The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions
|
|
|
- Gertrude Shepherd
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 The States: Experiments in Republicanism State constitutions served as experiments in republican government The people demand written constitutions provide clear definition of rights describe clear limits of government Lessons later applied to constructing central government Major break with England s unwritten constitution
3 Natural Rights and the State Constitutions State constitutions guaranteed natural rights Freedom of religion, speech, and the press. Private property Trial by jury Governors weakened Elected legislatures given most power
4 African Americans in the New Republic African-Americans embrace Declaration s stress on natural rights Demand right to freedom in petitions, suits Northern states gradually abolish slavery Southerners debate abolition Some privately free slaves Economic motives overcome republican ideals
5 Limiting Women s Freedom Women demand the natural right of equality Contribute to new society through Republican Motherhood Women more assertive in divorce, economic life Denied political and legal rights
6 Postponing full liberty Revolution limited in extension of rights Introduced ideal of freedom and equality
7 Government under Articles of Confederation In charge of foreign and Native American relations, military, and disputes between states
8 Weaknesses of Articles of Confederation Articles of Confederation severely limited central government s authority over states Each state had one vote No executive or judicial branch No taxing power States taxed each other s goods Amendments required unanimity No national currency
9 Crises of Lack of Power Barbary pirates raided ships in Mediterranean Unable to protect settlers from Indians Shay s Rebellion (1787) Tax revolt of indebted veterans Symbolized breakdown in law and order as perceived by propertied classes Strengthened support for new central government
10 Northwest Ordinance: The Confederation s Major Achievement Provided for eventual statehood of new lands Created three to five new territories in Northwest Population of 5000 may elect Assembly Population of 60,000 may petition for statehood Bill of Rights provided Slavery outlawed
11 The Nationalist Critique Restoration of trade with Britain caused trade deficit and hard currency shortage Congress unable to address trade, inflation, and debt Dissatisfaction with Articles of Confederation
12 Constitutional Convention Philadelphia: May to September Delegates George Washington: Chairman Federalists those who favored a strong National Government Anti-Federalists those who favored stronger state governments
13 Virginia Plan vs. New Jersey Plan Virginia Plan Both New Jersey Plan Called for a bicameral legislature (two houses) Representatives in legislatures based on state population Supported by large states Want a strong central government with three branches Called for a unicameral legislature (one house) Each state given one representative each. Supported by small states who fear losing power under a national government
14 The Great Compromise Bicameral Legislature House of Representatives based on population--a victory for the large states Each state given two delegates in the Senate--a victory for the small states
15 The Issue of Slavery Slavery threatens Convention s unity Northerners tend to be opposed Southerners threaten to bolt if slavery weakened Slave trade permitted to continue to 1808 Great as the evil is, a dismemberment of the Union would be worse. --James Madison Three-fifths Compromise: slaves were counted as 3/5 of one person for purposes of taxation and representation
16 Road to Ratification Convention seeks to bypass vested interests of state legislatures Power of ratification to special state conventions Constitution to go into effect on approval by nine state conventions New York Federalist Papers written by Madison, Hamilton, and Jay
17 Federalists vs. Anti-federalists Federalists Supported the Constitution Supported a strong central government Well-organized The Federalist Papers Anti-federalists Opposed to the Constitution Distrusted any government removed from direct control of the people Suspected the new Constitution favored the rich and powerful
18 Progress of Ratification No clear correlation between social status and support for Constitution Succeeded in winning ratification in eleven states by June 1788 North Carolina ratified November 1789 Rhode Island ratified May 1790
19 Adding the Bill of Rights The fruit of anti-federalist activism Adding Bill of Rights forestalled Second Constitutional Convention Purpose was to protect individual rights from government interference Rights included: Freedom of assembly, speech, religion, the press, and bearing arms Speedy trial by a jury of peers No unreasonable searches First ten amendments added by December 1791
New Nation. establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s
 New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
CHAPTER 9 THE CONFEDERATION & CONSTITUTION DEFINE REVOLUTION" Slavery after the Revolution 9/22/15 WAS THIS REALLY A REVOLUTION?
 CHAPTER 9 THE CONFEDERATION & CONSTITUTION DEFINE REVOLUTION" A SUDDEN AND MOMENTOUS CHANGE IN A SITUATION THE OVERTHROW AND SUDDEN CHANGE OF A GOVERNMENT WAS THIS REALLY A REVOLUTION? Slavery after the
CHAPTER 9 THE CONFEDERATION & CONSTITUTION DEFINE REVOLUTION" A SUDDEN AND MOMENTOUS CHANGE IN A SITUATION THE OVERTHROW AND SUDDEN CHANGE OF A GOVERNMENT WAS THIS REALLY A REVOLUTION? Slavery after the
AIM: How did the Articles of Confederation impact the U.S.?
