PAKISTAN & THE TALIBAN
|
|
|
- Annabel Horton
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Published on South Asia Analysis Group ( Home > PAKISTAN & THE TALIBAN PAKISTAN & THE TALIBAN Submitted by asiaadmin2 on Thu, 09/20/ :37 paper by B. Raman In its keenness to assert the primacy of its national interests and strategic objectives through any means, the US has over the years made heroes out of surrogates, whose only qualification was that they were prepared to do its bidding. Ultimately, it ended up with the mortification of seeing these heroes of yesterday becoming the Frankensteins of today, endangering the very US national interests to protect which they were initially created. Afghanistan provides a good case study of this. The dramatis personae in the more than two-decade-old Afghan tragedy --whether Osama bin Laden and his terrorists' mafia, Mullah Mohammed Omar Akhund and his Taliban Shoora or the innumerable "Mujahideen" commanders and Pakistani jehadis playing havoc in different parts of the country in the name of Islam--- were all the original creations of the CIA, ably assisted by Pakistan's Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI). Through their depredations, they have made Afghanistan perhaps the only country in the world to register a decline in population with that of Kabul reduced by half and with the largest proportion, anywhere in the world, of widows with no male relatives. They have turned Afghanistan into a breeding ground of medieval obscurantist forces which have been spreading their tentacles to Dagestan and Chechnya in Russia, the Central Asian Republics (CARs), Xinjiang in China, Pakistan itself, Jammu & Kashmir in India, Bangladesh, Myanmar and Southern Philippines.
2 And the Americans have created for themselves a situation where the choice is not among various policy options, but policy nightmares. The way the Taliban, which was backed by the US from its creation in July,1994, to its capture of Kabul in September,1996, has heaped indignities on the women of Afghanistan and reduced them to less than human beings in the name of Islam, is without parallel anywhere else in the world. While justifying the attitude of the Taliban towards women's role in society, the then Taliban Ambassador in Islamabad, Maulvi Saeedur Rahman Haqqani, said at a seminar at Islamabad on May 2, 1999: "In Muslim societies, we respect and cherish our women. We treat them like precious jewels and keep them in an ornamental box." What is the ground reality? Under the pre-1992 Najibullah Government, 70 per cent of the academics--members of the teaching faculties of schools and colleges per cent of the medical personnel and 30 per cent of the Government servants in Afghanistan were women. They played an active role in politics and diplomacy too. This high percentage was due to the spread of higher education amongst women and also due to the shortage of men to occupy civilian jobs because of the enlistment of a large number of men in the army to fight the "mujahideen". After its capture of Kabul in 1996, the Taliban removed all girls from educational institutions, banned any fresh induction and sacked all women from jobs where they might have to interact with men. They are now allowed only in those jobs in which their interaction would be only with other women. Wearing of burqa was made obligatory. The Taliban promised to at least partially restore the educational rights of women after the war against the Northern Alliance ended and after the economic situation improved. One doesn't know when that would be, now that it is facing two wars---one against the Northern Alliance and the other against the USled international coalition. The results since 1996: * An Increase in the instances of suicide by war widows unable to support their children. * Before 1992, Kabul did not have a single woman beggar. In 1999, the figures for which are available, it had an estimated 35,000, most of them widows with children--former academics, doctors, nurses and government servants--with no other means of feeding their children. Visitors to Kabul had remarked on their shock and indignation at the Taliban when they discovered that behind many a burqa of beggars approaching them for alms stood an English or French or Russian-speaking woman, highly educated with a sophisticated and cultured mind. They were heartlessly sacked for no other reason than that they were women. The Mullahs' anger was particularly directed at women who had their higher education in Hindu India, Communist USSR or the "decadent" West, where, according to the Mullahs, women were allowed to
3 "run around like wild animals." * Some Western non-governmental Organisations (NGOs) started a vocational training centre where the children of these widows could be trained in some craft so that they could support themselves and their mothers. The Taliban banned the enrollment of girls in this centre. As a Pakistani columnist remarked: " It would seem that for the Taliban, training boys and girls together would be unislamic, but letting them beg together in the streets is not so." It is many of these begging women and children who have now been killed by the US air strikes. They had no place where they could take cover from the air strikes. * Women were banned from witnessing any sports meet. The only public gathering at which their presence was allowed and even encouraged was to witness the stoning to death of convicts for adultery. The anti-woman attitude of the Taliban was evident even from October,1994, onwards when it started curtailing the rights of women in town after town captured by it, but the outside world, particularly the US and West Europe, reacted against it only after the Mullahs started enforcing their orders not only against Afghan women in the entire territory under their control, but also against foreign women working in the offices of international organisations and NGOs after the capture of Kabul. Next to women, the Shias were a major target of the brutalities and indignities of the Wahabi-Sunni-dominated Taliban Shoora and its militia called Lashkar Mohammadi. Public observance of Moharrum was banned. So too the Shia tradition of their women joining the men in prayers during Moharrum and visits to graves of their relatives. The "News" of Pakistan (April 26,1999) quoted Mr.Ghulam Mohiuddin, a Shia leader of Afghanistan, as stating as follows: " Even the Hindus in India allow the Shias to practise their religion, but the Taliban are denying us this basic right." After the Taliban captured Herat on the Iran border and, subsequently, the Bamiyan province, there were reportedly large-scale massacres of the Shias and forcible re-settlement of the Shias in the Sunni-majority villages in the rest of Afghanistan and their replacement by Sunnis brought to Herat and Bamiyan from other provinces. This was done to reduce the Shias to a minority in their traditional homelands. Before October 7,2001,the Taliban had only three achievements to its credit---improvement of law and order, restoration of electricity supply in towns and resumption of farming in 70 per cent of the cultivable land in the country. Better law and order was through rigorous enforcement of Islamic punishments such as amputation of arms and stoning and crushing to death. Some Pakistani analysts pointed out that such punishments were more frequent against non-pashtoons and Shias than against Pashtoons and Sunnis.
4 The Taliban's agricultural policy benefitted poppy cultivation more, through priority in fertiliser distribution to poppy farmers than to cultivators of other agricultural products. While offences such as theft, housebreaking, murder, rape, adultery, sodomy etc were immediately punished after a sham of a trial, there was no Islamic punishment for heroin production and smuggling. There was a strongly suspected nexus involving the poppy farmers, all of them Afghan citizens, the heroin producers, all of them Pakistani drug barons resident in the North-West Frontier Province (NWFP) and in the Federally-Administered Tribal areas (FATA) of Pakistan and 30 Mullahs constituting the Kandahar-based Taliban Shoora with Mullah Mohammad Omar, the Amir, at the top. The only effective arm of the Taliban administration was the militia, which brought 90 per cent of the country under its control within five years, and the Ministry for the Promotion of Islamic Virtue and the Prevention of Vice. A new intelligence agency, largely officered and headed by serving and retired ISI officers, was created and placed under the direct control of the Amir. The militia was a hotchpotch of students from the madrasas in the NWFP, Balochistan and Sindh, former Pashtoon officers and soldiers of the late Najibullah's Soviet-trained armed forces and Pakistani ex-servicemen and serving military personnel, given leave of absence by the Pakistani military, to enable them assist the Taliban. The Pakistanis constituted about 70 per cent plus of the strength of the Taliban militia. During important battles, the militia was also assisted by Pakistani militant organisations such as the Harkat-ul-Mujahideen, the virulently anti-shia Sipahe- Sahaba Pakistan, the Harkat-ul-Jehad-e-Islami and the Lashkar-e-Toiba and the Arab volunteers of bin Laden's Al Quaeda (055 Brigade). Despite its hotchpotch character, the discipline and religious motivation of the militia have remained surprisingly strong. It fought extremely well against the forces of the Northern Alliance led by the late Gen. Ahmed Shah Masood and is now withstanding the US onslaught with no apparent signs of demoralisation as yet. The large casualties suffered by the militia during the battles for Mazar-e-Sharif in 1997 and 1998 and the battles in Bamiyan in 1998 and 1999 did not affect its morale. However, there were reports of difficulties being faced by the Taliban in making fresh recruitment to make up for the losses--particularly from the Durrani sub-tribe of the Pashtoons, which was the main recruiting ground in Afghanistan. These shortages were, however, made up by a fresh influx of madrasa jehadis and ex-servicemen from Pakistan. The rest of the administration was in a chaotic state. There was no functioning central bank; nor were there any gold reserves and officially accounted for foreign exchange reserves. The tax collection machinery was ineffective.
5 There was no public scrutiny of Government policies, decisions and actions, no open discussion of the state budget, no policy and decision making infrastructure. Policy and decision options were not examined for their likely impact on Afghanistan's future and on its relations with the rest of the world before being adopted. The Amir and his associates in the Shoora look upon themselves as on a divine mission and there is a touching, but disturbing faith in divine intervention to help them out of problems. Since they have convinced themselves that they have been the beneficiaries of divine guidance, they do not feel the need for human guidance and advice from the non-clerical, civilian bureaucracy, which has consequently been reduced to merely an instrument for carrying out the decisions of the clerics, without any voice in policy and decision-making. This delusion of a divine mission also made the Amir insensitive to public opinion not only inside the country, but also in the rest of the world. The Amir is strongly motivated by the Pashtoon concept of "izzat" (self-respect) and tends to look upon any suggestion of concessions to international opinion as an affront to his "izzat". This should explain his obstinate refusal to respond to outside pressures for controlling the spread of terrorism, to expel bin Laden and to control heroin production and smuggling. Afghanistan, under the Taliban, has two capitals --the administrative capital at Kabul, which is the seat of the Government which interacts with foreign interlocutors, and the spiritual capital at Kandahar, where the Amir, his Shoora and the intelligence agency headquarters were located before October 7,2001. The Amir was hoping that Kandahar would one day become the spiritual capital of triumphant Wahabi-Sunni forces in Dagestan, Chechnya, Xinjiang, Pakistan, Kashmir in India, Bangladesh, Myanmar and Southern Philippines. The Amir hails from village Nodeh and grew up in village Singesar in the Mewand District near Kandahar. Mewand is as holy and historic a place for the Pashtoons of Afghanistan as Kosovo is for the Serbs. According to Afghan historians, it was at Mewand that the Pashtoons trounced the advancing British troops. Malalai, a Pashtoon woman of Mewand, earned a heroic reputation by fighting shoulder to shoulder with her male brethren and rallying them against the British troops. What an irony of fate that the descendants of this heroic woman should find themselves chained inside a burqa by the descendants of her male brethren! It was as a protector of women's honour that the Amir won the admiration of the Pashtoons of Kandahar in July, 1994, when he gathered a group of boys from the local madrasas, raided the house of a local "Mujahideen" commander, who had become notorious as a rapist, and killed him. From a protector, he degenerated into an oppressor of women's rights.
