THE SECOND WAR FOR INDEPENDENCE AND THE UPSURGE OF NATIONALISM ( )
|
|
|
- Linda Park
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 THE SECOND WAR FOR INDEPENDENCE AND THE UPSURGE OF NATIONALISM ( ) Period 4 ( ) Key Concept 4.1 The United States began to develop a modern democracy and celebrated a new national culture, while Americans sought to define the nation s democratic ideals and change their socitey and institutions to match them. 1
2 WAR OF 1812: LEGACY Established European respect: our right to exist Lead the rise of US as a military force. Increased economic opportunities: new trades, skills, private businesses Opened the door to western expansion Ushered in an era of nationalism and a belief in ourselves as a new, special and unique American culture and republican government man s greatest experiment 2
3 POLITICAL NATIONALISM ( s) On the Surface ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS President James Monroe ( ) Democrat-Republican Growing Nationalism: acquired Florida; agreed to Missouri Compromise; adopted Monroe Doctrine. End of the Federalist Party; no organized opposition party. Pres JMon elected by new, younger generation; an era of unlimited prosperity. But Underneath sectional issues debated; tariffs, national bank, slavery, public land sales 3
4 POLITICAL NATIONALISM 1816 Election 1820 Election GROWTH IN DEMOCRACY states begin eliminating suffrage land ownership prerequisite for white landowners Increased awareness that citizenship in a republic requires privileges AND obligations (duties) Increase interest in politics and obligation of voting Republican Motherhood prestigious role women had as the keepers of the nation's conscience; a citizen should be to his country as a mother is to her child. the nurturers of the next generation of Am heroes and leaders Investing in education: academies for women 4
5 Republican Motherhood 5
6 CULTURAL NATIONALISM SHARED EXPERIENCES Increased mobility, interaction and communication George Washington Portrait Gilbert Stuart schools, art, books to promote/exploit Am culture, history, republicanism. 6
7 CULTURAL NATIONALISM EXPANDING PUBLIC EDUCATION Lead Common School Movement universal education paid by local taxes Education brings social, political harmony; a strong republic. Created teacher schools; women as teachers. Horace Mann ( ) Father of Education Education reformer of Massachusetts Noah Webster s American Dictionary and blue-backed speller 7
8 CULTURAL NATIONALISM Horace Mann ( ) 8
9 NATIONALISM: FOREIGN POLICY MONROE DOCTRINE a statement of policy mentioned in Pres Monroe s State of the Union Address Warning to limit Europe s interference in colonization of Latin Am republics. Short Term: no one paid attention could we enforce it? BUT Long Term: matched our new attitude that we can compete on the world stage with Europe increased US intervention in Latin Am in 20 th Century 9
10 10
11 CULTURAL NATIONALISM Genre Painting George Caleb Bingham Common Ams doing Am activities The Jolly Flatboatmen Am s first artistic fraternity; New York City-based landscape painters under influence of Thomas Cole ( ) Romanticism: heroic beauty of Am landscapes; interest in nature Hudson River School Art County Election Family Life on the Frontier 11
12 ECONOMIC NATIONALISM BELIEF IN CAPITALISM Free enterprise: private ownership competition profit limited government Adam Smith( ) Philosopher, Political Scientist Smith s Invisible Hand The natural force that guides free market (capitalism) through competition. In a free market, participants try to maximize selfinterest in the exchange of goods and services and it encourages excellence of each participant than when simply producing for himself. In a free market, no government regulation is needed to ensure that the mutually beneficial exchange of goods and services took place, since this "invisible hand" would guide market participants to trade in the most mutually beneficial manner. Adam Smith s Wealth of Nations 12
13 THE FACTORY SYSTEM ECONOMIC NATIONALISM Switching from putting-out and bartering system to efficient, mass production by machines Samuel Slater ( ) Father of the Industrial Revolution Creeping Mechanization Slow to develop until after (1814) ie. mercantilism, embargo land ownership over factory work/city life Limited capital/credit in young nation Marvels in Manufacturing mechanization and interchangeable parts - made by machine instead of man (craftsman) Federal Laws Encouraging Risk: Patent Office private ownership rights Limited Liability: private ownership protection rights 13
14 development of the company town Slater s Mill Pawtucket Rhode Island Remington Arms Ilion, NY
15 The patent system secured to the inventor for a limited time exclusive use of his invention, and thereby added the fuel of interest to the fire of genius in the discovery and production of new and useful things Abraham Lincoln Entrepreneurship: a risk-taker: a capitalist economy need people with an idea and sweat 15
16 BUILDING ONE NATIONAL ECONOMY Whitney s Cotton Gin Patent (1794) Mother Necessity 16
17 THE AMERICAN SYSTEM BUILDING ONE NATIONAL ECONOMY CONGRESSIONAL ACTION Plan to use the influence of the fed govt to create a nurturing environment to encourage economic growth ($$) 1. Strong National Banking System Renewal of National Bank 2 nd Charter: credit, currency stability, economic growth Henry Clay ( ) House of Representatives 2. High Tariffs to really protect Am Indust; Tariff of 1816?Why would Pres JMonroe veto bills to spend federal funds on infrastructure? 3. Infrastructure federal monies to invest in national roads canals RRs to move people, raw materials and manufactured goods East West efficiently. 17
18 PANIC OF 1819 A strategy used by the national bank to protect the value of the Am dollar was to regulate the amount of money in the economy: Encouraging consumer borrowing (credit) or (loose money supply) or discouraging consumer borrowing (credit) (tight money supply). Capitalist Business Cycle Second National Bank: had tight money supply to control inflation banks closed, unemployed, bankruptcies, foreclosures on western farmland. Political Change Anti-centralized authority 18
19 MANIFEST DESTINY Reasons for Westward Movement Acquisition of American Indians Lands AmInds chased from Indiana and Florida (General AJacks) Economic Pressures NewEnglanders leave for better opportunities (embargo); Southern plantation owners need new land to replace exhausted soil. Immigrants Cheap land offered by speculators; GrLakes, Ohio Mississ River Valleys Improved Transportation Roads-canals-RRs 19
