CBSE Continuous and Comprehensive Evaluation (CCE) QUESTION. Term 2 (October to March 2015) Social Science. Published by : OSWAAL BOOKS
|
|
|
- Pamela Day
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CBSE Continuous and Comprehensive Evaluation (CCE) SAMPLE QUESTION PAPERS solutions Term 2 (October to March 2015) Social Science Class 10 Published by : OSWAAL BOOKS Oswaal House 1/11, Sahitya Kunj, M.G. Road, AGRA Ph.: , , Fax : , contact@oswaalbooks.com, website :
2 SOLUTIONS SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER-6 Self Assessment Ans. 1. Napoleonic Code Huynh Phu So. Ans. 2. Madhya Pradesh. Ans. 3. Mahatma Gandhi Ans. 4. Wangari Maathai Ans. 5. Money lenders. Ans Ans %. Ans. 8. To liberalise international trade. Ans. 9. Features of Landed aristocracy of Europe : (i) They were small in numbers. Members of this class were united by common way of life that cut across regional divisions. (ii) They owned estates in the countryside and also townhouses. (iii) They spoke French for the purpose of diplomacy and in high society. (iv) Their families were often connected by the ties of marriage. (Any three) 1 3=3 Like colonial policy of other imperial powers, the French also subjected the Vietnamese economy to interests of the homeland. Vietnam had to supply its natural resources and other essential goods to France on their terms. No doubt the French irrigation took up vast irrigation works and built canals but mainly with forced labour consisting of Vietnamese people. Increased rice production was aimed to export rice to the international market to make profit. Colonial economy of Vietnam was primarily based on rice cultivation and rubber plantation. 3 Ans. 10. The main features of the Boycott and Swadeshi Movement : (i) Boycott of foreign goods, institutions and services. (ii) Picketing of foreign goods shops. (iii) Bonfires of foreign cloth. (iv) Increased production of Indian handloom and textiles. (Any three) 3 Ans. 11. Coal is the most abundant fossil fuel in India. Features of coal : (i) It provides a substantial part of the nation s energy needs. (ii) It supplies energy to industry as well as for domestic needs. (iii) It is used for power generation. (Any two) 1+2=3 SOCIAL SCIENCE Oswaal CBSE Class -10, SA-2 Examination Sample Question Paper
3 2 OSWAAL CBSE (CCE), Social Science Class 10 Ans. 12. Non-conventional sources of energy : (i) The Sun, winds, tides, geothermal energy, biomass, farm and animals waste are non - conventional sources of energy. (ii) They are renewable and inexhaustible sources of energy. (iii) They are not very convenient and versatile forms of energy. (iv) They are very expensive. Conventional sources of energy : (i) Coal, oil, natural gas, hydroelectricity and nuclear energy are the conventional sources of energy. (ii) They are exhaustible and cannot be replenished. (iii) They are more convenient and versatile forms of energy. (iv) They are less expensive. Ans. 13. Odisha is the largest prodcer of manganese in India. Uses of manganese : (i) It is used in manufacturing of steel. (ii) It is used in manufacture of bleaching power and insecticides. (iii) It is used as depolariser in cells. (iv) It is used as decolourising agent for glass that has been coloured green. 1½+1½=3 1+½+½+½+½=3 Ans. 14. Firewood and cattle dung cake are most common in rural India. According to the estimate, more than 70 percent energy requirement in rural households is met by these two fuels; continuation of these is increasingly becoming difficult due to decreasing forest area. Moreover, using dung cake too is being discouraged because it consumes most valuable manure which could be used in agriculture. (or any other relevant points) (CBSE Marking Scheme 2014, Set-SPXOUWE) 1+2=3 Ans. 15. The word defection in democracy means changing party allegiance from the party on which a person got elected to a different party. In order to get some benefit, various party leaders took this way. (CBSE Marking Scheme 2014, Set-ABTAF1R) 1+2=3 Ans. 16. Democracy is a better form of government as compared to dictatorship because : (i) A democratic government is people s own government. That is why, it receives overwhelming support from all parts of the world. (ii) Unlike dictatorship, people wished to be ruled representatives elected by them. (iii) Democracy s ability to generate its own support is itself an outcome that cannot be ignored. (iv) The examples from South Asia show the support exists in countries with democratic as well as non-democratic regimes. 3 Ans. 17. (i) Challenge of expansion involves applying the basic principle of democratic government across all the regions, different social groups and various institutions. (ii) Ensuring greater power to local government, extension of federal principles to all the units of federation, inclusion of women and minorities, etc. falls under this challenge. (iii) It means that less and less decisions should remain outside the arena of democratic control. 3 Ans. 18. MNC s help in the growth of local companies in the following manner : (i) MNC s are spreading their production and interacting with local producers in various countries across the globe. (ii) By setting up partnerships with local companies. (iii) By using the local companies for supply. (iv) By closely competing with the local companies or buying them. 3
4 Sample Question Papers (SA-2) 3 Ans. 19. The problems that forced India to take New Economy Policy of 1991 are as follows : (i) The performance of the public sector was not good. (ii) Inability of the public sector to achieve desired goals. (iii) Balance of payment defict of India was rising continuously since (iv) Excess of anticipated expenditure over estimated revenue (i.e., fiscal deficit). (v) Rising prices. 3 Ans. 20. Under COPRA,three-tier-quasi judicial machinery at the district, state and national levels was set up for redressal of consumer disputes. (i) The district level court deals with the cases involving claims up to ` 20 lakhs. (ii) The state level courts deals with the cases involving claims between ` 20 lakhs and ` 1 crore. (iii) The national level court deals with the cases involving exceeding ` 1 crore. (iv) If a case is dismissed in the district level court, the consumer can also appeal at the state and then at the national level court. 3 Ans. 21. Greek War : (i) Greece had been part of the Ottoman empire since the 15th century. The growth of revolutionary nationalism in Europe sparked off a struggle for independence amongst the Greeks which began in (ii) Nationalist in Greece got support from other Greeks living in exile and also from many West Europeans who had sympathy for ancient Greek culture. (iii) Poets and artists lauded Greece as the cradle of European civilisation and mobilised public opinion to support its struggle against a Muslim empire. (iv) The English poet Lord Byron organised funds and later went to fight in the war, where he died of fever in (v) Finally, the Treaty of Constantinople of 1832 recognised Greece as an independent nation. 1 5=5 (i) Hoa Hao Movement began in 1939 and gained popularity in the fertile Mekong delta area. (ii) It drew upon religious ideas popular in anti-french uprisings of the 19th century. (iii) Founder of Hoa Hao Movement was Huynh Phu So. He performed miracles, his criticism against useless expenditure, sale of child brides, gambling and use of alchohol and opium had a wide apeal. (iv) He was treated mad and was expelled to Laos and many of his followers to concentration camps. (v) It was against colonial rule and its significance in arousing anti-imperialist sentiment should not be under-estimated. 1 5=5 Ans. 22. The Non-Cooperation Movement gradually slowed down in the cities due to the following reasons : (i) Khadi cloth was often more expensive-than mass produced mill cloth and poor people could not afford to buy it. (ii) For the movement to be successful, alternative Indian institutions had to be set up so that they could be used in place of British ones. (iii) These were slow to come up. So, students and teachers began trickling back to Government schools and lawyers joined back their work in government courts. (iv) Since businessmen were incurring a huge loss in their market, so they did not give support in this movement. 1¼ 4=5
5 4 OSWAAL CBSE (CCE), Social Science Class 10 Ans. 23. Gandhiji s idea of Satyagraha : (i) The idea of Satyagraha emphasized the power of truth and the need to search for truth. (ii) It suggested that if the cause was true and, if the struggle was against injustice, then physical force was not necessary to fight the oppressor. (iii) Without seeking vengeance or being aggressive, a Satyagrahi could win the battle through non-violence. (iv) This could be done by appealing to the conscience of the oppressor. (v) Gandhiji believed that truth was bound to ultimately triumph. (vi) He believed that the Dharma of non-violence could unite all Indians. (Any five) 1 5=5 Ans. 24. Transportation and communication are called the lifelines of a nation and its economy because : (i) Economy development of a region or country very largely depends upon the dense network of transport and communication. (ii) They link areas of production with consumption, agriculture with industry and village with town and cities. (iii) They help the industries by providing raw materials and distribution of finished goods. (iv) They help in the development of all the three sectors : primary, secondary and tertiary. (v) They help in the balanced regional development. (vi) They have accelerated the development of the industry and agriculture. Ans. 25. The following could be some of the reasons why a democracy is a better form of government : (i) Freedom of expression granted in a democratic nation. (ii) The ruling authority would be the choice of the people. (iii) Useful method of representation for large masses. (iv) A tool to represent diverse interests. (v) Lends stability to the political system. (vi) Develops a political culture which creates apt environment for political socialization. 1 5=5 Ans. 26. (i) The financial accounts of every political party should be made public. (ii) These accounts should be examined by government s auditors. (iii) There should be state funding of elections. Parties should be given some money by the government to meet their election expenditure. (iv) Citizens should be encouraged to give more donations to parties. (v) Such donations should be exempted from income tax. (CBSE Marking Scheme 2014, Set-ABTAF1R) 1 5=5 Ans. 27. (i) Banks are not present everywhere in rural India whereas informal sources are easily available in all villages. (ii) Getting a loan from a bank is much more difficult than taking a loan from the informal resources because bank loans require proper loans and collaterals. (iii) Money lenders provide loan to the poor people without any collateral. (iv) Formal sources provide loan only for productive purpose, whereas the informal sources provide credit both for productive and non-productive purposes. (v) Other informal sources of credit are friends and relatives, or traders and landlords, who know the borrowers personally and therefore they do not demand collaterals. 1 5=5 Ans. 28. There has been a change in the nature of our international trade : (i) Till , the share of agriculture and allied products, ores and minerals, chemical engineering goods have been increasing. (ii) Exchange of commodities and goals have been superseded by the exchange of information and knowledge.
