CH. 8: GROWTH OF A NATIONAL ECONOMY
|
|
|
- Jasper Bell
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 CH. 8: GROWTH OF A NATIONAL ECONOMY Mr. Anderson, M.Ed., J.D. Review Who was John Marshall? Which president appointed him? What is he best remembered for? The Industrial Revolution Section 1 Quick review: started in Britain in the early 1700 s w/ changes in textile industry. Spread around the world allowing production of products by machinery rather than people and animals Steam shovel, steamboat, muskets, interchangeable parts, cotton mills, canning factories, internal combustion engine, and THE COTTON GIN (Eli Whitney of New Haven, CT patented it in 1794) Samuel Slater (later emigrated to the US from Britain): developed textile mills using steam power ú cotton would become KING in the south after this invention The Industrial Revolution (con t.) Led to a revolution in travel and communication Roads, canals, rivers, railroads, postal service, led to Americans with the ability to read information previously unattainable since mail incl.: newspapers, magazines, & books 5 The Industrial Revolution (con t.) It also led to a stronger economy: Manufacturing - USE OF WATER POWER (New England colonies) Shopping Specialization Role of banks changed: THEY PROVIDED CAPITAL FOR INVESTMENTS 1
2 Role of banks changed: THEY PROVIDED CAPITAL FOR INVESTMENTS ú Bank notes (free enterprise system) 6 Differences in the North and South Sections 2 & 3 North New England, NY, NJ & PA OH, MI, WI, MN Farming & Industries Cities growing (pop. outgrowing avail. land) Products from industries incl.: Coal-mining, furniture, clocks, glass, tinware, carpet, bricks, shoes, ships, lumber, iron, leather, textiles, muskets South DE, MD, VA, WV, NC, SC, GA KY, TN, AL, MS, MO, LA, TX, AR King Cotton, tobacco, cattle, lumber, textiles, mining, rice & sugar cane, lumber, grain, iron & steel Slavery System 7 Slave Revolts Vesey and Turner Denmark Vesey Charleston, SC self educated won freedom with $ street lottery 35 hanged Nat Turner - Virginia; divine inspiration killed > 50 whites 20 hanged Results of these two uprisings: Harsher slave laws cannot teach slaves to read, meet or move freely 8 Notable Supreme Court Decisions Section 4 Chief Justice John Marshall strengthened the federal government s role in the nation s economy: 2
3 Chief Justice John Marshall strengthened the federal government s role in the nation s economy: Dartmouth v. Woodward (1819)- states cannot interfere with private contracts ( stability to the economy by encouraging growth) McCulloch v. Maryland (1819)- 2 nd bank of the US (held up implied powers of the Constitution) Congress did have the authority to charter the bank Gibbons v. Ogden (1824)- gave the federal government the power to regulate all interstate commerce Cherokee Nation v. Georgia (1832) domestic, dependent nation, rather than a sovereign nation - Art. III 9 10 Monroe Doctrine 1823 Short term-effects: U.S. would not get involved in internal affairs of European countries, nor would it take sides in wars among them U.S. recognized all countries in the western hemisphere and would not interfere with them in any way U.S. would not permit any more colonization of the western hemisphere Any attempt by a European power to do so would result in hostile action by U.S. Monroe Doctrine (con t) Long term effects: The Roosevelt Corollary (1904); Dollar Diplomacy (Taft); The Good Neighbor Policy; The Truman Doctrine; The Domino Theory; The Nixon Doctrine; The Reagan Doctrine; The Bush Doctrine 3
4 The Bush Doctrine 11 Presidential Election of 1824 Andrew Jackson (Man of the People Old Hickory ), John Quincy Adams (Experienced Diplomat), John Calhoun (Champion of the South) and Henry Clay (Passionate Orator) The Corrupt Bargain Jackson won most electoral college votes, but not a majority Const. says House must decide Clay used his influence as speaker of the House to swing enough votes to give Adams the victory Jackson denied win Jacksonian Democracy ( ) Section 5 The Spoils System: patronage is official policy of his administration jobs to friends & supporters Believed in limited government: vetoed a lot of laws that he agreed with but disagreed with how it should be done Believed in State s rights - they could nullify those federal laws they didn t like [Tariff Act of 1828 (tax on imports to boost northern American manufacturing) Southerners called it Tariff of Abominations ] The Indian Crisis The Bank War Defining moment of Andrew Jackson s (A.J.) Presidency Vetoed the bill to renew the charter of the Bank of the U.S. ( monster ) A.J. believed that the Bank was responsible for the Panic of 1819 The Bank was controlled by a small group of wealthy Easterners A.J. won reelection in 1828 The First 9 Presidents 4
5 1. George Washington (John Adams) John Adams (Thomas Jefferson) Thomas Jefferson (Aaron Burr) James Madison James Monroe John Quincy Adams Andrew Jackson Martin Van Buren William Henry Harrison
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism
 7 QUIT Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE GRAPH SECTION 1 Regional Economics Create Differences SECTION 2 Nationalism at Center Stage MAP SECTION 3
7 QUIT Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE GRAPH SECTION 1 Regional Economics Create Differences SECTION 2 Nationalism at Center Stage MAP SECTION 3
The Americans (Survey)
 The Americans (Survey) Chapter 7: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OVERVIEW American leaders devise a farsighted policy of improvements as North, South, and West develop
The Americans (Survey) Chapter 7: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OVERVIEW American leaders devise a farsighted policy of improvements as North, South, and West develop
The Role of Politics in Sectionalism
 The Role of Politics in Sectionalism James Monroe 1758 1831 Dem.-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former Gov. of VA, Secretary of State, and Secretary
The Role of Politics in Sectionalism James Monroe 1758 1831 Dem.-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former Gov. of VA, Secretary of State, and Secretary
Chapter 7 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism
 Chapter 7 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Changes in manufacturing launch an Industrial Revolution. Slavery and other issues divide the North and South. Andrew Jackson has popular appeal but uproots
Chapter 7 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Changes in manufacturing launch an Industrial Revolution. Slavery and other issues divide the North and South. Andrew Jackson has popular appeal but uproots
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism
 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Regional Economies Create Differences Samuel Slater brought the Water Frame to Rhode Island from Great Britain in 1789. It was used to spin raw cotton into cotton
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Regional Economies Create Differences Samuel Slater brought the Water Frame to Rhode Island from Great Britain in 1789. It was used to spin raw cotton into cotton
America: Pathways to the Present. Chapter 8. The Growth of a National Economy ( )
 America: Pathways to the Present Chapter 8 The Growth of a National Economy (1790 1850) Copyright 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey. All rights
America: Pathways to the Present Chapter 8 The Growth of a National Economy (1790 1850) Copyright 2005 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey. All rights
Consequences of the War of 1812
 Consequences of the War of 1812 Collapse of Federalist Party Era of Good Feelings Monroe Presidency 18161824 Bring factions togethersimilar to Washington Last of Revolutionary Founding Fathers Appointed
