Design of Question Paper Social Science (087), Summative Assessment-II Class X ( )
|
|
|
- Tracy Hawkins
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Design of Question Paper Social Science (087), Summative Assessment-II Class X ( ) S. Form of questions Marks of each Number of Total Marks question questions 1 MCQ Short Answer (SA) Long Answer (LA) Map Question Total The question paper will include value based question(s) to the extent of 3-5 marks. S. No. Unit No. Marks 1 History Geography 23 3 Political Science Economics 22 Total
2 Sample Questions Social Science (087), Summative Assessment-II Class X ( ) Multiple Choice Questions History 1 Mark each Q1. In Prussia, large landowners were known as A. Junkers B. Jacobins C. Habsburg D. Conservatives Ans. (A) Junkers Q. 2 Who formed a secret society called young Italy? A. Givseppe Mazzini B. Otto von Bismarck C. Victor Emmannel II D. Count Camillo de Cavour 1M Ans. (A) Givseppe Mazzini 1M 128
3 Q. 3. When did the creation of Indo-China Union, including Cochinchina, Annam, Tonkin and Cambodia (and later Laos) took place? 1M A B C D Ans Q4. Which film of John F. Coppola reflected the moral confusion that the U.S Vietnamese war had created in the U.S.A. 1M A. Apocalypse Now B. Green Berets C. No Mans Land D. Saving Private Ryan Ans. Apocalypse Now Q5. What was Vietminh? 1M A. League for the Independence of Vietnam B. League for the Independence of China C. League for the Independence of Japan D. League for the Independence of Korea Ans. League for the Independence of Vietnam 129
4 Q. 6. Who wrote Hind Swaraj? 1M A. Mahatma Gandhi B. Jawaharlal Nehru C. Subhash Chandra Bose D. Sarojini Naidu Q 7. In which Congress session the demand for Purna Swaraj adopted? A. Lahore session B. Calcutta Session C. Nagpur Session D. Belgaum Session Q.8. Who threw the bomb in the Legislative Assembly in April 1929? A. Bhagat Singh and Batukeshwar Dutt B. Jatin Das and Ajay Ghosh C. Chandra Shekhar Azad and Sukhdev D. Rajguru and Rash Behari Ghosh 3 Marks Questions 1M 1M Q.1. What was the Civil Code of 1804? Ans. The civil Code of 1804 usually known as the Napoleonic code abolished all the privileges based on birth, created quality before the law and secured the right to property. control. Moreover, this code was also exported to the regions under French 130
5 Q.2. Briefly describe Zollverein? Ans. In 1834, Zollverein or customs union was established at the initiative of Prussia and joined by most of the German states. The union did away with tariff barriers and decreased the number of currencies from over thirty to only two. Q 3. Which was the Balkans region? Ans. The Balkans was a region of geographical and ethnic diversity consisting modern day Albania, Bulgaria, Romania, Croatia, Bosnia Harzegoina, Macedonia, Greece, Serbia, Slovenia and Montenegro whose inhabitants were broadly called as Slavs. Q.4. Who was Confucius Ans. Confucius ( ) BCE was a Chinese thinker and philosopher who developed a philosophical system based on practical wisdom, good behaviour and proper social relationships. The people were taught to respect their parents and obey their elders. The relationship between the ruler and the people was described as between the parents and children. Q5 Why did the French thought that colonies were necessary? Ans. The Colonies were considered necessary to supply natural resources and other important goods and commodities. They were also guided by the idea of civilizing mission. In other words, they claimed that it was their duty to introduce modern ideas to civilize backward people. Q6 What were the obstacles in economic growth of Vietnam? Ans. There were a number of barriers in economic growth of Vietnam: high population levels, low agricultural productivity and widespread indebtedness among 131
6 the farmers. Moreover, increasing unemployment and lack of industrialization led to increased landlordism and declining standard of living. Q 7.What was Rowlatt Act? Rowlett Act gave the government enormous powers to suppress political activities and allowed detention of political prisons without trial for two years. In other words, the act proposed no appeal, no vakil and no daleel. Q.8 Why was the Khilafat Movement started? Ans. Khilafat movement was started by Mahatma Gandhi and Ali brothers Mohammed Ali and Shaukat Ali in response to the harsh treatment given to Caliph of Ottomon Empire and the dismemberment of the Ottoman Empire by the British. Q. 9. Who formed the Swaraj Party and why? Ans. Swaraj Party was formed by C.R Das and Motilal Nehru. They felt that it was necessary to oppose British policies within the councils, argue for reform and also show that these councils were not truly democratic. That is why they wanted to contest elections and carry on their battles in the councils. 5 Mark Questions Q1. What was Romanticism? How was it linked to Nationalism? 5M Ans. Romanticism was a cultural movement which sought to develop a specific from of nationalist sentiment. Romantic artists and poets usually were critical of glorification of science and reason. They gave greater importance to intuition, emotions and mystical feelings. Their attempt was to create a sense of a shared collective heritage, a common cultural past, as the basis of a nation. They gave 132
7 importance to vernacular language and collection of local folklore to recover not only an ancient national spirit but also to take forward the modern Nationalist ideas to a larger audience. Q2. Discuss the stages of the formation of Great Britain as a National state? 5M Ans. In Britain, the formation of the nation state was the consequence of a long drawn out process. There was no British nation before the 18 th century. The people who inhabitated British Isles were of ethnic groups like English, Irish, Scot or Welsh. In 1688, English Parliament wrested control from the monarchy. The Act of Union (1707) between England and Scotland led to creation of United Kingdom of Great Britain. The English now dominated Scotland s culture and its political institutions. The catholic people of Scottish highlands were forbidden to speak their Gaelic language and a large number of them were forced out of their habitats. Ireland met the same fate, the English supported the Protestants of Ireland and increased their domination over this largely catholic nation. In 1801, Ireland was forcibly incorporated into the United Kingdom. A new British nation with symbols like British flag (union Jack), National anthem (God save our Noble King) and the English language became forbearer of English culture and the older nations became subservient partners in this Union. Q 3.Write a character sketch of Ho Chi Minh? 5M Ans. Ho Chi Minh ( ) was born as Nguyen Van Thanh in central Vietnam. He briefly became a teacher in He later became an active member of the Comintern and met Lenin and other revolutionary leaders. In February 1930, Ho Chi Minh brought together competing nationalist groups to establish the Vietnamese 133
8 Communist (Vietnam Cong San Dang) Party, later renamed the Indochinese Communist Party. In 1943, he took the name Ho Chi Minh (He who enlightens). He became President of the Vietnam Democratic Republic in He led the Party successfully for around 40 years, struggling to preserve Vietnamese autonomy. He breathed his last on 3 rd Sep Q4. Discuss the consequences of U.S. Vietnamese War? 5M Ans. The U.S. failed to achieve its objectives: The Vietnamese resistance had not been crushed and the support of the Vietnamese for U.S. action had not been won. The war had caused death of thousands of soldiers both U.S and Vietnamese and destruction of property and peace. It was also called first television war as battle scenes were shown on the daily news programme. It created strong reactions in the U.S and many who became disillusioned with U.S. policies praised Vietnamese heroic defense of their nation. Noam Chomsky famous linguist and theoretician, called the war the greatest threat to peace to national self determination and to international cooperation. Q.5 Discuss the programmes in Non cooperation Movement? 5M Ans. Gandhi proposed that the movement should unfold in stages. It began with surrender of titles that the government had awarded, and a boycott of army, courts, legislative councils, civil services and police. Later, in case of government repression, full civil disobedience campaign will be launched. Foreign goods were boycotted, liquor shops were picketed and bonfires of foreign cloth was undertaken. There was also emphasis on using of Khadi cloth and swadeshi (indigenous) goods and commodities. 134
9 Q 6. Discuss the background and provisions of Poona Pact? 5M Ans: Dr. B.R. Ambedkar, who organized the dalits into the Depressed Classes Association in 1930 demanded separate electorates for dalits in the Second Round Table Conference organized in London. When British accepted this demand in the name of Communal Award Gandhi ji started a fast unto death. He believed that separate electorate for dalits would slow down the process of their integration into the society. Ambedkar and Gandhi came to an agreement with Ambedkar accepting Gandhi s position and the result was the Poona Pact of September It gave the depressed classes (later to be known as Schedule castes) reserved seats in provincial and central legislative councils, but they were to be voted in by the general electorate. 135
10 (Political Science) Class X Multiple Choice Questions 1 Marks each Q1. In what respect is a democratic government better than its alternatives? 1 a) Efficiency b) Responsiveness c) Transparency d) Legitimacy Ans: d) Legitimacy (Chapter 7, P-91) Q2. Which one of the following is a special feature that distinguishes a movement from an interest group? 1M a) Its functioning continues even after the goal is achieved. b) Most of them are issue specific to achieve a single objective within a limited time frame. c) It includes a very wide variety of objectives to achieve with no time limit. d) It has no political aspirations. (Chapter 5, P-65) Ans: b) Most of them are issue specific to achieve a single objective within a limited time frame. Q3. What does Universal Adult suffrage stand for? A. Right to vote B. Right to Education C. Right to Marriage D. Right to Religion Ans. (A) Right to vote 1M 136
