Several early American leaders believed that Tariffs were the best way for the government to generate funds that could be used to improve the country
|
|
|
- Madlyn Manning
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Several early American leaders believed that Tariffs were the best way for the government to generate funds that could be used to improve the country s transportation network as well as other government projects. Not everyone liked tariffs--southern farmers, in particular, resented the fact that they helped northern manufacturers but hurt southern farmer; when farmers sold their crops to Europeans they usually bought Europe-made products in return, but tariffs make these items more expensive. Many consumers did not like tariffs because they made manufactured items more expensive. John C. Calhoun was an important opponent of tariffs and his opposition caused the Nullification Crisis in 1828.
3 1. In the years before the American Civil War, which of these people would have been most likely to oppose high tariffs? A. Manufacturer from New York B. Craftsman with a shop in Massachusetts C. Plantation owner in South Carolina D. Slave working in Kentucky
4 NORTH SOUTH The Cold Climate meant a short growing season Industrialization changed how northerners--worked and lived Urbanization-workers moved to the cities to find jobs. The warm climate meant a long growing season. Agriculture was the primary economic activity Farms and large plantations produced agricultural products Slaves did most of the farm work There were few cities--it was mostly a rural area.
5 2. What was on of the major economic differences between the South and the North before the Civil War? A. The South was much larger than the North and therefore had a greater economic economic base. B. Fewer southern farmers than northern farmers owned land. C. The South produced a wider variety of products than the North produced. D. The South s economy relied on slave labor, while the North s economy relied on wage labor.
6 3. Why did manufacturing become an important part of the Northern economy? A. The climate was too arid to produce many crops B. There were not enough cities where farmers could ship their crops C. There was a shorter growing season, and farmers could not produce as many crops in the rocky soil. D. There were not enough rivers to run water powered factories.
7 New England Colonies Middle Colonies Southern Colonies Tobacco 48% Dried Fish and Whale Oil Livestock Wood Products Other 44% 17% 13% 26% Grain Iron Wood Products Other 73% 5% 5% 17% Rice Bread, Flour, Grain (not rice) Indigo Ot her 20% 13% 7% 12% Use this chart to answer the question on the next slide.
8 4. How did the products grown in the South differ from those grown in the Middle or Mid-Atlantic Colonies? A. The New England Colonies grew a greater variety of farm products. B. The South developed mining and lumbering as secondary industries C. The Middle Colonies did not depend on grain products for most of their income D. The South grew luxury crops for cash, not only food products
9 Good Soil Slave Labor Numerous Rivers and Waterways 5. What economic development do the conditions listed in the box help to explain? A. Plantation system B. Mercantilism C. Fishing Industry D. Water-powered mills
10 Congress voted to outlaw the slave trade, but owning slaves was still legal in the South. Slavery was still able to spread. The invention of the cotton gin in 1793 made it even easier and cheaper to grow cotton but growing cotton still required a lot of workers so more and more farmers used slaves to help them grow it. As America acquired new territories in the 19th century, slavery became a controversial issue; many farmers wanted to be able to use slaves in the new territories, but others wanted to outlaw slavery in the new territories. In the 19th century, many Americans migrated west, and grew cottons on the new lands.
11 6. Which of the following was not a reason for the spread of slavery? A. The cotton gin made it easier to produce cotton. B. More farmers began to grow cotton as they moved westward C. America acquired new territories which were suitable for growing cash crops D. Congress banned the slave trade
12 7. What affect did the Cotton Gin have on slavery? A. There is no relationship between the Cotton Gin and the spread of Slavery. B. The Cotton Gin made the sale of Cotton an extremely profitable Industry which increased demand for slave labor. C. The need for slaves in Europe increased because of the large scale production of the Cotton Gin. D. It decreased the need for slaves in the south because of the lowering of tariffs by the Federal government.
13 Missouri Compromise (1820) Compromise of 1850 Kansas Nebraska Act (1854)
14 D. These compromises led to spread of slavery into California as it became a slave state in The goal of the compromises listed in the box on the previous page was to maintain a balance between slave states and free states, which of the following statements is true about their effect on the spread of slavery. A. The Missouri Compromise did not effect the spread of slavery because it was declared unconstitutional by the Dred Scott Decision. B. All three of these compromises actually allowed for the further spread of slavery C. Only Kansas, Missouri and Nebraska were truly affected by these compromises
15 Factors that Led to Urbanization Factories were built in towns and cities because there was often better transportation and communication links with the rest of the country; and there were more unemployed people that the factories could hire as workers. Once the factories were there, this encouraged more people to move to towns and cities; there were many push factors (reasons that people had to move away from farms) and pull factors that explained the growth of cities.
16 9. Which of the following might be a reason for rapid urbanization within a country? A. Factories might be built in a city, providing new jobs and this will attract more people including immigrants B. The need for workers on a plantation increased. C. The demand for soldiers for the military brought large groups of men to the cities D. New jobs for women where pay was equal to that of the local men were available in cities
17 10. Which of the following was a push factor that caused people to begin to move to cities? A. Slaves were a source of cheap labor, and white workers refused to work as cheaply as slaves did. B. It was becoming more difficult to find good farm land. C. People who had moved west, found out that it wasn t so great, so they returned to cities on the east coast D. Factories provided jobs in cities.
18 11. Why did people decide to move to cities? A. There were more jobs in cities. B. It was more healthy to live there. C. They could not earn a living as farmers. D. They wanted to get rich quick
19 Mercantilism Free Enterprise 1. British government imposed very strict controls on colonial economy. 2. America discouraged from producing manufactured goods 3. America encouraged to buy British goods 4. America trade with other countries is restricted 1. Government does not control economy; does create regulations to monitor fair participation. 2. Individuals free to produce whatever manufactured goods it wanted 3. Individuals free to buy goods from any country 4. Free Trade: the United States can trade with any country it chooses.
20 12. Using the chart on the previous page, what conclusion can be drawn about the reason why a free enterprise system of economic developed in the United States. A. The American Colonies enjoyed to great rewards of mercantilism, and developed a similar economic system. B. The American colonies chose to develop a system by which the government would tightly control industry. C. British mercantilist policy tightly controlled the American colonist, and a free enterprise system freed those controls and allowed the people to more control over their own economic success or failure. D. Mercantilism gave too much favor to competition. Competition is the enemy of the free enterprise system.
21 Features of the Free Enterprise System in the New Nation In a free enterprise economy, individual Americans--not the government--control the economy; they decide what products they want to make, what to sell those products for, and what products they want to buy. The free enterprise system says that if individuals are free to make those decisions without interference by the government they will make decisions that are best for themselves. The following list outlines the main features of the free enterprise system.
