First Contact & Early Settlement Of Canada
|
|
|
- Jesse Williamson
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 First Contact & Early Settlement Of Canada Ms. Ross Name: Socials 9 Block:
2 FIRST CONTACT AND CULTURAL DIFFERENCES The First Nations of Canada first came into contact with Europeans who were fishing in the Grand Banks off the coast of Newfoundland. Their daily lives and activities brought them into contact. When two cultures share and borrow ideas, as well as influence each other, this is known as cultural exchange. The change that results in both cultures is called acculturation. The First Nations influenced the Europeans in the following ways: Taught Europeans survival skills such as hunting, trapping, snowshoeing, canoeing Provided Europeans with remedies for illness such as scurvy Provided Europeans with food and showed them where important resources were located The Europeans influenced the First Nations in the following ways: Supplied the First Nations with goods made out of iron, such as tools and cooking utensils Supplied the First Nations with guns and alcohol Attempted to civilize the First Nations and convert them to Catholicism When two cultures meet, there is often misunderstanding: some of this is due to the language barrier, but it can also result from a lack of knowledge about the beliefs and values of each culture. When people have lived in their culture all their life, they may believe that their culture is the best because it meets their needs and they are used to it: why would anyone do things differently? The belief that one culture is better than others is known as ethnocentrism. Europeans can definitely be described as ethnocentric during early contact. They believed their way of doing things was better than those who lived here before them. This would lead to conflict and domination. 2
3 Use Focus On: Points of View Cultural Differences p. 25 in Canada Revisited to learn the viewpoints of each culture on the provided topics. Social Organization French Viewpoint Aboriginal Viewpoint Land Ownership Settlement Governance Production and Ownership of Wealth Rule of Law Religion 3
4 JACQUES CARTIER CLAIMS CANADA Use pp in Crossroads 2 nd edition e-text to complete the following summary. In 1534, Jacques Cartier set sail to find the fabled. Instead, he sailed into the Gulf of St. Lawrence and the St. Lawrence River. He claimed the area in the name of France by erecting a cross on the Gaspe Peninsula. Before leaving, he kidnapped 2 of Iroquois Chief Donnacona s sons and and took them back to France. In 1535, Cartier returned with the 2 Iroquois men who saw the possibility of trade alliances forming with the French. Instead of staying at the Iroquois village of Stadacona, Cartier preceded to sail upriver to. When he arrived, he realized the St. Lawrence River was not the Northwest Passage to Asia. 4
5 Cartier and his crew had to spend the winter in amongst the Iroquois. The kidnapping of 2 of their people plus the refusal to follow their advice led to a strained relationship between the two groups. The French were not prepared for winter and many began dying of. Even though the Iroquois had been mistreated by the French, they shared their knowledge of how to make a vitamin C rich tea that saved many lives. How did Cartier show his thanks? When the weather improved, he sailed back to France, taking with him, his sons and 7 other Iroquois who could tell the King of France about all the riches in the New World. Cartier believed there was gold and diamonds to be found. The 10 kidnapped Iroquois would never return to their homeland. The Iroquois became suspicious of the French and their opinion of them didn t improve when they saw Cartier defy orders in 1542 and leave his countrymen to spend the winter in this new world. The Iroquois refused to trade and threatened on the French. Once Cartier returned home he discovered his riches were worthless. This was not the end of French voyages to the New Land. Continued expeditions would focus on acquiring other riches such as fish and fur. It would not be until the early 17 th century that France would make a second attempt at establishing permanent settlements. 5
6 CREATING A ROYAL COLONY Initially, France was not interested in colonizing Canada because the country was able to make profit without having to live here permanently. Plus, France was too busy fighting wars in Europe to invest money in colonization (settling and controlling other lands). However, in the 1600s the King of France and the Roman Catholic Church both became interested in creating permanent settlements in the New World, but for very different reasons. The Royal Colony began! First Attempt at Colonization Use pp in Crossroads 2 nd Edition e-text to answer the following questions. 1. Who was given the responsibility of establishing the first permanent colony? 2. What does it mean to have a monopoly? How would this benefit the colony? 3. The first location of settlement was Ste. Croix Island but this was soon abandoned for another location,, in What was Samuel de Champlain s main job? 5. Why was this colony abandoned in 1607? 6. Where should the French have established their first colony? Why? (*critical thinking) 6
7 LIFE IN ACADIA Acadia was one of two permanent settlements in the Royal Colony. This settlement spanned the areas of present day New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and PEI. Acadia was an attractive place for settlement because of its mild climate, fertile land, wealth of timber, access to harbours, and close location to the Grand Banks for fishing. By 1640, a small, successful farming settlement had developed in the region. Use pp in Canada Revisited to learn more about life in Acadia. 1. Britain and France both wanted to occupy and control Acadia. Use the map on p. 34 to help you, explain this statement: If you controlled Acadia, you controlled North America and the fur trade. 2. What was the primary occupation of settlers in Acadia? 3. Identify the invention that allowed Acadians to grow food on the marshy plains and explain how it worked. 4. Describe a typical Acadian family and their daily activities. 5. Who did the Acadians trade with? What items were traded between the two groups? 6. What Aboriginal group originally inhabited the land? How do you think the Acadian settlement affected their ways of life? (* critical thinking question use your brain, not the book!) 7
8 SECOND ATTEMPT AT COLONIZATION In 1608, Samuel de Champlain established a permanent settlement in the St. Lawrence River Valley. He believed this was a better location than Port Royal to maintain a monopoly because it was in the heart of fur trade territory. A habitation in this area would provide the opportunity to establish strong trading alliances with the Aboriginals and provide better access to furs. This habitation was located along the St. Lawrence River in present day Quebec City. He picked this site because the land is located on top of towering cliffs the geography of the region could provide natural fortifications from any invaders. The habitation would be both a living and working space. The buildings and surrounding lands would create the colony of New France. Trading companies were supposed to bring settlers to the region; however, they were more interested in making profits from the fur trade than building a colony. One company that did fulfill its mandate was the Company of 100 Associates, led by Cardinal Richelieu. In 1627, they were given a monopoly on the fur trade in New France and in return promised to bring 4,000 settlers to New France. Life for Champlain was not easy. He was constantly worried about attacks by the British from the south and his separate trade alliance with the Huron (Wendat) made the Algonkians and Montagnais (Innu) suspicious of his motives. When Champlain s colony was attacked by the British in 1629, the Algonkians actually sided with the British and refused to help the French! Champlain established new trading posts at locations along the St. Lawrence for the Company of 100 Associates in order to reclaim control of New France: these included Montreal and Trois Rivieres. While the company was successful in bringing settlers to the region, it was a business failure. The company lost its monopoly and eventually went bankrupt. Samuel de Champlain died on Christmas Day, His efforts in the royal colony earned him the titles Father of New France and Father of Canada. 8
