Era of Good Feelings:
|
|
|
- Alyson Casey
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Era of Good Feelings:
2 After the War of 1812 Americans finally have international respect The Republicans are the only political party James Monroe, the third member of the Virginia Dynasty, is president A time of economic prosperity
3 Shift in Republican Ideology: Federalism without Elitism Industrialism, not farming as future of America Broad, or loose, construction of the Constitution Nationalism, not states rights
4 Election of 1816 Federalist candidate: Rufus King (N.Y.) Republican candidate: James Monroe (V.A.) Monroe wins 183 to 34; Daniel D. Tompkins is V.P Last election with a Federalist candidate James Monroe
5 Laws of Tariff of to protect new American industry developed as a result of the Embargo of 1807 and the War of Bank of U.S. re-chartered (had expired in 1811) 3. Military Expansion (West Point Academy)to avoid mistreatment by foreign nations
6 Era of Good Feelings Refers to lack of political parties Coined by James Monroe as he toured the country, it is misleading New political factions were forming Sectionalism was beginning to heat up between the North and the South
7 First Wave of Industrialization Samuel Slateremigrated from England and had memorized plans for machinery Founder of Cotton Textile Industry in America: Pawtucket, Rhode Island, 1793
8 Working in a Mill Slater Mill Workers were from 7 to 12 Farmers distrusted factory work and thought it shameful real men work outside with the land Few families could survive without children s income
9 Eli Whitney: More than just Cotton He created the technique for interchangeable parts The muskets his workmen made by methods comparable to those of modern mass industrial production were the first to have standardized, interchangeable parts. Cotton Gin, 1793
10 Mills in the North: The vast majority of Americans still farmed, but a small percentage began to fill the new factories developing in the North
11 Powered by water, these factories depended on women and children. Single women left home to either gain independence or help their family financially.
12 Transportation Revolution: Part One As the West opened up it became essential for transportation to improve in order for the North to sell to the West and for the West to get their raw products to market.
13 By Water One of the U.S. s best natural transportation resources was its rivers and lakes The development of both the steamboat and the canal would make this an even more efficient travel option
14 The Steamboat Flatboats were the main vessel utilized by farmers and merchants along the Mississippi. Problem: They only float down river! Solution: The steamboat,invented by Robert Fulton in 1807, with its engine could also travel upstream!
15
16 Erie Canal, 1825 When it opened in 1825, the Erie Canal was a marvel of engineering and human labor. From Albany to Buffalo, it opened up the American frontier and made westward expansion inevitable. It turned New York Harbor into the nation's number one port. It shaped social and economic development. Cities and industries developed along the canal and flourished.
17 How Locks Work
18 National (Cumberland) Road First highway built entirely with federal funds Authorized by Jefferson in 1806 By 1818 the road stretched from Maryland to Ohio In the 1830s construction ceased due to lack of funding The road fell into disrepair
19 National Road
20 Henry Clay s American System A national bank The protective tariff National program of internal improvements to bind the country together and build the economy The tariff and bank would provide funds for these improvements
21 American System New England and New York were against internal improvements South and Southwest were against the protective tariff Sectionalism was becoming entrenched
22 Missouri Compromise Missouri petitions to be admitted as a slave state Would upset balance of 11 free and 11 slave states Tallmadge Amendment- Compromise
23
24 John Marshall Was a loose constructionist who was a strong Federalist (Hamiltonian) that believed in implied powers Dartmouth College v. Woodward(1819)- McCulloch v. Maryland (1819)-
25 John Marshall Let the end be legitimate, let it be within the scope of the constitution, and all means which are appropriate, which are plainly adapted to that end, which are not prohibited, but consistent with the letter and spirit of the constitution, are constitutional.
26 Foreign Policy Adams-Onis Treaty of 1819 Monroe Doctrine America recognizes independence of Spain s Latin America colonies
27
28 Hudson River Art School The Creation of American Culture A group of painters led by Thomas Cole who painted images of America s wilderness in the Hudson River Valley (N.Y.) and in the newly opened West.
29
30
31
32 Noah Webster 1828-Webster s dictionary contained 70,000 words He wrote his dictionary to have a uniform American, not British, language since different parts of the country used different spellings
33 Education Most children who received education did so with private tutors in the home Massachusetts leads way in public financing for education: Boston s English Classical School (1821) was the first public high school in the country Concept of training teachers just beginning book 1820
34 Status of Women Women will gain some standing legally Serve on committees in churches Higher education available Divorce is allowed, but difficult Single women can own property, enter into contracts, file law suites and pay taxes CANNOT serve on juries, vote or practice law (New Jersey changed law in 1807)
35 Federal Architecture Found mainly in the East in homes owned by the wealthy (or in public buildings) the architecture was inspired by ancient Roman architecture, the first republic!
Division of Labor: giving each worker one or two simple jobs.
 Chapter 12 The Nation Grows (1815-1830) Section 1 Industries take Root Industrial Revolution: the growth of industry eventually produced changes so great that this time in history is called the Industrial
Chapter 12 The Nation Grows (1815-1830) Section 1 Industries take Root Industrial Revolution: the growth of industry eventually produced changes so great that this time in history is called the Industrial
Economic Growth. Guided Reading Activity. Growth and Expansion. Answering Questions DIRECTIONS: As you read the section, answer the questions below.