22 13. What is the government s role in a free enterprise system? A. Control the economy B. Set fair prices for manufactured goods, to allow for all citizens to have an equal chance to be successful C. Tell people how to run their businesses D. Make a minimum number of regulations to ensure fairness
23 14. Which of the following is not a feature of the free enterprise system? A.Supply and Demand B.Competition C.Individual Choice D.Slavery
24 Multiculturalism American culture and society has always been influenced and shaped by the contributions of different racial, ethnic, and religious groups. The goal of many groups, especially immigrants, was to assimilate. This means that they tried to adopt the traditions and way of life of other Americans. These groups, however, also brought with them their own language, customs and way of life, and these different cultures influenced American culture and society. This process is called the melting pot. The melting pot is an appropriate image because it demonstrates the idea that American society is a blending of cultures, each group s culture contributing to the larger American culture.
25 15. Which statement is not true? I. Since Africans arrived as slaves they could not have any influence on American culture? II. Only groups of people who arrived in America before the American Revolution had an influence on American culture. III. Only a few groups of people had an impact on American culture. A. I and II B. II only C. I, II and III D. I and III
26 16. Which of the following statements about the development of America culture is not true? A. The early success of American colonists depended largely on the skills taught to them by African Americans and Native Americans B. The metaphor that best represents American culture is a melting pot C. Different religious groups had an important influence on American culture. D. Though the great contributions of women in America can be seen easily today, women were unable to truly contribute to America until they were granted voting rights.
27 17. How were women in the North and South able to contribute during the American Civil War? A. They protested food shortages brought on by blockades B. The worked as nurses in the field and ran hospitals C. The collected and transported supplies for the troops D. All of the above
28 We are assembled to protest against a form of government, existing without the consent of the governed to declare our right to be represented in the government which we are taxed to support, to have such disgraceful laws as give man the power to chastise and imprison his wife, to take the wages which she earns, the property which she inherits, and, in case of separation, the children of her love; laws as these that we are assembled to-day, and to have them, if possible, forever erased from our staute-books, deeming them a shame and a disgrace... Elizabeth Cady Stanton, Address Delivered at Seneca Falls and Rochester, N.Y. (1870)
29 18. In the previous passage, Elizabeth Cady Stanton tried to show that A. Marriage laws were unjust to women B. Thomas Jefferson would have supported the movement for woman s suffrage C. The Declaration of Independence applied to both men and women D. Women were being denied their constitutional rights
30 ABOLITIONISM Almost from the beginning of slavery in America some people declared that it was wrong, During the American Revolution, many Americans believed that they were fighting for the principles of liberty and equality. It became harder to justify keeping slaves and saying that they were inferior to white people. Congress banned the slave trade in Northern states outlawed slavery altogether, and some Northerners wanted the southern states to do the same. These people became known as abolitionist because they fought for the abolition of slavery in the South.
31 William Lloyd Garrison Fredrick Douglass Sarah & Angelina Grimke Sojourner Truth 19. Which reform movement belongs in the center circle? A. Public education reform B. Women s rights movement C. Abolitionist movement D. Temperance Movement
32 20. Abolitionist such as William Lloyd Garrison had been very successful in spreading the word of the abolitionist movement, but Fredrick Douglass and Sojourner Truth were able to bring added credibility to abolitionist movement. Why was this the case? A. They both were very wealthy, and common people looked up to them. B. They worked much harder than most other abolitionist C. They were both former slaves and had an understanding of what they were speaking about D. They had both participated in John Browns raid on Harper s Ferry, but survived and escaped unharmed.
33 Lack of money to live on Family problems Drunkenness undermining ability to work 21. The problems listed above resulted in what movement and reform in the 1830s? A. Temperance movement and the prohibition of the sale of alcohol in many states B. Labor union strikes and safer working conditions in factories C. Prison improvement and the separation of child offenders from adult prisoners D. Dorthea Dix s campaign for the mentally ill and the building of new hospitals.
34 Canals connecting interior areas to Lake Erie The National Road Steamboat travel on the Ohio and Mississippi River Railroads
35 22. How did the innovations in transportation listed on the previous page affect the national economy? A. They enabled different regions to specialize in the production of certain products which they could market to other parts of the country. B. They encouraged the federal government to impose protective tariffs on foreign technologies that might compete with them. C. They made it possible for immigrants to travel west where land and most new jobs were available. D. They led to the creation of a single currency for the entire country that would make it easier to calculate the cost of shipping goods by different means.
36 Transportation Systems Trade allowed some cities on the east coast to grow rapidly. Many people moved to the cities to find jobs, and improved roads and canals make it much easier to transport people and goods to and from the cities.
37 23. How did the transportation system affect urbanization? A. People could not travel west, so they moved to cities instead. B. There were more jobs in the cities because of the increased trade. C. Land became more expensive, so people had to move to cities D. Southern farmers could ship their crops to northern cities.
38 Technology Led to Industrialization The above list shows how inventions make industrialization possible. Steam power allowed factories to produce large amounts of goods quickly and cheaply; machines like power looms replaced workers and make the use of cheap, unskilled workers possible. New transportation technology like steamboats allowed the manufactured goods to be sold to more people.
39 24. Which of the following could be an affect of the development of the steamboat as a productive form of transportation? A. It became easier and cheaper for farmers to ship crops to cities B. The railroad would begin to die out as the most important form of transportation C. The United States Navy began to travel all over the world in these newer faster ships D. There would no longer be a need for government Tariffs on foreign goods.
40 Industrialization and Everyday Life In the years after the War of 1812, life in America changed dramatically. Advances in technology changed the way the Americans worked, farmed, lived and traveled. This process of change was known as industrialization. New machines replaced many workers and work was now done in factories instead of small workshops. Machines made it unnecessary for workers to take years to learn work skills; this allowed more women and children to work outside the home; many of these women and children worked at mills making textiles. Workers now worked for wages and worked for a set period of time each day for a long work day.
41 25. How did work change for many American after industrialization? A. Many more worked in small workshops. B. Many more worked on farms. C. Many more lost their jobs. D. Many more worked in factories.