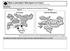
6 Sample Question Papers (SA-2) 5 (iii) India has emerged as a software giant at international level. (iv) India is earning large foreign exchange through the export of information technology. (v) Imports : Commodities imports include petroleum and petroleum products upto 41.87% and coal, coke upto 94.17%. 1 5=5 Ans =6 Amritsar A INDIA POLITICAL C Bardoli B Calcutta (iii) Berhampur (i) Kaiga (ii) Tuticorin Seaport SRI LANKA I N D I A N O C E A N
7 SOCIAL SCIENCE Oswaal CBSE Class -10, SA-2 Examination Sample Question Paper SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER-7 Self Assessment Ans. 1. Metternich 1 History of the Loss of Vietnam. Ans. 2. Manganese. 1 Ans. 3. Allahabad and Haldiya. 1 Ans th, December. 1 Ans. 5. Strengthening of institutions to increase people s participation and control. 1 Ans. 6. BAMCEF. 1 Ans. 7. Myanmar. 1 Ans. 8. To safeguard the domestic producers. 1 Ans. 9. The 1830 s were years of great economic hardship in Europe due to following reasons : (i) There were enormous increase in population all over Europe. (ii) There were more seekers of job than employment. (iii) Population migrated from rural areas to the cities. (iv) Peasants struggled under the burden of feudal dues and obligations. (Any three) 3 Impact of Great Depression on Vietnam : (i) The Great Depression of the 1930 s had a profound impact on Vietnam. (ii) The prices of rubber and rice fell, leading to rising rural debts, unemployment and rural uprisings, such as in the provinces of Nghea and Ha Tinh. (iii) The French put these uprisings down with great severity, even using planes to bomb demonstrators. 1 3=3 Ans. 10. (i) As a woman it was a proud movement for me to participate in Gandhiji s Civil Disobedience Movement. It was a time when women were kept inside walls. (ii) Though I had got good education, I was not allowed to take part in social or political activities. At the call of Gandhiji, I couldn t resist myself. Revolting against my family traditions, I became an active member of the movement. (iii) I organised the women of my locality and began the activities of the movement. I was full of nationalistic fervour. It was the most memorable and proud phase of my life. 1 3=3 Ans. 11. (i) Natural gas is used as source of energy as well as an industrial raw material. (ii) It can be transported easily through pipelines. (iii) Pipelines have helped in setting up fertilizer plants and power plants on its way. (iv) It is an environment-friendly fuel because of the low carbon emission. (Any three) 3
8 Sample Question Papers (SA-2) 7 Ans. 12. Non-conventional sources of energy are : (i) Solar energy : India is a tropical. It has enormous possibilities of tapping solar energy. Photovoltaic technology converts sunlight directly into electricity. (ii) Wind energy : India now ranks as a wind super power in the world. The largest wind farm cluster is located in Tamilnadu from Nagarcoil to Madurai. (iii) Biogas : Shrubs, farm waste, animal and human waste are used to produce biogas for domestic consumption in rural areas. Biogas plants using cattle dung are known as Gobar gas plants in rural India. 1 3=3 Ans. 13. Factors responsible for the location of an industry : (i) Availability of raw material. (ii) Availability of Labour. (iii) Capital, power and market. (iv) Services like Banking, Insurance, transport etc. (Any three) 1 3=3 Ans. 14. Factors : (i) Northern plains of India are vast and level land. Construction of railway tracks is easy and cheap in these plains. Plains have dense railway network. (ii) In hilly terrians of peninsular regions, rail tracks are laid through low hills and tunnels. In this region, railway network is not so dense as of plains. (iii) In sandy plain of western Rajasthan, construction of railway lines is always difficult. 3 Ans. 15. Bhartiya Janta Party (BJP). The four features of BJP are as follows : (i) Cultural nationalism is an important element in its conception of Indian nationhood and politics. (ii) It wants a uniform civil code for all people living in the country irrespective of religion. (iii) It came into power in 1998 as the leader of the National Democratic Alliance including several state and regional parties. (iv) It lost elections in 2004 and is the principal opposition party in Lok Sabha. 3 Ans. 16. (i) Democracies throughout the world have recognise the act that people should be treated with due respect. The passion for respect and freedom is the basis of democracy. (ii) Democracies recognise all individuals equal. The equality is a big thing for societies which have been built for a long on the basis of subordination and domination. (iii) Most societies across the world were male dominated but democracies have created sensitivity. That equal treatment of women are necessary ingredients of a democratic society. 3 Ans. 17. Definition of democracy shall be expanded by adding following features : (i) The rulers elected by the people must take all the decisions. (ii) Elections must offer a choice and fair opportunity to the people to change the current rulers. (iii) The choice and opportunity should be available to all the people on an equal basis. (iv) The exercise of this choice must lead to a government limited by the basic rules of the constitution and citizen s rights. (Any three) 3
9 8 OSWAAL CBSE (CCE), Social Science Class 10 Ans. 18. MNC s set up production units at such a place where : (i) Markets are closer. (ii) Skilled and unskilled labour are available at low cost. (iii) Other factors of production are assured. (iv) Government policies are favourable. (Any three) 3 Ans. 19. (i) MNC s set up units in those countries where labour is available at cheaper rate and has large market to sell their products. 3 (ii) MNC s setup production jointly with some of the local companies of the countries. (iii) MNG s purchase local companies and then expend production. Ans. 20. Consumers are exploited in the market in the following ways : 3 (i) Deceptive advertising : False informations are passed on through the media. (ii) Adulteration : Adulterated or defective goods are sold. (iii) Underweight : Traders indulge in unfair trade practices such as weighing less than what they should. Ans. 21. Culture played an important role in creating the idea of a nation by : (i) Art and poetry, stories, music helped in shaping nationalist feelings in Europe. (ii) Romanticism was a cultural movement which played a role in this context. Romantic poets and artists were critical of reason and science. (iii) A sense of shared collective heritage developed. (iv) Folk dance, Folk poetry, Folk songs were considered the true expression of the spirit of the nation. (v) Speaking in the vernacular language was another expression of nationalism. 5 (i) In February 1930, Ho Chi Minh brought together competing nationalist groups to establish Vietnamese Communist Party, later known as Indo-Chinese Communist Party. (ii) In 1940, when Japan occupied Vietnam, nationalists under Ho Chi Minh had to fight both against the French and the Japanese. (iii) The League for the Independence of Vietnam later known as Vietminh fought the Japanese and recaptured Hanoi in (iv) The Democratic Republic was formed and Ho Chi Minh became its Chairman. (v) After eight years of fighting, the French too was defeated by Vietminh under Ho Chi Minh. According to Geneva Convention, Vietnam was split into North and South Vietnam. Ho Chi Minh and the communists took power in the North. Till the end of his life, Ho Chi Minh struggled for the creation of united Vietnam. 5 Ans. 22. The main causes of limited Dalit participation are as follows : (i) Dr. B.R. Ambedkar who organized Dalits into depressed classes association in 1930, clashed with Mahatma Gandhi at the second round table conference as he asked for separate electorates for Dalits. (ii) Gandhiji believed that separate electorates will down the process of integration in society. (iii) Poona Pact of September, 1932 was the result of acceptance of Gandhiji s position.
10 Sample Question Papers (SA-2) 9 (iv) Also, Dalit were looked down upon by society since ages. (v) Political empowerment, they believed, would resolve the problem of social disabilities. (vi) Their organisation was strong all over. (vii) It gave the depressed classes reserved seats in provincial and central legislative councils, but they were to be voted in by the general electorate. 5 Ans. 23. The benefits of globalisation can be shared better in the following ways : (i) The government policy must protect the interest, not only of the rich and the powerful, but of all the people in the country. (ii) The government can ensure that labour laws are properly implemented and workers get their rights. (iii) It can support small producers to improve their performance till they became strong enough to compete. (iv) It can use trade and investment barriers. (v) It can negotiate at the WTO for fairer rules. 5 Ans. 24. Democracies do not appeal to be reducing inequalities : (i) The poor constitutes a large proportion of voters and no party likes to lose their votes, yet democratically elected governments have not addressed the question of poverty as one would have expected them to. (ii) The people in several poor countries are now dependent on rich countries even for food supplies. Argument in support : (i) It enhances the dignity of individual. (ii) Improves the quality of decision making. (iii) Provides a method to resolve conflicts. 5 Ans. 25. The following conclusion can be drawn from the two struggles : (i) The movement in Nepal was to establish democracy, while the struggle in Bolivia involved claims on an elected democratic government. (ii) The popular struggle in Bolivia was about one specific policy, while the struggle in Nepal was about the foundations of the country s politics. (ii) Both these are instances of political conflict that led to popular struggles. (iv) Both the cases of struggle involve mass mobilisations. Ans. 26. The different types of party systems and their merits : (i) One - party system Merit : The decisions are taken quickly and frequently. (ii) Bi-party or Two Party system 1¼ 4=5 Merit : It gives fair chance for the competing parties to come to power. Generally, one party forms government and other party sits in opposition. England is a good example of Bi-party system. (iii) Multi-party system Merit : It is more representative and accountable. This system creates internal checks and balances within a coalition government. (iv) India has a multi-party system. 5
11 10 OSWAAL CBSE (CCE), Social Science Class 10 Ans. 27. The joint efforts of seven party alliance, the Nepalese communist party, labour union and their federations, organization of the indigenous people, teachers, lawyers all taught the lesson of mobilization and organization. The struggle of Nepali people set the example of peaceful revolution, that established democracy and brought down the rule of monarchy. It also taught that direct participation in competetive politics can be done by creating parties contesting politics and forming governments. 5 Ans. 28. Characteristics of Kandla Sea Port : (i) Kandla in Kuchchh was the first port that developed soon after Independence. (ii) It was built so that the volume of trade on the Mumbai port gets eased after the loss of Karachi port to Pakistan after the Partition. (iii) It is a tidal port. (iv) Catering to the convenient handling of exports and imports of highly productive granary, it stretches along a huge industrial belt across the states of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and Gujarat. (v) It is a free trade zone. 5 Ans =6 (i) Narora INDIA POLITICAL B Champaran (iii) Kandla Dandi C (ii) Rourkela A Madras SRI LANKA I N D I A N O C E A N
12 SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER-8 Self Assessment Ans. 1. Led to the transfer of sovereignty from the monarchy to a body of citizens. 1 Phan Boi Chau. Ans. 2. Kalpakkam. 1 Ans. 3. Oil India Limited. 1 Ans. 4. United Kingdom. 1 Ans. 5. Thorium. 1 Ans. 6. They hold regular elections. 1 Ans. 7. Tax on import. 1 Ans. 8. Consumer international. 1 Ans. 9. Characteristics features : (i) Otto Von Bismarck, Chief Minister of Prussia was the architect of this process of unification. (ii) The wars over seven years with Austria, Denmark and France, ended in Prussian victory and completed the process of unification. (iii) The Prussian King, William-I was proclaimed the German Emperor. 1 3=3 The role of Trung Sisters in the nationalist movement of Vietnam : (i) Trung Sisters had fought against Chinese domination in CE. (ii) These sisters fought as patriot to save Vietnam from the Chinese. (iii) Phan Boi Chau wrote a play based on their lives and they were idealized and glorified. (iv) They were depicted in paintings, plays and novels as representing their intense patriotism towards Vietnam. (Any three) 3 Ans. 10. The Rowlatt Act of 1919 was opposed in the following ways : (i) People organised hartals in cities, railways went on strike. (ii) Shops were closed down. (iii) Rallies were organised in various cities. Jalianwala bagh massacre took place in opposition of the Rowlatt Act. 3 Ans. 11. (i) Aluminium is extracted from the Bauxite ore. (ii) Aluminium is gaining importance because of its extreme lightness, good conductivity and great malleability. It combines the strength of metals such as Iron. (iii) It is mainly found in Amarkantak plateau, Maikal hills and the plateau region of Bilaspur Katni. Koraput district in Odisha has large deposits. Odisha is the largest bauxite producing state. Others are Gujarat, Maharashtra and Jharkhand =3 SOCIAL SCIENCE Oswaal CBSE Class -10, SA-2 Examination Sample Question Paper
