Global Security Threat of Terrorism, Muslim Jihadi Organizations and U.S Foreign Policy
|
|
|
- Cathleen Jefferson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Global Security Threat of Terrorism, Muslim Jihadi Organizations and U.S Foreign Policy 11 Rani Erum* ABSTRACT Terrorism is a phenomenon that is specifically associated with the 21st century, though it has a relation with history. It is an international framework of organized violence transcending state boundaries through suicide bombing, terrorist attacks, airplane crashes etc. The attacks of 9/11 were the landmark of the emergence of this phenomenon in a globalized world of modern era because they were completely different from all previous incidents of terror. Global terrorism has been linked with Islamic Jihadi Organizations and state sponsored terrorism since this catastrophic event. This theory has both its supporters and opponents. The opponents of this theory generally emphasize the limited role and infrastructure of these Jihadi organizations and object to exaggerated propaganda of the West, especially USA, whereas, the supporters of the theory consider global terrorism the biggest threat to global security. This article analyzes this global issue to explore its hidden complexities in relation to US counter terrorism strategy and Jihadi organizations. Key words: Security, Terrorism, Jihadi Organizations, Violance, US Foreign Policy. INTRODUCTION Terrorism emerged as the greatest threat to global security in the new millennium. Attacks of September 11 th 2001 on the World Trade Center and the Pentagon shocked Americans as well as the world because of their complexity and precision. Although it is not completely a new phenomenon, its execution in the 21 st Century horrified the world and attained the focus of foreign policies of all major powers. It is a highly contested and deeply controversial phenomenon; critical theorists believe that major part of the commonly accepted knowledge about it is stereotypical and based on misconceptions. It is largely an overstated concept on ideological grounds and over promoted by media, which most of the time is used to achieve national objectives by world powers. Thus, there is a need to understand its origin and all its complexities and transformations in the modern. Terrorism, as a word in its usual usage, has basically a connotation of evil, indiscriminate violence or brutality 1. However, due to the complexity of the phenomenon, there have been a variety of definitions provided by theorists of world politics. Some of them are extremely complicated or consist of too many elements. To Walter Laqueur (1987, 1999) terrorism constitutes the illegitimate use of force to achieve a political objective by targeting innocent people 2. Robert Goodin describes it as a form of political violence that aims to achieve its objectives through creating a climate of fear and apprehension 3. James Lutz and Brenda Lutz gathered the work of Crenshaw (1983), Hoffman (2006) and Claridge, and have given a comprehensive definition of terrorism that is: * Assistant professor, Department of Political Science, Federal Urdu University, Karachi. rani.irum@fuuast.edu.pk Date of Receipt:
2 Terrorism involves political aims and motives. It is violent or threatens violence. It is designed to generate fear in a target audience that extends beyond the immediate victims of the violence. The violence involves a non-state actor as either the perpetrator, the victim of the violence, or both. Finally, the acts of violence are designed to create power in situations in which power previously had been lacking (i.e., the violence attempts to enhance the power base of the organization undertaking the action) 4. The first element of the definition states that the violence is initiated fundamentally for political reasons. In fact it is supposed to be the succession of politics. Political goals are a key factor that separate terrorist acts from other forms of violence 5. Political objectives may vary; terrorist acts can be undertaken for sake of change of leadership or of entire government or system, or they may seek to alter national boundaries and create altogether a new state. The second element is that the violence or persuasive threat of violence principally exists in the respective terrorist activities. This component illustrates that any attempts to bring change without violence are not terrorism, no matter how disturbing they may be to a government. The third key element of terrorism is, only those violent actions are qualified as terrorism, which have a potential to affect a massive crowd or their target audience is beyond the immediate victims and that influence a huge crowd as part of the strive to obtain the political objectives of the organization, therefore, Peter Chalk defined it as form of psychological warfare that intends to influence governments and general public 6. Fourth, political violence is supposed to be propagated by recognized organizations because it is very difficult for any individual to carry out terrorist actions solely. According to Badey, effective terrorism rests on the potential for repetition and the systematic use of violence 7.Terrorist organizations like to work with temporary members who work together for a specific attack and then separate, in other words they use part timers. Hoffman believes that these part timer groups may accept central direction in how they proceed, but they are not centrally controlled 8. The success rate of these loosely aligned individuals is far better than permanent members because they are more willing to inflict higher fatality and more eager to use lethal weapons than conventional groups. Fifth, this definition excludes state violence from terrorism, which limits its focus, because to exclude actions of state is to ignore violence undertaken by states. Governments also endeavor terrorist actions against their own population in order to achieve some political goals, though they officially deny such kind of actions. Finally, terrorist activities are used primarily to enhance the power position by such organizations. Terrorism usually inspires weaker groups because it assures them high reward despite limited resources. Other groups also make it the technique of choice and use it, when other methods take too long or do not work. All these features are essential for an action to be identified as a terrorist act. HISTORY OF TERRORISM Terrorism has had a long history and is by no means a modern phenomenon. Before the 19 th century it was mostly recognized on the basis of religion. The 12
3 Sicarri (dagger men) was the extreme splinter wing of Jewish Zealots, which is the most ancient example of terrorist group found in 1 st century from 66 to 71 AD. They used killing and kidnapping in their campaign against the Roman Judea and Jews who collaborated with Romans 9. Another early example of violence can be traced in India. It was the Thugee or Thugs, a cult that carried out ritual killings supposedly in honor of the goddess of Kali. It emerged in 13 th century but came to prominence in 17 th century. The Assassins, a group that sought to purify Islam by stabbing infidels from 1090 to is the third example. The term was used for the first time during French revolution, when the mass execution carried out by the Jacobins under the leadership of Robespierre was termed as the Reign of Terror ( ), during which almost 40,000 alleged enemies of revolution were put to death 11. Russian anarchist nihilists and populists of the 19 th century refined it as a tool for political, economic and social change 12. They introduced a new term in world politics named as anarchist terrorism, which was a form of propaganda by the dead. European anarchists used violence as a means to achieve political attention and to provoke the masses to revolt against subjugation and exploitation. Activities of anarchists groups reached their peak in Amongst the victims were Tsar Alexander II (1881), Empress Elizabeth of Austria (1898), King Umberto of Italy (1900) and President Carnot of France (1894) and McKinley of USA (1901) 13. A further wave of anarchist violence broke out in the decade of 1960 to 1970 undertaken by groups such as the Baader Meinhof group of West Germany, the Italian Red Brigade, the Japanese Red Army and the Angry Brigade in UK 14.However, nationalist and ethnic motives were essentially present behind terrorism after WWII. During the 1940s and 1950s, it was associated with third world anti-colonial struggle in Africa, Asia and the Middle East, later being taken up by national liberation movements such as the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) and groups such as Black September. It was also used by disaffected national or ethnic minorities in developed western societies, notably by the Irish Republican Army (IRA) in Northern Ireland, by ETA (Euskadi Ta Askatasuna or Basque Homeland and Liberty) in Spain and by the FLQ (Front de libération du Québec or Quebec Liberation Front) in Quebec, Canada 15.History provides evidence that states have sponsored terrorism and revolutionary France was its ancient example but from the 1980s many countries of the world such as Libya, Cuba and Syria instigated it. TERRORISM IN THE UNITED STATES Although the topic of terrorism has always been, and continues to be, a hotly debated and generally interpreted subject in the US, the first recorded instance of what might be argued as terrorism in America took place in 1622 when the Powhatan Native Americans attacked the Jamestown colony in 1622, killing 30 percent of its inhabitants 16.Although, there were occasional mutinies and rebellions in early United States history, the white supremacist organization, the Ku Klux Klan (KKK) was the first terrorist organization established after the 13
4 creation of the American republic. It was formed in 1867 and was primarily a non-violent social organization led by former Confederate general Nathan Bedford Forrest. It shortly turned towards violence in 1868, murdering, abusing and threatening black voters and white supporters of the Republican Party. Their assaults and terrorist activities were particularly effective in forming voting patterns, and resulted into conservative white Democratic control by late After a massive Federal crackdown involving suspension of Habeas Corpus, legal convictions of "dubious constitutionality" and tough anti-klan laws during , the KKK disbanded itself. After the end of early KKK violence in 1872, a new threat from anarchist movements emerged: "first wave" of modern international terrorism struck America with Haymarket square bombing in Anarchist terrorism ended in USA in 1927 with the execution of two Italian men, Nicola Sacco and Bartolommeo Vanzetti, who were arrested on charges of robbery involving murder. During that period a chain of bombings and murders took place that included the assassination of President McKinley in 1901, a stream of mail bombings directed at government officials that included a failed attempt at the Attorney General in 1919, and the bombing of Wall Street in 1920 which killed at least 30 people 18. From 1920 to 1960 relatively few terrorist attacks on the United States soil had been registered and that period is classified as the "anti-colonial wave". America experienced a significant increase of terrorism on its main land in the early 1960s because of Soviet communist regime. These groups included Symbionese Liberation Army, Weather Underground Organization, Black Liberation Army, Armed Forces of National Liberation and other Puerto Rican militants. All these groups were eradicated with the collapse of USSR and from early 1990s till now the majority of terrorist attacks on the US mainland came from white nationalists and others sects of the world. Most of the attacks before 9/11 were successfully prevented like the 1993 World Trade Center attack and the 1995 Oklahoma City bombing. The intensity was exhibited to the American people on the morning of September 11, INCIDENT OF 9/11: THE RISE OF NEW TERRORISM Terrorism emerged as a new experience on 9/11; it altered the global security environment of the world. On the morning of 11 September 2001 terrorists hijacked four American civilian aircrafts with passengers aboard and used them as devastating flying bombs. Two of them crashed into the twin towers of WTC (World Trade Center) in New York City with a force that measured 2.4 on the Richter scale, equivalent to a minor earthquake. Their hi-octane fuel exploded following the massive impact, bringing the 110 store-y buildings down one after the other and turning them into 450 tons of ruin. The site of the devastation came to be known as ground zero. The third aircraft wheeled and ripped into the Pentagon, headquarters of the US military in Washington DC. The western side of the gigantic building, which is the living icon of America s military, might and superpower status, lay in smoke and ruins 19.Fourth aircraft was off target and crashed into the forests of Pennsylvania. The sophistication of the attacks and the scope of the destruction horrified the world. It was the first direct attack on the 14
