AP UNITED STATES HISTORY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES
|
|
|
- Elisabeth Harmon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 AP UNITED STATES HISTORY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 To what extent did the role of the federal government change under President Theodore Roosevelt in regard to TWO of the following: Labor Trusts Conservation World affairs The 8 9 Essay Contains a clear, well-developed thesis that evaluates to what extent the role of the federal government changed under President Theodore Roosevelt with regard to TWO topics. Develops the thesis with substantial and specific relevant historical information. Provides effective analysis of the extent of change regarding TWO topics; treatment of topics may be somewhat uneven. May contain minor errors that do not detract from the overall quality of the essay. Is well organized and well written. The 5 7 Essay Contains a thesis that partially evaluates to what extent the role of the federal government changed under President Theodore Roosevelt with regard to TWO topics. Supports the thesis with some relevant historical information. Provides some analysis of the extent of change regarding TWO topics; treatment of topics may be substantially uneven. May contain errors that do not seriously detract from the quality of the essay. Has acceptable organization and writing. The 2 4 Essay Contains an undeveloped, confused, or unfocused thesis, or may simply restate the question. Provides minimal relevant information or lists facts with little or no application to the question. Addresses extent of change regarding only one topic, OR, describes two topics in a general way. May contain major errors. May be poorly organized and/or written. The 0 1 Essay Lacks a thesis or paraphrases the question. Demonstrates an incompetent or inappropriate response. Has little or no understanding of the question. Contains substantial errors. Is poorly organized and/or written. The Essay Is completely off topic or blank The College Board. All rights reserved.
2 AP UNITED STATES HISTORY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 Fact Sheet Theodore Roosevelt s general approach to the presidency was characterized by his broad view of executive power under the Constitution. He sought to avoid the extremes both of socialism and pure laissez-faire individualism, but he became more committed to Progressive reform during his second term. FEDERAL GOVERNMENT AND LABOR Prior to TR Not much support of labor by the federal government. Broke strikes with troops (railroad strikes, 1877; Pullman strike, 1894). Use of injunctions against labor unions for violating Sherman Anti-Trust Act (Pullman strike, 1894). During Presidency of TR ( ) Anthracite coal strike, 1902 o TR wanted compromise between miners and mine owners. o Considered using the army to take over and reopen mines. o Convinced mine owners to accept arbitration by the federal government (Anthracite Coal Strike Commission), but TR did not recognize the miners union (United Mine Workers). Square Deal for labor, business, and the public. Department of Commerce and Labor, 1903 (created Bureau of Corporations). Lochner v. New York (1905): struck down 10-hour workday for bakers. 1907: TR proposed eight-hour day for workers and broader compensation for industrial accidents. Muller v. Oregon (1908): upheld maximum working hours for females The College Board. All rights reserved.
3 FEDERAL GOVERNMENT AND TRUSTS AP UNITED STATES HISTORY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 Fact Sheet (continued) Prior to TR Santa Clara County v. Southern Pacific Railroad (1886): corporations are treated as persons under the law and get the protection of the Fourteenth Amendment. Interstate Commerce Act (1887). Sherman Antitrust Act (1890). United States v. E. C. Knight (1895): protected manufacturers from antitrust law. William McKinley: very probusiness, but in 1898, was appointed to the U.S. Industrial Commission on Trusts, which did look into the issue of trusts and industrial combinations (among other issues). During Presidency of TR ( ) TR and Trust Busting Congress did not want to pass regulatory legislation when TR took office. o TR accepted the idea of business centralization and believed government should regulate big business rather than eliminate it; good trusts vs. bad trusts ; historians have argued that TR was not as much of a trust buster as he is often portrayed to be. o TR used trust busting selectively: some informal understandings ( gentlemen s agreements ) between corporations and the federal government, for example, U.S. Steel got TR s consent before it took over Tennessee Coal and Iron Company in o During his second term, TR turned more toward regulation of business rather than trust busting. Justice Department went after Northern Securities Company in 1902; Northern Securities v. United States (1904). Supreme Court ruled Northern Securities violated the Sherman Act. Swift and Company v. United States (1905) ( beef trust case): Supreme Court ruled that meatpackers had avoided competitive bidding when purchasing livestock and as a result had violated the Sherman Antitrust Act; stream-of-commerce doctrine; livestock and meat products were part of interstate commerce and subject to federal regulation. Standard Oil and American Tobacco cases began (Supreme Court ruled to break up Standard Oil and reorganize American Tobacco in 1911). Under TR, the Justice Department filed cases under the Sherman Act (but most came to trial after he left office). Expedition Act (1903): hastened prosecution of antitrust suits. Department of Commerce and Labor (1903): created Bureau of Corporations, which could investigate activities of interstate corporations, but many corporations cooperated with the bureau to alleviate the need for antitrust lawsuits by federal government. Examples of Regulation of Business Not Directly Related to Trusts Pure Food and Drug Act (1906). Meat Inspection Act (1906). Elkins Act (1903): no rebates by railroads. Hepburn Act (1906): ICC established maximum freight rates The College Board. All rights reserved.
4 AP UNITED STATES HISTORY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 Fact Sheet (continued) FEDERAL GOVERNMENT AND CONSERVATION Prior to TR Federal government often debated with western states about water rights but did not consider the impact of water policies on the environment. Desert Land Act (1877): federal government sold arid land on the condition it be irrigated. Division of Forestry created by Congress in 1881 (part of the Department of the Interior). Forest Reserves Act (1891): president had power to establish forest reserves to protect watersheds. (Harrison established 15 forest reserves of over 16 million acres; Cleveland added 21 million acres.) Carey Act (1894): distributed federal land to states with the condition of irrigation. Forest Management Act (1897) (Organic Administration Act of 1897): established most national forests for purposes of managed harvesting of timber, mining of mineral resources, and use of water ; directed by secretary of the interior. Yellowstone National Park created in 1872; Yosemite National Park created in Sierra Club founded in 1892 (involvement of John Muir). During Presidency of TR ( ) TR was a strong supporter of conservation but believed in managed development; saw government as manager of the development of wilderness; battled both commercial interests and romantic preservationists. Federal government withdrew federal timber and grazing land from public sale or use. Strengthened national park system: 5 national parks, 53 wildlife preserves, 16 national monuments established. 1901: 41 national forest reserves (41 million acres); 1909: 159 national forest reserves (150 million acres). Gifford Pinchot: adviser to TR on conservation. Newlands Reclamation Act (1902): federal construction of irrigation projects, dams. TR drew on his relationship with John Muir (Yosemite National Park expanded by Congress in 1906). U.S. Forest Service established in 1905 with Pinchot as first head. Antiquities Act (1906): designated objects of historic or scientific interest and national monuments. (TR interpreted this broadly for scenic preservation, whereas Congress had only intended it to apply to small areas around artifacts like American Indian cliff dwellings in the Southwest.) Controversy over Pinchot s endorsement of supplying water to San Francisco from Hetch Hetchy Valley in Yosemite National Park in 1906; Congressional committee voted against the bill; public outcry against plan; TR postponed a decision. Bureau of Reclamation established in Congress rescinded president s authority to create national forests in six western states; TR signed the bill after he set aside 16 million acres as national forests in the six states. Conference of Governors (1908) held at White House: state and national politicians and conservation organizations looked at national resources issues of grazing land, timber, water, soil quality, public health; recommended creation of National Conservation Commission. Conservative Congressmen did not like TR s approach (never funded National Conservation Commission) The College Board. All rights reserved.