 Guided Reading Activity Growth and Expansion Section Economic Growth Give yourself enough time to read and understand the text. Don t rush through it. Take your time and pause to reread sections or to
Guided Reading Activity Growth and Expansion Section Economic Growth Give yourself enough time to read and understand the text. Don t rush through it. Take your time and pause to reread sections or to
Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages ) Economic Growth
 Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages 304 309) Economic Growth Essential Question What effects did the Industrial Revolution have on the U. S. economy? Directions: As you read, complete a graphic organizer like
Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages 304 309) Economic Growth Essential Question What effects did the Industrial Revolution have on the U. S. economy? Directions: As you read, complete a graphic organizer like
1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation
 Topic 3 1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg 88-89 They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation agreements 2. How did the British respond to the Boston Tea
Topic 3 1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg 88-89 They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation agreements 2. How did the British respond to the Boston Tea
Varieties of American Nationalism. Chapter 8: History 103
 Varieties of American Nationalism Chapter 8: History 103 Boom to Bust post war boom leads to Panic of 1819 Why did the Panic of 1819 occur? Banking and Currency 1811: First Bank of the United States expired
Varieties of American Nationalism Chapter 8: History 103 Boom to Bust post war boom leads to Panic of 1819 Why did the Panic of 1819 occur? Banking and Currency 1811: First Bank of the United States expired
DRAWING FROM EXPERIENCEII
 Chapter 10, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 306 311 ECONOMIC GROWTH KEY TERMS Industrial Revolution A new way of working and producing goods (page 307) capital Money invested to start new businesses
Chapter 10, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 306 311 ECONOMIC GROWTH KEY TERMS Industrial Revolution A new way of working and producing goods (page 307) capital Money invested to start new businesses
The Missouri Compromise and The Monroe Doctrine
 The Missouri Compromise and The Monroe Doctrine President James Monroe Monroe ran for President in 1816 as a Democratic-Republican and won easily against the last Federalist presidential candidate Rufus
The Missouri Compromise and The Monroe Doctrine President James Monroe Monroe ran for President in 1816 as a Democratic-Republican and won easily against the last Federalist presidential candidate Rufus
THE SECOND WAR FOR INDEPENDENCE AND THE UPSURGE OF NATIONALISM ( )
 THE SECOND WAR FOR INDEPENDENCE AND THE UPSURGE OF NATIONALISM (1812-1824) Period 4 (1800-1848) Key Concept 4.1 The United States began to develop a modern democracy and celebrated a new national culture,
THE SECOND WAR FOR INDEPENDENCE AND THE UPSURGE OF NATIONALISM (1812-1824) Period 4 (1800-1848) Key Concept 4.1 The United States began to develop a modern democracy and celebrated a new national culture,
Level 2 THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS
 Level 2 THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS Vocabulary Sectionalism: loyalty to a section of a country instead of the nation itself Inflation: Protective Tariff: tax on imported goods Internal Expansion: continued
Level 2 THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS Vocabulary Sectionalism: loyalty to a section of a country instead of the nation itself Inflation: Protective Tariff: tax on imported goods Internal Expansion: continued
Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change
 Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change 1800-1860 Nationalism and Economic Growth By 1815, following the end of The War of 1812, America had shown: That it could defend its sovereignty against
Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change 1800-1860 Nationalism and Economic Growth By 1815, following the end of The War of 1812, America had shown: That it could defend its sovereignty against
THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN THE U.S. How the War of 1812 & Technological Progress Change the Country
 THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN THE U.S. How the War of 1812 & Technological Progress Change the Country TECHNOLOGY MEANS PROGRESS Developments in technology begin to transform life in the U.S. in the
THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN THE U.S. How the War of 1812 & Technological Progress Change the Country TECHNOLOGY MEANS PROGRESS Developments in technology begin to transform life in the U.S. in the
The Americans (Survey)
 The Americans (Survey) Chapter 7: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OVERVIEW American leaders devise a farsighted policy of improvements as North, South, and West develop
The Americans (Survey) Chapter 7: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OVERVIEW American leaders devise a farsighted policy of improvements as North, South, and West develop
Chapter 7 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism
 Chapter 7 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Changes in manufacturing launch an Industrial Revolution. Slavery and other issues divide the North and South. Andrew Jackson has popular appeal but uproots
Chapter 7 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Changes in manufacturing launch an Industrial Revolution. Slavery and other issues divide the North and South. Andrew Jackson has popular appeal but uproots
History 1301 U.S. to Unit 2 - Lecture 4 ~
 History 1301 U.S. to 1877 Unit 2 - Lecture 4 ~ The Era of Good Feeling Post-war Economics: Post-war boom led to bust in 1819 National weaknesses shown by War experience Second National Bank chartered in
History 1301 U.S. to 1877 Unit 2 - Lecture 4 ~ The Era of Good Feeling Post-war Economics: Post-war boom led to bust in 1819 National weaknesses shown by War experience Second National Bank chartered in
Democratic Republican Era
 Democratic Republican Era Thomas Jefferson s Administration James Madison s Administration James Monroe s Administration Jefferson Madison Monroe Following the election of 1800, the Democratic Republicans
Democratic Republican Era Thomas Jefferson s Administration James Madison s Administration James Monroe s Administration Jefferson Madison Monroe Following the election of 1800, the Democratic Republicans
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism
 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Regional Economies Create Differences Samuel Slater brought the Water Frame to Rhode Island from Great Britain in 1789. It was used to spin raw cotton into cotton
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Regional Economies Create Differences Samuel Slater brought the Water Frame to Rhode Island from Great Britain in 1789. It was used to spin raw cotton into cotton
HIST 1301 Part Three. 9: Nation Building and Nationalism
 HIST 1301 Part Three 9: Nation Building and Nationalism Territorial Expansion Between 1792 and 1821 several new states joined the Union. Kentucky, 1792 Tennessee, 1796 Ohio, 1803 Louisiana, 1812 Indiana,
HIST 1301 Part Three 9: Nation Building and Nationalism Territorial Expansion Between 1792 and 1821 several new states joined the Union. Kentucky, 1792 Tennessee, 1796 Ohio, 1803 Louisiana, 1812 Indiana,
NAME DATE CLASS. Maine N.H. Vt. Manchester Lowell N.Y. Boston. Pawtucket. Conn. RI Pa. New York City Philadelphia. Baltimore Del. Md.