13 12 OSWAAL CBSE (CCE), Social Science Class 10 Ans. 12. Conservation of energy resources is essential because : (i) Every sector of the National Economy needs inputs of energy. (ii) Consumption of energy is increasing, hence resources are getting exhausted. (iii) Energy is required for future hence conservation is essential. (iv) Energy saved is energy produced. So, judicious use of energy is essential. (Any three) 3 Ans. 13. Challenges faced by the jute industry : Ans. 14. Analysis : (i) Stiff competition in the international market. (ii) Lack of demand due to synthetic substitutes available. Government policy is trying to revive the market. (iii) Low productivity and high cost of production. (i) Agro-industries in India have given a major boost to agriculture by raising of its productivity. (ii) Industries depend on agriculture for their raw material. (iii) Industries set all their products such as irrigation pumps, fertilisers etc. to the farmers. 3 Ans. 15. (i) Democracies do not appear to be very successful in reducing economic inequalities. Although majority of voters constitute the poverty ridden group, yet democratically elected government do not appear to be as keen to address the question of poverty as you would expect them to. (ii) Situation is much worse in some of the countries where people depend upon rich countries for food supplies. (iii) But even then democracy is favoured because it provides the opportunity to change the rulers. (Any three) 1 3=3 Ans. 16. Pressure group is a group of people which tries to exert pressure on administration to get these laws passed which do not go against their interest. They also use persuasive methods to get favourable decisions. They do not participate in politics directly. But political parties take participates in politics directly. The relation between the two are direct and indirect both. (CBSE Marking Scheme 2014, Set-SPXOUWE) 3 Ans. 17. Democracy is rated as better and successful if it : (i) Promotes equality among citizens. (ii) Enhances the dignity of the individuals. (iii) Improves the quality of decision making. (iv) Provides a method to resolve conflicts. (v) Allows room to correct mistakes. (Any three) 3 Ans. 18. (i) Telecommunication facilities are used to contact and communicate and to access information. (ii) Internet includes transfer of technology, money and capital across countries. (iii) Speedy transfer of information technology, money and capital integrates different countries of the world. 3 Ans. 19. Free and fair trade : (i) Government policies must protect the interests not only of the rich and powerful but all the people in the country. (ii) The Government can ensure that labour laws are properly implemented and the workers get their rights. (iii) It can support small producers to improve their performance till the time they become strong enough to compete. (iv) The government can use trade and investment barriers. It can also negotiate at the WTO for fairer rules. (Any three) 1 3=3
14 Sample Question Papers (SA-2) 13 Ans. 20. Right to choose : (i) Consumers have the right to be protected against the marketing of goods and delivery of services. (ii) Consumers have the right to avail safety against hazardous and electrical goods. (iii) Many goods and services require special attention to safety as pressure cooker, Geysers, Gas cylinders, etc. Ans. 21. Role of Giuseppe Mazzini in the unification of Italy : (i) He became member of various secret societies such as Young Italy or Young Europe. (ii) He attempted revolution in liguris. (iii) He wanted unification with wider alliance of nations. (iv) He frightened conservatives through opposition to Monarchy and vision of democratic republics. (v) He favoured war for unification of Italy. (vi) He wanted Economic development and Political dominance. (Any five) 5 Vietnamese shared an amicable relationship with Japan and China. They provide a refuge for those who were trying to escape from the French police, models for those who were looking for change. They also provided a location where Asian network of revolutionaries could be established. In , some 300 Vietnamese students went to Japan to get modern education. They also established a branch of Restoration society in Tokyo. Developments associated with China also inspired Vietnamese. The long established monarchy of China was overthrown by a popular movement under Sun-Yet-Sen, In 1911, a republic was set up. Later Vietnamese students established an association for restoration of Vietnam Viet Nam Quan Phuc Hoi. 5 Ans. 22. Reasons of grievances of the peasants against the government were : (i) Due to forest laws of the colonial government. (ii) Depriving them of the traditional rights of entering the forest. (iii) High land Revenue. (iv) Forced to perform beggary. Steps taken to organise peasant movement : (i) Many Kisan Sabhas were set. (ii) ganised Guerrilla militant movement. (iii) Attacked police station and attempted to kill police officials. (iv) Gandhiji declared that no tax should be paid. 2½+2½ 5 Ans. 23. (i) The sense of collective beloging meant that people began to feel that they all are the part of the same nation. This discovered a sense of unity which bound them together. (ii) They were the part of variety of cultural processes through which nationalism captured people s imagination. (iii) Indian folklore, history and fiction, popular prints and symbols all developed a sense of pride in the past. (iv) The sense of belonging came partly through the experience of united struggles. (v) Carrying a flag and holding it along during marches became a symbol of defiance. 5
15 14 OSWAAL CBSE (CCE), Social Science Class 10 Ans. 24. (i) Our spinning mills are competitive at the global level but the weaving, knitting and processing units cannot use much of the high quality yarn that is produced in the country. (ii) We need to import good quality staple cotton. (iii) Low output of labour and stiff competition with the synthetic fibre industry (iv) The world trade of cotton yarn is much larger than the trade of cotton garments. 1¼ 4=5 Ans. 25. Influence of pressure groups and movements : (i) They try to gain public support and sympathy for their goals by carrying out campaigns, meetings, filings, etc. (ii) They often organize protest activities like strikes. (iii) Many of them may participate in official bodies and committies that offer advice to the government. (iv) They seek to exert influence on political parties without participating in politics themselves. (v) Many a times pressure groups of movements are led by political parties. 1 5=5 Ans. 26. Suggestions to reform the political parties : (i) A law should be made to regulate the internal affairs of political parties. It should be made compulsory for political parties to maintain a register of its members, to follow its constitution, to act as a judge in case of party disputes, to hold open elections to the highest posts. (ii) It should be made mandatory for political parties to give a maximum number of tickets to women. (iii) Similarly, a 33% quota for women can be fixed in the decision-making body of the party. (iv) There should be state funding of elections. The government should give parties money to support their election expenses. (v) Every political party should disclose the source of their income. It should be made compulsory. 1 5=5 Ans. 27. (a) Bank would need for the specified loan amount and duration of loan. (b) Bank would know about the mode of repayment. (c) After that, Bank would require collateral and proper documentation for getting a loan. (d) A reasonable rate of interest would be charged for the loan. (e) Proper records would be maintained. (CBSE Marking Scheme 2014, Set-SPXOUWE) 1 5=5 Ans. 28. Water pollution is caused by organic and inorganic industrial wastes and affluents discharged into rivers. The main culprits in this regard are paper, pulp, chemical, textile and dyeing, petroleum refineries, tanneries and electroplating industries that let out dyes, detergents, acids, salts and heavy metals like lead and mercury pesticides, fertilisers, synthetic chemicals with carbon, plastics and rubber, etc. into the water bodies. To minimize environment degradation by industries : (i) Rainwater harvesting needs to be practised. (ii) Overdrawing of ground water reserves by industries where there is a threat to ground water should be prohibited. (iii) Minimizing use of water for processing by reusing and recycling it at every two or more successive stages. 5
16 Sample Question Papers (SA-2) 15 Ans =6 C Amritsar INDIA POLITICAL (iii) Raja Sansi (International Airport) B Ahmedabad (i) Bhilai A Calcutta (ii) Coimbatore SRI LANKA I N D I A N O C E A N
17 SOCIAL SCIENCE Oswaal CBSE Class -10, SA-2 Examination Sample Question Paper SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER-9 Self Assessment Ans. 1. Young Italy. 1 Success of collective bargaining. Ans. 2. Chauri Chaura. 1 Ans. 3. Textile Industry. 1 Ans. 4. Expressway National Highway. 1 Ans. 5. BAMCEF. 1 Ans. 6. Political party that runs government. 1 Ans. 7. Bureau of Indian Standards. 1 Ans. 8. Absence of collaterals. 1 Ans. 9. Cavour was the Chief Minister of Sardinia - Piedmont. His contribution to the unification of Italy was : 1+2=3 (i) He was a good administrator and worked for the unification of Italy. (ii) He led the movement to unify the regions of state. (i) Phan Chu Trinh was a nationalist and sought to end France s brutal occupation of Vietnam. (ii) He was intensely hostile to monarchy and opposed the idea of resisting the French with the help of court. (iii) He wanted to establish a democratic republic. (iv) He was influenced by western ideals like liberty. (Any three) 1 3=3 Ans. 10. Gandhiji issued an eleven point ultimatum to Lord Irwin, combining some general and specific demands. Some of them are as follows : (i) Release of political prisoners. (ii) Cuts in army expenses, civil services salaries. (iii) Lowering of rupee sterling rate. (iv) Abolition of both salt tax and government salt monopoly. The abolition of salt tax was the most stirring demand because it was the most essential item of the food and consumed by the rich and the poor alike. ½+½+½+½+1=3 Ans. 11. Ways for the judicious use of energy resources : (i) By using public transport system. (ii) Switching off electricity when not in use. (iii) Using power saving devices. (iv) Using non-conventional sources of energy. (Any three) 3
18 Sample Question Papers (SA-2) 17 Ans. 12. Factors responsible for location of jute textiles : Proximity of the jute producing area, the areas that produce jute in abundance are located near west bengal around hoogli river. This is one of the factor affecting the localisation of jute industies inexpensive water transport: hoogli river provides a good network of water ways suported by a good network of railways roadways nd waterways that allows easier transportation of raw materials n finished goods abundance of water: The jute industry requires abundance of water for processing raw material to finished goods this requirement is well fulfilled by hoogli river cheap labour: Cheap labour from bihar uttar pradesh and orrisa is available. (Any three) 1 3=3 Ans. 13. India is not able to perform her full potential in iron and steel production because of : (i) high costs and limited availability of cooking coal. (ii) Low production of labour. (iii) Irregular supply of energy/power. (iv) Poor infrastructure. (Any three) 1 3=3 Ans. 14. Importance of tourism as trade : (i) Our country earns foreign exchange through tourism. More than 15 million people are directly engaged in the tourism industry. (ii) It promotes National Integration and provides support to local handicrafts and cultural pursuits. (iii) It also helps in the development of international understanding about our culture and heritage. 1 3=3 Ans. 15. (i) Pressure groups have a strong organisation but movement groups have a loose organisation. (ii) Decision making in pressure groups is formal but informal in case of movement groups. (iii) Pressure groups depend on the participation of its members, but movement groups depend much more on spontaneous mass participation. 1 3=3 Ans. 16. Bahujan Samaj Party. Features : (i) It was formed in 1984 under the leadership of Kanshi Ram. (ii) It stands for the welfare of dalits and oppressed people. 1+2=3 Ans. 17. (i) The financial accounts of every political party should be made public. These accounts should be examined by Government auditors. (ii) There should be state funding of elections. (iii) Citizen should be encouraged to give more donations to parties and to political workers. Such donations should be exempt from income tax. (CBSE Marking Scheme 2014, Set-SPXOUWE) (1 3=3) Ans. 18. Factors that have enabled Globalisation are : (i) Improvement in transportation : This has made the delivery of goods much faster across long distances, possible at lower costs. (ii) Improvement in Information and Technology : It has played a major role in spreading out production of services across countries. Tele-communication facilities are used to contact one another around the world to access information instantly and to communicate from remote areas. Computers have now entered almost every field of activity. So, also the internet, at negligible costs.