9 GOVERNING THE ROYAL COLONY Originally, the colony of New France was governed by the trading companies. But they were more interested in making profit from the fur trade, not establishing settlements and all the elements that come with it (government, churches, schools, roads, etc.) Louis XIV (aka the Sun King ) appointed Jean-Baptiste Colbert to run the colony, establish a form of government in the region, and make the colony profitable for France. The Royal Government was both inexpensive and efficient and would govern the region for over 100 years. Interestingly, Colbert was the Chief Official of New France but never visited the colony! The first problem they had to solve was populating the colony: the few settlers that lived in New France were constantly being attacked by the Iroquois. There needed to be a stronger presence in the region. While Champlain wanted the coureur de bois ( runner of the woods ) fur traders to marry First Nations women and create one nation as a way to maintain control, the French government decided that sending French immigrants to the region was a better idea. Immigration grants were given to families with over 10 children 4,000 settlers were brought to New France at the expense of the government between o One third were retired soldiers o 1000 were single women, known as filles du roi, sent to marry single men in the royal colony and begin families The government of New France was called the Sovereign Council. Government officials were appointed by the King to carry out his orders for governing the colony. In reality, with the large distance and harsh winters, it was difficult for the mother country and colony to communicate; so, the government officials in New France actually had more power to govern than was originally intended. Appointed Governor General Intendant Bishop Sovereign Council For the settlers of New France, this government was just like the one they had left back home: the people did not have any power over the Sovereign Council, could not pick who would hold each position, and could not change any decision made by the Sovereign Council. Thus, the people had little influence over government and government was not always responsible or accountable to the citizens of the colony. 9
10 PORTRAIT OF AN IMMIGRANT TO NEW FRANCE Who came? Entrepreneurs, merchants, missionaries, government officials, orphans, single women, soldiers, criminals, farmers, lower class who couldn t afford land in France Why did they travel to New France? Push Factors In France there was unemployment, oppressive taxes, famine, absolute monarchy. There is a connection between hard times in France and peaks of immigration. Pull Factors New land, new opportunity, adventure, independence, break the social class system How did they get to New France? Boat fare (the cost of a craftman s annual income) Sign a contract to be an indentured labourer and you would work off your fee Recruited by the government What did they think when they arrived? France was successful at sending immigrants to New France, but were unable to keep them there: 1/3 to 2/3 of colonists didn t want to stay after they realized how much political, social, and economic building had to be done to make New France anything remotely similar to the mother country. Immigrants were greeted with rough living conditions, threats from First Nations, few marriageable women. Those who benefitted from the old class system in France discovered the rules didn t necessarily apply here in New France. Brainstorm the challenges an immigrant would have had when he/she moved to New France. 10
11 LIFE IN NEW FRANCE Use pp and in Crossroads 2 nd Edition e-text to learn more about life in New France. 1. owned the land in New France and farmed the land. 2. Describe what type of pattern a seigneurial system makes on the landscape. 3. Describe the responsibilities of both the seigneur and the habitant. 4. Habitant life was centered around the, the, and the. 5. Why would a habitant prefer to work land in the first row than the second row? (critical thinking question!) 6. What types of food did they eat? 7. Who were the first women to populate New France? Why did they come? 8. What types of roles did women have in New France? 11
12 FINDING SALVATION: THE JESUIT MISSIONARIES AND URSULINE NUNS Jesuit Missionaries The Black Robes The Company of 100 Associates, led by Cardinal Richelieu, was given a monopoly over the fur trade in the royal colony in exchange for bringing settlers to the region. Jesuit missionaries (Roman Catholic priests) were partners with Richelieu. These men, nicknamed the Black Robes, were brought to New France to spread Christianity. The French were very ethnocentric and believed the First Nations were uncivilized savages. It was thought that if they followed Catholicism, this would bring them salvation and civilization. While other missionaries were unsuccessful in converting Aboriginals to their religion, the Jesuits were different. They actually went to live amongst the First Nations, learned the language, and adapted to the culture: this allowed them to learn more about the First Nations, develop trust, and successfully communicate their message. One of the biggest missionaries was Saint Marie Among the Hurons in Huronia. The Jesuit missionaries had both success and failure. They were able to convert some First Nations to Catholicism and limited the sale of alcohol in the fur trade. Many First Nations were suspicious of the Black Robes and did not see why they should convert to another religion when they already had their own. In addition, during this time period Aboriginal communities were infected with devastating epidemics like smallpox and measles. These European diseases were unknowingly brought by the missionaries and rapidly spread amongst the Aboriginal population: wherever the Black Robes went soon came disease and death. For example, within 6 years of coming to Huronia, almost half of the population died. Aboriginal communities started to believe that the Jesuits were practicing witchcraft. The Jesuits tried to convince Aboriginals to convert to Catholicism while on their death bed: the sick were told if they didn t convert, they would not go to heaven. So one has to wonder how many of the conversions were true conversions to the faith or last ditched attempts at survival. In some instances, there was division within Aboriginal communities amongst those who converted to Catholicism and those who did not. The French gave perks to those who converted, such as guns and privileges in the fur trade. The Huron (Wendat) was one such nation negatively impacted by the actions of the French and Jesuits: they became weak and vulnerable and could not withstand attacks by the Iroquois (Haudenosaunee) The Ursuline Nuns Men were not the only ones who came to New France to spread the Roman Catholic faith. The Ursuline Nuns established religious settlements where they spread the word of God, ran schools for girls, created hospitals to help the sick and dying, and helped new female immigrants find a husband. Here are three important Ursuline Nuns and their contributions to the colony: Marie de l Incarnation Marguerite Bourgeoys Marguerite d Youville Educated girls and her letters Set up a school and cared Dedicated her life to helping home to France were for the poor and sick. She the poor and homeless. She important descriptors was canonized in 1982 & was canonized in 1990 and of life in New France is Canada s 1 st female saint is the 1 st person born in Canada to become a saint 12
13 THE ROLE OF THE ROMAN CATHOLIC CHURCH IN NEW FRANCE Use pp in Canada Revisited to learn more the role of the Catholic Church in New France. 1. In what way did the Church hold influential power in the colony? 2. Conversely, how was the power of the church limited? 3. Describe the services performed by priests on seigneuries. 4. Compare and contrast the education of boys and girls in New France under the Catholic Church. 5. Why was the Catholic Church, especially the Ursuline Nuns, given the responsibility of providing health care? (*critical thinking question) 13
P & S- French Regime (ALL)
 Name: Group: 404- Date: P & S- French Regime (ALL) Chapter 1 Population & Settlement Section 2: The French Regime (1608-1760) Jacques Cartier First French explorer to discover what is now Canada 1534,
Name: Group: 404- Date: P & S- French Regime (ALL) Chapter 1 Population & Settlement Section 2: The French Regime (1608-1760) Jacques Cartier First French explorer to discover what is now Canada 1534,
Chapter 2 The French Regime. Introduction. Chapter 2 The French Regime ( )
 Introduction Chapter 2 The French Regime (1608 1760) Exploration and Colonization Objectives in exploration: 1. To find a route to Asia The route for European merchants to Asia through Constantinople was
Introduction Chapter 2 The French Regime (1608 1760) Exploration and Colonization Objectives in exploration: 1. To find a route to Asia The route for European merchants to Asia through Constantinople was
Unit 2 Part 3, 4 & 5 New France
 Royal Government is established Unit 2 Part 3, 4 & 5 New France 1663-1760 A new government is formed in New France in 1663. King Louis XIV (known as the Sun King ) wanted New France to develop more in
Royal Government is established Unit 2 Part 3, 4 & 5 New France 1663-1760 A new government is formed in New France in 1663. King Louis XIV (known as the Sun King ) wanted New France to develop more in
Grade 9 History of Québec and Canada Program Knowledge to be acquired
 Grade 9 History of Québec and Canada Program Knowledge to be acquired UNIT 1: The experience of the Native peoples and the colonization attempts (30000BCE 1608) First occupants of the territory a. Migrations
Grade 9 History of Québec and Canada Program Knowledge to be acquired UNIT 1: The experience of the Native peoples and the colonization attempts (30000BCE 1608) First occupants of the territory a. Migrations
2.2 New France
 Name: Date: 2.2 New France 1627-1663 I. Population in 1627 Population - 1627 Situation in New France: 100 colonists lived in New France Mostly 11 women 96 men II. Company of 100 Associates A) Company Creation:
Name: Date: 2.2 New France 1627-1663 I. Population in 1627 Population - 1627 Situation in New France: 100 colonists lived in New France Mostly 11 women 96 men II. Company of 100 Associates A) Company Creation:
The Struggle for Control of North America. Vs.