6 The fact that the about 40-year-old Amir hailed from the legendary Mewand District gave him a halo in the eyes of the simple, God-fearing, proud Pashtoons and they followed his commands implicitly. Instead of leading them into the new millennium to make Afghanistan once again a tolerant, progressive Islamic state with equal rights for women and men, for Muslims and non-muslims, for Pashtoons and non-pashtoons, for Sunnis and Shias, he chose to lead them back to the middle ages in the name of God. The Amir is a man with little exposure to the world outside Kandahar and its environs. It is said that he has never travelled to the non-pashtoon areas. Many say he had never been to Kabul since it was captured by the Taliban in September,1996, but some others assert that he had visited it once. He hardly knows Pakistan outside Peshawar and Quetta. He lets the Mullahs of the Government in Kabul interact with domestic as well as foreign interlocutors. Since they do not know the Amir's mind while negotiating, one had the strange spectacle of the interlocutors from Kabul reaching agreements in principle to subsequently find these agreements rejected by the Amir. This was happening repeatedly. Before October 7,2001, the Pakistan Government's predominant influence in Taliban-controlled territory was mainly in the civilian administration, which had and continues to have many Pakistani advisers, the intelligence agency and the militia. Its influence in matters religious was limited. However, Pakistani religious leaders such as Maulana Fazlur Rahman and Maulana Samiul Haq had and continue to have very strong influence over the Amir and the other members of the Taliban leadership. The former Prime Minister, Mr.Nawaz Sharif, was intelligent and rational enough to realise that the obstinacy of the Amir and his Kandahar-based Shoora in dealing with issues such as the deportation of bin Laden, women's rights etc was creating serious difficulties for Pakistan in its relations with the US, that the anti-shia and anti-iran policies had caused a set-back to Pakistan's relations with Iran and that the Taliban's obscurantism had frustrated Pakistani aspirations of emerging as the gateway of Central Asia. However, he was unable to assert himself because there were---just as there are still--- too many Pakistani cooks spoiling the Afghan broth. These included the religious fundamentalist parties with Maulana Fazlur Rahman of the Jamaat-ul- Ulema Islam (JUI) in the forefront egging on the Amir and his Shoora to stick to their hard line, the Intelligence Bureau (IB), the ISI, the Directorate of Military Intelligence (DMI), Gen. Pervez Musharraf, and his then Chief of the General Staff (CGS), Lt.Gen. Mohammad Aziz, who is now a full General and is the Chairman of the Chiefs of Staff Committee.
7 During her second tenure as Prime Minister ( ), Mrs. Benazir Bhutto, who distrusted the ISI, let the IB working under the supervision of her Interior Minister, Maj.Gen. (retd) Nasirullah Babar, handle the Amir and his Taliban. Maj.Gen. Babar, a trusted officer of her father, the late Zulfiquar Ali Bhutto, was the head of the Afghan desk of the ISI under her father and used to claim that he could make the Afghan Pashtoons dance to Pakistan's tune. He used Musharraf, then Director-General of Military Operations (DGMI) and Mohammad Aziz in his Taliban operations despite Aziz's association with the ISI, which was distrusted by Benazir. On coming back to power in February, 1997,Sharif transferred the responsibility back to the ISI. The then Maj.Gen. Mohammad Aziz, who was the No.2 in the ISI, also directly supervised the Afghan desk. When Sharif appointed Lt.Gen. Khwaja Ziauddin, who comes from a family of Pakistan Muslim League loyalists, as the DG of the ISI in October,1998, Musharraf, who distrusted Ziauddin, had Maj.Gen.Aziz, then Deputy DG,ISI, promoted as Lt.Gen. and posted as the CGS instead of posting an already serving Lt.Gen. to this important post as was the tradition. Simultaneously, he had the responsibility for handling the Taliban transferred to the DMI and reportedly ordered that Lt.Gen. Aziz would continue to supervise this work. Addressing the English-speaking Union of Pakistan at Karachi on April 13,1999, Musharraf said that the collapse of the Taliban would lead to a disintegration of Afghanistan, which would not be in Pakistan's interest. He was of the view that Pakistan should continue to back the Taliban unmindful of US pressures and let time moderate the policies of the Mullahs. Since the middle of 1998, there were indications of unhappiness amongst the Mullahs of the administration in Kabul, who had to bear the brunt of the international criticism regarding the Taliban's policies on bin Laden and women's rights, over the unbending obstinacy of the Amir and his Mullahs of Kandahar. The Shoora was even reported to have foiled a coup attempt and made a number of arrests. The late Mullah Mohammad Rabbani, the then head of the interim ruling council in Kabul, who occupied the No 2 position in the Shoora and who was projected as the most trusted man of the Amir, was reported to have developed differences with the Amir when the latter rebuked him for not taking a strong line during the visit of Mr.Bill Richardson, the then US Permanent Representative to the UN, to Kabul in April, 1998 to discuss the terrorism issue. Thereafter, Mullah Rabbani did not enjoy the trust of the Amir and spent more time in Dubai for medical treatment than for doing his job in Kabul. He died of cancer in April last. The Amir has not so far appointed a regular head of Government in his place. The Shias of not only Afghanistan, but also Pakistan have been seething with anger against the Amir for the massacres of the Shias of Herat and Bamiyan. The Shias have a long memory for atrocities perpetrated on them as one saw in the death of Zia-ul-Haq in the plane crash of August,1988.
8 The NWFP has many Hazaras, the same tribe to which the Shias of Bamiyan belong, and the Hazaras are known to bide their time, even if it meant years, before avenging atrocities committed on them. On August 24, 1999, there was an unsuccessful attempt by unidentified elements allegedly to kill the Taliban Amir at Kandahar through an explosion outside his house. The explosion killed some bystanders, including a close relative of the Amir, but the Amir himself escaped. The Shias were suspected of having organised the explosion. Under Musharraf: After Musharraf seized power on October 12,1999, the presence of the Pakistani military-intelligence establishment in the Taliban-controlled territory increased and Afghanistan became a veritable Pakistani colony. This was facilitated by the past nexus of many of the Mullahs of the Taliban with Pakistan's military-intelligence establishment. Certain common characteristics define these Mullahs: * Many of them, though stated to be Kandahari Pashtoons, feel more comfortable talking in Urdu, the Pakistani official language, than in Pushtoo, their mother tongue, or Dari or Farsi, taught in the schools of Afghanistan before 1992 and used for official purposes by the then Government of the country. This is attributable to the fact that they were either born in Pakistan or grew up there. * Few of them except some like the Amir and Jalaluddin Haqqani had distinguished themselves in the jehad against the troops of the erstwhile USSR and of the then President Najibullah before Accounts by Taliban spokesmen and its supporters in Pakistan project the Amir as having played a legendary role in the jehad against the Soviet troops, during which, according to them, he lost an eye. However, these accounts are unverifiable and his detractors allege that he actually lost his eye as a child while playing with other children.
9 * Many of them started their career as clerics in Pakistan Army units. The late Zia-ul-Haq, a devout Deobandi, had a large number of clerics inducted into the Education Department to teach the Holy Koran and the Arabic language to school students and in Army units to teach the Holy Koran and to conduct the daily prayers. This policy was continued by the subsequent civilian Governments too under pressure from the military- intelligence establishment and the religious parties. Thus, even before their capture of power in Kandahar, Herat, Jalalabad and Kabul between 1994 and 1996, many of these clerics had a long history of association with Pakistan's military-intelligence establishment, having been paid Government servants of Pakistan. * Having spent a large part of their lives in Pakistan, few of them knew Afghanistan outside Kandahar before they were placed in power by Pakistan's military-intelligence establishment. * Not having fought before 1994, few of them had any military experience and hardly ever having lived in the country before 1994, none of them had any political and administrative acumen. The post-1994 battles, which led to the Taliban ostensibly assuming control over 90 per cent of the country's territory, were largely waged by militias, consisting of Pakistani servicemen and ex-servicemen, trained jehadists of Pakistan's Islamic parties and the dregs of Najibullah's army and of the various Pashtoon-dominant Mujahideen groups, which had distinguished themselves in the battles against the Soviet troops in the 1980s. Since the Taliban has had no experience of running the administration, the administrative chores in the capital Kabul and in the rest of the country were largely performed by retired Pakistani civil servants assisted by the civil administrators of Najibullah. Before October 7, 2001, there was a clear division of responsibilities between the clerics of the Taliban on the one side and the serving and retired public servants of the Pakistani military-intelligence establishment and civilian Government services on the other. While retaining a strict control over political, military and administrative affairs, Pakistan's military-intelligence establishment had left considerable autonomy of functioning to the Taliban in religious matters. As a result, the obscurantist fervour of the Taliban assumed an autonomous momentum of its own as was seen in its suppression of the political, economic and social rights of women, its export of terrorism in the name of jehad to the Central Asian Republics (CARs), Chechnya and Dagestan in Russia and even Xinjiang in China, much to the discomfiture of Pakistan, and its destruction of the Buddha statues of Bamiyan in the beginning of this year. The Taliban rejected foreign allegations that it was running training camps for Islamic terrorists in its territory. It did admit, however, that there were camps where Muslims from different nations studied the Holy Koran and the Sharia, learnt to live, work and eat together and were trained in the use of weapons of self-defence so that they could protect themselves and their religion. It compared such camps to the Israeli kibbutz and criticised what it described as the hypocrisy of the non-islamic world in accepting the kibbutz as legitimate centres for community living and self-defence, but denouncing similar camps in its territory as terrorist training camps. It did not deny that Osama bin Laden, reportedly related by marriage to the Amir, had been given sanctuary and hospitality in its territory. It pointed out that the decision to let him come and live in Afghan territory was taken by the Burhanuddin Rabbani Government, in consultation with the Benazir Bhutto
10 Government, before the Taliban captured Kabul in September, 1996, and criticised the US for campaigning against the presence of bin Laden only after the fall of the Rabbani Government. It asserted that it kept a tight watch over his activities to prevent him from indulging in terrorism and said that it was prepared to hand him over for a trial only if the trial was to be held according to the Sharia in an Islamic country. The Taliban's obscurantist fervour started threatening to infect the civil society in Pakistan itself, aggravating the sectarian divide between the Sunnis and the Shias and the medievalisation and the warlordisation of the die-hard Islamic elements, particularly in the Federally-Administered Tribal Areas (FATA) and the North-West Frontier Province (NWFP). This consequently gave rise to the oft-expressed fears of a possible Talibanisation and medievalisation of Pakistan itself. Pakistan is not the first country to be affected by the contagion of Islamic fundamentalism. Many other Islamic countries had earlier seen the rise and, sometimes, even triumph of fundamentalist elements. But, what distinguishes Islamic fundamentalism in Pakistan from that in other countries is the irrational mindset of those in the forefront of the fundamentalist drive. This irrational mindset is seen in their words and actions such as their emphasis on the religious duty of the Muslims to acquire weapons of mass destruction (WMD) not only to defend the Islamic State of which they form part, but also their religion, their oft-expressed willingness to consider using WMD, if necessary, to defend Islam, their chattelisation of women etc. The Pakistani madrasas, which have been the breeding ground of this religious irrationality, had infected the clerics too, whom Pakistan's militaryintelligence establishment had constituted into the Taliban. The establishment turned a blind eye to it in its eagerness to use the Mullahs to assume control over Afghanistan, but its folly came home to roost, post September 11,2001. The action of the Taliban earlier this year in dynamiting the statues of the Buddha in Bamiyan was but one more expression of this irrationality inherited by the Mullahs of the Taliban from their mentors and masters in Pakistan. Earlier, they enslaved the women of Afghanistan in the name of Allah, looted the Buddhist cultural treasures in the Kabul museum in 1996 in the name of Allah, massacred the Uzbecks of Mazar-e-Sharif and the Shias of Bamiyan in the name of Allah and then sought to destroy Allah Himself or rather a manifestation of Allah in the name of Allah. However, the destruction of the statues of the Buddha was not the first act of cultural and religious vandalism in Afghanistan. An equally outrageous act of vandalism was seen after Najibullah was overthrown in April 1992 and after the Pakistani led and staffed militias captured Kabul in September, In April 1992, after the Mujahideen captured power in Kabul, Lt.Gen. (retd) Hamid Gul, Ms.Benazir Bhutto's Director-General of the Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI) in her first tenure, Lt.Gen. (retd) Javed Nasir, DG, ISI, under Mr.Nawaz Sharif, and many other senior officers of the militaryintelligence establishment rushed to Kabul to take possession of the Soviet-supplied Scud missiles from the armoury of the fallen Najibullah's army. After doing so, they helped themselves to whatever Buddhist artifacts they could lay hands on in the Kabul museum.
