Answer Key. CHAPTER 8 Anglo American Colonization
|
|
|
- Candice Stevenson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CHAPTER 8 Anglo American Colonization Skillbuilder: Reading Social Studies Comparing and Contrasting Information 8 Person or group; Goal(s); Accomplishments Empresarios George Morgan; to bring settlers from the United States to Texas; founded New Madrid, served as an example to other empresarios Moses Austin; to bring settlers to Texas to make money and pay off his debts; obtained approval to start an Anglo American colony in Texas Stephen F. Austin; to realize his father s dream of colonizing Texas; first years of the colony were plagued by drought, suffered attacks by Karankawas, some families returned to the United States, colony eventually prospered until it burned during the Texas Revolution Green DeWitt; to bring settlers to Texas; founded a colony southwest of San Felipe de Austin Martín de León; to bring settlers to Texas from Mexico; settled 200 families, founded Victoria in 1824 Arthur Wavell and Ben Milam; to bring settlers to Texas; received a grant in northeastern Texas along the Red River Haden Edwards; to settle colonists in East Texas; received land grant for financing some of Austin s dealings with the government but later lost it due to disputes with the Mexican government Joseph Vehlein and David Burnet; to bring settlers to Texas; were allowed to bring settlers to the lands formerly granted to Edwards James Power, James Hewetson, John McMullen, James McGloin; to bring Irish settlers to Texas; Power and Hewetson settled an Irish colony along the Gulf Coast, McMullen and McGloin established an Irish colony along the Nueces River Filibusters Philip Nolan; to capture wild horses to sell in the United States; made Spanish authorities suspicious by visiting with General Wilkinson, warned he would be arrested if he returned, killed during a fight with Spanish soldiers near Waco Lieutenant Augustus Magee and Bernardo Gutiérrez de Lara; to free New Spain from Spanish control; organized the Republic of the North, proclaimed Texas independent of Spain, defeated by Spanish forces James Long; to colonize Texas and declare Texas s independence from Spain; after two attempts to gain Texas s independence, he was sent to Mexico City and was shot by a prison guard Spanish officials Juan Bautista Elguezábal; to keep Nolan out of Texas; threatened to arrest Nolan if he returned General Simón Herrera; to keep the peace between Texas and Louisiana; signed the Neutral Ground Agreement Governor Manuel Salcedo; to maintain Spanish rule of Texas; his forces killed Augustus Magee, he was defeated by filibusters at the Battle of Salado U.S. officials General James Wilkinson; to maintain U.S. control of the frontier and to maintain peace along the Texas-Louisiana border; signed the Neutral Ground Agreement General Andrew Jackson; rid the United States of Native Americans by pursuing them into Spanish Florida; actions in Florida led to the Adams-Onís Treaty, in which Spain ceded Florida to the United States Revolutionaries Francisco Xavier Mina and Henry Perry; to attack Spanish ships in the Gulf; organized revolutionaries and enlisted the help of pirate Louis Michel Aury Pirates Louis Michel Aury; to help revolutionaries; led an unsuccessful attack on Spain along the Mexican coast Jean Laffite; to take Spanish treasures; U.S. Navy drove him from the Texas coast when he began raiding U.S. ships Colonists Jane Long; to settle in Texas; managed a hotel and a plantation, became one of the most prominent pioneer women in Texas Mary Austin Holley; to encourage people to move to Texas; wrote series of letters, diary entries, and books that prompted many settlers to come to Texas from other states Religious leaders Father Michael Muldoon; to baptize colonists as Catholic; baptized so many dishonest converts that these people became known as Muldoon Catholics Samuel Doak McMahan; to preach his faith to colonists; established a Methodist church near San Augustine Joseph E. Bays and Thomas J. Pilgrim; to preach their faith to colonists; preached their faith in relative freedom Sumner Bacon; to preach his faith to colonists; preached his faith in relative freedom Discussion Questions 1. Spanish and U.S. officials both worked to maintain peace along the Texas-Louisiana border. Spanish officials sought to protect Texas from U.S. control, while U.S. officials sought to protect the U.S. frontier from Spanish control. 2. The empresarios brought settlers to Texas with the permission of the Spanish government. The filibusters carried on illegal activities. 3. Empresarios faced the challenges of bringing settlers to Texas and protecting them once they had arrived. Guided Reading 8.1 A. Filibusters Philip Nolan, Bernardo Gutiérrez de Lara, Augustus Magee, James Long, Samuel Kemper, Henry Perry, José Àlvarez de Toledo Empresario: George Morgan Government officials: General James Wilkinson, General Simón Herrera, Juan Bautista Elguezábal, Governor Manuel Salcedo, General Joaquín de Arredondo, General Andrew Jackson Revolutionaries: Francisco Xavier Mina, Henry Perry Colonist: Jane Long Pirates: Louis Michel Aury, Jean Laffite 52 UNIT 3
2 B. Agreement; Notes Neutral Ground Agreement; created a neutral zone between the Arroyo Hondo and the Sabine River, stopped border clashes between military patrols, created a shelter for lawless citizens of both nations Adams-Onís Treaty; Spain ceded Florida to the United States, the Sabine River would be the boundary between Spanish Texas and Louisiana, the United States agreed not to press claims west of the boundary Guided Reading 8.2 A. Box 2: Austin visits San Antonio de Béxar and meets with Governor Martínez. Box 4: Austin chooses land between the Lavaca and San Jacinto Rivers for his colony. Box 6: Beginning in 1821, settlers begin to arrive. Box 8: With Austin waiting at the Colorado River, some of the frustrated settlers give up and return home. Box 10: Austin learns that Mexico has gained its independence from Spain. Box 12: Austin learns to speak Spanish and wins the trust of Mexican leaders. B. Stephen F. Austin was such a good leader because he attended to the needs of his colonists. He influenced laws that benefited colonists. He learned to speak Spanish in order to communicate more effectively with the Mexican officials, to translate Spanish laws, and to communicate government policies to the colonists. Guided Reading 8.3 A. Where did the settlers come from?: United States, Mexico, Germany, Ireland, Poland, Africa What kinds of foods did the settlers eat?: fish, geese, deer, turkey, berries, nuts, salt, sugar, flour, dried vegetables, corn What kinds of homes did the settlers build?: log cabins, rock structures, one- or two-room cabins with breezeways, cooking was done in open fireplaces or outside, floor was often bare or covered by raised boards, mattresses were made of moss or corn husks, furniture was made from trees How were the settlers children educated?: no real system of education, few children attended formal classes, most children were taught at home by their parents What challenges did the settlers face?: disease, injury, limited or no medical care, conflicts with Native Texans, tension between colonists and Mexican government B. Some settlers were seeking adventure. Others may have been attracted by the inexpensive land. Skillbuilder: Vocabulary Terms and Names 8 A. Completion 1. Neutral Ground Agreement 2. Mary Austin Holley 3. Gutiérrez-Magee expedition 4. militia 5. Jane Long 6. San Felipe de Austin 7. compromise 8. Stephen F. Austin B. Matching 1. f 6. i 2. a 7. e 3. c 8. j 4. b 9. h 5. g 10. d C. Writing Students accounts should reflect information from the chapter and include all listed terms. Skillbuilder: Social Studies Identifying Bias to describe the beauty of Texas 2. No state is more eminently favored by nature; abundant; valuable; stately; magnificent; rich; splendid; luxuriant; endless variety; indescribable and surpassing loveliness; paradise 3. The excerpt refers to fertile soil and varied landscape in Texas. 4. Holley views Texas as a sort of paradise. 5. Holley was a cousin of Stephen F. Austin, wanted to move to Texas herself, and had land there. 6. to persuade people to colonize in Texas; She wanted to help Austin succeed in his colonization efforts, to increase the value of her land, and to secure her future in a successful colony. Skillbuilder: Map & Geography The Louisiana Purchase and the Adams-Onís Treaty, between the Sabine and Red Rivers 2. The new boundary followed the Sabine River and then went straight north to the Red River. 3. Red River and Arkansas River 4. Mississippi River 5. gained territory; The boundary was extended north of the Red River in West Texas and to the Red River in East and Central Texas. 6. Arkansas River, Red River, Sabine River, hundredth meridian, thirty-second parallel, forty-second parallel 7. Using rivers and latitude and longitude lines provided exact boundaries, even in unexplored areas, to prevent further disagreements on which country possessed which areas. 53