 The Struggle for Control of North America Vs. Ms. Ross Socials 9 Name Block THE STRUGGLE FOR CONTROL OF NORTH AMERICA Canada Revisited - Chapter 4 Crossroads 2 nd Edition - Chapter 2 Student Learning Outcomes
The Struggle for Control of North America Vs. Ms. Ross Socials 9 Name Block THE STRUGGLE FOR CONTROL OF NORTH AMERICA Canada Revisited - Chapter 4 Crossroads 2 nd Edition - Chapter 2 Student Learning Outcomes
Grade 7 Social Studies Final Exam Study Guide
 Grade 7 Social Studies Final Exam Study Guide Canada Before and After Confederation Vocabulary and Terms: 1. Assimilation - a process by which culture or individual is absorbed into a more dominant culture
Grade 7 Social Studies Final Exam Study Guide Canada Before and After Confederation Vocabulary and Terms: 1. Assimilation - a process by which culture or individual is absorbed into a more dominant culture
Grade 7 Social Studies Modified Study Guide
 Grade 7 Social Studies Modified Study Guide Chapter 1: Aboriginal Societies Culture: is a way of life or a way of being that is shared by a group of people. Ethnocentrism: Believing one s own ethnic group
Grade 7 Social Studies Modified Study Guide Chapter 1: Aboriginal Societies Culture: is a way of life or a way of being that is shared by a group of people. Ethnocentrism: Believing one s own ethnic group
Chapter 1 Population & Settlement
 Chapter 1 Population & Settlement Chapter 1 Population & Settlement Section 3: British Rule / British Regime (1760-1867) The 7 Year War & the Conquest In 1760, the British took control of what was New
Chapter 1 Population & Settlement Chapter 1 Population & Settlement Section 3: British Rule / British Regime (1760-1867) The 7 Year War & the Conquest In 1760, the British took control of what was New
A BRIEF HISTORY OF KAHNAWÀ:KE. 1-Overview - written historical records
 A BRIEF HISTORY OF KAHNAWÀ:KE 1-Overview - written historical records The written records of early explorers, such as Cartier, Noel, and Champlain, place Iroquoian peoples throughout the St. Lawrence Basin.
A BRIEF HISTORY OF KAHNAWÀ:KE 1-Overview - written historical records The written records of early explorers, such as Cartier, Noel, and Champlain, place Iroquoian peoples throughout the St. Lawrence Basin.
Grade 7 Social Studies Final Exam Study Guide
 Grade 7 Social Studies Final Exam Study Guide Canada Before and After Confederation Vocabulary and Terms: 1. - a process by which culture or individual is absorbed into a more dominant culture because
Grade 7 Social Studies Final Exam Study Guide Canada Before and After Confederation Vocabulary and Terms: 1. - a process by which culture or individual is absorbed into a more dominant culture because
Complementary activities (Chapter 2)
 COMPLEMENTARY ACTIVITIES Complementary activities (Chapter 2) PART 1 The colonization of New France in the early 17th century Textbook, pp. 62 67 1 Consult Document 7, on page 62 in your textbook. What
COMPLEMENTARY ACTIVITIES Complementary activities (Chapter 2) PART 1 The colonization of New France in the early 17th century Textbook, pp. 62 67 1 Consult Document 7, on page 62 in your textbook. What
Australia and Canada Unit Test-DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST
 Australia and Canada Unit Test-DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST 1. Which U-shaped rocky land covering is mineral rich and covers eastern and central Canada? A. Canadian Shield B. Rocky Mountains C. Lake Huron
Australia and Canada Unit Test-DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST 1. Which U-shaped rocky land covering is mineral rich and covers eastern and central Canada? A. Canadian Shield B. Rocky Mountains C. Lake Huron
Name: 8 th Grade U.S. History. STAAR Review. Colonization
 Name: _ 8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Colonization FORT BURROWS 2018 Name: _ VOCABULARY Agriculture - Farming, raising crops and livestock. Assembly a group of people who make and change laws for
Name: _ 8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Colonization FORT BURROWS 2018 Name: _ VOCABULARY Agriculture - Farming, raising crops and livestock. Assembly a group of people who make and change laws for
Niagara Falls forms what type of boundary between Canada and the United States (Little map on the right)?
 Chapter 6 Canada pg. 154 183 6 1 Mountains, Prairies, and Coastlines pg. 157 161 Connecting to Your World What is Canada s rank in largest countries of the world? **Where does Canada rank in size among
Chapter 6 Canada pg. 154 183 6 1 Mountains, Prairies, and Coastlines pg. 157 161 Connecting to Your World What is Canada s rank in largest countries of the world? **Where does Canada rank in size among
Chapter : The Formation of the Canadian Federal System Section 9: Migrations
 Chapter 1 1840-1896: The Formation of the Canadian Federal System Section 9: Migrations Pages that correspond to this presentation Rural Exodus in the Late 19 th Century: Page 68 Emigration to the United
Chapter 1 1840-1896: The Formation of the Canadian Federal System Section 9: Migrations Pages that correspond to this presentation Rural Exodus in the Late 19 th Century: Page 68 Emigration to the United
How did the French and English colonize Canada?
 SS6H4 and SS6H5 Essential Questions How did the French and English colonize Canada? How did life change for indigenous people in Canada when colonizers settled? What influence did the French and English
SS6H4 and SS6H5 Essential Questions How did the French and English colonize Canada? How did life change for indigenous people in Canada when colonizers settled? What influence did the French and English
I. Western Europe s Monarchs A. France and the Age of Absolutism 1. Henry IV (The first of the Bourbon line) a) Huguenot (Protestant) converts to
 I. Western Europe s Monarchs A. France and the Age of Absolutism 1. Henry IV (The first of the Bourbon line) a) Huguenot (Protestant) converts to Catholicism to unite country (1) Paris is well worth a
I. Western Europe s Monarchs A. France and the Age of Absolutism 1. Henry IV (The first of the Bourbon line) a) Huguenot (Protestant) converts to Catholicism to unite country (1) Paris is well worth a
Each of the following seven images tells us something about New France. Try to tell the story of New France by looking at these pictures.
