American History Unit 1 American Unification (Part I) The Big Picture:
|
|
|
- Francine Parker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 American History Unit 1 American Unification (Part I) The Big Picture: Compromises in 1820, 1833, and 1850 worked temporarily, but the emergence of sectional parties (Republicans and Democrats) as a result of the Kansas-Nebraska Act and the election of Abraham Lincoln in 1860 led key Southern states to secede from the Union. As a result of the American System, the country became connected through a network of roads and canals and regional trade with southern cotton, northern textiles, and western grains. Despite the surge in nationalism, American also experienced growing sectionalism as western expansion and slavery made evident differences between the North and South. The end of this era is marked by a major shift in American politics. Last Unit: Westward Expansion Current Unit: The Road to Secession and the Seeds of War Next Unit: The Civil War and Reconstruction Unit Pacing: Day 1 Sectionalism and Slavery Sectionalism and Slavery Day 2 Sectionalism and Slavery Abolitionists and Other Reform Movements Day 3 Abolitionists and Other Reform Movements Day 4 The Republicans and Secession The Republicans and Secession Day 5 Unit 1.1 Review Notes 1. Cotton gin 2. Sectionalism 3. Tariffs 4. Secede 5. Popular sovereignty 6. Fugitive Slave Law 7. Wilmot Proviso 8. Dred Scott v Sanford 9. John Brown's Raid 10. Antebellum 11. Abolitionist Movement 12. William Lloyd Garrison 13. Frederick Douglass Key Terms and Phrases: 14. Grimke Sisters 15. Stephen Douglas 16. Uncle Tom's Cabin 17. Horace Mann 18. Dorothea Dix Essentials Questions: 1. Why was maintaining slavery more important to the southern economy than to the northern economy? 2. The Missouri Compromise, Compromise of 1850, Wilmot Proviso, and the Kansas-Nebraska Act were all intended to do what? 3. What was unusual about the Grimke sister's role in the abolitionist movement? 4. Why did the south fear the election of Abraham Lincoln? 19. Susan B. Anthony 20. Sojourner Truth 21. Free Soilers Party 22. Republican Party 23. Election of Abraham Lincoln 25. Seceding 26. Jefferson Davis NOTES
2 Unit 1.1 Section 1 1. What role did Eli Whitney play in the industrialization of cotton? 2. Why did northern businessmen resent the plantation owners in the south? 3. What were the major differences politically between the north and south? 4. Why did southerners oppose tariffs? 5. Describe Henry Clay's "American system". 6. Why did Andrew Jackson denounce the presidential election of 1824 a corrupt bargain? 7. What was John C. Calhoun's pamphlet Exposition and Protest related to? 8. Which act of Congress repealed the Missouri Compromise of 1820 and replaced it with popular sovereignty in the territories of the Louisiana Purchase north of 36 30? 9. The Compromise of 1850 allowed for the passage of a new federal law which was an attempt to please the South - which law? 10. Which section of the United States opposed the passage of the Wilmot Proviso in 1846? 11. The Compromise of 1850 would allow the admission of which state? 12. Who was Dred Scott? 13. Why did the Supreme Court rule the Missouri Compromise unconstitutional as a result of the Dred Scott v. Sanford (1857) decision? 14. What was the impact in the North and the South after John Brown was hanged in 1859? Unit 1.1 Section The Second Great Awakening emphasized what? 16. What was the function of the Underground Railroad and who was Harriet Tubman? 17. What was Harriet Beecher Stowe's contribution to the abolitionist movement? 18. During the 19 th century what was the movement called that advocated the moderate use of alcohol? 19. Who helped organize the first women's rights convention at Seneca Falls in 1848? Unit 1.1 Section What issue divided the Whig Party, eventually causing its destruction? 21. Why did the Republican Party form in 1854? 22. Who was elected president in 1856? 23. How did the Lincoln-Douglas debates in 1858 bring national attention to Lincoln? 24. Who were the major candidates for president in 1860? Northern Democrat: Southern Democrat: Republican: 25. Which state was the first to secede following Abraham Lincoln's electoral victory? 26. Who was elected President of the Confederate States of America? 27. The Capitol of the Confederacy moved from Montgomery, Alabama to? 28. The first battle of the civil War occurred at?
3 UNIT THE ROAD TO SECESSION AND THE SEEDS OF WAR #1 Name The Transportation & Market Revolutions I. The Market Revolution From 1800 to 1840, the U.S. developed a "national" economy: A. New allowed the North (industry), South (cotton), & West (commercial farming) to develop specialized economies B. Improved reduced travel time & cost to ship goods which helped the country B. Regional Economy: The North 1. Technology: By 1840, Eli Whitney's & other textile technology led to a Revolution in the North 2. Specialized Regional Economy: By 1840, Northern factories textiles, farm equipment, other finished goods 3. The growth of in the North led to an increase in cities ( ) 4. The in Massachusetts was the most famous textile mill; Lowell managers hired young, single to work & live at the factory C. Regional Economy: The West 1. Technology: Cyrus McCormick's & John Deere's allowed western farmers to grow enough food to sell 2. Specialized Regional Economy: The West became a network of cash-crop farms producing, corn, hogs, & A. Regional Economy: The South 1. Technology: In 1793, invented the cotton gin making cotton easy to refine & very 2. Specialized Regional Economy: By 1820, became the dominant cash crop of the Deep South 3. The spread of cotton increased & plantation agriculture in the South 4. Southern cotton was so important to the antebellum economy that it was known as " " a. The South provided % of world's cotton b. Southern cotton stimulated the growth of Northern industry, shipping, & marketing
4 II. Connecting Regional Economies into a National Market Economy A. During the antebellum era, these 3 economies became as a result of: 1. Henry Clay's American System (2 nd Bank of the U.S., tariff on foreign manufacturing, & national funding for transportation) 2. A transportation revolution of roads, canals, & early railroads that built America's infrastructure s The Transportation Revolution A. & helped connect the West & East: 1. Western farmers could now get industrial equipment 2. Canals & Robert Fulton's steamboat helped cut costs by % for farmers 3. As a result, western farmers could produce more & make more 4. The most important canal was the (1825) because it provided the 1 st major between the East & West 5. Because the Erie Canal brought so much down the Hudson River, became the commercial capital of the U.S. B. Railroads 1. In the 1830s, construction first began 2. By 1860, railroads had become the greatest transportation network in America Immigration A. In the 1840s, millions of & immigrated to the U.S. 1. Immigrants filled low-paying jobs in factories or moved to become farmers 2. Immigrants, especially, faced from native-born Americans (called ) 3. The Party was formed to limit immigration & keep immigrant men from
5 UNIT THE ROAD TO SECESSION AND THE SEEDS OF WAR # : Increasing Sectionalism & the Road to the Civil War Name I. Sectionalism in the Antebellum Era From , the North & South became vastly different regions A. " " had transformed the South into a rural region with, little manufacturing, & few railroads B. The North had industrial, cities, paid immigrant workers, railroads, & larger C. These regional differences increased sectionalism-placing the interests of a above the interests of the II : Sectionalism was mild & resolved by compromise A. Missouri Compromise of The first major issue regarding slavery in the antebellum era focused on becoming a state in 1820: a. Northerners & Southerners did not want to upset the equal of free & slave states in the b. Northerners did not want slavery to spread beyond the " " c. Southerners did not think Congress had the to stop slavery 2. In 1820, negotiated the Missouri Compromise: Missouri became a slave state, broke from Massachusetts & became a free state, Slavery was outlawed in all western territories above the latitude of B. Nullification Crisis of In the 1830s, the issue of divided North & South a. Southerners argued that tariffs benefited only the & made manufactured goods too b. of SC attempted nullification & threatened 2. President Jackson fought this argument C. The Nat Turner rebellion increased the barbarity of slavery in the South 1. In 1831, freed slaves on Virginia farms & killed whites 2. Southern whites responded by making more severe D. Manifest Destiny & the Wilmot Proviso 1. was not annexed for 9 