11 Three Marks Questions Q1. Explain any three most effective ways in which the pressure groups and movements influence the politics of a country. 3x1 = Ans: Ways to influence polities i) The pressure groups try to gain public support and sympathy for their goals through campaigns, meetings, filing petitions etc. ii) They often organize protest activities like strikes or disrupting government programmes iii) Some persons from pressure groups or movements may participate in official bodies and committees Q2. Identify and explain any three challenges which political parties need to face and overcome in order to remain effective instruments of democracy. 3x1 = Ans: The Challenges which Political Parties need to face our Lack of internal democracy within the parties. There is a tendency towards the concentration of power in one or few top leaders. i) ii) iii) iv) Parties do not keep membership registers. They do not hold organizational meetings. They also do not hold internal elections regularly. The leaders assure greater power to make decisions in the name of the party. Since one or a few leaders exercise paramount power in the party, those who disagree with the leadership find it difficult to continue in the party. Due to dynastic succession and lack of open and transparent procedures, it becomes difficult for an ordinary worker to rise to the top of the party. 137
12 v) Growing role of money and muscle power in parties, increasing role of rich people and big companies, support to criminals etc influence the policies and decisions of the party. vi) Very often parties do not offer a meaningful choice to the voters. (Any three points) (Chapter 76, P-83) Five Marks Questions Q1. How far has India succeeded in overcoming, the challenge of expansion before its democracy? Evaluate. 5M Ans: Like most of the established democracies of the world, India, too, faces the challenge of expansion. i) India applies basic principles of democracy across all the regions, different social groups and various institutions. ii) Federal principles have been extended to all the units of the federation giving the right to make laws on the subjects in the state list. iii) Local governments both rural and urban have been ensured more powers. iv) Reservation of seats has ensured the participation of women, the minority groups SCs, STs and BCs in the governance of the country. v) All the above points mean that less and less decisions are taken outside the arena of democratic control. (Chapter 8, P-102) Q2. `Democracy is seen to be good in principle, but felt, to be not so good in practice. Justify the statement with suitable arguments
13 Ans: If we look at some of the democratic policies being implemented in more than one hundred countries of the world, democracy seems to be good. For example, having a formal Constitution, holding regular elections, guaranteeing the citizens certain rights, working for the welfare of the people etc. make us advocate that democracy is good. But if look in terms of social situations, their economic achievements and varied culture, we find a very big difference in most of the democracies. The vast economics disparities, social injustice based on discrimination, standard of life, sex discrimination etc. creates many doubts about the merit of democracy. Whenever some of our expectations are not met, we start blaming the idea of democracy. Since democracy is first a form of government, it can only create conditions for achieving our goals if they are reasonable. (Chapter 7, P-90) 139
14 Economics Class X Multiple Choice Questions 1 mark each Q 1. The ISI, A-Mark or Hallmark logo on a package assures:- i) Quality ii) Right price iii) No preservative used iv) Eco friendly products Ans i) Q. 2. A shopkeeper insists that you buy a guide with your NCERT textbook. Which right of the consumer is being violated:- i) Right to be informed ii) Right to choose iii) Right to information iv) Right to safety Ans ii) Q. 3. The consumer Protection Act 1986 ensures i) Right to see a movie ii) Right to consumer education. iii) Right to having a computer. iv) Right to a facebook account. Ans: ii) 3 Mark Questions 140
15 Q. 1. In spite of Globalization creating good quality product and expanding market, how is it affecting stability in jobs for the workers? Ans.: a) Employment of flexible workers b) Increased competition, objective to lower costs, the axe falls on the labour costs temporary jobs given. c) Longer working hours for labour to get suitable salaries. Q.2. How is the M.N.C able to cope with large demands all over the world and control prices? Ans. 1. Large MNCs in developed countries place order for production with small producers. 2. The MNC s sell these under their own. 3. As they control the market with the huge demand they are able to control prices. Five Marks Questions Q. 1. How have the SHG s affecting the economic weaker section 5M Ans. 1. Bank not present everywhere in rural areas 2. Difficulties in getting loans 3. Weaker section may not have collaterals 4. High rates at interest by money lenders 141
16 SHG s members, savings of Rs , lower rates of interest, no collaterals, give loans to each other.-1 group avails loan from bank. Group decides to disperse loans. Q. 2. Cheap and affordable credit is crucial for the countries development. Highlight the role of loans in reference to India. 5M Ans. 1. High cost of borrowing leads to a major share of profits to be paid as interest. 2. At time higher rates leads to more interests than the principal. 3. Debt trap discourages new entrants 4. More loans given by banks and co-operatives 5. Promotion of small scale industries. 142
17 (Geography) Class X Multiple Choice Questions One Mark Questions Q1. Identify the power plant which is different from the other three power plants? 1M A) Narora B) Korba C) Naively D) Talc her (Page 61) 1. Ans: A Q2. Which one of the following is finest quality of Coal? 1M A) Peat B) Lignite C) Anthracite D]Bituminous (Page 51) 2. Ans: C Q3. Identify the state from the following which is famous for the productions of cotton and woolen textiles? 1M A) Srinagar B) Ahmadabad C) Bangalore D) Varanasi (Page 69) 3. Ans: C Q4. Which one of the following is a major seaport as well as international airport? 1M A) Chennai B) Vishakhapatnam C) Tiruvanthapuram D) Marmangoa (Page 89) 4. Ans: A 143
18 Three Marks Questions Q2. Explain any three reasons for shifting sugar industry from Northern India to South India Ans:. Reasons for shifting of sugar industry 1. The production of sugarcane per hectare is higher in peninsular Industry. 2. The sucrose content is higher. 3. The crushing season is longer in south India. 4. The co-operatives are more successful in southern states Q3. Why is the air transport more popular in the North Eastern Part of the country? Give three reasons. Ans: Air transport is more useful in North eastern part of India because of 1. There is a marked presence of big rivers. 2. Dissected relief features 3. Frequent floods. 4. Presence of dense forests. 5. International frontiers. Five Marks Questions Q1. The Iron and Steel industry is the basic as well as heavy industry. Support the statement with suitable examples. 5M Ans.: The iron and steel is called basic industry because all other industries depend on it for their Machinery. Steel is needed to manufacture a variety of engineering goods, construction material, defense, medical, telephones, scientific equipment and variety of consumer goods. Iron and steel is a heavy industry because all the raw materials and finished goods are heavy. They are bulky also. They are entailing heavy transportation costs. Iron ore and limestone are required in high quantity. All very heavy. 144
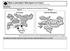
19 Q 2 What is trade? Why tourism is called invisible trade? 5M (Page 90-91) Ans.: The exchange of goods among people states and countries is referred as trade. The services referred to foreign tourists are the invisible products of tourist industry. These products are included hospitality services. In the year 2004 we got Rs crore of foreign exchange from foreign tourist. Tourism also promotes national integration. It provides support to handicrafts and cultural pursuits. It also helps in the understanding about our culture and heritage. We can attract more tourists by providing facilities. Q3. I) Two features A and B are shown in the given political outline map of India. Identify these features with the help of following information and write their correct names on the lines marked on the map. 2+3=5 (A) Iron Ore mines (B) Terminal station of North South Corridor II) On the same political outline map of India, locate and label the following items with appropriate symbols: (C) Bangalore-Software Technology Park (D) Kandla-Sea Port Note: The following questions are for the visually impaired candidates only in lieu of Q. No M 10.1 Name any two iron-mines of Chhattisgarh 10.2 Which is the northernmost terminal station of North-South Corridor? 10.3 Name the software technology park located in Orissa Which is the southern most major sea port of India? 145
20 Value Based Questions Social Science (087), Summative Assessment-II Class X ( ) Q. 1. Self Help Groups support has brought about a revolutionary change in the rural sector. Which values according to you is it able to support. Ans. Values (Any three) 1. Women empowerment 2. Team work 3. Self sufficiency 4. Eradication of poverty Q 2. How can we save our limited energy sources? Suggest any three ways for its judicious use. (Page 63) Ans.: Ways for the judicious use of energy resources: 1. By using public transport system 2. Switching off electricity when not in use. 3. Using power saving devices. 4. Using non-conventional sources of energy. 146
21 Q3 `Democracy in India has strengthened the claims of the disadvantaged and disseminated castes for equal status and equal opportunity. 3x1 = 3 Read the above statement carefully and answer the following questions : Ans. i) Identify the Fundamental Right which is related to this statement. ii) How do you feel when you come across words like `disadvantaged and `disseminated being used for a sections of citizens of free India? iii) How far can `equal status and `equal opportunity restore back the dignity and freedom of these deprived classes? i) The Right to Equality ii) Even after more than 60 years of independence, when such words are still used, it looks to me a slier on the name of the country. Every citizen of India is equal in the eyes of laws which means they should be equal: politically, economically and socially. iii) If equal opportunities are provided and availed of, it will raise and uplift the status of the people which in turn restore them the dignity and freedom. So, all out efforts should be made to bring social and economic equality. 147
Q1. India has enormous diversity in the availability of resources. Explain.
