Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation
|
|
|
- Irene Johnston
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation Explain how the states new constitutions reflected republican ideals. Describe the structure and powers of the national government under the Articles of Confederation. Summarize the Congress s plan for the settlement and governance of western lands. List the main weaknesses of the Articles. 1
2 Articles of Confederation ( ): America s system of during most of the American Revolution & years after. Established a / friendship between the 13 free and states. Established only a or -making body (Congress) of government. Results: Congress asked for $ million from states and received less than $ million. The U.S. was deeply in. The U.S. could not fund an or. Under The Articles of Confederation: 1. National (Federal) Government Lacked the Power to : America owed & foreign nations from the American Revolution. To get ($) the federal government had to money from the states. 2. States Used Different : - Each used different money. Results: Money had a different in each state. Some states would accept other states money. 2
3 Trouble on Two Fronts The Confederation government did not have the power to deal with the country s financial problems. Problems continued with Britain and Spain over land and trade issues. By 1781 money printed during the Revolutionary War had fallen in value, or depreciated, and was almost worthless. Congress and the states printed paper money without the gold and silver to back it up. Neither had the power to tax the citizens. The Continental Congress owed other countries and many citizens a lot of money after the war. The government failed to enforce the Treaty of Paris of 1783 and make British troops leave the lands east of the Mississippi River. British troops still held forts in the Great Lakes Region. British merchants succeeded in preventing Americans from trading in the West Indies and other markets. Americans slowly began to realize that the United States government needed to be given more power. In order to prevent westward expansion, Spain blocked the lower Mississippi River to American shipping in This cut off the Americans trade. In 1786 Spain agreed with America on the border between Georgia and Spanish Florida. In return, Americans agreed to limit shipping on the Mississippi River. Leaders, including George Washington, were worried about the future of America. 3. States Controlled Interstate & Foreign (Trade): Interstate Commerce = trading with other Foreign Commerce = trading with other - States taxed and when traveling through their state with products/produce. - States made trade agreements/policies with foreign nations. Results: In many cases it was to ship products /produce to nations. Some merchants & farmers began goods across state borders. Why did the American economy fail after the American Revolution? 3
4 Thirteen Independent States ( Britain did not believe the American government was very strong or effective. It ignored the Treaty of Paris and kept soldiers at posts on the American frontier. In May 1776, the Americans were busy forming their own governments. Each state organized their government and adopted a constitution, or plan that explains how the government will operate. By 1780 Connecticut and Rhode Island were the only states that followed their colonial charters instead of creating new constitutions. Most states included provisions to prevent abuses of power. Most constitutions included provisions for two-house, or bicameral, legislatures. The legislatures, made up of elected representatives of the people, were the most powerful branch of government. Pennsylvania replaced the office of governor with an elected 12-member council. In order to vote, one had to be at least a 21 year old male and own property or pay taxes. Most states limited voting to white males, but a few permitted free black males to vote. There were disagreements as each state became self-governing. 1. How did the British ignore the Treaty of Paris? Give evidence Results: Foreign nations had to deal with 13 countries (states) to secure trade agreements with the U.S. New York and New Hampshire almost went to war over. 7 of the 13 states had land claims. refused to join the U.S. if Virginia and others did not (give up) there western land claims. 4. States Acted as Countries: - States drafted their own & agreements with foreign nations. - States argued over land claims and other land disputes. 4
5 Britain did not believe the American government was very strong or effective. It ignored the Treaty of Paris and kept soldiers at posts on the American frontier. In May 1776, the Americans were busy forming their own governments. Each state organized their government and adopted a constitution, or plan that explains how the government will operate. By 1780 Connecticut and Rhode Island were the only states that followed their colonial charters instead of creating new constitutions. Most states included provisions to prevent abuses of power. Most constitutions included provisions for two-house, or bicameral, legislatures. The legislatures, made up of elected representatives of the people, were the most powerful branch of government. Pennsylvania replaced the office of governor with an elected 12-member council. In order to vote, one had to be at least a 21 year old male and own property or pay taxes. Most states limited voting to white males, but a few permitted free black males to vote. There were disagreements as each state became self-governing. 5. Lacked Funds for & : - U.S. could not fund or maintain a standing army or navy. Results: refused to allow American farmers access to the River. The British army refused to troops from forts on American soil. Barbary attacked and seized American trade (ships) off the coast of Africa (Mediterranean Sea). 1. How did the British ignore the Treaty of Paris? Give evidence 2. Following the end of the American Revolution, what did 11 of the 13 colonies form for each of their states? 5
6 6. No Strong Executive (President): No one person to make important decisions during or help settle problems between states or other countries. Federal government could pass, but not them. 7. Each State Only Received 1 Vote: - Each state received only 1 vote regardless of their. - Laws had to pass with at least votes. Results: Very laws were passed. Americans were not represented. Results: If an emergency occurred the federal government could not respond. England & other European nations had to deal with each of the states individually. Example:, had the least amount of people, while had the largest amount of people. However, both states received the number of votes. III - Impacts of Articles of Confederation: 1. Rebellion (1786): - In an effort to pay off debts, Massachusetts raised. - Many farmers were not able to pay their taxes and state courts their farms. Results: Daniel Shays, a Massachusetts farmer and American Revolution war led an armed. More than 1,000 armed attacked and closed state houses for months. The Massachusetts broke up Shays Rebellion. 6
