Attached are letters from the following distinguished professionals against a convention:
|
|
|
- Kelly Gardner
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Opposition to HJR 7 or SJR 5 (Calling for an Article V convention) Dave Black, Willoughby Ohio 11/9/13 Attached are letters from the following distinguished professionals against a convention: Supreme Court Chief Justice Burger Rex Lee, President of BYU Supreme Court Nominee Bork Associate Justice of the Supreme Court Arthur Goldbeg University Professor, Professor of Constitutional Law, Harvard Law School, L Tribe University of Texas, Law Professor C. Wright. I. HJR 7/SJR 5 is very risky for the following reasons: 1. Although it appears to ask for a limited convention regarding balancing the budget, it combines with other applications to get to the 2/3 needed. Have you looked at the other applications, because if they vary in their requests in the slightest degree or call for different amendments within their application, it would open it up to an unlimited convention. Congress could use their discretion to say the 2/3 have been met even though the requests may differ. The letters attached support this risk. 2. The safeguard of ¾ ratification is unsound as the original articles of confederation required ratification by all 13 states, and yet the convention charged that ratification by 9 was acceptable. Also, article V offers the Congress the option of ratifying through state legislatures or state conventions. They can use the mode that would most accomplish what they want. 3. HJR 7 does not mention the process of picking delegates. As I show the Compact for America proposes to have the Governor of each state pick the sole delegate for that state. There are numerous examples around the Country where a Governor goes against even their own party in favor of centralized power. 4. HJR 7 asks for a balanced budget amendment with no specifics on how large the federal budget may be. If this passes with no alteration. The federal government would have the power to raise taxes 40% to reach the amount needed to balance the budget based on the current expenditures. This would virtually eliminate the states as there would be no money left for state budgets. 5. Article V states Congress shall call convention, and Congress shall propose mod of ratification. This opens up a lot of authority over the Convention by Congress. II. The Bill of Rights are at Risk.
2 The last 10 years we ve seen a consistent attack on virtually all of the 10 amendments of the bill of rights. The first amendment: Freedom of Religion, of the press, Second Amendment: the right to bear arms, Fourth Amendment: the right to privacy without unwarranted search and seizure, Fifth Amendment, no one to be deprived of life or liberty without due process. Sixth Amendment: right to trial by jury. Seventh Amendment: Right to jury trial in common law. Eighth Amendment: No cruel or unusual punishment. Tenth Amendment: States authority of things not delegated to the Federal Government. III. Our only precedent was the original convention of Three major violations occurred then: 1. The convention was called only to amend the articles of confederation. It was not called to change the constitution. With the sole and express purpose of revising the Articles of Confederation. Federalist 40: James Madison. Articles of Confederation: 2. The articles required full ratification by all 13 states. The convention changed the rules to ratification by only 9 states. Article XIII: Every State shall abide by the determinations of the United States, in congress assembled, on all questions which by this confederation are submitted to them. And the Articles of this confederation shall be inviolably observed by every state, and the union shall be perpetual; nor shall any alteration at any time hereafter be made in any of them, unless such alteration be agreed to in a congress of the united states, and be afterwards con-firmed by the legislatures of every state. 3. The constitution changed the structure from a confederation of States to a Consolidated Government. In doing so risked the Bill of Rights totally insecure that were in such states as Virginia. Articles of CONFEDERATION and PERPETUAL UNION between the states of New Hampshire, Massachusetts Bay, Rhode Island and providence plantations, Connecticut New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia.
3 US Constitution: We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union Patrick Henry: THURSDAY, June 5, The fate of this question and of America may depend on this. Have they said, We, the states? Have they made a proposal of a compact between states? If they had, this would be a confederation. It is otherwise most clearly a consolidated government. Patrick Henry: THURSDAY, June 5, The rights of conscience, trial by jury, liberty of the press, all your immunities and franchises, all pretensions to human rights and privileges, are rendered insecure, if not lost, by this change, so loudly talked of by some, and inconsiderately by others. Is this tame relinquishment of rights worthy of freemen? Is it worthy of that manly fortitude that ought to characterize republicans? You are not to inquire how your trade may be increased, nor how you are to become a great and powerful people, but how your liberties can be secured; for liberty ought to be the direct end of your government. IV: Our only precedent before inclusion of the bill of rights risked our very freedom: The original convention showed that those seeking to consolidate power at the expense of personal liberty were able to maneuver into position to pull it off. Federal Farmer, October 8th, 1787 (Richard Henry Lee, signer of Declaration of Independence, and President under the Articles of Confederation.) when by the evils, on the one hand, and by the secret instigations of artful men, on the other, the minds of men were become sufficiently uneasy, a bold step was taken, which is usually followed by a revolution, or a civil war. A general convention for mere commercial purposes was moved for the authors of this measure saw that the people's attention was turned solely to the amendment of the federal system; and that, had the idea of a total change been started, probably no state would have appointed members to the convention. The idea of destroying, ultimately, the state government, and forming one consolidated system, could not have been admitted a convention, therefore, merely for vesting in congress power to regulate trade was proposed.
