Introduction to East and Southeast Asia. Second World War. The most noticeable group was Vietminh (Viet Nam Doc Lap Dong Minh:
|
|
|
- Delphia Parker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Introduction In Vietnam, political movements against colonizer emerged significantly before the Second World War. The most noticeable group was Vietminh (Viet Nam Doc Lap Dong Minh: League for Independence of Vietnam) led by communist party. At the early 1945, there was a revolt against the Japanese imperialism which led to the August Revolution. After the Japanese was defeated, the ally British troops occupied the south and Chinese troops occupied the north at the 16 th parallel waiting for the French to reinstate its colony. However, the French return was not that easy and successful because of resistance. While French reoccupied the south and exercised its direct control, Ho Chi Minh government in Hanoi resisted the French return until there was an Franco-Vietnamese agreement allowing the North to be an independent state in the French Union. The agreement did not ensure the security and stability, and the conflict was still on the stage. In December 1946, the French shelled the city of Haiphong and forcibly reentered the capital Hanoi. In 1949, likewise, the French took the Rice War to cut off the rice supports to Vietminh. This action provoked the conflict between the French and the Vietminh which later turned out to be the war, known as the First Indochina War. From 1947 until the Dien Bien Phu battle, the French mastered the skies, but were unable to stop the flow of supplies reaching the Vietnamese guerilla. The French expeditionary corps occupied Dien Bien Phu in 1954 and set up a group of fortresses equipped with many state-of-the-art weapons to prevent the Viet Minh from gaining control of Northern Laos and the middle of lower Mekong River Valley. Despite supports from the United States, the French was defeated severely in the Dien Bien Phu battle. The day after the battle, the International Peace Conference began in Geneva and brought the war to an end on July 20, This led to the end of the First Indochina War ( ). Following the fall of Diem Bien Phu battle, the 1954 Geneva Accords came into existence facilitating the withdrawal of French military from Indochina and provided The Fall of Saigon: Internal causes 2
3 independence for Cambodia, Laos and Vietnam; but preserved the division of Vietnam: the North and the South at 17 th parallel. However, the side effects of the Cold War and the involvement of United States in the conflict turned it into the full-scale war, the Vietnam War or Second Indochina War. After 15 years of bloody and tragic fighting, North Vietnam triumphed and Saigon fell into the communist control in April Regarding Vietnam War, the major studies focused mostly on U.S. involvement and international causes. However, this essay will investigate deeply the domestic causes contributed to the victory of North Vietnam over the South and the fall of Saigon rather than external factors. The domestic factors are: 1) authoritarian South Vietnam government was gravely weak that it could not control the situation in the country; 2) anti-government movement received strong supports from peasants; 3) South Vietnamese military was immoral and weakly trained; 4) north Vietnamese military was wellexperienced and committed and used the suitable geo-military strategies. These major factors will be studied in details along with proofs and evidences in the following parts of the essay to discover how VC and North Vietnamese troops won the battle leading to the fall of Saigon. Cold War Effect After the World War II came to an end, there was another war which lasted nearly five decades ( ). The war, known as Cold War or East-West conflict, was the ideological rival and arm race between two superpowers: the United States and Soviet Union. It was the economic competition, military tension, and political conflict between Western bloc led by the United States and Eastern bloc led by Soviet Union due to different ideology. The two superpowers found danger within one another, so they started to build up much stronger military forces and more advanced weapons, as well as provided aids, equipment and weaponry to client countries to fight in other battles around the world for their sack. Being afraid of communism spread over, U.S. adopted Containment Policy which meant to isolate and surround Soviet The Fall of Saigon: Internal causes 3
4 Union by preventing non-communist states from communist aggressors. This Containment Policy was applied on Korea and Vietnam causing the division of the two countries. In the prospect of stopping the expanded communism alliances in the world, U.S. applied the Domino Theory initiated by U.S. president Dwight D. Eisenhower. This theory led U.S. to involve in the battles of the two countries. Since these superpowers sought to unite Korea approaching their own protection, the civil war broke out in 1950 when North Korea invaded South Korea. Likewise, Vietnam experienced the division and later the tragic war, Vietnam War. Two Vietnam: North and South After the Geneva Conference in 1954, Vietnam was temporary divided into two zones at the 17 th parallel. In the North, the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (DRV) was established in Hanoi under presidency of Ho Chi Minh, and the old emperor Bao Dai was chosen to rule the South. In 1955, Ngo Dinh Diem became the prime minister of Bao Dai and later became the head of state after a referendum which ended the power of emperor Bao Dai. After division, the Democratic Republic of Vietnam in the North organized the structure of the state with its own currency and constitution. The country was ruled by the Labour Party (Dang Lao Dong). With the loss of relations with the South, North Vietnam government started to build its own economy depending on industrial infrastructures left from the colony and mineral resources, but it was far from successful. In addition, North Vietnam was regarded by the U.S. as the aggressive communist government and its role in the Vietnam War was obviously prominent. During the war years, North Vietnamese government sent many underground fighters to the South through Ho Chi Minh Trail along Cambodian and Laos border line to assist Viet Cong. As a result, it had to fight directly with the U.S. troops at the peak of the war ( ) and suffered for U.S. bombardment. The Fall of Saigon: Internal causes 4
5 In the South, Diem refused to held the election scheduled in 1956 by Geneva Accord, for he knew that he would lose to the strong popularity of Ho Chi Minh. Ngo was considered to be the anti-communist leader who was determined not to unite Vietnam. The refusal to held the election revoked anger among Viet Minh veterans who waited in the South for unification since the independence. The Communist Party, which was mainly formed by Viet Minh veterans, gained benefits from this dissatisfaction. On the other hand, there were many movements in the villages opposing Diem government policies and authoritarian styles (McWilliams, & Piotrowski, 2001). Firstly, there was a protest, especially led by the former Viet Minh soldiers. However, this protect was unsuccessful since these protestors was arrested. Secondly, Diem failed the promise to give the rural people, peasants, in the South a land reform, so they ran a program of forceful resistance which was mainly formed or led by Viet Minh veterans. Unfortunately, they was captured and placed in camps. Continuously, revolutionary movement still existed again and again in order to fight against Diem s government, and it was increasingly violent in the late 1950s and early 1960s. The emergence of another communist group which was known as NLF (National Liberation Front) or called by its enemy Viet Cong (Viet Nam Cong San) troubled Diem government even more. Viet Cong was established in 1960 and settled in South Vietnam. The creation of this political group was for the purpose of fighting against the Saigon regime backed by the U.S. This group was powerful and became larger; hence, Diem s popularity declined from time to time even in the cities. During Diem regime, there was also a religious forceful conflict. Various Buddhist organizations were resorted, and when they resisted, Nhu used force against them. Then there was a protest which several monks burned themselves in the public. This tragic event was broadcasted around the world by mass media, so the opposition to Diem grew stronger in both The Fall of Saigon: Internal causes 5
6 national and international stage. Accordingly, U.S. concluded that Diem had become so brutal especially the attack on the Buddhists, and his popularity was so weak both in the countryside and in the cities. Supported by Viet Minh and North Vietnam in term of weaponry, NLF force became increasingly stronger and furthered their attacks on Diem s government. Unrest continued in the South until Diem and his brother Nhu were overthrown and killed in a military coup on 1 November, After Diem assassin, an election supported by the U.S. was conducted to prove the public opinion that the U.S. government fought for democracy. However, the government ruled by Nguyen Van Thieu and Ly Kao Ky was also an ineffective one and the uprising became even more severe. The Vietnam War: U.S. and escalation of the war By 1965, there were only 23,300 U.S. soldiers and military advisors in South Vietnam (Gifford, 2005). Following the Gulf of Tonkin incident, which was reported that US naval ship, the destroyer Maddox, was attacked by North Vietnamese; US congress approved the Gulf of Tonkin resolution that allowed the president to take all necessary means to repel attacks and prevent further aggression. First, president Johnson commanded on air strikes, so called Operation Rolling Thunder, on the North. After air strike operation, US deployed its combat troops directly to take up battle in South Vietnam. The number of US military troops increased gradually throughout the year, and the scale of the war was also escalated. The weary war continued throughout 1966 and At this point it was no longer the Vietnamese war as it had already become the direct confrontation between North Vietnamese troops and those of the U.S.. At the end of January 1968, North Vietnamese troops launched out an surprising offensive throughout South Vietnam; it was on the Tet, the Lunar New Year holiday. In response, U.S. employed more severe attacks on North Vietnam; The Fall of Saigon: Internal causes 6
