VOTING SYSTEMS AND ARROW S THEOREM
|
|
|
- Alexis Hardy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 VOTING SYSTEMS AND ARROW S THEOREM AKHIL MATHEW Abstract. The following is a brief discussion of Arrow s theorem in economics. I wrote it for an economics class in high school. 1. Background Arrow s theorem is a central result in modern economics and social science, which states that any voting system satisfying reasonable assumptions has inherent limitations, and in particular that the problem of spoilers cannot be resolved within this framework. First, recall that voting is used to make decisions in democratic societies, but that many decisions can be made through the market system. The decision about how much corn will be produced in a given year is made not by central planning but by the cumulative choices of independent farmers and farming companies, each guided by market forces. However, many decisions must be made by the government: for instance, the provision of public goods such as military defense, or more simply the choice of a candidate. Some such decisions are between two alternatives (e.g. whether or not to support a given bill in a system of direct democracy), and there is a clear way to decide, namely, to make everyone vote and choose the side with the majority (choosing randomly if both options collect the same number of votes). In practice, however, one often has at least three alternatives, and it is quite possible no option will have a majority. Of course, one can select the winning alternative as the one that receives a plurality of votes, as is usually done. The problem with this approach is the existence of spoilers, as demonstrated for instance in the 2000 presidential election. Suppose there are three candidates A, B, C. A is a conservative, B a moderate liberal, and C a staunch liberal. The country, leaning left, is split: 49% for A, 48% for B, and 3% for C. The plurality approach will give A the victory, though the liberal 51% of the country would have preferred B to A. 1 In 2000, Ralph Nader was candidate C. Moreover, it is entirely possible that, according to pairwise match-ups, society will paradoxically prefer A > B, B > C, and C > A. In other words, even if each individual is rational i.e., each individual imposes a total ordering on the candidates society may be irrational. The Concordet criterion, named after the founder of voting theory, of choosing the candidate that defeats any other in a head-to-head match may not be applicable. Date: November 25, In the American political system, the situation is complicated by the electoral college system. 1
2 2 AKHIL MATHEW There are various methods at ameliorating the situation. For instance, one could perform a run-off election between the top two candidates, though this incurs additional expense, and in fact need not fully resolve the spoiler problem what if the split were between candidates A, B, C as above, and some of the moderately liberal B voters swung to A in the second (A versus C) round? An improvement to this model is instant-runoff voting (IRV), 2 which works as follows. Each voter is asked to rank the candidates from favorite to least favorite. Then, the first choices of all voters are tabulated; a candidate with a majority here wins. If there is no candidate with a majority, the candidate with the fewest number of first-choice votes is eliminated. Those voters who voted for the eliminated candidate now have their second-choice votes counted, and the candidate left in the round with the fewest votes is eliminated. The process repeats. In general, at each step, one scans through the list of all ballots and marks a vote for the highest-ranked candidate on each ballot that has not been eliminated. Then one eliminates the candidate with the fewest votes and resets all vote counts to zero. One repeats until a candidate has a majority. Nevertheless, Arrow s theorem shows that this method is also imperfect. Arrow s theorem itself is a purely mathematical statement, but it comes from the modelling of voting phenomena. Suppose we have a society, i.e. a finite set S (corresponding to the individuals of a population), and a finite set C of candidates. Each individual has a preference between candidates in a rational manner, i.e. if A, B, C C and an individual prefers A to B and B to C, then she prefers A to C. This means that each individual induces a total ordering on the set S by her preferences. A voting system associates to each system of preferences by each member of society a societal preference, or equivalently a total ordering on C. In other words, it is a function V : L(C) S L(C), where for a set T, we let L(T ) denote the set of total orders on it. We shall consider certain seemingly natural assumptions on V. (1) (Unanimity) Suppose A, B C. If all voters prefer A to B, then society prefers A to B. I.e., if A > B in each ordering in L(C) S, then A > B in V ( ). (2) (Independence of irrelevant alternatives) The societal preference of A relative to B depends only on the preferences (between A, B) of each individual in the society. In other words, if, L(C) S are societal preferences and A > B for an ordering in if and only if A > B in the corresponding -ordering, then A > B in V ( ) iff A > B in V ( ). The meaning of the first is clear. For the second, it means that whether society prefers A to B depends only on the individual preferences of A versus B (and not of any irrelevant alternatives C A, B). A simple way of constructing a voting system satisfying both conditions above is as follows. Pick d S and define V by sending (d). Equivalently, the 2 See [3].
3 VOTING SYSTEMS AND ARROW S THEOREM 3 societal ranking is simply that of d. The individual d for which this occurs is evidently unique, and is called a dictator. Theorem 1 (Arrow [5]). Any voting system satisfying unanimity and the independence of irrelevant alternatives has a dictator, when C has at least three elements. The theorem stunned mathematicians and economists, because it demonstrates that (within this framework), no perfect voting system can exist! Various proofs, all somewhat technical, are presented in [6]. 2. Proof of Arrow s theorem Henceforth, we assume V is a voting system satisfying unanimity and the independence of irrelevant alternatives. We present a proof due to Geanakopolous that a dictator exists. Step 1: An extremal lemma. Lemma. Suppose that each individual ranks A C either at the top or at the bottom. Then society ranks A either at the top or the bottom. Of course, this is an immediate consequence of unanimity when each individual chooses the same way (i.e. all top or bottom). For convenience, call a profile an element of L(C) S, i.e. a system of preferences. Suppose, to the contrary, that B > A > C in society, i.e. A is not in any extreme position. Since A is always at the extreme of each voter s list, we can tweak each voter s list so as to leave A fixed but shift the positions of B, C suitably such that C > B for each voter. In this modified profile P, clearly B > A, A > C societally because the relative preferences with respect to A have remained constant A is at the extreme and we have the independence of irrelevant alternatives. So B > C in V (P ). But also B < C for P by unanimity, contradiction. Step 2: Existence of a limited dictator. We now construct an element d S that will become the dictator. Lemma. Fix A C. There exists an individual d S and a profile P such that: (1) d ranks A at the bottom in P and V (P ) ranks A at the bottom. (2) Consider the modified profile P obtained by moving d s preference of A to the top. Then V (P ) ranks A at the top. (3) In the profile P, each voter ranks A either at the top of the bottom In other words, there is a profile P and an individual d such that by only d s changing its preference of A from the bottom to the top, society changes its preference of A from the bottom to the top. To see this, consider a profile P 0 where all individuals rank A at the bottom. Consider the profiles P 1,..., P s (where s = card S) where to obtain P s, we consider the profile P s 1 and, for one new voter, switch the preference of A from the
4 4 AKHIL MATHEW bottom to the top. Then in P 0, A is at the bottom of all voters preferences; in P s, A is at the top of all voters preferences. Since A is always at an extreme position in any voter in any profile P i, A is at either the top or the bottom of each V (P i ). When i = 0 it is at the bottom and when i = s at the top, by unanimity. There must be some P j such that A is at the bottom of V (P j ) and at the top of V (P j+1 ). Since P j+1 is obtained from P j by shifting the preference of A from the top to the bottom at some voter (call it d), the lemma is now clear. Step 3: Denoument. I claim that the individual d S from the previous lemma is a dictator. Step 3a. First, we show that: Lemma. If B, C C are distinct from A, then society (in any profile) ranks B > C iff d does. We can express this by saying that d is a dictator with respect to B, C. Consider the profiles P, P in the previous lemma; recall that each voter ranked A at the top or the bottom. Consider another profile Q in which, say, d ranks B > C. We will show that V (Q) ranks B > C as well. Now, modify P in the following way to get a new profile R. At the voter d, B is at the top, A right below, and C further down. At other voters, A remains at the extreme position (either top or bottom), and B, C are ordered in the same way as they are in Q. Note then that a voter ranks B > C in R iff she does so in Q. In particular, B > C in V (R) iff B > C in V (Q), by the independence of irrelevant alternatives. I now claim that B > C in V (R). Indeed, I will show that B > A and A > C. First, R and P have the same relative B, A preferences (e.g. at d, B > A), and A is at the bottom in V (P ). So B > A in V (P ) and hence in V (R). Second, R and P have the same relative A, C preferences (e.g. at d, A > C), and in V (P ), A is at the top. So by necessity B > A and A > C in V (R), implying B > C in V (R). Since V (R) and V (Q) have the same relative B, C preference, we are done. Step 3b. Now, I claim that if B C, then society ranks A > B if and only if d does. This handles the other case, and completes the proof that d is a (full) dictator. First, there is an individual d S such that society (for any profile) ranks A > B if and only if d does; this can be seen by choosing C A, B (recall that C has at least three elements!) and using the construction of the previous lemma, interchanging C and A. So we get an individual d S which is a dictator respect to any pair of elements not containing C. However, in the profiles P, P constructed for A, the societal preference of A, B shifts, even though only at d is there a difference between P, P. It follows that d = d, proving the result. Arrow s theorem is proved.
