What post-war issues caused the Western Allies and the Soviet Union to disagree? What did Churchill mean by an iron curtain has descended?
|
|
|
- Brandon Rogers
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Cold War I. Friend and Foe A. During WWII the US and USSR were. B. The could not have been beaten without the Soviets. C. Near the end of the war the allies met to discuss the. II. The A. Roosevelt, Stalin and Churchill met in Yalta. B. There, they decided to and occupy Germany temporarily. C. Stalin promised there would be in Eastern Europe. D. Germany Divided 1. For the time being Germany was divided up into to be governed by the victorious allies. 2. The Capital of was also divided into 4 pieces. III. Two : Different Goals A. United States 1. The US left WWII relatively unscathed. 2. We wanted to make $ and. B. Soviet Union: Post WWII Goals 1. Stalin had no plans to fulfill his 2. Stalin had two goals in a. To spread communism b. To create a of friendly governments as a defense against Germany (who had invaded Russia twice in the 20th century, killing millions) What post-war issues caused the Western Allies and the Soviet Union to disagree? 3. Occupying Eastern Europe a. As the Soviet Army returned to Russia, many troops countries b. Local in these countries, backed by the Red Army, took over, even assassinating democratic leaders What did Churchill mean by an iron curtain has descended? c. Yalta Violation i. These communist countries became Stalin s. ii. He directly violated his promise at the d. Until 1991, the world will be divided between East and West
2 IV. Cold War A. These disagreements over the in Eastern Europe and arguments over caused tensions B. Both the US and the Soviet Union felt deep C. The Cold War had begun What was the Cold War? What were some causes? 1. State of between nations aligned with the US on one side and the Soviet Union on the other, without between the major rivals V. Cold War will lead to: A. 1. The Soviets wanted to keep Germany divided into pieces. 2. The US wanted to, and allow them to rebuild (just not their military) 3. The Western Allies and allowed the people to write their own constitution 4. Berlin Blockade a. The Soviets were angry about the rebuilding of Germany b. Soviets responded by cutting off access to in June of c. Stalin believed that the West would give in rather than watch West Berlin starve. 5. The Berlin Airlift a. The West refused to give up West Berlin. b. For nearly a year the allies flew 278,000 missions to bring of supplies to West Berlin. 6. Crises Averted a. Eventually the Soviets. b. The airlift was a tremendous success, and showed the world that the US would not to the communists. Why was the Berlin Crisis so significant? What did it show? B. Opposing Alliances 1. This initial crisis led the US to make a military alliance with several nations pledging to protect each other a. 2. The Soviets responded with their own a. How might these alliances have increased tensions between the East and West?
3 C. The Arms Race 1. The US was the only country to have until the Soviets built one in The US wanted to keep its, and began to develop increasingly powerful nuclear weapons. 3. In 1952 The United States tested the first successful. a. One year later, the Soviets had their own Hydrogen bomb. 4. ICBMs a. In 1957 the Soviets developed a new method of delivering a nuclear device to its target. b. Inter Continental could travel long distances, and could not be shot down easily. 5. MAD a. With ICBMs, if one side launched a full scale, the other side would be able to hit back. b. Thus a nuclear strike would result in (MAD), or nuclear annihilation What role did nuclear weapons play in the Cold War? D. Space Race 1. On October 4, 1957 the USSR used an ICBM to launch, the first artificial into orbit. 2. The US feared that they had fallen behind in science and technology. 3. Space Race competition with the Soviets would lead to the creation of, billions of dollars in research, and a How was Neil Armstrong landing on the moon related to the Cold War? E. 3rd World Competition 1. 1st World: 2. 2nd World: Soviet Union and its Allies 3. 3rd World: Nation allied with 4. The U.S. and Soviets promoted their to 3rd World countries hoping to gain supportive nations 5. Would lead to wars and both nations reaching out to aid Cold War hotspots
4 THE BERLIN WALL East West rivalry. Why? What elements of the Cold War exist here? Berlin divided contrast the two halves. WEST EAST What they wanted WEST EAST Nikita Khrushchev died in His successor as leader of the Soviet Union was Nikita Khrushchev. Khrushchev was no Stalin, but he was smart, ruthless and extremely. "We will you!" John F. Kennedy Sworn in as President of the United States January 20,. Ask not what your country can do for ; ask what can do for your country. Kennedy aggressively combats Khrushchev. Khrushchev sees Kennedy as intelligent, but. The Berlin Wall: Split between East and West The Wall Goes Up In the Summer of 1961 The Soviets shocked the world. Should They have been shocked?
5 The object of the wall was not to keep West Berliners in, but rather to keep East Germans. John F. Kennedy s Berlin Speech Is this a convincing speech or not? Give two examples to support your point. Results for Berlin, Germany and the Cold War: Berlin was divided, free access ended between East and West, many families split, many attempted to escape to the West-between 1961 and 1989; almost people died trying to cross the Berlin Wall Who do you think came out on top? Khrushchev or Kennedy? Khrushchev lost face by failing to the West from Berlin JFK, though looking weak to some, is able to save face with his Berlin. The wall will prevent crossing until and will be demolished in KRUSHCHEV SPEECH
6 COLD WAR: AREAS OF TENSION I. US Policy Towards USSR A. The US feared that if one country fell to communism, others around it would fall as well 1. theory B. Because any country could start the falling dominos, the U.S. developed a policy of: 1. : Containing communism in its borders at all costs (with military and economic aid) C. Containment at Work 1. Doctrine Truman promises aid to any friend in need against communists, particularly to Turkey and Greece 2. Plan US gives $12.5 billion to help rebuild and stabilize Europe. II. Areas of Tension A. Europe 1. The Berlin Wall 2. Poland, Hungary, Czechoslovakia a) Some Eastern European countries revolted against Soviet domination b) In each case, Soviet forces the rebellions, while the U.S. failed to act Poland 1956 Hungary 1956 Czechoslovakia 1968 B. CHINA 1. War Continues a) The civil war that had been raging in China was put on hold during WWII. b) Now that the Japanese had been defeated, the war resumed in earnest. 2. Kai-shek a) Leader of the b) Supported by the c) Unpopular, Incompetent/corrupt military 3. ZeDong a) Leader of the Communists. b) Supported by Soviets. c) Popular, Experienced army. 4. Communist Victory a) Mao s guerilla army was able to gain control in mainland China by b) It was renamed The People s of China. c) Chiang fled to where he set up his own government 5. China Transforms a) Mao was determined to reshape the Chinese according the his version of Marxism. b) Created a command economy c) The Hundred Campaign i. At first Mao welcomed other opinions
7 ii. Hundred Flowers campaign sought the advice of intellectuals iii. Eventually the program ended, and those who spoke out were d) The Great Leap Forward i. In order to expand agricultural production, Mao announced the creation of vast farms. ii. Experts were rarely consulted, and things were done poorly. iii. The great leap forward, became a great leap backward for China. e) The Revolution i. In 1966 Mao ordered the organization of the Red youth militia. ii. They promoted an anti- intellectual society where the hard working was the new hero. f) The Little Book i. Mao set himself up to be revered by his people ii. Mao s teachings were published in the little red book, iii. It is the second most published book. C. Korea 1. The Korean War a) Communist North Koreans attacked U.S. backed South Korea b) The U.S. responded (in form of forces) to attack by sending Douglas to push North Koreans back c) Initial U.S. success will result in stalemate after China joins the fray 2. Korea Remains Divided a) No peace treaty was ever signed ending the conflict, but a cease fire was declared in. b) After nearly 4 million people had died, the border ended up right where it began on the parallel. c) Virtually nothing had been accomplished. D. Cuba 1. Revolution a) In 1959, communist Fidel took over Cuba after a bloody revolution b) He was backed by the c) The U.S. was not happy with an enemy so close to home 2. Cuban Missile Crisis a) In October, 1962 US spy planes discovered the USSR was putting missiles in Cuba. b) Kennedy demanded that Khrushchev have them removed, and a nuclear showdown followed. i. Kennedy ordered the Navy to stop Soviet ships bound for Cuba. ii. Soviet Ships continued to Cuba, risking nuclear war with the US. c) The Secret Deal
8 E. The Vietnam War i. At the last minute a deal was struck between Kennedy and Khrushchev and the crisis was averted. ii. The US promised never to invade if the USSR would take its missiles. First a handful of advisers. Then the Marines. Finally an army of half a million. That was the Vietnam War. It was an undeclared war. A war without front lines or clear objectives. A war against an elusive enemy. A war.