 AIM: How did the Articles of Confederation impact the U.S.? Do Now: How do you think Hale Charter Academy would function if we got rid of the assistant principal, and the dean, and we allowed the individual
AIM: How did the Articles of Confederation impact the U.S.? Do Now: How do you think Hale Charter Academy would function if we got rid of the assistant principal, and the dean, and we allowed the individual
LECTURE 3-3: THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION AND THE CONSTITUTION
 LECTURE 3-3: THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION AND THE CONSTITUTION The American Revolution s democratic and republican ideals inspired new experiments with different forms of government. I. Allegiances A.
LECTURE 3-3: THE ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION AND THE CONSTITUTION The American Revolution s democratic and republican ideals inspired new experiments with different forms of government. I. Allegiances A.
The United States Constitution. The Supreme Law of the Land
 The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States
The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States
Unit 4 Writing the Constitution Concepts to Review
 Unit 4 Writing the Constitution Concepts to Review CAUSE AND EFFECTS OF MAJOR ERAS AND EVENTS IN U.S. HISTORY THROUGH 1877 Writing the Constitution Shays Rebellion Philadelphia Convention 1787 Great Compromise
Unit 4 Writing the Constitution Concepts to Review CAUSE AND EFFECTS OF MAJOR ERAS AND EVENTS IN U.S. HISTORY THROUGH 1877 Writing the Constitution Shays Rebellion Philadelphia Convention 1787 Great Compromise
End of American Revolution and Creation of American government
 End of American Revolution and Creation of American government American Revolution concludes, an independent nation develops, 1781. Articles of Confederation ratified by states March 1781 - framework for
End of American Revolution and Creation of American government American Revolution concludes, an independent nation develops, 1781. Articles of Confederation ratified by states March 1781 - framework for
A More Perfect Union. Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation
 A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
A More Perfect Union Chapter 7 Lesson 1 The Articles of Confederation 1. Eleven of the thirteen states adopted state constitutions. Connecticut and Rhode Island kept its colonial charter as its constitution
3. Popular sovereignty - Rule by the people - People give their consent to be governed by government officials - People have the right to revolution
 Unit I Notes Purposes of Government - Maintain social order - Provide public services - Provide security and defense - Provide for the economy - Governments get authority from: o Their legitimacy o Ability
Unit I Notes Purposes of Government - Maintain social order - Provide public services - Provide security and defense - Provide for the economy - Governments get authority from: o Their legitimacy o Ability
How Shall We Govern Ourselves?
 How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
How Shall We Govern Ourselves? The Articles of Confederation America s First Constitution What kind of government would the FREEDOM loving Americans create to balance LIBERTY with enough AUTHORITY to get
Chapter 25 Section 1. Section 1. Terms and People
 Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
Chapter 25 Terms and People republic a government in which the people elect their representatives unicameral legislature a lawmaking body with a single house whose representatives are elected by the people
OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS
 CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
The United States Constitution. The Supreme Law of the Land
 The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land The Articles Prove Unstable Federal gov t could declare war and other foreign affairs Federal gov t have no power to collect taxes, relying only
The United States Constitution The Supreme Law of the Land The Articles Prove Unstable Federal gov t could declare war and other foreign affairs Federal gov t have no power to collect taxes, relying only
Learning Goal. Main Points 10/24/2012. Discuss the philosophical underpinnings of the U.S. Constitution.
 Learning Goal Discuss the philosophical underpinnings of the U.S. Constitution. Main Points The weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the adoption of a new form of government Federalism becomes
Learning Goal Discuss the philosophical underpinnings of the U.S. Constitution. Main Points The weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the adoption of a new form of government Federalism becomes
The Critical Period The early years of the American Republic
 The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
The Critical Period 1781-1789 The early years of the American Republic America after the War New Political Ideas: - Greater power for the people Republic: Represent the Public America after the War State
Basic Concepts of Government The English colonists brought 3 ideas that loom large in the shaping of the government in the United States.
 Civics Honors Chapter Two: Origins of American Government Section One: Our Political Beginnings Limited Government Representative government Magna Carta Petition of Right English Bill of Rights Charter
Civics Honors Chapter Two: Origins of American Government Section One: Our Political Beginnings Limited Government Representative government Magna Carta Petition of Right English Bill of Rights Charter
During the, the majority of delegates voted to declare independence from Britain. What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution?