5 VOTING SYSTEMS AND ARROW S THEOREM 5 3. Approval Voting and Near-counterexamples It turns out, however, that there do exist instances of what one might colloquially call voting systems that do satisfy the conditions of unanimity, independence of irrelevant alternatives, and non-dictatorship. Consider the following procedure, called approval voting. Each citizen is given a ballot with a list of all the candidates and marks 1 or 0 for each one according as she approves or disapproves of the candidate. The candidate with the largest number of 1 s wins. It is clear that this method of voting, in theory, satisfies the relevant conditions. It does not contradict Arrow s theorem because each individual does not choose a total ordering on the candidates. 3 Approval voting is used in certain organizations such as the National Academy of Sciences and the Mathematical Association of America, but it lacks real-world testing. Moreover, a potential flaw in the model is that it may fail to elect a candidate who is the clear favorite of a majority of voters due to a new version of the spoiler problem. For instance, suppose there are three candidates A, B, C, and 51% of voters have the preference A > B but approve of both A and B. Suppose 49% of voters have the preference B > A but approve of only B. Then, B will win the election via approval voting. This is pointed out, for instance, in [1]. However, the problem diminishes in importance when {0, 1} is replaced with a larger set, allowing more expressivity; sometimes this variant of approval voting is called range voting. Range voting, unlike strict approval voting, allows voters to register a preference. Finally, another potential benefit of range voting is the boost given to third parties. Under the present system, it is unlikely that someone will cast a vote for a third-party candidate, but a range-wote allows her to express tepid support for a potentially too extreme but not out-of-the-question candidate. As a result, range-voting might increase the activity and strength of minor parties; given the disenchantment of many Americans with both the Republicans and the Democrats, this may be a serious consideration. References [1] Approval voting vs. instant runoff voting. htm. [2] Citizens for approval voting. [3] Instant runoff voting. [4] Rangevoting.org Center for range voting. [5] Kenneth J. Arrow. A difficulty in the concept of social welfare. Journal of Political Economy, 58(4): , [6] John Geanakoplos. Three brief proofs of Arrow s impossibility theorem. Economic Theory, 26: , Available at [7] Dana Mackenzie. Making sense out of consensus php?id=674. [8] Ben Webster. Why Arrow s theorem is a scam, Blog post available at sbseminar. wordpress.com. 3 See the discussion at [8].
Arrow s Impossibility Theorem
 Arrow s Impossibility Theorem Some announcements Final reflections due on Monday. You now have all of the methods and so you can begin analyzing the results of your election. Today s Goals We will discuss
Arrow s Impossibility Theorem Some announcements Final reflections due on Monday. You now have all of the methods and so you can begin analyzing the results of your election. Today s Goals We will discuss
1.6 Arrow s Impossibility Theorem
 1.6 Arrow s Impossibility Theorem Some announcements Homework #2: Text (pages 33-35) 51, 56-60, 61, 65, 71-75 (this is posted on Sakai) For Monday, read Chapter 2 (pages 36-57) Today s Goals We will discuss
1.6 Arrow s Impossibility Theorem Some announcements Homework #2: Text (pages 33-35) 51, 56-60, 61, 65, 71-75 (this is posted on Sakai) For Monday, read Chapter 2 (pages 36-57) Today s Goals We will discuss
Chapter 9: Social Choice: The Impossible Dream Lesson Plan
 Lesson Plan For All Practical Purposes An Introduction to Social Choice Majority Rule and Condorcet s Method Mathematical Literacy in Today s World, 9th ed. Other Voting Systems for Three or More Candidates
Lesson Plan For All Practical Purposes An Introduction to Social Choice Majority Rule and Condorcet s Method Mathematical Literacy in Today s World, 9th ed. Other Voting Systems for Three or More Candidates
Arrow s Impossibility Theorem on Social Choice Systems
 Arrow s Impossibility Theorem on Social Choice Systems Ashvin A. Swaminathan January 11, 2013 Abstract Social choice theory is a field that concerns methods of aggregating individual interests to determine
Arrow s Impossibility Theorem on Social Choice Systems Ashvin A. Swaminathan January 11, 2013 Abstract Social choice theory is a field that concerns methods of aggregating individual interests to determine
Recall: Properties of ranking rules. Recall: Properties of ranking rules. Kenneth Arrow. Recall: Properties of ranking rules. Strategically vulnerable
 Outline for today Stat155 Game Theory Lecture 26: More Voting. Peter Bartlett December 1, 2016 1 / 31 2 / 31 Recall: Voting and Ranking Recall: Properties of ranking rules Assumptions There is a set Γ
Outline for today Stat155 Game Theory Lecture 26: More Voting. Peter Bartlett December 1, 2016 1 / 31 2 / 31 Recall: Voting and Ranking Recall: Properties of ranking rules Assumptions There is a set Γ
Main idea: Voting systems matter.