11 Those left behind by them were loaded into Pakistani army trucks by Pakistani military and intelligence officers in September 1996 and shifted to Pakistan for being sold to international art smugglers. Major-General Babar and Musharraf justified the shifting of the artifacts to Pakistan by saying that they would be kept in the safe custody of the Pakistan Government and restored to Afghanistan once the fighting ended and a Government enjoying the support of all ethnic groups was set up in Kabul. International media and public opinion closed their eyes to this cultural vandalism reminiscent of the vandalism perpetrated by the Nazis in the occupied territories during the World War till the "Guardian" of the UK and the "Sydney Morning Herald" of Australia exposed it in articles published last year. Against this background, the absence of feelings of outrage in large sections of Pakistani society and in the regime itself and the muted reactions Musharraf over the destruction of the Buddha statues was not a matter of surprise. What was a matter of surprise and concern to all right-thinking persons was that after the initial expression of outrage, the rest of the world tried to rationalise, in retrospect, the Taliban's act of vandalism with the argument that the isolation of the Taliban and the lack of engagement with it might have contributed to its outrageous act. This was exactly what Pakistan and the Taliban wanted the world to believe. Since taking over as the Chief of the Army Staff (COAS) in October, 1998, Musharraf's conduct in relation to the bin Laden issue was anything but straight. On seizing power on October 12,1999, he countermanded the orders of Sharif to the ISI to co-operate with the CIA in a commando operation to capture bin Laden and take him away to the US just as it had co-operated in the capture and the whisking away to the US of Mir Aimal Kansi, who assassinated two CIA officers in Langley in January, 1993, and Ramzi Yousef, involved in the explosion in the New York World Trade Centre in February, When the then President Clinton visited Pakistan in March, 2000, Musharraf assured him that he would himself visit Kandahar and persuade the Amir to co-operate with the US in the bin Laden case. He went back on this assurance. Instead, he sent to Kandahar his Interior Minister, Lt.Gen.(retd) Moinudeen Haider, to meet the Amir. Haider came back and reported the failure of his mission. Musharraf thereupon advised the US to interact directly with the Taliban since, according to him, the Taliban was not amenable to Pakistani influence. Musharraf continued to give the impression to Washington as if he was still trying hard to moderate the Taliban and persuade it to co-operate with the US in the deportation and trial of bin Laden and to release the American, German and Australian volunteers of the Shelter Now International organisation, who are currently detained in Kabul on charges of indulging in Christian missionary work under the cover of humanitarian relief.
12 He was under tremendous pressure from Washington on the Taliban issue. The US was more concerned over the threats to its nationals emanating from the Taliban, bin Laden and his International Islamic Front For Jehad against the US and Israel than over the escalation in terrorism in J & K and over the threats to the lives of non-americans from the same jehadis in other parts of the world. Moderating, if not countering, the Taliban was one of the main themes of the discussions during the feverish comings and goings between Islamabad and Washington between June and September,2001--the visits Mr.Abdul Sattar, the Pakistani Foreign Minister, to the US in June, of Mrs.Christina Rocca, the US Assistant Secretary of State for South Asia, to Pakistan July-end/beginning August, of a three-member team of the US Congressional Intelligence Oversight Committees led by Mr.Bob Graham, Chairman of the Senate Select Committee on Intelligence, to Pakistan in August, of Mr.Inamul Haq, the Pakistani Foreign Secretary, to Washington in August, of Gen.Charles F.Wald, chief of the US Air Force in the US Central Command, to Pakistan in August and of Lt.Gen.Mahmood Ahmed, the then Director-General of the Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI), to Washington in September. During these meetings, Pakistan, as in the past, claimed that it had very little influence over the Taliban and, at the same time, promised that, despite this, it would try its best to moderate the Taliban. One of the main purposes of the ISI chief's visit to the US was also to plead with the US to delay the stationing of UN monitors in Pakistani territory to monitor the implementation of the UN sanctions against the Taliban regime, which was strongly opposed by the religious organisations. Musharraf was also attributing the unabated activities of Islamic extremists from the Pakistan-Afghanistan region to India's alleged atrocities in J&K, which, according to him, was acting as fuel and oxygen to the religious extremist fire. While thus projecting to the US the image of a reasonable, co-operative man, who was as concerned as the US over the activities of the Taliban, he and Aziz covertly egged on the Taliban and bin Laden's forces to escalate their attacks on the Northern Alliance and complete quickly their conquest of the areas under the control of the Alliance before the US pressure became irresistible and Washington resorted to a more active response against the Taliban. The Taliban, at the urging of Musharraf, stepped up its offensive against the Northern Alliance, and the explosion triggered off on September 9,2001, by two Arab (Algerian?) suicide bombers of bin Laden, who were interviewing Ahmed Shah Masood, the Commander of the Northern Alliance, under the cover of TV journalists, was choreographed from the ISI headquarters in Pakistan. On September 12,2001, within 24 hours of the jehadi terrorist attacks in New York and Washington DC,Musharraf, after consulting his Corps Commanders, ordered an emergency scram to evacuate from the Taliban-controlled Afghan territory, all Pakistani Govt. personnel, serving as well as retired, serving in the Taliban's militia, civil administration and intelligence agency, and all jehadis belonging to the Harkat-ul-Mujahideen (HUM), the Lashkar-e-Toiba (LET), the Jaish-e-Mohammad (JEM) and the Al Badr undergoing training in the training camps in Afghan territory.
