Unit # 1: Industrialization and Imperialism 10 Instructional Days
|
|
|
- Marvin Montgomery
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit Plan: 11 th Grade US History Unit # 1: Industrialization and Imperialism 10 Instructional Days Unit Overview Big Idea: Industrialization would radically transform the practices of labor and the condition of American working people. This new industrial culture would spur a burst of imperialistic expansionism for the United States that culminated in a bold and sometimes controversial new policy of asserting America s influence abroad Unit Goals: A. Evaluate a historical source for point of view and historical context B. Gather and analyze historical information, including contradictory data, from a variety of primary and secondary sources, including sources located on the Internet, to support or reject hypotheses C. Construct and defend a written historical argument using relevant primary and secondary sources as evidence D. Differentiate between facts and historical interpretations, recognizing that a historian s narrative reflects his or her judgment about the significance of particular facts E. Investigate causes and effects of significant events in United States history. Topics to include but not limited to WWI, Great Depression, Cold War F. Analyze continuity and change in eras over the course of United States history G. Investigate causes and effects of significant events in United States history. Analyze the complexity of events in United States history. H. Examine and evaluate issues of unity and diversity from Reconstruction to present. Enduring Understanding Connections America accomplished heavy industrialization in the post-civil War era. Spurred by the transcontinental rail network, business grew and consolidated into giant corporate trusts, as epitomized by the oil and steel industries. Industrialization radically transformed the practices of labor and the condition of American working people. But despite frequent industrial strife and the efforts of various reformers and unions, workers failed to develop effective labor organizations to match the corporate forms of business. With the concentration of capital in the hands of a few, new moralities arose to advance justifications for this social and economic phenomenon. A survival of the fittest theory emerged, a popular theory based on the thought of Herbert Spencer and William Graham Sumner, which argued that millionaires were products of natural selection. Another theory known as the Gospel of Wealth argued that societies well-to-do had to prove themselves morally responsible. In the 1890s a number of economic and political forces sparked a spectacular burst of imperialistic expansionism for the United States that culminated in the Spanish-American War- a war that began over freeing Cuba and ended with the highly controversial acquisition of the Philippines and other territories. In the wake of the Spanish-American War, President Theodore Roosevelt pursued a bold and sometimes controversial new policy of asserting America s influence abroad, particularly in East Asia and Latin America.
2 Course Enduring Understandings A. The development of the United States has been affected in significant ways by its geography. B. The ideals of freedom, equality, democracy, and economic well-being have been powerful motivators throughout our history. C. The tensions between liberty and equality, liberty and order, region and nation, individualism and the common welfare, cultural diversity and civic unity have shaped U.S. history. D. The history of the United States is a story of diverse groups struggling to realize the American ideal. These groups have contributed to the American heritage and contemporary society. E. The development of the United States has been shaped dramatically by economic growth. F. Issues in and between other countries dramatically affect the United States and in turn, U. S. policy dramatically affects other countries. Essential Questions A. In what ways has geography shaped the economic, political, and social development of the United States? B. How has our understanding of the meaning of freedom, democracy, and economic well-being changed over time? C. What factors lead to unity? To division? D. In what ways and to what extent have diverse groups shaped American society, economics, politics, and culture? What does it mean to be an American? E. What is the American Dream? Are all groups in the United States able to achieve the American Dream? F. How has economic growth shaped society, politics, and culture in the U.S.? G. What issues drive our relations with other nations? What is America s role in the world in regard to these issues? Chapter 24 Guided Reading Questions 1. How did the transcontinental railroad network provide the basis for the great post-civil War industrial transformation? 2. What were the abuses in the railroad industry and how did these lead to the first efforts at industrial regulation by the federal government? 3. How did the economy come to be dominated by giant trusts, such as those headed by Carnegie and Rockefeller in the steel and oil industries? 