5 US since Pearl Harbor in December 1941 and even first ever on its mainland. On the night of the 9/11 attacks, President of United States George W. Bush noted in his diary, The Pearl Harbor of the 21 st century took place today. 20 More Americans were killed on September 11 than Pearl Harbor and more importantly, all of them were civilians. It was the greatest loss of lives in a single day since the civil war of 1812 and killed almost 3,000 people including nationals of 90 different countries and cost an estimated $500, US president immediately declared the War on Terror against the terrorists and their supporters. It was not just an immediate but also a precisely articulated reaction by the United States that is evident by the momentum of its foreign and domestic policy thereafter. They propagated that the War on Terror was the fight of all who believed in progress and pluralism, tolerance and freedom. There was no room for other states to remain neutral in this global war and therefore, they were pressurized to change, willingly or not, their foreign and domestic policies. In the United States, the Bush administration worked with Congress to legislate and implement a revised definition of terrorism, introducing new internal search arrest and surveillance powers, and appropriated huge increases in federal spending on homeland security and war on terror programs designed to enhance and develop new military, law enforcement, surveillance, data base management, border control, capital control and intelligence capacities particularly aimed at Islamic extremists. The inherent, plenary power awarded to President Bush gave him full discretion including license to ignore the Geneva Conventions, administration officials also effectively authorized and organized state kidnapping of alleged terrorists both in US and abroad, detaining suspects in military facilities in the US and abroad without access to legal redress, and sanctioned abuse of detainees, including torture, by US personnel and outsourcing of abuse to private contractors and officials of foreign governments 22. The US President also declared that United States would not make any distinction between terrorists and those who harbored them, and therefore, as a consequence of this approach it attacked Afghanistan on 7 th October, 2001 because the then incumbent Afghan regime had refused to hand over Osama Bin Laden, the Al Qaeda chief. Thus, analysts of the world proclaim this incident a new Terrorism. UNITED STATES COUNTER TERRORISM STRATEGY The 9/11 attacks opened a period for US in which national security concerns would loom large in the domestic arena. The passage by wide margins and without much debate of legislation to provide tools required to intercept and obstruct terrorism in the so called Patriot Act of 2001 strengthened the powers available to law enforcement agencies in a number of respects, including the powers to conduct wiretap and other surveillance operations on citizens, and to detain and deport immigrants who are suspected of being involved with terrorism. According to this act, US terrorism strategy has two directions, one is to counter non-state terrorist organizations and other is to counter state sponsored terrorism and rogue states. 15
6 TERRORIST ORGANIZATIONS According to section 2656f of US code terrorist organizations are those who involved in any terrorist activities against American citizens during the last five years; hence a list of designated Foreign Terrorist Organizations (FTOs) was issued. This list includes all Islamic jihadist organizations with some other Latin American and European organizations of the world but the core focus of US remains on Islamic Jihadist groups and organizations which are active in Afghanistan, Pakistan, Iran, Iraq, Syria, Egypt, Lebanon, Palestine and other Islamic countries. The US believes that such organizations are the major threat for global peace. Therefore, the focal point of US strategists is to counter these terrorist organizations. The FTOs list is given below 23 : DESIGNATED FOREIGN TERRORIST ORGANIZATIONS Date Designated Name 10/8/1997 Abu Nidal Organization (ANO) 10/8/1997 Abu Sayyaf Group (ASG) 10/8/1997 Aum Shinrikyo (AUM) 10/8/1997 Basque Fatherland and Liberty (ETA) 10/8/1997 Gama a al-islamiyya (Islamic Group) (IG) 10/8/1997 HAMAS 10/8/1997 Harakat ul-mujahidin (HUM) 10/8/1997 Hizballah 10/8/1997 Kahane Chai (Kach) 10/8/1997 Kurdistan Workers Party (PKK) (Kongra-Gel) 10/8/1997 Liberation Tigers of Tamil Eelam (LTTE) 10/8/1997 National Liberation Army (ELN) 10/8/1997 Palestine Liberation Front (PLF) 10/8/1997 Palestinian Islamic Jihad (PIJ) 10/8/1997 Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine (PFLF) 10/8/1997 PFLP-General Command (PFLP-GC) 10/8/1997 Revolutionary Armed Forces of Colombia (FARC) 10/8/1997 Revolutionary Organization 17 November (17N) 10/8/1997 Revolutionary People s Liberation Party/Front (DHKP/C) 10/8/1997 Shining Path (SL) 10/8/1999 al-qaida (AQ) 9/25/2000 Islamic Movement of Uzbekistan (IMU) 5/16/2001 Real Irish Republican Army (RIRA) 9/10/2001 United Self Defense Forces of Colombia (AUC) 12/26/2001 Jaish-e-Mohammed (JEM) 12/26/2001 Lashkar-e Tayyiba (LeT) 3/27/2002 Al-Aqsa Martyrs Brigade (AAMB) 3/27/2002 Asbat al-ansar (AAA) 16
7 3/27/2002 al-qaida in the Islamic Maghreb (AQIM) 8/9/2002 Communist Party of the Philippines/New People's Army (CPP/NPA) 10/23/2002 Jemaah Islamiya (JI) 1/30/2003 Lashkar i Jhangvi (LJ) 3/22/2004 Ansar al-islam (AAI) 7/13/2004 Continuity Irish Republican Army (CIRA) 12/17/2004 Libyan Islamic Fighting Group (LIFG) 12/17/2004 al-qaida in Iraq (AQI) 6/17/2005 Islamic Jihad Union (IJU) 10/11/2005 Moroccan Islamic Combatant Group (GICM) 3/5/2008 Harakat ul-jihad-i-islami/bangladesh (HUJI-B) 3/18/2008 al-shabaab 5/18/2009 Revolutionary Struggle (RS) 7/2/2009 Kata'ib Hizballah (KH) 1/19/2010 al-qaida in the Arabian Peninsula (AQAP) 8/6/2010 Harakat ul-jihad-i-islami (HUJI) 9/1/2010 Tehrik-e Taliban Pakistan (TTP) 11/4/2010 Jundallah 5/23/2011 Army of Islam (AOI) 9/19/2011 Indian Mujahedeen (IM) 3/13/2012 Jemaah Anshorut Tauhid (JAT) 5/30/2012 Abdallah Azzam Brigades (AAB) 9/19/2012 Haqqani Network (HQN) These declared FTOs need to be discussed because of their popularity, advance techniques and objectives. Most of the terrorist organizations of 21 st century are the outcome of wars and regional disputes of territories. These organizations initially began as freedom fighting movements for their homeland, which turned towards terrorism later. Al-Qaida Al-Qaida al-sulbah, an Arabic word that means "the Solid Base," is an international terrorist network established by Osama bin Laden in the late 1980s 24. It seeks to cleanse Muslim countries from the influence of the West and replace their governments with Islamic regimes. Al-Qaida s efforts are based on following principles: 1. Muslims are under attack everywhere. 2. Al-Qaida and its followers are fighting the oppressors of Islam. 3. Al-Qaida sees its mission to be the vanguard of the uprising of the oppressed and to inspire the masses with an uplifting message intended to create a revolution. 17
8 Al-Qaida along with its worldwide network is the most advanced, well equipped, self-sufficient and religiously motivated organization of the 21 st century. After the Soviet withdrawal from Afghanistan, Bin Laden saw the West, especially the US, as the greatest threat to Islam because of its negative policies for the Middle East. Members of Al-Qaida network see themselves as fighting against the evil influence made by the secular culture of West; they see the United States as being responsible for attacks on Muslim populations in many parts of the World, including Bosnia, Lebanon and Chechnya 25. According to them, United States involvement in Bosnia allowed Christian Serbs to attempt brutal violence against local Muslims. They are also concerned about US policies that favour Israel over the Palestinians, but the trigger point for them was the Persian Gulf conflict that arose after the Iraqi occupation of Kuwait, turning bin Laden against the US. He criticized the UN sanctions against Iraq as well as the presence of Western troops on Saudi Arabia where the holy cities of Makkah and Medina are situated. Bin Laden believed that all of these activities were a part of Christen-Judeo conspiracy. According to US officials Bin Laden led Al Qaida supported the Somali groups that attacked US forces in 1993, although there was no significant evidence of its direct role in those attacks. It apparently had some role in the bombing of the US barracks in Dhahran, Saudi Arabia in 1996 that killed nineteen US service personnel and wounded over 500, and it was clearly involved in the suicide attack on the US destroyer Cole in 2000 in Aden harbour that killed 17 service personnel and wounded thirty-nine others. Bin laden network was also responsible for the attacks in 1998 on the US embassies in Nairobi, Kenya and Dares-Salaam in Tanzania, which resulted in the death of over 200 people and the wounding of thousands, most of whom were the nationals of these countries 26. But 9/11 attacks gained major attention of the world and after these attacks, the United States launched a war in Afghanistan to destroy its bases there and overthrow the Taliban, the country's Muslim rulers who harboured bin Laden and his followers. Most of the analysts believed that Bush responded against this challenge not only in a radical but also in an incompetent way. He not only addressed the issue aggressively but also went on offensive to reform the world. He convinced the world that the United States confronted an unusual threat and needed support by other states. The extreme emotions of Bush administration against Al-Qaeda fighters and their supporters brought two wars in 21st century. Like his predecessor, Barack Obama has perused the same strategy of destroying al- Qaida's safe havens in the Afghanistan-Pakistan region, and limiting the group'sability to strike on US targets. In July 2007, US intelligence agencies found that despite the targeted killings of senior al-qaeda leaders that shrank its command and control capabilities, organization was regrouping and regaining strength in the tribal areas of Pakistan located along the border with Afghanistan. The killing of al-qaida's top leader Osama bin Laden by US forces in Pakistan on 2 nd May 2011 served a severe blow to the organization, but analysts still believed 18
9 that al-qaeda remains existing with its networks spread all over the world, plus, a number of affiliated groups have gained prominence in recent years. Taliban The Taliban movement was formed primarily in response to the failure of the Mujahedeen to establish a stable government following the withdrawal of the Soviet troops from Afghanistan in 1989 and the collapse in 1992 of the Najibullah government. It was the group of Madrassa teachers and students led by Mullah Muhammad Omar that came forward to put an end to the ongoing power struggle of the Mujahedeen warlords and establish a pure form of Islamic regime in This regime fell down in 2001 after the attack of US and its allied NATO forces 27. The Taliban s rural-based Pashtun ethno-tribal association produced great support to its network in Afghanistan and Pakistan. A very large section of Taliban was based in Pakistan and they gathered significant support from Pashtun of Khyber Pakhtun Khwa (KPK) and Baluchistan. Basically they were freedom fighters and not the terrorists, and it was the ideological and tactical bindings with Al-Qaida, which presented them as terrorists. They became the subject of US counterterrorism policy only when they started a counter insurgency against US troops and NATO forces in spring They conducted wide variety of attacks against US, coalition and Afghan security forces. They used the tactic of yielding population centres to US and Afghan forces, operating from rural areas. In a response to the Taliban insurgency the transnational counter insurgent states (US and NATO forces) assimilated strikes and local operations with Afghan forces, but these actions have not achieved their task and they are still active against Hamid Karzai s Afghan regime and NATO allied forces. Afghan Taliban influenced the tribal people of Pakistan and they emerged as Pakistani Taliban in FATA (Federally Administrated Tribal Area). Pakistani Taliban They are organizationally different from the Afghan group and emerged in 2002 in retaliation to the Pakistan army s foray into the tribal area for a militant hunt down. The Taliban tried to impose Islamic Shariah law; they beheaded opponents, kidnapped and terrorized government officials, bombed girls schools, outlawed entertainment and operated a war against the state. The insurgency, which was at the beginning limited to North and South Waziristan only, extended throughout FATA in a few years. Moreover, several insurgent militias emerged between 2002 and On December 13, 2007 these militant groups formed the Tehrik-e-Taliban Pakistan (TTP; Student Movement of Pakistan) to coordinate their activities against the American and NATO forces in Afghanistan and against the Pakistan Army in FATA and Khyber-Pakhtun Khwa (KPK) 28. By 2007, the Swat district had also fallen under rebel control and within two years the Pakistani Taliban controlled towns situated mere sixty miles away from Islamabad. The fight between Pakistan armed forces and pro-taliban militants was going on when government signed a ceasefire in February 2009 in Swat under the term of imposition of Shariah in the region. 19