7 Shays Rebellion During the American Revolution, the states and the Continental Congress had borrowed large sums of money from wealthy merchants. After the war, the merchants demanded that they be repaid, but the national government under the Articles of Confederation had no power to raise money. The states had to repay their own debts, and the only way for them to raise the money was to tax their citizens heavily. Many farmers in the western part of Massachusetts had an especially hard time paying their bills at this time. The Massachusetts farmers, many of whom were war veterans who had never been paid, owed about one-third of their income for state taxes, and the Massachusetts legislature refused to issue paper money as other states had done. Those farmers who could not pay their taxes had their farms taken away by state courts. Court officials then auctioned off the farms and used the money from the sale to pay the taxes. Farmers who could not pay their personal debts were often put into prison. The farmers asked the Massachusetts legislature to lower taxes and let them pay taxes and other debts with farm produce. They begged the legislature to stop jailing people who could not pay their debts. Instead the legislature listened to merchants and bankers to whom the farmers owed money. It refused to pass laws to help the farmers. Because they could not get help through legal means, a group of farmers decided they had no choice but to rebel. Their leader was Daniel Shays, a former Revolutionary War captain. In the fall of 1786, Shays led armed farmers in marches outside county courthouses in Springfield, Northampton and other towns in western Massachusetts. The purpose was to keep the courts from meeting. If the courts did not meet, bankers and others to whom farmers owed money could not take away their farms. In January 1787, Shays men attacked a Springfield building where they government stored guns. Wealthy merchants from as far away as Baltimore, Maryland paid to raise a militia and the governor of Massachusetts sent the soldiers to fight the rebels. The soldiers shot and killed four men, and soon the rest of Shays followers fled. Several rebel leaders were caught. The men were brought to trial, found guilty, and sentenced to death. Later the court set them all free, including Shays. Shays Rebellion did not succeed. For many, the rebellion symbolized a fatal weakness of the national government under the Articles of Confederation. Because Congress had no power to raise money, it could not help the states pay off their war debts, which forced the states to tax their citizens heavily. Moreover, Congress could not raise a national army without unanimous consent of the states, so it was unable to act in time to assist Massachusetts. The realization of this weakness helped spur the events of the summer of 1787, when the Constitutional Convention that met in Philadelphia wrote a constitution that defined a stronger and more capable federal government. 7
8 8
9 Document A Excerpts of Letters Written by George Washington in Response to Shays Rebellion Source: The George Washington Papers at the Library of Congress, American Memory, Library of Congress. Washington, D.C. Accessed 8/5/14. ibin/query/r?ammem/m gw:@field(docid+@lit(g w290026)) : 9
10 Document B Excerpts of Letters Written by Thomas Jefferson in Response to Shays Rebellion Source: Jefferson, Thomas to William Smith, November 13, Library of Congress, Manuscript Division. Washington, D.C. Accessed 8/6/14. v/exhibits/jefferso n/105.html 10
11 Purpose for reading: Interpret specific words and phrases in the letters written by George Washington and the letters written by Thomas Jefferson to determine each author s point of view on the rebellion. 11
12 Purpose for reading: Interpret specific words and phrases in the letters written by George Washington and the letters written by Thomas Jefferson to determine each author s point of view on the rebellion. 12
13 Analysis: Compare and contrast Washington s and Jefferson s viewpoints on the rebellion. 13
14 Shay s Rebellion - Newspaper Rubric 10pts Newspaper header and setup - Introduce a topic or text clearly, state an opinion, and create an Organizational structure in which ideas are logically grouped to support the Writer s purpose. 10pts Washington- corroborate multiple primary sources to draw conclusions about the founding fathers views of Shays Rebellion. 10pts Jefferson- corroborate multiple primary sources to draw conclusions about the founding fathers views of Shays Rebellion. 20pts 2 quotes Use quotes to support that that although they had very different viewpoints, both leaders recognized that the government did need reform in order to govern more effectively. Quotes should be cited correctly 25pts Explanation of Shays Rebellion Includes in detail all 6 parts from the w s chart and may include quotes from the text 25pts Connection of Historical Significance or outcome - create the foundation of the American political system based on the U.S. Constitution and the Bill of Rights or the need to do away with the A of C and create a government with a strong central base. justify your opinion with evidence from your research about what the Founding Fathers had to say and what they believed. inform the people of what happened; formulate an opinion on whether or not Shays rebellion was good for the United States; 14 Assignment: You are a newspaper journalist for the Hampshire Gazette, and your boss just gave you the most important assignment of your career. You have been chosen to cover the story of the recent rebellion in Massachusetts. Your boss expects you to:
15 2. Ordinance (1787): - Divided the Northwest into separate territories for future. -Outlawed in the Northwest Territory. Provided a method to admit new into the. Results: New states needed at least, free settlers and a state. Eventually, free (non-slave) states,, Indiana, Illinois, Michigan, and Wisconsin were created from the Northwest Territory CRQ - New Land Policies As the population west of the Appalachian Mountains grew, settlers wanted to form states and join the union. The Articles had no provisions for adding new states. In 1784, the Western territory was divided into smaller, self-governing districts with the approval of Congress. The districts could petition, or apply for statehood when their population equaled that of the smallest state. A law, or ordinance, passed by Congress in 1785, resulted in the division of Western lands north of the Ohio River into townships. Land was sold for a minimum of a dollar an acre. Speculators, or people who hoped to make a profit from their investment, bought large areas of inexpensive land. The lands north of the Ohio River and east of the Mississippi River became the Northwest Territory under the Northwest Ordinance of This territory was then divided into three to five smaller territories. These territories were permitted to petition, or apply, for statehood when the population reached 60,000. The ordinance protected settlers rights, including freedom of religion and trial by jury. The law was the first in the United States to ban slavery and involuntary servitude. 1. Who are Speculators? 2. How could a territory become a state under the Northwest Ordinance? 15
