Possible voting reforms in the United States
|
|
|
- Franklin Simon
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Possible voting reforms in the United States Since the disputed 2000 Presidential election, there have numerous proposals to improve how elections are conducted. While most proposals have attempted to focus upon the voting machines the election also helped revisit numerous questions about the anachronism of the Electoral College and whether further radical reform of the plurality based voting system to another system entirely. The first class of reforms involve changes in the electoral college, and those that move from the current plurality election method system without a runoff election to another election method that more accurately reflects voter opinions. Electoral College related reforms One of the biggest criticisms of the US Presidential elections is that the winner of the popular vote does not always win the Electoral College. Since the Electoral College was established in the 1787 US Constitution, there have been numerous attempts to change the system. Other from the Twelfth Amendment, which changed the process for when no candidate achieved a majority of the votes in the electoral college and put the Vice President and President on a slate together, and the Twenty-third Amendment that gave the District of Columbia there have been no constitutional revisions to the electoral college since the Federal Constitution of Clearly changing the federal constitution on this matter is very difficult, but it doesn't stop people from making suggestions for constitutional revisions. There are also some changes that could be made at the state level. The move towards using the popular vote to determine the allotment of electors was a state level change not an national change. Most, but not all states originally did not use a popular vote to determine the winner of the electors, but rather through the state legislature. Contrary to popular belief the popular vote was not instituted by constitutional revision, but rather through state legislatures changing their election codes to change how presidential electors were determined. Elimination of the Electoral College This was a perennially popular suggestion after the 2000 Presidential elections. The arguments for this are clearly obvious in that it would eliminate the indirect nature of US Presidential Elections. It would ensure that the winner of the popular vote would win every elections unlike the several occurrences in US History in which the electoral votes did not match the popular votes. It would eliminate the weighted vote advantage that smaller states have by the unproportional two votes that every state receives by the status of having two Senators. It would also encourage Presidential candidates to campaign outside of the so-called swing states and to campaign in any place where they could garner more votes for themselves. U.S. Senators Hillary Clinton and Arlen Specter both called for the abolition of the Electoral College in 2000 after the electoral debacle, but this motion never faced serious consideration. There are the obvious criticisms of the elimination of the electoral college in that were there to be a closely contested election (1960 and 2000 elections) one could have
2 protests in any county in the United States. There could be a nationwide recount with possibly legal disputes in every state. The Electoral College limits recounts and disputes to a few counties in a few disputed states. Furthermore, the elimination of the Electoral College would require a constitutional amendment that would likely not be able to pass in the state legislatures of smaller states that receive greater power under the status quo. In addition, there are several reforms that could be implemented without a constitutional amendment. Proportional vote One proposal that has been considered is having states select their electors proportionally to the vote margin that they garner. Colorado's Amendment 36 would have instituted a proportional representation of their electors in the state of Colorado. There were legal questions about the initiative that would have likely prevented the implementation including the post de facto implementation affecting the 2004 election and of course the constitutional question of whether voter initiatives can even constitutional remove that power from the state legislature where it currently resides, but any state legislature could implement such a plan without an amendment to the US Constitution. Maine-Nebraska method The states of Maine and Nebraska both allot their two electors representing their Senators are given towards the winners of the popular vote and the other electoral votes go towards the winners of each individual congressional district. Obviously, this allows a presidential candidate to not entirely ignore a state for which the candidate believes that they will lose if they still stand a chance to garner additional electors through the congressional district electors. Other states could use this system, but the problem much like the proportional system voters probably wouldn't support their state legislature changing towards this system because it would decrease the attention that their state might receive from candidates. Furthermore, the problem of greater representation amongst less populous states would remain. Abolishing the non-proportional electors Amongst the final major Electoral College changes is to eliminate the nonproportional electors, those representing the two Senators that every state has in the US Senate. This plan would eliminate the unfair bias towards the smallest states in the union. Such a reform would require a constitutional revision to eliminate these nonproportional electors, which would make passing such a measure through the US Senate difficult if not impossible. If combined with proportional representation of electors within states it would be almost impossible for the winner of the popular vote not to win the presidency. Election methods Most people think that developing a system of voting that accurately reflects voter
3 opinions is a simple process, but that isn't always the case. If there are two options one will always have a clear winner. There are only two options and the winner is the person whom receives the most votes, but the process becomes far more complicated went the number of options increases to three. The possibility that a candidate fails to receive a majority of the votes becomes a possibility and the chance that this occurs becomes even more likely for every additional option above three. In most elections in the United States, except for Louisiana and some municipal elections, there are no runoff elections therefore whomever wins the plurality is declared the winner of the contest. This system is called the plurality election method and while rather popular in the United States has considerable criticism amongst voting theorists. Donald Saari, a mathematics professor at UC Irvine, notes that CIA repeatedly aided left wing parties in Chile to run candidates in order to divide the vote amongst left wing parties to ensure the defeat of all of the left leaning or socialist candidates in favor of a more palatable right wing candidate. While the United States doesn't routinely have this spoiler effect problem (many contests are one sided) there have been several examples in which less popular candidates have encouraged voters to vote for the lesser of the two evils. The recent examples include: the 1992 Presidential Election, the 2000 Presidential Election, and the 2003 California Recall Election. In the 1992 election, Ross Perot ran as an independent and garnered 19% of the popular vote and hence denying Bill Clinton or George H.W. Bush the ability to receive a majority of the popular vote. Hence, had there been a runoff election the voters for Perot could have easily shifted the election towards Bush instead of Clinton. Four years later Perot garnered only 9%, but still denied both Clinton a majority of the popular vote. In 2000, Ralph Nader acted as a spoiler in Florida according to Democrats because his vote exceeded the slim margin of victory for George W. Bush. While it is difficult to be completely certain that Nader voters would have bothered to vote and to have voted for Gore had Nader not been on the ballot the possibility that Nader shifted the election towards Bush is widely accepted by many Republicans and Democrats alike. In the 2003 California Recall election 135 candidates ultimately qualified for the ballot due to the the low ballot qualification standards 1 combined with the media frenzy that noted that theoretically a candidate might win with as little as 10% of the vote. Superior resources ultimately reduced the number of major candidates to three major candidates: Lt. Gov Cruz Bustamante, State Senator Tom McClintock, and Arnold Schwarzenegger. Both McClintock and Schwarzenegger are Republicans and despite Schwarzenegger's stronger polling numbers McClintock refused to leave the contest. Hence, Republicans became divided and the possibility that McClintock could throw the contest to Democrat Cruz Bustamante became a real possibility. While ultimately Schwarzenegger won ~48% of the vote and McClintock merely ~13% 2 one wonders whether Schwarzenegger won merely because of his early opinion polling success encouraged undecided and more pragmatic Republicans to vote for Arnold or whether Arnold really was more preferred by voters. Since McClintock had the highest approval rating amongst candidates one has to wonder whether early success in opinion polls skewed the results towards Schwarzenegger. Thanks to these examples and others many critics of the plurality based voting without a runoff election believe that the United States ought to move towards a non- 1 See: 2 See:
4 plurality based voting system. The other major election methods include plurality with runoff elections, approval voting, preferential voting (sometimes called Instant Runoff Voting(IRV)), the Borda Count method, and finally the Condorcet method. Plurality voting with runoff elections Amongst the least radical election method that the United States could move towards would be a plurality election system with a runoff election. While most US elections don't have runoffs, some local elections (San Francisco until 2004) and Louisiana's state elections do utilize runoff elections. Several foreign countries utilize runoff elections notably France and Russia. While this ensures that the winner receives a majority because runoffs usually only have two candidates it doesn't ensure that the most popular candidate amongst voters wins. The candidate that is the most popular amongst voters may ironically be eliminated in the first round. Two extremist candidates are the more likely to advance than two moderate candidates. A candidate that most voters don't like such as Jean-Marie Le Pen 3 can advance into the runoff over a candidate that may be closer to the majority of the voters. Another criticism of this plan is that there is a significantly higher cost to running runoff elections. The 2003 California Recall Election cost the state and counties an aggregate of $59 million dollars. While the 2003 California Recall Election was an unusual election in the large number of candidates (135) running an election costs millions of dollars and hence many voters may not support spending millions of dollars even if it would result in a more popular candidate being elected. Approval Voting The Approval Voting method is a bit different from the status quo, but still rather simple to understand. In Approval Voting every voter votes for as many candidates as they approve to do the job. Approval voting is currently used by the United Nations to elect their Secretary General and also by the National Academy of Sciences. Because most major candidates have approval rates that exceed 50% the winner of such a race would be the candidate that was the least disliked candidate. As a added side effect it would discourage dirty campaigning because candidates whom attack opponents not only harm their opponents, but also frequently harm their own approval ratings. 4 Therefore, in order to prevent some third candidate from winning most candidates would probably try to stay away from any type of advertising that might backfire as being too negative. Furthermore, in most cases there would be little cost in implementation of approval voting because most current voting technologies can easily support this voting method. There is the obvious criticism that approval voting does not give voter the option of giving preference of one candidate over when one approves of multiple candidates. In addition, the winner is likely to merely be the least disliked not necessarily any voters first choice. Preferential voting (Instant Runoff voting) Preferential voting is a system where the voter ranks their choices. In preferential 3 See: 4 See:
5 voting the concept of the spoiler candidate is largely eliminated because one can vote for the candidate they most desire to win first and their pragmatic choice second. This election method is used by some parliamentary seats in Australia 5, various student governments (Berkeley, Harvard, Stanford,...), the National Forensic League, and San Francisco municipal elections as of Therefore, if their candidate is eliminated they still get to have some role determining the winner unlike the current plurality based voting system. In addition, unlike approval voting one can make further degradations between candidates beyond simply whether one approves or disapproves of the candidate. Some of the criticisms of preferential voting should be somewhat obvious to anyone whom has ever used this voting system. One problem is that the system encourages individuals to put candidates that they want to lose lower than they may actually be if they were voting honest to their desires. Hence, virtually every time this system was used a the National Forensic League qualifier for Student Congress I always remember dropping those I didn't want to win off of the ballot entirely. I would pack my ballot beyond the one of two choices that I wanted to win with individuals whom I knew had no chance of winning. Therefore, the person I didn't want to win could never receive a 2 nd, 3 rd, 4 th,... xth place vote from my ballot. Almost every other strategy minded voter I knew did the same. Considering this was a room of high school students I wouldn't find it a stretch of the imagination for a majority of adult voters to do the same. In addition, it sometimes forces voters to make decisions in differences where they may not obviously exist. Furthermore, much like plurality based voting with a runoff election ironically the candidate that is tolerated for the job could be eliminated in the first ballot. One candidate may be more popular amongst voters than another candidate, but be eliminated earlier merely because they received less first place votes. 7 Many critics of preferential voting note that the system systematically encourages disingenuous voting. 8 In theory preferential voting sounds good because if the voters voted honest to whom they really think would do the best in the precise order of quality the system would work great, but in practice preferential voting may not work as elegantly. The Borda Count The Borda Count method was a preferential voting system devised by Jean- Charles de Borda in The Borda Count election method takes the number of candidates x and assign each place a value of x-p where p is the place. Hence a 1 st place in a four candidate race would be worth 3(4-1). 9 It is fairly easy to see how this method can involve a candidate whom receives few or even no first place votes and still be in first place. Many sports polls and MVP voting run on a variation of this system where 1 st place may be 2-3 points more than second place instead of the customary 1 point to make it harder for a team to be ranked number 1 with no first place votes. A variation of the Borda Count is used in Naura, Kiribati, some private organizations and as noted some sporting polls use a modified version of the Borda count. 10 Much like preferential voting 5 See: See: 7 See: 8 See: 9 See: Saari, Donald. Basic Geometry of Voting (Basic Geometry of Voting). N.p.: Springer, See:
6 this system would encourage a voter to place a candidate they didn't want to win as low as possible even if one preferred that candidate over all others except one. Condorcet Voting The last and probably least practical voting system is the Condorcet voting method. In this method the voter selects their preference for every single head to head on a matrix. Under this system the voter would have a great amount of power to give preferences for any head to head contest. The problem is that while many academics tout this as the ultimate voting system it would prove difficult to implement for large elections. For example had this system been used in the California Recall Election there would have been a matrix with 18,090 head to heads (135x ). Voters would easily have so many head to heads to vote for that it could easily take two, three, or four times as long as the current ballot. Add in the additional ballot costs and the confusion amongst voters and this system while perfect in voting theory wouldn't be practical for contests of any significant size.
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems. Voting I 1/31
 Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems Voting I 1/31 In 2014 every member of the house is up for election and about a third of the senate seats will be up for grabs. Most people do not realize that there
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems Voting I 1/31 In 2014 every member of the house is up for election and about a third of the senate seats will be up for grabs. Most people do not realize that there
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems
 Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems 3 March 2014 Voting I 3 March 2014 1/27 In 2014 every member of the house is up for election and about a third of the senate seats will be up for grabs. Most people
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems 3 March 2014 Voting I 3 March 2014 1/27 In 2014 every member of the house is up for election and about a third of the senate seats will be up for grabs. Most people
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems. Voting I 1/36
 Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems Voting I 1/36 Each even year every member of the house is up for election and about a third of the senate seats are up for grabs. Most people do not realize that there
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems Voting I 1/36 Each even year every member of the house is up for election and about a third of the senate seats are up for grabs. Most people do not realize that there
Main idea: Voting systems matter.
 Voting Systems Main idea: Voting systems matter. Electoral College Winner takes all in most states (48/50) (plurality in states) 270/538 electoral votes needed to win (majority) If 270 isn t obtained -
Voting Systems Main idea: Voting systems matter. Electoral College Winner takes all in most states (48/50) (plurality in states) 270/538 electoral votes needed to win (majority) If 270 isn t obtained -
9.3 Other Voting Systems for Three or More Candidates
 9.3 Other Voting Systems for Three or More Candidates With three or more candidates, there are several additional procedures that seem to give reasonable ways to choose a winner. If we look closely at
9.3 Other Voting Systems for Three or More Candidates With three or more candidates, there are several additional procedures that seem to give reasonable ways to choose a winner. If we look closely at
What is the Best Election Method?