42
Inventor Invention Impact
 Industrialization and Reform Test Review Test Date: Name 1. Fill in the missing boxes Inventor Invention Impact Eli Whitney Cotton Gin -Increased slavery -Made cleaning cotton faster and more efficient
Industrialization and Reform Test Review Test Date: Name 1. Fill in the missing boxes Inventor Invention Impact Eli Whitney Cotton Gin -Increased slavery -Made cleaning cotton faster and more efficient
U.S. History Chapter Millionaire Review
 U.S. History Chapter 14-15 Millionaire Review #1 Which of the following best describes the cotton gin s contribution to industrialization? Created jobs for A: B: immigrants Lowered price of cotton in South
U.S. History Chapter 14-15 Millionaire Review #1 Which of the following best describes the cotton gin s contribution to industrialization? Created jobs for A: B: immigrants Lowered price of cotton in South
Unit 8. Innovation Brings Change 1800 s-1850 s
 Unit 8 Innovation Brings Change 1800 s-1850 s Unit Overview: Industrialization Era This unit addresses the development of the economies in the North and the South, innovations in technology and the application
Unit 8 Innovation Brings Change 1800 s-1850 s Unit Overview: Industrialization Era This unit addresses the development of the economies in the North and the South, innovations in technology and the application
Inventor Invention Impact
 Industrialization and Reform Test Review Test Date: Name 1. Fill in the missing boxes Inventor Invention Impact Eli Whitney Cotton Gin Robert Fulton Decreased the amount of time needed for travel. Decreased
Industrialization and Reform Test Review Test Date: Name 1. Fill in the missing boxes Inventor Invention Impact Eli Whitney Cotton Gin Robert Fulton Decreased the amount of time needed for travel. Decreased
Unit 3 Test Review (Study Guide) 1) Who were some of the important figures in George Washington's administration?
 Name: Unit 3 Test Review (Study Guide) 1) Who were some of the important figures in George Washington's administration? 2) What were the primary beliefs of the Democratic Republican Party? Who was the
Name: Unit 3 Test Review (Study Guide) 1) Who were some of the important figures in George Washington's administration? 2) What were the primary beliefs of the Democratic Republican Party? Who was the
Unit Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution
 Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
In the early Antebellum era ( ), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that
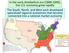 In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
American History Unit 1 American Unification (Part I) The Big Picture:
 American History Unit 1 American Unification (Part I) The Big Picture: Compromises in 1820, 1833, and 1850 worked temporarily, but the emergence of sectional parties (Republicans and Democrats) as a result
American History Unit 1 American Unification (Part I) The Big Picture: Compromises in 1820, 1833, and 1850 worked temporarily, but the emergence of sectional parties (Republicans and Democrats) as a result
Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy?
 Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.4: Clickers Questions Market Revolution inquiry activity
Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.4: Clickers Questions Market Revolution inquiry activity
Industrialization & Reform Learning Targets
 Industrialization & Reform Learning Targets Topic: History I can identify major eras and events in U.S. History and explain: Industrial Revolution Age of Reform Topic: Economics I can understand the origins
Industrialization & Reform Learning Targets Topic: History I can identify major eras and events in U.S. History and explain: Industrial Revolution Age of Reform Topic: Economics I can understand the origins
INDUSTRY AND MIGRATION/THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH. pp
 INDUSTRY AND MIGRATION/THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH pp 382-405 What drives history? Table Talk: Brainstorm some things that have driven history forward What do these things have in common? What changes have
INDUSTRY AND MIGRATION/THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH pp 382-405 What drives history? Table Talk: Brainstorm some things that have driven history forward What do these things have in common? What changes have
The Americans (Survey)
 The Americans (Survey) Chapter 7: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OVERVIEW American leaders devise a farsighted policy of improvements as North, South, and West develop
The Americans (Survey) Chapter 7: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OVERVIEW American leaders devise a farsighted policy of improvements as North, South, and West develop
8-4.3 Notes - Causes of Secession: Why South Carolina Left the Union
 8-4.3 Notes - Causes of Secession: Why South Carolina Left the Union Objectives - Analyze key issues that led to South Carolina s secession from the Union, including the nullification controversy and John
8-4.3 Notes - Causes of Secession: Why South Carolina Left the Union Objectives - Analyze key issues that led to South Carolina s secession from the Union, including the nullification controversy and John
Nuts and Bolts of Civil War/Reconstruction Unit
 Sectionalism Nuts and Bolts of Civil War/Reconstruction Unit Differences between the various regions of the United States had a great impact on the events leading up to the Civil War. The North Industrialized
Sectionalism Nuts and Bolts of Civil War/Reconstruction Unit Differences between the various regions of the United States had a great impact on the events leading up to the Civil War. The North Industrialized
Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages ) Economic Growth
 Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages 304 309) Economic Growth Essential Question What effects did the Industrial Revolution have on the U. S. economy? Directions: As you read, complete a graphic organizer like
Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages 304 309) Economic Growth Essential Question What effects did the Industrial Revolution have on the U. S. economy? Directions: As you read, complete a graphic organizer like
DRAWING FROM EXPERIENCEII
 Chapter 10, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 306 311 ECONOMIC GROWTH KEY TERMS Industrial Revolution A new way of working and producing goods (page 307) capital Money invested to start new businesses
Chapter 10, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 306 311 ECONOMIC GROWTH KEY TERMS Industrial Revolution A new way of working and producing goods (page 307) capital Money invested to start new businesses
WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer
 WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer Subject(s) Social Studies Conceptual Lenses Grade/Course 8 th Grade Leadership Unit of Study Expansion and Reform (1801-1861) Innovation Unit Title Unit 4 Growing Up: Expanding
WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer Subject(s) Social Studies Conceptual Lenses Grade/Course 8 th Grade Leadership Unit of Study Expansion and Reform (1801-1861) Innovation Unit Title Unit 4 Growing Up: Expanding
In the first half of the nineteenth century, economic changes called by historians the market revolution transformed the United States.
 1 2 In the first half of the nineteenth century, economic changes called by historians the market revolution transformed the United States. Innovations in transportation and communication sparked these
1 2 In the first half of the nineteenth century, economic changes called by historians the market revolution transformed the United States. Innovations in transportation and communication sparked these
How did the Industrial Revolution impact geography, city design, and transportation?
 5 th 6 WEEKS PROGRESS REPORT TEST REVIEW Know the map on page 394 How did the Industrial Revolution impact geography, city design, and transportation? Most factories were built along rivers because they
5 th 6 WEEKS PROGRESS REPORT TEST REVIEW Know the map on page 394 How did the Industrial Revolution impact geography, city design, and transportation? Most factories were built along rivers because they
SSWH 15 Presentation. Describe the impact of industrialization and urbanization.