 Lesson 1 A Growing Economy ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does geography influence the way people live? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. How did new technology affect the way things were made? 2. Why did agriculture remain
Lesson 1 A Growing Economy ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does geography influence the way people live? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. How did new technology affect the way things were made? 2. Why did agriculture remain
In the early Antebellum era ( ), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that
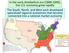 In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
CH. 8: GROWTH OF A NATIONAL ECONOMY
 1 2 3 4 CH. 8: GROWTH OF A NATIONAL ECONOMY 1790-1850 Mr. Anderson, M.Ed., J.D. Review Who was John Marshall? Which president appointed him? What is he best remembered for? The Industrial Revolution Section
1 2 3 4 CH. 8: GROWTH OF A NATIONAL ECONOMY 1790-1850 Mr. Anderson, M.Ed., J.D. Review Who was John Marshall? Which president appointed him? What is he best remembered for? The Industrial Revolution Section
An Early Republic. George Washington. Dept./Office Head Function
 Name An Early Republic George Washington What does the Executive Branch look like? Dept./Office Head Function State Department Thomas Jefferson Dept. of Treasury Alexander Hamilton Dept. of War Henry Knox
Name An Early Republic George Washington What does the Executive Branch look like? Dept./Office Head Function State Department Thomas Jefferson Dept. of Treasury Alexander Hamilton Dept. of War Henry Knox
The Presidency of James Monroe
 The Presidency of James Monroe James Monroe 1758 1831 Democratic-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former Governor of Virginia, Secretary of State,
The Presidency of James Monroe James Monroe 1758 1831 Democratic-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former Governor of Virginia, Secretary of State,
Chapter 9 A New National Identity The Big Idea The United States peacefully settled disputes with foreign powers. Holt McDougal,
 Chapter 9 A New National Identity The Big Idea The United States peacefully settled disputes with foreign powers. MAIN IDEA 1: THE UNITED STATES AND GREAT BRITAIN SETTLED THEIR DISPUTES OVER BOUNDARIES
Chapter 9 A New National Identity The Big Idea The United States peacefully settled disputes with foreign powers. MAIN IDEA 1: THE UNITED STATES AND GREAT BRITAIN SETTLED THEIR DISPUTES OVER BOUNDARIES
378. Purchase of Florida Under the Adams-Onis Treaty, Spain sold Florida to the U.S., and the U.S. gave up its claims to Texas.
 Note Cards 351. Embargo of 1807, opposition This act issued by Jefferson forbade American trading ships from leaving the U.S. It was meant to force Britain and France to change their policies towards neutral
Note Cards 351. Embargo of 1807, opposition This act issued by Jefferson forbade American trading ships from leaving the U.S. It was meant to force Britain and France to change their policies towards neutral
Unit Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution
 Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
Chapter 8: Varieties of American Nationalism
 Chapter 8: Varieties of American Nationalism "...but this momentous question, like a fire bell in the night, awakened and filled me with terror. I considered it at once as the death knell of the Union.
Chapter 8: Varieties of American Nationalism "...but this momentous question, like a fire bell in the night, awakened and filled me with terror. I considered it at once as the death knell of the Union.
CHAPTER 2, SECTION 2. The Growth of the Nation
 CHAPTER 2, SECTION 2 The Growth of the Nation Big Ideas: After the War of 1812, more Americans began to see themselves as members of a nation rather than only identifying themselves by a region or state.
CHAPTER 2, SECTION 2 The Growth of the Nation Big Ideas: After the War of 1812, more Americans began to see themselves as members of a nation rather than only identifying themselves by a region or state.
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism
 7 QUIT Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE GRAPH SECTION 1 Regional Economics Create Differences SECTION 2 Nationalism at Center Stage MAP SECTION 3
7 QUIT Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE GRAPH SECTION 1 Regional Economics Create Differences SECTION 2 Nationalism at Center Stage MAP SECTION 3
Chapter 9 and part of Chapter 8: Transforming the Economy,
 Chapter 9 and part of Chapter 8: Transforming the Economy, 1790-1860 The Big Questions: What were the causes and consequences of the industrial and market revolutions, and how did they change the way ordinary
Chapter 9 and part of Chapter 8: Transforming the Economy, 1790-1860 The Big Questions: What were the causes and consequences of the industrial and market revolutions, and how did they change the way ordinary
The Westward Movement
 The Westward Movement The American West- the most typically American part of America Young America- half of all Americans were under the age of 30 Life in the West was grim for American families Poorly
The Westward Movement The American West- the most typically American part of America Young America- half of all Americans were under the age of 30 Life in the West was grim for American families Poorly
The Treaty of Ghent War of 1812 is considered a stalemate Dec. 1814
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Map war1812 The Battle of Thames River, Oct. 5, 1813 US military victory led by General William H. Harrison Tecumseh was killed during this battle Naval Battles The Battle of Lake Erie
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Map war1812 The Battle of Thames River, Oct. 5, 1813 US military victory led by General William H. Harrison Tecumseh was killed during this battle Naval Battles The Battle of Lake Erie
Chapter 8 Exam. Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Multiple Choice
 Multiple Choice Chapter 8 Exam Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which statement about the election of 1824 is true? a. Most people did not think a military
Multiple Choice Chapter 8 Exam Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which statement about the election of 1824 is true? a. Most people did not think a military
Economic Issues and Growth
 Economic Issues and Growth 1800-1848 Tariff of 1816 Passed to protect American industries after War of 1812 What would be advantages and disadvantages of high tariffs? Would different regions of the country
Economic Issues and Growth 1800-1848 Tariff of 1816 Passed to protect American industries after War of 1812 What would be advantages and disadvantages of high tariffs? Would different regions of the country
HUSH Unit 4. Jefferson, The War of 1812, and the Beginning of the Market Economy
 HUSH Unit 4 Jefferson, The War of 1812, and the Beginning of the Market Economy Post War Economic Development A Market Economy is Born The Transportation Revolution Three Stages: Canals - man made waterways
HUSH Unit 4 Jefferson, The War of 1812, and the Beginning of the Market Economy Post War Economic Development A Market Economy is Born The Transportation Revolution Three Stages: Canals - man made waterways
The election of George Washington as the first president under the Constitution was not exactly unanimous
 The election of George Washington as the first president under the Constitution was not exactly unanimous -2 electors from VA and 2 electors from MD did not vote -NY was entitled to 8 electoral votes but
The election of George Washington as the first president under the Constitution was not exactly unanimous -2 electors from VA and 2 electors from MD did not vote -NY was entitled to 8 electoral votes but
Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy?
 Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.4: Clickers Questions Market Revolution inquiry activity
Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.4: Clickers Questions Market Revolution inquiry activity
2) Use your notes, information collected from my classroom website or other internet resources
 1) Create an episode map on the Presidency of James Madison 2) Use your notes, information collected from my classroom website or other internet resources 1817-1825 I. In the election of 1816 James Monroe
1) Create an episode map on the Presidency of James Madison 2) Use your notes, information collected from my classroom website or other internet resources 1817-1825 I. In the election of 1816 James Monroe
Nationalism at Center Stage
 Nationalism at Center Stage 1807-Robert Fulton installed a steam engine on a boat, & cruised up the Hudson River from New York City to Albany- 150 miles in 32 hours The boat-the Clermont-luxurious, with
Nationalism at Center Stage 1807-Robert Fulton installed a steam engine on a boat, & cruised up the Hudson River from New York City to Albany- 150 miles in 32 hours The boat-the Clermont-luxurious, with
The Monroe Doctrine. President James Monroe. Adams-Onis Treaty, Spain gives up control of Florida
 President James Monroe Foreign Policy: The policy of how we interact with other countries 5 th th President- 1816-1824 1824 Democratic Republican Significant Positions Secretary of State Adams-Onis Treaty,
President James Monroe Foreign Policy: The policy of how we interact with other countries 5 th th President- 1816-1824 1824 Democratic Republican Significant Positions Secretary of State Adams-Onis Treaty,
President James Monroe. Elected in 1816 (Democratic- Republican [Republican]) Two Terms: Era of Good Feelings Monroe Doctrine
![President James Monroe. Elected in 1816 (Democratic- Republican [Republican]) Two Terms: Era of Good Feelings Monroe Doctrine President James Monroe. Elected in 1816 (Democratic- Republican [Republican]) Two Terms: Era of Good Feelings Monroe Doctrine](/thumbs/72/66263504.jpg) President James Monroe Elected in 1816 (Democratic- Republican [Republican]) Two Terms: 1816-1824 Era of Good Feelings Monroe Doctrine John Quincy Adams Monroe s Secretary of State Architect of the Monroe
President James Monroe Elected in 1816 (Democratic- Republican [Republican]) Two Terms: 1816-1824 Era of Good Feelings Monroe Doctrine John Quincy Adams Monroe s Secretary of State Architect of the Monroe
James Monroe and The Era of Good Feelings. The Role of Politics in Sectionalism
 James Monroe and The Era of Good Feelings The Role of Politics in Sectionalism James Monroe 1758 1831 Dem.-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former
James Monroe and The Era of Good Feelings The Role of Politics in Sectionalism James Monroe 1758 1831 Dem.-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former
JEFFERSONIAN DEMOCRACY ( ) ELECTION OF 1800 ELECTION OF 1800 JEFFERSON S PHILOSOPHY EXAMPLE POLICIES A NATION OF FARMERS
 JEFFERSONIAN DEMOCRACY (1800 1828) ELECTION OF 1800 Revolution of 1800 Adams v. Jefferson (again) Major Issues: - Expansion of Military - Foreign Affairs - Alien & Sedition Acts 1 2 ELECTION OF 1800 DR
JEFFERSONIAN DEMOCRACY (1800 1828) ELECTION OF 1800 Revolution of 1800 Adams v. Jefferson (again) Major Issues: - Expansion of Military - Foreign Affairs - Alien & Sedition Acts 1 2 ELECTION OF 1800 DR
attorney general(314)- plan nation s top legal officer; today also the head of the Department of Justice
 UNIT FOUR: The Early Republic (1789-1844) CHAPTER NINE: Launching a New Republic (1789-1800) LESSON 9-1: Washington s Presidency, pgs. 312-317 1) Explain challenges Washington encountered as the first
UNIT FOUR: The Early Republic (1789-1844) CHAPTER NINE: Launching a New Republic (1789-1800) LESSON 9-1: Washington s Presidency, pgs. 312-317 1) Explain challenges Washington encountered as the first
Chapter 7 Politics and Society in the New Republic,
 Chapter 7 Politics and Society in the New Republic, 1787-1820 The Political Crisis of the 1790s Thomas Jefferson vs. Alexander Hamilton The Federalist Implement the Constitution Swept the election of 1788
Chapter 7 Politics and Society in the New Republic, 1787-1820 The Political Crisis of the 1790s Thomas Jefferson vs. Alexander Hamilton The Federalist Implement the Constitution Swept the election of 1788
Section 1: The era begins with the end of the War of 1812 (1815) & the election of James Monroe (1816)
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Ch. 8 AMSCO or other resources for Period 4 content. Directions: Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before you read the chapter.
Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Ch. 8 AMSCO or other resources for Period 4 content. Directions: Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before you read the chapter.
