Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change
|
|
|
- Rafe Boyd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change
2 Nationalism and Economic Growth By 1815, following the end of The War of 1812, America had shown: That it could defend its sovereignty against European nations Jackson's victory in New Orleans spawned a wave of American nationalism The Federalist Party was essentially dead, allowing the Democratic-Republicans to implement new economic development goals Madison asked for a protective tariff following the end of the war between Britain and France Congress passed the Tariff of 1816, on imported goods to protect American-made producers from competition with the flood of British goods after the war Most previous tariffs were primarily to make money for the federal government The tariff generally had wide American support, even in the South, and was also used to finance roads and canals
3 Early Industrialisation The Industrial Revolution began during the late 18th century in Britain, made it to America during the early 19th century Industrialisation generally consisted of technological innovations and organizational changes Technological innovation included thing such as steam engines and other mechanical devices that made it easier to produce goods than by hand Organizational changes included the shift to factories and away from homes and farms to consolidate production
4 Early Industrialisation Revolution in Transportation - James Watts invented the steam engine in Britain in During the early 19th century inventors used the steam engine to power ships and locomotives, drastically lowering transportation costs and travel times. First ships powered entirely by steam crossed the Atlantic in 1838 First public railway in Britain in 1830
5 Early Industrialisation The Market Revolution - the changeover in the market due to the changes from manual to machine labor, helped by the addition of transportation, and a focus on factories. First American textile (fabric) mill built in Rhode Island in 1791 by Samuel Slate First American Factory built in Pawtucket 1793 by Samuel Slater Focused on using spinning jennies to make yarn Before the 1860s much of North America s Industry focused on food and lumber By the end of the 19th century the focus had shift toward the the s teel and iron industries Most early factories were concentrated along the Northeastern coast of the United States due to populations and locations favorable to trade. Boston, Washington D.C., New York break-of-bulk : transferring cargo from one type of carrier to another
6 Eli Whitney and the Cotton Gin Processing cotton was difficult and time consuming, due to the need to remove seed by hand. Whitney s Cotton Gin quickly and easily separated the seeds from of the cotton. Allowed for the growing, selling, and usage of cotton on a much larger scale. Increased the demand for slaves. Cotton became the South s primary crop. King Cotton By the 1840 s the South produced 2/3s of the world s cotton. The demand for cotton from textile factories was already high, this just increased demand and production. Textile factories were located primarily in the Northeast and Midwest, while the South remained primarily rural.
7 Roads, Canals, and Railroads During the early 19th century the federal and state governments started charting private companies to build turnpikes (toll roads) in well settled areas. By 1830 the Middle Atlantic States chartered over 900 road companies. Congress authorized the National Road in 1811 which ran from Cumberland, Maryland to Vandalia, Illinois by 1839 Effective for helping settling to the West, but less effective for commerce. Robert Fulton introduced steamboat travel on the Hudson River in 1807, paving the way for steamboats on the Mississippi by Steamboats common by 1830 The construction of the Erie Canal from was one of the most important components of the transportation revolution of the early 19th century The canal was 363 miles long (the previous longest was 28) Connected markets in the Great Lakes to New York Shorted the trip from New York to Buffalo from 20 to 6 days
8 Roads, Canals, and Railroads First railroad in America began near Baltimore in 1830 Tom Thumb Just 13 miles long First long distance line in South Carolina in miles ,000 miles of railroad track in the United States ,000 miles of railroad track in the United States, more than the rest of the world combined. Samuel Morse put the telegraph into commercial operation in 1844, revolutionizing communications. 50,000 mile of telegraph wire across the country by 1860
9 Population Growth and Movement As the national economy grew, so did the population Many new states admitted to the Union : Ohio, Louisiana, Indiana, Mississippi, Illinois, Alabama, Main, Missouri Rise of the West - Constant stream of migration to the West 9.6 million in million in 1845 cheap land, often $1.25-$2 an acre squatters rights recognized in 1841 Following a military conflict with Spain, Spain was persuaded to sell Florida to the United States in the Adams-Onis Treaty of 1819.
10 Population Growth and Movement Between 1815 and 1860 railroads and canals continued to link the Northwest and the Midwest, increasing the solidarity of the two regions through trade and transportation. John Deere is a good example of Midwestern manufacturing Produced steel plows starting in 1837 Opened a factory in 1847 Led to increasing industry and other mass produced agricultural products such as reapers. Greatly increased Midwest grain production and export to foreign markets The South continued to focus on Cotton, and lacked the industrialization of the Northeast and Midwest
11 Urbanization The market revolution led to a dramatic population shift to the cities, as well as growth American cities with populations exceeding 5,000 People living in American cities or towns of more than 2, , ,844, over 6 million Occurred mostly in the Northeast and Midwest Atlantic seaports that were the center of foreign trade also became centers for finance and manufacturing. Immigrant labor - Irish and German
12 Urbanization The Factory System and Factory Towns Centralizing machinery near production areas Workers doing specialized tasks Towns were sometimes created around a factory to maximize production Such as Lowell near Boston Managers directly supervised and disciplined workers Incorporated in 1836 Specialized in Textiles By 1850 had 52 mills for producing textiles Interchangeable Parts Previously most machine parts and tools were custom made and made to order Consisted of identical parts which could be replaced as needed Allows for standardization of machines, tools and equipment Needed for the complex machines to run factories Embraced by Eli Whitney while manufacturing muskets
13 Urbanization Western cities began to grow at phenomenal rate during the 1830s and 1840s Detroit and St. Louis became centers of commerce, providing essential services to surrounding farms, merchants, and the rural population. Chicago became the largest of the western cities, acting as a rail hub for farming goods to be gathered and shipped East by railroad. Western cities became critical links between western farmers and eastern markets. Increasing sale of crops and animals by farmer led to higher farming incomes, which in turn lead to higher demand for manufactured goods, leading to more manufacturing in Midwestern cities. Increasing manufacturing led to urban issues including: tenements, wage inequality, poor police protection, and inadequate water, sewage, and garbage disposal.