19 18 OSWAAL CBSE (CCE), Social Science Class 10 (iii) Liberalisation nations have removed the barriers to foreign trade and foreign investment and thus promoted and facilitated globalization. 3 Ans. 19. Yes. (i) Consumers need to engage lawyers which costs money. (ii) Cases require time for filing and attending court. (iii) Purchases are mostly small and cash memos are rarely issued. (Any two) 1+2=3 Ans. 20. Particulars about the goods and services are available as given below : (i) Ingredients used in the product. (ii) Date of manufacture. (iii) Expiry date (upto which date can be used). (iv) Address of the manufacturing. (v) Directions for proper use. (Any three) 3 Ans. 21. Reasons : (i) The first half of the 19th century saw an enormous increase in population all over Europe. (ii) Job seekers were more and employment opportunities were less. (iii) People from rural areas migrated to cities and made cities overcrowded slums. (iv) Small producers often faced stiff competition from imports of cheap machine made goods. (v) Peasants struggled under the burden of feudal dues and obligations. 5 (i) In , some 300 Vietnamese students went to Japan to acquire modern education. This is to Go East Movement. (ii) The main objective was to drive out the French from Vietnam and overthrow the puppet emperor. (iii) These note analysts-established the Nguyen dynasty that had been deposed by the French. (iv) They worked for foreign arms and help. (v) They appealed to the Japanese as fellow Asians for help. Ans. 22. Gandhiji converted the National Movement into a mass movement in the following manner : (i) His simple and saintly life and style of convincing the masses made him popular. (ii) His undisputed leadership and magnetic personality. (iii) His policy of non-violent Satyagraha. (iv) His programmes of social reforms like fighting against untouchability. (v) His commitment to Hindu-Muslim unity. 5 Ans. 23. Industrial locations are complex in nature. They are influenced by a number of factors that determine their location in region. The physical factors that influence that location of industries are as follows : Availability of raw materials Raw materials for industries range from agricultural products to minerals. Raw material required for the industry must be available cheaply and at close range or at well-linked places. In case of industries using bulky raw materials like iron, bauxite, etc., the ideal location is near the sources of raw materials. 5
20 Sample Question Papers (SA-2) 19 Ans. 24. Railways are the most important mode of transport in India : (i) Railways are the principal mode of transportation for freight and passengers in India, as they link different parts of the country. (ii) They carry huge loads and bulky goods to long distances. (iii) Railways make it possible to conduct multifarious activities like business, sightseeing, pilgrimage along with transportation of goods over longer distances. (iv) Railways have been a great integrating force for the nation, for more than 150 years now. (v) They have been helpful in binding the economic life of the country and cultural fusion. (vi) They have accelerated the development of the industry and agriculture. (Any five) 5 Ans. 25. If several parties compete for power and more than two parties have a reasonable chance of coming to power, either on their own strength or in alliance with others, we call it a multiparty system. Merits : (i) This system allows a variety of interests and opinions. (ii) People have to make a choice between several candidates. (iii) The ruling party will be checked by opposition parties, so that mal practices will reduce. Demerits : (i) It appears messy. (ii) It leads to political instability. (iii) With three or more parties, a party has a much more likely chance of being elected without holding the same beliefs of the majority of people. 2+1½+1½=5 Ans. 26. The challenge of deepening of democracy is faced by every democracy in one form or the other. This involves strengthening of the institutions and practices of democracy. This should happen in such a way that people can realize their expectations of democracy. But ordinary people have different expectations from democracy in different societies. Therefore, challenge takes different meanings and paths in different parts of the world. In general terms, it usually means strengthening those institutions that help people s participation and control. This requires an attempt to bring down the control and influence of the rich and powerful people in making governmental decisions. 5 Ans. 27. Objective of Self Help Groups (SHG) : (i) Helps in pooling the savings of the women members who are poor. (ii) Timely loans are given for a variety of purposes. (iii) Reasonable rate of interest and lack of collateral. (iv) Provides platform to discuss variety of social issues. (v) The pooled savings can be used as a callateral to take a loan from a bank. 5 Ans. 28. WTO : World Trade ganisation Features : (i) To Liberalise International Trade. (ii) To make rules regarding International Trade. (iii) To see that these rules are followed by every member countries. (iv) Encouraging the adoption of liberal economic policies by governments. (CBSE Marking Scheme 2014, Set-SPXOUWE) 5
21 20 OSWAAL CBSE (CCE), Social Science Class 10 Ans =6 (iii) Amritsar INDIA POLITICAL B Bokaro (i) Kheda A Bellary (ii) Nagpur C Kolkata SRI LANKA I N D I A N O C E A N
22 SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER-10 Self Assessment Ans. 1. Red, green and yellow. 1 Ans. 2. Ludhiana. 1 Ans. 3. ganisation that led Bolivian mass protest. 1 Ans. 4. Manikaran. 1 Ans. 5. The Election Commission of India. 1 Ans. 6. About 1/4 th. 1 Ans. 7. Goods are exchanged for goods. 1 Ans % (CBSE Marking Scheme 2014, Set-ABTAF1R) 1 Ans. 9. Representatives of the European power, Britain, Russia, Prussia and Austria signed treaty of Vienna in The impacts of treaty were : (i) Deposed Bourbon dynasty was restored to power. Future expansion of French was prevented. (ii) Prussia was given important new territories on its Western frontiers, while Austria was given control of Northern Italy. (iii) In the East, Russia was given part of Poland while Prussia was given a portion of Saxony. (iv) The treaty slowed down the growth of nationalism. There was an effort to restore Monarchies that had been overthrown by Napoleon and to create a new conservatives order in Europe. 3 French colonization was not based only on economic exploitation. It was also driven by the idea of a Civilizing Mission. Like the British in India, the French claimed that they were bringing modern civilization to the Vietnamese. They took for granted that Europe had developed the most advanced civilization. So, it became the duty of the Europeans to introduce these modern ideas to the colony even if this meant destroying local cultures, religions and traditions, because were seen as outdated and prevented modern development. Education was seen as one way to civilize the native. Colonies were considered essential to supply natural resources and other essential goods. Like other Western nations, France also thought it was the mission of the advanced European countries to bring the benefits of civilization to backward peoples. Ans. 10. In the countryside, rich peasant communities such as the Patidars of Gujarat and the Jats of Uttar Pradesh took active participation in the movement. (i) They were very hard hit by the trade depression and falling prices being producers of commercial crops. SOCIAL SCIENCE Oswaal CBSE Class -10, SA-2 Examination Sample Question Paper
23 22 OSWAAL CBSE (CCE), Social Science Class 10 Ans. 11. (ii) As their cash income disappeared, they found it impossible to fulfil the government s revenue demand. (iii) Refusal of the government to reduce the revenue demand led to widespread resentment. (iv) These rich peasants became enthusiastic supporters of the Civil Disobedience Movement, organizing their communities and at times forcing reluctant members, to participate in the boycott programmes. (v) The fight for Swaraj was a struggle for them against high revenues. (Any three) 3 No. Ferrous Minerals Non-Ferrous Minerals (i) (ii) (iii) The minerals containing iron content are called ferrous minerals. They are used in iron and steel industry. Example : Iron, manganese, cobalt etc. The minerals which do not contain iron content are called non-ferrous minerals. They have their own utility and are used in electrical, electronic and chemical industries. Example : Copper, lead, aluminium, etc. Ans. 12. (i) It is essential for construction activities like buildings, bridges etc. (ii) It requires bulky and heavy raw material like- limestone, silica, alumina and gypsum. (iii) Coal and electric power are also required. (iv) At present 166 large plants and 350 mini plants are there in India as on (v) This industry is doing well in terms of production as well as export. (Any three) 1 3=3 Ans. 13. Iron and steel industries are called basic industry because all the industries depend on them for their machinery. The problems faced by this industry are : (i) This industry faces difficulty in buying coal because of its high cost and limited availability. (ii) There is an irregular supply of energy and electricity in India, so that work becomes more difficult. 1+2=3 Ans. 14. (i) They enable goods to reach newer markets and allows people greater accessibility to goods and services. (ii) They help in increasing cooperation and assistance between countries by easy movement of goods and material between countries. (iii) They help in trade and commerce within country. 1 3=3 Ans. 15. Pressure groups are organizations that attempt to influence government policies. Differences : (i) Unlike political parties, pressure group does not aim to share or directly control political power. (ii) These organizations are formed when people with common occupation, interests, aspirations, or opinions come together in order to achieve a common objective. Whereas in political parties are those which come together to contest elections and hold power in the government. (iii) A pressure group represents their own single interests while political party represents various interests. 1 3=3 Ans. 16. A democratic government can be made accountable by : (i) Conducting discussions and negotiations. (ii) By ensuring transparency. (iii) Holding regular, free and fair elections. (iv) Having open public debates. 1 3=3 3
24 Sample Question Papers (SA-2) 23 Ans. 17. Democratic principles cannot be implemented only on the basis of legal constitutional changes. It lies in the application of expansion of democratic principles to all social groups across regions. It requires the support of political parties, groups etc. These laws have been formulated to overcome the problems. Expansion includes taking democracy to the grass root level through local governments. It includes empowerment of women and applies federal principles to ensure autonomous decisionmaking and decentralization. 3 Ans. 18. (a) Awareness of one s right. (b) Responsibility of the consumer. (c) Social ethics of morality. (CBSE Marking Scheme 2014, Set-SPXOUWE) 1 3=3 Ans. 19. A consumer needs to be well informed as : A well informed consumer knows how to fight for his own rights. An educated consumer becomes a rational consumer i.e., he knows how to spend money to derive the maximum satisfaction out of d product he/she buys. A well informed consumer cannot be cheated easily by the shopkeepers,traders etc. 3 Ans. 20. Limitation of consumer movement : (i) It is cumbersome, expensive and time consuming. (ii) Evidences are not easy to gather. (iii) Existing laws are not clear. (vi) Lack of consumer awareness. (v) Rules and regulations are not clear. (Any three) 1 3=3 Ans. 21. (i) During the middle of the nineteenth century, Italy was divided into seven states, of which only one Piedmont and Sardinia was ruled by a Italian princely house. The North was under Austrian Habsburgs. Centers were under the pope and Southern states were under the Bourbon king of Spain. (ii) By 1830, Giuseppe Mazzini put forward coherent programme of unitary Italian republic. Formed secret society named young Italy to inspire them with ideas of unification. (iii) After the failure of revolutionary movement, the responsibility of unification lay on Victor Emmanuel-II who along with the chief minister Cavour led the movement to unify the regions of Italy. (iv) Through a tactful diplomatic alliance with France he defeated Austrian force in (v) Garibaldi, another leader in Italian unification, along with his armed volunteers marched into southern kingdom of Two Sicily s and drove away the rulers with the local peasants. In 1861, Victor Emmanuel-II was proclaimed the king of united Italy. 5 An incident which happened in Saigon Native Girls school in 1926 created much bad blood in Vietnam. It so happened when a Vietnamese girl sitting on one of the front seats was asked to vacate her seat for a local French student. When she refused to do so, she was expelled from the school by the principal. When the angry students protested, they too were expelled leading to further spread of the agitation and the protest. Seeing the situation getting out of control, the school authorities forced the school to take back the students. Such incidence went a long way in instilling the national feelings among the Vietnamese people. 5 Ans. 22. (i) Socialy and politically, a landed aristocracy was the dominant class on the continent. The members of this class were united by a common way of life that cut across regional division. (ii) They spoke French for purpose of diplomacy and in high society.
Social Science. Marking Scheme. Class X. 1. (d) or (b) 1 2. (b) 1 3. (c) (c ) 1 5. (d) 1 6. (a) (b) 1 8. (a) 1 9.