 Discuss and Take Notes: Each of the following seven images tells us something about New France. Try to tell the story of New France by looking at these pictures. Samuel de Champlain Coureurs de Bois OR
Discuss and Take Notes: Each of the following seven images tells us something about New France. Try to tell the story of New France by looking at these pictures. Samuel de Champlain Coureurs de Bois OR
Social Studies 7 Final Exam Study Guide
 Social Studies 7 Final Exam Study Guide Name: 7- Review key words and vocabulary lists. More Focus will be on chapter 5 to 9 Some more things to know: Chapter 1 How were the First Nations, Mi kmaq, Haudenosaunee
Social Studies 7 Final Exam Study Guide Name: 7- Review key words and vocabulary lists. More Focus will be on chapter 5 to 9 Some more things to know: Chapter 1 How were the First Nations, Mi kmaq, Haudenosaunee
Final Exam Review Every topic in every chapter in every unit
 Grade 10 History and Citizenship Education Final Exam Review Every topic in every chapter in every unit Unit 1 The First Occupants (1500 1608) Topics: Population: Asian Migration Theory Iroquois Algonquian
Grade 10 History and Citizenship Education Final Exam Review Every topic in every chapter in every unit Unit 1 The First Occupants (1500 1608) Topics: Population: Asian Migration Theory Iroquois Algonquian
Put the following vocabulary definitions in your own words /15
 Social Studies 7 Ch 5 Study Guide KEY /58 NAME Put the following vocabulary definitions in your own words /15 Anglophones- Any person that English is their first language and they live in an area that
Social Studies 7 Ch 5 Study Guide KEY /58 NAME Put the following vocabulary definitions in your own words /15 Anglophones- Any person that English is their first language and they live in an area that
Language & Religion Impacted by England. The Impact of English colonization on the language and religion of Australia
 Language & Religion Impacted by England The Impact of English colonization on the language and religion of Australia SS6G14 The student will describe the cultural characteristics of people who live in
Language & Religion Impacted by England The Impact of English colonization on the language and religion of Australia SS6G14 The student will describe the cultural characteristics of people who live in
A person who moves to a new country
 Chapter 6- Becoming Canada Name: Big Idea: How did the War of 1812 and its political consequences affect the developing Canadian identity? VOCABULARY Chateau Clique Deadlock Discrimination Family Compact
Chapter 6- Becoming Canada Name: Big Idea: How did the War of 1812 and its political consequences affect the developing Canadian identity? VOCABULARY Chateau Clique Deadlock Discrimination Family Compact
Immigration. How Do We Define Citizenship
 Immigration How Do We Define Citizenship Citizenship and the Aboriginal Peoples of Canada. Aboriginal Peoples were the first inhabitants of the land that is now Canada. Aboriginal peoples of Canada include:
Immigration How Do We Define Citizenship Citizenship and the Aboriginal Peoples of Canada. Aboriginal Peoples were the first inhabitants of the land that is now Canada. Aboriginal peoples of Canada include:
Chapter 6, Lesson 1 Physical Geography of Canada
 Chapter 6, Lesson 1 Physical Geography of Canada Canada 10 provinces (like states) & 3 territories 5 Regions o Maritime Provinces o Quebec & Ontario o Prairie Provinces o British Columbia o Northern Territories
Chapter 6, Lesson 1 Physical Geography of Canada Canada 10 provinces (like states) & 3 territories 5 Regions o Maritime Provinces o Quebec & Ontario o Prairie Provinces o British Columbia o Northern Territories
Unit 2- Population. The Human Landscape- Who We Are
 Unit 2- Population The Human Landscape- Who We Are Population Measure of the # of people who live in a specific place at a specific time. Usually follow a political boundary such as a country, province
Unit 2- Population The Human Landscape- Who We Are Population Measure of the # of people who live in a specific place at a specific time. Usually follow a political boundary such as a country, province
Chapter 5 War and British Conquest. Test Review
 Chapter 5 War and British Conquest Test Review True or False The struggle to control North America had three main geographic divisions. The struggle focused partly on the Atlantic coast, where Britain
Chapter 5 War and British Conquest Test Review True or False The struggle to control North America had three main geographic divisions. The struggle focused partly on the Atlantic coast, where Britain
EXAM INFORMATION. Human Geography II of the United States and Canada. European Exploration. Europe in North America. Age of Discovery 2/28/2013
 Human Geography II of the United States and Canada Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 13 EXAM INFORMATION Exam One is Tuesday, March 5. Bring a # pencil, eraser and a pen. Multiple choice short answer plus choice
Human Geography II of the United States and Canada Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 13 EXAM INFORMATION Exam One is Tuesday, March 5. Bring a # pencil, eraser and a pen. Multiple choice short answer plus choice
Chapter 8- Empresarios and Colonization
 Chapter 8- Empresarios and Colonization Empresario *In 1789 George Morgan became the first empresario for the Spanish government as he brought U.S. settlers into New Madrid, Missouri. His example would
Chapter 8- Empresarios and Colonization Empresario *In 1789 George Morgan became the first empresario for the Spanish government as he brought U.S. settlers into New Madrid, Missouri. His example would
Name: Group: Date: REVIEW Chapter 1
 REVIEW Chapter 1 REVIEW Textbook, pp. 360 361 1 What political change was introduced by the Act of Union? The legislative union of Upper and Lower Canada 2 What was the main demand of the Reform members
REVIEW Chapter 1 REVIEW Textbook, pp. 360 361 1 What political change was introduced by the Act of Union? The legislative union of Upper and Lower Canada 2 What was the main demand of the Reform members
Duty to Consult and the Aboriginal Reconciliation Process in New Brunswick. Aboriginal Affairs Secretariat November 6, 2015
 Duty to Consult and the Aboriginal Reconciliation Process in New Brunswick Aboriginal Affairs Secretariat November 6, 2015 Historical Context (400 Years) Aboriginal and Treaty Rights in New Brunswick Jacques
Duty to Consult and the Aboriginal Reconciliation Process in New Brunswick Aboriginal Affairs Secretariat November 6, 2015 Historical Context (400 Years) Aboriginal and Treaty Rights in New Brunswick Jacques
First Nations Groups in Canada
 First Nations Groups in Canada First Nations in BC Over 200 First Nations Amazing diversity 60% of FN languages in Canada are in BC Terminology Indian an older/outdated term for Aboriginal person First
First Nations Groups in Canada First Nations in BC Over 200 First Nations Amazing diversity 60% of FN languages in Canada are in BC Terminology Indian an older/outdated term for Aboriginal person First
COMPLEMENTARY ACTIVITIES (cont.) Worksheet 2.8
 PART 3 New France from 1663 to 1701 Textbook, pp. 86 101 1 Among the following statements, circle the ones that correspond to the king s two main objectives when he established the royal government in
PART 3 New France from 1663 to 1701 Textbook, pp. 86 101 1 Among the following statements, circle the ones that correspond to the king s two main objectives when he established the royal government in
Victorian: during the reign of Queen Victoria, or someone who shares the values of that period
 Victorian: during the reign of Queen Victoria, or someone who shares the values of that period The Province of Canada: now Canada East and Canada West After the Rebellions of 1837, there was a big increase
Victorian: during the reign of Queen Victoria, or someone who shares the values of that period The Province of Canada: now Canada East and Canada West After the Rebellions of 1837, there was a big increase
Module 4: British North America
 Module 4: British North America 1791-1867 Population and Settlement Who were the people of the British wave and where did they settle? What happens to the French population? Economy and Development How
Module 4: British North America 1791-1867 Population and Settlement Who were the people of the British wave and where did they settle? What happens to the French population? Economy and Development How
Canadian History 11 Exam Review
 Exam Outline: Name: Canadian History 11 Exam Review Section A: Multiple Choice (50 points) o 50 Multiple Choice questions Section B: Fill in the Blanks (10 points) o 10 questions 1 point each o Mostly
Exam Outline: Name: Canadian History 11 Exam Review Section A: Multiple Choice (50 points) o 50 Multiple Choice questions Section B: Fill in the Blanks (10 points) o 10 questions 1 point each o Mostly
Chapter 3 Notes Earth s Human and Cultural Geography
 Chapter 3 Notes Earth s Human and Cultural Geography Section 1: World Population Geographers study how people and physical features are distributed on Earth s surface. Although the world s population is
Chapter 3 Notes Earth s Human and Cultural Geography Section 1: World Population Geographers study how people and physical features are distributed on Earth s surface. Although the world s population is
EXAM INFORMATION. Human Geography II of the United States and Canada. L Anse aux Meadows World Heritage Site, NFD. Early European Exploration
 /4/017 EXAM INFORMATION Exam One is Tues, Mar 7th. Format. Multiple choice questions on material covered through Human Geog III; some aimed at maps/diagrams and essay topics from a choice. See Study Guide.