7 and it was the peaking year of the war. However, it was a major psychological and political victory for North Vietnam. Richard Nixon, the successor of Johnson, introduced a new strategy called Vietnamization from 1969 to 1973 aiming to disengage gradually from South Vietnam, but it was a failure. Following the unsuccessful peace talk in 1965 and 1969, a new secret negotiation was renewed since 1972 in Paris. On January 27, 1973 an agreement between Washington and Hanoi was reached, and here come the exit of the United States from the Vietnam War. Despite disengagement of the US, South Vietnamese troops were in the stage of fighting on its own. Finally, North Vietnamese troops defeated the South Vietnamese troops and captured Saigon in April, Analysis: Vietnamization of studies over the fall of Saigon As mentioned above, North Vietnam defeated the Saigon government and reunified the country in April, But how could North Vietnam grant victory? and what factors contributed to the fall of Saigon? Vietnam War has long been studied as part of American history rather than Vietnamese history itself, so the analysis and studies in many works are found America-centric. Regarding the fall of Saigon, many factors have been emphasized exclusively on the American role and external context rather than the internals. At this point, this essay will be devoted to the analysis of domestic or internal causes which led VC and North Vietnamese troops towards the victory with regardless of the importance of external factors. The Vietnamization of study on the victory of North Vietnamese troops is indisputably a new challenge and noteworthy. The earliest important factor that shall be noticed is the weakness of Saigon government itself. A prominent leader of the South was Ngo Dinh Diem. Becoming the president after referendum in 1955, Diem immediately launched out his anti-communism campaign and ruled The Fall of Saigon: Internal causes 7
8 with authoritarian leadership. Basically, Diem government not only failed to conduct land reforms as promised, but also gave privileges to rich landlords and Catholic group. This failure provoked the anger of poor peasants, as well as Viet Minh veterans, so the demonstrations erupted. To restrict people from communist groups, he employed a policy of relocating people into the protective hamlet communities. This Strategic Hamlets failed and consequently caused the enmity among people and the popularity of Diem declined sharply. The revolt evolved into violence when NLF, later known as Viet Cong, was created to fight against his government. Besides repression on commoners, Diem was also known as a leader who employed religious repression. Diem was a Catholic among Buddhist groups and his policy harmed the Buddhist sects; this religious tension broke the ground for revolts. The event that the Buddhist monks burned themselves in the public squares and the brutality of South Vietnamese soldiers were broadcasted by mass media around the world shocked the public opinion in the United States. One of the major factors leading to the disengagement of U.S. from the war was anti-vietnam War campaign in the United States. At this turning point, question might be raised why that campaign broke out in U.S.. The fact that severity of the situation in South Vietnam under Diem and brutality of his troops was broadcasted shall be articulated provoking U.S. public opinion. Therefore, the external factors were just the evolution of internal ones. One more factor is that Diem was reluctant to the important of peasants roles in preventing communism and ignored them. Consequently, he lost the strong hold in rural areas. The later government under Nguyen Van Thieu was not a better one, and the situation was already out of control. In this regards, assumption can be made that it was the domestic factors rather than external ones that led to revolts against Saigon government and later the failure of Saigon, and it was because of the inability of Diem s government itself that led to the shortfall of supports from people for his government and even for later government. The Fall of Saigon: Internal causes 8
9 Another factor contributing to fall of Saigon was that North Vietnamese troops were supported strongly by people. The more the U.S. fought and the more South Vietnamese government put the pressure on their enemy, the stronger NLF or VC became. When the U.S. involved directly into the war, the sense of nationalism among Vietnamese became even stronger than ever the Vietnamese history indicates that there have always been the unity against foreign invaders (Miller & Tuong, 2009); for example, the revolt against Chinese, French, Japanese and later the American. VC and North Vietnamese troops usually employ popular warfare which means they sought supports from peasantry. Goure, in his memorandum conducted in 1966, suggested that the communists had always relied heavily on peasant cooperation for manpower, materials, and intelligence; and the introduction of North Vietnamese Army combat forces only increased the need for local support. In some cases, peasants helped hide Viet Cong when the U.S. troops were seeking for them, and other peasants even enlisted themselves in VC. This made the ARVN and U.S troops found it difficult to find and attack VC; and the war became more and more weary. This can also be considered as a cause of victory of VC and North Vietnamese troops. The most prominent factor was the inability and ineffectiveness of ARVN itself. Although equipped with modern weaponry supported by the U.S., they were still unable to fight and defeated its enemy because they were less-committed, weakly-trained, and immoral. Some peasants joined VC because of misbehavior of ARVN and mistreatment by local officials and police rather than being forced to join by VC (Goure et al., 1966). Unlike VC or North Vietnamese troops who fought for survival, ARVN troops were not strongly committed and they were forced to fight; as a result, they are easily defeated. During the years of Vietnamization, U.S. military supported flew into the South in a vast amounts in order to strengthen ARVN to fight against communist troops. Yet, ARVN was still in a low level no matter how well they The Fall of Saigon: Internal causes 9
10 were equipped because of corruption and indiscipline (Edkins & Nick, 2009). After the disengagement of U.S. from the war, the situation of ARVN in the battle was even worse than ever. No matter how long the U.S. support ARVN or U.S. continued to fight the battle, the defeat can still be seen as the future since ARVN was not a good partner for U.S.. Misbehavior, corruption, inability and indiscipline within ARVN were all the factors that VC and North Vietnamese troops could take advantages for their victory and those factors were responsible for the fall of Saigon. One last but not least cause that contributed to the victory of North Vietnam was VC and North Vietnamese force itself. Unlike ARVN or U.S., VC and North Vietnamese (Viet Minh) were well-experienced in the guerilla warfare which suits the geography of Vietnam the best. In the First Indochina War, they had employed the right geo-military strategies and successfully defeated the French. Besides, VC and North Vietnamese troops were courageous and strongly committed since they fought for the unification and liberation of their country from American imperialism (Goure et al., 1966). With supports from peasants, communist troops found it easy to recruit more fighters. Furthermore, North Vietnamese women served in military as Youth Shock Brigades to protect the Ho Chi Minh Trail, and this made the battle even more difficult and tough for U.S. troops, who dared not to fight against women. Although VC and North Vietnamese troops tended to be immoral at the very end of the war, they were well-conducted, disciplined and well-organized since the first place. Many peasant enlisted themselves in VC due to its policies (Goure et al., 1966). More importantly, VC and North Vietnamese troops were exactly persistent and known as the strongest fighters in the region. All the characteristics of VC and North Vietnamese troops were the active ingredients for their victory. Without these qualifications, they would not be able to defeat their enemies. The Fall of Saigon: Internal causes 10