4 a few men from the middle states met at Annapolis, and hastily proposed a convention to be held in May, 1787, for the purpose, generally, of amending the confederation still not a word was said about destroying the old constitution, and making a new one The states still unsuspecting, and not aware that they were passing the Rubicon, appointed members to the new convention, for the sole and express purpose of revising and amending the confederation and, probably, not one man in ten thousand in the United States, till within these ten or twelve days, had an idea that the old ship was to be destroyed, and he put to the alternative of embarking in the new ship presented, or of being left in danger of sinking Virginia made a very respectable appointment, and placed at the head of it the first man in America: In this appointment there was a mixture of political characters; but Pennsylvania appointed principally those men who are esteemed aristocratical. Here the favourite moment for changing the government was evidently discerned by a few men, who seized it with address The Address and Reasons of Dissent of the Minority of the Convention of PennsylvaniaTo Their Constituents Pennsylvania Packet and Daily Advertiser 18 December 1787 With this view a convention was first proposed by Virginia, and finally recommended by Congress for the different states to appoint deputies to meet in convention, "for the purposes of revising and amending the present articles of confederation, so as to make them adequate to the exigencies of the union." The Continental convention met in the city of Philadelphia at the time appointed. It was composed of some men of excellent characters; of others who were more remarkable for their ambition and cunning, than their patriotism; and of some who had been opponents to the independence of the United States. The delegates from Pennsylvania were, six of them, uniform and decided opponents to the constitution of this commonwealth. The convention sat upwards of four months. The doors were kept shut, and the members brought under the most solemn engagements of secrecy. Some of those who opposed their going so far beyond their powers, retired, hopeless, from the convention, others had the firmness to refuse signing the plan altogether; and many who did sign it, did it not as a system they wholly approved, but as the best that could
5 be then obtained, and notwithstanding the time spent on this subject, it is agreed on all hands to be a work of haste and accommodation. Whilst the gilded chains were forging in the secret conclave, the meaner instruments of despotism without, were busily employed in alarming the fears of the people with dangers which did not exist, and exciting their hopes of greater advantages from the expected plan than even the best government on earth could produce. The proposed plan had not many hours issued forth from the womb of suspicious secrecy, until such as were prepared for the purpose, were carrying about petitions for people to sign, signifying their approbation of the system, and requesting the legislature to call a convention. While every measure was taken to intimidate the people against opposing it, the public papers teemed with the most violent threats against those who should dare to think for themselves, and tar and feathers were liberally promised to all those who would not immediately join in supporting the proposed government be it what it would. The continental convention in direct violation of the 13th article of confederation, have declared "that the ratification of nine states shall be sufficient for the establishment of this constitution, between the states so ratifying the same." Patrick Henry: MONDAY, June 9, 1788 A number of characters, of the greatest eminence in this country, object to this government for its consolidating tendency. This is not imaginary. It is a formidable reality. If consolidation proves to be as mischievous to this country as it has been to other countries, what will the poor inhabitants of this country do? This government will operate like an ambuscade. It will destroy the state governments, and swallow the liberties of the people, without giving previous notice. Sept 7, 10 or 15 at convention: Colonel Mason and Mr. Randolph of Virginia delegation at the convention refused to sign the constitution. This delegation is the same group the introduced the Virginia Plan, which presented the platform to expand the federal powers under the Articles of Confederation. (Anti Federalist Papers, Ralph Ketcham, 1986) Colonel Mason concluded it would end either in monarchy or a tyrannical aristocracy, which he was in doubt, but one or the other, he was sure. This Constitution had been formed without the knowledge or idea of the people. A second convention will know more of the sense of the people and be able to provide a system more consonant to it. It was improper to say to the people take this or nothing. (Papers of George Mason, III, Rutland)
6 V. Additional information to consider: Beware of Article V video, Presented by Mark Stubbs, Former member of Idaho Legislature includes warnings from: Associate Justice of Supreme Court: Arthur Goldberg. Attached is report by him on dangers of a constitutional convention. Chief Justice Warren Berger. Rex E. Lee, President of Brigham Young University. COMPACT FOR AMERICA: ARTICLE V RESOLUTION APPLYING FOR CONVENTION Section 1. Be it resolved, as provided for in Article V of the Constitution of the United States, the Legislature of each Member State herewith applies to Congress for a convention for proposing amendments. Section 2. To the furthest extent permitted by law, the Convention shall be entirely focused upon and exclusively limited to the subject matter of introducing, debating, voting upon, and rejecting or proposing for ratification the Balanced Budget Amendment. ARTICLE VI DELEGATE APPOINTMENT, LIMITATIONS AND INSTRUCTIONS Section 1. Number of Delegates. Each Member State shall be entitled to one delegate as its sole and exclusive representative at the Convention as set forth in this Article. Section 2. Identity of Delegates. Each Member State s chief executive officer, who is serving on the enactment date of this Compact, is appointed in an individual capacity to
7 represent his or her respective State at the Convention as its sole and exclusive delegate. :. Laurence H. Tribe University Professor and Professor of Constitutional Law Harvard Law School Conference on constitutional convention: 9/24/2011 Harvard Law School. Paraphrased: There remain too many questions such as: Can a state limit the convention to one amendment? May Congress prescribe the rules of the convention? Are states to be equally represented by one vote per state? Can delegates be bound to instruction from State legislation on the actions of the delegates. I feel there are too many unknowns on how an Article V will be handled to put the whole constitution up for grabs." Possible bad amendments: All laws shall be subject to National Security as determined by the Executive Branch. Department of Education shall be under the jurisdiction of the Federal Government. The US shall have authority over settling the debt of any state. Nationalized Healthcare shall be a right of all citizens.
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
Document Based Essay Grade 7 The Constitution
 Document Based Essay Grade 7 The Constitution Directions: The following question is based on the accompanying documents (1-5). This question is designed to test your ability to work with historic documents.
Document Based Essay Grade 7 The Constitution Directions: The following question is based on the accompanying documents (1-5). This question is designed to test your ability to work with historic documents.
The Constitution. Karen H. Reeves
 The Constitution Karen H. Reeves Toward a New Union Annapolis Convention (Sept. 1786) Met to determine commercial regulation Nationalists called for Constitutional Convention Constitutional Convention
The Constitution Karen H. Reeves Toward a New Union Annapolis Convention (Sept. 1786) Met to determine commercial regulation Nationalists called for Constitutional Convention Constitutional Convention
Major Problem. Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government.
 The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
From VOA Learning English, welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in Special English. I m Steve Ember.