 What is the Best Election Method? E. Maskin Harvard University Gorman Lectures University College, London February 2016 Today and tomorrow will explore 2 Today and tomorrow will explore election methods
What is the Best Election Method? E. Maskin Harvard University Gorman Lectures University College, London February 2016 Today and tomorrow will explore 2 Today and tomorrow will explore election methods
Font Size: A A. Eric Maskin and Amartya Sen JANUARY 19, 2017 ISSUE. 1 of 7 2/21/ :01 AM
 1 of 7 2/21/2017 10:01 AM Font Size: A A Eric Maskin and Amartya Sen JANUARY 19, 2017 ISSUE Americans have been using essentially the same rules to elect presidents since the beginning of the Republic.
1 of 7 2/21/2017 10:01 AM Font Size: A A Eric Maskin and Amartya Sen JANUARY 19, 2017 ISSUE Americans have been using essentially the same rules to elect presidents since the beginning of the Republic.
Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 12 Notes
 Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 12 Notes Voting Methods David J. Gisch Voting: Does the Majority Always Rule? Choosing a Winner In elections with more then 2 candidates, there are several acceptable
Math for Liberal Arts MAT 110: Chapter 12 Notes Voting Methods David J. Gisch Voting: Does the Majority Always Rule? Choosing a Winner In elections with more then 2 candidates, there are several acceptable
To understand the U.S. electoral college and, more generally, American democracy, it is critical to understand that when voters go to the polls on
 To understand the U.S. electoral college and, more generally, American democracy, it is critical to understand that when voters go to the polls on Tuesday, November 8th, they are not voting together in
To understand the U.S. electoral college and, more generally, American democracy, it is critical to understand that when voters go to the polls on Tuesday, November 8th, they are not voting together in
How Should Members of Parliament (and Presidents) Be Elected? E. Maskin Institute for Advanced Study
 How Should Members of Parliament (and Presidents) Be Elected? E. Maskin Institute for Advanced Study What s wrong with this picture? 2005 U.K. General Election Constituency of Croyden Central vote totals
How Should Members of Parliament (and Presidents) Be Elected? E. Maskin Institute for Advanced Study What s wrong with this picture? 2005 U.K. General Election Constituency of Croyden Central vote totals
The Electoral College
 The Electoral College H. FRY 2014 What is the Electoral College? The Electoral College is NOT a University! College: -noun An organized association of persons having certain powers and rights, and performing
The Electoral College H. FRY 2014 What is the Electoral College? The Electoral College is NOT a University! College: -noun An organized association of persons having certain powers and rights, and performing
that changes needed to be made when electing their Presidential nominee. Iowa, at the time had a
 Part I The Iowa caucuses are perhaps the most important yet mysterious contest in American politics. It all began after the 1968 Democratic National Convention protest, the party decided that changes needed
Part I The Iowa caucuses are perhaps the most important yet mysterious contest in American politics. It all began after the 1968 Democratic National Convention protest, the party decided that changes needed
PROBLEM SET #2: VOTING RULES
 POLI 309 Fall 2006 due 10/13/06 PROBLEM SET #2: VOTING RULES Write your answers directly on this page. Unless otherwise specified, assume all voters vote sincerely, i.e., in accordance with their preferences.
POLI 309 Fall 2006 due 10/13/06 PROBLEM SET #2: VOTING RULES Write your answers directly on this page. Unless otherwise specified, assume all voters vote sincerely, i.e., in accordance with their preferences.
LWV Oklahoma Instant Runoff Voting (IRV) or Ranked Choice Voting (RCV) Study
 LWV Oklahoma Instant Runoff Voting (IRV) or Ranked Choice Voting (RCV) Study Contents Study background 2 Election Systems 2 Plurality 2 Two Round Runoff 3 Instant Runoff or Ranked Choice Voting 3 Election
LWV Oklahoma Instant Runoff Voting (IRV) or Ranked Choice Voting (RCV) Study Contents Study background 2 Election Systems 2 Plurality 2 Two Round Runoff 3 Instant Runoff or Ranked Choice Voting 3 Election
Chapter 1 Practice Test Questions
 0728 Finite Math Chapter 1 Practice Test Questions VOCABULARY. On the exam, be prepared to match the correct definition to the following terms: 1) Voting Elements: Single-choice ballot, preference ballot,
0728 Finite Math Chapter 1 Practice Test Questions VOCABULARY. On the exam, be prepared to match the correct definition to the following terms: 1) Voting Elements: Single-choice ballot, preference ballot,
Electing a President. The Electoral College
 Electing a President The Electoral College The Original Electoral College System Compromise between allowing Congress to choose a chief executive and direct popular election -Allowing Congress goes against
Electing a President The Electoral College The Original Electoral College System Compromise between allowing Congress to choose a chief executive and direct popular election -Allowing Congress goes against
The Mathematics of Voting Transcript
 The Mathematics of Voting Transcript Hello, my name is Andy Felt. I'm a professor of Mathematics at the University of Wisconsin- Stevens Point. This is Chris Natzke. Chris is a student at the University
The Mathematics of Voting Transcript Hello, my name is Andy Felt. I'm a professor of Mathematics at the University of Wisconsin- Stevens Point. This is Chris Natzke. Chris is a student at the University
Electoral College Reform: Evaluation and Policy Recommendations
 Electoral College Reform: Evaluation and Policy Recommendations Albert Qian, Alex Hider, Amanda Khan, Caroline Reisch, Madeline Goossen, and Araksya Nordikyan Research Question What are alternative ways
Electoral College Reform: Evaluation and Policy Recommendations Albert Qian, Alex Hider, Amanda Khan, Caroline Reisch, Madeline Goossen, and Araksya Nordikyan Research Question What are alternative ways
The California Primary and Redistricting
 The California Primary and Redistricting This study analyzes what is the important impact of changes in the primary voting rules after a Congressional and Legislative Redistricting. Under a citizen s committee,
The California Primary and Redistricting This study analyzes what is the important impact of changes in the primary voting rules after a Congressional and Legislative Redistricting. Under a citizen s committee,
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems, Continued
 Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems, Continued 7 March 2014 Voting III 7 March 2014 1/27 Last Time We ve discussed several voting systems and conditions which may or may not be satisfied by a system.
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems, Continued 7 March 2014 Voting III 7 March 2014 1/27 Last Time We ve discussed several voting systems and conditions which may or may not be satisfied by a system.
Voting Methods for Municipal Elections: Propaganda, Field Experiments and what USA voters want from an Election Algorithm
 Voting Methods for Municipal Elections: Propaganda, Field Experiments and what USA voters want from an Election Algorithm Kathryn Lenz, Mathematics and Statistics Department, University of Minnesota Duluth
Voting Methods for Municipal Elections: Propaganda, Field Experiments and what USA voters want from an Election Algorithm Kathryn Lenz, Mathematics and Statistics Department, University of Minnesota Duluth
Campaigning in General Elections (HAA)
 Campaigning in General Elections (HAA) Once the primary season ends, the candidates who have won their party s nomination shift gears to campaign in the general election. Although the Constitution calls
Campaigning in General Elections (HAA) Once the primary season ends, the candidates who have won their party s nomination shift gears to campaign in the general election. Although the Constitution calls
Issue Overview: How the U.S. elects its presidents
 Issue Overview: How the U.S. elects its presidents By Bloomberg, adapted by Newsela staff on 09.27.16 Word Count 660 TOP: Voters head to the polls on Super Tuesday during the primaries. Photo by Alex Wong.