11 The orthodox interpretation of the fall of Saigon was the disengagement of U.S. from the war. Many studies attributed the causes of disengagement solely to the internal factors economic cost, economic depression or public opinion of the United Sates and the fact that the U.S. attempted to avoid direct confrontation with USSR and China during the Cold War. However, one-side view can be far from complete. Question should be asked whether what caused economic depression and reaction of public opinion in the U.S.. This question can be settle by investigating the real situation of the war. Unlike other battles, U.S. encountered a tough time defeating VC and North Vietnamese troops because ARVN was ineffective and corrupted, while VC and North Vietnamese were obviously strong with suitable geo-military strategies. The U.S. military strategies and weaponries were not quite suitable with mountainous area of Vietnam which was rather suitable for guerilla warfare. This situation prolonged the war, and consequently the expenditures and the death toll of U.S. troops increased sharply. These factors provoked the economic depression and reaction of public opinion. Additionally, the fact that U.S. were afraid of direct confrontation with USSR or China like what happened in the Korean War cannot be articulated. In case of Korean War, in fact, Moscow, Beijing and Pyong Yang had agreed on a military pact for mutual assistant if the war with the U.S. broke out. In the pact, China and USSR agreed to deployed their forces directly to help North Korea in the battle. As indicated in history, however, USSR did not send its troops to North Korea when the war broke out in 1950 because USSR, as a superpower, attempted to avoid direct confrontation with U.S. only China did send its military to North Korea. More importantly, Sino-Soviet relation spilt since 1959 because of ideology rival. Therefore, it was not a possible case that both major countries would send its force collectively to fight the battle in Vietnam. The most important factor is the resistance of Vietnamese in general. Ho Chi Minh would never accept and attempted to restrict China intervention at any cost, for he knew that sovereignty of Vietnam would be at The Fall of Saigon: Internal causes 11
12 risk if he did so. Consequently, Ho Chi Minh appealed to Soviet Union, whose physical boundary does not link with Vietnam, because it was not the direct threat to Vietnam. In brief, direct confrontation between USSR and U.S. or between China and U.S. could not be a possible outcome and shall not be taken into account. Conclusion The orthodox interpretation of the Vietnam War focused only on American involvement, for it was regarded mostly as part of American history. However, the Vietnamization of studies on Vietnam War and North Vietnamese victory is absolutely indispensible for deep understanding of the causes of victory and the fall of Saigon. Through discussion and analysis on victory of North Vietnam in the war and the fall of Saigon, conclusion can be made that there were not only America-centric causes or external causes exclusively, but also internal causes and factors which contributed to the victory of North Vietnam and the fall of Saigon. The four major factors which shall be taken into accounts are: weakness of South Vietnamese Government, revolts of people against government, inability and ineffectiveness of ARVN, and strong VC and North Vietnamese troops. In this regard, the internal factors contributing to the fall of Saigon shall be more important in comparison to external factors. For further research, domestic social factors of Vietnam should be consulted for the benefits of a complete interpretation. The Fall of Saigon: Internal causes 12
13 Bibliography 1. Gifford, C. (2005). How Did it Happen? The Vietnam War. Sydney: Franklin Watts. 2. McWilliams, W. C., & Piotrowski, H. (2001). The world since 1945: A history of international relations (5th ed.). The United States of America: Lynne Rienner Publishers, Inc. 3. Miller, E., & Tuong, V. (2009). The Vietnam War as a Vietnamese War: Agency and Society in the Study of the Second Indochina War. Journal of Vietnamese Studies, 4 (4), L. Goure et al., Some Findings of the Viet Cong Motivation and Morale Study: June December 1965 (Santa Monica, CA: Rand Corporation, 1966), Ooi, K. G. (Ed.). (2004). Southeast Asia: A historical encyclopedia from Angkor Wat to East Timor Part II. The United States of America: ABC-CLIO. The Fall of Saigon: Internal causes 13
Ch 29-1 The War Develops
 Ch 29-1 The War Develops The Main Idea Concern about the spread of communism led the United States to become increasingly violent in Vietnam. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze how the Cold war and
Ch 29-1 The War Develops The Main Idea Concern about the spread of communism led the United States to become increasingly violent in Vietnam. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze how the Cold war and
OBJECTIVES. Describe and evaluate the events that led to the war between North Vietnam and South Vietnam.
 OBJECTIVES Describe and evaluate the events that led to the war between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. Identify and explain the foreign policy of the United States at this time, and how it relates to
OBJECTIVES Describe and evaluate the events that led to the war between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. Identify and explain the foreign policy of the United States at this time, and how it relates to
VIETNAM WAR
 VIETNAM WAR 1955-1975 #30 http://www.military.com/video/offduty/movies/classic-forrest-gump-invietnam-war/1069387728001 PRESIDENTS DURING THE VIETNAM WAR Dwight D. Eisenhower. John F. Kennedy. Lyndon B.
VIETNAM WAR 1955-1975 #30 http://www.military.com/video/offduty/movies/classic-forrest-gump-invietnam-war/1069387728001 PRESIDENTS DURING THE VIETNAM WAR Dwight D. Eisenhower. John F. Kennedy. Lyndon B.
VUS.13b. The Vietnam War. U. S. government s anti- Communist strategy of containment in Asia
 VUS.13b The Vietnam War U. S. government s anti- Communist strategy of containment in Asia Help the French and send some advisors- Increase advisors, send some troops- Escalate- we can not lose a war Peace
VUS.13b The Vietnam War U. S. government s anti- Communist strategy of containment in Asia Help the French and send some advisors- Increase advisors, send some troops- Escalate- we can not lose a war Peace
ANSWER KEY..REVIEW FOR Friday s QUIZ #15 Chapter: 29 -Vietnam
 ANSWER KEY..REVIEW FOR Friday s QUIZ #15 Chapter: 29 -Vietnam Ch. 29 sec. 1 - skim and scan pages 908-913 and then answer the questions. French Indochina: French ruled colony made up of Vietnam, Laos,
ANSWER KEY..REVIEW FOR Friday s QUIZ #15 Chapter: 29 -Vietnam Ch. 29 sec. 1 - skim and scan pages 908-913 and then answer the questions. French Indochina: French ruled colony made up of Vietnam, Laos,
Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs. non Communist South Organized by Ho Chi Minh
 1956 Elections are cancelled (1 of Geneva Accords) 1957 The Vietcong attack in South Vietnam Vietcong are South Vietnamese communists Guerrilla fighters Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs.
1956 Elections are cancelled (1 of Geneva Accords) 1957 The Vietcong attack in South Vietnam Vietcong are South Vietnamese communists Guerrilla fighters Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs.
There will be some disturbing images and footage as we cover this unit, please do your best to act as adults, and learn from this war.
 There will be some disturbing images and footage as we cover this unit, please do your best to act as adults, and learn from this war. Vietnam Intro Before WWII, Vietnam was a colony of the French Japanese
There will be some disturbing images and footage as we cover this unit, please do your best to act as adults, and learn from this war. Vietnam Intro Before WWII, Vietnam was a colony of the French Japanese
Ended French rule in Indo-China
 Vietnam Review Dien Bien Phu in 1954 the main French forces were surrounded at this location in the north of Vietnam and forced to surrender. This was a turning point in that it ended the French control
Vietnam Review Dien Bien Phu in 1954 the main French forces were surrounded at this location in the north of Vietnam and forced to surrender. This was a turning point in that it ended the French control
UNIT Y222 THE COLD WAR IN ASIA
 UNIT Y222 THE COLD WAR IN ASIA 1945-1993 NOTE: BASED ON 2 X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources Western Policies
UNIT Y222 THE COLD WAR IN ASIA 1945-1993 NOTE: BASED ON 2 X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources Western Policies
THEMES. 1) EXPANDING DEMOCRACY: America s mission in Vietnam was to halt the spread of communism-a threat to democracy.
 THEMES 1) EXPANDING DEMOCRACY: America s mission in Vietnam was to halt the spread of communism-a threat to democracy. 2) CONSTITUTIONAL CONCERNS: Among the constitutional issues of the Vietnam War era
THEMES 1) EXPANDING DEMOCRACY: America s mission in Vietnam was to halt the spread of communism-a threat to democracy. 2) CONSTITUTIONAL CONCERNS: Among the constitutional issues of the Vietnam War era
Chapter 30-1 CN I. Early American Involvement in Vietnam (pages ) A. Although little was known about Vietnam in the late 1940s and early
 Chapter 30-1 CN I. Early American Involvement in Vietnam (pages 892 894) A. Although little was known about Vietnam in the late 1940s and early 1950s, American officials felt Vietnam was important in their
Chapter 30-1 CN I. Early American Involvement in Vietnam (pages 892 894) A. Although little was known about Vietnam in the late 1940s and early 1950s, American officials felt Vietnam was important in their
Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos Annotation
 Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos Annotation Name Directions: A. Read the entire article, CIRCLE words you don t know, mark a + in the margin next to paragraphs you understand and a next to paragraphs you don t
Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos Annotation Name Directions: A. Read the entire article, CIRCLE words you don t know, mark a + in the margin next to paragraphs you understand and a next to paragraphs you don t
Conflict U.S. War
 Conflict - 1945-1975 U.S. War 1964-1973 Overview of the Vietnam War Why is Vietnam still a painful war to remember? Longest war in U.S. history and only war we lost It showed Americans that our power is
Conflict - 1945-1975 U.S. War 1964-1973 Overview of the Vietnam War Why is Vietnam still a painful war to remember? Longest war in U.S. history and only war we lost It showed Americans that our power is
Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs. non Communist South Organized by Ho Chi Minh
 1956 Elections are cancelled (1 of Geneva Accords) 1957 The Vietcong attack in South Vietnam Vietcong are South Vietnamese communists Guerrilla fighters Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs.