 From VOA Learning English, welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in Special English. I m Steve Ember. Today, we continue our story of the United States Constitution. In recent weeks, we told
From VOA Learning English, welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in Special English. I m Steve Ember. Today, we continue our story of the United States Constitution. In recent weeks, we told
Ratification of the Constitution. Issues
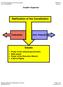 Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Basic Concepts of Government The English colonists brought 3 ideas that loom large in the shaping of the government in the United States.
 Civics Honors Chapter Two: Origins of American Government Section One: Our Political Beginnings Limited Government Representative government Magna Carta Petition of Right English Bill of Rights Charter
Civics Honors Chapter Two: Origins of American Government Section One: Our Political Beginnings Limited Government Representative government Magna Carta Petition of Right English Bill of Rights Charter
The United States Constitution. The Supreme Law of the Land
 The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land The Articles Prove Unstable Federal gov t could declare war and other foreign affairs Federal gov t have no power to collect taxes, relying only
The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land The Articles Prove Unstable Federal gov t could declare war and other foreign affairs Federal gov t have no power to collect taxes, relying only
Constitutional Convention. May 1787
 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Annapolis Convention September 11 to September 14, 1786 Annapolis, Maryland Purpose - How to fix the articles of confederation Alexander Hamilton (New York) MUST resolve
Constitutional Convention May 1787 Annapolis Convention September 11 to September 14, 1786 Annapolis, Maryland Purpose - How to fix the articles of confederation Alexander Hamilton (New York) MUST resolve
The Constitutional Convention formed the plan of government that the United States still has today.
 2 Creating the Constitution MAIN IDEA The states sent delegates to a convention to solve the problems of the Articles of Confederation. WHY IT MATTERS NOW The Constitutional Convention formed the plan
2 Creating the Constitution MAIN IDEA The states sent delegates to a convention to solve the problems of the Articles of Confederation. WHY IT MATTERS NOW The Constitutional Convention formed the plan
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Articles of Confederation. Essential Question:
 Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton
 Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
Ratifying the Constitution
 Ratifying the Constitution Signing the Constitution Once the debate ended, Governor Morris of New Jersey put the Constitution in its final form. He competed the task of hand-writing 4,300 words in two
Ratifying the Constitution Signing the Constitution Once the debate ended, Governor Morris of New Jersey put the Constitution in its final form. He competed the task of hand-writing 4,300 words in two
Unit 4 Writing the Constitution Concepts to Review
 Unit 4 Writing the Constitution Concepts to Review CAUSE AND EFFECTS OF MAJOR ERAS AND EVENTS IN U.S. HISTORY THROUGH 1877 Writing the Constitution Shays Rebellion Philadelphia Convention 1787 Great Compromise
Unit 4 Writing the Constitution Concepts to Review CAUSE AND EFFECTS OF MAJOR ERAS AND EVENTS IN U.S. HISTORY THROUGH 1877 Writing the Constitution Shays Rebellion Philadelphia Convention 1787 Great Compromise
Section Preview. Toward a New Constitution. Section Chapter 14: With Libery and Justice, the Federal Government
 Section Preview As you read, look for: reasons for calling for a constitutional convention, important issues at the Constitutional Convention, method of amending the Constitution, basic principles of our
Section Preview As you read, look for: reasons for calling for a constitutional convention, important issues at the Constitutional Convention, method of amending the Constitution, basic principles of our
Chapter 25 Section 1. Section 1. Terms and People
 Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
Chapter 2. Government
 Chapter 2 Government The way the United States government is organized, its powers, and its limitations, are based on ideas about government that were brought to these shores by the English colonist. Three
Chapter 2 Government The way the United States government is organized, its powers, and its limitations, are based on ideas about government that were brought to these shores by the English colonist. Three
OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS
 CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
Establishing A New Government: Creating a Government. Chapter 4 Concept 2
 Establishing A New Government: Creating a Government Chapter 4 Concept 2 4.2 Creating a Government How did the decisions made at the Constitutional Convention affect the balance of power in the new nation?
Establishing A New Government: Creating a Government Chapter 4 Concept 2 4.2 Creating a Government How did the decisions made at the Constitutional Convention affect the balance of power in the new nation?
The United States Constitution. The Supreme Law of the Land
 The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States
The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States
Constitution Unit Test
 Constitution Unit Test Eighth Amendment Excessive fines cannot be imposed. Excessive bail cannot be required. 1. Which sentence completes this diagram? A. People cannot be forced to be witnesses against
Constitution Unit Test Eighth Amendment Excessive fines cannot be imposed. Excessive bail cannot be required. 1. Which sentence completes this diagram? A. People cannot be forced to be witnesses against
Chapter 3 Constitution. Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook
 Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
Gov t was needed to maintain peace. Gov t is not all powerful Power is limited to what the people give to it
 Ordered Government Gov t was needed to maintain peace Limited Government*********** Gov t is not all powerful Power is limited to what the people give to it Representative Government Gov t should serve
Ordered Government Gov t was needed to maintain peace Limited Government*********** Gov t is not all powerful Power is limited to what the people give to it Representative Government Gov t should serve
CREATING A GOVERNMENT
 Let us not be afraid to view with a steady eye the dangers with which we are surrounded. Are we not on the eve of a war, which is only to be prevented by the hopes from this convention? CREATING A GOVERNMENT
Let us not be afraid to view with a steady eye the dangers with which we are surrounded. Are we not on the eve of a war, which is only to be prevented by the hopes from this convention? CREATING A GOVERNMENT
HIST 1301 Part Two. 6: The Republican Experiment
 HIST 1301 Part Two 6: The Republican Experiment The States and the Confederation 1776-1788 During the Revolution, state Governments formed first. 2 min. 40 sec. Each state had a written constitution. Each
HIST 1301 Part Two 6: The Republican Experiment The States and the Confederation 1776-1788 During the Revolution, state Governments formed first. 2 min. 40 sec. Each state had a written constitution. Each
Why do you think the Framers organized the new country as a republic, when most countries in the world (in 1783) were ruled by a king or queen?