Consequences of the War of 1812 Collapse of Federalist Party Era of Good Feelings Monroe Presidency 18161824 Bring factions togethersimilar to Washington Last of Revolutionary Founding Fathers Appointed
The Antebellum Era ( ): The Rise of Jacksonian Democracy Part 1
 The Antebellum Era (1781-1860): The Rise of Jacksonian Democracy Part 1 B. Building a Nation (Colonization-ca. 1877) 1. Colonization and Forging a Nation K. Identify and evaluate the political and territorial
The Antebellum Era (1781-1860): The Rise of Jacksonian Democracy Part 1 B. Building a Nation (Colonization-ca. 1877) 1. Colonization and Forging a Nation K. Identify and evaluate the political and territorial
REVIEW FOR 4 TH 6 WEEKS COMPREHENSIVE EXAM
 REVIEW FOR 4 TH 6 WEEKS COMPREHENSIVE EXAM 1. What were the main foreign policy issues faced by Washington (include an evaluation of his farewell address)? Keeping the USA neutral during the war between
REVIEW FOR 4 TH 6 WEEKS COMPREHENSIVE EXAM 1. What were the main foreign policy issues faced by Washington (include an evaluation of his farewell address)? Keeping the USA neutral during the war between
1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation
 Topic 3 1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg 88-89 They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation agreements 2. How did the British respond to the Boston Tea
Topic 3 1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg 88-89 They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation agreements 2. How did the British respond to the Boston Tea
Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages ) Economic Growth
 Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages 304 309) Economic Growth Essential Question What effects did the Industrial Revolution have on the U. S. economy? Directions: As you read, complete a graphic organizer like
Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages 304 309) Economic Growth Essential Question What effects did the Industrial Revolution have on the U. S. economy? Directions: As you read, complete a graphic organizer like
1. It disappeared after President James Monroe s landslide election victory in 1816.
 Chapter 10: A Changing Nation 1815-1840 Section 1: Building National Identity 1. It disappeared after President James Monroe s landslide election victory in 1816. 2. You were to put an X on the chart next
Chapter 10: A Changing Nation 1815-1840 Section 1: Building National Identity 1. It disappeared after President James Monroe s landslide election victory in 1816. 2. You were to put an X on the chart next
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER 7
 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER 7 Section 1 Regional Economies Create Differences Do Now: An industrial revolution is a change in economic and social conditions marked by a significant increase
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER 7 Section 1 Regional Economies Create Differences Do Now: An industrial revolution is a change in economic and social conditions marked by a significant increase
Division of Labor: giving each worker one or two simple jobs.
 Chapter 12 The Nation Grows (1815-1830) Section 1 Industries take Root Industrial Revolution: the growth of industry eventually produced changes so great that this time in history is called the Industrial
Chapter 12 The Nation Grows (1815-1830) Section 1 Industries take Root Industrial Revolution: the growth of industry eventually produced changes so great that this time in history is called the Industrial
Jackson s Administration
 SECTION2 Jackson s Administration What You Will Learn Main Ideas 1. Regional differences grew during Jackson s presidency. 2. The rights of the states were debated amid arguments about a national tariff.
SECTION2 Jackson s Administration What You Will Learn Main Ideas 1. Regional differences grew during Jackson s presidency. 2. The rights of the states were debated amid arguments about a national tariff.
James Monroe and The Era of Good Feelings. The Role of Politics in Sectionalism
 James Monroe and The Era of Good Feelings The Role of Politics in Sectionalism James Monroe 1758 1831 Dem.-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former
James Monroe and The Era of Good Feelings The Role of Politics in Sectionalism James Monroe 1758 1831 Dem.-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former
Level 2 THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS
 Level 2 THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS Vocabulary Sectionalism: loyalty to a section of a country instead of the nation itself Inflation: Protective Tariff: tax on imported goods Internal Expansion: continued
Level 2 THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS Vocabulary Sectionalism: loyalty to a section of a country instead of the nation itself Inflation: Protective Tariff: tax on imported goods Internal Expansion: continued
Warm Up. the north & south. slavery in the southern USA: economic landscape of the United States: 1) Using a Venn Diagram compare and contrast
 Warm Up 1) Using a Venn Diagram compare and contrast the north & south 2) Explain the impact of the cotton gin on slavery in the southern USA: 3) Discuss how industrialization changed the economic landscape
Warm Up 1) Using a Venn Diagram compare and contrast the north & south 2) Explain the impact of the cotton gin on slavery in the southern USA: 3) Discuss how industrialization changed the economic landscape
Election of Rise of Popular Politics. Republican Candidates. A Democratic Revolution. New Democracy franchise
 Rise of Popular Politics Chapter 10 A Democratic Revolution New Democracy franchise 1810s many states: all white men only place in world laborers, small farmers new western states Republican Candidates
Rise of Popular Politics Chapter 10 A Democratic Revolution New Democracy franchise 1810s many states: all white men only place in world laborers, small farmers new western states Republican Candidates
Unit Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution
 Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
Binder Page Name Period Andrew Jackson and the Growth of American Democracy
 Binder Page Name Period Andrew Jackson and the Growth of American Democracy Date Chapter 6.1 Jackson Wins the Presidency- (p. 302-312) 1. Democracy was growing in the United States. In other words, the
Binder Page Name Period Andrew Jackson and the Growth of American Democracy Date Chapter 6.1 Jackson Wins the Presidency- (p. 302-312) 1. Democracy was growing in the United States. In other words, the
Unit 4: { Politics Economics Society
 Unit 4: 1800-1848 { Politics Economics Society Established Cabinet of close advisers French Revolution Neutrality Proclamation Organized troops against Whiskey Rebellion BIG PICTURE IMPACT: Promoted unity;
Unit 4: 1800-1848 { Politics Economics Society Established Cabinet of close advisers French Revolution Neutrality Proclamation Organized troops against Whiskey Rebellion BIG PICTURE IMPACT: Promoted unity;
Varieties of American Nationalism. Chapter 8: History 103
 Varieties of American Nationalism Chapter 8: History 103 Boom to Bust post war boom leads to Panic of 1819 Why did the Panic of 1819 occur? Banking and Currency 1811: First Bank of the United States expired
Varieties of American Nationalism Chapter 8: History 103 Boom to Bust post war boom leads to Panic of 1819 Why did the Panic of 1819 occur? Banking and Currency 1811: First Bank of the United States expired
Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy?
 Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.4: Clickers Questions Market Revolution inquiry activity
Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.4: Clickers Questions Market Revolution inquiry activity
President James Monroe. Elected in 1816 (Democratic- Republican [Republican]) Two Terms: Era of Good Feelings Monroe Doctrine
![President James Monroe. Elected in 1816 (Democratic- Republican [Republican]) Two Terms: Era of Good Feelings Monroe Doctrine President James Monroe. Elected in 1816 (Democratic- Republican [Republican]) Two Terms: Era of Good Feelings Monroe Doctrine](/thumbs/72/66263504.jpg) President James Monroe Elected in 1816 (Democratic- Republican [Republican]) Two Terms: 1816-1824 Era of Good Feelings Monroe Doctrine John Quincy Adams Monroe s Secretary of State Architect of the Monroe
President James Monroe Elected in 1816 (Democratic- Republican [Republican]) Two Terms: 1816-1824 Era of Good Feelings Monroe Doctrine John Quincy Adams Monroe s Secretary of State Architect of the Monroe
Era of Good Feelings:
 Era of Good Feelings: 1815-1825 After the War of 1812 Americans finally have international respect The Republicans are the only political party James Monroe, the third member of the Virginia Dynasty, is
Era of Good Feelings: 1815-1825 After the War of 1812 Americans finally have international respect The Republicans are the only political party James Monroe, the third member of the Virginia Dynasty, is
The Big Idea The expansion of voting rights and the election of Andrew Jackson signaled the growing power of the American people.
 Jacksonian Democracy The Big Idea The expansion of voting rights and the election of Andrew Jackson signaled the growing power of the American people. Main Ideas Democracy expanded in the 1820s as more
Jacksonian Democracy The Big Idea The expansion of voting rights and the election of Andrew Jackson signaled the growing power of the American people. Main Ideas Democracy expanded in the 1820s as more
CHAPTER 2, SECTION 2. The Growth of the Nation
 CHAPTER 2, SECTION 2 The Growth of the Nation Big Ideas: After the War of 1812, more Americans began to see themselves as members of a nation rather than only identifying themselves by a region or state.
CHAPTER 2, SECTION 2 The Growth of the Nation Big Ideas: After the War of 1812, more Americans began to see themselves as members of a nation rather than only identifying themselves by a region or state.
What four men ran for president and what parts of the country did they represent?
 Chapter 12 The Age of Jackson pg. 366 389 12 1 Politics of the People The Election of 1824 What four men ran for president and what parts of the country did they represent? Why was the election of 1824
Chapter 12 The Age of Jackson pg. 366 389 12 1 Politics of the People The Election of 1824 What four men ran for president and what parts of the country did they represent? Why was the election of 1824
UNIT THREE STUDY QUESTIONS AND TERMS Chapter 7, 8, 9
 UNIT THREE STUDY QUESTIONS AND TERMS Chapter 7, 8, 9 Chapter 7: The Jeffersonian Era 1. What were Jefferson s ideas about education? 2. How were southern private schools different from northern private
UNIT THREE STUDY QUESTIONS AND TERMS Chapter 7, 8, 9 Chapter 7: The Jeffersonian Era 1. What were Jefferson s ideas about education? 2. How were southern private schools different from northern private
The Age of Jackson. A. As you read about the Jacksonian era, write answers to the questions about events that appear on the time line.