13 Airports, including the one in Islamabad, were temporarily closed for traffic to enable the evacuation by air from Kabul and Kandahar of all senior Army officers, serving and retired, serving in the Taliban. Under the UN sanctions, there is a ban on all flights to and from the Taliban-controlled territory. Despite this, Musharraf and his officers decided to take a risk by evacuating the senior officers by air. All junior officers and civilian personnel were ordered to return to Pakistan by road as best as they could. Similar instructions were issued to the jehadis undergoing training in Afghan territory, preparatory to their induction into Jammu & Kashmir. The two visits by Lt.Gen.Mahmood Ahmed, the then DG, ISI, to Kandahar---on the second occasion with a group of Pakistani Mullahs---ostensibly to pressurise Mulla Mohammad Omer to hand over bin Laden to the US or to an European country was at least partly meant to gain time to complete the evacuation of Pakistani Government personnel and the jehadis. However, there was no evacuation, either actual or ordered, of the Pakistani students of the various madrasas in Pakistan, most of them belonging to Maulana Fazlur Rahman's JUI, who have been fighting along with the Taliban Militia against the Northern Alliance troops. They were reportedly asked to stay on and continue to assist the Taliban Militia. Islamabad's military junta was worried that the evacuation of the Pakistani Army personnel and any disruption of the Taliban's Militia set-up by US air strikes might enable the Northern Alliance to re-capture Kabul and other territory lost to the Taliban since September,1996. The junta was and continues to be worried that if the Taliban's resistance against the Northern Alliance collapses and the Burhanuddin Rabbani Government returns to power in Kabul, it would be strongly anti-pakistan and pro-india, pro-russia and pro-iran. It wants to prevent this from happening. In the meanwhile, the death of at least 35 jehadis of the HUM fighting with the Taliban against the Northern Alliance due to the US air strikes created considerable embarrassment for Musharraf, who has till now been maintaining that the HUM is an India-based indigenous Kashmiri freedom-fighters' organisation despite its offices being located in Pakistan and its leaders indulging in open activities in Pakistani territory and that there are no Pakistanis in the Taliban. Renowned international defence experts have been saying since the Taliban captured Kabul in September,1996, that it is a largely Pakistani organisation, clandestinely controlled and guided by the military-intelligence establishment. In a special assessment on the Taliban's fighting potential issued on October 8,2001, the day after the US air strikes started, the "Jane's Defence Weekly" of London stated as follows:
14 * "The Taliban have displayed an innovative approach to warfare characterised by the use of surprise, mobility, speed, impressive logistics support and an efficient command, control, communications and intelligence (C3I) network. * " All unusual in the context of warfare in Afghanistan, these elements, along with other evidence, have lent credence in the past to reports of involvement at both planning and operational levels by Pashto-speaking Pakistani military intelligence advisers or technically retired Pakistani military personnel acting on secondment. This was the case during the Taliban's 1998 Summer and Autumn campaign and 1999 Summer offensive. * "Taliban forces have generally come from three distinct backgrounds: former students of madrassas (religious schools) in both Pakistan and Afghanistan, who constitute the ideological core of the movement; former Mujahideen or jihadi (holy war) groups whose commanders joined the Taliban for financial or ethnic reasons; and officers of the former pre-1992 Afghan Army, many from the hard line, Pashtun nationalist Khalq (Masses) wing of the communist party. The latter have formed a skilled, professional core in artillery, armour, communications and in the air force, but some of these former communists were purged in late * "More recently, another distinct element has been playing an important military role: Pakistani and Arab religious volunteers. The Arabs, mostly deployed on front lines north of Kabul, are estimated to number between 500 and 600. Pakistani volunteers are far more numerous. By late 1998, as many as 9,000 to 10,000 Pakistanis were serving in Taliban ranks. These different backgrounds have inevitably resulted in some friction. To minimise this, Taliban troops are kept in separate units based on nationality and, in some cases, region, district, or tribe. " Since the beginning of the US-UK air strikes, at least another 3,000 volunteers from the Binori (Karachi) and other madrasas in Pakistan are estimated to have been rushed to the North to join the jehad against the US declared by the Taliban Amir. Some of the jehadis of organisations such as the HUM, the Lashkar-e-Toiba, the Harkat-ul-Jehad-e-Islami etc, who were withdrawn post-haste after September 11, have been sent back to North Afghanistan to assist the Taliban against the Northern Alliance. Initially, the US and the UK heeded the request of Musharraf to refrain from bombing the forward positions lest this enable the Northern Alliance capture Kabul. However, there has been an unannounced change in their position since October 18,2001, when they not only started bombing the forward positions ignoring Musharraf's pleas not to do so, but also concentrating the air strikes against the 055 Brigade of bin Laden and the Pakistani units, which are identifiable distinctly. Reports from the North say that the American commanders, who have been surprised by the continuing good morale of the Taliban leadership, the unity of its leaders and by their dogged resistance, have concluded that it is the presence of the large number of well-trained Pakistani jehadis and Arabs which has
15 been preventing the collapse of the Afghan component of the Taliban. They seem to feel that till the Arabs and the Pakistanis are neutralised, the Taliban cannot be defeated. This has been resulting in increasing number of casualties among the Pakistanis. The initial refusal of the Pakistani junta to let the dead bodies of the HUM jehadis killed by US strikes be brought to Karachi for burial on October 24 under the pretext that they were not Pakistanis led to violent demonstrations in Karachi with the Police being forced to open fire to control the demonstrators. Ultimately, the military junta relented and let the bodies be taken to Karachi. The Harkat-ul-Jehad-e-Islami announced in Karachi on November 8,2001, that 85 of its jehadis, including two senior commanders, have been killed in North Afghanistan. Their body bags have not yet been brought to Pakistan. Two significant aspects of the first month of the US "war" in Afghanistan need to be highlighted: * Almost all the civilians killed (estimate 2,000 plus) are poor Afghans. * Almost all the Taliban militia personnel killed (500 plus, including about 20 Arabs) are Pakistanis. The HUM and the Harkat-ul-Jehad-e- Islami have publicly admitted their fatal casualties ( a total of 120 ). The JUI, the Sipah-e-Sahaba, the LET and other Pakistani organisations have not admitted theirs. The USA seems to be determined to continue the air strikes on the Pakistani units with the Taliban even at the risk of the continued arrival of body bags in Karachi, Peshawar, Quetta and Lahore inflaming the local population and weakening further the position of Musharraf. It is said in Islamabad that the US military commanders have started showing signs of disquiet over the wisdom of depending on the assurances of Musharraf. There is a creeping feeling that Musharraf has not been sharing with them real time intelligence of value, has been deliberately avoiding giving any intelligence about the location of the Taliban and the Al Qaeda leadership and has not been taking any action to stop the fresh influx of jehadis to join the Taliban ranks and against many retired officers of Pakistan's military-intelligence establishment, who have been advising the Taliban on how to counter the US. It is these retired officers, who had learnt Psywar techniques from the CIA in the 1980s, who are behind the Psywar savvy being displayed by the Taliban. In the US media, one could already discern increasing signs of doubts over the wisdom of their action in having hastily embraced Musharraf and showering lollipops on him in anticipation of his helping the US capture bin Laden and his brains trust, which he shows no signs of doing. The Pakistani military-intelligence establishment has practically been running till September 10,2001, the Taliban militia and intelligence. If it had sincerely wanted to help the US capture bin Laden and his associates, they would have been by now dead or alive in US custody. The fact that this has not yet happened is eloquent testimony to Pakistan's double game.
16 Note: This is an updated and consolidated version of the papers on the subject disseminated by us since September, (The writer is Additional Secretary (retd), Cabinet Secretariat, Govt. of India, and, presently, Director, Institute for Topical Studies, Chennai. [1] ) Category: Papers [2] Countries: Afganistan [3] Copyright All Rights are Reserved. Source URL: Links [1] mailto:corde@vsnl.com [2] [3]
US-LED WAR AGAINST TERRORISM
 Published on South Asia Analysis Group (http://www.southasiaanalysis.org) Home > US-LED WAR AGAINST TERRORISM US-LED WAR AGAINST TERRORISM Submitted by asiaadmin2 on Tue, 09/25/2012-13:28 Paper No. 386
Published on South Asia Analysis Group (http://www.southasiaanalysis.org) Home > US-LED WAR AGAINST TERRORISM US-LED WAR AGAINST TERRORISM Submitted by asiaadmin2 on Tue, 09/25/2012-13:28 Paper No. 386
Americans to blame too August 29, 2007
 Americans to blame too August 29, 2007 India has celebrated the 60th anniversary of its independence. Sixty years is a long time in the life of a nation. On August 15, 1947, Jawaharlal Nehru announced
Americans to blame too August 29, 2007 India has celebrated the 60th anniversary of its independence. Sixty years is a long time in the life of a nation. On August 15, 1947, Jawaharlal Nehru announced
A Historical Timeline of Afghanistan
 A Historical Timeline of Afghanistan Soviet soldiers in Afghanistan The land that is now Afghanistan has a long history of domination by foreign conquerors and strife among internally warring factions.
A Historical Timeline of Afghanistan Soviet soldiers in Afghanistan The land that is now Afghanistan has a long history of domination by foreign conquerors and strife among internally warring factions.
Pakistan After Musharraf
 CARNEGIE ENDOWMENT FOR INTERNATIONAL PEACE Pakistan After Musharraf Q&A with: Frederic Grare, visiting scholar, Carnegie South Asia Program Wednesday, August 20, 2008 What are the implications of Musharraf
CARNEGIE ENDOWMENT FOR INTERNATIONAL PEACE Pakistan After Musharraf Q&A with: Frederic Grare, visiting scholar, Carnegie South Asia Program Wednesday, August 20, 2008 What are the implications of Musharraf
Weekly Geopolitical Report
 August 17, 2009 Pakistan and the Death of Baitullah Mehsud Reports indicated that on Aug. 5, Baitullah Mehsud, the notorious leader of the Taliban in Pakistan, died from a U.S. missile strike. In this
August 17, 2009 Pakistan and the Death of Baitullah Mehsud Reports indicated that on Aug. 5, Baitullah Mehsud, the notorious leader of the Taliban in Pakistan, died from a U.S. missile strike. In this
fragility and crisis
 strategic asia 2003 04 fragility and crisis Edited by Richard J. Ellings and Aaron L. Friedberg with Michael Wills Country Studies Pakistan: A State Under Stress John H. Gill restrictions on use: This
strategic asia 2003 04 fragility and crisis Edited by Richard J. Ellings and Aaron L. Friedberg with Michael Wills Country Studies Pakistan: A State Under Stress John H. Gill restrictions on use: This
CRS Report for Congress
 Order Code RS21584 Updated August 4, 2003 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Summary Pakistan: Chronology of Events K. Alan Kronstadt Analyst in Asian Affairs Foreign Affairs, Defense,
Order Code RS21584 Updated August 4, 2003 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Summary Pakistan: Chronology of Events K. Alan Kronstadt Analyst in Asian Affairs Foreign Affairs, Defense,
ANNEX 5. Public. Chronology of relevant events
 ICC-02/17-7-Anx5 20-11-2017 1/6 NM PT ANNEX 5 Public Chronology of relevant events ICC-02/17-7-Anx5 20-11-2017 2/6 NM PT CHRONOLOGY OF RELEVANT EVENTS In accordance with Regulation 49(3), the Prosecution
ICC-02/17-7-Anx5 20-11-2017 1/6 NM PT ANNEX 5 Public Chronology of relevant events ICC-02/17-7-Anx5 20-11-2017 2/6 NM PT CHRONOLOGY OF RELEVANT EVENTS In accordance with Regulation 49(3), the Prosecution
The top leaders of the Movement of the Taliban in Pakistan:
 Downloaded from: justpaste.it/1b04 Pakistani Taliban - Leaders // Ethnic Groups Map of northwestern Pakistan. By BILL ROGGIO May 17, 2010 After the failed car bomb attack in New York City's Times Square,
Downloaded from: justpaste.it/1b04 Pakistani Taliban - Leaders // Ethnic Groups Map of northwestern Pakistan. By BILL ROGGIO May 17, 2010 After the failed car bomb attack in New York City's Times Square,
one time. Any additional use of this file, whether for
 one time. Any additional use of this file, whether for Islamabad and The Taliban sales, alterations or copying is strictly prohibited without written permission and fair compensation to BENAZIR BHUTTO,
one time. Any additional use of this file, whether for Islamabad and The Taliban sales, alterations or copying is strictly prohibited without written permission and fair compensation to BENAZIR BHUTTO,
AFGHANISTAN. The Trump Plan R4+S. By Bill Conrad, LTC USA (Ret) October 6, NSF Presentation
 AFGHANISTAN The Trump Plan R4+S By Bill Conrad, LTC USA (Ret) October 6, 2017 --NSF Presentation Battle Company 2 nd of the 503 rd Infantry Regiment 2 Battle Company 2 nd of the 503 rd Infantry Regiment
AFGHANISTAN The Trump Plan R4+S By Bill Conrad, LTC USA (Ret) October 6, 2017 --NSF Presentation Battle Company 2 nd of the 503 rd Infantry Regiment 2 Battle Company 2 nd of the 503 rd Infantry Regiment
Unit 7 Station 2: Conflict, Human Rights Issues, and Peace Efforts. Name: Per:
 Name: Per: Station 2: Conflicts, Human Rights Issues, and Peace Efforts Part 1: Vocab Directions: Use the reading below to locate the following vocab words and their definitions. Write their definitions
Name: Per: Station 2: Conflicts, Human Rights Issues, and Peace Efforts Part 1: Vocab Directions: Use the reading below to locate the following vocab words and their definitions. Write their definitions
Operation OMID PANJ January 2011 Naweed Barikzai 1
 Operation OMID PANJ January 2011 Naweed Barikzai 1 With the passage of every day, as the security situation becomes more volatile in Afghanistan, international forces in coordination with the Afghan National
Operation OMID PANJ January 2011 Naweed Barikzai 1 With the passage of every day, as the security situation becomes more volatile in Afghanistan, international forces in coordination with the Afghan National
The most important geostrategic issue for the UK? Pakistan with friends like these.