1956 Elections are cancelled (1 of Geneva Accords) 1957 The Vietcong attack in South Vietnam Vietcong are South Vietnamese communists Guerrilla fighters Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs.
1969 U.S. troops begin their withdrawal from Vietnam
 Vietnam War Years Timeline 1964 LBJ becomes President 1965 First major combat units arrive in Vietnam 1968 M.L.King and Robert Kennedy are assassinated 1969 U.S. troops begin their withdrawal from Vietnam
Vietnam War Years Timeline 1964 LBJ becomes President 1965 First major combat units arrive in Vietnam 1968 M.L.King and Robert Kennedy are assassinated 1969 U.S. troops begin their withdrawal from Vietnam
 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 The reason the French did not want to give up Vietnam.
$100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 The reason the French did not want to give up Vietnam.
Chapter 19: Going To war in Vietnam
 Heading Towards War Vietnam during WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the. returned to Vietnam
Heading Towards War Vietnam during WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the. returned to Vietnam
VIETNAM WAR
 VIETNAM WAR 1965-1972 FRENCH CONTROL French controlled Vietnam until World War II Vietnam taken by Japan Ho Chi Minh called for an independence of Vietnam Eight Year war between France and Ho Chi Minh
VIETNAM WAR 1965-1972 FRENCH CONTROL French controlled Vietnam until World War II Vietnam taken by Japan Ho Chi Minh called for an independence of Vietnam Eight Year war between France and Ho Chi Minh
The War in Vietnam. Chapter 30
 The War in Vietnam Chapter 30 Vietnam A colony of France until after World War II 1954- War for Independence led by Ho Chi Minh Ho Chi Minh The Geneva Accords The Geneva Accords divided the country into
The War in Vietnam Chapter 30 Vietnam A colony of France until after World War II 1954- War for Independence led by Ho Chi Minh Ho Chi Minh The Geneva Accords The Geneva Accords divided the country into
1. America slowly involves itself in the war in Vietnam as it seeks to halt the spread of communism.
 The War in Vietnam Indochina was still another Cold War battlefield. France had controlled Vietnam since the middle of the 19th century, only to be supplanted by Japan during the Second World War. Meanwhile,
The War in Vietnam Indochina was still another Cold War battlefield. France had controlled Vietnam since the middle of the 19th century, only to be supplanted by Japan during the Second World War. Meanwhile,
Chapter 20. The Vietnam War Era
 Chapter 20 The Vietnam War Era 1954-1975 Ho Chi Minh The most important voice who demanded independence for Vietnam. Communist leader of the Vietminh. Vietminh The term initially used to describe all Vietnamese
Chapter 20 The Vietnam War Era 1954-1975 Ho Chi Minh The most important voice who demanded independence for Vietnam. Communist leader of the Vietminh. Vietminh The term initially used to describe all Vietnamese
National Nightmare Begins: Origins of Vietnam War
 National Nightmare Begins: Origins of Vietnam War From late 1800 s until WWII (When Japan took over) France ruled Indochina (Vietnam, Laos & Cambodia). French took land from peasants & built large plantations,
National Nightmare Begins: Origins of Vietnam War From late 1800 s until WWII (When Japan took over) France ruled Indochina (Vietnam, Laos & Cambodia). French took land from peasants & built large plantations,
SECTION 1: MOVING TOWARD CONFLICT PAGE 730
 CHAPTER 22 SECTION 1: MOVING TOWARD CONFLICT PAGE 730 Main Idea: America gets involved in Vietnam to stop the spread of communism TERMS AND NAMES: Ho Chi Minh Ngo Dinh Diem Vietcong Vietminh domino theory
CHAPTER 22 SECTION 1: MOVING TOWARD CONFLICT PAGE 730 Main Idea: America gets involved in Vietnam to stop the spread of communism TERMS AND NAMES: Ho Chi Minh Ngo Dinh Diem Vietcong Vietminh domino theory
Vietnam War. Andrew Rodgers, Jeda Niyomkul, Marcus Johnson, Oliver Gray, Annemarie Rakoski, and Langley McEntyre
 Vietnam War Andrew Rodgers, Jeda Niyomkul, Marcus Johnson, Oliver Gray, Annemarie Rakoski, and Langley McEntyre Before the War The Modern-day countries of Vietnam, Cambodia and Laos known as Indochina
Vietnam War Andrew Rodgers, Jeda Niyomkul, Marcus Johnson, Oliver Gray, Annemarie Rakoski, and Langley McEntyre Before the War The Modern-day countries of Vietnam, Cambodia and Laos known as Indochina
Standard 8.0- Demonstrate an understanding of social, economic and political issues in contemporary America. Closing: Quiz
 Standard 8.0- Demonstrate an understanding of social, economic and political issues in contemporary America. Opening: Great Society Chart Work Period: Vietnam War Notes Political Cartoon Double Flow Map
Standard 8.0- Demonstrate an understanding of social, economic and political issues in contemporary America. Opening: Great Society Chart Work Period: Vietnam War Notes Political Cartoon Double Flow Map
TRUMAN S ROLE IN VIETNAM. = America is busy!!!!!
 TRUMAN S ROLE IN VIETNAM Saw Vietnam as extension of Cold War - democracy v. communism! France fighting to re-gain Vietnam Truman supported France with money supplies because didn t want Something going
TRUMAN S ROLE IN VIETNAM Saw Vietnam as extension of Cold War - democracy v. communism! France fighting to re-gain Vietnam Truman supported France with money supplies because didn t want Something going
Gulf of Tonkin Resolution Lesson Plan
 Resolution Lesson Plan Central Historical Question: Was the U.S. planning to go to war with North Vietnam before the Resolution? Materials: Powerpoint Timeline Documents A-D Guiding Questions Plan of Instruction:
Resolution Lesson Plan Central Historical Question: Was the U.S. planning to go to war with North Vietnam before the Resolution? Materials: Powerpoint Timeline Documents A-D Guiding Questions Plan of Instruction:
Ho Declares Independence of Vietnam British Forces Land in Saigon, Return Authority to French First American Dies in Vietnam
 1945 Ho Chi Minh Creates Provisional Government Following the surrender of Japan to Allied forces, Ho Chi Minh and his People's Congress form a provisional government. Japan transfers all power to Ho's
1945 Ho Chi Minh Creates Provisional Government Following the surrender of Japan to Allied forces, Ho Chi Minh and his People's Congress form a provisional government. Japan transfers all power to Ho's
The Vietnam War. Summary
 The Vietnam War Summary The Vietnam War grew out of the American commitment to the containment of communism during the Cold War. For approximately fifteen years, the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (North
The Vietnam War Summary The Vietnam War grew out of the American commitment to the containment of communism during the Cold War. For approximately fifteen years, the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (North
The Vietnam War,
 The Vietnam War, 1954 1975 Who was Ho Chi Minh? Vietnamese Communist who wanted self rule for Vietnam. Why did the United States aid the French? The French returned to Vietnam in 1946. As the Vietminh
The Vietnam War, 1954 1975 Who was Ho Chi Minh? Vietnamese Communist who wanted self rule for Vietnam. Why did the United States aid the French? The French returned to Vietnam in 1946. As the Vietminh
History Skill Builder. Perspective Taking
 History Skill Builder Perspective Taking Perspective Taking History is a written by people, with different points of view and biases. Conflicts arise from differences of opinion, competing interests. Compromises
History Skill Builder Perspective Taking Perspective Taking History is a written by people, with different points of view and biases. Conflicts arise from differences of opinion, competing interests. Compromises
Vietnam Introduction. Answer the following questions on a sticky note...
 Vietnam Introduction Answer the following questions on a sticky note... https://www.youtube.c om/watch?v=epfnsk5l 26U Burning Monk 1. Why was the burning monk event significant? How did people in the U.S.