 Date CHAPTER Section 3 GUIDED READING The Age of Jackson A. As you read about the Jacksonian era, write answers to the questions about events that appear on the time line. 182 1830 By this point, the Cherokee
Date CHAPTER Section 3 GUIDED READING The Age of Jackson A. As you read about the Jacksonian era, write answers to the questions about events that appear on the time line. 182 1830 By this point, the Cherokee
Henry Clay met with Adams, and said he would use his influence as Speaker of the House to elect Adams if Adams named him Sec. of State Adams was
 Election of 1824 Monroe ends 2 nd term, four candidates ran William Crawford Georgia Andrew Jackson Tennessee Henry Clay Kentucky John Quincy Adams Massachusetts each candidate had regional support and
Election of 1824 Monroe ends 2 nd term, four candidates ran William Crawford Georgia Andrew Jackson Tennessee Henry Clay Kentucky John Quincy Adams Massachusetts each candidate had regional support and
Age of Jackson. 7 pages
 Age of Jackson 7 pages James Monroe 1817-1825 He is still president U.S. Territory The United States in 1819 (the light orange and light green areas were not then U.S. territory). The Missouri Compromise
Age of Jackson 7 pages James Monroe 1817-1825 He is still president U.S. Territory The United States in 1819 (the light orange and light green areas were not then U.S. territory). The Missouri Compromise
Jeopardy Monroe Harrison
 Jeopardy Monroe Harrison 1817-1841 Good Vibrations Eccentric Elections Jackson: Good or Bad? Monroe -Tyler Jeopardy Court Conundrums Get this Party started! $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200
Jeopardy Monroe Harrison 1817-1841 Good Vibrations Eccentric Elections Jackson: Good or Bad? Monroe -Tyler Jeopardy Court Conundrums Get this Party started! $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200
An ERA OF GOOD & BAD FEELINGS. Nationalism & Sectionalism after the War of 1812 A07EW
 An ERA OF GOOD & BAD FEELINGS Nationalism & Sectionalism after the War of 1812 A07EW 10.1015 Results of the War of 1812 Draw militarily Small war and insignificant in military terms. Important consequences
An ERA OF GOOD & BAD FEELINGS Nationalism & Sectionalism after the War of 1812 A07EW 10.1015 Results of the War of 1812 Draw militarily Small war and insignificant in military terms. Important consequences
Industrial Revolution
 The student will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and the different responses to it. a. Explain the impact of the Industrial
The student will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and the different responses to it. a. Explain the impact of the Industrial
Economic Issues and Growth
 Economic Issues and Growth 1800-1848 Tariff of 1816 Passed to protect American industries after War of 1812 What would be advantages and disadvantages of high tariffs? Would different regions of the country
Economic Issues and Growth 1800-1848 Tariff of 1816 Passed to protect American industries after War of 1812 What would be advantages and disadvantages of high tariffs? Would different regions of the country
In the early Antebellum era ( ), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that
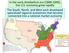 In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
Monroe, the Era of Good Feelings, and the Election of 1824
 Monroe, the Era of Good Feelings, and the Election of 1824 A Boston newspaper coined the years of the Monroe Administration as the Era of Good Feelings After the War of 1812, Americans felt a sense of
Monroe, the Era of Good Feelings, and the Election of 1824 A Boston newspaper coined the years of the Monroe Administration as the Era of Good Feelings After the War of 1812, Americans felt a sense of
netw rks Reading Essentials and Study Guide Growth and Division, Lesson 1 American Nationalism ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Reading HELPDESK
 and Study Guide Lesson 1 American Nationalism ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How did the nation s economy help shape its politics? How did the economic differences between the North and the South cause tension? Reading
and Study Guide Lesson 1 American Nationalism ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How did the nation s economy help shape its politics? How did the economic differences between the North and the South cause tension? Reading
13.1 Jacksonian Democracy
 Name: Per: 1. Define the following terms: 13.1 Jacksonian Democracy Mudslinging Bureaucracy Spoils System New Parties Emerge 2. Read about the Election of 1824 and fill in the information below: Andrew
Name: Per: 1. Define the following terms: 13.1 Jacksonian Democracy Mudslinging Bureaucracy Spoils System New Parties Emerge 2. Read about the Election of 1824 and fill in the information below: Andrew
Chapter 8: Varieties of American Nationalism
 Chapter 8: Varieties of American Nationalism "...but this momentous question, like a fire bell in the night, awakened and filled me with terror. I considered it at once as the death knell of the Union.
Chapter 8: Varieties of American Nationalism "...but this momentous question, like a fire bell in the night, awakened and filled me with terror. I considered it at once as the death knell of the Union.
History 1301 U.S. to Unit 2 - Lecture 4 ~
 History 1301 U.S. to 1877 Unit 2 - Lecture 4 ~ The Era of Good Feeling Post-war Economics: Post-war boom led to bust in 1819 National weaknesses shown by War experience Second National Bank chartered in
History 1301 U.S. to 1877 Unit 2 - Lecture 4 ~ The Era of Good Feeling Post-war Economics: Post-war boom led to bust in 1819 National weaknesses shown by War experience Second National Bank chartered in
Period 4: ( ) Chapter 12: 2 nd War of Independence/Upsurge in Nationalism ( )
 Period 4: (1800-1848) Chapter 12: 2 nd War of Independence/Upsurge in Nationalism (1812-1824) EQ: What economic, political and social challenges did the new nation face in its infancy in the early 19 th
Period 4: (1800-1848) Chapter 12: 2 nd War of Independence/Upsurge in Nationalism (1812-1824) EQ: What economic, political and social challenges did the new nation face in its infancy in the early 19 th
Madison & Monroe. Presidencies
 James James Madison & Monroe Presidencies Where we are March 1797: President John Adams takes office. 1796-1800: XYZ Affair, Quasi-War with France, Alien & Sedition Acts, VA & KY Resolutions 1801-1804:
James James Madison & Monroe Presidencies Where we are March 1797: President John Adams takes office. 1796-1800: XYZ Affair, Quasi-War with France, Alien & Sedition Acts, VA & KY Resolutions 1801-1804:
CHAPTER 10 A GROWING NATION:
 Section 1: Building a National Identity 1. I. The Era of Good Feeling CHAPTER 10 A GROWING NATION: 1815 1840 With the end of the War of 1812, the Republicans took firm control of the government. The presidential
Section 1: Building a National Identity 1. I. The Era of Good Feeling CHAPTER 10 A GROWING NATION: 1815 1840 With the end of the War of 1812, the Republicans took firm control of the government. The presidential
3. Shay s Rebellion mobocracy Need a strong govt. to maintain order AOC could not
 Born in Virginia, 1755 Served as an officer with General Washington during the Revolution Attended College of William and Mary and became a practicing attorney. 2 nd cousin of Thomas Jefferson. Marshall
Born in Virginia, 1755 Served as an officer with General Washington during the Revolution Attended College of William and Mary and became a practicing attorney. 2 nd cousin of Thomas Jefferson. Marshall
The Jacksonian Era & the Rise of Sectionalism. (c. 1820s c. 1840s)
 The Jacksonian Era & the Rise of Sectionalism (c. 1820s c. 1840s) SSUSH7 Students will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and
The Jacksonian Era & the Rise of Sectionalism (c. 1820s c. 1840s) SSUSH7 Students will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and
CHAPTER 9: THE ASCENSION AND PRESIDENCY OF ANDREW JACKSON
 CHAPTER 9: THE ASCENSION AND PRESIDENCY OF ANDREW JACKSON How did the Panic of 1819, and the Missouri Crisis increase citizens awareness of politics and government? The recession caused by the panic made
CHAPTER 9: THE ASCENSION AND PRESIDENCY OF ANDREW JACKSON How did the Panic of 1819, and the Missouri Crisis increase citizens awareness of politics and government? The recession caused by the panic made
APUSH Reading Quiz 13 The Rise of Mass Democracy ( )
 APUSH Reading Quiz 13 The Rise of Mass Democracy (1824-1840) Period 2 1. Though an ardent advocate for states rights, Andrew Jackson believed that the preservation of the Union was a higher political priority.
