Introduction to the Theory of Voting
|
|
|
- Lionel Bishop
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 November 11, 2015
2 1 Introduction What is Voting? Motivation 2 Axioms I Anonymity, Neutrality and Pareto Property Issues 3 Voting Rules I Condorcet Extensions and Scoring Rules 4 Axioms II Reinforcement and Monotonicity Issues 5 Impossibilities Strategy-Proofness
3 What is Voting? Voting Definition Voting is the process of achieving a collective decision based on the preferences among all alternatives from the voters.
4 What is Voting? Definitions N = {1, 2,..., n} a finite set of voters. A a finite set of m alternatives, m 2 A ballot cast by voter i N, which is a linear ordering i of A (transitive, complete, reflexive and antisymmetric) and induces a preference ranking A profile P = ( 1, 2,..., n ), which specifies a ballot for each voter i N a b c b c b c a a
5 What is Voting? Definitions A social choice function (SCF) f : L(A) n C(A) that returns the winning alternatives for each profile of strict preferences A social welfare function (SWF) yields a weak ranking f : L(A) n R(A) of the set alternatives (pre-linear ordering) for each profile of strict preferences
6 Motivation From school: Elections Definition A fair election should be free, equal, secret, general, direct, public/transparent and effective.
7 Motivation 2015 UK General Elections
8 Motivation 2015 UK General Elections First-Past-The-Post system (FPTP) 650 constituencies between 60,000 and 80,000 voters per constituency 1 seat per constituency for candidate with the most votes Is used, because of uneven population distribution, otherwise major part of representatives would be from London and thus legislation biased towards it.
9 Motivation 2015 UK General Elections Issues: not representative favors major parties not every vote is equal Possible changes: have larger constituencies and give multiple seats (better representation) do not use constituencies (favor of denser populated areas) develop some system which distributes seats over constituencies after the fact
10 Motivation Hamburg Bürgerschafts (City-State-Parliament) Elections New voting system (since 2011) two lists: candidates and parties 5 votes per list Kumulieren (accumulation) and Panaschieren (vote splitting) Issue: Too complicated for many voters!
11 Anonymity, Neutrality and Pareto Property Anonymity Definition An SCF f is anonymous if each pair of voters play interchangeable roles: f (P) = f (P ) holds whenever P is obtained from P by swapping the ballots cast by two voters Example (of nonanonymity) voters with veto rights, for example the 5 permanent members of the UNO in the UN Security Council votes, which have to pass the two houses of parliament any organization where board members have more votes than regular members (or they count more).
12 Anonymity, Neutrality and Pareto Property Neutrality Definition An SCF f is neutral if each pair of alternatives are interchangeable: when P is obtained from P by swapping the positions of two alternatives in every ballot and f (P ) is obtained from f (P) via a similar swap Example (of nonneutrality) legislative voting systems, where the YES alternative needs a 2/3 majority.
13 Anonymity, Neutrality and Pareto Property Pareto Property Definition In P alternative x Pareto dominates alternative y if every voter ranks x over y; y is Pareto dominated if such an x exists. Then an SCF f is Pareto (optimal) if f (P) never contains a Pareto dominated alternative.
14 Issues Issues Theorem (Moulin, 1983) Let m 2 be the number of alternatives and n be the number of voters. If n is divisible by any integer r with 1 < r m, then no neutral, anonymous and Pareto SCF is resolute (single valued). Example obviously for two alternatives, where the number of voters is even, ties may exist How do you break ties?
15 Issues How do you break ties? Example In 2013 the mayoral election in San Teodoro, Philipines, the tie was settled via coin toss. The French electoral code states, that ties are broken in favor of the older candidate (consequently in some elections parties favor older candidates).
16 Condorcet Extensions and Scoring Rules Condorcet Extensions Definition A Condorcet winner for P is an alternative x that defeats every other alternative in the strict pairwise majority sense: x > µ P y for all y x. Pairwise Majority Rule (PMR) declares the winning alternative to be the Condorcet winner and is undefined when a profile has no such winner. An SCF is a Condorcet extension (or Condorcet consistent) if it selects the Condorcet winner alone, when it exists. Problems are caused by majority cycles (e.g. a > µ b, b > µ c and c > µ a). These are known as Condorcet s voting paradox and relate to the intransitivity of > µ.
17 Condorcet Extensions and Scoring Rules Condorcet s Voting Paradox Reminder: a b c c b c a b c a b a Net p (a > b) = {j N a j b} {j N b j a} b a 100 c
18 Condorcet Extensions and Scoring Rules Condorcet Extensions Example The Copeland score of a Condorcet winner is m 1 and uniquely highest, thus is a Condorce extension. Borda can fail to elect an alternative, which is top-ranked by a majority of voters and is thus not a Condorcet extension. Reminder: Net p (a > b) = {j N a j b} {j N b j a} Copeland(x) = {y A x > µ y} {y A y > µ x} Where x > µ y denotes that Net P (x > y) > 0 Borda sym P (x) = y A Net P(x > y)
19 Condorcet Extensions and Scoring Rules Scoring Rules Definition A score vector w = (w 1, w 2,..., w m ) consists of real number scoring weights and is proper if w 1 w 2 w m 1 w m and w 1 > w m. The weights are awarded as points to each alternative from top ranked to lowest. The winner is the alternative with the largest sum of awarded points. A proper scoring rule is induced by a proper score vector. Example Plurality with w = (1, 0,, 0,..., 0) Borda count with w = (m 1, m 2,..., 1, 0)
20 Condorcet Extensions and Scoring Rules Instant Run-off Voting Definition (Instant Run-off Voting) At each stage the alternative with the lowest plurality score is dropped from all ballots and at the first stage at which and alternative x sits atop the majority of ballots, it is declared the winner. Example (Irish presidential election, 1990) Candidate Round 1 Round 2 Mary Robinson 612,265 (38.9%) 817,830 (51.6%) Brian Lenihan 694,484 (43.8%) 731,273 (46.2%) Austin Currie 267,902 (16.9%) -
21 Reinforcement and Monotonicity Reinforcement Definition Reinforcement means that the common winning alternatives (if they exist) of two disjoint sets of voters be exactly those chosen by the union: f (s) f (t) f (s + t) = f (s) f (t) for all voting situations s and t. Example Scoring rules are reinforcing, since if an alternative has the highest score for s and t, it also has the highest for s + t (the sum of the scores for s and t). Condorcet extensions for three or more alternatives violate reinforcement.
22 Reinforcement and Monotonicity Monotonicity Definition A resolute SCF (no ties) f satisfies (weak) monotonicity if whenever P is modified to P by having one voter i switch i to i by lifting the winning alternative x = f (P) simply (increasing its relative preference without changing others), f (P ) = f (P). Example Copeland and all proper Scoring Rules are monotonic.