4. Describe the growing class conflict caused by industrial growth and combustion, and the early efforts to alleviate it. 5. How did industrialist supporters attempt to explain and justify great wealth and increasing class division through natural law and the Gospel of Wealth? 6. Why was the South generally excluded from industrial development and fall into a third world economic dependency? 7. What were the social changes brought by industrialization, particularly the altered position of working men and women? 8. What were the failures of the Knights of Labor and the modest success of the American Federation of Labor? Chapter 27 Guided Reading Questions 1. Why did the United States suddenly abandon its isolationism and turn outward at the end of the nineteenth century? 2. What were the forces pushing for American overseas expansion, and the causes of the Spanish-America War? 3. What were the unintended results of the Spanish-American War, especially with the conquest of Puerto
3 Rico and the Philippines? 4. Explain McKinley s decision to keep the Philippines, and list the opposing arguments in the debate about imperialism. 5. Analyze the consequences of the Spanish-America War, including the Filipino rebellion against U.S. rule and the war to suppress it. 6. How did U.S. involvement in East Asia expand and what was America s Open Door policy towards China? 7. What was the significance of the pro-imperialist Republican victory in 1900 and the rise of Theodore Roosevelt as a strong advocate of American power in international affairs? 8. Describe Roosevelt s assertive policies in Panama and elsewhere in Latin America, and explain why his corollary to the Monroe Doctrine aroused such controversy. 9. Discuss Roosevelt s foreign policies and diplomatic achievements, especially regarding Japan. Unit Learning Goals (tied to Unit Goals) LG 1 Analyze how the industrialization of America during the late nineteenth century began to shape the politics, economy, and culture of the nation This should include discussion of The Railroads: 1865vs. 1900,transcontinental railroads, government subsidies, land grants, Grover Cleveland and the land grants, frontier villages, The Civil War, Union Pacific Railroad, Credit Mobilier, the Irish and the railroad, Central Pacific Railroad, Leland Stanford, Collis P. Huntington, The Big Four, Chinese Laborers, Ogden, Utah, The Great Northern, Cornelius Vanderbilt, steel rail, air brake, telegraph, Industrialization brought about by the railroads (pg. 536),Corruption, Jay Gould, stock watering, promoters profits, abuse of the public, the pool, the Grange, Wabash Case, Interstate Commerce Commission, Interstate Commerce Act, Industrialization: millionaire, natural resources, immigration, Eli Whitney, Alexander Graham Bell, Thomas Alva Edison, Andrew Carnegie, John D. Rockefeller, J.P. Morgan, horizontal integration, the trust, Standard Oil, Steel is King, Bessemer Process, Carnegie and Steel, Morgan and Steel, Rockefeller s successes, The Gospel of Wealth, Survival of the Fittest, Plutocracy, Sherman Anti- Trust Act of 1890, The Impact: sharecropping, south as a supplier, Pittsburgh Plus, textile mills in the south, increased wealth, impact on time, impact on women, oligarchy of wealth, foreign trade, displacement of employees, forced organization, scabs, Jay Gould Quote, federal courts, lockouts, black list, National Labor Union, Knights of Labor, ten hour workday, May Day Strikes, Haymarket Learning Goal Guiding Questions Habits of Mind Documents and Readings What were the costs and benefits of the industrial transformation of the post-civil War era? Should industrialists like Vanderbilt, Carnegie, and Rockefeller be viewed as robber barons or captains of industry? Was the growing class division of the time a threat to American democracy? Why did American workers have such trouble responding to the new industrial conditions of labor? Habits of Mind: Significance of the Past Understand the significance of the past to one s own life and to one s society. Documents A Defense of Long Haul Rates (1885) Railroad President Sidney Dillon Supports Stock Watering (1891) General James B. Weaver Deplores Stock Watering (1892) John D. Rockefeller Justifies Rebates (1909) An Oil Man Goes Bankrupt (1899) Weaver Attacks the Trust (1892) Andrew Carnegie s Gospel of Wealth (1889) The Nation Challenges Carnegie (1901) Russell Conwell Deifies the Dollar (c. 1900) Henry Grady Issues a Challenge (1889) A Yankee Visits the New South (1887) Life in a Southern Mill (1910) In Praise of Mechanization (1897) A Tailor Testifies (1883) The Life of a Sweatshop Girl (1902) Our Daily Life is not a Pleasant One (1902) Risking Life and Limb inb the Pittsburgh Steel Mills The Knights of Labor Champion Reform (1887) Samuel Gompers Condemns the Knights (c. 1886) Capital Versus Labor (1871) Upton Sinclair Describes Smoke Pollution (1911)