 Voting Systems Main idea: Voting systems matter. Electoral College Winner takes all in most states (48/50) (plurality in states) 270/538 electoral votes needed to win (majority) If 270 isn t obtained -
Voting Systems Main idea: Voting systems matter. Electoral College Winner takes all in most states (48/50) (plurality in states) 270/538 electoral votes needed to win (majority) If 270 isn t obtained -
The Mathematics of Voting
 Math 165 Winston Salem, NC 28 October 2010 Voting for 2 candidates Today, we talk about voting, which may not seem mathematical. President of the Math TA s Let s say there s an election which has just
Math 165 Winston Salem, NC 28 October 2010 Voting for 2 candidates Today, we talk about voting, which may not seem mathematical. President of the Math TA s Let s say there s an election which has just
Fairness Criteria. Review: Election Methods
 Review: Election Methods Plurality method: the candidate with a plurality of votes wins. Plurality-with-elimination method (Instant runoff): Eliminate the candidate with the fewest first place votes. Keep
Review: Election Methods Plurality method: the candidate with a plurality of votes wins. Plurality-with-elimination method (Instant runoff): Eliminate the candidate with the fewest first place votes. Keep
MATH4999 Capstone Projects in Mathematics and Economics Topic 3 Voting methods and social choice theory
 MATH4999 Capstone Projects in Mathematics and Economics Topic 3 Voting methods and social choice theory 3.1 Social choice procedures Plurality voting Borda count Elimination procedures Sequential pairwise
MATH4999 Capstone Projects in Mathematics and Economics Topic 3 Voting methods and social choice theory 3.1 Social choice procedures Plurality voting Borda count Elimination procedures Sequential pairwise
The Mathematics of Voting. The Mathematics of Voting
 1.3 The Borda Count Method 1 In the Borda Count Method each place on a ballot is assigned points. In an election with N candidates we give 1 point for last place, 2 points for second from last place, and
1.3 The Borda Count Method 1 In the Borda Count Method each place on a ballot is assigned points. In an election with N candidates we give 1 point for last place, 2 points for second from last place, and
Voting Criteria: Majority Criterion Condorcet Criterion Monotonicity Criterion Independence of Irrelevant Alternatives Criterion
 We have discussed: Voting Theory Arrow s Impossibility Theorem Voting Methods: Plurality Borda Count Plurality with Elimination Pairwise Comparisons Voting Criteria: Majority Criterion Condorcet Criterion
We have discussed: Voting Theory Arrow s Impossibility Theorem Voting Methods: Plurality Borda Count Plurality with Elimination Pairwise Comparisons Voting Criteria: Majority Criterion Condorcet Criterion
Desirable properties of social choice procedures. We now outline a number of properties that are desirable for these social choice procedures:
 Desirable properties of social choice procedures We now outline a number of properties that are desirable for these social choice procedures: 1. Pareto [named for noted economist Vilfredo Pareto (1848-1923)]
Desirable properties of social choice procedures We now outline a number of properties that are desirable for these social choice procedures: 1. Pareto [named for noted economist Vilfredo Pareto (1848-1923)]
The search for a perfect voting system. MATH 105: Contemporary Mathematics. University of Louisville. October 31, 2017
 The search for a perfect voting system MATH 105: Contemporary Mathematics University of Louisville October 31, 2017 Review of Fairness Criteria Fairness Criteria 2 / 14 We ve seen three fairness criteria
The search for a perfect voting system MATH 105: Contemporary Mathematics University of Louisville October 31, 2017 Review of Fairness Criteria Fairness Criteria 2 / 14 We ve seen three fairness criteria
Mathematics and Social Choice Theory. Topic 4 Voting methods with more than 2 alternatives. 4.1 Social choice procedures
 Mathematics and Social Choice Theory Topic 4 Voting methods with more than 2 alternatives 4.1 Social choice procedures 4.2 Analysis of voting methods 4.3 Arrow s Impossibility Theorem 4.4 Cumulative voting
Mathematics and Social Choice Theory Topic 4 Voting methods with more than 2 alternatives 4.1 Social choice procedures 4.2 Analysis of voting methods 4.3 Arrow s Impossibility Theorem 4.4 Cumulative voting
Voting Criteria April
 Voting Criteria 21-301 2018 30 April 1 Evaluating voting methods In the last session, we learned about different voting methods. In this session, we will focus on the criteria we use to evaluate whether
Voting Criteria 21-301 2018 30 April 1 Evaluating voting methods In the last session, we learned about different voting methods. In this session, we will focus on the criteria we use to evaluate whether
Economics 470 Some Notes on Simple Alternatives to Majority Rule
 Economics 470 Some Notes on Simple Alternatives to Majority Rule Some of the voting procedures considered here are not considered as a means of revealing preferences on a public good issue, but as a means
Economics 470 Some Notes on Simple Alternatives to Majority Rule Some of the voting procedures considered here are not considered as a means of revealing preferences on a public good issue, but as a means
Mathematical Thinking. Chapter 9 Voting Systems
 Mathematical Thinking Chapter 9 Voting Systems Voting Systems A voting system is a rule for transforming a set of individual preferences into a single group decision. What are the desirable properties
Mathematical Thinking Chapter 9 Voting Systems Voting Systems A voting system is a rule for transforming a set of individual preferences into a single group decision. What are the desirable properties
Fairness Criteria. Majority Criterion: If a candidate receives a majority of the first place votes, that candidate should win the election.
 Fairness Criteria Majority Criterion: If a candidate receives a majority of the first place votes, that candidate should win the election. The plurality, plurality-with-elimination, and pairwise comparisons
Fairness Criteria Majority Criterion: If a candidate receives a majority of the first place votes, that candidate should win the election. The plurality, plurality-with-elimination, and pairwise comparisons
Section Voting Methods. Copyright 2013, 2010, 2007, Pearson, Education, Inc.
 Section 15.1 Voting Methods What You Will Learn Plurality Method Borda Count Method Plurality with Elimination Pairwise Comparison Method Tie Breaking 15.1-2 Example 2: Voting for the Honor Society President
Section 15.1 Voting Methods What You Will Learn Plurality Method Borda Count Method Plurality with Elimination Pairwise Comparison Method Tie Breaking 15.1-2 Example 2: Voting for the Honor Society President
Voting rules: (Dixit and Skeath, ch 14) Recall parkland provision decision:
 rules: (Dixit and Skeath, ch 14) Recall parkland provision decision: Assume - n=10; - total cost of proposed parkland=38; - if provided, each pays equal share = 3.8 - there are two groups of individuals
rules: (Dixit and Skeath, ch 14) Recall parkland provision decision: Assume - n=10; - total cost of proposed parkland=38; - if provided, each pays equal share = 3.8 - there are two groups of individuals
Section Voting Methods. Copyright 2013, 2010, 2007, Pearson, Education, Inc.