 NAME: Date: U.S. History CHAPTER 7 PACKET ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is a constitution? 2. What is a republic? 3. What was the Articles of Confederation? 4. How was state and national power divided under
NAME: Date: U.S. History CHAPTER 7 PACKET ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS: 1. What is a constitution? 2. What is a republic? 3. What was the Articles of Confederation? 4. How was state and national power divided under
FEDERALISTS, ANTI-FEDERALISTS AND THE CONSTITUTION SS.7.C.1.8
 FEDERALISTS, ANTI-FEDERALISTS AND THE CONSTITUTION SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the ratification of the Constitution and inclusion of a bill of
FEDERALISTS, ANTI-FEDERALISTS AND THE CONSTITUTION SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the ratification of the Constitution and inclusion of a bill of
Wednesday, February 29 th
 Ratification & New Government 1 Wednesday, February 29 th Final version of Essay 1 and Change Memo: due March 8 th or 9 th at the beginning of lab. Post a digital copy of final version of Essay 1 to Turn-It-In
Ratification & New Government 1 Wednesday, February 29 th Final version of Essay 1 and Change Memo: due March 8 th or 9 th at the beginning of lab. Post a digital copy of final version of Essay 1 to Turn-It-In
The Constitution. Multiple-Choice Questions
 2 The Constitution Multiple-Choice Questions 1. At the Constitutional Convention, the delegates agreed that slaves would be counted as of a person for determining population for representation in the House
2 The Constitution Multiple-Choice Questions 1. At the Constitutional Convention, the delegates agreed that slaves would be counted as of a person for determining population for representation in the House
Creating Our. Constitution. Key Terms. delegates equal representation executive federal system framers House of Representatives judicial
 Lesson 2 Creating Our Constitution Key Terms delegates equal representation executive federal system framers House of Representatives judicial What You Will Learn to Do Explain how the Philadelphia Convention
Lesson 2 Creating Our Constitution Key Terms delegates equal representation executive federal system framers House of Representatives judicial What You Will Learn to Do Explain how the Philadelphia Convention
T H E C O N F E D E R A T I O N A N D T H E C O N S T I T U T I O N C H A P T E R 7 A P U S H I S T O R Y
 T H E C O N F E D E R A T I O N A N D T H E C O N S T I T U T I O N C H A P T E R 7 A P U S H I S T O R Y LEARNING GOAL: Students will be able to explain the growth of the new governing systems in the
T H E C O N F E D E R A T I O N A N D T H E C O N S T I T U T I O N C H A P T E R 7 A P U S H I S T O R Y LEARNING GOAL: Students will be able to explain the growth of the new governing systems in the
Creating the Constitution
 Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50
 Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
The Constitution: From Ratification to Amendments. US Government Fall, 2014
 The Constitution: From Ratification to Amendments US Government Fall, 2014 Origins of American Government Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely, from England
The Constitution: From Ratification to Amendments US Government Fall, 2014 Origins of American Government Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely, from England
2:Forging a New Constitution. Essential Question How do new ideas change the way people live?
 2:Forging a New Constitution Essential Question How do new ideas change the way people live? The Need for Change Bold action helped the nation overcome the serious shortcomings of the Articles of Confederation.
2:Forging a New Constitution Essential Question How do new ideas change the way people live? The Need for Change Bold action helped the nation overcome the serious shortcomings of the Articles of Confederation.
The Convention Leaders
 The Convention Leaders When Thomas Jefferson heard who was attending the Constitutional Convention, he called it an assembly of demigods because the members were so rich in education and political experience.
The Convention Leaders When Thomas Jefferson heard who was attending the Constitutional Convention, he called it an assembly of demigods because the members were so rich in education and political experience.
Land Ordinance of 1785
 Unit 3 SSUSH5 Investigate specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution. a. Examine the strengths of the Articles of Confederation,
Unit 3 SSUSH5 Investigate specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution. a. Examine the strengths of the Articles of Confederation,
Debating the Constitution
 SECTION 3 A Bill of Rights A bill of rights is what the people are entitled to against every government on earth, general or particular; and what no just government should refuse or rest on inference.
SECTION 3 A Bill of Rights A bill of rights is what the people are entitled to against every government on earth, general or particular; and what no just government should refuse or rest on inference.
Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings. Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings. Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings. Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings
 Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings The US government has its roots in English history Limited Government The concept that government is limited in what it can and cannot do Representative Government Government
Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings The US government has its roots in English history Limited Government The concept that government is limited in what it can and cannot do Representative Government Government
2. Divided Convention. 3. Inside the Constitution. Constitution replaced the Articles---becomes the law of the land.
 2. Divided Convention notes7 9/13 states needed to ratify (to approve) Political parties begin Federalists: supported the Constitution The Federalist ---essays support Constitution Anti-Federalists: against
2. Divided Convention notes7 9/13 states needed to ratify (to approve) Political parties begin Federalists: supported the Constitution The Federalist ---essays support Constitution Anti-Federalists: against
Constitutional Convention
 Constitutional Convention I INTRODUCTION Constitutional Convention, meeting during the summer of 1787 at which delegates from 12 states wrote the Constitution of the United States. At the convention in
Constitutional Convention I INTRODUCTION Constitutional Convention, meeting during the summer of 1787 at which delegates from 12 states wrote the Constitution of the United States. At the convention in
Chinmay Sridhar, Angel Weng, Benjamin Zhang APUS, Buggé, Period 1 Chapter 7, Topic 2: Newburgh Conspiracy
 Chinmay Sridhar, Angel Weng, Benjamin Zhang APUS, Buggé, Period 1 Chapter 7, Topic 2: Newburgh Conspiracy Land Grants Land Ordinance (1785) Northwest Ordinance (1787) Who Made by Congress under Articles
Chinmay Sridhar, Angel Weng, Benjamin Zhang APUS, Buggé, Period 1 Chapter 7, Topic 2: Newburgh Conspiracy Land Grants Land Ordinance (1785) Northwest Ordinance (1787) Who Made by Congress under Articles
Roles: Narrator One Narrator Two Narrator Three Narrator Four Connecticut New York Pennsylvania Massachusetts New Jersey
 ead the book aloud to the class so that they may become acquainted with the story and vocabulary. Next, hand out copies of The Reader s Theater script to seventeen students. Ask any remaining students
ead the book aloud to the class so that they may become acquainted with the story and vocabulary. Next, hand out copies of The Reader s Theater script to seventeen students. Ask any remaining students
Chapter 9: The Confederation and the Constitution,
 APUSH CH 9+10 Lecture Name: Hour: Chapter 9: The Confederation and the Constitution, 1776-1790 I. From Confederation to Constitution A. The Articles of Confederation: An Attempt at Constitution-Making
APUSH CH 9+10 Lecture Name: Hour: Chapter 9: The Confederation and the Constitution, 1776-1790 I. From Confederation to Constitution A. The Articles of Confederation: An Attempt at Constitution-Making
Shays. Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt.