APUSH Reading Quiz 13 The Rise of Mass Democracy (1824-1840) Period 2 1. Though an ardent advocate for states rights, Andrew Jackson believed that the preservation of the Union was a higher political priority.
Issues that Challenged Old Hickory
 Issues that Challenged Old Hickory The Corrupt Bargain The Candidates Andrew Jackson- Democrat John Quincy Adams- Whig Henry Clay- Whig William Crawford- Democrat Jackson won the popular vote, but no candidate
Issues that Challenged Old Hickory The Corrupt Bargain The Candidates Andrew Jackson- Democrat John Quincy Adams- Whig Henry Clay- Whig William Crawford- Democrat Jackson won the popular vote, but no candidate
ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS
 ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS Big Idea As the US expanded, there was more debate over slavery and new attempts at compromise New western states continued to enter the Union -New states: IN, IL, MS, AL President
ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS Big Idea As the US expanded, there was more debate over slavery and new attempts at compromise New western states continued to enter the Union -New states: IN, IL, MS, AL President
UNIT 4 REVIEW PACKET The Early 19 th Century
 Name: UNIT 4 REVIEW PACKET The Early 19 th Century Due Date: Part 1: Content Review You will define and explain the significance of important terms from the historical period. Part 2: Key Concepts You
Name: UNIT 4 REVIEW PACKET The Early 19 th Century Due Date: Part 1: Content Review You will define and explain the significance of important terms from the historical period. Part 2: Key Concepts You
The Treaty of Ghent War of 1812 is considered a stalemate Dec. 1814
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Map war1812 The Battle of Thames River, Oct. 5, 1813 US military victory led by General William H. Harrison Tecumseh was killed during this battle Naval Battles The Battle of Lake Erie
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Map war1812 The Battle of Thames River, Oct. 5, 1813 US military victory led by General William H. Harrison Tecumseh was killed during this battle Naval Battles The Battle of Lake Erie
Chapter 9 and part of Chapter 8: Transforming the Economy,
 Chapter 9 and part of Chapter 8: Transforming the Economy, 1790-1860 The Big Questions: What were the causes and consequences of the industrial and market revolutions, and how did they change the way ordinary
Chapter 9 and part of Chapter 8: Transforming the Economy, 1790-1860 The Big Questions: What were the causes and consequences of the industrial and market revolutions, and how did they change the way ordinary
s Era of Good Feelings s Why was it called this?
 s Era of Good Feelings s Why was it called this? s For such an era to exist, what would have to be NOT present in other words what stressful issues would have to be reslved in order to have an Era of Good
s Era of Good Feelings s Why was it called this? s For such an era to exist, what would have to be NOT present in other words what stressful issues would have to be reslved in order to have an Era of Good
Going to War? Learning Target 1: I can discuss the causes and effects of the War of Learning Target 2: I can discuss the impact of James Madison
 Going to War? Learning Target 1: I can discuss the causes and effects of the War of 1812 Learning Target 2: I can discuss the impact of James Madison A-James Madison was elected President in 1808 and 1812
Going to War? Learning Target 1: I can discuss the causes and effects of the War of 1812 Learning Target 2: I can discuss the impact of James Madison A-James Madison was elected President in 1808 and 1812
The Triumph of Democracy
 Name: Give Me Liberty!, Chapter 10 Video Guide Big Idea Questions Who wrote The Liberator? What is the cult of domesticity? Guided Notes The Triumph of Democracy Jackson s inauguration Seen as the Man
Name: Give Me Liberty!, Chapter 10 Video Guide Big Idea Questions Who wrote The Liberator? What is the cult of domesticity? Guided Notes The Triumph of Democracy Jackson s inauguration Seen as the Man
WARM UP. 1 Get into the Kahoot game on the board. 2 We will review the week & the winner will receive a prize!
 WARM UP 1 Get into the Kahoot game on the board 2 We will review the week & the winner will receive a prize! PRESIDENCY OF JOHN QUINCY ADAMS ELECTION OF 1824 I. Sectionalism replaced nationalism in the
WARM UP 1 Get into the Kahoot game on the board 2 We will review the week & the winner will receive a prize! PRESIDENCY OF JOHN QUINCY ADAMS ELECTION OF 1824 I. Sectionalism replaced nationalism in the
Democratic Republican Era
 Democratic Republican Era Thomas Jefferson s Administration James Madison s Administration James Monroe s Administration Jefferson Madison Monroe Following the election of 1800, the Democratic Republicans
Democratic Republican Era Thomas Jefferson s Administration James Madison s Administration James Monroe s Administration Jefferson Madison Monroe Following the election of 1800, the Democratic Republicans
Describe why the election of 1824 was called a Corrupt Bargain by Jackson supporters. Explain one way in which voting rights were expanded.