16 3. The Articles of Confederation : After Shays Rebellion, leaders from several states called for a framework of government to be created. - The Articles of Confederation failed because the had too much power. - The Articles of Confederation failed because it lacked a strong / / government. - The Articles of Confederation failed because the document had many. Result: In 1787, the began to develop a new government for America. What is a republic? What were two powers the Confederation of Congress were given to handle CRQ -2 Forming a Republic The states agreed the government should be a republic, a form of government ruled by the people through their elected representatives. A committee drafted a constitution that was approved by the Second Continental Congress in November The plan was called the Articles of Confederation. The plan gave each state its freedom and independence. The central government, or Confederation of Congress, was given the power to handle relations with other countries, establish an army, borrow money, and issue currency or forms of money. The Confederation of Congress did not have the power to tax the states, force people to join the army, or regulate trade. Congress had to ask the state legislatures for money or troops. The states could choose whether or not they would contribute. Congressional committees took the place of a chief executive or president. The Confederation of Congress officially became the United States after all 13 states approved the Articles of Confederation on March 1, Each state had one vote. All states agreed to give up land claims west of the Appalachian Mountains. The Confederation won the war for independence and provided for new states in the West. However, the government, under the Articles of Confederation, was not strong enough to handle all of the problems it faced. Its authority was limited. Nine states had to vote in favor of any new laws. Any change to the Articles required the agreement of all 13 states. What authority did the Confederation of Congress lack that was given to the states instead? 16
17 Analysis: Compare and contrast Washington s and Jefferson s viewpoints on the rebellion. George Washington was extremely embarrassed that it appeared that Americans were unable to govern themselves well. He was unhappy with the lack of a strong central government and the weakness of the Articles of Confederation Both men believed that changes (reforms) were necessary in order to provide a more effective government. Thomas Jefferson believed that any rebellion was a good thing because it helped to protect the people s liberty and limit the power of the government. Rebellion didn t mean that a government was bad, just that it needed to be amended to work better. 17
11/30 What are some things we need now that we are our own Nation? List as many things as you can. Moves on the chart.
 11/30 What are some things we need now that we are our own Nation? List as many things as you can. Moves on the chart. 12/1 Predict some problems moving forward under one gov t: (Think back to some issues
11/30 What are some things we need now that we are our own Nation? List as many things as you can. Moves on the chart. 12/1 Predict some problems moving forward under one gov t: (Think back to some issues
SS7 Civics Ch 3.1: Early State Governments
 SS7 Civics Ch 3.1: Early State Governments I. State Constitutions A. Even before the Declaration of Independence was signed, American colonists thought about independence. Independence would mean an end
SS7 Civics Ch 3.1: Early State Governments I. State Constitutions A. Even before the Declaration of Independence was signed, American colonists thought about independence. Independence would mean an end
Colonies Become States
 Colonies Become States Colonies already had their own individual governments before the 1776 Declaration 11 of 13 colonies had State Constitutions Constitution a document that states rules under which
Colonies Become States Colonies already had their own individual governments before the 1776 Declaration 11 of 13 colonies had State Constitutions Constitution a document that states rules under which
The Confederation Era
 1 The Confederation Era MAIN IDEA The Articles of Confederation were too weak to govern the nation after the war ended. WHY IT MATTERS NOW The weakness of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing
1 The Confederation Era MAIN IDEA The Articles of Confederation were too weak to govern the nation after the war ended. WHY IT MATTERS NOW The weakness of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing
The Articles of Confederation: Chapter 3, Section 1
 The Articles of Confederation: Chapter 3, Section 1 Political ideas and major events shape how people form governments. When the American colonies broke their political ties with Great Britain, they faced
The Articles of Confederation: Chapter 3, Section 1 Political ideas and major events shape how people form governments. When the American colonies broke their political ties with Great Britain, they faced
How Shall We Govern Ourselves?
 How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
Indirect representation: when elected officials elect higher officials Interstate commerce: trade between states Legislature: a law making body of
 Level 2 Indirect representation: when elected officials elect higher officials Interstate commerce: trade between states Legislature: a law making body of government Tariff: a tax on imports Amendment:
Level 2 Indirect representation: when elected officials elect higher officials Interstate commerce: trade between states Legislature: a law making body of government Tariff: a tax on imports Amendment:
Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation
 Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A constitution is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government.
Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A constitution is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government.
Once a year, each state would select a delegation to send to the capital city.
 In November 1777, the Continental Congress adopted the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union. This was a plan for a loose union of the states under Congress. Once a year, each state would select
In November 1777, the Continental Congress adopted the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union. This was a plan for a loose union of the states under Congress. Once a year, each state would select
11 1 THE BIG QUESTION: WHO WILL BE IN CHARGE? SHIFTING BALANCE OF POWER: AN OVERVIEW
 11 1 THE BIG QUESTION: WHO WILL BE IN CHARGE? SHIFTING BALANCE OF POWER: AN OVERVIEW 152 11 2 ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION: 13 SOVEREIGN STATES sovereign supreme power; independent THE CONFEDERATION GOVERNMENT
11 1 THE BIG QUESTION: WHO WILL BE IN CHARGE? SHIFTING BALANCE OF POWER: AN OVERVIEW 152 11 2 ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION: 13 SOVEREIGN STATES sovereign supreme power; independent THE CONFEDERATION GOVERNMENT
Objectives: Students will be able to explain that the success and failures of the articles of confederation and be able to give some examples of each.