Madison & Monroe. Presidencies
 James James Madison & Monroe Presidencies Where we are March 1797: President John Adams takes office. 1796-1800: XYZ Affair, Quasi-War with France, Alien & Sedition Acts, VA & KY Resolutions 1801-1804:
James James Madison & Monroe Presidencies Where we are March 1797: President John Adams takes office. 1796-1800: XYZ Affair, Quasi-War with France, Alien & Sedition Acts, VA & KY Resolutions 1801-1804:
Chapter 8:THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS:
 Chapter 8:THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS: Objectives: We will the study the effects of postwar expansion and continued economic growth in shaping the nation during the "era of good feelings" We will study the
Chapter 8:THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS: Objectives: We will the study the effects of postwar expansion and continued economic growth in shaping the nation during the "era of good feelings" We will study the
Imperialism by the US
 Imperialism by the US Quick Class Discussion: Based on this image, what important changes took place in the United States from 1783 to 1900? 115 years after gaining independence from Britain, the United
Imperialism by the US Quick Class Discussion: Based on this image, what important changes took place in the United States from 1783 to 1900? 115 years after gaining independence from Britain, the United
Forging a National Economy ANTEBELLUM AMERICAN SOCIETY
 Forging a National Economy ANTEBELLUM AMERICAN SOCIETY FORGING THE NATIONAL ECONOMY Theme 1: The American population expanded and changed in character as more people moved to the West, cities, and immigrant
Forging a National Economy ANTEBELLUM AMERICAN SOCIETY FORGING THE NATIONAL ECONOMY Theme 1: The American population expanded and changed in character as more people moved to the West, cities, and immigrant
In this chapter, you will learn about life in the new nation, from the Presidency of George Washington to that of James Monroe.
 In this chapter, you will learn about life in the new nation, from the Presidency of George Washington to that of James Monroe. Our earliest Presidents established many new traditions that have survived
In this chapter, you will learn about life in the new nation, from the Presidency of George Washington to that of James Monroe. Our earliest Presidents established many new traditions that have survived
The election of George Washington as the first president under the Constitution was not exactly unanimous
 The election of George Washington as the first president under the Constitution was not exactly unanimous -2 electors from VA and 2 electors from MD did not vote -NY was entitled to 8 electoral votes but
The election of George Washington as the first president under the Constitution was not exactly unanimous -2 electors from VA and 2 electors from MD did not vote -NY was entitled to 8 electoral votes but
Period 4: ( ) Chapter 12: 2 nd War of Independence/Upsurge in Nationalism ( )
 Period 4: (1800-1848) Chapter 12: 2 nd War of Independence/Upsurge in Nationalism (1812-1824) EQ: What economic, political and social challenges did the new nation face in its infancy in the early 19 th
Period 4: (1800-1848) Chapter 12: 2 nd War of Independence/Upsurge in Nationalism (1812-1824) EQ: What economic, political and social challenges did the new nation face in its infancy in the early 19 th
An ERA OF GOOD & BAD FEELINGS. Nationalism & Sectionalism after the War of 1812 A07EW
 An ERA OF GOOD & BAD FEELINGS Nationalism & Sectionalism after the War of 1812 A07EW 10.1015 Results of the War of 1812 Draw militarily Small war and insignificant in military terms. Important consequences
An ERA OF GOOD & BAD FEELINGS Nationalism & Sectionalism after the War of 1812 A07EW 10.1015 Results of the War of 1812 Draw militarily Small war and insignificant in military terms. Important consequences
Guided Reading & Analysis: Nationalism and Economic Development, Chapter 8- Nationalism and Economic Development, pp
 THIS IS A TRADITIONAL & OPTIONAL ASSIGNMENT IT MUST BE PRINTED AND COMPLETED IN INK! Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Guided Reading & Analysis: Nationalism and Economic Development, 1816-1848 Chapter
THIS IS A TRADITIONAL & OPTIONAL ASSIGNMENT IT MUST BE PRINTED AND COMPLETED IN INK! Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Guided Reading & Analysis: Nationalism and Economic Development, 1816-1848 Chapter
After the War of 1812 THE BEGINNING OF CHANGE IN AMERICAN POLITICS, ECONOMY, AND SOCIETY
 After the War of 1812 THE BEGINNING OF CHANGE IN AMERICAN POLITICS, ECONOMY, AND SOCIETY Consequences of the War of 1812 Why was the War of 1812 fought? Impressment Violation of neutral shipping rights
After the War of 1812 THE BEGINNING OF CHANGE IN AMERICAN POLITICS, ECONOMY, AND SOCIETY Consequences of the War of 1812 Why was the War of 1812 fought? Impressment Violation of neutral shipping rights
The March of Millions
 The March of Millions Around 1850 the population was doubling every 25 years. By 186 there were 33 states. America was the fourth most populous nation in the world. Cities were rapidly developing as were
The March of Millions Around 1850 the population was doubling every 25 years. By 186 there were 33 states. America was the fourth most populous nation in the world. Cities were rapidly developing as were
8.46 Analyze the physical obstacles to and the economic and political factors involved in building a network of roads, canals and railroads,
 8.46 Analyze the physical obstacles to and the economic and political factors involved in building a network of roads, canals and railroads, including Henry Clay s American System. United States in 1815
8.46 Analyze the physical obstacles to and the economic and political factors involved in building a network of roads, canals and railroads, including Henry Clay s American System. United States in 1815
The War of 1812 and the Upsurge of Nationalism APUSH Guide for American Pageant chapter 12 & AMSCO chapters 7 (last few pages) and 8
 Name: Class Period: The War of 1812 and the Upsurge of Nationalism 1812-1824 APUSH Guide for American Pageant chapter 12 & AMSCO chapters 7 (last few pages) and 8 Directions Print document and take notes
Name: Class Period: The War of 1812 and the Upsurge of Nationalism 1812-1824 APUSH Guide for American Pageant chapter 12 & AMSCO chapters 7 (last few pages) and 8 Directions Print document and take notes
ID-Irish and German Immigration by Decade (291) Summary 1- What decade brought the greatest number of Irish immigrants? Summary 2- What
 Ch 14 Insights Goals Questions Part 1 Identify the two largest immigrant groups to the US in the first half of the 1800 s and explain how their experiences were different Explain how those different experiences
Ch 14 Insights Goals Questions Part 1 Identify the two largest immigrant groups to the US in the first half of the 1800 s and explain how their experiences were different Explain how those different experiences
The Early Republic
 The Early Republic 1789-1828 Essential Questions What challenges faced the new nation under the Constitution? How did the first American political parties emerge? How did the Supreme Court establish its