3 Primary Sources Memoirs of a Tejano Hero San Antonio 2. Colonel Miguel Menchaca 3. It shows her courage and independence. 4. He admires their efforts. The Early Colonies women; because of the friends left behind, hardships, lack of necessities, and boredom 2. horses 3. from an old ship (possibly La Salle s) 4. DeWitt Colony; because of the rude cabins, lack of comfort, alligators, mosquitoes, etc. 5. Both events triggered an influx of people moving to frontier areas to seek a better life. Colonial Texas Life It ran aground and wrecked during a storm. 2. the flooding of the Brazos and Colorado Rivers 3. helping each other without expecting pay 4. The corn crop was ruined, so there was very little corn to be ground. CHAPTER 9 The Road to Revolution Skillbuilder: Reading Social Studies Identifying Cause and Effect 9 Row 1: Mexican officials fear that the colonists are becoming too independent; Haden Edwards leads the Fredonian Rebellion; John Quincy Adams offers to purchase Texas for $1 million; Mier y Terán reports that Anglo American settlers outnumber Mexican settlers in Texas; his report also points out that the influence of the United States is growing in Texas and that many settlers ignore laws against trading with the United States. Row 2: The Texans resent the presence of Mexican troops and dislike the new taxes; shippers are upset about Fisher s order that all ships must receive clearance papers from the customs officials in Anahuac; Bradburn arrests Madero for issuing land grants that violate the Law of April 6, 1830; tension sets the stage for further conflict. Row 3: Delegates vote against an immediate declaration of independence; they declare that they are still loyal citizens of Mexico; they set up a provisional government and choose Henry Smith as governor; Sam Houston is appointed commander of the Texas military forces. Discussion Questions 1. Texas colonists traded freely with the United States and participated in the Fredonian Rebellion. 2. The Law of April 6, 1830, was not successful; It led to increased tensions between Mexicans and Texans. 3. Santa Anna s violations of the Constitution of 1824; Colonists wanted the state rather than the federal government to control local affairs. 54 UNIT 3 Guided Reading 9.1 A. Haden Edwards: disputed Mexican land grants; overturned an election for alcalde of Nacogdoches; negotiated treaty with some of the Cherokees in the area; formed the Fredonian Republic Benjamin Edwards: led the Fredonian Rebellion John Quincy Adams: offered to pay as much as $1 million for all or part of Texas Joel Poinsett: sent to Mexico to present the purchase offer to Mexican officials Manuel Mier y Terán: reported his findings that U.S. influence was growing in Texas and that many settlers were ignoring laws against trading with the United States B. outlawed immigration from the United States; canceled all empresarial grants that had not been fulfilled; provided land and money for European and Mexican settlers to relocate to Texas; outlawed the transportation of slaves into Mexico; established new forts and presidios to stop illegal immigration; placed customs duties on all goods brought from the United States Guided Reading 9.2 A. Antonio López de Santa Anna: Mexican; launched a revolution against President Bustamante George Fisher: Mexican; appointed to collect customs duties and stop smuggling of goods into and out of the country, ordered that all ships report to the customs house at the mouth of the Brazos River John Davis Bradburn: Mexican; arrested Francisco Madero for issuing land titles to people who already lived in Texas, forced settlers to provide free materials and labor to construct a new fort, used colonists slaves to help with his public works program, ordered the arrests of William B. Travis and Patrick Jack William B. Travis: Texan; tried to retrieve William T. Logan s slaves from Bradburn, arrested by Bradburn and held at Anahuac Domingo de Ugartechea: Mexican; refused to let settlers pass along the Brazos River, initiated the Battle of Velasco Stephen F. Austin: Texan; traveled to Mexico to deliver Texans resolutions, met with Santa Anna to discuss Texans requests, was arrested and imprisoned for challenging the authority of the Mexican government William Wharton: Texan; elected leader of the Convention of 1833 Valentín Gómez Farías: Mexican; ran the Mexican government while Santa Anna was away, initially met with Austin to discuss his resolutions B. Convention of 1832: resolved to appoint a land commissioner to issue land titles in East Texas; resolved to donate government lands for the maintenance of primary schools; resolved to request the Nacogdoches governing council to prevent Anglo American invasion of Native American lands;
4 established a plan to create militias; created committees of vigilance, safety, and correspondence Convention of 1833: resolved to obtain adequate defense from Native American raids; resolved to stop African slave traffic in Texas; created a state constitution Both: resolved to split Coahuila y Tejas and grant Texas statehood; resolved to extend tax exemption; resolved to modify the Law of April 6, 1830, to permit more immigration Guided Reading 9.3 A. Row 1: Cos sends Tenorio to Anahuac to resume Bradburn s duties. Row 2: Settlers treat Travis and his men with disrespect to show their loyalty to Mexico. Row 3: Stephen F. Austin is imprisoned in Mexico. Row 4: Moore s men cross the river and fire the cannon at the Mexican soldiers. Row 5: Cos continues his march to San Antonio. Row 6: Santa Anna immediately begins gathering an army south of the Rio Grande to deal with the Texas revolutionaries. B. voted against an immediate declaration of independence; adopted the Declaration of the People in Texas in General Convention Assembled; declared that they had fought to protect themselves; encouraged other Mexicans to join in the fight for the Constitution of 1824; set up a provisional government with Henry Smith as governor; decided to meet again on March 1, 1836, to make a decision about Texas s independence; asked Stephen F. Austin and two revolutionaries to go to the United States to raise troops and money for their cause; appointed Sam Houston as overall commander of their military forces Skillbuilder: Vocabulary Terms and Names 9 A. Completion 1. Constitution of Fredonian Rebellion 3. Law of April 6, Turtle Bayou Resolutions 5. provisional government B. Matching 1. e 6. c 11. b 2. h 7. a 12. l 3. g 8. k 13. i 4. j 9. o 14. f 5. m 10. n 15. d C. Writing Students speeches should reflect information from the chapter and include all of the listed terms. Skillbuilder: Social Studies Distinguishing Fact from Opinion Mexicans lived in Nacogdoches, Mexicans were poor, and some foreign colonists had visited the Mexican capital. 2. lowest class, very poor, very ignorant, degraded condition, most ignorant 3. They are not of the type that take any thought for the improvement of its public institutions or the betterment of its degraded condition. 4. They are poor and ignorant and care nothing about educating themselves or bettering their communities. 5. to inform 6. Mier y Terán fears that a revolution might result in Texas because the Mexicans and foreigners do not get along and are different from one another. Skillbuilder: Map & Geography Departments of Texas, three 2. Department of Béxar 3. San Felipe de Austin 4. Saltillo 5. Some settlements were along the Old San Antonio Road; most others were located southeast of the road. 6. Department of Béxar 7. Most of the settlers in the eastern municipalities had come from the United States, so they were Anglo Texans. Many Hispanics lived in San Antonio because the city was closer to Mexico. Primary Sources A Report 9.1A 1. They do very little, do not know the laws of their own country, and are corrupt. 2. They want Texas to be a territory separate from Coahuila. 3. They bring with them their ideas about rights guaranteed by the U.S. Constitution. 4. Many wealthy Anglo Americans would come to Texas, and Texas would become very powerful. On Slavery 9.1B 1. whether he would be allowed to bring slaves 2. It was hard to find farm workers, and colonists would not come unless they could bring slaves. 3. He supported slavery as necessary; he opposed it; he supported it as necessary. 4. It was the wish of the people. To Stephen F. Austin 9.2A 1. Stephen F. Austin 2. supportively 3. No; His letter shows bias and is very emotional. 4. get along with the Mexican government and laws as much as possible 55
5 From Stephen F. Austin 9.2B 1. people confined for political crimes 2. independence from Mexico and annexation to the United States 3. probably not; because his earlier letter was intercepted and read by Mexican officials 4. surprised and angry Attack on San Antonio send ammunition (powder and lead) and men 2. He sent ammunition and issued a call for volunteers. 3. He means that the outcome is extremely important to the people of Texas and they eagerly await the outcome. 4. Many would probably be moved to go to the aid of Burleson. CHAPTER 10 The Texas Revolution Skillbuilder: Reading Social Studies Sequencing Events 10 Students may wish to review information about sequencing on page 276 of the Pupil s Edition before answering. Mexican Troops; Texas Troops December: Cos retreats from Texas; Burleson turns troops over to Neill. January: Santa Anna travels up the Old San Antonio Road, Urrea travels up the Atascosito Road; Jamison helps fortify the Alamo. February: Santa Anna arrives at the Alamo, Urrea defeats 50 Texans at San Patricio; Travis raises 29 soldiers to help defend the Alamo, Crockett raises 12 soldiers. March: Santa Anna wages last attack on the Alamo and wins, Urrea defeats 50 Texas soldiers led by Grant; Consultation delegates declare Texas independent, Fannin receives orders to retreat, Fannin s troops surrender to Urrea at the Battle of Coleto, Texan troops executed at Goliad. April: Santa Anna captures Harrisburg, Santa Anna captured by Texan forces; Texas victory at San Jacinto, Burnet negotiates Treaties of Velasco. Discussion Questions 1. The Texan troops probably wanted to win more than ever and to get revenge on the Mexican troops for attacking the Alamo and killing all the defenders, as well as for executing the troops at Goliad. In April the Texan troops turned their misfortune around by capturing Santa Anna, winning at San Jacinto, and negotiating the Treaties of Velasco. 2. execution of Texan troops at Goliad and the attack on Mexican troops at San Jacinto; Santa Anna s capture and the negotiation of the Treaties of Velasco 3. Students may conclude that Texas s defeat at San Patricio as well as Santa Anna s arrival at the Alamo led to the Consultation s decision to declare Texas an independent republic. Guided Reading 10.1 A. 1. Texan and Mexican troops 2. Mexican leaders wanted to rid Texas of Anglo American and Tejano rebels, and Texans wanted independence from the Mexican centralist government. 3. at the Alamo, a former mission that had been turned into a fort in San Antonio 4. General Antonio López de Santa Anna, Colonel James Bowie, Lieutenant Colonel William B. Travis, David Crockett 5. Santa Anna s troops defeated the Alamo defenders. 6. Survivors warned other Texans about Santa Anna s approach. B. James Walker Fannin: a colonel in the Texas army; he commanded a force near Goliad; he and his troops were at Presidio La Bahía ready to defend the Atascosito Road. Antonio López de Santa Anna: wanted to reestablish Texas under Mexican control; wanted to rid Texas of Anglo American and Tejano rebels; he led Mexican troops to San Antonio to seek revenge for the previous defeat in San Antonio; defeated the Alamo defenders William Barret Travis: recruited defenders to fight at the Alamo; commanded forces at the Alamo Guided Reading 10.2 A. Attack at Refugio: Mexican soldiers kill or capture Captain Amon B. King and his men while they are on a reconnaissance mission. Battle of Coleto: Fannin and troops stop to rest in an open prairie near Coleto Creek on their way to Victoria and are attacked by Urrea and his men; Fannin surrenders his command. Execution at Goliad: Texan captives are marched to Goliad, held for a week, and then executed. Runaway Scrape: Gonzales area families panic upon learning of advancing Mexican army; Anglo settlers in the area flee to eastern settlements. Battle of San Jacinto: Texas troops attack Mexican army, catching them off guard; Santa Anna is captured. B. Texas troops wanted revenge for the events at Goliad and the Alamo; General Houston finally got enough men gathered together and trained; Mexican troops did not have many remaining supplies, including food and ammunition; Texas troops attacked the Mexican army, catching them off guard; Deaf Smith burned Vince s Bridge, preventing the Mexican army from retreating. 56 UNIT 3