years because its would unbalance the number of free & slave states 2. The addition of the after the Mexican-American War gave Southerners hope that would spread to the Pacific Ocean 3. In 1846, Northern Congressmen tried to pass the : a. This law would have outlawed all from the Mexican Cession b. Rather than voting along party lines (Democrats & Whigs), Congressmen voting according to their 4. In 1848, the Party was formed to keep slavery from West E. California and the Compromise of In 1850, asked to enter the Union as a free state: a. Southerners did not want more free states & wanted slavery to be allowed in the territories b. Northerners wanted to keep out of the SW & wanted other laws to protect who made it to freedom in the North 2. The Compromise of 1850 solved the sectional dispute between North & South: California entered as a, The people of Utah & New Mexico could to allow or ban slavery ( ), The slave trade ended in Washington DC, A stronger Fugitive Slave Law was created that allowed Southerners to slaves in the North F. From 1820 to 1850, sectionalism in America increased due to 1. Differences in & the use of slavery, Westward expansion & the entry of new states to the Union, Growing in the North 2. But, each time a dispute threatened the nation, a was reached III : The growth of abolitionism & westward expansion intensified the question of the "morality" of slavery A. & many Northerners despised the Compromise of 1850: 1. The Fugitive Slave Law allowed runaway slaves (& sometimes ) to be recaptured & enslaved 2. Northerners formed committees to protect runaways 3. Abolitionism grew in the North a. formed the American Anti-Slavery Society & published The Liberator b. Ex-slave Frederick Douglass published c. The Sisters revealed that some Southerners opposed slavery d. The Underground Railroad was a network of to help slaves escape to freedom B. In 1852 Harriet Beecher Stowe published
6 1. Depicted slavery as a ; Became the best selling book of the 19 th century 2. many in the North to join the abolitionist cause C. Kansas-Nebraska Act of In 1854, Congress passed Kansas-Nebraska Act a. The law used to give the residents of the territories the right to vote to determine slavery b. To do this, Congress (ended) the Missouri Compromise line at 36º30' in the western territories 2. Northerners were outraged by the Act: a. Congress allowed to spread into an area of the U.S. where slavery was already b. Northerners formed the Party in 1854 & became committed to the "free soil" movement 3. Popular sovereignty to settle the slavery question in the West: a. When a vote was held in Kansas in 1855 to decide on slavery, thousands of Missouri residents b. This illegal vote gave Kansas when its residents voted against it c. In 1856, a began between Kansas & Missouri ( ) D. From 1850 to 1856, sectionalism in America increased due to 1. The growth of due to the Fugitive Slave Law, Uncle Tom's Cabin, & the Kansas-Nebraska Act 2. The birth of (not national) political parties like the Republicans 3. Sectional tensions were becoming so bad that was not an option IV : The slave issue became "irreconcilable" & led to the Civil War A. The election of 1856 was the first time in which political parties represented of the country, not the nation 1. became the most important political issue in American politics 2. Even though the lost in 1856, they realized that they had enough electoral votes to win the presidency without support B. Dred Scott v Sanford (1857) 1. In 1857, a slave named sued for his freedom after traveling with his master from Missouri to Wisconsin 2. The Dred Scott case presented the Supreme Court with 2 major questions: (a) Does Congress have the to decide on slavery in the territories? (b) Is the Missouri Compromise? 3. In Dred Scott v. Sanford (1857), the Supreme Court ruled: a. Dred Scott had no right to because blacks are not b. Congress did not have the power to stop in western territories so the was ruled unconstitutional c. Northern abolitionists were furious C. Lincoln-Douglas Debates (1858) 1. In 1858, Democrat Stephen Douglas ran against Republican Abraham Lincoln for the Illinois 2. Lincoln was at the time, but during the campaign he argued that Congress must stop the spread of slavery (free soil argument); Lincoln lost the Senate election, but his argument against slavery made him a popular figure D. John Brown's Raid at Harper's Ferry, Virginia (1859) 1. In 1859, abolitionist led an unsuccessful raid on a federal armory at Harper's Ferry, VA in an attempt to free slaves in a massive slave 2. Brown was caught & executed, but he was seen as a by many in the North 3. Southerners believed Northerners were using to to end slavery E. The Election of 1860 proved to be the final straw for the South: 1. Republicans nominated Abraham Lincoln who argued for " " & a strong national gov't 2. Democrats in the North & South were over the issue of slavery: (a) Northern Democrats nominated Stephen Douglas who argued for popular sovereignty; (b) Southern Democrats nominated John Breckenridge who argued for & the protection of slavery 3. Lincoln the election without a single vote; Southerners assumed slavery would soon be abolished & began to discuss the possibility of (breaking away) from the USA 4. In December 1860, became the first state to secede from the Union; In 1861, more Southern states seceded & the between North & South began F. From 1856 to 1860, sectionalism in America increased due to: 1. Slavery became the most important political issue of the time 2. Growing Southern that the North would end slavery (John Brown's raid, election of Lincoln) 3. No could prevent a Civil War between the North & South
7 UNIT THE ROAD TO SECESSION AND THE SEEDS OF WAR #3 Name Identifying Multiple Perspectives on Slavery A. In the 1830s, a number of emerged that tried to fix problems in America: 1. Temperance (end abuse) 2. Horace Mann & reform 3. Seneca Falls ( rights) 4. (Garrison & Douglass) B. By the 1840s, became the most significant reform & added to tension in North & South Directions: Working with a partner, examine the placard image and read the text on the back. Each placard represents a different person's viewpoint on slavery. Analyze the placard carefully and then record their view on slavery and the actions taken to support that view in the matrix below. Person Three Details of the Person's View on Slavery Actions Person Took to Support Viewpoint John C Calhoun Frederick Douglass
8 Person Three Details of the Person's View on Slavery Actions Person Took to Support Viewpoint William Lloyd Garrison The Grimke Sisters Hinton Helper George Fitzhugh
9
10
11
12
13
14
15 UNIT THE ROAD TO SECESSION AND THE SEEDS OF WAR #4 Name The Presidency of Andrew Jackson I. The Growth of Democracy A. From 1800 to 1840, increased in America: 1. Before 1800, less than % of white men could vote because of & tax restrictions 2. By 1840, these restrictions were removed which allowed % of " " white men to vote ("universal white male ") B. Because more "common men" could vote, used new techniques to get votes 1., parades, & slogans that appealed to the "common man"; Well organized political parties to rally voters 2. As a result of these changes, the 1830s & 1840s saw massive in elections II. The Presidency of Andrew Jackson ( ) A. In 1828, Andrew Jackson was elected president: 1. The 1 st " " candidate (Old Hickory) 2. He split from Jefferson's Democratic-Republican Party & helped form the Party (the 1 st party) 3. He greatly expanded presidential B. President Jackson changed American government: 1. He loyal supporters with gov't jobs ( system) 2. He used the presidential more often than any president for the next 100 years 3. Critics of Jackson's Democrats formed the Party (which maintained the system) C. The 2 nd Two-Party System 1. Democrats a. -Jackson supporters b., farming, & Western expansion c. Supported in South & West, by common farmers 2. Whigs a. Jackson's b. central gov't, industry, trade, & national c. Supported in NE, by merchants & bankers III. Jackson's 8 years as president were defined by 3 controversies: A. In 1830, Jackson signed the Act to remove remaining Indians from the East 1. Jackson faced a problem with Indians in the American South: a. was discovered in north Georgia in 1828 in lands controlled by the Cherokee who refused to move from GA b. Jackson asked Congress for the Indian Removal Act of 1830 to relocate Indians across the River 2. In 1838, the U.S. Army forced the west on the " " B. The Nullification Crisis ( ) exposed sectionalism between the states & national government 1. By the 1830s, was becoming more obvious, especially over the issue of : a. Southerners argued that tariffs helped industry but made higher for farmers b. When Congress passed a high tariff in 1832, Southerners claimed " " & threatened to nullify the tariff c. is the argument that states have the right to ignore federal laws that they think are unfair 2. President Jackson viewed nullification as a to the U.S. a. The national gov't is over the states b. Urged Congress to pass the to enforce the tariff 4. In 1833, Congress created a tariff & the crisis ended 3. VP from South Carolina urged nullification a. States have the right to themselves from the national government b. As a last resort, states can from the Union 5. Significance of Nullification Crisis: a. Revealed between North & South; South used "states' rights" to argue that secession was possible b. President Jackson was willing to use to protect the power of the gov't over the states
