Imperialism by the US
|
|
|
- David O’Neal’
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Imperialism by the US
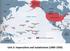
3 Quick Class Discussion: Based on this image, what important changes took place in the United States from 1783 to 1900?
4 115 years after gaining independence from Britain, the United States was an industrial and imperial power How did this happen?
5 The United States: The U.S. Economy: From 1790 to 1820, most Americans were small-scale farmers But, a few early textile mills were built in New England and...eli Whitney s cotton gin led to a boom in southern cotton and slavery
6 The United States: U.S. Territorial Expansion: The American population expanded across the Appalachian Mountains In 1803, Jefferson doubled the size of the USA and gained control of the Mississippi River when he bought Louisiana from French Emperor Napoleon
7 The United States: The U.S. Economy: From 1820 to 1860, Southern cotton made up 60% of American exports The North had a diverse economy based on farming textile production, and manufacturing Western farmers were connected to Northern industry by roads, canals, and railroads
8 The United States: U.S. Territorial Expansion: From 1820 to 1860, the USA claimed its Manifest Destiny and gained new western lands in Texas, Oregon, and the southwest By 1850, the USA had all lands from the Atlantic to the Pacific
9 The United States: The U.S. Economy: From 1860 to 1900, the United States experienced an industrial revolution The USA became a world leader in railroads, oil, steel, and electricity As America became more industrialized, it experienced a rise in urbanization and immigration
10 The United States: U.S. Territorial Expansion: The USA expanded beyond North America and imperialized by gaining new colonies in Latin America and Asia
11 Why did the United States imperialize? American factories needed new sources of raw materials and markets to sell their goods By 1890, there were no new lands in the west to expand into and Americans wanted overseas colonies
12 Why did the United States imperialize? Americans felt the need to keep up with European imperialists The U.S. had a modern navy and belief that it could compete with other powerful nations
13 Why did the United States imperialize? Like Europeans, Americans believed in Social Darwinism and that they had a duty to civilize the inferior races of the world So, what did the USA gain during Age of Imperialism?
14 Americans were interested in Hawaii to convert natives to Christianity, profit from fruit plantations, and its location as a fueling center midway to Asia
15 Americans overthrew Queen Liliuokalani and created a new republic in 1893; The USA annexed Hawaii as a territory in 1898
16 By the 1890s, European powers gained exclusive trade rights in Chinese ports the United States was left out of Chinese trade
17 In 1899, the USA negotiated an Open Door policy allowing all nations to trade in Chinese ports
18 The USA helped Cuba gain its independence and went to war with Spain in 1898
19 After winning the Spanish-American War in 1898, the USA gained Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines
20 The USA wanted to protect the newly independent Latin American republics from imperialism by European powers
21 By 1904, the USA was a world power and declared itself the police power of the Western Hemisphere
22 The USA wanted to build a canal through Central America but could not negotiate a treaty with the government of Colombia
23 The USA encouraged Panama to revolt from Colombia and allow America to build the Panama Canal
24 Click here to see how the Panama Canal works
25 By the 20 th century, the United States was a world leader in industry and had one of the world s most powerful militaries Imperialism in Asia and Latin America transformed the United States into a major world power
Essential Question: & Latin America? Clicker Review. What role did the United States play as an imperial power in Asia. CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.
 Essential Question: What role did the United States play as an imperial power in Asia & Latin America? CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.8: Clicker Review Imperialism by the USA notes Today s HW: 28.3 Unit 10 Test:
Essential Question: What role did the United States play as an imperial power in Asia & Latin America? CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.8: Clicker Review Imperialism by the USA notes Today s HW: 28.3 Unit 10 Test:
Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914?
 Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914? From 1890 to 1914, the United States expanded its role in world affairs and gained new overseas colonies Class Activity:
Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914? From 1890 to 1914, the United States expanded its role in world affairs and gained new overseas colonies Class Activity:
Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism ( )
 Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism (1890-1930) What is an empire? Is imperialism the same as colonization? Why would the U.S. get involved in this practice? What is the difference between acquiring and
Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism (1890-1930) What is an empire? Is imperialism the same as colonization? Why would the U.S. get involved in this practice? What is the difference between acquiring and
BECOMING A WORLD POWER
 BECOMING A WORLD POWER CHAPTER 10 IMPERIALISM THE PRESSURE TO EXPAND Americans had always sought to expand the size of their nation, and throughout the 19th century they extended their control toward the
BECOMING A WORLD POWER CHAPTER 10 IMPERIALISM THE PRESSURE TO EXPAND Americans had always sought to expand the size of their nation, and throughout the 19th century they extended their control toward the
Letter from President Fillmore asking Japan. American ships to stop for supplies safety reasons
 Chapter 19-21 Introduction Japan 1853 Not open to trading with other countries Commodore Matthew Perry went to Japan with a small fleet of warships (Gunboat Diplomacy) Letter from President Fillmore asking
Chapter 19-21 Introduction Japan 1853 Not open to trading with other countries Commodore Matthew Perry went to Japan with a small fleet of warships (Gunboat Diplomacy) Letter from President Fillmore asking
Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power
 Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power Objective: Why did the United States become imperialistic and what were the outcomes? Goal: Students will be able to understand the causes and effects of imperialism
Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power Objective: Why did the United States become imperialistic and what were the outcomes? Goal: Students will be able to understand the causes and effects of imperialism
Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism
 Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism 1. List the ideas that fueled American Imperialism. 2. How were yellow journalists able to influence Americans opinions on foreign policy? 3. The person who urged
Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism 1. List the ideas that fueled American Imperialism. 2. How were yellow journalists able to influence Americans opinions on foreign policy? 3. The person who urged
Unit 8: Imperialism. February 15th & 16th
 Unit 8: Imperialism February 15th & 16th WarmUp - February 15th & 16th Pick up papers from front table Jot down anything that comes to mind when you see the word IMPERIALISM (this is our next topic Unit
Unit 8: Imperialism February 15th & 16th WarmUp - February 15th & 16th Pick up papers from front table Jot down anything that comes to mind when you see the word IMPERIALISM (this is our next topic Unit
Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War
 Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War 1 Imperialism & Expansion CH 14-1 Imperialism & War Name Reasons why the United States becomes an imperialist nation. 1-New Markets 2-Anglo-Saxonism 3-Modern Navy 4-Into
Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War 1 Imperialism & Expansion CH 14-1 Imperialism & War Name Reasons why the United States becomes an imperialist nation. 1-New Markets 2-Anglo-Saxonism 3-Modern Navy 4-Into
Growing Pains in the Americas THE EUROPEAN MOMENT ( )
 Growing Pains in the Americas THE EUROPEAN MOMENT (1750 1900) Or we could call today s notes: The history of the Western Hemisphere in the 19 th century as they face problems keeping order and confront
Growing Pains in the Americas THE EUROPEAN MOMENT (1750 1900) Or we could call today s notes: The history of the Western Hemisphere in the 19 th century as they face problems keeping order and confront
APUSH. U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! EMPIRE & EXPANSION
 APUSH 1890-1909 EMPIRE & EXPANSION U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 27 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 19 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 21 Important Ideas Since the
APUSH 1890-1909 EMPIRE & EXPANSION U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 27 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 19 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 21 Important Ideas Since the
Agenda for Monday/Tuesday. CNN 10 Westward Expansion Notes Manifest Destiny Map Assignment
 Agenda for Monday/Tuesday CNN 10 Westward Expansion Notes Manifest Destiny Map Assignment Learning Objectives I can describe the treaties such as the Adams-Onis treaty and/or the Treaty of Guadelupe-Hidalgo
Agenda for Monday/Tuesday CNN 10 Westward Expansion Notes Manifest Destiny Map Assignment Learning Objectives I can describe the treaties such as the Adams-Onis treaty and/or the Treaty of Guadelupe-Hidalgo
Economic History of the US
 Economic History of the US Revolution to Civil War, 1776-1860 Lecture #2 Peter Allen Econ 120 Map 8.1 US Land Expansion Early Western Migrations Population at independence (in thousands) Total White African
Economic History of the US Revolution to Civil War, 1776-1860 Lecture #2 Peter Allen Econ 120 Map 8.1 US Land Expansion Early Western Migrations Population at independence (in thousands) Total White African
Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea
 Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea In the last half of the 1800s, the United States joined the race for control of overseas territories.
Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea In the last half of the 1800s, the United States joined the race for control of overseas territories.
The United States Lesson 2: History of the United States
 Lesson 2: History of the United States ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is history important? Terms to Know indigenous living or occurring naturally in a particular place nomadic describes a way of life in which
Lesson 2: History of the United States ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is history important? Terms to Know indigenous living or occurring naturally in a particular place nomadic describes a way of life in which
18 America Claims an Empire QUIT
 18 America Claims an Empire QUIT CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE SECTION 1 Imperialism and America GRAPH MAP SECTION 2 The Spanish-American War SECTION 3 Acquiring New Lands SECTION 4
18 America Claims an Empire QUIT CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE SECTION 1 Imperialism and America GRAPH MAP SECTION 2 The Spanish-American War SECTION 3 Acquiring New Lands SECTION 4
Chapter 17. Becoming a World Power ( )
 Chapter 17 Becoming a World Power (1872 1912) 1 Chapter Overview: During this era, economic and military competition from world powers convinced the United States it must be a world power. The United States
Chapter 17 Becoming a World Power (1872 1912) 1 Chapter Overview: During this era, economic and military competition from world powers convinced the United States it must be a world power. The United States
Between 1870 and 1900, Europeans had taken over 1/5 of land and 1/10 of population of the world Germany became America s biggest imperialist foe and
 U.S. Imperialism Between 1870 and 1900, Europeans had taken over 1/5 of land and 1/10 of population of the world Germany became America s biggest imperialist foe and largely spurred U.S. into imperialism;
U.S. Imperialism Between 1870 and 1900, Europeans had taken over 1/5 of land and 1/10 of population of the world Germany became America s biggest imperialist foe and largely spurred U.S. into imperialism;
Social Studies U.S. History and Government-Academic Unit 7: The Manifest Destiny Era
 Understandings Questions With the Louisiana Purchase, America was faced with determining the value of the new territory and how to deal with the people already living there. The feeling of nationalism
Understandings Questions With the Louisiana Purchase, America was faced with determining the value of the new territory and how to deal with the people already living there. The feeling of nationalism
American Foreign Policy, : The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly.