 RS 57 The most important geostrategic issue for the UK? Pakistan with friends like these. By Professor Shaun Gregory PSRU, Department of Peace Studies, University of Bradford This paper is taken from an
RS 57 The most important geostrategic issue for the UK? Pakistan with friends like these. By Professor Shaun Gregory PSRU, Department of Peace Studies, University of Bradford This paper is taken from an
Center for Strategic & Regional Studies
 Center for Strategic & Regional Studies Kabul Weekly Analysis-Issue Number 164 (May 7-14, 2016) Weekly Analysis is one of CSRS publications, which significantly analyses weekly economic and political events
Center for Strategic & Regional Studies Kabul Weekly Analysis-Issue Number 164 (May 7-14, 2016) Weekly Analysis is one of CSRS publications, which significantly analyses weekly economic and political events
USA s Pak Strategy Blown - A New Round of Challenges for the Region
 Published on South Asia Analysis Group (http://www.southasiaanalysis.org) Home > USA s Pak Strategy Blown - A New Round of Challenges for the Region USA s Pak Strategy Blown - A New Round of Challenges
Published on South Asia Analysis Group (http://www.southasiaanalysis.org) Home > USA s Pak Strategy Blown - A New Round of Challenges for the Region USA s Pak Strategy Blown - A New Round of Challenges
The Geopolitical Importance of Pakistan
 The Geopolitical Importance of Pakistan A Country Caught between the Threat of Talibanisation and the Return to Democracy by Dr. Heinrich Kreft The murder of Benazir Bhutto on 27 December focused world
The Geopolitical Importance of Pakistan A Country Caught between the Threat of Talibanisation and the Return to Democracy by Dr. Heinrich Kreft The murder of Benazir Bhutto on 27 December focused world
Securing Indian Interests in Afghanistan Beyond 2014
 Securing Indian Interests in Afghanistan Beyond 2014 C. Christine Fair Asia Policy, Number 17, January 2014, pp. 27-32 (Article) Published by National Bureau of Asian Research DOI: https://doi.org/10.1353/asp.2014.0016
Securing Indian Interests in Afghanistan Beyond 2014 C. Christine Fair Asia Policy, Number 17, January 2014, pp. 27-32 (Article) Published by National Bureau of Asian Research DOI: https://doi.org/10.1353/asp.2014.0016
Country Summary January 2005
 Country Summary January 2005 Afghanistan Despite some improvements, Afghanistan continued to suffer from serious instability in 2004. Warlords and armed factions, including remaining Taliban forces, dominate
Country Summary January 2005 Afghanistan Despite some improvements, Afghanistan continued to suffer from serious instability in 2004. Warlords and armed factions, including remaining Taliban forces, dominate
CRS Report for Congress
 Order Code RS21584 Updated November 3, 2003 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Summary Pakistan: Chronology of Events K. Alan Kronstadt Analyst in Asian Affairs Foreign Affairs, Defense,
Order Code RS21584 Updated November 3, 2003 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Summary Pakistan: Chronology of Events K. Alan Kronstadt Analyst in Asian Affairs Foreign Affairs, Defense,
Pakistan and China: cooperation in counter-terrorism
 Pakistan and China: cooperation in counter-terrorism Rashid Ahmad Khan * Introduction T he Pakistan-China strategic relationship is based on multi-faceted bilateral cooperation in diverse fields. During
Pakistan and China: cooperation in counter-terrorism Rashid Ahmad Khan * Introduction T he Pakistan-China strategic relationship is based on multi-faceted bilateral cooperation in diverse fields. During
The motivations behind Afghan Taliban leaders arrest in Pakistan. Saifullah Ahmadzai 1 15 th March 2010
 The motivations behind Afghan Taliban leaders arrest in Pakistan Saifullah Ahmadzai 1 15 th March 2010 The Christian Science Monitor reported that Pakistani officials had arrested seven out of fifteen
The motivations behind Afghan Taliban leaders arrest in Pakistan Saifullah Ahmadzai 1 15 th March 2010 The Christian Science Monitor reported that Pakistani officials had arrested seven out of fifteen
Cover Story. - by Shraddha Bhandari. 24 JANUARY-FEBRUARY 2016 FSAI Journal
 - by Shraddha Bhandari 24 JANUARY-FEBRUARY 2016 FSAI Journal Following the spate of terror attacks in Paris, Beirut, and downing of the Russian Metrojet liner in November 2015, concerns have been raised
- by Shraddha Bhandari 24 JANUARY-FEBRUARY 2016 FSAI Journal Following the spate of terror attacks in Paris, Beirut, and downing of the Russian Metrojet liner in November 2015, concerns have been raised
Center for Strategic & Regional Studies
 Center for Strategic & Regional Studies Kabul Weekly Analysis-Issue Number 272 (Oct 20-27, 2018) Weekly Analysis is one of CSRS publications, which significantly analyses weekly economic and political
Center for Strategic & Regional Studies Kabul Weekly Analysis-Issue Number 272 (Oct 20-27, 2018) Weekly Analysis is one of CSRS publications, which significantly analyses weekly economic and political
Center for Strategic & Regional Studies
 Center for Strategic & Regional Studies Kabul Weekly Analysis-Issue Number 256 (June 16-23, 2018) Weekly Analysis is one of CSRS publications, which significantly analyses weekly economic and political
Center for Strategic & Regional Studies Kabul Weekly Analysis-Issue Number 256 (June 16-23, 2018) Weekly Analysis is one of CSRS publications, which significantly analyses weekly economic and political
Terrorist Groups: Lashkar-e-Taiba and Jamaat-ud-Dawa:
 Pakistan Pakistan has long been accused by its neighbours India and Afghanistan, and western nations like the United States and the United Kingdom of its involvement in terrorist activities in the region
Pakistan Pakistan has long been accused by its neighbours India and Afghanistan, and western nations like the United States and the United Kingdom of its involvement in terrorist activities in the region
Teaching International Humanitarian Law
 No. 02 March 2004 The ICRC's mission is to protect and assist the civilian and military victims of armed conflict and internal disturbances on a strictly neutral and impartial basis. Since 1986, the ICRC
No. 02 March 2004 The ICRC's mission is to protect and assist the civilian and military victims of armed conflict and internal disturbances on a strictly neutral and impartial basis. Since 1986, the ICRC
CRS Report for Congress
 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Order Code RS21658 November 3, 2003 Summary International Terrorism in South Asia K. Alan Kronstadt Analyst in Asian Affairs Foreign Affairs, Defense,
CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Order Code RS21658 November 3, 2003 Summary International Terrorism in South Asia K. Alan Kronstadt Analyst in Asian Affairs Foreign Affairs, Defense,
FIGHTING DRUGS AND CREATING ALTERNATIVE LIVELIHOODS
 FIGHTING DRUGS AND CREATING ALTERNATIVE LIVELIHOODS 1.01 The Government of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan is committed to tackling and ending the cultivation and trafficking of drugs. At the National
FIGHTING DRUGS AND CREATING ALTERNATIVE LIVELIHOODS 1.01 The Government of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan is committed to tackling and ending the cultivation and trafficking of drugs. At the National
Globalization and Human Rights: Focus on Afghan Women
 Globalization and Human Rights: Focus on Afghan Women By Linda Lindsey, Maryville University The sociological story of human rights as related to women in the developing world is rapidly unfolding. This
Globalization and Human Rights: Focus on Afghan Women By Linda Lindsey, Maryville University The sociological story of human rights as related to women in the developing world is rapidly unfolding. This
International Protection Needs of Asylum-Seekers from Afghanistan 12 March 2018 Vienna, Austria
 International Protection Needs of Asylum-Seekers from Afghanistan 12 March 2018 Vienna, Austria Contents A brief history Major incidents in Kabul, 2016-2018 Afghanistan at war Attacks on religious leaders
International Protection Needs of Asylum-Seekers from Afghanistan 12 March 2018 Vienna, Austria Contents A brief history Major incidents in Kabul, 2016-2018 Afghanistan at war Attacks on religious leaders
CRS Report for Congress
 Order Code RS21584 Updated February 5, 2004 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Pakistan: Chronology of Recent Events Summary K. Alan Kronstadt Analyst in Asian Affairs Foreign Affairs,
Order Code RS21584 Updated February 5, 2004 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Pakistan: Chronology of Recent Events Summary K. Alan Kronstadt Analyst in Asian Affairs Foreign Affairs,
White Paper of the Interagency Policy Group's Report on U.S. Policy toward Afghanistan and Pakistan INTRODUCTION
 White Paper of the Interagency Policy Group's Report on U.S. Policy toward Afghanistan and Pakistan INTRODUCTION The United States has a vital national security interest in addressing the current and potential
White Paper of the Interagency Policy Group's Report on U.S. Policy toward Afghanistan and Pakistan INTRODUCTION The United States has a vital national security interest in addressing the current and potential
confronting terrorism in the pursuit of power
 strategic asia 2004 05 confronting terrorism in the pursuit of power Edited by Ashley J. Tellis and Michael Wills Regional Studies South Asia: A Selective War on Terrorism? Walter K. Andersen restrictions
strategic asia 2004 05 confronting terrorism in the pursuit of power Edited by Ashley J. Tellis and Michael Wills Regional Studies South Asia: A Selective War on Terrorism? Walter K. Andersen restrictions
The Future of Extremism in Pakistan
 The Future of Extremism in Pakistan A Twenty Year Forward Look to 2028 is a Private Limited Company registered in England and Wales www.jan-consulting.com VIOLENT EXTREMISM IN PAKISTAN Extremism is politically
The Future of Extremism in Pakistan A Twenty Year Forward Look to 2028 is a Private Limited Company registered in England and Wales www.jan-consulting.com VIOLENT EXTREMISM IN PAKISTAN Extremism is politically
Q2. (IF RIGHT DIRECTION) Why do you say that? (Up to two answers accepted.)