16 C. Jackson's decision to kill the 2 nd Bank of the United States 1. In 1816, Congress created the. as part of Henry Clay's American System a. The BUS held ~$10 million in federal money & it to state banks which forced small banks to be when issuing loans b. State banks loaned money to individual, businesses, or local governments to finance roads, canals,, & farms 2. President Jackson hated the BUS: a. He thought it was unconstitutional & gave too much to the b. In 1832, he a law that would have extended the of the BUS another 20 years c. In 1833, he ordered all federal to be removed from the BUS & put in 23 " " state banks d. Without the BUS, the economy entered a 6-year 3. Jackson was criticized as his Constitutional powers as president IV. Conclusions Andrew Jackson represented a new era in American democracy: A. Forming the Party, campaigning for the votes of the " man," & spoils system B. Jackson's use of the strengthened presidential C. Opposition to Jackson led to the permanent system The Early Antebellum American Presidents: Heroes or Villains? You Decide! Directions: During this unit we have studied the events of each President's administration. While some of the things that they have done have helped our country tremendously, some have caused hurt and destruction. How do YOU think our Presidents should be rem embered? For each President in Unit 4, complete the following chart that looks at both the good and bad sides of thei r presidencies. Considered some of the most important events of each President's terms and decide how their supporters wo uld want them to be remembered and what their critics would say. After looking at each President, decide which way YOU think they should be remembered and explain WHY. The President Why should they be remembered favorably? What would their supporters say? Why should they be remembered unfavorably? What would their critics say? How do you think that they should be remembered? WHY? Thomas Jefferson ( ) James Madison ( ) James Monroe ( ) Andrew Jackson ( ) Who is the biggest hero? Why? Who is the biggest villain? Why?
17 UNIT THE ROAD TO SECESSION AND THE SEEDS OF WAR #5 Social Reforms in the Early Antebellum Era Name Directions: Students will visit 10 learning stations about social reform in the 1830s. There are two groups of stations: 5 stations examine the social problems of the era and 5 stations explore ways in which these problems were addressed by reformers. In each station, examine the image or document quotation and guess what the problem or reform is. After you have made your guess, flip the placard, read the background information, and take notes in the chart below. Problem? Reform? Problem? Reform? Problem? Problem? Problem? Reform? Reform? Reform?
Nuts and Bolts of Civil War/Reconstruction Unit
 Sectionalism Nuts and Bolts of Civil War/Reconstruction Unit Differences between the various regions of the United States had a great impact on the events leading up to the Civil War. The North Industrialized
Sectionalism Nuts and Bolts of Civil War/Reconstruction Unit Differences between the various regions of the United States had a great impact on the events leading up to the Civil War. The North Industrialized
Unit 3 Test Review (Study Guide) 1) Who were some of the important figures in George Washington's administration?
 Name: Unit 3 Test Review (Study Guide) 1) Who were some of the important figures in George Washington's administration? 2) What were the primary beliefs of the Democratic Republican Party? Who was the
Name: Unit 3 Test Review (Study Guide) 1) Who were some of the important figures in George Washington's administration? 2) What were the primary beliefs of the Democratic Republican Party? Who was the
REVIEW FOR CHAPTERS 15, 16, AND 17 TEST
 Define the following with detail: REVIEW FOR CHAPTERS 15, 16, AND 17 TEST 1. Wilmot Proviso A bill passed by the House of Representatives but not by the Senate that would have outlawed slavery in the Mexican
Define the following with detail: REVIEW FOR CHAPTERS 15, 16, AND 17 TEST 1. Wilmot Proviso A bill passed by the House of Representatives but not by the Senate that would have outlawed slavery in the Mexican
Road to Civil War ( ) North - South Debates HW
 Road to Civil War (1850 1861) North - South Debates HW Crash Course US History Episode #18 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ronmeoojcdy&list=pl8dpuualjxtmwmepbjtsg593eg7obzo7s&index=18 Review of some examples
Road to Civil War (1850 1861) North - South Debates HW Crash Course US History Episode #18 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ronmeoojcdy&list=pl8dpuualjxtmwmepbjtsg593eg7obzo7s&index=18 Review of some examples
SWBAT. Explain the role of compromise in the preservation of the Union
 Union in Crisis SWBAT Explain the role of compromise in the preservation of the Union Do Now I hold it to be a good and it will continue to prove so if not disturbed by the spirit of abolition John C.
Union in Crisis SWBAT Explain the role of compromise in the preservation of the Union Do Now I hold it to be a good and it will continue to prove so if not disturbed by the spirit of abolition John C.
1/22/18 Monday Organize Your Notebook for Unit 6
 1/22/18 Monday Organize Your Notebook for Unit 6 #65 African-American Response to Slavery #66 Typical Day for the Enslaved #67 The Civil War Video Notes #68 Sectionalism New #69 1+2 Causes of the Civil
1/22/18 Monday Organize Your Notebook for Unit 6 #65 African-American Response to Slavery #66 Typical Day for the Enslaved #67 The Civil War Video Notes #68 Sectionalism New #69 1+2 Causes of the Civil
A Divided Nation. Chapter 15 Page 472
 A Divided Nation Chapter 15 Page 472 The Debate Over Slavery Chapter 15 Section 1 Page 476 New Land Renews Slavery Disputes The Missouri Compromise of 1820 had divided the Louisiana Purchase into either
A Divided Nation Chapter 15 Page 472 The Debate Over Slavery Chapter 15 Section 1 Page 476 New Land Renews Slavery Disputes The Missouri Compromise of 1820 had divided the Louisiana Purchase into either
Unit 6: A Divided Union
 Unit 6: A Divided Union Name: Lecture 6.1 The Abolition Movement The idea that slavery was morally wrong grew out of two different sets of beliefs or principles: political - The Constitution says that,
Unit 6: A Divided Union Name: Lecture 6.1 The Abolition Movement The idea that slavery was morally wrong grew out of two different sets of beliefs or principles: political - The Constitution says that,
How did the Industrial Revolution impact geography, city design, and transportation?
 5 th 6 WEEKS PROGRESS REPORT TEST REVIEW Know the map on page 394 How did the Industrial Revolution impact geography, city design, and transportation? Most factories were built along rivers because they
5 th 6 WEEKS PROGRESS REPORT TEST REVIEW Know the map on page 394 How did the Industrial Revolution impact geography, city design, and transportation? Most factories were built along rivers because they
Events Leading to the Civil War
 Events Leading to the Civil War (1820-1861) Chapter 16 This is how it all began... Missouri Compromise (1820) Missouri Compromise (1820) devised by Henry Clay, kept the balance of free states (12) and
Events Leading to the Civil War (1820-1861) Chapter 16 This is how it all began... Missouri Compromise (1820) Missouri Compromise (1820) devised by Henry Clay, kept the balance of free states (12) and
Unit 6: A Divided Union
 Unit 6: A Divided Union Lecture 6.1 The Abolition Movement The idea that slavery was morally wrong grew out of two different sets of beliefs or principles: political - The Constitution says that, All men
Unit 6: A Divided Union Lecture 6.1 The Abolition Movement The idea that slavery was morally wrong grew out of two different sets of beliefs or principles: political - The Constitution says that, All men
Political Divide. Sam Houston, though he never joined the party, supported the Know-Nothing party which opposed immigration to the United States.