20 Meanwhile migration West addition of new states new US Senators in Congress and potential shift of power: slave v. free states 20
21 MISSOURI COMPROMISE of 1820 SLAVERY: CAN WE STAY UNITED? Keeping the US United; The Balance of Power in the Senate Same Tallmadge Amendment (NY Rep) Limiting new slaves into Missouri; emancipating slaves at age 25: REJECTED Missouri Comp Line Dividing the nation N/S Kept Senate Power equal Cooled tempers for now 21
22 OLD IMMIGRATION (1820s-1850s) CULTURAL NATIONALISM OPEN DOOR IMMIGRATION Mostly from NW Europe: English, Irish, Scotch Irish, German, Dutch, Danish Why They Left: persecution prosecution Irish Potato Famine Why They Came: what some faced: OPPORTUNITY NATIVISM = anti-immigration J-O-B-S: canal digging, factory work, laying RRs, etc. land ownership 22
23 POLITICAL NATIONALISM ( s) THE JOHN MARSHALL COURT ( ) Appointed by Federalist Pres Adams as Chief Justice Powers written into the Constitution at the Const Conv (1789) to make sure the federal govt could keep the states united elastic clause interstate commerce clause John Marshall ( ) supremacy clause contract clause It is emphatically the province and duty of the judicial department to say what the law is Chief Justice John Marshall Marbury v. Madison (1803) judicial review established 9 justices Interpreted and used by Marshall to validate the appointed by president: powers of the new Constitution/federal govt ratified by Senate Serve for life: insulated from politics and public opinion 23
Era of Good Feelings:
 Era of Good Feelings: 1815-1825 After the War of 1812 Americans finally have international respect The Republicans are the only political party James Monroe, the third member of the Virginia Dynasty, is
Era of Good Feelings: 1815-1825 After the War of 1812 Americans finally have international respect The Republicans are the only political party James Monroe, the third member of the Virginia Dynasty, is
The Americans (Survey)
 The Americans (Survey) Chapter 7: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OVERVIEW American leaders devise a farsighted policy of improvements as North, South, and West develop
The Americans (Survey) Chapter 7: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OVERVIEW American leaders devise a farsighted policy of improvements as North, South, and West develop
Division of Labor: giving each worker one or two simple jobs.
 Chapter 12 The Nation Grows (1815-1830) Section 1 Industries take Root Industrial Revolution: the growth of industry eventually produced changes so great that this time in history is called the Industrial
Chapter 12 The Nation Grows (1815-1830) Section 1 Industries take Root Industrial Revolution: the growth of industry eventually produced changes so great that this time in history is called the Industrial
The Antebellum Era ( ): The Rise of Jacksonian Democracy Part 1
 The Antebellum Era (1781-1860): The Rise of Jacksonian Democracy Part 1 B. Building a Nation (Colonization-ca. 1877) 1. Colonization and Forging a Nation K. Identify and evaluate the political and territorial
The Antebellum Era (1781-1860): The Rise of Jacksonian Democracy Part 1 B. Building a Nation (Colonization-ca. 1877) 1. Colonization and Forging a Nation K. Identify and evaluate the political and territorial
An Early Republic. George Washington. Dept./Office Head Function
 Name An Early Republic George Washington What does the Executive Branch look like? Dept./Office Head Function State Department Thomas Jefferson Dept. of Treasury Alexander Hamilton Dept. of War Henry Knox
Name An Early Republic George Washington What does the Executive Branch look like? Dept./Office Head Function State Department Thomas Jefferson Dept. of Treasury Alexander Hamilton Dept. of War Henry Knox
Unit 4: { Politics Economics Society
 Unit 4: 1800-1848 { Politics Economics Society Established Cabinet of close advisers French Revolution Neutrality Proclamation Organized troops against Whiskey Rebellion BIG PICTURE IMPACT: Promoted unity;
Unit 4: 1800-1848 { Politics Economics Society Established Cabinet of close advisers French Revolution Neutrality Proclamation Organized troops against Whiskey Rebellion BIG PICTURE IMPACT: Promoted unity;
Economic Growth. Guided Reading Activity. Growth and Expansion. Answering Questions DIRECTIONS: As you read the section, answer the questions below.
 Guided Reading Activity Growth and Expansion Section Economic Growth Give yourself enough time to read and understand the text. Don t rush through it. Take your time and pause to reread sections or to
Guided Reading Activity Growth and Expansion Section Economic Growth Give yourself enough time to read and understand the text. Don t rush through it. Take your time and pause to reread sections or to
Chapter 7 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism
 Chapter 7 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Changes in manufacturing launch an Industrial Revolution. Slavery and other issues divide the North and South. Andrew Jackson has popular appeal but uproots
Chapter 7 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Changes in manufacturing launch an Industrial Revolution. Slavery and other issues divide the North and South. Andrew Jackson has popular appeal but uproots
Democratic Republican Era
 Democratic Republican Era Thomas Jefferson s Administration James Madison s Administration James Monroe s Administration Jefferson Madison Monroe Following the election of 1800, the Democratic Republicans
Democratic Republican Era Thomas Jefferson s Administration James Madison s Administration James Monroe s Administration Jefferson Madison Monroe Following the election of 1800, the Democratic Republicans
Related Thematic Learning Objectives. Concept Outline
 NAT-2.0: Explain how interpretations of the Constitution and debates over rights, liberties, and definitions of citizenship have affected American values, politics, and society. NAT-4.0: Analyze relationships
NAT-2.0: Explain how interpretations of the Constitution and debates over rights, liberties, and definitions of citizenship have affected American values, politics, and society. NAT-4.0: Analyze relationships
History 1301 U.S. to Unit 2 - Lecture 4 ~
 History 1301 U.S. to 1877 Unit 2 - Lecture 4 ~ The Era of Good Feeling Post-war Economics: Post-war boom led to bust in 1819 National weaknesses shown by War experience Second National Bank chartered in
History 1301 U.S. to 1877 Unit 2 - Lecture 4 ~ The Era of Good Feeling Post-war Economics: Post-war boom led to bust in 1819 National weaknesses shown by War experience Second National Bank chartered in