5 AP UNITED STATES HISTORY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 Fact Sheet (continued) FEDERAL GOVERNMENT AND WORLD AFFAIRS Prior to TR Increased interest in world affairs in Olney Corollary/Interpretation of Monroe Doctrine (1895): United States predominant in Western Hemisphere; boundary dispute between Venezuela and British Guiana. Interest in expanding United States navy (Alfred Thayer Mahan, TR s assistant secretary of the navy): by 1896, 11 new battleships had been built or authorized. Spanish American War (1898)/Treaty of Paris (1898). United States annexation of Hawaii (1898). Eastern parts of Samoa annexed (1899): tripartite agreement (United States, Great Britain, and Germany) on Samoa (1889). Platt Amendment proposed by McKinley administration. Foraker Act (1900): Puerto Rico gets legislature, but Puerto Ricans are not citizens of United States. Filipino insurrection ( ): Philippines annexed in China: Open Door Policy (1899, 1900): United States sends military forces to suppress Boxer Rebellion in Hay Pauncefote Treaties between United States and Great Britain (1900, 1901): United States got the exclusive right to build, control, and fortify a canal through Central America. During Presidency of TR ( ) Big stick ; United States as policeman of Western Hemisphere; concern with balance of power in Asia/Pacific; United States as civilizer and transmitter WASP values; Social Darwinism. Panama o Hay Herran Treaty (1903) signed between the United States and Colombia but rejected by Colombian Senate. o United States support for revolution in Panama. o Hay Bunau Varilla Treaty (1903): United States got control over Canal Zone; Panama became a U.S. protectorate. o Canal built between 1904 and Cuba became a U.S. protectorate (Cuban American Treaty, 1903); United States landed Marines in Filipino insurrection ended in Venezuela debt dispute (1903): Great Britain, Germany, and Italy blockaded Venezuela over debts owed to private investors; TR feared armed intervention by Europeans. Roosevelt Corollary (1904): preventive intervention. Dominican Republic became a U.S. protectorate in 1905; United States took over customs house. Insular cases (1901, 1903, 1904): the Constitution does not follow the flag. TR arbitrates Russo Japanese War ( ); Treaty of Portsmouth (1905). Taft Katsura Memorandum (1905): Japan and the United States respect one another s territories in the Pacific and Asia. Act of Algeciras (1906): independence of Morocco; open door for trade; France and Spain could train and control Moroccan police. Gentlemen s Agreement with Japan ( ). TR sends Great White Fleet on world cruise ( ); arrives in Japan in The College Board. All rights reserved.
6 AP UNITED STATES HISTORY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 Fact Sheet (continued) Root Takahira Agreement (1908): Japan and United States maintain status quo in Pacific; respect Open Door Policy in China. Spring 1908: Congress endorsed a policy of building two new battleships per year The College Board. All rights reserved.
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15 AP UNITED STATES HISTORY 2007 SCORING COMMENTARY Question 4 Overview The question evaluated students understanding of the shift in the role of the federal government in the economy, society, and international affairs from the late nineteenth century to the early twentieth century, using the presidential administration of Theodore Roosevelt as a transitional period. It was a straightforward question that required students to analyze the changing role of the federal government in four areas: labor, trusts, conservation, and world affairs. Sample: 4A Score: 9 This essay offers a strong thesis, asserting that Theodore Roosevelt s use of federal power to bust trusts and promote conservation set an important precedent. It contains excellent analysis supported by specific historical information on trusts (Beef Trust, Northern Securities, Standard Oil, regulation versus elimination of trusts) and conservation (Desert Land Act, Newlands Act, conservation versus preservation, Pinchot affair). The student demonstrates a clear understanding of the larger historical context for change. This outstanding essay is thoughtful, well written, and organized logically. Sample: 4B Score: 5 This essay analyzes Roosevelt s handling of both world affairs and trusts with some specific information on each subject. Topic treatment is uneven with much better information on world affairs. The essay mentions good and bad trusts to distinguish between the two and offers an illustration of each. The student inaccurately references the Hay Pauncefote Treaty but demonstrates an understanding of what was involved. Sample: 4C Score: 3 This essay s thesis attempts to address the question but is undeveloped. The student includes minimal relevant information in a general way ( good and bad trusts, and the Roosevelt Corollary). This information, however, is not analyzed in terms of the extent of change in the role of government The College Board. All rights reserved.
Monday October 30. All Electronics Off & away
 Monday October 30 1) Bellringer: Identify Teddy Roosevelt (ID = who, what, when, where, why, how, significance) from pages 233, 234, & 237. (Infographic too) Discussion 2) Chapter 8.4: Create a Chart of
Monday October 30 1) Bellringer: Identify Teddy Roosevelt (ID = who, what, when, where, why, how, significance) from pages 233, 234, & 237. (Infographic too) Discussion 2) Chapter 8.4: Create a Chart of
America s Path to Empire. APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8
 America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8 1890-1892 Foreign Policy The Influence of Sea Power upon History (1890): Alfred Thayer Mahan Sea power throughout history gives advantages US lies
America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8 1890-1892 Foreign Policy The Influence of Sea Power upon History (1890): Alfred Thayer Mahan Sea power throughout history gives advantages US lies
Chapter 27: The Path of Empire, (Pages )
 Chapter 27: The Path of Empire, 1890 1899 (Pages 626 653) I. America Turns Outward A. Motives for overseas expansion 1. Farmers and industrialists Name Per. Date Row 2. The yellow press 3. Role of religion
Chapter 27: The Path of Empire, 1890 1899 (Pages 626 653) I. America Turns Outward A. Motives for overseas expansion 1. Farmers and industrialists Name Per. Date Row 2. The yellow press 3. Role of religion
APUSH. U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! EMPIRE & EXPANSION
 APUSH 1890-1909 EMPIRE & EXPANSION U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 27 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 19 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 21 Important Ideas Since the
APUSH 1890-1909 EMPIRE & EXPANSION U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 27 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 19 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 21 Important Ideas Since the
Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power,
 Name: Class Period: Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1865-1917 Amsco Chapter 20 Reading Assignment: Ch. 21 AMSCO Purpose: This guide is intended to provide a space for you to record
Name: Class Period: Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1865-1917 Amsco Chapter 20 Reading Assignment: Ch. 21 AMSCO Purpose: This guide is intended to provide a space for you to record
U.S. History PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT REVIEWED! THE PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT
 9/28/17 U.S. History 1890-1912 PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT REVIEWED! THE PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT WHY: Industrialization, urbanization, and immigration created significant changes and challenges for the United States.