 Class:- X Delhi Public School, Jammu Question Bank Session:- 2017-18 Subject- Social-Science Q1. India has enormous diversity in the availability of resources. Explain. Ans- i) The states of Jharkhand,
Class:- X Delhi Public School, Jammu Question Bank Session:- 2017-18 Subject- Social-Science Q1. India has enormous diversity in the availability of resources. Explain. Ans- i) The states of Jharkhand,
Social Science. Marking Scheme. Class X. 1. (d) or (b) 1 2. (b) 1 3. (c) (c ) 1 5. (d) 1 6. (a) (b) 1 8. (a) 1 9.
 Social Science Marking Scheme Class X 1. (d) or (b) 1 2. (b) 1. (c) 1 4. (c ) 1 5. (d) 1 6. (a) 1 7. (b) 1 8. (a) 1 9. (b) 1 10. Unification of Italy Mazzini formed a secret society called young Italy-
Social Science Marking Scheme Class X 1. (d) or (b) 1 2. (b) 1. (c) 1 4. (c ) 1 5. (d) 1 6. (a) 1 7. (b) 1 8. (a) 1 9. (b) 1 10. Unification of Italy Mazzini formed a secret society called young Italy-
CBSE Sample Paper-03 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science
 CBSE Sample Paper-03 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science Time allowed: 3 hours ANSWER Maximum Marks: 90 1. In 1834, a customs union or Zollverein was formed at the initiative of Prussia and
CBSE Sample Paper-03 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science Time allowed: 3 hours ANSWER Maximum Marks: 90 1. In 1834, a customs union or Zollverein was formed at the initiative of Prussia and
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, 2012 II, Class X / Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks :
 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, 202 II, 202 SOCIAL SCIENCE / Class X / X SS-200 Time allowed : hours Maximum Marks : 80 80 General Instructions : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) The question paper has 6 questions
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, 202 II, 202 SOCIAL SCIENCE / Class X / X SS-200 Time allowed : hours Maximum Marks : 80 80 General Instructions : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) The question paper has 6 questions
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT TEST- 2, SOCIAL SCIENCE
 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, ERNAKULAM REGION SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT TEST- 2, 2013-14 SOCIAL SCIENCE SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER CLASS: 10 MAX MARKS: 90 TIME ALLOWED: 3 Hrs 1. The question paper has 30 questions
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, ERNAKULAM REGION SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT TEST- 2, 2013-14 SOCIAL SCIENCE SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER CLASS: 10 MAX MARKS: 90 TIME ALLOWED: 3 Hrs 1. The question paper has 30 questions
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (FOREIGN)
 MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (FOREIGN) Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION MARCH 205 CODE NO. 32/2/3 Requirement for a political party to be recognized as a State Party Page
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (FOREIGN) Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION MARCH 205 CODE NO. 32/2/3 Requirement for a political party to be recognized as a State Party Page
2018 SOCIAL SCIENCE SOLVED SAMPLE PAPER 5
 Class: X General Instructions: 2018 SOCIAL SCIENCE SOLVED SAMPLE PAPER 5 Marks: 80 Time: 3 hr 1. All questions are compulsory. Marks are indicated against each question. 2. Questions from serial number
Class: X General Instructions: 2018 SOCIAL SCIENCE SOLVED SAMPLE PAPER 5 Marks: 80 Time: 3 hr 1. All questions are compulsory. Marks are indicated against each question. 2. Questions from serial number
NATIONALISM IN INDIA. Q. 1. Why Gandhiji wanted 1920 movement as broad based movement? Q. 2. What was 'The Rowlatt Act, 1919'?
 NATIONALISM IN INDIA Q. 1. Why Gandhiji wanted 1920 movement as broad based movement? Q. 2. What was 'The Rowlatt Act, 1919'? Q. 3. Why did Gandhiji perceived salt as a powerful symbol that can unites
NATIONALISM IN INDIA Q. 1. Why Gandhiji wanted 1920 movement as broad based movement? Q. 2. What was 'The Rowlatt Act, 1919'? Q. 3. Why did Gandhiji perceived salt as a powerful symbol that can unites
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, 2012 II, Class X / Time allowed : 3 hours Marks :
 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, 202 II, 202 SOCIAL SCIENCE / Class X / X SS 2076 Time allowed : 3 hours Marks : 80 3 80 Maximum General Instructions : (i) The question paper has 36 questions in all. All questions
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, 202 II, 202 SOCIAL SCIENCE / Class X / X SS 2076 Time allowed : 3 hours Marks : 80 3 80 Maximum General Instructions : (i) The question paper has 36 questions in all. All questions
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, 2012 II, Class X / Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks :
 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, 202 II, 202 SOCIAL SCIENCE / Class X / X SS-2080 Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 80 3 80 General Instructions : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) The question paper has 36 questions
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, 202 II, 202 SOCIAL SCIENCE / Class X / X SS-2080 Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 80 3 80 General Instructions : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) The question paper has 36 questions
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (NSQF)
 Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS 2 MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (NSQF) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION SA-II MARCH 205 CODE NO. 532/2 Government sold the rights of water supply to a MNC. MNC increased
Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS 2 MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (NSQF) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION SA-II MARCH 205 CODE NO. 532/2 Government sold the rights of water supply to a MNC. MNC increased
The National Movement and Mahatma Gandhi ( )
 The National Movement and Mahatma Gandhi (1915-34) The Nationalist Movement of India - An Introduction In India, the rise of nationalism was intricately linked with the opposition of colonialism. The revolt
The National Movement and Mahatma Gandhi (1915-34) The Nationalist Movement of India - An Introduction In India, the rise of nationalism was intricately linked with the opposition of colonialism. The revolt
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (FOREIGN)
 MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (FOREIGN) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION MARCH 205 CODE NO. 32/2/ Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS Major issues taken up by the liberal nationalists Freedom of the Press
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (FOREIGN) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION MARCH 205 CODE NO. 32/2/ Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS Major issues taken up by the liberal nationalists Freedom of the Press
NATIONAL MOVEMENT AND MAHATMA GANDHI
 NATIONAL MOVEMENT AND MAHATMA GANDHI M E T H O D S A D O P T E D B Y G A N D H I I N T H E N A T I O N A L M O V E M E N T [ S A T Y A G R A H A & S W A D E S H I ] T H E C A U S E S F O R T H E N O N
NATIONAL MOVEMENT AND MAHATMA GANDHI M E T H O D S A D O P T E D B Y G A N D H I I N T H E N A T I O N A L M O V E M E N T [ S A T Y A G R A H A & S W A D E S H I ] T H E C A U S E S F O R T H E N O N
CBSE Board Class X Summative Assessment II Social Science Board Question Paper 2014 Set 2
 CBSE Board Class X Summative Assessment II Social Science Board Question Paper 2014 Set 2 Time: 3 hrs Max. Marks: 90 Note: Please check that this question paper contains 13 printed pages + 1Map. Code number
CBSE Board Class X Summative Assessment II Social Science Board Question Paper 2014 Set 2 Time: 3 hrs Max. Marks: 90 Note: Please check that this question paper contains 13 printed pages + 1Map. Code number
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (FOREIGN)
 MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (FOREIGN) Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS Logo like to see on a tin of edible oil- SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION MARCH 205 CODE NO. 32/2/2 Page MARKS 2 Agmark Pg-85(E)
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (FOREIGN) Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS Logo like to see on a tin of edible oil- SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION MARCH 205 CODE NO. 32/2/2 Page MARKS 2 Agmark Pg-85(E)
Nationalism movement wanted to: UNIFICATION: peoples of common culture from different states were joined together
 7-3.2 Analyze the effects of the Napoleonic Wars on the development and spread of nationalism in Europe, including the Congress of Vienna, the revolutionary movements of 1830 and 1848, and the unification
7-3.2 Analyze the effects of the Napoleonic Wars on the development and spread of nationalism in Europe, including the Congress of Vienna, the revolutionary movements of 1830 and 1848, and the unification
THE QUESTION PAPER WILL INCLUDE VALUE BASED QUESTION(S) TO THE EXTENT OF 3-5 MARKS.