Industrial Revolution
 The student will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and the different responses to it. a. Explain the impact of the Industrial
The student will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and the different responses to it. a. Explain the impact of the Industrial
Industrialization & Reform Learning Targets
 Industrialization & Reform Learning Targets Topic: History I can identify major eras and events in U.S. History and explain: Industrial Revolution Age of Reform Topic: Economics I can understand the origins
Industrialization & Reform Learning Targets Topic: History I can identify major eras and events in U.S. History and explain: Industrial Revolution Age of Reform Topic: Economics I can understand the origins
Inventor Invention Impact
 Industrialization and Reform Test Review Test Date: Name 1. Fill in the missing boxes Inventor Invention Impact Eli Whitney Cotton Gin Robert Fulton Decreased the amount of time needed for travel. Decreased
Industrialization and Reform Test Review Test Date: Name 1. Fill in the missing boxes Inventor Invention Impact Eli Whitney Cotton Gin Robert Fulton Decreased the amount of time needed for travel. Decreased
DRAWING FROM EXPERIENCEII
 Chapter 10, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 306 311 ECONOMIC GROWTH KEY TERMS Industrial Revolution A new way of working and producing goods (page 307) capital Money invested to start new businesses
Chapter 10, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 306 311 ECONOMIC GROWTH KEY TERMS Industrial Revolution A new way of working and producing goods (page 307) capital Money invested to start new businesses
The Triumph of Democracy
 Name: Give Me Liberty!, Chapter 10 Video Guide Big Idea Questions Who wrote The Liberator? What is the cult of domesticity? Guided Notes The Triumph of Democracy Jackson s inauguration Seen as the Man
Name: Give Me Liberty!, Chapter 10 Video Guide Big Idea Questions Who wrote The Liberator? What is the cult of domesticity? Guided Notes The Triumph of Democracy Jackson s inauguration Seen as the Man
James Monroe and The Era of Good Feelings. The Role of Politics in Sectionalism
 James Monroe and The Era of Good Feelings The Role of Politics in Sectionalism James Monroe 1758 1831 Dem.-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former
James Monroe and The Era of Good Feelings The Role of Politics in Sectionalism James Monroe 1758 1831 Dem.-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former
The term Era of Good Feelings refers to the period of American history when there seemed to be political harmony during the Monroe administration.
 The term Era of Good Feelings refers to the period of American history when there seemed to be political harmony during the Monroe administration. 1 2 In 1816, James Monroe became president, inaugurating
The term Era of Good Feelings refers to the period of American history when there seemed to be political harmony during the Monroe administration. 1 2 In 1816, James Monroe became president, inaugurating
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism
 7 QUIT Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE GRAPH SECTION 1 Regional Economics Create Differences SECTION 2 Nationalism at Center Stage MAP SECTION 3
7 QUIT Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE GRAPH SECTION 1 Regional Economics Create Differences SECTION 2 Nationalism at Center Stage MAP SECTION 3
1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation
 Topic 3 1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg 88-89 They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation agreements 2. How did the British respond to the Boston Tea
Topic 3 1. How did the colonists protest British taxes? Pg 88-89 They boycotted, petitioned the English government, and signed nonimportation agreements 2. How did the British respond to the Boston Tea
JEFFERSONIAN DEMOCRACY ( ) ELECTION OF 1800 ELECTION OF 1800 JEFFERSON S PHILOSOPHY EXAMPLE POLICIES A NATION OF FARMERS
 JEFFERSONIAN DEMOCRACY (1800 1828) ELECTION OF 1800 Revolution of 1800 Adams v. Jefferson (again) Major Issues: - Expansion of Military - Foreign Affairs - Alien & Sedition Acts 1 2 ELECTION OF 1800 DR
JEFFERSONIAN DEMOCRACY (1800 1828) ELECTION OF 1800 Revolution of 1800 Adams v. Jefferson (again) Major Issues: - Expansion of Military - Foreign Affairs - Alien & Sedition Acts 1 2 ELECTION OF 1800 DR
Chapter 9 and part of Chapter 8: Transforming the Economy,
 Chapter 9 and part of Chapter 8: Transforming the Economy, 1790-1860 The Big Questions: What were the causes and consequences of the industrial and market revolutions, and how did they change the way ordinary
Chapter 9 and part of Chapter 8: Transforming the Economy, 1790-1860 The Big Questions: What were the causes and consequences of the industrial and market revolutions, and how did they change the way ordinary
Inventor Invention Impact
 Industrialization and Reform Test Review Test Date: Name 1. Fill in the missing boxes Inventor Invention Impact Eli Whitney Cotton Gin -Increased slavery -Made cleaning cotton faster and more efficient
Industrialization and Reform Test Review Test Date: Name 1. Fill in the missing boxes Inventor Invention Impact Eli Whitney Cotton Gin -Increased slavery -Made cleaning cotton faster and more efficient
Academic Vocabulary CONTENT BUILDER FOR THE PLC SOCIAL STUDIES GRADE 8
 Academic Vocabulary CONTENT BUILDER FOR THE PLC SOCIAL STUDIES GRADE 8 : academic vocabulary directly taken from the standard : academic vocabulary used on the assessment (source released tests) STANDARD
Academic Vocabulary CONTENT BUILDER FOR THE PLC SOCIAL STUDIES GRADE 8 : academic vocabulary directly taken from the standard : academic vocabulary used on the assessment (source released tests) STANDARD
Economic Issues and Growth
 Economic Issues and Growth 1800-1848 Tariff of 1816 Passed to protect American industries after War of 1812 What would be advantages and disadvantages of high tariffs? Would different regions of the country
Economic Issues and Growth 1800-1848 Tariff of 1816 Passed to protect American industries after War of 1812 What would be advantages and disadvantages of high tariffs? Would different regions of the country
Period 4 Content Outline,
 Period 4 Content Outline, 1800-1848 The content for APUSH is divided into 9 periods. The outline below contains the required course content for Period 4. The Thematic Learning Objectives are included as