 Social Science Marking Scheme Class X 1. (d) or (b) 1 2. (b) 1. (c) 1 4. (c ) 1 5. (d) 1 6. (a) 1 7. (b) 1 8. (a) 1 9. (b) 1 10. Unification of Italy Mazzini formed a secret society called young Italy-
Social Science Marking Scheme Class X 1. (d) or (b) 1 2. (b) 1. (c) 1 4. (c ) 1 5. (d) 1 6. (a) 1 7. (b) 1 8. (a) 1 9. (b) 1 10. Unification of Italy Mazzini formed a secret society called young Italy-
CBSE Sample Paper-04 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science
 CBSE Sample Paper-04 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science Time allowed: 3 hours ANSWERS Maximum Marks: 90 1. China 2. Periodically, banks have to submit information to the RBI on how much they
CBSE Sample Paper-04 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science Time allowed: 3 hours ANSWERS Maximum Marks: 90 1. China 2. Periodically, banks have to submit information to the RBI on how much they
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (NSQF)
 Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS 2 MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (NSQF) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION SA-II MARCH 205 CODE NO. 532/2 Government sold the rights of water supply to a MNC. MNC increased
Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS 2 MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (NSQF) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION SA-II MARCH 205 CODE NO. 532/2 Government sold the rights of water supply to a MNC. MNC increased
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, 2012 II, Class X / Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks :
 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, 202 II, 202 SOCIAL SCIENCE / Class X / X SS-200 Time allowed : hours Maximum Marks : 80 80 General Instructions : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) The question paper has 6 questions
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, 202 II, 202 SOCIAL SCIENCE / Class X / X SS-200 Time allowed : hours Maximum Marks : 80 80 General Instructions : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) The question paper has 6 questions
NATIONALISM IN INDIA. Q. 1. Why Gandhiji wanted 1920 movement as broad based movement? Q. 2. What was 'The Rowlatt Act, 1919'?
 NATIONALISM IN INDIA Q. 1. Why Gandhiji wanted 1920 movement as broad based movement? Q. 2. What was 'The Rowlatt Act, 1919'? Q. 3. Why did Gandhiji perceived salt as a powerful symbol that can unites
NATIONALISM IN INDIA Q. 1. Why Gandhiji wanted 1920 movement as broad based movement? Q. 2. What was 'The Rowlatt Act, 1919'? Q. 3. Why did Gandhiji perceived salt as a powerful symbol that can unites
THE QUESTION PAPER WILL INCLUDE VALUE BASED QUESTION(S) TO THE EXTENT OF 3-5 MARKS.
 ANNEXURE 'H' SYLLABUS SOCIAL SCIENCE SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-II (2013-14) Class-X Time : 3 Hours Marks : 90 UNIT TERM 1 TERM 2 1 India and the Contemporary World - II 23 23 2 India - Resources and their Development
ANNEXURE 'H' SYLLABUS SOCIAL SCIENCE SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-II (2013-14) Class-X Time : 3 Hours Marks : 90 UNIT TERM 1 TERM 2 1 India and the Contemporary World - II 23 23 2 India - Resources and their Development
CBSE Sample Paper-04 (Solved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science. Time allowed: 3 hours ANSWERS Maximum Marks: 90
 CBSE Sample Paper-04 (Solved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science Time allowed: 3 hours ANSWERS Maximum Marks: 90 1. Bourbon Kings OR 1873 2. 32 kg per annum 3. In this system of voting the
CBSE Sample Paper-04 (Solved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science Time allowed: 3 hours ANSWERS Maximum Marks: 90 1. Bourbon Kings OR 1873 2. 32 kg per annum 3. In this system of voting the
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, 2012 II, Class X / Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks :
 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, 202 II, 202 SOCIAL SCIENCE / Class X / X SS-2080 Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 80 3 80 General Instructions : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) The question paper has 36 questions
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, 202 II, 202 SOCIAL SCIENCE / Class X / X SS-2080 Time allowed : 3 hours Maximum Marks : 80 3 80 General Instructions : (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) (v) (vi) The question paper has 36 questions
Note: Please ensure that these instructions are not printed with the question paper being administered to the examinees.
 Important Instructions for the School Principal (Not to be printed with the question paper) ) This question paper is strictly meant for the use in School Based Summative Assessment-II, March-202 only.
Important Instructions for the School Principal (Not to be printed with the question paper) ) This question paper is strictly meant for the use in School Based Summative Assessment-II, March-202 only.
Nationalism movement wanted to: UNIFICATION: peoples of common culture from different states were joined together
 7-3.2 Analyze the effects of the Napoleonic Wars on the development and spread of nationalism in Europe, including the Congress of Vienna, the revolutionary movements of 1830 and 1848, and the unification
7-3.2 Analyze the effects of the Napoleonic Wars on the development and spread of nationalism in Europe, including the Congress of Vienna, the revolutionary movements of 1830 and 1848, and the unification
Q1. India has enormous diversity in the availability of resources. Explain.
 Class:- X Delhi Public School, Jammu Question Bank Session:- 2017-18 Subject- Social-Science Q1. India has enormous diversity in the availability of resources. Explain. Ans- i) The states of Jharkhand,
Class:- X Delhi Public School, Jammu Question Bank Session:- 2017-18 Subject- Social-Science Q1. India has enormous diversity in the availability of resources. Explain. Ans- i) The states of Jharkhand,
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (DELHI)
 Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS 1 MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (DELHI) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION MARCH 2015 CODE NO. 32/1/1 The French Revolution led to the transfer of sovereignty from the monarchy
Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS 1 MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (DELHI) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION MARCH 2015 CODE NO. 32/1/1 The French Revolution led to the transfer of sovereignty from the monarchy
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, 2012 II, Class X / Time allowed : 3 hours Marks :
 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, 202 II, 202 SOCIAL SCIENCE / Class X / X SS 2076 Time allowed : 3 hours Marks : 80 3 80 Maximum General Instructions : (i) The question paper has 36 questions in all. All questions
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II, 202 II, 202 SOCIAL SCIENCE / Class X / X SS 2076 Time allowed : 3 hours Marks : 80 3 80 Maximum General Instructions : (i) The question paper has 36 questions in all. All questions
CBSE Sample Paper-03 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science
 CBSE Sample Paper-03 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science Time allowed: 3 hours ANSWER Maximum Marks: 90 1. In 1834, a customs union or Zollverein was formed at the initiative of Prussia and
CBSE Sample Paper-03 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science Time allowed: 3 hours ANSWER Maximum Marks: 90 1. In 1834, a customs union or Zollverein was formed at the initiative of Prussia and
CBSE Guide Teacher' Jobs CBSE News
 Time: 3hrs. Social Science Max Marks :80 Guess Paper Class X General Instructions:- 1. The question paper has 36 questions in all. All questions are compulsory. 2. Marks are indicated against each question.
Time: 3hrs. Social Science Max Marks :80 Guess Paper Class X General Instructions:- 1. The question paper has 36 questions in all. All questions are compulsory. 2. Marks are indicated against each question.
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (FOREIGN)
 MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (FOREIGN) Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS Logo like to see on a tin of edible oil- SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION MARCH 205 CODE NO. 32/2/2 Page MARKS 2 Agmark Pg-85(E)
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (FOREIGN) Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS Logo like to see on a tin of edible oil- SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION MARCH 205 CODE NO. 32/2/2 Page MARKS 2 Agmark Pg-85(E)
2018 SOCIAL SCIENCE SOLVED SAMPLE PAPER 5
 Class: X General Instructions: 2018 SOCIAL SCIENCE SOLVED SAMPLE PAPER 5 Marks: 80 Time: 3 hr 1. All questions are compulsory. Marks are indicated against each question. 2. Questions from serial number
Class: X General Instructions: 2018 SOCIAL SCIENCE SOLVED SAMPLE PAPER 5 Marks: 80 Time: 3 hr 1. All questions are compulsory. Marks are indicated against each question. 2. Questions from serial number
Literarysources.wordpress.com
 QUESTION BANK - HISTORY - CLASS X NATIONALISM IN INDIA 1. How did the First World War help in the growth of national movement in India? 2. What is meant by the idea of satyagraha? Or A satyagrahi wins
QUESTION BANK - HISTORY - CLASS X NATIONALISM IN INDIA 1. How did the First World War help in the growth of national movement in India? 2. What is meant by the idea of satyagraha? Or A satyagrahi wins
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - II SESSION SOCIAL SCIENCE (CODE NO. 087) Set - 2 CLASS-X
 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - II SESSION 20-6 SOCIAL SCIENCE (CODE NO. 087) Set - 2 CLASS-X Time Allowed: Hours Maximum Marks: 90 General Instructions:. There are 29 questions in all. All questions are compulsory.
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT - II SESSION 20-6 SOCIAL SCIENCE (CODE NO. 087) Set - 2 CLASS-X Time Allowed: Hours Maximum Marks: 90 General Instructions:. There are 29 questions in all. All questions are compulsory.
THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL DUBAI SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II MODEL QUESTION PAPER ( ) SOCIAL SCIENCE- CLASSX (BOYS)
 THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL DUBAI SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II MODEL QUESTION PAPER (2016-17) SOCIAL SCIENCE- CLASSX (BOYS) Time allotted- 3hours Maximum Marks-90 Date-15-1-2017 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS (1) The question
THE INDIAN HIGH SCHOOL DUBAI SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II MODEL QUESTION PAPER (2016-17) SOCIAL SCIENCE- CLASSX (BOYS) Time allotted- 3hours Maximum Marks-90 Date-15-1-2017 GENERAL INSTRUCTIONS (1) The question
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II SOCIAL SCIENCE Sample Paper 2 Class X. Time: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 90
 SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II SOCIAL SCIENCE Sample Paper 2 Class X Time: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 90 Instructions: The question paper has 32 questions in all. All questions are compulsory. Marks are indicated
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II SOCIAL SCIENCE Sample Paper 2 Class X Time: 3 hours Maximum Marks: 90 Instructions: The question paper has 32 questions in all. All questions are compulsory. Marks are indicated
Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain????
 Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain???? Read textbook pages 612-615. Write a paragraph explaining why the industrial revolution began in Great Britain. Please include something about
Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain???? Read textbook pages 612-615. Write a paragraph explaining why the industrial revolution began in Great Britain. Please include something about
B. Directions: Use the words from the sentences to fill in the words in this puzzle. The letters in the box reading down name a part of nationalism.