 What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution? A. The Stamp Act B. Boston Tea Party C. Quartering Act D. Battle of Lexington and Concord During the, the majority of delegates voted
What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution? A. The Stamp Act B. Boston Tea Party C. Quartering Act D. Battle of Lexington and Concord During the, the majority of delegates voted
Standard Indicator SOUTH CAROLINA AND THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION IN PHILADELPHIA
 Standard Indicator 8-3.2 SOUTH CAROLINA AND THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION IN PHILADELPHIA ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION First plan of government for US Adopted during Revolutionary War Weak plan of government
Standard Indicator 8-3.2 SOUTH CAROLINA AND THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION IN PHILADELPHIA ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION First plan of government for US Adopted during Revolutionary War Weak plan of government
New Nation. establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s
 New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
New Nation establishing the government of the US during the 1780s & 1790s CREATING THE CONSTITUTION From the Articles of Confederation to the Bill of Rights (1780s) The Articles of Confederation After
Chapter 2 TEST Origins of American Government
 US Government - Ried Chapter 2 TEST Origins of American Government 1)The Magna Carta was originally intended to protect the rights of which group? A. religious leaders B. kings and queens C. common people
US Government - Ried Chapter 2 TEST Origins of American Government 1)The Magna Carta was originally intended to protect the rights of which group? A. religious leaders B. kings and queens C. common people
Constitution Day September 17
 Constitution Day September 17 The Constitution Pages 61-71 How many articles are there? What are each of the first THREE articles about? ( What( it Means boxes) Based on their length, which seems most
Constitution Day September 17 The Constitution Pages 61-71 How many articles are there? What are each of the first THREE articles about? ( What( it Means boxes) Based on their length, which seems most
Creating a Nation Test Review
 Creating a Nation Test Review Question #1: Multiple Choice The Northwest ordinance of 1787 is important because. A. It sent troops to the Northwest to protect the colonies from Native Americans. B. It
Creating a Nation Test Review Question #1: Multiple Choice The Northwest ordinance of 1787 is important because. A. It sent troops to the Northwest to protect the colonies from Native Americans. B. It
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government
 Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government United States Government Fall, 2017 Origins of American Political Ideals Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely,
Chapter 2: The Beginnings of American Government United States Government Fall, 2017 Origins of American Political Ideals Colonial Period Where did ideas for government in the colonies come from? Largely,
CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT
 CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT The Constitution set out our rules for government. It explains what our government can and cannot do. It reflects are experience as a colony as well as ideas from Europe
CHAPTER 7 CREATING A GOVERNMENT The Constitution set out our rules for government. It explains what our government can and cannot do. It reflects are experience as a colony as well as ideas from Europe
Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ:
 Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ: 6.1 Introduction Like Washington, most Americans did not want to be ruled by a monarch. What they did want, though, was an effective government. Articles of Confederation,
Ch. 6 Creating the Constitution /EQ: 6.1 Introduction Like Washington, most Americans did not want to be ruled by a monarch. What they did want, though, was an effective government. Articles of Confederation,
Chapter 6. APUSH Mr. Muller
 Chapter 6 APUSH Mr. Muller Aim: How is the New Republic tested? Do Now: Thus I consent, sir, to this Constitution, because I expect no better, and because I am not sure that it is not the best. The opinions
Chapter 6 APUSH Mr. Muller Aim: How is the New Republic tested? Do Now: Thus I consent, sir, to this Constitution, because I expect no better, and because I am not sure that it is not the best. The opinions
Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation
 Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A constitution is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government.
Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A constitution is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government.
Articles of Confederation
 Articles of Confederation Do Now How is power divided in our country today? SWBAT Analyze government problems under the Articles of Confederation Activity Review the Articles of Confederation chart and
Articles of Confederation Do Now How is power divided in our country today? SWBAT Analyze government problems under the Articles of Confederation Activity Review the Articles of Confederation chart and
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Articles of Confederation. Essential Question:
 Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
Articles of Confederation Essential Question: Why was the central government s power too weak under the Articles of Confederation? Objectives Discuss the ideas that guided the new state governments. Describe
FORMING A NEW GOVERNMENT
 FORMING A NEW GOVERNMENT These questions are in random order. They will be in a different order in class tomorrow. Seven Principles Checks & Balances Federalism Individual Rights Limited Government Popular
FORMING A NEW GOVERNMENT These questions are in random order. They will be in a different order in class tomorrow. Seven Principles Checks & Balances Federalism Individual Rights Limited Government Popular
Chapter Two: Learning Objectives. Learning Objectives. The Constitution
 1 Chapter Two: The Constitution Learning Objectives 2 Explain the impact of events in the early settlements, including Jamestown (representative assembly) and Plymouth (social contract) on later political
1 Chapter Two: The Constitution Learning Objectives 2 Explain the impact of events in the early settlements, including Jamestown (representative assembly) and Plymouth (social contract) on later political
Chapter 5 section 3: Creating the Constitution textbook pages
 Chapter 5 section 3: Creating the Constitution textbook pages 163-168 The Big Idea A new constitution provided a framework for a stronger national government. Main Idea 1:The Constitutional Convention
Chapter 5 section 3: Creating the Constitution textbook pages 163-168 The Big Idea A new constitution provided a framework for a stronger national government. Main Idea 1:The Constitutional Convention
Name: 8 th Grade U.S. History. STAAR Review. Constitution
 8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Constitution FORT BURROWS 2018 VOCABULARY Confederation - A group of loosely connected nations or states that work together for mutual benefit. Republic - A system
8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Constitution FORT BURROWS 2018 VOCABULARY Confederation - A group of loosely connected nations or states that work together for mutual benefit. Republic - A system
Ratification of the Constitution. Issues
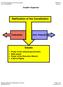 Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Constitutional Convention. May 1787
 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Annapolis Convention September 11 to September 14, 1786 Annapolis, Maryland Purpose - How to fix the articles of confederation Alexander Hamilton (New York) MUST resolve
Constitutional Convention May 1787 Annapolis Convention September 11 to September 14, 1786 Annapolis, Maryland Purpose - How to fix the articles of confederation Alexander Hamilton (New York) MUST resolve
CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION
 CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Objectives Why did the Constitutional Convention draft a new plan for government? How did the rival plans for the new government differ? What other conflicts required the Framers
CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Objectives Why did the Constitutional Convention draft a new plan for government? How did the rival plans for the new government differ? What other conflicts required the Framers
Chapter 2. Government
 Chapter 2 Government The way the United States government is organized, its powers, and its limitations, are based on ideas about government that were brought to these shores by the English colonist. Three
Chapter 2 Government The way the United States government is organized, its powers, and its limitations, are based on ideas about government that were brought to these shores by the English colonist. Three
SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution.
 Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution. a. Explain how weaknesses in the Articles of
Standards SSUSH5 The student will explain specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution. a. Explain how weaknesses in the Articles of
What types of things did the new states do to make the governments more democratic?
 Chapter 8 Confederation to Constitution pg. 218 241 8 1 The Confederation Era pg. 221 225 Moving West and New State Governments Into which areas did American settlement expand in the late 1700s? What types
Chapter 8 Confederation to Constitution pg. 218 241 8 1 The Confederation Era pg. 221 225 Moving West and New State Governments Into which areas did American settlement expand in the late 1700s? What types
Creating the Constitution
 Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
Creating the Constitution 1776-1791 US Timeline 1777-1791 1777 Patriots win Battles of Saratoga. Continental Congress passes the Articles of Confederation. 1781 Articles of Confederation go into effect.
BEGINNINGS: Political essentials and foundational ideas
 BEGINNINGS: Political essentials and foundational ideas 1689 LOCKE S SECOND TREATISE ON GOVERNMENT: Natural Rights: Life, Liberty & Property which existed before government Legitimate government depends
BEGINNINGS: Political essentials and foundational ideas 1689 LOCKE S SECOND TREATISE ON GOVERNMENT: Natural Rights: Life, Liberty & Property which existed before government Legitimate government depends
The Beginnings of a New American Government
 The Constitution The Beginnings of a New American Government Dissatisfaction grew with the Articles of Confederation as disagreements over control of waterways and trade developed. In 1785 the first meeting
The Constitution The Beginnings of a New American Government Dissatisfaction grew with the Articles of Confederation as disagreements over control of waterways and trade developed. In 1785 the first meeting
The Constitutional Convention
 The Constitutional Convention Problems like Shay s Rebellion revealed the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation This event convinced many U.S. citizens that our 1 st written plan of government needed
The Constitutional Convention Problems like Shay s Rebellion revealed the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation This event convinced many U.S. citizens that our 1 st written plan of government needed
Constitutional Convention
 Constitutional Convention How did the United States overcome the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation and provide for the organization of the new government? What role did compromise play in the
Constitutional Convention How did the United States overcome the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation and provide for the organization of the new government? What role did compromise play in the
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50
 Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
Read the Federalist #47,48,& 51 How to read the Constitution In the Woll Book Pages 40-50 The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from religious persecution Economic opportunity Independent
Name Class Date. MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term or person that matches each description. Some answers will not be used.