 Section 15.1 Voting Methods INB Table of Contents Date Topic Page # February 24, 2014 Test #3 Practice Test 38 February 24, 2014 Test #3 Practice Test Workspace 39 March 10, 2014 Test #3 40 March 10, 2014
Section 15.1 Voting Methods INB Table of Contents Date Topic Page # February 24, 2014 Test #3 Practice Test 38 February 24, 2014 Test #3 Practice Test Workspace 39 March 10, 2014 Test #3 40 March 10, 2014
answers to some of the sample exercises : Public Choice
 answers to some of the sample exercises : Public Choice Ques 1 The following table lists the way that 5 different voters rank five different alternatives. Is there a Condorcet winner under pairwise majority
answers to some of the sample exercises : Public Choice Ques 1 The following table lists the way that 5 different voters rank five different alternatives. Is there a Condorcet winner under pairwise majority
Measuring Fairness. Paul Koester () MA 111, Voting Theory September 7, / 25
 Measuring Fairness We ve seen FOUR methods for tallying votes: Plurality Borda Count Pairwise Comparisons Plurality with Elimination Are these methods reasonable? Are these methods fair? Today we study
Measuring Fairness We ve seen FOUR methods for tallying votes: Plurality Borda Count Pairwise Comparisons Plurality with Elimination Are these methods reasonable? Are these methods fair? Today we study
How should we count the votes?
 How should we count the votes? Bruce P. Conrad January 16, 2008 Were the Iowa caucuses undemocratic? Many politicians, pundits, and reporters thought so in the weeks leading up to the January 3, 2008 event.
How should we count the votes? Bruce P. Conrad January 16, 2008 Were the Iowa caucuses undemocratic? Many politicians, pundits, and reporters thought so in the weeks leading up to the January 3, 2008 event.
Elections with Only 2 Alternatives
 Math 203: Chapter 12: Voting Systems and Drawbacks: How do we decide the best voting system? Elections with Only 2 Alternatives What is an individual preference list? Majority Rules: Pick 1 of 2 candidates
Math 203: Chapter 12: Voting Systems and Drawbacks: How do we decide the best voting system? Elections with Only 2 Alternatives What is an individual preference list? Majority Rules: Pick 1 of 2 candidates
Voting Definitions and Theorems Spring Dr. Martin Montgomery Office: POT 761
 Voting Definitions and Theorems Spring 2014 Dr. Martin Montgomery Office: POT 761 http://www.ms.uky.edu/~martinm/m111 Voting Method: Plurality Definition (The Plurality Method of Voting) For each ballot,
Voting Definitions and Theorems Spring 2014 Dr. Martin Montgomery Office: POT 761 http://www.ms.uky.edu/~martinm/m111 Voting Method: Plurality Definition (The Plurality Method of Voting) For each ballot,
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems. Voting I 1/36
 Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems Voting I 1/36 Each even year every member of the house is up for election and about a third of the senate seats are up for grabs. Most people do not realize that there
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems Voting I 1/36 Each even year every member of the house is up for election and about a third of the senate seats are up for grabs. Most people do not realize that there
In deciding upon a winner, there is always one main goal: to reflect the preferences of the people in the most fair way possible.
 Voting Theory 1 Voting Theory In many decision making situations, it is necessary to gather the group consensus. This happens when a group of friends decides which movie to watch, when a company decides
Voting Theory 1 Voting Theory In many decision making situations, it is necessary to gather the group consensus. This happens when a group of friends decides which movie to watch, when a company decides
Many Social Choice Rules
 Many Social Choice Rules 1 Introduction So far, I have mentioned several of the most commonly used social choice rules : pairwise majority rule, plurality, plurality with a single run off, the Borda count.
Many Social Choice Rules 1 Introduction So far, I have mentioned several of the most commonly used social choice rules : pairwise majority rule, plurality, plurality with a single run off, the Borda count.
Math116Chap1VotingPart2.notebook January 12, Part II. Other Methods of Voting and Other "Fairness Criteria"
 Part II Other Methods of Voting and Other "Fairness Criteria" Plurality with Elimination Method Round 1. Count the first place votes for each candidate, just as you would in the plurality method. If a
Part II Other Methods of Voting and Other "Fairness Criteria" Plurality with Elimination Method Round 1. Count the first place votes for each candidate, just as you would in the plurality method. If a
MATH 1340 Mathematics & Politics
 MATH 1340 Mathematics & Politics Lecture 6 June 29, 2015 Slides prepared by Iian Smythe for MATH 1340, Summer 2015, at Cornell University 1 Basic criteria A social choice function is anonymous if voters
MATH 1340 Mathematics & Politics Lecture 6 June 29, 2015 Slides prepared by Iian Smythe for MATH 1340, Summer 2015, at Cornell University 1 Basic criteria A social choice function is anonymous if voters
Math Circle Voting Methods Practice. March 31, 2013
 Voting Methods Practice 1) Three students are running for class vice president: Chad, Courtney and Gwyn. Each student ranked the candidates in order of preference. The chart below shows the results of
Voting Methods Practice 1) Three students are running for class vice president: Chad, Courtney and Gwyn. Each student ranked the candidates in order of preference. The chart below shows the results of
(67686) Mathematical Foundations of AI June 18, Lecture 6
 (67686) Mathematical Foundations of AI June 18, 2008 Lecturer: Ariel D. Procaccia Lecture 6 Scribe: Ezra Resnick & Ariel Imber 1 Introduction: Social choice theory Thus far in the course, we have dealt
(67686) Mathematical Foundations of AI June 18, 2008 Lecturer: Ariel D. Procaccia Lecture 6 Scribe: Ezra Resnick & Ariel Imber 1 Introduction: Social choice theory Thus far in the course, we have dealt
Social welfare functions
 Social welfare functions We have defined a social choice function as a procedure that determines for each possible profile (set of preference ballots) of the voters the winner or set of winners for the
Social welfare functions We have defined a social choice function as a procedure that determines for each possible profile (set of preference ballots) of the voters the winner or set of winners for the
Social Choice: The Impossible Dream. Check off these skills when you feel that you have mastered them.
 Chapter Objectives Check off these skills when you feel that you have mastered them. Analyze and interpret preference list ballots. Explain three desired properties of Majority Rule. Explain May s theorem.
Chapter Objectives Check off these skills when you feel that you have mastered them. Analyze and interpret preference list ballots. Explain three desired properties of Majority Rule. Explain May s theorem.