23 Reinforcement and Monotonicity Strategy-Proofness Definition A resolute SCF (no ties) f satisfies strategy-proofness if whenever a profile P is modified to P by having one voter i switch i to i, f (P) i f (P ). Other monotonicity properties exist, such as Maskin, Down, One-way, Half-way monotinicity and Participation. For all of these including (weak) monotonicity it holds, that they are weak forms of strategy proofness.
24 Issues Issues Definition A resolute SCF (no ties) f satisfies Half-way monotinicity if whenever P is modified to P by having one voter i switch i to rev i (z w w rev z), f (P) i f (P ). Theorem Let f be a resolute SCF for m 4 alternatives and sufficiently large odd n. If f is neutral and anonymous and has a Condorcet winner, then either f fails to be strategy proof or f violates half-way monotinicity.
25 Issues Issues Definition A resolute SCF (no ties) f satisfies Participation (the absence of no show paradoxes) if whenever P is modified to P by adding one voter i with ballot i to the electorate, f (P ) i f (P). Theorem Let f be a resolute Condorcet extension for m 4 alternatives. Then f violates participation (if f is a variable-electorate SCF) half-way monotinicity (if f is a fixed-electorate SCF for sufficiently large n)
26 Strategy-Proofness Strategic manipulation Reminder: e d a c e b a b c d c d b a e Net p (a > b) = {j N a j b} {j N b j a} Copeland(x) = {y A x > µ y} {y A y > µ x} Where x > µ y denotes that Net P (x > y) > 0 Borda sym P (x) = y A Net P(x > y) Copeland and Borda are single voter manipulable.
27 Strategy-Proofness Impossibilities Definition (Independence of Irrelevant Alternatives (IIA), Kenneth Arrow) The collective voter opinion to the relative merits of two alternatives should not be influenced by the individual opinion towards an irrelevant third. Theorem (Arrow Impossibility) Every weakly-paretian SWF for m 3 alternatives either violates IIA or is a dictatorship. (Where weakly-paretian means, that if every voter strictly prefers a over b, then the SWF ranks a strictly over b.)
28 Strategy-Proofness Impossibilities Theorem (Gibbard-Satterhwaite (GST)) Any resolute, nonimposed (no alternative is unelectable) and strategy-proof SCF for m 3 alternatives must be a dictatorship.
29 Strategy-Proofness Not everything is hopeless! In practice the voter needs to know the intended ballot of the other voters. to be sure that no other voter will similarly engage in strategic vote-switching the computational resources to predict whether some switch in her ballot can change the outcome into one she prefers
Introduction to Theory of Voting. Chapter 2 of Computational Social Choice by William Zwicker
 Introduction to Theory of Voting Chapter 2 of Computational Social Choice by William Zwicker If we assume Introduction 1. every two voters play equivalent roles in our voting rule 2. every two alternatives
Introduction to Theory of Voting Chapter 2 of Computational Social Choice by William Zwicker If we assume Introduction 1. every two voters play equivalent roles in our voting rule 2. every two alternatives
Exercises For DATA AND DECISIONS. Part I Voting
 Exercises For DATA AND DECISIONS Part I Voting September 13, 2016 Exercise 1 Suppose that an election has candidates A, B, C, D and E. There are 7 voters, who submit the following ranked ballots: 2 1 1
Exercises For DATA AND DECISIONS Part I Voting September 13, 2016 Exercise 1 Suppose that an election has candidates A, B, C, D and E. There are 7 voters, who submit the following ranked ballots: 2 1 1
Chapter 10. The Manipulability of Voting Systems. For All Practical Purposes: Effective Teaching. Chapter Briefing
 Chapter 10 The Manipulability of Voting Systems For All Practical Purposes: Effective Teaching As a teaching assistant, you most likely will administer and proctor many exams. Although it is tempting to
Chapter 10 The Manipulability of Voting Systems For All Practical Purposes: Effective Teaching As a teaching assistant, you most likely will administer and proctor many exams. Although it is tempting to
Chapter 9: Social Choice: The Impossible Dream Lesson Plan
 Lesson Plan For All Practical Purposes An Introduction to Social Choice Majority Rule and Condorcet s Method Mathematical Literacy in Today s World, 9th ed. Other Voting Systems for Three or More Candidates
Lesson Plan For All Practical Purposes An Introduction to Social Choice Majority Rule and Condorcet s Method Mathematical Literacy in Today s World, 9th ed. Other Voting Systems for Three or More Candidates
Mathematics and Social Choice Theory. Topic 4 Voting methods with more than 2 alternatives. 4.1 Social choice procedures
 Mathematics and Social Choice Theory Topic 4 Voting methods with more than 2 alternatives 4.1 Social choice procedures 4.2 Analysis of voting methods 4.3 Arrow s Impossibility Theorem 4.4 Cumulative voting
Mathematics and Social Choice Theory Topic 4 Voting methods with more than 2 alternatives 4.1 Social choice procedures 4.2 Analysis of voting methods 4.3 Arrow s Impossibility Theorem 4.4 Cumulative voting
MATH4999 Capstone Projects in Mathematics and Economics Topic 3 Voting methods and social choice theory
 MATH4999 Capstone Projects in Mathematics and Economics Topic 3 Voting methods and social choice theory 3.1 Social choice procedures Plurality voting Borda count Elimination procedures Sequential pairwise
MATH4999 Capstone Projects in Mathematics and Economics Topic 3 Voting methods and social choice theory 3.1 Social choice procedures Plurality voting Borda count Elimination procedures Sequential pairwise
Fairness Criteria. Review: Election Methods
 Review: Election Methods Plurality method: the candidate with a plurality of votes wins. Plurality-with-elimination method (Instant runoff): Eliminate the candidate with the fewest first place votes. Keep
Review: Election Methods Plurality method: the candidate with a plurality of votes wins. Plurality-with-elimination method (Instant runoff): Eliminate the candidate with the fewest first place votes. Keep
Arrow s Impossibility Theorem
 Arrow s Impossibility Theorem Some announcements Final reflections due on Monday. You now have all of the methods and so you can begin analyzing the results of your election. Today s Goals We will discuss
Arrow s Impossibility Theorem Some announcements Final reflections due on Monday. You now have all of the methods and so you can begin analyzing the results of your election. Today s Goals We will discuss
Elections with Only 2 Alternatives
 Math 203: Chapter 12: Voting Systems and Drawbacks: How do we decide the best voting system? Elections with Only 2 Alternatives What is an individual preference list? Majority Rules: Pick 1 of 2 candidates
Math 203: Chapter 12: Voting Systems and Drawbacks: How do we decide the best voting system? Elections with Only 2 Alternatives What is an individual preference list? Majority Rules: Pick 1 of 2 candidates
The search for a perfect voting system. MATH 105: Contemporary Mathematics. University of Louisville. October 31, 2017
 The search for a perfect voting system MATH 105: Contemporary Mathematics University of Louisville October 31, 2017 Review of Fairness Criteria Fairness Criteria 2 / 14 We ve seen three fairness criteria
The search for a perfect voting system MATH 105: Contemporary Mathematics University of Louisville October 31, 2017 Review of Fairness Criteria Fairness Criteria 2 / 14 We ve seen three fairness criteria
Public Choice. Slide 1
 Public Choice We investigate how people can come up with a group decision mechanism. Several aspects of our economy can not be handled by the competitive market. Whenever there is market failure, there
Public Choice We investigate how people can come up with a group decision mechanism. Several aspects of our economy can not be handled by the competitive market. Whenever there is market failure, there
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems, Continued
 Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems, Continued 7 March 2014 Voting III 7 March 2014 1/27 Last Time We ve discussed several voting systems and conditions which may or may not be satisfied by a system.