The Early Republic 1789-1828 Essential Questions What challenges faced the new nation under the Constitution? How did the first American political parties emerge? How did the Supreme Court establish its
Monroe, the Era of Good Feelings, and the Election of 1824
 Monroe, the Era of Good Feelings, and the Election of 1824 A Boston newspaper coined the years of the Monroe Administration as the Era of Good Feelings After the War of 1812, Americans felt a sense of
Monroe, the Era of Good Feelings, and the Election of 1824 A Boston newspaper coined the years of the Monroe Administration as the Era of Good Feelings After the War of 1812, Americans felt a sense of
AP U.S. History: Unit 4.3 HistorySage.com The Era of Good Feelings :
 AP U.S. History: Unit 4.3 HistorySage.com The Era of Good Feelings : 1816-1824 I. U.S. emerged from the War of 1812 with a heightened sense of nationalism A. Madison more popular when leaving office in
AP U.S. History: Unit 4.3 HistorySage.com The Era of Good Feelings : 1816-1824 I. U.S. emerged from the War of 1812 with a heightened sense of nationalism A. Madison more popular when leaving office in
UNIT THREE STUDY QUESTIONS AND TERMS Chapter 7, 8, 9
 UNIT THREE STUDY QUESTIONS AND TERMS Chapter 7, 8, 9 Chapter 7: The Jeffersonian Era 1. What were Jefferson s ideas about education? 2. How were southern private schools different from northern private
UNIT THREE STUDY QUESTIONS AND TERMS Chapter 7, 8, 9 Chapter 7: The Jeffersonian Era 1. What were Jefferson s ideas about education? 2. How were southern private schools different from northern private
The Early Industrial and Transportation Revolution Chapter 14
 The Early Industrial and Transportation Revolution Chapter 14 1. Population growth 1800 = 5.5 million to 33 million by 1861 13 states to 33 states by 1861 Expansion of cities 2. Flow of Immigration 1830
The Early Industrial and Transportation Revolution Chapter 14 1. Population growth 1800 = 5.5 million to 33 million by 1861 13 states to 33 states by 1861 Expansion of cities 2. Flow of Immigration 1830
Advanced Placement United States History Test: Jeffersonian Democracy
 Advanced Placement United States History Test: Jeffersonian Democracy Bradberry 1. Which of the following statements about the American System is correct? a) it was set up by the Treaty of Ghent at the
Advanced Placement United States History Test: Jeffersonian Democracy Bradberry 1. Which of the following statements about the American System is correct? a) it was set up by the Treaty of Ghent at the
The term Era of Good Feelings refers to the period of American history when there seemed to be political harmony during the Monroe administration.
 The term Era of Good Feelings refers to the period of American history when there seemed to be political harmony during the Monroe administration. 1 2 In 1816, James Monroe became president, inaugurating
The term Era of Good Feelings refers to the period of American history when there seemed to be political harmony during the Monroe administration. 1 2 In 1816, James Monroe became president, inaugurating
Early Republic Addressing Challenges
 Early Republic Addressing Challenges 1789-1828 In this chapter, you will learn about life in the new nation, from the Presidency of to that of. Our earliest Presidents established many new traditions that
Early Republic Addressing Challenges 1789-1828 In this chapter, you will learn about life in the new nation, from the Presidency of to that of. Our earliest Presidents established many new traditions that
ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS
 ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS Big Idea As the US expanded, there was more debate over slavery and new attempts at compromise New western states continued to enter the Union -New states: IN, IL, MS, AL President
ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS Big Idea As the US expanded, there was more debate over slavery and new attempts at compromise New western states continued to enter the Union -New states: IN, IL, MS, AL President
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER 7
 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER 7 Section 1 Regional Economies Create Differences Do Now: An industrial revolution is a change in economic and social conditions marked by a significant increase
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER 7 Section 1 Regional Economies Create Differences Do Now: An industrial revolution is a change in economic and social conditions marked by a significant increase
Characteristics Families Clustered near rivers Regional settlement
 Population 1790 Majority lives East of Appalachian mountains and within a few miles of ocean 1840 1/3 lives between Appalachian mountains and Mississippi River The Sweep West Series of bursts 1790s 1791-1803
Population 1790 Majority lives East of Appalachian mountains and within a few miles of ocean 1840 1/3 lives between Appalachian mountains and Mississippi River The Sweep West Series of bursts 1790s 1791-1803
In the first half of the nineteenth century, economic changes called by historians the market revolution transformed the United States.
 1 2 In the first half of the nineteenth century, economic changes called by historians the market revolution transformed the United States. Innovations in transportation and communication sparked these
1 2 In the first half of the nineteenth century, economic changes called by historians the market revolution transformed the United States. Innovations in transportation and communication sparked these
The Jacksonian Era & the Rise of Sectionalism. (c. 1820s c. 1840s)
 The Jacksonian Era & the Rise of Sectionalism (c. 1820s c. 1840s) SSUSH7 Students will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and
The Jacksonian Era & the Rise of Sectionalism (c. 1820s c. 1840s) SSUSH7 Students will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and
FORGING THE NATIONAL ECONOMY, Chapter 14
 FORGING THE NATIONAL ECONOMY, 1790 1860 Chapter 14 WESTWARD MOVEMENT & SHAPING THE WESTERN LANDSCAPE America West of the Alleghenies Population center shifts Life is brutal, primitive, isolated Land becomes
FORGING THE NATIONAL ECONOMY, 1790 1860 Chapter 14 WESTWARD MOVEMENT & SHAPING THE WESTERN LANDSCAPE America West of the Alleghenies Population center shifts Life is brutal, primitive, isolated Land becomes
This painting is titled Fourth of July Celebration in Centre Square, Philadelphia, This painting by John Krimmel ( ) is courtesy of
 LEQ: What is the name given to feelings of pride and devotion to one s country? This painting is titled Fourth of July Celebration in Centre Square, Philadelphia, 1819. This painting by John Krimmel (1786-1821)
LEQ: What is the name given to feelings of pride and devotion to one s country? This painting is titled Fourth of July Celebration in Centre Square, Philadelphia, 1819. This painting by John Krimmel (1786-1821)
Question: Based on the picture above, what assumptions can we make about the period of time following the War of 1812?