 ANNEXURE 'H' SYLLABUS SOCIAL SCIENCE SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-II (2013-14) Class-X Time : 3 Hours Marks : 90 UNIT TERM 1 TERM 2 1 India and the Contemporary World - II 23 23 2 India - Resources and their Development
ANNEXURE 'H' SYLLABUS SOCIAL SCIENCE SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-II (2013-14) Class-X Time : 3 Hours Marks : 90 UNIT TERM 1 TERM 2 1 India and the Contemporary World - II 23 23 2 India - Resources and their Development
Note: Please ensure that these instructions are not printed with the question paper being administered to the examinees.
 Important Instructions for the School Principal (Not to be printed with the question paper) ) This question paper is strictly meant for the use in School Based Summative Assessment-II, March-202 only.
Important Instructions for the School Principal (Not to be printed with the question paper) ) This question paper is strictly meant for the use in School Based Summative Assessment-II, March-202 only.
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II SOCIAL SCIENCE Sample Paper 2 Class X. Time: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 90
 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II SOCIAL SCIENCE Sample Paper 2 Class X Time: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 90 Instructions: The question paper has 32 questions in all. All questions are compulsory. Marks are indicated
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II SOCIAL SCIENCE Sample Paper 2 Class X Time: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 90 Instructions: The question paper has 32 questions in all. All questions are compulsory. Marks are indicated
*Agricultural Revolution Came First. Working Class Political Movement
 1848-1914 *Agricultural Revolution Came First. 1. Great Britain led the Way 2. Migration from Rural to Urban (Poor Living Conditions) 3. Proletarianization of the Workforce (Poor Working Conditions) 4.
1848-1914 *Agricultural Revolution Came First. 1. Great Britain led the Way 2. Migration from Rural to Urban (Poor Living Conditions) 3. Proletarianization of the Workforce (Poor Working Conditions) 4.
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - II SESSION SOCIAL SCIENCE (CODE NO. 087) Set - 2 CLASS-X
 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - II SESSION 20-6 SOCIAL SCIENCE (CODE NO. 087) Set - 2 CLASS-X Time Allowed: Hours Maximum Marks: 90 General Instructions:. There are 29 questions in all. All questions are compulsory.
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - II SESSION 20-6 SOCIAL SCIENCE (CODE NO. 087) Set - 2 CLASS-X Time Allowed: Hours Maximum Marks: 90 General Instructions:. There are 29 questions in all. All questions are compulsory.
Ch 29-1 The War Develops
 Ch 29-1 The War Develops The Main Idea Concern about the spread of communism led the United States to become increasingly violent in Vietnam. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze how the Cold war and
Ch 29-1 The War Develops The Main Idea Concern about the spread of communism led the United States to become increasingly violent in Vietnam. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze how the Cold war and
African Independence Movements. After World War I, many Africans organized to end colonial rule in their countries.
 African Independence Movements After World War I, many Africans organized to end colonial rule in their countries. African Independence Movements (cont.) Opposition to colonial rule escalated and Africans
African Independence Movements After World War I, many Africans organized to end colonial rule in their countries. African Independence Movements (cont.) Opposition to colonial rule escalated and Africans
4 Rebuilding a World Economy: The Post-war Era
 4 Rebuilding a World Economy: The Post-war Era The Second World War broke out a mere two decades after the end of the First World War. It was fought between the Axis powers (mainly Nazi Germany, Japan
4 Rebuilding a World Economy: The Post-war Era The Second World War broke out a mere two decades after the end of the First World War. It was fought between the Axis powers (mainly Nazi Germany, Japan
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT FIRST PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION SUBJECT : SOCIAL SCIENCE MARKING SCHEME
 Roll Number Code Number 87/2 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT FIRST PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION SUBJECT : SOCIAL SCIENCE MARKING SCHEME CLASS: X Sub. Code: 087 Time Allotted: Hrs.2.207 Max. Marks: 80 Q. No. mar ks To
Roll Number Code Number 87/2 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT FIRST PRELIMINARY EXAMINATION SUBJECT : SOCIAL SCIENCE MARKING SCHEME CLASS: X Sub. Code: 087 Time Allotted: Hrs.2.207 Max. Marks: 80 Q. No. mar ks To
History The Rise of Nationalism in Europe
 Class X.A History The Rise of Nationalism in Europe 1. Explain Frederic Sorrieu s utopian vision of a world made up of democratic and social republics? *Frederic Sorrieu was a French artist who prepared
Class X.A History The Rise of Nationalism in Europe 1. Explain Frederic Sorrieu s utopian vision of a world made up of democratic and social republics? *Frederic Sorrieu was a French artist who prepared
Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe
 Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe Frederic Sorrieu He was a French artist famous for prints prepared in 1948 that visualized the dream of a world consisting of Democratic and Social Republics.
Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe Frederic Sorrieu He was a French artist famous for prints prepared in 1948 that visualized the dream of a world consisting of Democratic and Social Republics.
THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL DUBAI SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II MODEL QUESTION PAPER ( ) SOCIAL SCIENCE- CLASSX (BOYS)
 THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL DUBAI SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II MODEL QUESTION PAPER (2016-17) SOCIAL SCIENCE- CLASSX (BOYS) Time allotted- 3hours Maximum Marks-90 Date-15-1-2017 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS (1) The question
THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL DUBAI SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II MODEL QUESTION PAPER (2016-17) SOCIAL SCIENCE- CLASSX (BOYS) Time allotted- 3hours Maximum Marks-90 Date-15-1-2017 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS (1) The question
TOPIC: FORESTS, SOCIETY AND COLONIALISM
 TOPIC: FORESTS, SOCIETY AND COLONIALISM 1) Mention any few provisions which prompted the Samins to revolt against the Dutch. 2) Who was Huitotos? 3) How tendu leaves enhance the income of people living
TOPIC: FORESTS, SOCIETY AND COLONIALISM 1) Mention any few provisions which prompted the Samins to revolt against the Dutch. 2) Who was Huitotos? 3) How tendu leaves enhance the income of people living
Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain????
 Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain???? Read textbook pages 612-615. Write a paragraph explaining why the industrial revolution began in Great Britain. Please include something about
Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain???? Read textbook pages 612-615. Write a paragraph explaining why the industrial revolution began in Great Britain. Please include something about
Clash of Philosophies: 11/10/2010
 1. Notebook Entry: Nationalism Vocabulary 2. What does nationalism look like? EQ: What role did Nationalism play in 19 th century political development? Common Language, Romanticism, We vs. They, Irrational
1. Notebook Entry: Nationalism Vocabulary 2. What does nationalism look like? EQ: What role did Nationalism play in 19 th century political development? Common Language, Romanticism, We vs. They, Irrational
Literarysources.wordpress.com
 QUESTION BANK - HISTORY - CLASS X NATIONALISM IN INDIA 1. How did the First World War help in the growth of national movement in India? 2. What is meant by the idea of satyagraha? Or A satyagrahi wins
QUESTION BANK - HISTORY - CLASS X NATIONALISM IN INDIA 1. How did the First World War help in the growth of national movement in India? 2. What is meant by the idea of satyagraha? Or A satyagrahi wins
PT-1 Answer Key Set-1. History
 PT-1 Answer Key Set-1 History Q1. Conservative regimes set up in 1815 were autocratic. A) They did not tolerate criticism and dissent. B) They tried to curb the activities that questioned the legitimacy
PT-1 Answer Key Set-1 History Q1. Conservative regimes set up in 1815 were autocratic. A) They did not tolerate criticism and dissent. B) They tried to curb the activities that questioned the legitimacy
Grade X. Social Science (HOTS) #GrowWithGreen
 Grade X Social Science (HOTS) #GrowWithGreen Questions 1. Culture had played an important role in the development of nationalism in Europe during eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. Explain. 2. Do you
Grade X Social Science (HOTS) #GrowWithGreen Questions 1. Culture had played an important role in the development of nationalism in Europe during eighteenth and nineteenth centuries. Explain. 2. Do you
Ch. 15: The Industrial Revolution
 Ch. 15: The Industrial Revolution I. Understanding Economics a. The Three Economic Questions i. People have unlimited wants, but limited resources. ii. 3 basic questions: 1. What should be produced? 2.
Ch. 15: The Industrial Revolution I. Understanding Economics a. The Three Economic Questions i. People have unlimited wants, but limited resources. ii. 3 basic questions: 1. What should be produced? 2.
CBSE Guide Teacher' Jobs CBSE News
 Time: 3hrs. Social Science Max Marks :80 Guess Paper Class X General Instructions:- 1. The question paper has 36 questions in all. All questions are compulsory. 2. Marks are indicated against each question.
Time: 3hrs. Social Science Max Marks :80 Guess Paper Class X General Instructions:- 1. The question paper has 36 questions in all. All questions are compulsory. 2. Marks are indicated against each question.
Indian Freedom Struggle: Important Events 1857 Mutiny against the British
 Year Indian Freedom Struggle: Important Events 1857 Mutiny against the British 1858 Government Of India Act 1858 1861 Indian Councils Act 1861 1875 Arya Samaj founder on 10 April 1875 by Sawami Dayananda
Year Indian Freedom Struggle: Important Events 1857 Mutiny against the British 1858 Government Of India Act 1858 1861 Indian Councils Act 1861 1875 Arya Samaj founder on 10 April 1875 by Sawami Dayananda
Curriculum Pacing Guide Grade/Course: World History and Geography 1500 to the Present Grading Period: 1 st 9 Weeks
 2011-12 Curriculum Pacing Guide Grade/Course: World History and Geography 1500 to the Present Grading Period: 1 st 9 Weeks Time Frame 1 Week Geography, Trade, and Religions Review: A. Basic Map and globe
2011-12 Curriculum Pacing Guide Grade/Course: World History and Geography 1500 to the Present Grading Period: 1 st 9 Weeks Time Frame 1 Week Geography, Trade, and Religions Review: A. Basic Map and globe
SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS X SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER II
 SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS X SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER II Time Allowed : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 80 INSTRUCTIONS 1. There are 29 questions in all. All questions are compulsory. 2. Marks for each question are indicated
SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS X SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER II Time Allowed : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 80 INSTRUCTIONS 1. There are 29 questions in all. All questions are compulsory. 2. Marks for each question are indicated
India and Vietnam Independence Activator
 India and Vietnam Independence Activator Essential Question: How did nationalism lead to independence in India and Vietnam? Standards: SS7H3a. Describe how nationalism led to independence in India and
India and Vietnam Independence Activator Essential Question: How did nationalism lead to independence in India and Vietnam? Standards: SS7H3a. Describe how nationalism led to independence in India and
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (DELHI)
 MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (DELHI) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION MARCH 2015 CODE NO. 32/1/3 Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS Page No. MARKS 1 Role of FEDECOR: 2 3 The protest against water privatization
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (DELHI) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION MARCH 2015 CODE NO. 32/1/3 Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS Page No. MARKS 1 Role of FEDECOR: 2 3 The protest against water privatization
Downloaded from
 INDIA AFTER INDEPENDENCE Ques1) Mention the challenges faced by independent India. 1. Framing a new constitution for India 2. Integration of states into the Indian union. 3. Planning for development of
INDIA AFTER INDEPENDENCE Ques1) Mention the challenges faced by independent India. 1. Framing a new constitution for India 2. Integration of states into the Indian union. 3. Planning for development of
Chapter 3 Nationalism in India
 Chapter 3 Nationalism in India Nationalism It involves a strong identification of a group of individuals with a political entity defined in national terms, i.e., a nation. Modern nationalism was associated
Chapter 3 Nationalism in India Nationalism It involves a strong identification of a group of individuals with a political entity defined in national terms, i.e., a nation. Modern nationalism was associated
B. Directions: Use the words from the sentences to fill in the words in this puzzle. The letters in the box reading down name a part of nationalism.
 Name Date Period Nationalism Puzzle Chapter 22 Activity 64 A. Directions: Write the correct word from the Word Bank to complete each sentence. 1) Customs, religion, music, beliefs, and way of life make
Name Date Period Nationalism Puzzle Chapter 22 Activity 64 A. Directions: Write the correct word from the Word Bank to complete each sentence. 1) Customs, religion, music, beliefs, and way of life make
CLASS IX MID TERM EXAM SUBJECT: - HISTORY & POLITICAL SCIENCE SET C1/2
 CLASS IX MID TERM EXAM 207-8 SUBJECT: - HISTORY & POLITICAL SCIENCE SET C/2 C C2 VALUE POINTS MARKS Q. What did the Red Phrygian cap signify to the French? Ans.The Red Phrygian cap symbolized Liberty.
CLASS IX MID TERM EXAM 207-8 SUBJECT: - HISTORY & POLITICAL SCIENCE SET C/2 C C2 VALUE POINTS MARKS Q. What did the Red Phrygian cap signify to the French? Ans.The Red Phrygian cap symbolized Liberty.
Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman Perspectives
 STANDARD 10.1.1 Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman Perspectives Specific Objective: Analyze the similarities and differences in Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman views of law, reason and faith, and duties of
STANDARD 10.1.1 Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman Perspectives Specific Objective: Analyze the similarities and differences in Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman views of law, reason and faith, and duties of
POLITICAL PHILOSOPHY UNDERLYING THE CONSTITUTION
 Page No.1 INTRODUCTION: The political philosophy of the constitution consists of three things. a) The conceptual structure; meaning of the terms used in constitution like democracy, rights, citizenship
Page No.1 INTRODUCTION: The political philosophy of the constitution consists of three things. a) The conceptual structure; meaning of the terms used in constitution like democracy, rights, citizenship
Country Dead Wounded POW/MIA Total Mobilized Austria-Hungary 1,200,000 3,620,000 2,200,000 7,020,000 7,800,000 Belgium 13,716 44,686 34,659 93,061
 Europe before WWI Europe after WWI Country Dead Wounded POW/MIA Total Mobilized Austria-Hungary 1,200,000 3,620,000 2,200,000 7,020,000 7,800,000 Belgium 13,716 44,686 34,659 93,061 267,000 British Empire
Europe before WWI Europe after WWI Country Dead Wounded POW/MIA Total Mobilized Austria-Hungary 1,200,000 3,620,000 2,200,000 7,020,000 7,800,000 Belgium 13,716 44,686 34,659 93,061 267,000 British Empire
Europe Faces Revolution
 8.2 Notes: Europe Faces Revolution World History 9 th Mr. Sanderson Europe, 1815 Napoleon was defeated ended 25 years of war in Europe Old monarchs were restored to power (with limited powers) The Congress
8.2 Notes: Europe Faces Revolution World History 9 th Mr. Sanderson Europe, 1815 Napoleon was defeated ended 25 years of war in Europe Old monarchs were restored to power (with limited powers) The Congress
Balance of Power. Balance of Power, theory and policy of international relations that asserts that the most effective
 Balance of Power I INTRODUCTION Balance of Power, theory and policy of international relations that asserts that the most effective check on the power of a state is the power of other states. In international
Balance of Power I INTRODUCTION Balance of Power, theory and policy of international relations that asserts that the most effective check on the power of a state is the power of other states. In international
GRADE 10 5/31/02 WHEN THIS WAS TAUGHT: MAIN/GENERAL TOPIC: WHAT THE STUDENTS WILL KNOW OR BE ABLE TO DO: COMMENTS:
 1 SUB- Age of Revolutions (1750-1914) Continued from Global I Economic and Social Revolutions: Agrarian and Industrial Revolutions Responses to industrialism (Karl Marx) Socialism Explain why the Industrial
1 SUB- Age of Revolutions (1750-1914) Continued from Global I Economic and Social Revolutions: Agrarian and Industrial Revolutions Responses to industrialism (Karl Marx) Socialism Explain why the Industrial
What is nationalism? What impact can it have? Objective: Explain what nationalism is and what effect it can have on individuals and on society.
 What is nationalism? What impact can it have? Objective: Explain what nationalism is and what effect it can have on individuals and on society. Introduction Directions: Examine the images and information
What is nationalism? What impact can it have? Objective: Explain what nationalism is and what effect it can have on individuals and on society. Introduction Directions: Examine the images and information
Unit 11: Age of Nationalism, Garibaldi in Naples
 Unit 11: Age of Nationalism, 1850-1914 Garibaldi in Naples Learning Objectives Explain why nationalism became an almost universal faith in Europe. Describe the unifications of both Germany and Italy-in
Unit 11: Age of Nationalism, 1850-1914 Garibaldi in Naples Learning Objectives Explain why nationalism became an almost universal faith in Europe. Describe the unifications of both Germany and Italy-in
CLASS VIII: OUR PASTS III
 CLASS VIII: OUR PASTS III Where, When, How (a) An overview of the period. (b) Introduction to the new geographical categories. (c) An outline of the time frame. (d) An introduction to the sources. (a)
CLASS VIII: OUR PASTS III Where, When, How (a) An overview of the period. (b) Introduction to the new geographical categories. (c) An outline of the time frame. (d) An introduction to the sources. (a)
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, 2012 II, Class X / Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks :
 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, 202 II, 202 SOCIAL SCIENCE / Class X / X 68043 Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 80 3 80 General Instructions : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) The question paper has 36 questions
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, 202 II, 202 SOCIAL SCIENCE / Class X / X 68043 Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 80 3 80 General Instructions : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) The question paper has 36 questions
Unit 7. Historical Background for Southern and Eastern Asia
 Unit 7 Historical Background for Southern and Eastern Asia What You Will Learn Historical events in Southern and Eastern Asia have shaped the governments, nations, economies, and culture through conflict
Unit 7 Historical Background for Southern and Eastern Asia What You Will Learn Historical events in Southern and Eastern Asia have shaped the governments, nations, economies, and culture through conflict
Southeast Asia: Violence, Economic Growth, and Democratization. April 9, 2015
 Southeast Asia: Violence, Economic Growth, and Democratization April 9, 2015 Review Is the Democratic People s Republic of Korea really a republic? Why has the economy of the DPRK fallen so far behind
Southeast Asia: Violence, Economic Growth, and Democratization April 9, 2015 Review Is the Democratic People s Republic of Korea really a republic? Why has the economy of the DPRK fallen so far behind
CBSE Sample Paper-05 (Solved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science. Time allowed: 3 hours ANSWERS Maximum Marks: 90
 CBSE Sample Paper-05 (Solved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science Time allowed: 3 hours ANSWERS Maximum Marks: 90 1. Young Italy in Marseilles and Young Europe in Berne. OR Military and Economic
CBSE Sample Paper-05 (Solved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science Time allowed: 3 hours ANSWERS Maximum Marks: 90 1. Young Italy in Marseilles and Young Europe in Berne. OR Military and Economic
CBSE Sample Paper-04 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science
 CBSE Sample Paper-04 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science Time allowed: 3 hours ANSWERS Maximum Marks: 90 1. China 2. Periodically, banks have to submit information to the RBI on how much they
CBSE Sample Paper-04 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science Time allowed: 3 hours ANSWERS Maximum Marks: 90 1. China 2. Periodically, banks have to submit information to the RBI on how much they
CHAPTER 23 The Emergence of Industrial Society in the West,
 CHAPTER 23 The Emergence of Industrial Society in the West, 1760-1914 World Civilizations: The Global Experience Fifth Edition Stearns/Adas/Schwartz/Gilbert Copyright 2007, Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
CHAPTER 23 The Emergence of Industrial Society in the West, 1760-1914 World Civilizations: The Global Experience Fifth Edition Stearns/Adas/Schwartz/Gilbert Copyright 2007, Pearson Education, Inc., publishing
BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (TELANGANA) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - II
 BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (TELANGANA) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - II TENTH CLASS SOCIAL STUDIES MODEL PAPER PAPER - II (ENGLISH VERSION) Time: 2 hrs. 45 mins. PART - A & B Maximum Marks: 40 INSTRUCTIONS:
BOARD OF SECONDARY EDUCATION (TELANGANA) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - II TENTH CLASS SOCIAL STUDIES MODEL PAPER PAPER - II (ENGLISH VERSION) Time: 2 hrs. 45 mins. PART - A & B Maximum Marks: 40 INSTRUCTIONS:
COUNTRY DATA: UNITED KINGDOM: Information from the CIA World INTRODUCTION GEOGRAPHY
 COUNTRY DATA: UNITED KINGDOM: Information from the CIA World INTRODUCTION The United Kingdom has historically played a leading role in developing parliamentary democracy and in advancing literature and
COUNTRY DATA: UNITED KINGDOM: Information from the CIA World INTRODUCTION The United Kingdom has historically played a leading role in developing parliamentary democracy and in advancing literature and
HISTORY CHAPTER 4: RISE OF ASSERTIVE NATIONALISM
 CLASS 9 HISTORY CHAPTER 4: RISE OF ASSERTIVE NATIONALISM Q1. Highlight the different methods of struggle adopted by the Moderates and the Assertive Nationalists. Ans: MODERATES The moderates wanted to
CLASS 9 HISTORY CHAPTER 4: RISE OF ASSERTIVE NATIONALISM Q1. Highlight the different methods of struggle adopted by the Moderates and the Assertive Nationalists. Ans: MODERATES The moderates wanted to
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (DELHI)
 Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS 1 MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (DELHI) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION MARCH 2015 CODE NO. 32/1/1 The French Revolution led to the transfer of sovereignty from the monarchy
Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS 1 MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (DELHI) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION MARCH 2015 CODE NO. 32/1/1 The French Revolution led to the transfer of sovereignty from the monarchy
Period V ( ): Industrialization and Global Integration
 Period V (1750-1900): Industrialization and Global Integration 5.1 Industrialization and Global Capitalism I. I can describe and explain how industrialism fundamentally changed how goods were produced.
Period V (1750-1900): Industrialization and Global Integration 5.1 Industrialization and Global Capitalism I. I can describe and explain how industrialism fundamentally changed how goods were produced.