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems, Continued 7 March 2014 Voting III 7 March 2014 1/27 Last Time We ve discussed several voting systems and conditions which may or may not be satisfied by a system.
Voting Criteria: Majority Criterion Condorcet Criterion Monotonicity Criterion Independence of Irrelevant Alternatives Criterion
 We have discussed: Voting Theory Arrow s Impossibility Theorem Voting Methods: Plurality Borda Count Plurality with Elimination Pairwise Comparisons Voting Criteria: Majority Criterion Condorcet Criterion
We have discussed: Voting Theory Arrow s Impossibility Theorem Voting Methods: Plurality Borda Count Plurality with Elimination Pairwise Comparisons Voting Criteria: Majority Criterion Condorcet Criterion
(67686) Mathematical Foundations of AI June 18, Lecture 6
 (67686) Mathematical Foundations of AI June 18, 2008 Lecturer: Ariel D. Procaccia Lecture 6 Scribe: Ezra Resnick & Ariel Imber 1 Introduction: Social choice theory Thus far in the course, we have dealt
(67686) Mathematical Foundations of AI June 18, 2008 Lecturer: Ariel D. Procaccia Lecture 6 Scribe: Ezra Resnick & Ariel Imber 1 Introduction: Social choice theory Thus far in the course, we have dealt
1.6 Arrow s Impossibility Theorem
 1.6 Arrow s Impossibility Theorem Some announcements Homework #2: Text (pages 33-35) 51, 56-60, 61, 65, 71-75 (this is posted on Sakai) For Monday, read Chapter 2 (pages 36-57) Today s Goals We will discuss
1.6 Arrow s Impossibility Theorem Some announcements Homework #2: Text (pages 33-35) 51, 56-60, 61, 65, 71-75 (this is posted on Sakai) For Monday, read Chapter 2 (pages 36-57) Today s Goals We will discuss
The Manipulability of Voting Systems. Check off these skills when you feel that you have mastered them.
 Chapter 10 The Manipulability of Voting Systems Chapter Objectives Check off these skills when you feel that you have mastered them. Explain what is meant by voting manipulation. Determine if a voter,
Chapter 10 The Manipulability of Voting Systems Chapter Objectives Check off these skills when you feel that you have mastered them. Explain what is meant by voting manipulation. Determine if a voter,
The Impossibilities of Voting
 The Impossibilities of Voting Introduction Majority Criterion Condorcet Criterion Monotonicity Criterion Irrelevant Alternatives Criterion Arrow s Impossibility Theorem 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide
The Impossibilities of Voting Introduction Majority Criterion Condorcet Criterion Monotonicity Criterion Irrelevant Alternatives Criterion Arrow s Impossibility Theorem 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. Slide
answers to some of the sample exercises : Public Choice
 answers to some of the sample exercises : Public Choice Ques 1 The following table lists the way that 5 different voters rank five different alternatives. Is there a Condorcet winner under pairwise majority
answers to some of the sample exercises : Public Choice Ques 1 The following table lists the way that 5 different voters rank five different alternatives. Is there a Condorcet winner under pairwise majority
Social Choice: The Impossible Dream. Check off these skills when you feel that you have mastered them.
 Chapter Objectives Check off these skills when you feel that you have mastered them. Analyze and interpret preference list ballots. Explain three desired properties of Majority Rule. Explain May s theorem.
Chapter Objectives Check off these skills when you feel that you have mastered them. Analyze and interpret preference list ballots. Explain three desired properties of Majority Rule. Explain May s theorem.
Desirable properties of social choice procedures. We now outline a number of properties that are desirable for these social choice procedures:
 Desirable properties of social choice procedures We now outline a number of properties that are desirable for these social choice procedures: 1. Pareto [named for noted economist Vilfredo Pareto (1848-1923)]
Desirable properties of social choice procedures We now outline a number of properties that are desirable for these social choice procedures: 1. Pareto [named for noted economist Vilfredo Pareto (1848-1923)]
Recall: Properties of ranking rules. Recall: Properties of ranking rules. Kenneth Arrow. Recall: Properties of ranking rules. Strategically vulnerable
 Outline for today Stat155 Game Theory Lecture 26: More Voting. Peter Bartlett December 1, 2016 1 / 31 2 / 31 Recall: Voting and Ranking Recall: Properties of ranking rules Assumptions There is a set Γ
Outline for today Stat155 Game Theory Lecture 26: More Voting. Peter Bartlett December 1, 2016 1 / 31 2 / 31 Recall: Voting and Ranking Recall: Properties of ranking rules Assumptions There is a set Γ
Introduction to Social Choice
 for to Social Choice University of Waterloo January 14, 2013 Outline for 1 2 3 4 for 5 What Is Social Choice Theory for Study of decision problems in which a group has to make the decision The decision
for to Social Choice University of Waterloo January 14, 2013 Outline for 1 2 3 4 for 5 What Is Social Choice Theory for Study of decision problems in which a group has to make the decision The decision
Computational Social Choice: Spring 2007
 Computational Social Choice: Spring 2007 Ulle Endriss Institute for Logic, Language and Computation University of Amsterdam Ulle Endriss 1 Plan for Today This lecture will be an introduction to voting
Computational Social Choice: Spring 2007 Ulle Endriss Institute for Logic, Language and Computation University of Amsterdam Ulle Endriss 1 Plan for Today This lecture will be an introduction to voting
Social choice theory
 Social choice theory A brief introduction Denis Bouyssou CNRS LAMSADE Paris, France Introduction Motivation Aims analyze a number of properties of electoral systems present a few elements of the classical
Social choice theory A brief introduction Denis Bouyssou CNRS LAMSADE Paris, France Introduction Motivation Aims analyze a number of properties of electoral systems present a few elements of the classical
Social Choice Theory. Denis Bouyssou CNRS LAMSADE
 A brief and An incomplete Introduction Introduction to to Social Choice Theory Denis Bouyssou CNRS LAMSADE What is Social Choice Theory? Aim: study decision problems in which a group has to take a decision
A brief and An incomplete Introduction Introduction to to Social Choice Theory Denis Bouyssou CNRS LAMSADE What is Social Choice Theory? Aim: study decision problems in which a group has to take a decision
Mathematical Thinking. Chapter 9 Voting Systems
 Mathematical Thinking Chapter 9 Voting Systems Voting Systems A voting system is a rule for transforming a set of individual preferences into a single group decision. What are the desirable properties
Mathematical Thinking Chapter 9 Voting Systems Voting Systems A voting system is a rule for transforming a set of individual preferences into a single group decision. What are the desirable properties