10 The war in the tribal areas has become very important in the perspective of both Pakistan s national security and US foreign and national security policy objectives. Most of the Afghan Taliban have moved away from al-qaeda and their aims linger in Afghanistan, but the Pakistani Taliban have moved in the opposite direction due to their affiliation with al-qaeda and its affiliated groups. Al-Qaeda has been involved in several attacks inside Pakistan and, with the nomination of Ayman al-zawahiri as the new leader, has pledged to continue fighting against the US. Both United States and Pakistan cannot afford safe havens of al-qaeda in the tribal areas and therefore, both the countries launched an armed operation in tribal areas of Pakistan. Pakistani Army has fought on ground; the US targets locations and fighters that Pakistan is either unwilling or unable to tackle militarily. These operations increase the innocent casualties in tribal areas especially by the drone attacks and the killing of common people has developed immense hatred against the US and Pakistan Army not only in affected areas but also in the entire country. Yet, the long-term challenge for Pakistan and the US remains the execution of a complex strategy through which the Pakistani Taliban can be significantly weakened. Hezbollah Hezbollah is a Shiite Islamist militia, declared as a terrorist organization by US. It has traditionally defined itself and justified its paramilitary actions as a legitimate resistance force to Israeli occupation of Lebanese territory in response to the relative weakness of Lebanese state security institutions. It is one of the most ambiguous organizations in the Middle East due to the manner in which it was formed, its historical transformation and its desire to execute a leading role in Lebanon s politics. It grew out of the Iranian Revolution ( ) and still maintains close links with Iran. Some analysts argue that it is an instrument of Iranian foreign policy, but others insist that Tehran does not and cannot control the organization 29. The United States government holds Hezbollah responsible for a number of kidnappings and high-profile terrorist attacks against US, European, and Israeli interests since the early 1980s. Hezbollah continues to define itself as a resistance movement and remains viscerally opposed to what it views as illegitimate US and Israeli intervention in Lebanese and regional affairs. According to the Director of National Intelligence Dennis Blair, it is the largest recipient of Iranian financial aid, training and weaponry, and Iran s senior leadership has cited it as a model for other militant groups 30. In August 2010, the Obama Administration reported that it is the most technically capable terrorist group in the world and stated that the group has thousands of supporters, several thousand members, and a few hundred terrorist operatives. 31 Americans recognize that it is not directly targeting them and their interests today and they are aware that things could change if tensions increase with Iran over that country s nuclear program. 20
11 Hamas Hamas was formed in late 1987 with the beginning of first Palestinian Intifada (uprising). It originated from the Palestinian branch of Muslim Brotherhood, and it is supported by a vigorous social and political configuration inside the Palestinian territories. According to its charter, Hamas's goal is to liberate Palestine and return it to its rightful place. It strives to liberate Palestine by resisting the Israeli occupation, and seeks to serve and spread Islam 32. The group s manifesto is to establish an Islamic Palestinian state in place of Israel and it refuses all settlements made between the PLO and Israel. It has recently publicized willingness to obtain a long-term cessation of war, if Israel agrees to recognize a Palestinian state based on the 1967 borders with Jerusalem as its capital. Hamas s strength is concentrated in the Gaza Strip and areas of the West Bank. It has a paramilitary-armed force known as the Izz-al-Din al-qassam Brigades, which was formed in the 1990s and has conducted many anti-israeli attacks in Israeli and the Palestinian territories 33. In 2004, Israel assassinated Hamas s spiritual leader, Sheik Ahmed Yassin. As soon as Hamas appointed a new leader, the Israelis killed him too 34. In early 2006 Hamas won legislative elections in the Palestinian territories that ended the secular Fatah party s hold on the Palestinian Authority (PA) and challenged Fatah s leadership of the Palestinian national movement. Although the League of Arab States has only recognized the PLO as a national liberation movement, and does not recognize Hamas, but this does not undermine its importance as a national liberation movement. While the international community has recognized the Palestinian right to self-determination and endorsed the idea of a Palestinian state, Hamas has not gained international recognition because of its militant tactics. While Hamas is a representative organization capable of negotiating with the international community, the international community is not ready to negotiate with Hamas. Instead, US Government has declared it as a Foreign Terrorist Organization. Jaish-E- Mohammad (Jem) The Jaish-e-Mohammed ( Army of Mohammed, JeM in short) is a relatively new terrorist organization, which came into existence on January 31, It is chiefly based in Peshawar and Muzaffarabad and operates in Jammu and Kashmir, Balakot, Rawalpindi, Karachi and Islamabad and it heavily depends on Fedayeen (suicide bombers) suicide attacks. JeM was involved in abduction and murder of Daniel Pearl in 2002, a Jewish reporter working as a South Asian bureau chief for Wall Street Journal. It attempted to assassinate President General Pervez Musharraf of Pakistan in December It has been alleged as a terrorist organization by USA, UK, Canada and Australia. Lashkar-E-Tayyiba (Let) Lashkar-e-Tayyiba (LeT) was formed in 1993 as an armed wing of Markaz-ud- Dawa-wal-Irshad (MDI), which was a religious organization of Sunni sect based in Pakistan under the leadership of Professor Hafiz Mohammad Saeed, an instructor at the University of Lahore. The organization was banned by Pakistan 21
12 in 2002 and black listed by United States in April Lashkar was designated as a foreign terrorist organization by the United States in 2001 and banned in UK 36. Many people believed that it was the brainchild of Pakistani Inter-service Intelligence (ISI), and funded by wealthy donors from the Persian Gulf states. It was involved in bombing of London subway on According to Daniel Benjamin, a counterterrorism official with the United States State Department, Lashkar e-tayyiba has made it clear that it is willing to undertake bold, masscasualty operations with a target set that would please al-qaida planners. Very few things worry me as much as the strength and ambition of LeT, a truly malign presence in South Asia. 37 Lashkar and al-qaida began their relation in mid 1990s and it developed further after 9/11 and the succeeding American crackdown on al-qaida in Afghanistan. US officials believe that Lashkar has a capability to fill the gaps left by Osama bin Laden s organization because it has a clear command-and control structure, with its top leader Hafiz Saeed operating openly from Pakistan. Indian Government claimed that Mumbai attacks on 2008 were done by Jammat- ud-dawa (JuD) that was also created by Hafiz Saeed after the banning of Lashkar. These allegations are yet to be proved. The Westerners who have passed through LeT s training camps include an Australian-born al Qaida operative named David Hicks, convicted shoe bomber Richard Reid, and the mastermind of a failed gas-cylinder bombing in London, Dhiren Barot 38. US administration believes that the dismantling of Lashkar-e-Tayyiba is as necessary as of al-qaida for global security and peace. Haqqani Network The Haqqani group is the most fatal fighter group active in Afghanistan having close ties with al Qaeda and other regional insurgent groups, such as the Quetta Shura Taliban, Pakistani Taliban, Islamic Movement of Uzbekistan, Lashkar-e- Tayyiba (LeT) and others. Jalaluddin Haqqani, a prominent freedom fighter of Afghanistan against Soviet invasion, established it. The Haqqanis maintain considerable sanctuary and support nodes inside Pakistan s Federally Administered Tribal Areas (FATA) and use these Pakistani bases as training areas for multiple terrorist groups, including Lashkar-e Tayyiba, the Islamic Movement of Uzbekistan, and Tehrik-e Taliban Pakistan 39. Haqqani fighters were responsible for the storming of the Serena Hotel in Kabul during a high-level visit by Norwegian officials in January 2008, a suicide attack against the Indian embassy in Kabul in July 2008 that killed two senior Indian officials and over 50 others, a suicide attack on a CIA base in Khost Province in December 2009 that marked the most deadly attack on the CIA in 25 years, an attack on the US Bagram Air Base in mid-may 2010, a multi-hour siege of the US embassy in Kabul in September 2011, and a complex and coordinated attack on Salerno, a US base camp in Khost Province on June According to the estimate of American government 15% of casualties of coalition forces in Afghanistan are due to the attacks of Haqqani network. Former US Ambassador to Afghanistan, Ryan Crocker, recently called the Haqqani fighters the worst of the worst, a group of killers, pure and simple. 41 Since 2004, United States has used drone 22
13 attacks against them inside Pakistan that have though not proved very effective; hence the US has put a reward of 5 million US dollars on capturing the ruling elite of the network such as Sirajuddin Haqqani. STATE SPONSORED TERRORISM AND ROGUE STATES United States, in 1979, formed a list of countries that were giving either direct or indirect support to terrorist groups, which was later compiled in the Export Administration Act under the Secretary of State's authority. The annual list is declared in the Code of Federal Regulations and in Country Reports on Terrorism. States sponsoring terrorism have also been named 'rogue states' or have been identified with other similar terms such as the 'axis of evil' by President Bush 42. US believe that state sponsored terrorism provides crucial support to non-state terrorist groups. Terrorist groups would have faced much more difficulty to attaining the funds, weapons, materials, and secure areas for their plans and operations without state sponsors. The list of State Sponsors was revisited in 2007 and has included five countries: Cuba (as of March 1, 1982), Iran (January 19, 1984), North Korea (January 20, 1988), Sudan (August 12, 1993), Syria (December 29, 1979). The three countries that were previously on the list that are Iraq, Libya and South Yemen have been removed. President Bush removed the name of North Korea from the list, in June 2008 in exchange for disclosure of its nuclear activities.the People's Democratic Republic of Yemen, or "South Yemen," was placed on the list in 1979, and removed when it was merged with the Yemen Arab Republic (North Yemen). Libya, which was put on the list in 1979, was removed in Libya took responsibility for the explosion of Pan Am flight 103 in The explosion over Lockerbie, Scotland killed 270 people. Libya agreed to compensate families of the flight's victims and to cooperate in the investigation and trial of the event. Libya also agreed to abandon its fledgling WMD program. Perhaps most important, Libya agreed to cooperate with the United States in new anti-terrorism efforts. On May 15, 2006, Secretary of State, Condoleezza Rice, announced that normal diplomatic relations would resume 43.The inclusion of other states on the list is based on the cooperation with US goals in its global war on terrorism. Cuba, for example, remains on the list despite the judgment of the CIA in 2003that, We have no credible evidence that the Cuban government has engaged in or directly supported international terrorist operations in the past decade, although our information is insufficient to say beyond a doubt that no collaboration has occurred." 44 Cuba's resistance to the American "war" is undoubtedly an important factor in its continued presence on the list. Syria also continuously holds a place in the respective list. According to the State Department s Country Reports on Terrorism 2008, Damascus continued to provide political and material support to Hezbollah and allowed Iran to use Syrian territory as a transit point for assistance to the Shiite militia group in Lebanon. Hamas, Palestine Islamic Jihad, the Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine, and the PLFP-GC, among others, have based their external leadership within Syria's borders 45. Syrian President Bashar al Assad s views on the support for Palestinian terrorist groups also strengthen US perception regarding its 23