Issue Overview: How the U.S. elects its presidents By Bloomberg, adapted by Newsela staff on 09.27.16 Word Count 660 TOP: Voters head to the polls on Super Tuesday during the primaries. Photo by Alex Wong.
Chapter 9: Social Choice: The Impossible Dream Lesson Plan
 Lesson Plan For All Practical Purposes An Introduction to Social Choice Majority Rule and Condorcet s Method Mathematical Literacy in Today s World, 9th ed. Other Voting Systems for Three or More Candidates
Lesson Plan For All Practical Purposes An Introduction to Social Choice Majority Rule and Condorcet s Method Mathematical Literacy in Today s World, 9th ed. Other Voting Systems for Three or More Candidates
Math Circle Voting Methods Practice. March 31, 2013
 Voting Methods Practice 1) Three students are running for class vice president: Chad, Courtney and Gwyn. Each student ranked the candidates in order of preference. The chart below shows the results of
Voting Methods Practice 1) Three students are running for class vice president: Chad, Courtney and Gwyn. Each student ranked the candidates in order of preference. The chart below shows the results of
U.S Presidential Election
 U.S Presidential Election The US has had an elected president since its constitution went into effect in 1789. Unlike in many countries, the Presidential election in the US is rather a year-long process
U.S Presidential Election The US has had an elected president since its constitution went into effect in 1789. Unlike in many countries, the Presidential election in the US is rather a year-long process
Rock the Vote or Vote The Rock
 Rock the Vote or Vote The Rock Tom Edgar Department of Mathematics University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, Indiana October 27, 2008 Graduate Student Seminar Introduction Basic Counting Extended Counting Introduction
Rock the Vote or Vote The Rock Tom Edgar Department of Mathematics University of Notre Dame Notre Dame, Indiana October 27, 2008 Graduate Student Seminar Introduction Basic Counting Extended Counting Introduction
Election Campaigns GUIDE TO READING
 Election Campaigns GUIDE TO READING Main Idea Every two years for Congress and every four years for the president, voters respond to political campaigns by going to the polls and casting their ballots.
Election Campaigns GUIDE TO READING Main Idea Every two years for Congress and every four years for the president, voters respond to political campaigns by going to the polls and casting their ballots.
THE CITY OF LOS ANGELES RUNOFF ELECTIONS: EXPENSIVE, WASTEFUL AND LOW VOTER PARTICIPATION
 THE CITY OF LOS ANGELES RUNOFF ELECTIONS: EXPENSIVE, WASTEFUL AND LOW VOTER PARTICIPATION OVERVIEW The City of Los Angeles currently uses a two-round runoff system to elect its mayor, city attorney, city
THE CITY OF LOS ANGELES RUNOFF ELECTIONS: EXPENSIVE, WASTEFUL AND LOW VOTER PARTICIPATION OVERVIEW The City of Los Angeles currently uses a two-round runoff system to elect its mayor, city attorney, city
Chapter 5: Political Parties Section 1
 Chapter 5: Political Parties Section 1 What is a Party? The party organization is the party professionals who run the party at all levels by contributing time, money, and skill. The party in government
Chapter 5: Political Parties Section 1 What is a Party? The party organization is the party professionals who run the party at all levels by contributing time, money, and skill. The party in government
The Mathematics of Voting
 Math 165 Winston Salem, NC 28 October 2010 Voting for 2 candidates Today, we talk about voting, which may not seem mathematical. President of the Math TA s Let s say there s an election which has just
Math 165 Winston Salem, NC 28 October 2010 Voting for 2 candidates Today, we talk about voting, which may not seem mathematical. President of the Math TA s Let s say there s an election which has just
Computational Social Choice: Spring 2007
 Computational Social Choice: Spring 2007 Ulle Endriss Institute for Logic, Language and Computation University of Amsterdam Ulle Endriss 1 Plan for Today This lecture will be an introduction to voting
Computational Social Choice: Spring 2007 Ulle Endriss Institute for Logic, Language and Computation University of Amsterdam Ulle Endriss 1 Plan for Today This lecture will be an introduction to voting
US History, October 8
 US History, October 8 Entry Task: Write down your FAVORITE cartoon character. We will narrow it down to 2 or 3 - you ll need a piece of paper (FYI) Announcements Fill out worksheet - ONLY Executive side
US History, October 8 Entry Task: Write down your FAVORITE cartoon character. We will narrow it down to 2 or 3 - you ll need a piece of paper (FYI) Announcements Fill out worksheet - ONLY Executive side
A New Electoral System for a New Century. Eric Stevens
 A New Electoral System for a New Century Eric There are many difficulties we face as a nation concerning public policy, but of these difficulties the most pressing is the need for the reform of the electoral
A New Electoral System for a New Century Eric There are many difficulties we face as a nation concerning public policy, but of these difficulties the most pressing is the need for the reform of the electoral
Simulating Electoral College Results using Ranked Choice Voting if a Strong Third Party Candidate were in the Election Race
 Simulating Electoral College Results using Ranked Choice Voting if a Strong Third Party Candidate were in the Election Race Michele L. Joyner and Nicholas J. Joyner Department of Mathematics & Statistics
Simulating Electoral College Results using Ranked Choice Voting if a Strong Third Party Candidate were in the Election Race Michele L. Joyner and Nicholas J. Joyner Department of Mathematics & Statistics
Is Majority Rule the Best Voting Method? Partha Dasgupta and Eric Maskin
 Is Majority Rule the Best Voting Method? by Partha Dasgupta and Eric Maskin June 2003 The authors are, respectively, the Frank Ramsey Professor of Economics at the University of Cambridge, UK, and the
Is Majority Rule the Best Voting Method? by Partha Dasgupta and Eric Maskin June 2003 The authors are, respectively, the Frank Ramsey Professor of Economics at the University of Cambridge, UK, and the
The Iowa Caucuses. (See Attached Page Below) B R C T R B R R C C B C T T T B
 Date: 9/27/2016 The Iowa Caucuses Part I: Research the Iowa Caucuses and explain how they work. Your response should be a one-page (250-word) narrative. Be sure to include a brief history, how a caucus
Date: 9/27/2016 The Iowa Caucuses Part I: Research the Iowa Caucuses and explain how they work. Your response should be a one-page (250-word) narrative. Be sure to include a brief history, how a caucus
Simple methods for single winner elections
 Simple methods for single winner elections Christoph Börgers Mathematics Department Tufts University Medford, MA April 14, 2018 http://emerald.tufts.edu/~cborgers/ I have posted these slides there. 1 /
Simple methods for single winner elections Christoph Börgers Mathematics Department Tufts University Medford, MA April 14, 2018 http://emerald.tufts.edu/~cborgers/ I have posted these slides there. 1 /
Battleground 59: A (Potentially) Wasted Opportunity for the Republican Party Republican Analysis by: Ed Goeas and Brian Nienaber
 Battleground 59: A (Potentially) Wasted Opportunity for the Republican Party Republican Analysis by: Ed Goeas and Brian Nienaber In what seems like so long ago, the 2016 Presidential Election cycle began
Battleground 59: A (Potentially) Wasted Opportunity for the Republican Party Republican Analysis by: Ed Goeas and Brian Nienaber In what seems like so long ago, the 2016 Presidential Election cycle began
American Dental Association
 American Dental Association May 2, 2016 Bill McInturff SLIDE 1 Heading into the Election Year SLIDE 2 Direction of country remains strongly negative for over a decade. Right Track Wrong Direction WT 80
American Dental Association May 2, 2016 Bill McInturff SLIDE 1 Heading into the Election Year SLIDE 2 Direction of country remains strongly negative for over a decade. Right Track Wrong Direction WT 80
The search for a perfect voting system. MATH 105: Contemporary Mathematics. University of Louisville. October 31, 2017
 The search for a perfect voting system MATH 105: Contemporary Mathematics University of Louisville October 31, 2017 Review of Fairness Criteria Fairness Criteria 2 / 14 We ve seen three fairness criteria
The search for a perfect voting system MATH 105: Contemporary Mathematics University of Louisville October 31, 2017 Review of Fairness Criteria Fairness Criteria 2 / 14 We ve seen three fairness criteria
Josh Engwer (TTU) Voting Methods 15 July / 49
 Voting Methods Contemporary Math Josh Engwer TTU 15 July 2015 Josh Engwer (TTU) Voting Methods 15 July 2015 1 / 49 Introduction In free societies, citizens vote for politicians whose values & opinions
Voting Methods Contemporary Math Josh Engwer TTU 15 July 2015 Josh Engwer (TTU) Voting Methods 15 July 2015 1 / 49 Introduction In free societies, citizens vote for politicians whose values & opinions
Explaining the Impossible: Kenneth Arrow s Nobel Prize Winning Theorem on Elections
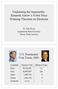 Explaining the Impossible: Kenneth Arrow s Nobel Prize Winning Theorem on Elections Dr. Rick Klima Appalachian State University Boone, North Carolina U.S. Presidential Vote Totals, 2000 Candidate Bush
Explaining the Impossible: Kenneth Arrow s Nobel Prize Winning Theorem on Elections Dr. Rick Klima Appalachian State University Boone, North Carolina U.S. Presidential Vote Totals, 2000 Candidate Bush
The Arrow Impossibility Theorem: Where Do We Go From Here?