6 Guided Reading 10.3 A. Texas Declaration of Independence: first section declares the right of revolution; second section lists complaints against the Mexican government; third section declares Texas s independence from Mexico; adopted by the Consultation on March 2, 1836 Constitution of 1836: based on the U.S. Constitution; created the Republic of Texas; set up ad interim government and selected leaders Treaties of Velasco: (public treaty) Santa Anna agrees never to fight against Texas again; Santa Anna agrees to withdraw all Mexican troops from Texas; all Mexican and Texas prisoners to be exchanged; (secret treaty) Santa Anna promises to recognize Texas s independence; Santa Anna agrees to establish the Rio Grande as the border between Texas and Mexico B. David G. Burnet, president Lorenzo de Zavala, vice-president Samuel P. Carson, secretary of state David Thomas, attorney general Thomas J. Rusk, secretary of war Robert Potter, secretary of the navy Sam Houston, secretary of the army Skillbuilder: Vocabulary Terms and Names 10 A. Completion 1. Green B. Jamison 2. fortify 3. William Barret Travis 4. David Crockett 5. Antonio López de Santa Anna 6. Battle of the Alamo B. Matching 1. n 6. o 11. b 2. e 7. c 12. h 3. f 8. d 13. l 4. g 9. m 14. k 5. a 10. j 15. i C. Writing Students newspaper articles should reflect information from the chapter and include all of the listed terms. Skillbuilder: Social Studies Reading a Time Line 10.2 Students may wish to review information about reading a time line on page 208 of the Pupil s Edition before answering. 1. from February 1836 to April one month 3. The Battle of Coleto takes place after Fannin begins his retreat to Victoria and before the execution of Texas soldiers at Goliad. 4. Several hundred Texas soldiers were executed at Goliad. 5. in an open prairie near Coleto Creek; Lack of shelter and water might have contributed to their defeat. 6. Anger over the executions at Goliad might have helped Texan troops win the Battle of San Jacinto. Skillbuilder: Map & Geography Migration from the United States to Texas, 1824 to west or southwest 2. Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, Georgia, Alabama, Tennessee, Missouri, and Arkansas 3. Tennessee is hilly, forested, landlocked, and unsuitable for farming; Texas is flat, accessible to the coast, and suitable for farming. 4. Tennessee and Arkansas 5. the Lower South 6. the northeast, especially near the border of Arkansas 7. the Upper South 8. migrants from the Upper South Primary Sources An Alamo Defender Washington (on the Brazos) acres of land plus 444 more acres if he settled his family 3. A lawyer might be interested in writing the constitution and laws and serving in the new government. 4. Answers may include I go whole hog in the cause of Texas. I expect to help them gain their independence. 5. Autry seems confident that Santa Anna will be defeated quickly. The Runaway Scrape 10.2A 1. They expected Santa Anna s army to arrive immediately and to destroy everything in its path. 2. They arrived days later and took all the livestock. 3. The first is from the point of view of a soldier describing the overall situation; the second is from the point of view of a slave, who describes the physical details of the hardships suffered. 4. The colonists believed that Santa Anna might force them to leave Texas forever, and they lost many things they had worked very hard to build up. Battle of San Jacinto 10.2B 1. to justify Santa Anna s actions and losses in Texas 2. Santa Anna, General Cos, General Castrillón 3. Answers may include emotional phrases such as enthusiasm of my troops, pitiful tone, All hope lost, noble kindness, etc. 4. The reasons included the disobedience of General Cos in leaving men behind, allowing the men to rest, and the failure of General Castrillón to wake him promptly. 5. Other people probably viewed Santa Anna as a poor leader and a coward for running away. 57
7 The Birth of a Republic providing supplies and weapons for war 2. Answers may include determination, courage, energy, boldness, quickness, etc. 3. Smith means that the Texans have had trouble agreeing on their government. 4. The delegates were probably inspired by the speech. CHAPTER 11 An Independent Texas Skillbuilder: Reading Social Studies Comparing and Contrasting Information 11 Houston: limited government spending, established peaceful relations with Mexico and the Native Texans, reduced army, eliminated navy Lamar: encouraged renewal of war with Mexico, wanted to force Native Texans out of Texas, increased government spending, supported military expeditions, wanted Texas to remain independent and expand its territory, established the public education system, expanded the use of redbacks, implemented policies that increased public debt Jones: announced the annexation of Texas Houston/Lamar: faced financial problems Lamar/Jones: served one term as president of the Republic of Texas Jones/Houston: supported annexation Houston/Lamar/Jones: served as president of the Republic of Texas, faced issue of how to handle Texas s status as a republic Discussion Questions 1. Many Texans did not agree with Houston s policies; they elected Lamar because he had a different approach. 2. The most positive result of Lamar s presidency was the creation of the public education system. The most negative result was the large debt he left behind. 3. Sam Houston was the most effective president because he worked to keep peace with Mexico and the Native Texans. He was also influential in the fight for annexation. Guided Reading 11.1 A. Problem: Texas was $1 million in debt; Solution: cut government expenses and issued promissory notes Problem: Tensions still existed between Mexico and Texas; Solution: reduced the army to prevent Felix Huston from renewing the war Problem: Native Texans resented the large number of Anglo American settlers who were moving into the area, so they began raiding; Solution: sent the Texas Rangers to patrol the frontier and control Native Texan raiding parties B. 1. He thought it was the best way to solve Texas s post-revolution problems, which included debt and trouble with Mexico and with the Native Texans. 2. Most Texans had immigrated from the United States. Texans language, customs, and ideas about law and government were similar to those of most Americans. 3. Texas would have entered the Union as a slave state. 4. The government s financial situation did not improve, and many people feared that the promise of future payment would not be kept. 5. Sam Houston thought that Felix Huston would start another war with Mexico. 6. The Cherokees land was highly desired by settlers. Also, many settlers wanted to rid the Republic of all Native Texans. Guided Reading 11.2 Policies; Results A. 1. wanted Texas to remain independent and expand its territory, returned to the empresarial system; new settlements were established in Texas 2. wanted to force Native Texans out of Texas; Cherokees were forced into present-day Oklahoma 3. wanted to expand Texas s boundaries into Mexican territory; tensions between Texas and Mexico increased 4. wanted to create a public education system; Congress set aside almost 18,000 acres of land for public schools and more than 220,000 acres for two universities 5. expanded the use of redbacks and spent money he did not have on battles with Native Americans and the Santa Fe expedition; public debt increased to almost $7 million B. Chief Bowles: Cherokee chief who Lamar ordered to lead the Cherokees out of Texas; when he refused, Lamar ordered General Douglass to drive them out; Bowles was killed and the Cherokees were forced into Oklahoma Council House Fight: Comanches agreed to discuss peace and to release all Anglo captives; when they released only one, the Texans refused to let the Comanche leaders leave until all captives were released; when the Comanches tried to leave by saying the captives were being held by other bands that weren t present, the Texans attacked them Battle of Plum Creek: prompted by the Council House Fight; Comanches killed all remaining Texas prisoners and raided Linnville and Victoria; the Texans fought back and killed 100 Comanches Commodore Edwin Moore: Texas navy commander 58 UNIT 3
8 who was sent by Lamar to aid Yucatecan rebels in their revolt against the Mexican government General Hugh McLeod: led the Santa Fe expedition to convince New Mexicans that they were Texans; surrendered to Mexican authorities; imprisoned in Perote until 1842 Texas Land Policy: Texas government used land to attract new settlers and pay its debts; through Texas Constitution, promised land to Anglo families already living in Texas and those who immigrated at that time; promised more land to immigrants who served for three months in the army; sold land to private investors; returned to the empresarial system Guided Reading 11.3 A. Election of 1841: Sam Houston defeated David G. Burnet; Edward Burleson won the vice-presidency; clear division existed between those who supported Houston and those who supported Lamar; Houston put plans from his previous presidency back into action Mier Expedition: General Vásquez took control of San Antonio and declared Mexican control; General Woll led 1,400 Mexican soldiers into Texas and retreated with 67 hostages; General Somervell pursued them into Mexico and demanded that the citizens of Mier give them supplies; Mexican soldiers captured them and marched them to Mexico City; Santa Anna ordered one of every ten soldiers shot and the others imprisoned for life; the survivors were released in 1844 Archives War: Houston moved the capital to Washington-on-the-Brazos, but the archives stayed in Austin; Houston tried to have the archives moved, but the citizens of Austin chased after the wagons carrying the archives and returned them to Austin Regulator-Moderator War: feud between two groups in East Texas that started after the Neutral Ground Agreement went into effect; regulators used excessive force to control the lawlessness of the area; moderators wanted to stop the excessive use of force; Houston sent in troops, which eventually ended the feuding Election of 1844: Texans elected Dr. Anson Jones; he defeated Edward Burleson; Jones continued Houston s pro-annexation policies Annexation of Texas: U.S. Congress approved a joint resolution on February 26, 1845; Mexican government agreed to recognize Texas as independent if the Texas Congress would reject annexation; the Texas Congress voted for annexation and ratified a state constitution; President Jones announced annexation on February 19, 1846; Texas became the twenty-eighth state B. Mexico did not want Texas to become a part of the United States because that would extend the U.S. border south and west. Mexico saw the United States as a bigger threat to its frontiers than Texas. If Texas remained independent, Mexico had a better chance of retaking the land. If Texas became a part of the United States, however, Mexico would have to declare war on the entire country to take back Texas. Skillbuilder: Vocabulary Terms and Names 11 A. Completion 1. John Allen 2. Augustus Allen 3. Houston 4. Mirabeau B. Lamar 5. Archive War B. Matching 1. c 7. i 2. l 8. k 3. h 9. f 4. g 10. d 5. a 11. b 6. j 12. e C. Writing Students speeches should reflect information from the chapter and include all of the listed terms. Skillbuilder: Social Studies Drawing Conclusions The United States expanded its southwestern border. 