9 I. Roots of the Conflict Vietnam A. before WWII Vietnam had been colonized by. 1. Opposition to French colonial rule came from. B. Ho Chi Minh 1. Vietnamese nationalist leader Well educated, fluent in many languages and well traveled. 2. Embraced communism as a means to. C. Role in WWII 1. During WWII, Vietnam was taken by the Japanese. 2. Ho returned to Vietnam in 1941 to fight for Vietnamese independence. a. He was supported in secret by the. 3. Ho believed Vietnam would become independent after Surrendered Instead, the Chinese began moving into Northern Vietnam. Reluctantly, The Viet Minh allowed the French back in. D. Things Fall Apart. 1. The Viet Minh and French could not agree on anything at all. 2. Ho and his followers began an insurgency from the. E. First Indochina War 1. The US backed France, and Ho was forced to turn to for aid. 2. Ho was VERY popular in the countryside. 3. Viet Minh used tactics. F. Dien Bien Phu Viet Minh victory at Bien Phu. 2. The French were forced to surrender to Ho Chi Minh, and Vietnam was divided into North and South. G. Ngo Dinh Diem II. US Involvement 1. Ngo Dinh Diem became the President of South Vietnam after rigging an. He was extremely unpopular 2. communist guerillas called the Vietcong (VC), or the National Front (NLF), began to take power in the countryside. 3. Strategic Program In an attempt to limit his people s exposure to VC, Diem put his people into camps. 4. Assassination a.in 1963, The US learned that Diem s were plotting to kill him. b. Diem and his brother were both shot in November,. c. A communist victory seemed.
10 A. Truman 1. Provides upwards of 1 billion dollars to support France against the Vietminh. Why? 2.Authorizes U.S. military advisors to aid French troops B. Eisenhower continues this policy believing in the D Effect. 1. Geneva Conference and Accords July 1954 a. consensus that Vietnam would become reunited in 1956 (likely communist) b. Neither the U.S., nor Vietnam sign this 2.Nov. 1, Authorizes U.S. military to aid South Vietnamese troops 3. official beginning of U.S. involvement in Vietnam C. Escalation! 1. On November 22, 1963 John F. was assassinated in Dallas Texas 2. at 2:38, VP Lyndon was the new president D. Gulf of Tonkin Incident III. Jungle Fighting USS Maddox reported being attacked, twice by NLF torpedo boats in the Gulf of 2. With the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution, without declaring, Johnson was now able to send over 180,000 US troops to Vietnam A. US army was far larger and far better than the Vietcong. B. the Vietcong were familiar with the jungle terrain which the US technological advantage. C. C. Ho Chi Minh VIETNAM VIDEO 1. America s involvement in Vietnam began in 1954 when a political split the country in two. 2. August 2, 1964 The USS is attacked by three North Vietnamese torpedo boats. 3. Both the Vietcong and the North Vietnamese view the Gulf of Tonkin resolution as a declaration of by the U.S. 4. On March 8 th 1965 at 8:15 3,500 marines land in south. 5. With South Vietnam near collapse, General Westmoreland asks President Johnson for permission to take the. IV. Further Escalation A. Early failures lead to increasing troop build ups in Vietnam. 1. the would have to be expanded more than half a US troops were serving in Vietnam. B. Long, Costly, and Unpleasant.
11 V. Tet Offensive 1. The South Vietnamese government was becoming increasingly unpopular. 2.The American presence in Vietnam was also becoming a source of for the Vietnamese people, and Americans back home. A despite assurances from the Johnson administration that the war was going well and would soon reach a successful conclusion, the Vietcong launched a series of attacks all over South Vietnam. 1. beginning of the end for the in Vietnam. VI. America attempts to control the situation A. The U.S. used million gallons Agent Orange to eliminate jungle and regain control of the fight 1. later revealed to cause serious health issues including tumors, birth defects, rashes, psychological symptoms and B. Operation Rolling VII. US Withdrawal 1. Due to politics and borders, the U.S. was unable to attack the Ho Chi Minh trail 2. sustained bombing against the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (North Vietnam) 3. Killed ,ooo people. A. Richard Nixon began winding down American involvement in Vietnam. VIII. Aftermath 1. The last US troops left in. A. By 1975 South Vietnam was overrun by the communists. B. Cambodia 1. million Vietnamese had died 2. American deaths. 3. War Powers Act a. U.S. President can send U.S. Armed Forces into action abroad only by declaration of by Congress 1. overrun by communist insurgents called the Khmer. 2. Their leader,, violently transformed Cambodia into an agrarian communist society. 3. Cambodians were murdered. VIETNAM VIDEO You are to decide whether or not the Vietnam war was worth it. As you watch the video, you need to find 10 pieces of evidence to help you decide, Was the Vietnam war worth fighting? Be sure to be specific!!! 1.
12
13 END OF THE COLD WAR:FALL OF THE USSR I. What caused the fall of Communism in Eastern Europe? A. When Gorbachev took over, Soviet military expenditures accounted for of the Soviet GDP (at the peak of the Reagan defense buildup, US defense spending was 6.5% of the US GDP). B. is the Soviet Vietnam 1. The war was going poorly for the Soviets 2. Gorbachev allocated more money to defense, and authorized an offensive to break the stalemate of the Afghanistan War ,000 + Soviet casualties 4. In April 1988, Gorbachev ordered a phased Soviet from Afghanistan that was completed in February C. By the end of the 1980s the entire Soviet Union had just desktop computers while the US had 25 million. D. Soviet s realized there was little incentive to work harder. II. The Final Players Mikhail Gorbachev A. Was born in 1931 B. Came to power in 1985 C. He sought, and the end of Cold War confrontations D. He pulled troops out of Afghanistan and looked to fix the USSR s Ronald Reagan A. President from B. Thought that the US needed an stance against communism C. Called the Soviets, the Empire D. Worked tirelessly to the Soviet Union in Cold War conflicts III. Soviet Union Reforms! A. Gorbachev initiates reform 1. Glasnost - 2. Perestroika was Gorbachev s attempt to reform the economy and government by B. Impact of Reforms a. Reducing the size of the b. Endorsing enterprise 1. Increased in the Soviet Empire 2. Demand for more and reform 3. uprisings spread throughout Eastern Europe - Gorbachev stepped down Reagan Berlin Wall Speech - Is this an effective or ineffective speech? Cite two Examples C. Communism collapses in Europe
14 largely peaceful revolutions swept through eastern Europe 2. October 1989, Berliners tore down the Berlin Wall 3. Eastern Europe rapidly became IV. Fall of Communism in Eastern Europe - demands of Freedom increase A. Hungary 1970 s small economic reform s criticize the USSR New freedoms allowed. B. In April 1989 the Polish held national elections led by Lech. C anti-communist dissident Vaclav came out of prison and was elected president of Czechoslovakia V. Russian Republic A is the beginning of a in Russia that lasts 10 years. B. Gorbachev is for everything C. Boris is elected Russian president in June 1991, but there is still a Gorbachev to deal with. D. After a coup, Gorbachev signs over nuclear arsenal to Yeltsin, 1991 which symbolically ends the USSR the USSR ceases to Which quote fits how you feel about the Cold War. In your opinion, did the United States win the Cold War? Consider the costs (Vietnam, Korea, Nuclear arms, McCarthy, etc.) Cite two pieces of evidence to support your answer. As the world s leading military power, is it the responsibility of the United States to be the World s Policeman?