Chapter 8 National Self-Determination
 Chapter 8 National Self-Determination Chapter Issue: Should national self-determination be pursued? Related Issue #2: Should nations pursue national interest? Name: #1 Chapter 8: National Self-Determination
Chapter 8 National Self-Determination Chapter Issue: Should national self-determination be pursued? Related Issue #2: Should nations pursue national interest? Name: #1 Chapter 8: National Self-Determination
World History SGM Review Ch 1+2 Review Ch 5 Review Ch 6 Review Multiple Choice
 World History SGM Review 2017-2018 Ch 1+2 Review 2017-2018 Increasing numbers of people learned to read after the mid-1400s because The Renaissance focused on a new idea of human interaction rather than
World History SGM Review 2017-2018 Ch 1+2 Review 2017-2018 Increasing numbers of people learned to read after the mid-1400s because The Renaissance focused on a new idea of human interaction rather than
Notes on the Industrial Revolution ( ) A. Machines start to replace human & animal power in production and manufacturing of goods
 I. Overview of Industrial Revolution (IR) Notes on the Industrial Revolution (1780-1850) A. Machines start to replace human & animal power in production and manufacturing of goods B. Europe gradually transforms
I. Overview of Industrial Revolution (IR) Notes on the Industrial Revolution (1780-1850) A. Machines start to replace human & animal power in production and manufacturing of goods B. Europe gradually transforms
Part Read about the regions of great Britain and Northern Ireland. Briefly describe its two regions:
 Social Studies 9 Unit 3 Worksheet Chapter 2, Part 1. 1. Democracy and have only been won after much. Many Canadian democratic traditions come originally from. The was signed in 1215 and recognized individual
Social Studies 9 Unit 3 Worksheet Chapter 2, Part 1. 1. Democracy and have only been won after much. Many Canadian democratic traditions come originally from. The was signed in 1215 and recognized individual
Teacher Overview Objectives: Nationalism and the Unification of Germany and Italy
 Teacher Overview Objectives: Nationalism and the Unification of Germany and Italy NYS Social Studies Framework Alignment: Key Idea Conceptual Understanding Content Specification 10.2: ENLIGHTENMENT, REVOLUTION,
Teacher Overview Objectives: Nationalism and the Unification of Germany and Italy NYS Social Studies Framework Alignment: Key Idea Conceptual Understanding Content Specification 10.2: ENLIGHTENMENT, REVOLUTION,
Regional Economic Integration : the European Union Process.
 INTERNATIONAL AFFAIRS Regional Economic Integration : the European Union Process. IAE - Paris, April 21 st 2015 Marie-Christine HENRIOT 1 INTERNATIONAL AFFAIRS United in diversity 2 INTERNATIONAL AFFAIRS
INTERNATIONAL AFFAIRS Regional Economic Integration : the European Union Process. IAE - Paris, April 21 st 2015 Marie-Christine HENRIOT 1 INTERNATIONAL AFFAIRS United in diversity 2 INTERNATIONAL AFFAIRS
IRELAND: A DIVIDED COUNTRY
 IRELAND: A DIVIDED COUNTRY Key Focus: Why is Ireland a divided nation? Level Effort (1-5) House Points (/10) Comment: Target: Ipad/Internet research task Find a map of the British Isles and sketch or print
IRELAND: A DIVIDED COUNTRY Key Focus: Why is Ireland a divided nation? Level Effort (1-5) House Points (/10) Comment: Target: Ipad/Internet research task Find a map of the British Isles and sketch or print
Chapter 12. Chapter 12 Section 1 China Resist Outside Influence. Transformations Around The Globe Confucianism. Confucius (K'ung-tzu)
 Chapter 12 Transformations Around The Globe 1800-1914 Chapter 12 Section 1 China Resist Outside Influence Confucius (K'ung-tzu) Kong" 551 BC 479 BC Chinese and social philosopher. emphasized and governmental
Chapter 12 Transformations Around The Globe 1800-1914 Chapter 12 Section 1 China Resist Outside Influence Confucius (K'ung-tzu) Kong" 551 BC 479 BC Chinese and social philosopher. emphasized and governmental
The Roots of the Cold War
 The Roots of the Cold War Communism No real wealthy people State/country controls everything business related No free enterprise system 1 ruler that can easily turn into a dictatorship Roots of the Cold
The Roots of the Cold War Communism No real wealthy people State/country controls everything business related No free enterprise system 1 ruler that can easily turn into a dictatorship Roots of the Cold
Albania: Country of Opportunities
 Albania: Country of Opportunities Four reasons to invest in Albania A Export-oriented B Competitive C Promising D Comprehensive Growth Human Capital Sectoral Opportunities Structural Reforms A Export-oriented
Albania: Country of Opportunities Four reasons to invest in Albania A Export-oriented B Competitive C Promising D Comprehensive Growth Human Capital Sectoral Opportunities Structural Reforms A Export-oriented
EUROPEAN NATIONALISM. Mid 19 th Century
 EUROPEAN NATIONALISM Mid 19 th Century What is Nationalism? the belief that a person s greatest loyalty should not be to a king or an empire but to a nation of people who share a common culture and history.
EUROPEAN NATIONALISM Mid 19 th Century What is Nationalism? the belief that a person s greatest loyalty should not be to a king or an empire but to a nation of people who share a common culture and history.
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION. called the Scheduled Castes, is the constitutionally recognized.
 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION According to John C. B. Webster, the term Dalit (oppressed or broken) is not a new word it was used in the year 1930s as a Hindi, and Marathi Translation of depressed classes, the
CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION According to John C. B. Webster, the term Dalit (oppressed or broken) is not a new word it was used in the year 1930s as a Hindi, and Marathi Translation of depressed classes, the
I. The Agricultural Revolution
 I. The Agricultural Revolution A. The Agricultural Revolution Paves the Way 1. Wealthy farmers cultivated large fields called enclosures. 2. The enclosure movement caused landowners to try new methods.
I. The Agricultural Revolution A. The Agricultural Revolution Paves the Way 1. Wealthy farmers cultivated large fields called enclosures. 2. The enclosure movement caused landowners to try new methods.
The Early Industrial Revolution Chapter 22 AP World History
 The Early Industrial Revolution 1760-1851 Chapter 22 AP World History Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
The Early Industrial Revolution 1760-1851 Chapter 22 AP World History Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
1: Population* and urbanisation for want of more hands
 1: Population* and urbanisation for want of more hands *Remember that the study of population is called Demographics By 1900 there were nearly five times as many people in Britain as there were in 1750.
1: Population* and urbanisation for want of more hands *Remember that the study of population is called Demographics By 1900 there were nearly five times as many people in Britain as there were in 1750.