 American Foreign Policy, 1880-1920: The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly. Each group will become experts on their assigned country. Create poster showing how U.S. policy toward your respective country was good,
American Foreign Policy, 1880-1920: The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly. Each group will become experts on their assigned country. Create poster showing how U.S. policy toward your respective country was good,
Unit 7: America Comes of Age FRQ Outlines
 Prompt: 2. Analyze the extent to which the Spanish-American War was a turning point in American foreign policy. Re-written as a Question: What was the extent to which the Spanish American war a turning
Prompt: 2. Analyze the extent to which the Spanish-American War was a turning point in American foreign policy. Re-written as a Question: What was the extent to which the Spanish American war a turning
China Resists Outside Influence
 Name CHAPTER 28 Section 1 (pages 805 809) China Resists Outside Influence BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about imperialism in Asia. In this section, you will see how China dealt with foreign
Name CHAPTER 28 Section 1 (pages 805 809) China Resists Outside Influence BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about imperialism in Asia. In this section, you will see how China dealt with foreign
BELLRINGER. Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies?
 BELLRINGER Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies? U.S. INTERVENTION ABROAD Ms. Luco IB Hist Americas LEARNING
BELLRINGER Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies? U.S. INTERVENTION ABROAD Ms. Luco IB Hist Americas LEARNING
Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power,
 Name: Class Period: Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1865-1917 Amsco Chapter 20 Reading Assignment: Ch. 21 AMSCO Purpose: This guide is intended to provide a space for you to record
Name: Class Period: Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1865-1917 Amsco Chapter 20 Reading Assignment: Ch. 21 AMSCO Purpose: This guide is intended to provide a space for you to record
throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not.
 1. Tell what at least three of the symbols you see on this flag represent. 2. Do you think these three symbols would be recognized throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not. 3. Why would this
1. Tell what at least three of the symbols you see on this flag represent. 2. Do you think these three symbols would be recognized throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not. 3. Why would this
Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of???
 Need to know What was President Roosevelt s Gentlemen s Agreement with Japan? Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of??? imperialism Stronger nations dominating
Need to know What was President Roosevelt s Gentlemen s Agreement with Japan? Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of??? imperialism Stronger nations dominating
Warm up: We have discussed the Chinese role in constructing the railroads in the west. How do you think that the Chinese were treated by other
 Warm up: We have discussed the Chinese role in constructing the railroads in the west. How do you think that the Chinese were treated by other groups? SSUSH14 Explain America s evolving relationship with
Warm up: We have discussed the Chinese role in constructing the railroads in the west. How do you think that the Chinese were treated by other groups? SSUSH14 Explain America s evolving relationship with
3. THINK: How did American businesses on the East Coast of the USA benefit when the United States built a canal in Panama?
 DOCUMENT 1: Japan Alaska China USA Panama Philippines Hawaii Guam 1. The United States wanted to expand trade with China. What islands were located between the United States and China? 2. THINK: For what
DOCUMENT 1: Japan Alaska China USA Panama Philippines Hawaii Guam 1. The United States wanted to expand trade with China. What islands were located between the United States and China? 2. THINK: For what
Imperialism. U.S. Foreign Policy. U.S. Foreign Policy 10/30/13. Chapter 10. Monroe Doctrine. Many Spanish colonies revolting
 Imperialism Chapter 10 U.S. Foreign Policy Monroe Doctrine No new colonization by Europe in western hemisphere U.S. stays out of European affairs If Europe attempts to colonize in the west, U.S. would
Imperialism Chapter 10 U.S. Foreign Policy Monroe Doctrine No new colonization by Europe in western hemisphere U.S. stays out of European affairs If Europe attempts to colonize in the west, U.S. would
Empire and Expansion. Chapter 27
 Empire and Expansion Chapter 27 Imperialism Stronger nations attempt to create empires by dominating weaker nations. The late 1800s marked the peak of European imperialism, with much of Africa and Asia
Empire and Expansion Chapter 27 Imperialism Stronger nations attempt to create empires by dominating weaker nations. The late 1800s marked the peak of European imperialism, with much of Africa and Asia
CHAPTER 25: The Industrial Revolution
 Due Monday, March 24, 2014 NAME Period CHAPTER 25: The Industrial Revolution 25.1: The Beginnings of Industrialization (pg. 717-722) I. Industrial Revolution Begins in England A. What is the definition
Due Monday, March 24, 2014 NAME Period CHAPTER 25: The Industrial Revolution 25.1: The Beginnings of Industrialization (pg. 717-722) I. Industrial Revolution Begins in England A. What is the definition
Indiana Academic Standards Social Studies
 A Correlation of To the Introduction This document demonstrates how,, meets the for,. Correlation page references are to the Student Edition and Teacher Edition. The all new myworld Interactive encourages
A Correlation of To the Introduction This document demonstrates how,, meets the for,. Correlation page references are to the Student Edition and Teacher Edition. The all new myworld Interactive encourages
In the early Antebellum era ( ), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that
 In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
1. Since the founding of Jamestown, Americans had a hunger for land. Some wanted their own farms, others were interested in land speculation.