Unit 7: The Cold War
 Unit 7: The Cold War Standard 7-5 Goal: The student will demonstrate an understanding of international developments during the Cold War era. Vocabulary 7-5.1 OCCUPIED 7-5.2 UNITED NATIONS NORTH ATLANTIC
Unit 7: The Cold War Standard 7-5 Goal: The student will demonstrate an understanding of international developments during the Cold War era. Vocabulary 7-5.1 OCCUPIED 7-5.2 UNITED NATIONS NORTH ATLANTIC
Chapter 17 Lesson 1: Two Superpowers Face Off. Essential Question: Why did tension between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R increase after WWII?
 Chapter 17 Lesson 1: Two Superpowers Face Off Essential Question: Why did tension between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R increase after WWII? Post WWII Big Three meet in Yalta Divide Germany into 4 zones (U.S.,
Chapter 17 Lesson 1: Two Superpowers Face Off Essential Question: Why did tension between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R increase after WWII? Post WWII Big Three meet in Yalta Divide Germany into 4 zones (U.S.,
Write 3 words you think of when you hear Cold War? THE COLD WAR ( )
 THE Write 3 words you think of when you hear Cold War? COLD WAR (1948-1989) ORIGINS of the Cold War: (1945-1948) Tension or rivalry but NO FIGHTING between the United States and the Soviet Union This rivalry
THE Write 3 words you think of when you hear Cold War? COLD WAR (1948-1989) ORIGINS of the Cold War: (1945-1948) Tension or rivalry but NO FIGHTING between the United States and the Soviet Union This rivalry
THE COLD WAR ( )
 THE COLD WAR (1948-1989) ORIGINS of the Cold War: (1945-1948) Tension or rivalry but NO FIGHTING between the United States and the Soviet Union This rivalry divided the world into two teams (capitalism
THE COLD WAR (1948-1989) ORIGINS of the Cold War: (1945-1948) Tension or rivalry but NO FIGHTING between the United States and the Soviet Union This rivalry divided the world into two teams (capitalism
Ch 29-1 The War Develops
 Ch 29-1 The War Develops The Main Idea Concern about the spread of communism led the United States to become increasingly violent in Vietnam. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze how the Cold war and
Ch 29-1 The War Develops The Main Idea Concern about the spread of communism led the United States to become increasingly violent in Vietnam. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze how the Cold war and
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Cold War Tensions (Chapter 30 Quiz)
 Cold War Tensions (Chapter 30 Quiz) What were the military and political consequences of the Cold War in the Soviet Union, Europe, and the United States? After World War II ended, the United States and
Cold War Tensions (Chapter 30 Quiz) What were the military and political consequences of the Cold War in the Soviet Union, Europe, and the United States? After World War II ended, the United States and
World History Chapter 23 Page Reading Outline
 World History Chapter 23 Page 601-632 Reading Outline The Cold War Era: Iron Curtain: a phrased coined by Winston Churchill at the end of World War I when her foresaw of the impending danger Russia would
World History Chapter 23 Page 601-632 Reading Outline The Cold War Era: Iron Curtain: a phrased coined by Winston Churchill at the end of World War I when her foresaw of the impending danger Russia would
Communism. Soviet Union government State (government) controls everything Opposite of democracy and capitalism (USA)
 Cold War VS Communism Soviet Union government State (government) controls everything Opposite of democracy and capitalism (USA) United Nations (UN) Started with 50 member countries Created to promote peace
Cold War VS Communism Soviet Union government State (government) controls everything Opposite of democracy and capitalism (USA) United Nations (UN) Started with 50 member countries Created to promote peace
Chapter 33 Summary/Notes
 Chapter 33 Summary/Notes Unit 8 Perspectives on the Present Chapter 33 Section 1. The Cold War Superpowers Face off We learned about the end of WWII. Now we learn about tensions that followed the war.
Chapter 33 Summary/Notes Unit 8 Perspectives on the Present Chapter 33 Section 1. The Cold War Superpowers Face off We learned about the end of WWII. Now we learn about tensions that followed the war.
World History (Survey) Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present
 World History (Survey) Chapter 33: Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present Section 1: Two Superpowers Face Off The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February
World History (Survey) Chapter 33: Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present Section 1: Two Superpowers Face Off The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February
ALLIES BECOME ENEMIES
 Cold War: Super Powers Face Off ALLIES BECOME ENEMIES What caused the Cold War? The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February 1945, they agreed to divide Germany into
Cold War: Super Powers Face Off ALLIES BECOME ENEMIES What caused the Cold War? The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February 1945, they agreed to divide Germany into
Cold War: Superpowers Face Off
 Cold War: Superpowers Face Off ALLIES BECOME ENEMIES What caused the Cold War? The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February 1945, they agreed to divide Germany into
Cold War: Superpowers Face Off ALLIES BECOME ENEMIES What caused the Cold War? The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February 1945, they agreed to divide Germany into
The Cold War Begins. After WWII
 The Cold War Begins After WWII After WWII the US and the USSR emerged as the world s two. Although allies during WWII distrust between the communist USSR and the democratic US led to the. Cold War tension
The Cold War Begins After WWII After WWII the US and the USSR emerged as the world s two. Although allies during WWII distrust between the communist USSR and the democratic US led to the. Cold War tension
THE IRON CURTAIN. From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic an iron curtain has descended across the continent. - Winston Churchill
 COLD WAR 1945-1991 1. The Soviet Union drove the Germans back across Eastern Europe. 2. They occupied several countries along it s western border and considered them a necessary buffer or wall of protection
COLD WAR 1945-1991 1. The Soviet Union drove the Germans back across Eastern Europe. 2. They occupied several countries along it s western border and considered them a necessary buffer or wall of protection
1969 U.S. troops begin their withdrawal from Vietnam
 Vietnam War Years Timeline 1964 LBJ becomes President 1965 First major combat units arrive in Vietnam 1968 M.L.King and Robert Kennedy are assassinated 1969 U.S. troops begin their withdrawal from Vietnam
Vietnam War Years Timeline 1964 LBJ becomes President 1965 First major combat units arrive in Vietnam 1968 M.L.King and Robert Kennedy are assassinated 1969 U.S. troops begin their withdrawal from Vietnam
Ended French rule in Indo-China
 Vietnam Review Dien Bien Phu in 1954 the main French forces were surrounded at this location in the north of Vietnam and forced to surrender. This was a turning point in that it ended the French control
Vietnam Review Dien Bien Phu in 1954 the main French forces were surrounded at this location in the north of Vietnam and forced to surrender. This was a turning point in that it ended the French control
Unit 15 Cold War-Present
 Unit 15 Cold War-Present Section 1: Introduction Cold War Definition A cold war in general is a state of political hostility between countries characterized by threats, propaganda, and other measures short
Unit 15 Cold War-Present Section 1: Introduction Cold War Definition A cold war in general is a state of political hostility between countries characterized by threats, propaganda, and other measures short
Bell Ringers - April 21
 WWII: Bell Ringers - April 21 What were the Nuremburg Trials? Trials set up by the Allies (International Military Tribunal) to make sure the NAZIs were punished for their crimes for waging a war of aggression
WWII: Bell Ringers - April 21 What were the Nuremburg Trials? Trials set up by the Allies (International Military Tribunal) to make sure the NAZIs were punished for their crimes for waging a war of aggression
Chapter 17: Restructuring the Postwar World: 1945-Present I. Cold War: Superpowers Face Off (Section 1) a. Allies Become Enemies i.