/4/017 EXAM INFORMATION Exam One is Tues, Mar 7th. Format. Multiple choice questions on material covered through Human Geog III; some aimed at maps/diagrams and essay topics from a choice. See Study Guide.
Module 1: The Formation of the Canadian Federal System Review
 Module 1: The Formation of the Canadian Federal System Review Frotin, Sylvain, Dominique Lapointe, Remi Lavoie, and Alain Parent. Reflections.qc.ca: 1840 to Our Times. Montreal, QC: Cheneliere Education,
Module 1: The Formation of the Canadian Federal System Review Frotin, Sylvain, Dominique Lapointe, Remi Lavoie, and Alain Parent. Reflections.qc.ca: 1840 to Our Times. Montreal, QC: Cheneliere Education,
Aboriginal The Blues bribery Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms Acadian Canadien(ne) alliance assembly line Catholic school cause
 Glossary Aboriginal The descendants of the original inhabitants of North America. First Nations, Inuit and Métis peoples have unique heritages, languages, cultural practices, and spiritual beliefs. Aboriginal
Glossary Aboriginal The descendants of the original inhabitants of North America. First Nations, Inuit and Métis peoples have unique heritages, languages, cultural practices, and spiritual beliefs. Aboriginal
ANCIENT GREECE & ROME
 ANCIENT GREECE & ROME 3.1 The student will explain how the contributions of ancient Greece and Rome have influenced the present world in terms of architecture, government (direct and representative democracy),
ANCIENT GREECE & ROME 3.1 The student will explain how the contributions of ancient Greece and Rome have influenced the present world in terms of architecture, government (direct and representative democracy),
Fill in the Blanks Use your study sheet to find the correct answers.
 Canada Homework 1 Fill in the Blanks Use your study sheet to find the correct answers. Canada is the world s s largest nation. Only R has more l. Canada is a vast land with many attributes. The nation
Canada Homework 1 Fill in the Blanks Use your study sheet to find the correct answers. Canada is the world s s largest nation. Only R has more l. Canada is a vast land with many attributes. The nation
The Red River Settlement 50 years of instability
 The Red River Settlement 50 years of instability 1820-1870 Merger of HBC and NWC The turmoil over the Pemmican Proclamation and Battle of Seven Oaks were examples of a larger struggle between the HBC and
The Red River Settlement 50 years of instability 1820-1870 Merger of HBC and NWC The turmoil over the Pemmican Proclamation and Battle of Seven Oaks were examples of a larger struggle between the HBC and
Grade 8 History. Confederation
 Grade 8 History Confederation Factors Leading To Confederation Defence Issues During the war of 1812, England successfully defended the colonies in North America against the United States. England had
Grade 8 History Confederation Factors Leading To Confederation Defence Issues During the war of 1812, England successfully defended the colonies in North America against the United States. England had
Grade 7 Social Studies Study Guide
 Grade 7 Social Studies Study Guide Chapter 1: Aboriginal Societies Culture: is a way of life or a way of being that is shared by a group of people. Ethnocentrism: Believing ones own ethnic group is better
Grade 7 Social Studies Study Guide Chapter 1: Aboriginal Societies Culture: is a way of life or a way of being that is shared by a group of people. Ethnocentrism: Believing ones own ethnic group is better
1.2 Pocahontas. what really happened?
 1.2 Pocahontas what really happened? Controversy Pocahontas float at high school homecoming parade sparks outrage from Native American students FOX NEWS POSTED 6:46 PM, SEPTEMBER 29, 2015, BY TAMARA VAIFANUA,
1.2 Pocahontas what really happened? Controversy Pocahontas float at high school homecoming parade sparks outrage from Native American students FOX NEWS POSTED 6:46 PM, SEPTEMBER 29, 2015, BY TAMARA VAIFANUA,
Early US History Part 1. Your Notes. Goal 9/5/2012. How did the United States became a country?
 Questions / Themes 9/5/2012 Early US History Part 1 How did the United States became a country? Your Notes You will need these notes to prepare for exams. Remember to paraphrase and generalize. Avoid copying
Questions / Themes 9/5/2012 Early US History Part 1 How did the United States became a country? Your Notes You will need these notes to prepare for exams. Remember to paraphrase and generalize. Avoid copying
LEARNING INTENTIONS Understanding the following events contributed to the anti-british Sentiment American Revolution Stamp Act, 1765 Boston Massacre,
 LEARNING INTENTIONS Understanding the following events contributed to the anti-british Sentiment American Revolution Stamp Act, 1765 Boston Massacre, 1770 The Tea Act, 1773 Boston Tea Party, 1773 The Intolerable
LEARNING INTENTIONS Understanding the following events contributed to the anti-british Sentiment American Revolution Stamp Act, 1765 Boston Massacre, 1770 The Tea Act, 1773 Boston Tea Party, 1773 The Intolerable
Absolutism and Enlightenment
 Absolutism and Enlightenment The Commercial Revolution Most of Europe remained agricultural between 1600-1770 The Commercial Revolution marked an important step in the transition from the local economies
Absolutism and Enlightenment The Commercial Revolution Most of Europe remained agricultural between 1600-1770 The Commercial Revolution marked an important step in the transition from the local economies
-rocky soil. -forests. -clean water. -rivers. -forests. -good soil for farming. -harsh winters. -summer rain
 John Winthrop lead Puritans here to freely practice their religion. -rocky soil -forests -clean water -lumbering -fishing -democratic -decisions were made at town meetings; majority rules -cold winters
John Winthrop lead Puritans here to freely practice their religion. -rocky soil -forests -clean water -lumbering -fishing -democratic -decisions were made at town meetings; majority rules -cold winters
I. SSUSH1: The student will describe European settlement in North America during the 17th century
 Unit I Review Sheet I. SSUSH1: The student will describe European settlement in North America during the 17th century 1. The Virginia Company A joint stock company. A group of investors share the risk
Unit I Review Sheet I. SSUSH1: The student will describe European settlement in North America during the 17th century 1. The Virginia Company A joint stock company. A group of investors share the risk
HISTORY OF QUEBEC AND CANADA. Secondary 4. Based off of Reflections textbook by Chenelière
 HISTORY OF QUEBEC AND CANADA Secondary 4 Based off of Reflections textbook by Chenelière GOOD MORNING! HERE S WHAT WE LL BE DOING TODAY Recap of the past few lessons (5 mins) Presentation of new material
HISTORY OF QUEBEC AND CANADA Secondary 4 Based off of Reflections textbook by Chenelière GOOD MORNING! HERE S WHAT WE LL BE DOING TODAY Recap of the past few lessons (5 mins) Presentation of new material
The History of the Huguenots. Western Civilization II Marshall High School Mr. Cline Unit ThreeDA
 The History of the Huguenots Western Civilization II Marshall High School Mr. Cline Unit ThreeDA Reformation Comes to France When the Reformation came to France, its message spread quickly. By 1534, there
The History of the Huguenots Western Civilization II Marshall High School Mr. Cline Unit ThreeDA Reformation Comes to France When the Reformation came to France, its message spread quickly. By 1534, there
HISTORY AND SOCIAL SCIENCE
 Nashoba Regional School District HISTORY AND SOCIAL SCIENCE Grade 5 Nashoba Regional School District History and Social Science, 2008. Work in this document is based upon the standards outlined in the
Nashoba Regional School District HISTORY AND SOCIAL SCIENCE Grade 5 Nashoba Regional School District History and Social Science, 2008. Work in this document is based upon the standards outlined in the
Evaluation of knowledge (Chapter 1)
 EVALUATION OF KNOWLEDGE SECTION 1 /65 The Act of Union Evaluation of knowledge (Chapter 1) PART 1 The Act of Union and the early days of the Province of Canada (1840 1849) 1 a) Of the following two proposals
EVALUATION OF KNOWLEDGE SECTION 1 /65 The Act of Union Evaluation of knowledge (Chapter 1) PART 1 The Act of Union and the early days of the Province of Canada (1840 1849) 1 a) Of the following two proposals
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions.
 SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. Known as the Sun
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. Known as the Sun
2. List some reasons why the Quebec Act was seen by the French Canadiens as a favorable law.
 Name/Date: Social Studies 9 Unit 3: Building a Nation 3A The American Influence 1774-1815 References: Cranny, M. (1998) Crossroads: A Meeting of Nations, Ch. 10 video or filmstrip titles (e.g. Origins
Name/Date: Social Studies 9 Unit 3: Building a Nation 3A The American Influence 1774-1815 References: Cranny, M. (1998) Crossroads: A Meeting of Nations, Ch. 10 video or filmstrip titles (e.g. Origins
Grade 5 Concepts and Skills
 G RADE 5 UNITED STATES HISTORY, GEOGRAPHY, ECONOMICS, AND GOVERNMENT: EARLY EXPLORATION TO WESTWARD MOVEMENT Students study the major pre-columbian civilizations in the New World; the 15th and 16th century
G RADE 5 UNITED STATES HISTORY, GEOGRAPHY, ECONOMICS, AND GOVERNMENT: EARLY EXPLORATION TO WESTWARD MOVEMENT Students study the major pre-columbian civilizations in the New World; the 15th and 16th century
5.1 Prosperity in the 1920 s
 Social Studies 9 Chapter 5 : Prosperity and Depression 5.1 Prosperity in the 1920 s During the Great War, Canada s industries were focused on wartime goods which drove up the cost of everyday goods. Returning
Social Studies 9 Chapter 5 : Prosperity and Depression 5.1 Prosperity in the 1920 s During the Great War, Canada s industries were focused on wartime goods which drove up the cost of everyday goods. Returning
UNIT 4: Defining Canada Chapter 7: The Emergence of Modern Canada
 UNIT 4: Defining Canada Chapter 7: The Emergence of Modern Canada Laurier: The Compromiser In 1896, 20 years of Conservative rule ended when the Liberals won a majority government in an election Wilfrid
UNIT 4: Defining Canada Chapter 7: The Emergence of Modern Canada Laurier: The Compromiser In 1896, 20 years of Conservative rule ended when the Liberals won a majority government in an election Wilfrid
Events Leading to the American Revolution
 Events Leading to the American Revolution Colonization Main Reason was for Mercantilism: Making money for the mother country Joint-stock company: investors share ownership and profits Charters: grants
Events Leading to the American Revolution Colonization Main Reason was for Mercantilism: Making money for the mother country Joint-stock company: investors share ownership and profits Charters: grants
SAMPLE Group Presentation
 SAMPLE Group Presentation What follows is a presentation (with some modifications) created by 3 students in History 146 for the group project called "The Way I See It" in which groups explored a topic
SAMPLE Group Presentation What follows is a presentation (with some modifications) created by 3 students in History 146 for the group project called "The Way I See It" in which groups explored a topic
SOCIAL JUSTICE AND ABORIGINAL POVERTY IN CANADA
 SOCIAL JUSTICE AND ABORIGINAL POVERTY IN CANADA DISTRIBUTION OF WEALTH IN CANADA Section of Population Top 20% 75 Second to top 17.4 Middle 20% 6.9 Second from bottom 1.3 Bottom 20% Share (%) of Wealth
SOCIAL JUSTICE AND ABORIGINAL POVERTY IN CANADA DISTRIBUTION OF WEALTH IN CANADA Section of Population Top 20% 75 Second to top 17.4 Middle 20% 6.9 Second from bottom 1.3 Bottom 20% Share (%) of Wealth
The French Texans. Rene-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle. THE INSTITUTE OF TEXAN CULTURES 2014 Texans One and All The French Texans Page 1
 The French Texans Although a French flag of some sort is represented in six flags over Texas displays, France never in any sense of political control or official claims flew a flag over Texas and never
The French Texans Although a French flag of some sort is represented in six flags over Texas displays, France never in any sense of political control or official claims flew a flag over Texas and never
ECONOMY AND DEVELOPMENT FROM THEN TO NOW TAKEN FROM
 ECONOMY AND DEVELOPMENT FROM THEN TO NOW TAKEN FROM HTTP://MISSVHISTORY.BLOGSPOT.CA/ FIRST OCCUPANTS 1. TRADE NETWORKS BARTER BETWEEN NATIVES; NOMADIC GROUPS EXCHANGED GOODS WITH OTHERS, LIKE SEDENTARY
ECONOMY AND DEVELOPMENT FROM THEN TO NOW TAKEN FROM HTTP://MISSVHISTORY.BLOGSPOT.CA/ FIRST OCCUPANTS 1. TRADE NETWORKS BARTER BETWEEN NATIVES; NOMADIC GROUPS EXCHANGED GOODS WITH OTHERS, LIKE SEDENTARY
Ancient Rome and the Origins of Christianity. Lesson 1: The Roman Republic
 Ancient Rome and the Origins of Christianity Lesson 1: The Roman Republic Lesson 1 Objectives Describe the development of the classical civilization of Rome Outline how the Roman republic was structured
Ancient Rome and the Origins of Christianity Lesson 1: The Roman Republic Lesson 1 Objectives Describe the development of the classical civilization of Rome Outline how the Roman republic was structured
English Colonies in an Age of Empire 1660s 1763 English Colonies in an Age of Empire 1660s 1763 Video Series: Key Topics in U.S.
 1 2 3 4 5 6 English Colonies in an Age of Empire 1660s 1763 Economic Development and Imperial Trade in the British Colonies How did trade policy shape the relationship between Britain and the colonies?
1 2 3 4 5 6 English Colonies in an Age of Empire 1660s 1763 Economic Development and Imperial Trade in the British Colonies How did trade policy shape the relationship between Britain and the colonies?