14 Urbanization
15 Public Schools No public schools outside of New England Every state offered some public education to urban white children. Horace Mann - Massachusetts State Board of Education Advocated free universal education as a tool to provide better opportunities to the urban poor, including immigrants. Public schools could provide a common American identity. Hoped education could narrow gap between the rich and poor. Black students generally ignored. First state sponsored universities were in the South. University of North Carolina 1795 University of Virginia 1819
16 Immigration Between 1830 and 1860 approximately 5 million people immigrated to the United States Almost 2 million Irish migrated to the United States during the 1840s due to the potato famine in Ireland. In % of the white population of the United States was foreign-born. Largest groups were Irish and German. Largest non-european group were the Chinese with 41,000 entering in the 1850s. Generally poor. Took low paying urban jobs. Established large communities in Easter urban areas. Most German immigrants were craftsmen, shopkeepers, or educated refugees. Generally had more wealth, and were more readily welcomed into existing communities than the Irish. Many moved West into Pennsylvania and other rural areas.
17 Immigration
18 Immigration Most Irish and some Germans who immigrated to America were Roman Catholic. Nativists - Americans who feared the impact of immigrants on American culture and politics The large majority of American were Protestant. blamed immigrants for various problems such as crime, corruption, and stealing native jobs. The Irish were primarily targeted. The American Party was formed in 1854 with the express purpose of reserving political office for native born Americans and keeping the Catholic Church suppressed from public life. Had wide success in the 1854 elections, winning the governor s seat, the legislature, and many mayor s seats in Massachusetts. Also known as the Know Nothings due to meeting in secret and saying I know nothing to questions regarding their meetings.
19 Black American and Economic Opportunity Most new opportunities from the market revolution were not open to free black Americans. Most free blacks lived in poor sections of Eastern cities, and were occasionally subjected to white mobs. Many of their opportunities resulted from black institutions, such as local churches, that focused on serving the needs of local black communities. Many northern free blacks were skilled craftsmen, but were often barred from various employment, and only received the lowest paying jobs. Moving West was not generally an available option. Federal law forbid access to public lands. Indiana, Illinois, Iowa, and Oregon prohibited entry. As a result nearly all blacks moving West were slaves.
20 Social Class Distinctions In the South, social class distinctions remained primarily based upon land ownership. In the North, the wealthiest people were often the owners of large factories and businesses. Opportunities to become wealthy were increasing, but often were risky and required a large amount of money for initial costs. The Factory System created a strict division between workers and management. Managers often became part of the middle class. Workers received low wages. Child workers were common. Workers often had to spend ⅔-¾ of their wages on food. Workers generally received little protection or warnings in hazardous environments, leading to many accidents and injuries.
21 Social Class Distinctions Major changes in family life due to the separation of the workplace from family life. Cult of Domesticity - The new way women were often viewed in relation to the home. Many family members were often gone all day, working in factories. Working class wives often worked to provide a second income to survive. Middle and upper class husbands often took pride in the fact that their wives did not need to work. The chief goal of women was to provide a private refuge for men at home after long day at work. Men were often interested in leisure activities depending on their classes. Self improvement and reading for the wealthy, and going to pubs for workers. Women were also often responsible for managing the finances, correspondence, and maintaining their status as paragons of virtue. The gap between the rich and poor continued to grow. Accentuated regional differences.
THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN THE U.S. How the War of 1812 & Technological Progress Change the Country
 THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN THE U.S. How the War of 1812 & Technological Progress Change the Country TECHNOLOGY MEANS PROGRESS Developments in technology begin to transform life in the U.S. in the
THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN THE U.S. How the War of 1812 & Technological Progress Change the Country TECHNOLOGY MEANS PROGRESS Developments in technology begin to transform life in the U.S. in the
In the first half of the nineteenth century, economic changes called by historians the market revolution transformed the United States.
 1 2 In the first half of the nineteenth century, economic changes called by historians the market revolution transformed the United States. Innovations in transportation and communication sparked these
1 2 In the first half of the nineteenth century, economic changes called by historians the market revolution transformed the United States. Innovations in transportation and communication sparked these
Industrial Revolution
 Chapter 9 Economic Transformation Industrial Revolution Division of Labor Industry in America 1790 1820 aided by transportation Industrial Revolution outwork system work done outside of shop modern factory
Chapter 9 Economic Transformation Industrial Revolution Division of Labor Industry in America 1790 1820 aided by transportation Industrial Revolution outwork system work done outside of shop modern factory
DRAWING FROM EXPERIENCEII
 Chapter 10, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 306 311 ECONOMIC GROWTH KEY TERMS Industrial Revolution A new way of working and producing goods (page 307) capital Money invested to start new businesses
Chapter 10, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 306 311 ECONOMIC GROWTH KEY TERMS Industrial Revolution A new way of working and producing goods (page 307) capital Money invested to start new businesses
INDUSTRY AND MIGRATION/THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH. pp
 INDUSTRY AND MIGRATION/THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH pp 382-405 What drives history? Table Talk: Brainstorm some things that have driven history forward What do these things have in common? What changes have
INDUSTRY AND MIGRATION/THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH pp 382-405 What drives history? Table Talk: Brainstorm some things that have driven history forward What do these things have in common? What changes have
The March of Millions
 The March of Millions Around 1850 the population was doubling every 25 years. By 186 there were 33 states. America was the fourth most populous nation in the world. Cities were rapidly developing as were
The March of Millions Around 1850 the population was doubling every 25 years. By 186 there were 33 states. America was the fourth most populous nation in the world. Cities were rapidly developing as were
Transformation. Society
 Transformation of the Economy & Society in Antebellum America 1820-1860 A09W 10.11.01 Guiding Question Analyze the causes of the transformation of the American economy in the first half of the nineteenth
Transformation of the Economy & Society in Antebellum America 1820-1860 A09W 10.11.01 Guiding Question Analyze the causes of the transformation of the American economy in the first half of the nineteenth
In the early Antebellum era ( ), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that