 Shays Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt. 1. Constitutional Convention: May to Sept. 1787 2. Divided Convention 9/13 states needed to
Shays Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt. 1. Constitutional Convention: May to Sept. 1787 2. Divided Convention 9/13 states needed to
INTRODUCTION TO UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT: Foundations of U.S. Democracy. Constitutional Convention: Key Agreements and the Great Compromise
 Constitutional Convention: Key Agreements and the Great Compromise Virginia Plan proposed on May 29, 1787 This plan was also known as the Randolph Resolution, since it was proposed by Edmund Randolph of
Constitutional Convention: Key Agreements and the Great Compromise Virginia Plan proposed on May 29, 1787 This plan was also known as the Randolph Resolution, since it was proposed by Edmund Randolph of
but given the customs of the time touching personal honor, it made perfect sense. by Charles Wilson
 3 A New Constitution How are you today, my dear General! W ith these words, Gouverneur Morris greeted General George Washington, after slapping him genially on the back. Morris, a Pennsylvania delegate
3 A New Constitution How are you today, my dear General! W ith these words, Gouverneur Morris greeted General George Washington, after slapping him genially on the back. Morris, a Pennsylvania delegate
US Government Chapter 2 Section 1 Review
 Class: Date: US Government Chapter 2 Section 1 Review True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. Freedom of [people] under government is to have a standing rule to live by... made by the
Class: Date: US Government Chapter 2 Section 1 Review True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. Freedom of [people] under government is to have a standing rule to live by... made by the
Wednesday, September 28 th
 Wednesday, September 28 th Midterm #1: Monday, Sept. 26 th to Thursday, Sept. 29 th Wednesday ($5 late fee) Thursday ($7 late fee) Must have test in hand by 11 am Exam in Testing Center. Be sure to go
Wednesday, September 28 th Midterm #1: Monday, Sept. 26 th to Thursday, Sept. 29 th Wednesday ($5 late fee) Thursday ($7 late fee) Must have test in hand by 11 am Exam in Testing Center. Be sure to go
The Bill of Rights to the United States Constitution. What does the term amend mean?
 The Bill of Rights to the United States Constitution What does the term amend mean? The Bill of Rights First ten amendments to the United States Constitution Introduced by James Madison to the First United
The Bill of Rights to the United States Constitution What does the term amend mean? The Bill of Rights First ten amendments to the United States Constitution Introduced by James Madison to the First United
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes
 Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
Once a year, each state would select a delegation to send to the capital city.
 In November 1777, the Continental Congress adopted the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union. This was a plan for a loose union of the states under Congress. Once a year, each state would select
In November 1777, the Continental Congress adopted the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union. This was a plan for a loose union of the states under Congress. Once a year, each state would select
U.S. Constitution PSCI 1040
 PSCI 1040 Purposes of a Constitution Organize and empower the government Limit the powers of government. Many consider limited government to be the essence of constitutional government. 2 Articles of Confederation
PSCI 1040 Purposes of a Constitution Organize and empower the government Limit the powers of government. Many consider limited government to be the essence of constitutional government. 2 Articles of Confederation
Colonies Become States
 Colonies Become States Colonies already had their own individual governments before the 1776 Declaration 11 of 13 colonies had State Constitutions Constitution a document that states rules under which
Colonies Become States Colonies already had their own individual governments before the 1776 Declaration 11 of 13 colonies had State Constitutions Constitution a document that states rules under which
Four reasons we need government
 Four reasons we need government 1. Need for Law and Order - Government makes laws to protect citizens, and punishes those who break the law. Laws provide order in a society. This allows citizens to live
Four reasons we need government 1. Need for Law and Order - Government makes laws to protect citizens, and punishes those who break the law. Laws provide order in a society. This allows citizens to live
Constitutional Convention
 2014 Delegates Remember a delegate is someone who is chosen to speak for others, or to represent them. The delegates represented each of the states and consisted of: Wealthy and educated landowners, business
2014 Delegates Remember a delegate is someone who is chosen to speak for others, or to represent them. The delegates represented each of the states and consisted of: Wealthy and educated landowners, business
The Federalist Papers. Day 1: Constitutional Convention 2/9/2018. In Search of Original Intent
 The Federalist Papers In Search of Original Intent Day 1: Background 10of Constitutional Convention; Purpose of Federalist Papers; Federalist No. 1 Constitutional Convention 1 Facts about the Constitutional
The Federalist Papers In Search of Original Intent Day 1: Background 10of Constitutional Convention; Purpose of Federalist Papers; Federalist No. 1 Constitutional Convention 1 Facts about the Constitutional
The Three Branches of Government include the executive, the legislative, and the
 Three Branches of the US Government The Three Branches of Government include the executive, the legislative, and the judicial branches. Each branch has a special role in the function of the United States
Three Branches of the US Government The Three Branches of Government include the executive, the legislative, and the judicial branches. Each branch has a special role in the function of the United States
Amuse Their Minds Publishing. Read, Write and Learn Copybooks: Copywork with a Purpose. Historical US Documents Series: The Articles of Confederation
 Amuse Their Minds Publishing Read, Write and Learn Copybooks: Copywork with a Purpose. Historical US Documents Series: The Articles of Confederation The Articles of Confederation National Archives Grades
Amuse Their Minds Publishing Read, Write and Learn Copybooks: Copywork with a Purpose. Historical US Documents Series: The Articles of Confederation The Articles of Confederation National Archives Grades
A More Perfect Union. Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation
 A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
How Shall We Govern Ourselves?