 The Age of Jackson in United States History: Beginnings to 1877 SWBATs: Describe why the election of 1824 was called a Corrupt Bargain by Jackson supporters. Explain one way in which voting rights were
The Age of Jackson in United States History: Beginnings to 1877 SWBATs: Describe why the election of 1824 was called a Corrupt Bargain by Jackson supporters. Explain one way in which voting rights were
DRAWING FROM EXPERIENCEII
 Chapter 10, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 306 311 ECONOMIC GROWTH KEY TERMS Industrial Revolution A new way of working and producing goods (page 307) capital Money invested to start new businesses
Chapter 10, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 306 311 ECONOMIC GROWTH KEY TERMS Industrial Revolution A new way of working and producing goods (page 307) capital Money invested to start new businesses
378. Purchase of Florida Under the Adams-Onis Treaty, Spain sold Florida to the U.S., and the U.S. gave up its claims to Texas.
 Note Cards 351. Embargo of 1807, opposition This act issued by Jefferson forbade American trading ships from leaving the U.S. It was meant to force Britain and France to change their policies towards neutral
Note Cards 351. Embargo of 1807, opposition This act issued by Jefferson forbade American trading ships from leaving the U.S. It was meant to force Britain and France to change their policies towards neutral
Chapter 8:THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS:
 Chapter 8:THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS: Objectives: We will the study the effects of postwar expansion and continued economic growth in shaping the nation during the "era of good feelings" We will study the
Chapter 8:THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS: Objectives: We will the study the effects of postwar expansion and continued economic growth in shaping the nation during the "era of good feelings" We will study the
Trends in Antebellum America:
 Mr. Cegielski Trends in Antebellum America: 1810-1860 Covered last unit: 1. New intellectual and religious movements 2. Social reforms 3. Increase in federal power Marshall Ct. decisions. This Unit: 1.
Mr. Cegielski Trends in Antebellum America: 1810-1860 Covered last unit: 1. New intellectual and religious movements 2. Social reforms 3. Increase in federal power Marshall Ct. decisions. This Unit: 1.
The Presidency of James Monroe
 The Presidency of James Monroe James Monroe 1758 1831 Democratic-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former Governor of Virginia, Secretary of State,
The Presidency of James Monroe James Monroe 1758 1831 Democratic-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former Governor of Virginia, Secretary of State,
APUSH Chapter Lecture Notes
 APUSH Chapter 11+12 Lecture Notes Chapter 11: The Triumphs and Travails of the Jeffersonian Republic, 1800 1812 I. The Triumphs and Travails of the Jeffersonian Republic A. The Election of 1800: Adams
APUSH Chapter 11+12 Lecture Notes Chapter 11: The Triumphs and Travails of the Jeffersonian Republic, 1800 1812 I. The Triumphs and Travails of the Jeffersonian Republic A. The Election of 1800: Adams
JACKSONIAN DEMOCRACY. Ch. 7 Section 4 & 5
 JACKSONIAN DEMOCRACY Ch. 7 Section 4 & 5 ELECTION OF 1824 The Candidates in the Election of 1824 John Quincy Adams Andrew Jackson Henry Clay Jackson wins plurality of electoral votes (99), but no one wins
JACKSONIAN DEMOCRACY Ch. 7 Section 4 & 5 ELECTION OF 1824 The Candidates in the Election of 1824 John Quincy Adams Andrew Jackson Henry Clay Jackson wins plurality of electoral votes (99), but no one wins
VIDEO OBJECTIVES. 1. Analyze the key characteristics of Jacksonian Democracy and the elections of 1824 and 1828.
 When Jackson wasn t battling Calhoun or his wife, over the Peggy Eaton affair, he was locking horns with Nicholas Biddle, president of the Bank of the United States, over re-charting the Bank of the United
When Jackson wasn t battling Calhoun or his wife, over the Peggy Eaton affair, he was locking horns with Nicholas Biddle, president of the Bank of the United States, over re-charting the Bank of the United
After the War of 1812 THE BEGINNING OF CHANGE IN AMERICAN POLITICS, ECONOMY, AND SOCIETY
 After the War of 1812 THE BEGINNING OF CHANGE IN AMERICAN POLITICS, ECONOMY, AND SOCIETY Consequences of the War of 1812 Why was the War of 1812 fought? Impressment Violation of neutral shipping rights
After the War of 1812 THE BEGINNING OF CHANGE IN AMERICAN POLITICS, ECONOMY, AND SOCIETY Consequences of the War of 1812 Why was the War of 1812 fought? Impressment Violation of neutral shipping rights
Chapter 12 Social Studies Test Prep
 Chapter 12 Social Studies Test Prep!e Jacksonian Era 1. A New Era in Politics 2. Jackson in the White House 3. A New Crisis Section 1, A New Era in Politics Growing Spirit of Equality Many U.S. citizens
Chapter 12 Social Studies Test Prep!e Jacksonian Era 1. A New Era in Politics 2. Jackson in the White House 3. A New Crisis Section 1, A New Era in Politics Growing Spirit of Equality Many U.S. citizens
Key Concept 4.3, I: The US needed a foreign policy and an expansion policy
 Key Concept 4.3, I: The US needed a foreign policy and an expansion policy Key Concept 4.3: U.S. interest in increasing foreign trade, expanding its national borders, and isolating itself from European
Key Concept 4.3, I: The US needed a foreign policy and an expansion policy Key Concept 4.3: U.S. interest in increasing foreign trade, expanding its national borders, and isolating itself from European
Name Date Class KEY TERMS AND NAMES
 Chapter 7, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 240 244 AMERICAN NATIONALISM KEY TERMS AND NAMES Era of Good Feelings phrase used to describe James Monroe s presidency because of the harmony in national
Chapter 7, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 240 244 AMERICAN NATIONALISM KEY TERMS AND NAMES Era of Good Feelings phrase used to describe James Monroe s presidency because of the harmony in national
INDUSTRY AND MIGRATION/THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH. pp
 INDUSTRY AND MIGRATION/THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH pp 382-405 What drives history? Table Talk: Brainstorm some things that have driven history forward What do these things have in common? What changes have