Period 4 Content Outline, 1800-1848 The content for APUSH is divided into 9 periods. The outline below contains the required course content for Period 4. The Thematic Learning Objectives are included as
Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages ) Economic Growth
 Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages 304 309) Economic Growth Essential Question What effects did the Industrial Revolution have on the U. S. economy? Directions: As you read, complete a graphic organizer like
Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages 304 309) Economic Growth Essential Question What effects did the Industrial Revolution have on the U. S. economy? Directions: As you read, complete a graphic organizer like
Level 2 THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS
 Level 2 THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS Vocabulary Sectionalism: loyalty to a section of a country instead of the nation itself Inflation: Protective Tariff: tax on imported goods Internal Expansion: continued
Level 2 THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS Vocabulary Sectionalism: loyalty to a section of a country instead of the nation itself Inflation: Protective Tariff: tax on imported goods Internal Expansion: continued
UNIT 4 REVIEW PACKET The Early 19 th Century
 Name: UNIT 4 REVIEW PACKET The Early 19 th Century Due Date: Part 1: Content Review You will define and explain the significance of important terms from the historical period. Part 2: Key Concepts You
Name: UNIT 4 REVIEW PACKET The Early 19 th Century Due Date: Part 1: Content Review You will define and explain the significance of important terms from the historical period. Part 2: Key Concepts You
Madison & Monroe. Presidencies
 James James Madison & Monroe Presidencies Where we are March 1797: President John Adams takes office. 1796-1800: XYZ Affair, Quasi-War with France, Alien & Sedition Acts, VA & KY Resolutions 1801-1804:
James James Madison & Monroe Presidencies Where we are March 1797: President John Adams takes office. 1796-1800: XYZ Affair, Quasi-War with France, Alien & Sedition Acts, VA & KY Resolutions 1801-1804:
FORGING THE NATIONAL ECONOMY, Chapter 14
 FORGING THE NATIONAL ECONOMY, 1790 1860 Chapter 14 WESTWARD MOVEMENT & SHAPING THE WESTERN LANDSCAPE America West of the Alleghenies Population center shifts Life is brutal, primitive, isolated Land becomes
FORGING THE NATIONAL ECONOMY, 1790 1860 Chapter 14 WESTWARD MOVEMENT & SHAPING THE WESTERN LANDSCAPE America West of the Alleghenies Population center shifts Life is brutal, primitive, isolated Land becomes
President James Monroe. Elected in 1816 (Democratic- Republican [Republican]) Two Terms: Era of Good Feelings Monroe Doctrine
![President James Monroe. Elected in 1816 (Democratic- Republican [Republican]) Two Terms: Era of Good Feelings Monroe Doctrine President James Monroe. Elected in 1816 (Democratic- Republican [Republican]) Two Terms: Era of Good Feelings Monroe Doctrine](/thumbs/72/66263504.jpg) President James Monroe Elected in 1816 (Democratic- Republican [Republican]) Two Terms: 1816-1824 Era of Good Feelings Monroe Doctrine John Quincy Adams Monroe s Secretary of State Architect of the Monroe
President James Monroe Elected in 1816 (Democratic- Republican [Republican]) Two Terms: 1816-1824 Era of Good Feelings Monroe Doctrine John Quincy Adams Monroe s Secretary of State Architect of the Monroe
2) Use your notes, information collected from my classroom website or other internet resources
 1) Create an episode map on the Presidency of James Madison 2) Use your notes, information collected from my classroom website or other internet resources 1817-1825 I. In the election of 1816 James Monroe
1) Create an episode map on the Presidency of James Madison 2) Use your notes, information collected from my classroom website or other internet resources 1817-1825 I. In the election of 1816 James Monroe
Texas Assessment of Knowledge and Skills - Answer Key
 Texas Assessment of Knowledge and Skills - Answer Key Grade: 08 Subject: Social Studies Administration: April 2006 Item Correct Objective Student Number Answer Measured Expectations 01 A 03 8.24 (E) 02
Texas Assessment of Knowledge and Skills - Answer Key Grade: 08 Subject: Social Studies Administration: April 2006 Item Correct Objective Student Number Answer Measured Expectations 01 A 03 8.24 (E) 02
Grade 8 Social Studies
 Standard 1: History Students will examine the relationship and significance of themes, concepts, and movements in the development of United States history, including review of key ideas related to the
Standard 1: History Students will examine the relationship and significance of themes, concepts, and movements in the development of United States history, including review of key ideas related to the
In the early Antebellum era ( ), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that
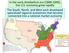 In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change
 Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change 1800-1860 Nationalism and Economic Growth By 1815, following the end of The War of 1812, America had shown: That it could defend its sovereignty against
Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change 1800-1860 Nationalism and Economic Growth By 1815, following the end of The War of 1812, America had shown: That it could defend its sovereignty against
The Early Industrial Revolution Chapter 22 AP World History
 The Early Industrial Revolution 1760-1851 Chapter 22 AP World History Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
The Early Industrial Revolution 1760-1851 Chapter 22 AP World History Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
Chapter 8 Exam. Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. Multiple Choice
 Multiple Choice Chapter 8 Exam Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which statement about the election of 1824 is true? a. Most people did not think a military
Multiple Choice Chapter 8 Exam Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which statement about the election of 1824 is true? a. Most people did not think a military
This era corresponds to information in Unit 5 ( ), Unit 6 ( ) and Unit 7 ( )
 PERIOD 4: 1800 1848 The content for APUSH is divided into 9 periods. The outline below contains the required course content for Period 4. The Thematic Learning Objectives (historical themes) are included
PERIOD 4: 1800 1848 The content for APUSH is divided into 9 periods. The outline below contains the required course content for Period 4. The Thematic Learning Objectives (historical themes) are included
Advanced Placement United States History Test: Jeffersonian Democracy