 SSWH 15 Presentation Describe the impact of industrialization and urbanization. Vocabulary Industrial Revolution Industrialization Adam Smith Capitalism Laissiez-Faire Wealth of Nations Karl Marx Communism
SSWH 15 Presentation Describe the impact of industrialization and urbanization. Vocabulary Industrial Revolution Industrialization Adam Smith Capitalism Laissiez-Faire Wealth of Nations Karl Marx Communism
To get to Santa Fe, New Mexico. New opportunities, more land, gold, trade route
 Regionalism and Expansion (1800-1850s) Learning Targets Name: Hour: Essential Questions: How did the expansion of U.S. territory impact the roles, responsibilities and relationship between the American
Regionalism and Expansion (1800-1850s) Learning Targets Name: Hour: Essential Questions: How did the expansion of U.S. territory impact the roles, responsibilities and relationship between the American
THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN THE U.S. How the War of 1812 & Technological Progress Change the Country
 THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN THE U.S. How the War of 1812 & Technological Progress Change the Country TECHNOLOGY MEANS PROGRESS Developments in technology begin to transform life in the U.S. in the
THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN THE U.S. How the War of 1812 & Technological Progress Change the Country TECHNOLOGY MEANS PROGRESS Developments in technology begin to transform life in the U.S. in the
Q3/Q4 Sectionalism Vocab
 Q3/Q4 Sectionalism Vocab North: Industrial Revolution Sectionalism: loyalty to one region (section) of the country rather than the whole country Industrial Revolution: period of rapid growth in the use
Q3/Q4 Sectionalism Vocab North: Industrial Revolution Sectionalism: loyalty to one region (section) of the country rather than the whole country Industrial Revolution: period of rapid growth in the use
8.46 Analyze the physical obstacles to and the economic and political factors involved in building a network of roads, canals and railroads,
 8.46 Analyze the physical obstacles to and the economic and political factors involved in building a network of roads, canals and railroads, including Henry Clay s American System. United States in 1815
8.46 Analyze the physical obstacles to and the economic and political factors involved in building a network of roads, canals and railroads, including Henry Clay s American System. United States in 1815
Practice for the TOEFL & other Reading Tests
 Practice for the TOEFL & other Reading Tests Practice for important reading tests by reading this six-paragraph passage on early industry and mechanized agriculture in the U.S. and answering the questions
Practice for the TOEFL & other Reading Tests Practice for important reading tests by reading this six-paragraph passage on early industry and mechanized agriculture in the U.S. and answering the questions
The March of Millions
 The March of Millions Around 1850 the population was doubling every 25 years. By 186 there were 33 states. America was the fourth most populous nation in the world. Cities were rapidly developing as were
The March of Millions Around 1850 the population was doubling every 25 years. By 186 there were 33 states. America was the fourth most populous nation in the world. Cities were rapidly developing as were
Readiness Knowledge and Skills Social Studies 8 STAAR Review
 Answer is A Major Era 1 Exploration and Colonial Era 1492-1763 Exploration Reasons for exploration: Religion (God) Wealth (Gold) Fame and International recognition (Glory) Leads to discovery of North America
Answer is A Major Era 1 Exploration and Colonial Era 1492-1763 Exploration Reasons for exploration: Religion (God) Wealth (Gold) Fame and International recognition (Glory) Leads to discovery of North America
Industrial Revolution
 The student will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and the different responses to it. a. Explain the impact of the Industrial
The student will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and the different responses to it. a. Explain the impact of the Industrial
R E A D T H I S F I R S T!
 R E A D T H I S F I R S T! Period 4 (1800 1848) Review Sheet Chapters 9 12 the America s History Textbook Welcome to Period 4! This period accounts for roughly 10% of the exam. In past exams, this period
R E A D T H I S F I R S T! Period 4 (1800 1848) Review Sheet Chapters 9 12 the America s History Textbook Welcome to Period 4! This period accounts for roughly 10% of the exam. In past exams, this period
Washington to Madison Practice Questions
 1 Washington s Proclamation of Neutrality (1793), Jefferson s Embargo Act (1807), and the Monroe Doctrine (1823) were all efforts to (1) avoid political conflicts with European nations (2) directly support
1 Washington s Proclamation of Neutrality (1793), Jefferson s Embargo Act (1807), and the Monroe Doctrine (1823) were all efforts to (1) avoid political conflicts with European nations (2) directly support
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER 7
 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER 7 Section 1 Regional Economies Create Differences Do Now: An industrial revolution is a change in economic and social conditions marked by a significant increase
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER 7 Section 1 Regional Economies Create Differences Do Now: An industrial revolution is a change in economic and social conditions marked by a significant increase
Name: 8 th Grade U.S. History. STAAR Review. Colonization
 Name: _ 8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Colonization FORT BURROWS 2018 Name: _ VOCABULARY Agriculture - Farming, raising crops and livestock. Assembly a group of people who make and change laws for
Name: _ 8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Colonization FORT BURROWS 2018 Name: _ VOCABULARY Agriculture - Farming, raising crops and livestock. Assembly a group of people who make and change laws for
Standard 3: Causes of the American Revolution. e. Declaration of Independence
 Name Date Hour U.S. History to 1877 OCCT Review Study Guide Use your notes, your textbook and all of the knowledge gained this year to complete this O.C.C.T. Review Study Guide. This study guide will be
Name Date Hour U.S. History to 1877 OCCT Review Study Guide Use your notes, your textbook and all of the knowledge gained this year to complete this O.C.C.T. Review Study Guide. This study guide will be
REVIEW FOR CHAPTERS 15, 16, AND 17 TEST
 Define the following with detail: REVIEW FOR CHAPTERS 15, 16, AND 17 TEST 1. Wilmot Proviso A bill passed by the House of Representatives but not by the Senate that would have outlawed slavery in the Mexican
Define the following with detail: REVIEW FOR CHAPTERS 15, 16, AND 17 TEST 1. Wilmot Proviso A bill passed by the House of Representatives but not by the Senate that would have outlawed slavery in the Mexican
Economic History of the US
 Economic History of the US Revolution to Civil War, 1776-1860 Lecture #4 Peter Allen Econ 120 US in 1819 First organization of labor After 1815 Rapid industrialization and urbanization Esp. NE and Mid-Atlantic
Economic History of the US Revolution to Civil War, 1776-1860 Lecture #4 Peter Allen Econ 120 US in 1819 First organization of labor After 1815 Rapid industrialization and urbanization Esp. NE and Mid-Atlantic
Early to Mid 1800's Practice Quiz
 1 Which action is most closely associated with the term Manifest Destiny? (1) declaring independence from Great Britain (2) deciding to end the War of 1812 (3) acquiring territory from Mexico in 1848 (4)
1 Which action is most closely associated with the term Manifest Destiny? (1) declaring independence from Great Britain (2) deciding to end the War of 1812 (3) acquiring territory from Mexico in 1848 (4)
The Market Revolution:
 The Market Revolution: By midcentury (1850s), capital and technology were converting enough central workshops into mechanized factories to convert the market revolution into a staggeringly productive industrial
The Market Revolution: By midcentury (1850s), capital and technology were converting enough central workshops into mechanized factories to convert the market revolution into a staggeringly productive industrial
1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation
 Topic 3 1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg 88-89 They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation agreements 2. How did the British respond to the Boston Tea
Topic 3 1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg 88-89 They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation agreements 2. How did the British respond to the Boston Tea
Northern Industry. Unit III: Expansion, Nationalism, Sectionalism
 Northern Industry Unit III: Expansion, Nationalism, Sectionalism Using simple tools Technology advances Using complex machines Using natural sources of power Technology advances Using artificial sources
Northern Industry Unit III: Expansion, Nationalism, Sectionalism Using simple tools Technology advances Using complex machines Using natural sources of power Technology advances Using artificial sources
Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change
 Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change 1800-1860 Nationalism and Economic Growth By 1815, following the end of The War of 1812, America had shown: That it could defend its sovereignty against
Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change 1800-1860 Nationalism and Economic Growth By 1815, following the end of The War of 1812, America had shown: That it could defend its sovereignty against
Sectional disagreements moved settlers into the new territories. Settlers remained Northerners or Southerners.