14 terrorist s ties. US State Department believes that its revolutionary leadership has sponsored a number of terrorist organizations such as Hezbollah in Lebanon and Hamas in Palestine, and its intelligence agents have undertaken a number of terrorist assassinations abroad. In the reports on Terrorism 2008, Iran s involvement in the planning and financial support of terrorist attacks throughout the Middle East, Europe, and Central Asia had a direct impact on international efforts to promote peace, threatened economic stability in the Gulf, and undermined the growth of democracy 46. United States believes that if there is one country that can equip the terrorist organizations with WMD, it is Iran because of its leadership s clear support to the terrorist organizations and its publically admitted desire of Israel s destruction. CONCLUSION Terrorism has been very severe and devastating especially in the 21st Century, as it has frightened the world completely. It is because of three reasons: first, modern terrorism is by nature difficult, and may be impossible, to defend; for how can protection be provided against such attackers who are willing to sacrifice their own lives in order to kill others? This contributes to the idea that, although it may be possible to reduce the likelihood of terrorist attack, the threat can never be eradicated. Second, the potential scope and scale of terrorism has greatly increased as a result of modern technology and particularly the prospect of WMDs falling into the hands of terrorists. Since September 11, governments have been trying to plan a strategy if chemical or biological weapons play into the hands of terrorists, and the prospect of nuclear terrorism can no longer be dismissed as a fanciful fear. Third, some people believe that modern terrorists not only have easier access to WMDs but also a greater enthusiasm to use them. This, allegedly, is because they may be less constrained by moral or humanitarian principles than others. However, there are other analysts who argue that the threat of terrorism, whether new or global has been greatly overstated, because there are doubts about the military effectiveness of terrorism. Though, terrorists attacks have a devastating impact but this impact is different from systemic destruction wreaked by mass warfare among states. Although, Islamist terrorism has played a significant role as part of insurgent war in Iraq, Afghanistan and elsewhere, it does not, and cannot, pose a serious threat to Western societies. Fear about Islamist terrorism may also be exaggerated because it is based on questionable assumptions about a civilizational conflict between Islam and the West. There is very little evidence that Muslim populations generally are aggressive towards Western values like human rights and democracy. Critical theorists, indeed, have gone further and argued that the war on terror, and the overstated fear of terrorism on which it is based, serve both to legitimize US attempts to maintain its global supremacy (in particular, helping to justify the US presence in the oil-rich Middle East) and to promote a wider politics of fear. Therefore, the war on terror is primarily an ideological construct, which has been created by the US and other Western states 24
15 to generate internal unity and a sense of purpose in societies that are no longer afraid of the communist threat. According to this view, ruling elites, in democratic and authoritarian societies, strengthen their positions by creating myths about threatening others. In 21st Century this role may be filled by global terrorism especially when linking it with WMDs and the phantom of nuclear terrorism can bolster fear about terrorism. Lastly, global security appears as the new world order for the entire world. It raises the ideology that security provision is the duty of all. Despite the fact that these security threats largely jeopardized the poor and underdeveloped world, they were considered as the source of all malpractices. Thus those who are provoked most are less victimized such as the rich global north and those who were victimized most are also charged with the most provocation. A distance was created between developed and underdeveloped countries as well as between the Muslim and non-muslim world which generated the anti-american feelings all over. REFERENCES 1. Rapoport, D. C. (Sep 1984). Fear and Trembling: Terrorism in Three Religious traditions, American Political Science Review. 78(3), pp White, J. R. (2012). Terrorism and Homeland Security. USA: Wadsworth, Cengage Learning, p Goodin, R. (2006). What s Wrong with Terrorism. Cambridge: Polity Press, p Lutz, J. M. & Lutz, B. J. (2 nd ed 2008) Global Terrorism. London & New York: Routledge Taylor and Francis, p Long, D. E. (1990). The Anatomy of Terrorism. New York: Free Press, p Chalk, P. (1996). West European Terrorism and Counter Terrorism: The Evolving Dynamic. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan, p Badey, T. J. (1998). Defining International Terrorism: A Pragmatic Approach. Terrorism and Political Violence. 10(1), p Hoffman, B. (1995). Holy Terror: The Implications of Terrorism Motivated by a Religious Imperative. Studies in Conflict and Terrorism. 18(4), p Op. Cit., Rapoport, p Robertson, A. E. (2010). Terrorism and Global Security. New Delhi: Viva Books, p Heywood, A. (2011). Global Politics. New York: Palgrave Foundation, p Op. Cit., Robertson, A. E., p Ford, F. L. (1985). Political Murder: From Tyranncide to Terrorism. Cambridge M.A: Harvard University Press, pp Drake, C. J. M. (1998). The Role of Ideology in Terrorist Target Selection. Terrorism and Political Violence. 10(2), p Hoffman, B. (2006). Inside Terrorism. Revised and Expanded Edition. New York: Columbia University Press, p Beutel, A. J. Perils of Empire: Islamophobia, Religious Extremism and the New Imperialism, Amss 36th Annual Conference, The Department of Government and Politics University of Maryland, College Park, Maryland October , p. 2, Rapoport, (2003). The Four Waves of Modern Terrorism, pp , Terrorism.pdf, (Accessed on 20 December, 2012) 18. Op. Cit., Beutel, A. J., p CNN, 15 th Sep, 2001, 8:45 p.m. 20. Op. Cit., White, J. R., p
16 21. Owens, J. E.& Pelizzo, R. (2010). The War on Terror and the Growth of Executive Power? A comparative analysis. London and New York: Routledge Taylor & Francis Group, p Pfiffner, J. P. (2009). Torture as Public Policy, Boulder, CO: Paradigm Publishers, p Retrieved from: Gunaratna, R. (2002). Inside Al- Qaeda: Global Network of Terror. Lahore: Vanguard, p Doran, M. S. (2002). Somebody Eles s Civil War. Foreign Affairs. 81(1), pp Lutz, J. M. & Lutz, B. J. Op. cit, p Arpita, A. eds. (2012). Non-State Armed Groups in South Asia: A Preliminary Structured Focused Comparison, New Delhi: Pentagon Security International, p Hassan, A. (2009). Pakistan s Troubled Frontier. Washington DC: Jamestown Foundation, pp Perry, M. (2010). Talking to Terrorists: Why America Must Engage with Its Enemies, New York: Basic Books, p Drug trafficking also provides support to other terrorists, such as Hizballah. Director of National Intelligence, Dennis C. Blair, Annual Threat Assessment of the Intelligence Community for the Senate Select Committee on Intelligence, February 2, U.S. Department of State. Country Reports on Terrorism 2009, August 5, Hroub, K. (2000). Hamas Charter art, Hamas Political Thought and Practice app, p Salih, Abdelrahim. (2007). HAMAS: An organization working towards the goals of the Palestinian people militarily, socially and politically, P. 6, Retrieved on March 2007, from: =UTF-8&fr=yfp-t-701&pstart=1&b= Op. Cit., White, J. R., p Op. Cit., Arpita, A., p Benjamin, D. The Obama Administration s Counterterrorism Policy at One Year, CATO Institute, Retrieved on 13/1/2010, form: 37. Susan Schmidt and Siobhan Gorman, Lashkar-e-Taiba served as Gateway for Western Converts Turning to Jihad, Wall Street JournalRetrieved on 4/12/2008 form: See also Bobby Ghosh, Beyond Times Square: The Threat from Pakistan, Time Magazine (May 6, 2010) available at (explaining that At least one of the plotters of the 2005 London subway bombings was an LeT trainee, and British investigators believe the group has been connected to other plots in the U.K. ). 38. Dressler, J., Retrieved from: 39. Curtis,Lisa., Retrieved from: CurtisL pdf 40. McDonald, M. Taliban Rages over U.S. Decision on Terrorist Group, International Herald Tribune, Retrieved on 9/9/2012, from: Gareau, F. (2004). State Terrorism and the United States: From Counterinsurgency to the War on Terrorism. London: Zed Books, p Op. Cit., Robertson, A. E., p Zalman, A., Retrieved from: Ahmad,I., p. 17, Retrieved from: 45. Green, J.D. (1995). Terrorism and Politics in Iran, in Crenshaw. M (ed.) Terrorism in Context, University Park. PA: Pennsylvania State University Press, p Ibid, p
Banning Biological Weapons - Challenges and Efforts in South East Asia -
 COUNTER TERRORISM CBRNE Jakarta, Indonesia 10-13 December 2013 Banning Biological Weapons - Challenges and Efforts in South East Asia - Dr Teck-Mean Chua IFBA A-PBA Biosecurity Challenges Preparing for
COUNTER TERRORISM CBRNE Jakarta, Indonesia 10-13 December 2013 Banning Biological Weapons - Challenges and Efforts in South East Asia - Dr Teck-Mean Chua IFBA A-PBA Biosecurity Challenges Preparing for
August 2013 Security Threat to Americans Abroad
 Number of Attacks BACKGROUND REPORT August 2013 Security Threat to Americans Abroad On Aug. 2, 2013 the U.S. State Department issued an alert 1 to Americans traveling abroad, particularly in the Middle
Number of Attacks BACKGROUND REPORT August 2013 Security Threat to Americans Abroad On Aug. 2, 2013 the U.S. State Department issued an alert 1 to Americans traveling abroad, particularly in the Middle
Instructor's Manual for Chapter Six. Corporate and Non-Governmental Actors
 World Politics in the Twenty-First Century Instructor's Manual for Chapter Six Corporate and Non-Governmental Actors Active and Collaborative Teaching Techniques 1) Intergovernmental Organizations, NGOs,
World Politics in the Twenty-First Century Instructor's Manual for Chapter Six Corporate and Non-Governmental Actors Active and Collaborative Teaching Techniques 1) Intergovernmental Organizations, NGOs,
Unit 7 Station 2: Conflict, Human Rights Issues, and Peace Efforts. Name: Per:
 Name: Per: Station 2: Conflicts, Human Rights Issues, and Peace Efforts Part 1: Vocab Directions: Use the reading below to locate the following vocab words and their definitions. Write their definitions
Name: Per: Station 2: Conflicts, Human Rights Issues, and Peace Efforts Part 1: Vocab Directions: Use the reading below to locate the following vocab words and their definitions. Write their definitions
WCAML Forum. The Challenges of Terrorist Financing in 2014 and Beyond. May 7, Dennis M. Lormel President & CEO DML Associates, LLC
 The Challenges of Terrorist Financing in 2014 and Beyond May 7, 2014 Dennis M. Lormel President & CEO DML Associates, LLC Al-Qaeda s Most Dangerous Member: Nasir al-wuhayshi 2 Terrorist Threats 2014 Introduction
The Challenges of Terrorist Financing in 2014 and Beyond May 7, 2014 Dennis M. Lormel President & CEO DML Associates, LLC Al-Qaeda s Most Dangerous Member: Nasir al-wuhayshi 2 Terrorist Threats 2014 Introduction
Domestic policy WWI. Foreign Policy. Balance of Power
 Domestic policy WWI The decisions made by a government regarding issues that occur within the country. Healthcare, education, Social Security are examples of domestic policy issues. Foreign Policy Caused
Domestic policy WWI The decisions made by a government regarding issues that occur within the country. Healthcare, education, Social Security are examples of domestic policy issues. Foreign Policy Caused
Weekly Geopolitical Report
 August 17, 2009 Pakistan and the Death of Baitullah Mehsud Reports indicated that on Aug. 5, Baitullah Mehsud, the notorious leader of the Taliban in Pakistan, died from a U.S. missile strike. In this
August 17, 2009 Pakistan and the Death of Baitullah Mehsud Reports indicated that on Aug. 5, Baitullah Mehsud, the notorious leader of the Taliban in Pakistan, died from a U.S. missile strike. In this
TERRORISM Fervour is the weapon of choice of the impotent. FRANZ FANON, B l a c k S k i n, White Ma s k s (1952)
 TERRORISM Fervour is the weapon of choice of the impotent. FRANZ FANON, B l a c k S k i n, White Ma s k s (1952) Until the 1990s, terrorism was widely considered to be a security concern of the second
TERRORISM Fervour is the weapon of choice of the impotent. FRANZ FANON, B l a c k S k i n, White Ma s k s (1952) Until the 1990s, terrorism was widely considered to be a security concern of the second
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES DESIGNING INSTITUTIONS TO DEAL WITH TERRORISM IN THE UNITED STATES. Martin S. Feldstein
 NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES DESIGNING INSTITUTIONS TO DEAL WITH TERRORISM IN THE UNITED STATES Martin S. Feldstein Working Paper 13729 http://www.nber.org/papers/w13729 NATIONAL BUREAU OF ECONOMIC RESEARCH
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES DESIGNING INSTITUTIONS TO DEAL WITH TERRORISM IN THE UNITED STATES Martin S. Feldstein Working Paper 13729 http://www.nber.org/papers/w13729 NATIONAL BUREAU OF ECONOMIC RESEARCH
India-US Counterterrorism Cooperation: The Way Forward
 India-US Counterterrorism Cooperation: The Way Forward by Vinay Kaura BESA Center Perspectives Paper No. 555, August 8, 2017 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: Narendra Modi s visit to the Trump White House in June was
India-US Counterterrorism Cooperation: The Way Forward by Vinay Kaura BESA Center Perspectives Paper No. 555, August 8, 2017 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: Narendra Modi s visit to the Trump White House in June was
1/13/ What is Terrorism? The Globalization of Terrorism. What is Terrorism? Geography of Terrorism. Global Patterns of Terrorism
 What is Terrorism? The Globalization of Terrorism Global Issues 621 Chapter 23 Page 364 1/13/2009 Terrorism 2 Unfortunately, the term terrorism is one that has become a part of our everyday vocabulary
What is Terrorism? The Globalization of Terrorism Global Issues 621 Chapter 23 Page 364 1/13/2009 Terrorism 2 Unfortunately, the term terrorism is one that has become a part of our everyday vocabulary
10/15/2013. The Globalization of Terrorism. What is Terrorism? What is Terrorism?
