US History 1877 to Present Flashcard Set
|
|
|
- Winfred Warner
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 US History 1877 to Present Flashcard Set 1
2 QUESTIONS ANSWERS USII.2a - What are the physical features and climate of the Great Plains? Flatlands that rise gradually from east to west Land eroded by wind and water Low rainfall Frequent dust storms USII.2a - Before the Civil War, how did people view the Great Plains? The area was considered a "treeless wasteland" - not a good place to settle. USII.2a - How did perceptions of the Great Plains change after the Civil War? New technologies allowed people to see the Great Plains not as a treeless wasteland but as a vast area to be settled. USII.2a - What were some of the technologies and inventions that allowed people to settle in the Great Plains after the Civil War? Barbed wire Steel plows Dry farming Sod houses Beef cattle raising Wheat farming Windmills Railroads 2
3 USII.2b -What are three industries that emerged after the Civil War in specialized manufacturing areas? New England textile industry Detroit automobile industry Pittsburgh steel industry Chicago meat packing (somewhat later) USII.2b - New manufacturing and industrial areas emerged after the Civil War. Where was the textile industry centered? New England USII.2b - What city emerged as the center of the automobile industry? Detroit, Michigan USII.2b - What city emerged as the center of the steel industry? Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania USII.2c - Name the 7 political regions of the U.S. Northeast Southeast Midwest Southwest Rocky Mountain Pacific Noncontiguous USII.2c - Name the 9 states of the Northeast region. Hint: below are the first letters of the states listed from north to south (more or less). M V N C M R N N P Maine Vermont New Hampshire Connecticut Massachusetts Rhode Island New York New Jersey Pennsylvania 3
4 USII.2c - Name the 14 states of the Southeast region. Hint: below are the first letters of the states listed from north to south (more or less). M D W V K T N S G F A M L A Maryland Delaware West Virginia Virginia Kentucky Tennessee North Carolina South Carolina Georgia Florida Alabama Mississippi Louisiana Arkansas USII.2c - Name the 12 states of the Midwest region. Hint: below are the first letters of the states listed from east to west (more or less). O I I M W M I M K N S N Ohio Indiana Illinois Michigan Wisconsin Minnesota Iowa Missouri Kansas Nebraska South Dakota North Dakota USII.2c - Name the 4 states of the Southwest region. Hint: below are the first letters of the states. T O N A Texas Oklahoma New Mexico Arizona USII.2c - Name the 6 states of the Rocky Mountain region. Hint: below are the first letters of the states. C U N M W I Colorado Utah Nevada Montana Wyoming Idaho USII.2c - Name the 3 states of the Pacific region. Washington Oregon California USII.2c - Name the 2 noncontiguous states. Alaska Hawaii 4
5 USII.2c - A state is an example of a region. political USII.2c - Name the states in which these cities are located. Boston New York City Boston, Massachusetts New York, New York USII.2c - Name the states in which these cities are located. Pittsburgh Philadelphia Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania Philadelphia, Pennsylvania USII.2c - Name the states in which these cities are located. Atlanta New Orleans Atlanta, Georgia New Orleans, Louisiana USII.2c - Name the states in which these cities are located. Chicago St. Louis Chicago, Illinois St. Louis, Missouri USII.2c - Name the states in which these cities are located. Detroit San Antonio Detroit, Michigan San Antonio, Texas 5
6 USII.2c - Name the states in which these cities are located. Santa Fe Denver Santa Fe, New Mexico Denver, Colorado USII.2c - Name the states in which these cities are located. Salt Lake City San Francisco Salt Lake City, Utah San Francisco, California USII.2c - Name the states in which these cities are located. Los Angeles Seattle Los Angeles, California Seattle, Washington USII.2c - Name the states in which these cities are located. Juneau Honolulu Juneau, Alaska Honolulu, Hawaii USII.3a - What were some reasons for the period of westward expansion after Civil War? The Homestead Act resulted in opportunities for land ownership. The Transcontinental Railroad The discovery of gold and silver Adventure A new beginning for former slaves USII.3b - What were some of the factors leading to increased immigration after the Civil War? Some of the factors which led to increased immigration: hope for better opportunities adventure religious freedom. escape from oppressive governments. 6
7 USII.3b - Why did cities grow rapidly after the Civil War? Immigration from other countries (immigrants usually lived in cities) Movement of Americans from rural to urban areas for job opportunities Specialized industries developed in cities steel in Pittsburgh, meat packing in Chicago USII.3a - What were some inventions that contributed to change and industrial growth in the late 1800s? Lighting and mechanical uses of electricity Thomas Edison Expansion of telephone service Alexander Graham Bell USII.3a - What were some challenges faced by cities in the late 1800s and early 1900s? Overcrowded immigrant neighborhoods and tenements Political corruption USII.3a - What were some of the efforts made to solve immigration problems? Settlement Houses, such as Hull House founded by Jane Addams Political machines that gained power by attending to the needs of new immigrants (jobs, housing) USII.3a - How did political machines gain power in the cities? By helping immigrants with jobs, housing and other needs USII.3a - Who is Jane Addams? The founder of Hull House, a settlement house that offered a variety of services to immigrants 7
8 USII.3b - By 1865, skirmishes between Indians and white settlers were frequent. The government tried to convince Indians tribes to give up their land and relocate onto - reservations (land set aside for Indian communities) USII.3b - In 1876, the federal government decided to force the Sioux, led by Crazy Horse and Sitting Bull, back onto their reservation. In this famous battle, Custer led his troops against more than 2,000 Sioux Indians. He and all of his men died. the Battle of Little Bighorn USII.3b - In 1877, when the federal government sent troops into the Washington territory to force the Nez Percé off their lands and into a reservation, this Indian chief led 400, 000 of his people toward Canada on a long but unsuccessful escape. Chief Joseph USII.3b - During the 1880s, settlers on the West Coast blamed declining wages and economic problems on these workers. Chinese workers USII.3b - In 1882, Congress passed the first significant law restricting immigration into the United States. What was it? Chinese Exclusion Act USII.3b - This group of immigrants began to arrive in large numbers after their potato crop failed in the 1840s. By 1860, they had largely replaced the New England mill girls as textile workers. Irish immigrants 8
9 USII.3c - What were Jim Crow laws? Laws that institutionalized a system of legal segregation, creating unequal opportunities for African Americans in housing, work, education, and government USII.3c - What is racial segregation? Separation based on race USII.3c - "Jim Crow" laws made discrimination in many states. legal USII.3c - Who was Booker T. Washington and how did he respond to the issue of segregation? An African American leader who, believing that African Americans would achieve equality in time through education, was willing to put up temporarily with social segregation. USII.3c - Who was W.E.B. Du Bois, and how did he respond to the issue of segregation and discrimination? An African American leader who wanted immediate political, civil and social equality for African Americans at any cost USII.3c - How did Booker T. Washington and W.E.B. Du Bois differ in their responses to discrimination? Washington was willing to accept some degree of segregation while African Americans slowly achieved equal treatment through education. DuBois, on the other hand, demanded immediate equality for African Americans. 9
10 USII.3d - Between the Civil War and World War I, the U.S. was transformed from a(n) to a(n) nation. agricultural --- industrial USII.3d - What created the rise in big business in the late 1800s? National markets created by transportation advances Captains of industry like Rockefeller (oil) Carnegie (steel), and Ford (cars) Advertising Lower-cost production USII.3d - What caused industrialization in the late 1800s? Access to raw materials and energy Availability of a large work force Inventions Financial resources USII.3d - What are some examples of "big business" that emerged after the Civil War? Railroads, Oil, Steel USII.3d - Who was the oil "captain of industry"? John D. Rockefeller USII.3d - Who emerged as the captain of the steel industry? Andrew Carnegie 10
11 USII.3d - Who emerged as the captain of the auto industry? Henry Ford USII.3d - How did farm life change after the Civil War? Mechanization (e.g., the reaper) reduced farm labor needs and increased production. Industrialization provided access to consumer goods by mail order USII.3d - Industrial development in the cities increased the need for - labor USII.3d - How did changes in farm life fuel industrialization? Mechanization meant fewer workers were needed on the farms, so labor was freed up for the cities. USII.3d - What effect did mechanization (e.g., the reaper) have on the farms? Mechanization increased productivity and reduced labor needs. Farm laborers left for the cities to work in industry. USII.3e - What were some of the negative effects of industrialization? Child labor Low wages and long hours Unsafe working conditions 11
12 USII.3e - What were some of the workplace reforms brought about by the Progressive Movement? Improved safety conditions Reduced work hours Restrictions on child labor USII.3e - What did Progressive reformers want? Reformers wanted laws to protect workers and poor people, to reform government, and to regulate business. USII.3e - What did the women's suffrage movement want? voting rights for women increased educational opportunities for women USII.3e - The negative effects of industrialization led to: the rise of organized labor progressive movement and workplace reforms USII.3e - This union pushed for higher wages, shorter hours and better working conditions. It was stronger in the skilled trades than the factories, and preferred to bargain rather than to strike. The AFL - American Federation of Labor USII.3e - In 1892, 13 men were killed in a battle between striking steelworkers and strikebreakers at Carnegie's steel plant in Pittsburgh. This strike is known as the - Homestead Strike 12
13 USII.3e - What was an important result of the Homestead Strike? Americans turned against unions and organized labor, whom they blamed for the violence. USII.3e - Which Constitutional Amendment finally gave women the right to vote? When was it adopted? The 19 th amendment, adopted in 1920, gave women the right to vote. USII.3e - What did Susan B. Anthony do? She worked for women's suffrage. USII.3e - What was the movement against alcohol consumption and production? The Temperance Movement USII.3e - What was the 18th amendment? It prohibited the manufacture, sale, and transport of alcoholic beverages. USII.4a - In what year did the Spanish American War take place?