Exercises For DATA AND DECISIONS. Part I Voting
 Exercises For DATA AND DECISIONS Part I Voting September 13, 2016 Exercise 1 Suppose that an election has candidates A, B, C, D and E. There are 7 voters, who submit the following ranked ballots: 2 1 1
Exercises For DATA AND DECISIONS Part I Voting September 13, 2016 Exercise 1 Suppose that an election has candidates A, B, C, D and E. There are 7 voters, who submit the following ranked ballots: 2 1 1
Chapter 9: Social Choice: The Impossible Dream Lesson Plan
 Lesson Plan For ll Practical Purposes Voting and Social hoice Majority Rule and ondorcet s Method Mathematical Literacy in Today s World, 7th ed. Other Voting Systems for Three or More andidates Plurality
Lesson Plan For ll Practical Purposes Voting and Social hoice Majority Rule and ondorcet s Method Mathematical Literacy in Today s World, 7th ed. Other Voting Systems for Three or More andidates Plurality
Social Choice & Mechanism Design
 Decision Making in Robots and Autonomous Agents Social Choice & Mechanism Design Subramanian Ramamoorthy School of Informatics 2 April, 2013 Introduction Social Choice Our setting: a set of outcomes agents
Decision Making in Robots and Autonomous Agents Social Choice & Mechanism Design Subramanian Ramamoorthy School of Informatics 2 April, 2013 Introduction Social Choice Our setting: a set of outcomes agents
Introduction to the Theory of Voting
 November 11, 2015 1 Introduction What is Voting? Motivation 2 Axioms I Anonymity, Neutrality and Pareto Property Issues 3 Voting Rules I Condorcet Extensions and Scoring Rules 4 Axioms II Reinforcement
November 11, 2015 1 Introduction What is Voting? Motivation 2 Axioms I Anonymity, Neutrality and Pareto Property Issues 3 Voting Rules I Condorcet Extensions and Scoring Rules 4 Axioms II Reinforcement
Head-to-Head Winner. To decide if a Head-to-Head winner exists: Every candidate is matched on a one-on-one basis with every other candidate.
 Head-to-Head Winner A candidate is a Head-to-Head winner if he or she beats all other candidates by majority rule when they meet head-to-head (one-on-one). To decide if a Head-to-Head winner exists: Every
Head-to-Head Winner A candidate is a Head-to-Head winner if he or she beats all other candidates by majority rule when they meet head-to-head (one-on-one). To decide if a Head-to-Head winner exists: Every
Chapter 1 Practice Test Questions
 0728 Finite Math Chapter 1 Practice Test Questions VOCABULARY. On the exam, be prepared to match the correct definition to the following terms: 1) Voting Elements: Single-choice ballot, preference ballot,
0728 Finite Math Chapter 1 Practice Test Questions VOCABULARY. On the exam, be prepared to match the correct definition to the following terms: 1) Voting Elements: Single-choice ballot, preference ballot,
Rock the Vote or Vote The Rock
 Rock the Vote or Vote The Rock Tom Edgar Department of Mathematics University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, Indiana October 27, 2008 Graduate Student Seminar Introduction Basic Counting Extended Counting Introduction
Rock the Vote or Vote The Rock Tom Edgar Department of Mathematics University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, Indiana October 27, 2008 Graduate Student Seminar Introduction Basic Counting Extended Counting Introduction
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems, Continued. Voting II 1/27
 Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems, Continued Voting II 1/27 Last Time Last time we discussed some elections and some issues with plurality voting. We started to discuss another voting system, the Borda
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems, Continued Voting II 1/27 Last Time Last time we discussed some elections and some issues with plurality voting. We started to discuss another voting system, the Borda
12.2 Defects in Voting Methods
 12.2 Defects in Voting Methods Recall the different Voting Methods: 1. Plurality - one vote to one candidate, the others get nothing The remaining three use a preference ballot, where all candidates are
12.2 Defects in Voting Methods Recall the different Voting Methods: 1. Plurality - one vote to one candidate, the others get nothing The remaining three use a preference ballot, where all candidates are
SOCIAL CHOICES (Voting Methods) THE PROBLEM. Social Choice and Voting. Terminologies
 SOCIAL CHOICES (Voting Methods) THE PROBLEM In a society, decisions are made by its members in order to come up with a situation that benefits the most. What is the best voting method of arriving at a
SOCIAL CHOICES (Voting Methods) THE PROBLEM In a society, decisions are made by its members in order to come up with a situation that benefits the most. What is the best voting method of arriving at a
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems, Continued
 Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems, Continued 7 March 2014 Voting III 7 March 2014 1/27 Last Time We ve discussed several voting systems and conditions which may or may not be satisfied by a system.
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems, Continued 7 March 2014 Voting III 7 March 2014 1/27 Last Time We ve discussed several voting systems and conditions which may or may not be satisfied by a system.
Voting Methods
 1.3-1.5 Voting Methods Some announcements Homework #1: Text (pages 28-33) 1, 4, 7, 10, 12, 19, 22, 29, 32, 38, 42, 50, 51, 56-60, 61, 65 (this is posted on Sakai) Math Center study sessions with Katie
1.3-1.5 Voting Methods Some announcements Homework #1: Text (pages 28-33) 1, 4, 7, 10, 12, 19, 22, 29, 32, 38, 42, 50, 51, 56-60, 61, 65 (this is posted on Sakai) Math Center study sessions with Katie
Chapter 9: Social Choice: The Impossible Dream
 Chapter 9: Social Choice: The Impossible Dream The application of mathematics to the study of human beings their behavior, values, interactions, conflicts, and methods of making decisions is generally
Chapter 9: Social Choice: The Impossible Dream The application of mathematics to the study of human beings their behavior, values, interactions, conflicts, and methods of making decisions is generally
Make the Math Club Great Again! The Mathematics of Democratic Voting
 Make the Math Club Great Again! The Mathematics of Democratic Voting Darci L. Kracht Kent State University Undergraduate Mathematics Club April 14, 2016 How do you become Math Club King, I mean, President?
Make the Math Club Great Again! The Mathematics of Democratic Voting Darci L. Kracht Kent State University Undergraduate Mathematics Club April 14, 2016 How do you become Math Club King, I mean, President?
The Manipulability of Voting Systems. Check off these skills when you feel that you have mastered them.
 Chapter 10 The Manipulability of Voting Systems Chapter Objectives Check off these skills when you feel that you have mastered them. Explain what is meant by voting manipulation. Determine if a voter,
Chapter 10 The Manipulability of Voting Systems Chapter Objectives Check off these skills when you feel that you have mastered them. Explain what is meant by voting manipulation. Determine if a voter,
Computational Social Choice: Spring 2007
 Computational Social Choice: Spring 2007 Ulle Endriss Institute for Logic, Language and Computation University of Amsterdam Ulle Endriss 1 Plan for Today This lecture will be an introduction to voting
Computational Social Choice: Spring 2007 Ulle Endriss Institute for Logic, Language and Computation University of Amsterdam Ulle Endriss 1 Plan for Today This lecture will be an introduction to voting
The mathematics of voting, power, and sharing Part 1
 The mathematics of voting, power, and sharing Part 1 Voting systems A voting system or a voting scheme is a way for a group of people to select one from among several possibilities. If there are only two
The mathematics of voting, power, and sharing Part 1 Voting systems A voting system or a voting scheme is a way for a group of people to select one from among several possibilities. If there are only two
Chapter 10. The Manipulability of Voting Systems. For All Practical Purposes: Effective Teaching. Chapter Briefing
 Chapter 10 The Manipulability of Voting Systems For All Practical Purposes: Effective Teaching As a teaching assistant, you most likely will administer and proctor many exams. Although it is tempting to
Chapter 10 The Manipulability of Voting Systems For All Practical Purposes: Effective Teaching As a teaching assistant, you most likely will administer and proctor many exams. Although it is tempting to
Math for Liberal Studies
 Math for Liberal Studies As we have discussed, when there are only two candidates in an election, deciding the winner is easy May s Theorem states that majority rule is the best system However, the situation
Math for Liberal Studies As we have discussed, when there are only two candidates in an election, deciding the winner is easy May s Theorem states that majority rule is the best system However, the situation
Math for Liberal Studies
 Math for Liberal Studies There are many more methods for determining the winner of an election with more than two candidates We will only discuss a few more: sequential pairwise voting contingency voting
Math for Liberal Studies There are many more methods for determining the winner of an election with more than two candidates We will only discuss a few more: sequential pairwise voting contingency voting
Today s plan: Section : Plurality with Elimination Method and a second Fairness Criterion: The Monotocity Criterion.
