Independent to Imperialist -- The Spanish American War
|
|
|
- Rodney Stanley
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 St. Cloud State University therepository at St. Cloud State Curriculum Unit on the Gilded Age in the United States American History Lesson Plans Independent to Imperialist -- The Spanish American War Tom Stoffel St. Cloud State University Follow this and additional works at: Part of the Curriculum and Instruction Commons, and the United States History Commons Recommended Citation Stoffel, Tom, "Independent to Imperialist -- The Spanish American War" (2016). Curriculum Unit on the Gilded Age in the United States. Book This lesson is brought to you for free and open access by the American History Lesson Plans at therepository at St. Cloud State. It has been accepted for inclusion in Curriculum Unit on the Gilded Age in the United States by an authorized administrator of therepository at St. Cloud State. For more information, please contact
2 Title: Independent to Imperialist The Spanish American War Author: Lower East Side Tenement Museum Adapter: Tom Stoffel Grade Levels: 9-12 Time: 1 Day Lesson 50 Min Classes Focus Statement: By utilizing primary sources without knowing what the outcome is supposed to be, students will perceive events and issues as people experienced them at the time, to develop historical empathy as opposed to present-mindedness. Students will evaluate the message Theodore Roosevelt sent to Dewey and decide if Roosevelt made the correct decision. Students will also learn key terms relating to what lead to the Spanish American War, what events happened in Cuba and debate if Yellow Journalism still occurs today. To finish the day we will cover how and if the Spanish American War changed the course of American foreign policy. MN Standard: MN Standard As the United States shifted from its agrarian roots into an industrial and global power, the rise of big business, urbanization and immigration led to institutionalized racism, ethnic and class conflict and new efforts at reform. (Development of an industrial United States ) Benchmark: Explain how the United States became a world power via trade and imperialist acquisition of new territories. (Development of an Industrial United States: ) Habit of Mind: Perceive past events and issues as they were experienced by people at the time, to develop historical empathy as opposed to present-mindedness. Learning Objective(s): (Both Content and Skill) Students will locate: Cuba, Philippines, Guam and Hawaii on a Map Students will define the following: Imperialism, Isolationism, Martial Law and Yellow Journalism Students will articulate how the Spanish American War changed the course of American Foreign Policy Resources: Attached at End Copy of telegram from Theodore Roosevelt to Admiral Dewey Writings from Cleveland and McKinley In the Shadow of Glory: The Story of the Thirteenth Minnesota in the Spanish American War and Philippine American War, (Use for Images and story for students to relate to) Painting of USS Maine explosion Powerpoint in order to give students definitions of key terms and main points
3 Day 1 Methods/Procedures Beginning (10 minutes): Display the painting of the USS Main exploding, ask the students what they think happened. Write answers on the board. Ask how U.S. citizens might have reacted, what would it be like to be there. Note the huge range of answers, write the conspiracies that were going around the United States during the time of the explosion: Spanish forces blew it up, Cuban Rebels blew it up to bring the United States into the war and the ship blew up because the ammunition was stored too closely to the boiler room. Display Roosevelt s telegram to Admiral Dewey and see if any of the kids can tell you what it means. If they cannot inform them it authorized Dewey to engage the Spanish fleet without letting everyone else know what is going on. Should Roosevelt have done this? Middle: Instructional Strategies / Learning Activities (30 minutes): First show where Cuba is in relation to the United States as well as Hawaii, Guam and the Philippines. Use a Map and ensure all students know the basic geography of the region we re talking about. Tell the class what the Spanish were doing to the native Cubans and talk about the camps they were putting them into. Talk about the harsh living conditions with so many people living in a confined space under martial law and subject to disease and dirty water. Describe Yellow Journalism and how this was used to change the opinions of Americans and government officials by exaggerating the facts and not showing all sides of what was going on. Discuss the USS Maine blowing up. Why this happened and how the U.S. population took the news. Was it because of the Spanish or Cubans, or was it just bad placement of the ammunition. U.S. citizens were already getting mad at the Spanish because they were treating people inhumanely just 90 miles off the coast of Florida. Again display Roosevelt s telegram to Admiral Dewey and tell the class how Dewey was able to destroy all of the Spanish Ships in the Philippines. Talk about how German and English fleets flocked to the area seeing if the United States was going to take over the Philippines or not. If the United States did not they were going to move in for their own purposes. Ask if America wants to expand during this time period or remain isolationist? Between the Gilded Age and until after World War II there was the discussion of being a world power or should we use the oceans to our advantage and be isolationist. Break the class up into groups of 2-3 and hand out two different points of view, one from Cleveland and McKinley. Have the students answer who, what, where, when and why. Do students think the way these two politicians did? Pick students to discuss what their group wrote. Ask the students if this is the only two viewpoints? Can we today completely understand what was going on during this time from just primary sources? Talk about the buildup of the military and staging in Florida as well as Roosevelt s Rough Riders. Tell students we did not even have enough naval ships to ship troops the 90 miles and had to use merchant ships. Show students about Buffalo soldiers and how they are the unsung heroes of the Cuban Campaign. The Battle of Santiago De Cuba which resulted in the destruction of the Spanish Navy s Caribbean Squadron. Discuss imperialism and how the Spanish American War changed foreign policy, was it good that we were in control of areas that were not part of the United States? End / Summary (10 minutes): Fill out an Exit Card defining vocab words Discuss whether or not Yellow Journalism still occurs today
4 How did America view of its role change from time period of the Civil War to the time period of the Spanish American War Afterwards Provisions for Individual Differences (physical, emotional, mental, language, etc.): Once I find out what Individual Education Program (IEP) I have in the class I will make appropriate adjustments so that all students get the most out of their education Self-Reflection (What worked? What needs Improvement? What changes would I make before doing the lesson again?) I will fill out after trying in a classroom to better incorporate new ideas and how to teach this lesson better
5 Bibliography Hickman, Kennedy. "The Spanish-American War." About Education Accessed November 25, Roosevelt, Theodore. Telegram in Code from Theodore Roosevelt to Admiral Dewy, 2/26/1898. National Archives. Accessed October 17, Splendid Little War : The Spanish American War. Edsitement. Accessed October 17, of an American Empire Lesson02.pdf. Ward, Kyle. In the Shadow of Glory: The Story of the Thirteenth Minnesota in the Spanish American War and Philippine American War, St Coud, Minnesota: North Star Press of St Cloud MN, 1999.
6 Name: Date: Exit Card 1. Define the following: Imperialism: Isolationism: Yellow Journalism: Martial Law: 2. Does Yellow Journalism still occur today? 3. How did America s view of its role change from time period of the Civil War to the time period of the Spanish American War
7 Painting of the explosion of the USS Maine Document for May 1st: Telegram, in code, from Theodore Roosevelt to Commodore Dewey, 02/26/1898 This telegram, in code from Assistant Secretary of the Navy Theodore Roosevelt to Commodore George Dewey, Commander of the U.S. Asiatic Squadron, was sent without the knowledge of Secretary of the Navy Long. The telegram authorized Dewey to engage the Spanish fleet. On May 1, 1898, Dewey would destroy the Spanish fleet at the Battle of Manila Bay.