14 USII.4a - Where did the fighting take place during the Spanish American War? Mostly Cuba and the Philippines USII.4a - The United States emerged as a as a result of victory over Spain in the Spanish American War. world power USII.4a - The Spanish American War started when Cuban nationalists revolted against the ruling Spanish government. Whom did the U.S. support? Cuban nationalists USII.4a - Reporters covering the Spanish American War exaggerated Spanish atrocities in order to sell newspapers. This became known as - yellow journalism USII.4a - What were some of the reasons for the Spanish American War? Protection of American business interests in Cuba American support of Cuban rebels to gain independence from Spain Tensions resulting from the sinking of the U.S.S. Maine in Havana Harbor Exaggerated news reports of events (Yellow Journalism) USII.4a - What was important about the U.S. battleship Maine? The U.S. blamed the Spanish for sinking the Maine, and used it as an excuse to declare war on Spain. 14
15 USII.4a - What possessions did the U.S. gain as a result of the Spanish American War? The Philippines, Guam and Puerto Rico USII.4a - What was the outcome of the Spanish American War for Cuba? Cuba gained independence from Spain. USII.4a - What was the Spanish American War all about? In 1898, Cuban rebels wanted independence from Spain and the U.S. supported them. USII.4a - When and why was the term Yellow Journalism first used During the Spanish American War to describe sensational reporting on the war. USII.4b - What happened in 1914? World War I broke out in Europe USII.4b - What was the U.S. response when war broke out in Europe in 1914? Americans did not want to become involved in European conflicts, and did not enter the war until 3 years later. 15
16 USII.4b - The U.S. policy before World War I of avoiding involvement in world affairs is called -. Isolationist USII.4b - Why did the US finally enter the war in Europe in 1917? Inability to remain neutral German submarine warfare sinking of Lusitania U.S. economic and political ties to Great Britain USII.4b - What was the significance of the Lusitania? A ship carrying American passengers that was sunk by a German sub during World War I. This and other incidents of German sub warfare prompted the U.S. to enter the war in Europe. USII.4b - Who were the World War I Allies? Great Britain France Russia Serbia Belgium USII.4b - The countries fighting the Allies during World War I were called: Central Powers USII.4b - Who were the Central Powers? Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, the Ottoman Empire (Turkey) 16
17 USII.4b - In what year did World War I break out? In what year did the U.S. enter the fighting in World War I? World War I broke out in The US entered the war in USII.4b - What did President Woodrow Wilson propose after WWI? A peace plan that called for the formation of the League of Nations, a peacekeeping organization USII.4b - What was the League of Nations? A peacekeeping organization proposed by Woodrow Wilson, that the US never joined USII.4b - Why did Woodrow Wilson propose the League of Nations? To help prevent further wars USII.4b - Why did the U.S. refuse to join the League of Nations? Americans did not want the U.S. tangled in world affairs, preferring the isolationist policy of the past USII.5a - How was life in the early 20 th century different from 19 th century life? Technology extended into even rural areas and to all aspects of American life. 17
18 USII.5a - What were some of the technologies that changed American life in the early 20 th century? The affordable automobile The invention of the airplane The use of the assembly line Communication changes- availability of the telephone, radio and broadcast industry, and movies Electrification labor saving home products USII.5a - How did the affordable automobile change American life in the 20 th century? Greater mobility Creation of jobs Growth of transportation-related industries road construction, oil, steel, automobile Movement to suburban areas USII.5a - Who invented the airplane? The Wright brothers USII.5a - Who made popular the use of the moving assembly line? Henry Ford and the automobile industry USII.5a - How did communications change in the early 20 th century? - Increased availability of the telephone - Development of the radio and broadcast industry (Marconi and Sarnoff) - Development of movies USII.5a - How did electrification change American life? - Labor-saving products - the washing machine, electric stove, water pumps - Electric lighting - Entertainment radio 18
19 USII.5a - Who had an important role in the development of the radio? Guglielmo Marconi USII.5a - Who had an important role in the development of the broadcast industry? David Sarnoff USII.5b - What was Prohibition? Refers to a time when a constitutional amendment made it illegal to manufacture, transport and sell alcoholic beverages. USII.5b - What was a lesson we learned from Prohibition? It is difficult to legislate how people behave. Speakeasies were created as places for people to drink. Bootleggers smuggled illegal alcohol and promoted organized crime. USII.5b - What were speakeasies? Places for people to drink alcoholic beverages during the period of Prohibition USII.5b - Who were bootleggers? Those who smuggled illegal alcohol and promoted organized crime. 19
20 USII.5b - What was the Great Migration North? African Americans left the South where jobs were low-paying and scarce and migrated to northern cities. USII.5b - Did African Americans who left the South during the Great Migration manage to escape discrimination and violence? No, they faced discrimination and violence in the North as they had in the South. USII.5c - When was the Harlem Renaissance? 1920s and 1930s USII.5c - What was the Harlem Renaissance? African Americans in Harlem revealed the freshness and variety of African American culture through their art, music and writing. USII.5c - Who was a Harlem Renaissance painter who chronicled through art the experiences of the Great Migration north? Jacob Lawrence USII.5c - Who was a Harlem Renaissance poet who combined the experiences of African and American cultural roots? Langston Hughes 20
21 USII.5c - Who were two Harlem Renaissance jazz composers? Duke Ellington and Louis Armstrong USII.5c - Who was a Harlem Renaissance blues singer? Bessie Smith USII.5c - Other artists of the 1920s and 1930s included this artist, known for urban scenes and paintings of the Southwest. Georgia O'Keeffe USII.5c - Who wrote novels about the Jazz Age of the 1920s? F. Scott Fitzgerald USII.5c - Who wrote Grapes of Wrath, a novel about poor migrant worker during the 1930s? John Steinbeck USII.5c - Who were composers of the 1920s and 1930s who wrote uniquely American music? Aaron Copland and George Gershwin 21
22 USII.5d - What was a primary cause of the Great Depression? People over speculated on stocks, using borrowed money that they could not repay when stock prices crashed. The failed to prevent the collapse of the banking system which triggered the Great Depression. Federal Reserve USII.5d - Another cause of the Great Depression was the strangling of international trade by - high tariffs USII.5d Describe the impact of the Great Depression on Americans? - One fourth of workers were without jobs - Banks and businesses failed - People were hungry and homeless - Farmers incomes fell USII.5d - What was the New Deal? President Franklin Roosevelt's plan to use government programs to help the nation recover from the Depression. USII.5d - Name some of the features of the New Deal. - Social Security - Federal work programs - Environmental improvement programs - Farm assistance programs - Increased rights for labor 22
23 USII.6a - What were the conditions in Europe after World War I that led to the rise of fascism and World War II? Worldwide depression High war debt owed by Germany High inflation Massive unemployment. USII.6a - What is fascism? A political philosophy in which total power is given to a dictator and individual freedoms are denied. USII.6a - Name three fascist dictators - Adolf Hitler - Germany Benito Mussolini - Italy Hideki Tojo - Japan USII.6a - Describe America s foreign policy when WWII broke out in Europe in Policy of neutrality and isolationism a legacy from WWI and the Great Depression USII.6a - How did America s foreign policy evolve as the conflict grew in Europe? It evolved from a policy of isolationism to indirect involvement (economic aid) to direct involvement. USII.6a - Which nations were known as the Allies? The United States, Great Britain, Canada, and the Soviet Union after it was invaded by Germany. 23
24 USII.6a - Who were the Allied leaders? The U.S. FDR and after he died, Truman Great Britain Winston Churchill Soviet Union Joseph Stalin USII.6a Which countries became known as the Axis Powers? Germany, Italy and Japan USII.6a - When was the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor? December 7, 1941 USII.6a - Who was the leader of Great Britain during WWII? Prime Minister Winston Churchill USII.6a - What event caused the United States to declare war on Japan? The bombing of Pearl Harbor on Dec USII.6a - What happened after the U.S. declared war on Japan after the bombing of Pearl Harbor? Germany declared war on the United States 24
25 USII.6b On September 1, 1939, Hitler invaded. World War II had begun. Poland USII.6b Soon after Hitler invaded Poland, troops moved into Eastern Poland. Poland was split in half by two occupying countries- Germany and the Soviet Union. Soviet USII.6b In June of 1940, German troops marched victoriously into what important city? Paris, France USII.6b After the defeat of France, which country stood in the way of Hitler s plan to dominate Europe? Great Britain USII.6b From August until October 1940, Germans bombed British cities, shipyards and industries. This was known as the - the Battle of Britain USII.6b What was the outcome of the Battle of Britain? Hitler could not defeat Great Britain and ended his air attacks. 25