Measuring Fairness. Paul Koester () MA 111, Voting Theory September 7, / 25
 Measuring Fairness We ve seen FOUR methods for tallying votes: Plurality Borda Count Pairwise Comparisons Plurality with Elimination Are these methods reasonable? Are these methods fair? Today we study
Measuring Fairness We ve seen FOUR methods for tallying votes: Plurality Borda Count Pairwise Comparisons Plurality with Elimination Are these methods reasonable? Are these methods fair? Today we study
Social welfare functions
 Social welfare functions We have defined a social choice function as a procedure that determines for each possible profile (set of preference ballots) of the voters the winner or set of winners for the
Social welfare functions We have defined a social choice function as a procedure that determines for each possible profile (set of preference ballots) of the voters the winner or set of winners for the
Notes for Session 7 Basic Voting Theory and Arrow s Theorem
 Notes for Session 7 Basic Voting Theory and Arrow s Theorem We follow up the Impossibility (Session 6) of pooling expert probabilities, while preserving unanimities in both unconditional and conditional
Notes for Session 7 Basic Voting Theory and Arrow s Theorem We follow up the Impossibility (Session 6) of pooling expert probabilities, while preserving unanimities in both unconditional and conditional
Chapter 1 Practice Test Questions
 0728 Finite Math Chapter 1 Practice Test Questions VOCABULARY. On the exam, be prepared to match the correct definition to the following terms: 1) Voting Elements: Single-choice ballot, preference ballot,
0728 Finite Math Chapter 1 Practice Test Questions VOCABULARY. On the exam, be prepared to match the correct definition to the following terms: 1) Voting Elements: Single-choice ballot, preference ballot,
MATH 1340 Mathematics & Politics
 MATH 1340 Mathematics & Politics Lecture 6 June 29, 2015 Slides prepared by Iian Smythe for MATH 1340, Summer 2015, at Cornell University 1 Basic criteria A social choice function is anonymous if voters
MATH 1340 Mathematics & Politics Lecture 6 June 29, 2015 Slides prepared by Iian Smythe for MATH 1340, Summer 2015, at Cornell University 1 Basic criteria A social choice function is anonymous if voters
Fairness Criteria. Majority Criterion: If a candidate receives a majority of the first place votes, that candidate should win the election.
 Fairness Criteria Majority Criterion: If a candidate receives a majority of the first place votes, that candidate should win the election. The plurality, plurality-with-elimination, and pairwise comparisons
Fairness Criteria Majority Criterion: If a candidate receives a majority of the first place votes, that candidate should win the election. The plurality, plurality-with-elimination, and pairwise comparisons
Computational Social Choice: Spring 2017
 Computational Social Choice: Spring 2017 Ulle Endriss Institute for Logic, Language and Computation University of Amsterdam Ulle Endriss 1 Plan for Today So far we saw three voting rules: plurality, plurality
Computational Social Choice: Spring 2017 Ulle Endriss Institute for Logic, Language and Computation University of Amsterdam Ulle Endriss 1 Plan for Today So far we saw three voting rules: plurality, plurality
Voting rules: (Dixit and Skeath, ch 14) Recall parkland provision decision:
 rules: (Dixit and Skeath, ch 14) Recall parkland provision decision: Assume - n=10; - total cost of proposed parkland=38; - if provided, each pays equal share = 3.8 - there are two groups of individuals
rules: (Dixit and Skeath, ch 14) Recall parkland provision decision: Assume - n=10; - total cost of proposed parkland=38; - if provided, each pays equal share = 3.8 - there are two groups of individuals
The Mathematics of Voting
 Math 165 Winston Salem, NC 28 October 2010 Voting for 2 candidates Today, we talk about voting, which may not seem mathematical. President of the Math TA s Let s say there s an election which has just
Math 165 Winston Salem, NC 28 October 2010 Voting for 2 candidates Today, we talk about voting, which may not seem mathematical. President of the Math TA s Let s say there s an election which has just
CS 886: Multiagent Systems. Fall 2016 Kate Larson
 CS 886: Multiagent Systems Fall 2016 Kate Larson Multiagent Systems We will study the mathematical and computational foundations of multiagent systems, with a focus on the analysis of systems where agents
CS 886: Multiagent Systems Fall 2016 Kate Larson Multiagent Systems We will study the mathematical and computational foundations of multiagent systems, with a focus on the analysis of systems where agents
CSC304 Lecture 16. Voting 3: Axiomatic, Statistical, and Utilitarian Approaches to Voting. CSC304 - Nisarg Shah 1
 CSC304 Lecture 16 Voting 3: Axiomatic, Statistical, and Utilitarian Approaches to Voting CSC304 - Nisarg Shah 1 Announcements Assignment 2 was due today at 3pm If you have grace credits left (check MarkUs),
CSC304 Lecture 16 Voting 3: Axiomatic, Statistical, and Utilitarian Approaches to Voting CSC304 - Nisarg Shah 1 Announcements Assignment 2 was due today at 3pm If you have grace credits left (check MarkUs),
Voting Protocols. Introduction. Social choice: preference aggregation Our settings. Voting protocols are examples of social choice mechanisms
 Voting Protocols Yiling Chen September 14, 2011 Introduction Social choice: preference aggregation Our settings A set of agents have preferences over a set of alternatives Taking preferences of all agents,
Voting Protocols Yiling Chen September 14, 2011 Introduction Social choice: preference aggregation Our settings A set of agents have preferences over a set of alternatives Taking preferences of all agents,
12.2 Defects in Voting Methods
 12.2 Defects in Voting Methods Recall the different Voting Methods: 1. Plurality - one vote to one candidate, the others get nothing The remaining three use a preference ballot, where all candidates are
12.2 Defects in Voting Methods Recall the different Voting Methods: 1. Plurality - one vote to one candidate, the others get nothing The remaining three use a preference ballot, where all candidates are
2-Candidate Voting Method: Majority Rule
 2-Candidate Voting Method: Majority Rule Definition (2-Candidate Voting Method: Majority Rule) Majority Rule is a form of 2-candidate voting in which the candidate who receives the most votes is the winner
2-Candidate Voting Method: Majority Rule Definition (2-Candidate Voting Method: Majority Rule) Majority Rule is a form of 2-candidate voting in which the candidate who receives the most votes is the winner
Lecture 12: Topics in Voting Theory
 Lecture 12: Topics in Voting Theory Eric Pacuit ILLC, University of Amsterdam staff.science.uva.nl/ epacuit epacuit@science.uva.nl Lecture Date: May 11, 2006 Caput Logic, Language and Information: Social