 Origins of American Government Section 1 MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term or person that matches each description. Some answers will not be used. 1. Idea that people should
Origins of American Government Section 1 MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term or person that matches each description. Some answers will not be used. 1. Idea that people should
Chapter Two: The Constitution
 Chapter Two: The Constitution Learning Outcomes 1. Explain how the colonial experience prepared Americans for independence. 2. Discuss the restrictions that Britain placed on the colonies and the American
Chapter Two: The Constitution Learning Outcomes 1. Explain how the colonial experience prepared Americans for independence. 2. Discuss the restrictions that Britain placed on the colonies and the American
From Revolution to Government
 From Revolution to Government The Second Continental Congress declared independence from Britain in 1776. The Revolutionary War lasted from 1775 to 1783. Congress developed a new government for America:
From Revolution to Government The Second Continental Congress declared independence from Britain in 1776. The Revolutionary War lasted from 1775 to 1783. Congress developed a new government for America:
THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION. Compromises Federalists v. Anti-Federalists
 THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Compromises Federalists v. Anti-Federalists QUICK REVIEW: FIND SOMEONE WHO Second Continental Congress Drafting of the Articles of Confederation Weaknesses International Relations
THE CONSTITUTIONAL CONVENTION Compromises Federalists v. Anti-Federalists QUICK REVIEW: FIND SOMEONE WHO Second Continental Congress Drafting of the Articles of Confederation Weaknesses International Relations
Unit 3 Section 1 Articles and Early Government.notebook. January 18, Vocabulary. Westward Ho! Need for State and National Government
 8.1 Vocabulary Wilderness Road Republic Articles of Confederation Land Ordinance of 1785 Northwest Territory Northwest Ordinance Shays's Rebellion Chapter Connection: Articles of Confederation were not
8.1 Vocabulary Wilderness Road Republic Articles of Confederation Land Ordinance of 1785 Northwest Territory Northwest Ordinance Shays's Rebellion Chapter Connection: Articles of Confederation were not
The Constitutional Convention. Chapter 2 Section 4
 The Constitutional Convention Chapter 2 Section 4 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 74 delegates allowed, 55 attended, 39 signed final Delegates to the Convention Had lots of
The Constitutional Convention Chapter 2 Section 4 Constitutional Convention May 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 74 delegates allowed, 55 attended, 39 signed final Delegates to the Convention Had lots of
What is Compromise? My friend wanted a boat more than anything. His wife kept refusing, but he bought one anyway. "I'll tell you what," he told her,
 What is Compromise? My friend wanted a boat more than anything. His wife kept refusing, but he bought one anyway. "I'll tell you what," he told her, "In the spirit of compromise, why don't you name the
What is Compromise? My friend wanted a boat more than anything. His wife kept refusing, but he bought one anyway. "I'll tell you what," he told her, "In the spirit of compromise, why don't you name the
HIST 1301 Part Two. 6: The Republican Experiment
 HIST 1301 Part Two 6: The Republican Experiment The States and the Confederation 1776-1788 During the Revolution, state Governments formed first. 2 min. 40 sec. Each state had a written constitution. Each
HIST 1301 Part Two 6: The Republican Experiment The States and the Confederation 1776-1788 During the Revolution, state Governments formed first. 2 min. 40 sec. Each state had a written constitution. Each
2. Divided Convention. 3. Inside the Constitution. Constitution replaced the Articles---becomes the law of the land.
 2. Divided Convention notes7 9/13 states needed to ratify (to approve) Political parties begin Federalists: supported the Constitution The Federalist ---essays support Constitution Anti-Federalists: against
2. Divided Convention notes7 9/13 states needed to ratify (to approve) Political parties begin Federalists: supported the Constitution The Federalist ---essays support Constitution Anti-Federalists: against
Articles of Condederation Very weak government. Why??? Five pages, 13 articles
 Articles of Condederation Very weak government. Why??? Five pages, 13 articles Establishes the name of the confederation as "The United States of America." Asserts the precedence of the separate states
Articles of Condederation Very weak government. Why??? Five pages, 13 articles Establishes the name of the confederation as "The United States of America." Asserts the precedence of the separate states
Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation
 Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation Explain how the states new constitutions reflected republican ideals. Describe the structure and powers of the national government under the Articles of Confederation.
Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation Explain how the states new constitutions reflected republican ideals. Describe the structure and powers of the national government under the Articles of Confederation.
The Constitutional Convention
 The Constitutional Convention Review Why was the Constitution necessary? Article Text Congress had no power to tax Problem Created Congress had no power to enforce treaties Every state, despite size, had
The Constitutional Convention Review Why was the Constitution necessary? Article Text Congress had no power to tax Problem Created Congress had no power to enforce treaties Every state, despite size, had
Unit 3: Building the New Nation FRQ Outlines. Prompt:Analyze the reasons for the Anti-Federalists opposition to ratifying the Constitution.
 Prompt:Analyze the reasons for the Anti-Federalists opposition to ratifying the Constitution. Re-written as a Question: What were the reasons for the Anti-Federalist opposition to ratifying the constitution?
Prompt:Analyze the reasons for the Anti-Federalists opposition to ratifying the Constitution. Re-written as a Question: What were the reasons for the Anti-Federalist opposition to ratifying the constitution?
Articles of Confederation
 Articles of Confederation What was the nation facing after the Revolutionary War? -An agrarian or agricultural nation (Farmland) -A Confederate Nation-joined by an agreement or treaty -Debt -Major economic
Articles of Confederation What was the nation facing after the Revolutionary War? -An agrarian or agricultural nation (Farmland) -A Confederate Nation-joined by an agreement or treaty -Debt -Major economic
May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington
 May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington -May 1787 Philadelphia Met in Independence Hall in Philadelphia George Washington leader -12 of 13 states Rhode Island
May, 1787 Philadelphia, Pennsylvania ~Independence Hall~ Leader: George Washington -May 1787 Philadelphia Met in Independence Hall in Philadelphia George Washington leader -12 of 13 states Rhode Island
Ch.8, Sec.2 Creating the Constitution
 ü A al Convention Is Called - during the summer of 1787, 12 states sent delegates to Philadelphia to discuss amending the Articles of Confederation - the example set by Shays Rebellion proved our young
ü A al Convention Is Called - during the summer of 1787, 12 states sent delegates to Philadelphia to discuss amending the Articles of Confederation - the example set by Shays Rebellion proved our young
Shays. Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt.