Vietnam Introduction Answer the following questions on a sticky note... https://www.youtube.c om/watch?v=epfnsk5l 26U Burning Monk 1. Why was the burning monk event significant? How did people in the U.S.
Modern American History Unit 8: The 1960s The Vietnam War Notes and Questions
 Modern American History Unit 8: The 1960s The Vietnam War Notes and Questions The Vietnam War A. Vietnam: A Painful War U.S. involvement in conflicts in Vietnam lasted from mid-1940s to 1975 Only war the
Modern American History Unit 8: The 1960s The Vietnam War Notes and Questions The Vietnam War A. Vietnam: A Painful War U.S. involvement in conflicts in Vietnam lasted from mid-1940s to 1975 Only war the
VIETNAM 04/14/15 ORIGINS OF THE VIETNAM WAR s French establish control over Indochina - Southeast Asia
 VIETNAM Have you seen Charlie? 04/12/15 2 ORIGINS OF THE VIETNAM WAR 1800 s French establish control over Indochina - Southeast Asia Modern countries: Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos Transplanted French laws
VIETNAM Have you seen Charlie? 04/12/15 2 ORIGINS OF THE VIETNAM WAR 1800 s French establish control over Indochina - Southeast Asia Modern countries: Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos Transplanted French laws
The Cold War Finally Thaws Out. Korean War ( ) Vietnam War ( ) Afghan War ( )
 The Cold War Finally Thaws Out Korean War (1950-1953) Vietnam War (1963-1973) Afghan War (1979-1989) Korean war Split after WWII between US and USSR Temporary gov ts created in images of their major allies
The Cold War Finally Thaws Out Korean War (1950-1953) Vietnam War (1963-1973) Afghan War (1979-1989) Korean war Split after WWII between US and USSR Temporary gov ts created in images of their major allies
The Vietnam War Years. B. Domino theory C. Vietcong D. Tonkin Gulf Resolution E. Napalm F. Credibility gap
 study guide Chapter Name The Vietnam War Years Period Due Directions: Write Definitions on a separate sheet of paper. 1. A. Ho Chi Minh B. Domino theory C. Vietcong D. Tonkin Gulf Resolution E. Napalm
study guide Chapter Name The Vietnam War Years Period Due Directions: Write Definitions on a separate sheet of paper. 1. A. Ho Chi Minh B. Domino theory C. Vietcong D. Tonkin Gulf Resolution E. Napalm
The Vietnam War: Tragic Conflict in Asia Affected an American Generation
 The Vietnam War: Tragic Conflict in Asia Affected an American Generation By History.com on 05.02.17 Word Count 2,327 Level MAX Hovering U.S. Army helicopters pour machine gun fire into a tree line to cover
The Vietnam War: Tragic Conflict in Asia Affected an American Generation By History.com on 05.02.17 Word Count 2,327 Level MAX Hovering U.S. Army helicopters pour machine gun fire into a tree line to cover
20 th /Raffel The Vietnam War: Containment Leads to Disaster About this Assignment: The Vietnam war was one of the most controversial wars in
 20 th /Raffel The Vietnam War: Containment Leads to Disaster About this Assignment: The Vietnam war was one of the most controversial wars in American history. In retrospect, there were many missed opportunities
20 th /Raffel The Vietnam War: Containment Leads to Disaster About this Assignment: The Vietnam war was one of the most controversial wars in American history. In retrospect, there were many missed opportunities
Chapter 19 GOING TO WAR IN VIETNAM
 Chapter 19 GOING TO WAR IN VIETNAM VIETNAM DURING WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the Japanese.
Chapter 19 GOING TO WAR IN VIETNAM VIETNAM DURING WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the Japanese.
Conflict in Indochina
 Conflict in Indochina 1954 French defeat at Dien Bien Phu Ba.le took place over 4 stages: 13 March: cut off French supply routes 30 March: start of a 5- day assault 5 April: encroachment; digging trenches
Conflict in Indochina 1954 French defeat at Dien Bien Phu Ba.le took place over 4 stages: 13 March: cut off French supply routes 30 March: start of a 5- day assault 5 April: encroachment; digging trenches
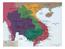
(i Nha Trang;,:: Cam Ranht
 CWA 4.1- Origins of the Vietnam War (Page 1 of 6) Ck History. Instructions: On each page, first, underline the dates and time markers (for example, "In the same year... ') in the text below. Next, write
CWA 4.1- Origins of the Vietnam War (Page 1 of 6) Ck History. Instructions: On each page, first, underline the dates and time markers (for example, "In the same year... ') in the text below. Next, write
War. Ho Chi Minh. domino theory. Dien Bien Phu SEATO. Vietcong Gulf of Tonkin Resolution. the end of WWII? ce? supporting
 Chapter 29 Section 1 Origins of the Vietnam War Ho Chi Minh domino theory Dien Bien Phu SEATO Vietcong Gulf of Tonkin Resolution 1. Witness History: What countries made up French Indochina? 2. What state
Chapter 29 Section 1 Origins of the Vietnam War Ho Chi Minh domino theory Dien Bien Phu SEATO Vietcong Gulf of Tonkin Resolution 1. Witness History: What countries made up French Indochina? 2. What state
Name Period Date. Civil Rights Movement and Vietnam War Unit Test Review. Test Format- 50 questions 15 matching. 5 map, 3 reading a chart, 27 MC
 Name Period Date Civil Rights Movement and Vietnam War Unit Test Review Test Format- 50 questions 15 matching. 5 map, 3 reading a chart, 27 MC 1. What was LBJ s (President Johnson) program to end poverty
Name Period Date Civil Rights Movement and Vietnam War Unit Test Review Test Format- 50 questions 15 matching. 5 map, 3 reading a chart, 27 MC 1. What was LBJ s (President Johnson) program to end poverty
1) Read the article on American involvement in Vietnam
 Warm Up 1) Read the article on American involvement in Vietnam 1) Circle in the causes of the Vietnam War 2) Put a star next to the key people/ countries 3) Box in key events, battles, treaties 4) Put
Warm Up 1) Read the article on American involvement in Vietnam 1) Circle in the causes of the Vietnam War 2) Put a star next to the key people/ countries 3) Box in key events, battles, treaties 4) Put
Historical Security Council (1967)
 Research Report XXVII Annual Session Historical Security Council (1967) The Vietnam War Research Report Page 1 of 9 Mik Dijkman Maurits de Lint Forum: Historical Security Council (1967) Issue: Student
Research Report XXVII Annual Session Historical Security Council (1967) The Vietnam War Research Report Page 1 of 9 Mik Dijkman Maurits de Lint Forum: Historical Security Council (1967) Issue: Student
Ch. 16 Sec. 1: Origins of the Vietnam War
 CHAPTER 16 QUESTIONS 5 sections, and Document Based Questions Ch. 16 Sec. 1: Origins of the Vietnam War 1) French Indochina included which three cultures? 2) How many people lived in Indochina by the end
CHAPTER 16 QUESTIONS 5 sections, and Document Based Questions Ch. 16 Sec. 1: Origins of the Vietnam War 1) French Indochina included which three cultures? 2) How many people lived in Indochina by the end
Chapter 29 Section 4 The War s End and Impact
 Chapter 29 Section 4 The War s End and Impact President Nixon inherited an unpopular war and increasing troubles on the home front. Peace Talks Stall Formal peace talks began in May, 1968 in Paris US wanted
Chapter 29 Section 4 The War s End and Impact President Nixon inherited an unpopular war and increasing troubles on the home front. Peace Talks Stall Formal peace talks began in May, 1968 in Paris US wanted
C. Continuing protests Doves wanted an immediate withdrawal that was complete, unconditional, and irreversible.
 I. VIETNAM WAR spread across 5 presidencies and spanned 25 years Direct U.S involvement from 1963-1973 A. France lost control of Vietnam after the battle of Dien Bien Phu in 1954 1. U.S. by 1954 had financed
I. VIETNAM WAR spread across 5 presidencies and spanned 25 years Direct U.S involvement from 1963-1973 A. France lost control of Vietnam after the battle of Dien Bien Phu in 1954 1. U.S. by 1954 had financed
The Vietnam War Why does the United States get involved in Vietnam?