 How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
United States Constitutional Law: Theory, Practice, and Interpretation
 United States Constitutional Law: Theory, Practice, and Interpretation Class 1: Introduction to Course and Constitutional Law Monday, December 17, 2018 Dane S. Ciolino A.R. Christovich Professor of Law
United States Constitutional Law: Theory, Practice, and Interpretation Class 1: Introduction to Course and Constitutional Law Monday, December 17, 2018 Dane S. Ciolino A.R. Christovich Professor of Law
Federalist 55 James Madison
 FEDERALIST 319 Federalist James Madison Under the Constitution s original formula, the House would have sixtyfive members. This number was too small according to Anti-Federalists. Publius employs a number
FEDERALIST 319 Federalist James Madison Under the Constitution s original formula, the House would have sixtyfive members. This number was too small according to Anti-Federalists. Publius employs a number
The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions
 The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions provide clear definition of rights describe clear limits
The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions provide clear definition of rights describe clear limits
ARTICLES OF CONDEDERATION: RATIFICATION AND ATTEMPTS TO AMEND
 ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION ARTICLES OF CONDEDERATION: RATIFICATION AND ATTEMPTS TO AMEND TIME AND GRADE LEVEL One 45 or 50 minute class period in a Grade 9-12 US history, civics, or government course. PURPOSE
ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION ARTICLES OF CONDEDERATION: RATIFICATION AND ATTEMPTS TO AMEND TIME AND GRADE LEVEL One 45 or 50 minute class period in a Grade 9-12 US history, civics, or government course. PURPOSE
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government
 Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government United States Government Fall, 2017 Origins of American Political Ideals Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely,
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government United States Government Fall, 2017 Origins of American Political Ideals Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely,
Transcript of Articles of Confederation (1777)
 www.ourdocuments.gov October 21, 2010 Transcript of Articles of Confederation (1777) To all to whom these Presents shall come, we, the undersigned, Delegates of the States affixed to our Names, send greeting:
www.ourdocuments.gov October 21, 2010 Transcript of Articles of Confederation (1777) To all to whom these Presents shall come, we, the undersigned, Delegates of the States affixed to our Names, send greeting:
Chapter 8 and 9 Review
 Chapter 8 and 9 Review A constitution is a document that outlines the powers of government. Constitution (1787) James Madison formulated many of the ideas included in the Constitution and is known as the
Chapter 8 and 9 Review A constitution is a document that outlines the powers of government. Constitution (1787) James Madison formulated many of the ideas included in the Constitution and is known as the
THE CONSTITUTION AND ITS HISTORY
 THE CONSTITUTION AND ITS HISTORY 1 CHAPTER Outline I. Introduction II. History Leading up to the Constitution A. Articles of Confederation 1. A firm league of friendship a. Each state was to remain (1)
THE CONSTITUTION AND ITS HISTORY 1 CHAPTER Outline I. Introduction II. History Leading up to the Constitution A. Articles of Confederation 1. A firm league of friendship a. Each state was to remain (1)
We the People of the United States,
 We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings
We the People of the United States, in Order to form a more perfect Union, establish Justice, insure domestic Tranquility, provide for the common defence, promote the general Welfare, and secure the Blessings
Bill of Rights. 1. Meet the Source (2:58) Interview with Whitman Ridgway (Professor, University of Maryland, College Park)
 Interview with Whitman Ridgway (Professor, University of Maryland, College Park) Bill of Rights 1. Meet the Source (2:58) Well, the Bill of Rights, in my opinion, is a very remarkable document because
Interview with Whitman Ridgway (Professor, University of Maryland, College Park) Bill of Rights 1. Meet the Source (2:58) Well, the Bill of Rights, in my opinion, is a very remarkable document because
Articles of Confederation vs. Constitution
 Articles of Confederation vs. Analysis Objective What kind of government was set up by the Articles of Confederation? How does this compare to the US? Directions: Analyze the timeline below to understand
Articles of Confederation vs. Analysis Objective What kind of government was set up by the Articles of Confederation? How does this compare to the US? Directions: Analyze the timeline below to understand
American Democracy Now Chapter 2: The Constitution
 American Democracy Now Chapter 2: The Constitution Multiple-Choice Questions: 1. Which of these countries employs an unwritten constitution? a. the United States b. Great Britain c. Venezuela d. Kenya
American Democracy Now Chapter 2: The Constitution Multiple-Choice Questions: 1. Which of these countries employs an unwritten constitution? a. the United States b. Great Britain c. Venezuela d. Kenya
Handout B: Madison EXCERPTS FROM FEDERALIST NO. 47 BY JAMES MADISON. DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources
 DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources Unit 2: The Purpose of Government Reading: Separation of Powers and Checks and Balances Activity: Montesquieu and Madison Handout
DOCUMENTS of FREEDOM History, Government & Economics through Primary Sources Unit 2: The Purpose of Government Reading: Separation of Powers and Checks and Balances Activity: Montesquieu and Madison Handout
PEARCE PRESS. Is freedom a right or a privilege? Spelling quiz on Thursday. Reading test on Friday. iready mid-year assessment this Friday.