 Q1. Generally speaking, do you think things in Afghanistan today are going in the right direction, or do you think they are going in the wrong direction? 2005 2004 Right direction 40 54 55 77 64 Wrong
Q1. Generally speaking, do you think things in Afghanistan today are going in the right direction, or do you think they are going in the wrong direction? 2005 2004 Right direction 40 54 55 77 64 Wrong
PROGRESS AND PROSPECTS
 COUNTER TERRORISM EXPERIENCE OF PAKISTAN PROGRESS AND PROSPECTS 1 INTRODUCTION 2 BADAKSHAN MINTAKA NURISTAN CHITRAL AFGHANISTAN PAKTIA KHOWST PAKTIKA ZABUL KUNAR NANGARHAR NWA SWA BANNU KHYBER PESHAWAR
COUNTER TERRORISM EXPERIENCE OF PAKISTAN PROGRESS AND PROSPECTS 1 INTRODUCTION 2 BADAKSHAN MINTAKA NURISTAN CHITRAL AFGHANISTAN PAKTIA KHOWST PAKTIKA ZABUL KUNAR NANGARHAR NWA SWA BANNU KHYBER PESHAWAR
Who, Where,And When : USSR vs Afghanistan resistance group (80% mujahideen) Front: Mainland of Afghanistan December 1979-February 1989
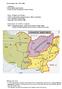 Soviet-Afghan War (1979-1989) Vocabulary: KHAD (Afghan secret police) LCOSF (Limited Contingent of Soviet Forces) Who, Where,And When : USSR vs Afghanistan resistance group (80% mujahideen) Front: Mainland
Soviet-Afghan War (1979-1989) Vocabulary: KHAD (Afghan secret police) LCOSF (Limited Contingent of Soviet Forces) Who, Where,And When : USSR vs Afghanistan resistance group (80% mujahideen) Front: Mainland
India-US Counterterrorism Cooperation: The Way Forward
 India-US Counterterrorism Cooperation: The Way Forward by Vinay Kaura BESA Center Perspectives Paper No. 555, August 8, 2017 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: Narendra Modi s visit to the Trump White House in June was
India-US Counterterrorism Cooperation: The Way Forward by Vinay Kaura BESA Center Perspectives Paper No. 555, August 8, 2017 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY: Narendra Modi s visit to the Trump White House in June was
Georgia Studies. Unit 7: Modern Georgia and Civil Rights. Lesson 3: Georgia in Recent History. Study Presentation
 Georgia Studies Unit 7: Modern Georgia and Civil Rights Lesson 3: Georgia in Recent History Study Presentation Lesson 3: Georgia in Recent History ESSENTIAL QUESTION: How did the policies and actions of
Georgia Studies Unit 7: Modern Georgia and Civil Rights Lesson 3: Georgia in Recent History Study Presentation Lesson 3: Georgia in Recent History ESSENTIAL QUESTION: How did the policies and actions of
IR History Post John Lee Department of Political Science Florida State University
 IR History Post-1950 John Lee Department of Political Science Florida State University World War II Germany initially expands, no one stops them. Allied v/s Axis Powers. USSR/Germany reach initial compromise,
IR History Post-1950 John Lee Department of Political Science Florida State University World War II Germany initially expands, no one stops them. Allied v/s Axis Powers. USSR/Germany reach initial compromise,
Report- Book Launch 88 Days to Kandahar A CIA Diary
 INSTITUTE OF STRATEGIC STUDIES web: www.issi.org.pk phone: +92-920-4423, 24 fax: +92-920-4658 Report- Book Launch 88 Days to Kandahar A CIA Diary March 11, 2016 Compiled by: Amina Khan 1 P a g e Pictures
INSTITUTE OF STRATEGIC STUDIES web: www.issi.org.pk phone: +92-920-4423, 24 fax: +92-920-4658 Report- Book Launch 88 Days to Kandahar A CIA Diary March 11, 2016 Compiled by: Amina Khan 1 P a g e Pictures
Center for Strategic & Regional Studies
 Center for Strategic & Regional Studies Kabul Weekly Analysis-Issue Number 284 (Jan 12-19, 2019) Weekly Analysis is one of CSRS publications, which significantly analyses weekly economic and political
Center for Strategic & Regional Studies Kabul Weekly Analysis-Issue Number 284 (Jan 12-19, 2019) Weekly Analysis is one of CSRS publications, which significantly analyses weekly economic and political
Continuing Conflict in SW Asia. EQ: What are the causes and effects of key conflicts in SW Asia that required U.S. involvement?
 Continuing Conflict in SW Asia EQ: What are the causes and effects of key conflicts in SW Asia that required U.S. involvement? Directions Today, we will be looking at the causes of important ongoing conflicts
Continuing Conflict in SW Asia EQ: What are the causes and effects of key conflicts in SW Asia that required U.S. involvement? Directions Today, we will be looking at the causes of important ongoing conflicts
Taliban. Troubles in the Middle East
 Taliban Troubles in the Middle East Where did they come from? The Taliban is a group that was not well known until they were tasked with protecting a trade convoy. When this job was finished they were
Taliban Troubles in the Middle East Where did they come from? The Taliban is a group that was not well known until they were tasked with protecting a trade convoy. When this job was finished they were
Electoral Failure of Religious Political Parties in Pakistan: An Analysis with Special Reference to Jamaat-E-Islami
 Lyallpur Historical & Cultural Research Journal June 2015, Vol. 1, No. 1 [19-25] ISSN Print 2523-2770 ISSN Online 2523-2789 Electoral Failure of Religious Political Parties in Pakistan: An Analysis with
Lyallpur Historical & Cultural Research Journal June 2015, Vol. 1, No. 1 [19-25] ISSN Print 2523-2770 ISSN Online 2523-2789 Electoral Failure of Religious Political Parties in Pakistan: An Analysis with
Pakistan: Political and Foreign Relations Outlook
 12 28 February 2017 Pakistan: Political and Foreign Relations Outlook Lindsay Hughes Research Analyst Indian Ocean Research Programme Key Points Pakistani politics have been influenced by the country s
12 28 February 2017 Pakistan: Political and Foreign Relations Outlook Lindsay Hughes Research Analyst Indian Ocean Research Programme Key Points Pakistani politics have been influenced by the country s
Round Table Discussion on Pak-Afghan Relations: Future Prospects
 Phone: +92 51 2514555 Email: info@muslim-institute.org www.muslim-institute.org Round Table Discussion on Pak-Afghan Relations: Future Prospects Organized by MUSLIM Institute MUSLIM Institute organized
Phone: +92 51 2514555 Email: info@muslim-institute.org www.muslim-institute.org Round Table Discussion on Pak-Afghan Relations: Future Prospects Organized by MUSLIM Institute MUSLIM Institute organized
AFGHANISTAN. Reports of torture, ill-treatment and extrajudicial execution of prisoners, late April - early May 1992
 AFGHANISTAN Reports of torture, ill-treatment and extrajudicial execution of prisoners, late April - early May 1992 Recent political developments On 16 April 1992, former president Najibullah was replaced
AFGHANISTAN Reports of torture, ill-treatment and extrajudicial execution of prisoners, late April - early May 1992 Recent political developments On 16 April 1992, former president Najibullah was replaced
US NSA s visit to South Asia implications for India
 Author: Amb. Yogendra Kumar 27.04.2016 CHARCHA Photograph: Kevin Lamarque/Reuters US NSA s visit to South Asia implications for India An indication of the Administration s regional priorities has been
Author: Amb. Yogendra Kumar 27.04.2016 CHARCHA Photograph: Kevin Lamarque/Reuters US NSA s visit to South Asia implications for India An indication of the Administration s regional priorities has been
SSUSH25 The student will describe changes in national politics since 1968.
 SSUSH25 The student will describe changes in national politics since 1968. a. Describe President Richard M. Nixon s opening of China, his resignation due to the Watergate scandal, changing attitudes toward
SSUSH25 The student will describe changes in national politics since 1968. a. Describe President Richard M. Nixon s opening of China, his resignation due to the Watergate scandal, changing attitudes toward
C. Christine Fair 1. The Timing of the Study
 Islamist Militancy in Pakistan: A View from the Provinces Companion to Pakistani Public Opinion on the Swat Conflict, Afghanistan and the U.S. July 10, 2009 C. Christine Fair 1 In Pakistan s struggles
Islamist Militancy in Pakistan: A View from the Provinces Companion to Pakistani Public Opinion on the Swat Conflict, Afghanistan and the U.S. July 10, 2009 C. Christine Fair 1 In Pakistan s struggles
Scott D. Sagan Stanford University Herzliya Conference, Herzliya, Israel,
 Scott D. Sagan Stanford University Herzliya Conference, Herzliya, Israel, 2009 02 04 Thank you for this invitation to speak with you today about the nuclear crisis with Iran, perhaps the most important
Scott D. Sagan Stanford University Herzliya Conference, Herzliya, Israel, 2009 02 04 Thank you for this invitation to speak with you today about the nuclear crisis with Iran, perhaps the most important
Pakistan. Gender-Based Violence and Legal Discrimination
 January 2007 Country Summary Pakistan In office since a 1999 coup d etat, President Pervez Musharraf s military-backed government did little in 2006 to address a rapidly deteriorating human rights situation.
January 2007 Country Summary Pakistan In office since a 1999 coup d etat, President Pervez Musharraf s military-backed government did little in 2006 to address a rapidly deteriorating human rights situation.
Afghanistan. Endemic corruption and violence marred parliamentary elections in September 2010.