 Unit 6 Notes Sectional disagreements moved settlers into the new territories. Settlers remained Northerners or Southerners. The opening of Oregon and the admission of California to the Union convinced
Unit 6 Notes Sectional disagreements moved settlers into the new territories. Settlers remained Northerners or Southerners. The opening of Oregon and the admission of California to the Union convinced
#1 INDUSTRIALIZATION
 #1 INDUSTRIALIZATION Industrialization the shift from an agricultural economy to one based on production and manufacturing completely changed the northern and western economy between 1820 and 1860. For
#1 INDUSTRIALIZATION Industrialization the shift from an agricultural economy to one based on production and manufacturing completely changed the northern and western economy between 1820 and 1860. For
An Early Republic. George Washington. Dept./Office Head Function
 Name An Early Republic George Washington What does the Executive Branch look like? Dept./Office Head Function State Department Thomas Jefferson Dept. of Treasury Alexander Hamilton Dept. of War Henry Knox
Name An Early Republic George Washington What does the Executive Branch look like? Dept./Office Head Function State Department Thomas Jefferson Dept. of Treasury Alexander Hamilton Dept. of War Henry Knox
Why did competing political parties develop during the 1790s?
 Standard VUS.6a The student will demonstrate knowledge of the major events from the last decade of the eighteenth century a) explaining the principles and issues that prompted Thomas Jefferson to organize
Standard VUS.6a The student will demonstrate knowledge of the major events from the last decade of the eighteenth century a) explaining the principles and issues that prompted Thomas Jefferson to organize
The Beginnings of Industrialization
 Name CHAPTER 25 Section 1 (pages 717 722) The Beginnings of BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about romanticism and realism in the arts. In this section, you will read about the beginning of
Name CHAPTER 25 Section 1 (pages 717 722) The Beginnings of BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about romanticism and realism in the arts. In this section, you will read about the beginning of
Eighth Grade Social Studies United States History Course Outline
 Crossings Christian School Academic Guide Middle School Division Grades 5-8 Eighth Grade Social Studies Chapter : Early Exploration of the Americas How do new ideas change the way people live? Why do people
Crossings Christian School Academic Guide Middle School Division Grades 5-8 Eighth Grade Social Studies Chapter : Early Exploration of the Americas How do new ideas change the way people live? Why do people
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism
 7 QUIT Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE GRAPH SECTION 1 Regional Economics Create Differences SECTION 2 Nationalism at Center Stage MAP SECTION 3
7 QUIT Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE GRAPH SECTION 1 Regional Economics Create Differences SECTION 2 Nationalism at Center Stage MAP SECTION 3
Chapter 7 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism
 Chapter 7 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Changes in manufacturing launch an Industrial Revolution. Slavery and other issues divide the North and South. Andrew Jackson has popular appeal but uproots
Chapter 7 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Changes in manufacturing launch an Industrial Revolution. Slavery and other issues divide the North and South. Andrew Jackson has popular appeal but uproots
AGS United States Government Michigan Grade 8 Grade Level Content Expectations
 Correlated to Michigan Grade 8 Grade Level Content Expectations 5910 Rice Creek Pkwy, Suite 1000 Shoreview, MN 55126 Copyright 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliate(s). All rights reserved. F1
Correlated to Michigan Grade 8 Grade Level Content Expectations 5910 Rice Creek Pkwy, Suite 1000 Shoreview, MN 55126 Copyright 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliate(s). All rights reserved. F1
The Early Industrial Revolution Chapter 22 AP World History
 The Early Industrial Revolution 1760-1851 Chapter 22 AP World History Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
The Early Industrial Revolution 1760-1851 Chapter 22 AP World History Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
8 th grade American Studies sample test questions
 8 th grade American Studies sample test questions PASS 1.2 Standard 1. The student will develop and practice process skills in social studies. PASS OBJECTIVE 1.2: Identify, analyze, and interpret primary
8 th grade American Studies sample test questions PASS 1.2 Standard 1. The student will develop and practice process skills in social studies. PASS OBJECTIVE 1.2: Identify, analyze, and interpret primary
Related Thematic Learning Objectives. Concept Outline
 NAT-2.0: Explain how interpretations of the Constitution and debates over rights, liberties, and definitions of citizenship have affected American values, politics, and society. NAT-4.0: Analyze relationships
NAT-2.0: Explain how interpretations of the Constitution and debates over rights, liberties, and definitions of citizenship have affected American values, politics, and society. NAT-4.0: Analyze relationships
The Westward Movement
 The Westward Movement The American West- the most typically American part of America Young America- half of all Americans were under the age of 30 Life in the West was grim for American families Poorly
The Westward Movement The American West- the most typically American part of America Young America- half of all Americans were under the age of 30 Life in the West was grim for American families Poorly
America: History of Our Nation, Survey Edition 2009 Correlated to: Michigan Grade Level Content Expectations for Social Studies for Grade 8 (Grade 8)
 FOUNDATIONS IN UNITED STATES HISTORY AND GEOGRAPHY ERAS 1-3 These foundational expectations are included to help students draw upon their previous study of American history and connect 8th grade United
FOUNDATIONS IN UNITED STATES HISTORY AND GEOGRAPHY ERAS 1-3 These foundational expectations are included to help students draw upon their previous study of American history and connect 8th grade United
Division of Labor: giving each worker one or two simple jobs.