 Archimedean Academy November 26, 2018 PEARCE PRESS Is freedom a right or a privilege? Monday Reading passage: Compromise: Creating the US Constitution Review spelling/vocabulary BrainPOP due Wednesday
Archimedean Academy November 26, 2018 PEARCE PRESS Is freedom a right or a privilege? Monday Reading passage: Compromise: Creating the US Constitution Review spelling/vocabulary BrainPOP due Wednesday
Foundations of American Government
 Foundations of American Government Government The institution through which a society makes and enforces its public policies made up of those people who have authority and control over other people public
Foundations of American Government Government The institution through which a society makes and enforces its public policies made up of those people who have authority and control over other people public
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes
 Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
Name: 8 th Grade U.S. History. STAAR Review. Constitution
 8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Constitution FORT BURROWS 2018 VOCABULARY Confederation - A group of loosely connected nations or states that work together for mutual benefit. Republic - A system
8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Constitution FORT BURROWS 2018 VOCABULARY Confederation - A group of loosely connected nations or states that work together for mutual benefit. Republic - A system
AKS M 49 C 30 a-d D 32 a-c D 33 a-c D 34 a-b BUILDING A NEW NATION
 AKS M 49 C 30 a-d D 32 a-c D 33 a-c D 34 a-b BUILDING A NEW NATION The official end of the Revolutionary War was the signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1783. The newly independent US and GA now faced the
AKS M 49 C 30 a-d D 32 a-c D 33 a-c D 34 a-b BUILDING A NEW NATION The official end of the Revolutionary War was the signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1783. The newly independent US and GA now faced the
Primary Sources: The Articles of Confederation
 Primary Sources: The Articles of Confederation By Original document from the public domain, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.29.16 Word Count 1,995 The original cover of the Articles of Confederation, printed
Primary Sources: The Articles of Confederation By Original document from the public domain, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.29.16 Word Count 1,995 The original cover of the Articles of Confederation, printed
Learning Check. You CAN use your notes. You CAN NOT use your neighbor!
 Learning Check You CAN use your notes. You CAN NOT use your neighbor! Constitution and Bill of Rights QC Standards B.1.i. Interpret the ideas and principles expressed in the U.S. Constitution B.1.j. Explain
Learning Check You CAN use your notes. You CAN NOT use your neighbor! Constitution and Bill of Rights QC Standards B.1.i. Interpret the ideas and principles expressed in the U.S. Constitution B.1.j. Explain
CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION
 CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Objectives Why did the Constitutional Convention draft a new plan for government? How did the rival plans for the new government differ? What other conflicts required the Framers
CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Objectives Why did the Constitutional Convention draft a new plan for government? How did the rival plans for the new government differ? What other conflicts required the Framers
What types of things did the new states do to make the governments more democratic?
 Chapter 8 Confederation to Constitution pg. 218 241 8 1 The Confederation Era pg. 221 225 Moving West and New State Governments Into which areas did American settlement expand in the late 1700s? What types
Chapter 8 Confederation to Constitution pg. 218 241 8 1 The Confederation Era pg. 221 225 Moving West and New State Governments Into which areas did American settlement expand in the late 1700s? What types
10/13/14 GOVERNMENT BY THE STATES OPPOSITION TO THE ARTICLES CHAPTER 5 THE CONSTITUTION OF THE UNITED STATES ( )
 1 CHAPTER 5 THE CONSTITUTION OF THE UNITED STATES (1776 1800) Mr. Anderson, M.Ed., J.D. GOVERNMENT BY THE STATES Early Gov t Articles of Confederation Set of laws to govern the U.S. most power w/ the states
1 CHAPTER 5 THE CONSTITUTION OF THE UNITED STATES (1776 1800) Mr. Anderson, M.Ed., J.D. GOVERNMENT BY THE STATES Early Gov t Articles of Confederation Set of laws to govern the U.S. most power w/ the states
The Electoral College: A Scripted Conversation
 The Electoral College: A Scripted Conversation Rick Kelm Ripon High School Ripon, WI Introduction One of the most difficult and contentious issues in the Constitutional Convention of 1787 was provisions
The Electoral College: A Scripted Conversation Rick Kelm Ripon High School Ripon, WI Introduction One of the most difficult and contentious issues in the Constitutional Convention of 1787 was provisions
1. According to Washington, what is needed to prevent an uprising like Shays Rebellion? [1]
![1. According to Washington, what is needed to prevent an uprising like Shays Rebellion? [1] 1. According to Washington, what is needed to prevent an uprising like Shays Rebellion? [1]](/thumbs/83/87708147.jpg) Part A Short-Answer Questions Directions: Analyze the documents and answer the short-answer questions that follow each document in the space provided. Document 1 We are fast verging to anarchy and confusion!
Part A Short-Answer Questions Directions: Analyze the documents and answer the short-answer questions that follow each document in the space provided. Document 1 We are fast verging to anarchy and confusion!
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #70 Aims: SWBAT understand and explain the debate over representation SWBAT identify and explain the Virginia Plan and
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #70 Aims: SWBAT understand and explain the debate over representation SWBAT identify and explain the Virginia Plan and
3: A New Plan of Government. Essential Question: How Do Governments Change?
 3: A New Plan of Government Essential Question: How Do Governments Change? The Constitution s Source Guiding Question: From where did the Framers of the Constitution borrow their ideas about government?
3: A New Plan of Government Essential Question: How Do Governments Change? The Constitution s Source Guiding Question: From where did the Framers of the Constitution borrow their ideas about government?