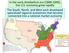 In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
Unit 8. Innovation Brings Change 1800 s-1850 s
 Unit 8 Innovation Brings Change 1800 s-1850 s Unit Overview: Industrialization Era This unit addresses the development of the economies in the North and the South, innovations in technology and the application
Unit 8 Innovation Brings Change 1800 s-1850 s Unit Overview: Industrialization Era This unit addresses the development of the economies in the North and the South, innovations in technology and the application
The Westward Movement
 The Westward Movement The American West- the most typically American part of America Young America- half of all Americans were under the age of 30 Life in the West was grim for American families Poorly
The Westward Movement The American West- the most typically American part of America Young America- half of all Americans were under the age of 30 Life in the West was grim for American families Poorly
FORGING THE NATIONAL ECONOMY, Chapter 14
 FORGING THE NATIONAL ECONOMY, 1790 1860 Chapter 14 WESTWARD MOVEMENT & SHAPING THE WESTERN LANDSCAPE America West of the Alleghenies Population center shifts Life is brutal, primitive, isolated Land becomes
FORGING THE NATIONAL ECONOMY, 1790 1860 Chapter 14 WESTWARD MOVEMENT & SHAPING THE WESTERN LANDSCAPE America West of the Alleghenies Population center shifts Life is brutal, primitive, isolated Land becomes
HUSH Unit 4. Jefferson, The War of 1812, and the Beginning of the Market Economy
 HUSH Unit 4 Jefferson, The War of 1812, and the Beginning of the Market Economy Post War Economic Development A Market Economy is Born The Transportation Revolution Three Stages: Canals - man made waterways
HUSH Unit 4 Jefferson, The War of 1812, and the Beginning of the Market Economy Post War Economic Development A Market Economy is Born The Transportation Revolution Three Stages: Canals - man made waterways
Unit Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution
 Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
Forging a National Economy ANTEBELLUM AMERICAN SOCIETY
 Forging a National Economy ANTEBELLUM AMERICAN SOCIETY FORGING THE NATIONAL ECONOMY Theme 1: The American population expanded and changed in character as more people moved to the West, cities, and immigrant
Forging a National Economy ANTEBELLUM AMERICAN SOCIETY FORGING THE NATIONAL ECONOMY Theme 1: The American population expanded and changed in character as more people moved to the West, cities, and immigrant
Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages ) Economic Growth
 Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages 304 309) Economic Growth Essential Question What effects did the Industrial Revolution have on the U. S. economy? Directions: As you read, complete a graphic organizer like
Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages 304 309) Economic Growth Essential Question What effects did the Industrial Revolution have on the U. S. economy? Directions: As you read, complete a graphic organizer like
Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy?
 Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.4: Clickers Questions Market Revolution inquiry activity
Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.4: Clickers Questions Market Revolution inquiry activity
netw rks Reading Essentials and Study Guide Growth and Division, Lesson 2 Early Industry ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Reading HELPDESK
 and Study Guide Lesson 2 Early Industry ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How did the nation s economy help shape its politics? How did the economic differences between the North and the South cause tension? Reading
and Study Guide Lesson 2 Early Industry ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How did the nation s economy help shape its politics? How did the economic differences between the North and the South cause tension? Reading
Chapter 9 and part of Chapter 8: Transforming the Economy,
 Chapter 9 and part of Chapter 8: Transforming the Economy, 1790-1860 The Big Questions: What were the causes and consequences of the industrial and market revolutions, and how did they change the way ordinary
Chapter 9 and part of Chapter 8: Transforming the Economy, 1790-1860 The Big Questions: What were the causes and consequences of the industrial and market revolutions, and how did they change the way ordinary
Era of Good Feelings:
 Era of Good Feelings: 1815-1825 After the War of 1812 Americans finally have international respect The Republicans are the only political party James Monroe, the third member of the Virginia Dynasty, is
Era of Good Feelings: 1815-1825 After the War of 1812 Americans finally have international respect The Republicans are the only political party James Monroe, the third member of the Virginia Dynasty, is
Division of Labor: giving each worker one or two simple jobs.
 Chapter 12 The Nation Grows (1815-1830) Section 1 Industries take Root Industrial Revolution: the growth of industry eventually produced changes so great that this time in history is called the Industrial
Chapter 12 The Nation Grows (1815-1830) Section 1 Industries take Root Industrial Revolution: the growth of industry eventually produced changes so great that this time in history is called the Industrial
UNIT 4: EXPANSION & REFORM LESSON 4.1: EFFECTS OF MANIFEST DESTINY & INDUSTRIALIZATION
 UNIT 4: EXPANSION & REFORM LESSON 4.1: EFFECTS OF MANIFEST DESTINY & INDUSTRIALIZATION ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does expansion and industrialization contribute to growing sectionalism within the United States
UNIT 4: EXPANSION & REFORM LESSON 4.1: EFFECTS OF MANIFEST DESTINY & INDUSTRIALIZATION ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does expansion and industrialization contribute to growing sectionalism within the United States
Economic Issues and Growth
 Economic Issues and Growth 1800-1848 Tariff of 1816 Passed to protect American industries after War of 1812 What would be advantages and disadvantages of high tariffs? Would different regions of the country
Economic Issues and Growth 1800-1848 Tariff of 1816 Passed to protect American industries after War of 1812 What would be advantages and disadvantages of high tariffs? Would different regions of the country
Chapter 7 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism
 Chapter 7 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Changes in manufacturing launch an Industrial Revolution. Slavery and other issues divide the North and South. Andrew Jackson has popular appeal but uproots
Chapter 7 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Changes in manufacturing launch an Industrial Revolution. Slavery and other issues divide the North and South. Andrew Jackson has popular appeal but uproots
AMERICA S ECONOMIC REVOLUTION. HIST 103 Chapter 10
 AMERICA S ECONOMIC REVOLUTION HIST 103 Chapter 10 The Changing American Population Population increased rapidly between 1820-1840 - improvements in public health - high birth rate - decreasing child mortality
AMERICA S ECONOMIC REVOLUTION HIST 103 Chapter 10 The Changing American Population Population increased rapidly between 1820-1840 - improvements in public health - high birth rate - decreasing child mortality
ID-Irish and German Immigration by Decade (291) Summary 1- What decade brought the greatest number of Irish immigrants? Summary 2- What
 Ch 14 Insights Goals Questions Part 1 Identify the two largest immigrant groups to the US in the first half of the 1800 s and explain how their experiences were different Explain how those different experiences
Ch 14 Insights Goals Questions Part 1 Identify the two largest immigrant groups to the US in the first half of the 1800 s and explain how their experiences were different Explain how those different experiences
Chapter 13 Sections 1 & 2 THE NORTH!