 Advanced Placement United States History Test: Jeffersonian Democracy Bradberry 1. Which of the following statements about the American System is correct? a) it was set up by the Treaty of Ghent at the
Advanced Placement United States History Test: Jeffersonian Democracy Bradberry 1. Which of the following statements about the American System is correct? a) it was set up by the Treaty of Ghent at the
Indiana Academic Standards Social Studies
 A Correlation of To the Introduction This document demonstrates how,, meets the for,. Correlation page references are to the Student Edition and Teacher Edition. The all new myworld Interactive encourages
A Correlation of To the Introduction This document demonstrates how,, meets the for,. Correlation page references are to the Student Edition and Teacher Edition. The all new myworld Interactive encourages
Standard 3: Causes of the American Revolution. e. Declaration of Independence
 Name Date Hour U.S. History to 1877 OCCT Review Study Guide Use your notes, your textbook and all of the knowledge gained this year to complete this O.C.C.T. Review Study Guide. This study guide will be
Name Date Hour U.S. History to 1877 OCCT Review Study Guide Use your notes, your textbook and all of the knowledge gained this year to complete this O.C.C.T. Review Study Guide. This study guide will be
Unit 3- Hammering Out a Federal Republic
 Name: Class Period: Unit 3- Hammering Out a Federal Republic Key Concepts FOR PERIOD 3: Key Concept 3.2: The American Revolution s democratic and republican ideals inspired new experiments with different
Name: Class Period: Unit 3- Hammering Out a Federal Republic Key Concepts FOR PERIOD 3: Key Concept 3.2: The American Revolution s democratic and republican ideals inspired new experiments with different
Varieties of American Nationalism. Chapter 8: History 103
 Varieties of American Nationalism Chapter 8: History 103 Boom to Bust post war boom leads to Panic of 1819 Why did the Panic of 1819 occur? Banking and Currency 1811: First Bank of the United States expired
Varieties of American Nationalism Chapter 8: History 103 Boom to Bust post war boom leads to Panic of 1819 Why did the Panic of 1819 occur? Banking and Currency 1811: First Bank of the United States expired
The Early Republic
 The Early Republic 1789-1828 Essential Questions What challenges faced the new nation under the Constitution? How did the first American political parties emerge? How did the Supreme Court establish its
The Early Republic 1789-1828 Essential Questions What challenges faced the new nation under the Constitution? How did the first American political parties emerge? How did the Supreme Court establish its
Unit Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution
 Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
The Monroe Doctrine. President James Monroe. Adams-Onis Treaty, Spain gives up control of Florida
 President James Monroe Foreign Policy: The policy of how we interact with other countries 5 th th President- 1816-1824 1824 Democratic Republican Significant Positions Secretary of State Adams-Onis Treaty,
President James Monroe Foreign Policy: The policy of how we interact with other countries 5 th th President- 1816-1824 1824 Democratic Republican Significant Positions Secretary of State Adams-Onis Treaty,
Chapter 8:THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS:
 Chapter 8:THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS: Objectives: We will the study the effects of postwar expansion and continued economic growth in shaping the nation during the "era of good feelings" We will study the
Chapter 8:THE ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS: Objectives: We will the study the effects of postwar expansion and continued economic growth in shaping the nation during the "era of good feelings" We will study the
7th Grade Social Studies GLEs
 7th Grade Social Studies GLEs Geography The World in Spatial Terms. Analyze various types of maps, charts, graphs, and diagrams related to U.S. history (G-A-M2) Places and Regions 2. Explain how physical
7th Grade Social Studies GLEs Geography The World in Spatial Terms. Analyze various types of maps, charts, graphs, and diagrams related to U.S. history (G-A-M2) Places and Regions 2. Explain how physical
The Role of Politics in Sectionalism
 The Role of Politics in Sectionalism James Monroe 1758 1831 Dem.-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former Gov. of VA, Secretary of State, and Secretary
The Role of Politics in Sectionalism James Monroe 1758 1831 Dem.-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former Gov. of VA, Secretary of State, and Secretary
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism
 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Regional Economies Create Differences Samuel Slater brought the Water Frame to Rhode Island from Great Britain in 1789. It was used to spin raw cotton into cotton
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism Regional Economies Create Differences Samuel Slater brought the Water Frame to Rhode Island from Great Britain in 1789. It was used to spin raw cotton into cotton
Grade 8 Social Studies Assessment. Eligible Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills
 Grade 8 Social Studies Assessment Eligible Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills STAAR Grade 8 Social Studies Assessment Based on Revised Curriculum Reporting Category 1: History The student will demonstrate
Grade 8 Social Studies Assessment Eligible Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills STAAR Grade 8 Social Studies Assessment Based on Revised Curriculum Reporting Category 1: History The student will demonstrate
HIST 1301 Part Three. 9: Nation Building and Nationalism
 HIST 1301 Part Three 9: Nation Building and Nationalism Territorial Expansion Between 1792 and 1821 several new states joined the Union. Kentucky, 1792 Tennessee, 1796 Ohio, 1803 Louisiana, 1812 Indiana,
HIST 1301 Part Three 9: Nation Building and Nationalism Territorial Expansion Between 1792 and 1821 several new states joined the Union. Kentucky, 1792 Tennessee, 1796 Ohio, 1803 Louisiana, 1812 Indiana,
Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation
 Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A constitution is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government.
Name: Date: Chapter 8 Study Guide Section 8-1: The Articles of Confederation 1. A constitution is a set of basic principles and laws, usually in written form, that state the powers and duties of a government.