The Birth of the American Identity
 The Birth of the American Identity 1689-1763 Colonial Life In England, less than 5% of the population owned land As a result, more Americans could vote than British Land ownership Cheap farmland Natural
The Birth of the American Identity 1689-1763 Colonial Life In England, less than 5% of the population owned land As a result, more Americans could vote than British Land ownership Cheap farmland Natural
4: TELESCOPING THE TIMES
 The Americans (Survey) Chapter 4: TELESCOPING THE TIMES The War for Independence CHAPTER OVERVIEW The colonists clashes with the British government lead them to declare independence. With French aid, they
The Americans (Survey) Chapter 4: TELESCOPING THE TIMES The War for Independence CHAPTER OVERVIEW The colonists clashes with the British government lead them to declare independence. With French aid, they
Chinese regulations ensured China had favorable balance of trade with other nations Balance of trade: difference between how much a country imports
 Chinese regulations ensured China had favorable balance of trade with other nations Balance of trade: difference between how much a country imports and how much it exports By 1800s, western nations were
Chinese regulations ensured China had favorable balance of trade with other nations Balance of trade: difference between how much a country imports and how much it exports By 1800s, western nations were
4th 9 weeks study guide.notebook May 19, 2014
 What was the main reason that the Puritans started the Massachusetts Bay Colony? to live according to their religious beliefs What was the main purpose of town meetings in the New England colonies? To
What was the main reason that the Puritans started the Massachusetts Bay Colony? to live according to their religious beliefs What was the main purpose of town meetings in the New England colonies? To
Evaluation of competencies (Chapter 4)
 Name: Group: Date: EVALUATION OF COMPETENCIES Evaluation Criterion 2 result: /25 Criterion 3 result: /8 Criterion 4 result: /12 Final result: /45 Evaluation of competencies () DOCUMENTS DOCUMENT 1 The
Name: Group: Date: EVALUATION OF COMPETENCIES Evaluation Criterion 2 result: /25 Criterion 3 result: /8 Criterion 4 result: /12 Final result: /45 Evaluation of competencies () DOCUMENTS DOCUMENT 1 The
Confederation: Primary Source Analysis 1. Source B
 Confederation: Primary Source Analysis 1 Source B We don t know each other. We have no trade with each other. We have no facilities, or resources, or incentives, to mingle with each other. We are shut
Confederation: Primary Source Analysis 1 Source B We don t know each other. We have no trade with each other. We have no facilities, or resources, or incentives, to mingle with each other. We are shut
SUBJECT: History and Social Studies Grade Level: 5 United States History, Geography, Economics, and Government: Early Exploration to Westward Movement
 Unit: Pre-Columbian Civilizations of the New World and European Exploration, Colonization, and Settlement to 1700 Learning Standards / Essential Knowledge Concepts and Skills Essential Questions 5.1 Describe
Unit: Pre-Columbian Civilizations of the New World and European Exploration, Colonization, and Settlement to 1700 Learning Standards / Essential Knowledge Concepts and Skills Essential Questions 5.1 Describe
Atlantic Provinces. Deciduous forests. Smallest region-5% of Canada s land and 8% of its people.
 Canada Chapter 8 Canada s Regions Canada s 10 provinces and 3 territories are divided into 5 regions based on physical features, culture, and economy. Regions are more distinct than those in the US. -Smaller
Canada Chapter 8 Canada s Regions Canada s 10 provinces and 3 territories are divided into 5 regions based on physical features, culture, and economy. Regions are more distinct than those in the US. -Smaller
History- Confederation Review. The Great Migration
 History- Confederation Review The Great Migration This contributed to the diversity in Canada s makeup. Many Irish came over as a result of the Potato famine, and these people were Protestants. This conflicted
History- Confederation Review The Great Migration This contributed to the diversity in Canada s makeup. Many Irish came over as a result of the Potato famine, and these people were Protestants. This conflicted
Grade Three Introduction to History and Social Science
 2008 Curriculum Framework Grade Three Introduction to History and Social Science Commonwealth of Virginia Board of Education Richmond, Virginia Approved July 17, 2008 STANDARD 3.1 The student will explain
2008 Curriculum Framework Grade Three Introduction to History and Social Science Commonwealth of Virginia Board of Education Richmond, Virginia Approved July 17, 2008 STANDARD 3.1 The student will explain
'FTER. Canadians CHAPTER 10
 CLASH OF EMPIRES: THE BRITISH, FRENCH & INDIAN WAR 1754-1763 CHAPTER 10 Canadians 'FTER THE SEPTEMBER 1760 SURRENDER OF MONTREAL, British Commander-intChief Jeffrey Amherst established a temporary military
CLASH OF EMPIRES: THE BRITISH, FRENCH & INDIAN WAR 1754-1763 CHAPTER 10 Canadians 'FTER THE SEPTEMBER 1760 SURRENDER OF MONTREAL, British Commander-intChief Jeffrey Amherst established a temporary military
Social Studies Content Expectations
 The fifth grade social studies content expectations mark a departure from the social studies approach taken in previous grades. Building upon the geography, civics and government, and economics concepts
The fifth grade social studies content expectations mark a departure from the social studies approach taken in previous grades. Building upon the geography, civics and government, and economics concepts
The War of British, local militia and First Nations fought together against the invaders and won many key battles.
 The War of 1812 Tensions between Britain and the U.S. heated up again. -Britain stopped the Americans form trading with the French. - They kidnapped American sailors and forced them in to service for the
The War of 1812 Tensions between Britain and the U.S. heated up again. -Britain stopped the Americans form trading with the French. - They kidnapped American sailors and forced them in to service for the
Name: Final Exam Date: Period: Texas History Fall Semester Final Exam Review
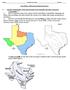 Name: Final Exam Date: Period: Texas History Fall Semester Final Exam Review I.) Unit One: Natural/Native Texas and its People (Texas Geography and Native Americans) ***Geography *** 1.) MAP A: Label the
Name: Final Exam Date: Period: Texas History Fall Semester Final Exam Review I.) Unit One: Natural/Native Texas and its People (Texas Geography and Native Americans) ***Geography *** 1.) MAP A: Label the
Chapter 12. The study of population numbers, distribution, trends, and issues.
 Chapter 12 Population Challenges Demography: The study of population numbers, distribution, trends, and issues. Population Statistics for October, 2004, Land Area (Square Km.) And Population Density Canada
Chapter 12 Population Challenges Demography: The study of population numbers, distribution, trends, and issues. Population Statistics for October, 2004, Land Area (Square Km.) And Population Density Canada
Causes of French Revolution. 3 Causes
 Causes of French Revolution 3 Causes Contextualization 1. Burdens of absolutism 2. Enlightenment present solutions to absolutism 1. Burdens of Absolutism Louis XIV: gold standard of absolute monarchs When
Causes of French Revolution 3 Causes Contextualization 1. Burdens of absolutism 2. Enlightenment present solutions to absolutism 1. Burdens of Absolutism Louis XIV: gold standard of absolute monarchs When
Nations and Nation Building: Canada's Evolutionary Changes!