 Unit Name: Unit 2B - Expanding Markets and Manifest Destiny Author: Steve Schweizer UNIT Subject: Social Studies Country: Course/Grade: U.S. History I State/Group: NJ School: EHTHS UNIT SUMMARY The result
Unit Name: Unit 2B - Expanding Markets and Manifest Destiny Author: Steve Schweizer UNIT Subject: Social Studies Country: Course/Grade: U.S. History I State/Group: NJ School: EHTHS UNIT SUMMARY The result
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e. Chapter Nineteen: From Crisis to Empire
 Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e The Politics of Equilibrium Electoral Stability High Turnout for Elections Cultural Basis of Party Identification Catholics Tended to Vote Democrat 2 The Politics of
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e The Politics of Equilibrium Electoral Stability High Turnout for Elections Cultural Basis of Party Identification Catholics Tended to Vote Democrat 2 The Politics of
Chapter 19: Republic To Empire
 Chapter 19: Republic To Empire Objectives: o We will examine the policies America implemented in their newly conquered territories after the Spanish American War. o We will examine the various changes
Chapter 19: Republic To Empire Objectives: o We will examine the policies America implemented in their newly conquered territories after the Spanish American War. o We will examine the various changes
After the War of 1812 THE BEGINNING OF CHANGE IN AMERICAN POLITICS, ECONOMY, AND SOCIETY
 After the War of 1812 THE BEGINNING OF CHANGE IN AMERICAN POLITICS, ECONOMY, AND SOCIETY Consequences of the War of 1812 Why was the War of 1812 fought? Impressment Violation of neutral shipping rights
After the War of 1812 THE BEGINNING OF CHANGE IN AMERICAN POLITICS, ECONOMY, AND SOCIETY Consequences of the War of 1812 Why was the War of 1812 fought? Impressment Violation of neutral shipping rights
Imperialism. Creation of the U.S. Empire
 Imperialism Creation of the U.S. Empire Please Note: The images included in this presentation, some of which are copyrighted, are being used under the fair use provision (for educational purposes) of the
Imperialism Creation of the U.S. Empire Please Note: The images included in this presentation, some of which are copyrighted, are being used under the fair use provision (for educational purposes) of the
Chapter 12 Section 1 The Imperialist Vision. Click on a hyperlink to view the corresponding slides.
 Chapter 12 Section 1 The Imperialist Vision Click on a hyperlink to view the corresponding slides. Click the Speaker button to listen to the audio again. continued on next slide Guide to Reading Main
Chapter 12 Section 1 The Imperialist Vision Click on a hyperlink to view the corresponding slides. Click the Speaker button to listen to the audio again. continued on next slide Guide to Reading Main
Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages ) Economic Growth
 Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages 304 309) Economic Growth Essential Question What effects did the Industrial Revolution have on the U. S. economy? Directions: As you read, complete a graphic organizer like
Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages 304 309) Economic Growth Essential Question What effects did the Industrial Revolution have on the U. S. economy? Directions: As you read, complete a graphic organizer like
Reasons for American Imperialism
 Name: Reasons for American Introduction: Expansion has always been a part of America s history. At first, expansion headed towards the Pacific within North America. In the 1700 s and 1800 s, European nations
Name: Reasons for American Introduction: Expansion has always been a part of America s history. At first, expansion headed towards the Pacific within North America. In the 1700 s and 1800 s, European nations
Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power ( )
 Name: Period Page# Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power (1890 1915) Section 1: The Pressure to Expand What factors led to the growth of imperialism around the world? In what ways did the United States begin
Name: Period Page# Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power (1890 1915) Section 1: The Pressure to Expand What factors led to the growth of imperialism around the world? In what ways did the United States begin
Period V ( ): Industrialization and Global Integration
 Period V (1750-1900): Industrialization and Global Integration 5.1 Industrialization and Global Capitalism I. I can describe and explain how industrialism fundamentally changed how goods were produced.
Period V (1750-1900): Industrialization and Global Integration 5.1 Industrialization and Global Capitalism I. I can describe and explain how industrialism fundamentally changed how goods were produced.
Welcome to History 12 Political and Social History of the U.S. II From 1876 to the present Prof. Valadez
 Welcome to History 12 Political and Social History of the U.S. II From 1876 to the present Prof. Valadez 1 Topics The U.S. as a World Power Progressive Era 2 Becoming a World Power The New Imperialism
Welcome to History 12 Political and Social History of the U.S. II From 1876 to the present Prof. Valadez 1 Topics The U.S. as a World Power Progressive Era 2 Becoming a World Power The New Imperialism
World History (Survey) Chapter 28: Transformations Around the Globe,
 World History (Survey) Chapter 28: Transformations Around the Globe, 1800 1914 Section 1: China Responds to Pressure from the West In the late 1700s, China was self-sufficient. It had a strong farming
World History (Survey) Chapter 28: Transformations Around the Globe, 1800 1914 Section 1: China Responds to Pressure from the West In the late 1700s, China was self-sufficient. It had a strong farming
Unit Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution
 Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
The term Era of Good Feelings refers to the period of American history when there seemed to be political harmony during the Monroe administration.