 Why does the United States get involved in Vietnam? Vietnam had been a French colony since the late 1800s. After World War II, the French began to battle the Viet Minh, who wanted to kick out the French
Why does the United States get involved in Vietnam? Vietnam had been a French colony since the late 1800s. After World War II, the French began to battle the Viet Minh, who wanted to kick out the French
The Invasion of Cambodia and Laos during the Vietnam War
 June 9th. 2014 World Geography 11 The Invasion of Cambodia and Laos during the Vietnam War Daphne Wood! On October 4th, 1965, the United States Air Force begun a secret bombing campaign in Cambodia and
June 9th. 2014 World Geography 11 The Invasion of Cambodia and Laos during the Vietnam War Daphne Wood! On October 4th, 1965, the United States Air Force begun a secret bombing campaign in Cambodia and
THE COLD WAR IN SOUTH EAST ASIA,
 THE COLD WAR IN SOUTH EAST ASIA, 1945-1979 Today s Themes Decolonization/Cold War. Regional dynamics Problem of objectivity in Vietnam War scholarship. American centrism. Boomers: memory of lived history
THE COLD WAR IN SOUTH EAST ASIA, 1945-1979 Today s Themes Decolonization/Cold War. Regional dynamics Problem of objectivity in Vietnam War scholarship. American centrism. Boomers: memory of lived history
World History Flashpoint #2 Vietnam
 World History 3201 Flashpoint #2 Vietnam KEY TERMS: Viet Cong : Communists in South Vietnam who opposed the Diem (Capitalist South Vietnamese Leader) government. Viet Minh : Vietnamese nationalists who
World History 3201 Flashpoint #2 Vietnam KEY TERMS: Viet Cong : Communists in South Vietnam who opposed the Diem (Capitalist South Vietnamese Leader) government. Viet Minh : Vietnamese nationalists who
VIETNAM: LEAD UP TO WAR
 VIETNAM: LEAD UP TO WAR Southeast Asia s Colonial History France gained control of Vietnam by 1883 despite fierce resistance from the Vietnamese. The French combined Vietnam with Laos and Cambodia to form
VIETNAM: LEAD UP TO WAR Southeast Asia s Colonial History France gained control of Vietnam by 1883 despite fierce resistance from the Vietnamese. The French combined Vietnam with Laos and Cambodia to form
Moving Toward Conflict
 The Vietnam War Years Moving Toward Conflict Terms and Names Ho Chi Minh Leader of North Vietnam Vietminh Communist group led by Ho Chi Minh domino theory Eisenhower s explanation for stopping communism
The Vietnam War Years Moving Toward Conflict Terms and Names Ho Chi Minh Leader of North Vietnam Vietminh Communist group led by Ho Chi Minh domino theory Eisenhower s explanation for stopping communism
Chapter 22. The Vietnam War Years
 Chapter 22 The Vietnam War Years Chapter 22-1 Moving Toward Conflict French Indochina 3 countries Vietnam Laos Cambodia French colonies late 1800s-WWII French Indochina French took land from native people
Chapter 22 The Vietnam War Years Chapter 22-1 Moving Toward Conflict French Indochina 3 countries Vietnam Laos Cambodia French colonies late 1800s-WWII French Indochina French took land from native people
A HISTORY OF THE VIETNAM WAR
 A HISTORY OF THE VIETNAM WAR EXAM INFORMATION This exam was developed to enable schools to award credit to students for knowledge equivalent to that learned by students taking the course. This examination
A HISTORY OF THE VIETNAM WAR EXAM INFORMATION This exam was developed to enable schools to award credit to students for knowledge equivalent to that learned by students taking the course. This examination
UNDERGROUND COMPLEXES
 UNDERGROUND COMPLEXES TET OFFENSIVE Morale among U.S. soldiers remained generally high from 1965-1968. Many battlefield successes. Johnson Admin. reported that the war was all but won. Temporary ceasefire
UNDERGROUND COMPLEXES TET OFFENSIVE Morale among U.S. soldiers remained generally high from 1965-1968. Many battlefield successes. Johnson Admin. reported that the war was all but won. Temporary ceasefire
Chapter 29. Section 3 and 4
 Chapter 29 Section 3 and 4 The War Divides America Section 3 Objectives Describe the divisions within American society over the Vietnam War. Analyze the Tet Offensive and the American reaction to it. Summarize
Chapter 29 Section 3 and 4 The War Divides America Section 3 Objectives Describe the divisions within American society over the Vietnam War. Analyze the Tet Offensive and the American reaction to it. Summarize
CWA 4.1 Origins of the Vietnam War (Page 4 of 6)
 CWA 4.1 Origins of the Vietnam War (Page 4 of 6) Ho Chi Minh, 1946. Cropped version Source: Wikipedia Commons, Vietnamese Public Domain, http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:ho_chi _Minh_1946_and_signature.jpg
CWA 4.1 Origins of the Vietnam War (Page 4 of 6) Ho Chi Minh, 1946. Cropped version Source: Wikipedia Commons, Vietnamese Public Domain, http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/file:ho_chi _Minh_1946_and_signature.jpg
The Sixties and Seventies. The Cold War cools down, Civil Rights get complicated, and the Baby Boomers come of age.
 The Sixties and Seventies The Cold War cools down, Civil Rights get complicated, and the Baby Boomers come of age. Learning Targets Describe the Kennedy years, with specific detail covering: The election
The Sixties and Seventies The Cold War cools down, Civil Rights get complicated, and the Baby Boomers come of age. Learning Targets Describe the Kennedy years, with specific detail covering: The election
Is it Justified for the President to expand executive power during war time?
 Paul Bennis Goshen High School, Goshen N.Y. U.S. Military History Is it Justified for the President to expand executive power during war time? Wilson F.D.R. 1. Japanese Internment 2. Schenk v. U.S. J.F.K.
Paul Bennis Goshen High School, Goshen N.Y. U.S. Military History Is it Justified for the President to expand executive power during war time? Wilson F.D.R. 1. Japanese Internment 2. Schenk v. U.S. J.F.K.
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Cold War Tensions (Chapter 30 Quiz)
 Cold War Tensions (Chapter 30 Quiz) What were the military and political consequences of the Cold War in the Soviet Union, Europe, and the United States? After World War II ended, the United States and
Cold War Tensions (Chapter 30 Quiz) What were the military and political consequences of the Cold War in the Soviet Union, Europe, and the United States? After World War II ended, the United States and
Vietnam Before WWII During the early 1900s, nationalism was strong in. As the Vietnamese sought or reform of the colonial government, several
 Name Date Per Vietnam Before WWII During the early 1900s, nationalism was strong in. As the Vietnamese sought or reform of the colonial government, several political parties formed. One of the leaders
Name Date Per Vietnam Before WWII During the early 1900s, nationalism was strong in. As the Vietnamese sought or reform of the colonial government, several political parties formed. One of the leaders
Chapter 17 Lesson 1: Two Superpowers Face Off. Essential Question: Why did tension between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R increase after WWII?
 Chapter 17 Lesson 1: Two Superpowers Face Off Essential Question: Why did tension between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R increase after WWII? Post WWII Big Three meet in Yalta Divide Germany into 4 zones (U.S.,
Chapter 17 Lesson 1: Two Superpowers Face Off Essential Question: Why did tension between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R increase after WWII? Post WWII Big Three meet in Yalta Divide Germany into 4 zones (U.S.,
World History (Survey) Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present
 World History (Survey) Chapter 33: Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present Section 1: Two Superpowers Face Off The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February
World History (Survey) Chapter 33: Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present Section 1: Two Superpowers Face Off The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February
The Vietnam War Vietnamization and Peace with Honor
 The Vietnam War Vietnamization and Peace with Honor Name: Class: Vietnamization General Creighton Abrams, who replaced General Westmoreland as U.S. Commander in Vietnam in 1968, had very different ideas
The Vietnam War Vietnamization and Peace with Honor Name: Class: Vietnamization General Creighton Abrams, who replaced General Westmoreland as U.S. Commander in Vietnam in 1968, had very different ideas
Notes: LG: Analyze how the 1960s changed America.