 The Arrow Impossibility Theorem: Where Do We Go From Here? Eric Maskin Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton Arrow Lecture Columbia University December 11, 2009 I thank Amartya Sen and Joseph Stiglitz
The Arrow Impossibility Theorem: Where Do We Go From Here? Eric Maskin Institute for Advanced Study, Princeton Arrow Lecture Columbia University December 11, 2009 I thank Amartya Sen and Joseph Stiglitz
VOTING SYSTEMS AND ARROW S THEOREM
 VOTING SYSTEMS AND ARROW S THEOREM AKHIL MATHEW Abstract. The following is a brief discussion of Arrow s theorem in economics. I wrote it for an economics class in high school. 1. Background Arrow s theorem
VOTING SYSTEMS AND ARROW S THEOREM AKHIL MATHEW Abstract. The following is a brief discussion of Arrow s theorem in economics. I wrote it for an economics class in high school. 1. Background Arrow s theorem
Elections with Only 2 Alternatives
 Math 203: Chapter 12: Voting Systems and Drawbacks: How do we decide the best voting system? Elections with Only 2 Alternatives What is an individual preference list? Majority Rules: Pick 1 of 2 candidates
Math 203: Chapter 12: Voting Systems and Drawbacks: How do we decide the best voting system? Elections with Only 2 Alternatives What is an individual preference list? Majority Rules: Pick 1 of 2 candidates
Today s plan: Section : Plurality with Elimination Method and a second Fairness Criterion: The Monotocity Criterion.
 1 Today s plan: Section 1.2.4. : Plurality with Elimination Method and a second Fairness Criterion: The Monotocity Criterion. 2 Plurality with Elimination is a third voting method. It is more complicated
1 Today s plan: Section 1.2.4. : Plurality with Elimination Method and a second Fairness Criterion: The Monotocity Criterion. 2 Plurality with Elimination is a third voting method. It is more complicated
CHOICE VOTING: ONE YEAR LATER
 CHOICE VOTING: ONE YEAR LATER CHRISTOPHER JERDONEK SONNY MOHAMMADZADEH CONTENTS 1. Introduction 1 2. Choice Voting Background 2 3. Part 1 of Analysis: Slate Representation 3 4. Part 2 of Analysis: Candidate
CHOICE VOTING: ONE YEAR LATER CHRISTOPHER JERDONEK SONNY MOHAMMADZADEH CONTENTS 1. Introduction 1 2. Choice Voting Background 2 3. Part 1 of Analysis: Slate Representation 3 4. Part 2 of Analysis: Candidate
Political Sophistication and Third-Party Voting in Recent Presidential Elections
 Political Sophistication and Third-Party Voting in Recent Presidential Elections Christopher N. Lawrence Department of Political Science Duke University April 3, 2006 Overview During the 1990s, minor-party
Political Sophistication and Third-Party Voting in Recent Presidential Elections Christopher N. Lawrence Department of Political Science Duke University April 3, 2006 Overview During the 1990s, minor-party
Fairness Criteria. Review: Election Methods
 Review: Election Methods Plurality method: the candidate with a plurality of votes wins. Plurality-with-elimination method (Instant runoff): Eliminate the candidate with the fewest first place votes. Keep
Review: Election Methods Plurality method: the candidate with a plurality of votes wins. Plurality-with-elimination method (Instant runoff): Eliminate the candidate with the fewest first place votes. Keep
The Electoral College. What is it?, how does it work?, the pros, and the cons
 The Electoral College What is it?, how does it work?, the pros, and the cons What is the Electoral College? n E lec tor al College- A body of electors chosen to elect the President and Vice President of
The Electoral College What is it?, how does it work?, the pros, and the cons What is the Electoral College? n E lec tor al College- A body of electors chosen to elect the President and Vice President of
Presidential Election Democrat Grover Cleveland versus Benjamin Harrison. ************************************ Difference of 100,456
 Presidential Election 1886 Democrat Grover Cleveland versus Benjamin Harrison Cleveland 5,540,309 Harrison 5,439,853 ************************************ Difference of 100,456 Electoral College Cleveland
Presidential Election 1886 Democrat Grover Cleveland versus Benjamin Harrison Cleveland 5,540,309 Harrison 5,439,853 ************************************ Difference of 100,456 Electoral College Cleveland
Political Sophistication and Third-Party Voting in Recent Presidential Elections
 Political Sophistication and Third-Party Voting in Recent Presidential Elections Christopher N. Lawrence Department of Political Science Duke University April 3, 2006 Overview During the 1990s, minor-party
Political Sophistication and Third-Party Voting in Recent Presidential Elections Christopher N. Lawrence Department of Political Science Duke University April 3, 2006 Overview During the 1990s, minor-party
Why The National Popular Vote Bill Is Not A Good Choice
 Why The National Popular Vote Bill Is Not A Good Choice A quick look at the National Popular Vote (NPV) approach gives the impression that it promises a much better result in the Electoral College process.
Why The National Popular Vote Bill Is Not A Good Choice A quick look at the National Popular Vote (NPV) approach gives the impression that it promises a much better result in the Electoral College process.
