul Bennis Goshen High School, Goshen N.Y. U.S. Military History Is it Justified for the President to expand executive power during war time? Wilson F.D.R. 1. Japanese Internment 2. Schenk v. U.S. J.F.K.
The Vietnam War: Chapter 22
 The Vietnam War: Chapter 22 EQ: Evaluate the war aims for the US going to war in Vietnam, and whether these aims were met during the US s time in Vietnam. Timeline: What s Happening? United States: 1965
The Vietnam War: Chapter 22 EQ: Evaluate the war aims for the US going to war in Vietnam, and whether these aims were met during the US s time in Vietnam. Timeline: What s Happening? United States: 1965
The Vietnam War: [CUL] How and why have changes in moral, philosophical, and cultural values affected US history?
![The Vietnam War: [CUL] How and why have changes in moral, philosophical, and cultural values affected US history? The Vietnam War: [CUL] How and why have changes in moral, philosophical, and cultural values affected US history?](/thumbs/95/123299360.jpg) The Vietnam War: [CUL] How and why have changes in moral, philosophical, and cultural values affected US history? Timeline: What s Happening? United States: 1965 first major US combat units arrive in Vietnam
The Vietnam War: [CUL] How and why have changes in moral, philosophical, and cultural values affected US history? Timeline: What s Happening? United States: 1965 first major US combat units arrive in Vietnam
Politics of the Cold War
 Politics of the Cold War Standards SSUSH20 The student will analyze the domestic and international impact of the Cold War on the United States. c. Describe the Cuban Revolution, the Bay of Pigs, and the
Politics of the Cold War Standards SSUSH20 The student will analyze the domestic and international impact of the Cold War on the United States. c. Describe the Cuban Revolution, the Bay of Pigs, and the
Chapter 17 Lesson 1: Two Superpowers Face Off. Essential Question: Why did tension between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R increase after WWII?
 Chapter 17 Lesson 1: Two Superpowers Face Off Essential Question: Why did tension between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R increase after WWII? Post WWII Big Three meet in Yalta Divide Germany into 4 zones (U.S.,
Chapter 17 Lesson 1: Two Superpowers Face Off Essential Question: Why did tension between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R increase after WWII? Post WWII Big Three meet in Yalta Divide Germany into 4 zones (U.S.,
The 1960s ****** Two young candidates, Senator John F. Kennedy (D) and Vice-President Richard M. Nixon (R), ran for president in 1960.
 The 1960s A PROMISING TIME? As the 1960s began, many Americans believed they lived in a promising time. The economy was doing well, the country seemed poised for positive changes, and a new generation
The 1960s A PROMISING TIME? As the 1960s began, many Americans believed they lived in a promising time. The economy was doing well, the country seemed poised for positive changes, and a new generation
A HISTORY OF THE VIETNAM WAR
 A HISTORY OF THE VIETNAM WAR EXAM INFORMATION This exam was developed to enable schools to award credit to students for knowledge equivalent to that learned by students taking the course. This examination
A HISTORY OF THE VIETNAM WAR EXAM INFORMATION This exam was developed to enable schools to award credit to students for knowledge equivalent to that learned by students taking the course. This examination
The Vietnam War: Tragic Conflict in Asia Affected an American Generation
 The Vietnam War: Tragic Conflict in Asia Affected an American Generation By History.com on 05.02.17 Word Count 2,327 Level MAX Hovering U.S. Army helicopters pour machine gun fire into a tree line to cover
The Vietnam War: Tragic Conflict in Asia Affected an American Generation By History.com on 05.02.17 Word Count 2,327 Level MAX Hovering U.S. Army helicopters pour machine gun fire into a tree line to cover