 January 2011 country summary Afghanistan While fighting escalated in 2010, peace talks between the government and the Taliban rose to the top of the political agenda. Civilian casualties reached record
January 2011 country summary Afghanistan While fighting escalated in 2010, peace talks between the government and the Taliban rose to the top of the political agenda. Civilian casualties reached record
Adopted by the Security Council at its 4251st meeting, on 19 December 2000
 United Nations S/RES/1333 (2000) Security Council Distr.: General 19 December 2000 Resolution 1333 (2000) Adopted by the Security Council at its 4251st meeting, on 19 December 2000 The Security Council,
United Nations S/RES/1333 (2000) Security Council Distr.: General 19 December 2000 Resolution 1333 (2000) Adopted by the Security Council at its 4251st meeting, on 19 December 2000 The Security Council,
Engaging Regional Players in Afghanistan Threats and Opportunities
 Engaging Regional Players in Afghanistan Threats and Opportunities A Report of the CSIS Post-Conflict Reconstruction Project author Shiza Shahid codirectors Rick Barton Karin von Hippel November 2009 CSIS
Engaging Regional Players in Afghanistan Threats and Opportunities A Report of the CSIS Post-Conflict Reconstruction Project author Shiza Shahid codirectors Rick Barton Karin von Hippel November 2009 CSIS
Center for Strategic & Regional Studies
 Center for Strategic & Regional Studies Kabul Weekly Analysis-Issue Number 248 (April 14-21, 2018) Weekly Analysis is one of CSRS publications, which significantly analyses weekly economic and political
Center for Strategic & Regional Studies Kabul Weekly Analysis-Issue Number 248 (April 14-21, 2018) Weekly Analysis is one of CSRS publications, which significantly analyses weekly economic and political
An Unarguable Fact: American Security is Tied to Afghanistan and Pakistan
 Statement before the House Committee on Foreign Affairs Subcommittee on the Middle East and North Africa and Subcommittee on Asia and the Pacific on After the Withdrawal: The Way Forward in Afghanistan
Statement before the House Committee on Foreign Affairs Subcommittee on the Middle East and North Africa and Subcommittee on Asia and the Pacific on After the Withdrawal: The Way Forward in Afghanistan
Afghanistan has become terrain for India-Pakistan proxy war
 Afghanistan has become terrain for India-Pakistan proxy war Ramananda Sengupta* March 2010 Al Jazeera Centre for Studies Tel: +974-4930181 Fax: +974-4831346 jcforstudies@aljazeera.net www.aljazeera.net/studies
Afghanistan has become terrain for India-Pakistan proxy war Ramananda Sengupta* March 2010 Al Jazeera Centre for Studies Tel: +974-4930181 Fax: +974-4831346 jcforstudies@aljazeera.net www.aljazeera.net/studies
US DRONE ATTACKS INSIDE PAKISTAN TERRITORY: UN CHARTER
 US DRONE ATTACKS INSIDE PAKISTAN TERRITORY: UN CHARTER Nadia Sarwar * The US President, George W. Bush, in his address to the US. Military Academy at West point on June 1, 2002, declared that America could
US DRONE ATTACKS INSIDE PAKISTAN TERRITORY: UN CHARTER Nadia Sarwar * The US President, George W. Bush, in his address to the US. Military Academy at West point on June 1, 2002, declared that America could
CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web
 CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Order Code RS21041 October 5, 2001 Summary Taliban and the Drug Trade Raphael F. Perl Specialist in International Affairs Foreign Affairs, Defense,
CRS Report for Congress Received through the CRS Web Order Code RS21041 October 5, 2001 Summary Taliban and the Drug Trade Raphael F. Perl Specialist in International Affairs Foreign Affairs, Defense,
FINAL/NOT FOR DISTRIBUTION
 Statement of General Stanley A. McChrystal, USA Commander, NATO International Security Assistance Force House Armed Services Committee December 8, 2009 Mr. Chairman, Congressman McKeon, distinguished members
Statement of General Stanley A. McChrystal, USA Commander, NATO International Security Assistance Force House Armed Services Committee December 8, 2009 Mr. Chairman, Congressman McKeon, distinguished members
ADDRESS TO A JOINT SESSION OF CONGRESS AND THE AMERICAN PEOPLE 2001
 ADDRESS TO A JOINT SESSION OF CONGRESS AND THE AMERICAN PEOPLE 2001 George W. Bush On the morning of September 11, 2001, the most destructive act of terrorism in modern history was inflicted on the United
ADDRESS TO A JOINT SESSION OF CONGRESS AND THE AMERICAN PEOPLE 2001 George W. Bush On the morning of September 11, 2001, the most destructive act of terrorism in modern history was inflicted on the United
1. Issue of concern: Impunity
 A Human Rights Watch Submission to the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights regarding the Universal Periodic Review of the Republic of India 1. Issue of concern: Impunity India has always claimed
A Human Rights Watch Submission to the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights regarding the Universal Periodic Review of the Republic of India 1. Issue of concern: Impunity India has always claimed
Guided Reading Activity 32-1
 Guided Reading Activity 32-1 DIRECTIONS: Recalling the Facts Use the information in your textbook to answer the questions below. Use another sheet of paper if necessary. 1. What conservative view did many
Guided Reading Activity 32-1 DIRECTIONS: Recalling the Facts Use the information in your textbook to answer the questions below. Use another sheet of paper if necessary. 1. What conservative view did many
PRESS BRIEFING BY PROF. ABDUL SATTAR SIRAT, HEAD OF THE ROME GROUP DELEGATION, AND OTHER MEMBERS OF THE DELEGATION
 For information, not an official record - Zur Information, kein offizielles Dokument - document sans caractère officiel Königswinter, 29 November 2001 PRESS BRIEFING BY PROF. ABDUL SATTAR SIRAT, HEAD OF
For information, not an official record - Zur Information, kein offizielles Dokument - document sans caractère officiel Königswinter, 29 November 2001 PRESS BRIEFING BY PROF. ABDUL SATTAR SIRAT, HEAD OF
MEDIA COVERAGE. Pakistan-Austria Roundtable Afghanistan and Regional Security 28 March 2019 NATIONAL ONLINE NEWSPAPERS
 ISLAMABAD POLICY RESEARCH INSTITUTE 5 th Floor, Evacuee Trust Complex, Sir Aga Khan Road, F-5/1, Islamabad, Pakistan Tel: + 92 51 9211346-49; Fax + 92 51 9211350 Email: ipripak@ipripak.org; Website: www.ipripak.org
ISLAMABAD POLICY RESEARCH INSTITUTE 5 th Floor, Evacuee Trust Complex, Sir Aga Khan Road, F-5/1, Islamabad, Pakistan Tel: + 92 51 9211346-49; Fax + 92 51 9211350 Email: ipripak@ipripak.org; Website: www.ipripak.org
Press Conference June
 Press Conference PRESS CONFERENCE (near verbatim transcript) Ambassador Peter Wittig, Germany s Permanent Representative to the United Nations; Chair of the UN Security Council Working Group on Children
Press Conference PRESS CONFERENCE (near verbatim transcript) Ambassador Peter Wittig, Germany s Permanent Representative to the United Nations; Chair of the UN Security Council Working Group on Children
Center for Strategic & Regional Studies
 Center for Strategic & Regional Studies Kabul Weekly Analysis-Issue Number 246 (March 31-7 April, 2018) Weekly Analysis is one of CSRS publications, which significantly analyses weekly economic and political
Center for Strategic & Regional Studies Kabul Weekly Analysis-Issue Number 246 (March 31-7 April, 2018) Weekly Analysis is one of CSRS publications, which significantly analyses weekly economic and political
Homepage. Web. 14 Oct <
 Civilian Casualties Rise Naweed Barikzai 1 A report on civilian casualties, published by the United Nations Assistance Mission in Afghanistan (UNAMA) evaluates civilian casualties in the first six months
Civilian Casualties Rise Naweed Barikzai 1 A report on civilian casualties, published by the United Nations Assistance Mission in Afghanistan (UNAMA) evaluates civilian casualties in the first six months
THE AFGHAN SUMMER OF WAR Paul Rogers
 International Security Monthly Briefing September 2006 THE AFGHAN SUMMER OF WAR Paul Rogers Lebanon During September, substantial numbers of foreign troops entered southern Lebanon to act as an enhanced
International Security Monthly Briefing September 2006 THE AFGHAN SUMMER OF WAR Paul Rogers Lebanon During September, substantial numbers of foreign troops entered southern Lebanon to act as an enhanced
MUSHARRAF AND TERRORISM
 Published on South Asia Analysis Group (http://www.southasiaanalysis.org) Home > MUSHARRAF AND TERRORISM MUSHARRAF AND TERRORISM Submitted by asiaadmin2 on Wed, 09/26/2012-04:47 Paper No. 283 24.07.2001
Published on South Asia Analysis Group (http://www.southasiaanalysis.org) Home > MUSHARRAF AND TERRORISM MUSHARRAF AND TERRORISM Submitted by asiaadmin2 on Wed, 09/26/2012-04:47 Paper No. 283 24.07.2001
Pakistani Public Opinion on Democracy, Islamist Militancy, and Relations with the US
 Pakistani Public Opinion on Democracy, Islamist Militancy, and Relations with the US A Joint Study of WorldPublicOpinion.org and the United States Institute of Peace January 7, 2008 C. CHRISTINE FAIR CLAY
Pakistani Public Opinion on Democracy, Islamist Militancy, and Relations with the US A Joint Study of WorldPublicOpinion.org and the United States Institute of Peace January 7, 2008 C. CHRISTINE FAIR CLAY
Summary of the Report on Civilian Casualties in Armed Conflict in 1396
 Afghanistan Independent Human Rights Commission Summary of the Report on Civilian Casualties in Armed Conflict in 1396 Special Investigation Team April 2018 Humanitarian law is a set of rules and principles
Afghanistan Independent Human Rights Commission Summary of the Report on Civilian Casualties in Armed Conflict in 1396 Special Investigation Team April 2018 Humanitarian law is a set of rules and principles
Unit 5: empowering women globally
 Susan Retik lost her husband David on American Airlines Flight 11, which was flown into the North Tower of the World Trade Center on September 11, 2001. At the time, they had two children, and Susan was
Susan Retik lost her husband David on American Airlines Flight 11, which was flown into the North Tower of the World Trade Center on September 11, 2001. At the time, they had two children, and Susan was
ECOSOC I Adam McMahon (Deputy Chair) MY-MUNOFS VI Feb 28 Mar
 ECOSOC I Adam McMahon (Deputy Chair) MY-MUNOFS VI Feb 28 Mar 01 2015 Introduction: Pakistan is a country that continuously finds itself caught up in the middle of a lot of tricky situations as it faces
ECOSOC I Adam McMahon (Deputy Chair) MY-MUNOFS VI Feb 28 Mar 01 2015 Introduction: Pakistan is a country that continuously finds itself caught up in the middle of a lot of tricky situations as it faces
Strategy, Diplomacy and Neighborhood: Af-Pak Region
 Strategy, Diplomacy and Neighborhood: Af-Pak Region Dr. Manish Kumar Assistant Professor Dept. Of Defence and Strategic Studies Post Graduate Government College, Sector-11 Chandigarh Abstract: The modern
Strategy, Diplomacy and Neighborhood: Af-Pak Region Dr. Manish Kumar Assistant Professor Dept. Of Defence and Strategic Studies Post Graduate Government College, Sector-11 Chandigarh Abstract: The modern