9/28/17 U.S. History 1890-1912 PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT REVIEWED! THE PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT WHY: Industrialization, urbanization, and immigration created significant changes and challenges for the United States.
The Progressive Presidents
 The Progressive Presidents Main Ideas o The federal government responded to grassroots reform efforts by enacting progressive policies. o Progressive reforms sought to established a greater degree of democratic
The Progressive Presidents Main Ideas o The federal government responded to grassroots reform efforts by enacting progressive policies. o Progressive reforms sought to established a greater degree of democratic
APUSH REVIEWED! PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT
 APUSH 1890-1912 PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 28 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 20 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 19-20 THE PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT WHY: Industrialization,
APUSH 1890-1912 PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 28 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 20 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 19-20 THE PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT WHY: Industrialization,
Empire and Expansion. Chapter 27
 Empire and Expansion Chapter 27 Imperialism Stronger nations attempt to create empires by dominating weaker nations. The late 1800s marked the peak of European imperialism, with much of Africa and Asia
Empire and Expansion Chapter 27 Imperialism Stronger nations attempt to create empires by dominating weaker nations. The late 1800s marked the peak of European imperialism, with much of Africa and Asia
Presidents in general are not lovable. They ve had to do too much to get where they are. But there was one president who was lovable Teddy Roosevelt
 Presidents in general are not lovable. They ve had to do too much to get where they are. But there was one president who was lovable Teddy Roosevelt and I loved him Walter Lippmann Theodore Roosevelt brought
Presidents in general are not lovable. They ve had to do too much to get where they are. But there was one president who was lovable Teddy Roosevelt and I loved him Walter Lippmann Theodore Roosevelt brought
Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism
 Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism 1. List the ideas that fueled American Imperialism. 2. How were yellow journalists able to influence Americans opinions on foreign policy? 3. The person who urged
Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism 1. List the ideas that fueled American Imperialism. 2. How were yellow journalists able to influence Americans opinions on foreign policy? 3. The person who urged
Imperalism.notebook March 03, 2015
 Agenda Bell ringer Notability 1 Objective: I can discuss and explain why the United States Foreign Policy changed during the late 19th century. Bell Ringer Notability HW: Due Thursday 2 1 A B C D 3 2 A
Agenda Bell ringer Notability 1 Objective: I can discuss and explain why the United States Foreign Policy changed during the late 19th century. Bell Ringer Notability HW: Due Thursday 2 1 A B C D 3 2 A
Chapter 8 Section 2 Roosevelt and Taft (p )
 MAIN IDEAS Theodore Roosevelt Review NOTES Theodore Roosevelt Became president at age 42 Took over after the assassination of William McKinley Believed in Social Darwinism The fittest country in the world
MAIN IDEAS Theodore Roosevelt Review NOTES Theodore Roosevelt Became president at age 42 Took over after the assassination of William McKinley Believed in Social Darwinism The fittest country in the world
Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of???
 Need to know What was President Roosevelt s Gentlemen s Agreement with Japan? Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of??? imperialism Stronger nations dominating
Need to know What was President Roosevelt s Gentlemen s Agreement with Japan? Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of??? imperialism Stronger nations dominating
1 Use your ipad, notes or phone to complete the Progressive Movement worksheet
 1 Use your ipad, notes or phone to complete the Progressive Movement worksheet 2 You may work together on this assignment but you each must turn in a separate worksheet 3 The answers are a blend of old
1 Use your ipad, notes or phone to complete the Progressive Movement worksheet 2 You may work together on this assignment but you each must turn in a separate worksheet 3 The answers are a blend of old
Define the following: a. Neutrality Policy. b. Louisiana Purchase. c. War of d. Monroe Doctrine. e. Mexican-American War
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Chapter 20 in AMSCO or other resource covering the Spanish American War. Directions: 1. Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before
Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Chapter 20 in AMSCO or other resource covering the Spanish American War. Directions: 1. Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before
America s Path to Empire. APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 2
 America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 2 Major Events 1890-1892 McKinley Tariff October 1, 1890 Raised the average duty on imports to almost fifty percent Intended to protect domestic industries
America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 2 Major Events 1890-1892 McKinley Tariff October 1, 1890 Raised the average duty on imports to almost fifty percent Intended to protect domestic industries
-Born into a wealthy NY family -Had severe asthma (not expected to live past age 5) -His father stressed physical fitness TR always pushed himself
 -Born into a wealthy NY family -Had severe asthma (not expected to live past age 5) -His father stressed physical fitness TR always pushed himself physically -Loved sports, especially boxing and hunting
-Born into a wealthy NY family -Had severe asthma (not expected to live past age 5) -His father stressed physical fitness TR always pushed himself physically -Loved sports, especially boxing and hunting
Letter from President Fillmore asking Japan. American ships to stop for supplies safety reasons
 Chapter 19-21 Introduction Japan 1853 Not open to trading with other countries Commodore Matthew Perry went to Japan with a small fleet of warships (Gunboat Diplomacy) Letter from President Fillmore asking
Chapter 19-21 Introduction Japan 1853 Not open to trading with other countries Commodore Matthew Perry went to Japan with a small fleet of warships (Gunboat Diplomacy) Letter from President Fillmore asking
American Foreign Policy, : The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly.
 American Foreign Policy, 1880-1920: The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly. Each group will become experts on their assigned country. Create poster showing how U.S. policy toward your respective country was good,
American Foreign Policy, 1880-1920: The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly. Each group will become experts on their assigned country. Create poster showing how U.S. policy toward your respective country was good,
18 America Claims an Empire QUIT
 18 America Claims an Empire QUIT CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE SECTION 1 Imperialism and America GRAPH MAP SECTION 2 The Spanish-American War SECTION 3 Acquiring New Lands SECTION 4
18 America Claims an Empire QUIT CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE SECTION 1 Imperialism and America GRAPH MAP SECTION 2 The Spanish-American War SECTION 3 Acquiring New Lands SECTION 4
America s Path to Empire. APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 5
 America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 5 Mariam Haider, Emma Tresch, 5th Period America s Path to Empire 1892-1894 Feb 29, 1892: Britain and US sign treaty on seal hunting in the Bering
America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 5 Mariam Haider, Emma Tresch, 5th Period America s Path to Empire 1892-1894 Feb 29, 1892: Britain and US sign treaty on seal hunting in the Bering
U.S. Imperialism s Impact on Other Nations
 U.S. Imperialism s Impact on Other Nations U.S.-Japanese Relations Japan had closed itself to outsiders in the late 1400s; held a strong mistrust of Western cultures In mid-1800s, US businesses began to
U.S. Imperialism s Impact on Other Nations U.S.-Japanese Relations Japan had closed itself to outsiders in the late 1400s; held a strong mistrust of Western cultures In mid-1800s, US businesses began to
Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism ( )
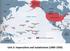 Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism (1890-1930) What is an empire? Is imperialism the same as colonization? Why would the U.S. get involved in this practice? What is the difference between acquiring and
Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism (1890-1930) What is an empire? Is imperialism the same as colonization? Why would the U.S. get involved in this practice? What is the difference between acquiring and
Progressivism. Definition of Progressivism A movement of the people to curb the powers of the special interests When did it occur?