 Texans Go to War Political Divide The Democrats were the dominant political party, and had very little competition from the Whig party. the -Texans would vote for southern democrats until 1980 s! Sam Houston,
Texans Go to War Political Divide The Democrats were the dominant political party, and had very little competition from the Whig party. the -Texans would vote for southern democrats until 1980 s! Sam Houston,
The United States Expands West. 1820s 1860s
 The United States Expands West 1820s 1860s Georgia Standards SSUSH8 The student will explain the relationship between growing northsouth divisions and westward expansion. a. Explain how slavery became
The United States Expands West 1820s 1860s Georgia Standards SSUSH8 The student will explain the relationship between growing northsouth divisions and westward expansion. a. Explain how slavery became
Name: Date: Class: The Antebellum Era ( ): TEST
 Name: Date: Class: The Antebellum Era (1781-1860): TEST Part A: Multiple Choice: Instructions: Choose the option that answers the question or completes the sentence. 1. What did the Judiciary Act of 1789
Name: Date: Class: The Antebellum Era (1781-1860): TEST Part A: Multiple Choice: Instructions: Choose the option that answers the question or completes the sentence. 1. What did the Judiciary Act of 1789
SOCIAL STUDIES PACING GUIDE: 3rd Nine Weeks
 Week Standards Learning Targets Name of Unit Lessons 8.55 Explain the events and impact I can explain the events of the presidency of Andrew and impact of the Jackson, including the corrupt presidency
Week Standards Learning Targets Name of Unit Lessons 8.55 Explain the events and impact I can explain the events of the presidency of Andrew and impact of the Jackson, including the corrupt presidency
Chapter 15 Worksheet: The Nation Breaking Apart Growing Tensions Between North and South Read pages Name 8
 Chapter 15 Worksheet: The Nation Breaking Apart 1846-1861 15.1 Growing Tensions Between North and South Read pages 441-445 Name 8 1. Wilmot Proviso- 2. Free-Soil Party- 3. Henry Clay- 4. Daniel Webster-
Chapter 15 Worksheet: The Nation Breaking Apart 1846-1861 15.1 Growing Tensions Between North and South Read pages 441-445 Name 8 1. Wilmot Proviso- 2. Free-Soil Party- 3. Henry Clay- 4. Daniel Webster-
8-4.3 Notes - Causes of Secession: Why South Carolina Left the Union
 8-4.3 Notes - Causes of Secession: Why South Carolina Left the Union Objectives - Analyze key issues that led to South Carolina s secession from the Union, including the nullification controversy and John
8-4.3 Notes - Causes of Secession: Why South Carolina Left the Union Objectives - Analyze key issues that led to South Carolina s secession from the Union, including the nullification controversy and John
Social Studies 7 Final Exam Review MRS. MCLEAN
 Social Studies 7 Final Exam Review MRS. MCLEAN 2012-2013 Articles of Confederation America's first constitution that had a central government with limited powers (A constitution is a written plan of government)
Social Studies 7 Final Exam Review MRS. MCLEAN 2012-2013 Articles of Confederation America's first constitution that had a central government with limited powers (A constitution is a written plan of government)
America: History of Our Nation, Survey Edition 2009 Correlated to: Michigan Grade Level Content Expectations for Social Studies for Grade 8 (Grade 8)
 FOUNDATIONS IN UNITED STATES HISTORY AND GEOGRAPHY ERAS 1-3 These foundational expectations are included to help students draw upon their previous study of American history and connect 8th grade United
FOUNDATIONS IN UNITED STATES HISTORY AND GEOGRAPHY ERAS 1-3 These foundational expectations are included to help students draw upon their previous study of American history and connect 8th grade United
The Asher Questions are to be done in advance of the Test. (see my website to download copies of these Study Questions).
 U. S. History Survey Study Guide Test #2 Please bring a Green Scantron form for this test, (available in the GPC bookstore) along with a number 2 pencil. The professor will not provide them. If you forget
U. S. History Survey Study Guide Test #2 Please bring a Green Scantron form for this test, (available in the GPC bookstore) along with a number 2 pencil. The professor will not provide them. If you forget
In the early Antebellum era ( ), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that
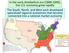 In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
Standard 3: Causes of the American Revolution. e. Declaration of Independence
 Name Date Hour U.S. History to 1877 OCCT Review Study Guide Use your notes, your textbook and all of the knowledge gained this year to complete this O.C.C.T. Review Study Guide. This study guide will be
Name Date Hour U.S. History to 1877 OCCT Review Study Guide Use your notes, your textbook and all of the knowledge gained this year to complete this O.C.C.T. Review Study Guide. This study guide will be
CHAPTER 10: THE NATION SPLITS APART The Big Picture: After the war with Mexico, one questions stirred national politics: Would these new territories
 CHAPTER 10: THE NATION SPLITS APART The Big Picture: After the war with Mexico, one questions stirred national politics: Would these new territories be slave or free? By 1860 the nation had split along
CHAPTER 10: THE NATION SPLITS APART The Big Picture: After the war with Mexico, one questions stirred national politics: Would these new territories be slave or free? By 1860 the nation had split along
AGS United States Government Michigan Grade 8 Grade Level Content Expectations
 Correlated to Michigan Grade 8 Grade Level Content Expectations 5910 Rice Creek Pkwy, Suite 1000 Shoreview, MN 55126 Copyright 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliate(s). All rights reserved. F1
Correlated to Michigan Grade 8 Grade Level Content Expectations 5910 Rice Creek Pkwy, Suite 1000 Shoreview, MN 55126 Copyright 2007 Pearson Education, Inc. or its affiliate(s). All rights reserved. F1
Notes on the Pendulum Swing in American Presidential Elections,
 Notes on the Pendulum Swing in American Presidential Elections, 1789-1865 I Trends and Fluctuations Political Competition and Franchise Extension Parties compete against one another: Franchise extended
Notes on the Pendulum Swing in American Presidential Elections, 1789-1865 I Trends and Fluctuations Political Competition and Franchise Extension Parties compete against one another: Franchise extended
Unit Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution
 Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
Industrialization & Reform Learning Targets
 Industrialization & Reform Learning Targets Topic: History I can identify major eras and events in U.S. History and explain: Industrial Revolution Age of Reform Topic: Economics I can understand the origins
Industrialization & Reform Learning Targets Topic: History I can identify major eras and events in U.S. History and explain: Industrial Revolution Age of Reform Topic: Economics I can understand the origins
Chapter 15: The Nation Breaking Apart
 Chapter 15: The Nation Breaking Apart Teacher 1 SQ3R Chapter 15 The Nation Breaking Apart, Section 1 Tensions Rise Between North and South p.480-487 SURVEY Headings and Subheadings: SURVEY continued 1)
Chapter 15: The Nation Breaking Apart Teacher 1 SQ3R Chapter 15 The Nation Breaking Apart, Section 1 Tensions Rise Between North and South p.480-487 SURVEY Headings and Subheadings: SURVEY continued 1)
FINAL EXAM (2018) STUDY GUIDE
 FINAL EXAM (2018) STUDY GUIDE *Semester Final will be divided into two parts: Part 1 DBQ Essay December 14 (B Day), December 17 (A Day) You will use one of the outlines you created to write ONE document-based
FINAL EXAM (2018) STUDY GUIDE *Semester Final will be divided into two parts: Part 1 DBQ Essay December 14 (B Day), December 17 (A Day) You will use one of the outlines you created to write ONE document-based
B) Henry Clay was made Adams Secretary of State E) The Embargo Act after throwing his support to Adams after he was out of the election.