4 Case, Samuel Gompers, The AFL, LG 2 Analyze the how America s shift in foreign policy in the late decades of the nineteenth century began to shape the politics and economy of the United States while cemented America s foreign influence in the world as an empire. This should include discussion of America Turns Outward: Yellow Press, Randolph Hearst, Henry Cabot Lodge, Theodore Roosevelt, Chinese Empire and its problems, Alfred Thayer Mahan, James G. Blaine, American Samoa, Diplomatic Crisis in late 1880s, The British Conflict, Richard Olney, President Cleveland, The Great Reproachment, Hawaii, Queen Liliuokalani, failure of annexation, Cuba, Insurrectos, General Butcher Weyler, Deputy de Lome, de Lome Letter, U.S.S. Maine, Teller Amendment, Admiral George Dewey, Manila, Philippine Invasion, William McKinley, Theodore Roosevelt, Rough Riders, Kettle Hill, Spanish-American War Empire: Treaty of Paris, Guam, Puerto Rico, Christianize and Civilize the Philippines, $20 Million, Imperialism, anti-imperialist League, Foraker Act, citizenship to Puerto Ricans, insular cases, Platt Amendment, Sphere of Influence: US as a world power, John Hay, Elihu Root, Philippine insurrection, Guerrilla warfare, Emilio Aguinaldo, reconcentration, William Howard Taft, benevolent Assimilation, Open Door Policy (notes), Boxer Rebellion, Nine Power Treaty, Teddy: TR, William Jennings Bryan, McKinley, murder of McKinley, President Roosevelt, Jingoism, spheres of influence, Roosevelt Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine, Big-stick diplomacy, Hay- Pauncefote Treaty, Clayton-Bulwar Treaty, Hay- Bunau-Varilla Treaty, Philippe Bunau-Varilla, Panama Canal, Russo-Japanese War Portsmouth Conference, Gentlemen s Agreement, Great White Fleet Readings: Rose Schniederman and the Triangle Fire by Bonnie Mitelman Taking Sides: Was John D\. Rockefeller a Robber Baron? Taking Sides: Did the Industrial Revolution Disrupt the American Family Industrialization: A Brief Introduction by Jonathan Rees How was American expansionism overseas similar to previous continental expansion westward and how was it different? Was the taking of Hawaii, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines really a violation of fundamental American ideals of selfgovernment and democracy? Did Roosevelt more often speak softly or use the big stick? Was the United States essentially acting as a white, Western imperialist power, or did American democratic ideals substantially restrain the imperialist impulse? Habits of Mind: Multi-Causality Understand the complexity of historical cause-effect relationships in order to avoid simplified generalizations. Documents: Joseph Pulitzer Demands Intervention (1897) William Randolph Hearst Stages a Rescue (1897) President McKinley Submits a War Message (1898) Professor Charles Elliot Norton s Patriotic Protest (1898) Albert Beveridge Trumpets Imperialism (1898) Professor William Sumner Spurns Empire (1898) William Jennings Bryan Vents His Bitterness (1901) The Nation Denounces Atrocities (1902) John Hay Twists Columbia s Arm (1903) Official Connivance in Washington (1903) Roosevelt Launches a Corollary (1904) A Latin American Protests (1943) President Roosevelt Anticipate Trouble (1905) Japan Resents Discrimination (1906) The Gentlemen s Agreement (1908) Readings: Point Counter Point: Should Puerto Rico Be Granted Statehood Taking Sides: Did Yellow Journalism Cause the Spanish American War?
5 Measuring and Tracking Learning Goals Measuring Progress of Learning Goals Tracking Student Progress Daily checks for understanding Weekly averages of Learning Goal objective Daily demonstrators of learning to be completed for each Lesson objective demonstrations of learning Assessing the progress of the Learning Goals Students complete formative assessments during and after the completion of each learning goal. Formative assessment consists of: A Multiple choice formative assessment at the completion of the learning goal Chapter reading and guided reading questions Formative assignments throughout the learning goal Socratic seminars, formative writing assignments, and class discussions on the primary sources and secondary readings associated with the learning goal Measuring and Tracking of Progress towards Unit Goals Measuring the Unit Goals Tracking Student Progress Students complete Formative writing assessments after the completion of each learning goal. Weekly graphing of student progress on learning goal formative writing assessments Measuring Progress to Unit Goals: Students score proficient or advanced on 80% of learning goal formative assessments Students score proficient or advanced on 80% of learning goal formative writing assignments Students score proficient or advanced on 100% of take home practice Measuring and Tracking Unit Goals Measuring the Unit Goal Tracking Student Progress Document Based Question Assessment Weekly graphing of student progress on learning goal Summative Writing Assessment formative assessments Formative Writing Assessment Historical Interview Summative Assessment Measuring Progress to Unit Goal: Students score proficient or advanced on 80% of learning goal formative assessments Students score proficient or advanced on 80% of formative assignments LG1 LG2 Common Summative Assessment Common Summative Assessment Learning Goal Summative Assessments Blog Post 1: Blog Post 2: Blog Post 3: Blog Posts Blog Site: What were the costs and benefits of the industrial transformation of the post-civil War era? Should industrialists like Vanderbilt, Carnegie, and Rockefeller be viewed as robber barons or captains of industry? During the American expansion of the late nineteenth century was the United States essentially acting as a white, Western imperialist power, or did American democratic ideals substantially restrain the imperialist impulse?