26 USII.6b Ignoring the pact he had made with Stalin, in June 1941, Hitler launched an attack on - the Soviet Union USII.6b Before Pearl Harbor, how did the U.S, help Britain? The United States gave Britain war supplies and old naval warships in return for military bases in Bermuda and the Caribbean. USII.6b What was the turning point in the war in the Pacific? The Battle of Midway, June The U.S. was victorious over Japan. USII.6b What battle was the turning point of the war in Eastern Europe? The Battle of Stalingrad where the Soviet Union defeated Germany USII.6b Where did the American and Allied troops land to begin the liberation of Western Europe? In Normandy, France USII.6b The United States was victorious over Japan in the Battle of. This victory was the turning point of the war in the Pacific. Midway 26
27 USII.6b The Soviet Union defeated Germany at, marking the turning point of the war in Eastern Europe. Stalingrad USII.6b American and Allied troops landed in Normandy, France, on to begin the liberation of Western Europe. June 6, 1944 known as D-Day USII.6b How did the US force Japan to surrender and thus bring an end to World War II? The United States dropped two atomic bombs on Japan (Hiroshima and Nagasaki) in 1945 USII.6b Despite initial success in both Europe and the Pacific, the Allies persevered and ultimately defeated Germany and Japan. Axis USII.6b Wiping out an entire group of people is - genocide USII.6b As many a six million Jews died during - the Holocaust 27
28 USII.6b Nazi troops crammed Jews into railroad cars and took them to prison camps for civilians called - concentration camps USII.6b What is anti-semitism? Hatred of the Jews USII.6b What is Aryan supremacy? Hitler and the Nazis portrayed the German people as superior to all others. USII.6b Whom did Hitler blame for Germany s problems? the Jews USII.6b Jews in Germany were persecuted from the time Hitler came to power through such means as: Boycotts of Jewish stores Threats Segregation USII.6b In the early 1940s. the Nazis embarked on their final solution. What was it? to destroy the Jews 28
29 USII.6b The Nazis built death camps where they killed thousands of people a day in gas chambers. These were called: concentration camps USII.6b Allied forces liberated the camps and freed the Jews that survived. When did this happen? After V-E Day (Victory in Europe Day) 1945 USII.6c - Why did American involvement in WWII bring an end to the Depression? Factories and workers were needed to produce goods to win the war. USII.6c As millions of men joined the war effort, who entered the labor force? Women USII.6c Many women had not worked before WWII. An advertising campaign which encouraged women to take factory jobs featured a character called- Rosie the Riveter USII.6c American involvement in World War II brought an end to - the Great Depression 29
30 USII.6c Americans at home supported the war (WWII) by - conserving and rationing resources USII.6c What impact did WWII have on race relations in America? The need for workers temporarily broke down some racial barriers (e.g., hiring in defense plants) although discrimination against African Americans continued. USII.6c How were Japanese Americans treated during WWII? Some were treated with distrust and prejudice, and many were forced into internment camps. In what condition was most of Europe after World War II? in ruins What parts of Europe did Soviet forces occupy after WWII? most of Eastern and Central Europe and the eastern part of Germany. USII.7a - Why did the US feel it was in its best interest to rebuild Europe after WWII? To prevent political and economic instability which could lead to the spread of communism. 30
31 USII.7a - What was the US plan to rebuild Europe called and what did it do? The Marshall Plan it provided massive financial aid to rebuild European economies and prevent the spread of communism. USII.7a - What happened to Germany after WWII? Germany was partitioned into East and West Germany. West Germany became democratic and resumed self-government after a few years of American, British, and French occupation. East Germany remained under the domination of the Soviet Union and did not adopt democratic institutions. USII.7a - What happened to Japan after WWII? Following its defeat, Japan was occupied by American forces. It soon adopted a democratic form of government, resumed selfgovernment, and became a strong ally of the United States. USII.7a - When and why was the United Nations established? The United Nations was formed near the end of World War II to create a body for the nations of the world to try to prevent future global wars. USII.6c - How did American involvement in WWII affect the role of women? Thousands of American women took jobs in defense plants during the war (e.g., Rosie the Riveter). USII.6c - How did Americans at home support the war effort? By conserving and rationing resources 31
32 USII.6c - How did American involvement in WWII effect race relations? The need for workers temporarily broke down some racial barriers. The high demand for labor opened up doors for African Americans. However, discrimination against African Americans continued. USII.6c - How were Japanese Americans treated? Many were treated with distrust and prejudice, and some were forced into internment camps. USII.7a - In what condition was Europe after WWII? In ruins USII.7a - After WWII, what lands did the Soviet Union occupy? Soviet forces occupied most of Eastern and Central Europe and the eastern portion of Germany USII.7a - Why did the U.S. feel it was in its best interests to rebuild Europe and Japan? To prevent political and economic instability. USII.7a - What was America s plan to rebuild Europe called? The Marshall Plan 32
33 USII.7a What did the Marshall Plan do? It provided massive financial aid to rebuild European economies. USII.7a The Marshall Plan was intended to prevent the spread of - communism What happened to Germany after WWII? Germany was partitioned into East and West Germany. USII.7a What happened to West Germany after a few years of American, British and French occupation? West Germany became democratic and resumed self-government. USII.7a What happened to East Germany after WWII? East Germany remained under the domination of the Soviet Union and did not adopt democratic institutions. USII.7a Following its defeat in WWII, Japan was occupied by - American forces 33
34 USII.7a Soon after WWII, Japan adopted a form of government. democratic USII.7a Soon after WWII, Japan became a strong of the U.S. ally USII.7a Near the end of WWII, what was done to try to prevent future world wars? The United Nations (U.N.) was formed In the U.S., the period following WWII was one of economic - growth and prosperity USII.7b How did WWII help bring the Depression to an end? Wartime production stimulated America s economy. USII.7b - What contributed to the rapid growth of America s economy after WWII? With rationing of consumer goods over, business converted from production of war materials to consumer goods. Americans purchased goods on credit. 34
35 USII.7b - What happened to labor unions after WWII? They merged and became more powerful. USII.7b - How did the more powerful labor unions that emerged after WWII help workers? Workers gained new benefits and higher salaries. USII.7b - What changes occurred in the American workforce after WWII? The workforce shifted back to men, and most women returned to family responsibilities. USII.7b - After WWII, women left the workforce and returned to their families. Did they stay out of the workforce? No, the next generation of women reentered the labor force in large numbers. USII.7c -The United States and the Soviet Union emerged from World War II as: world powers or superpowers USII.7c - What was the result of the he state of tension which developed between the two superpowers the United States and the Soviet Union? A rivalry over ideology and national security which divided the world into two camps 35
36 USII.7c - The rivalry or state of tension that developed between the U.S. and the Soviet Union was called - the Cold War USII.7c - How were the U.S. and the Soviet Union ideologically different? The United States was democratic and capitalist; the Soviet Union was dictatorial and communist USII.7c - The United States was and. In contrast, the Soviet Union was and. democratic, capitalist dictatorial, communist USII.7c - Among the causes of the Cold War were- - differing ideologies - the Soviet domination of East Europe - U.S. policy of containment - NATO vs. Warsaw Pact military rivalry USII.7c - What is containment? The U.S. policy aimed at stopping the spread of communism USII.7c - Our allies in Europe formed a military alliance called: NATO North Atlantic Treaty Organization 36
37 USII.7c - A military alliance of nations dominated by the Soviet Union was called: the Warsaw Pact USII.7c - Since World War II, the United States has been directly involved in various Cold War conflicts such as - North/South Korea Cuban Missile Crisis Vietnam USII.7c - Describe the Korean conflict. South Korea and the United States resisted Chinese and North Korean aggression. The conflict ended in a stalemate. USII.7c - Describe the Cuban Missile Crisis. The Cuban Missile Crisis occurred when the Soviet Union tried to place missiles in Cuba. The Soviets removed the missiles in response to a U.S. blockade. USII.7c - The United States intervened to stop the spread of into South Vietnam. communism USII.7c - According to the Theory, if the U.S. did not intervene to prevent the spread of communism to South Vietnam, communism would spread throughout countries of Asia like falling dominoes. Domino 37