 Nations and Nation Building: Canada's Evolutionary Changes! Movements Toward Confederation! Initial Reasons for Confederation! Fear of USA domination! Belief that Britain was reluctant to defend against
Nations and Nation Building: Canada's Evolutionary Changes! Movements Toward Confederation! Initial Reasons for Confederation! Fear of USA domination! Belief that Britain was reluctant to defend against
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY TEACHER S GUIDE. 9th Grade
 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY TEACHER S GUIDE 9th Grade Author: Alpha Omega Publications Editor: Alan Christopherson, M.S. 2 25 History & Geography 900 Teacher Notes INSTRUCTIONS FOR HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY The LIFEPAC
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY TEACHER S GUIDE 9th Grade Author: Alpha Omega Publications Editor: Alan Christopherson, M.S. 2 25 History & Geography 900 Teacher Notes INSTRUCTIONS FOR HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY The LIFEPAC
Aboriginal Peoples. New France British Rule Confederation. Aboriginal Peoples and European Settlement Settling the West
 THE HISTORT Canada's History Get Ready to Learn Unit 1 Unit Z Unit 3 Unit 4 UnitS Unit 6 Unit 7 UnitS Unit 9 Unit 10 Unit 11 Unit 12 Aboriginal Peoples New France British Rule Confederation Aboriginal
THE HISTORT Canada's History Get Ready to Learn Unit 1 Unit Z Unit 3 Unit 4 UnitS Unit 6 Unit 7 UnitS Unit 9 Unit 10 Unit 11 Unit 12 Aboriginal Peoples New France British Rule Confederation Aboriginal
The US Government Policy towards the Plains Indians
 The US Government Policy towards the Plains Indians Learning Objective To know the US Government policy towards the Plains Indians in the 1830s 1850s and assess the reasons for the changes in policy that
The US Government Policy towards the Plains Indians Learning Objective To know the US Government policy towards the Plains Indians in the 1830s 1850s and assess the reasons for the changes in policy that
Topic Page: Iroquois. https://search.credoreference.com/content/topic/iroquois. Definition: Iroquois from Merriam-Webster's Collegiate(R) Dictionary
 Topic Page: Iroquois Definition: Iroquois from Merriam-Webster's Collegiate(R) Dictionary pronunciation (1666) 1 pl : an American Indian confederacy orig. of New York consisting of the Cayuga, Mohawk,
Topic Page: Iroquois Definition: Iroquois from Merriam-Webster's Collegiate(R) Dictionary pronunciation (1666) 1 pl : an American Indian confederacy orig. of New York consisting of the Cayuga, Mohawk,
Cultural diffusion- a person using something from another culture (Middle Eastern lady wearing Levi jeans)
 First Semester Review: Location-absolute and relative Region vs. place Human Environment Interaction Technology and its impact Continents and Hemispheres Tsunami -giant wave that starts with an earthquake
First Semester Review: Location-absolute and relative Region vs. place Human Environment Interaction Technology and its impact Continents and Hemispheres Tsunami -giant wave that starts with an earthquake
Wednesday, September 20, 2017
 Wednesday, September 20, 2017 Human Geography of Canada, eh Content Objective: WG.7B Explain how political, economic, social, and environmental push and pull factors and physical geography affect the routes
Wednesday, September 20, 2017 Human Geography of Canada, eh Content Objective: WG.7B Explain how political, economic, social, and environmental push and pull factors and physical geography affect the routes
Chapter 5 - Overview The chapter explores the social and economic classes developing in the colonies as well as the new religious and philosophical mo
 Chapter 5 Beginnings of an American Identity Chapter 5 - Overview The chapter explores the social and economic classes developing in the colonies as well as the new religious and philosophical movements.
Chapter 5 Beginnings of an American Identity Chapter 5 - Overview The chapter explores the social and economic classes developing in the colonies as well as the new religious and philosophical movements.
Note on the historical background for European industrialization. Social organization. Trade in Feudal era. Social norms 9/20/2017
 European Feudalism, ca. 800-1450AD Note on the historical background for European industrialization Roman empire weakens after 4 th Century AD plague, decadence, too big and complex.. Infrastructure, law
European Feudalism, ca. 800-1450AD Note on the historical background for European industrialization Roman empire weakens after 4 th Century AD plague, decadence, too big and complex.. Infrastructure, law
1. Identify different ways of dating historical narrative ( 17th century, seventeenth century, 1600s, colonial period) (H, G)
 Andover Public Schools Social Studies Benchmarks ~ 2004 Grade 5 United States History, Geography, Economics, and Government: Early Exploration to Westward Movement Students study major pre-columbian civilizations
Andover Public Schools Social Studies Benchmarks ~ 2004 Grade 5 United States History, Geography, Economics, and Government: Early Exploration to Westward Movement Students study major pre-columbian civilizations
Social Studies 4th Grade Sept June 2018 SAS Pacing Guide
 Social Studies 4th Grade Sept. 2017- June 2018 SAS Pacing Guide Questions Sept. 4.1: 4.1a, 4.1b Geography of New Question(s): How do maps provide information about people, places, and physical and cultural
Social Studies 4th Grade Sept. 2017- June 2018 SAS Pacing Guide Questions Sept. 4.1: 4.1a, 4.1b Geography of New Question(s): How do maps provide information about people, places, and physical and cultural
The Federalist Papers
 The Federalist Papers If men were angels, no government would be necessary. James Madison During the Revolutionary War, Americans set up a new national government. They feared a strong central government.
The Federalist Papers If men were angels, no government would be necessary. James Madison During the Revolutionary War, Americans set up a new national government. They feared a strong central government.
British Landlords. You made sure that you were off in London or Paris so you didn t have to personally witness the suffering in Ireland.
 British Landlords You are directly responsible for the terrible famine resulting from the potato blight. You owned the land that the Irish peasants worked. When the potato crop failed, you had a choice:
British Landlords You are directly responsible for the terrible famine resulting from the potato blight. You owned the land that the Irish peasants worked. When the potato crop failed, you had a choice:
Date Standards/Essential Questions Essential Knowledge/Skills/Understanding Resources/Assessment & Activities September MAP SKILLS
 During the summer of 2010, the pacing guide for third grade History was reviewed based on input from third grade teachers and the following changes were made: Economics concepts were moved to November.
During the summer of 2010, the pacing guide for third grade History was reviewed based on input from third grade teachers and the following changes were made: Economics concepts were moved to November.
Book Review of Upper Peninsula of Michigan: A History by Russell, M. Magnaghi
 Upper Country: A Journal of the Lake Superior Region Volume 5 Article 6 2017 Book Review of Upper Peninsula of Michigan: A History by Russell, M. Magnaghi Gabe Logan Northern Michigan University, glogan@nmu.edu
Upper Country: A Journal of the Lake Superior Region Volume 5 Article 6 2017 Book Review of Upper Peninsula of Michigan: A History by Russell, M. Magnaghi Gabe Logan Northern Michigan University, glogan@nmu.edu
I. SPANISH POWER GROWS pg 504 A. Charles V* Inherits Two Crowns 1. Ruling the Hapsburg Empire* a. Charles=grandson of Ferdinand & Isabella b.
 I. SPANISH POWER GROWS pg 504 A. Charles V* Inherits Two Crowns 1. Ruling the Hapsburg Empire* a. Charles=grandson of Ferdinand & Isabella b.=ruler of Spain + Holy Roman Empire A Kingdom Too Spread Out
I. SPANISH POWER GROWS pg 504 A. Charles V* Inherits Two Crowns 1. Ruling the Hapsburg Empire* a. Charles=grandson of Ferdinand & Isabella b.=ruler of Spain + Holy Roman Empire A Kingdom Too Spread Out