CBSE Sample Paper-04 (Solved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science. Time allowed: 3 hours ANSWERS Maximum Marks: 90
 CBSE Sample Paper-04 (Solved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science Time allowed: 3 hours ANSWERS Maximum Marks: 90 1. Bourbon Kings OR 1873 2. 32 kg per annum 3. In this system of voting the
CBSE Sample Paper-04 (Solved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science Time allowed: 3 hours ANSWERS Maximum Marks: 90 1. Bourbon Kings OR 1873 2. 32 kg per annum 3. In this system of voting the
HISTORY. March 21, 2018
 HISTORY March 21, 2018 Capitalism-System in which the means of production is in the hands of an individual The economy was well balanced between agriculture and industry. Three stages of Capitalism in
HISTORY March 21, 2018 Capitalism-System in which the means of production is in the hands of an individual The economy was well balanced between agriculture and industry. Three stages of Capitalism in
Scientific Revolution. 17 th Century Thinkers. John Locke 7/10/2009
 1 Scientific Revolution 17 th Century Thinkers John Locke Enlightenment an intellectual movement in 18 th Century Europe which promote free-thinking, individualism Dealt with areas such as government,
1 Scientific Revolution 17 th Century Thinkers John Locke Enlightenment an intellectual movement in 18 th Century Europe which promote free-thinking, individualism Dealt with areas such as government,
BLOOM PUBLIC SCHOOL Vasant Kunj, New Delhi Lesson Plan Subject: Political Science. Month: April No of Periods: 19
 Class: XI BLOOM PUBLIC SCHOOL Vasant Kunj, New Delhi Lesson Plan Subject: Political Science Month: April No of Periods: 19 Chapter: Chapter 1 and 10: Constitution: Why and How? Philosophy of the Constitution
Class: XI BLOOM PUBLIC SCHOOL Vasant Kunj, New Delhi Lesson Plan Subject: Political Science Month: April No of Periods: 19 Chapter: Chapter 1 and 10: Constitution: Why and How? Philosophy of the Constitution
Secondary School Exam. (March, 2017) Social Science (Summative Assessment 2) Marking Scheme (Delhi) 32/1/1, 32/1/2, 32/1/3
 Secondary School Exam. (March, 2017) Social Science (Summative Assessment 2) Marking Scheme (Delhi) 32/1/1, 32/1/2, 32/1/3 General Instructions: 1. The Marking scheme provides general guidelines to reduce
Secondary School Exam. (March, 2017) Social Science (Summative Assessment 2) Marking Scheme (Delhi) 32/1/1, 32/1/2, 32/1/3 General Instructions: 1. The Marking scheme provides general guidelines to reduce
COUNTRY DATA: Belgium : Information from the CIA World Factbook
 COUNTRY DATA: Belgium : Information from the CIA World Factbook INTRODUCTION Belgium became independent from the Netherlands in 1830; it was occupied by Germany during World Wars I and II. The country
COUNTRY DATA: Belgium : Information from the CIA World Factbook INTRODUCTION Belgium became independent from the Netherlands in 1830; it was occupied by Germany during World Wars I and II. The country
Absolutism and Enlightenment
 Absolutism and Enlightenment The Commercial Revolution Most of Europe remained agricultural between 1600-1770 The Commercial Revolution marked an important step in the transition from the local economies
Absolutism and Enlightenment The Commercial Revolution Most of Europe remained agricultural between 1600-1770 The Commercial Revolution marked an important step in the transition from the local economies
OBJECTIVES. Describe and evaluate the events that led to the war between North Vietnam and South Vietnam.
 OBJECTIVES Describe and evaluate the events that led to the war between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. Identify and explain the foreign policy of the United States at this time, and how it relates to
OBJECTIVES Describe and evaluate the events that led to the war between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. Identify and explain the foreign policy of the United States at this time, and how it relates to
ELITE AND MASS ATTITUDES ON HOW THE UK AND ITS PARTS ARE GOVERNED DEMOCRATIC ENGAGEMENT WITH THE PROCESS OF CONSTITUTIONAL CHANGE
 BRIEFING ELITE AND MASS ATTITUDES ON HOW THE UK AND ITS PARTS ARE GOVERNED DEMOCRATIC ENGAGEMENT WITH THE PROCESS OF CONSTITUTIONAL CHANGE Lindsay Paterson, Jan Eichhorn, Daniel Kenealy, Richard Parry
BRIEFING ELITE AND MASS ATTITUDES ON HOW THE UK AND ITS PARTS ARE GOVERNED DEMOCRATIC ENGAGEMENT WITH THE PROCESS OF CONSTITUTIONAL CHANGE Lindsay Paterson, Jan Eichhorn, Daniel Kenealy, Richard Parry
WORLD HISTORY Curriculum Map
 WORLD HISTORY Curriculum Map (1 st Semester) WEEK 1- ANCIENT HISTORY Suggested Chapters 1 SS Standards LA.910.1.6.1-3 LA.910.2.2.1-3 SS.912.G.1-3 SS.912.G.2.1-3 SS.912.G.4.1-9 SS.912.H.1.3 SS.912.H.3.1
WORLD HISTORY Curriculum Map (1 st Semester) WEEK 1- ANCIENT HISTORY Suggested Chapters 1 SS Standards LA.910.1.6.1-3 LA.910.2.2.1-3 SS.912.G.1-3 SS.912.G.2.1-3 SS.912.G.4.1-9 SS.912.H.1.3 SS.912.H.3.1
Land and Natural Resources. Factors of Production. Capital: funding, investments
 AP* World History Study Guide and Graphic Organizers Unit 5: The Dawn of the Industrial Age, 1750 CE 1914 CE 1. Factors of Production A defining characteristic of this era is the Industrial Revolution.
AP* World History Study Guide and Graphic Organizers Unit 5: The Dawn of the Industrial Age, 1750 CE 1914 CE 1. Factors of Production A defining characteristic of this era is the Industrial Revolution.
India Then and Now! By: Ankit Sood Matrikel Nu.:
 India Then and Now! By: Ankit Sood Matrikel Nu.: 871123 7. April 2018 1 Facts & Figures India is world s largest, oldest and continuously existing civilization. Dates back to 9000 BC. India had world s
India Then and Now! By: Ankit Sood Matrikel Nu.: 871123 7. April 2018 1 Facts & Figures India is world s largest, oldest and continuously existing civilization. Dates back to 9000 BC. India had world s
Guidelines for CBSE Proficiency Test in Social Science 2011
 Guidelines for CBSE Proficiency Test in Social Science 2011 This document provides some general guidelines for the CBSE Proficiency Test in Social Science to be held in May-June, 2011. It aims to introduce
Guidelines for CBSE Proficiency Test in Social Science 2011 This document provides some general guidelines for the CBSE Proficiency Test in Social Science to be held in May-June, 2011. It aims to introduce
Our objective is to evaluate the U.S. Policy of containment in response to the causes and effects of the Korean and Vietnam Wars.
 Our objective is to evaluate the U.S. Policy of containment in response to the causes and effects of the Korean and Vietnam Wars. Do Now: This OR That Write below if this relates to the Korean War, War
Our objective is to evaluate the U.S. Policy of containment in response to the causes and effects of the Korean and Vietnam Wars. Do Now: This OR That Write below if this relates to the Korean War, War
MRS. OSBORN S APWH CRAM PACKET:
 MRS. OSBORN S APWH CRAM PACKET: Period 5 Industrialization & Global Integration, 1750-1900, chapters 23-29 (20% of APWH Exam) (NOTE: Some material overlaps into Period 6, 1900-1914) Questions of periodization:
MRS. OSBORN S APWH CRAM PACKET: Period 5 Industrialization & Global Integration, 1750-1900, chapters 23-29 (20% of APWH Exam) (NOTE: Some material overlaps into Period 6, 1900-1914) Questions of periodization:
Henry6SS5 (H6SSALL) 4. In which economic system are the production and distribution of goods owned by private individuals or corporations?
 Name: Date: 1. Which word has the same meaning as the economic term "tariff"? A. tax B. savings C. debt D. money 2. Which of these factors best helps to explain why a strong navy and a large fleet of trading
Name: Date: 1. Which word has the same meaning as the economic term "tariff"? A. tax B. savings C. debt D. money 2. Which of these factors best helps to explain why a strong navy and a large fleet of trading
AMERICA AND THE WORLD. Chapter 13 Section 1 US History
 AMERICA AND THE WORLD Chapter 13 Section 1 US History AMERICA AND THE WORLD THE RISE OF DICTATORS MAIN IDEA Dictators took control of the governments of Italy, the Soviet Union, Germany, and Japan End
AMERICA AND THE WORLD Chapter 13 Section 1 US History AMERICA AND THE WORLD THE RISE OF DICTATORS MAIN IDEA Dictators took control of the governments of Italy, the Soviet Union, Germany, and Japan End
Social Studies Part 3 - Implications and Consequences of Globalization. Chapter 11 - Economic Globalization
 Social Studies 10-2 Part 3 - Implications and Consequences of Globalization Chapter 11 - Economic Globalization Why are there different understandings of economic globalization? Name: Chapter 11 - Economic
Social Studies 10-2 Part 3 - Implications and Consequences of Globalization Chapter 11 - Economic Globalization Why are there different understandings of economic globalization? Name: Chapter 11 - Economic
Ch. 6.3 Radical Period of the French Revolution. leader of the Committee of Public Safety; chief architect of the Reign of Terror
 the right to vote Ch. 6.3 Radical Period of the French Revolution leader of the Committee of Public Safety; chief architect of the Reign of Terror period from September 1793 to July 1794 when those who
the right to vote Ch. 6.3 Radical Period of the French Revolution leader of the Committee of Public Safety; chief architect of the Reign of Terror period from September 1793 to July 1794 when those who