 Chapter 12 The Nation Grows (1815-1830) Section 1 Industries take Root Industrial Revolution: the growth of industry eventually produced changes so great that this time in history is called the Industrial
Chapter 12 The Nation Grows (1815-1830) Section 1 Industries take Root Industrial Revolution: the growth of industry eventually produced changes so great that this time in history is called the Industrial
Indiana Academic Standards Social Studies
 A Correlation of To the Introduction This document demonstrates how,, meets the for,. Correlation page references are to the Student Edition and Teacher Edition. The all new myworld Interactive encourages
A Correlation of To the Introduction This document demonstrates how,, meets the for,. Correlation page references are to the Student Edition and Teacher Edition. The all new myworld Interactive encourages
Imperialism by the US
 Imperialism by the US Quick Class Discussion: Based on this image, what important changes took place in the United States from 1783 to 1900? 115 years after gaining independence from Britain, the United
Imperialism by the US Quick Class Discussion: Based on this image, what important changes took place in the United States from 1783 to 1900? 115 years after gaining independence from Britain, the United
White 1 Monday 1.30 Homework: Assignment 1
 2016-17 Honors History Unit 4: Reforming American Society, 1820-1850 Calendar Blue 1 Friday 1.17 Essay Writing (Typing?) White 1 Monday 1.30 Homework: Assignment 1 Blue 1 Tuesday 1.31 Due: Assignment 1
2016-17 Honors History Unit 4: Reforming American Society, 1820-1850 Calendar Blue 1 Friday 1.17 Essay Writing (Typing?) White 1 Monday 1.30 Homework: Assignment 1 Blue 1 Tuesday 1.31 Due: Assignment 1
Political Divide. Sam Houston, though he never joined the party, supported the Know-Nothing party which opposed immigration to the United States.
 Texans Go to War Political Divide The Democrats were the dominant political party, and had very little competition from the Whig party. the -Texans would vote for southern democrats until 1980 s! Sam Houston,
Texans Go to War Political Divide The Democrats were the dominant political party, and had very little competition from the Whig party. the -Texans would vote for southern democrats until 1980 s! Sam Houston,
EOCT Practice Questions Answer Key. 1) How was the settlement of Virginia different from the settlement of Massachusetts?
 1) How was the settlement of Virginia different from the settlement of Massachusetts? A. Massachusetts was created as a haven for Quakers from England. B. Virginia was settled primarily for economic reasons
1) How was the settlement of Virginia different from the settlement of Massachusetts? A. Massachusetts was created as a haven for Quakers from England. B. Virginia was settled primarily for economic reasons
THE JACKSON PRESIDENCY AND JACKSONIAN DEMOCRACY
 THE JACKSON PRESIDENCY AND JACKSONIAN DEMOCRACY 1828 ushered in the beginning of the modern political party system Jackson had been denied the presidency in 1824 despite winning a plurality of the vote
THE JACKSON PRESIDENCY AND JACKSONIAN DEMOCRACY 1828 ushered in the beginning of the modern political party system Jackson had been denied the presidency in 1824 despite winning a plurality of the vote
netw rks Reading Essentials and Study Guide Growth and Division, Lesson 2 Early Industry ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Reading HELPDESK
 and Study Guide Lesson 2 Early Industry ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How did the nation s economy help shape its politics? How did the economic differences between the North and the South cause tension? Reading
and Study Guide Lesson 2 Early Industry ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How did the nation s economy help shape its politics? How did the economic differences between the North and the South cause tension? Reading
I. The Agricultural Revolution
 I. The Agricultural Revolution A. The Agricultural Revolution Paves the Way 1. Wealthy farmers cultivated large fields called enclosures. 2. The enclosure movement caused landowners to try new methods.
I. The Agricultural Revolution A. The Agricultural Revolution Paves the Way 1. Wealthy farmers cultivated large fields called enclosures. 2. The enclosure movement caused landowners to try new methods.
SWBAT. Explain the role of compromise in the preservation of the Union
 Union in Crisis SWBAT Explain the role of compromise in the preservation of the Union Do Now I hold it to be a good and it will continue to prove so if not disturbed by the spirit of abolition John C.
Union in Crisis SWBAT Explain the role of compromise in the preservation of the Union Do Now I hold it to be a good and it will continue to prove so if not disturbed by the spirit of abolition John C.
US History. Immigrants and Urban Challenges. The Big Idea. Main Ideas
 Immigrants and Urban Challenges The Big Idea The population of the United States grew rapidly in the early 1800s with the arrival of millions of immigrants. Main Ideas Millions of immigrants, mostly German
Immigrants and Urban Challenges The Big Idea The population of the United States grew rapidly in the early 1800s with the arrival of millions of immigrants. Main Ideas Millions of immigrants, mostly German
Grade Eight. Integrated United States History INTEGRATED * UNITED STATES HISTORY, ORGANIZED BY ERA (USHG)
 Integrated United States History INTEGRATED * UNITED STATES HISTORY, ORGANIZED BY ERA (USHG) Eras 1-3 Addressed in 5th Grade Eras 3-5 Addressed in 8th Grade USHG ERA 1 Beginnings to 1620 (Grade 5) 1.1
Integrated United States History INTEGRATED * UNITED STATES HISTORY, ORGANIZED BY ERA (USHG) Eras 1-3 Addressed in 5th Grade Eras 3-5 Addressed in 8th Grade USHG ERA 1 Beginnings to 1620 (Grade 5) 1.1
Name Period Teacher. Wantagh Middle School 7 th Grade Social Studies Final Exam Review Guide
 Name Period Teacher Wantagh Middle School 7 th Grade Social Studies Final Exam Review Guide 1. How did the earliest people migrate to North America? 2. How did Native Americans use the environment around
Name Period Teacher Wantagh Middle School 7 th Grade Social Studies Final Exam Review Guide 1. How did the earliest people migrate to North America? 2. How did Native Americans use the environment around
Age of Jackson. 7 pages
 Age of Jackson 7 pages James Monroe 1817-1825 He is still president U.S. Territory The United States in 1819 (the light orange and light green areas were not then U.S. territory). The Missouri Compromise
Age of Jackson 7 pages James Monroe 1817-1825 He is still president U.S. Territory The United States in 1819 (the light orange and light green areas were not then U.S. territory). The Missouri Compromise
Industrial Revolution
 Chapter 9 Economic Transformation Industrial Revolution Division of Labor Industry in America 1790 1820 aided by transportation Industrial Revolution outwork system work done outside of shop modern factory
Chapter 9 Economic Transformation Industrial Revolution Division of Labor Industry in America 1790 1820 aided by transportation Industrial Revolution outwork system work done outside of shop modern factory
Characteristics Families Clustered near rivers Regional settlement
 Population 1790 Majority lives East of Appalachian mountains and within a few miles of ocean 1840 1/3 lives between Appalachian mountains and Mississippi River The Sweep West Series of bursts 1790s 1791-1803
Population 1790 Majority lives East of Appalachian mountains and within a few miles of ocean 1840 1/3 lives between Appalachian mountains and Mississippi River The Sweep West Series of bursts 1790s 1791-1803
United States History I
 PEABODY VETERANS MEMORIAL HIGH SCHOOL SOCIAL STUDIES DEPARTMENT United States History I Mid Year Exam Review Packet 2013-14 Exam Overview The Mid Year Exam serves as a summative assessment to measure your
PEABODY VETERANS MEMORIAL HIGH SCHOOL SOCIAL STUDIES DEPARTMENT United States History I Mid Year Exam Review Packet 2013-14 Exam Overview The Mid Year Exam serves as a summative assessment to measure your
UNIT 4: EXPANSION & REFORM LESSON 4.1: EFFECTS OF MANIFEST DESTINY & INDUSTRIALIZATION
 UNIT 4: EXPANSION & REFORM LESSON 4.1: EFFECTS OF MANIFEST DESTINY & INDUSTRIALIZATION ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does expansion and industrialization contribute to growing sectionalism within the United States
UNIT 4: EXPANSION & REFORM LESSON 4.1: EFFECTS OF MANIFEST DESTINY & INDUSTRIALIZATION ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does expansion and industrialization contribute to growing sectionalism within the United States
Chapter 6 Shaping an Abundant Land. Page 135
 Chapter 6 Shaping an Abundant Land Page 135 Waves of immigrants came to the U.S. in order to find a better life. Push-pull factors were at play. Immigration is not the only movement of people in the U.S.