 1 Today s plan: Section 1.2.4. : Plurality with Elimination Method and a second Fairness Criterion: The Monotocity Criterion. 2 Plurality with Elimination is a third voting method. It is more complicated
1 Today s plan: Section 1.2.4. : Plurality with Elimination Method and a second Fairness Criterion: The Monotocity Criterion. 2 Plurality with Elimination is a third voting method. It is more complicated
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems. Voting I 1/31
 Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems Voting I 1/31 In 2014 every member of the house is up for election and about a third of the senate seats will be up for grabs. Most people do not realize that there
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems Voting I 1/31 In 2014 every member of the house is up for election and about a third of the senate seats will be up for grabs. Most people do not realize that there
Introduction: The Mathematics of Voting
 VOTING METHODS 1 Introduction: The Mathematics of Voting Content: Preference Ballots and Preference Schedules Voting methods including, 1). The Plurality Method 2). The Borda Count Method 3). The Plurality-with-Elimination
VOTING METHODS 1 Introduction: The Mathematics of Voting Content: Preference Ballots and Preference Schedules Voting methods including, 1). The Plurality Method 2). The Borda Count Method 3). The Plurality-with-Elimination
Mathematics of Voting Systems. Tanya Leise Mathematics & Statistics Amherst College
 Mathematics of Voting Systems Tanya Leise Mathematics & Statistics Amherst College Arrow s Impossibility Theorem 1) No special treatment of particular voters or candidates 2) Transitivity A>B and B>C implies
Mathematics of Voting Systems Tanya Leise Mathematics & Statistics Amherst College Arrow s Impossibility Theorem 1) No special treatment of particular voters or candidates 2) Transitivity A>B and B>C implies
Topics on the Border of Economics and Computation December 18, Lecture 8
 Topics on the Border of Economics and Computation December 18, 2005 Lecturer: Noam Nisan Lecture 8 Scribe: Ofer Dekel 1 Correlated Equilibrium In the previous lecture, we introduced the concept of correlated
Topics on the Border of Economics and Computation December 18, 2005 Lecturer: Noam Nisan Lecture 8 Scribe: Ofer Dekel 1 Correlated Equilibrium In the previous lecture, we introduced the concept of correlated
In deciding upon a winner, there is always one main goal: to reflect the preferences of the people in the most fair way possible.
 Voting Theory 35 Voting Theory In many decision making situations, it is necessary to gather the group consensus. This happens when a group of friends decides which movie to watch, when a company decides
Voting Theory 35 Voting Theory In many decision making situations, it is necessary to gather the group consensus. This happens when a group of friends decides which movie to watch, when a company decides
Lecture 11. Voting. Outline
 Lecture 11 Voting Outline Hanging Chads Again Did Ralph Nader cause the Bush presidency? A Paradox Left Middle Right 40 25 35 Robespierre Danton Lafarge D L R L R D A Paradox Consider Robespierre versus
Lecture 11 Voting Outline Hanging Chads Again Did Ralph Nader cause the Bush presidency? A Paradox Left Middle Right 40 25 35 Robespierre Danton Lafarge D L R L R D A Paradox Consider Robespierre versus
VOTING TO ELECT A SINGLE CANDIDATE
 N. R. Miller 05/01/97 5 th rev. 8/22/06 VOTING TO ELECT A SINGLE CANDIDATE This discussion focuses on single-winner elections, in which a single candidate is elected from a field of two or more candidates.
N. R. Miller 05/01/97 5 th rev. 8/22/06 VOTING TO ELECT A SINGLE CANDIDATE This discussion focuses on single-winner elections, in which a single candidate is elected from a field of two or more candidates.
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems
 Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems 3 March 2014 Voting I 3 March 2014 1/27 In 2014 every member of the house is up for election and about a third of the senate seats will be up for grabs. Most people
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems 3 March 2014 Voting I 3 March 2014 1/27 In 2014 every member of the house is up for election and about a third of the senate seats will be up for grabs. Most people
Voting Methods for Municipal Elections: Propaganda, Field Experiments and what USA voters want from an Election Algorithm
 Voting Methods for Municipal Elections: Propaganda, Field Experiments and what USA voters want from an Election Algorithm Kathryn Lenz, Mathematics and Statistics Department, University of Minnesota Duluth
Voting Methods for Municipal Elections: Propaganda, Field Experiments and what USA voters want from an Election Algorithm Kathryn Lenz, Mathematics and Statistics Department, University of Minnesota Duluth
The Impossibilities of Voting
 The Impossibilities of Voting Introduction Majority Criterion Condorcet Criterion Monotonicity Criterion Irrelevant Alternatives Criterion Arrow s Impossibility Theorem 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide
The Impossibilities of Voting Introduction Majority Criterion Condorcet Criterion Monotonicity Criterion Irrelevant Alternatives Criterion Arrow s Impossibility Theorem 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide
Social Choice Theory. Denis Bouyssou CNRS LAMSADE
 A brief and An incomplete Introduction Introduction to to Social Choice Theory Denis Bouyssou CNRS LAMSADE What is Social Choice Theory? Aim: study decision problems in which a group has to take a decision
A brief and An incomplete Introduction Introduction to to Social Choice Theory Denis Bouyssou CNRS LAMSADE What is Social Choice Theory? Aim: study decision problems in which a group has to take a decision
Notes for Session 7 Basic Voting Theory and Arrow s Theorem
 Notes for Session 7 Basic Voting Theory and Arrow s Theorem We follow up the Impossibility (Session 6) of pooling expert probabilities, while preserving unanimities in both unconditional and conditional
Notes for Session 7 Basic Voting Theory and Arrow s Theorem We follow up the Impossibility (Session 6) of pooling expert probabilities, while preserving unanimities in both unconditional and conditional
Font Size: A A. Eric Maskin and Amartya Sen JANUARY 19, 2017 ISSUE. 1 of 7 2/21/ :01 AM
 1 of 7 2/21/2017 10:01 AM Font Size: A A Eric Maskin and Amartya Sen JANUARY 19, 2017 ISSUE Americans have been using essentially the same rules to elect presidents since the beginning of the Republic.