 Name Date Period Nationalism Puzzle Chapter 22 Activity 64 A. Directions: Write the correct word from the Word Bank to complete each sentence. 1) Customs, religion, music, beliefs, and way of life make
Name Date Period Nationalism Puzzle Chapter 22 Activity 64 A. Directions: Write the correct word from the Word Bank to complete each sentence. 1) Customs, religion, music, beliefs, and way of life make
Secondary School Exam. (March, 2017) Social Science (Summative Assessment 2) Marking Scheme (Delhi) 32/1/1, 32/1/2, 32/1/3
 Secondary School Exam. (March, 2017) Social Science (Summative Assessment 2) Marking Scheme (Delhi) 32/1/1, 32/1/2, 32/1/3 General Instructions: 1. The Marking scheme provides general guidelines to reduce
Secondary School Exam. (March, 2017) Social Science (Summative Assessment 2) Marking Scheme (Delhi) 32/1/1, 32/1/2, 32/1/3 General Instructions: 1. The Marking scheme provides general guidelines to reduce
BRAIN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL
 BRAIN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL TERM-II CLASS-X 2018-19 SUBJECT:- SOCIAL SCIENCE REVISION SHEET HISTORY CHAPTER-1-NATIONALISM IN INDIA Q1. Examine the importance of the Noncooperation Movement. Q2. What was
BRAIN INTERNATIONAL SCHOOL TERM-II CLASS-X 2018-19 SUBJECT:- SOCIAL SCIENCE REVISION SHEET HISTORY CHAPTER-1-NATIONALISM IN INDIA Q1. Examine the importance of the Noncooperation Movement. Q2. What was
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (DELHI)
 MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (DELHI) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION MARCH 2015 CODE NO. 32/1/3 Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS Page No. MARKS 1 Role of FEDECOR: 2 3 The protest against water privatization
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (DELHI) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION MARCH 2015 CODE NO. 32/1/3 Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS Page No. MARKS 1 Role of FEDECOR: 2 3 The protest against water privatization
CBSE Board Class X Summative Assessment II Social Science Board Question Paper 2014 Set 2
 CBSE Board Class X Summative Assessment II Social Science Board Question Paper 2014 Set 2 Time: 3 hrs Max. Marks: 90 Note: Please check that this question paper contains 13 printed pages + 1Map. Code number
CBSE Board Class X Summative Assessment II Social Science Board Question Paper 2014 Set 2 Time: 3 hrs Max. Marks: 90 Note: Please check that this question paper contains 13 printed pages + 1Map. Code number
What is nationalism? What impact can it have? Objective: Explain what nationalism is and what effect it can have on individuals and on society.
 What is nationalism? What impact can it have? Objective: Explain what nationalism is and what effect it can have on individuals and on society. Introduction Directions: Examine the images and information
What is nationalism? What impact can it have? Objective: Explain what nationalism is and what effect it can have on individuals and on society. Introduction Directions: Examine the images and information
Nationalism in Europe Section 1
 Preview Italian Unification Starting Points Map: Europe,1815 Main Idea / Reading Focus Stirrings of Nationalism Quick Facts: Elements of Nationalism The Path Toward Unity Garibaldi and the Red Shirts Preview,
Preview Italian Unification Starting Points Map: Europe,1815 Main Idea / Reading Focus Stirrings of Nationalism Quick Facts: Elements of Nationalism The Path Toward Unity Garibaldi and the Red Shirts Preview,
Chapter 6 Political Parties
 Chapter 6 Political Parties Political Parties Political parties are one of the most visible institutions in a democracy. Is a group of people who come together to contest elections and hold power in the
Chapter 6 Political Parties Political Parties Political parties are one of the most visible institutions in a democracy. Is a group of people who come together to contest elections and hold power in the
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (OUTSIDE DELHI) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION SA - II MARCH, Series JSR CODE NO. 32/1, 32/2, 32/3 SET-3
 MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (OUTSIDE DELHI) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION SA - II MARCH, 2016 Series JSR CODE NO. 32/1, 32/2, 32/3 SET-3 Q. No EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS Page No. Marks 1 Victor Emmanuel
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (OUTSIDE DELHI) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION SA - II MARCH, 2016 Series JSR CODE NO. 32/1, 32/2, 32/3 SET-3 Q. No EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS Page No. Marks 1 Victor Emmanuel
Chapter 3 Nationalism in India
 Chapter 3 Nationalism in India Nationalism It involves a strong identification of a group of individuals with a political entity defined in national terms, i.e., a nation. Modern nationalism was associated
Chapter 3 Nationalism in India Nationalism It involves a strong identification of a group of individuals with a political entity defined in national terms, i.e., a nation. Modern nationalism was associated
Nationalism in Europe Section 1
 Preview Italian Unification Starting Points Map: Europe,1815 Main Idea / Reading Focus Stirrings of Nationalism Quick Facts: Elements of Nationalism The Path Toward Unity Garibaldi and the Red Shirts Preview,
Preview Italian Unification Starting Points Map: Europe,1815 Main Idea / Reading Focus Stirrings of Nationalism Quick Facts: Elements of Nationalism The Path Toward Unity Garibaldi and the Red Shirts Preview,
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (FOREIGN)
 MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (FOREIGN) Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION MARCH 205 CODE NO. 32/2/3 Requirement for a political party to be recognized as a State Party Page
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (FOREIGN) Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION MARCH 205 CODE NO. 32/2/3 Requirement for a political party to be recognized as a State Party Page
CBSE Sample Paper-05 (Solved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science. Time allowed: 3 hours ANSWERS Maximum Marks: 90
 CBSE Sample Paper-05 (Solved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science Time allowed: 3 hours ANSWERS Maximum Marks: 90 1. Young Italy in Marseilles and Young Europe in Berne. OR Military and Economic
CBSE Sample Paper-05 (Solved) SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT II Class X Social Science Time allowed: 3 hours ANSWERS Maximum Marks: 90 1. Young Italy in Marseilles and Young Europe in Berne. OR Military and Economic
HISTORY. March 21, 2018
 HISTORY March 21, 2018 Capitalism-System in which the means of production is in the hands of an individual The economy was well balanced between agriculture and industry. Three stages of Capitalism in
HISTORY March 21, 2018 Capitalism-System in which the means of production is in the hands of an individual The economy was well balanced between agriculture and industry. Three stages of Capitalism in
Chapter- 5 Political Parties. Prepared by - Sudiksha Pabbi
 Chapter- 5 Political Parties Prepared by - Sudiksha Pabbi 1 1. Why do we need parties? Areas of Study 2. What are Political Parties? 3.How many parties are good for a democracy? 4.National and regional
Chapter- 5 Political Parties Prepared by - Sudiksha Pabbi 1 1. Why do we need parties? Areas of Study 2. What are Political Parties? 3.How many parties are good for a democracy? 4.National and regional
SSWH 15 Presentation. Describe the impact of industrialization and urbanization.
 SSWH 15 Presentation Describe the impact of industrialization and urbanization. Vocabulary Industrial Revolution Industrialization Adam Smith Capitalism Laissiez-Faire Wealth of Nations Karl Marx Communism
SSWH 15 Presentation Describe the impact of industrialization and urbanization. Vocabulary Industrial Revolution Industrialization Adam Smith Capitalism Laissiez-Faire Wealth of Nations Karl Marx Communism
History The Rise of Nationalism in Europe
 Class X.A History The Rise of Nationalism in Europe 1. Explain Frederic Sorrieu s utopian vision of a world made up of democratic and social republics? *Frederic Sorrieu was a French artist who prepared
Class X.A History The Rise of Nationalism in Europe 1. Explain Frederic Sorrieu s utopian vision of a world made up of democratic and social republics? *Frederic Sorrieu was a French artist who prepared
The National Movement and Mahatma Gandhi ( )
 The National Movement and Mahatma Gandhi (1915-34) The Nationalist Movement of India - An Introduction In India, the rise of nationalism was intricately linked with the opposition of colonialism. The revolt
The National Movement and Mahatma Gandhi (1915-34) The Nationalist Movement of India - An Introduction In India, the rise of nationalism was intricately linked with the opposition of colonialism. The revolt
*Agricultural Revolution Came First. Working Class Political Movement
 1848-1914 *Agricultural Revolution Came First. 1. Great Britain led the Way 2. Migration from Rural to Urban (Poor Living Conditions) 3. Proletarianization of the Workforce (Poor Working Conditions) 4.
1848-1914 *Agricultural Revolution Came First. 1. Great Britain led the Way 2. Migration from Rural to Urban (Poor Living Conditions) 3. Proletarianization of the Workforce (Poor Working Conditions) 4.
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (OUTSIDE DELHI) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION SA - II MARCH, Series JSR CODE NO. 32/1, 32/2, 32/3 SET-1
 MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (OUTSIDE DELHI) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION SA - II MARCH, 2016 Series JSR CODE NO. 32/1, 32/2, 32/3 SET-1 Q. No EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS Page No. Marks 1 When France
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (OUTSIDE DELHI) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION SA - II MARCH, 2016 Series JSR CODE NO. 32/1, 32/2, 32/3 SET-1 Q. No EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS Page No. Marks 1 When France
NATIONALISM CASE STUDIES: ITALY AND GERMANY
 NATIONALISM CASE STUDIES: ITALY AND GERMANY NATIONALISM Nationalism is the belief that one s greatest loyalty should not be to a king or an empire but to a nation of people who share a common culture and
NATIONALISM CASE STUDIES: ITALY AND GERMANY NATIONALISM Nationalism is the belief that one s greatest loyalty should not be to a king or an empire but to a nation of people who share a common culture and
CH 17: The European Moment in World History, Revolutions in Industry,
 CH 17: The European Moment in World History, 1750-1914 Revolutions in Industry, 1750-1914 Explore the causes & consequences of the Industrial Revolution Root Europe s Industrial Revolution in a global
CH 17: The European Moment in World History, 1750-1914 Revolutions in Industry, 1750-1914 Explore the causes & consequences of the Industrial Revolution Root Europe s Industrial Revolution in a global
Unit 11: Age of Nationalism, Garibaldi in Naples
 Unit 11: Age of Nationalism, 1850-1914 Garibaldi in Naples Learning Objectives Explain why nationalism became an almost universal faith in Europe. Describe the unifications of both Germany and Italy-in
Unit 11: Age of Nationalism, 1850-1914 Garibaldi in Naples Learning Objectives Explain why nationalism became an almost universal faith in Europe. Describe the unifications of both Germany and Italy-in
Ch. 15: The Industrial Revolution
 Ch. 15: The Industrial Revolution I. Understanding Economics a. The Three Economic Questions i. People have unlimited wants, but limited resources. ii. 3 basic questions: 1. What should be produced? 2.
Ch. 15: The Industrial Revolution I. Understanding Economics a. The Three Economic Questions i. People have unlimited wants, but limited resources. ii. 3 basic questions: 1. What should be produced? 2.
NATIONAL MOVEMENT AND MAHATMA GANDHI
 NATIONAL MOVEMENT AND MAHATMA GANDHI M E T H O D S A D O P T E D B Y G A N D H I I N T H E N A T I O N A L M O V E M E N T [ S A T Y A G R A H A & S W A D E S H I ] T H E C A U S E S F O R T H E N O N
NATIONAL MOVEMENT AND MAHATMA GANDHI M E T H O D S A D O P T E D B Y G A N D H I I N T H E N A T I O N A L M O V E M E N T [ S A T Y A G R A H A & S W A D E S H I ] T H E C A U S E S F O R T H E N O N
Unit 7. Historical Background for Southern and Eastern Asia
 Unit 7 Historical Background for Southern and Eastern Asia What You Will Learn Historical events in Southern and Eastern Asia have shaped the governments, nations, economies, and culture through conflict
Unit 7 Historical Background for Southern and Eastern Asia What You Will Learn Historical events in Southern and Eastern Asia have shaped the governments, nations, economies, and culture through conflict
African Independence Movements. After World War I, many Africans organized to end colonial rule in their countries.