Husain Haqqani. An Interview with
 An Interview with Husain Haqqani Muhammad Mustehsan What does success in Afghanistan look like from a Pakistani perspective, and how might it be achieved? HH: From Pakistan s perspective, a stable Afghanistan
An Interview with Husain Haqqani Muhammad Mustehsan What does success in Afghanistan look like from a Pakistani perspective, and how might it be achieved? HH: From Pakistan s perspective, a stable Afghanistan
CRS Report for Congress
 CRS Report for Congress.Received through the CRS Web Order Code RS21584 Updated June 22, 2005 Pakistan: Chronology of Recent Events Summary K. Alan Kronstadt Analyst in Asian Affairs Foreign Affairs, Defense,
CRS Report for Congress.Received through the CRS Web Order Code RS21584 Updated June 22, 2005 Pakistan: Chronology of Recent Events Summary K. Alan Kronstadt Analyst in Asian Affairs Foreign Affairs, Defense,
CURRENT GOVERNMENT & ITS EXISTING PROBLEMS AND THE WAY TO GET RID OF IT
 CURRENT GOVERNMENT & ITS EXISTING PROBLEMS AND THE WAY TO GET RID OF IT د افغانستان د بشرى حقوقو او چاپيريال ساتنى سازمان Afghan Organization of Human Rights & Environmental Protection No: Date: 1. Distrust
CURRENT GOVERNMENT & ITS EXISTING PROBLEMS AND THE WAY TO GET RID OF IT د افغانستان د بشرى حقوقو او چاپيريال ساتنى سازمان Afghan Organization of Human Rights & Environmental Protection No: Date: 1. Distrust
AFGHANISTAN: TRANSITION UNDER THREAT WORKSHOP REPORT
 AFGHANISTAN: TRANSITION UNDER THREAT WORKSHOP REPORT On December 17-18, 2006, a workshop was held near Waterloo, Ontario Canada to assess Afghanistan s progress since the end of the Taliban regime. Among
AFGHANISTAN: TRANSITION UNDER THREAT WORKSHOP REPORT On December 17-18, 2006, a workshop was held near Waterloo, Ontario Canada to assess Afghanistan s progress since the end of the Taliban regime. Among
World Conflicts: Asia and the Middle East Afghanistan
 World Conflicts: Asia and the Middle East Afghanistan A country long plagued by foreign occupations, repressive governments, political instability, and warfare, Afghanistan became a center of international
World Conflicts: Asia and the Middle East Afghanistan A country long plagued by foreign occupations, repressive governments, political instability, and warfare, Afghanistan became a center of international
The Falange Espanola: Spanish Fascism
 Spanish Civil War The Falange Espanola: Spanish Fascism Fascism reared its ugly head. Similar to Nazi party and Italian Fascist party. Anti-parliamentary and sought one-party rule. Not racist but attached
Spanish Civil War The Falange Espanola: Spanish Fascism Fascism reared its ugly head. Similar to Nazi party and Italian Fascist party. Anti-parliamentary and sought one-party rule. Not racist but attached
India-Pakistan Relations: Post Pathankot
 INSTITUTE OF STRATEGIC STUDIES web: www.issi.org.pk phone: +92-920-4423, 24 fax: +92-920-4658 Issue Brief India-Pakistan Relations: Post Pathankot Tooba Khurshid, Research Fellow, ISSI February 11, 2016
INSTITUTE OF STRATEGIC STUDIES web: www.issi.org.pk phone: +92-920-4423, 24 fax: +92-920-4658 Issue Brief India-Pakistan Relations: Post Pathankot Tooba Khurshid, Research Fellow, ISSI February 11, 2016
5. Unaccountable Supply Chain Security Contractors Undermine U.S. Counterinsurgency Strategy
 5. Unaccountable Supply Chain Security Contractors Undermine U.S. Counterinsurgency Strategy Finding: While outsourcing principal responsibility for the supply chain in Afghanistan to local truckers and
5. Unaccountable Supply Chain Security Contractors Undermine U.S. Counterinsurgency Strategy Finding: While outsourcing principal responsibility for the supply chain in Afghanistan to local truckers and
The following text is an edited transcript of Professor. Fisher s remarks at the November 13 meeting. Afghanistan: Negotiation in the Face of Terror
 1 The following text is an edited transcript of Professor Fisher s remarks at the November 13 meeting. Afghanistan: Negotiation in the Face of Terror Roger Fisher Whether negotiation will be helpful or
1 The following text is an edited transcript of Professor Fisher s remarks at the November 13 meeting. Afghanistan: Negotiation in the Face of Terror Roger Fisher Whether negotiation will be helpful or
The Benefit of Negative Examples: What We Can Learn About Leadership from the Taliban
 The Benefit of Negative Examples: What We Can Learn About Leadership from the Taliban Douglas R. Lindsay, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Behavioral Sciences & Leadership United States Air Force
The Benefit of Negative Examples: What We Can Learn About Leadership from the Taliban Douglas R. Lindsay, Ph.D. Associate Professor Department of Behavioral Sciences & Leadership United States Air Force
Afghanistan: Researched and compiled by the Refugee Documentation Centre of Ireland on 12 September 2011
 Afghanistan: Researched and compiled by the Refugee Documentation Centre of Ireland on 12 September 2011 Do the Taliban in Afghanistan have a record of forcibly recruiting locals to fight for them? If
Afghanistan: Researched and compiled by the Refugee Documentation Centre of Ireland on 12 September 2011 Do the Taliban in Afghanistan have a record of forcibly recruiting locals to fight for them? If
Any response to Uri must factor in the Pakistani state s relationship with non-state actors.
 Inside, outside Any response to Uri must factor in the Pakistani state s relationship with non-state actors. Soldiers guard outside the army base which was attacked suspected militants in Uri, Jammu and
Inside, outside Any response to Uri must factor in the Pakistani state s relationship with non-state actors. Soldiers guard outside the army base which was attacked suspected militants in Uri, Jammu and
Yemen. By September 2014, 334,512 people across Yemen were officially registered as internally displaced due to fighting.
 JANUARY 2015 COUNTRY SUMMARY Yemen The fragile transition government that succeeded President Ali Abdullah Saleh in 2012 following mass protests failed to address multiple human rights challenges in 2014.
JANUARY 2015 COUNTRY SUMMARY Yemen The fragile transition government that succeeded President Ali Abdullah Saleh in 2012 following mass protests failed to address multiple human rights challenges in 2014.
Pakistan Elections 2018: Imran Khan and a new South Asia. C Raja Mohan 1
 ISAS Brief No. 595 2 August 2018 Institute of South Asian Studies National University of Singapore 29 Heng Mui Keng Terrace #08-06 (Block B) Singapore 119620 Tel: (65) 6516 4239 Fax: (65) 6776 7505 www.isas.nus.edu.sg
ISAS Brief No. 595 2 August 2018 Institute of South Asian Studies National University of Singapore 29 Heng Mui Keng Terrace #08-06 (Block B) Singapore 119620 Tel: (65) 6516 4239 Fax: (65) 6776 7505 www.isas.nus.edu.sg
IRI Index: Pakistan. Voters were also opposed to the various measures that accompanied the state of emergency declaration.
 IRI Index: Pakistan State of Emergency On November 3, 2007, Pakistan President Pervez Musharraf, who was then Army Chief of Staff, declared a state of emergency and suspended the constitution. IRI s most
IRI Index: Pakistan State of Emergency On November 3, 2007, Pakistan President Pervez Musharraf, who was then Army Chief of Staff, declared a state of emergency and suspended the constitution. IRI s most
Ms. Susan M. Pojer & Mrs. Lisbeth Rath Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NY
 Ms. Susan M. Pojer & Mrs. Lisbeth Rath Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NY Border problems Jawarlal Nehru Ally of Gandhi. 1 st Prime Minister of India, 1947-1964. Advocated Industrialization. Promoted Green
Ms. Susan M. Pojer & Mrs. Lisbeth Rath Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NY Border problems Jawarlal Nehru Ally of Gandhi. 1 st Prime Minister of India, 1947-1964. Advocated Industrialization. Promoted Green
 Modern day Kashmir consist of three parts: Pakistan occupied Kashmir (POK) Azad Jammu and Kashmir (AJK) Gilgit-Baltistan India occupied Kashmir China has occupied Aksai Chin since the early 1950s and,
Modern day Kashmir consist of three parts: Pakistan occupied Kashmir (POK) Azad Jammu and Kashmir (AJK) Gilgit-Baltistan India occupied Kashmir China has occupied Aksai Chin since the early 1950s and,
Press Conference March Dr Sima Samar, Chairperson of Afghan Independent Human Rights Commission (AIHRC)
 Press Conference PRESS CONFERENCE (near verbatim transcript) Ivan Simonovic, UN Assistant Secretary-General for Human Rights Dr Sima Samar, Chairperson of Afghan Independent Human Rights Commission (AIHRC)
Press Conference PRESS CONFERENCE (near verbatim transcript) Ivan Simonovic, UN Assistant Secretary-General for Human Rights Dr Sima Samar, Chairperson of Afghan Independent Human Rights Commission (AIHRC)
Traditional Loya Jirga 4: lacklustre political theatre (amended)
 Traditional Loya Jirga 4: lacklustre political theatre (amended) Author : Kate Clark Published: 19 November 2011 Downloaded: 1 September 2017 Download URL: https://www.afghanistan-analysts.org/traditional-loya-jirga-4-lacklustre-political-theatre-amended/?format=pdf
Traditional Loya Jirga 4: lacklustre political theatre (amended) Author : Kate Clark Published: 19 November 2011 Downloaded: 1 September 2017 Download URL: https://www.afghanistan-analysts.org/traditional-loya-jirga-4-lacklustre-political-theatre-amended/?format=pdf
Chapter 8: The Use of Force
 Chapter 8: The Use of Force MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. According to the author, the phrase, war is the continuation of policy by other means, implies that war a. must have purpose c. is not much different from
Chapter 8: The Use of Force MULTIPLE CHOICE 1. According to the author, the phrase, war is the continuation of policy by other means, implies that war a. must have purpose c. is not much different from
Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Pakistan Studies (4PA0/01) Paper 01: The History & Heritage of Pakistan
 Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2016 Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Pakistan Studies (4PA0/01) Paper 01: The History & Heritage of Pakistan Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications
Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2016 Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Pakistan Studies (4PA0/01) Paper 01: The History & Heritage of Pakistan Edexcel and BTEC Qualifications Edexcel and BTEC qualifications
It was carried out by Charney Research of New York. The fieldwork was done by the Afghan Centre for Social and Opinion Research in Kabul.
 This poll, commissioned by BBC World Service in conjunction with ABC News and ARD (Germany), was conducted via face-to-face interviews with 1,377 randomly selected Afghan adults across the country between
This poll, commissioned by BBC World Service in conjunction with ABC News and ARD (Germany), was conducted via face-to-face interviews with 1,377 randomly selected Afghan adults across the country between