U.S. History Chapter Millionaire Review
 U.S. History Chapter 14-15 Millionaire Review #1 Which of the following best describes the cotton gin s contribution to industrialization? Created jobs for A: B: immigrants Lowered price of cotton in South
U.S. History Chapter 14-15 Millionaire Review #1 Which of the following best describes the cotton gin s contribution to industrialization? Created jobs for A: B: immigrants Lowered price of cotton in South
Monroe, the Era of Good Feelings, and the Election of 1824
 Monroe, the Era of Good Feelings, and the Election of 1824 A Boston newspaper coined the years of the Monroe Administration as the Era of Good Feelings After the War of 1812, Americans felt a sense of
Monroe, the Era of Good Feelings, and the Election of 1824 A Boston newspaper coined the years of the Monroe Administration as the Era of Good Feelings After the War of 1812, Americans felt a sense of
ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS
 ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS Big Idea As the US expanded, there was more debate over slavery and new attempts at compromise New western states continued to enter the Union -New states: IN, IL, MS, AL President
ERA OF GOOD FEELINGS Big Idea As the US expanded, there was more debate over slavery and new attempts at compromise New western states continued to enter the Union -New states: IN, IL, MS, AL President
7th Grade Illinois Social Studies Standards Teacher Implementation Guide
 7th Grade Illinois Social Studies Standards Teacher Implementation Guide The Illinois Social Science Learning Standards: The standards build the knowledge, dispositions, and skills necessary for success
7th Grade Illinois Social Studies Standards Teacher Implementation Guide The Illinois Social Science Learning Standards: The standards build the knowledge, dispositions, and skills necessary for success
Name Period Teacher. Wantagh Middle School 7 th Grade Social Studies Final Exam Review Guide
 Name Period Teacher Wantagh Middle School 7 th Grade Social Studies Final Exam Review Guide 1. How did the earliest people migrate to North America? 2. How did Native Americans use the environment around
Name Period Teacher Wantagh Middle School 7 th Grade Social Studies Final Exam Review Guide 1. How did the earliest people migrate to North America? 2. How did Native Americans use the environment around
CH. 8: GROWTH OF A NATIONAL ECONOMY
 1 2 3 4 CH. 8: GROWTH OF A NATIONAL ECONOMY 1790-1850 Mr. Anderson, M.Ed., J.D. Review Who was John Marshall? Which president appointed him? What is he best remembered for? The Industrial Revolution Section
1 2 3 4 CH. 8: GROWTH OF A NATIONAL ECONOMY 1790-1850 Mr. Anderson, M.Ed., J.D. Review Who was John Marshall? Which president appointed him? What is he best remembered for? The Industrial Revolution Section
An ERA OF GOOD & BAD FEELINGS. Nationalism & Sectionalism after the War of 1812 A07EW
 An ERA OF GOOD & BAD FEELINGS Nationalism & Sectionalism after the War of 1812 A07EW 10.1015 Results of the War of 1812 Draw militarily Small war and insignificant in military terms. Important consequences
An ERA OF GOOD & BAD FEELINGS Nationalism & Sectionalism after the War of 1812 A07EW 10.1015 Results of the War of 1812 Draw militarily Small war and insignificant in military terms. Important consequences
Eighth Grade, page 1 rev. May 10, 2011
 Eighth Grade, page 1 rev. May 10, 2011 PROCESS OBJECTIVES--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1 st 9 Weeks 1 st 9 Weeks 1. Explain the political
Eighth Grade, page 1 rev. May 10, 2011 PROCESS OBJECTIVES--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------1 st 9 Weeks 1 st 9 Weeks 1. Explain the political
TAKS Diagnostic and Practice Tests
 Teacher s Edition Texas Assessment Consultant Sharon Sicinski Skeans Texas Consultant Sue Hudson Lubbock Independent School District Lubbock, Texas To the Teacher This booklet is designed to help students
Teacher s Edition Texas Assessment Consultant Sharon Sicinski Skeans Texas Consultant Sue Hudson Lubbock Independent School District Lubbock, Texas To the Teacher This booklet is designed to help students
The Jacksonian Era & the Rise of Sectionalism. (c. 1820s c. 1840s)
 The Jacksonian Era & the Rise of Sectionalism (c. 1820s c. 1840s) SSUSH7 Students will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and
The Jacksonian Era & the Rise of Sectionalism (c. 1820s c. 1840s) SSUSH7 Students will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER 7
 Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER 7 Section 1 Regional Economies Create Differences Do Now: An industrial revolution is a change in economic and social conditions marked by a significant increase
Balancing Nationalism and Sectionalism CHAPTER 7 Section 1 Regional Economies Create Differences Do Now: An industrial revolution is a change in economic and social conditions marked by a significant increase
The Treaty of Ghent War of 1812 is considered a stalemate Dec. 1814
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Map war1812 The Battle of Thames River, Oct. 5, 1813 US military victory led by General William H. Harrison Tecumseh was killed during this battle Naval Battles The Battle of Lake Erie
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Map war1812 The Battle of Thames River, Oct. 5, 1813 US military victory led by General William H. Harrison Tecumseh was killed during this battle Naval Battles The Battle of Lake Erie
Unit III Outline Organizing Principles
 Unit III Outline Organizing Principles British imperial attempts to reassert control over its colonies and the colonial reaction to these attempts produced a new American republic, along with struggles
Unit III Outline Organizing Principles British imperial attempts to reassert control over its colonies and the colonial reaction to these attempts produced a new American republic, along with struggles
WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer
 WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer Subject(s) Social Studies Conceptual Lenses Grade/Course American History 1 Conflict Unit of Study Unit 4: Political Conflict, Industrialization, and Reform (4.1, 4.2, 4.3,
WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer Subject(s) Social Studies Conceptual Lenses Grade/Course American History 1 Conflict Unit of Study Unit 4: Political Conflict, Industrialization, and Reform (4.1, 4.2, 4.3,
SOCIAL STUDIES GRADE 8. I Can Checklist U.S. STUDIES FROM 1492 TO 1877: EXPLORATION THROUGH RECONSTRUCTION
 SOCIAL STUDIES U.S. STUDIES FROM 1492 TO 1877: EXPLORATION THROUGH RECONSTRUCTION GRADE 8 I Can Checklist 2015-2016 Aligned with Ohio s New Learning Standards for Social Studies Office of Teaching and
SOCIAL STUDIES U.S. STUDIES FROM 1492 TO 1877: EXPLORATION THROUGH RECONSTRUCTION GRADE 8 I Can Checklist 2015-2016 Aligned with Ohio s New Learning Standards for Social Studies Office of Teaching and
Section 1: The era begins with the end of the War of 1812 (1815) & the election of James Monroe (1816)
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Ch. 8 AMSCO or other resources for Period 4 content. Directions: Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before you read the chapter.
Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Ch. 8 AMSCO or other resources for Period 4 content. Directions: Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before you read the chapter.
Industrial Revolution
 Chapter 9 Economic Transformation Industrial Revolution Division of Labor Industry in America 1790 1820 aided by transportation Industrial Revolution outwork system work done outside of shop modern factory
Chapter 9 Economic Transformation Industrial Revolution Division of Labor Industry in America 1790 1820 aided by transportation Industrial Revolution outwork system work done outside of shop modern factory
GRADE 8 United States History Growth and Development (to 1877)
 GRADE 8 United States History Growth and Development (to 1877) Course 0470-08 In Grade 8, students focus upon United States history, beginning with a brief review of early history, including the Revolution
GRADE 8 United States History Growth and Development (to 1877) Course 0470-08 In Grade 8, students focus upon United States history, beginning with a brief review of early history, including the Revolution
After the War of 1812 THE BEGINNING OF CHANGE IN AMERICAN POLITICS, ECONOMY, AND SOCIETY
 After the War of 1812 THE BEGINNING OF CHANGE IN AMERICAN POLITICS, ECONOMY, AND SOCIETY Consequences of the War of 1812 Why was the War of 1812 fought? Impressment Violation of neutral shipping rights
After the War of 1812 THE BEGINNING OF CHANGE IN AMERICAN POLITICS, ECONOMY, AND SOCIETY Consequences of the War of 1812 Why was the War of 1812 fought? Impressment Violation of neutral shipping rights
8 th grade American Studies sample test questions
 8 th grade American Studies sample test questions PASS 1.2 Standard 1. The student will develop and practice process skills in social studies. PASS OBJECTIVE 1.2: Identify, analyze, and interpret primary
8 th grade American Studies sample test questions PASS 1.2 Standard 1. The student will develop and practice process skills in social studies. PASS OBJECTIVE 1.2: Identify, analyze, and interpret primary
#1 INDUSTRIALIZATION
 #1 INDUSTRIALIZATION Industrialization the shift from an agricultural economy to one based on production and manufacturing completely changed the northern and western economy between 1820 and 1860. For
#1 INDUSTRIALIZATION Industrialization the shift from an agricultural economy to one based on production and manufacturing completely changed the northern and western economy between 1820 and 1860. For
TEKS Snapshot - Grade 8 Social Studies
 Process Standards (Social Studies Skills and Processes) 8.29 Social Studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies
Process Standards (Social Studies Skills and Processes) 8.29 Social Studies skills. The student applies critical-thinking skills to organize and use information acquired through established research methodologies
CHAPTER 113. TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS (TEKS) FOR SOCIAL STUDIES Subchapter B. Middle School Social Studies, Grade 8.
 CHAPTER 113. TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS (TEKS) FOR SOCIAL STUDIES Subchapter B. Middle School 113.24. Social Studies, Grade 8. Correlated to HISTORY OF OUR NATION: 2005 4201 Woodland Road Circle
CHAPTER 113. TEXAS ESSENTIAL KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS (TEKS) FOR SOCIAL STUDIES Subchapter B. Middle School 113.24. Social Studies, Grade 8. Correlated to HISTORY OF OUR NATION: 2005 4201 Woodland Road Circle
Unit 8. Innovation Brings Change 1800 s-1850 s
 Unit 8 Innovation Brings Change 1800 s-1850 s Unit Overview: Industrialization Era This unit addresses the development of the economies in the North and the South, innovations in technology and the application
Unit 8 Innovation Brings Change 1800 s-1850 s Unit Overview: Industrialization Era This unit addresses the development of the economies in the North and the South, innovations in technology and the application
Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy?
 Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.4: Clickers Questions Market Revolution inquiry activity
Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.4: Clickers Questions Market Revolution inquiry activity
THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN THE U.S. How the War of 1812 & Technological Progress Change the Country
 THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN THE U.S. How the War of 1812 & Technological Progress Change the Country TECHNOLOGY MEANS PROGRESS Developments in technology begin to transform life in the U.S. in the
THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN THE U.S. How the War of 1812 & Technological Progress Change the Country TECHNOLOGY MEANS PROGRESS Developments in technology begin to transform life in the U.S. in the
America s History Eighth Edi(on
 James A. Henretta! Eric Hinderaker! Rebecca Edwards! Robert O. Self! America s History Eighth Edi(on America: A Concise History Sixth Edi(on CHAPTER 8 nd 9 Review= Unit 4 Crea=ng a Republican Culture 1790
James A. Henretta! Eric Hinderaker! Rebecca Edwards! Robert O. Self! America s History Eighth Edi(on America: A Concise History Sixth Edi(on CHAPTER 8 nd 9 Review= Unit 4 Crea=ng a Republican Culture 1790
The Industrial Revolution. The Start of Mass Production
 The Industrial Revolution The Start of Mass Production Section 1 Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
The Industrial Revolution The Start of Mass Production Section 1 Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
Guided Reading & Analysis: Nationalism and Economic Development, Chapter 8- Nationalism and Economic Development, pp
 THIS IS A TRADITIONAL & OPTIONAL ASSIGNMENT IT MUST BE PRINTED AND COMPLETED IN INK! Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Guided Reading & Analysis: Nationalism and Economic Development, 1816-1848 Chapter
THIS IS A TRADITIONAL & OPTIONAL ASSIGNMENT IT MUST BE PRINTED AND COMPLETED IN INK! Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Guided Reading & Analysis: Nationalism and Economic Development, 1816-1848 Chapter
The Westward Movement
 The Westward Movement The American West- the most typically American part of America Young America- half of all Americans were under the age of 30 Life in the West was grim for American families Poorly
The Westward Movement The American West- the most typically American part of America Young America- half of all Americans were under the age of 30 Life in the West was grim for American families Poorly
REVIEW FOR 4 TH 6 WEEKS COMPREHENSIVE EXAM
 REVIEW FOR 4 TH 6 WEEKS COMPREHENSIVE EXAM 1. What were the main foreign policy issues faced by Washington (include an evaluation of his farewell address)? Keeping the USA neutral during the war between
REVIEW FOR 4 TH 6 WEEKS COMPREHENSIVE EXAM 1. What were the main foreign policy issues faced by Washington (include an evaluation of his farewell address)? Keeping the USA neutral during the war between
How did the Industrial Revolution impact geography, city design, and transportation?