Nevada Poll Results Tarkanian 39%, Heller 31% (31% undecided) 31% would renominate Heller (51% want someone else, 18% undecided)
 Nevada Poll Results Tarkanian 39%, Heller 31% (31% undecided) 31% would renominate Heller (51% want someone else, 18% undecided) POLLING METHODOLOGY For this poll, a sample of likely Republican households
Nevada Poll Results Tarkanian 39%, Heller 31% (31% undecided) 31% would renominate Heller (51% want someone else, 18% undecided) POLLING METHODOLOGY For this poll, a sample of likely Republican households
ELECTORAL COLLEGE AND BACKGROUND INFO
 ELECTORAL COLLEGE AND BACKGROUND INFO 1. Go to www.270towin.com and select the year 2000 2. How many total popular votes did George W. Bush receive? Al Gore? 3. How many total electoral votes did George
ELECTORAL COLLEGE AND BACKGROUND INFO 1. Go to www.270towin.com and select the year 2000 2. How many total popular votes did George W. Bush receive? Al Gore? 3. How many total electoral votes did George
CONSTITUTIONAL ISSUES
 LWVUS National Popular Vote Compact Study, Supporting Arguments by Gail Dryden(CA), Barbara Klein (AZ), Sue Lederman (NJ), Carol Mellor (NY), and Jack Sullivan ( CA) The National Popular Vote (NPV) Compact
LWVUS National Popular Vote Compact Study, Supporting Arguments by Gail Dryden(CA), Barbara Klein (AZ), Sue Lederman (NJ), Carol Mellor (NY), and Jack Sullivan ( CA) The National Popular Vote (NPV) Compact
Mathematics of Voting Systems. Tanya Leise Mathematics & Statistics Amherst College
 Mathematics of Voting Systems Tanya Leise Mathematics & Statistics Amherst College Arrow s Impossibility Theorem 1) No special treatment of particular voters or candidates 2) Transitivity A>B and B>C implies
Mathematics of Voting Systems Tanya Leise Mathematics & Statistics Amherst College Arrow s Impossibility Theorem 1) No special treatment of particular voters or candidates 2) Transitivity A>B and B>C implies
The second step of my proposed plan involves breaking states up into multi-seat districts.
 Multi-Seat Districts The second step of my proposed plan involves breaking states up into multi-seat districts. This will obviously be easy to do, and to understand, in a small, densely populated state
Multi-Seat Districts The second step of my proposed plan involves breaking states up into multi-seat districts. This will obviously be easy to do, and to understand, in a small, densely populated state
Voting Methods
 1.3-1.5 Voting Methods Some announcements Homework #1: Text (pages 28-33) 1, 4, 7, 10, 12, 19, 22, 29, 32, 38, 42, 50, 51, 56-60, 61, 65 (this is posted on Sakai) Math Center study sessions with Katie
1.3-1.5 Voting Methods Some announcements Homework #1: Text (pages 28-33) 1, 4, 7, 10, 12, 19, 22, 29, 32, 38, 42, 50, 51, 56-60, 61, 65 (this is posted on Sakai) Math Center study sessions with Katie
Mathematics of the Electoral College. Robbie Robinson Professor of Mathematics The George Washington University
 Mathematics of the Electoral College Robbie Robinson Professor of Mathematics The George Washington University Overview Is the US President elected directly? No. The president is elected by electors who
Mathematics of the Electoral College Robbie Robinson Professor of Mathematics The George Washington University Overview Is the US President elected directly? No. The president is elected by electors who
AP Gov Chapter 09 Outline
 I. TURNING OUT TO VOTE Although most presidents have won a majority of the votes cast in the election, no modern president has been elected by more than 38 percent of the total voting age population. In
I. TURNING OUT TO VOTE Although most presidents have won a majority of the votes cast in the election, no modern president has been elected by more than 38 percent of the total voting age population. In
Safe Votes, Sincere Votes, and Strategizing
 Safe Votes, Sincere Votes, and Strategizing Rohit Parikh Eric Pacuit April 7, 2005 Abstract: We examine the basic notion of strategizing in the statement of the Gibbard-Satterthwaite theorem and note that
Safe Votes, Sincere Votes, and Strategizing Rohit Parikh Eric Pacuit April 7, 2005 Abstract: We examine the basic notion of strategizing in the statement of the Gibbard-Satterthwaite theorem and note that
Many Social Choice Rules
 Many Social Choice Rules 1 Introduction So far, I have mentioned several of the most commonly used social choice rules : pairwise majority rule, plurality, plurality with a single run off, the Borda count.
Many Social Choice Rules 1 Introduction So far, I have mentioned several of the most commonly used social choice rules : pairwise majority rule, plurality, plurality with a single run off, the Borda count.
Introduction What are political parties, and how do they function in our two-party system? Encourage good behavior among members
 Chapter 5: Political Parties Section 1 Objectives Define a political party. Describe the major functions of political parties. Identify the reasons why the United States has a two-party system. Understand
Chapter 5: Political Parties Section 1 Objectives Define a political party. Describe the major functions of political parties. Identify the reasons why the United States has a two-party system. Understand
Bush Wins Over Gore in Contested 2000 Election
 23 August 2012 MP3 at voaspecialenglish.com Bush Wins Over Gore in Contested 2000 Election STEVE EMBER: Welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember. This
23 August 2012 MP3 at voaspecialenglish.com Bush Wins Over Gore in Contested 2000 Election STEVE EMBER: Welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in VOA Special English. I m Steve Ember. This
Fair Division in Theory and Practice
 Fair Division in Theory and Practice Ron Cytron (Computer Science) Maggie Penn (Political Science) Lecture 5b: Alternative Voting Systems 1 Increasing minority representation Public bodies (juries, legislatures,
Fair Division in Theory and Practice Ron Cytron (Computer Science) Maggie Penn (Political Science) Lecture 5b: Alternative Voting Systems 1 Increasing minority representation Public bodies (juries, legislatures,
Federal Primary Election Runoffs and Voter Turnout Decline,
 Federal Primary Election Runoffs and Voter Turnout Decline, 1994-2010 July 2011 By: Katherine Sicienski, William Hix, and Rob Richie Summary of Facts and Findings Near-Universal Decline in Turnout: Of
Federal Primary Election Runoffs and Voter Turnout Decline, 1994-2010 July 2011 By: Katherine Sicienski, William Hix, and Rob Richie Summary of Facts and Findings Near-Universal Decline in Turnout: Of
Voting Criteria April
 Voting Criteria 21-301 2018 30 April 1 Evaluating voting methods In the last session, we learned about different voting methods. In this session, we will focus on the criteria we use to evaluate whether
Voting Criteria 21-301 2018 30 April 1 Evaluating voting methods In the last session, we learned about different voting methods. In this session, we will focus on the criteria we use to evaluate whether
Empowering Moderate Voters Implement an Instant Runoff Strategy
 Empowering Moderate Voters Implement an Instant Runoff Strategy Rep. John Porter Summary U.S. elections and the conduct of elected representatives in recent years have been characterized by excessive partisanship
Empowering Moderate Voters Implement an Instant Runoff Strategy Rep. John Porter Summary U.S. elections and the conduct of elected representatives in recent years have been characterized by excessive partisanship
Approval Voting. Simple, Effective Voting Method Reform. Neal McBurnett. for the League of Women Voters, Boulder County Revised
 Approval Voting Simple, Effective Voting Method Reform Neal McBurnett for the League of Women Voters, Boulder County 2017-02-21 Revised 2017-04-02 Center for Election Science 501(c)(3) founded in 2011
Approval Voting Simple, Effective Voting Method Reform Neal McBurnett for the League of Women Voters, Boulder County 2017-02-21 Revised 2017-04-02 Center for Election Science 501(c)(3) founded in 2011
Elections. How we choose the people who govern us
 Elections How we choose the people who govern us Electing the President Questions 1. What is an example of popular sovereignty? 2. Who are you really voting for when you vote in a presidential election?