8 Grover Cleveland: American Interests in the Cuban Revolution (1896): THE INSURRECTION IN CUBA still continues with all its perplexities. It is difficult to perceive that any progress has thus far been made toward the pacification of the island or that the situation of affairs as depicted in my last annual message has in the least improved. Indeed, as the contest has gone on, the pretense that civil government exists on the island, except so far as Spain is able to maintain it, has been practically abandoned. Spain does keep on foot such a government, more or less imperfectly, in the large towns and their immediate suburbs. But, that exception being made, the entire country is either given over to anarchy or is subject to the military occupation of one or the other party. Meanwhile, as in all cases of protracted civil strife, the passions of the combatants grow more and more inflamed, and excesses on both sides become more frequent and more deplorable. They are also participated in by bands of marauders, who, now in the name of one party and now in the name of the other, as may best suit the occasion, harry the country at will and plunder its wretched inhabitants for their own advantage The sure result would seem to be that the industrial value of the island is fast diminishing, and that unless there is a speedy and radical change in existing conditions, it will soon disappear altogether. That value consists very largely, of course, in its capacity to produce sugar - a capacity already much reduced by the interruptions to tillage which have taken place during the last two years The spectacle of the utter ruin of an adjoining country, by nature one of the most fertile and charming on the globe, would engage the serious attention of the government and people of the United States in any circumstances It is reasonably estimated that at least from $30 million to $50 million of American capital are invested in plantations and in railroad, mining, and other business enterprises on the island. The volume of trade between the United States and Cuba, which in 1889 amounted to about $64 million, rose in 1893 to about $103 million, and in 1894, the year before the present insurrection broke out, amounted to nearly $96 million. These inevitable entanglements of the United States with the rebellion in Cuba, the large American property interests affected, and considerations of philanthropy and humanity in general, have led to a vehement demand in various quarters for some sort of positive intervention on the part of the United States It is now also suggested that the United States should buy the island - a suggestion possibly worthy of consideration if there were any evidence of a desire or willingness on the part of Spain to entertain such a proposal. It is urged, finally, that, all other methods failing, the existing internecine strife in Cuba should be terminated by our intervention, even at the cost of a war between the United States and Spain - a war which its advocates confidently prophesy could be neither large in its proportions nor doubtful in its issue. The correctness of this forecast need be neither affirmed nor denied. The United States has nevertheless a character to maintain as a nation, which plainly dictates that right and not might should be the rule of its conduct. Further, though the United States is not a nation to which peace is a necessity, it is in truth the most pacific of powers and desires nothing so much as to live in amity with all the world. Its own ample and diversified domains satisfy all possible longings for territory, preclude all dreams of conquest, and prevent any casting of covetous eyes upon neighboring regions, however attractive. Nevertheless, realizing that suspicions and precautions on the part of the weaker of two combatants are always natural and not always unjustifiable, being sincerely desirous in the interest of both as well as on its own account that the Cuban problem should be solved with the least possible delay, it was intimated by this government to the government of Spain some months ago that, if a satisfactory measure of home rule were tendered the Cuban insurgents and would be accepted by them upon a guarantee of its execution, the United States would endeavor to find a way not objectionable to Spain of furnishing such guarantee. While no definite response to this intimation has yet been received from the Spanish government, it is believed to be not altogether unwelcome, while, as already suggested, no reason is perceived why it should not be approved by the insurgents. Neither party can fail to see the importance of early action, and both must realize that to prolong the present state of things for even a short period will add enormously to the time and labor and expenditure necessary to bring about the industrial recuperation of the island. It is therefore fervently hoped on all grounds that earnest
9 efforts for healing the breach between Spain and the insurgent Cubans, upon the lines above indicated, may be at once inaugurated and pushed to an immediate and successful is-sue. The friendly offices of the United States, either in the manner above outlined or in any other way consistent with our Constitution and laws, will always be at the disposal of either party. Whatever circumstances may arise, our policy and our interests would constrain us to object to the acquisition of the island or an interference with its control by any other power. It should be added that it cannot be reasonably assumed that the hitherto expectant attitude of the United States will be indefinitely maintained. While we are anxious to accord all due respect to the sovereignty of Spain, we cannot view the pending conflict in all its features and properly apprehend our inevitably close relations to it and its possible results without considering that, by the course of events, we may be drawn into such an unusual and unprecedented condition as will fix a limit to our patient waiting for Spain to end the contest, either alone and in her own way or with our friendly cooperation
10 President McKinley s Declaration of War, 1898: The present revolution is but the successor of other similar insurrections which have occurred in Cuba against the dominion of Spain, extending over a period of nearly half a century, each of which, during its progress, has subjected the United States to great effort and expense in enforcing its neutrality laws, caused enormous losses to American trade and commerce, caused irritation, annoyance, and disturbance among our citizens, and, by the exercise of cruel, barbarous, and uncivilized practices of warfare, shocked the sensibilities and offended the humane sympathies of our people....the grounds for such intervention may be briefly summarized as follows: First, in the cause of humanity and to put an end to the barbarities, bloodshed, starvation, and horrible miseries now existing there, and which the parties to the conflict are either unable or unwilling to stop or mitigate. It is no answer to say this is all in another country, belonging to another nation, and is therefore none of our business. It is specially our duty, for it is right at our door. Second, we owe it to our citizens in Cuba to afford them that protection and indemnity for life and property which no government there can or will afford, and to that end to terminate the conditions that deprive them of legal protection. Third, the right to intervene may be justified by the very serious injury to the commerce, trade, and business of our people, and by the wanton destruction of property and devastation of the island. Fourth, and which is of the utmost importance, the present condition of affairs in Cuba is a constant menace to our peace, and entails upon this government an enormous expense. With such a conflict waged for years in an island so near us and with which our people have such trade and business relations; when the lives and liberty of our citizens are in constant danger and their property destroyed and themselves ruined; where our trading vessels are liable to seizure and are seized at our very door by warships of a foreign nation, the expeditions of filibustering that we are powerless to prevent altogether, and the irritating questions and entanglements thus arising -- all these and others that I need not mention, with the resulting strained relations, are a constant menace to our peace, and compel us to keep on a semiwar footing with a nation with which we are at peace. These elements of danger and disorder already pointed out have been strikingly illustrated by a tragic event which has deeply and justly moved the American people. I have already transmitted to Congress the report of the Naval Court of Inquiry on the destruction of the battleship Maine in the harbor of Havana during the night of the 15th of February. The destruction of that noble vessel has filled the national heart with inexpressible horror. Two hundred and fifty-eight brave sailors and marines and two officers of our Navy, reposing in the fancied security of a friendly harbor, have been hurled to death, grief and want brought to their homes, and sorrow to the nation. The Naval Court of Inquiry, which, it is needless to say, commands the unqualified confidence of the government, was unanimous in its conclusion that the destruction of the Maine was caused by an exterior explosion, that of a submarine mine. It did not assume to place the responsibility. That remains to be fixed. In any event, the destruction of the Maine, by whatever exterior cause, is a patent and impressive proof of a state of things in Cuba that is intolerable. That condition is thus shown to be such that the Spanish government cannot assure safety and security to a vessel of the American Navy in the harbor of Havana on a mission of peace, and rightfully there.... The long trial has proved that the object for which Spain has waged the war cannot be attained. The fire of insurrection may flame or may smolder with varying seasons, but it has not been, and it is plain that it cannot be, extinguished by present methods. The only hope of relief and repose from a condition which can no longer be endured is the enforced pacification of Cuba. In the name of humanity, in the name of civilization, in behalf of endangered American interests which give us the right and the duty to speak and to act, the war in Cuba must stop. In view of these facts and of these considerations, I ask the Congress to authorize and empower the President to take measures to secure a full and final termination of hostilities between the government of Spain and the people of Cuba, and to secure in the island the establishment of a stable government, capable of maintaining order and observing its international obligations, insuring peace and tranquillity and the security of its
11 citizens as well as our own, and to use the military and naval forces of the United States as may be necessary for these purposes. And in the interest of humanity and to aid in preserving the lives of the starving people of the island, I recommend that the distribution of food and supplies be continued, and that an appropriation be made out of the public Treasury to supplement the charity of our citizens...