 The Globalization of Terrorism Global Issues 621 Chapter 23 Page 364 What is Terrorism? 10/15/2013 Terrorism 2 What is Terrorism? Unfortunately, the term terrorism is one that has become a part of our
The Globalization of Terrorism Global Issues 621 Chapter 23 Page 364 What is Terrorism? 10/15/2013 Terrorism 2 What is Terrorism? Unfortunately, the term terrorism is one that has become a part of our
Period 9 Notes. Coach Hoshour
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Unit 9: 1980-present Chapters 40-42 Election 1988 George Bush Republican 426 47,946,000 Michael S. Dukakis Democratic 111 41,016,000 1988-1992 Domestic Issues The Only Remaining
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 Unit 9: 1980-present Chapters 40-42 Election 1988 George Bush Republican 426 47,946,000 Michael S. Dukakis Democratic 111 41,016,000 1988-1992 Domestic Issues The Only Remaining
US DRONE ATTACKS INSIDE PAKISTAN TERRITORY: UN CHARTER
 US DRONE ATTACKS INSIDE PAKISTAN TERRITORY: UN CHARTER Nadia Sarwar * The US President, George W. Bush, in his address to the US. Military Academy at West point on June 1, 2002, declared that America could
US DRONE ATTACKS INSIDE PAKISTAN TERRITORY: UN CHARTER Nadia Sarwar * The US President, George W. Bush, in his address to the US. Military Academy at West point on June 1, 2002, declared that America could
States & Types of States
 States & Types of States Political Geography Nation: a group of people with a common culture - Tightly knit group of people possessing shared cultural beliefs & unity: genous - Ancestry or historical events
States & Types of States Political Geography Nation: a group of people with a common culture - Tightly knit group of people possessing shared cultural beliefs & unity: genous - Ancestry or historical events
After the Cold War. Europe and North America Section 4. Main Idea
 Main Idea Content Statements: After the Cold War The Soviet Union collapsed in 1991 and the Cold War came to an end, bringing changes to Europe and leaving the United States as the world s only superpower.
Main Idea Content Statements: After the Cold War The Soviet Union collapsed in 1991 and the Cold War came to an end, bringing changes to Europe and leaving the United States as the world s only superpower.
The Key Groups: The Irish Republican Army (IRA) The Palestinian Liberation Organisation (PLO) Al-Qaeda
 In this section, you need to know the following key themes: What exactly is meant by terrorism? The motivation of terrorist groups? Similarities and differences between terrorist groups? How governments
In this section, you need to know the following key themes: What exactly is meant by terrorism? The motivation of terrorist groups? Similarities and differences between terrorist groups? How governments
TERRORISM CASES: THE TENSION BETWEEN CRIMINAL PROSECUTION AND INTELLIGENCE GATHERING
 TERRORISM CASES: THE TENSION BETWEEN CRIMINAL PROSECUTION AND INTELLIGENCE GATHERING Gregg N. Sofer Counterterrorism Section US Department of Justice May 11, 2006 Cartagena, Colombia 1 COUNTERTERRORISM
TERRORISM CASES: THE TENSION BETWEEN CRIMINAL PROSECUTION AND INTELLIGENCE GATHERING Gregg N. Sofer Counterterrorism Section US Department of Justice May 11, 2006 Cartagena, Colombia 1 COUNTERTERRORISM
The Terror OCTOBER 18, 2001
 The Terror OCTOBER 18, 2001 Philip C. Wilcox Jr. Font Size: A A A The author, a retired US Foreign Service officer, served as US Ambassador at Large for Counterterrorism between 1994 and 1997. The Bush
The Terror OCTOBER 18, 2001 Philip C. Wilcox Jr. Font Size: A A A The author, a retired US Foreign Service officer, served as US Ambassador at Large for Counterterrorism between 1994 and 1997. The Bush
SSUSH25 The student will describe changes in national politics since 1968.
 SSUSH25 The student will describe changes in national politics since 1968. a. Describe President Richard M. Nixon s opening of China, his resignation due to the Watergate scandal, changing attitudes toward
SSUSH25 The student will describe changes in national politics since 1968. a. Describe President Richard M. Nixon s opening of China, his resignation due to the Watergate scandal, changing attitudes toward
THE AFGHAN SUMMER OF WAR Paul Rogers
 International Security Monthly Briefing September 2006 THE AFGHAN SUMMER OF WAR Paul Rogers Lebanon During September, substantial numbers of foreign troops entered southern Lebanon to act as an enhanced
International Security Monthly Briefing September 2006 THE AFGHAN SUMMER OF WAR Paul Rogers Lebanon During September, substantial numbers of foreign troops entered southern Lebanon to act as an enhanced
LECTURE: TERRORISM DEFINING TERRORISM
 DEFINING TERRORISM I) What is terrorism? a. According to Joseph Nye, Harvard professor, it is a method of violence with roots that stretch far back in history. i. Terrorism reaches back to Greece and Rome
DEFINING TERRORISM I) What is terrorism? a. According to Joseph Nye, Harvard professor, it is a method of violence with roots that stretch far back in history. i. Terrorism reaches back to Greece and Rome
confronting terrorism in the pursuit of power
 strategic asia 2004 05 confronting terrorism in the pursuit of power Edited by Ashley J. Tellis and Michael Wills Regional Studies South Asia: A Selective War on Terrorism? Walter K. Andersen restrictions
strategic asia 2004 05 confronting terrorism in the pursuit of power Edited by Ashley J. Tellis and Michael Wills Regional Studies South Asia: A Selective War on Terrorism? Walter K. Andersen restrictions
ANNEX 5. Public. Chronology of relevant events
 ICC-02/17-7-Anx5 20-11-2017 1/6 NM PT ANNEX 5 Public Chronology of relevant events ICC-02/17-7-Anx5 20-11-2017 2/6 NM PT CHRONOLOGY OF RELEVANT EVENTS In accordance with Regulation 49(3), the Prosecution
ICC-02/17-7-Anx5 20-11-2017 1/6 NM PT ANNEX 5 Public Chronology of relevant events ICC-02/17-7-Anx5 20-11-2017 2/6 NM PT CHRONOLOGY OF RELEVANT EVENTS In accordance with Regulation 49(3), the Prosecution
White Paper of the Interagency Policy Group's Report on U.S. Policy toward Afghanistan and Pakistan INTRODUCTION
 White Paper of the Interagency Policy Group's Report on U.S. Policy toward Afghanistan and Pakistan INTRODUCTION The United States has a vital national security interest in addressing the current and potential
White Paper of the Interagency Policy Group's Report on U.S. Policy toward Afghanistan and Pakistan INTRODUCTION The United States has a vital national security interest in addressing the current and potential
The Embassy Closings
 The Embassy Closings August 20, 2013 by Bill O'Grady of Confluence Investment Management In the first week of August, the Obama administration announced the closing of 22 embassies and consulates across
The Embassy Closings August 20, 2013 by Bill O'Grady of Confluence Investment Management In the first week of August, the Obama administration announced the closing of 22 embassies and consulates across
Lecture 2: What is Terrorism? Is this man a Terrorist or a Freedom Fighter?