38 USII.7c - How did Cold War tensions cause divisiveness at home? Americans were divided over whether the United States should be involved militarily in Vietnam. USII.7c - How did the war in Vietnam end? The conflict ended in a cease-fire agreement in which U.S. troops withdrew, but immediately after South Vietnam fell to communist forces. USII.7c - The late 1980s, communism in Eastern Europe began to - collapse USII.7c - What happened to the Soviet Union in the early 1990s? The Soviet Union broke up into independent countries. USII.7c - What event signal became symbolic of the collapse of communism in Eastern Europe? the destruction of the Berlin Wall USII.7c What were some of the new challenges faced by the U.S. after the Cold War ended? Role of U.S. military intervention Environmental challenges Global issues including trade, jobs, diseases 38
39 USII.7d Changes in society after WWII included expanded educational and economic opportunities for - military veterans, women and minorities USII.7d - Some of the factors leading to changes in US society after WWII were- Strong economy Greater investment in education The Baby Boom, Interstate highway system Evolving role of women - Role of Eleanor Roosevelt in expanding rights African Americans aspirations for equal opportunities Changes in makeup of immigrants USII.7d One of the factors leading to changes in US society after WWII was a strong US economy which was the result of - a healthy job market, increased productivity, increased demand for American products USII.7d When and what was The Baby Boom? After WWII, returning soldiers married and for the next decade or so, more babies than usual were born. A strong economy also contributed to the baby boom. USII.7d - This president s wife helped to helped to expand women s rights. Eleanor Roosevelt USII.7d - How did immigration change in the period after 1965? more Hispanic Americans, Asian Americans 39
40 USII.7d - What policies and programs expanded educational and employment opportunities for minorities? The Civil Rights Movement resulted in legislation that ensured constitutional rights to all citizens regardless of race. USII.8a - Women activists were inspired by the achievements of the and took action to gain equality for themselves, particularly in the workplace. Civil Rights Movement USII.8a - After World War II, women sought equality in the. workplace USII.8a - What were some effects of segregation on American society? Separate educational facilities and resources for white and African American students Separate restrooms, drinking fountains, restaurants Social isolation of races USII.8a - The Supreme Court decision in Plessy v. Ferguson allowed schools and other facilities that were - Separate but equal USII.8a - Which Supreme Court decision called for the desegregation of schools? Brown v. Board of Education 40
41 USII.8a - Who called for passive resistance against segregated schools? Martin Luther King, Jr. USII.8a - Rosa Park s actions resulted in the bus boycott. Montgomery USII.8a - What does NAACP stand for? National Association for the Advancement of Colored People USII.8a - Which laws supported the struggle for equality for African Americans? Civil Rights Act of 1964 Voting Rights Act of 1965 USII.8a - How were women disadvantaged in the workplace? Discrimination in hiring practices against women Lower wages for women than for men doing the same job USII.8a - This organization campaigned for women s rights - NOW National Organization for Women 41
42 USII.8a - What actions were taken to improve conditions for women? Federal legislation to force colleges to give women equal athletic opportunities focus on equal opportunity employment created a wider range of options and opportunities USII.8a - What gave educational, housing, and employment benefits to World War II veterans? G.I. Bill of Rights USII.8a Which president desegregated the armed forces? Truman USII.8a - led to increased educational, economic, and political opportunities for women and minorities. Civil Rights legislation USII.8b - Identify the industries that benefited the most from the new technologies of the second half of the twentieth century. Include the following: Airline industry Jets Auto industry and interstate highway system Entertainment and news Exploration of space Computer industry Satellite telecommunications Internet USII.8a What impact did the new technologies of the twentieth century have on American life? -Increased travel -Greater access to information -Better and cheaper communication -Better heating and air conditioning -More widespread and even distribution throughout the country of access to communication technologies 42
People You Gotta Know
 People You Gotta Know W.E.B. Dubois Booker T. Washington Chief Joseph Believed in full Believed equality Chief of the Political, civil, and could be achieved Nez Perce Social rights for through vocational
People You Gotta Know W.E.B. Dubois Booker T. Washington Chief Joseph Believed in full Believed equality Chief of the Political, civil, and could be achieved Nez Perce Social rights for through vocational
US Review. United States History
 US Review United States History How can we group the United States? Rocky Mountains Midwest Northeast Pacific Noncontiguous Southwest Southeast Examples of Manufacturing areas Automobile Industry Detroit
US Review United States History How can we group the United States? Rocky Mountains Midwest Northeast Pacific Noncontiguous Southwest Southeast Examples of Manufacturing areas Automobile Industry Detroit
3. Theodore Roosevelt expanded the Monroe Doctrine as a way to prevent. European involvement in the affairs of Latin American countries.
 Block Name Date USII.5a-6c Post Test Review USII.5a: The Spanish American War 1. What were the causes/reasons for the Spanish American War? (complete answers!) American Business interests in Cuba (sugar)
Block Name Date USII.5a-6c Post Test Review USII.5a: The Spanish American War 1. What were the causes/reasons for the Spanish American War? (complete answers!) American Business interests in Cuba (sugar)
United States History: 1865 to Present SOL USII. 2 : The student will use maps, globes, photographs, pictures, or tables for explaining:
 United States History: 1865 to Present SOL USII. 2 : The student will use maps, globes, photographs, pictures, or tables for explaining: USII.2a Westward Movement after 1865 : how the physical features
United States History: 1865 to Present SOL USII. 2 : The student will use maps, globes, photographs, pictures, or tables for explaining: USII.2a Westward Movement after 1865 : how the physical features
Curriculum Framework. United States History: 1877 to the Present
 Curriculum Framework United States History: 1877 to the Present Commonwealth of Virginia Board of Education Richmond, Virginia 2001 STANDARD USII.1 a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h The student will demonstrate skills
Curriculum Framework United States History: 1877 to the Present Commonwealth of Virginia Board of Education Richmond, Virginia 2001 STANDARD USII.1 a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h The student will demonstrate skills
CONCEPTUAL UNIT QUESTION
 UNIT VI: The Boom to Bust Period This unit will address the following objectives: SOL USII.5 a) explaining how developments in transportation (including the use of the automobile), communication, and rural
UNIT VI: The Boom to Bust Period This unit will address the following objectives: SOL USII.5 a) explaining how developments in transportation (including the use of the automobile), communication, and rural
SOL Review for United States History 1865 to the Present
 SOL Review for United States History 1865 to the Present Physical Features/ Climate of the Great Plains (USII.2a) to west Technological advances allowed people to live in more challenging environments.
SOL Review for United States History 1865 to the Present Physical Features/ Climate of the Great Plains (USII.2a) to west Technological advances allowed people to live in more challenging environments.
SOL Review for United States History 1865 to the Present
 SOL Review for United States History 1865 to the Present Physical Features/ Climate of the Great Plains (USII.2a) Flatlands that rise gradually from east to west Land eroded by wind and water Low rainfall
SOL Review for United States History 1865 to the Present Physical Features/ Climate of the Great Plains (USII.2a) Flatlands that rise gradually from east to west Land eroded by wind and water Low rainfall
The Spanish American-War 4 Causes of the War: Important Events 1/7/2018. Effects of the Spanish American War
 The Spanish American-War 4 Causes of the War: Sugar (Economic) Spanish Cruelties (Humanitarian) The Sinking of the USS Maine (Self-Defense/National Pride) Spanish Brutalities and Yellow Journalism (Political
The Spanish American-War 4 Causes of the War: Sugar (Economic) Spanish Cruelties (Humanitarian) The Sinking of the USS Maine (Self-Defense/National Pride) Spanish Brutalities and Yellow Journalism (Political
Interpret ideas and events from different historical perspectives. (USII.1d)
 Reporting Category 1: Reconstruction to Modern America STANDARD USII.3b-c The student will demonstrate knowledge of the effects of Reconstruction on American life by b) describing the impact of Reconstruction
Reporting Category 1: Reconstruction to Modern America STANDARD USII.3b-c The student will demonstrate knowledge of the effects of Reconstruction on American life by b) describing the impact of Reconstruction
GRADE 5. United States Studies: 1865 to the Present
 Standard 5-1: The student will demonstrate an understanding of Reconstruction and its impact on the United States. Reconstruction was a period of great hope, incredible change, and efforts at rebuilding.
Standard 5-1: The student will demonstrate an understanding of Reconstruction and its impact on the United States. Reconstruction was a period of great hope, incredible change, and efforts at rebuilding.
Chapter 6 Shaping an Abundant Land. Page 135
 Chapter 6 Shaping an Abundant Land Page 135 Waves of immigrants came to the U.S. in order to find a better life. Push-pull factors were at play. Immigration is not the only movement of people in the U.S.
Chapter 6 Shaping an Abundant Land Page 135 Waves of immigrants came to the U.S. in order to find a better life. Push-pull factors were at play. Immigration is not the only movement of people in the U.S.