Platform of the American Anti-Imperialist League (1899)
 Platform of the American Anti-Imperialist League (1899) Those opposed to the new expansionism included Republicans and Democrats, business leaders such as Andrew Carnegie, the philosopher William James,
Platform of the American Anti-Imperialist League (1899) Those opposed to the new expansionism included Republicans and Democrats, business leaders such as Andrew Carnegie, the philosopher William James,
Chapter 17. Becoming a World Power ( )
 Chapter 17 Becoming a World Power (1872 1912) 1 Chapter Overview: During this era, economic and military competition from world powers convinced the United States it must be a world power. The United States
Chapter 17 Becoming a World Power (1872 1912) 1 Chapter Overview: During this era, economic and military competition from world powers convinced the United States it must be a world power. The United States
Letter from President Fillmore asking Japan. American ships to stop for supplies safety reasons
 Chapter 19-21 Introduction Japan 1853 Not open to trading with other countries Commodore Matthew Perry went to Japan with a small fleet of warships (Gunboat Diplomacy) Letter from President Fillmore asking
Chapter 19-21 Introduction Japan 1853 Not open to trading with other countries Commodore Matthew Perry went to Japan with a small fleet of warships (Gunboat Diplomacy) Letter from President Fillmore asking
Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power
 Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power Objective: Why did the United States become imperialistic and what were the outcomes? Goal: Students will be able to understand the causes and effects of imperialism
Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power Objective: Why did the United States become imperialistic and what were the outcomes? Goal: Students will be able to understand the causes and effects of imperialism
Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea
 Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea In the last half of the 1800s, the United States joined the race for control of overseas territories.
Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea In the last half of the 1800s, the United States joined the race for control of overseas territories.
Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War
 Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War 1 Imperialism & Expansion CH 14-1 Imperialism & War Name Reasons why the United States becomes an imperialist nation. 1-New Markets 2-Anglo-Saxonism 3-Modern Navy 4-Into
Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War 1 Imperialism & Expansion CH 14-1 Imperialism & War Name Reasons why the United States becomes an imperialist nation. 1-New Markets 2-Anglo-Saxonism 3-Modern Navy 4-Into
(Think in reverse for America s products)
 Foreign countries put tariffs on incoming American goods. This made American goods more expensive in those countries and less desirable. Having more control over other countries and their economies would
Foreign countries put tariffs on incoming American goods. This made American goods more expensive in those countries and less desirable. Having more control over other countries and their economies would
The United States Looks Overseas
 The United States Looks Overseas 1853-1915 Interact with History In 1893, American sugar planters in the Kingdom of Hawaii thought they could make more money if Hawaii were an American state. So they staged
The United States Looks Overseas 1853-1915 Interact with History In 1893, American sugar planters in the Kingdom of Hawaii thought they could make more money if Hawaii were an American state. So they staged
STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015
 STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015 AGE OF IMPERIALISM! (1900s- 1914) MILITARY Alfred T. Mahan argued for a strong NAVY in his book Influence of Sea Power Upon History Easier
STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015 AGE OF IMPERIALISM! (1900s- 1914) MILITARY Alfred T. Mahan argued for a strong NAVY in his book Influence of Sea Power Upon History Easier
Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power ( )
 Name: Period Page# Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power (1890 1915) Section 1: The Pressure to Expand What factors led to the growth of imperialism around the world? In what ways did the United States begin
Name: Period Page# Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power (1890 1915) Section 1: The Pressure to Expand What factors led to the growth of imperialism around the world? In what ways did the United States begin
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e. Chapter Nineteen: From Crisis to Empire
 Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e The Politics of Equilibrium Electoral Stability High Turnout for Elections Cultural Basis of Party Identification Catholics Tended to Vote Democrat 2 The Politics of
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e The Politics of Equilibrium Electoral Stability High Turnout for Elections Cultural Basis of Party Identification Catholics Tended to Vote Democrat 2 The Politics of
Chapter 17, Section 1 I. Building Support for Imperialism (pages ) A. Beginning in the 1880s, Americans wanted the United States to become a
 Chapter 17, Section 1 I. Building Support for Imperialism (pages 520 522) A. Beginning in the 1880s, Americans wanted the United States to become a world power. Their change in attitude was a result of
Chapter 17, Section 1 I. Building Support for Imperialism (pages 520 522) A. Beginning in the 1880s, Americans wanted the United States to become a world power. Their change in attitude was a result of
Key Term Sheet UNIT #4: IMPERIALISM Chapter 7, Sections 1-3 (Pages )
 Key Term Sheet UNIT #4: IMPERIALISM Chapter 7, Sections 1-3 (Pages 260-276) Name: ANSWER KEY Hour: Term Imperialism Definition Refers to when a larger more powerful country exerts influence over another
Key Term Sheet UNIT #4: IMPERIALISM Chapter 7, Sections 1-3 (Pages 260-276) Name: ANSWER KEY Hour: Term Imperialism Definition Refers to when a larger more powerful country exerts influence over another
APUSH. U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! EMPIRE & EXPANSION
 APUSH 1890-1909 EMPIRE & EXPANSION U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 27 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 19 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 21 Important Ideas Since the
APUSH 1890-1909 EMPIRE & EXPANSION U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 27 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 19 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 21 Important Ideas Since the
Imperialism. Policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker territories
 Imperialism Policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker territories Global Competition European nations had been establishing colonies for years Asia
Imperialism Policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker territories Global Competition European nations had been establishing colonies for years Asia
Empire and Expansion. Chapter 27
 Empire and Expansion Chapter 27 Imperialism Stronger nations attempt to create empires by dominating weaker nations. The late 1800s marked the peak of European imperialism, with much of Africa and Asia
Empire and Expansion Chapter 27 Imperialism Stronger nations attempt to create empires by dominating weaker nations. The late 1800s marked the peak of European imperialism, with much of Africa and Asia
The Spanish-American War
 Activities Using Photographs The Spanish-American War Rough Riders Objectives Explain events, ideas, or concepts in a historical text, including what happened and why, based on specific information in
Activities Using Photographs The Spanish-American War Rough Riders Objectives Explain events, ideas, or concepts in a historical text, including what happened and why, based on specific information in
Unit 4: Imperialism. Name: Word Definition Analysis
 Name: Unit 4: Imperialism Word Definition Analysis 1. Imperialism (191) Policy by which strong nations Did America practice imperialism? extend their political, military, If so where? and economic control
Name: Unit 4: Imperialism Word Definition Analysis 1. Imperialism (191) Policy by which strong nations Did America practice imperialism? extend their political, military, If so where? and economic control
BECOMING A WORLD POWER
 BECOMING A WORLD POWER CHAPTER 10 IMPERIALISM THE PRESSURE TO EXPAND Americans had always sought to expand the size of their nation, and throughout the 19th century they extended their control toward the
BECOMING A WORLD POWER CHAPTER 10 IMPERIALISM THE PRESSURE TO EXPAND Americans had always sought to expand the size of their nation, and throughout the 19th century they extended their control toward the
American Upon the Global Stage Was America Imperialist? Or Was America Exceptional?