 Hook Answer the following question on the top of pg. 65 (Notebook). Cue Column 2 ½ in. Study Questions/Main Ideas Fourth of July Celebration in Centre Square, Philadelphia (1819) by John Lewis Krimmel
Hook Answer the following question on the top of pg. 65 (Notebook). Cue Column 2 ½ in. Study Questions/Main Ideas Fourth of July Celebration in Centre Square, Philadelphia (1819) by John Lewis Krimmel
Essential Question: How did President Jefferson change U.S. government, territory, & foreign policy?
 Essential Question: How did President Jefferson change U.S. government, territory, & foreign policy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.1: Clicker Preview Questions President Jefferson notes & Marbury v Madison activity
Essential Question: How did President Jefferson change U.S. government, territory, & foreign policy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.1: Clicker Preview Questions President Jefferson notes & Marbury v Madison activity
America s History Eighth Edi(on
 James A. Henretta! Eric Hinderaker! Rebecca Edwards! Robert O. Self! America s History Eighth Edi(on America: A Concise History Sixth Edi(on CHAPTER 8 nd 9 Review= Unit 4 Crea=ng a Republican Culture 1790
James A. Henretta! Eric Hinderaker! Rebecca Edwards! Robert O. Self! America s History Eighth Edi(on America: A Concise History Sixth Edi(on CHAPTER 8 nd 9 Review= Unit 4 Crea=ng a Republican Culture 1790
APUSH- Unit 4: Early Federal Period
 APUSH- Unit 4: Early Federal Period Launching the New Ship of State, 1789-1800 (Chapter 10) I can explain why George Washington was pivotal to inaugurating the new federal government. (Pages 190-193) Cabinet
APUSH- Unit 4: Early Federal Period Launching the New Ship of State, 1789-1800 (Chapter 10) I can explain why George Washington was pivotal to inaugurating the new federal government. (Pages 190-193) Cabinet
Key Terms. Era of Good. Feelings. sectionalism American System internal improvements McCulloch v. Maryland Gibbons v. Ogden interstate commerce
 Name Period BifOI\E,ou READ Reading Focus What role did sectionalism play In the nation during the Era of Good Feelings? How did Congress help American Industry after the War of 1812? What was Henry Clay's
Name Period BifOI\E,ou READ Reading Focus What role did sectionalism play In the nation during the Era of Good Feelings? How did Congress help American Industry after the War of 1812? What was Henry Clay's
Guided Reading & Analysis: Nationalism and Economic Development, Chapter 8- Nationalism and Economic Development, pp
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Guided Reading & Analysis: Nationalism and Economic Development, 1816-1848 Chapter 8- Nationalism and Economic Development, pp 150-166 Reading Assignment: Ch. 8 AMSCO;
Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Guided Reading & Analysis: Nationalism and Economic Development, 1816-1848 Chapter 8- Nationalism and Economic Development, pp 150-166 Reading Assignment: Ch. 8 AMSCO;
Name: 8 th Grade U.S. History. STAAR Review. Early Republic
 8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Early Republic FORT BURROWS 2018 VOCABULARY Rebellion- an effort by many people to change the government or leader of a country by the use of protest or violence Excise
8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Early Republic FORT BURROWS 2018 VOCABULARY Rebellion- an effort by many people to change the government or leader of a country by the use of protest or violence Excise
AP U.S. History (Mr. Broach)
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 NATIONALISM AND THE JACKSONIAN PERIOD AP United States History (Kennedy, Chapters 12-15) Unit 4 UNIT THEMES Nationalism / one-party system after the War of 1812 Emerging sectional tensions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 NATIONALISM AND THE JACKSONIAN PERIOD AP United States History (Kennedy, Chapters 12-15) Unit 4 UNIT THEMES Nationalism / one-party system after the War of 1812 Emerging sectional tensions
America: Pathways to the Present. Chapter 8. The Growth of a National Economy ( )
 America: Pathways to the Present Chapter 8 The Growth of a National Economy (1790 1850) Copyright 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey. All rights
America: Pathways to the Present Chapter 8 The Growth of a National Economy (1790 1850) Copyright 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey. All rights
Comparing Regions,
 Comparing Regions, 1800-1850 You ve studied data about the three main regions of the United States in the period from 1800 to 1850, and you ve considered the ways in which people in those regions thought
Comparing Regions, 1800-1850 You ve studied data about the three main regions of the United States in the period from 1800 to 1850, and you ve considered the ways in which people in those regions thought
Unit 3- Hammering Out a Federal Republic
 Name: Class Period: Unit 3- Hammering Out a Federal Republic Key Concepts FOR PERIOD 3: Key Concept 3.2: The American Revolution s democratic and republican ideals inspired new experiments with different
Name: Class Period: Unit 3- Hammering Out a Federal Republic Key Concepts FOR PERIOD 3: Key Concept 3.2: The American Revolution s democratic and republican ideals inspired new experiments with different
The Antebellum Era ( ): The Rise of Jacksonian Democracy Part 1
 The Antebellum Era (1781-1860): The Rise of Jacksonian Democracy Part 1 B. Building a Nation (Colonization-ca. 1877) 1. Colonization and Forging a Nation K. Identify and evaluate the political and territorial
The Antebellum Era (1781-1860): The Rise of Jacksonian Democracy Part 1 B. Building a Nation (Colonization-ca. 1877) 1. Colonization and Forging a Nation K. Identify and evaluate the political and territorial
Trends in Antebellum America:
 Mr. Cegielski Trends in Antebellum America: 1810-1860 Covered last unit: 1. New intellectual and religious movements 2. Social reforms 3. Increase in federal power Marshall Ct. decisions. This Unit: 1.