 1. The most unpopular act of Thomas Jefferson's administration was which of the following? A) The repeal of the excise tax B) The creation of 12th Amendment C) The reduction of the size of the army D)
1. The most unpopular act of Thomas Jefferson's administration was which of the following? A) The repeal of the excise tax B) The creation of 12th Amendment C) The reduction of the size of the army D)
Grade Eight. Integrated United States History INTEGRATED * UNITED STATES HISTORY, ORGANIZED BY ERA (USHG)
 Integrated United States History INTEGRATED * UNITED STATES HISTORY, ORGANIZED BY ERA (USHG) Eras 1-3 Addressed in 5th Grade Eras 3-5 Addressed in 8th Grade USHG ERA 1 Beginnings to 1620 (Grade 5) 1.1
Integrated United States History INTEGRATED * UNITED STATES HISTORY, ORGANIZED BY ERA (USHG) Eras 1-3 Addressed in 5th Grade Eras 3-5 Addressed in 8th Grade USHG ERA 1 Beginnings to 1620 (Grade 5) 1.1
SSUSH8 Explore the relationship
 SSUSH8 Explore the relationship between slavery, growing northsouth divisions, and westward expansion that led to the outbreak of the Civil War. a. Explain the impact of the Missour i Compromise on the
SSUSH8 Explore the relationship between slavery, growing northsouth divisions, and westward expansion that led to the outbreak of the Civil War. a. Explain the impact of the Missour i Compromise on the
U.S. History Chapter Millionaire Review
 U.S. History Chapter 14-15 Millionaire Review #1 Which of the following best describes the cotton gin s contribution to industrialization? Created jobs for A: B: immigrants Lowered price of cotton in South
U.S. History Chapter 14-15 Millionaire Review #1 Which of the following best describes the cotton gin s contribution to industrialization? Created jobs for A: B: immigrants Lowered price of cotton in South
CHAPTER 15. A Divided Nation
 CHAPTER 15 A Divided Nation Trouble in Kansas SECTION 15.2 ELECTION OF 1852 1852 - four candidates for the Democratic presidential nomination. Many turned to Franklin Pierce, a little-known politician
CHAPTER 15 A Divided Nation Trouble in Kansas SECTION 15.2 ELECTION OF 1852 1852 - four candidates for the Democratic presidential nomination. Many turned to Franklin Pierce, a little-known politician
Why did competing political parties develop during the 1790s?
 Standard VUS.6a The student will demonstrate knowledge of the major events from the last decade of the eighteenth century a) explaining the principles and issues that prompted Thomas Jefferson to organize
Standard VUS.6a The student will demonstrate knowledge of the major events from the last decade of the eighteenth century a) explaining the principles and issues that prompted Thomas Jefferson to organize
THE ROAD TO CIVIL WAR
 THE ROAD TO CIVIL WAR DIFFERENCES BETWEEN NORTH & SOUTH: SECTIONALISM NORTH: Favored a stronger central government (remember Federalist) More dependency on government Growing industrial economy Larger
THE ROAD TO CIVIL WAR DIFFERENCES BETWEEN NORTH & SOUTH: SECTIONALISM NORTH: Favored a stronger central government (remember Federalist) More dependency on government Growing industrial economy Larger
Sectionalism and Compromise
 Sectionalism and Compromise Steps to Civil War CA 8 th Grade US History Standard 8.9.5 In 1818, Missouri asked to Join the Union as a slave state. At that time the number of slave and free states were
Sectionalism and Compromise Steps to Civil War CA 8 th Grade US History Standard 8.9.5 In 1818, Missouri asked to Join the Union as a slave state. At that time the number of slave and free states were
Chapter 14: The Sectional Crisis
 Chapter 14: The Sectional Crisis AP United States History Week of January 25, 2016 The Buildup to a Tumultuous Decade Both the Democrats and Whigs wanted to resolve the crisis Emotion and ideology became
Chapter 14: The Sectional Crisis AP United States History Week of January 25, 2016 The Buildup to a Tumultuous Decade Both the Democrats and Whigs wanted to resolve the crisis Emotion and ideology became
Uncle Tom s Cabin Harriett Beecher Stowe Connecticut teacher
 Uncle Tom s Cabin 1852 Harriett Beecher Stowe Connecticut teacher Goal was to expose the reality of slavery Humanity can be saved through Christianity No. 1 Novel for Century. Sectionalism North Horrified
Uncle Tom s Cabin 1852 Harriett Beecher Stowe Connecticut teacher Goal was to expose the reality of slavery Humanity can be saved through Christianity No. 1 Novel for Century. Sectionalism North Horrified
Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy?
 Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.4: Clickers Questions Market Revolution inquiry activity
Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.4: Clickers Questions Market Revolution inquiry activity
netw rks Where in the world? When did it happen? Toward Civil War Lesson 1 The Search for Compromise ESSENTIAL QUESTION Terms to Know
 Lesson 1 The Search for Compromise ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why does conflict develop? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. What political compromises were made because of slavery? 2. What is the Kansas-Nebraska Act? Terms
Lesson 1 The Search for Compromise ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why does conflict develop? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. What political compromises were made because of slavery? 2. What is the Kansas-Nebraska Act? Terms
Chapter Introduction Section 1: Slavery and the West Section 2: A Nation Dividing Section 3: Challenges to Slavery Section 4: Secession and War
 Chapter Introduction Section 1: Slavery and the West Section 2: A Nation Dividing Section 3: Challenges to Slavery Section 4: Secession and War Visual Summary Slavery and the West Essential Question Did
Chapter Introduction Section 1: Slavery and the West Section 2: A Nation Dividing Section 3: Challenges to Slavery Section 4: Secession and War Visual Summary Slavery and the West Essential Question Did
Industrial Revolution
 The student will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and the different responses to it. a. Explain the impact of the Industrial
The student will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and the different responses to it. a. Explain the impact of the Industrial
A Thematic approach to Sectionalism and the Civil War
 Jason Scott Abington High School CHARMS Year 2 Final Project A Thematic approach to Sectionalism and the Civil War Background and Objective: Through this 5 day unit, students will take a thematic approach
Jason Scott Abington High School CHARMS Year 2 Final Project A Thematic approach to Sectionalism and the Civil War Background and Objective: Through this 5 day unit, students will take a thematic approach
Standard 1. Standard 2. Standard 3. Choices have consequences. Individuals have rights and responsibilities
 Standard 1 Choices have consequences 1.1 The student will recognize and evaluate significant choices made by individuals, communities, states and nations that have impacted our lives and futures. 1.2 The
Standard 1 Choices have consequences 1.1 The student will recognize and evaluate significant choices made by individuals, communities, states and nations that have impacted our lives and futures. 1.2 The
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 4: TELESCOPING THE TIMES The Union in Peril CHAPTER OVERVIEW Slavery becomes an issue that divides the nation. North and South enter a long and
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 4: TELESCOPING THE TIMES The Union in Peril CHAPTER OVERVIEW Slavery becomes an issue that divides the nation. North and South enter a long and
Name Period Teacher. Wantagh Middle School 7 th Grade Social Studies Final Exam Review Guide
 Name Period Teacher Wantagh Middle School 7 th Grade Social Studies Final Exam Review Guide 1. How did the earliest people migrate to North America? 2. How did Native Americans use the environment around
Name Period Teacher Wantagh Middle School 7 th Grade Social Studies Final Exam Review Guide 1. How did the earliest people migrate to North America? 2. How did Native Americans use the environment around
Several early American leaders believed that Tariffs were the best way for the government to generate funds that could be used to improve the country
 Several early American leaders believed that Tariffs were the best way for the government to generate funds that could be used to improve the country s transportation network as well as other government
Several early American leaders believed that Tariffs were the best way for the government to generate funds that could be used to improve the country s transportation network as well as other government
Q3/Q4 Sectionalism Vocab