 APUSH Kind American Imperialism American Upon the Global Stage Was America Imperialist? Or Was America Exceptional? History of American Foreign Policy Neutrality & Isolationism Neutrality Proclamation
APUSH Kind American Imperialism American Upon the Global Stage Was America Imperialist? Or Was America Exceptional? History of American Foreign Policy Neutrality & Isolationism Neutrality Proclamation
Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914?
 Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914? From 1890 to 1914, the United States expanded its role in world affairs and gained new overseas colonies Class Activity:
Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914? From 1890 to 1914, the United States expanded its role in world affairs and gained new overseas colonies Class Activity:
Chapters 18 Review American History
 Chapters 18 Review American History I. Policy of Imperialism: a. Imperialism is a countries policy and practice of creating an empire and maintaining control to expand their control of raw materials, and
Chapters 18 Review American History I. Policy of Imperialism: a. Imperialism is a countries policy and practice of creating an empire and maintaining control to expand their control of raw materials, and
President William McKinley
 President William McKinley William McKinley was born in Niles, Ohio on January 29, 1843 to a large family where he was the seventh of eight children. His family moved to Poland, Ohio when he was ten years
President William McKinley William McKinley was born in Niles, Ohio on January 29, 1843 to a large family where he was the seventh of eight children. His family moved to Poland, Ohio when he was ten years
18 America Claims an Empire QUIT
 18 America Claims an Empire QUIT CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE SECTION 1 Imperialism and America GRAPH MAP SECTION 2 The Spanish-American War SECTION 3 Acquiring New Lands SECTION 4
18 America Claims an Empire QUIT CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE SECTION 1 Imperialism and America GRAPH MAP SECTION 2 The Spanish-American War SECTION 3 Acquiring New Lands SECTION 4
Imperialism Practice Test
 Imperialism Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What did Liliuokalani propose after she became Queen of the Hawaiian Islands?
Imperialism Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What did Liliuokalani propose after she became Queen of the Hawaiian Islands?
Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism
 Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism 1. List the ideas that fueled American Imperialism. 2. How were yellow journalists able to influence Americans opinions on foreign policy? 3. The person who urged
Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism 1. List the ideas that fueled American Imperialism. 2. How were yellow journalists able to influence Americans opinions on foreign policy? 3. The person who urged
Unit 8: Imperialism. February 15th & 16th
 Unit 8: Imperialism February 15th & 16th WarmUp - February 15th & 16th Pick up papers from front table Jot down anything that comes to mind when you see the word IMPERIALISM (this is our next topic Unit
Unit 8: Imperialism February 15th & 16th WarmUp - February 15th & 16th Pick up papers from front table Jot down anything that comes to mind when you see the word IMPERIALISM (this is our next topic Unit
SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR VOCAB
 SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR VOCAB 1. War of 1812 2. Monroe Doctrine 3. Mexican War 4. Yellow journalism 5. USS Maine 6. Rough Riders 7. San Juan Hill 8. Anti-Imperialist League 9. Platt Amendment 10.Diplomacy
SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR VOCAB 1. War of 1812 2. Monroe Doctrine 3. Mexican War 4. Yellow journalism 5. USS Maine 6. Rough Riders 7. San Juan Hill 8. Anti-Imperialist League 9. Platt Amendment 10.Diplomacy
Imperialism and America
 CHAPTER 10 Section 1 ( pages 342 345) Imperialism and America BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about Woodrow Wilson. In this section, you will learn how economic activity led to political
CHAPTER 10 Section 1 ( pages 342 345) Imperialism and America BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about Woodrow Wilson. In this section, you will learn how economic activity led to political
Imperialism and America
 Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire CHAPTER 10 Section 1 (pages 342-345) Imperialism and America American Expansionism (pages 342-344) Why did Americans support imperialism? In 1893, Queen Liliuokalani
Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire CHAPTER 10 Section 1 (pages 342-345) Imperialism and America American Expansionism (pages 342-344) Why did Americans support imperialism? In 1893, Queen Liliuokalani
Expanding Horizons: Imperialism
 Expanding Horizons: Imperialism In August 1914, World War I broke out in Europe, which drowned out the Progressive Era. Leading up to this, U.S. foreign policy had been drastically changing. IMPERIALISM
Expanding Horizons: Imperialism In August 1914, World War I broke out in Europe, which drowned out the Progressive Era. Leading up to this, U.S. foreign policy had been drastically changing. IMPERIALISM
U.S. Imperialism s Impact on Other Nations
 U.S. Imperialism s Impact on Other Nations U.S.-Japanese Relations Japan had closed itself to outsiders in the late 1400s; held a strong mistrust of Western cultures In mid-1800s, US businesses began to
U.S. Imperialism s Impact on Other Nations U.S.-Japanese Relations Japan had closed itself to outsiders in the late 1400s; held a strong mistrust of Western cultures In mid-1800s, US businesses began to
Imperialism. Creation of the U.S. Empire
 Imperialism Creation of the U.S. Empire Please Note: The images included in this presentation, some of which are copyrighted, are being used under the fair use provision (for educational purposes) of the
Imperialism Creation of the U.S. Empire Please Note: The images included in this presentation, some of which are copyrighted, are being used under the fair use provision (for educational purposes) of the
INQUIRY: Was American expansion abroad justified? AIM: Should the United States go to war with Spain in 1898? Spanish-American War Debate
 INQUIRY: Was American expansion abroad justified? AIM: Should the United States go to war with Spain in 1898? Name Spanish-American War Debate Directions: With your partner, read and annotate the documents.
INQUIRY: Was American expansion abroad justified? AIM: Should the United States go to war with Spain in 1898? Name Spanish-American War Debate Directions: With your partner, read and annotate the documents.