 Progressivism Definition of Progressivism A movement of the people to curb the powers of the special interests When did it occur? Where did Progressivism originate? Who were the Progressives? Middle Class
Progressivism Definition of Progressivism A movement of the people to curb the powers of the special interests When did it occur? Where did Progressivism originate? Who were the Progressives? Middle Class
AP UNITED STATES HISTORY 2006 SCORING GUIDELINES. Question 4
 AP UNITED STATES HISTORY 2006 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 Historians have argued that Progressive reform lost momentum in the 1920 s. Evaluate this statement with respect to TWO of the following: Regulation
AP UNITED STATES HISTORY 2006 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 Historians have argued that Progressive reform lost momentum in the 1920 s. Evaluate this statement with respect to TWO of the following: Regulation
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e. Chapter Nineteen: From Crisis to Empire
 Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e The Politics of Equilibrium Electoral Stability High Turnout for Elections Cultural Basis of Party Identification Catholics Tended to Vote Democrat 2 The Politics of
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e The Politics of Equilibrium Electoral Stability High Turnout for Elections Cultural Basis of Party Identification Catholics Tended to Vote Democrat 2 The Politics of
Guided Reading & Analysis: Becoming a World Power, Chapter 20- Spanish American War, American Imperialism pp
 COMPLETE IN INK. Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Guided Reading & Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1898-1917 Chapter 20- Spanish American War, American Imperialism pp 380-391 Reading Assignment: Chapter
COMPLETE IN INK. Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Guided Reading & Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1898-1917 Chapter 20- Spanish American War, American Imperialism pp 380-391 Reading Assignment: Chapter
Who Were the Progressives? Big Ideas: President Roosevelt used his charisma and influence to curb what he saw as abuses by big business.
 Roosevelt & Taft Who Were the Progressives? Big Ideas: President Roosevelt used his charisma and influence to curb what he saw as abuses by big business. Roosevelt Takes on the Trusts Theodore Roosevelt
Roosevelt & Taft Who Were the Progressives? Big Ideas: President Roosevelt used his charisma and influence to curb what he saw as abuses by big business. Roosevelt Takes on the Trusts Theodore Roosevelt
1869 Wyoming Territory gave women the right to vote Comstock Law passed illegal to use the U.S. post office to mail obscene material
 Unit 6 (Period 7 Part 1) Timeline Review.Important Dates and Chronological Review Keep in mind that memorizing dates is not required, however sometimes significant years do pop up on tests. Those dates
Unit 6 (Period 7 Part 1) Timeline Review.Important Dates and Chronological Review Keep in mind that memorizing dates is not required, however sometimes significant years do pop up on tests. Those dates
Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power ( )
 Name: Period Page# Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power (1890 1915) Section 1: The Pressure to Expand What factors led to the growth of imperialism around the world? In what ways did the United States begin
Name: Period Page# Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power (1890 1915) Section 1: The Pressure to Expand What factors led to the growth of imperialism around the world? In what ways did the United States begin
Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War
 Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War 1 Imperialism & Expansion CH 14-1 Imperialism & War Name Reasons why the United States becomes an imperialist nation. 1-New Markets 2-Anglo-Saxonism 3-Modern Navy 4-Into
Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War 1 Imperialism & Expansion CH 14-1 Imperialism & War Name Reasons why the United States becomes an imperialist nation. 1-New Markets 2-Anglo-Saxonism 3-Modern Navy 4-Into
Quick Class Discussion: What problems existed within the city, state, and national gov ts?
 During the Gilded Age, city, state, and national governments were in need of reform Corrupt political machines controlled city gov ts Political positions were gained based on patronage not merit Corruption
During the Gilded Age, city, state, and national governments were in need of reform Corrupt political machines controlled city gov ts Political positions were gained based on patronage not merit Corruption
Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt. Chapter 28
 Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt Chapter 28 Progressive Reformers Progressives wanted government actively involved protecting poor and needy Attacked monopolies, corruption, inefficiency and
Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt Chapter 28 Progressive Reformers Progressives wanted government actively involved protecting poor and needy Attacked monopolies, corruption, inefficiency and
Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power
 Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power Objective: Why did the United States become imperialistic and what were the outcomes? Goal: Students will be able to understand the causes and effects of imperialism
Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power Objective: Why did the United States become imperialistic and what were the outcomes? Goal: Students will be able to understand the causes and effects of imperialism
Chapter 18. American Claims an Empire
 Chapter 18 American Claims an Empire Section 1: Imperialism and American Imperialism 1880s U.S. interest in building an Empire builds Imperialism = Stronger : Economic, political, or military control Europeans
Chapter 18 American Claims an Empire Section 1: Imperialism and American Imperialism 1880s U.S. interest in building an Empire builds Imperialism = Stronger : Economic, political, or military control Europeans
BELLRINGER. Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies?
 BELLRINGER Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies? U.S. INTERVENTION ABROAD Ms. Luco IB Hist Americas LEARNING
BELLRINGER Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies? U.S. INTERVENTION ABROAD Ms. Luco IB Hist Americas LEARNING
Between 1870 and 1900, Europeans had taken over 1/5 of land and 1/10 of population of the world Germany became America s biggest imperialist foe and
 U.S. Imperialism Between 1870 and 1900, Europeans had taken over 1/5 of land and 1/10 of population of the world Germany became America s biggest imperialist foe and largely spurred U.S. into imperialism;
U.S. Imperialism Between 1870 and 1900, Europeans had taken over 1/5 of land and 1/10 of population of the world Germany became America s biggest imperialist foe and largely spurred U.S. into imperialism;
Chapter 22, The Battle for National Reform Theodore Roosevelt and the Modern Presidency
 Chapter 22, The Battle for National Reform Theodore Roosevelt and the Modern Presidency I. The Accidental President A. When William McKinley died of assassination, vice president, Roosevelt, a young (42
Chapter 22, The Battle for National Reform Theodore Roosevelt and the Modern Presidency I. The Accidental President A. When William McKinley died of assassination, vice president, Roosevelt, a young (42
Chapter 17. Becoming a World Power ( )
 Chapter 17 Becoming a World Power (1872 1912) 1 Chapter Overview: During this era, economic and military competition from world powers convinced the United States it must be a world power. The United States
Chapter 17 Becoming a World Power (1872 1912) 1 Chapter Overview: During this era, economic and military competition from world powers convinced the United States it must be a world power. The United States
FINISH PROJ/ PROGESSIVES / JUMP ON PAGE 672!!!