 Lecture 2: What is Terrorism? Is this man a Terrorist or a Freedom Fighter? International Terrorism: What is Terrorism? A. Dr. Jim Ray (2010) argues that terrorism has been around for a long time- terrorist
Lecture 2: What is Terrorism? Is this man a Terrorist or a Freedom Fighter? International Terrorism: What is Terrorism? A. Dr. Jim Ray (2010) argues that terrorism has been around for a long time- terrorist
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF STATE Bureau of Diplomatic Security. Top Private-Sector Security Concerns in 2008
 U.S. DEPARTMENT OF STATE Bureau of Diplomatic Security For Immediate Release Jan. 7, 2009 Contact: Brian Leventhal 571-345-2499 (office) 202-997-5747 (cell) LeventhalBH@state.gov Top Private-Sector Security
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF STATE Bureau of Diplomatic Security For Immediate Release Jan. 7, 2009 Contact: Brian Leventhal 571-345-2499 (office) 202-997-5747 (cell) LeventhalBH@state.gov Top Private-Sector Security
IR History Post John Lee Department of Political Science Florida State University
 IR History Post-1950 John Lee Department of Political Science Florida State University World War II Germany initially expands, no one stops them. Allied v/s Axis Powers. USSR/Germany reach initial compromise,
IR History Post-1950 John Lee Department of Political Science Florida State University World War II Germany initially expands, no one stops them. Allied v/s Axis Powers. USSR/Germany reach initial compromise,
The Emotive Context of Terrorism: Part II. Explaining Terrorism in the Context of Political Violence
 The Emotive Context of Terrorism: Part II Explaining Terrorism in the Context of Political Violence Spring 2010 Masaryk University Department of Int l Relations & European Studies Dave McCuan What Makes
The Emotive Context of Terrorism: Part II Explaining Terrorism in the Context of Political Violence Spring 2010 Masaryk University Department of Int l Relations & European Studies Dave McCuan What Makes
Who, Where,And When : USSR vs Afghanistan resistance group (80% mujahideen) Front: Mainland of Afghanistan December 1979-February 1989
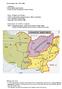 Soviet-Afghan War (1979-1989) Vocabulary: KHAD (Afghan secret police) LCOSF (Limited Contingent of Soviet Forces) Who, Where,And When : USSR vs Afghanistan resistance group (80% mujahideen) Front: Mainland
Soviet-Afghan War (1979-1989) Vocabulary: KHAD (Afghan secret police) LCOSF (Limited Contingent of Soviet Forces) Who, Where,And When : USSR vs Afghanistan resistance group (80% mujahideen) Front: Mainland
Research Report. Leiden Model United Nations 2015 ~ fresh ideas, new solutions ~
 Forum: Issue: Student Officer: Position: General Assembly First Committee: Disarmament and International Security Foreign combatants in internal militarised conflicts Ethan Warren Deputy Chair Introduction
Forum: Issue: Student Officer: Position: General Assembly First Committee: Disarmament and International Security Foreign combatants in internal militarised conflicts Ethan Warren Deputy Chair Introduction
WINTER. March 24. Template
 March 24 WINTER EQ- What are the different state shapes and types of boundaries? Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Review 3. Nation, State, Nation-States Gallery walk 4. Types of Boundaries Notes 4. Shapes of
March 24 WINTER EQ- What are the different state shapes and types of boundaries? Agenda: 1. Daily Sheet 2. Review 3. Nation, State, Nation-States Gallery walk 4. Types of Boundaries Notes 4. Shapes of
fragility and crisis
 strategic asia 2003 04 fragility and crisis Edited by Richard J. Ellings and Aaron L. Friedberg with Michael Wills Country Studies Pakistan: A State Under Stress John H. Gill restrictions on use: This
strategic asia 2003 04 fragility and crisis Edited by Richard J. Ellings and Aaron L. Friedberg with Michael Wills Country Studies Pakistan: A State Under Stress John H. Gill restrictions on use: This
2015 Biennial American Survey May, Questionnaire - The Chicago Council on Global Affairs 2015 Public Opinion Survey Questionnaire
 2015 Biennial American Survey May, 2015 - Questionnaire - The Chicago Council on Global Affairs 2015 Public Opinion Survey Questionnaire [DISPLAY] In this survey, we d like your opinions about some important
2015 Biennial American Survey May, 2015 - Questionnaire - The Chicago Council on Global Affairs 2015 Public Opinion Survey Questionnaire [DISPLAY] In this survey, we d like your opinions about some important
UNIT SIX: CHALLENGES OF THE MODERN ERA Part II
 UNIT SIX: CHALLENGES OF THE MODERN ERA Part II ARMS PROLIFERATION Spread of weapons of mass destruction (WMDs) (nuclear, chemical & biological weapons) throughout the world.* This is seen as dangerous
UNIT SIX: CHALLENGES OF THE MODERN ERA Part II ARMS PROLIFERATION Spread of weapons of mass destruction (WMDs) (nuclear, chemical & biological weapons) throughout the world.* This is seen as dangerous
Permanent Mission of United States of America to the United Nations
 Permanent Mission of United States of America to the United Nations Address by H.E. Mr. George W. Bush, President of the United States of America, at the 61 st session of the UN General Assembly, New York,
Permanent Mission of United States of America to the United Nations Address by H.E. Mr. George W. Bush, President of the United States of America, at the 61 st session of the UN General Assembly, New York,
AFGHANISTAN. The Trump Plan R4+S. By Bill Conrad, LTC USA (Ret) October 6, NSF Presentation
 AFGHANISTAN The Trump Plan R4+S By Bill Conrad, LTC USA (Ret) October 6, 2017 --NSF Presentation Battle Company 2 nd of the 503 rd Infantry Regiment 2 Battle Company 2 nd of the 503 rd Infantry Regiment
AFGHANISTAN The Trump Plan R4+S By Bill Conrad, LTC USA (Ret) October 6, 2017 --NSF Presentation Battle Company 2 nd of the 503 rd Infantry Regiment 2 Battle Company 2 nd of the 503 rd Infantry Regiment
GCSE HISTORY (8145) EXAMPLE RESPONSES. Marked Papers 1B/E - Conflict and tension in the Gulf and Afghanistan,
 GCSE HISTORY (8145) EXAMPLE RESPONSES Marked Papers 1B/E - Conflict and tension in the Gulf and Afghanistan, 1990-2009 Understand how to apply the mark scheme for our sample assessment papers. Version
GCSE HISTORY (8145) EXAMPLE RESPONSES Marked Papers 1B/E - Conflict and tension in the Gulf and Afghanistan, 1990-2009 Understand how to apply the mark scheme for our sample assessment papers. Version
Putin s Predicament: Russia and Afghanistan after 2014
 Putin s Predicament: Russia and Afghanistan after 2014 Mark N. Katz Asia Policy, Number 17, January 2014, pp. 13-17 (Article) Published by National Bureau of Asian Research DOI: https://doi.org/10.1353/asp.2014.0009
Putin s Predicament: Russia and Afghanistan after 2014 Mark N. Katz Asia Policy, Number 17, January 2014, pp. 13-17 (Article) Published by National Bureau of Asian Research DOI: https://doi.org/10.1353/asp.2014.0009
Security in a Dangerous World
 4 Vocabulary Builder Use the information below and the following resources to teach the high-use word from this section. Teaching Resources, Unit 5, p. 87; Teaching Resources, Skills Handbook, p. 3 High-Use
4 Vocabulary Builder Use the information below and the following resources to teach the high-use word from this section. Teaching Resources, Unit 5, p. 87; Teaching Resources, Skills Handbook, p. 3 High-Use
Drug trafficking and the case study in narco-terrorism. "If you quit drugs, you join the fight against terrorism." President George W.
 1 Drug trafficking and the case study in narco-terrorism "If you quit drugs, you join the fight against terrorism." President George W.Bush, 2001 Introduction Drug trafficking has a long history as a world-wide
1 Drug trafficking and the case study in narco-terrorism "If you quit drugs, you join the fight against terrorism." President George W.Bush, 2001 Introduction Drug trafficking has a long history as a world-wide
Terrorist Groups Are Aligning To Conduct Global Terrorism. By: John R. Fraser. A Dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements
 Terrorist Groups Are Aligning To Conduct Global Terrorism By: John R. Fraser A Dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Political Science
Terrorist Groups Are Aligning To Conduct Global Terrorism By: John R. Fraser A Dissertation submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in Political Science
CRS Report for Congress
 Order Code RS21584 Updated August 4, 2003 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Summary Pakistan: Chronology of Events K. Alan Kronstadt Analyst in Asian Affairs Foreign Affairs, Defense,
Order Code RS21584 Updated August 4, 2003 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Summary Pakistan: Chronology of Events K. Alan Kronstadt Analyst in Asian Affairs Foreign Affairs, Defense,
President Jimmy Carter
 President Jimmy Carter E. America Enters World War II (1945-Present) g. Analyze the origins of the Cold War, foreign policy developments, and major events of the administrations from Truman to present
President Jimmy Carter E. America Enters World War II (1945-Present) g. Analyze the origins of the Cold War, foreign policy developments, and major events of the administrations from Truman to present
CRS Report for Congress
 Order Code RL32417 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web The Department of State s Patterns of Global Terrorism Report: Trends, State Sponsors, and Related Issues June 1, 2004 Raphael Perl
Order Code RL32417 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web The Department of State s Patterns of Global Terrorism Report: Trends, State Sponsors, and Related Issues June 1, 2004 Raphael Perl
Lecture 2: What is Terrorism? Is this man a Terrorist or a Freedom Fighter?