Let's discuss: to stop human rights abuses under no circumstances
 Let's discuss: When do you think it is appropriate for the US to send soldiers to fight and face death on foreign soil? (Choose up to 3 of the following and briefly explain your choices) to assist an ally
Let's discuss: When do you think it is appropriate for the US to send soldiers to fight and face death on foreign soil? (Choose up to 3 of the following and briefly explain your choices) to assist an ally
Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power,
 Name: Class Period: Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1865-1917 Amsco Chapter 20 Reading Assignment: Ch. 21 AMSCO Purpose: This guide is intended to provide a space for you to record
Name: Class Period: Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1865-1917 Amsco Chapter 20 Reading Assignment: Ch. 21 AMSCO Purpose: This guide is intended to provide a space for you to record
Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism ( )
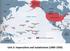 Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism (1890-1930) What is an empire? Is imperialism the same as colonization? Why would the U.S. get involved in this practice? What is the difference between acquiring and
Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism (1890-1930) What is an empire? Is imperialism the same as colonization? Why would the U.S. get involved in this practice? What is the difference between acquiring and
American Foreign Policy, : The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly.
 American Foreign Policy, 1880-1920: The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly. Each group will become experts on their assigned country. Create poster showing how U.S. policy toward your respective country was good,
American Foreign Policy, 1880-1920: The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly. Each group will become experts on their assigned country. Create poster showing how U.S. policy toward your respective country was good,
Chapter 17 NOTES Spanish American War Cuban people revolting against Spain Yellow journalism-printing of sensational stories intended to excite the
 Chapter 17 NOTES Spanish American War Cuban people revolting against Spain Yellow journalism-printing of sensational stories intended to excite the reader US battleship Maine sent to protect Americans
Chapter 17 NOTES Spanish American War Cuban people revolting against Spain Yellow journalism-printing of sensational stories intended to excite the reader US battleship Maine sent to protect Americans
Lesson 9: An Emerging World Power Imperialist = Expansionist (Chapter 9 in Textbook)
 Lesson 9: An Emerging World Power Imperialist = Expansionist (Chapter 9 in Textbook) Time Period: Late 1800s- 1914 Presidents William Mckinley 1897-1901 Theodore Roosevelt 1901-1909 William Howard Taft
Lesson 9: An Emerging World Power Imperialist = Expansionist (Chapter 9 in Textbook) Time Period: Late 1800s- 1914 Presidents William Mckinley 1897-1901 Theodore Roosevelt 1901-1909 William Howard Taft
Unit 5. US Foreign Policy, Friday, December 9, 11
 Unit 5 US Foreign Policy, 1890-1920 I. American Imperialism A. What is Imperialism? B. Stated motivations (how we were helping others) Helping free countries from foreign domination Spreading Christianity
Unit 5 US Foreign Policy, 1890-1920 I. American Imperialism A. What is Imperialism? B. Stated motivations (how we were helping others) Helping free countries from foreign domination Spreading Christianity
throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not.
 1. Tell what at least three of the symbols you see on this flag represent. 2. Do you think these three symbols would be recognized throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not. 3. Why would this
1. Tell what at least three of the symbols you see on this flag represent. 2. Do you think these three symbols would be recognized throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not. 3. Why would this
America s Path to Empire. APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8
 America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8 1890-1892 Foreign Policy The Influence of Sea Power upon History (1890): Alfred Thayer Mahan Sea power throughout history gives advantages US lies
America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8 1890-1892 Foreign Policy The Influence of Sea Power upon History (1890): Alfred Thayer Mahan Sea power throughout history gives advantages US lies
The Progressive Movement
 Section4 The Progressive Movement As you read, look for: the impact of the progressive movement in the state, and vocabulary terms progressive movement and workers compensation. Above: Louisiana s first
Section4 The Progressive Movement As you read, look for: the impact of the progressive movement in the state, and vocabulary terms progressive movement and workers compensation. Above: Louisiana s first
God Bless the USA! (4) Mr. Cegielski
 God Bless the USA! (4) Mr. Cegielski 1 IMPERIALISM Imperialism is the quest for colonial empires and it often involves the use of economic, political, or military power 2 The Main Idea The United States
God Bless the USA! (4) Mr. Cegielski 1 IMPERIALISM Imperialism is the quest for colonial empires and it often involves the use of economic, political, or military power 2 The Main Idea The United States
Drill 12/20/2010 What, according to this quote, is most responsible for the war with Spain?
 Drill 12/20/2010 What, according to this quote, is most responsible for the war with Spain? The Spanish-American War of 1898 marked a turning point in American history. Within a few years of the war's
Drill 12/20/2010 What, according to this quote, is most responsible for the war with Spain? The Spanish-American War of 1898 marked a turning point in American history. Within a few years of the war's
THE EMERGENCE OF THE AMERICAS IN GLOBAL AFFAIRS,
 THE EMERGENCE OF THE AMERICAS IN GLOBAL AFFAIRS, 1880-1929 INTRODUCTION END OF 19 TH C. MARKED BY GLOBAL INTEGRATION 2 ND HALF OF 19 TH C. U.S. MOVES INTO A PERIOD OF ECONOMIC EXPANSION AND IMPERIALIZATION
THE EMERGENCE OF THE AMERICAS IN GLOBAL AFFAIRS, 1880-1929 INTRODUCTION END OF 19 TH C. MARKED BY GLOBAL INTEGRATION 2 ND HALF OF 19 TH C. U.S. MOVES INTO A PERIOD OF ECONOMIC EXPANSION AND IMPERIALIZATION
Imperialism. U.S. Foreign Policy. U.S. Foreign Policy 10/30/13. Chapter 10. Monroe Doctrine. Many Spanish colonies revolting
 Imperialism Chapter 10 U.S. Foreign Policy Monroe Doctrine No new colonization by Europe in western hemisphere U.S. stays out of European affairs If Europe attempts to colonize in the west, U.S. would
Imperialism Chapter 10 U.S. Foreign Policy Monroe Doctrine No new colonization by Europe in western hemisphere U.S. stays out of European affairs If Europe attempts to colonize in the west, U.S. would
America s Path to Empire. APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 2
 America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 2 Major Events 1890-1892 McKinley Tariff October 1, 1890 Raised the average duty on imports to almost fifty percent Intended to protect domestic industries
America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 2 Major Events 1890-1892 McKinley Tariff October 1, 1890 Raised the average duty on imports to almost fifty percent Intended to protect domestic industries
Convention (X) for the Adaptation to Maritime Warfare of the Principles of the Geneva Convention. The Hague, 18 October 1907.
 Convention (X) for the Adaptation to Maritime Warfare of the Principles of the Geneva Convention. The Hague, 18 October 1907. (List of Contracting Parties) Animated alike by the desire to diminish, as
Convention (X) for the Adaptation to Maritime Warfare of the Principles of the Geneva Convention. The Hague, 18 October 1907. (List of Contracting Parties) Animated alike by the desire to diminish, as
Imperialism and WWI US History Unit 4. Name:
 Imperialism and WWI US History Unit 4 Name: 2 Imperialism and WWI [all homework assignments must be turned in prior to taking your assessment] 4.1: Due Pages 187-207 1. Imperialism 2. Annexing Hawaii 3.
Imperialism and WWI US History Unit 4 Name: 2 Imperialism and WWI [all homework assignments must be turned in prior to taking your assessment] 4.1: Due Pages 187-207 1. Imperialism 2. Annexing Hawaii 3.