2. The Republic was still new, and many expected that Mexico would attempt to reclaim the land it lost. 3. The United States could annex an independent country, but it would not attempt to annex part of Mexico. 4. The United States was dividing states that supported slavery and those that opposed it. 5. People who opposed slavery did not want to add another slave state to the Union. 6. The United States decided that the benefits outweighed any problems that annexation might cause. Skillbuilder: Map & Geography Texas Capitals, 1521 Present approximately 150 miles; approximately 80 miles 2. Los Adaes 3. Galveston and Velasco 4. Saltillo, Monclova, and Mexico City 5. Colorado River 6. Austin 7. Mexico City; approximately 750 miles Primary Sources A Treaty with the Cherokees forever 2. no 3. They had little choice; the settlers were crowding them out. 4. Texas settlers wanted the land. 59
9 A Letter from Lamar They were too far away and isolated. 2. They will be forced to do so. 3. Lamar is asking them to allow Texas to take over New Mexico peacefully. 4. They probably felt the Texas government was being arrogant. The Mier Expedition 11.3A 1. death 2. kill him instead of his men 3. They were brave and defiant and cared deeply about one another. 4. Similar: Men who had surrendered and expected to be held prisoner were executed at Santa Anna s order. Different: Only one out of every ten of the Mier prisoners was executed. Annexation 11.3B 1. because it was bound by domestic and political ties to the United States 2. California 3. the movement westward and the increase in population 4. glorious, natural, right, proper, inevitable, Providence, etc. TAKS Skillbuilder 1. C 2. B 3. A TAKS Practice 1. C 2. F 3. D 4. H 60 UNIT 3
Chapter 6 Steps Toward Revolution:
 Lone Star: The Story of Texas Chapter 6 Steps Toward Revolution: 1827-1836 Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Lone Star:
Lone Star: The Story of Texas Chapter 6 Steps Toward Revolution: 1827-1836 Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Lone Star:
Texas Revolution and Independence Guided Notes
 Texas Revolution and Independence Guided Notes Era Code Rev Student Expectations 1. Trace the development of events that led to the Texas Revolution 2. Explain the roles played by significant individuals
Texas Revolution and Independence Guided Notes Era Code Rev Student Expectations 1. Trace the development of events that led to the Texas Revolution 2. Explain the roles played by significant individuals
Name Period November 3-Test. 1. After touring Texas, what was Mier y Teran s greatest concern? Page 219
 Name Period November 3-Test Chapters 9-12 Review Texas Revolution Answer the following questions: Chapter 9-The Road to Revolution Lesson One-Difficulties with Mexico 1. After touring Texas, what was Mier
Name Period November 3-Test Chapters 9-12 Review Texas Revolution Answer the following questions: Chapter 9-The Road to Revolution Lesson One-Difficulties with Mexico 1. After touring Texas, what was Mier
PoliticAL unrest IN TEXAS
 Road To Revolution PoliticAL unrest IN TEXAS Haden Edwards received his Empresario contract from the Mexican Government in 1825. This contract allowed him to settle 800 families near Nacogdoches. Upon
Road To Revolution PoliticAL unrest IN TEXAS Haden Edwards received his Empresario contract from the Mexican Government in 1825. This contract allowed him to settle 800 families near Nacogdoches. Upon
Chapter 8 Anglo American Colonization of Texas
 Chapter 8 Anglo American Colonization of Texas Essential Questions Could the British have done anything differently to keep from losing their American colonies? What was the legacy of the American Revolution?
Chapter 8 Anglo American Colonization of Texas Essential Questions Could the British have done anything differently to keep from losing their American colonies? What was the legacy of the American Revolution?
Name: Final Exam Date: Period: Texas History Fall Semester Final Exam Review
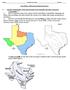 Name: Final Exam Date: Period: Texas History Fall Semester Final Exam Review I.) Unit One: Natural/Native Texas and its People (Texas Geography and Native Americans) ***Geography *** 1.) MAP A: Label the
Name: Final Exam Date: Period: Texas History Fall Semester Final Exam Review I.) Unit One: Natural/Native Texas and its People (Texas Geography and Native Americans) ***Geography *** 1.) MAP A: Label the
Unit 4 Mexican Colonization and the Empresario System
 Unit 4 Mexican Colonization and the Empresario System 1821-1836 For these notes you write the slides with the red titles!!! Unit 4 Vocab empresario an agent who makes all the arrangements to bring settlers
Unit 4 Mexican Colonization and the Empresario System 1821-1836 For these notes you write the slides with the red titles!!! Unit 4 Vocab empresario an agent who makes all the arrangements to bring settlers
Spring Final Review TEXAS HISTORY
 Spring Final Review TEXAS HISTORY Immigration to Mexico from U.S. Mexican General Mier y Teran warned of the growing American influence in East Texas. He recommended: increasing trade between TX and Mexico.
Spring Final Review TEXAS HISTORY Immigration to Mexico from U.S. Mexican General Mier y Teran warned of the growing American influence in East Texas. He recommended: increasing trade between TX and Mexico.
G.T.T Gone to Texas. Anglo Colonization of Texas
 G.T.T Gone to Texas Anglo Colonization of Texas Vocabulary Terms Anglo American a person whose ancestors moved from Europe and live in the U.S. Empresario An agent who makes all arrangements to bring settlers
G.T.T Gone to Texas Anglo Colonization of Texas Vocabulary Terms Anglo American a person whose ancestors moved from Europe and live in the U.S. Empresario An agent who makes all arrangements to bring settlers
Issues Faced By the Republic of Texas
 Grade 7, Unit: 06 Lesson: 04 Issues Faced By the Republic of Texas 1836-1845 Grade 7 Unit 6, Lesson 4 President Houston 1836-1838, 1841-1844 Frontier bold and popular First president of Texas Limited government
Grade 7, Unit: 06 Lesson: 04 Issues Faced By the Republic of Texas 1836-1845 Grade 7 Unit 6, Lesson 4 President Houston 1836-1838, 1841-1844 Frontier bold and popular First president of Texas Limited government
Social Studies Grade 7
 FORMATIVE MINI ASSESSMENTS Second Grading Period 2010-11 December 7-10 STUDENT NAME DATE PERIOD Social Studies Grade 7 Use your knowledge of social studies to answer the following questions. Event Resolutions
FORMATIVE MINI ASSESSMENTS Second Grading Period 2010-11 December 7-10 STUDENT NAME DATE PERIOD Social Studies Grade 7 Use your knowledge of social studies to answer the following questions. Event Resolutions
Chapter 8- Empresarios and Colonization
 Chapter 8- Empresarios and Colonization Empresario *In 1789 George Morgan became the first empresario for the Spanish government as he brought U.S. settlers into New Madrid, Missouri. His example would
Chapter 8- Empresarios and Colonization Empresario *In 1789 George Morgan became the first empresario for the Spanish government as he brought U.S. settlers into New Madrid, Missouri. His example would
2. Anglo Americans were the most supportive of Texas independence.
 Republic of Texas and Statehood Study Guide Houston focused on ensuring peace especially with Native Americans A tariff a tax on imported goods to encourage the purchase of the nation made goods. Continued
Republic of Texas and Statehood Study Guide Houston focused on ensuring peace especially with Native Americans A tariff a tax on imported goods to encourage the purchase of the nation made goods. Continued
7th Grade Texas Middle School Social Studies - Completely TEKS Aligned
 7th Grade Middle School Social Studies - Completely TEKS Aligned Collection Part Experience Objectives Geography of the Mountains and Basins Describe how the Mountains and Basins region differs from the
7th Grade Middle School Social Studies - Completely TEKS Aligned Collection Part Experience Objectives Geography of the Mountains and Basins Describe how the Mountains and Basins region differs from the
Texas Independence
 Texas Independence Introduction WARM UP: Some Canadians are angry that the state of Maine, prominently located between Quebec and New Brunswick, is part of the United States, and should be given up to
Texas Independence Introduction WARM UP: Some Canadians are angry that the state of Maine, prominently located between Quebec and New Brunswick, is part of the United States, and should be given up to
Texas Wins Independence. Chapter 13 Section 2 Pages
 Texas Wins Independence Chapter 13 Section 2 Pages 351-355 355 I. Americans in Mexican Texas A. Since the early 1800s the Spanish colony called Texas was longed after by many Americans for its rich farming
Texas Wins Independence Chapter 13 Section 2 Pages 351-355 355 I. Americans in Mexican Texas A. Since the early 1800s the Spanish colony called Texas was longed after by many Americans for its rich farming
Welcome to 7 th Grade Texas History!