 U.S. History Mr. Boothby 1/24/2018 Target Chapter 29: America on the World Stage PT2 http://www.apnotes.net/notes-12e/ch29-12e.html Roosevelt & Environment/ Taft: Dollar Diplomacy/THE JUNGLE = PROGRESS!?!?!
U.S. History Mr. Boothby 1/24/2018 Target Chapter 29: America on the World Stage PT2 http://www.apnotes.net/notes-12e/ch29-12e.html Roosevelt & Environment/ Taft: Dollar Diplomacy/THE JUNGLE = PROGRESS!?!?!
1. Commercial/Business Interests. U. S. Foreign Investments:
 1. Commercial/Business Interests U. S. Foreign Investments: 1869-1908 1. Commercial/Business Interests American Foreign Trade: 1870-1914 2. Military/Strategic Interests Alfred T. Mahan The Influence of
1. Commercial/Business Interests U. S. Foreign Investments: 1869-1908 1. Commercial/Business Interests American Foreign Trade: 1870-1914 2. Military/Strategic Interests Alfred T. Mahan The Influence of
Guided Reading & Analysis: Becoming a World Power, Chapter 20- Spanish American War, American Imperialism pp
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Guided Reading & Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1898-1917 Chapter 20- Spanish American War, American Imperialism pp 380-391 Reading Assignment: Ch. 20 AMSCO; If you
Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Guided Reading & Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1898-1917 Chapter 20- Spanish American War, American Imperialism pp 380-391 Reading Assignment: Ch. 20 AMSCO; If you
Difficult choice. Republican ideals? Imperial power?
 Difficult choice Republican ideals? Imperial power? Anti-Imperialist League Founded in 1899. Mark Twain, Andrew Carnegie, William James, and William Jennings Bryan among the leaders. Campaigned against
Difficult choice Republican ideals? Imperial power? Anti-Imperialist League Founded in 1899. Mark Twain, Andrew Carnegie, William James, and William Jennings Bryan among the leaders. Campaigned against
Lesson 9: An Emerging World Power Imperialist = Expansionist (Chapter 9 in Textbook)
 Lesson 9: An Emerging World Power Imperialist = Expansionist (Chapter 9 in Textbook) Time Period: Late 1800s- 1914 Presidents William Mckinley 1897-1901 Theodore Roosevelt 1901-1909 William Howard Taft
Lesson 9: An Emerging World Power Imperialist = Expansionist (Chapter 9 in Textbook) Time Period: Late 1800s- 1914 Presidents William Mckinley 1897-1901 Theodore Roosevelt 1901-1909 William Howard Taft
Essential Question: & Latin America? Clicker Review. What role did the United States play as an imperial power in Asia. CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.
 Essential Question: What role did the United States play as an imperial power in Asia & Latin America? CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.8: Clicker Review Imperialism by the USA notes Today s HW: 28.3 Unit 10 Test:
Essential Question: What role did the United States play as an imperial power in Asia & Latin America? CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.8: Clicker Review Imperialism by the USA notes Today s HW: 28.3 Unit 10 Test:
2.5 - PROGRESSIVE ERA POLITICS UNIT 2 THE PROGRESSIVE ERA SECTION 5 POLITICS
 2.5 - PROGRESSIVE ERA POLITICS UNIT 2 THE PROGRESSIVE ERA SECTION 5 POLITICS Learning Targets & Key Words The Students Will Be Able To (TSWBAT): Identify the major accomplishments of Progressive Era presidents
2.5 - PROGRESSIVE ERA POLITICS UNIT 2 THE PROGRESSIVE ERA SECTION 5 POLITICS Learning Targets & Key Words The Students Will Be Able To (TSWBAT): Identify the major accomplishments of Progressive Era presidents
Progressivism Takes Hold. American History Chapter 9
 Progressivism Takes Hold American History Chapter 9 Theodore Roosevelt & the Modern Presidency Early Political Career 1880 Graduate of Harvard 1881 Elected to the N.Y. State Assembly 1884 Moved to Dakota
Progressivism Takes Hold American History Chapter 9 Theodore Roosevelt & the Modern Presidency Early Political Career 1880 Graduate of Harvard 1881 Elected to the N.Y. State Assembly 1884 Moved to Dakota
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved.
 Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. US History Immigration and Foreign policy Blizzard Bag 2014-2015 1. In a 1904 address to Congress, President Theodore Roosevelt stated that the United States
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. US History Immigration and Foreign policy Blizzard Bag 2014-2015 1. In a 1904 address to Congress, President Theodore Roosevelt stated that the United States
Chapter 28: Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt
 Chapter 28: Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt Progressive Roots New reformists went back to the Greenback Labor Party of 1870 s, Populists 1890 s, because of the trusts Laissez-faire was out dated,
Chapter 28: Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt Progressive Roots New reformists went back to the Greenback Labor Party of 1870 s, Populists 1890 s, because of the trusts Laissez-faire was out dated,
Objectives. What did Roosevelt think government should do for citizens? Discuss Theodore Roosevelt s ideas on the role of government.
 Objectives Discuss Theodore Roosevelt s ideas on the role of government. Analyze how Roosevelt changed the government s role in the economy. Explain the impact of Roosevelt s actions on natural resources.
Objectives Discuss Theodore Roosevelt s ideas on the role of government. Analyze how Roosevelt changed the government s role in the economy. Explain the impact of Roosevelt s actions on natural resources.
Unit 8: Imperialism. February 15th & 16th
 Unit 8: Imperialism February 15th & 16th WarmUp - February 15th & 16th Pick up papers from front table Jot down anything that comes to mind when you see the word IMPERIALISM (this is our next topic Unit
Unit 8: Imperialism February 15th & 16th WarmUp - February 15th & 16th Pick up papers from front table Jot down anything that comes to mind when you see the word IMPERIALISM (this is our next topic Unit
Becoming a World Power
 20 Becoming a World Power (1) CHAPTER OUTLINE As the United States Senate debates whether to annex the Philippine Isls, tension mounts near Manila as Filipinos Americans confront each other across an uneasy
20 Becoming a World Power (1) CHAPTER OUTLINE As the United States Senate debates whether to annex the Philippine Isls, tension mounts near Manila as Filipinos Americans confront each other across an uneasy
ID- Captured Filipino Insurrectionists (642) Summary 1-How many Filipinos died in the three year insurrection against the US? 600,000 Summary 2- How
 Ch 27 P2 Insights 1) Define and explain why the US issued the Open Door Policy 2) Explain how the Open Door Policy changed the United States role in the world. 3) Was the US a good neighbor to Latin America?