 African Independence Movements After World War I, many Africans organized to end colonial rule in their countries. African Independence Movements (cont.) Opposition to colonial rule escalated and Africans
African Independence Movements After World War I, many Africans organized to end colonial rule in their countries. African Independence Movements (cont.) Opposition to colonial rule escalated and Africans
CLASS X SOCIAL SCIENCE (CODE 087) MARKING SCHEME
 CLASS X SOCIAL SCIENCE (CODE 087) MARKING SCHEME 208-9 SECTION A ( X 7=7) Ans To define their identity and independence. Ch-,Nationalism in Europe, Page no. 26 To bring the benefits of civilization to
CLASS X SOCIAL SCIENCE (CODE 087) MARKING SCHEME 208-9 SECTION A ( X 7=7) Ans To define their identity and independence. Ch-,Nationalism in Europe, Page no. 26 To bring the benefits of civilization to
Europe Faces Revolution
 8.2 Notes: Europe Faces Revolution World History 9 th Mr. Sanderson Europe, 1815 Napoleon was defeated ended 25 years of war in Europe Old monarchs were restored to power (with limited powers) The Congress
8.2 Notes: Europe Faces Revolution World History 9 th Mr. Sanderson Europe, 1815 Napoleon was defeated ended 25 years of war in Europe Old monarchs were restored to power (with limited powers) The Congress
Teacher Overview Objectives: Nationalism and the Unification of Germany and Italy
 Teacher Overview Objectives: Nationalism and the Unification of Germany and Italy NYS Social Studies Framework Alignment: Key Idea Conceptual Understanding Content Specification 10.2: ENLIGHTENMENT, REVOLUTION,
Teacher Overview Objectives: Nationalism and the Unification of Germany and Italy NYS Social Studies Framework Alignment: Key Idea Conceptual Understanding Content Specification 10.2: ENLIGHTENMENT, REVOLUTION,
SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS]
![SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS] SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS]](/thumbs/76/73770788.jpg) POLITICAL PARTIES SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS] 1. How do political parties shape public opinion? Explain with three examples. Political parties shape public opinion in the following ways. They
POLITICAL PARTIES SHORT ANSWER TYPE QUESTIONS [3 MARKS] 1. How do political parties shape public opinion? Explain with three examples. Political parties shape public opinion in the following ways. They
World History (Survey) Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present
 World History (Survey) Chapter 33: Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present Section 1: Two Superpowers Face Off The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February
World History (Survey) Chapter 33: Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present Section 1: Two Superpowers Face Off The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (FOREIGN)
 MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (FOREIGN) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION MARCH 205 CODE NO. 32/2/ Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS Major issues taken up by the liberal nationalists Freedom of the Press
MARKING SCHEME SOCIAL SCIENCE (FOREIGN) SECONDARY SCHOOL EXAMINATION MARCH 205 CODE NO. 32/2/ Q.NO. EXPECTED ANSWERS/ VALUE POINTS Major issues taken up by the liberal nationalists Freedom of the Press
SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT TEST- 2, SOCIAL SCIENCE
 KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, ERNAKULAM REGION SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT TEST- 2, 2013-14 SOCIAL SCIENCE SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER CLASS: 10 MAX MARKS: 90 TIME ALLOWED: 3 Hrs 1. The question paper has 30 questions
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN, ERNAKULAM REGION SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT TEST- 2, 2013-14 SOCIAL SCIENCE SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER CLASS: 10 MAX MARKS: 90 TIME ALLOWED: 3 Hrs 1. The question paper has 30 questions
India Then and Now! By: Ankit Sood Matrikel Nu.:
 India Then and Now! By: Ankit Sood Matrikel Nu.: 871123 7. April 2018 1 Facts & Figures India is world s largest, oldest and continuously existing civilization. Dates back to 9000 BC. India had world s
India Then and Now! By: Ankit Sood Matrikel Nu.: 871123 7. April 2018 1 Facts & Figures India is world s largest, oldest and continuously existing civilization. Dates back to 9000 BC. India had world s
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 3 The Rise of Napoleon and the Napoleonic Wars ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What causes revolution? How does revolution change society? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary capable having or showing ability
Lesson 3 The Rise of Napoleon and the Napoleonic Wars ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What causes revolution? How does revolution change society? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary capable having or showing ability
SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS X SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER II
 SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS X SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER II Time Allowed : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 80 INSTRUCTIONS 1. There are 29 questions in all. All questions are compulsory. 2. Marks for each question are indicated
SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS X SAMPLE QUESTION PAPER II Time Allowed : 3 Hours Max. Marks : 80 INSTRUCTIONS 1. There are 29 questions in all. All questions are compulsory. 2. Marks for each question are indicated
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Unification of Italy
 Unification of Italy Objectives List the key obstacles to Italian unity. Understand the roles Count Camillo Cavour and Giuseppe Garibaldi played in the struggle for Italy. Describe the challenges that
Unification of Italy Objectives List the key obstacles to Italian unity. Understand the roles Count Camillo Cavour and Giuseppe Garibaldi played in the struggle for Italy. Describe the challenges that
The Colonies after WW1
 The Colonies after WW1 Africa - Summary Wanted to be independent Learned new ideas about freedom and nationalism New leaders were educated in Europe and the United States Africa Important People Harry
The Colonies after WW1 Africa - Summary Wanted to be independent Learned new ideas about freedom and nationalism New leaders were educated in Europe and the United States Africa Important People Harry
SUBJECT : POLITICAL SCIENCE
 SUBJECT : POLITICAL SCIENCE CH.1 : THE COLD WAR ERA 1. Describe the Cuban Missile Crises. 2. Explain the cold war. 3. Discuss the ideology of USSR and USA. 4. Why did USA decided to drop atom bomb on Japan?
SUBJECT : POLITICAL SCIENCE CH.1 : THE COLD WAR ERA 1. Describe the Cuban Missile Crises. 2. Explain the cold war. 3. Discuss the ideology of USSR and USA. 4. Why did USA decided to drop atom bomb on Japan?
10th Social Science Sample Paper SA-2 issued by CBSE (for 2015)
 Summative Assessment-II SAMPLE QUESTIONS 10th Social Science Sample Paper SA-2 issued by CBSE (for 2015) SUBJECT- SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS-X Very short answers -VSA (1 mark) 1. What did the inland Emigrating
Summative Assessment-II SAMPLE QUESTIONS 10th Social Science Sample Paper SA-2 issued by CBSE (for 2015) SUBJECT- SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS-X Very short answers -VSA (1 mark) 1. What did the inland Emigrating
The Making of Modern India: Indian Nationalism and Independence
 The Making of Modern India: Indian Nationalism and Independence Theme: How Indians adopt and adapt nationalist ideas that ultimately fostered the end of imperialism and make for a pattern of politics and
The Making of Modern India: Indian Nationalism and Independence Theme: How Indians adopt and adapt nationalist ideas that ultimately fostered the end of imperialism and make for a pattern of politics and
LATIN AMERICA POST-INDEPENDENCE ( )
 LATIN AMERICA POST-INDEPENDENCE (1820-1920) Socially, not much changed w/ independencelarge gap between wealthy landowners & poor laborers Politically unstable- military dictators called caudillos often
LATIN AMERICA POST-INDEPENDENCE (1820-1920) Socially, not much changed w/ independencelarge gap between wealthy landowners & poor laborers Politically unstable- military dictators called caudillos often
CBSE Class 10 Social Notes Civics
 CBSE Class 10 Social Notes Civics 1 CBSE Class 10 Social Notes Civics Table of Contents 1. Power Sharing... 2... 2 2. Federalism... 3... 3 3. Democracy and Diversity... 4... 4 4. Gender, Religion and Caste...
CBSE Class 10 Social Notes Civics 1 CBSE Class 10 Social Notes Civics Table of Contents 1. Power Sharing... 2... 2 2. Federalism... 3... 3 3. Democracy and Diversity... 4... 4 4. Gender, Religion and Caste...
World History Chapter 24
 World History Chapter 24 Problem: How to bring stability & security back to Europe which was destroyed by the French Revolution & Napoleon Solution: Dominant 5 form an alliance (dominated by Russia, Prussia,
World History Chapter 24 Problem: How to bring stability & security back to Europe which was destroyed by the French Revolution & Napoleon Solution: Dominant 5 form an alliance (dominated by Russia, Prussia,
Chapter 12 Section 3 Indian Nationalism Grows. Essential Question: How did Gandhi and the Congress party work for independence in India?
 Chapter 12 Section 3 Indian Nationalism Grows Essential Question: How did Gandhi and the Congress party work for independence in India? Chapter 12 Section 3 India Seeks Self-Rule Indian Nationalism Grows
Chapter 12 Section 3 Indian Nationalism Grows Essential Question: How did Gandhi and the Congress party work for independence in India? Chapter 12 Section 3 India Seeks Self-Rule Indian Nationalism Grows
Summary The Beginnings of Industrialization KEY IDEA The Industrial Revolution started in Great Britain and soon spread elsewhere.
 Summary The Beginnings of Industrialization KEY IDEA The Industrial Revolution started in Great Britain and soon spread elsewhere. In the early 1700s, large landowners in Britain bought much of the land
Summary The Beginnings of Industrialization KEY IDEA The Industrial Revolution started in Great Britain and soon spread elsewhere. In the early 1700s, large landowners in Britain bought much of the land
Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman Perspectives
 STANDARD 10.1.1 Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman Perspectives Specific Objective: Analyze the similarities and differences in Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman views of law, reason and faith, and duties of
STANDARD 10.1.1 Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman Perspectives Specific Objective: Analyze the similarities and differences in Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman views of law, reason and faith, and duties of
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Age of Napoleon
 The Age of Napoleon Objectives Understand Napoleon s rise to power and why the French strongly supported him. Explain how Napoleon built an empire and what challenges the empire faced. Analyze the events
The Age of Napoleon Objectives Understand Napoleon s rise to power and why the French strongly supported him. Explain how Napoleon built an empire and what challenges the empire faced. Analyze the events
Ch 29-1 The War Develops
 Ch 29-1 The War Develops The Main Idea Concern about the spread of communism led the United States to become increasingly violent in Vietnam. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze how the Cold war and
Ch 29-1 The War Develops The Main Idea Concern about the spread of communism led the United States to become increasingly violent in Vietnam. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze how the Cold war and
NCERT Class 9th Social Science Economics Chapter 3: Poverty as a Challenge
 NCERT Class 9th Social Science Economics Chapter 3: Poverty as a Challenge Question 1. Describe how poverty line is estimated in India. A common method used to measure poverty is based on income or consumption
NCERT Class 9th Social Science Economics Chapter 3: Poverty as a Challenge Question 1. Describe how poverty line is estimated in India. A common method used to measure poverty is based on income or consumption
The Beginnings of Industrialization
 Name CHAPTER 25 Section 1 (pages 717 722) The Beginnings of BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about romanticism and realism in the arts. In this section, you will read about the beginning of
Name CHAPTER 25 Section 1 (pages 717 722) The Beginnings of BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about romanticism and realism in the arts. In this section, you will read about the beginning of
Aravali International School Assessment sheet- Class X Subject: Economics (Development)
 Subject: Economics (Development) Short answer questions 1. What is the most common method of measuring the economic development of a country? a) Equal treatment c) Security b) Freedom d) Income 2. Which
Subject: Economics (Development) Short answer questions 1. What is the most common method of measuring the economic development of a country? a) Equal treatment c) Security b) Freedom d) Income 2. Which
THE INDIAN COMMUNITY SCHOOL, KUWAIT
 THE INDIAN COMMUNITY SCHOOL, KUWAIT SERIES : II TERM /FN/ 2018-2019 CODE : L 087 TIME ALLOWED : 3 HOURS NAME OF STUDENT : MAX. MARKS : 80 ROLL NO. :.. CLASS/SEC :.. NO. OF PAGES : 3 + 1 MAP SOCIAL SCIENCE
THE INDIAN COMMUNITY SCHOOL, KUWAIT SERIES : II TERM /FN/ 2018-2019 CODE : L 087 TIME ALLOWED : 3 HOURS NAME OF STUDENT : MAX. MARKS : 80 ROLL NO. :.. CLASS/SEC :.. NO. OF PAGES : 3 + 1 MAP SOCIAL SCIENCE
Communism in the Far East. China
 Communism in the Far East China Terms and Players KMT PLA PRC CCP Sun Yat-Sen Mikhail Borodin Chiang Kai-shek Mao Zedong Shaky Start In 1913 the newly formed Chinese government was faced with the assassination
Communism in the Far East China Terms and Players KMT PLA PRC CCP Sun Yat-Sen Mikhail Borodin Chiang Kai-shek Mao Zedong Shaky Start In 1913 the newly formed Chinese government was faced with the assassination
Unification of Italy & Germany. Ideologies of Change: Europe
 Unification of Italy & Germany Ideologies of Change: Europe 1815 1914 Creation of Italy and Germany Revolutions reverberated throughout Western Europe: Failures did not diminish impact: To what extent
Unification of Italy & Germany Ideologies of Change: Europe 1815 1914 Creation of Italy and Germany Revolutions reverberated throughout Western Europe: Failures did not diminish impact: To what extent
World History Unit 12 Lesson 1 The Congress of Vienna
 Unit 12 Lesson 1 The Congress of Vienna After the Napoleonic Wars, Europe faced many problems: 1) Many countries leaders had been replaced by Napoleon. 2) Some countries had been eliminated. 3) The liberalism
Unit 12 Lesson 1 The Congress of Vienna After the Napoleonic Wars, Europe faced many problems: 1) Many countries leaders had been replaced by Napoleon. 2) Some countries had been eliminated. 3) The liberalism
Period V ( ): Industrialization and Global Integration
 Period V (1750-1900): Industrialization and Global Integration 5.1 Industrialization and Global Capitalism I. I can describe and explain how industrialism fundamentally changed how goods were produced.