 Notes: LG: Analyze how the 1960s changed America. USSR Nikita Khrushchev 1953-1964 1. Cold War Abroad in the 1960s a. 1961, Bay of Pigs Invasion (Cuba) i. President Eisenhower and CIA train Cuban
Notes: LG: Analyze how the 1960s changed America. USSR Nikita Khrushchev 1953-1964 1. Cold War Abroad in the 1960s a. 1961, Bay of Pigs Invasion (Cuba) i. President Eisenhower and CIA train Cuban
The Vietnam War
 The Vietnam War 1968-1973 LBJ: Grew increasingly unpopular over the course of his term. In 1968, his popularity dropped from 48% to 36%. Getting out of Vietnam As much as Nixon wanted to stop the protests
The Vietnam War 1968-1973 LBJ: Grew increasingly unpopular over the course of his term. In 1968, his popularity dropped from 48% to 36%. Getting out of Vietnam As much as Nixon wanted to stop the protests
The Vietnam War
 The Vietnam War 1968-1973 LBJ: As his term was coming to an end, he cut back on bombing North Vietnam and called for peace talks which failed. Nixon: Claimed in 1968 election that he had a secret plan
The Vietnam War 1968-1973 LBJ: As his term was coming to an end, he cut back on bombing North Vietnam and called for peace talks which failed. Nixon: Claimed in 1968 election that he had a secret plan
East Asia in the Postwar Settlements
 Chapter 34 " Rebirth and Revolution: Nation-building in East Asia and the Pacific Rim East Asia in the Postwar Settlements Korea was divided between a Russian zone of occupation in the north and an American
Chapter 34 " Rebirth and Revolution: Nation-building in East Asia and the Pacific Rim East Asia in the Postwar Settlements Korea was divided between a Russian zone of occupation in the north and an American
Unit 7: The Cold War
 Unit 7: The Cold War Standard 7-5 Goal: The student will demonstrate an understanding of international developments during the Cold War era. Vocabulary 7-5.1 OCCUPIED 7-5.2 UNITED NATIONS NORTH ATLANTIC
Unit 7: The Cold War Standard 7-5 Goal: The student will demonstrate an understanding of international developments during the Cold War era. Vocabulary 7-5.1 OCCUPIED 7-5.2 UNITED NATIONS NORTH ATLANTIC
Communism in the Far East. China
 Communism in the Far East China Terms and Players KMT PLA PRC CCP Sun Yat-Sen Mikhail Borodin Chiang Kai-shek Mao Zedong Shaky Start In 1913 the newly formed Chinese government was faced with the assassination
Communism in the Far East China Terms and Players KMT PLA PRC CCP Sun Yat-Sen Mikhail Borodin Chiang Kai-shek Mao Zedong Shaky Start In 1913 the newly formed Chinese government was faced with the assassination
Bell Ringer: April 18(19), 2018
 Announcements: 1: Test 5/4! Review is on the Weebly! Bell Ringer: April 18(19), 2018 Materials: 1: Spiral/blank sheet of paper 2: Vietnam War DBQ (PREAP) 1. Set up your Cornell notes 2. Across the top
Announcements: 1: Test 5/4! Review is on the Weebly! Bell Ringer: April 18(19), 2018 Materials: 1: Spiral/blank sheet of paper 2: Vietnam War DBQ (PREAP) 1. Set up your Cornell notes 2. Across the top
Check for Understanding. Why was Birmingham (1963) a turning point in the Civil Rights Movement? Include at least 3 specific reasons as to why.
 Check for Understanding Why was Birmingham (1963) a turning point in the Civil Rights Movement? Include at least 3 specific reasons as to why. Part I: Korea and Vietnam War Part II: JFK Presidency 1950-1963
Check for Understanding Why was Birmingham (1963) a turning point in the Civil Rights Movement? Include at least 3 specific reasons as to why. Part I: Korea and Vietnam War Part II: JFK Presidency 1950-1963
Our objective is to evaluate the U.S. Policy of containment in response to the causes and effects of the Korean and Vietnam Wars.
 Our objective is to evaluate the U.S. Policy of containment in response to the causes and effects of the Korean and Vietnam Wars. Do Now: This OR That Write below if this relates to the Korean War, War
Our objective is to evaluate the U.S. Policy of containment in response to the causes and effects of the Korean and Vietnam Wars. Do Now: This OR That Write below if this relates to the Korean War, War
China Summit. Situation in Taiwan Vietnam War Chinese Relationship with Soviet Union c. By: Paul Sabharwal and Anjali. Jain
 China Summit Situation in Taiwan Vietnam War Chinese Relationship with Soviet Union c. By: Paul Sabharwal and Anjali Jain I. Introduction In the 1970 s, the United States decided that allying with China
China Summit Situation in Taiwan Vietnam War Chinese Relationship with Soviet Union c. By: Paul Sabharwal and Anjali Jain I. Introduction In the 1970 s, the United States decided that allying with China
The Vietnam War The Never-Ending Tunnel
 The Vietnam War The Never-Ending Tunnel Introduction The shared nature of conflicts in and around Vietnam after the Second World War is that of a national struggle to free the country from the grip of
The Vietnam War The Never-Ending Tunnel Introduction The shared nature of conflicts in and around Vietnam after the Second World War is that of a national struggle to free the country from the grip of
INTRODUCTION. Major countries involved
 15.03 17.03 RESEARCH REPORT COMMITTEE : HISTORICAL COUNCIL ISSUE: IMPROVING ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL CONDITIONS IN VIETNAM AND RESTORING PEACEFUL INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS IN EASTERN ASIA CHAIRS : ZOE GAILLOT
15.03 17.03 RESEARCH REPORT COMMITTEE : HISTORICAL COUNCIL ISSUE: IMPROVING ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL CONDITIONS IN VIETNAM AND RESTORING PEACEFUL INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS IN EASTERN ASIA CHAIRS : ZOE GAILLOT
And The Republicans VIETNAM. BY Leonard P. Liggio. of it.
 VIETNAM And The Republicans The War In Vietnam. The Text of the Controversial Republican White Paper Prepared by the Staff of the Senate Republican Policy Committee, Washington,.D.C., Public Affairs Press.
VIETNAM And The Republicans The War In Vietnam. The Text of the Controversial Republican White Paper Prepared by the Staff of the Senate Republican Policy Committee, Washington,.D.C., Public Affairs Press.
What post-war issues caused the Western Allies and the Soviet Union to disagree? What did Churchill mean by an iron curtain has descended?
 The Cold War I. Friend and Foe A. During WWII the US and USSR were. B. The could not have been beaten without the Soviets. C. Near the end of the war the allies met to discuss the. II. The A. Roosevelt,
The Cold War I. Friend and Foe A. During WWII the US and USSR were. B. The could not have been beaten without the Soviets. C. Near the end of the war the allies met to discuss the. II. The A. Roosevelt,
PRESIDENT NIXON & THE WITHDRAWAL FROM VIETNAM. L obj: to consider whether the USA lost the war in Vietnam, or whether the Vietcong won it.
 PRESIDENT NIXON & THE WITHDRAWAL FROM VIETNAM L obj: to consider whether the USA lost the war in Vietnam, or whether the Vietcong won it. US Presidents (during Vietnam) Dwight Eisenhower 1953 61 John F
PRESIDENT NIXON & THE WITHDRAWAL FROM VIETNAM L obj: to consider whether the USA lost the war in Vietnam, or whether the Vietcong won it. US Presidents (during Vietnam) Dwight Eisenhower 1953 61 John F
qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqw ertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwert yuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyui opasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopa sdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdf
 qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqw ertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwert yuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyui opasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopa China and Vietnam: An Enigma in Southeast Asian International Relations sdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdf
qwertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqw ertyuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwert yuiopasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyui opasdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopa China and Vietnam: An Enigma in Southeast Asian International Relations sdfghjklzxcvbnmqwertyuiopasdf
Assess Nixon s new approach to the war, and explain why protests continued.