5. Base your answer on the map below and on your knowledge of social studies.
 Name: 1. To help pay for World War II, the United States government relied heavily on the 1) money borrowed from foreign governments 2) sale of war bonds 3) sale of United States manufactured goods to
Name: 1. To help pay for World War II, the United States government relied heavily on the 1) money borrowed from foreign governments 2) sale of war bonds 3) sale of United States manufactured goods to
U.S. TAKS Review. 11th
 11th U.S. TAKS Review Add a background color or design template to the following slides and use as a Power Point presentation. Print as slides in black and white on colored paper to use as placards for
11th U.S. TAKS Review Add a background color or design template to the following slides and use as a Power Point presentation. Print as slides in black and white on colored paper to use as placards for
USSR United Soviet Socialist Republic
 USSR United Soviet Socialist Republic United States Great Britain FDR Joseph Stalin Winston Churchill Truman Major Leaders of the War Franklin D. Roosevelt (Allied Power) U.S. President Elected in 1933
USSR United Soviet Socialist Republic United States Great Britain FDR Joseph Stalin Winston Churchill Truman Major Leaders of the War Franklin D. Roosevelt (Allied Power) U.S. President Elected in 1933
Review. Geographic Change Essay. Essay Blocking. Possible Thematic Essays 6/7/2013
 Review Essay Blocking Possible Thematic Essays Study 2 of the following: 5 W s- Who, What, When, Why - Reform Movements (Women, Civil Rights, Progressive Era) - Manifest Destiny ( Louisiana Purchase, Homestead
Review Essay Blocking Possible Thematic Essays Study 2 of the following: 5 W s- Who, What, When, Why - Reform Movements (Women, Civil Rights, Progressive Era) - Manifest Destiny ( Louisiana Purchase, Homestead
Unit 6 World War II & Aftermath
 Unit 6 World War II & Aftermath Following WWI and the Gr. Depr US wanted to stay out of world affairs Needed to rebuild economy Pursued policies of: isolationism neutrality Neutrality Taking no side in
Unit 6 World War II & Aftermath Following WWI and the Gr. Depr US wanted to stay out of world affairs Needed to rebuild economy Pursued policies of: isolationism neutrality Neutrality Taking no side in
World War II. Benito Mussolini Adolf Hitler Fascism Nazi. Joseph Stalin Axis Powers Appeasement Blitzkrieg
 Mr. Martin U.S. History Name: Date: Block: World War II The effects of World War I and the Great Depression touched almost every corner of the world. In some countries, these upheavals led to the rise
Mr. Martin U.S. History Name: Date: Block: World War II The effects of World War I and the Great Depression touched almost every corner of the world. In some countries, these upheavals led to the rise
Standard 7 Review. Opening: Answer the multiple-choice questions on pages and
 Opening: Standard 7 Review Answer the multiple-choice questions on pages 186-188 and 201-204. Correct answers we be counted as extra credit on your quiz. Standard USHC-7: The student will demonstrate an
Opening: Standard 7 Review Answer the multiple-choice questions on pages 186-188 and 201-204. Correct answers we be counted as extra credit on your quiz. Standard USHC-7: The student will demonstrate an
5th Social Studies practice test
 Name: Instructions: Bubble in the correct answer. Read all choices before marking your answer. Copyright 2000-2002 Measured Progress, All Rights Reserved : 1. Which of the following was developed during
Name: Instructions: Bubble in the correct answer. Read all choices before marking your answer. Copyright 2000-2002 Measured Progress, All Rights Reserved : 1. Which of the following was developed during
GRADE 5. United States Studies: 1865 to the Present
 Students continue their study of the history of the United States in grade five, beginning with Reconstruction and continuing through the present day. They learn about the renewal of the country after
Students continue their study of the history of the United States in grade five, beginning with Reconstruction and continuing through the present day. They learn about the renewal of the country after
USII.4bd, 6a Immigration & Big Business
 Block# Name: Today s Date: Due Date: USII.4bd, 6a Immigration & Big Business 1870 1910 Special Note: pages 2, & 3 are the Essential Knowledge of this SOL. It is your responsibility to study this information,
Block# Name: Today s Date: Due Date: USII.4bd, 6a Immigration & Big Business 1870 1910 Special Note: pages 2, & 3 are the Essential Knowledge of this SOL. It is your responsibility to study this information,
Map of the Foreign Born Population of the United States, 1900
 Introduction According to the 1900 census, the population of the United States was then 76.3 million. Nearly 14 percent of the population approximately 10.4 million people was born outside of the United
Introduction According to the 1900 census, the population of the United States was then 76.3 million. Nearly 14 percent of the population approximately 10.4 million people was born outside of the United
Introduction to World War II By USHistory.org 2017
 Name: Class: Introduction to World War II By USHistory.org 2017 World War II was the second global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. The war involved a majority of the world s countries, and it is considered
Name: Class: Introduction to World War II By USHistory.org 2017 World War II was the second global war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. The war involved a majority of the world s countries, and it is considered
RECONSTRUCTION. Poll Tax 1. Fee people had to pay on order to vote 2. Because African Americans could not afford the tax, they could not vote
 RECONSTRUCTION Jim Crow Laws 1. Required African Americans and whites to be separated in almost every public place 2. African Americans continued to feel oppressed or put down Segregation 1. Separation
RECONSTRUCTION Jim Crow Laws 1. Required African Americans and whites to be separated in almost every public place 2. African Americans continued to feel oppressed or put down Segregation 1. Separation
From D-Day to Doomsday Part A - Foreign
 UNIT 4 : 1930-1960 From D-Day to Doomsday Part A - Foreign World War I Unresolved Treaty of Versailles increases German nationalism Hitler violates treaty to re-militarize League of Nations has no way
UNIT 4 : 1930-1960 From D-Day to Doomsday Part A - Foreign World War I Unresolved Treaty of Versailles increases German nationalism Hitler violates treaty to re-militarize League of Nations has no way
Georgia High School Graduation Test Tutorial. World History from World War I to World War II
 Georgia High School Graduation Test Tutorial World History from World War I to World War II Causes of World War I 1. Balkan Nationalism Causes of World War I 2. Entangled Alliances Causes of World War
Georgia High School Graduation Test Tutorial World History from World War I to World War II Causes of World War I 1. Balkan Nationalism Causes of World War I 2. Entangled Alliances Causes of World War
Fascism is a nationalistic political philosophy which is anti-democratic, anticommunist, and anti-liberal. It puts the importance of the nation above
 1939-1945 Fascism is a nationalistic political philosophy which is anti-democratic, anticommunist, and anti-liberal. It puts the importance of the nation above the rights of the individual. The word Fascism
1939-1945 Fascism is a nationalistic political philosophy which is anti-democratic, anticommunist, and anti-liberal. It puts the importance of the nation above the rights of the individual. The word Fascism
5 th Grade Social Studies
 5 th Grade Social Studies UNITED STATES HISTORY Year 3: Industrialization to the Digital Age In fifth grade, students are in the final year of a three year study of United States history in which all four
5 th Grade Social Studies UNITED STATES HISTORY Year 3: Industrialization to the Digital Age In fifth grade, students are in the final year of a three year study of United States history in which all four
Seventh Grade United States History 1865 to the Present
 Seventh Grade United States History 1865 to the Present Revised: April 2016 for the 2016-2017 School Year Waynesboro Public Schools 301 Pine Avenue Waynesboro, Virginia 22980 www.waynesboro.k12.va.us Important
Seventh Grade United States History 1865 to the Present Revised: April 2016 for the 2016-2017 School Year Waynesboro Public Schools 301 Pine Avenue Waynesboro, Virginia 22980 www.waynesboro.k12.va.us Important
U.S. History II Review Notes for Parents and Students
 U.S. History II Review Notes for Parents and Students Grade 6 U. S. History II 1 st /3 rd Nine Weeks, 2017-2018 1 United States History II: 1865-Present Content Review Notes: Standards of Learning in Detail
U.S. History II Review Notes for Parents and Students Grade 6 U. S. History II 1 st /3 rd Nine Weeks, 2017-2018 1 United States History II: 1865-Present Content Review Notes: Standards of Learning in Detail
USII.1 The student will demonstrate skills for historical and geographical analysis, including the ability to
 Prentice Hall The American Nation 2005, Civil War to the Present Edition Virginia Social Studies Standards of Learning, United States History: 1877 to the Present (Grade 7) History and Social Science Standards
Prentice Hall The American Nation 2005, Civil War to the Present Edition Virginia Social Studies Standards of Learning, United States History: 1877 to the Present (Grade 7) History and Social Science Standards
EOC Preparation: WWII and the Early Cold War Era
 EOC Preparation: WWII and the Early Cold War Era WWII Begins Adolf Hitler and Nazi Party were elected to power and took over the German government Hitler held a strict rule over Germany and set his sights
EOC Preparation: WWII and the Early Cold War Era WWII Begins Adolf Hitler and Nazi Party were elected to power and took over the German government Hitler held a strict rule over Germany and set his sights
Create Your Cover Page on The Roaring Twenties Page1
 Create Your Cover Page on The Roaring Twenties Page1 SOL Standard USII. 6a Results of improved transportation brought about by affordable automobiles Greater mobility Creation of jobs Growth of transportation-related
Create Your Cover Page on The Roaring Twenties Page1 SOL Standard USII. 6a Results of improved transportation brought about by affordable automobiles Greater mobility Creation of jobs Growth of transportation-related
U.S. History & Government Unit 12 WWII Do Now
 1. Which precedent was established by the Nuremberg war crimes trials? (1) National leaders can be held responsible for crimes against humanity. (2) Only individuals who actually commit murder during a
1. Which precedent was established by the Nuremberg war crimes trials? (1) National leaders can be held responsible for crimes against humanity. (2) Only individuals who actually commit murder during a
USH Vocabulary From Closing the West
 USH Vocabulary From Closing the West 16th Amendment 17th Amendment 18th Amendment 19th Amendment 1960 Nixon/Kennedy TV Debate 1968 Turmoil 38th Parallel Acquittal Affirmative Action Alliances Alphabet
USH Vocabulary From Closing the West 16th Amendment 17th Amendment 18th Amendment 19th Amendment 1960 Nixon/Kennedy TV Debate 1968 Turmoil 38th Parallel Acquittal Affirmative Action Alliances Alphabet
Here we go again. EQ: Why was there a WWII?