 Chapter 13 Sections 1 & 2 THE NORTH! Definitions Telegraph- Invention by Samuel Morse that electronically transmitted signals over long distances. Clipper Ship- Narrow hulled ships with tall sails that
Chapter 13 Sections 1 & 2 THE NORTH! Definitions Telegraph- Invention by Samuel Morse that electronically transmitted signals over long distances. Clipper Ship- Narrow hulled ships with tall sails that
The Early Industrial and Transportation Revolution Chapter 14
 The Early Industrial and Transportation Revolution Chapter 14 1. Population growth 1800 = 5.5 million to 33 million by 1861 13 states to 33 states by 1861 Expansion of cities 2. Flow of Immigration 1830
The Early Industrial and Transportation Revolution Chapter 14 1. Population growth 1800 = 5.5 million to 33 million by 1861 13 states to 33 states by 1861 Expansion of cities 2. Flow of Immigration 1830
Economic Growth. Guided Reading Activity. Growth and Expansion. Answering Questions DIRECTIONS: As you read the section, answer the questions below.
 Guided Reading Activity Growth and Expansion Section Economic Growth Give yourself enough time to read and understand the text. Don t rush through it. Take your time and pause to reread sections or to
Guided Reading Activity Growth and Expansion Section Economic Growth Give yourself enough time to read and understand the text. Don t rush through it. Take your time and pause to reread sections or to
America s Economic Revolution
 America s Economic Revolution The Industrial Revolution has two phases: one material, the other social; one concerning the making of things, the other concerning the making of men. Charles A. Beard The
America s Economic Revolution The Industrial Revolution has two phases: one material, the other social; one concerning the making of things, the other concerning the making of men. Charles A. Beard The
HIST 1301 Part Three. 9: Nation Building and Nationalism
 HIST 1301 Part Three 9: Nation Building and Nationalism Territorial Expansion Between 1792 and 1821 several new states joined the Union. Kentucky, 1792 Tennessee, 1796 Ohio, 1803 Louisiana, 1812 Indiana,
HIST 1301 Part Three 9: Nation Building and Nationalism Territorial Expansion Between 1792 and 1821 several new states joined the Union. Kentucky, 1792 Tennessee, 1796 Ohio, 1803 Louisiana, 1812 Indiana,
#1 INDUSTRIALIZATION
 #1 INDUSTRIALIZATION Industrialization the shift from an agricultural economy to one based on production and manufacturing completely changed the northern and western economy between 1820 and 1860. For
#1 INDUSTRIALIZATION Industrialization the shift from an agricultural economy to one based on production and manufacturing completely changed the northern and western economy between 1820 and 1860. For
CHAPTER 2, SECTION 2. The Growth of the Nation
 CHAPTER 2, SECTION 2 The Growth of the Nation Big Ideas: After the War of 1812, more Americans began to see themselves as members of a nation rather than only identifying themselves by a region or state.
CHAPTER 2, SECTION 2 The Growth of the Nation Big Ideas: After the War of 1812, more Americans began to see themselves as members of a nation rather than only identifying themselves by a region or state.
Q3/Q4 Sectionalism Vocab
 Q3/Q4 Sectionalism Vocab North: Industrial Revolution Sectionalism: loyalty to one region (section) of the country rather than the whole country Industrial Revolution: period of rapid growth in the use
Q3/Q4 Sectionalism Vocab North: Industrial Revolution Sectionalism: loyalty to one region (section) of the country rather than the whole country Industrial Revolution: period of rapid growth in the use
Industrial Revolution
 The student will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and the different responses to it. a. Explain the impact of the Industrial
The student will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and the different responses to it. a. Explain the impact of the Industrial
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism
 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Regional Economies Create Differences Samuel Slater brought the Water Frame to Rhode Island from Great Britain in 1789. It was used to spin raw cotton into cotton
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Regional Economies Create Differences Samuel Slater brought the Water Frame to Rhode Island from Great Britain in 1789. It was used to spin raw cotton into cotton
National Transformation
 Slide 1 National Transformation Unit 4 Chapters 9-11 Slide 2 The Market Revolution -In the early 1800s, the Jeffersonian dream of a nation of independent farmers remained strong in rural areas. As the
Slide 1 National Transformation Unit 4 Chapters 9-11 Slide 2 The Market Revolution -In the early 1800s, the Jeffersonian dream of a nation of independent farmers remained strong in rural areas. As the
Trends in Antebellum America:
 Mr. Cegielski Trends in Antebellum America: 1810-1860 Covered last unit: 1. New intellectual and religious movements 2. Social reforms 3. Increase in federal power Marshall Ct. decisions. This Unit: 1.
Mr. Cegielski Trends in Antebellum America: 1810-1860 Covered last unit: 1. New intellectual and religious movements 2. Social reforms 3. Increase in federal power Marshall Ct. decisions. This Unit: 1.