 The term Era of Good Feelings refers to the period of American history when there seemed to be political harmony during the Monroe administration. 1 2 In 1816, James Monroe became president, inaugurating
The term Era of Good Feelings refers to the period of American history when there seemed to be political harmony during the Monroe administration. 1 2 In 1816, James Monroe became president, inaugurating
Unit III Outline Organizing Principles
 Unit III Outline Organizing Principles British imperial attempts to reassert control over its colonies and the colonial reaction to these attempts produced a new American republic, along with struggles
Unit III Outline Organizing Principles British imperial attempts to reassert control over its colonies and the colonial reaction to these attempts produced a new American republic, along with struggles
Today s Topics. Quiz 1 Populism & The Segregated South The U.S. as a World Power
 Today s Topics Quiz 1 Populism & The Segregated South The U.S. as a World Power 1 The Transformation of the West 2 The Transformation of the West Remaking Indian Life Forced assimilation The Dawes Act
Today s Topics Quiz 1 Populism & The Segregated South The U.S. as a World Power 1 The Transformation of the West 2 The Transformation of the West Remaking Indian Life Forced assimilation The Dawes Act
Chapter 12: Transformations Around the Globe,
 Chapter 12: Transformations Around the Globe, 1800 1914 China and Japan respond differently to the European powers. The United States influences Latin America, and Mexico undergoes a revolution. Theodore
Chapter 12: Transformations Around the Globe, 1800 1914 China and Japan respond differently to the European powers. The United States influences Latin America, and Mexico undergoes a revolution. Theodore
Varieties of American Nationalism. Chapter 8: History 103
 Varieties of American Nationalism Chapter 8: History 103 Boom to Bust post war boom leads to Panic of 1819 Why did the Panic of 1819 occur? Banking and Currency 1811: First Bank of the United States expired
Varieties of American Nationalism Chapter 8: History 103 Boom to Bust post war boom leads to Panic of 1819 Why did the Panic of 1819 occur? Banking and Currency 1811: First Bank of the United States expired
An Early Republic. George Washington. Dept./Office Head Function
 Name An Early Republic George Washington What does the Executive Branch look like? Dept./Office Head Function State Department Thomas Jefferson Dept. of Treasury Alexander Hamilton Dept. of War Henry Knox
Name An Early Republic George Washington What does the Executive Branch look like? Dept./Office Head Function State Department Thomas Jefferson Dept. of Treasury Alexander Hamilton Dept. of War Henry Knox
Chapter 17, Section 1 I. Building Support for Imperialism (pages ) A. Beginning in the 1880s, Americans wanted the United States to become a
 Chapter 17, Section 1 I. Building Support for Imperialism (pages 520 522) A. Beginning in the 1880s, Americans wanted the United States to become a world power. Their change in attitude was a result of
Chapter 17, Section 1 I. Building Support for Imperialism (pages 520 522) A. Beginning in the 1880s, Americans wanted the United States to become a world power. Their change in attitude was a result of
Review. Geographic Change Essay. Essay Blocking. Possible Thematic Essays 6/7/2013
 Review Essay Blocking Possible Thematic Essays Study 2 of the following: 5 W s- Who, What, When, Why - Reform Movements (Women, Civil Rights, Progressive Era) - Manifest Destiny ( Louisiana Purchase, Homestead
Review Essay Blocking Possible Thematic Essays Study 2 of the following: 5 W s- Who, What, When, Why - Reform Movements (Women, Civil Rights, Progressive Era) - Manifest Destiny ( Louisiana Purchase, Homestead
Era of Good Feelings:
 Era of Good Feelings: 1815-1825 After the War of 1812 Americans finally have international respect The Republicans are the only political party James Monroe, the third member of the Virginia Dynasty, is
Era of Good Feelings: 1815-1825 After the War of 1812 Americans finally have international respect The Republicans are the only political party James Monroe, the third member of the Virginia Dynasty, is
Tuesday, September 12, 2017 United States Human Geography
 Tuesday, September 12, 2017 United States Human Geography Objective: Explain how the United States acquired its geographic boundaries. Examine patterns of immigration to and migration within the United
Tuesday, September 12, 2017 United States Human Geography Objective: Explain how the United States acquired its geographic boundaries. Examine patterns of immigration to and migration within the United
Unit 8. Innovation Brings Change 1800 s-1850 s
 Unit 8 Innovation Brings Change 1800 s-1850 s Unit Overview: Industrialization Era This unit addresses the development of the economies in the North and the South, innovations in technology and the application
Unit 8 Innovation Brings Change 1800 s-1850 s Unit Overview: Industrialization Era This unit addresses the development of the economies in the North and the South, innovations in technology and the application
Imperialism. Policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker territories
 Imperialism Policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker territories Global Competition European nations had been establishing colonies for years Asia
Imperialism Policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker territories Global Competition European nations had been establishing colonies for years Asia
Imperialism and America
 Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire CHAPTER 10 Section 1 (pages 342-345) Imperialism and America American Expansionism (pages 342-344) Why did Americans support imperialism? In 1893, Queen Liliuokalani
Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire CHAPTER 10 Section 1 (pages 342-345) Imperialism and America American Expansionism (pages 342-344) Why did Americans support imperialism? In 1893, Queen Liliuokalani
Early to Mid 1800's Practice Quiz
 1 Which action is most closely associated with the term Manifest Destiny? (1) declaring independence from Great Britain (2) deciding to end the War of 1812 (3) acquiring territory from Mexico in 1848 (4)
1 Which action is most closely associated with the term Manifest Destiny? (1) declaring independence from Great Britain (2) deciding to end the War of 1812 (3) acquiring territory from Mexico in 1848 (4)
Summary The Beginnings of Industrialization KEY IDEA The Industrial Revolution started in Great Britain and soon spread elsewhere.