 Welcome to 7 th Grade Texas History! Natural Texas and People Age of Contact Spanish Colonial The Battle of San Jacinto & Texas Independence Mexican National 10/16/17 Revolution and Republic Early Statehood
Welcome to 7 th Grade Texas History! Natural Texas and People Age of Contact Spanish Colonial The Battle of San Jacinto & Texas Independence Mexican National 10/16/17 Revolution and Republic Early Statehood
Why Texas Wanted Independence from Mexico
 Why Texas Wanted Independence from Mexico By Christopher Minster, ThoughtCo.com on 10.11.17 Word Count 1,559 Level MAX The Battle of San Jacinto, which saw the capture of Mexican President Santa Anna,
Why Texas Wanted Independence from Mexico By Christopher Minster, ThoughtCo.com on 10.11.17 Word Count 1,559 Level MAX The Battle of San Jacinto, which saw the capture of Mexican President Santa Anna,
Texas and the Mexican War PowerPoint Notes
 Name: _ Date: Texas Texas and the Mexican War PowerPoint Notes 1. 1821 The first settlers from the arrive from looking for. 2. At this time, Texas was a part of. 3. Within ten years, there were more in
Name: _ Date: Texas Texas and the Mexican War PowerPoint Notes 1. 1821 The first settlers from the arrive from looking for. 2. At this time, Texas was a part of. 3. Within ten years, there were more in
Florida Notes. had colonized Florida in the late 1500 s By the 1800 s the population of Florida was diverse with and
 Florida Notes Florida had colonized Florida in the late 1500 s By the 1800 s the population of Florida was diverse with and Attempt at Diplomacy Jefferson sent in 1804 to Spain to attempt to buy Florida
Florida Notes Florida had colonized Florida in the late 1500 s By the 1800 s the population of Florida was diverse with and Attempt at Diplomacy Jefferson sent in 1804 to Spain to attempt to buy Florida
Level 2. Manifest Destiny and the Acquisition of Land
 Level 2 Manifest Destiny and the Acquisition of Land Vocabulary Sectionalism: a loyalty to a section of the country instead of the nation itself Diplomats: a person appointed by a government to conduct
Level 2 Manifest Destiny and the Acquisition of Land Vocabulary Sectionalism: a loyalty to a section of the country instead of the nation itself Diplomats: a person appointed by a government to conduct
Texas Independence. April 20, 2012
 Texas Independence April 20, 2012 DO NOW 1. Why would people move to Texas? (According to the quote and graph?) 2. Why might people choose to go to Texas instead of Oregon? Guided Notes Native Americans
Texas Independence April 20, 2012 DO NOW 1. Why would people move to Texas? (According to the quote and graph?) 2. Why might people choose to go to Texas instead of Oregon? Guided Notes Native Americans
Natural Texas and People. Age of Contact. Spanish Colonial. Mexican National. Revolution and Republic. Early Statehood
 Slide 1 Welcome to 7 th Grade Texas History! Natural Texas and People Age of Contact Spanish Colonial Mexican National Revolution and Republic Early Statehood Texas in the Civil War and Reconstruction
Slide 1 Welcome to 7 th Grade Texas History! Natural Texas and People Age of Contact Spanish Colonial Mexican National Revolution and Republic Early Statehood Texas in the Civil War and Reconstruction
Main idea: Americans moved west, energized by their belief in the rightful expansion of the United States from the Atlantic to the Pacific.
 VUS.6.b: Expansion Objectives p. 002 VUS.6The student will demonstrate knowledge of the major events from the last decade of the eighteenth century through the first half of the nineteenth century by b)
VUS.6.b: Expansion Objectives p. 002 VUS.6The student will demonstrate knowledge of the major events from the last decade of the eighteenth century through the first half of the nineteenth century by b)
VUS.6.b: Expansion Filled In
 Name: Date: Period: VUS6b: Expansion Filled In Notes VUS6b: Expansion 1 Objectives about Expansion and the Coming of the Civil War VUS6 VUS7 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the major events from
Name: Date: Period: VUS6b: Expansion Filled In Notes VUS6b: Expansion 1 Objectives about Expansion and the Coming of the Civil War VUS6 VUS7 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the major events from
Chapter 12, Section 2 Independence for Texas
 Chapter 12, Section 2 Independence for Texas (pages 362-368) Setting a Purpose for Reading Think about these questions as you read: Why did problems arise between the Mexican government and the American
Chapter 12, Section 2 Independence for Texas (pages 362-368) Setting a Purpose for Reading Think about these questions as you read: Why did problems arise between the Mexican government and the American
Texas. Remember the Alamo
 Texas Remember the Alamo Americans in Texas Stephen Austin Moses Austin Made agreement with Spanish that American s could move there Americans Promised to become Mexican Citizens and Catholics Stephen
Texas Remember the Alamo Americans in Texas Stephen Austin Moses Austin Made agreement with Spanish that American s could move there Americans Promised to become Mexican Citizens and Catholics Stephen
Name Period Test Date-December 13. Second Nine Weeks DCA-Review
 Name Period Test Date-December 13 Chapter 9-The Road to Revolution Second Nine Weeks DCA-Review 1. Which era to the following belong? Chapter 9 Fredonian Rebellion Turtle Bayou Resolutions Constitution
Name Period Test Date-December 13 Chapter 9-The Road to Revolution Second Nine Weeks DCA-Review 1. Which era to the following belong? Chapter 9 Fredonian Rebellion Turtle Bayou Resolutions Constitution
Mexico s Independence Mexico declared its independence from Spain on September 16, 1810 The Mexican war for independence then lasted from
 Mexico s Independence Mexico declared its independence from Spain on September 16, 1810 The Mexican war for independence then lasted from 1810-1821. Texas was the north-east territory of Mexico. Few people
Mexico s Independence Mexico declared its independence from Spain on September 16, 1810 The Mexican war for independence then lasted from 1810-1821. Texas was the north-east territory of Mexico. Few people
UNIT 5, PART 3. Expansion and Reform ( )
 UNIT 5, PART 3 Expansion and Reform (1801 1850) WHIG PARTY 1) New political party formed in 1834 2) Organized to oppose Pres. Andrew Jackson s Democratic Party policies 3) Was formed by members of the
UNIT 5, PART 3 Expansion and Reform (1801 1850) WHIG PARTY 1) New political party formed in 1834 2) Organized to oppose Pres. Andrew Jackson s Democratic Party policies 3) Was formed by members of the
THE TEXAS CONSTITUTION PART I
 THE TEXAS CONSTITUTION PART I Half the ballot items are ridiculous because they deal with doing away with a constable s position in Erath County or somewhere and the other half no one can understand because
THE TEXAS CONSTITUTION PART I Half the ballot items are ridiculous because they deal with doing away with a constable s position in Erath County or somewhere and the other half no one can understand because
Traveling in Texas By Clint Williams
 Traveling in Texas 1700-1870 By Clint Williams I sent that Ancestry site some information on My Family Tree They sent me back a pack of seeds and suggested that I just start over Mary Maverick quote December
Traveling in Texas 1700-1870 By Clint Williams I sent that Ancestry site some information on My Family Tree They sent me back a pack of seeds and suggested that I just start over Mary Maverick quote December
Level 1. Manifest Destiny and the Addition of Land
 Level 1 Manifest Destiny and the Addition of Land Vocabulary Sectionalism: a loyalty to a section of the country instead of the nation itself Diplomats: a person appointed by a government to conduct negotiations
Level 1 Manifest Destiny and the Addition of Land Vocabulary Sectionalism: a loyalty to a section of the country instead of the nation itself Diplomats: a person appointed by a government to conduct negotiations
16.1 The Mexican War
 16.1 The Mexican War Fighting Breaks Out The border conflict arose from tensions between Mexico and the United States after the annexation of Texas and the signing of the Texas Admission Act on December
16.1 The Mexican War Fighting Breaks Out The border conflict arose from tensions between Mexico and the United States after the annexation of Texas and the signing of the Texas Admission Act on December
Educational Packet :Power-Hewetson Irish Colonists as Settlers
 Enduring Understanding: The Irish immigrants who settled in Coahuila y Texas exemplify the Mexican government s empresario system in contrast to the popular Texas myth of Anglo-American settlement of Texas.
Enduring Understanding: The Irish immigrants who settled in Coahuila y Texas exemplify the Mexican government s empresario system in contrast to the popular Texas myth of Anglo-American settlement of Texas.