Ch 27 P2 Insights 1) Define and explain why the US issued the Open Door Policy 2) Explain how the Open Door Policy changed the United States role in the world. 3) Was the US a good neighbor to Latin America?
8 TH GRADE UNITS OF INSTRUCTION
 Name Date Per. Social Studies 8 1/3 Review Packet Mrs. Myles McAnally 8 TH GRADE UNITS OF INSTRUCTION Reconstruction: Economic Expansion: a. Immigration b. Industrialization c. US Expansion and Imperialism
Name Date Per. Social Studies 8 1/3 Review Packet Mrs. Myles McAnally 8 TH GRADE UNITS OF INSTRUCTION Reconstruction: Economic Expansion: a. Immigration b. Industrialization c. US Expansion and Imperialism
I. Elements of reform
 APUSH Unit 10- Roosevelt & Wilson Progressivism Chapter Guide/Lecture Notes Chapter 29 I. Elements of reform A. Diverse goals of progressivism- greater democracy, honest and efficient gov t, more efficient
APUSH Unit 10- Roosevelt & Wilson Progressivism Chapter Guide/Lecture Notes Chapter 29 I. Elements of reform A. Diverse goals of progressivism- greater democracy, honest and efficient gov t, more efficient
Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea
 Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea In the last half of the 1800s, the United States joined the race for control of overseas territories.
Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea In the last half of the 1800s, the United States joined the race for control of overseas territories.
CHAPTER 22. The Quest for Empire, Learning Objectives. Thematic Guide
 CHAPTER 22 The Quest for Empire, 1865 1914 Learning Objectives After you have studied Chapter 22 in your textbook and worked through this study guide chapter, you should be able to: 1. Examine the late-nineteenth-century
CHAPTER 22 The Quest for Empire, 1865 1914 Learning Objectives After you have studied Chapter 22 in your textbook and worked through this study guide chapter, you should be able to: 1. Examine the late-nineteenth-century
10/11/2018. Progressive Politics Video. Coal Strike of Theodore Roosevelt
 Theodore Roosevelt Theodore Roosevelt Progressive Politics Video Theodore Roosevelt Youngest President in American history - 42 President from 1901 to 1909. Trust Buster and Progressive. The Square Deal
Theodore Roosevelt Theodore Roosevelt Progressive Politics Video Theodore Roosevelt Youngest President in American history - 42 President from 1901 to 1909. Trust Buster and Progressive. The Square Deal
OUTLINE 7-3: THE PROGRESSIVE ERA, II
 OUTLINE 7-3: THE PROGRESSIVE ERA, II Growth expanded opportunity, while economic instability led to new efforts to reform U.S. society and its economic system. In the Progressive Era of the early 20 th
OUTLINE 7-3: THE PROGRESSIVE ERA, II Growth expanded opportunity, while economic instability led to new efforts to reform U.S. society and its economic system. In the Progressive Era of the early 20 th
Becoming A World Power,
 Becoming A World Power, 1890-1915 United States History Week of April 27, 2015 What Factors Caused Imperialism? Economic factors: need for natural resources, new markets for manufactured goods Nationalistic
Becoming A World Power, 1890-1915 United States History Week of April 27, 2015 What Factors Caused Imperialism? Economic factors: need for natural resources, new markets for manufactured goods Nationalistic
Background. 0 PASSIONATE HUNTER 0 Remarried & had six kids. 0 abandoned politics
 Background 0 Born Oct 27, 1858 into wealthy family 0 Asthma as a child 0 Harvard at 18 excelled in school and athletics (marksmanship and horseback riding) 0 Wife and mother died 1884 from illness 0 abandoned
Background 0 Born Oct 27, 1858 into wealthy family 0 Asthma as a child 0 Harvard at 18 excelled in school and athletics (marksmanship and horseback riding) 0 Wife and mother died 1884 from illness 0 abandoned
Born New York City, 1858 Sickly child (asthma) forced himself into better physical shape Harvard New York legislature (1882) Progressive Republican
 Born New York City, 1858 Sickly child (asthma) forced himself into better physical shape Harvard New York legislature (1882) Progressive Republican moral righteousness Not afraid to use power First wife
Born New York City, 1858 Sickly child (asthma) forced himself into better physical shape Harvard New York legislature (1882) Progressive Republican moral righteousness Not afraid to use power First wife
Bridging the Gap. Filling the holes between 9 th Grade World Civilization and 10 th Grade American History
 Bridging the Gap Filling the holes between 9 th Grade World Civilization and 10 th Grade American History (1)Review of Industrial Revolution 1790-1860: 36,000 patents issued in U.S. 1860-1890:500,000 patents
Bridging the Gap Filling the holes between 9 th Grade World Civilization and 10 th Grade American History (1)Review of Industrial Revolution 1790-1860: 36,000 patents issued in U.S. 1860-1890:500,000 patents
throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not.
 1. Tell what at least three of the symbols you see on this flag represent. 2. Do you think these three symbols would be recognized throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not. 3. Why would this
1. Tell what at least three of the symbols you see on this flag represent. 2. Do you think these three symbols would be recognized throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not. 3. Why would this
What Was Progressivism
 Chapter 6 Progressivism What Was Progressivism Progressivism- address the social problems that industrialization created Improve living conditions, question business practices, improve/fix government Muckrakers-
Chapter 6 Progressivism What Was Progressivism Progressivism- address the social problems that industrialization created Improve living conditions, question business practices, improve/fix government Muckrakers-
Theodore Roosevelt, William Howard Taft, and Woodrow Wilson
 Theodore Roosevelt, William Howard Taft, and Woodrow Wilson Theodore Roosevelt is the most prominent Progressive President in United States History. He consistently supported Progressive goals like consumer
Theodore Roosevelt, William Howard Taft, and Woodrow Wilson Theodore Roosevelt is the most prominent Progressive President in United States History. He consistently supported Progressive goals like consumer
BECOMING A WORLD POWER
 BECOMING A WORLD POWER CHAPTER 10 IMPERIALISM THE PRESSURE TO EXPAND Americans had always sought to expand the size of their nation, and throughout the 19th century they extended their control toward the
BECOMING A WORLD POWER CHAPTER 10 IMPERIALISM THE PRESSURE TO EXPAND Americans had always sought to expand the size of their nation, and throughout the 19th century they extended their control toward the
In the early 1900's the United States engaged in conflicts with Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines.