The Market Revolution:
 The Market Revolution: By midcentury (1850s), capital and technology were converting enough central workshops into mechanized factories to convert the market revolution into a staggeringly productive industrial
The Market Revolution: By midcentury (1850s), capital and technology were converting enough central workshops into mechanized factories to convert the market revolution into a staggeringly productive industrial
Industrialization & Reform Learning Targets
 Industrialization & Reform Learning Targets Topic: History I can identify major eras and events in U.S. History and explain: Industrial Revolution Age of Reform Topic: Economics I can understand the origins
Industrialization & Reform Learning Targets Topic: History I can identify major eras and events in U.S. History and explain: Industrial Revolution Age of Reform Topic: Economics I can understand the origins
Characteristics Families Clustered near rivers Regional settlement
 Population 1790 Majority lives East of Appalachian mountains and within a few miles of ocean 1840 1/3 lives between Appalachian mountains and Mississippi River The Sweep West Series of bursts 1790s 1791-1803
Population 1790 Majority lives East of Appalachian mountains and within a few miles of ocean 1840 1/3 lives between Appalachian mountains and Mississippi River The Sweep West Series of bursts 1790s 1791-1803
The Factors Affecting American Economy From : Which Were. The United States economy was stimulated by many factors between
 The Factors Affecting American Economy From 1800 1860: Which Were Most Important And Why William Heegaard Sometime in High School The United States economy was stimulated by many factors between 1800 and
The Factors Affecting American Economy From 1800 1860: Which Were Most Important And Why William Heegaard Sometime in High School The United States economy was stimulated by many factors between 1800 and
1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation
 Topic 3 1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg 88-89 They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation agreements 2. How did the British respond to the Boston Tea
Topic 3 1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg 88-89 They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation agreements 2. How did the British respond to the Boston Tea
After the War of 1812 THE BEGINNING OF CHANGE IN AMERICAN POLITICS, ECONOMY, AND SOCIETY
 After the War of 1812 THE BEGINNING OF CHANGE IN AMERICAN POLITICS, ECONOMY, AND SOCIETY Consequences of the War of 1812 Why was the War of 1812 fought? Impressment Violation of neutral shipping rights
After the War of 1812 THE BEGINNING OF CHANGE IN AMERICAN POLITICS, ECONOMY, AND SOCIETY Consequences of the War of 1812 Why was the War of 1812 fought? Impressment Violation of neutral shipping rights
The Early Industrial Revolution Chapter 22 AP World History
 The Early Industrial Revolution 1760-1851 Chapter 22 AP World History Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
The Early Industrial Revolution 1760-1851 Chapter 22 AP World History Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
Comparing Regions,
 Comparing Regions, 1800-1850 You ve studied data about the three main regions of the United States in the period from 1800 to 1850, and you ve considered the ways in which people in those regions thought
Comparing Regions, 1800-1850 You ve studied data about the three main regions of the United States in the period from 1800 to 1850, and you ve considered the ways in which people in those regions thought
Inventor Invention Impact
 Industrialization and Reform Test Review Test Date: Name 1. Fill in the missing boxes Inventor Invention Impact Eli Whitney Cotton Gin Robert Fulton Decreased the amount of time needed for travel. Decreased
Industrialization and Reform Test Review Test Date: Name 1. Fill in the missing boxes Inventor Invention Impact Eli Whitney Cotton Gin Robert Fulton Decreased the amount of time needed for travel. Decreased
The Start of the Industrial Revolution
 The Start of the Industrial Revolution I. Agricultural Revolution A. Industrial Revolution changed Europe from a mostly agricultural economy to industrialization- work driven by machinery B. Improved Farm
The Start of the Industrial Revolution I. Agricultural Revolution A. Industrial Revolution changed Europe from a mostly agricultural economy to industrialization- work driven by machinery B. Improved Farm
8.46 Analyze the physical obstacles to and the economic and political factors involved in building a network of roads, canals and railroads,
 8.46 Analyze the physical obstacles to and the economic and political factors involved in building a network of roads, canals and railroads, including Henry Clay s American System. United States in 1815
8.46 Analyze the physical obstacles to and the economic and political factors involved in building a network of roads, canals and railroads, including Henry Clay s American System. United States in 1815
Forging the National Economy,
 CHAPTER 14 Forging the National Economy, 1790 1860 PART I: REVIEWING THE CHAPTER A. Checklist of Learning Objectives After mastering this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe the growth and movement
CHAPTER 14 Forging the National Economy, 1790 1860 PART I: REVIEWING THE CHAPTER A. Checklist of Learning Objectives After mastering this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe the growth and movement
Forging the National Economy
 Forging the National Economy 1790-1860 Western Demographics By 1840: demographic center of American population had crossed over the Alleghenies 1850: half of Americans under age 30 Pioneer Americans: ill-informed,
Forging the National Economy 1790-1860 Western Demographics By 1840: demographic center of American population had crossed over the Alleghenies 1850: half of Americans under age 30 Pioneer Americans: ill-informed,
attorney general(314)- plan nation s top legal officer; today also the head of the Department of Justice
 UNIT FOUR: The Early Republic (1789-1844) CHAPTER NINE: Launching a New Republic (1789-1800) LESSON 9-1: Washington s Presidency, pgs. 312-317 1) Explain challenges Washington encountered as the first
UNIT FOUR: The Early Republic (1789-1844) CHAPTER NINE: Launching a New Republic (1789-1800) LESSON 9-1: Washington s Presidency, pgs. 312-317 1) Explain challenges Washington encountered as the first
Chronological Reasoning and Continuity/Change over Time Economic Development Market Revolution
 Chronological Reasoning and Continuity/Change over Time Economic Development Market Revolution From the 2015 Revised Framework: Patterns of Continuity and Change over Time Historical thinking involves
Chronological Reasoning and Continuity/Change over Time Economic Development Market Revolution From the 2015 Revised Framework: Patterns of Continuity and Change over Time Historical thinking involves
The North s People. Guide to Reading
 The North s People Guide to Reading Main Idea Many cities grew tremendously during this period. Key Terms trade union, strike, prejudice, discrimination, famine, nativist Reading Strategy Determining Cause
The North s People Guide to Reading Main Idea Many cities grew tremendously during this period. Key Terms trade union, strike, prejudice, discrimination, famine, nativist Reading Strategy Determining Cause
Inventor Invention Impact
 Industrialization and Reform Test Review Test Date: Name 1. Fill in the missing boxes Inventor Invention Impact Eli Whitney Cotton Gin -Increased slavery -Made cleaning cotton faster and more efficient
Industrialization and Reform Test Review Test Date: Name 1. Fill in the missing boxes Inventor Invention Impact Eli Whitney Cotton Gin -Increased slavery -Made cleaning cotton faster and more efficient
Chapter 14, Section 1 Immigrants and Urban Challenges
 Chapter 14, Section 1 Immigrants and Urban Challenges Pages 438-442 The revolutions in industry, transportation, and technology were not the only major changes in the United States in the mid-1800s. Millions
Chapter 14, Section 1 Immigrants and Urban Challenges Pages 438-442 The revolutions in industry, transportation, and technology were not the only major changes in the United States in the mid-1800s. Millions
Forging the National Economy ( ) Chapter 14
 Forging the National Economy (1790-1860) Chapter 14 1. What did Ralph Waldo Emerson mean in 1844 when he said, Europe stretches to the Alleghenies; America lies beyond? ** Bonus After reading the section
Forging the National Economy (1790-1860) Chapter 14 1. What did Ralph Waldo Emerson mean in 1844 when he said, Europe stretches to the Alleghenies; America lies beyond? ** Bonus After reading the section
378. Purchase of Florida Under the Adams-Onis Treaty, Spain sold Florida to the U.S., and the U.S. gave up its claims to Texas.