Elections How we choose the people who govern us Electing the President Questions 1. What is an example of popular sovereignty? 2. Who are you really voting for when you vote in a presidential election?
FOR RELEASE: SUNDAY, OCTOBER 13, 1991, A.M.
 FOR RELEASE: SUNDAY, OCTOBER 13, 1991, A.M. Two In Three Want Candidates To Discuss Economic Issues "DON'T KNOW" LEADS KERREY IN EARLY DEMOCRATIC NOMINATION SWEEPS "Don't Know" leads in the early stages
FOR RELEASE: SUNDAY, OCTOBER 13, 1991, A.M. Two In Three Want Candidates To Discuss Economic Issues "DON'T KNOW" LEADS KERREY IN EARLY DEMOCRATIC NOMINATION SWEEPS "Don't Know" leads in the early stages
In deciding upon a winner, there is always one main goal: to reflect the preferences of the people in the most fair way possible.
 Voting Theory 1 Voting Theory In many decision making situations, it is necessary to gather the group consensus. This happens when a group of friends decides which movie to watch, when a company decides
Voting Theory 1 Voting Theory In many decision making situations, it is necessary to gather the group consensus. This happens when a group of friends decides which movie to watch, when a company decides
ELECTING CANDIDATES WITH FAIR REPRESENTATION VOTING: RANKED CHOICE VOTING AND OTHER METHODS
 November 2013 ELECTING CANDIDATES WITH FAIR REPRESENTATION VOTING: RANKED CHOICE VOTING AND OTHER METHODS A voting system translates peoples' votes into seats. Because the same votes in different systems
November 2013 ELECTING CANDIDATES WITH FAIR REPRESENTATION VOTING: RANKED CHOICE VOTING AND OTHER METHODS A voting system translates peoples' votes into seats. Because the same votes in different systems
The Mathematics of Voting
 The Mathematics of Voting Voting Methods Summary Last time, we considered elections for Math Club President from among four candidates: Alisha (A), Boris (B), Carmen (C), and Dave (D). All 37 voters submitted
The Mathematics of Voting Voting Methods Summary Last time, we considered elections for Math Club President from among four candidates: Alisha (A), Boris (B), Carmen (C), and Dave (D). All 37 voters submitted
Sanders runs markedly better than Clinton in a general election with Donald Trump;
 March 28, 2016 To: From: Re: Interested Parties Ben Tulchin, Ben Krompak, and Kiel Brunner; Tulchin Research Sanders is Best Candidate to Lead Democrats to Victory in 2016; Offers Real Strengths While
March 28, 2016 To: From: Re: Interested Parties Ben Tulchin, Ben Krompak, and Kiel Brunner; Tulchin Research Sanders is Best Candidate to Lead Democrats to Victory in 2016; Offers Real Strengths While
Moral Values Take Back Seat to Partisanship and the Economy In 2004 Presidential Election
 Moral Values Take Back Seat to Partisanship and the Economy In 2004 Presidential Election Lawrence R. Jacobs McKnight Land Grant Professor Director, 2004 Elections Project Humphrey Institute University
Moral Values Take Back Seat to Partisanship and the Economy In 2004 Presidential Election Lawrence R. Jacobs McKnight Land Grant Professor Director, 2004 Elections Project Humphrey Institute University
December 30, 2008 Agreement Among the States to Elect the President by National Popular Vote
 STATE OF VERMONT HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES STATE HOUSE 115 STATE STREET MONTPELIER, VT 05633-5201 December 30, 2008 Agreement Among the States to Elect the President by National Popular Vote To Members
STATE OF VERMONT HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES STATE HOUSE 115 STATE STREET MONTPELIER, VT 05633-5201 December 30, 2008 Agreement Among the States to Elect the President by National Popular Vote To Members
10/23/2012. Chapter 13: The Presidency Section 5
 Chapter 13: The Presidency Section 5 Objectives 1. Describe the features of the presidential campaign. 2. Explain how the electoral college provides for the election of the President. 3. Identify several
Chapter 13: The Presidency Section 5 Objectives 1. Describe the features of the presidential campaign. 2. Explain how the electoral college provides for the election of the President. 3. Identify several
Chapter 13: The Presidency Section 5
 Chapter 13: The Presidency Section 5 Objectives 1. Describe the features of the presidential campaign. 2. Explain how the electoral college provides for the election of the President. 3. Identify several
Chapter 13: The Presidency Section 5 Objectives 1. Describe the features of the presidential campaign. 2. Explain how the electoral college provides for the election of the President. 3. Identify several
Chapter 5: Political Parties Ms. Nguyen American Government Bell Ringer: 1. What is this chapter s EQ? 2. Interpret the quote below: No America
 Chapter 5: Political Parties Ms. Nguyen American Government Bell Ringer: 1. What is this chapter s EQ? 2. Interpret the quote below: No America without democracy, no democracy without politics, no politics
Chapter 5: Political Parties Ms. Nguyen American Government Bell Ringer: 1. What is this chapter s EQ? 2. Interpret the quote below: No America without democracy, no democracy without politics, no politics
THE PRO S AND CON S OF THE ELECTORAL COLLEGE SYSTEM
 High School: U.S. Government Background Information THE PRO S AND CON S OF THE ELECTORAL COLLEGE SYSTEM There have, in its 200-year history, been a number of critics and proposed reforms to the Electoral
High School: U.S. Government Background Information THE PRO S AND CON S OF THE ELECTORAL COLLEGE SYSTEM There have, in its 200-year history, been a number of critics and proposed reforms to the Electoral
NBC News/WSJ/Marist Poll. April New York Questionnaire
 Residents: n=2,521, MOE +/- 2.0% Registered Voters: n=1,987, MOE +/- 2.2% NBC News/WSJ/Marist Poll New York Questionnaire Potential Republican Electorate: n=477, MOE +/- 4.5% Likely Republican Primary
Residents: n=2,521, MOE +/- 2.0% Registered Voters: n=1,987, MOE +/- 2.2% NBC News/WSJ/Marist Poll New York Questionnaire Potential Republican Electorate: n=477, MOE +/- 4.5% Likely Republican Primary
Patrick J. Lingane February 7, 2008 A Letter to the Author Improvements to Spitzer s Chapter on Elections
 Patrick J. Lingane February 7, 2008 A Letter to the Author Improvements to Spitzer s Chapter on Elections Although Spitzer (et al.), in the sixth chapter of their book Essentials of American Politics,
Patrick J. Lingane February 7, 2008 A Letter to the Author Improvements to Spitzer s Chapter on Elections Although Spitzer (et al.), in the sixth chapter of their book Essentials of American Politics,
Amy Tenhouse. Incumbency Surge: Examining the 1996 Margin of Victory for U.S. House Incumbents
 Amy Tenhouse Incumbency Surge: Examining the 1996 Margin of Victory for U.S. House Incumbents In 1996, the American public reelected 357 members to the United States House of Representatives; of those