Progressive Era, Imperialism, and World War 1
 Progressive Era, Imperialism, and World War 1 Section 7.1 Imperialism- a nation desires to gain more territory outside it s borders Reasons for US Imperialism: Economic growth- new people to sell to National
Progressive Era, Imperialism, and World War 1 Section 7.1 Imperialism- a nation desires to gain more territory outside it s borders Reasons for US Imperialism: Economic growth- new people to sell to National
Imperalism.notebook March 03, 2015
 Agenda Bell ringer Notability 1 Objective: I can discuss and explain why the United States Foreign Policy changed during the late 19th century. Bell Ringer Notability HW: Due Thursday 2 1 A B C D 3 2 A
Agenda Bell ringer Notability 1 Objective: I can discuss and explain why the United States Foreign Policy changed during the late 19th century. Bell Ringer Notability HW: Due Thursday 2 1 A B C D 3 2 A
Between 1870 and 1900, Europeans had taken over 1/5 of land and 1/10 of population of the world Germany became America s biggest imperialist foe and
 U.S. Imperialism Between 1870 and 1900, Europeans had taken over 1/5 of land and 1/10 of population of the world Germany became America s biggest imperialist foe and largely spurred U.S. into imperialism;
U.S. Imperialism Between 1870 and 1900, Europeans had taken over 1/5 of land and 1/10 of population of the world Germany became America s biggest imperialist foe and largely spurred U.S. into imperialism;
Chapter 27: The Path of Empire, (Pages )
 Chapter 27: The Path of Empire, 1890 1899 (Pages 626 653) I. America Turns Outward A. Motives for overseas expansion 1. Farmers and industrialists Name Per. Date Row 2. The yellow press 3. Role of religion
Chapter 27: The Path of Empire, 1890 1899 (Pages 626 653) I. America Turns Outward A. Motives for overseas expansion 1. Farmers and industrialists Name Per. Date Row 2. The yellow press 3. Role of religion
The Age of Empire
 The Age of Empire 1890-1900 Overview Competition for markets Acquisition of land (Primarily in Pacific) Yellow Journalism Spanish American War McKinley vs. Bryan Why Empire? Why Empire? Markets Export
The Age of Empire 1890-1900 Overview Competition for markets Acquisition of land (Primarily in Pacific) Yellow Journalism Spanish American War McKinley vs. Bryan Why Empire? Why Empire? Markets Export
Chapter 18. American Claims an Empire
 Chapter 18 American Claims an Empire Section 1: Imperialism and American Imperialism 1880s U.S. interest in building an Empire builds Imperialism = Stronger : Economic, political, or military control Europeans
Chapter 18 American Claims an Empire Section 1: Imperialism and American Imperialism 1880s U.S. interest in building an Empire builds Imperialism = Stronger : Economic, political, or military control Europeans
Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of???
 Need to know What was President Roosevelt s Gentlemen s Agreement with Japan? Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of??? imperialism Stronger nations dominating
Need to know What was President Roosevelt s Gentlemen s Agreement with Japan? Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of??? imperialism Stronger nations dominating
America s Path to Empire. APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 5
 America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 5 Mariam Haider, Emma Tresch, 5th Period America s Path to Empire 1892-1894 Feb 29, 1892: Britain and US sign treaty on seal hunting in the Bering
America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 5 Mariam Haider, Emma Tresch, 5th Period America s Path to Empire 1892-1894 Feb 29, 1892: Britain and US sign treaty on seal hunting in the Bering
Standards US History 10-25
 Standards US History 10-25 Progressivism Progressivism A reform movement focused on improving living conditions, education, working conditions, stopping political corruption, and gain women the right to
Standards US History 10-25 Progressivism Progressivism A reform movement focused on improving living conditions, education, working conditions, stopping political corruption, and gain women the right to
Reasons for American Imperialism
 Name: Reasons for American Introduction: Expansion has always been a part of America s history. At first, expansion headed towards the Pacific within North America. In the 1700 s and 1800 s, European nations
Name: Reasons for American Introduction: Expansion has always been a part of America s history. At first, expansion headed towards the Pacific within North America. In the 1700 s and 1800 s, European nations
IT S STORY TIME! UNIT 4 AMERICAN IMPERIALISM Part 1 The Imperialist Vision Part 2 The Spanish-American War Part 3 New American Diplomacy
 IT S STORY TIME! UNIT 4 AMERICAN IMPERIALISM 1872-1912 Part 1 The Imperialist Vision Part 2 The Spanish-American War Part 3 New American Diplomacy AMERICAN DIPLOMACY in ASIA Each LEASEHOLD became center
IT S STORY TIME! UNIT 4 AMERICAN IMPERIALISM 1872-1912 Part 1 The Imperialist Vision Part 2 The Spanish-American War Part 3 New American Diplomacy AMERICAN DIPLOMACY in ASIA Each LEASEHOLD became center
Unit 7: America Comes of Age FRQ Outlines
 Prompt: 2. Analyze the extent to which the Spanish-American War was a turning point in American foreign policy. Re-written as a Question: What was the extent to which the Spanish American war a turning
Prompt: 2. Analyze the extent to which the Spanish-American War was a turning point in American foreign policy. Re-written as a Question: What was the extent to which the Spanish American war a turning
IMPERIALISM. Policing the Western Hemisphere
 Alaska William Seward Sec. of State purchased from Russia for $7 million. Twice the size of Texas Nicknamed Seward s Folly or Seward s Icebox 1890 gold found there Hawaii IMPERIALISM Grew sugar that was
Alaska William Seward Sec. of State purchased from Russia for $7 million. Twice the size of Texas Nicknamed Seward s Folly or Seward s Icebox 1890 gold found there Hawaii IMPERIALISM Grew sugar that was
Resources for Navigating Successes, Failures, & Consequences
 Researching Debate & Diplomacy: Resources for Navigating Successes, Failures, & Consequences History Day @ Your Library 11/10/10 Jennifer Hootman Minitex Reference Services Coordinator hootm001@umn.edu
Researching Debate & Diplomacy: Resources for Navigating Successes, Failures, & Consequences History Day @ Your Library 11/10/10 Jennifer Hootman Minitex Reference Services Coordinator hootm001@umn.edu
Unit 9 Imperialism and WWI. New US Power and Diplomacy
 Unit 9 Imperialism and WWI New US Power and Diplomacy Attitudes Toward an International Role Arguments for Expansion Economics: new markets/investment opportunities/raw materials Culture: Social Darwinism/Protestant
Unit 9 Imperialism and WWI New US Power and Diplomacy Attitudes Toward an International Role Arguments for Expansion Economics: new markets/investment opportunities/raw materials Culture: Social Darwinism/Protestant
BELLRINGER. Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies?