 Note Cards 351. Embargo of 1807, opposition This act issued by Jefferson forbade American trading ships from leaving the U.S. It was meant to force Britain and France to change their policies towards neutral
Note Cards 351. Embargo of 1807, opposition This act issued by Jefferson forbade American trading ships from leaving the U.S. It was meant to force Britain and France to change their policies towards neutral
Note Taking Study Guide DAWN OF THE INDUSTRIAL AGE
 SECTION 1 DAWN OF THE INDUSTRIAL AGE Focus Question: What events helped bring about the Industrial Revolution? As you read this section in your textbook, complete the following flowchart to list multiple
SECTION 1 DAWN OF THE INDUSTRIAL AGE Focus Question: What events helped bring about the Industrial Revolution? As you read this section in your textbook, complete the following flowchart to list multiple
Industrialism. Sophia Wright, David Suescun, Oliver Santos, Kayla Gardner
 Industrialism Sophia Wright, David Suescun, Oliver Santos, Kayla Gardner Industrialism- What is It? Before industrialism, mainly farming and agriculture took place in the United States, despite Alexander
Industrialism Sophia Wright, David Suescun, Oliver Santos, Kayla Gardner Industrialism- What is It? Before industrialism, mainly farming and agriculture took place in the United States, despite Alexander
America s History Eighth Edi(on
 James A. Henretta! Eric Hinderaker! Rebecca Edwards! Robert O. Self! America s History Eighth Edi(on America: A Concise History Sixth Edi(on CHAPTER 8 nd 9 Review= Unit 4 Crea=ng a Republican Culture 1790
James A. Henretta! Eric Hinderaker! Rebecca Edwards! Robert O. Self! America s History Eighth Edi(on America: A Concise History Sixth Edi(on CHAPTER 8 nd 9 Review= Unit 4 Crea=ng a Republican Culture 1790
NAME DATE CLASS. Maine N.H. Vt. Manchester Lowell N.Y. Boston. Pawtucket. Conn. RI Pa. New York City Philadelphia. Baltimore Del. Md.
 Lesson 1 A Growing Economy ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does geography influence the way people live? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. How did new technology affect the way things were made? 2. Why did agriculture remain
Lesson 1 A Growing Economy ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does geography influence the way people live? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. How did new technology affect the way things were made? 2. Why did agriculture remain
The Beginnings of Industrialization
 Name CHAPTER 25 Section 1 (pages 717 722) The Beginnings of BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about romanticism and realism in the arts. In this section, you will read about the beginning of
Name CHAPTER 25 Section 1 (pages 717 722) The Beginnings of BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about romanticism and realism in the arts. In this section, you will read about the beginning of
Unit 4: { Politics Economics Society
 Unit 4: 1800-1848 { Politics Economics Society Established Cabinet of close advisers French Revolution Neutrality Proclamation Organized troops against Whiskey Rebellion BIG PICTURE IMPACT: Promoted unity;
Unit 4: 1800-1848 { Politics Economics Society Established Cabinet of close advisers French Revolution Neutrality Proclamation Organized troops against Whiskey Rebellion BIG PICTURE IMPACT: Promoted unity;
The Americans (Survey)
 The Americans (Survey) Chapter 7: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OVERVIEW American leaders devise a farsighted policy of improvements as North, South, and West develop
The Americans (Survey) Chapter 7: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OVERVIEW American leaders devise a farsighted policy of improvements as North, South, and West develop
Level 2 THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS
 Level 2 THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS Vocabulary Sectionalism: loyalty to a section of a country instead of the nation itself Inflation: Protective Tariff: tax on imported goods Internal Expansion: continued
Level 2 THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS Vocabulary Sectionalism: loyalty to a section of a country instead of the nation itself Inflation: Protective Tariff: tax on imported goods Internal Expansion: continued
AP U.S. History: Unit 4.3 Student Edition The Market Revolution:
 AP U.S. History: Unit 4.3 Student Edition The Market Revolution: 1790-1860 The "Market Revolution" in antebellum America encompassed several areas: Industrial Revolution (and its impact on American society)
AP U.S. History: Unit 4.3 Student Edition The Market Revolution: 1790-1860 The "Market Revolution" in antebellum America encompassed several areas: Industrial Revolution (and its impact on American society)
The Industrial Revolution. The Start of Mass Production
 The Industrial Revolution The Start of Mass Production Section 1 Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
The Industrial Revolution The Start of Mass Production Section 1 Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
Chapter 9: Chapter Outline Instructions: I. The American Industrial Revolution Market Revolution division of labor factories mechanics
 Chapter 9: Chapter Outline The following annotated chapter outline will help you review the major topics covered in this chapter. Instructions: Review the outline to recall events and their relationships
Chapter 9: Chapter Outline The following annotated chapter outline will help you review the major topics covered in this chapter. Instructions: Review the outline to recall events and their relationships
The election of George Washington as the first president under the Constitution was not exactly unanimous
 The election of George Washington as the first president under the Constitution was not exactly unanimous -2 electors from VA and 2 electors from MD did not vote -NY was entitled to 8 electoral votes but
The election of George Washington as the first president under the Constitution was not exactly unanimous -2 electors from VA and 2 electors from MD did not vote -NY was entitled to 8 electoral votes but
The Industrial Revolution Begins ( )
 Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 20, Section World History: Connection to Today Chapter 20 The Industrial Revolution
Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 20, Section World History: Connection to Today Chapter 20 The Industrial Revolution
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism
 7 QUIT Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE GRAPH SECTION 1 Regional Economics Create Differences SECTION 2 Nationalism at Center Stage MAP SECTION 3
7 QUIT Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE GRAPH SECTION 1 Regional Economics Create Differences SECTION 2 Nationalism at Center Stage MAP SECTION 3