Lecture 12: Topics in Voting Theory Eric Pacuit ILLC, University of Amsterdam staff.science.uva.nl/ epacuit epacuit@science.uva.nl Lecture Date: May 11, 2006 Caput Logic, Language and Information: Social
Algorithms, Games, and Networks February 7, Lecture 8
 Algorithms, Games, and Networks February 7, 2013 Lecturer: Ariel Procaccia Lecture 8 Scribe: Dong Bae Jun 1 Overview In this lecture, we discuss the topic of social choice by exploring voting rules, axioms,
Algorithms, Games, and Networks February 7, 2013 Lecturer: Ariel Procaccia Lecture 8 Scribe: Dong Bae Jun 1 Overview In this lecture, we discuss the topic of social choice by exploring voting rules, axioms,
SOCIAL CHOICES (Voting Methods) THE PROBLEM. Social Choice and Voting. Terminologies
 SOCIAL CHOICES (Voting Methods) THE PROBLEM In a society, decisions are made by its members in order to come up with a situation that benefits the most. What is the best voting method of arriving at a
SOCIAL CHOICES (Voting Methods) THE PROBLEM In a society, decisions are made by its members in order to come up with a situation that benefits the most. What is the best voting method of arriving at a
Australian AI 2015 Tutorial Program Computational Social Choice
 Australian AI 2015 Tutorial Program Computational Social Choice Haris Aziz and Nicholas Mattei www.csiro.au Social Choice Given a collection of agents with preferences over a set of things (houses, cakes,
Australian AI 2015 Tutorial Program Computational Social Choice Haris Aziz and Nicholas Mattei www.csiro.au Social Choice Given a collection of agents with preferences over a set of things (houses, cakes,
The Mathematics of Voting. The Mathematics of Voting
 1.3 The Borda Count Method 1 In the Borda Count Method each place on a ballot is assigned points. In an election with N candidates we give 1 point for last place, 2 points for second from last place, and
1.3 The Borda Count Method 1 In the Borda Count Method each place on a ballot is assigned points. In an election with N candidates we give 1 point for last place, 2 points for second from last place, and
Write all responses on separate paper. Use complete sentences, charts and diagrams, as appropriate.
 Math 13 HW 5 Chapter 9 Write all responses on separate paper. Use complete sentences, charts and diagrams, as appropriate. 1. Explain why majority rule is not a good way to choose between four alternatives.
Math 13 HW 5 Chapter 9 Write all responses on separate paper. Use complete sentences, charts and diagrams, as appropriate. 1. Explain why majority rule is not a good way to choose between four alternatives.
Social Choice. CSC304 Lecture 21 November 28, Allan Borodin Adapted from Craig Boutilier s slides
 Social Choice CSC304 Lecture 21 November 28, 2016 Allan Borodin Adapted from Craig Boutilier s slides 1 Todays agenda and announcements Today: Review of popular voting rules. Axioms, Manipulation, Impossibility
Social Choice CSC304 Lecture 21 November 28, 2016 Allan Borodin Adapted from Craig Boutilier s slides 1 Todays agenda and announcements Today: Review of popular voting rules. Axioms, Manipulation, Impossibility
Chapter 4: Voting and Social Choice.
 Chapter 4: Voting and Social Choice. Topics: Ordinal Welfarism Condorcet and Borda: 2 alternatives for majority voting Voting over Resource Allocation Single-Peaked Preferences Intermediate Preferences
Chapter 4: Voting and Social Choice. Topics: Ordinal Welfarism Condorcet and Borda: 2 alternatives for majority voting Voting over Resource Allocation Single-Peaked Preferences Intermediate Preferences
Many Social Choice Rules
 Many Social Choice Rules 1 Introduction So far, I have mentioned several of the most commonly used social choice rules : pairwise majority rule, plurality, plurality with a single run off, the Borda count.
Many Social Choice Rules 1 Introduction So far, I have mentioned several of the most commonly used social choice rules : pairwise majority rule, plurality, plurality with a single run off, the Borda count.
Voting Lecture 3: 2-Candidate Voting Spring Morgan Schreffler Office: POT Teaching.
 Voting Lecture 3: 2-Candidate Voting Spring 2014 Morgan Schreffler Office: POT 902 http://www.ms.uky.edu/~mschreffler/ Teaching.php 2-Candidate Voting Method: Majority Rule Definition (2-Candidate Voting
Voting Lecture 3: 2-Candidate Voting Spring 2014 Morgan Schreffler Office: POT 902 http://www.ms.uky.edu/~mschreffler/ Teaching.php 2-Candidate Voting Method: Majority Rule Definition (2-Candidate Voting
Voting Criteria April
 Voting Criteria 21-301 2018 30 April 1 Evaluating voting methods In the last session, we learned about different voting methods. In this session, we will focus on the criteria we use to evaluate whether
Voting Criteria 21-301 2018 30 April 1 Evaluating voting methods In the last session, we learned about different voting methods. In this session, we will focus on the criteria we use to evaluate whether
CSC304 Lecture 14. Begin Computational Social Choice: Voting 1: Introduction, Axioms, Rules. CSC304 - Nisarg Shah 1
 CSC304 Lecture 14 Begin Computational Social Choice: Voting 1: Introduction, Axioms, Rules CSC304 - Nisarg Shah 1 Social Choice Theory Mathematical theory for aggregating individual preferences into collective
CSC304 Lecture 14 Begin Computational Social Choice: Voting 1: Introduction, Axioms, Rules CSC304 - Nisarg Shah 1 Social Choice Theory Mathematical theory for aggregating individual preferences into collective
Math116Chap1VotingPart2.notebook January 12, Part II. Other Methods of Voting and Other "Fairness Criteria"
 Part II Other Methods of Voting and Other "Fairness Criteria" Plurality with Elimination Method Round 1. Count the first place votes for each candidate, just as you would in the plurality method. If a
Part II Other Methods of Voting and Other "Fairness Criteria" Plurality with Elimination Method Round 1. Count the first place votes for each candidate, just as you would in the plurality method. If a
Voting System: elections
 Voting System: elections 6 April 25, 2008 Abstract A voting system allows voters to choose between options. And, an election is an important voting system to select a cendidate. In 1951, Arrow s impossibility
Voting System: elections 6 April 25, 2008 Abstract A voting system allows voters to choose between options. And, an election is an important voting system to select a cendidate. In 1951, Arrow s impossibility
9.3 Other Voting Systems for Three or More Candidates
 9.3 Other Voting Systems for Three or More Candidates With three or more candidates, there are several additional procedures that seem to give reasonable ways to choose a winner. If we look closely at
9.3 Other Voting Systems for Three or More Candidates With three or more candidates, there are several additional procedures that seem to give reasonable ways to choose a winner. If we look closely at
Main idea: Voting systems matter.