Write the Following? s in your Journal then re-read the last paragraph on p. 167
 Important Info: We will be having an Open Notes, Summative Assessment next class: B-Day 12/5, A-Day 12/6 Stack your Come to MX-TX Ad on your desk or if it is not complete, your Character Card Write the
Important Info: We will be having an Open Notes, Summative Assessment next class: B-Day 12/5, A-Day 12/6 Stack your Come to MX-TX Ad on your desk or if it is not complete, your Character Card Write the
MANIFEST DESTINY WESTWARD EXPANSION
 MANIFEST DESTINY WESTWARD EXPANSION DONE IN STAGES Up to 1776 East Coast Colonies After 1783 E. of Mississippi R. Treaty of Paris (HL) After 1787 G.Lakes & Ohio R. Valley Ordinance of 1787 (HL) After 1803
MANIFEST DESTINY WESTWARD EXPANSION DONE IN STAGES Up to 1776 East Coast Colonies After 1783 E. of Mississippi R. Treaty of Paris (HL) After 1787 G.Lakes & Ohio R. Valley Ordinance of 1787 (HL) After 1803
Name: Date: Period: VUS.6.b: Expansion. Notes VUS.6.b: Expansion 1
 Name: Date: Period: VUS6b: Expansion Notes VUS6b: Expansion 1 Objectives about Expansion and the Coming of the Civil War VUS6 VUS7 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the major events from the last
Name: Date: Period: VUS6b: Expansion Notes VUS6b: Expansion 1 Objectives about Expansion and the Coming of the Civil War VUS6 VUS7 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the major events from the last
MANIFEST DESTINY, THE OREGON TRAIL, AND THE MEXICAN AMERICAN WAR
 What do you see? MANIFEST DESTINY, THE OREGON TRAIL, AND THE MEXICAN AMERICAN WAR Manifest Destiny Manifest Destiny was the belief that it was the destiny of the U.S. to expand its territory over the whole
What do you see? MANIFEST DESTINY, THE OREGON TRAIL, AND THE MEXICAN AMERICAN WAR Manifest Destiny Manifest Destiny was the belief that it was the destiny of the U.S. to expand its territory over the whole
CONSTITUTIONAL RIGHTS FOUNDATION Bill of Rights in Action Winter 2004 (20:1) Conflict of Cultures
 CONSTITUTIONAL RIGHTS FOUNDATION Bill of Rights in Action Winter 2004 (20:1) Conflict of Cultures BRIA 20:1 Home President Polk and the Taking of the West Muslim Conquests in Europe The Rise of Islamist
CONSTITUTIONAL RIGHTS FOUNDATION Bill of Rights in Action Winter 2004 (20:1) Conflict of Cultures BRIA 20:1 Home President Polk and the Taking of the West Muslim Conquests in Europe The Rise of Islamist
US History. Jefferson Becomes President. The Big Idea. Main Ideas. Thomas Jefferson s election began a new era in American government.
 Jefferson Becomes President The Big Idea Thomas Jefferson s election began a new era in American government. Main Ideas The election of 1800 marked the first peaceful transition in power from one political
Jefferson Becomes President The Big Idea Thomas Jefferson s election began a new era in American government. Main Ideas The election of 1800 marked the first peaceful transition in power from one political
Documents of lexas History
 Documents of lexas History SECOND EDITION edited by Ernest Wallace David M. Vigness & George B. Ward Texas State Historical Association Austin, Texas 2002 of Contents 1. The First Europeans in Texas, 1528-1536...
Documents of lexas History SECOND EDITION edited by Ernest Wallace David M. Vigness & George B. Ward Texas State Historical Association Austin, Texas 2002 of Contents 1. The First Europeans in Texas, 1528-1536...
Washington, Jefferson, Madison, Monroe, Jackson, and Polk Presidencies
 Washington, Jefferson, Madison, Monroe, Jackson, and Polk Presidencies 1. George Washington (1789-1797) - Created a cabinet of advisors 1. Secretary of War - Henry Knox 2. Secretary of the Treasury - Alexander
Washington, Jefferson, Madison, Monroe, Jackson, and Polk Presidencies 1. George Washington (1789-1797) - Created a cabinet of advisors 1. Secretary of War - Henry Knox 2. Secretary of the Treasury - Alexander
Anahuac, June 1832: An Episode in Mexico s Federalist Wars By: Dr. Bruce Winders, Alamo Historian & Curator
 Anahuac, June 1832: An Episode in Mexico s Federalist Wars By: Dr. Bruce Winders, Alamo Historian & Curator The traditional story of the 1832 disturbance at Anahuac revolves around two personalities: Juan
Anahuac, June 1832: An Episode in Mexico s Federalist Wars By: Dr. Bruce Winders, Alamo Historian & Curator The traditional story of the 1832 disturbance at Anahuac revolves around two personalities: Juan
Lecture: Going West. Learning Target 1: I can describe why people wanted to move west.
 Lecture: Going West Learning Target 1: I can describe why people wanted to move west. Learning Target 2: I can describe the two conflicts with Mexico. I-Expansion to the Pacific A-Manifest Destiny: Belief
Lecture: Going West Learning Target 1: I can describe why people wanted to move west. Learning Target 2: I can describe the two conflicts with Mexico. I-Expansion to the Pacific A-Manifest Destiny: Belief
How a former Eutaw Ranger helped Shape the Boundaries of the State of Texas. By Clinton F. Cross (Great-grandson of James F. Cross, a Eutaw Ranger)
 How a former Eutaw Ranger helped Shape the Boundaries of the State of Texas By Clinton F. Cross (Great-grandson of James F. Cross, a Eutaw Ranger) When the Republic of Texas obtained its independence from
How a former Eutaw Ranger helped Shape the Boundaries of the State of Texas By Clinton F. Cross (Great-grandson of James F. Cross, a Eutaw Ranger) When the Republic of Texas obtained its independence from
Close Read: Texas Annexation. What were the arguments for and against the annexation of Texas?
 Close Read: Texas Annexation CR Objective What were the arguments for and against the annexation of Texas? Directions: Read the timeline below. Analyze the content of the timeline by choosing the best
Close Read: Texas Annexation CR Objective What were the arguments for and against the annexation of Texas? Directions: Read the timeline below. Analyze the content of the timeline by choosing the best
1st Nine Weeks 2nd Nine Weeks 3rd Nine Weeks 4th Nine Weeks. Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit 7 Unit 8 Unit 9
 YEAR AT A GLANCE SUBJECT 7TH GRADE TEXAS HISTORY GRADE(S) 7TH UNIT(S) 9 Program Transfer Goals - Students will independently use their learning to Evaluate information and issues in order to critically
YEAR AT A GLANCE SUBJECT 7TH GRADE TEXAS HISTORY GRADE(S) 7TH UNIT(S) 9 Program Transfer Goals - Students will independently use their learning to Evaluate information and issues in order to critically
Woo hoo! We won the Mexican War!
 Woo hoo! We won the Mexican War! After the capture of Mexico City, Mexican officials had few options. Mexican officials met with U.S. diplomat Nicholas Trist, near Mexico City, at the town of Guadelupe-Hidago.
Woo hoo! We won the Mexican War! After the capture of Mexico City, Mexican officials had few options. Mexican officials met with U.S. diplomat Nicholas Trist, near Mexico City, at the town of Guadelupe-Hidago.
The Confederation Era
 1 The Confederation Era MAIN IDEA The Articles of Confederation were too weak to govern the nation after the war ended. WHY IT MATTERS NOW The weakness of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing
1 The Confederation Era MAIN IDEA The Articles of Confederation were too weak to govern the nation after the war ended. WHY IT MATTERS NOW The weakness of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing
Vertical Alignment Document. Social Studies Grade 4, Grade
 Vertical Alignment Document Social Studies Grade 4, Grade 7 2012 2013 TEXAS HISTORY GRADES 4 AND 7 113.10. Implementation of Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Social Studies, Elementary, Beginning
Vertical Alignment Document Social Studies Grade 4, Grade 7 2012 2013 TEXAS HISTORY GRADES 4 AND 7 113.10. Implementation of Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Social Studies, Elementary, Beginning
1. Chapter Eight 2. Columbus discovered America in Jefferson wrote the Declaration of Independence in Washington became President
 1. Chapter Eight 2. Columbus discovered America in 1492. 3. Jefferson wrote the Declaration of Independence in 1776. 4. Washington became President and our US Constitution went into effect in 1789. 5.
1. Chapter Eight 2. Columbus discovered America in 1492. 3. Jefferson wrote the Declaration of Independence in 1776. 4. Washington became President and our US Constitution went into effect in 1789. 5.