 Lecture 2: What is Terrorism? Is this man a Terrorist or a Freedom Fighter? International Terrorism: What is Terrorism? A. Dr. Jim Ray (2010) argues that terrorism has been around for a long time- terrorist
Lecture 2: What is Terrorism? Is this man a Terrorist or a Freedom Fighter? International Terrorism: What is Terrorism? A. Dr. Jim Ray (2010) argues that terrorism has been around for a long time- terrorist
United States Foreign Policy
 United States Foreign Policy Contemporary US F.P. Timeline In the early 20th century, U.S. isolates and remains neutral ahead of 1 st and 2 nd World Wars, US has to intervene to help end them, after 2
United States Foreign Policy Contemporary US F.P. Timeline In the early 20th century, U.S. isolates and remains neutral ahead of 1 st and 2 nd World Wars, US has to intervene to help end them, after 2
The enemies list: the foreign terrorist organization list and its role in defining terrorism
 Calhoun: The NPS Institutional Archive DSpace Repository Theses and Dissertations 1. Thesis and Dissertation Collection, all items 2014-03 The enemies list: the foreign terrorist organization list and
Calhoun: The NPS Institutional Archive DSpace Repository Theses and Dissertations 1. Thesis and Dissertation Collection, all items 2014-03 The enemies list: the foreign terrorist organization list and
The following text is an edited transcript of Professor. Fisher s remarks at the November 13 meeting. Afghanistan: Negotiation in the Face of Terror
 1 The following text is an edited transcript of Professor Fisher s remarks at the November 13 meeting. Afghanistan: Negotiation in the Face of Terror Roger Fisher Whether negotiation will be helpful or
1 The following text is an edited transcript of Professor Fisher s remarks at the November 13 meeting. Afghanistan: Negotiation in the Face of Terror Roger Fisher Whether negotiation will be helpful or
Civil War and Political Violence. Paul Staniland University of Chicago
 Civil War and Political Violence Paul Staniland University of Chicago paul@uchicago.edu Chicago School on Politics and Violence Distinctive approach to studying the state, violence, and social control
Civil War and Political Violence Paul Staniland University of Chicago paul@uchicago.edu Chicago School on Politics and Violence Distinctive approach to studying the state, violence, and social control
Negotiating with Terrorists an Option Not to Be Forgone
 KOMMENTARE /COMMENTS Negotiating with Terrorists an Option Not to Be Forgone MICHAEL DAUDERSTÄDT I t is very tempting, in the wake of the many shocking terrorist attacks of recent times such as those in
KOMMENTARE /COMMENTS Negotiating with Terrorists an Option Not to Be Forgone MICHAEL DAUDERSTÄDT I t is very tempting, in the wake of the many shocking terrorist attacks of recent times such as those in
Threat Convergence Profile Series. The Haqqani Network
 Threat Convergence Profile Series The Haqqani Network October 2011 The Fund for Peace is an independent, nonpartisan, 501(c)(3) non-profit research and educational organization that works to prevent violent
Threat Convergence Profile Series The Haqqani Network October 2011 The Fund for Peace is an independent, nonpartisan, 501(c)(3) non-profit research and educational organization that works to prevent violent
The War in Iraq. The War on Terror
 The War in Iraq The War on Terror Daily Writing: How should the United States respond to the threat of terrorism at home or abroad? Should responses differ if the threat has not taken tangible shape but
The War in Iraq The War on Terror Daily Writing: How should the United States respond to the threat of terrorism at home or abroad? Should responses differ if the threat has not taken tangible shape but
IPB Congres War in Syria and The Future Of the Middle-East 30/09-03/ Haytham Manna
 IPB Congres War in Syria and The Future Of the Middle-East 30/09-03/10-2016 Haytham Manna 1 Half a century of authoritarian State Within nearly half a century, the authoritarian power in the Middle East,
IPB Congres War in Syria and The Future Of the Middle-East 30/09-03/10-2016 Haytham Manna 1 Half a century of authoritarian State Within nearly half a century, the authoritarian power in the Middle East,
An Unarguable Fact: American Security is Tied to Afghanistan and Pakistan
 Statement before the House Committee on Foreign Affairs Subcommittee on the Middle East and North Africa and Subcommittee on Asia and the Pacific on After the Withdrawal: The Way Forward in Afghanistan
Statement before the House Committee on Foreign Affairs Subcommittee on the Middle East and North Africa and Subcommittee on Asia and the Pacific on After the Withdrawal: The Way Forward in Afghanistan
Securing Indian Interests in Afghanistan Beyond 2014
 Securing Indian Interests in Afghanistan Beyond 2014 C. Christine Fair Asia Policy, Number 17, January 2014, pp. 27-32 (Article) Published by National Bureau of Asian Research DOI: https://doi.org/10.1353/asp.2014.0016
Securing Indian Interests in Afghanistan Beyond 2014 C. Christine Fair Asia Policy, Number 17, January 2014, pp. 27-32 (Article) Published by National Bureau of Asian Research DOI: https://doi.org/10.1353/asp.2014.0016
Ch 19-1 Postwar Havoc
 Ch 19-1 Postwar Havoc The Main Idea Although the end of World War I brought peace, it did not ease the minds of many Americans, who found much to fear in postwar years. Content Statement 12/Learning Goal
Ch 19-1 Postwar Havoc The Main Idea Although the end of World War I brought peace, it did not ease the minds of many Americans, who found much to fear in postwar years. Content Statement 12/Learning Goal
The top leaders of the Movement of the Taliban in Pakistan:
 Downloaded from: justpaste.it/1b04 Pakistani Taliban - Leaders // Ethnic Groups Map of northwestern Pakistan. By BILL ROGGIO May 17, 2010 After the failed car bomb attack in New York City's Times Square,
Downloaded from: justpaste.it/1b04 Pakistani Taliban - Leaders // Ethnic Groups Map of northwestern Pakistan. By BILL ROGGIO May 17, 2010 After the failed car bomb attack in New York City's Times Square,
Agenda: Protecting and Promoting Human Rights to Prevent and Counter Violent Extremism
 Agenda: Protecting and Promoting Human Rights to Prevent and Counter Violent Extremism Committee: Human Rights Council Student Officer: Soo Young Yun, President from Wikimedia Commons Introduction: With
Agenda: Protecting and Promoting Human Rights to Prevent and Counter Violent Extremism Committee: Human Rights Council Student Officer: Soo Young Yun, President from Wikimedia Commons Introduction: With
The Situation in Syria
 The Situation in Syria Topic Background Over 465,000 people have been killed in the civil war that is ongoing in Syria. Over one million others have been injured, and more than 12 million individuals -
The Situation in Syria Topic Background Over 465,000 people have been killed in the civil war that is ongoing in Syria. Over one million others have been injured, and more than 12 million individuals -
Foreign Policy Discussion Guide
 Foreign Policy Discussion Guide AGENDA: Social Time (30 minutes) Within each group identify who will be: Timekeeper to ensure that everyone has a chance to speak Scribe to take a few notes of what has
Foreign Policy Discussion Guide AGENDA: Social Time (30 minutes) Within each group identify who will be: Timekeeper to ensure that everyone has a chance to speak Scribe to take a few notes of what has
Post-Cold War Era- Today. 1990s-2000s
 Post-Cold War Era- Today 1990s-2000s Presidential Review (The guys you already learned about) #37: Nixon: 1968 and 1972- Watergate scandal leads to resignation to avoid impeachment in 1974 #38: Gerald
Post-Cold War Era- Today 1990s-2000s Presidential Review (The guys you already learned about) #37: Nixon: 1968 and 1972- Watergate scandal leads to resignation to avoid impeachment in 1974 #38: Gerald
A Historical Timeline of Afghanistan
 A Historical Timeline of Afghanistan Soviet soldiers in Afghanistan The land that is now Afghanistan has a long history of domination by foreign conquerors and strife among internally warring factions.
A Historical Timeline of Afghanistan Soviet soldiers in Afghanistan The land that is now Afghanistan has a long history of domination by foreign conquerors and strife among internally warring factions.
How to Prevent an Iranian Bomb
 How to Prevent an Iranian Bomb The Case for Deterrence By Michael Mandelbaum, FOREIGN AFFAIRS, Nov/Dec 2015 The Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), reached by Iran, six other countries, and the
How to Prevent an Iranian Bomb The Case for Deterrence By Michael Mandelbaum, FOREIGN AFFAIRS, Nov/Dec 2015 The Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), reached by Iran, six other countries, and the
Situation in Iraq and Syria and the IS offensive including the persecution of minorities
 EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT 2014-2019 TEXTS ADOPTED Provisional edition P8_TA-PROV(2014)0027 Situation in Iraq and Syria and the IS offensive including the persecution of minorities European Parliament resolution
EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT 2014-2019 TEXTS ADOPTED Provisional edition P8_TA-PROV(2014)0027 Situation in Iraq and Syria and the IS offensive including the persecution of minorities European Parliament resolution
This is the End? Last Two Weeks
 This is the End? Last Two Weeks Quick Questions (May 11-12) 1.) What was President Carter s successful diplomacy that brought temporary peace to the Middle East called? a.) Suez Canal Crisis b.) Potsdam
This is the End? Last Two Weeks Quick Questions (May 11-12) 1.) What was President Carter s successful diplomacy that brought temporary peace to the Middle East called? a.) Suez Canal Crisis b.) Potsdam
From King Stork to King Log: America s Negative Message Overseas
 From King Stork to King Log: America s Negative Message Overseas Anthony H. Cordesman October 26, 2015 There are so many different views of America overseas that any effort to generalize is dangerous,
From King Stork to King Log: America s Negative Message Overseas Anthony H. Cordesman October 26, 2015 There are so many different views of America overseas that any effort to generalize is dangerous,
The Israel-Lebanon War of 2006 and the Ceyhan-Haifa Pipeline
 - Iakovos Alhadeff The Israel-Lebanon War of 2006 and the Ceyhan-Haifa Pipeline By Iakovos Alhadeff Release Date : 2014-09-13 Genre : Politics & Current Affairs FIle Size : 0.65 MB is Politics & Current
- Iakovos Alhadeff The Israel-Lebanon War of 2006 and the Ceyhan-Haifa Pipeline By Iakovos Alhadeff Release Date : 2014-09-13 Genre : Politics & Current Affairs FIle Size : 0.65 MB is Politics & Current
United Nations General Assembly 1st
 ASMUN CONFERENCE 2018 "New problems create new opportunities: 7.6 billion people together towards a better future" United Nations General Assembly 1st "Paving the way to a world without a nuclear threat"!
ASMUN CONFERENCE 2018 "New problems create new opportunities: 7.6 billion people together towards a better future" United Nations General Assembly 1st "Paving the way to a world without a nuclear threat"!
2010 Arab Public Opinion Poll
 2010 Arab Public Opinion Poll Conducted by the University of Maryland in conjunction with Zogby International With special thanks to the Carnegie Corporation of New York Shibley Telhami, Principal Investigator
2010 Arab Public Opinion Poll Conducted by the University of Maryland in conjunction with Zogby International With special thanks to the Carnegie Corporation of New York Shibley Telhami, Principal Investigator
Measures to eliminate international terrorism
 Forum: General Assembly 6 Issue: Measures to eliminate international terrorism Student Officer: Sama Ayoub Position: Head Chair Introduction Terrorism acts are often carried as an attempt to cause disruption
Forum: General Assembly 6 Issue: Measures to eliminate international terrorism Student Officer: Sama Ayoub Position: Head Chair Introduction Terrorism acts are often carried as an attempt to cause disruption
one time. Any additional use of this file, whether for
 one time. Any additional use of this file, whether for Islamabad and The Taliban sales, alterations or copying is strictly prohibited without written permission and fair compensation to BENAZIR BHUTTO,
one time. Any additional use of this file, whether for Islamabad and The Taliban sales, alterations or copying is strictly prohibited without written permission and fair compensation to BENAZIR BHUTTO,
Yemen. Yemen faces a growing humanitarian crisis, with nearly half the population lacking sufficient food, according to UN agencies.
 JANUARY 2014 COUNTRY SUMMARY Yemen The fragile transition government that succeeded President Ali Abdullah Saleh in 2012 following mass protests failed to address multiple human rights challenges. Conflictrelated
JANUARY 2014 COUNTRY SUMMARY Yemen The fragile transition government that succeeded President Ali Abdullah Saleh in 2012 following mass protests failed to address multiple human rights challenges. Conflictrelated
CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE HMSY 1342 UNDERSTANDING AND COMBATING TERRORISM. Semester Hours Credit: 3 INSTRUCTOR: OFFICE HOURS:
 I. INTRODUCTION CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE HMSY 1342 UNDERSTANDING AND COMBATING TERRORISM Semester Hours Credit: 3 INSTRUCTOR: OFFICE HOURS: A. It is important for an individual to understand the history of
I. INTRODUCTION CENTRAL TEXAS COLLEGE HMSY 1342 UNDERSTANDING AND COMBATING TERRORISM Semester Hours Credit: 3 INSTRUCTOR: OFFICE HOURS: A. It is important for an individual to understand the history of
U.S.-INDIA COUNTERTERRORISM COOPERATION: DEEPENING THE PARTNERSHIP
 U.S.-INDIA COUNTERTERRORISM COOPERATION: DEEPENING THE PARTNERSHIP THE U.S. HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES COMMITTEE ON FOREIGN AFFAIRS SUBCOMMITTEE ON TERRORISM, NON-PROLIFERATION AND TRADE SEPTEMBER 14, 2011
U.S.-INDIA COUNTERTERRORISM COOPERATION: DEEPENING THE PARTNERSHIP THE U.S. HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES COMMITTEE ON FOREIGN AFFAIRS SUBCOMMITTEE ON TERRORISM, NON-PROLIFERATION AND TRADE SEPTEMBER 14, 2011
PIPA-Knowledge Networks Poll: Americans on Iraq & the UN Inspections II. Questionnaire
 PIPA-Knowledge Networks Poll: Americans on Iraq & the UN Inspections II Questionnaire Dates of Survey: Feb 12-18, 2003 Margin of Error: +/- 2.6% Sample Size: 3,163 respondents Half sample: +/- 3.7% [The
PIPA-Knowledge Networks Poll: Americans on Iraq & the UN Inspections II Questionnaire Dates of Survey: Feb 12-18, 2003 Margin of Error: +/- 2.6% Sample Size: 3,163 respondents Half sample: +/- 3.7% [The
The Geography of Terrorism
 The Geography of Terrorism More than 80 percent of last year's terrorism fatalities occurred in just five countries. KATHY GILSINANNOV 18 2014, 6:08 PM ET Institute for Economics and Peace Of the 17,958
The Geography of Terrorism More than 80 percent of last year's terrorism fatalities occurred in just five countries. KATHY GILSINANNOV 18 2014, 6:08 PM ET Institute for Economics and Peace Of the 17,958
Conflating Terrorism and Insurgency
 Page 1 of 6 MENU FOREIGN POLICY ESSAY Conflating Terrorism and Insurgency By John Mueller, Mark Stewart Sunday, February 28, 2016, 10:05 AM Editor's Note: What if most terrorism isn t really terrorism?