 Shays Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt. 1. Constitutional Convention: May to Sept. 1787 2. Divided Convention 9/13 states needed to
Shays Daniel Shay 1784 to 1785, unfair taxes, debt and foreclosure Farmer s rebellion to overthrow Mass. Govt. 1. Constitutional Convention: May to Sept. 1787 2. Divided Convention 9/13 states needed to
Beginnings of a New Nation
 The period between the Treaty of Paris and the writing of the Constitution, the states were united only by a rope of sand. George Washington Beginnings of a New Nation Officers were disgusted with Congress
The period between the Treaty of Paris and the writing of the Constitution, the states were united only by a rope of sand. George Washington Beginnings of a New Nation Officers were disgusted with Congress
The constitution supercedes ordinary law even when the law represents the wishes of a majority of citizens.
 AP Government Chapter 2 The Constitution The constitution supercedes ordinary law even when the law represents the wishes of a majority of citizens. The Constitution is this nation s basic law: It creates
AP Government Chapter 2 The Constitution The constitution supercedes ordinary law even when the law represents the wishes of a majority of citizens. The Constitution is this nation s basic law: It creates
U.S. Constitution PSCI 1040
 PSCI 1040 Purposes of a Constitution Organize and empower the government Limit the powers of government. Many consider limited government to be the essence of constitutional government. 2 Articles of Confederation
PSCI 1040 Purposes of a Constitution Organize and empower the government Limit the powers of government. Many consider limited government to be the essence of constitutional government. 2 Articles of Confederation
The Constitutional Convention
 The Constitutional Convention Problems like Shay s Rebellion revealed the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation This event convinced many U.S. citizens that our 1 st written plan of government needed
The Constitutional Convention Problems like Shay s Rebellion revealed the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation This event convinced many U.S. citizens that our 1 st written plan of government needed
Charles de Montesquieu
 Unit III He first created the idea of consent of the governed where people have a vote in who leads them (democracy). Every person has the right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. John Locke
Unit III He first created the idea of consent of the governed where people have a vote in who leads them (democracy). Every person has the right to life, liberty and the pursuit of happiness. John Locke
The U.S. Constitution: Who, What, Where, When, Why & How
 The U.S. Constitution: Who, What, Where, When, Why & How 'a ^Va&o/z Fighting between the American colonists and British forces under King George III was in its second year when the Declaration of Independence
The U.S. Constitution: Who, What, Where, When, Why & How 'a ^Va&o/z Fighting between the American colonists and British forces under King George III was in its second year when the Declaration of Independence
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton
 Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
Constitutional Democracy: Promoting Liberty and Self-Government. Chapter 2
 Constitutional Democracy: Promoting Liberty and Self-Government Chapter 2 Before the Constitution: Colonial and Revolutionary Experiences The Rights of Englishmen Life, liberty and property to which all
Constitutional Democracy: Promoting Liberty and Self-Government Chapter 2 Before the Constitution: Colonial and Revolutionary Experiences The Rights of Englishmen Life, liberty and property to which all
Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings. Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings. Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings. Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings
 Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings The US government has its roots in English history Limited Government The concept that government is limited in what it can and cannot do Representative Government Government
Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings The US government has its roots in English history Limited Government The concept that government is limited in what it can and cannot do Representative Government Government
Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution
 Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution The Articles of Confederation After declaring independence from Britain in 1776, Congress tried to unite the states under one national government. However, many feared
Ch. 8: Creating the Constitution The Articles of Confederation After declaring independence from Britain in 1776, Congress tried to unite the states under one national government. However, many feared
Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation
 Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government. 2. is
Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government. 2. is
Chapter 3 Constitution. Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook
 Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
Chapter 3 Constitution Read the article Federalist 47,48,51 & how to read the Constitution on www.pknock.com Read Chapter 3 in the Textbook The Origins of a New Nation Colonists from New World Escape from
United States Constitution 101
 Constitution 101: An Introduction & Overview to the US Constitution United States Constitution 101 This PPT can be used alone or in conjunction with the Consortium s Goal 1 & 2 lessons, available in the
Constitution 101: An Introduction & Overview to the US Constitution United States Constitution 101 This PPT can be used alone or in conjunction with the Consortium s Goal 1 & 2 lessons, available in the
THE CONSTITUTION. Chapter 2
 THE CONSTITUTION Chapter 2 ROOTS OF THE CONSTITUTION 2.1 TRADE AND TAXATION 2.1 Mercantilism Strict import/export controls Widely ignored Costly French and Indian War New taxes on sugar and paper items
THE CONSTITUTION Chapter 2 ROOTS OF THE CONSTITUTION 2.1 TRADE AND TAXATION 2.1 Mercantilism Strict import/export controls Widely ignored Costly French and Indian War New taxes on sugar and paper items
The Learning Target :REVIEW/SYNTHESIS CH 7-8
 U.S. History Mr. Boothby 10/5/2017 The Learning Target :REVIEW/SYNTHESIS CH 7-8 -QUIZ #3 is in 10 MINUTES- -Turn in CHAPTER 9 ALL NOTES TOMORROW- -Grab the handout for TONIGHT!- -READ ALL OF CHAPTER 9
U.S. History Mr. Boothby 10/5/2017 The Learning Target :REVIEW/SYNTHESIS CH 7-8 -QUIZ #3 is in 10 MINUTES- -Turn in CHAPTER 9 ALL NOTES TOMORROW- -Grab the handout for TONIGHT!- -READ ALL OF CHAPTER 9