 Voting Systems Main idea: Voting systems matter. Electoral College Winner takes all in most states (48/50) (plurality in states) 270/538 electoral votes needed to win (majority) If 270 isn t obtained -
Voting Systems Main idea: Voting systems matter. Electoral College Winner takes all in most states (48/50) (plurality in states) 270/538 electoral votes needed to win (majority) If 270 isn t obtained -
Rationality of Voting and Voting Systems: Lecture II
 Rationality of Voting and Voting Systems: Lecture II Rationality of Voting Systems Hannu Nurmi Department of Political Science University of Turku Three Lectures at National Research University Higher
Rationality of Voting and Voting Systems: Lecture II Rationality of Voting Systems Hannu Nurmi Department of Political Science University of Turku Three Lectures at National Research University Higher
Head-to-Head Winner. To decide if a Head-to-Head winner exists: Every candidate is matched on a one-on-one basis with every other candidate.
 Head-to-Head Winner A candidate is a Head-to-Head winner if he or she beats all other candidates by majority rule when they meet head-to-head (one-on-one). To decide if a Head-to-Head winner exists: Every
Head-to-Head Winner A candidate is a Head-to-Head winner if he or she beats all other candidates by majority rule when they meet head-to-head (one-on-one). To decide if a Head-to-Head winner exists: Every
Economics 470 Some Notes on Simple Alternatives to Majority Rule
 Economics 470 Some Notes on Simple Alternatives to Majority Rule Some of the voting procedures considered here are not considered as a means of revealing preferences on a public good issue, but as a means
Economics 470 Some Notes on Simple Alternatives to Majority Rule Some of the voting procedures considered here are not considered as a means of revealing preferences on a public good issue, but as a means
How should we count the votes?
 How should we count the votes? Bruce P. Conrad January 16, 2008 Were the Iowa caucuses undemocratic? Many politicians, pundits, and reporters thought so in the weeks leading up to the January 3, 2008 event.
How should we count the votes? Bruce P. Conrad January 16, 2008 Were the Iowa caucuses undemocratic? Many politicians, pundits, and reporters thought so in the weeks leading up to the January 3, 2008 event.
Democratic Rules in Context
 Democratic Rules in Context Hannu Nurmi Public Choice Research Centre and Department of Political Science University of Turku Institutions in Context 2012 (PCRC, Turku) Democratic Rules in Context 4 June,
Democratic Rules in Context Hannu Nurmi Public Choice Research Centre and Department of Political Science University of Turku Institutions in Context 2012 (PCRC, Turku) Democratic Rules in Context 4 June,
that changes needed to be made when electing their Presidential nominee. Iowa, at the time had a
 Part I The Iowa caucuses are perhaps the most important yet mysterious contest in American politics. It all began after the 1968 Democratic National Convention protest, the party decided that changes needed
Part I The Iowa caucuses are perhaps the most important yet mysterious contest in American politics. It all began after the 1968 Democratic National Convention protest, the party decided that changes needed
How Should Members of Parliament (and Presidents) Be Elected? E. Maskin Institute for Advanced Study
 How Should Members of Parliament (and Presidents) Be Elected? E. Maskin Institute for Advanced Study What s wrong with this picture? 2005 U.K. General Election Constituency of Croyden Central vote totals
How Should Members of Parliament (and Presidents) Be Elected? E. Maskin Institute for Advanced Study What s wrong with this picture? 2005 U.K. General Election Constituency of Croyden Central vote totals
VOTING SYSTEMS AND ARROW S THEOREM
 VOTING SYSTEMS AND ARROW S THEOREM AKHIL MATHEW Abstract. The following is a brief discussion of Arrow s theorem in economics. I wrote it for an economics class in high school. 1. Background Arrow s theorem
VOTING SYSTEMS AND ARROW S THEOREM AKHIL MATHEW Abstract. The following is a brief discussion of Arrow s theorem in economics. I wrote it for an economics class in high school. 1. Background Arrow s theorem
Section Voting Methods. Copyright 2013, 2010, 2007, Pearson, Education, Inc.
 Section 15.1 Voting Methods INB Table of Contents Date Topic Page # February 24, 2014 Test #3 Practice Test 38 February 24, 2014 Test #3 Practice Test Workspace 39 March 10, 2014 Test #3 40 March 10, 2014
Section 15.1 Voting Methods INB Table of Contents Date Topic Page # February 24, 2014 Test #3 Practice Test 38 February 24, 2014 Test #3 Practice Test Workspace 39 March 10, 2014 Test #3 40 March 10, 2014
What is the Best Election Method?
 What is the Best Election Method? E. Maskin Harvard University Gorman Lectures University College, London February 2016 Today and tomorrow will explore 2 Today and tomorrow will explore election methods
What is the Best Election Method? E. Maskin Harvard University Gorman Lectures University College, London February 2016 Today and tomorrow will explore 2 Today and tomorrow will explore election methods
Intro to Contemporary Math
 Intro to Contemporary Math Independence of Irrelevant Alternatives Criteria Nicholas Nguyen nicholas.nguyen@uky.edu Department of Mathematics UK Agenda Independence of Irrelevant Alternatives Criteria
Intro to Contemporary Math Independence of Irrelevant Alternatives Criteria Nicholas Nguyen nicholas.nguyen@uky.edu Department of Mathematics UK Agenda Independence of Irrelevant Alternatives Criteria
Rationality & Social Choice. Dougherty, POLS 8000
 Rationality & Social Choice Dougherty, POLS 8000 Social Choice A. Background 1. Social Choice examines how to aggregate individual preferences fairly. a. Voting is an example. b. Think of yourself writing
Rationality & Social Choice Dougherty, POLS 8000 Social Choice A. Background 1. Social Choice examines how to aggregate individual preferences fairly. a. Voting is an example. b. Think of yourself writing
Approaches to Voting Systems
 Approaches to Voting Systems Properties, paradoxes, incompatibilities Hannu Nurmi Department of Philosophy, Contemporary History and Political Science University of Turku Game Theory and Voting Systems,
Approaches to Voting Systems Properties, paradoxes, incompatibilities Hannu Nurmi Department of Philosophy, Contemporary History and Political Science University of Turku Game Theory and Voting Systems,
Social Choice & Mechanism Design
 Decision Making in Robots and Autonomous Agents Social Choice & Mechanism Design Subramanian Ramamoorthy School of Informatics 2 April, 2013 Introduction Social Choice Our setting: a set of outcomes agents
Decision Making in Robots and Autonomous Agents Social Choice & Mechanism Design Subramanian Ramamoorthy School of Informatics 2 April, 2013 Introduction Social Choice Our setting: a set of outcomes agents
Arrow s Impossibility Theorem on Social Choice Systems
 Arrow s Impossibility Theorem on Social Choice Systems Ashvin A. Swaminathan January 11, 2013 Abstract Social choice theory is a field that concerns methods of aggregating individual interests to determine
Arrow s Impossibility Theorem on Social Choice Systems Ashvin A. Swaminathan January 11, 2013 Abstract Social choice theory is a field that concerns methods of aggregating individual interests to determine
Topics on the Border of Economics and Computation December 18, Lecture 8
 Topics on the Border of Economics and Computation December 18, 2005 Lecturer: Noam Nisan Lecture 8 Scribe: Ofer Dekel 1 Correlated Equilibrium In the previous lecture, we introduced the concept of correlated
Topics on the Border of Economics and Computation December 18, 2005 Lecturer: Noam Nisan Lecture 8 Scribe: Ofer Dekel 1 Correlated Equilibrium In the previous lecture, we introduced the concept of correlated
Voting Definitions and Theorems Spring Dr. Martin Montgomery Office: POT 761
 Voting Definitions and Theorems Spring 2014 Dr. Martin Montgomery Office: POT 761 http://www.ms.uky.edu/~martinm/m111 Voting Method: Plurality Definition (The Plurality Method of Voting) For each ballot,
Voting Definitions and Theorems Spring 2014 Dr. Martin Montgomery Office: POT 761 http://www.ms.uky.edu/~martinm/m111 Voting Method: Plurality Definition (The Plurality Method of Voting) For each ballot,
Problems with Group Decision Making
 Problems with Group Decision Making There are two ways of evaluating political systems: 1. Consequentialist ethics evaluate actions, policies, or institutions in regard to the outcomes they produce. 2.