 Here we go again. EQ: Why was there a WWII? In the 1930s, all the world was suffering from a depression not just the U.S.A. Europeans were still trying to rebuild their lives after WWI. Many of them could
Here we go again. EQ: Why was there a WWII? In the 1930s, all the world was suffering from a depression not just the U.S.A. Europeans were still trying to rebuild their lives after WWI. Many of them could
Grade Seven History and Social Science: United States History, 1865 to the Present
 Grade Seven History and Social Science: United States History, 1865 to the Present Grade 7 Curriculum for Loudoun County Public Schools Dr. Edgar B. Hatrick, Superintendent Sharon D. Ackerman, Assistant
Grade Seven History and Social Science: United States History, 1865 to the Present Grade 7 Curriculum for Loudoun County Public Schools Dr. Edgar B. Hatrick, Superintendent Sharon D. Ackerman, Assistant
Standard Standard
 Standard 10.8.4 Describe the political, diplomatic, and military leaders during the war (e.g. Winston Churchill, Franklin Delano Roosevelt, Emperor Hirohito, Adolf Hitler, Benito Mussolini, Joseph Stalin,
Standard 10.8.4 Describe the political, diplomatic, and military leaders during the war (e.g. Winston Churchill, Franklin Delano Roosevelt, Emperor Hirohito, Adolf Hitler, Benito Mussolini, Joseph Stalin,
Domestic policy WWI. Foreign Policy. Balance of Power
 Domestic policy WWI The decisions made by a government regarding issues that occur within the country. Healthcare, education, Social Security are examples of domestic policy issues. Foreign Policy Caused
Domestic policy WWI The decisions made by a government regarding issues that occur within the country. Healthcare, education, Social Security are examples of domestic policy issues. Foreign Policy Caused
World War II Leaders Battles Maps
 World War II Leaders Battles Maps Reign of the Dictator Italy Germany Soviet Union Japan Joseph Stalin Born in Gori, Georgia in 1879. Last name means steel in Russian. Seized power in USSR after Lenin
World War II Leaders Battles Maps Reign of the Dictator Italy Germany Soviet Union Japan Joseph Stalin Born in Gori, Georgia in 1879. Last name means steel in Russian. Seized power in USSR after Lenin
Unit Eight Test Review
 Unit Eight Test Review 1. How had the Treaty of Versailles laid the groundwork for the outbreak of World War Two? 2. What worldwide event led to the rise of Adolf Hitler in Germany? 3. Explain the importance
Unit Eight Test Review 1. How had the Treaty of Versailles laid the groundwork for the outbreak of World War Two? 2. What worldwide event led to the rise of Adolf Hitler in Germany? 3. Explain the importance
The United States Lesson 2: History of the United States
 Lesson 2: History of the United States ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is history important? Terms to Know indigenous living or occurring naturally in a particular place nomadic describes a way of life in which
Lesson 2: History of the United States ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is history important? Terms to Know indigenous living or occurring naturally in a particular place nomadic describes a way of life in which
5th Grade History and Government
 Q 1. How were the contributions of Louis Armstrong and Langston Hughes similar? A) Both men expanded interest in African-American culture. B) Both men were African-American members of Congress. C) Both
Q 1. How were the contributions of Louis Armstrong and Langston Hughes similar? A) Both men expanded interest in African-American culture. B) Both men were African-American members of Congress. C) Both
American History I Can Statements
 American History I Can Statements I can recognize important figures in big business, such as Rockefeller and Carnegie, and describe their impact on the American economy. I can identify major labor unions
American History I Can Statements I can recognize important figures in big business, such as Rockefeller and Carnegie, and describe their impact on the American economy. I can identify major labor unions
5th Grade Social Studies Test
 5th Grade Social Studies Practice Name: Instructions: Copyright 2000-2002 Measured Progress, All Rights Reserved : 5th Grade Social Studies Practice 1. What is the economic term used for the skills and
5th Grade Social Studies Practice Name: Instructions: Copyright 2000-2002 Measured Progress, All Rights Reserved : 5th Grade Social Studies Practice 1. What is the economic term used for the skills and
STANDARD VUS.8a. Essential Questions What factors influenced American growth and expansion in the late nineteenth and early twentieth century?
 STANDARD VUS.8a through the early twentieth century by explaining the relationship among territorial expansion, westward movement of the population, new immigration, growth of cities, and the admission
STANDARD VUS.8a through the early twentieth century by explaining the relationship among territorial expansion, westward movement of the population, new immigration, growth of cities, and the admission
DIOCESE OF HARRISBURG SOCIAL STUDIES CURRICULUM GRADE 7/8 United States History: Westward Expansion to Present Day
 5.1.9 Identify the goals of the constitution and the basic principles of American government. Recognize the Preamble to the Constitution and briefly explain how our government meets each goal. List and
5.1.9 Identify the goals of the constitution and the basic principles of American government. Recognize the Preamble to the Constitution and briefly explain how our government meets each goal. List and
The Cold War Begins. After WWII
 The Cold War Begins After WWII After WWII the US and the USSR emerged as the world s two. Although allies during WWII distrust between the communist USSR and the democratic US led to the. Cold War tension
The Cold War Begins After WWII After WWII the US and the USSR emerged as the world s two. Although allies during WWII distrust between the communist USSR and the democratic US led to the. Cold War tension
Unit 7 Test Review: The Great Depression, New Deal, & WWII
 Name: Unit 7 Test Review: The Great Depression, New Deal, & WWII 1) Describe the economy of the late 1920's: 2) How did wages for the AVERAGE AMERICAN worker compare to overall economic profits during
Name: Unit 7 Test Review: The Great Depression, New Deal, & WWII 1) Describe the economy of the late 1920's: 2) How did wages for the AVERAGE AMERICAN worker compare to overall economic profits during
Granite School District U.S. History II: 11 th Grade Curriculum Map
 1 st Quarter : America s early history directs the nation s course in the 19 th and 20 th centuries. Note: The first standard of the U.S. History II core is designed to apply 8 th grade content in more
1 st Quarter : America s early history directs the nation s course in the 19 th and 20 th centuries. Note: The first standard of the U.S. History II core is designed to apply 8 th grade content in more
World War II Causes of World War II
 Name World War II Causes of World War II U.S. History: Cold War & World War II Treaty of Versailles Caused Germany to: Admit war guilt Give up overseas colonies Lose land to France (Alsace Loraine) Give
Name World War II Causes of World War II U.S. History: Cold War & World War II Treaty of Versailles Caused Germany to: Admit war guilt Give up overseas colonies Lose land to France (Alsace Loraine) Give
Countries Of The World: The United States
 Countries Of The World: The United States By National Geographic Kids, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.26.18 Word Count 859 Level MAX Image 1: U.S. Route 101 in Oregon. This highway runs along the entire
Countries Of The World: The United States By National Geographic Kids, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.26.18 Word Count 859 Level MAX Image 1: U.S. Route 101 in Oregon. This highway runs along the entire
Red, white, and blue. One for each state. Question 1 What are the colors of our flag? Question 2 What do the stars on the flag mean?
 1 What are the colors of our flag? Red, white, and blue 2 What do the stars on the flag mean? One for each state 3 How many stars are there on our flag? There are 50 stars on our flag. 4 What color are
1 What are the colors of our flag? Red, white, and blue 2 What do the stars on the flag mean? One for each state 3 How many stars are there on our flag? There are 50 stars on our flag. 4 What color are
WW2 Practice Quiz (2) More women and minorities found employment in factories. (4) assist countries fighting the Axis Powers
 1 Which statement describes a major social and economic impact on American society during World War II? (1) The Great Depression continued to worsen. (2) More women and minorities found employment in factories.
1 Which statement describes a major social and economic impact on American society during World War II? (1) The Great Depression continued to worsen. (2) More women and minorities found employment in factories.
1 Run Up To WWII 2 Legacies of WWI Isolationism: US isolated themselves from world affairs during 1920s & 1930s Disarmament: US tried to reduce size
 1 Run Up To WWII 2 Legacies of WWI Isolationism: US isolated themselves from world affairs during 1920s & 1930s Disarmament: US tried to reduce size of militaries throughout world -- did NOT work Kellog-Brand
1 Run Up To WWII 2 Legacies of WWI Isolationism: US isolated themselves from world affairs during 1920s & 1930s Disarmament: US tried to reduce size of militaries throughout world -- did NOT work Kellog-Brand
1. Base your answer to the following question on the cartoon below and on your knowledge of social studies.
 1. Base your answer to the following question on the cartoon below and on your knowledge of social studies. 3. Base your answer on the map below and on your knowledge of social studies. In the cartoon,
1. Base your answer to the following question on the cartoon below and on your knowledge of social studies. 3. Base your answer on the map below and on your knowledge of social studies. In the cartoon,
25% Tests, Finals and long term projects 25% Homework 25% Class Participation/Classwork
 Course Description: Class Policies: 8 TH GRADE AMERICAN HISTORY CURRICULUM MAP Unit One: Development of Industrial America Unit Two: The Emergence of Modern America Unit Three: The Depression and World
Course Description: Class Policies: 8 TH GRADE AMERICAN HISTORY CURRICULUM MAP Unit One: Development of Industrial America Unit Two: The Emergence of Modern America Unit Three: The Depression and World
Unit 7.4: World War II
 Unit 7.4: World War II 1942-1945 Germany used blitzkrieg tactics to dominate Eastern & Western Europe England was wounded from German attacks in the Battle of Britain Hitler broke the Nazi-Soviet Nonaggression
Unit 7.4: World War II 1942-1945 Germany used blitzkrieg tactics to dominate Eastern & Western Europe England was wounded from German attacks in the Battle of Britain Hitler broke the Nazi-Soviet Nonaggression
US History Mr. Martin Unit 7: The Birth of Modern America Chapters 13-16
 US History Mr. Martin Unit 7: The Birth of Modern America Chapters 13-16 This unit explores the transformation of the US from a rural nation into an industrial, urban nation during the period from 1865
US History Mr. Martin Unit 7: The Birth of Modern America Chapters 13-16 This unit explores the transformation of the US from a rural nation into an industrial, urban nation during the period from 1865
Jeopardy Chapter 26. Sec. 3 Sec. 3 Sec. 3 Sec. 3 Sec. 3 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200
 Jeopardy Chapter 26 Sec. 3 Sec. 3 Sec. 3 Sec. 3 Sec. 3 Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400
Jeopardy Chapter 26 Sec. 3 Sec. 3 Sec. 3 Sec. 3 Sec. 3 Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400
First Nine Weeks. 1. Have students define region.