Period V (1750-1900): Industrialization and Global Integration 5.1 Industrialization and Global Capitalism I. I can describe and explain how industrialism fundamentally changed how goods were produced.
C.B.S.E Class X
 SOLVED PAPER With CBSE Marking Scheme C.B.S.E. 2018 Class X Delhi & Outside Delhi Social Science Time Allowed : 3 Hrs. M.M. : 80 Instructions : 1. The question paper has 26 questions in all. All questions
SOLVED PAPER With CBSE Marking Scheme C.B.S.E. 2018 Class X Delhi & Outside Delhi Social Science Time Allowed : 3 Hrs. M.M. : 80 Instructions : 1. The question paper has 26 questions in all. All questions
4 Rebuilding a World Economy: The Post-war Era
 4 Rebuilding a World Economy: The Post-war Era The Second World War broke out a mere two decades after the end of the First World War. It was fought between the Axis powers (mainly Nazi Germany, Japan
4 Rebuilding a World Economy: The Post-war Era The Second World War broke out a mere two decades after the end of the First World War. It was fought between the Axis powers (mainly Nazi Germany, Japan
MRS. OSBORN S APWH CRAM PACKET:
 MRS. OSBORN S APWH CRAM PACKET: Period 5 Industrialization & Global Integration, 1750-1900, chapters 23-29 (20% of APWH Exam) (NOTE: Some material overlaps into Period 6, 1900-1914) Questions of periodization:
MRS. OSBORN S APWH CRAM PACKET: Period 5 Industrialization & Global Integration, 1750-1900, chapters 23-29 (20% of APWH Exam) (NOTE: Some material overlaps into Period 6, 1900-1914) Questions of periodization:
10 th CBSE (SESSION : ) SUBJECT : SOCIAL SCIENCE SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-II SOLUTION _SET-2_CODE NO. 32/2
 Pre-foundation Career Care Programmes (PCCP) Division 10 th CBSE (SESSION : 2015-16) SUBJECT : SOCIAL SCIENCE SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-II SOLUTION _SET-2_CODE NO. 32/2 SECTION # A 1. In January 1871, the Prussian
Pre-foundation Career Care Programmes (PCCP) Division 10 th CBSE (SESSION : 2015-16) SUBJECT : SOCIAL SCIENCE SUMMATIVE ASSESSMENT-II SOLUTION _SET-2_CODE NO. 32/2 SECTION # A 1. In January 1871, the Prussian
The Early Industrial Revolution Chapter 22 AP World History
 The Early Industrial Revolution 1760-1851 Chapter 22 AP World History Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
The Early Industrial Revolution 1760-1851 Chapter 22 AP World History Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos Annotation
 Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos Annotation Name Directions: A. Read the entire article, CIRCLE words you don t know, mark a + in the margin next to paragraphs you understand and a next to paragraphs you don t
Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos Annotation Name Directions: A. Read the entire article, CIRCLE words you don t know, mark a + in the margin next to paragraphs you understand and a next to paragraphs you don t
5th Grade Social Studies Test
 5th Grade Social Studies Practice Name: Instructions: Copyright 2000-2002 Measured Progress, All Rights Reserved : 5th Grade Social Studies Practice 1. What is the economic term used for the skills and
5th Grade Social Studies Practice Name: Instructions: Copyright 2000-2002 Measured Progress, All Rights Reserved : 5th Grade Social Studies Practice 1. What is the economic term used for the skills and
Name Class Date. The French Revolution and Napoleon Section 3
 Name Class Date Section 3 MAIN IDEA Napoleon Bonaparte rose through military ranks to become emperor over France and much of Europe. Key Terms and People Napoleon Bonaparte ambitious military leader who
Name Class Date Section 3 MAIN IDEA Napoleon Bonaparte rose through military ranks to become emperor over France and much of Europe. Key Terms and People Napoleon Bonaparte ambitious military leader who
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX TOPIC/CHAPTER: 03-Poverty As A Challenge WORKSHEET No.
 INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX TOPIC/CHAPTER: 0-Poverty As A Challenge WORKSHEET No. : 4 (206-7) SUMMARY WRITE THESE QUESTIONS IN YOUR CLASS WORK NOTE BOOK 5,
INDIAN SCHOOL MUSCAT SENIOR SECTION DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SCIENCE CLASS: IX TOPIC/CHAPTER: 0-Poverty As A Challenge WORKSHEET No. : 4 (206-7) SUMMARY WRITE THESE QUESTIONS IN YOUR CLASS WORK NOTE BOOK 5,
Key Terms. Franco-Prussian War. The Second Reich Otto Von Bismarck Junker Blood & Iron Realpolitik. War with Denmark War with Austria
 German Unification Key Terms The Second Reich Otto Von Bismarck Junker Blood & Iron Realpolitik War with Denmark War with Austria Franco-Prussian War Kaiser King Wilhelm I Germany in the1700s German people
German Unification Key Terms The Second Reich Otto Von Bismarck Junker Blood & Iron Realpolitik War with Denmark War with Austria Franco-Prussian War Kaiser King Wilhelm I Germany in the1700s German people
Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe
 Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe Frederic Sorrieu He was a French artist famous for prints prepared in 1948 that visualized the dream of a world consisting of Democratic and Social Republics.
Chapter 1 The Rise of Nationalism in Europe Frederic Sorrieu He was a French artist famous for prints prepared in 1948 that visualized the dream of a world consisting of Democratic and Social Republics.
Business Globalization
 Business Globalization Introduction In today s business environment, most of the big companies are becoming global in nature. Companies are realizing that globalization provides an opportunity in terms
Business Globalization Introduction In today s business environment, most of the big companies are becoming global in nature. Companies are realizing that globalization provides an opportunity in terms
EUROPEAN NATIONALISM. Mid 19 th Century
 EUROPEAN NATIONALISM Mid 19 th Century What is Nationalism? the belief that a person s greatest loyalty should not be to a king or an empire but to a nation of people who share a common culture and history.
EUROPEAN NATIONALISM Mid 19 th Century What is Nationalism? the belief that a person s greatest loyalty should not be to a king or an empire but to a nation of people who share a common culture and history.
CHAPTER 11 KEY ISSUE TWO: WHERE IS INDUSTRY DISTRIBUTED?
 CHAPTER 11 KEY ISSUE TWO: WHERE IS INDUSTRY DISTRIBUTED? WORLD INDUSTRIAL REGIONS North America Industrialized areas in North America Changing distribution of U.S. manufacturing Europe Western Europe Eastern
CHAPTER 11 KEY ISSUE TWO: WHERE IS INDUSTRY DISTRIBUTED? WORLD INDUSTRIAL REGIONS North America Industrialized areas in North America Changing distribution of U.S. manufacturing Europe Western Europe Eastern
I. The Agricultural Revolution
 I. The Agricultural Revolution A. The Agricultural Revolution Paves the Way 1. Wealthy farmers cultivated large fields called enclosures. 2. The enclosure movement caused landowners to try new methods.
I. The Agricultural Revolution A. The Agricultural Revolution Paves the Way 1. Wealthy farmers cultivated large fields called enclosures. 2. The enclosure movement caused landowners to try new methods.
KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN GURGAON REGION SPLIT UP SYLLABUS SUB: Social Science CLASS: IX
 S. No Month First Term Expected No.of working Days KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN GURGAON REGION SPLIT UP SYLLABUS 2015-16 SUB: Social Science CLASS: IX Branch of Subject Chapter No & Chapter Detailed Split-up
S. No Month First Term Expected No.of working Days KENDRIYA VIDYALAYA SANGATHAN GURGAON REGION SPLIT UP SYLLABUS 2015-16 SUB: Social Science CLASS: IX Branch of Subject Chapter No & Chapter Detailed Split-up
Lecture Outline, The French Revolution,
 Lecture Outline, The French Revolution, 1789-1799 A) Causes growth of "liberal" public opinion the spread of Enlightenment ideas re. rights, liberty, limited state power, need for rational administrative
Lecture Outline, The French Revolution, 1789-1799 A) Causes growth of "liberal" public opinion the spread of Enlightenment ideas re. rights, liberty, limited state power, need for rational administrative
National Self-Determination
 What is National Self-Determination? People are trying to gain or keep the power to their own They want to make their decisions about what is in their interests. National Self-Determination Case Study
What is National Self-Determination? People are trying to gain or keep the power to their own They want to make their decisions about what is in their interests. National Self-Determination Case Study
3.1 How does the economy of the globalised world function in different places?
 3.1 How does the economy of the globalised world function in different places? a. The balance between employment sectors (primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary) varies spatially and is changing.
3.1 How does the economy of the globalised world function in different places? a. The balance between employment sectors (primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary) varies spatially and is changing.
PT-1 Answer Key Set-1. History
 PT-1 Answer Key Set-1 History Q1. Conservative regimes set up in 1815 were autocratic. A) They did not tolerate criticism and dissent. B) They tried to curb the activities that questioned the legitimacy
PT-1 Answer Key Set-1 History Q1. Conservative regimes set up in 1815 were autocratic. A) They did not tolerate criticism and dissent. B) They tried to curb the activities that questioned the legitimacy