 Summary The Beginnings of Industrialization KEY IDEA The Industrial Revolution started in Great Britain and soon spread elsewhere. In the early 1700s, large landowners in Britain bought much of the land
Summary The Beginnings of Industrialization KEY IDEA The Industrial Revolution started in Great Britain and soon spread elsewhere. In the early 1700s, large landowners in Britain bought much of the land
America s Path to Empire. APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8
 America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8 1890-1892 Foreign Policy The Influence of Sea Power upon History (1890): Alfred Thayer Mahan Sea power throughout history gives advantages US lies
America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8 1890-1892 Foreign Policy The Influence of Sea Power upon History (1890): Alfred Thayer Mahan Sea power throughout history gives advantages US lies
UNIT 4: EXPANSION & REFORM LESSON 4.1: EFFECTS OF MANIFEST DESTINY & INDUSTRIALIZATION
 UNIT 4: EXPANSION & REFORM LESSON 4.1: EFFECTS OF MANIFEST DESTINY & INDUSTRIALIZATION ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does expansion and industrialization contribute to growing sectionalism within the United States
UNIT 4: EXPANSION & REFORM LESSON 4.1: EFFECTS OF MANIFEST DESTINY & INDUSTRIALIZATION ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does expansion and industrialization contribute to growing sectionalism within the United States
Name Period Teacher. Wantagh Middle School 7 th Grade Social Studies Final Exam Review Guide
 Name Period Teacher Wantagh Middle School 7 th Grade Social Studies Final Exam Review Guide 1. How did the earliest people migrate to North America? 2. How did Native Americans use the environment around
Name Period Teacher Wantagh Middle School 7 th Grade Social Studies Final Exam Review Guide 1. How did the earliest people migrate to North America? 2. How did Native Americans use the environment around
The Americans (Survey)
 The Americans (Survey) Chapter 7: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OVERVIEW American leaders devise a farsighted policy of improvements as North, South, and West develop
The Americans (Survey) Chapter 7: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OVERVIEW American leaders devise a farsighted policy of improvements as North, South, and West develop
Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy?
 Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.4: Clickers Questions Market Revolution inquiry activity
Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.4: Clickers Questions Market Revolution inquiry activity
Essential Question: What was the impact of European imperialism on China?
 Essential Question: What was the impact of European imperialism on China? CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.8: Clicker questions Imperialism in China notes Today s HW: 27.5 Unit 10 Test: Friday, February 22 The
Essential Question: What was the impact of European imperialism on China? CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.8: Clicker questions Imperialism in China notes Today s HW: 27.5 Unit 10 Test: Friday, February 22 The
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism
 7 QUIT Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE GRAPH SECTION 1 Regional Economics Create Differences SECTION 2 Nationalism at Center Stage MAP SECTION 3
7 QUIT Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE GRAPH SECTION 1 Regional Economics Create Differences SECTION 2 Nationalism at Center Stage MAP SECTION 3
I. The Agricultural Revolution
 I. The Agricultural Revolution A. The Agricultural Revolution Paves the Way 1. Wealthy farmers cultivated large fields called enclosures. 2. The enclosure movement caused landowners to try new methods.
I. The Agricultural Revolution A. The Agricultural Revolution Paves the Way 1. Wealthy farmers cultivated large fields called enclosures. 2. The enclosure movement caused landowners to try new methods.
I. Articles of Confederation
 The New Nation I. Articles of Confederation A. The A.O.C. were the nations 1 st Constitution 1. Adopted by congress during the rev. war 2. Set up a loose alliance among the 13 states 3. it reflects a fear
The New Nation I. Articles of Confederation A. The A.O.C. were the nations 1 st Constitution 1. Adopted by congress during the rev. war 2. Set up a loose alliance among the 13 states 3. it reflects a fear
Madison & Monroe. Presidencies
 James James Madison & Monroe Presidencies Where we are March 1797: President John Adams takes office. 1796-1800: XYZ Affair, Quasi-War with France, Alien & Sedition Acts, VA & KY Resolutions 1801-1804:
James James Madison & Monroe Presidencies Where we are March 1797: President John Adams takes office. 1796-1800: XYZ Affair, Quasi-War with France, Alien & Sedition Acts, VA & KY Resolutions 1801-1804:
IMPERIALISM. Policing the Western Hemisphere
 Alaska William Seward Sec. of State purchased from Russia for $7 million. Twice the size of Texas Nicknamed Seward s Folly or Seward s Icebox 1890 gold found there Hawaii IMPERIALISM Grew sugar that was
Alaska William Seward Sec. of State purchased from Russia for $7 million. Twice the size of Texas Nicknamed Seward s Folly or Seward s Icebox 1890 gold found there Hawaii IMPERIALISM Grew sugar that was
Progressive Era, Imperialism, and World War 1
 Progressive Era, Imperialism, and World War 1 Section 7.1 Imperialism- a nation desires to gain more territory outside it s borders Reasons for US Imperialism: Economic growth- new people to sell to National
Progressive Era, Imperialism, and World War 1 Section 7.1 Imperialism- a nation desires to gain more territory outside it s borders Reasons for US Imperialism: Economic growth- new people to sell to National
The Beginnings of Industrialization
 Name CHAPTER 25 Section 1 (pages 717 722) The Beginnings of BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about romanticism and realism in the arts. In this section, you will read about the beginning of
Name CHAPTER 25 Section 1 (pages 717 722) The Beginnings of BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about romanticism and realism in the arts. In this section, you will read about the beginning of