 First Nine Weeks : USII.2c The student will use maps, globes, pictures or tables for locating the 50 states and the cities most significant to the historical development of the United States. USII.1f,g
First Nine Weeks : USII.2c The student will use maps, globes, pictures or tables for locating the 50 states and the cities most significant to the historical development of the United States. USII.1f,g
PERMISSIBILITY OF ELECTRONIC VOTING IN THE UNITED STATES. Member Electronic Vote/ . Alabama No No Yes No. Alaska No No No No
 PERMISSIBILITY OF ELECTRONIC VOTING IN THE UNITED STATES State Member Conference Call Vote Member Electronic Vote/ Email Board of Directors Conference Call Vote Board of Directors Electronic Vote/ Email
PERMISSIBILITY OF ELECTRONIC VOTING IN THE UNITED STATES State Member Conference Call Vote Member Electronic Vote/ Email Board of Directors Conference Call Vote Board of Directors Electronic Vote/ Email
EOCT Practice Questions. 1) The Spanish-American War was the first war fought by the United States in which it
 1) The Spanish-American War was the first war fought by the United States in which it A. acquired overseas possessions B. tested tanks in battle C. used the Panama Canal D. allied with a foreign power
1) The Spanish-American War was the first war fought by the United States in which it A. acquired overseas possessions B. tested tanks in battle C. used the Panama Canal D. allied with a foreign power
AMERICA AND THE WORLD. Chapter 13 Section 1 US History
 AMERICA AND THE WORLD Chapter 13 Section 1 US History AMERICA AND THE WORLD THE RISE OF DICTATORS MAIN IDEA Dictators took control of the governments of Italy, the Soviet Union, Germany, and Japan End
AMERICA AND THE WORLD Chapter 13 Section 1 US History AMERICA AND THE WORLD THE RISE OF DICTATORS MAIN IDEA Dictators took control of the governments of Italy, the Soviet Union, Germany, and Japan End
One Stop Shop For Educators. Grade Five
 Grade Five UNITED STATES HISTORY SINCE 1860 In fifth grade, students continue their formal study of United States history. As with fourth grade, the strands of history, geography, civics, and economics
Grade Five UNITED STATES HISTORY SINCE 1860 In fifth grade, students continue their formal study of United States history. As with fourth grade, the strands of history, geography, civics, and economics
CPWH Agenda for Unit 12.3: Clicker Review Questions World War II: notes Today s HW: 31.4 Unit 12 Test: Wed, April 13
 Essential Question: What caused World War II? What were the major events during World War II from 1939 to 1942? CPWH Agenda for Unit 12.3: Clicker Review Questions World War II: 1939-1942 notes Today s
Essential Question: What caused World War II? What were the major events during World War II from 1939 to 1942? CPWH Agenda for Unit 12.3: Clicker Review Questions World War II: 1939-1942 notes Today s
Write the letter of the description that does NOT match the name or term.
 Page 1 Write the letter of the description that does NOT match the name or term. 1. Joseph Stalin a. totalitarian b. Communist c. launched a massive drive to collectivize agriculture d. entered into a
Page 1 Write the letter of the description that does NOT match the name or term. 1. Joseph Stalin a. totalitarian b. Communist c. launched a massive drive to collectivize agriculture d. entered into a
STATE LAWS SUMMARY: CHILD LABOR CERTIFICATION REQUIREMENTS BY STATE
 STATE LAWS SUMMARY: CHILD LABOR CERTIFICATION REQUIREMENTS BY STATE THE PROBLEM: Federal child labor laws limit the kinds of work for which kids under age 18 can be employed. But as with OSHA, federal
STATE LAWS SUMMARY: CHILD LABOR CERTIFICATION REQUIREMENTS BY STATE THE PROBLEM: Federal child labor laws limit the kinds of work for which kids under age 18 can be employed. But as with OSHA, federal
ACTION: Notice announcing addresses for summons and complaints. SUMMARY: Our Office of the General Counsel (OGC) is responsible for processing
 This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 02/23/2017 and available online at https://federalregister.gov/d/2017-03495, and on FDsys.gov 4191-02U SOCIAL SECURITY ADMINISTRATION
This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 02/23/2017 and available online at https://federalregister.gov/d/2017-03495, and on FDsys.gov 4191-02U SOCIAL SECURITY ADMINISTRATION
Name 1. Why were the League of Nations and the United Nations created? A.
 Name 1. Why were the League of Nations and the United Nations created? A. to end world hunger B. to prevent future wars C. to unify the world economy D. to spread democracy in the world 2. How did the
Name 1. Why were the League of Nations and the United Nations created? A. to end world hunger B. to prevent future wars C. to unify the world economy D. to spread democracy in the world 2. How did the
Fifth Grade Social Studies Essential Facts
 Fifth Grade Social Studies Essential Facts Reconstruction 1. Reconstruction was the rebuilding and healing of the country after the Civil War. 2. The 13 th amendment abolished slavery in 1865. 3. The 14th
Fifth Grade Social Studies Essential Facts Reconstruction 1. Reconstruction was the rebuilding and healing of the country after the Civil War. 2. The 13 th amendment abolished slavery in 1865. 3. The 14th
VUS. 8.c&d: Immigration, Discrimination, and The Progressive Era
 Name: Date: Period: VUS 8c&d: Immigration, Discrimination, and The Progressive Era Notes VUS8c&d: Immigration, Discrimination, and the Progressive Era 1 Objectives about Title VUS8 The student will demonstrate
Name: Date: Period: VUS 8c&d: Immigration, Discrimination, and The Progressive Era Notes VUS8c&d: Immigration, Discrimination, and the Progressive Era 1 Objectives about Title VUS8 The student will demonstrate
FIGHTING WWII CHAPTERS 36-37
 FIGHTING WWII CHAPTERS 36-37 AFTER PEARL HARBOR The U.S. was not prepared Not enough navy vessels German U-boats were destroying ships off the Atlantic coast Hard to send men and supplies Could not fight
FIGHTING WWII CHAPTERS 36-37 AFTER PEARL HARBOR The U.S. was not prepared Not enough navy vessels German U-boats were destroying ships off the Atlantic coast Hard to send men and supplies Could not fight
Europe and North America Section 1
 Europe and North America Section 1 Europe and North America Section 1 Click the icon to play Listen to History audio. Click the icon below to connect to the Interactive Maps. Europe and North America Section
Europe and North America Section 1 Europe and North America Section 1 Click the icon to play Listen to History audio. Click the icon below to connect to the Interactive Maps. Europe and North America Section
Unit 7 Study Guide. Period 7.2:
 Unit 7 Study Guide Period 7.2: 1920 1945 In a Nutshell An increasingly pluralistic United States faced profound domestic and global challenges, debated the proper degree of government activism, and sought
Unit 7 Study Guide Period 7.2: 1920 1945 In a Nutshell An increasingly pluralistic United States faced profound domestic and global challenges, debated the proper degree of government activism, and sought
WARM UP: Today s Topics What were the major turning points. in WW2? How did the Allies compromise with one another?
 WARM UP: Today s Topics What were the major turning points in WW2? How did the Allies compromise with one another? From 1939 to 1942, the Axis Powers dominated Europe, North Africa, & Asia Germany used
WARM UP: Today s Topics What were the major turning points in WW2? How did the Allies compromise with one another? From 1939 to 1942, the Axis Powers dominated Europe, North Africa, & Asia Germany used
Matthew Miller, Bureau of Legislative Research
 Matthew Miller, Bureau of Legislative Research Arkansas (reelection) Georgia (reelection) Idaho (reelection) Kentucky (reelection) Michigan (partisan nomination - reelection) Minnesota (reelection) Mississippi
Matthew Miller, Bureau of Legislative Research Arkansas (reelection) Georgia (reelection) Idaho (reelection) Kentucky (reelection) Michigan (partisan nomination - reelection) Minnesota (reelection) Mississippi
Case 3:15-md CRB Document 4700 Filed 01/29/18 Page 1 of 5
 Case 3:15-md-02672-CRB Document 4700 Filed 01/29/18 Page 1 of 5 Michele D. Ross Reed Smith LLP 1301 K Street NW Suite 1000 East Tower Washington, D.C. 20005 Telephone: 202 414-9297 Fax: 202 414-9299 Email:
Case 3:15-md-02672-CRB Document 4700 Filed 01/29/18 Page 1 of 5 Michele D. Ross Reed Smith LLP 1301 K Street NW Suite 1000 East Tower Washington, D.C. 20005 Telephone: 202 414-9297 Fax: 202 414-9299 Email:
World War II Exam One &
 World War II Exam One 2.11.09 & 2.12.09 Standards Assessed: SS5H6 The student will explain the reasons for America s involvement in World War II. a. Describe Germany s aggression in Europe and Japanese
World War II Exam One 2.11.09 & 2.12.09 Standards Assessed: SS5H6 The student will explain the reasons for America s involvement in World War II. a. Describe Germany s aggression in Europe and Japanese
Addressed Identify various roles each branch of the government has.