 Day 1 Objectives: Students will be able to explain that the success and failures of the articles of confederation and be able to give some examples of each. Procedure: Do Now: Why is it important to have
Day 1 Objectives: Students will be able to explain that the success and failures of the articles of confederation and be able to give some examples of each. Procedure: Do Now: Why is it important to have
Unit 7. Our First Government. Bellwork. Essential Questions (What I need to know):
 Unit 7 Our First Government Name Date Period Essential Questions (What I need to know): Date Bellwork Answer(s) 1. What is government? 2. How did the first United States government operate? 3. How did
Unit 7 Our First Government Name Date Period Essential Questions (What I need to know): Date Bellwork Answer(s) 1. What is government? 2. How did the first United States government operate? 3. How did
Chapter 25 Section 1. Section 1. Terms and People
 Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
Creating the Constitution
 Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
The Origins of the Constitution
 The Origins of the Constitution Before the colonies signed the Treaty of Paris ending the Revolutionary War in 1783, they ratified the Articles of Confederation in 1781, The Articles provided a weak union
The Origins of the Constitution Before the colonies signed the Treaty of Paris ending the Revolutionary War in 1783, they ratified the Articles of Confederation in 1781, The Articles provided a weak union
The First Government: How it Worked
 IQ S 1. Describe the role of government in securing freedom, opportunity, prosperity, and security (FOP S) for the people. 2. Without FOP S, can a government of the people be successful? 3. Is there a
IQ S 1. Describe the role of government in securing freedom, opportunity, prosperity, and security (FOP S) for the people. 2. Without FOP S, can a government of the people be successful? 3. Is there a
The Articles of Confederation
 The Articles of Confederation 1781-1789 The United States was the first nation in modern times to have a government designed and run according to democratic principles. During the Revolutionary War the
The Articles of Confederation 1781-1789 The United States was the first nation in modern times to have a government designed and run according to democratic principles. During the Revolutionary War the
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #68 Aims: SWBAT identify and evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation DO NOW Directions:
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #68 Aims: SWBAT identify and evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation DO NOW Directions:
The Search for a National Government by Alan Brinkley
 The Search for a National Government by Alan Brinkley This reading is excerpted from Chapter Five of Brinkley s American History: A Survey (12th ed.). I wrote the footnotes. If you use the questions below
The Search for a National Government by Alan Brinkley This reading is excerpted from Chapter Five of Brinkley s American History: A Survey (12th ed.). I wrote the footnotes. If you use the questions below
The ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION. Mr. P s Class
 The ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION Mr. P s Class ANY NOTES IN YELLOW ARE MAIN POINTS AND GO IN THE LEFT COLUMN OF YOUR NOTES ANY NOTES IN RED ARE SUPPORTING DETAILS AND GO IN THE RIGHT COLUMN OF YOUR NOTES
The ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION Mr. P s Class ANY NOTES IN YELLOW ARE MAIN POINTS AND GO IN THE LEFT COLUMN OF YOUR NOTES ANY NOTES IN RED ARE SUPPORTING DETAILS AND GO IN THE RIGHT COLUMN OF YOUR NOTES
#1 State Constitutions
 #1 State Constitutions The American Revolution began the process of creating a new nation in a number of different ways. On May 10, 1776, the Continental Congress directed the colonies to suppress royal
#1 State Constitutions The American Revolution began the process of creating a new nation in a number of different ways. On May 10, 1776, the Continental Congress directed the colonies to suppress royal
The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783!
 Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Articles of Confederation. Essential Question:
 Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
The New Nation Faces Challenges
 SECTION 2 hat You ill Learn... Main Ideas 1. The United States had difficulties with other nations. 2. Internal economic problems plagued the new nation. 3. Shays s Rebellion pointed out weaknesses in
SECTION 2 hat You ill Learn... Main Ideas 1. The United States had difficulties with other nations. 2. Internal economic problems plagued the new nation. 3. Shays s Rebellion pointed out weaknesses in
The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783!
 Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
It s to late to apologize uzfrawatbvg&feature=player_de tailpage#t=4s
 It s to late to apologize http://www.youtube.com/watch?v= uzfrawatbvg&feature=player_de tailpage#t=4s War effectively comes to an end in October 1781 with the defeat of the British at Yorktown. Washington
It s to late to apologize http://www.youtube.com/watch?v= uzfrawatbvg&feature=player_de tailpage#t=4s War effectively comes to an end in October 1781 with the defeat of the British at Yorktown. Washington
Ratification. By March 1781, all 13 Colonies had ratified the Articles of Confederation, making it the official written plan of government.
 The Goal To form a confederation of states - A Firm League of Friendship To continue the form of government established by the Second Continental Congress Ratification By March 1781, all 13 Colonies had
The Goal To form a confederation of states - A Firm League of Friendship To continue the form of government established by the Second Continental Congress Ratification By March 1781, all 13 Colonies had
The Critical Period The early years of the American Republic
 The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
The Treaty of Paris in 1783 recognizes the United States independence from England and establishes our borders
 The Treaty of Paris in 1783 recognizes the United States independence from England and establishes our borders AFRICAN-AMERICANS in the AMERICAN REVOLUTION Over 5,000 served in the Continental Army Over
The Treaty of Paris in 1783 recognizes the United States independence from England and establishes our borders AFRICAN-AMERICANS in the AMERICAN REVOLUTION Over 5,000 served in the Continental Army Over
CHAPTER 9 THE CONFEDERATION & CONSTITUTION DEFINE REVOLUTION" Slavery after the Revolution 9/22/15 WAS THIS REALLY A REVOLUTION?
 CHAPTER 9 THE CONFEDERATION & CONSTITUTION DEFINE REVOLUTION" A SUDDEN AND MOMENTOUS CHANGE IN A SITUATION THE OVERTHROW AND SUDDEN CHANGE OF A GOVERNMENT WAS THIS REALLY A REVOLUTION? Slavery after the
CHAPTER 9 THE CONFEDERATION & CONSTITUTION DEFINE REVOLUTION" A SUDDEN AND MOMENTOUS CHANGE IN A SITUATION THE OVERTHROW AND SUDDEN CHANGE OF A GOVERNMENT WAS THIS REALLY A REVOLUTION? Slavery after the
Articles of Confederation
 Confederation Confederation A group of people, countries, organizations, etc., that are joined together in some activity or effort More or less permanently united for common purposes Articles of Confederation
Confederation Confederation A group of people, countries, organizations, etc., that are joined together in some activity or effort More or less permanently united for common purposes Articles of Confederation
LECTURE 3-3: THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION AND THE CONSTITUTION
 LECTURE 3-3: THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION AND THE CONSTITUTION The American Revolution s democratic and republican ideals inspired new experiments with different forms of government. I. Allegiances A.