Chapter 6 Shaping an Abundant Land Page 135 Waves of immigrants came to the U.S. in order to find a better life. Push-pull factors were at play. Immigration is not the only movement of people in the U.S.
X On record with the USOE.
 Textbook Alignment to the Utah Core 8 th Grade Social Studies U.S. History This alignment has been completed using an Independent Alignment Vendor from the USOE approved list (www.schools.utah.gov/curr/imc/indvendor.html.)
Textbook Alignment to the Utah Core 8 th Grade Social Studies U.S. History This alignment has been completed using an Independent Alignment Vendor from the USOE approved list (www.schools.utah.gov/curr/imc/indvendor.html.)
X On record with the USOE.
 Textbook Alignment to the Utah Core 8 th Grade Social Studies U.S. History This alignment has been completed using an Independent Alignment Vendor from the USOE approved list (www.schools.utah.gov/curr/imc/indvendor.html.)
Textbook Alignment to the Utah Core 8 th Grade Social Studies U.S. History This alignment has been completed using an Independent Alignment Vendor from the USOE approved list (www.schools.utah.gov/curr/imc/indvendor.html.)
Social Studies 7 Final Exam Review MRS. MCLEAN
 Social Studies 7 Final Exam Review MRS. MCLEAN 2012-2013 Articles of Confederation America's first constitution that had a central government with limited powers (A constitution is a written plan of government)
Social Studies 7 Final Exam Review MRS. MCLEAN 2012-2013 Articles of Confederation America's first constitution that had a central government with limited powers (A constitution is a written plan of government)
X On record with the USOE.
 Textbook Alignment to the Utah Core 8 th Grade Social Studies U.S. History This alignment has been completed using an Independent Alignment Vendor from the USOE approved list (www.schools.utah.gov/curr/imc/indvendor.html.)
Textbook Alignment to the Utah Core 8 th Grade Social Studies U.S. History This alignment has been completed using an Independent Alignment Vendor from the USOE approved list (www.schools.utah.gov/curr/imc/indvendor.html.)
Writing Prompts US History
 Writing Prompts US History In order to be successful in the classroom, students must have choice, write everyday and be able to defend positions. These prompts allow students to do all three. Please consider
Writing Prompts US History In order to be successful in the classroom, students must have choice, write everyday and be able to defend positions. These prompts allow students to do all three. Please consider
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism
 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Regional Economies Create Differences Samuel Slater brought the Water Frame to Rhode Island from Great Britain in 1789. It was used to spin raw cotton into cotton
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Regional Economies Create Differences Samuel Slater brought the Water Frame to Rhode Island from Great Britain in 1789. It was used to spin raw cotton into cotton
Name: Date: Class: The Antebellum Era ( ): TEST
 Name: Date: Class: The Antebellum Era (1781-1860): TEST Part A: Multiple Choice: Instructions: Choose the option that answers the question or completes the sentence. 1. What did the Judiciary Act of 1789
Name: Date: Class: The Antebellum Era (1781-1860): TEST Part A: Multiple Choice: Instructions: Choose the option that answers the question or completes the sentence. 1. What did the Judiciary Act of 1789
Chapter 6 - The Spirit of Reform Test
 Chapter 6 - The Spirit of Reform Test 1) Beginning in the early 1800s and continuing through the presidency of Andrew Jackson, ordinary citizens became a greater political force 2) Andrew Jackson believed
Chapter 6 - The Spirit of Reform Test 1) Beginning in the early 1800s and continuing through the presidency of Andrew Jackson, ordinary citizens became a greater political force 2) Andrew Jackson believed
Georgia Standards Covered. This module reinforces students understandings of grids on maps and globes to meet the 4 th Grade Skills requirement.
 Grade 4 Module Where People Live This module reinforces students understandings of grids on maps and globes to meet the 4 th Grade Skills requirement. Matters This module may be used at the start of the
Grade 4 Module Where People Live This module reinforces students understandings of grids on maps and globes to meet the 4 th Grade Skills requirement. Matters This module may be used at the start of the
Summary The Beginnings of Industrialization KEY IDEA The Industrial Revolution started in Great Britain and soon spread elsewhere.