 BELLRINGER Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies? U.S. INTERVENTION ABROAD Ms. Luco IB Hist Americas LEARNING
BELLRINGER Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies? U.S. INTERVENTION ABROAD Ms. Luco IB Hist Americas LEARNING
Unit 6 Review Sheets Foreign Policies: Imperialism Isolationism (Spanish-American War Great Depression)
 Speak softly & carry a big stick; you will go far -Theodore Roosevelt Work or fight -National War Labor Board Unit 6 Review Sheets Foreign Policies: Imperialism Isolationism (Spanish-American War Great
Speak softly & carry a big stick; you will go far -Theodore Roosevelt Work or fight -National War Labor Board Unit 6 Review Sheets Foreign Policies: Imperialism Isolationism (Spanish-American War Great
Foreign Policy: Setting a Course of Expansionism
 [Photo: SE19.00] 1796 1896 Chapter 19 Foreign Policy: Setting a Course of Expansionism Was American foreign policy during the 1800s motivated more by realism or idealism? 19.1 Introduction On July 8, 1853,
[Photo: SE19.00] 1796 1896 Chapter 19 Foreign Policy: Setting a Course of Expansionism Was American foreign policy during the 1800s motivated more by realism or idealism? 19.1 Introduction On July 8, 1853,
President Wilson's Declaration of Neutrality
 President Wilson's Declaration of Neutrality Woodrow Wilson, Message to Congress, 63rd Cong., 2d Sess., Senate Doc. No. 566 (Washington, 1914), pp. 3-4. The effect of the war upon the United States will
President Wilson's Declaration of Neutrality Woodrow Wilson, Message to Congress, 63rd Cong., 2d Sess., Senate Doc. No. 566 (Washington, 1914), pp. 3-4. The effect of the war upon the United States will
Warm up: We have discussed the Chinese role in constructing the railroads in the west. How do you think that the Chinese were treated by other
 Warm up: We have discussed the Chinese role in constructing the railroads in the west. How do you think that the Chinese were treated by other groups? SSUSH14 Explain America s evolving relationship with
Warm up: We have discussed the Chinese role in constructing the railroads in the west. How do you think that the Chinese were treated by other groups? SSUSH14 Explain America s evolving relationship with
The Spanish American-War 4 Causes of the War: Important Events 1/7/2018. Effects of the Spanish American War
 The Spanish American-War 4 Causes of the War: Sugar (Economic) Spanish Cruelties (Humanitarian) The Sinking of the USS Maine (Self-Defense/National Pride) Spanish Brutalities and Yellow Journalism (Political
The Spanish American-War 4 Causes of the War: Sugar (Economic) Spanish Cruelties (Humanitarian) The Sinking of the USS Maine (Self-Defense/National Pride) Spanish Brutalities and Yellow Journalism (Political
Unit 6: A New Role in the World
 Unit 6: A New Role in the World Study online at quizlet.com/_1fnvlz 1. alliances 5. conscription An agreement between nations to aid and protect each other. 2. Allies A military draft 6. dollar diplomacy
Unit 6: A New Role in the World Study online at quizlet.com/_1fnvlz 1. alliances 5. conscription An agreement between nations to aid and protect each other. 2. Allies A military draft 6. dollar diplomacy
THE AGE OF IMPERIALISM. The Emergence of the U.S. in World Affairs
 THE AGE OF IMPERIALISM The Emergence of the U.S. in World Affairs 1890-1914 IMPERIALISM Imperialism the policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker
THE AGE OF IMPERIALISM The Emergence of the U.S. in World Affairs 1890-1914 IMPERIALISM Imperialism the policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker
Becoming A World Power,
 Becoming A World Power, 1890-1915 United States History Week of April 27, 2015 What Factors Caused Imperialism? Economic factors: need for natural resources, new markets for manufactured goods Nationalistic
Becoming A World Power, 1890-1915 United States History Week of April 27, 2015 What Factors Caused Imperialism? Economic factors: need for natural resources, new markets for manufactured goods Nationalistic
Chapter 19: Republic To Empire
 Chapter 19: Republic To Empire Objectives: o We will examine the policies America implemented in their newly conquered territories after the Spanish American War. o We will examine the various changes
Chapter 19: Republic To Empire Objectives: o We will examine the policies America implemented in their newly conquered territories after the Spanish American War. o We will examine the various changes
STAAR Review Student Cards. Part 1
 STAAR Review Student Cards Part 1 Eras of U.S. Timeline Exploration Age of Exploration: Time period in which Europeans explored in search for Gold, Glory, and God Northwest Passage: Reason Gold Explanation
STAAR Review Student Cards Part 1 Eras of U.S. Timeline Exploration Age of Exploration: Time period in which Europeans explored in search for Gold, Glory, and God Northwest Passage: Reason Gold Explanation
Elihu Root, The Ethics of the Panama Question, 1904
 Elihu Root, The Ethics of the Panama Question, 1904 This document comes from a speech that Elihu Root delivered at the Union League Club of Chicago in February 1904 about U.S. action in Panama, shortly
Elihu Root, The Ethics of the Panama Question, 1904 This document comes from a speech that Elihu Root delivered at the Union League Club of Chicago in February 1904 about U.S. action in Panama, shortly
Woodrow Wilson: Address to the Senate on Peace Without Victory, 22 Jan. 1917
 Woodrow Wilson: Address to the Senate on Peace Without Victory, 22 Jan. 1917 ADDRESS OF THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES DELIVERED TO THE SENATE OF THE UNITED STATES JANUARY 22, 1917 WASHINGTON 1917
Woodrow Wilson: Address to the Senate on Peace Without Victory, 22 Jan. 1917 ADDRESS OF THE PRESIDENT OF THE UNITED STATES DELIVERED TO THE SENATE OF THE UNITED STATES JANUARY 22, 1917 WASHINGTON 1917
CHAPTER 34 Franklin D. Roosevelt and the Shadow of War,
 CHAPTER 34 Franklin D. Roosevelt and the Shadow of War, 1933 1941 Checklist of Learning Objectives After mastering this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe Franklin Roosevelt s early isolationist
CHAPTER 34 Franklin D. Roosevelt and the Shadow of War, 1933 1941 Checklist of Learning Objectives After mastering this chapter, you should be able to: 1. Describe Franklin Roosevelt s early isolationist
Japanese Attack Manchuria (1931)
 America clings to isolationism in the 1930s as war looms Japanese Attack Manchuria (1931) League of Nations condemned the action. Japan leaves the League. Hoover wanted no part in an American military
America clings to isolationism in the 1930s as war looms Japanese Attack Manchuria (1931) League of Nations condemned the action. Japan leaves the League. Hoover wanted no part in an American military
1. AMERICA BECOMES A WORLD POWER
 1. AMERICA BECOMES A WORLD POWER OVERVIEW OF THE VIDEO While Progressive leaders showed their distrust of power in their dealings with large corporations at home, they still grasped the growing need for
1. AMERICA BECOMES A WORLD POWER OVERVIEW OF THE VIDEO While Progressive leaders showed their distrust of power in their dealings with large corporations at home, they still grasped the growing need for
Introduction to World War II By USHistory.org 2017
 Name: Class: Introduction to World War II By USHistory.org 2017 World War II was the second global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. The war involved a majority of the world s countries, and it is considered
Name: Class: Introduction to World War II By USHistory.org 2017 World War II was the second global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. The war involved a majority of the world s countries, and it is considered
Neutrality and War (Delivered October 13, 1939)
 Neutrality and War (Delivered October 13, 1939) Tonight, I speak again to the people of this country who are opposed to the United States entering the war which is now going on in Europe. We are faced