2. Which of the following was not one of the rights granted in the Magna Carta?
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 Our Political Beginnings SECTION 2 The Coming of Independence
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 Our Political Beginnings SECTION 2 The Coming of Independence
Chapter 5, Section 3 Creating the Constitution. Pages
 Chapter 5, Section 3 Creating the Constitution Pages 163-168 It didn t take long for people to realize that the Articles of Confederation had many weaknesses. By the mid-1780s most political leaders agreed
Chapter 5, Section 3 Creating the Constitution Pages 163-168 It didn t take long for people to realize that the Articles of Confederation had many weaknesses. By the mid-1780s most political leaders agreed
Establishing A New Government: Creating a Government. Chapter 4 Concept 2
 Establishing A New Government: Creating a Government Chapter 4 Concept 2 4.2 Creating a Government How did the decisions made at the Constitutional Convention affect the balance of power in the new nation?
Establishing A New Government: Creating a Government Chapter 4 Concept 2 4.2 Creating a Government How did the decisions made at the Constitutional Convention affect the balance of power in the new nation?
Land Ordinance of 1785
 Unit 3 SSUSH5 Investigate specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution. a. Examine the strengths of the Articles of Confederation,
Unit 3 SSUSH5 Investigate specific events and key ideas that brought about the adoption and implementation of the United States Constitution. a. Examine the strengths of the Articles of Confederation,
When were the Bill of Rights ratified? 1791 What is the purpose of the Preamble? KNOW THE Give an introduction and summary of the Constitution
 STUDY GUIDE - CONSTITUTION FLASH CARDS NAME: Background information What was the first national government of the country called? Why was a new Constitution needed? What powers did Congress have under
STUDY GUIDE - CONSTITUTION FLASH CARDS NAME: Background information What was the first national government of the country called? Why was a new Constitution needed? What powers did Congress have under
C is for Constitution
 You can master the Constitution if you can remember this: C is for Constitution APUSH Exam Review May 3, 2012 Compromise Conservative Contradictory 1780s-Catalysts for the convention (under the AOC): 1.
You can master the Constitution if you can remember this: C is for Constitution APUSH Exam Review May 3, 2012 Compromise Conservative Contradictory 1780s-Catalysts for the convention (under the AOC): 1.
Constitution Test Study Guide
 Constitution Test Study Guide Part One: Development of the Constitution Articles of Confederation: America's first government. The 13 states were loosely unified but the government was very weak, with
Constitution Test Study Guide Part One: Development of the Constitution Articles of Confederation: America's first government. The 13 states were loosely unified but the government was very weak, with
Underpinnings of the Constitution
 Underpinnings of the Constitution A constitution is a nations basic laws creates political institutions assigns and divides power in government provides certain guarantees to citizens includes unwritten
Underpinnings of the Constitution A constitution is a nations basic laws creates political institutions assigns and divides power in government provides certain guarantees to citizens includes unwritten
SS.7.C.1.5. Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution
 SS.7.C.1.5. Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the
SS.7.C.1.5. Identify how the weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation led to the writing of the Constitution SS.7.C.1.8 Explain the viewpoints of the Federalists and the Anti-Federalists regarding the
Battle of Saratoga. British troops reached Saratoga from Quebec and were surrounded and severely outnumbered = Surrendered
 Battle of Saratoga British troops reached Saratoga from Quebec and were surrounded and severely outnumbered = Surrendered Huge military victory, and boosted morale Convinced the French & Spain to enter
Battle of Saratoga British troops reached Saratoga from Quebec and were surrounded and severely outnumbered = Surrendered Huge military victory, and boosted morale Convinced the French & Spain to enter
SSUSH5 A, B, C & D Creating a New Government
 SSUSH5 A, B, C & D Creating a New Government The Articles of Confederation Formally called the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, this agreement was created by the leaders of the original thirteen
SSUSH5 A, B, C & D Creating a New Government The Articles of Confederation Formally called the Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union, this agreement was created by the leaders of the original thirteen
AKS M 49 C 30 a-d D 32 a-c D 33 a-c D 34 a-b BUILDING A NEW NATION
 AKS M 49 C 30 a-d D 32 a-c D 33 a-c D 34 a-b BUILDING A NEW NATION The official end of the Revolutionary War was the signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1783. The newly independent US and GA now faced the
AKS M 49 C 30 a-d D 32 a-c D 33 a-c D 34 a-b BUILDING A NEW NATION The official end of the Revolutionary War was the signing of the Treaty of Paris in 1783. The newly independent US and GA now faced the