TEKS Clarification Document. Social Studies Grade
 TEKS Clarification Document Social Studies Grade 7 2012 2013 113.17. Implementation of Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Social Studies, Middle School, Beginning with School Year 2011-2012. Source:
TEKS Clarification Document Social Studies Grade 7 2012 2013 113.17. Implementation of Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Social Studies, Middle School, Beginning with School Year 2011-2012. Source:
The Alamo and the Making of Texas
 The Alamo and the Making of Texas Don Holder, LTG, US Army (re4red) 2015 Diamond6 Leadership and Strategy, LLC Historical Overview Purpose: Consider leadership through three presentations focused on the
The Alamo and the Making of Texas Don Holder, LTG, US Army (re4red) 2015 Diamond6 Leadership and Strategy, LLC Historical Overview Purpose: Consider leadership through three presentations focused on the
The United States Expands West. 1820s 1860s
 The United States Expands West 1820s 1860s Georgia Standards SSUSH8 The student will explain the relationship between growing northsouth divisions and westward expansion. a. Explain how slavery became
The United States Expands West 1820s 1860s Georgia Standards SSUSH8 The student will explain the relationship between growing northsouth divisions and westward expansion. a. Explain how slavery became
MARKING PERIOD 1. Shamokin Area 7 th Grade American History I Common Core I. UNIT 1: THREE WORLDS MEET. Assessments Formative/Performan ce
 Shamokin Area 7 th Grade American History I Common Core Marking Period Content Targets Common Core Standards Objectives Assessments Formative/Performan ce MARKING PERIOD 1 I. UNIT 1: THREE WORLDS MEET
Shamokin Area 7 th Grade American History I Common Core Marking Period Content Targets Common Core Standards Objectives Assessments Formative/Performan ce MARKING PERIOD 1 I. UNIT 1: THREE WORLDS MEET
TEKS Clarification. Social Studies. Grade page 1 of 1. Print Date 08/14/2014 Printed By Joe Nicks, KAUFMAN ISD
 TEKS Clarification Social Studies Grade 7 2014-2015 page 1 of 1 TEKS Clarification Social Studies Grade 7 2014-2015 GRADE 7 113.17. Implementation of Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Social Studies,
TEKS Clarification Social Studies Grade 7 2014-2015 page 1 of 1 TEKS Clarification Social Studies Grade 7 2014-2015 GRADE 7 113.17. Implementation of Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills for Social Studies,
Texas, Oregon and the War with Mexico
 Texas, Oregon and the War with Mexico Texas Settlement Revolt and Independence General Antonio Lopez de Santa Anna The Alamo Annexation Jackson and Van Buren Tyler Maine Border dispute between rival lumber
Texas, Oregon and the War with Mexico Texas Settlement Revolt and Independence General Antonio Lopez de Santa Anna The Alamo Annexation Jackson and Van Buren Tyler Maine Border dispute between rival lumber
Jefferson to Jackson Study Guide
 1. What is the significance of 36 30? a. It would grant each state north of this line the right to slavery and make slavery to the south illegal. b. It would grant each state south of this line the right
1. What is the significance of 36 30? a. It would grant each state north of this line the right to slavery and make slavery to the south illegal. b. It would grant each state south of this line the right
Grade 4 Social Studies
 Grade 4 Social Studies Unit 5 Mexico Rules Texas Title 3 rd Six Weeks 25 Days Suggested Time Frame Big Ideas/Enduring Understandings Texas experienced change in government style when Mexico took Texas
Grade 4 Social Studies Unit 5 Mexico Rules Texas Title 3 rd Six Weeks 25 Days Suggested Time Frame Big Ideas/Enduring Understandings Texas experienced change in government style when Mexico took Texas
War of Independence: Chapter 2, Section 4
 War of Independence: Chapter 2, Section 4 Political ideas and major events shape how people form governments. The United States declared independence in 1776, but it took several years of war and turmoil
War of Independence: Chapter 2, Section 4 Political ideas and major events shape how people form governments. The United States declared independence in 1776, but it took several years of war and turmoil
From Texas to Immigration: Transformations in America from Chapters 13 AP US History
 + From Texas to Immigration: Transformations in America from 1790-1860 Chapters 13 AP US History + Learning Objectives: Students will be able to Analyze how ideas about national identity changed in response
+ From Texas to Immigration: Transformations in America from 1790-1860 Chapters 13 AP US History + Learning Objectives: Students will be able to Analyze how ideas about national identity changed in response
Agenda for Monday/Tuesday. CNN 10 Westward Expansion Notes Manifest Destiny Map Assignment
 Agenda for Monday/Tuesday CNN 10 Westward Expansion Notes Manifest Destiny Map Assignment Learning Objectives I can describe the treaties such as the Adams-Onis treaty and/or the Treaty of Guadelupe-Hidalgo
Agenda for Monday/Tuesday CNN 10 Westward Expansion Notes Manifest Destiny Map Assignment Learning Objectives I can describe the treaties such as the Adams-Onis treaty and/or the Treaty of Guadelupe-Hidalgo
The United States Lesson 2: History of the United States
 Lesson 2: History of the United States ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is history important? Terms to Know indigenous living or occurring naturally in a particular place nomadic describes a way of life in which
Lesson 2: History of the United States ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is history important? Terms to Know indigenous living or occurring naturally in a particular place nomadic describes a way of life in which
Texas: Prelude to Civil War Teresa Goodin. Contextual Essay: Essential Question:
 Texas: Prelude to Civil War Teresa Goodin Contextual Essay Essential Question: How did the settling and annexation of Texas impact American foreign relations, politics and the growing sectionalism between
Texas: Prelude to Civil War Teresa Goodin Contextual Essay Essential Question: How did the settling and annexation of Texas impact American foreign relations, politics and the growing sectionalism between
The Americans (Survey)
 The Americans (Survey) Chapter 7: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OVERVIEW American leaders devise a farsighted policy of improvements as North, South, and West develop
The Americans (Survey) Chapter 7: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OVERVIEW American leaders devise a farsighted policy of improvements as North, South, and West develop
Influences on the Causes of the Civil War
 RM 44 Influences on the Causes of the Civil War You have been assigned one of the following roles to perform. As you read the assigned text, concentrate on your role and identify areas that relate to it.
RM 44 Influences on the Causes of the Civil War You have been assigned one of the following roles to perform. As you read the assigned text, concentrate on your role and identify areas that relate to it.
Chapter 9 A New National Identity The Big Idea The United States peacefully settled disputes with foreign powers. Holt McDougal,
 Chapter 9 A New National Identity The Big Idea The United States peacefully settled disputes with foreign powers. MAIN IDEA 1: THE UNITED STATES AND GREAT BRITAIN SETTLED THEIR DISPUTES OVER BOUNDARIES
Chapter 9 A New National Identity The Big Idea The United States peacefully settled disputes with foreign powers. MAIN IDEA 1: THE UNITED STATES AND GREAT BRITAIN SETTLED THEIR DISPUTES OVER BOUNDARIES
Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation
 Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation Explain how the states new constitutions reflected republican ideals. Describe the structure and powers of the national government under the Articles of Confederation.
Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation Explain how the states new constitutions reflected republican ideals. Describe the structure and powers of the national government under the Articles of Confederation.
Cause and Effect The Mexican-American War. Objective : Determining the causes of the Mexican American War
 Cause and Effect The Mexican-American War Objective : Determining the causes of the Mexican American War U.S.-Mexico Disputes The Annexation of Texas by the U.S. angered the Mexican Government. Mexico
Cause and Effect The Mexican-American War Objective : Determining the causes of the Mexican American War U.S.-Mexico Disputes The Annexation of Texas by the U.S. angered the Mexican Government. Mexico
Chapter 12 Territorial And Economic Expansion,
 Chapter 12 Territorial And Economic Expansion, 1830-1860 Manifest Destiny was the belief the U.S. had a God given mission to spread its civilization by conquest to the entire western hemisphere no matter
Chapter 12 Territorial And Economic Expansion, 1830-1860 Manifest Destiny was the belief the U.S. had a God given mission to spread its civilization by conquest to the entire western hemisphere no matter
4: TELESCOPING THE TIMES
 The Americans (Survey) Chapter 4: TELESCOPING THE TIMES The War for Independence CHAPTER OVERVIEW The colonists clashes with the British government lead them to declare independence. With French aid, they
The Americans (Survey) Chapter 4: TELESCOPING THE TIMES The War for Independence CHAPTER OVERVIEW The colonists clashes with the British government lead them to declare independence. With French aid, they
EOC Test Preparation: Expansion and the Antebellum Period
 EOC Test Preparation: Expansion and the Antebellum Period Territorial Expansion Northwest Territory, Northwest Ordinance Guidelines on how new states could be admitted Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Michigan,
EOC Test Preparation: Expansion and the Antebellum Period Territorial Expansion Northwest Territory, Northwest Ordinance Guidelines on how new states could be admitted Ohio, Indiana, Illinois, Michigan,
Antebellum Politics. Lagniappe. Section2
 Section2 Antebellum Politics Top: Jacques Villere was a Creole who was elected as the second governor of Louisiana. Above: Anglo American Thomas Bolling Robertson was the third governor of the state. As
Section2 Antebellum Politics Top: Jacques Villere was a Creole who was elected as the second governor of Louisiana. Above: Anglo American Thomas Bolling Robertson was the third governor of the state. As
Creating the Constitution
 Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
The term Era of Good Feelings refers to the period of American history when there seemed to be political harmony during the Monroe administration.
 The term Era of Good Feelings refers to the period of American history when there seemed to be political harmony during the Monroe administration. 1 2 In 1816, James Monroe became president, inaugurating
The term Era of Good Feelings refers to the period of American history when there seemed to be political harmony during the Monroe administration. 1 2 In 1816, James Monroe became president, inaugurating
Chapter 4. The American Revolution
 Chapter 4 The American Revolution 1 Raising Taxes Sugar Act- The first tax passed specifically to raise money in the colonies, rather than regulate trade. To crack down on smugglers Help pay for French
Chapter 4 The American Revolution 1 Raising Taxes Sugar Act- The first tax passed specifically to raise money in the colonies, rather than regulate trade. To crack down on smugglers Help pay for French
Great Emancipator or White Supremacist?