 Chapter 17: Restructuring the Postwar World: 1945-Present I. Cold War: Superpowers Face Off (Section 1) a. Allies Become Enemies i. Yalta Conference: A Postwar Plan 1. In February 1945, British, American
Chapter 17: Restructuring the Postwar World: 1945-Present I. Cold War: Superpowers Face Off (Section 1) a. Allies Become Enemies i. Yalta Conference: A Postwar Plan 1. In February 1945, British, American
The Cold War. Chapter 30
 The Cold War Chapter 30 Two Side Face Off in Europe Each superpower formed its own military alliance NATO USA and western Europe Warsaw Pact USSR and eastern Europe Berlin Wall 1961 Anti-Soviet revolts
The Cold War Chapter 30 Two Side Face Off in Europe Each superpower formed its own military alliance NATO USA and western Europe Warsaw Pact USSR and eastern Europe Berlin Wall 1961 Anti-Soviet revolts
Notes: LG: Analyze how the 1960s changed America.
 Notes: LG: Analyze how the 1960s changed America. USSR Nikita Khrushchev 1953-1964 1. Cold War Abroad in the 1960s a. 1961, Bay of Pigs Invasion (Cuba) i. President Eisenhower and CIA train Cuban
Notes: LG: Analyze how the 1960s changed America. USSR Nikita Khrushchev 1953-1964 1. Cold War Abroad in the 1960s a. 1961, Bay of Pigs Invasion (Cuba) i. President Eisenhower and CIA train Cuban
2014 Brain Wrinkles. Origins and Consequences
 Origins and Consequences Standards SS5H7 The student will discuss the origins and consequences of the Cold War. a. Explain the origin and meaning of the term Iron Curtain. b. Explain how the United States
Origins and Consequences Standards SS5H7 The student will discuss the origins and consequences of the Cold War. a. Explain the origin and meaning of the term Iron Curtain. b. Explain how the United States
UNIT Y222 THE COLD WAR IN ASIA
 UNIT Y222 THE COLD WAR IN ASIA 1945-1993 NOTE: BASED ON 2 X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources Western Policies
UNIT Y222 THE COLD WAR IN ASIA 1945-1993 NOTE: BASED ON 2 X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources Western Policies
This work is the intellectual property of MrHubbshistory.com. Content copyright MrHubbsHistory. All rights reserved.
 The Crumbling Alliance After World War II two powers, the United States and the Soviet Union became the world superpowers. These two countries had the economic resources and military force to dominate
The Crumbling Alliance After World War II two powers, the United States and the Soviet Union became the world superpowers. These two countries had the economic resources and military force to dominate
the Cold War The Cold War would dominate global affairs from 1945 until the breakup of the USSR in 1991
 U.S vs. U.S.S.R. ORIGINS OF THE COLD WAR After being Allies during WWII, the U.S. and U.S.S.R. soon viewed each other with increasing suspicion Their political differences created a climate of icy tension
U.S vs. U.S.S.R. ORIGINS OF THE COLD WAR After being Allies during WWII, the U.S. and U.S.S.R. soon viewed each other with increasing suspicion Their political differences created a climate of icy tension
TRUMAN S ROLE IN VIETNAM. = America is busy!!!!!
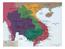 TRUMAN S ROLE IN VIETNAM Saw Vietnam as extension of Cold War - democracy v. communism! France fighting to re-gain Vietnam Truman supported France with money supplies because didn t want Something going
TRUMAN S ROLE IN VIETNAM Saw Vietnam as extension of Cold War - democracy v. communism! France fighting to re-gain Vietnam Truman supported France with money supplies because didn t want Something going
There will be some disturbing images and footage as we cover this unit, please do your best to act as adults, and learn from this war.
 There will be some disturbing images and footage as we cover this unit, please do your best to act as adults, and learn from this war. Vietnam Intro Before WWII, Vietnam was a colony of the French Japanese
There will be some disturbing images and footage as we cover this unit, please do your best to act as adults, and learn from this war. Vietnam Intro Before WWII, Vietnam was a colony of the French Japanese
OBJECTIVES. Describe and evaluate the events that led to the war between North Vietnam and South Vietnam.
 OBJECTIVES Describe and evaluate the events that led to the war between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. Identify and explain the foreign policy of the United States at this time, and how it relates to
OBJECTIVES Describe and evaluate the events that led to the war between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. Identify and explain the foreign policy of the United States at this time, and how it relates to
The Americans (Survey)
 The Americans (Survey) Chapter 26: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Cold War Conflicts CHAPTER OVERVIEW After World War II, tensions between the United States and the Soviet Union lead to a war without direct military
The Americans (Survey) Chapter 26: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Cold War Conflicts CHAPTER OVERVIEW After World War II, tensions between the United States and the Soviet Union lead to a war without direct military
Chapter 19: Going To war in Vietnam
 Heading Towards War Vietnam during WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the. returned to Vietnam
Heading Towards War Vietnam during WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the. returned to Vietnam
Cold War: Superpowers Face Off
 Section 1 Cold War: Superpowers Face Off Reading Comprehension Find the name or term in the second column that best matches the description in the first column. Then write the letter of your answer in
Section 1 Cold War: Superpowers Face Off Reading Comprehension Find the name or term in the second column that best matches the description in the first column. Then write the letter of your answer in
The Cold War Finally Thaws Out. Korean War ( ) Vietnam War ( ) Afghan War ( )
 The Cold War Finally Thaws Out Korean War (1950-1953) Vietnam War (1963-1973) Afghan War (1979-1989) Korean war Split after WWII between US and USSR Temporary gov ts created in images of their major allies
The Cold War Finally Thaws Out Korean War (1950-1953) Vietnam War (1963-1973) Afghan War (1979-1989) Korean war Split after WWII between US and USSR Temporary gov ts created in images of their major allies
Topic 5: The Cold War (Compiled from 10 Topic and 6 Topic Format) Revised 2014
 Topic 5: The Cold War (Compiled from 10 Topic and 6 Topic Format) Revised 2014 [Since 1998, the pattern is: two subject specific questions, two questions allowing a choice of examples, and one question
Topic 5: The Cold War (Compiled from 10 Topic and 6 Topic Format) Revised 2014 [Since 1998, the pattern is: two subject specific questions, two questions allowing a choice of examples, and one question
Chapter 25 Cold War America, APUSH Mr. Muller
 Chapter 25 Cold War America, 1945-1963 APUSH Mr. Muller Aim: How does the U.S. and U.S.S.R. go from allies to rivals? Do Now: Communism holds that the world is so deeply divided into opposing classes that
Chapter 25 Cold War America, 1945-1963 APUSH Mr. Muller Aim: How does the U.S. and U.S.S.R. go from allies to rivals? Do Now: Communism holds that the world is so deeply divided into opposing classes that
THE COLD WAR Part One Teachers Notes by Paul Latham
 THE COLD WAR Part One Teachers Notes by Paul Latham Notes also available on DVD disc as either a Word document or PDF file. Also available on the website. 1 2 The Cold War (Part 1) Teachers Notes ORIGINS
THE COLD WAR Part One Teachers Notes by Paul Latham Notes also available on DVD disc as either a Word document or PDF file. Also available on the website. 1 2 The Cold War (Part 1) Teachers Notes ORIGINS
ANSWER KEY..REVIEW FOR Friday s QUIZ #15 Chapter: 29 -Vietnam
 ANSWER KEY..REVIEW FOR Friday s QUIZ #15 Chapter: 29 -Vietnam Ch. 29 sec. 1 - skim and scan pages 908-913 and then answer the questions. French Indochina: French ruled colony made up of Vietnam, Laos,
ANSWER KEY..REVIEW FOR Friday s QUIZ #15 Chapter: 29 -Vietnam Ch. 29 sec. 1 - skim and scan pages 908-913 and then answer the questions. French Indochina: French ruled colony made up of Vietnam, Laos,
THEMES. 1) EXPANDING DEMOCRACY: America s mission in Vietnam was to halt the spread of communism-a threat to democracy.