Page 1 of 6 MENU FOREIGN POLICY ESSAY Conflating Terrorism and Insurgency By John Mueller, Mark Stewart Sunday, February 28, 2016, 10:05 AM Editor's Note: What if most terrorism isn t really terrorism?
World Youth Summit 2018 A Letter from Your Chair and Co-Chairs. Dear Delegates,
 A Letter from Your Chair and Co-Chairs Dear Delegates, On behalf of all staff members, it s my pleasure to welcome you all to World Youth Summit 2018! We are really honored to serve as Chair and Co-Chairs
A Letter from Your Chair and Co-Chairs Dear Delegates, On behalf of all staff members, it s my pleasure to welcome you all to World Youth Summit 2018! We are really honored to serve as Chair and Co-Chairs
Fallujah and its Aftermath
 OXFORD RESEARCH GROUP International Security Monthly Briefing - November 2004 Fallujah and its Aftermath Professor Paul Rogers Towards the end of October there were numerous reports of a substantial build-up
OXFORD RESEARCH GROUP International Security Monthly Briefing - November 2004 Fallujah and its Aftermath Professor Paul Rogers Towards the end of October there were numerous reports of a substantial build-up
Introduction. Definition of Key Terms. Special Conference. Measures to suppress the financing of terrorism
 Forum: Issue: Student Officer: Position: Special Conference Measures to suppress the financing of terrorism Sinan van der Hoeven Co-Chair Introduction Throughout the history of humanity we have always
Forum: Issue: Student Officer: Position: Special Conference Measures to suppress the financing of terrorism Sinan van der Hoeven Co-Chair Introduction Throughout the history of humanity we have always
The United States and Russia in the Greater Middle East
 MARCH 2019 The United States and Russia in the Greater Middle East James Dobbins & Ivan Timofeev Though the Middle East has not been the trigger of the current U.S.-Russia crisis, it is an area of competition.
MARCH 2019 The United States and Russia in the Greater Middle East James Dobbins & Ivan Timofeev Though the Middle East has not been the trigger of the current U.S.-Russia crisis, it is an area of competition.
Adopted by the Security Council at its 4251st meeting, on 19 December 2000
 United Nations S/RES/1333 (2000) Security Council Distr.: General 19 December 2000 Resolution 1333 (2000) Adopted by the Security Council at its 4251st meeting, on 19 December 2000 The Security Council,
United Nations S/RES/1333 (2000) Security Council Distr.: General 19 December 2000 Resolution 1333 (2000) Adopted by the Security Council at its 4251st meeting, on 19 December 2000 The Security Council,
The most important geostrategic issue for the UK? Pakistan with friends like these.
 RS 57 The most important geostrategic issue for the UK? Pakistan with friends like these. By Professor Shaun Gregory PSRU, Department of Peace Studies, University of Bradford This paper is taken from an
RS 57 The most important geostrategic issue for the UK? Pakistan with friends like these. By Professor Shaun Gregory PSRU, Department of Peace Studies, University of Bradford This paper is taken from an
Confronting the Terror Finance Challenge in Today s Middle East
 AP PHOTO/MANU BRABO Confronting the Terror Finance Challenge in Today s Middle East By Hardin Lang, Peter Juul, and Trevor Sutton November 2015 WWW.AMERICANPROGRESS.ORG Introduction and summary In the
AP PHOTO/MANU BRABO Confronting the Terror Finance Challenge in Today s Middle East By Hardin Lang, Peter Juul, and Trevor Sutton November 2015 WWW.AMERICANPROGRESS.ORG Introduction and summary In the
LEBANON ON THE BRINK OF ELECTIONS: KEY PUBLIC OPINION FINDINGS
 NUMBER 14 JUNE 00 LEBANON ON THE BRINK OF ELECTIONS: KEY PUBLIC OPINION FINDINGS Shibley Telhami OVERVIEW As the Lebanese approach a crucial election on June th that could alter not only internal Lebanese
NUMBER 14 JUNE 00 LEBANON ON THE BRINK OF ELECTIONS: KEY PUBLIC OPINION FINDINGS Shibley Telhami OVERVIEW As the Lebanese approach a crucial election on June th that could alter not only internal Lebanese
Can Obama Restore the US Image in the Middle East?
 Can Obama Restore the US Image in the Middle East? December 22, 2008 Analysis by Steven Kull Reprinted from the Harvard International Review Sitting in a focus group, a young Jordanian bewailed America's
Can Obama Restore the US Image in the Middle East? December 22, 2008 Analysis by Steven Kull Reprinted from the Harvard International Review Sitting in a focus group, a young Jordanian bewailed America's
Theory and the Levels of Analysis
 Theory and the Levels of Analysis Chapter 4 Ø Not be frightened by the word theory Ø Definitions of theory: p A theory is a proposition, or set of propositions, that tries to analyze, explain or predict
Theory and the Levels of Analysis Chapter 4 Ø Not be frightened by the word theory Ø Definitions of theory: p A theory is a proposition, or set of propositions, that tries to analyze, explain or predict
Cover Story. - by Shraddha Bhandari. 24 JANUARY-FEBRUARY 2016 FSAI Journal
 - by Shraddha Bhandari 24 JANUARY-FEBRUARY 2016 FSAI Journal Following the spate of terror attacks in Paris, Beirut, and downing of the Russian Metrojet liner in November 2015, concerns have been raised
- by Shraddha Bhandari 24 JANUARY-FEBRUARY 2016 FSAI Journal Following the spate of terror attacks in Paris, Beirut, and downing of the Russian Metrojet liner in November 2015, concerns have been raised
Guided Reading Activity 32-1
 Guided Reading Activity 32-1 DIRECTIONS: Recalling the Facts Use the information in your textbook to answer the questions below. Use another sheet of paper if necessary. 1. What conservative view did many
Guided Reading Activity 32-1 DIRECTIONS: Recalling the Facts Use the information in your textbook to answer the questions below. Use another sheet of paper if necessary. 1. What conservative view did many
National Security Policy. National Security Policy. Begs four questions: safeguarding America s national interests from external and internal threats
 National Security Policy safeguarding America s national interests from external and internal threats 17.30j Public Policy 1 National Security Policy Pattern of government decisions & actions intended
National Security Policy safeguarding America s national interests from external and internal threats 17.30j Public Policy 1 National Security Policy Pattern of government decisions & actions intended
Cipher Brief on Afghanistan, Pakistan, LeT, India Lashkar-e-Taiba Wreaks Havoc in South
 Cipher Brief on Afghanistan, Pakistan, LeT, India Cipher Brief on Afghanistan, Pakistan, LeT, India Lashkar-e-Taiba Wreaks Havoc in South Asia, Threatens the U.S. Lashkar-e-Taiba Wreaks Havoc in South
Cipher Brief on Afghanistan, Pakistan, LeT, India Cipher Brief on Afghanistan, Pakistan, LeT, India Lashkar-e-Taiba Wreaks Havoc in South Asia, Threatens the U.S. Lashkar-e-Taiba Wreaks Havoc in South
Worldwide Caution: Annotated
 Worldwide Caution: Annotated Terrorism 9/14/2017 On September 14, 2017, the U.S. Department of State s Bureau of Consular Affairs released an updated version of its Worldwide Caution. This report is an
Worldwide Caution: Annotated Terrorism 9/14/2017 On September 14, 2017, the U.S. Department of State s Bureau of Consular Affairs released an updated version of its Worldwide Caution. This report is an
Chapter 6 Foreign Aid
 Chapter 6 Foreign Aid FOREIGN AID REPRESENTS JUST 1% OF THE FEDERAL BUDGET FOREIGN AID 1% Defense 19% Education 4% Health 10% Medicare 13% Income Security 16% Social Security 21% Net Interest 6% Veterans
Chapter 6 Foreign Aid FOREIGN AID REPRESENTS JUST 1% OF THE FEDERAL BUDGET FOREIGN AID 1% Defense 19% Education 4% Health 10% Medicare 13% Income Security 16% Social Security 21% Net Interest 6% Veterans
ASSESSMENT REPORT. Obama s Visit to Saudi Arabia
 ASSESSMENT REPORT Obama s Visit to Saudi Arabia Policy Analysis Unit - ACRPS April 2014 Obama s Visit to Saudi Arabia Series: Assessment Report Policy Analysis Unit ACRPS April 2014 Copyright 2014 Arab
ASSESSMENT REPORT Obama s Visit to Saudi Arabia Policy Analysis Unit - ACRPS April 2014 Obama s Visit to Saudi Arabia Series: Assessment Report Policy Analysis Unit ACRPS April 2014 Copyright 2014 Arab
WATERGATE. In 1972, Nixon ran for reelection.
 THE MODERN ERA 1968-1992 RICHARD NIXON In 1968 conservative Richard Nixon became President. One of Nixon s greatest accomplishments was his 1972 visit to communist China. Visit opened China to American
THE MODERN ERA 1968-1992 RICHARD NIXON In 1968 conservative Richard Nixon became President. One of Nixon s greatest accomplishments was his 1972 visit to communist China. Visit opened China to American
Continuing Conflict in SW Asia. EQ: What are the causes and effects of key conflicts in SW Asia that required U.S. involvement?
 Continuing Conflict in SW Asia EQ: What are the causes and effects of key conflicts in SW Asia that required U.S. involvement? Directions Today, we will be looking at the causes of important ongoing conflicts
Continuing Conflict in SW Asia EQ: What are the causes and effects of key conflicts in SW Asia that required U.S. involvement? Directions Today, we will be looking at the causes of important ongoing conflicts
ADDRESS TO A JOINT SESSION OF CONGRESS AND THE AMERICAN PEOPLE 2001
 ADDRESS TO A JOINT SESSION OF CONGRESS AND THE AMERICAN PEOPLE 2001 George W. Bush On the morning of September 11, 2001, the most destructive act of terrorism in modern history was inflicted on the United
ADDRESS TO A JOINT SESSION OF CONGRESS AND THE AMERICAN PEOPLE 2001 George W. Bush On the morning of September 11, 2001, the most destructive act of terrorism in modern history was inflicted on the United
2010 Annual Arab Public Opinion Survey
 EMBAGOED UNTIL 10:00 AM, THURSDAY AUGUST 5TH Anwar Sadat Chair for Peace and Development University of Maryland with Zogby International 2010 Annual Arab Public Opinion Survey Survey conducted June-July
EMBAGOED UNTIL 10:00 AM, THURSDAY AUGUST 5TH Anwar Sadat Chair for Peace and Development University of Maryland with Zogby International 2010 Annual Arab Public Opinion Survey Survey conducted June-July