 1861-1865 Great Emancipator or White Supremacist? I have no purpose to introduce political and social equality between the white and black races. There is a physical difference between the two, which,
1861-1865 Great Emancipator or White Supremacist? I have no purpose to introduce political and social equality between the white and black races. There is a physical difference between the two, which,
Alamo. Daniel Boone. Davy Crockett. (noun) (noun) (noun)
 WORDS IN CONTEXT DAY 1 (Page 1 of 4) Alamo The Alamo is a former fort in Texas that was the site of a famous battle on March 6, 1836. The battle of the Alamo was fought between Mexican forces and Americans
WORDS IN CONTEXT DAY 1 (Page 1 of 4) Alamo The Alamo is a former fort in Texas that was the site of a famous battle on March 6, 1836. The battle of the Alamo was fought between Mexican forces and Americans
GACE Study Guide Laura Brittain March 6, 2011
 GACE Study Guide Laura Brittain March 6, 2011 GPS Standard: S4H6:The student will explain westward expansion of America between 1801 and 1861. a. Describe territorial expansion with emphasis on the Louisiana
GACE Study Guide Laura Brittain March 6, 2011 GPS Standard: S4H6:The student will explain westward expansion of America between 1801 and 1861. a. Describe territorial expansion with emphasis on the Louisiana
Key Concept 4.3, I: The US needed a foreign policy and an expansion policy
 Key Concept 4.3, I: The US needed a foreign policy and an expansion policy Key Concept 4.3: U.S. interest in increasing foreign trade, expanding its national borders, and isolating itself from European
Key Concept 4.3, I: The US needed a foreign policy and an expansion policy Key Concept 4.3: U.S. interest in increasing foreign trade, expanding its national borders, and isolating itself from European
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #107 Aims: SWBAT identify the causes of the Mexican-American War SWBAT identify two different perspectives on the Mexican-American
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #107 Aims: SWBAT identify the causes of the Mexican-American War SWBAT identify two different perspectives on the Mexican-American
Chapter 11, Section 3 The Mexican-American War. Pages
 Chapter 11, Section 3 The Mexican-American War Pages 354-363 Mexican independence set the stage for conflict and change in the West and Southwest. At the same time, American settlers continued to move
Chapter 11, Section 3 The Mexican-American War Pages 354-363 Mexican independence set the stage for conflict and change in the West and Southwest. At the same time, American settlers continued to move
Grade 07 Social Studies Unit 07 Exemplar Lesson 02 : Texas and the Quest for Manifest Destiny
 Unit: 07 Lesson: 02 Suggested Duration: 3 days Grade 07 Unit 07 Exemplar Lesson 02 : Texas and the Quest for Manifest Destiny This lesson is one approach to teaching the State Standards associated with
Unit: 07 Lesson: 02 Suggested Duration: 3 days Grade 07 Unit 07 Exemplar Lesson 02 : Texas and the Quest for Manifest Destiny This lesson is one approach to teaching the State Standards associated with
Toussaint L Ouverture, Simon Bolivar, & Miguel Hidalgo
 Toussaint L Ouverture, Simon Bolivar, & Miguel Hidalgo Spain conquered most of the lands in the Americas (while Portugal conquered Brazil0. It divided its empire into provinces. The two most important
Toussaint L Ouverture, Simon Bolivar, & Miguel Hidalgo Spain conquered most of the lands in the Americas (while Portugal conquered Brazil0. It divided its empire into provinces. The two most important
the election of abraham lincoln
 Scott pursed his freedom, with the case eventually reaching the United States Supreme Court. It became a political question on whether or not slavery should be legal. Abolitionists and those who supported
Scott pursed his freedom, with the case eventually reaching the United States Supreme Court. It became a political question on whether or not slavery should be legal. Abolitionists and those who supported
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Articles of Confederation. Essential Question:
 Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
Study Guide: Sunshine State Standards
 Chapter 11, Section 1 (continued) 1. How did John Quincy Adams win the election of 1824? The Election of 1828 (pages 335 336) The Republican Party was divided. The Democratic-Republicans supported Jackson.
Chapter 11, Section 1 (continued) 1. How did John Quincy Adams win the election of 1824? The Election of 1828 (pages 335 336) The Republican Party was divided. The Democratic-Republicans supported Jackson.
Chapter 8 Exam. Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Multiple Choice
 Multiple Choice Chapter 8 Exam Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which statement about the election of 1824 is true? a. Most people did not think a military
Multiple Choice Chapter 8 Exam Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which statement about the election of 1824 is true? a. Most people did not think a military
Learning Goal 5: Students will be able to explain the events which led to the start of the American
 American Revolution Learning Goal 5: Students will be able to explain the events which led to the start of the American Revolution. - Tea Act (Boston Tea Party, British East India Company, Sons of Liberty,
American Revolution Learning Goal 5: Students will be able to explain the events which led to the start of the American Revolution. - Tea Act (Boston Tea Party, British East India Company, Sons of Liberty,
NAME DATE CLASS John Quincy Adams becomes president
 Lesson 1 Jacksonian Democracy ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the characteristics of a leader? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. What new ways of campaigning appeared during the elections of 1824 and 1828? 2. How did Andrew
Lesson 1 Jacksonian Democracy ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the characteristics of a leader? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. What new ways of campaigning appeared during the elections of 1824 and 1828? 2. How did Andrew
Name Class Date. Forging the New Republic Section 1
 Name Class Date Section 1 MAIN IDEA President Washington and other leaders tried to solve the new nation s economic problems. This led to the rise of political parties. Key Terms and People cabinet heads
Name Class Date Section 1 MAIN IDEA President Washington and other leaders tried to solve the new nation s economic problems. This led to the rise of political parties. Key Terms and People cabinet heads
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 2: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Revolution and the Early Republic CHAPTER OVERVIEW Colonists declare their independence and win a war to gain the right
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 2: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Revolution and the Early Republic CHAPTER OVERVIEW Colonists declare their independence and win a war to gain the right
netw rks Reading Essentials and Study Guide Growth and Division, Lesson 1 American Nationalism ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Reading HELPDESK
 and Study Guide Lesson 1 American Nationalism ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How did the nation s economy help shape its politics? How did the economic differences between the North and the South cause tension? Reading
and Study Guide Lesson 1 American Nationalism ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How did the nation s economy help shape its politics? How did the economic differences between the North and the South cause tension? Reading
HERE WAS BURIED THOMAS JEFFERSON AUTHOR OF THE DECLARATION OF AMERICAN INDEPENDENCE OF THE STATUTE OF VIRGINIA FOR RELIGIOUS FREEDOM AND FATHER OF
 HERE WAS BURIED THOMAS JEFFERSON AUTHOR OF THE DECLARATION OF AMERICAN INDEPENDENCE OF THE STATUTE OF VIRGINIA FOR RELIGIOUS FREEDOM AND FATHER OF THE UNIVERSITY OF VIRGINIA BORN APRIL 13, 1743 DIED JULY
HERE WAS BURIED THOMAS JEFFERSON AUTHOR OF THE DECLARATION OF AMERICAN INDEPENDENCE OF THE STATUTE OF VIRGINIA FOR RELIGIOUS FREEDOM AND FATHER OF THE UNIVERSITY OF VIRGINIA BORN APRIL 13, 1743 DIED JULY
Madison & Monroe. Presidencies
 James James Madison & Monroe Presidencies Where we are March 1797: President John Adams takes office. 1796-1800: XYZ Affair, Quasi-War with France, Alien & Sedition Acts, VA & KY Resolutions 1801-1804:
James James Madison & Monroe Presidencies Where we are March 1797: President John Adams takes office. 1796-1800: XYZ Affair, Quasi-War with France, Alien & Sedition Acts, VA & KY Resolutions 1801-1804:
Eighth Grade Social Studies United States History Course Outline
 Crossings Christian School Academic Guide Middle School Division Grades 5-8 Eighth Grade Social Studies Chapter : Early Exploration of the Americas How do new ideas change the way people live? Why do people
Crossings Christian School Academic Guide Middle School Division Grades 5-8 Eighth Grade Social Studies Chapter : Early Exploration of the Americas How do new ideas change the way people live? Why do people
Texas Revolutionary War. Chair Letter Introduction... 3
 Contents Chair Letter... 2 Introduction... 3 Background and Timeline to the Revolution... 4 Events that caused rising tension... 6 Social and cultural situation... 8 An Expansionist United States... 10
Contents Chair Letter... 2 Introduction... 3 Background and Timeline to the Revolution... 4 Events that caused rising tension... 6 Social and cultural situation... 8 An Expansionist United States... 10
America A series that focuses on unique wrinkles in our survey heritage.
 the fabric of Surveying America A series that focuses on unique wrinkles in our survey heritage. By John Stanley Coalter, LS Surveying Texas Background Note: While a small band of heavily-outnumbered patriots
the fabric of Surveying America A series that focuses on unique wrinkles in our survey heritage. By John Stanley Coalter, LS Surveying Texas Background Note: While a small band of heavily-outnumbered patriots
Expansion, Nationalism,& Sectionalism ( )
 Expansion, Nationalism,& Sectionalism (1800-1865) President Adams John Adams was Washington s VP Adams ran for election in 1796 and won He faced 2 difficult tasks: war from abroad & growing political party
Expansion, Nationalism,& Sectionalism (1800-1865) President Adams John Adams was Washington s VP Adams ran for election in 1796 and won He faced 2 difficult tasks: war from abroad & growing political party