6 Unit Learning Goal Lesson Objectives Learning Goal Lesson Objectives LG 1 LO 1A SWBAT explain how the transcontinental railroad network provided the basis for the great post-civil War industrial transformation LO 1B SWBAT identify the abuses in the railroad industry and discuss how these led to the first efforts at industrial regulation by the federal government LO 1C SWBAT describe how the economy came to be dominated by giant trusts, such as those headed by Carnegie and Rockefeller in the steel and oil industries LO 1D SWBAT discuss the growing class conflict caused by industrial growth and combination, and the early efforts to alleviate it LO 1E SWBAT indicate how industrialists and their supporters attempted to explain and justify great wealth and increasing class division through natural law and the Gospel of Wealth. LO 1F SWBAT explain why the South was generally excluded from industrial development and fell into a third world economic dependency LO 1G SWBAT analyze the social changes brought by industrialization, particularly the altered position of working men and women LO 1H SWBAT explain the failures of the knights of Labor and the modest success of the American Federation of Labor LG 2 LO 2A SWBAT Explain why the United States suddenly abandoned its isolationism and turned outward at the end of the nineteenth century LO 2B SWBAT describe the forces pushing for American overseas expansion, and the causes of the Spanish-American War LO 2C SWBAT Describe and explain the unintended results of the Spanish-American War, especially the conquest of Puerto Rico and the Philippines LO 2D SWBAT explain McKinley s decision to keep the Philippines, and list the opposing arguments in the debate about imperialism LO 2E SWBAT Analyze the consequences of the Spanish-American War, including the Filipino rebellion against U.S. rule and the war to suppress it LO 2F SWBAT Explain the growing U.S. involvement in East Asia, and summarize America s Open Door policy toward China LO 2G SWBAT Discuss the significance of the pro-imperialist Republican victory in 1900 and the rise of Theodore Roosevelt as a strong advocate of American power in international affairs LO 2H SWBAT describe Roosevelt s assertive policies in Panama and elsewhere in Latin America, and explain why his corollary to the Monroe Doctrine aroused such controversy LO 2I SWBAT discuss Roosevelt s foreign policies and diplomatic achievements, especially regarding Japan
7 Lesson Objective Demonstrations of Learning Learning Goal Demonstration of Learning LG 1 LO 1A GSA: Using the information form class and your textbook pick a specific transcontinental railroad and explain how that railroad led to industrial transformation LO 1B GSA: What abuses were committed by the railroad industry and how did the government react to those abuses? Was this reaction successful? LO 1C GSA: Explain how the giant trusts, would be looked upon by society today. Use specifc examples such as those headed by Carnegie and Rockefeller in the steel and oil industries LO 1D GSA: What led to the growing class conflict on the late nineteenth century? Was this a natural reaction to industrialization? Why? LO 1E GSA: Using the Gospel of Wealth explain how the robber barons viewed their lifestyle. LO 1F GSA: What impacts of the Industrial Revolution on the South do we still see in America today? LO 1G GSA: Describe the daily life of an immigrant American during the time of industrialization. LO 1H GSA: Why did the Knights fail when the AFL succeeded? Which of these organizations visions do you think was best for the laborers of the day? LG 2 LO 2A GSA: Why did the United States suddenly abandoned its isolationism? Was this a good policy? LO 2B GSA: What? Who? Caused of the Spanish-American War? Why? LO 2C GSA: Why did America shift its policy towards Puerto Rico and the Philippines during the Spanish American war? Was this good foreign policy? LO 2D GSA: If you were McKinley would you have kept the Philippines or provide them a policy of self-determination? Justify your answer? LO 2E GSA: Were the consequences of the Spanish-American War foreseeable? Justify. LO 2F GSA: What was the open Door Policy? Was it a success? LO 2G GSA: Why did the Republicans win in 1900? Who would you have voted for? Justify. LO 2H GSA: Was the Monroe Corollary a strategic windfall or an extreme blunder? LO 2I Was Roosevelt a successful president or an American disaster? Justify. Instructional Calendar January 6 The Transcontinentals January 13 The Spanish American War January 7 The Trusts January 14 The Philippines January 8 Class Conflict January 15 Teddy Roosevelt January 9 The Gospel of Wealth January 16 Teddy Roosevelt January 10 Industrialization January 17 Teddy Roosevelt