 Unit 1: The Constitution of The United States Identify various roles each branch of the government has. Explain the organization of the Constitution. Define and translate the Preamble. Describe similarities
Unit 1: The Constitution of The United States Identify various roles each branch of the government has. Explain the organization of the Constitution. Define and translate the Preamble. Describe similarities
UNIT 5 World War II and Its Aftermath Date. Russia Renamed
 Chapter 16: World War Looms Dictators Threaten Peace Nationalism Joseph Stalin Takes Over Russia Russian Revolution (1917) Lenin Russia Renamed To control areas, the communists 1 2 3 Totalitarian Benito
Chapter 16: World War Looms Dictators Threaten Peace Nationalism Joseph Stalin Takes Over Russia Russian Revolution (1917) Lenin Russia Renamed To control areas, the communists 1 2 3 Totalitarian Benito
$100 People. WWII and Cold War. The man who made demands at Yalta who led to the dropping of the "iron curtain" around the eastern European countries.
 People WWII and Cold War Jeopardy Between the Geography Treaties and Battles of Wars WWII Hot Spots of the Cold War $100 People WWII and Cold War $100 People WWII and Cold War Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100
People WWII and Cold War Jeopardy Between the Geography Treaties and Battles of Wars WWII Hot Spots of the Cold War $100 People WWII and Cold War $100 People WWII and Cold War Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100
ii. Nazi strategy e. Battle of the Bulge, December 16, 1944 f. V-E day, May 8, 1945 V. Hitler s forced labor plan a. People from German occupied
 Outline of Content: (Suggestions: Take notes with each assignment and use this out line. You will be reading different sources so it is best for your learning to take notes from the beginning of the unit
Outline of Content: (Suggestions: Take notes with each assignment and use this out line. You will be reading different sources so it is best for your learning to take notes from the beginning of the unit
The Victim Rights Law Center thanks Catherine Cambridge for her research assistance.
 The Victim Rights Law Center thanks Catherine Cambridge for her research assistance. Privilege and Communication Between Professionals Summary of Research Findings Question Addressed: Which jurisdictions
The Victim Rights Law Center thanks Catherine Cambridge for her research assistance. Privilege and Communication Between Professionals Summary of Research Findings Question Addressed: Which jurisdictions
05 WLE SS All Domains (05wlessalldomains)
 05 WLE SS All Domains (05wlessalldomains) Name: Date: 1. Use the list below to answer this question. Germany invades Poland. the Holocaust V-E Day V-J Day All of these are associated with A. the Spanish-American
05 WLE SS All Domains (05wlessalldomains) Name: Date: 1. Use the list below to answer this question. Germany invades Poland. the Holocaust V-E Day V-J Day All of these are associated with A. the Spanish-American
Social Studies Curriculum Guide GSE FIFTH GRADE
 Social Studies Curriculum Guide GSE FIFTH GRADE March 2017 1 Grade/Course: Grade Five United States History Since 1860 Standards: H1a, b, c, d; G1a; G2a, b; CG1a-b; E1b, d; E3a-c 2.5 weeks Standards: H2a,
Social Studies Curriculum Guide GSE FIFTH GRADE March 2017 1 Grade/Course: Grade Five United States History Since 1860 Standards: H1a, b, c, d; G1a; G2a, b; CG1a-b; E1b, d; E3a-c 2.5 weeks Standards: H2a,
5 SUGGESTED CLASSROOM INSTRUCTIONAL TIME
 Grade 5 SUGGESTED CLASSROOM INSTRUCTIONAL TIME + + + 200 MINUTES PER WEEK + + + Grade 5 United States: Continuing Development of the United States Social Studies in grade five concentrates on the development
Grade 5 SUGGESTED CLASSROOM INSTRUCTIONAL TIME + + + 200 MINUTES PER WEEK + + + Grade 5 United States: Continuing Development of the United States Social Studies in grade five concentrates on the development
STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015
 STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015 AGE OF IMPERIALISM! (1900s- 1914) MILITARY Alfred T. Mahan argued for a strong NAVY in his book Influence of Sea Power Upon History Easier
STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015 AGE OF IMPERIALISM! (1900s- 1914) MILITARY Alfred T. Mahan argued for a strong NAVY in his book Influence of Sea Power Upon History Easier
7-45. Electronic Access to Legislative Documents. Legislative Documents
 Legislative Documents 7-45 Electronic Access to Legislative Documents Paper is no longer the only medium through which the public can gain access to legislative documents. State legislatures are using
Legislative Documents 7-45 Electronic Access to Legislative Documents Paper is no longer the only medium through which the public can gain access to legislative documents. State legislatures are using
The Building of Modern America, Part 1. The Transcontinental Railroad and the Rise of the American City
 The Building of Modern America, Part 1 The Transcontinental Railroad and the Rise of the American City SSUSH11 The student will describe the growth of big business and technological innovations after Reconstruction.
The Building of Modern America, Part 1 The Transcontinental Railroad and the Rise of the American City SSUSH11 The student will describe the growth of big business and technological innovations after Reconstruction.
D-Day Gives the Allies a Foothold in Europe
 D-Day Gives the Allies a Foothold in Europe On June 6, 1944, Allied forces under U.S. general Dwight D. Eisenhower landed on the Normandy beaches in history s greatest naval invasion: D-Day. Within three
D-Day Gives the Allies a Foothold in Europe On June 6, 1944, Allied forces under U.S. general Dwight D. Eisenhower landed on the Normandy beaches in history s greatest naval invasion: D-Day. Within three
Decision Analyst Economic Index United States Census Divisions April 2017
 United States s Arlington, Texas The Economic Indices for the U.S. s have increased in the past 12 months. The Middle Atlantic Division had the highest score of all the s, with an score of 114 for. The
United States s Arlington, Texas The Economic Indices for the U.S. s have increased in the past 12 months. The Middle Atlantic Division had the highest score of all the s, with an score of 114 for. The
Chapter 17 WS - Dr. Larson - Summer School
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Chapter 17 WS - Dr. Larson - Summer School Matching IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS, PEOPLE, AND PLACES Match each name with his or her description below. You will not use all the names. a.
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Chapter 17 WS - Dr. Larson - Summer School Matching IDENTIFYING KEY TERMS, PEOPLE, AND PLACES Match each name with his or her description below. You will not use all the names. a.
Academic Calendar: (In alignment with Civics Content Expectations)
 Academic Calendar: (In alignment with Civics Content Expectations) 1st Quarter Marking Period: 6.1 Growth of an Industrial and Urban America Explain the causes and consequences both positive and negative
Academic Calendar: (In alignment with Civics Content Expectations) 1st Quarter Marking Period: 6.1 Growth of an Industrial and Urban America Explain the causes and consequences both positive and negative
Grade Seven History and Social Science: United States History, 1865 to the Present
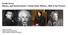 Grade Seven History and Social Science: United States History, 1865 to the Present Grade 7 Curriculum Loudoun County Public Schools Patricia Coggins, Instructional Supervisor The purpose of this curriculum
Grade Seven History and Social Science: United States History, 1865 to the Present Grade 7 Curriculum Loudoun County Public Schools Patricia Coggins, Instructional Supervisor The purpose of this curriculum
Content Connector. USH.2.4.a.1: Explain how the lives of American Indians changed with the development of the West.
 Standard 1: Early National Development: 1775 to 1877 Students review and summarize key ideas, events, and developments from the Founding Era through the Civil War and Reconstruction from 1775 to 1877.
Standard 1: Early National Development: 1775 to 1877 Students review and summarize key ideas, events, and developments from the Founding Era through the Civil War and Reconstruction from 1775 to 1877.
19 th Amendment. 16 th Amendment 17 th Amendment 18 TH Amendment established direct election of United States Senators by popular vote
 16 th Amendment 17 th Amendment 18 TH Amendment 1913-gave Congress the power to tax personal income 1913- established direct election of United States Senators by popular vote 1919- banned the sale of
16 th Amendment 17 th Amendment 18 TH Amendment 1913-gave Congress the power to tax personal income 1913- established direct election of United States Senators by popular vote 1919- banned the sale of
Unit 7: The Cold War
 Unit 7: The Cold War Standard 7-5 Goal: The student will demonstrate an understanding of international developments during the Cold War era. Vocabulary 7-5.1 OCCUPIED 7-5.2 UNITED NATIONS NORTH ATLANTIC
Unit 7: The Cold War Standard 7-5 Goal: The student will demonstrate an understanding of international developments during the Cold War era. Vocabulary 7-5.1 OCCUPIED 7-5.2 UNITED NATIONS NORTH ATLANTIC
THE IRON CURTAIN. From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic an iron curtain has descended across the continent. - Winston Churchill
 COLD WAR 1945-1991 1. The Soviet Union drove the Germans back across Eastern Europe. 2. They occupied several countries along it s western border and considered them a necessary buffer or wall of protection
COLD WAR 1945-1991 1. The Soviet Union drove the Germans back across Eastern Europe. 2. They occupied several countries along it s western border and considered them a necessary buffer or wall of protection