 Q3/Q4 Sectionalism Vocab North: Industrial Revolution Sectionalism: loyalty to one region (section) of the country rather than the whole country Industrial Revolution: period of rapid growth in the use
Q3/Q4 Sectionalism Vocab North: Industrial Revolution Sectionalism: loyalty to one region (section) of the country rather than the whole country Industrial Revolution: period of rapid growth in the use
PPT Accompaniment for To Secede or Not to Secede: Events Leading to Civil War
 PPT Accompaniment for To Secede or Not to Secede: Events Leading to Civil War To view this PDF as a projectable presentation, save the file, click View in the top menu bar of the file, and select Full
PPT Accompaniment for To Secede or Not to Secede: Events Leading to Civil War To view this PDF as a projectable presentation, save the file, click View in the top menu bar of the file, and select Full
The Great Debate- The Compromise of 1850
 Chapter 18 The Great Debate- The Compromise of 1850 The 1850 Crisis & Compromise 1. Nov. 1849- CA ratified a constitution that banned slavery. 2. The admission of California as a state threatened the balance
Chapter 18 The Great Debate- The Compromise of 1850 The 1850 Crisis & Compromise 1. Nov. 1849- CA ratified a constitution that banned slavery. 2. The admission of California as a state threatened the balance
North/South Split Made Complete
 North/South Split Made Complete In 1855, the American Party split into northern (antislavery) and southern (proslavery) wings Many people who had voted for the Know-Nothings shifted their support to the
North/South Split Made Complete In 1855, the American Party split into northern (antislavery) and southern (proslavery) wings Many people who had voted for the Know-Nothings shifted their support to the
Chapter Fifteen. The Coming Crisis, the 1850s
 Chapter Fifteen The Coming Crisis, the 1850s Part One: Introduction Chapter Focus Questions Why did the Whigs and Democrats fail to find a lasting political compromise on the issue of slavery? What caused
Chapter Fifteen The Coming Crisis, the 1850s Part One: Introduction Chapter Focus Questions Why did the Whigs and Democrats fail to find a lasting political compromise on the issue of slavery? What caused
Unit 5 Study Guide. 1. What did the Northwest Ordinance establish? Process for a territory to become a state
 Unit 5 Study Guide 1. What did the Northwest Ordinance establish? Process for a territory to become a state 2. Why was the Whig Party primarily created? Oppose Andrew Jackson s policies 3. What was the
Unit 5 Study Guide 1. What did the Northwest Ordinance establish? Process for a territory to become a state 2. Why was the Whig Party primarily created? Oppose Andrew Jackson s policies 3. What was the
Argument: American expansionism was an aggressive imperialism to a large extent. (Include both position as well as extent)
 TR Prompt: Although Americans perceived Manifest Destiny as a benevolent movement, it was in fact an aggressive imperialism pursued at the expense of others. Assess the validity of this statement with
TR Prompt: Although Americans perceived Manifest Destiny as a benevolent movement, it was in fact an aggressive imperialism pursued at the expense of others. Assess the validity of this statement with
Can the Civil War be prevented?
 Can the Civil War be prevented? Abraham Lincoln Abraham Lincoln Background Born in Kentucky; moved to Indiana then Illinois as a boy Didn t want to farm; went into business Elected to state legislature
Can the Civil War be prevented? Abraham Lincoln Abraham Lincoln Background Born in Kentucky; moved to Indiana then Illinois as a boy Didn t want to farm; went into business Elected to state legislature
Chapter 13 The Union In Peril,
 Chapter 13 The Union In Peril, 1848-1861 Zachary Taylor s presidency Almost immediately he had to deal with the admission of California into the union as a free state. California s population expanded
Chapter 13 The Union In Peril, 1848-1861 Zachary Taylor s presidency Almost immediately he had to deal with the admission of California into the union as a free state. California s population expanded
WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer
 WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer Subject(s) Social Studies Conceptual Lenses Grade/Course American History 1 Compromise Unit of Study Unit 6: The Civil War and (4.1, 4.2, 4.4, 5.2, 7.1, 7.2, 7.3) War Power
WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer Subject(s) Social Studies Conceptual Lenses Grade/Course American History 1 Compromise Unit of Study Unit 6: The Civil War and (4.1, 4.2, 4.4, 5.2, 7.1, 7.2, 7.3) War Power
Slavery was the topic
 Slavery was the topic » if slavery is legal or not?» where slavery is allowed (or not allowed)? » The United States had been experiencing rapid growth (in terms of population and in land acquisition)
Slavery was the topic » if slavery is legal or not?» where slavery is allowed (or not allowed)? » The United States had been experiencing rapid growth (in terms of population and in land acquisition)
WARM UP. 1 Get into the Kahoot game on the board. 2 We will review the week & the winner will receive a prize!
 WARM UP 1 Get into the Kahoot game on the board 2 We will review the week & the winner will receive a prize! PRESIDENCY OF JOHN QUINCY ADAMS ELECTION OF 1824 I. Sectionalism replaced nationalism in the
WARM UP 1 Get into the Kahoot game on the board 2 We will review the week & the winner will receive a prize! PRESIDENCY OF JOHN QUINCY ADAMS ELECTION OF 1824 I. Sectionalism replaced nationalism in the
X On record with the USOE.
 Textbook Alignment to the Utah Core 8 th Grade Social Studies U.S. History This alignment has been completed using an Independent Alignment Vendor from the USOE approved list (www.schools.utah.gov/curr/imc/indvendor.html.)
Textbook Alignment to the Utah Core 8 th Grade Social Studies U.S. History This alignment has been completed using an Independent Alignment Vendor from the USOE approved list (www.schools.utah.gov/curr/imc/indvendor.html.)
X On record with the USOE.
 Textbook Alignment to the Utah Core 8 th Grade Social Studies U.S. History This alignment has been completed using an Independent Alignment Vendor from the USOE approved list (www.schools.utah.gov/curr/imc/indvendor.html.)
Textbook Alignment to the Utah Core 8 th Grade Social Studies U.S. History This alignment has been completed using an Independent Alignment Vendor from the USOE approved list (www.schools.utah.gov/curr/imc/indvendor.html.)
X On record with the USOE.
 Textbook Alignment to the Utah Core 8 th Grade Social Studies U.S. History This alignment has been completed using an Independent Alignment Vendor from the USOE approved list (www.schools.utah.gov/curr/imc/indvendor.html.)
Textbook Alignment to the Utah Core 8 th Grade Social Studies U.S. History This alignment has been completed using an Independent Alignment Vendor from the USOE approved list (www.schools.utah.gov/curr/imc/indvendor.html.)
US HISTORY 1ST SEMESTER CUMULATIVE FORM A
 US HISTORY 1ST SEMESTER CUMULATIVE FORM A AP US History DO NOT 1st Sem Cumulative Test Ch. 2-15 WRITE ON Colonies to Reconstruction Form A THIS TEST Directions: Answer all questions on a separate sheet
US HISTORY 1ST SEMESTER CUMULATIVE FORM A AP US History DO NOT 1st Sem Cumulative Test Ch. 2-15 WRITE ON Colonies to Reconstruction Form A THIS TEST Directions: Answer all questions on a separate sheet
Civil War - Points of Conflict
 Civil War - Points of Conflict Missouri (Maine) Compromise (1820) proslavery in the early 1800s, tensions began to rise between and anti-slavery groups across the country by 1819 there were 11 free states
Civil War - Points of Conflict Missouri (Maine) Compromise (1820) proslavery in the early 1800s, tensions began to rise between and anti-slavery groups across the country by 1819 there were 11 free states
Chapter 16 : Slavery Divides a Nation
 Chapter 16 : Slavery Divides a Nation 1 Part 1: Slavery in the Territories Hooray for the free Soil Party! In 1848 the Free Soil Party formed. The free soil party was a group of antislavery supporters
Chapter 16 : Slavery Divides a Nation 1 Part 1: Slavery in the Territories Hooray for the free Soil Party! In 1848 the Free Soil Party formed. The free soil party was a group of antislavery supporters
The Americans (Survey)
 The Americans (Survey) Chapter 7: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OVERVIEW American leaders devise a farsighted policy of improvements as North, South, and West develop
The Americans (Survey) Chapter 7: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OVERVIEW American leaders devise a farsighted policy of improvements as North, South, and West develop
8th Grade U.S. History STAAR Study Packet.