 THEMES 1) EXPANDING DEMOCRACY: America s mission in Vietnam was to halt the spread of communism-a threat to democracy. 2) CONSTITUTIONAL CONCERNS: Among the constitutional issues of the Vietnam War era
THEMES 1) EXPANDING DEMOCRACY: America s mission in Vietnam was to halt the spread of communism-a threat to democracy. 2) CONSTITUTIONAL CONCERNS: Among the constitutional issues of the Vietnam War era
The Cold War
 The Cold War 1945-1989 What is the Cold War It was an intense rivalry between the United States and Russia between West and East and between capitalism and communism that dominated the years following
The Cold War 1945-1989 What is the Cold War It was an intense rivalry between the United States and Russia between West and East and between capitalism and communism that dominated the years following
Cold War. A war of words between countries. There is no actual fighting.
 Cold War Era Cold War A war of words between countries. There is no actual fighting. Iron Curtain The term Winston Churchill used to describe the communist countries in Europe Yalta Conference a conference
Cold War Era Cold War A war of words between countries. There is no actual fighting. Iron Curtain The term Winston Churchill used to describe the communist countries in Europe Yalta Conference a conference
Topic 5: The Cold War (Compiled from 10 Topic and 6 Topic Format) Revised 2012
 Topic 5: The Cold War (Compiled from 10 Topic and 6 Topic Format) Revised 2012 [Since 1998, the pattern is: two subject specific questions, two questions allowing a choice of examples, and one question
Topic 5: The Cold War (Compiled from 10 Topic and 6 Topic Format) Revised 2012 [Since 1998, the pattern is: two subject specific questions, two questions allowing a choice of examples, and one question
VUS.13b. The Vietnam War. U. S. government s anti- Communist strategy of containment in Asia
 VUS.13b The Vietnam War U. S. government s anti- Communist strategy of containment in Asia Help the French and send some advisors- Increase advisors, send some troops- Escalate- we can not lose a war Peace
VUS.13b The Vietnam War U. S. government s anti- Communist strategy of containment in Asia Help the French and send some advisors- Increase advisors, send some troops- Escalate- we can not lose a war Peace
Introduction to the Cold War
 Introduction to the Cold War What is the Cold War? The Cold War is the conflict that existed between the United States and Soviet Union from 1945 to 1991. It is called cold because the two sides never
Introduction to the Cold War What is the Cold War? The Cold War is the conflict that existed between the United States and Soviet Union from 1945 to 1991. It is called cold because the two sides never
Politics of the Cold War
 Politics of the Cold War Standards SSUSH20 The student will analyze the domestic and international impact of the Cold War on the United States. c. Describe the Cuban Revolution, the Bay of Pigs, and the
Politics of the Cold War Standards SSUSH20 The student will analyze the domestic and international impact of the Cold War on the United States. c. Describe the Cuban Revolution, the Bay of Pigs, and the
World History: Patterns of Interaction
 Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945-Present The United States and the Soviet Union vie for superiority, and both countries extend their control over other nations. Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945-Present
Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945-Present The United States and the Soviet Union vie for superiority, and both countries extend their control over other nations. Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945-Present
Chapter 28, Section 1: The Cold War Begins. Main Idea: After WWII, distrust between the US & USSR led to the Cold War.
 Chapter 28, Section 1: The Cold War Begins Main Idea: After WWII, distrust between the US & USSR led to the Cold War. The Cold War [1945-1991]: An Ideological Struggle US & the Western Democracies GOAL
Chapter 28, Section 1: The Cold War Begins Main Idea: After WWII, distrust between the US & USSR led to the Cold War. The Cold War [1945-1991]: An Ideological Struggle US & the Western Democracies GOAL
The Cold War An overview
 The Cold War An overview 1945-1960 I m takin you down, Freedom!! You and all your Western Friends! Neeeiiigggghhhh!! We re going to stamp you out, you and all your Commie cronies! What is the Cold War?
The Cold War An overview 1945-1960 I m takin you down, Freedom!! You and all your Western Friends! Neeeiiigggghhhh!! We re going to stamp you out, you and all your Commie cronies! What is the Cold War?
One war ends, another begins
 One war ends, another begins Communism comes from the word common, meaning to belong equally to more than one individual. The related word, commune is a place where people live together and share property
One war ends, another begins Communism comes from the word common, meaning to belong equally to more than one individual. The related word, commune is a place where people live together and share property
Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs. non Communist South Organized by Ho Chi Minh
 1956 Elections are cancelled (1 of Geneva Accords) 1957 The Vietcong attack in South Vietnam Vietcong are South Vietnamese communists Guerrilla fighters Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs.
1956 Elections are cancelled (1 of Geneva Accords) 1957 The Vietcong attack in South Vietnam Vietcong are South Vietnamese communists Guerrilla fighters Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs.
Period 8 and Period to Infinity
 Period 8 and Period 9 1945 to Infinity YOU AND THE DECADES: A TIME OF WONDER AND AMAZEMENT Using the textbook and your massive brains, spend time perusing the decades of the mid-20 th century. It is a
Period 8 and Period 9 1945 to Infinity YOU AND THE DECADES: A TIME OF WONDER AND AMAZEMENT Using the textbook and your massive brains, spend time perusing the decades of the mid-20 th century. It is a
The Cold War. Origins - Korean War
 The Cold War Origins - Korean War What is a Cold War? WW II left two nations of almost equal strength but differing goals Cold War A struggle over political differences carried on by means short of direct
The Cold War Origins - Korean War What is a Cold War? WW II left two nations of almost equal strength but differing goals Cold War A struggle over political differences carried on by means short of direct
Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present. Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present. Cold War: Superpowers Face Off. Allies Become Enemies
 Restructuring the Postwar World, 9 Present The United States and the Soviet Union vie for superiority, and both countries extend their control over other nations. Restructuring the Postwar World, 9 Present
Restructuring the Postwar World, 9 Present The United States and the Soviet Union vie for superiority, and both countries extend their control over other nations. Restructuring the Postwar World, 9 Present
Cold War Conflicts Chapter 26
 Cold War Conflicts Chapter 26 Former Allies Clash After World War II the US and the Soviets had very different goals for the future. Under Soviet communism the state controlled all property and economic
Cold War Conflicts Chapter 26 Former Allies Clash After World War II the US and the Soviets had very different goals for the future. Under Soviet communism the state controlled all property and economic
Journal # 11 04/30/15 Objective: Students will utilize various
 Journal # 11 04/30/15 Objective: Students will utilize various resources to identify, compare/contrast, and evaluate the origins, development and effects of the Cold War. Agenda: Journal Cold War PPT Guided
Journal # 11 04/30/15 Objective: Students will utilize various resources to identify, compare/contrast, and evaluate the origins, development and effects of the Cold War. Agenda: Journal Cold War PPT Guided
COLD WAR ORIGINS. U.S vs. U.S.S.R. Democ./Cap vs Comm.