 Ch 18-Section 3 - Acquiring New Lands In the early 1900's the United States engaged in conflicts with Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines. Puerto Rico Fearful of losing autonomy that they had won under
Ch 18-Section 3 - Acquiring New Lands In the early 1900's the United States engaged in conflicts with Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines. Puerto Rico Fearful of losing autonomy that they had won under
Chapter 17, Section 1 I. Building Support for Imperialism (pages ) A. Beginning in the 1880s, Americans wanted the United States to become a
 Chapter 17, Section 1 I. Building Support for Imperialism (pages 520 522) A. Beginning in the 1880s, Americans wanted the United States to become a world power. Their change in attitude was a result of
Chapter 17, Section 1 I. Building Support for Imperialism (pages 520 522) A. Beginning in the 1880s, Americans wanted the United States to become a world power. Their change in attitude was a result of
Imperialism. Creation of the U.S. Empire
 Imperialism Creation of the U.S. Empire Please Note: The images included in this presentation, some of which are copyrighted, are being used under the fair use provision (for educational purposes) of the
Imperialism Creation of the U.S. Empire Please Note: The images included in this presentation, some of which are copyrighted, are being used under the fair use provision (for educational purposes) of the
Imperialism by the US
 Imperialism by the US Quick Class Discussion: Based on this image, what important changes took place in the United States from 1783 to 1900? 115 years after gaining independence from Britain, the United
Imperialism by the US Quick Class Discussion: Based on this image, what important changes took place in the United States from 1783 to 1900? 115 years after gaining independence from Britain, the United
Unit 9 Imperialism and WWI. New US Power and Diplomacy
 Unit 9 Imperialism and WWI New US Power and Diplomacy Attitudes Toward an International Role Arguments for Expansion Economics: new markets/investment opportunities/raw materials Culture: Social Darwinism/Protestant
Unit 9 Imperialism and WWI New US Power and Diplomacy Attitudes Toward an International Role Arguments for Expansion Economics: new markets/investment opportunities/raw materials Culture: Social Darwinism/Protestant
Unit 4: Imperialism. Name: Word Definition Analysis
 Name: Unit 4: Imperialism Word Definition Analysis 1. Imperialism (191) Policy by which strong nations Did America practice imperialism? extend their political, military, If so where? and economic control
Name: Unit 4: Imperialism Word Definition Analysis 1. Imperialism (191) Policy by which strong nations Did America practice imperialism? extend their political, military, If so where? and economic control
Imperialism and America
 CHAPTER 10 Section 1 ( pages 342 345) Imperialism and America BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about Woodrow Wilson. In this section, you will learn how economic activity led to political
CHAPTER 10 Section 1 ( pages 342 345) Imperialism and America BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about Woodrow Wilson. In this section, you will learn how economic activity led to political
The Progressive Era,
 The Progressive Era, 1900-1920 Topics of Discussion I. Shift from Gilded Age to Progressive Era Reform III. Theodore Roosevelt and Republican Progressivism IV. William H. Taft, Roosevelt s protégé outdoes
The Progressive Era, 1900-1920 Topics of Discussion I. Shift from Gilded Age to Progressive Era Reform III. Theodore Roosevelt and Republican Progressivism IV. William H. Taft, Roosevelt s protégé outdoes
TR: FIRST MODERN PRESIDENT
 TR: FIRST MODERN PRESIDENT DYNAMIC CHARACTER TR personified America at the turn of the century with his youthful exuberance and strenuous life. He embodied modern American nationalism, militarism, and
TR: FIRST MODERN PRESIDENT DYNAMIC CHARACTER TR personified America at the turn of the century with his youthful exuberance and strenuous life. He embodied modern American nationalism, militarism, and
Warm up: We have discussed the Chinese role in constructing the railroads in the west. How do you think that the Chinese were treated by other
 Warm up: We have discussed the Chinese role in constructing the railroads in the west. How do you think that the Chinese were treated by other groups? SSUSH14 Explain America s evolving relationship with
Warm up: We have discussed the Chinese role in constructing the railroads in the west. How do you think that the Chinese were treated by other groups? SSUSH14 Explain America s evolving relationship with
Chapter 28: Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt, (Pages ) Per. Date Row
 Chapter 28: Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt, Name 1901-1912 (Pages 656-678) Per. Date Row I. Introduction A. Immigration at the turn of the century B. Progressive Reform Movement 1. What issues
Chapter 28: Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt, Name 1901-1912 (Pages 656-678) Per. Date Row I. Introduction A. Immigration at the turn of the century B. Progressive Reform Movement 1. What issues
American History 11R
 American History 11R Progressive Movement Goals Protecting Social Welfare Promoting Moral Improvement Creating Economic Reform Fostering Efficiency Reform Political System Protecting Social Welfare Tried
American History 11R Progressive Movement Goals Protecting Social Welfare Promoting Moral Improvement Creating Economic Reform Fostering Efficiency Reform Political System Protecting Social Welfare Tried
9/28/2007. The Progressive Era, The Progressive Era, The Progressive Era, Topics of Discussion
 Topics of Discussion I. Shift from Gilded Age to Progressive Era Reform II. Four Goals of the Progressive Era Reform Movement III. Theodore Roosevelt and Republican Progressivism IV. William H. Taft, Roosevelt
Topics of Discussion I. Shift from Gilded Age to Progressive Era Reform II. Four Goals of the Progressive Era Reform Movement III. Theodore Roosevelt and Republican Progressivism IV. William H. Taft, Roosevelt
The United States Looks Overseas
 The United States Looks Overseas 1853-1915 Interact with History In 1893, American sugar planters in the Kingdom of Hawaii thought they could make more money if Hawaii were an American state. So they staged
The United States Looks Overseas 1853-1915 Interact with History In 1893, American sugar planters in the Kingdom of Hawaii thought they could make more money if Hawaii were an American state. So they staged
The Progressive Era,
 The Progressive Era, 1900-1920 The Progressive Era, 1900-1920 Topics of Discussion I. Shift from Gilded Age to Progressive Era Reform II. Four Goals of the Progressive Era Reform Movement III. Theodore
The Progressive Era, 1900-1920 The Progressive Era, 1900-1920 Topics of Discussion I. Shift from Gilded Age to Progressive Era Reform II. Four Goals of the Progressive Era Reform Movement III. Theodore
Imperialism. U.S. Foreign Policy. U.S. Foreign Policy 10/30/13. Chapter 10. Monroe Doctrine. Many Spanish colonies revolting
 Imperialism Chapter 10 U.S. Foreign Policy Monroe Doctrine No new colonization by Europe in western hemisphere U.S. stays out of European affairs If Europe attempts to colonize in the west, U.S. would
Imperialism Chapter 10 U.S. Foreign Policy Monroe Doctrine No new colonization by Europe in western hemisphere U.S. stays out of European affairs If Europe attempts to colonize in the west, U.S. would
Imperialism and America
 Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire CHAPTER 10 Section 1 (pages 342-345) Imperialism and America American Expansionism (pages 342-344) Why did Americans support imperialism? In 1893, Queen Liliuokalani
Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire CHAPTER 10 Section 1 (pages 342-345) Imperialism and America American Expansionism (pages 342-344) Why did Americans support imperialism? In 1893, Queen Liliuokalani
Let's discuss: to stop human rights abuses under no circumstances
 Let's discuss: When do you think it is appropriate for the US to send soldiers to fight and face death on foreign soil? (Choose up to 3 of the following and briefly explain your choices) to assist an ally
Let's discuss: When do you think it is appropriate for the US to send soldiers to fight and face death on foreign soil? (Choose up to 3 of the following and briefly explain your choices) to assist an ally
Chapter 19: Republic To Empire
 Chapter 19: Republic To Empire Objectives: o We will examine the policies America implemented in their newly conquered territories after the Spanish American War. o We will examine the various changes
Chapter 19: Republic To Empire Objectives: o We will examine the policies America implemented in their newly conquered territories after the Spanish American War. o We will examine the various changes
The Progressive Era. Political, Social, and Economic Reform ( )
 The Progressive Era Political, Social, and Economic Reform (1901-1917) POLITICAL SOCIAL ECONOMIC Expanded Suffrage Decline of Political Machines Increased Party Influence Expanded Workers Rights Assimilation
The Progressive Era Political, Social, and Economic Reform (1901-1917) POLITICAL SOCIAL ECONOMIC Expanded Suffrage Decline of Political Machines Increased Party Influence Expanded Workers Rights Assimilation
Work Period: Latin America and China Foreign policies Notes President Chart Activity
 USHC 5.0 DEMONSTRATE AN UNDERSTANDING OF DOMESTIC AND FOREIGN DEVELOPMENTS THAT CONTRIBUTED TO THE EMERGENCE OF THE UNITED STATES AS A WORLD POWER IN THE 20 TH CENTURY Opening: Complete pages 185-188 in
USHC 5.0 DEMONSTRATE AN UNDERSTANDING OF DOMESTIC AND FOREIGN DEVELOPMENTS THAT CONTRIBUTED TO THE EMERGENCE OF THE UNITED STATES AS A WORLD POWER IN THE 20 TH CENTURY Opening: Complete pages 185-188 in
American Upon the Global Stage Was America Imperialist? Or Was America Exceptional?
 APUSH Kind American Imperialism American Upon the Global Stage Was America Imperialist? Or Was America Exceptional? History of American Foreign Policy Neutrality & Isolationism Neutrality Proclamation
APUSH Kind American Imperialism American Upon the Global Stage Was America Imperialist? Or Was America Exceptional? History of American Foreign Policy Neutrality & Isolationism Neutrality Proclamation
The Progressive Movement:
 1 The Progressive Movement: 1901-1912 Chapter Learning Objectives 2 Discuss the origins and nature of the progressive movement. Describe how the early progressive movement developed its roots at the city
1 The Progressive Movement: 1901-1912 Chapter Learning Objectives 2 Discuss the origins and nature of the progressive movement. Describe how the early progressive movement developed its roots at the city
Welcome to History 06 History of the Americas II Prof. Valadez
 Welcome to History 06 History of the Americas II Prof. Valadez 1 Topics Review: Positivism Participation Assignment #3 U.S. Foreign Policy In Latin America Early 20 th Century Revolutions in Latin America
Welcome to History 06 History of the Americas II Prof. Valadez 1 Topics Review: Positivism Participation Assignment #3 U.S. Foreign Policy In Latin America Early 20 th Century Revolutions in Latin America
Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914?
 Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914? From 1890 to 1914, the United States expanded its role in world affairs and gained new overseas colonies Class Activity:
Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914? From 1890 to 1914, the United States expanded its role in world affairs and gained new overseas colonies Class Activity:
-King Kalahaua: Queen Liliuokalani (Sandford B. Dole)
 Imperialism Causes of Imperialism If it were necessary to give the briefest possible definition of imperialism, we should have to say that imperialism is the monopoly stage of capitalism. --Vladimir Lenin
Imperialism Causes of Imperialism If it were necessary to give the briefest possible definition of imperialism, we should have to say that imperialism is the monopoly stage of capitalism. --Vladimir Lenin
Roosevelt Taft Wilson. Big Stick Diplomacy Dollar Diplomacy Moral Diplomacy
 Roosevelt Taft Wilson Big Stick Diplomacy Dollar Diplomacy Moral Diplomacy Definition: The art or practice of conducting international relations, as in negotiating alliances, treaties, and agreements.
Roosevelt Taft Wilson Big Stick Diplomacy Dollar Diplomacy Moral Diplomacy Definition: The art or practice of conducting international relations, as in negotiating alliances, treaties, and agreements.
Objective To explain how the progressive movement managed to increase the power of government to regulate business and to protect society from the
 Objective To explain how the progressive movement managed to increase the power of government to regulate business and to protect society from the injustices fostered by big business. What was Progressivism?
Objective To explain how the progressive movement managed to increase the power of government to regulate business and to protect society from the injustices fostered by big business. What was Progressivism?
Unit 7: America Comes of Age FRQ Outlines
 Prompt: 2. Analyze the extent to which the Spanish-American War was a turning point in American foreign policy. Re-written as a Question: What was the extent to which the Spanish American war a turning
Prompt: 2. Analyze the extent to which the Spanish-American War was a turning point in American foreign policy. Re-written as a Question: What was the extent to which the Spanish American war a turning
affairs of other countries
 Competency Goal 6: The Emergence of the United States in World Affairs (1890-1914), analyze causes and effects of the United States emergence as a world power 6.01: Examine the factors that led to the
Competency Goal 6: The Emergence of the United States in World Affairs (1890-1914), analyze causes and effects of the United States emergence as a world power 6.01: Examine the factors that led to the
IT S STORY TIME! UNIT 4 AMERICAN IMPERIALISM Part 1 The Imperialist Vision Part 2 The Spanish-American War Part 3 New American Diplomacy
 IT S STORY TIME! UNIT 4 AMERICAN IMPERIALISM 1872-1912 Part 1 The Imperialist Vision Part 2 The Spanish-American War Part 3 New American Diplomacy AMERICAN DIPLOMACY in ASIA Each LEASEHOLD became center
IT S STORY TIME! UNIT 4 AMERICAN IMPERIALISM 1872-1912 Part 1 The Imperialist Vision Part 2 The Spanish-American War Part 3 New American Diplomacy AMERICAN DIPLOMACY in ASIA Each LEASEHOLD became center
PROGRESSIVE ERA. 1890s A21w
 PROGRESSIVE ERA 1890s-1920 A21w 9.2.13 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Who were the Progressives, and in what ways did they seek to reform US society form 1890-1920? Consider: political change, social change (industrial
PROGRESSIVE ERA 1890s-1920 A21w 9.2.13 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Who were the Progressives, and in what ways did they seek to reform US society form 1890-1920? Consider: political change, social change (industrial