LECTURE 3-3: THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION AND THE CONSTITUTION The American Revolution s democratic and republican ideals inspired new experiments with different forms of government. I. Allegiances A.
The Articles of Confederation
 The Articles of Confederation Explain the weaknesses and strengths of the Articles of Confederation. Examine the need for a strong central government. Document that broke the 12 English colonies from British
The Articles of Confederation Explain the weaknesses and strengths of the Articles of Confederation. Examine the need for a strong central government. Document that broke the 12 English colonies from British
Land Ordinance of 1785
 Unit 3 SSUSH5 Investigate specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution. a. Examine the strengths of the Articles of Confederation,
Unit 3 SSUSH5 Investigate specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution. a. Examine the strengths of the Articles of Confederation,
Case Studies Articles of Confederation
 Name Case Studies Articles of Confederation Directions: Read the Case Study given to your group, and answer the questions below. Whose interests were pitted against each other is asking you to think about
Name Case Studies Articles of Confederation Directions: Read the Case Study given to your group, and answer the questions below. Whose interests were pitted against each other is asking you to think about
VUS. 5 (pt.1): Building a New Nation: The Constitutional Convention
 Name: Date: Period: VUS 5 (pt1): Building a New Nation: The Constitutional Convention Notes US 5 (pt1): Building a New Nation: The Constitutional Convention 1 Objectives about VUS5: Building a New Nation
Name: Date: Period: VUS 5 (pt1): Building a New Nation: The Constitutional Convention Notes US 5 (pt1): Building a New Nation: The Constitutional Convention 1 Objectives about VUS5: Building a New Nation
Second Continental Congress May 1775
 Second Continental Congress May 1775 Met in Philadelphia Representatives from each state Continental Congress Went to work on a new government Articles of Confederation (Nov. 1777) Set up a confederation
Second Continental Congress May 1775 Met in Philadelphia Representatives from each state Continental Congress Went to work on a new government Articles of Confederation (Nov. 1777) Set up a confederation
Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution
 Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution The Articles of Confederation After declaring independence from Britain in 1776, Congress tried to unite the states under one national government. However, many feared
Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution The Articles of Confederation After declaring independence from Britain in 1776, Congress tried to unite the states under one national government. However, many feared
Articles of Confederation and Constitutional Conventions
 Articles of Confederation and Constitutional Conventions The Declaration of Independence Recognized changes taking place in colonies; colonies becoming states subject to no higher authority Colonies begin
Articles of Confederation and Constitutional Conventions The Declaration of Independence Recognized changes taking place in colonies; colonies becoming states subject to no higher authority Colonies begin
CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT
 CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT The Constitution set out our rules for government. It explains what our government can and cannot do. It reflects are experience as a colony as well as ideas from Europe
CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT The Constitution set out our rules for government. It explains what our government can and cannot do. It reflects are experience as a colony as well as ideas from Europe
Conceived in Liberty. 5th Grade Social Studies Textbook
 Conceived in Liberty 5th Grade Social Studies Textbook Chapter 9 Creating the Constitution Chapter 9 Creating the Constiution When the American people won their independence, they had to decide what kind
Conceived in Liberty 5th Grade Social Studies Textbook Chapter 9 Creating the Constitution Chapter 9 Creating the Constiution When the American people won their independence, they had to decide what kind
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton
 Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
How did the Articles of Confederation organize the first. 11national government? What are the Articles of Confederation?
 11national government? How did the Articles of Confederation organize the first LESSON PURPOSE Our first government, the Continental Congress, drew up a constitution stating its powers. This constitution
11national government? How did the Articles of Confederation organize the first LESSON PURPOSE Our first government, the Continental Congress, drew up a constitution stating its powers. This constitution
Chapter 9: The Confederation and the Constitution,
 APUSH CH 9+10 Lecture Name: Hour: Chapter 9: The Confederation and the Constitution, 1776-1790 I. From Confederation to Constitution A. The Articles of Confederation: An Attempt at Constitution-Making
APUSH CH 9+10 Lecture Name: Hour: Chapter 9: The Confederation and the Constitution, 1776-1790 I. From Confederation to Constitution A. The Articles of Confederation: An Attempt at Constitution-Making
The Federalist Papers
 The Federalist Papers If men were angels, no government would be necessary. James Madison During the Revolutionary War, Americans set up a new national government. They feared a strong central government.
The Federalist Papers If men were angels, no government would be necessary. James Madison During the Revolutionary War, Americans set up a new national government. They feared a strong central government.