 8th Grade U.S. History STAAR Study Packet. NAME: HISTORY TEACHER: Complete the activities using your STAAR Review Sheet. Once you finish an assignment, check your answers by using the answer key provided
8th Grade U.S. History STAAR Study Packet. NAME: HISTORY TEACHER: Complete the activities using your STAAR Review Sheet. Once you finish an assignment, check your answers by using the answer key provided
Writing Prompts US History
 Writing Prompts US History In order to be successful in the classroom, students must have choice, write everyday and be able to defend positions. These prompts allow students to do all three. Please consider
Writing Prompts US History In order to be successful in the classroom, students must have choice, write everyday and be able to defend positions. These prompts allow students to do all three. Please consider
Years Before Secession. Buchanan s Presidency. ISSUE 1: Dred Scott Case 1/16/2013
 Years Before Secession Buchanan s Issues, Lincoln-Douglas Debates, Democratic Party Split, Election of Lincoln Buchanan s Presidency Three major events 1. Dred Scott Decision 2. Troubles in Kansas Lecompton
Years Before Secession Buchanan s Issues, Lincoln-Douglas Debates, Democratic Party Split, Election of Lincoln Buchanan s Presidency Three major events 1. Dred Scott Decision 2. Troubles in Kansas Lecompton
R E A D T H I S F I R S T!
 R E A D T H I S F I R S T! Period 4 (1800 1848) Review Sheet Chapters 9 12 the America s History Textbook Welcome to Period 4! This period accounts for roughly 10% of the exam. In past exams, this period
R E A D T H I S F I R S T! Period 4 (1800 1848) Review Sheet Chapters 9 12 the America s History Textbook Welcome to Period 4! This period accounts for roughly 10% of the exam. In past exams, this period
Chapter 19 Drifting Toward Disunion The Kansas Territory erupted in violence in 1855 between proslavery and antislavery arguments.
 The Kansas Territory erupted in violence in 1855 between proslavery and antislavery arguments. In 1857, the Supreme Court's Dred Scott decision invalidated the Missouri Compromise of 1820. 1. Stowe and
The Kansas Territory erupted in violence in 1855 between proslavery and antislavery arguments. In 1857, the Supreme Court's Dred Scott decision invalidated the Missouri Compromise of 1820. 1. Stowe and
The Path to Civil War
 The Path to Civil War It all started at the Constitutional Convention The Three-Fifths Compromise Allowed southern states to count 3/5 of their slave populations for purposes of determining how many representatives
The Path to Civil War It all started at the Constitutional Convention The Three-Fifths Compromise Allowed southern states to count 3/5 of their slave populations for purposes of determining how many representatives
Civil War 10/25/2018. The Union in Crisis! Gold found in CA- increase population CA wants to be a state Free or slave state?
 The Union in Crisis! Dred Scott Kansas-Nebraska Act Lincoln-Douglas Debates Compromise of 1850 Civil War Lincoln s Election Compromise of 1850 Gold found in CA- increase population CA wants to be a state
The Union in Crisis! Dred Scott Kansas-Nebraska Act Lincoln-Douglas Debates Compromise of 1850 Civil War Lincoln s Election Compromise of 1850 Gold found in CA- increase population CA wants to be a state
Civil War Open- Note Test. Directions: Using your notes from this unit answer the following questions.
 Civil War Open- Note Test Directions: Using your notes from this unit answer the following questions. 1. Which of the following was a cause of the Civil War? a. Northerners did not believe the South had
Civil War Open- Note Test Directions: Using your notes from this unit answer the following questions. 1. Which of the following was a cause of the Civil War? a. Northerners did not believe the South had
Binder Page Name Period Andrew Jackson and the Growth of American Democracy
 Binder Page Name Period Andrew Jackson and the Growth of American Democracy Date Chapter 6.1 Jackson Wins the Presidency- (p. 302-312) 1. Democracy was growing in the United States. In other words, the
Binder Page Name Period Andrew Jackson and the Growth of American Democracy Date Chapter 6.1 Jackson Wins the Presidency- (p. 302-312) 1. Democracy was growing in the United States. In other words, the
Expansion, Nationalism,& Sectionalism ( )
 Expansion, Nationalism,& Sectionalism (1800-1865) President Adams John Adams was Washington s VP Adams ran for election in 1796 and won He faced 2 difficult tasks: war from abroad & growing political party
Expansion, Nationalism,& Sectionalism (1800-1865) President Adams John Adams was Washington s VP Adams ran for election in 1796 and won He faced 2 difficult tasks: war from abroad & growing political party
APUSH REVIEWED! DRIFTING TOWARD DISUNION NORTHERN RESISTANCE 11/9/15. Result of the Kansas-Nebraska Act
 11/9/15 APUSH 1854-1861 DRIFTING TOWARD DISUNION REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 19 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 13 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 13 NORTHERN RESISTANCE Uncle
11/9/15 APUSH 1854-1861 DRIFTING TOWARD DISUNION REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 19 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 13 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 13 NORTHERN RESISTANCE Uncle
Andover Public Schools Social Studies Benchmarks 2004 Grade 8 U. S. History I The Revolution Through Reconstruction
 Students examine the historical and intellectual origins of the United States during the Revolutionary and Constitutional eras. They learn about the important political and economic factors that contributed
Students examine the historical and intellectual origins of the United States during the Revolutionary and Constitutional eras. They learn about the important political and economic factors that contributed
Inventor Invention Impact
 Industrialization and Reform Test Review Test Date: Name 1. Fill in the missing boxes Inventor Invention Impact Eli Whitney Cotton Gin -Increased slavery -Made cleaning cotton faster and more efficient
Industrialization and Reform Test Review Test Date: Name 1. Fill in the missing boxes Inventor Invention Impact Eli Whitney Cotton Gin -Increased slavery -Made cleaning cotton faster and more efficient
The Antebellum Era ( ): The Rise of Jacksonian Democracy Part 1
 The Antebellum Era (1781-1860): The Rise of Jacksonian Democracy Part 1 B. Building a Nation (Colonization-ca. 1877) 1. Colonization and Forging a Nation K. Identify and evaluate the political and territorial
The Antebellum Era (1781-1860): The Rise of Jacksonian Democracy Part 1 B. Building a Nation (Colonization-ca. 1877) 1. Colonization and Forging a Nation K. Identify and evaluate the political and territorial
COMPREHENSION AND CRITICAL THINKING
 Name Class Date Chapter Summary COMPREHENSION AND CRITICAL THINKING Use information from the graphic organizer to answer the following questions. 1. Recall What caused the sectional controversy that led
Name Class Date Chapter Summary COMPREHENSION AND CRITICAL THINKING Use information from the graphic organizer to answer the following questions. 1. Recall What caused the sectional controversy that led
SOWING THE SEEDS OF CONFLICT IN A HOUSE DIVIDED. By: Angelica Narvaez
 SOWING THE SEEDS OF CONFLICT IN A HOUSE DIVIDED By: Angelica Narvaez Timeline Cotton Gin (1784) Compromise of 1820 Nullification Crisis (1832) Mexican- American War (1846-1848) Compromise of 1850 Harriet
SOWING THE SEEDS OF CONFLICT IN A HOUSE DIVIDED By: Angelica Narvaez Timeline Cotton Gin (1784) Compromise of 1820 Nullification Crisis (1832) Mexican- American War (1846-1848) Compromise of 1850 Harriet
Warm Up. the north & south. slavery in the southern USA: economic landscape of the United States: 1) Using a Venn Diagram compare and contrast
 Warm Up 1) Using a Venn Diagram compare and contrast the north & south 2) Explain the impact of the cotton gin on slavery in the southern USA: 3) Discuss how industrialization changed the economic landscape
Warm Up 1) Using a Venn Diagram compare and contrast the north & south 2) Explain the impact of the cotton gin on slavery in the southern USA: 3) Discuss how industrialization changed the economic landscape
Chapter 15 Toward Civil War ( ) Section 3 Challenges to Slavery
 Chapter 15 Toward Civil War (1840-1861) Section 3 Challenges to Slavery Which political issue is most important to you? A. Foreign policy B. Domestic policy C. The economy D. Government reform A. A B.