D r a f t i n g, D r a w i n g & R e v i s i n g t h e A m e r i c a n
 Kind APUSH Critical to Federalist Periods D r a f t i n g, D r a w i n g & R e v i s i n g t h e A m e r i c a n N a t i o n P r i n c i p l e s o f G o v e r n m e n t t o b e I m p l e m e n t e d Natural
Kind APUSH Critical to Federalist Periods D r a f t i n g, D r a w i n g & R e v i s i n g t h e A m e r i c a n N a t i o n P r i n c i p l e s o f G o v e r n m e n t t o b e I m p l e m e n t e d Natural
ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION TO THE CONSTITUTION
 ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION TO THE CONSTITUTION Articles of Confederation The representatives of the thirteen states agree to create a confederacy called the United States of America, in which each state
ARTICLES OF CONFEDERATION TO THE CONSTITUTION Articles of Confederation The representatives of the thirteen states agree to create a confederacy called the United States of America, in which each state
The Constitutional Convention. Howard Chandler Christy, Scene at the Signing of the Constitution of the United States (1940)
 The Constitutional Convention Howard Chandler Christy, Scene at the Signing of the Constitution of the United States (1940) USHC 1.4 Analyze how dissatisfactions with the government under the Articles
The Constitutional Convention Howard Chandler Christy, Scene at the Signing of the Constitution of the United States (1940) USHC 1.4 Analyze how dissatisfactions with the government under the Articles
Constitution Unit Test
 Constitution Unit Test Eighth Amendment Excessive fines cannot be imposed. Excessive bail cannot be required. 1. Which sentence completes this diagram? A. People cannot be forced to be witnesses against
Constitution Unit Test Eighth Amendment Excessive fines cannot be imposed. Excessive bail cannot be required. 1. Which sentence completes this diagram? A. People cannot be forced to be witnesses against
The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783!
 Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
Creating a Republic The British did not even stay for the official portrait at the Treaty of Paris in 1783! The treaty ending the war with Britain, more than doubled the territory of the United States!
Articles of Confederation September 18, 2007
 Articles of Confederation September 18, 2007 Powers Given to Congress under the Articles Weaknesses under the Articles Results of the Articles during the Critical Period Use Page 44-46 to analyze the effects
Articles of Confederation September 18, 2007 Powers Given to Congress under the Articles Weaknesses under the Articles Results of the Articles during the Critical Period Use Page 44-46 to analyze the effects
Name Date Hour. Mid-Term Exam Study Guide
 Name Date Hour Mid-Term Exam Study Guide Following is a list of concepts and terms that may appear on the mid-term exam. Some definitions have been provided. **Exam Tip: Take extra time on graph and reading
Name Date Hour Mid-Term Exam Study Guide Following is a list of concepts and terms that may appear on the mid-term exam. Some definitions have been provided. **Exam Tip: Take extra time on graph and reading
[ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals
![[ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals [ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals](/thumbs/77/76341976.jpg) [ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals [ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals Key Terms limited government representative government due process bicameral unicameral [ 2.1 ] Origins of American
[ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals [ 2.1 ] Origins of American Political Ideals Key Terms limited government representative government due process bicameral unicameral [ 2.1 ] Origins of American
the states. decisions within its own borders) 1. A central government that would represent all 2. State sovereignty (the power to make
 The United States has operated under two constitutions. The first, The Articles of Confederation, was in effect from March 1, 1781. The Articles tried to balance two very different ideas: 1. A central
The United States has operated under two constitutions. The first, The Articles of Confederation, was in effect from March 1, 1781. The Articles tried to balance two very different ideas: 1. A central
The Pursuit of Equality-- background
 The Pursuit of Equality-- background The Pursuit of Equality-- background Constitution Making in the States Constitution Making in the States Economic Crosscurrents Economic Crosscurrents A Shaky Start
The Pursuit of Equality-- background The Pursuit of Equality-- background Constitution Making in the States Constitution Making in the States Economic Crosscurrents Economic Crosscurrents A Shaky Start
#1 State Constitutions
 #1 State Constitutions The American Revolution began the process of creating a new nation in a number of different ways. On May 10, 1776, the Continental Congress directed the colonies to suppress royal
#1 State Constitutions The American Revolution began the process of creating a new nation in a number of different ways. On May 10, 1776, the Continental Congress directed the colonies to suppress royal