Warm Up. 1 Create an episode map on the American Revolution. 2 Again you will have to use your notes from the last unit or from the classroom website
 Warm Up 1 Create an episode map on the American Revolution 2 Again you will have to use your notes from the last unit or from the classroom website Shay s Rebellion & The Articles of Confederation STRENGTHS
Warm Up 1 Create an episode map on the American Revolution 2 Again you will have to use your notes from the last unit or from the classroom website Shay s Rebellion & The Articles of Confederation STRENGTHS
4. After some negotiating, mostly with the promise of the Bill of Rights, the Constitution was ratified.
 Chapter #9: The Confederation and the Constitution Big Picture Ideas 1. The Articles of Confederation, the first government set up after the American Revolution, was structured out of fear of a too-strong
Chapter #9: The Confederation and the Constitution Big Picture Ideas 1. The Articles of Confederation, the first government set up after the American Revolution, was structured out of fear of a too-strong
Beginnings of a New Nation
 The period between the Treaty of Paris and the writing of the Constitution, the states were united only by a rope of sand. George Washington Beginnings of a New Nation Officers were disgusted with Congress
The period between the Treaty of Paris and the writing of the Constitution, the states were united only by a rope of sand. George Washington Beginnings of a New Nation Officers were disgusted with Congress
Chapter 6. APUSH Mr. Muller
 Chapter 6 APUSH Mr. Muller Aim: How is the New Republic tested? Do Now: Thus I consent, sir, to this Constitution, because I expect no better, and because I am not sure that it is not the best. The opinions
Chapter 6 APUSH Mr. Muller Aim: How is the New Republic tested? Do Now: Thus I consent, sir, to this Constitution, because I expect no better, and because I am not sure that it is not the best. The opinions
SSUSH5 A, B, C & D Creating a New Government
 SSUSH5 A, B, C & D Creating a New Government The Articles of Confederation Formally called the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, this agreement was created by the leaders of the original thirteen
SSUSH5 A, B, C & D Creating a New Government The Articles of Confederation Formally called the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, this agreement was created by the leaders of the original thirteen
Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed.
 Geography Challenge G e o G r a p h y C h a l l e n G e Geography Skills Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed. 1. Label each state
Geography Challenge G e o G r a p h y C h a l l e n G e Geography Skills Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed. 1. Label each state
Unit 3 Section 1 Articles and Early Government.notebook. January 18, Vocabulary. Westward Ho! Need for State and National Government
 8.1 Vocabulary Wilderness Road Republic Articles of Confederation Land Ordinance of 1785 Northwest Territory Northwest Ordinance Shays's Rebellion Chapter Connection: Articles of Confederation were not
8.1 Vocabulary Wilderness Road Republic Articles of Confederation Land Ordinance of 1785 Northwest Territory Northwest Ordinance Shays's Rebellion Chapter Connection: Articles of Confederation were not
Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation
 Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government. 2. is
Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government. 2. is
The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions
 The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions provide clear definition of rights describe clear limits
The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions provide clear definition of rights describe clear limits
netw rks Where in the world? When did it happen? The Federalist Era Lesson 1 The First President ESSENTIAL QUESTION Terms to Know GUIDING QUESTIONS
 Lesson 1 The First President ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the characteristics of a leader? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. What decisions did Washington and the new Congress have to make about the new government?
Lesson 1 The First President ESSENTIAL QUESTION What are the characteristics of a leader? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. What decisions did Washington and the new Congress have to make about the new government?
The Critical Period Test Review 2
 The Critical Period Test Review 2 1. What is republicanism? Republicanism is a form of government ruled through elected representatives. The idea government should be based on the consent of the people.
The Critical Period Test Review 2 1. What is republicanism? Republicanism is a form of government ruled through elected representatives. The idea government should be based on the consent of the people.
The United States Constitution. The Supreme Law of the Land
 The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States
The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States
Creating a Nation Test Review
 Creating a Nation Test Review Question #1: Multiple Choice The Northwest ordinance of 1787 is important because. A. It sent troops to the Northwest to protect the colonies from Native Americans. B. It
Creating a Nation Test Review Question #1: Multiple Choice The Northwest ordinance of 1787 is important because. A. It sent troops to the Northwest to protect the colonies from Native Americans. B. It
2:Forging a New Constitution. Essential Question How do new ideas change the way people live?
 2:Forging a New Constitution Essential Question How do new ideas change the way people live? The Need for Change Bold action helped the nation overcome the serious shortcomings of the Articles of Confederation.
2:Forging a New Constitution Essential Question How do new ideas change the way people live? The Need for Change Bold action helped the nation overcome the serious shortcomings of the Articles of Confederation.
During the, the majority of delegates voted to declare independence from Britain. What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution?
 What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution? A. The Stamp Act B. Boston Tea Party C. Quartering Act D. Battle of Lexington and Concord During the, the majority of delegates voted
What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution? A. The Stamp Act B. Boston Tea Party C. Quartering Act D. Battle of Lexington and Concord During the, the majority of delegates voted
OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS
 CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
understanding CONSTITUTION
 understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
Articles of Condederation Very weak government. Why??? Five pages, 13 articles
 Articles of Condederation Very weak government. Why??? Five pages, 13 articles Establishes the name of the confederation as "The United States of America." Asserts the precedence of the separate states
Articles of Condederation Very weak government. Why??? Five pages, 13 articles Establishes the name of the confederation as "The United States of America." Asserts the precedence of the separate states
i n t e r a C t i v e s t u d e n t n o t e b o o k Mapping Activity 11/02/17
 Mapping Activity 11/02/17 Geography Skills Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed. 1. Label each state on the map. Which two states
Mapping Activity 11/02/17 Geography Skills Analyze the maps in Setting the Stage. Then answer the following questions and fill out the map as directed. 1. Label each state on the map. Which two states
The Beginnings of a New American Government
 The Constitution The Beginnings of a New American Government Dissatisfaction grew with the Articles of Confederation as disagreements over control of waterways and trade developed. In 1785 the first meeting
The Constitution The Beginnings of a New American Government Dissatisfaction grew with the Articles of Confederation as disagreements over control of waterways and trade developed. In 1785 the first meeting
A More Perfect Union. Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation
 A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
We re Free Let s Grow!
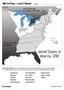 Atlantic Ocean Find Those States! The United States started out with just thirteen states. Use the list below to correctly identify each one on the map. Watch out: Things were a little different back then!