INDUSTRY AND MIGRATION/THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH pp 382-405 What drives history? Table Talk: Brainstorm some things that have driven history forward What do these things have in common? What changes have
SMALL FARMERS, FRONTIER SETTLERS & SLAVE HOLDERS
 8 th Grade American Studies Name Unit 6 The New Republic Date Topic: Jacksonian Democracy Period Chapter 10 Section 1 (322 324) & 326-327 & 329-331 Expansion of Democracy In the early 1800 s, how was life
8 th Grade American Studies Name Unit 6 The New Republic Date Topic: Jacksonian Democracy Period Chapter 10 Section 1 (322 324) & 326-327 & 329-331 Expansion of Democracy In the early 1800 s, how was life
Washington to Madison Practice Questions
 1 Washington s Proclamation of Neutrality (1793), Jefferson s Embargo Act (1807), and the Monroe Doctrine (1823) were all efforts to (1) avoid political conflicts with European nations (2) directly support
1 Washington s Proclamation of Neutrality (1793), Jefferson s Embargo Act (1807), and the Monroe Doctrine (1823) were all efforts to (1) avoid political conflicts with European nations (2) directly support
AP U.S. History (Mr. Broach)
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 NATIONALISM AND THE JACKSONIAN PERIOD AP United States History (Kennedy, Chapters 12-15) Unit 4 UNIT THEMES Nationalism / one-party system after the War of 1812 Emerging sectional tensions
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 NATIONALISM AND THE JACKSONIAN PERIOD AP United States History (Kennedy, Chapters 12-15) Unit 4 UNIT THEMES Nationalism / one-party system after the War of 1812 Emerging sectional tensions
The term Era of Good Feelings refers to the period of American history when there seemed to be political harmony during the Monroe administration.
 The term Era of Good Feelings refers to the period of American history when there seemed to be political harmony during the Monroe administration. 1 2 In 1816, James Monroe became president, inaugurating
The term Era of Good Feelings refers to the period of American history when there seemed to be political harmony during the Monroe administration. 1 2 In 1816, James Monroe became president, inaugurating
America s History, Chapter 10: A Democratic Revolution,
 America s History, Chapter 10: A Democratic Revolution, 1800 1844 Key Concept: Innovations in technology, agriculture, and commerce powerfully accelerated the American economy, precipitating profound changes
America s History, Chapter 10: A Democratic Revolution, 1800 1844 Key Concept: Innovations in technology, agriculture, and commerce powerfully accelerated the American economy, precipitating profound changes
Essential Question: How did President Jefferson change U.S. government, territory, & foreign policy?
 Essential Question: How did President Jefferson change U.S. government, territory, & foreign policy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.1: Clicker Preview Questions President Jefferson notes & Marbury v Madison activity
Essential Question: How did President Jefferson change U.S. government, territory, & foreign policy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.1: Clicker Preview Questions President Jefferson notes & Marbury v Madison activity
Study Guide: Sunshine State Standards
 Chapter 11, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 334 339 JACKSONIAN DEMOCRACY KEY TERMS favorite son Candidates backed by their home states instead of the national party (page 335) majority More than
Chapter 11, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 334 339 JACKSONIAN DEMOCRACY KEY TERMS favorite son Candidates backed by their home states instead of the national party (page 335) majority More than
Old Hickory. I was born for a storm, and a calm does not suit me. -Andrew Jackson
 Old Hickory I was born for a storm, and a calm does not suit me. -Andrew Jackson The Age of Jackson is also known as the Era of the Common Man It completely changed the landscape of American politics.
Old Hickory I was born for a storm, and a calm does not suit me. -Andrew Jackson The Age of Jackson is also known as the Era of the Common Man It completely changed the landscape of American politics.
JACKSONIAN AMERICA A08W
 JACKSONIAN AMERICA A08W 10.1015 A. EMERGENCE OF THE SECOND PARTY SYSTEM GUIDING QUESTION Why did a two party system reemerge in the period 1820-1840? Major political personalities Economic issues States
JACKSONIAN AMERICA A08W 10.1015 A. EMERGENCE OF THE SECOND PARTY SYSTEM GUIDING QUESTION Why did a two party system reemerge in the period 1820-1840? Major political personalities Economic issues States
Market revolution and political democracy expanded the public sphere and drastically increased printing Application of steam power led to the cost of
 1 2 3 4 Market revolution and political democracy expanded the public sphere and drastically increased printing Application of steam power led to the cost of printing being reduced, "alternative" newspapers
1 2 3 4 Market revolution and political democracy expanded the public sphere and drastically increased printing Application of steam power led to the cost of printing being reduced, "alternative" newspapers
Economic Growth. Guided Reading Activity. Growth and Expansion. Answering Questions DIRECTIONS: As you read the section, answer the questions below.
 Guided Reading Activity Growth and Expansion Section Economic Growth Give yourself enough time to read and understand the text. Don t rush through it. Take your time and pause to reread sections or to
Guided Reading Activity Growth and Expansion Section Economic Growth Give yourself enough time to read and understand the text. Don t rush through it. Take your time and pause to reread sections or to
Related Thematic Learning Objectives. Concept Outline
 NAT-2.0: Explain how interpretations of the Constitution and debates over rights, liberties, and definitions of citizenship have affected American values, politics, and society. NAT-4.0: Analyze relationships
NAT-2.0: Explain how interpretations of the Constitution and debates over rights, liberties, and definitions of citizenship have affected American values, politics, and society. NAT-4.0: Analyze relationships
Preview. If you were elected President, who would you put in government positions in the Executive Branch?