 Summary The Beginnings of Industrialization KEY IDEA The Industrial Revolution started in Great Britain and soon spread elsewhere. In the early 1700s, large landowners in Britain bought much of the land
Summary The Beginnings of Industrialization KEY IDEA The Industrial Revolution started in Great Britain and soon spread elsewhere. In the early 1700s, large landowners in Britain bought much of the land
Period 4 Content Outline,
 Period 4 Content Outline, 1800-1848 The content for APUSH is divided into 9 periods. The outline below contains the required course content for Period 4. The Thematic Learning Objectives are included as
Period 4 Content Outline, 1800-1848 The content for APUSH is divided into 9 periods. The outline below contains the required course content for Period 4. The Thematic Learning Objectives are included as
I. Articles of Confederation
 The New Nation I. Articles of Confederation A. The A.O.C. were the nations 1 st Constitution 1. Adopted by congress during the rev. war 2. Set up a loose alliance among the 13 states 3. it reflects a fear
The New Nation I. Articles of Confederation A. The A.O.C. were the nations 1 st Constitution 1. Adopted by congress during the rev. war 2. Set up a loose alliance among the 13 states 3. it reflects a fear
Eighth Grade, page 1 rev. May 10, 2011
 Eighth Grade, page 1 rev. May 10, 2011 PROCESS OBJECTIVES--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1 st 9 Weeks 1 st 9 Weeks 1. Explain the political
Eighth Grade, page 1 rev. May 10, 2011 PROCESS OBJECTIVES--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1 st 9 Weeks 1 st 9 Weeks 1. Explain the political
American History 100 Facts Mr. Ken Brown Ore City Middle School
 American History 100 Facts Mr. Ken Brown Ore City Middle School 1. Unalienable rights are rights that cannot be given up, taken away or transferred. Life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness are some
American History 100 Facts Mr. Ken Brown Ore City Middle School 1. Unalienable rights are rights that cannot be given up, taken away or transferred. Life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness are some
Grade 4: New York State and Local History and Government
 Grade 4: New York State and Local History and Government Grade 4 Social Studies is focused on New York State and local communities and their change over time, incorporating the study of geography, history,
Grade 4: New York State and Local History and Government Grade 4 Social Studies is focused on New York State and local communities and their change over time, incorporating the study of geography, history,
Geography 8th Grade Social Studies Standard 1
 Geography Standard 1 1. I can determine how geography affected the development of the United States. 8. 1. a I can identify the 5 aspects of geography including location, place, human-environmental interaction,
Geography Standard 1 1. I can determine how geography affected the development of the United States. 8. 1. a I can identify the 5 aspects of geography including location, place, human-environmental interaction,
THE RECONSTRUCTION ERA
 THE RECONSTRUCTION ERA 1865-1877 ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS I. What problems faced the nation during Reconstruction? II. How well did Reconstruction governments in the South succeed? III. What factors promoted
THE RECONSTRUCTION ERA 1865-1877 ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS I. What problems faced the nation during Reconstruction? II. How well did Reconstruction governments in the South succeed? III. What factors promoted
The Jacksonian Era & the Rise of Sectionalism. (c. 1820s c. 1840s)
 The Jacksonian Era & the Rise of Sectionalism (c. 1820s c. 1840s) SSUSH7 Students will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and
The Jacksonian Era & the Rise of Sectionalism (c. 1820s c. 1840s) SSUSH7 Students will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and
The Changing American Population
 The Changing American Population Population booms Improvements in public health, high birth rate, & immigration Immigration and Urban Growth English, French, Italian, Scandinavian, German, & Irish flood
The Changing American Population Population booms Improvements in public health, high birth rate, & immigration Immigration and Urban Growth English, French, Italian, Scandinavian, German, & Irish flood
WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer
 WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer Subject(s) Social Studies Conceptual Lenses Grade/Course American History 1 Conflict Unit of Study Unit 4: Political Conflict, Industrialization, and Reform (4.1, 4.2, 4.3,
WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer Subject(s) Social Studies Conceptual Lenses Grade/Course American History 1 Conflict Unit of Study Unit 4: Political Conflict, Industrialization, and Reform (4.1, 4.2, 4.3,
History 1301 U.S. to Unit 2 - Lecture 4 ~
 History 1301 U.S. to 1877 Unit 2 - Lecture 4 ~ The Era of Good Feeling Post-war Economics: Post-war boom led to bust in 1819 National weaknesses shown by War experience Second National Bank chartered in
History 1301 U.S. to 1877 Unit 2 - Lecture 4 ~ The Era of Good Feeling Post-war Economics: Post-war boom led to bust in 1819 National weaknesses shown by War experience Second National Bank chartered in
8th Grade U.S. History STAAR Study Packet.
 8th Grade U.S. History STAAR Study Packet. NAME: HISTORY TEACHER: Complete the activities using your STAAR Review Sheet. Once you finish an assignment, check your answers by using the answer key provided
8th Grade U.S. History STAAR Study Packet. NAME: HISTORY TEACHER: Complete the activities using your STAAR Review Sheet. Once you finish an assignment, check your answers by using the answer key provided
Critical Dates/Events to Remember Event Date Why it Matters Key Events Event Date Why it Matters
 Critical Dates/Events to Remember Event Date Jamestown 1607 First successful colony in North America Declaration of Independence 1776 Document stating that the 13 colonies were a free and independent nation
Critical Dates/Events to Remember Event Date Jamestown 1607 First successful colony in North America Declaration of Independence 1776 Document stating that the 13 colonies were a free and independent nation
Texas Assessment of Knowledge and Skills - Answer Key
 Texas Assessment of Knowledge and Skills - Answer Key Grade: 08 Subject: Social Studies Administration: April 2006 Item Correct Objective Student Number Answer Measured Expectations 01 A 03 8.24 (E) 02
Texas Assessment of Knowledge and Skills - Answer Key Grade: 08 Subject: Social Studies Administration: April 2006 Item Correct Objective Student Number Answer Measured Expectations 01 A 03 8.24 (E) 02
America, History of Our Nation Civil War to the Present 2014
 A Correlation of Civil War to the Present 2014 To the Utah Core State Standards for Resource Title:, Civil War to the Present Publisher: Pearson Education publishing as Prentice Hall ISBN: SE: 9780133231441
A Correlation of Civil War to the Present 2014 To the Utah Core State Standards for Resource Title:, Civil War to the Present Publisher: Pearson Education publishing as Prentice Hall ISBN: SE: 9780133231441
Test Booklet. Subject: SS, Grade: 08 Grade 8 Social Studies Practice Test Student name:
 Test Booklet Subject: SS, Grade: 08 Grade 8 Social Studies Practice Test 2006 Student name: Author: Ohio District: Ohio Released Tests Printed: Sunday September 02, 2012 1 According to Article I of the
Test Booklet Subject: SS, Grade: 08 Grade 8 Social Studies Practice Test 2006 Student name: Author: Ohio District: Ohio Released Tests Printed: Sunday September 02, 2012 1 According to Article I of the
SOCIAL STUDIES PACING GUIDE: 3rd Nine Weeks
 Week Standards Learning Targets Name of Unit Lessons 8.55 Explain the events and impact I can explain the events of the presidency of Andrew and impact of the Jackson, including the corrupt presidency
Week Standards Learning Targets Name of Unit Lessons 8.55 Explain the events and impact I can explain the events of the presidency of Andrew and impact of the Jackson, including the corrupt presidency