Chapter 15 Toward Civil War (1840-1861) Section 3 Challenges to Slavery Which political issue is most important to you? A. Foreign policy B. Domestic policy C. The economy D. Government reform A. A B.
America, History of Our Nation Civil War to the Present 2014
 A Correlation of Civil War to the Present 2014 To the Utah Core State Standards for Resource Title:, Civil War to the Present Publisher: Pearson Education publishing as Prentice Hall ISBN: SE: 9780133231441
A Correlation of Civil War to the Present 2014 To the Utah Core State Standards for Resource Title:, Civil War to the Present Publisher: Pearson Education publishing as Prentice Hall ISBN: SE: 9780133231441
THE FIRST 350-ISH YEARS:
 REVIEW AMERICAN HISTORY TUBBS THE FIRST 350-ISH YEARS: from the AGE OF COLUMBUS thru the SECTIONALISM CRISIS OF THE 1850s DIRECTIONS. Indicate the single best response, according to information provided
REVIEW AMERICAN HISTORY TUBBS THE FIRST 350-ISH YEARS: from the AGE OF COLUMBUS thru the SECTIONALISM CRISIS OF THE 1850s DIRECTIONS. Indicate the single best response, according to information provided
UNITED STATES HISTORY I COURSE SYLLABUS
 UNITED STATES HISTORY I COURSE SYLLABUS Course Title: United States History I H2 and H3 Department: Social Studies Primary Course Materials: America: Pathways to the Present Course Description: In the
UNITED STATES HISTORY I COURSE SYLLABUS Course Title: United States History I H2 and H3 Department: Social Studies Primary Course Materials: America: Pathways to the Present Course Description: In the
Slavery and Sectionalism. The Political Crisis of
 Slavery and Sectionalism The Political Crisis of 1848-1861 Slavery? In the Territories Gold Rush Slavery? In the Territories Compromise of 1850 Dead on arrival/president Taylor dies/douglas Separate Legislation
Slavery and Sectionalism The Political Crisis of 1848-1861 Slavery? In the Territories Gold Rush Slavery? In the Territories Compromise of 1850 Dead on arrival/president Taylor dies/douglas Separate Legislation
Drifting Toward Disunion, Chapter 19
 Drifting Toward Disunion, 1854-1861 Chapter 19 Stowe & Helper: Literary Incendiaries Harriet Beecher Stowe Uncle Tom s Cabin Revealed evil in slavery Rallied North around abolitionism Hinton R. Helper
Drifting Toward Disunion, 1854-1861 Chapter 19 Stowe & Helper: Literary Incendiaries Harriet Beecher Stowe Uncle Tom s Cabin Revealed evil in slavery Rallied North around abolitionism Hinton R. Helper
Slavery and Secession. Chapter 10.4
 Slavery and Secession Chapter 10.4 1856: Democrat James Buchanan elected president 1857: Dred Scott v. Sandford Missouri Compromise = unconstitutional 1857: Voters in Kansas reject proslavery state constitution
Slavery and Secession Chapter 10.4 1856: Democrat James Buchanan elected president 1857: Dred Scott v. Sandford Missouri Compromise = unconstitutional 1857: Voters in Kansas reject proslavery state constitution
CW1.9 Defining Ideas in Context: States Rights (page 1 of 3)
 CW1.9 Defining Ideas in Context: States Rights (page 1 of 3) One of the most important concepts in this unit is the noun phrase, States Rights. Understanding how this term was used in the 1800s requires
CW1.9 Defining Ideas in Context: States Rights (page 1 of 3) One of the most important concepts in this unit is the noun phrase, States Rights. Understanding how this term was used in the 1800s requires
8 th grade American Studies sample test questions
 8 th grade American Studies sample test questions PASS 1.2 Standard 1. The student will develop and practice process skills in social studies. PASS OBJECTIVE 1.2: Identify, analyze, and interpret primary
8 th grade American Studies sample test questions PASS 1.2 Standard 1. The student will develop and practice process skills in social studies. PASS OBJECTIVE 1.2: Identify, analyze, and interpret primary
1st CONTINENTAL CONGRESS 3/5 COMPROMISE Constitutional Amendment that OUTLAWED SLAVERY. 13th AMMENDMENT. To end slavery Anti-slavery ABOLITION
 1st CONTINENTAL CONGRESS 1774 in Philadelphia; A meeting of delegates (representatives) to decide how to respond to Britain... taxes, closing Boston Harbor, war??? One representative from each colony (except
1st CONTINENTAL CONGRESS 1774 in Philadelphia; A meeting of delegates (representatives) to decide how to respond to Britain... taxes, closing Boston Harbor, war??? One representative from each colony (except
United States History and Government
 Name: United States History and Government Period: Date: Regents Review #2: Early American Republic, Westward Expansion, Sectionalism, the Civil War, and Reconstruction Early American Republic: George
Name: United States History and Government Period: Date: Regents Review #2: Early American Republic, Westward Expansion, Sectionalism, the Civil War, and Reconstruction Early American Republic: George
The Role of Politics in Sectionalism
 The Role of Politics in Sectionalism James Monroe 1758 1831 Dem.-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former Gov. of VA, Secretary of State, and Secretary
The Role of Politics in Sectionalism James Monroe 1758 1831 Dem.-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former Gov. of VA, Secretary of State, and Secretary
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism
 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Regional Economies Create Differences Samuel Slater brought the Water Frame to Rhode Island from Great Britain in 1789. It was used to spin raw cotton into cotton
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Regional Economies Create Differences Samuel Slater brought the Water Frame to Rhode Island from Great Britain in 1789. It was used to spin raw cotton into cotton
THE DEBATE OVER SLAVERY
 THE DEBATE OVER SLAVERY THE MORALITY & LEGITIMACY OF SLAVERY Read either the William Lloyd Garrison or John C Calhoun Article. Complete the questions associated with your article in Complete Sentences
THE DEBATE OVER SLAVERY THE MORALITY & LEGITIMACY OF SLAVERY Read either the William Lloyd Garrison or John C Calhoun Article. Complete the questions associated with your article in Complete Sentences
WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer
 WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer Subject(s) Social Studies Conceptual Lenses Grade/Course American History 1 Conflict Unit of Study Unit 4: Political Conflict, Industrialization, and Reform (4.1, 4.2, 4.3,
WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer Subject(s) Social Studies Conceptual Lenses Grade/Course American History 1 Conflict Unit of Study Unit 4: Political Conflict, Industrialization, and Reform (4.1, 4.2, 4.3,
Washington to Madison Practice Questions
 1 Washington s Proclamation of Neutrality (1793), Jefferson s Embargo Act (1807), and the Monroe Doctrine (1823) were all efforts to (1) avoid political conflicts with European nations (2) directly support
1 Washington s Proclamation of Neutrality (1793), Jefferson s Embargo Act (1807), and the Monroe Doctrine (1823) were all efforts to (1) avoid political conflicts with European nations (2) directly support