Problems with Group Decision Making There are two ways of evaluating political systems: 1. Consequentialist ethics evaluate actions, policies, or institutions in regard to the outcomes they produce. 2.
Homework 7 Answers PS 30 November 2013
 Homework 7 Answers PS 30 November 2013 1. Say that there are three people and five candidates {a, b, c, d, e}. Say person 1 s order of preference (from best to worst) is c, b, e, d, a. Person 2 s order
Homework 7 Answers PS 30 November 2013 1. Say that there are three people and five candidates {a, b, c, d, e}. Say person 1 s order of preference (from best to worst) is c, b, e, d, a. Person 2 s order
Chapter 9: Social Choice: The Impossible Dream
 Chapter 9: Social Choice: The Impossible Dream The application of mathematics to the study of human beings their behavior, values, interactions, conflicts, and methods of making decisions is generally
Chapter 9: Social Choice: The Impossible Dream The application of mathematics to the study of human beings their behavior, values, interactions, conflicts, and methods of making decisions is generally
Constructing voting paradoxes with logic and symmetry
 Constructing voting paradoxes with logic and symmetry Part I: Voting and Logic Problem 1. There was a kingdom once ruled by a king and a council of three members: Ana, Bob and Cory. It was a very democratic
Constructing voting paradoxes with logic and symmetry Part I: Voting and Logic Problem 1. There was a kingdom once ruled by a king and a council of three members: Ana, Bob and Cory. It was a very democratic
Problems with Group Decision Making
 Problems with Group Decision Making There are two ways of evaluating political systems. 1. Consequentialist ethics evaluate actions, policies, or institutions in regard to the outcomes they produce. 2.
Problems with Group Decision Making There are two ways of evaluating political systems. 1. Consequentialist ethics evaluate actions, policies, or institutions in regard to the outcomes they produce. 2.
Simple methods for single winner elections
 Simple methods for single winner elections Christoph Börgers Mathematics Department Tufts University Medford, MA April 14, 2018 http://emerald.tufts.edu/~cborgers/ I have posted these slides there. 1 /
Simple methods for single winner elections Christoph Börgers Mathematics Department Tufts University Medford, MA April 14, 2018 http://emerald.tufts.edu/~cborgers/ I have posted these slides there. 1 /
Make the Math Club Great Again! The Mathematics of Democratic Voting
 Make the Math Club Great Again! The Mathematics of Democratic Voting Darci L. Kracht Kent State University Undergraduate Mathematics Club April 14, 2016 How do you become Math Club King, I mean, President?
Make the Math Club Great Again! The Mathematics of Democratic Voting Darci L. Kracht Kent State University Undergraduate Mathematics Club April 14, 2016 How do you become Math Club King, I mean, President?
Presidential Election Democrat Grover Cleveland versus Benjamin Harrison. ************************************ Difference of 100,456
 Presidential Election 1886 Democrat Grover Cleveland versus Benjamin Harrison Cleveland 5,540,309 Harrison 5,439,853 ************************************ Difference of 100,456 Electoral College Cleveland
Presidential Election 1886 Democrat Grover Cleveland versus Benjamin Harrison Cleveland 5,540,309 Harrison 5,439,853 ************************************ Difference of 100,456 Electoral College Cleveland
Voting Methods for Municipal Elections: Propaganda, Field Experiments and what USA voters want from an Election Algorithm
 Voting Methods for Municipal Elections: Propaganda, Field Experiments and what USA voters want from an Election Algorithm Kathryn Lenz, Mathematics and Statistics Department, University of Minnesota Duluth
Voting Methods for Municipal Elections: Propaganda, Field Experiments and what USA voters want from an Election Algorithm Kathryn Lenz, Mathematics and Statistics Department, University of Minnesota Duluth
Chapter 9: Social Choice: The Impossible Dream Lesson Plan
 Lesson Plan For ll Practical Purposes Voting and Social hoice Majority Rule and ondorcet s Method Mathematical Literacy in Today s World, 7th ed. Other Voting Systems for Three or More andidates Plurality
Lesson Plan For ll Practical Purposes Voting and Social hoice Majority Rule and ondorcet s Method Mathematical Literacy in Today s World, 7th ed. Other Voting Systems for Three or More andidates Plurality
The Borda Majority Count
 The Borda Majority Count Manzoor Ahmad Zahid Harrie de Swart Department of Philosophy, Tilburg University Box 90153, 5000 LE Tilburg, The Netherlands; Email: {M.A.Zahid, H.C.M.deSwart}@uvt.nl Abstract
The Borda Majority Count Manzoor Ahmad Zahid Harrie de Swart Department of Philosophy, Tilburg University Box 90153, 5000 LE Tilburg, The Netherlands; Email: {M.A.Zahid, H.C.M.deSwart}@uvt.nl Abstract
The Mathematics of Voting
 The Mathematics of Voting Voting Methods Summary Last time, we considered elections for Math Club President from among four candidates: Alisha (A), Boris (B), Carmen (C), and Dave (D). All 37 voters submitted
The Mathematics of Voting Voting Methods Summary Last time, we considered elections for Math Club President from among four candidates: Alisha (A), Boris (B), Carmen (C), and Dave (D). All 37 voters submitted
c M. J. Wooldridge, used by permission/updated by Simon Parsons, Spring
 Today LECTURE 8: MAKING GROUP DECISIONS CIS 716.5, Spring 2010 We continue thinking in the same framework as last lecture: multiagent encounters game-like interactions participants act strategically We
Today LECTURE 8: MAKING GROUP DECISIONS CIS 716.5, Spring 2010 We continue thinking in the same framework as last lecture: multiagent encounters game-like interactions participants act strategically We
Section Voting Methods. Copyright 2013, 2010, 2007, Pearson, Education, Inc.