U.S. Imperialism Practice Questions
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the map below and on your knowledge of social studies. 1 Which United States foreign policy was most often used to carry out the actions shown on the map? (1)
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the map below and on your knowledge of social studies. 1 Which United States foreign policy was most often used to carry out the actions shown on the map? (1)
DRAWING FROM EXPERIENCEII
 Chapter 10, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 306 311 ECONOMIC GROWTH KEY TERMS Industrial Revolution A new way of working and producing goods (page 307) capital Money invested to start new businesses
Chapter 10, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 306 311 ECONOMIC GROWTH KEY TERMS Industrial Revolution A new way of working and producing goods (page 307) capital Money invested to start new businesses
INTRODUCTION TO IMPERIALISM: A SPRITE APPROACH
 INTRODUCTION TO IMPERIALISM: A SPRITE APPROACH DEFINITION OF IMPERIALISM: Process by which one state, with superior military strength and more advanced technology, imposes its control over the land, resources,
INTRODUCTION TO IMPERIALISM: A SPRITE APPROACH DEFINITION OF IMPERIALISM: Process by which one state, with superior military strength and more advanced technology, imposes its control over the land, resources,
Q3/Q4 Sectionalism Vocab
 Q3/Q4 Sectionalism Vocab North: Industrial Revolution Sectionalism: loyalty to one region (section) of the country rather than the whole country Industrial Revolution: period of rapid growth in the use
Q3/Q4 Sectionalism Vocab North: Industrial Revolution Sectionalism: loyalty to one region (section) of the country rather than the whole country Industrial Revolution: period of rapid growth in the use
Imperialism and America
 CHAPTER 10 Section 1 ( pages 342 345) Imperialism and America BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about Woodrow Wilson. In this section, you will learn how economic activity led to political
CHAPTER 10 Section 1 ( pages 342 345) Imperialism and America BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about Woodrow Wilson. In this section, you will learn how economic activity led to political
1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation
 Topic 3 1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg 88-89 They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation agreements 2. How did the British respond to the Boston Tea
Topic 3 1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg 88-89 They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation agreements 2. How did the British respond to the Boston Tea
Let's discuss: to stop human rights abuses under no circumstances
 Let's discuss: When do you think it is appropriate for the US to send soldiers to fight and face death on foreign soil? (Choose up to 3 of the following and briefly explain your choices) to assist an ally
Let's discuss: When do you think it is appropriate for the US to send soldiers to fight and face death on foreign soil? (Choose up to 3 of the following and briefly explain your choices) to assist an ally
4. During the late 1800s, the port of entry for the majority of immigrants was a. Boston b. New York City c. Philadelphia d.
 Chapters 14-18 Presentations Test 1. The cruise of the Great White Fleet showed that a. the Atlantic could be crossed safely. b. Great Britain was a second-rate power. c. the United States was a naval
Chapters 14-18 Presentations Test 1. The cruise of the Great White Fleet showed that a. the Atlantic could be crossed safely. b. Great Britain was a second-rate power. c. the United States was a naval
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved.
 Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. US History Immigration and Foreign policy Blizzard Bag 2014-2015 1. In a 1904 address to Congress, President Theodore Roosevelt stated that the United States
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. US History Immigration and Foreign policy Blizzard Bag 2014-2015 1. In a 1904 address to Congress, President Theodore Roosevelt stated that the United States
Washington to Madison Practice Questions
 1 Washington s Proclamation of Neutrality (1793), Jefferson s Embargo Act (1807), and the Monroe Doctrine (1823) were all efforts to (1) avoid political conflicts with European nations (2) directly support
1 Washington s Proclamation of Neutrality (1793), Jefferson s Embargo Act (1807), and the Monroe Doctrine (1823) were all efforts to (1) avoid political conflicts with European nations (2) directly support
THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN THE U.S. How the War of 1812 & Technological Progress Change the Country
 THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN THE U.S. How the War of 1812 & Technological Progress Change the Country TECHNOLOGY MEANS PROGRESS Developments in technology begin to transform life in the U.S. in the
THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN THE U.S. How the War of 1812 & Technological Progress Change the Country TECHNOLOGY MEANS PROGRESS Developments in technology begin to transform life in the U.S. in the
Imperalism.notebook March 03, 2015
 Agenda Bell ringer Notability 1 Objective: I can discuss and explain why the United States Foreign Policy changed during the late 19th century. Bell Ringer Notability HW: Due Thursday 2 1 A B C D 3 2 A
Agenda Bell ringer Notability 1 Objective: I can discuss and explain why the United States Foreign Policy changed during the late 19th century. Bell Ringer Notability HW: Due Thursday 2 1 A B C D 3 2 A
MISSISSIPPI SOCIAL STUDIES FRAMEWORKS, UNITED STATES HISTORY TO 1877 EIGHTH GRADE
 Mississippi Social Studies Frameworks, Mississippi Social Studies Frameworks, United States History to 1877 (Grade 8) EIGHTH GRADE (United States History to 1877) STRANDS: (C-Civics); (H-History); (G-Geography);
Mississippi Social Studies Frameworks, Mississippi Social Studies Frameworks, United States History to 1877 (Grade 8) EIGHTH GRADE (United States History to 1877) STRANDS: (C-Civics); (H-History); (G-Geography);