America: Pathways to the Present. Chapter 8. The Growth of a National Economy ( )
 America: Pathways to the Present Chapter 8 The Growth of a National Economy (1790 1850) Copyright 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey. All rights
America: Pathways to the Present Chapter 8 The Growth of a National Economy (1790 1850) Copyright 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey. All rights
Chapter 10: America s Economic Revolution
 Chapter 10: America s Economic Revolution Lev_19:34 But the stranger that dwelleth with you shall be unto you as one born among you, and thou shalt love him as thyself; for ye were strangers in the land
Chapter 10: America s Economic Revolution Lev_19:34 But the stranger that dwelleth with you shall be unto you as one born among you, and thou shalt love him as thyself; for ye were strangers in the land
Forging a National Economy. Chapter 14
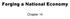 Forging a National Economy Chapter 14 Westward Movement Original Areas of settlement Oregon Territory California Territory Texas Northwest Territories Great Plains were not settled because it was hard
Forging a National Economy Chapter 14 Westward Movement Original Areas of settlement Oregon Territory California Territory Texas Northwest Territories Great Plains were not settled because it was hard
Chapter 9 1/14/2019. Alabama Standard. Ch.9 Section 1 (page #283)
 Chapter 9 THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION Alabama Standard Describe the impact of technological inventions, conditions of labor and economic theories of capitalism, liberalism, socialism, and Marxism during
Chapter 9 THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION Alabama Standard Describe the impact of technological inventions, conditions of labor and economic theories of capitalism, liberalism, socialism, and Marxism during
I. The Agricultural Revolution
 I. The Agricultural Revolution A. The Agricultural Revolution Paves the Way 1. Wealthy farmers cultivated large fields called enclosures. 2. The enclosure movement caused landowners to try new methods.
I. The Agricultural Revolution A. The Agricultural Revolution Paves the Way 1. Wealthy farmers cultivated large fields called enclosures. 2. The enclosure movement caused landowners to try new methods.
Warm Up. I. Create an episode map on the Market Revolution
 Warm Up I. Create an episode map on the Market Revolution The Rise of Industry I. The Market Revolution led to increased industrialization in the United States A. More products are made by machines than
Warm Up I. Create an episode map on the Market Revolution The Rise of Industry I. The Market Revolution led to increased industrialization in the United States A. More products are made by machines than
Democratic Republican Era
 Democratic Republican Era Thomas Jefferson s Administration James Madison s Administration James Monroe s Administration Jefferson Madison Monroe Following the election of 1800, the Democratic Republicans
Democratic Republican Era Thomas Jefferson s Administration James Madison s Administration James Monroe s Administration Jefferson Madison Monroe Following the election of 1800, the Democratic Republicans
Industrialization Spreads. Section 9.3
 Industrialization Spreads Section 9.3 England First country to industrialize on huge scale Inspired other countries to industrialize Copy the British miracle Class structure becomes more rigid Raises the
Industrialization Spreads Section 9.3 England First country to industrialize on huge scale Inspired other countries to industrialize Copy the British miracle Class structure becomes more rigid Raises the
Notes on the Industrial Revolution ( ) A. Machines start to replace human & animal power in production and manufacturing of goods
 I. Overview of Industrial Revolution (IR) Notes on the Industrial Revolution (1780-1850) A. Machines start to replace human & animal power in production and manufacturing of goods B. Europe gradually transforms
I. Overview of Industrial Revolution (IR) Notes on the Industrial Revolution (1780-1850) A. Machines start to replace human & animal power in production and manufacturing of goods B. Europe gradually transforms
CH. 8: GROWTH OF A NATIONAL ECONOMY
 1 2 3 4 CH. 8: GROWTH OF A NATIONAL ECONOMY 1790-1850 Mr. Anderson, M.Ed., J.D. Review Who was John Marshall? Which president appointed him? What is he best remembered for? The Industrial Revolution Section
1 2 3 4 CH. 8: GROWTH OF A NATIONAL ECONOMY 1790-1850 Mr. Anderson, M.Ed., J.D. Review Who was John Marshall? Which president appointed him? What is he best remembered for? The Industrial Revolution Section
Forging the National Economy,
 CHAPTER 14 Forging the National Economy, 1790 1860 PART I: REVIEWING THE CHAPTER A. Checklist of Learning Objectives After mastering this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe the growth and movement
CHAPTER 14 Forging the National Economy, 1790 1860 PART I: REVIEWING THE CHAPTER A. Checklist of Learning Objectives After mastering this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe the growth and movement
Industrial Cities in Great Britain and Ireland,
 Outline Map Industrial Cities in Great Britain and Ireland, 1800 1850 Directions: Locate and label the following: Bristol, London, Birmingham, Belfast, Liverpool, Manchester, Glasgow, Newcastle, Edinburgh,
Outline Map Industrial Cities in Great Britain and Ireland, 1800 1850 Directions: Locate and label the following: Bristol, London, Birmingham, Belfast, Liverpool, Manchester, Glasgow, Newcastle, Edinburgh,
Commerce and Industry Men and Women at Work. Adait Mou, Dewey Dugger, and Juliane Ponce
 Commerce and Industry Men and Women at Work Adait Mou, Dewey Dugger, and Juliane Ponce Nationalism and Economic Growth (1) (2) Juliane Ponce New wave of nationalism + growing geographic size = democratic
Commerce and Industry Men and Women at Work Adait Mou, Dewey Dugger, and Juliane Ponce Nationalism and Economic Growth (1) (2) Juliane Ponce New wave of nationalism + growing geographic size = democratic
In this chapter, you will learn about life in the new nation, from the Presidency of George Washington to that of James Monroe.
 In this chapter, you will learn about life in the new nation, from the Presidency of George Washington to that of James Monroe. Our earliest Presidents established many new traditions that have survived
In this chapter, you will learn about life in the new nation, from the Presidency of George Washington to that of James Monroe. Our earliest Presidents established many new traditions that have survived
SSWH 15 Presentation. Describe the impact of industrialization and urbanization.