1 of 7 2/21/2017 10:01 AM Font Size: A A Eric Maskin and Amartya Sen JANUARY 19, 2017 ISSUE Americans have been using essentially the same rules to elect presidents since the beginning of the Republic.
Voting Protocols. Introduction. Social choice: preference aggregation Our settings. Voting protocols are examples of social choice mechanisms
 Voting Protocols Yiling Chen September 14, 2011 Introduction Social choice: preference aggregation Our settings A set of agents have preferences over a set of alternatives Taking preferences of all agents,
Voting Protocols Yiling Chen September 14, 2011 Introduction Social choice: preference aggregation Our settings A set of agents have preferences over a set of alternatives Taking preferences of all agents,
Simple methods for single winner elections
 Simple methods for single winner elections Christoph Börgers Mathematics Department Tufts University Medford, MA April 14, 2018 http://emerald.tufts.edu/~cborgers/ I have posted these slides there. 1 /
Simple methods for single winner elections Christoph Börgers Mathematics Department Tufts University Medford, MA April 14, 2018 http://emerald.tufts.edu/~cborgers/ I have posted these slides there. 1 /
Explaining the Impossible: Kenneth Arrow s Nobel Prize Winning Theorem on Elections
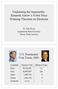 Explaining the Impossible: Kenneth Arrow s Nobel Prize Winning Theorem on Elections Dr. Rick Klima Appalachian State University Boone, North Carolina U.S. Presidential Vote Totals, 2000 Candidate Bush
Explaining the Impossible: Kenneth Arrow s Nobel Prize Winning Theorem on Elections Dr. Rick Klima Appalachian State University Boone, North Carolina U.S. Presidential Vote Totals, 2000 Candidate Bush
Rationality & Social Choice. Dougherty, POLS 8000
 Rationality & Social Choice Dougherty, POLS 8000 Social Choice A. Background 1. Social Choice examines how to aggregate individual preferences fairly. a. Voting is an example. b. Think of yourself writing
Rationality & Social Choice Dougherty, POLS 8000 Social Choice A. Background 1. Social Choice examines how to aggregate individual preferences fairly. a. Voting is an example. b. Think of yourself writing
Voting Systems. High School Circle I. June 4, 2017
 Voting Systems High School Circle I June 4, 2017 Today we are going to start our study of voting systems. Put loosely, a voting system takes the preferences of many people, and converted them into a group
Voting Systems High School Circle I June 4, 2017 Today we are going to start our study of voting systems. Put loosely, a voting system takes the preferences of many people, and converted them into a group
Lecture 16: Voting systems
 Lecture 16: Voting systems Economics 336 Economics 336 (Toronto) Lecture 16: Voting systems 1 / 18 Introduction Last lecture we looked at the basic theory of majority voting: instability in voting: Condorcet
Lecture 16: Voting systems Economics 336 Economics 336 (Toronto) Lecture 16: Voting systems 1 / 18 Introduction Last lecture we looked at the basic theory of majority voting: instability in voting: Condorcet
Approaches to Voting Systems
 Approaches to Voting Systems Properties, paradoxes, incompatibilities Hannu Nurmi Department of Philosophy, Contemporary History and Political Science University of Turku Game Theory and Voting Systems,
Approaches to Voting Systems Properties, paradoxes, incompatibilities Hannu Nurmi Department of Philosophy, Contemporary History and Political Science University of Turku Game Theory and Voting Systems,
Sect 13.2 Flaws of Voting Methods
 218 Sect 13.2 Flaws of Voting Methods From an example the previous section, we had 48 sports writers rank the top four Spurs players of all time. Below is the preference table. Number of votes 20 14 10
218 Sect 13.2 Flaws of Voting Methods From an example the previous section, we had 48 sports writers rank the top four Spurs players of all time. Below is the preference table. Number of votes 20 14 10
The Math of Rational Choice - Math 100 Spring 2015
 The Math of Rational Choice - Math 100 Spring 2015 Mathematics can be used to understand many aspects of decision-making in everyday life, such as: 1. Voting (a) Choosing a restaurant (b) Electing a leader
The Math of Rational Choice - Math 100 Spring 2015 Mathematics can be used to understand many aspects of decision-making in everyday life, such as: 1. Voting (a) Choosing a restaurant (b) Electing a leader
Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 12 Notes
 Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 12 Notes Voting Methods David J. Gisch Voting: Does the Majority Always Rule? Choosing a Winner In elections with more then 2 candidates, there are several acceptable
Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 12 Notes Voting Methods David J. Gisch Voting: Does the Majority Always Rule? Choosing a Winner In elections with more then 2 candidates, there are several acceptable
that changes needed to be made when electing their Presidential nominee. Iowa, at the time had a
 Part I The Iowa caucuses are perhaps the most important yet mysterious contest in American politics. It all began after the 1968 Democratic National Convention protest, the party decided that changes needed
Part I The Iowa caucuses are perhaps the most important yet mysterious contest in American politics. It all began after the 1968 Democratic National Convention protest, the party decided that changes needed
The Arrow Impossibility Theorem: Where Do We Go From Here?
 The Arrow Impossibility Theorem: Where Do We Go From Here? Eric Maskin Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton Arrow Lecture Columbia University December 11, 2009 I thank Amartya Sen and Joseph Stiglitz
The Arrow Impossibility Theorem: Where Do We Go From Here? Eric Maskin Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton Arrow Lecture Columbia University December 11, 2009 I thank Amartya Sen and Joseph Stiglitz
The Mathematics of Elections
 MTH 110 Week 1 hapter 1 Worksheet NME The Mathematics of Elections It s not the voting that s democracy; it s the counting. Tom Stoppard We have elections because we don t all think alike. Since we cannot
MTH 110 Week 1 hapter 1 Worksheet NME The Mathematics of Elections It s not the voting that s democracy; it s the counting. Tom Stoppard We have elections because we don t all think alike. Since we cannot
Social Choice. CSC304 Lecture 21 November 28, Allan Borodin Adapted from Craig Boutilier s slides
 Social Choice CSC304 Lecture 21 November 28, 2016 Allan Borodin Adapted from Craig Boutilier s slides 1 Todays agenda and announcements Today: Review of popular voting rules. Axioms, Manipulation, Impossibility
Social Choice CSC304 Lecture 21 November 28, 2016 Allan Borodin Adapted from Craig Boutilier s slides 1 Todays agenda and announcements Today: Review of popular voting rules. Axioms, Manipulation, Impossibility
CS 886: Multiagent Systems. Fall 2016 Kate Larson
 CS 886: Multiagent Systems Fall 2016 Kate Larson Multiagent Systems We will study the mathematical and computational foundations of multiagent systems, with a focus on the analysis of systems where agents
CS 886: Multiagent Systems Fall 2016 Kate Larson Multiagent Systems We will study the mathematical and computational foundations of multiagent systems, with a focus on the analysis of systems where agents
Mathematics and Democracy: Designing Better Voting and Fair-Division Procedures*
 Mathematics and Democracy: Designing Better Voting and Fair-Division Procedures* Steven J. Brams Department of Politics New York University New York, NY 10012 *This essay is adapted, with permission, from
Mathematics and Democracy: Designing Better Voting and Fair-Division Procedures* Steven J. Brams Department of Politics New York University New York, NY 10012 *This essay is adapted, with permission, from
French. Chinese. Mexican. Italian
 Lesson 1. rrow s onditions and pproval Voting Paradoxes, unfair results, and insincere voting are some of the problems that have caused people to look for better models for reaching group decisions. In
Lesson 1. rrow s onditions and pproval Voting Paradoxes, unfair results, and insincere voting are some of the problems that have caused people to look for better models for reaching group decisions. In
Safe Votes, Sincere Votes, and Strategizing
 Safe Votes, Sincere Votes, and Strategizing Rohit Parikh Eric Pacuit April 7, 2005 Abstract: We examine the basic notion of strategizing in the statement of the Gibbard-Satterthwaite theorem and note that
Safe Votes, Sincere Votes, and Strategizing Rohit Parikh Eric Pacuit April 7, 2005 Abstract: We examine the basic notion of strategizing in the statement of the Gibbard-Satterthwaite theorem and note that
Public Choice. Slide 1
 Public Choice We investigate how people can come up with a group decision mechanism. Several aspects of our economy can not be handled by the competitive market. Whenever there is market failure, there
Public Choice We investigate how people can come up with a group decision mechanism. Several aspects of our economy can not be handled by the competitive market. Whenever there is market failure, there
Arrow s Conditions and Approval Voting. Which group-ranking method is best?