 Objectives Assess Nixon s new approach to the war, and explain why protests continued. Explain what led to the Paris Peace Accords and why South Vietnam eventually fell to the communists. Evaluate the
Objectives Assess Nixon s new approach to the war, and explain why protests continued. Explain what led to the Paris Peace Accords and why South Vietnam eventually fell to the communists. Evaluate the
3/2/2017. Dwight Eisenhower & The Cold War. Election of Adlai Stevenson Democratic Candidate. Dwight D. Eisenhower Ike Republican Candidate
 1 2 3 4 Dwight Eisenhower & The Cold War Election of 1952 Adlai Stevenson Democratic Candidate Dwight D. Eisenhower Ike Republican Candidate 5 6 7 1952 Election Results Dwight D. Eisenhower 34 th President
1 2 3 4 Dwight Eisenhower & The Cold War Election of 1952 Adlai Stevenson Democratic Candidate Dwight D. Eisenhower Ike Republican Candidate 5 6 7 1952 Election Results Dwight D. Eisenhower 34 th President
xvi Chronology 2 Aug North Vietnamese patrol boats attack the Maddox in the Gulf of Tonkin near the North Vietnamese coast. 4 5 Aug Both t
 CHRONOLOGY May 1941 Formation of the Vietminh. 2 Sept. 1945 Ho Chi Minh publicly declares a provisional government and Vietnamese national independence. 23 Nov. 1946 French bombardment of Haiphong. Oct.
CHRONOLOGY May 1941 Formation of the Vietminh. 2 Sept. 1945 Ho Chi Minh publicly declares a provisional government and Vietnamese national independence. 23 Nov. 1946 French bombardment of Haiphong. Oct.
SS7H3e Brain Wrinkles
 SS7H3e End of WWII The United States, Soviet Union, and Great Britain made an agreement on how they would after World War II. Each country was supposed to the lands that were impacted by the war. They
SS7H3e End of WWII The United States, Soviet Union, and Great Britain made an agreement on how they would after World War II. Each country was supposed to the lands that were impacted by the war. They
The arms race meant that the US feared war in Vietnam because of potential nuclear attack from the Soviet Union.
 The situation in Vietnam by 1961 Vietnam was a French colony, known as French Indochina. Ho Chi Minh was at war with the French, fighting for Vietnamese independence. He won a decisive victory at Dien
The situation in Vietnam by 1961 Vietnam was a French colony, known as French Indochina. Ho Chi Minh was at war with the French, fighting for Vietnamese independence. He won a decisive victory at Dien
The Cold War Begins. After WWII
 The Cold War Begins After WWII After WWII the US and the USSR emerged as the world s two. Although allies during WWII distrust between the communist USSR and the democratic US led to the. Cold War tension
The Cold War Begins After WWII After WWII the US and the USSR emerged as the world s two. Although allies during WWII distrust between the communist USSR and the democratic US led to the. Cold War tension
U.S. wants to withdraw but cannot do so until the ARVN are ready.
 VIETNAMIZATION U.S. wants to withdraw but cannot do so until the ARVN are ready. The ARVN and RVNAF are supplied with modern weapons and aircraft in the hope that they can defend themselves. PACIFICATION-A
VIETNAMIZATION U.S. wants to withdraw but cannot do so until the ARVN are ready. The ARVN and RVNAF are supplied with modern weapons and aircraft in the hope that they can defend themselves. PACIFICATION-A
AUSTRALIA S VIETNAM WAR A PERSONAL PERSPECTIVE FORESTVILLE RSL SUB-BRANCH
 AUSTRALIA S VIETNAM WAR A PERSONAL PERSPECTIVE Introduction The aim of our talk is to provide you with: an overview of the Vietnam War from an Australian context, our personal perspectives of the War,
AUSTRALIA S VIETNAM WAR A PERSONAL PERSPECTIVE Introduction The aim of our talk is to provide you with: an overview of the Vietnam War from an Australian context, our personal perspectives of the War,
Inventing Vietnam: The United States and State Building, James Carter. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, ISBN:
 1 Inventing Vietnam: The United States and State Building, 1954-1968. James Carter. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2008. ISBN: 9780521716901 In Inventing Vietnam, James Carter attempts to counter
1 Inventing Vietnam: The United States and State Building, 1954-1968. James Carter. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, 2008. ISBN: 9780521716901 In Inventing Vietnam, James Carter attempts to counter
One war ends, another begins
 One war ends, another begins Communism comes from the word common, meaning to belong equally to more than one individual. The related word, commune is a place where people live together and share property
One war ends, another begins Communism comes from the word common, meaning to belong equally to more than one individual. The related word, commune is a place where people live together and share property
Wars in Korea and Vietnam
 Wars in Korea and Vietnam 3 MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW TERMS & NAMES REVOLUTION In Asia, the Cold War flared into actual wars supported mainly by the superpowers. Today, Vietnam is a Communist country,
Wars in Korea and Vietnam 3 MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW TERMS & NAMES REVOLUTION In Asia, the Cold War flared into actual wars supported mainly by the superpowers. Today, Vietnam is a Communist country,
netw rks Where in the world? When did it happen? The Vietnam Era Lesson 1 Kennedy s Foreign Policy ESSENTIAL QUESTION Terms to Know GUIDING QUESTIONS
 Lesson 1 Kennedy s Foreign Policy ESSENTIAL QUESTION What motivates people to act? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. Why did President Kennedy seek new ways to deal with the challenges and fears of the Cold War? 2.
Lesson 1 Kennedy s Foreign Policy ESSENTIAL QUESTION What motivates people to act? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. Why did President Kennedy seek new ways to deal with the challenges and fears of the Cold War? 2.
The Making of a Stalemate. The Vietnam War
 The Making of a Stalemate The Vietnam War 1965-1967 LBJ s search for advice - Eisenhower WhiteHouseTapes.org Transcript + Audio Clip WhiteHouseTapes.org Transcript + Audio Clip WhiteHouseTapes.org Transcript
The Making of a Stalemate The Vietnam War 1965-1967 LBJ s search for advice - Eisenhower WhiteHouseTapes.org Transcript + Audio Clip WhiteHouseTapes.org Transcript + Audio Clip WhiteHouseTapes.org Transcript
World History Chapter 23 Page Reading Outline
 World History Chapter 23 Page 601-632 Reading Outline The Cold War Era: Iron Curtain: a phrased coined by Winston Churchill at the end of World War I when her foresaw of the impending danger Russia would
World History Chapter 23 Page 601-632 Reading Outline The Cold War Era: Iron Curtain: a phrased coined by Winston Churchill at the end of World War I when her foresaw of the impending danger Russia would
Chapter 33 Summary/Notes
 Chapter 33 Summary/Notes Unit 8 Perspectives on the Present Chapter 33 Section 1. The Cold War Superpowers Face off We learned about the end of WWII. Now we learn about tensions that followed the war.
Chapter 33 Summary/Notes Unit 8 Perspectives on the Present Chapter 33 Section 1. The Cold War Superpowers Face off We learned about the end of WWII. Now we learn about tensions that followed the war.
Analyzing Attitudes on the Vietnam War through Political Cartoons
 Analyzing Attitudes on the Vietnam War through Political Cartoons The other ascent into the unknown During the presidential campaign of 1964, President Lyndon Johnson suggested that Republican candidate
Analyzing Attitudes on the Vietnam War through Political Cartoons The other ascent into the unknown During the presidential campaign of 1964, President Lyndon Johnson suggested that Republican candidate
2) How many cities in South Vietnam and how many U.S. air bases were attacked in the Tet Offensive?
 1) What is the Vietnamese holiday of Tet? 2) How many cities in South Vietnam and how many U.S. air bases were attacked in the Tet Offensive? 3) Why did American support for the Vietnam War change after
1) What is the Vietnamese holiday of Tet? 2) How many cities in South Vietnam and how many U.S. air bases were attacked in the Tet Offensive? 3) Why did American support for the Vietnam War change after
Chapter 24 The Vietnam War Section 1 The War Unfolds
 Chapter 24 The Vietnam War 1950-1975 Section 1 The War Unfolds 1 The Vietnam War Memorial in Washington, DC Over 58,000 American soldiers were killed in the Vietnam War. The names of all the soldiers that
Chapter 24 The Vietnam War 1950-1975 Section 1 The War Unfolds 1 The Vietnam War Memorial in Washington, DC Over 58,000 American soldiers were killed in the Vietnam War. The names of all the soldiers that