Atlantic Ocean Find Those States! The United States started out with just thirteen states. Use the list below to correctly identify each one on the map. Watch out: Things were a little different back then!
Early US History Part 1. Your Notes. Goal 9/5/2012. How did the United States became a country?
 Questions / Themes 9/5/2012 Early US History Part 1 How did the United States became a country? Your Notes You will need these notes to prepare for exams. Remember to paraphrase and generalize. Avoid copying
Questions / Themes 9/5/2012 Early US History Part 1 How did the United States became a country? Your Notes You will need these notes to prepare for exams. Remember to paraphrase and generalize. Avoid copying
Chapter 3 Constitution. Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook
 Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
The Articles of Confederation
 1 The Articles of Confederation Approved by Congress on November 15, 1777, Congress sent to the states for ratification the Articles of Confederation. This was the first governing constitution for the
1 The Articles of Confederation Approved by Congress on November 15, 1777, Congress sent to the states for ratification the Articles of Confederation. This was the first governing constitution for the
A More Perfect Union
 A More Perfect Union 1777 1790 Why It Matters When the American colonies broke their political ties with Great Britain, they faced the task of forming independent governments at both the state and national
A More Perfect Union 1777 1790 Why It Matters When the American colonies broke their political ties with Great Britain, they faced the task of forming independent governments at both the state and national
Underpinnings of the Constitution
 Underpinnings of the Constitution A constitution is a nations basic laws creates political institutions assigns and divides power in government provides certain guarantees to citizens includes unwritten
Underpinnings of the Constitution A constitution is a nations basic laws creates political institutions assigns and divides power in government provides certain guarantees to citizens includes unwritten
Test Day. October 3-4
 Test Day October 3-4 Sit Wherever Turn in your Study Guide to me When done with test, Turn in to the correct area up front (follow sticky notes) Pick up outline for Unit 3 Pick up a survey for Unit 3 Pick
Test Day October 3-4 Sit Wherever Turn in your Study Guide to me When done with test, Turn in to the correct area up front (follow sticky notes) Pick up outline for Unit 3 Pick up a survey for Unit 3 Pick
The Articles of!confederation
 The Articles of Confederation Our New Nation s First Constitution The Articles of Confederation When the Second Continental Congress appointed a committee to write a Declaration of Independence in 1776,
The Articles of Confederation Our New Nation s First Constitution The Articles of Confederation When the Second Continental Congress appointed a committee to write a Declaration of Independence in 1776,
THE CONSTITUTION. How do societies balance individual and community rights? How does social change influence government?
 CHAPTER 5 THE CONSTITUTION NGSSS SS.7.C.1.7 Describe how the Constitution limits the powers of government through separation of powers and checks and balances. ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why do people create,
CHAPTER 5 THE CONSTITUTION NGSSS SS.7.C.1.7 Describe how the Constitution limits the powers of government through separation of powers and checks and balances. ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why do people create,
Basic Concepts of Government The English colonists brought 3 ideas that loom large in the shaping of the government in the United States.
 Civics Honors Chapter Two: Origins of American Government Section One: Our Political Beginnings Limited Government Representative government Magna Carta Petition of Right English Bill of Rights Charter
Civics Honors Chapter Two: Origins of American Government Section One: Our Political Beginnings Limited Government Representative government Magna Carta Petition of Right English Bill of Rights Charter
7/10/2009. By Mr. Cegielski WARM UP:
 By Mr. Cegielski WARM UP: 1 PREVIEW: George Washington Presidential Accomplishments Washington voluntarily resigned as Commander-in-Chief of the Continental Army in 1783. Because of his victories in the
By Mr. Cegielski WARM UP: 1 PREVIEW: George Washington Presidential Accomplishments Washington voluntarily resigned as Commander-in-Chief of the Continental Army in 1783. Because of his victories in the
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50
 Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
LESSON TWO: THE FEDERALIST PAPERS
 LESSON TWO: THE FEDERALIST PAPERS OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Identify the Articles of Confederation and explain why it failed. Explain the argument over the need for a bill of rights
LESSON TWO: THE FEDERALIST PAPERS OVERVIEW OBJECTIVES Students will be able to: Identify the Articles of Confederation and explain why it failed. Explain the argument over the need for a bill of rights
What types of things did the new states do to make the governments more democratic?
 Chapter 8 Confederation to Constitution pg. 218 241 8 1 The Confederation Era pg. 221 225 Moving West and New State Governments Into which areas did American settlement expand in the late 1700s? What types
Chapter 8 Confederation to Constitution pg. 218 241 8 1 The Confederation Era pg. 221 225 Moving West and New State Governments Into which areas did American settlement expand in the late 1700s? What types
CHAPTER 2 NOTES Government Daily Lecture Notes 2-1 Even though the American colonists got many of their ideas about representative government and
 CHAPTER 2 NOTES Government Daily Lecture Notes 2-1 Even though the American colonists got many of their ideas about representative government and freedom from England, that country has no written constitution.
CHAPTER 2 NOTES Government Daily Lecture Notes 2-1 Even though the American colonists got many of their ideas about representative government and freedom from England, that country has no written constitution.