CONSTITUTION WRITE THE RED TEXT FOR NOTES! SCAVENGER HUNT AT THE END OF THE POWERPOINT USE LINK
 CONSTITUTION WRITE THE RED TEXT FOR NOTES! SCAVENGER HUNT AT THE END OF THE POWERPOINT USE LINK Why Recognize this Document? The Constitution is a handwritten document which is over 200 years old. It is
CONSTITUTION WRITE THE RED TEXT FOR NOTES! SCAVENGER HUNT AT THE END OF THE POWERPOINT USE LINK Why Recognize this Document? The Constitution is a handwritten document which is over 200 years old. It is
Articles of Confederation [first printing, first edition] Lancaster, Pennsylvania, 1777 Book, 26 pages. ARTICLES. OF [Illegible] 1777 CONFEDERATION
![Articles of Confederation [first printing, first edition] Lancaster, Pennsylvania, 1777 Book, 26 pages. ARTICLES. OF [Illegible] 1777 CONFEDERATION Articles of Confederation [first printing, first edition] Lancaster, Pennsylvania, 1777 Book, 26 pages. ARTICLES. OF [Illegible] 1777 CONFEDERATION](/thumbs/79/78892399.jpg) Articles of Confederation [first printing, first edition] Lancaster, Pennsylvania, 1777 Book, 26 pages. [2] ARTICLES OF [Illegible] 1777 CONFEDERATION AND Perpetual Union BETWEEN THE S T A T E S OF NEW-HAMPSHIRE,
Articles of Confederation [first printing, first edition] Lancaster, Pennsylvania, 1777 Book, 26 pages. [2] ARTICLES OF [Illegible] 1777 CONFEDERATION AND Perpetual Union BETWEEN THE S T A T E S OF NEW-HAMPSHIRE,
understanding CONSTITUTION
 understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
understanding the CONSTITUTION Contents The Articles of Confederation The Constitutional Convention The Principles of the Constitution The Preamble The Legislative Branch The Executive Branch The Judicial
Federalists and Antifederalists January 25, 2011 Biographies of the Nation Danice Toyias,
 Constitution Debate, pg. 1 of 1 Federalists and Antifederalists January 25, 2011 Biographies of the Nation Danice Toyias, danice.toyias@mchce.net Lesson Topic and Focus This lesson utilizes what I call
Constitution Debate, pg. 1 of 1 Federalists and Antifederalists January 25, 2011 Biographies of the Nation Danice Toyias, danice.toyias@mchce.net Lesson Topic and Focus This lesson utilizes what I call
Birth of a Nation. Founding Fathers. Benjamin Rush. John Hancock. Causes
 Birth of a Nation Causes British debts after the French and Indian War = new taxes Stamp Act Tea Act Many colonists felt their rights as Englishmen were being violated 1 2 The American Revolution After
Birth of a Nation Causes British debts after the French and Indian War = new taxes Stamp Act Tea Act Many colonists felt their rights as Englishmen were being violated 1 2 The American Revolution After
CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT
 CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT The Constitution set out our rules for government. It explains what our government can and cannot do. It reflects are experience as a colony as well as ideas from Europe
CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT The Constitution set out our rules for government. It explains what our government can and cannot do. It reflects are experience as a colony as well as ideas from Europe
Chapter 6: Framing the Constitution
 Chapter 6: Framing the Constitution Objectives: We will examine the positions of those who called for a strong centralized government. We will examine the issues, debates, and compromise of the Constitutional
Chapter 6: Framing the Constitution Objectives: We will examine the positions of those who called for a strong centralized government. We will examine the issues, debates, and compromise of the Constitutional
Points in opposition to OHIO HJR3
 Citizens Against an Article V Convention judicaler@hotmail.com Points in opposition to OHIO HJR3 I. How would HJR3 change the U.S. Constitution? HJR3 is an application to Congress from Ohio for Congress
Citizens Against an Article V Convention judicaler@hotmail.com Points in opposition to OHIO HJR3 I. How would HJR3 change the U.S. Constitution? HJR3 is an application to Congress from Ohio for Congress
AP American Government
 AP American Government WILSON, CHAPTER 2 The Constitution OVERVIEW The Framers of the Constitution sought to create a government capable of protecting liberty and preserving order. The solution they chose
AP American Government WILSON, CHAPTER 2 The Constitution OVERVIEW The Framers of the Constitution sought to create a government capable of protecting liberty and preserving order. The solution they chose
Unit 3 Section 1 Articles and Early Government.notebook. January 18, Vocabulary. Westward Ho! Need for State and National Government
 8.1 Vocabulary Wilderness Road Republic Articles of Confederation Land Ordinance of 1785 Northwest Territory Northwest Ordinance Shays's Rebellion Chapter Connection: Articles of Confederation were not
8.1 Vocabulary Wilderness Road Republic Articles of Confederation Land Ordinance of 1785 Northwest Territory Northwest Ordinance Shays's Rebellion Chapter Connection: Articles of Confederation were not
3. Popular sovereignty - Rule by the people - People give their consent to be governed by government officials - People have the right to revolution
 Unit I Notes Purposes of Government - Maintain social order - Provide public services - Provide security and defense - Provide for the economy - Governments get authority from: o Their legitimacy o Ability
Unit I Notes Purposes of Government - Maintain social order - Provide public services - Provide security and defense - Provide for the economy - Governments get authority from: o Their legitimacy o Ability
The Constitution CHAPTER 2 CHAPTER OUTLINE WITH KEYED-IN RESOURCES
 CHAPTER 2 The Constitution CHAPTER OUTLINE WITH KEYED-IN RESOURCES I. The problem of liberty (THEME A: THE POLITICAL PHILOSOPHY OF THE FOUNDERS) A. Colonists were focused on traditional liberties 1. The
CHAPTER 2 The Constitution CHAPTER OUTLINE WITH KEYED-IN RESOURCES I. The problem of liberty (THEME A: THE POLITICAL PHILOSOPHY OF THE FOUNDERS) A. Colonists were focused on traditional liberties 1. The
Constitution of the United States. Article. I.
 Constitution of the United States Article. I. Section. 1. All legislative Powers herein granted shall be vested in a Congress of the United States, which shall consist of a Senate and House of Representatives.
Constitution of the United States Article. I. Section. 1. All legislative Powers herein granted shall be vested in a Congress of the United States, which shall consist of a Senate and House of Representatives.