 Section 15.1 Voting Methods What You Will Learn Plurality Method Borda Count Method Plurality with Elimination Pairwise Comparison Method Tie Breaking 15.1-2 Example 2: Voting for the Honor Society President
Section 15.1 Voting Methods What You Will Learn Plurality Method Borda Count Method Plurality with Elimination Pairwise Comparison Method Tie Breaking 15.1-2 Example 2: Voting for the Honor Society President
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems, Continued. Voting II 1/27
 Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems, Continued Voting II 1/27 Last Time Last time we discussed some elections and some issues with plurality voting. We started to discuss another voting system, the Borda
Voting: Issues, Problems, and Systems, Continued Voting II 1/27 Last Time Last time we discussed some elections and some issues with plurality voting. We started to discuss another voting system, the Borda
Dictatorships Are Not the Only Option: An Exploration of Voting Theory
 Dictatorships Are Not the Only Option: An Exploration of Voting Theory Geneva Bahrke May 17, 2014 Abstract The field of social choice theory, also known as voting theory, examines the methods by which
Dictatorships Are Not the Only Option: An Exploration of Voting Theory Geneva Bahrke May 17, 2014 Abstract The field of social choice theory, also known as voting theory, examines the methods by which
Game Theory. Jiang, Bo ( 江波 )
 Game Theory Jiang, Bo ( 江波 ) Jiang.bo@mail.shufe.edu.cn Mechanism Design in Voting Majority voting Three candidates: x, y, z. Three voters: a, b, c. Voter a: x>y>z; voter b: y>z>x; voter c: z>x>y What
Game Theory Jiang, Bo ( 江波 ) Jiang.bo@mail.shufe.edu.cn Mechanism Design in Voting Majority voting Three candidates: x, y, z. Three voters: a, b, c. Voter a: x>y>z; voter b: y>z>x; voter c: z>x>y What
Voting and preference aggregation
 Voting and preference aggregation CSC304 Lecture 20 November 23, 2016 Allan Borodin (adapted from Craig Boutilier slides) Announcements and todays agenda Today: Voting and preference aggregation Reading
Voting and preference aggregation CSC304 Lecture 20 November 23, 2016 Allan Borodin (adapted from Craig Boutilier slides) Announcements and todays agenda Today: Voting and preference aggregation Reading
Grade 6 Math Circles Winter February 27/28 The Mathematics of Voting - Solutions
 Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles Winter 2018 - February 27/28 The Mathematics of Voting - Solutions Warm-up: Time
Faculty of Mathematics Waterloo, Ontario N2L 3G1 Centre for Education in Mathematics and Computing Grade 6 Math Circles Winter 2018 - February 27/28 The Mathematics of Voting - Solutions Warm-up: Time
Lecture 16: Voting systems
 Lecture 16: Voting systems Economics 336 Economics 336 (Toronto) Lecture 16: Voting systems 1 / 18 Introduction Last lecture we looked at the basic theory of majority voting: instability in voting: Condorcet
Lecture 16: Voting systems Economics 336 Economics 336 (Toronto) Lecture 16: Voting systems 1 / 18 Introduction Last lecture we looked at the basic theory of majority voting: instability in voting: Condorcet
Explaining the Impossible: Kenneth Arrow s Nobel Prize Winning Theorem on Elections
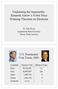 Explaining the Impossible: Kenneth Arrow s Nobel Prize Winning Theorem on Elections Dr. Rick Klima Appalachian State University Boone, North Carolina U.S. Presidential Vote Totals, 2000 Candidate Bush
Explaining the Impossible: Kenneth Arrow s Nobel Prize Winning Theorem on Elections Dr. Rick Klima Appalachian State University Boone, North Carolina U.S. Presidential Vote Totals, 2000 Candidate Bush
Voter Response to Iterated Poll Information
 Voter Response to Iterated Poll Information MSc Thesis (Afstudeerscriptie) written by Annemieke Reijngoud (born June 30, 1987 in Groningen, The Netherlands) under the supervision of Dr. Ulle Endriss, and
Voter Response to Iterated Poll Information MSc Thesis (Afstudeerscriptie) written by Annemieke Reijngoud (born June 30, 1987 in Groningen, The Netherlands) under the supervision of Dr. Ulle Endriss, and
Name Date I. Consider the preference schedule in an election with 5 candidates.
 Name Date I. Consider the preference schedule in an election with 5 candidates. 1. How many voters voted in this election? 2. How many votes are needed for a majority (more than 50% of the vote)? 3. How
Name Date I. Consider the preference schedule in an election with 5 candidates. 1. How many voters voted in this election? 2. How many votes are needed for a majority (more than 50% of the vote)? 3. How
Voting and preference aggregation
 Voting and preference aggregation CSC200 Lecture 38 March 14, 2016 Allan Borodin (adapted from Craig Boutilier slides) Announcements and todays agenda Today: Voting and preference aggregation Reading for
Voting and preference aggregation CSC200 Lecture 38 March 14, 2016 Allan Borodin (adapted from Craig Boutilier slides) Announcements and todays agenda Today: Voting and preference aggregation Reading for
Introduction: The Mathematics of Voting
 VOTING METHODS 1 Introduction: The Mathematics of Voting Content: Preference Ballots and Preference Schedules Voting methods including, 1). The Plurality Method 2). The Borda Count Method 3). The Plurality-with-Elimination
VOTING METHODS 1 Introduction: The Mathematics of Voting Content: Preference Ballots and Preference Schedules Voting methods including, 1). The Plurality Method 2). The Borda Count Method 3). The Plurality-with-Elimination
Categoric and Ordinal Voting: An Overview
 Categoric and Ordinal Voting: An Overview Harrie de Swart 1, Ad van Deemen 2, Eliora van der Hout 1 and Peter Kop 3 1 Tilburg University, Faculty of Philosophy, P.O. Box 90153 5000 LE Tilburg, The Netherlands;
Categoric and Ordinal Voting: An Overview Harrie de Swart 1, Ad van Deemen 2, Eliora van der Hout 1 and Peter Kop 3 1 Tilburg University, Faculty of Philosophy, P.O. Box 90153 5000 LE Tilburg, The Netherlands;
A Framework for the Quantitative Evaluation of Voting Rules
 A Framework for the Quantitative Evaluation of Voting Rules Michael Munie Computer Science Department Stanford University, CA munie@stanford.edu Yoav Shoham Computer Science Department Stanford University,
A Framework for the Quantitative Evaluation of Voting Rules Michael Munie Computer Science Department Stanford University, CA munie@stanford.edu Yoav Shoham Computer Science Department Stanford University,