Amy Tenhouse Incumbency Surge: Examining the 1996 Margin of Victory for U.S. House Incumbents In 1996, the American public reelected 357 members to the United States House of Representatives; of those
Electing the President. Chapter 12 Mathematical Modeling
 Electing the President Chapter 12 Mathematical Modeling Phases of the Election 1. State Primaries seeking nomination how to position the candidate to gather momentum in a set of contests 2. Conventions
Electing the President Chapter 12 Mathematical Modeling Phases of the Election 1. State Primaries seeking nomination how to position the candidate to gather momentum in a set of contests 2. Conventions
NEW JERSEY VOTERS TAKE ON 2008
 Contact: PATRICK MURRAY 732-263-5858 (office) 732-979-6769 (cell) pdmurray@monmouth.edu Released: Wednesday, 30, For more information: Monmouth University Polling Institute 400 Cedar Avenue West Long Branch,
Contact: PATRICK MURRAY 732-263-5858 (office) 732-979-6769 (cell) pdmurray@monmouth.edu Released: Wednesday, 30, For more information: Monmouth University Polling Institute 400 Cedar Avenue West Long Branch,
Subject: Sanders leads in Wisconsin; GOP Race Close; VA Privatization Issue Hurts Johnson
 From: Tom Jensen, Director of Public Policy Polling To: Interested Parties Subject: Sanders leads in Wisconsin; GOP Race Close; VA Privatization Issue Hurts Johnson Date: 3-31-16 A new Public Policy Polling
From: Tom Jensen, Director of Public Policy Polling To: Interested Parties Subject: Sanders leads in Wisconsin; GOP Race Close; VA Privatization Issue Hurts Johnson Date: 3-31-16 A new Public Policy Polling
AP US GOVERNMENT: CHAPER 7: POLITICAL PARTIES: ESSENTIAL TO DEMOCRACY
 AP US GOVERNMENT: CHAPER 7: POLITICAL PARTIES: ESSENTIAL TO DEMOCRACY Before political parties, candidates were listed alphabetically, and those whose names began with the letters A to F did better than
AP US GOVERNMENT: CHAPER 7: POLITICAL PARTIES: ESSENTIAL TO DEMOCRACY Before political parties, candidates were listed alphabetically, and those whose names began with the letters A to F did better than
Applying Ranked Choice Voting to Congressional Elections. The Case for RCV with the Top Four Primary and Multi-Member Districts. Rob Richie, FairVote
 Applying Ranked Choice Voting to Congressional Elections The Case for RCV with the Top Four Primary and Multi-Member Districts Rob Richie, FairVote American Exceptionalism: Inescapable Realities for Reformers
Applying Ranked Choice Voting to Congressional Elections The Case for RCV with the Top Four Primary and Multi-Member Districts Rob Richie, FairVote American Exceptionalism: Inescapable Realities for Reformers
ELECTION SYSTEMS. Plurality-Majority
 ELECTION SYSTEMS (The following mini-study Kit was written as an insert for the Sacramento VOTER. A member of that League, Pete Martineau, also an Election Systems study committee member, authored the
ELECTION SYSTEMS (The following mini-study Kit was written as an insert for the Sacramento VOTER. A member of that League, Pete Martineau, also an Election Systems study committee member, authored the
The Alternative Vote Referendum: why I will vote YES. Mohammed Amin
 The Alternative Vote Referendum: why I will vote YES By Mohammed Amin Contents The legislative framework...2 How the first past the post system works...4 How you vote...5 How the votes are counted...5
The Alternative Vote Referendum: why I will vote YES By Mohammed Amin Contents The legislative framework...2 How the first past the post system works...4 How you vote...5 How the votes are counted...5
EXAM: Parties & Elections
 AP Government EXAM: Parties & Elections Mr. Messinger INSTRUCTIONS: Mark all answers on your Scantron. Do not write on the test. Good luck!! 1. All of the following are true of the Electoral College system
AP Government EXAM: Parties & Elections Mr. Messinger INSTRUCTIONS: Mark all answers on your Scantron. Do not write on the test. Good luck!! 1. All of the following are true of the Electoral College system
Why We Should Abolish the Electoral College And How to Do It Script to Accompany Slide Presentation (shorter version)
 Why We Should Abolish the Electoral College And How to Do It Script to Accompany Slide Presentation (shorter version) 1 [No script here, just have this up while people are getting seated.] 2 The League
Why We Should Abolish the Electoral College And How to Do It Script to Accompany Slide Presentation (shorter version) 1 [No script here, just have this up while people are getting seated.] 2 The League
Campaign Finance Charges Raise Doubts Among 7% of Clinton Backers FINAL PEW CENTER SURVEY-CLINTON 52%, DOLE 38%, PEROT 9%
 FOR RELEASE: SUNDAY, NOVEMBER 3, 1996, 5:00 P.M. Campaign Finance Charges Raise Doubts Among 7% of Clinton Backers FINAL PEW CENTER SURVEY-CLINTON 52%, DOLE 38%, PEROT 9% FOR FURTHER INFORMATION CONTACT:
FOR RELEASE: SUNDAY, NOVEMBER 3, 1996, 5:00 P.M. Campaign Finance Charges Raise Doubts Among 7% of Clinton Backers FINAL PEW CENTER SURVEY-CLINTON 52%, DOLE 38%, PEROT 9% FOR FURTHER INFORMATION CONTACT:
Rationality & Social Choice. Dougherty, POLS 8000
 Rationality & Social Choice Dougherty, POLS 8000 Social Choice A. Background 1. Social Choice examines how to aggregate individual preferences fairly. a. Voting is an example. b. Think of yourself writing
Rationality & Social Choice Dougherty, POLS 8000 Social Choice A. Background 1. Social Choice examines how to aggregate individual preferences fairly. a. Voting is an example. b. Think of yourself writing
A Harsh Judgment on Davis Clears Schwarzenegger s Way
 CALIFORNIA EXIT POLL: THE RECALL 10/7/03 A Harsh Judgment on Davis Clears Schwarzenegger s Way In the end it was more about Gray Davis than about Arnold Schwarzenegger, and on Davis, the voters judgment
CALIFORNIA EXIT POLL: THE RECALL 10/7/03 A Harsh Judgment on Davis Clears Schwarzenegger s Way In the end it was more about Gray Davis than about Arnold Schwarzenegger, and on Davis, the voters judgment
Executive Summary of Economic Attitudes, Most Important Problems, Ratings of Top Political Figures, and an Early Look at the 2018 Texas Elections
 2017 of Economic Attitudes, Most Important Problems, Ratings of Top Political Figures, and an Early Look at the 2018 Texas Elections Summary of Findings The 2017 continues its long time-series assessing
2017 of Economic Attitudes, Most Important Problems, Ratings of Top Political Figures, and an Early Look at the 2018 Texas Elections Summary of Findings The 2017 continues its long time-series assessing
Math for Liberal Studies
 Math for Liberal Studies As we have discussed, when there are only two candidates in an election, deciding the winner is easy May s Theorem states that majority rule is the best system However, the situation
Math for Liberal Studies As we have discussed, when there are only two candidates in an election, deciding the winner is easy May s Theorem states that majority rule is the best system However, the situation