 SSWH 15 Presentation Describe the impact of industrialization and urbanization. Vocabulary Industrial Revolution Industrialization Adam Smith Capitalism Laissiez-Faire Wealth of Nations Karl Marx Communism
SSWH 15 Presentation Describe the impact of industrialization and urbanization. Vocabulary Industrial Revolution Industrialization Adam Smith Capitalism Laissiez-Faire Wealth of Nations Karl Marx Communism
The Changing American Population
 The Changing American Population Population booms Improvements in public health, high birth rate, & immigration Immigration and Urban Growth English, French, Italian, Scandinavian, German, & Irish flood
The Changing American Population Population booms Improvements in public health, high birth rate, & immigration Immigration and Urban Growth English, French, Italian, Scandinavian, German, & Irish flood
Summary The Beginnings of Industrialization KEY IDEA The Industrial Revolution started in Great Britain and soon spread elsewhere.
 Summary The Beginnings of Industrialization KEY IDEA The Industrial Revolution started in Great Britain and soon spread elsewhere. In the early 1700s, large landowners in Britain bought much of the land
Summary The Beginnings of Industrialization KEY IDEA The Industrial Revolution started in Great Britain and soon spread elsewhere. In the early 1700s, large landowners in Britain bought much of the land
Industrial Revolution Mechanical Change in the World
 Industrial Revolution Mechanical Change in the World STANDARD WHII.9a The student will demonstrate knowledge of the effects of the Industrial Revolution during the nineteenth century by a) citing scientific,
Industrial Revolution Mechanical Change in the World STANDARD WHII.9a The student will demonstrate knowledge of the effects of the Industrial Revolution during the nineteenth century by a) citing scientific,
The 19th Century. Its Place in the Flow of History. Sunday, February 17, 13
 The 19th Century Its Place in the Flow of History Industrialization Industrial Revolution By the 1830s writers began using the Industrial revolution to refer to the extraordinary changes in their economic
The 19th Century Its Place in the Flow of History Industrialization Industrial Revolution By the 1830s writers began using the Industrial revolution to refer to the extraordinary changes in their economic
Madison & Monroe. Presidencies
 James James Madison & Monroe Presidencies Where we are March 1797: President John Adams takes office. 1796-1800: XYZ Affair, Quasi-War with France, Alien & Sedition Acts, VA & KY Resolutions 1801-1804:
James James Madison & Monroe Presidencies Where we are March 1797: President John Adams takes office. 1796-1800: XYZ Affair, Quasi-War with France, Alien & Sedition Acts, VA & KY Resolutions 1801-1804:
Chapter 10. America s Economic Revolution
 Chapter 10 America s Economic Revolution Section 1: The Changing American Population 1820-1840 Trends Three trends contributed to economic growth: population increase, migration from the countryside to
Chapter 10 America s Economic Revolution Section 1: The Changing American Population 1820-1840 Trends Three trends contributed to economic growth: population increase, migration from the countryside to
Chapter 6 Shaping an Abundant Land. Page 135
 Chapter 6 Shaping an Abundant Land Page 135 Waves of immigrants came to the U.S. in order to find a better life. Push-pull factors were at play. Immigration is not the only movement of people in the U.S.
Chapter 6 Shaping an Abundant Land Page 135 Waves of immigrants came to the U.S. in order to find a better life. Push-pull factors were at play. Immigration is not the only movement of people in the U.S.
Early Republic Addressing Challenges
 Early Republic Addressing Challenges 1789-1828 In this chapter, you will learn about life in the new nation, from the Presidency of to that of. Our earliest Presidents established many new traditions that
Early Republic Addressing Challenges 1789-1828 In this chapter, you will learn about life in the new nation, from the Presidency of to that of. Our earliest Presidents established many new traditions that
U.S. History Chapter Millionaire Review
 U.S. History Chapter 14-15 Millionaire Review #1 Which of the following best describes the cotton gin s contribution to industrialization? Created jobs for A: B: immigrants Lowered price of cotton in South
U.S. History Chapter 14-15 Millionaire Review #1 Which of the following best describes the cotton gin s contribution to industrialization? Created jobs for A: B: immigrants Lowered price of cotton in South
Chapter 9: The Industrial Revolution,
 Chapter 9: The Industrial Revolution, 1700 1900 The Industrial Revolution begins in Britain, spreads to other countries, and has a strong impact on economics, politics, and society. Rail locomotives began
Chapter 9: The Industrial Revolution, 1700 1900 The Industrial Revolution begins in Britain, spreads to other countries, and has a strong impact on economics, politics, and society. Rail locomotives began
Several early American leaders believed that Tariffs were the best way for the government to generate funds that could be used to improve the country
 Several early American leaders believed that Tariffs were the best way for the government to generate funds that could be used to improve the country s transportation network as well as other government
Several early American leaders believed that Tariffs were the best way for the government to generate funds that could be used to improve the country s transportation network as well as other government
This era corresponds to information in Unit 5 ( ), Unit 6 ( ) and Unit 7 ( )
 PERIOD 4: 1800 1848 The content for APUSH is divided into 9 periods. The outline below contains the required course content for Period 4. The Thematic Learning Objectives (historical themes) are included
PERIOD 4: 1800 1848 The content for APUSH is divided into 9 periods. The outline below contains the required course content for Period 4. The Thematic Learning Objectives (historical themes) are included
Imperialism by the US
 Imperialism by the US Quick Class Discussion: Based on this image, what important changes took place in the United States from 1783 to 1900? 115 years after gaining independence from Britain, the United
Imperialism by the US Quick Class Discussion: Based on this image, what important changes took place in the United States from 1783 to 1900? 115 years after gaining independence from Britain, the United
Northern Industry. Unit III: Expansion, Nationalism, Sectionalism
 Northern Industry Unit III: Expansion, Nationalism, Sectionalism Using simple tools Technology advances Using complex machines Using natural sources of power Technology advances Using artificial sources
Northern Industry Unit III: Expansion, Nationalism, Sectionalism Using simple tools Technology advances Using complex machines Using natural sources of power Technology advances Using artificial sources