 Arrow s Conditions and Approval Voting Which group-ranking method is best? Paradoxes When a group ranking results in an unexpected winner, the situation is known as a paradox. A special type of paradox
Arrow s Conditions and Approval Voting Which group-ranking method is best? Paradoxes When a group ranking results in an unexpected winner, the situation is known as a paradox. A special type of paradox
Warm Up Day 2 Determine the Plurality, Borda, Runoff, and Sequential Runoff winners.
 Warm Up Day 2 Determine the Plurality, orda, Runoff, and Sequential Runoff winners. D D D D 10 4 7 8 HW Questions? Pairwise Voting Once all of the ballots are submitted, we consider all of the different
Warm Up Day 2 Determine the Plurality, orda, Runoff, and Sequential Runoff winners. D D D D 10 4 7 8 HW Questions? Pairwise Voting Once all of the ballots are submitted, we consider all of the different
Constructing voting paradoxes with logic and symmetry
 Constructing voting paradoxes with logic and symmetry Part I: Voting and Logic Problem 1. There was a kingdom once ruled by a king and a council of three members: Ana, Bob and Cory. It was a very democratic
Constructing voting paradoxes with logic and symmetry Part I: Voting and Logic Problem 1. There was a kingdom once ruled by a king and a council of three members: Ana, Bob and Cory. It was a very democratic
Voting System: elections
 Voting System: elections 6 April 25, 2008 Abstract A voting system allows voters to choose between options. And, an election is an important voting system to select a cendidate. In 1951, Arrow s impossibility
Voting System: elections 6 April 25, 2008 Abstract A voting system allows voters to choose between options. And, an election is an important voting system to select a cendidate. In 1951, Arrow s impossibility
Possible voting reforms in the United States
 Possible voting reforms in the United States Since the disputed 2000 Presidential election, there have numerous proposals to improve how elections are conducted. While most proposals have attempted to
Possible voting reforms in the United States Since the disputed 2000 Presidential election, there have numerous proposals to improve how elections are conducted. While most proposals have attempted to
Constructing voting paradoxes with logic and symmetry Teacher s Notes
 Constructing voting paradoxes with logic and symmetry Teacher s Notes Elena Galaktionova elena@problemtrove.org Mobile Math Circle This is a loose transcript of the Math Circle, with occasional notes on
Constructing voting paradoxes with logic and symmetry Teacher s Notes Elena Galaktionova elena@problemtrove.org Mobile Math Circle This is a loose transcript of the Math Circle, with occasional notes on
Introduction to Theory of Voting. Chapter 2 of Computational Social Choice by William Zwicker
 Introduction to Theory of Voting Chapter 2 of Computational Social Choice by William Zwicker If we assume Introduction 1. every two voters play equivalent roles in our voting rule 2. every two alternatives
Introduction to Theory of Voting Chapter 2 of Computational Social Choice by William Zwicker If we assume Introduction 1. every two voters play equivalent roles in our voting rule 2. every two alternatives
Strategy and Effectiveness: An Analysis of Preferential Ballot Voting Methods
 Strategy and Effectiveness: An Analysis of Preferential Ballot Voting Methods Maksim Albert Tabachnik Advisor: Dr. Hubert Bray April 25, 2011 Submitted for Graduation with Distinction: Duke University
Strategy and Effectiveness: An Analysis of Preferential Ballot Voting Methods Maksim Albert Tabachnik Advisor: Dr. Hubert Bray April 25, 2011 Submitted for Graduation with Distinction: Duke University
PROBLEM SET #2: VOTING RULES
 POLI 309 Fall 2006 due 10/13/06 PROBLEM SET #2: VOTING RULES Write your answers directly on this page. Unless otherwise specified, assume all voters vote sincerely, i.e., in accordance with their preferences.
POLI 309 Fall 2006 due 10/13/06 PROBLEM SET #2: VOTING RULES Write your answers directly on this page. Unless otherwise specified, assume all voters vote sincerely, i.e., in accordance with their preferences.
Josh Engwer (TTU) Voting Methods 15 July / 49
 Voting Methods Contemporary Math Josh Engwer TTU 15 July 2015 Josh Engwer (TTU) Voting Methods 15 July 2015 1 / 49 Introduction In free societies, citizens vote for politicians whose values & opinions
Voting Methods Contemporary Math Josh Engwer TTU 15 July 2015 Josh Engwer (TTU) Voting Methods 15 July 2015 1 / 49 Introduction In free societies, citizens vote for politicians whose values & opinions
9.3 Other Voting Systems for Three or More Candidates
 9.3 Other Voting Systems for Three or More Candidates With three or more candidates, there are several additional procedures that seem to give reasonable ways to choose a winner. If we look closely at
9.3 Other Voting Systems for Three or More Candidates With three or more candidates, there are several additional procedures that seem to give reasonable ways to choose a winner. If we look closely at
Theorising the Democratic State. Elizabeth Frazer: Lecture 4. Who Rules? I
 Theorising the Democratic State Elizabeth Frazer: http://users.ox.ac.uk/~efrazer/default.htm Lecture 4 Who Rules? I The Elite Theory of Government Democratic Principles 1. Principle of autonomy: Individuals
Theorising the Democratic State Elizabeth Frazer: http://users.ox.ac.uk/~efrazer/default.htm Lecture 4 Who Rules? I The Elite Theory of Government Democratic Principles 1. Principle of autonomy: Individuals