 Preview If you were elected President, who would you put in government positions in the Executive Branch? Title your page this! Andrew Jackson a. Nicknamed Old Hickory for his toughness b. Major General
Preview If you were elected President, who would you put in government positions in the Executive Branch? Title your page this! Andrew Jackson a. Nicknamed Old Hickory for his toughness b. Major General
Chapter 10 Test: The Age of Jackson
 Chapter 10 Test: The Age of Jackson PRACTICE TEST Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What effect did the Tariff of Abominations have on Andrew
Chapter 10 Test: The Age of Jackson PRACTICE TEST Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What effect did the Tariff of Abominations have on Andrew
Guided Reading & Analysis: Nationalism and Economic Development, Chapter 8- Nationalism and Economic Development, pp
 THIS IS A TRADITIONAL & OPTIONAL ASSIGNMENT IT MUST BE PRINTED AND COMPLETED IN INK! Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Guided Reading & Analysis: Nationalism and Economic Development, 1816-1848 Chapter
THIS IS A TRADITIONAL & OPTIONAL ASSIGNMENT IT MUST BE PRINTED AND COMPLETED IN INK! Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Guided Reading & Analysis: Nationalism and Economic Development, 1816-1848 Chapter
The Missouri Compromise and The Monroe Doctrine
 The Missouri Compromise and The Monroe Doctrine President James Monroe Monroe ran for President in 1816 as a Democratic-Republican and won easily against the last Federalist presidential candidate Rufus
The Missouri Compromise and The Monroe Doctrine President James Monroe Monroe ran for President in 1816 as a Democratic-Republican and won easily against the last Federalist presidential candidate Rufus
R E A D T H I S F I R S T!
 R E A D T H I S F I R S T! Period 4 (1800 1848) Review Sheet Chapters 9 12 the America s History Textbook Welcome to Period 4! This period accounts for roughly 10% of the exam. In past exams, this period
R E A D T H I S F I R S T! Period 4 (1800 1848) Review Sheet Chapters 9 12 the America s History Textbook Welcome to Period 4! This period accounts for roughly 10% of the exam. In past exams, this period
The Nullification Crisis
 The Nullification Crisis Warm up With your shoulder partner, you need to discuss the questions posted on the next slide. You will be EXPECTED to go to the board and write your answers. What issue is this
The Nullification Crisis Warm up With your shoulder partner, you need to discuss the questions posted on the next slide. You will be EXPECTED to go to the board and write your answers. What issue is this
Section 1: The era begins with the end of the War of 1812 (1815) & the election of James Monroe (1816)
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Ch. 8 AMSCO or other resources for Period 4 content. Directions: Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before you read the chapter.
Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Ch. 8 AMSCO or other resources for Period 4 content. Directions: Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before you read the chapter.
Presidency Chart Andrew Jackson ( )
 Presidency Chart Andrew Jackson (1829-1837) Election of 1824 Four Republicans ran for president. On election day Andrew Jackson of Tennessee led the popular vote and in the Electoral College but did not
Presidency Chart Andrew Jackson (1829-1837) Election of 1824 Four Republicans ran for president. On election day Andrew Jackson of Tennessee led the popular vote and in the Electoral College but did not
B) Henry Clay was made Adams Secretary of State E) The Embargo Act after throwing his support to Adams after he was out of the election.
 1. The most unpopular act of Thomas Jefferson's administration was which of the following? A) The repeal of the excise tax B) The creation of 12th Amendment C) The reduction of the size of the army D)
1. The most unpopular act of Thomas Jefferson's administration was which of the following? A) The repeal of the excise tax B) The creation of 12th Amendment C) The reduction of the size of the army D)
Wednesday, March 30, Pick Up 1824/1828 Election Packet 2. Ch 12.1 Notes on desk 3. Read & Annotate Election of 1824
 Wednesday, March 30, 2016 1. Pick Up 1824/1828 Election Packet 2. Ch 12.1 Notes on desk 3. Read & Annotate Election of 1824 p1 & 2 4. Complete 1824 Election Map based on electoral results table p2 & 3
Wednesday, March 30, 2016 1. Pick Up 1824/1828 Election Packet 2. Ch 12.1 Notes on desk 3. Read & Annotate Election of 1824 p1 & 2 4. Complete 1824 Election Map based on electoral results table p2 & 3
Study Guide: Sunshine State Standards
 Chapter 11, Section 1 (continued) 1. How did John Quincy Adams win the election of 1824? The Election of 1828 (pages 335 336) The Republican Party was divided. The Democratic-Republicans supported Jackson.
Chapter 11, Section 1 (continued) 1. How did John Quincy Adams win the election of 1824? The Election of 1828 (pages 335 336) The Republican Party was divided. The Democratic-Republicans supported Jackson.
AP U.S. History (Mr. Broach)
 AP United States History (Kennedy, Chapters 12-15) Unit 4 Nationalism / one-party system after the War of 1812 Emerging sectional tensions as people move west Some foreign concerns Universal white male
AP United States History (Kennedy, Chapters 12-15) Unit 4 Nationalism / one-party system after the War of 1812 Emerging sectional tensions as people move west Some foreign concerns Universal white male
New Republic Outline. American history I to 1865 Exam 2 Outlines. Articles of Confederation Ordinance of Northwest Ordinance
 American history I to 1865 Exam 2 Outlines New Republic Outline Articles of Confederation 1781-87 Ordinance of 1784 Northwest Ordinance Indian Conflicts Little Turtle Confederation Problems Shay Rebellion
American history I to 1865 Exam 2 Outlines New Republic Outline Articles of Confederation 1781-87 Ordinance of 1784 Northwest Ordinance Indian Conflicts Little Turtle Confederation Problems Shay Rebellion
Politics In An Age Of Passion
 Name: Give Me Liberty!, Chapter 8 Video Guide Big Idea Questions What was Washington s view of political parties? What is impressment? Guided Notes Politics In An Age Of Passion Hamilton s Program Hamilton
Name: Give Me Liberty!, Chapter 8 Video Guide Big Idea Questions What was Washington s view of political parties? What is impressment? Guided Notes Politics In An Age Of Passion Hamilton s Program Hamilton