JEFFERSONIAN DEMOCRACY ( ) ELECTION OF 1800 ELECTION OF 1800 JEFFERSON S PHILOSOPHY EXAMPLE POLICIES A NATION OF FARMERS
 JEFFERSONIAN DEMOCRACY (1800 1828) ELECTION OF 1800 Revolution of 1800 Adams v. Jefferson (again) Major Issues: - Expansion of Military - Foreign Affairs - Alien & Sedition Acts 1 2 ELECTION OF 1800 DR
JEFFERSONIAN DEMOCRACY (1800 1828) ELECTION OF 1800 Revolution of 1800 Adams v. Jefferson (again) Major Issues: - Expansion of Military - Foreign Affairs - Alien & Sedition Acts 1 2 ELECTION OF 1800 DR
Review. Declaration of Independence
 Declaration of Independence Review Letter giving reasons why they were revolting Influenced by John Locke Governments power comes from people (Consent of Governed) Natural Rights- life, liberty, pursuit
Declaration of Independence Review Letter giving reasons why they were revolting Influenced by John Locke Governments power comes from people (Consent of Governed) Natural Rights- life, liberty, pursuit
Eighth Grade Social Studies United States History Course Outline
 Crossings Christian School Academic Guide Middle School Division Grades 5-8 Eighth Grade Social Studies Chapter : Early Exploration of the Americas How do new ideas change the way people live? Why do people
Crossings Christian School Academic Guide Middle School Division Grades 5-8 Eighth Grade Social Studies Chapter : Early Exploration of the Americas How do new ideas change the way people live? Why do people
Level 1. Manifest Destiny and the Addition of Land
 Level 1 Manifest Destiny and the Addition of Land Vocabulary Sectionalism: a loyalty to a section of the country instead of the nation itself Diplomats: a person appointed by a government to conduct negotiations
Level 1 Manifest Destiny and the Addition of Land Vocabulary Sectionalism: a loyalty to a section of the country instead of the nation itself Diplomats: a person appointed by a government to conduct negotiations
EXAM INFORMATION. Human Geography II of the United States and Canada. L Anse aux Meadows World Heritage Site, NFD. Early European Exploration
 /4/017 EXAM INFORMATION Exam One is Tues, Mar 7th. Format. Multiple choice questions on material covered through Human Geog III; some aimed at maps/diagrams and essay topics from a choice. See Study Guide.
/4/017 EXAM INFORMATION Exam One is Tues, Mar 7th. Format. Multiple choice questions on material covered through Human Geog III; some aimed at maps/diagrams and essay topics from a choice. See Study Guide.
Chapter 27: The Path of Empire, (Pages )
 Chapter 27: The Path of Empire, 1890 1899 (Pages 626 653) I. America Turns Outward A. Motives for overseas expansion 1. Farmers and industrialists Name Per. Date Row 2. The yellow press 3. Role of religion
Chapter 27: The Path of Empire, 1890 1899 (Pages 626 653) I. America Turns Outward A. Motives for overseas expansion 1. Farmers and industrialists Name Per. Date Row 2. The yellow press 3. Role of religion
WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer
 WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer Subject(s) Social Studies Conceptual Lenses Grade/Course 8 th Grade Leadership Unit of Study Expansion and Reform (1801-1861) Innovation Unit Title Unit 4 Growing Up: Expanding
WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer Subject(s) Social Studies Conceptual Lenses Grade/Course 8 th Grade Leadership Unit of Study Expansion and Reform (1801-1861) Innovation Unit Title Unit 4 Growing Up: Expanding
Imperialism and WWI US History Unit 4. Name:
 Imperialism and WWI US History Unit 4 Name: 2 Imperialism and WWI [all homework assignments must be turned in prior to taking your assessment] 4.1: Due Pages 187-207 1. Imperialism 2. Annexing Hawaii 3.
Imperialism and WWI US History Unit 4 Name: 2 Imperialism and WWI [all homework assignments must be turned in prior to taking your assessment] 4.1: Due Pages 187-207 1. Imperialism 2. Annexing Hawaii 3.
Division of Labor: giving each worker one or two simple jobs.
 Chapter 12 The Nation Grows (1815-1830) Section 1 Industries take Root Industrial Revolution: the growth of industry eventually produced changes so great that this time in history is called the Industrial
Chapter 12 The Nation Grows (1815-1830) Section 1 Industries take Root Industrial Revolution: the growth of industry eventually produced changes so great that this time in history is called the Industrial
Acquiring and Managing Global Power
 1890 1917 Chapter 21 Acquiring and Managing Global Power Were U.S. interventions abroad between 1890 and 1917 motivated more by realism or idealism? 21.1 Introduction On May 1, 1901, the Pan-American Exposition
1890 1917 Chapter 21 Acquiring and Managing Global Power Were U.S. interventions abroad between 1890 and 1917 motivated more by realism or idealism? 21.1 Introduction On May 1, 1901, the Pan-American Exposition
Chapter 6 Shaping an Abundant Land. Page 135
 Chapter 6 Shaping an Abundant Land Page 135 Waves of immigrants came to the U.S. in order to find a better life. Push-pull factors were at play. Immigration is not the only movement of people in the U.S.
Chapter 6 Shaping an Abundant Land Page 135 Waves of immigrants came to the U.S. in order to find a better life. Push-pull factors were at play. Immigration is not the only movement of people in the U.S.
Transformations Around the Globe. Ch
 Transformations Around the Globe Ch 28 1800-1914 China + the West China looked down on foreigners China was self-sufficient Strong agricultural economy Extensive mining + industry China wasn t interested
Transformations Around the Globe Ch 28 1800-1914 China + the West China looked down on foreigners China was self-sufficient Strong agricultural economy Extensive mining + industry China wasn t interested
America s Path to Empire. APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 2
 America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 2 Major Events 1890-1892 McKinley Tariff October 1, 1890 Raised the average duty on imports to almost fifty percent Intended to protect domestic industries
America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 2 Major Events 1890-1892 McKinley Tariff October 1, 1890 Raised the average duty on imports to almost fifty percent Intended to protect domestic industries