1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation
 Topic 3 1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg 88-89 They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation agreements 2. How did the British respond to the Boston Tea
Topic 3 1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg 88-89 They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation agreements 2. How did the British respond to the Boston Tea
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government
 Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government United States Government Fall, 2017 Origins of American Political Ideals Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely,
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government United States Government Fall, 2017 Origins of American Political Ideals Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely,
Battle of Saratoga. British troops reached Saratoga from Quebec and were surrounded and severely outnumbered = Surrendered
 Battle of Saratoga British troops reached Saratoga from Quebec and were surrounded and severely outnumbered = Surrendered Huge military victory, and boosted morale Convinced the French & Spain to enter
Battle of Saratoga British troops reached Saratoga from Quebec and were surrounded and severely outnumbered = Surrendered Huge military victory, and boosted morale Convinced the French & Spain to enter
The Coming of Independence. Ratifying the Constitution
 C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 1 SECTION 1 SECTION 2 SECTION 3 SECTION 4 SECTION 5 Our Political Beginnings The Coming of Independence The Critical Period Creating the Constitution Ratifying
C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 1 SECTION 1 SECTION 2 SECTION 3 SECTION 4 SECTION 5 Our Political Beginnings The Coming of Independence The Critical Period Creating the Constitution Ratifying
Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ:
 Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ: 6.1 Introduction Like Washington, most Americans did not want to be ruled by a monarch. What they did want, though, was an effective government. Articles of Confederation,
Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ: 6.1 Introduction Like Washington, most Americans did not want to be ruled by a monarch. What they did want, though, was an effective government. Articles of Confederation,
Name Class Date. MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term or person that matches each description. Some answers will not be used.
 Origins of American Government Section 1 MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term or person that matches each description. Some answers will not be used. 1. Idea that people should
Origins of American Government Section 1 MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term or person that matches each description. Some answers will not be used. 1. Idea that people should
2. Divided Convention. 3. Inside the Constitution. Constitution replaced the Articles---becomes the law of the land.
 2. Divided Convention notes7 9/13 states needed to ratify (to approve) Political parties begin Federalists: supported the Constitution The Federalist ---essays support Constitution Anti-Federalists: against
2. Divided Convention notes7 9/13 states needed to ratify (to approve) Political parties begin Federalists: supported the Constitution The Federalist ---essays support Constitution Anti-Federalists: against
The Founding of American Democracy By Jessica McBirney 2016
 Name: Class: The Founding of American Democracy By Jessica McBirney 2016 The American colonies rose up in 1776 against Britain with the goal of becoming an independent state. They sent the King of England
Name: Class: The Founding of American Democracy By Jessica McBirney 2016 The American colonies rose up in 1776 against Britain with the goal of becoming an independent state. They sent the King of England
Chapter Seven. The Creation of the United States
 Chapter Seven The Creation of the United States 1776-1786 Part One Introduction The Creation of the United States 1776-1786 What does the painting tell us about who fought for the creation of the United
Chapter Seven The Creation of the United States 1776-1786 Part One Introduction The Creation of the United States 1776-1786 What does the painting tell us about who fought for the creation of the United
New Nation. establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s
 New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
The American Revolution & Confederation. The Birth of the United States
 The American Revolution & Confederation The Birth of the United States 1774-1787 Essential Question Evaluate the extent to which the Revolution fundamentally changed American society. The First Continental
The American Revolution & Confederation The Birth of the United States 1774-1787 Essential Question Evaluate the extent to which the Revolution fundamentally changed American society. The First Continental
THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION
 Tis really astonishing that the same people, who have just emerged from a long and cruel war in defense of liberty, should now agree to fix an elective despotism upon themselves and their posterity. Richard
Tis really astonishing that the same people, who have just emerged from a long and cruel war in defense of liberty, should now agree to fix an elective despotism upon themselves and their posterity. Richard
Essential Question Section 1: The Colonial Period Section 2: Uniting for Independence Section 3: The Articles of Confederation Section 4: The
 Essential Question Section 1: The Colonial Period Section 2: Uniting for Independence Section 3: The Articles of Confederation Section 4: The Constitutional Convention Chapter Summary Content Vocabulary
Essential Question Section 1: The Colonial Period Section 2: Uniting for Independence Section 3: The Articles of Confederation Section 4: The Constitutional Convention Chapter Summary Content Vocabulary
Building a Nation LEVELED READER Z. Visit for thousands of books and materials.
 Building a Nation A Reading A Z Level Z Leveled Reader Word Count: 2,183 LEVELED READER Z Building a Nation Part Three of The American Revolution Written by Terry Miller Shannon Visit www.readinga-z.com
Building a Nation A Reading A Z Level Z Leveled Reader Word Count: 2,183 LEVELED READER Z Building a Nation Part Three of The American Revolution Written by Terry Miller Shannon Visit www.readinga-z.com
Shays. Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt.
 Shays Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt. 1. Constitutional Convention: May to Sept. 1787 2. Divided Convention 9/13 states needed to
Shays Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt. 1. Constitutional Convention: May to Sept. 1787 2. Divided Convention 9/13 states needed to
American History Semester 1 Review - Shorter Answers
 American History Semester 1 Review - Shorter Answers Study online at quizlet.com/_30fd48 1. Name the first three attempts at British Colonies. 2. Which of the first three colonies attempted was settled
American History Semester 1 Review - Shorter Answers Study online at quizlet.com/_30fd48 1. Name the first three attempts at British Colonies. 2. Which of the first three colonies attempted was settled
Washington s Presidency
 !CHAPTER 9 SECTION 1 REVIEW Washington s Presidency Specific Objective Learn that George Washington and his advisers faced many challenges during his Presidency. Directions: Read the summary below to answer
!CHAPTER 9 SECTION 1 REVIEW Washington s Presidency Specific Objective Learn that George Washington and his advisers faced many challenges during his Presidency. Directions: Read the summary below to answer
Convention. Guide to Reading
 Convention and Compromise Main Idea The new Constitution corrected the weaknesses of government under the Articles of Confederation. Key Terms depression, manumission, proportional, compromise 1784 Rhode
Convention and Compromise Main Idea The new Constitution corrected the weaknesses of government under the Articles of Confederation. Key Terms depression, manumission, proportional, compromise 1784 Rhode
New Nation. establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s
 New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