 COLD WAR ORIGINS U.S vs. U.S.S.R. Democ./Cap vs Comm. Section One: Objectives By the end, I will be able to: 1. Explain the breakdown in relations between the United States and the Soviet Union after World
COLD WAR ORIGINS U.S vs. U.S.S.R. Democ./Cap vs Comm. Section One: Objectives By the end, I will be able to: 1. Explain the breakdown in relations between the United States and the Soviet Union after World
EOC Test Preparation: The Cold War Era
 EOC Test Preparation: The Cold War Era Conflict in Europe Following WWII, tensions were running high between western Allies and USSR US and Great Britain: Allies should not occupy territories they conquered
EOC Test Preparation: The Cold War Era Conflict in Europe Following WWII, tensions were running high between western Allies and USSR US and Great Britain: Allies should not occupy territories they conquered
What was the Cold War?
 The Cold War What was the Cold War? Period of tension (1945-1991) involving primarily the two superpowers (United States and Soviet Union) following W.W.II No Direct Conflict between the U.S. and U.S.S.R.
The Cold War What was the Cold War? Period of tension (1945-1991) involving primarily the two superpowers (United States and Soviet Union) following W.W.II No Direct Conflict between the U.S. and U.S.S.R.
The Cold War TOWARD A GLOBAL COMMUNITY (1900 PRESENT)
 The Cold War TOWARD A GLOBAL COMMUNITY (1900 PRESENT) Throughout WWII the U.S. and the Soviet Union began to view each other with increasing suspicion. He s a commie, and once made an alliance with Hitler...
The Cold War TOWARD A GLOBAL COMMUNITY (1900 PRESENT) Throughout WWII the U.S. and the Soviet Union began to view each other with increasing suspicion. He s a commie, and once made an alliance with Hitler...
Chapter 21 Review. AP World History
 Chapter 21 Review AP World History Essential Question: What led to the Cold War between the United States & Soviet Union? The end of World War II led to important changes in the world: The U.N. United
Chapter 21 Review AP World History Essential Question: What led to the Cold War between the United States & Soviet Union? The end of World War II led to important changes in the world: The U.N. United
Chapter 30-1 CN I. Early American Involvement in Vietnam (pages ) A. Although little was known about Vietnam in the late 1940s and early
 Chapter 30-1 CN I. Early American Involvement in Vietnam (pages 892 894) A. Although little was known about Vietnam in the late 1940s and early 1950s, American officials felt Vietnam was important in their
Chapter 30-1 CN I. Early American Involvement in Vietnam (pages 892 894) A. Although little was known about Vietnam in the late 1940s and early 1950s, American officials felt Vietnam was important in their
Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs. non Communist South Organized by Ho Chi Minh
 1956 Elections are cancelled (1 of Geneva Accords) 1957 The Vietcong attack in South Vietnam Vietcong are South Vietnamese communists Guerrilla fighters Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs.
1956 Elections are cancelled (1 of Geneva Accords) 1957 The Vietcong attack in South Vietnam Vietcong are South Vietnamese communists Guerrilla fighters Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs.
Modern World History Spring Final Exam 09
 1. What was the goal of the Marshall Plan? A. to provide aid to European countries damaged by World War II B. to protect member nations against Soviet Union aggression C. to protect the United States economically
1. What was the goal of the Marshall Plan? A. to provide aid to European countries damaged by World War II B. to protect member nations against Soviet Union aggression C. to protect the United States economically
The War in Vietnam. Chapter 30
 The War in Vietnam Chapter 30 Vietnam A colony of France until after World War II 1954- War for Independence led by Ho Chi Minh Ho Chi Minh The Geneva Accords The Geneva Accords divided the country into
The War in Vietnam Chapter 30 Vietnam A colony of France until after World War II 1954- War for Independence led by Ho Chi Minh Ho Chi Minh The Geneva Accords The Geneva Accords divided the country into
VIETNAM WAR
 VIETNAM WAR 1955-1975 #30 http://www.military.com/video/offduty/movies/classic-forrest-gump-invietnam-war/1069387728001 PRESIDENTS DURING THE VIETNAM WAR Dwight D. Eisenhower. John F. Kennedy. Lyndon B.
VIETNAM WAR 1955-1975 #30 http://www.military.com/video/offduty/movies/classic-forrest-gump-invietnam-war/1069387728001 PRESIDENTS DURING THE VIETNAM WAR Dwight D. Eisenhower. John F. Kennedy. Lyndon B.
Chapter 19 GOING TO WAR IN VIETNAM
 Chapter 19 GOING TO WAR IN VIETNAM VIETNAM DURING WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the Japanese.
Chapter 19 GOING TO WAR IN VIETNAM VIETNAM DURING WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the Japanese.
Early Cold War
 Early Cold War 1945-1972 Capitalism vs. Communism Capitalism Communism Free-Market Economy Upper, Middle and Working Class North Atlantic Treaty Organization Government Controlled Economy Classless Society
Early Cold War 1945-1972 Capitalism vs. Communism Capitalism Communism Free-Market Economy Upper, Middle and Working Class North Atlantic Treaty Organization Government Controlled Economy Classless Society
Unit 4 Notes - The Cold War
 Unit 4 Notes - The Cold War 4.1.1 Cold War: The period following WWII, 1945 to 1990, when increasing diplomatic and political tension between the West / United States and the East /Soviet Union created
Unit 4 Notes - The Cold War 4.1.1 Cold War: The period following WWII, 1945 to 1990, when increasing diplomatic and political tension between the West / United States and the East /Soviet Union created
National Nightmare Begins: Origins of Vietnam War
 National Nightmare Begins: Origins of Vietnam War From late 1800 s until WWII (When Japan took over) France ruled Indochina (Vietnam, Laos & Cambodia). French took land from peasants & built large plantations,
National Nightmare Begins: Origins of Vietnam War From late 1800 s until WWII (When Japan took over) France ruled Indochina (Vietnam, Laos & Cambodia). French took land from peasants & built large plantations,
Russian History. Lecture #1 Ancient History The Romanov s
 Russian History Lecture #1 Ancient History The Romanov s Outline Russia Lecture #1 Ancient Russia Settlement of Russia Yaroslav the Wise Mongol Invasion of Russia Retaking Russia Ivan the Great Ivan the
Russian History Lecture #1 Ancient History The Romanov s Outline Russia Lecture #1 Ancient Russia Settlement of Russia Yaroslav the Wise Mongol Invasion of Russia Retaking Russia Ivan the Great Ivan the
This opposition created a global atmosphere of tension which never developed into direct. There was a warlike relationship between the two nations.
 AIM: Explain the conflict between the two superpowers that led to the Cold War. Expansion of Communism Stalin agreed to allow free elections in Soviet occupied European countries. He did not fulfill his
AIM: Explain the conflict between the two superpowers that led to the Cold War. Expansion of Communism Stalin agreed to allow free elections in Soviet occupied European countries. He did not fulfill his
Vietnam Introduction. Answer the following questions on a sticky note...