Mr. Cegielski Trends in Antebellum America: 1810-1860 Covered last unit: 1. New intellectual and religious movements 2. Social reforms 3. Increase in federal power Marshall Ct. decisions. This Unit: 1.
Industrial Revolution
 The student will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and the different responses to it. a. Explain the impact of the Industrial
The student will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and the different responses to it. a. Explain the impact of the Industrial
The Young Republic: The Early Years. The Young Republic Test Packet due & test day:
 The Young Republic: The Early Years The Young Republic Test Packet due & test day: The Early Nation Vocabulary Name: Define each of the following words in regards to the early development of the nation:
The Young Republic: The Early Years The Young Republic Test Packet due & test day: The Early Nation Vocabulary Name: Define each of the following words in regards to the early development of the nation:
netw rks Reading Essentials and Study Guide Growth and Division, Lesson 2 Early Industry ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Reading HELPDESK
 and Study Guide Lesson 2 Early Industry ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How did the nation s economy help shape its politics? How did the economic differences between the North and the South cause tension? Reading
and Study Guide Lesson 2 Early Industry ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How did the nation s economy help shape its politics? How did the economic differences between the North and the South cause tension? Reading
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton
 Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
CHAPTER 10. Nationalism, Expansion, and the Market Economy, Learning Objectives
 CHAPTER 10 Nationalism, Expansion, and the Market Economy, 1816 1845 Learning Objectives After you have studied Chapter 10 in your textbook and worked through this study guide chapter, you should be able
CHAPTER 10 Nationalism, Expansion, and the Market Economy, 1816 1845 Learning Objectives After you have studied Chapter 10 in your textbook and worked through this study guide chapter, you should be able
Name Class Date. MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term or person that matches each description. Some answers will not be used.
 Origins of American Government Section 1 MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term or person that matches each description. Some answers will not be used. 1. Idea that people should
Origins of American Government Section 1 MATCHING In the space provided, write the letter of the term or person that matches each description. Some answers will not be used. 1. Idea that people should
Consequences of the War of 1812
 Consequences of the War of 1812 Collapse of Federalist Party Era of Good Feelings Monroe Presidency 18161824 Bring factions togethersimilar to Washington Last of Revolutionary Founding Fathers Appointed
Consequences of the War of 1812 Collapse of Federalist Party Era of Good Feelings Monroe Presidency 18161824 Bring factions togethersimilar to Washington Last of Revolutionary Founding Fathers Appointed
Chronological Reasoning and Continuity/Change over Time Economic Development Market Revolution
 Chronological Reasoning and Continuity/Change over Time Economic Development Market Revolution From the 2015 Revised Framework: Patterns of Continuity and Change over Time Historical thinking involves
Chronological Reasoning and Continuity/Change over Time Economic Development Market Revolution From the 2015 Revised Framework: Patterns of Continuity and Change over Time Historical thinking involves
Jeopardy Monroe Harrison
 Jeopardy Monroe Harrison 1817-1841 Good Vibrations Eccentric Elections Jackson: Good or Bad? Monroe -Tyler Jeopardy Court Conundrums Get this Party started! $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200
Jeopardy Monroe Harrison 1817-1841 Good Vibrations Eccentric Elections Jackson: Good or Bad? Monroe -Tyler Jeopardy Court Conundrums Get this Party started! $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200
Standard 3: Causes of the American Revolution. e. Declaration of Independence
 Name Date Hour U.S. History to 1877 OCCT Review Study Guide Use your notes, your textbook and all of the knowledge gained this year to complete this O.C.C.T. Review Study Guide. This study guide will be
Name Date Hour U.S. History to 1877 OCCT Review Study Guide Use your notes, your textbook and all of the knowledge gained this year to complete this O.C.C.T. Review Study Guide. This study guide will be
Industrial Revolution
 Chapter 9 Economic Transformation Industrial Revolution Division of Labor Industry in America 1790 1820 aided by transportation Industrial Revolution outwork system work done outside of shop modern factory
Chapter 9 Economic Transformation Industrial Revolution Division of Labor Industry in America 1790 1820 aided by transportation Industrial Revolution outwork system work done outside of shop modern factory
4.1 NATIONALISM & SECTIONALISM AMERICAN HISTORY I UNIT 4 ERA OF GROWTH AND DISUNION DAY 1 NATIONALISM & SECTIONALISM
 4.1 NATIONALISM & SECTIONALISM AMERICAN HISTORY I UNIT 4 ERA OF GROWTH AND DISUNION DAY 1 NATIONALISM & SECTIONALISM NATIONALISM: AN ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS What is NATIONALISM? First, let s define NATION.
4.1 NATIONALISM & SECTIONALISM AMERICAN HISTORY I UNIT 4 ERA OF GROWTH AND DISUNION DAY 1 NATIONALISM & SECTIONALISM NATIONALISM: AN ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS What is NATIONALISM? First, let s define NATION.
The Role of Politics in Sectionalism
 The Role of Politics in Sectionalism James Monroe 1758 1831 Dem.-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former Gov. of VA, Secretary of State, and Secretary
The Role of Politics in Sectionalism James Monroe 1758 1831 Dem.-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former Gov. of VA, Secretary of State, and Secretary