 5 th 6 WEEKS PROGRESS REPORT TEST REVIEW Know the map on page 394 How did the Industrial Revolution impact geography, city design, and transportation? Most factories were built along rivers because they
5 th 6 WEEKS PROGRESS REPORT TEST REVIEW Know the map on page 394 How did the Industrial Revolution impact geography, city design, and transportation? Most factories were built along rivers because they
The Factors Affecting American Economy From : Which Were. The United States economy was stimulated by many factors between
 The Factors Affecting American Economy From 1800 1860: Which Were Most Important And Why William Heegaard Sometime in High School The United States economy was stimulated by many factors between 1800 and
The Factors Affecting American Economy From 1800 1860: Which Were Most Important And Why William Heegaard Sometime in High School The United States economy was stimulated by many factors between 1800 and
Transformation. Society
 Transformation of the Economy & Society in Antebellum America 1820-1860 A09W 10.11.01 Guiding Question Analyze the causes of the transformation of the American economy in the first half of the nineteenth
Transformation of the Economy & Society in Antebellum America 1820-1860 A09W 10.11.01 Guiding Question Analyze the causes of the transformation of the American economy in the first half of the nineteenth
Immigration. Emigrants Leaving Ireland, a 19th-century painting
 Immigration German immigration: Rising land costs, overcrowding, and political instability Settled in Midwest to farm Irish immigration: Great Hunger (potato famine) Settled on East Coast for industrial
Immigration German immigration: Rising land costs, overcrowding, and political instability Settled in Midwest to farm Irish immigration: Great Hunger (potato famine) Settled on East Coast for industrial
The Presidency of James Monroe
 The Presidency of James Monroe James Monroe 1758 1831 Democratic-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former Governor of Virginia, Secretary of State,
The Presidency of James Monroe James Monroe 1758 1831 Democratic-Republican 5 th President (1817-25) Last President to have participated in the Revolution Former Governor of Virginia, Secretary of State,
ID-Irish and German Immigration by Decade (291) Summary 1- What decade brought the greatest number of Irish immigrants? Summary 2- What
 Ch 14 Insights Goals Questions Part 1 Identify the two largest immigrant groups to the US in the first half of the 1800 s and explain how their experiences were different Explain how those different experiences
Ch 14 Insights Goals Questions Part 1 Identify the two largest immigrant groups to the US in the first half of the 1800 s and explain how their experiences were different Explain how those different experiences
APUSH Chapter Lecture Notes
 APUSH Chapter 11+12 Lecture Notes Chapter 11: The Triumphs and Travails of the Jeffersonian Republic, 1800 1812 I. The Triumphs and Travails of the Jeffersonian Republic A. The Election of 1800: Adams
APUSH Chapter 11+12 Lecture Notes Chapter 11: The Triumphs and Travails of the Jeffersonian Republic, 1800 1812 I. The Triumphs and Travails of the Jeffersonian Republic A. The Election of 1800: Adams
US History Module 1 (A) Lesson 3. A New Nation
 US History Module 1 (A) Lesson 3 A New Nation Forming a New Government Fears and concerns about the form of government affects planning of new government Experimenting with Confederation 1781 Congress
US History Module 1 (A) Lesson 3 A New Nation Forming a New Government Fears and concerns about the form of government affects planning of new government Experimenting with Confederation 1781 Congress
Essential Question: How did President Jefferson change U.S. government, territory, & foreign policy?
 Essential Question: How did President Jefferson change U.S. government, territory, & foreign policy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.1: Clicker Preview Questions President Jefferson notes & Marbury v Madison activity
Essential Question: How did President Jefferson change U.S. government, territory, & foreign policy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.1: Clicker Preview Questions President Jefferson notes & Marbury v Madison activity
The March of Millions
 The March of Millions Around 1850 the population was doubling every 25 years. By 186 there were 33 states. America was the fourth most populous nation in the world. Cities were rapidly developing as were
The March of Millions Around 1850 the population was doubling every 25 years. By 186 there were 33 states. America was the fourth most populous nation in the world. Cities were rapidly developing as were
Course Title: Advanced Placement United States History I. American Beginnings to 1763
 Unit 1, September American Beginnings to 1763 What is the state if the Atlantic world in 1492 What are the results of the clash of cultures and the early explorations and settlements of the Western hemispheres?
Unit 1, September American Beginnings to 1763 What is the state if the Atlantic world in 1492 What are the results of the clash of cultures and the early explorations and settlements of the Western hemispheres?
Consequences of the War of 1812
 Consequences of the War of 1812 Collapse of Federalist Party Era of Good Feelings Monroe Presidency 18161824 Bring factions togethersimilar to Washington Last of Revolutionary Founding Fathers Appointed
Consequences of the War of 1812 Collapse of Federalist Party Era of Good Feelings Monroe Presidency 18161824 Bring factions togethersimilar to Washington Last of Revolutionary Founding Fathers Appointed
Amarillo ISD Social Studies Curriculum
 Amarillo Independent School District follows the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS). All of AISD curriculum and documents and resources are aligned to the TEKS. The State of Texas State Board
Amarillo Independent School District follows the Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS). All of AISD curriculum and documents and resources are aligned to the TEKS. The State of Texas State Board
MARKING PERIOD 1. Shamokin Area 7 th Grade American History I Common Core I. UNIT 1: THREE WORLDS MEET. Assessments Formative/Performan ce
 Shamokin Area 7 th Grade American History I Common Core Marking Period Content Targets Common Core Standards Objectives Assessments Formative/Performan ce MARKING PERIOD 1 I. UNIT 1: THREE WORLDS MEET
Shamokin Area 7 th Grade American History I Common Core Marking Period Content Targets Common Core Standards Objectives Assessments Formative/Performan ce MARKING PERIOD 1 I. UNIT 1: THREE WORLDS MEET