 Vietnam Introduction Answer the following questions on a sticky note... https://www.youtube.c om/watch?v=epfnsk5l 26U Burning Monk 1. Why was the burning monk event significant? How did people in the U.S.
Vietnam Introduction Answer the following questions on a sticky note... https://www.youtube.c om/watch?v=epfnsk5l 26U Burning Monk 1. Why was the burning monk event significant? How did people in the U.S.
THE COLD WAR Part Two Teachers Notes by Paul Latham
 THE COLD WAR Part Two Teachers Notes by Paul Latham Notes also available on DVD disc as either a Word document or PDF file. Also available on the website 1 2 The Cold War (Part 2) Teachers Notes CUBA AND
THE COLD WAR Part Two Teachers Notes by Paul Latham Notes also available on DVD disc as either a Word document or PDF file. Also available on the website 1 2 The Cold War (Part 2) Teachers Notes CUBA AND
WINNING the WAR / PLANNING the PEACE The Allies: US, England, USSR, and China Feb 1945 Yalta Conference: US-USSR-England GERMANY must agree to
 WINNING the WAR / PLANNING the PEACE The Allies: US, England, USSR, and China Feb 1945 Yalta Conference: US-USSR-England GERMANY must agree to UNCONDITIONAL SURRENDER Germany will be divided into 4 parts
WINNING the WAR / PLANNING the PEACE The Allies: US, England, USSR, and China Feb 1945 Yalta Conference: US-USSR-England GERMANY must agree to UNCONDITIONAL SURRENDER Germany will be divided into 4 parts
Note Taking Study Guide THE COLD WAR UNFOLDS
 SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide THE COLD WAR UNFOLDS Focus Question: What were the military and political consequences of the Cold War in the Soviet Union, Europe, and the United States? As you read
SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide THE COLD WAR UNFOLDS Focus Question: What were the military and political consequences of the Cold War in the Soviet Union, Europe, and the United States? As you read
East Asia in the Postwar Settlements
 Chapter 34 " Rebirth and Revolution: Nation-building in East Asia and the Pacific Rim East Asia in the Postwar Settlements Korea was divided between a Russian zone of occupation in the north and an American
Chapter 34 " Rebirth and Revolution: Nation-building in East Asia and the Pacific Rim East Asia in the Postwar Settlements Korea was divided between a Russian zone of occupation in the north and an American
The Cold War. Chap. 18, 19
 The Cold War Chap. 18, 19 Cold War 1945-1991 Political and economic conflict between U.S. and USSR Not fought on battlefield U.S. Vs. USSR Democracy- free elections private ownership Free market former
The Cold War Chap. 18, 19 Cold War 1945-1991 Political and economic conflict between U.S. and USSR Not fought on battlefield U.S. Vs. USSR Democracy- free elections private ownership Free market former
VIETNAM 04/14/15 ORIGINS OF THE VIETNAM WAR s French establish control over Indochina - Southeast Asia
 VIETNAM Have you seen Charlie? 04/12/15 2 ORIGINS OF THE VIETNAM WAR 1800 s French establish control over Indochina - Southeast Asia Modern countries: Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos Transplanted French laws
VIETNAM Have you seen Charlie? 04/12/15 2 ORIGINS OF THE VIETNAM WAR 1800 s French establish control over Indochina - Southeast Asia Modern countries: Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos Transplanted French laws
VIETNAM WAR
 VIETNAM WAR 1965-1972 FRENCH CONTROL French controlled Vietnam until World War II Vietnam taken by Japan Ho Chi Minh called for an independence of Vietnam Eight Year war between France and Ho Chi Minh
VIETNAM WAR 1965-1972 FRENCH CONTROL French controlled Vietnam until World War II Vietnam taken by Japan Ho Chi Minh called for an independence of Vietnam Eight Year war between France and Ho Chi Minh
Conflict U.S. War
 Conflict - 1945-1975 U.S. War 1964-1973 Overview of the Vietnam War Why is Vietnam still a painful war to remember? Longest war in U.S. history and only war we lost It showed Americans that our power is
Conflict - 1945-1975 U.S. War 1964-1973 Overview of the Vietnam War Why is Vietnam still a painful war to remember? Longest war in U.S. history and only war we lost It showed Americans that our power is
C. Continuing protests Doves wanted an immediate withdrawal that was complete, unconditional, and irreversible.
 I. VIETNAM WAR spread across 5 presidencies and spanned 25 years Direct U.S involvement from 1963-1973 A. France lost control of Vietnam after the battle of Dien Bien Phu in 1954 1. U.S. by 1954 had financed
I. VIETNAM WAR spread across 5 presidencies and spanned 25 years Direct U.S involvement from 1963-1973 A. France lost control of Vietnam after the battle of Dien Bien Phu in 1954 1. U.S. by 1954 had financed
Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present
 Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present Map Activity Define the following on a separate sheet of paper: Cold War, Brinkmanship, Détente, Containment, Communism, Capitalism, Democracy, Command Economy,
Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present Map Activity Define the following on a separate sheet of paper: Cold War, Brinkmanship, Détente, Containment, Communism, Capitalism, Democracy, Command Economy,
Main Idea. After WWII, China became a Communist nation and Korea was split into a communist north and democratic south.
 Objectives 1. Explain how Communists came to power in China and how the United States reacted. 2. Summarize the events of the Korean War. 3. Explain the conflict between President Truman and General MacArthur.
Objectives 1. Explain how Communists came to power in China and how the United States reacted. 2. Summarize the events of the Korean War. 3. Explain the conflict between President Truman and General MacArthur.
Chapter 37A: The Bipolar War
 Chapter 37A: The Bipolar War Key Concept 6.1 Science and the Environment Rapid advances in science altered the understanding of the universe and the natural world and led to the development of new technologies.
Chapter 37A: The Bipolar War Key Concept 6.1 Science and the Environment Rapid advances in science altered the understanding of the universe and the natural world and led to the development of new technologies.
netw rks Where in the world? When did it happen? The Vietnam Era Lesson 1 Kennedy s Foreign Policy ESSENTIAL QUESTION Terms to Know GUIDING QUESTIONS
 Lesson 1 Kennedy s Foreign Policy ESSENTIAL QUESTION What motivates people to act? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. Why did President Kennedy seek new ways to deal with the challenges and fears of the Cold War? 2.
Lesson 1 Kennedy s Foreign Policy ESSENTIAL QUESTION What motivates people to act? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. Why did President Kennedy seek new ways to deal with the challenges and fears of the Cold War? 2.