Neutrality and War (Delivered October 13, 1939) Tonight, I speak again to the people of this country who are opposed to the United States entering the war which is now going on in Europe. We are faced
Define the following: a. Neutrality Policy. b. Louisiana Purchase. c. War of d. Monroe Doctrine. e. Mexican-American War
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Chapter 20 in AMSCO or other resource covering the Spanish American War. Directions: 1. Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before
Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Chapter 20 in AMSCO or other resource covering the Spanish American War. Directions: 1. Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before
French on the Mexican-American border Expansion. Intervention confined to Latin America Europe
 French on the Mexican-American border Expansion Alaska Midway Islands left alone to pursue interests Reducing army and navy No longer interested in Caribbean Intervention confined to Latin America Europe
French on the Mexican-American border Expansion Alaska Midway Islands left alone to pursue interests Reducing army and navy No longer interested in Caribbean Intervention confined to Latin America Europe
U.S. Imperialism Practice Questions
 Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the map below and on your knowledge of social studies. 1 Which United States foreign policy was most often used to carry out the actions shown on the map? (1)
Base your answers to questions 1 and 2 on the map below and on your knowledge of social studies. 1 Which United States foreign policy was most often used to carry out the actions shown on the map? (1)
U.S. History / Geography I Final Exam Review
 U.S. History / Geography I Final Exam Review 1. Laissez-faire relies on to regulate prices and wages. 2. A shortage of workers in California forced the Central-Pacific railroad while building the Trans-Continental
U.S. History / Geography I Final Exam Review 1. Laissez-faire relies on to regulate prices and wages. 2. A shortage of workers in California forced the Central-Pacific railroad while building the Trans-Continental
Philippines? Have Annexed the. o Should the [Jnited States I. The Documents: A Mini Document Based Question (Mini-a)
 o Should the [Jnited States I Have Annexed the Philippines? Overview: In 1898 the United States successfully fought a short war with Spain. One of the results of the war was that several Spanish colonies
o Should the [Jnited States I Have Annexed the Philippines? Overview: In 1898 the United States successfully fought a short war with Spain. One of the results of the war was that several Spanish colonies
Thinking About a US-China War, Part 2
 Thinking About a US-China War, Part 2 Jan. 4, 2017 Sanctions and blockades as an alternative to armed conflict would lead to armed conflict. By George Friedman This article is the second in a series. Read
Thinking About a US-China War, Part 2 Jan. 4, 2017 Sanctions and blockades as an alternative to armed conflict would lead to armed conflict. By George Friedman This article is the second in a series. Read
UNITED STATES HISTORY SECTION I1 Part A (Suggested writing time-45 minutes) Percent of Section I1 score-45
 UNITED STATES HISTORY SECTION I1 Part A (Suggested writing time-45 minutes) Percent of Section I1 score-45 Directions: The following question requires you to construct a coherent essay that integrates
UNITED STATES HISTORY SECTION I1 Part A (Suggested writing time-45 minutes) Percent of Section I1 score-45 Directions: The following question requires you to construct a coherent essay that integrates
Espionage Act of 1917
 Espionage Act of 1917 This act, passed during World War I, strictly limited Americans' freedom of speech in the name of wartime security. Since the Alien and Sedition Acts of the late eighteenth century,
Espionage Act of 1917 This act, passed during World War I, strictly limited Americans' freedom of speech in the name of wartime security. Since the Alien and Sedition Acts of the late eighteenth century,
Chapter Twenty. Commonwealth and Empire
 Chapter Twenty Commonwealth and Empire 1870-1900 Part One: Introduction Commonwealth and Empire What does this painting suggest and American expansion? 3 Chapter Focus Questions What characterized the
Chapter Twenty Commonwealth and Empire 1870-1900 Part One: Introduction Commonwealth and Empire What does this painting suggest and American expansion? 3 Chapter Focus Questions What characterized the
DIOCESE OF HARRISBURG SOCIAL STUDIES CURRICULUM GRADE 7/8 United States History: Westward Expansion to Present Day
 5.1.9 Identify the goals of the constitution and the basic principles of American government. Recognize the Preamble to the Constitution and briefly explain how our government meets each goal. List and
5.1.9 Identify the goals of the constitution and the basic principles of American government. Recognize the Preamble to the Constitution and briefly explain how our government meets each goal. List and
Today s Topics. Quiz 1 Populism & The Segregated South The U.S. as a World Power
 Today s Topics Quiz 1 Populism & The Segregated South The U.S. as a World Power 1 The Transformation of the West 2 The Transformation of the West Remaking Indian Life Forced assimilation The Dawes Act
Today s Topics Quiz 1 Populism & The Segregated South The U.S. as a World Power 1 The Transformation of the West 2 The Transformation of the West Remaking Indian Life Forced assimilation The Dawes Act
Roosevelt Taft Wilson. Big Stick Diplomacy Dollar Diplomacy Moral Diplomacy
 Roosevelt Taft Wilson Big Stick Diplomacy Dollar Diplomacy Moral Diplomacy Definition: The art or practice of conducting international relations, as in negotiating alliances, treaties, and agreements.
Roosevelt Taft Wilson Big Stick Diplomacy Dollar Diplomacy Moral Diplomacy Definition: The art or practice of conducting international relations, as in negotiating alliances, treaties, and agreements.
Imperial America The United States in the World
 Imperial America The United States in the World 1890-1914 Gilded Age: A Tale of Today 1873 Novel by Mark Twain and Charles Warner: fictional account of political and economic corruption in the USA gild
Imperial America The United States in the World 1890-1914 Gilded Age: A Tale of Today 1873 Novel by Mark Twain and Charles Warner: fictional account of political and economic corruption in the USA gild
CHAPTER 22. The Quest for Empire, Learning Objectives. Thematic Guide
 CHAPTER 22 The Quest for Empire, 1865 1914 Learning Objectives After you have studied Chapter 22 in your textbook and worked through this study guide chapter, you should be able to: 1. Examine the late-nineteenth-century
CHAPTER 22 The Quest for Empire, 1865 1914 Learning Objectives After you have studied Chapter 22 in your textbook and worked through this study guide chapter, you should be able to: 1. Examine the late-nineteenth-century
19 th Amendment. 16 th Amendment 17 th Amendment 18 TH Amendment established direct election of United States Senators by popular vote
 16 th Amendment 17 th Amendment 18 TH Amendment 1913-gave Congress the power to tax personal income 1913- established direct election of United States Senators by popular vote 1919- banned the sale of
16 th Amendment 17 th Amendment 18 TH Amendment 1913-gave Congress the power to tax personal income 1913- established direct election of United States Senators by popular vote 1919- banned the sale of
FOREIGN POLICY AS A GUARANTEE FOR NATIONAL PROSPERITY. In constructing United States foreign policy in the past century, American
 PROMISED LAND OR A CRUSADER STATE: AMERICAN FOREIGN POLICY AS A GUARANTEE FOR NATIONAL PROSPERITY In constructing United States foreign policy in the past century, American politicians have been particularly
PROMISED LAND OR A CRUSADER STATE: AMERICAN FOREIGN POLICY AS A GUARANTEE FOR NATIONAL PROSPERITY In constructing United States foreign policy in the past century, American politicians have been particularly