At the end of World War II
 At the end of World War II the world was in ruins. People wanted peace and needed the world put back together again. But there were only two countries with the power to rebuild the world: The United States
At the end of World War II the world was in ruins. People wanted peace and needed the world put back together again. But there were only two countries with the power to rebuild the world: The United States
4/8/2015. April nations met. US and USSR on same side in WW II. Cold War Feb FDR, Churchill, Stalin Postwar issues
 Chapter 26 US and USSR on same side in WW II Not by choice Common enemy Cold War 1946 1991 Feb. 1945 FDR, Churchill, Stalin Postwar issues divide Germany free elections April 1945 50 nations met UN Charter
Chapter 26 US and USSR on same side in WW II Not by choice Common enemy Cold War 1946 1991 Feb. 1945 FDR, Churchill, Stalin Postwar issues divide Germany free elections April 1945 50 nations met UN Charter
unit 4: The Cold War
 unit 4: The Cold War Vocabulary & Important People 1. Cold War: the state of political hostility that existed between the Soviet bloc countries and the US-led Western powers from 1945 to 1990. 2. Harry
unit 4: The Cold War Vocabulary & Important People 1. Cold War: the state of political hostility that existed between the Soviet bloc countries and the US-led Western powers from 1945 to 1990. 2. Harry
The Cold War ( )
 The Cold War (1945-1991) Timeline USSR dissolves WWII Cold War 1939 1945 1989 1991 Revolutions of 1989 What is it US vs. USSR state of tension nuclear arms race Space Race propaganda war fighting through
The Cold War (1945-1991) Timeline USSR dissolves WWII Cold War 1939 1945 1989 1991 Revolutions of 1989 What is it US vs. USSR state of tension nuclear arms race Space Race propaganda war fighting through
Unit 8. 5th Grade Social Studies Cold War Study Guide. Additional study material and review games are available at at
 Unit 8 5th Grade Social Studies Cold War Study Guide Additional study material and review games are available at www.jonathanfeicht.com. are available at www.jonathanfeicht.com. Copyright 2015. For single
Unit 8 5th Grade Social Studies Cold War Study Guide Additional study material and review games are available at www.jonathanfeicht.com. are available at www.jonathanfeicht.com. Copyright 2015. For single
Modern American History Unit 8: The 1960s The Vietnam War Notes and Questions
 Modern American History Unit 8: The 1960s The Vietnam War Notes and Questions The Vietnam War A. Vietnam: A Painful War U.S. involvement in conflicts in Vietnam lasted from mid-1940s to 1975 Only war the
Modern American History Unit 8: The 1960s The Vietnam War Notes and Questions The Vietnam War A. Vietnam: A Painful War U.S. involvement in conflicts in Vietnam lasted from mid-1940s to 1975 Only war the
Making of the Modern World 15. Lecture #10 The Cold War and the American Century
 Making of the Modern World 15 Lecture #10 The Cold War and the American Century Uncle Joe Guess where. Origins of the Cold War US, USSR, Great Britain unnatural allies during World War II Tensions submerged
Making of the Modern World 15 Lecture #10 The Cold War and the American Century Uncle Joe Guess where. Origins of the Cold War US, USSR, Great Britain unnatural allies during World War II Tensions submerged
3/2/2017. Dwight Eisenhower & The Cold War. Election of Adlai Stevenson Democratic Candidate. Dwight D. Eisenhower Ike Republican Candidate
 1 2 3 4 Dwight Eisenhower & The Cold War Election of 1952 Adlai Stevenson Democratic Candidate Dwight D. Eisenhower Ike Republican Candidate 5 6 7 1952 Election Results Dwight D. Eisenhower 34 th President
1 2 3 4 Dwight Eisenhower & The Cold War Election of 1952 Adlai Stevenson Democratic Candidate Dwight D. Eisenhower Ike Republican Candidate 5 6 7 1952 Election Results Dwight D. Eisenhower 34 th President
5/8/2013. The Cold War Era. Chapter 23 THE COLD WAR ERA. Postwar Confrontation. Communist Motives. A Heritage of Mistrust
 Chapter 23 THE COLD WAR ERA An iron curtain has descended The Cold War Era After WWII, Soviet Expansion threatened to enslave Europe From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain
Chapter 23 THE COLD WAR ERA An iron curtain has descended The Cold War Era After WWII, Soviet Expansion threatened to enslave Europe From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic, an iron curtain
War. Ho Chi Minh. domino theory. Dien Bien Phu SEATO. Vietcong Gulf of Tonkin Resolution. the end of WWII? ce? supporting
 Chapter 29 Section 1 Origins of the Vietnam War Ho Chi Minh domino theory Dien Bien Phu SEATO Vietcong Gulf of Tonkin Resolution 1. Witness History: What countries made up French Indochina? 2. What state
Chapter 29 Section 1 Origins of the Vietnam War Ho Chi Minh domino theory Dien Bien Phu SEATO Vietcong Gulf of Tonkin Resolution 1. Witness History: What countries made up French Indochina? 2. What state
World History Unit 08a and 08b: Global Conflicts & Issues _Edited
 Name: Period: Date: Teacher: World History Unit 08a and 08b: Global Conflicts & Issues 2012-2013_Edited Test Date: April 25, 2013 Suggested Duration: 1 class period This test is the property of TESCCC/CSCOPE
Name: Period: Date: Teacher: World History Unit 08a and 08b: Global Conflicts & Issues 2012-2013_Edited Test Date: April 25, 2013 Suggested Duration: 1 class period This test is the property of TESCCC/CSCOPE
The Stormy Sixties. Chapter 38
 The Stormy Sixties Chapter 38 Kennedy Nixon Debates John F Kennedy and Richard Nixon had first presidential debate on TV Kennedy s New Frontier Spirit JFK elected by small margin over Nixon in 1960 Youngest
The Stormy Sixties Chapter 38 Kennedy Nixon Debates John F Kennedy and Richard Nixon had first presidential debate on TV Kennedy s New Frontier Spirit JFK elected by small margin over Nixon in 1960 Youngest
4.2.2 Korea, Cuba, Vietnam. Causes, Events and Results
 4.2.2 Korea, Cuba, Vietnam Causes, Events and Results This section will illustrate the extent of the Cold War outside of Europe & its impact on international affairs Our focus will be to analyze the causes
4.2.2 Korea, Cuba, Vietnam Causes, Events and Results This section will illustrate the extent of the Cold War outside of Europe & its impact on international affairs Our focus will be to analyze the causes
Review for final. 1. What type of ruler was Julius Caesar? 2. Who was the ruler of the Byzantine Empire during it s Golden Age?
 Review for final 1. What type of ruler was Julius Caesar? 2. Who was the ruler of the Byzantine Empire during it s Golden Age? 3. Tell me all you remember about the Crusades. 4. The 200 year period of
Review for final 1. What type of ruler was Julius Caesar? 2. Who was the ruler of the Byzantine Empire during it s Golden Age? 3. Tell me all you remember about the Crusades. 4. The 200 year period of
Gulf of Tonkin Resolution Lesson Plan
 Resolution Lesson Plan Central Historical Question: Was the U.S. planning to go to war with North Vietnam before the Resolution? Materials: Powerpoint Timeline Documents A-D Guiding Questions Plan of Instruction:
Resolution Lesson Plan Central Historical Question: Was the U.S. planning to go to war with North Vietnam before the Resolution? Materials: Powerpoint Timeline Documents A-D Guiding Questions Plan of Instruction:
Chapter 18: Cold War Conflicts
 Chapter 18: Cold War Conflicts Section 1: Origins of the Cold War United Nations Satellite Nation Containment Iron Curtain Cold War Truman Doctrine Marshall Plan Berlin Airlift North Atlantic Treaty Organization
Chapter 18: Cold War Conflicts Section 1: Origins of the Cold War United Nations Satellite Nation Containment Iron Curtain Cold War Truman Doctrine Marshall Plan Berlin Airlift North Atlantic Treaty Organization
Chapter 20. The Vietnam War Era
 Chapter 20 The Vietnam War Era 1954-1975 Ho Chi Minh The most important voice who demanded independence for Vietnam. Communist leader of the Vietminh. Vietminh The term initially used to describe all Vietnamese
Chapter 20 The Vietnam War Era 1954-1975 Ho Chi Minh The most important voice who demanded independence for Vietnam. Communist leader of the Vietminh. Vietminh The term initially used to describe all Vietnamese