Chapter 27: The Path of Empire, (Pages )
 Chapter 27: The Path of Empire, 1890 1899 (Pages 626 653) I. America Turns Outward A. Motives for overseas expansion 1. Farmers and industrialists Name Per. Date Row 2. The yellow press 3. Role of religion
Chapter 27: The Path of Empire, 1890 1899 (Pages 626 653) I. America Turns Outward A. Motives for overseas expansion 1. Farmers and industrialists Name Per. Date Row 2. The yellow press 3. Role of religion
APUSH. U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! EMPIRE & EXPANSION
 APUSH 1890-1909 EMPIRE & EXPANSION U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 27 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 19 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 21 Important Ideas Since the
APUSH 1890-1909 EMPIRE & EXPANSION U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 27 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 19 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 21 Important Ideas Since the
Empire and Expansion. Chapter 27
 Empire and Expansion Chapter 27 Imperialism Stronger nations attempt to create empires by dominating weaker nations. The late 1800s marked the peak of European imperialism, with much of Africa and Asia
Empire and Expansion Chapter 27 Imperialism Stronger nations attempt to create empires by dominating weaker nations. The late 1800s marked the peak of European imperialism, with much of Africa and Asia
Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power,
 Name: Class Period: Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1865-1917 Amsco Chapter 20 Reading Assignment: Ch. 21 AMSCO Purpose: This guide is intended to provide a space for you to record
Name: Class Period: Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1865-1917 Amsco Chapter 20 Reading Assignment: Ch. 21 AMSCO Purpose: This guide is intended to provide a space for you to record
18 America Claims an Empire QUIT
 18 America Claims an Empire QUIT CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE SECTION 1 Imperialism and America GRAPH MAP SECTION 2 The Spanish-American War SECTION 3 Acquiring New Lands SECTION 4
18 America Claims an Empire QUIT CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE SECTION 1 Imperialism and America GRAPH MAP SECTION 2 The Spanish-American War SECTION 3 Acquiring New Lands SECTION 4
Define the following: a. Neutrality Policy. b. Louisiana Purchase. c. War of d. Monroe Doctrine. e. Mexican-American War
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Chapter 20 in AMSCO or other resource covering the Spanish American War. Directions: 1. Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before
Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Chapter 20 in AMSCO or other resource covering the Spanish American War. Directions: 1. Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before
1. Commercial/Business Interests. U. S. Foreign Investments:
 1. Commercial/Business Interests U. S. Foreign Investments: 1869-1908 1. Commercial/Business Interests American Foreign Trade: 1870-1914 2. Military/Strategic Interests Alfred T. Mahan The Influence of
1. Commercial/Business Interests U. S. Foreign Investments: 1869-1908 1. Commercial/Business Interests American Foreign Trade: 1870-1914 2. Military/Strategic Interests Alfred T. Mahan The Influence of
Guided Reading & Analysis: Becoming a World Power, Chapter 20- Spanish American War, American Imperialism pp
 COMPLETE IN INK. Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Guided Reading & Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1898-1917 Chapter 20- Spanish American War, American Imperialism pp 380-391 Reading Assignment: Chapter
COMPLETE IN INK. Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Guided Reading & Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1898-1917 Chapter 20- Spanish American War, American Imperialism pp 380-391 Reading Assignment: Chapter
Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism
 Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism 1. List the ideas that fueled American Imperialism. 2. How were yellow journalists able to influence Americans opinions on foreign policy? 3. The person who urged
Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism 1. List the ideas that fueled American Imperialism. 2. How were yellow journalists able to influence Americans opinions on foreign policy? 3. The person who urged
Chapter 17. Becoming a World Power ( )
 Chapter 17 Becoming a World Power (1872 1912) 1 Chapter Overview: During this era, economic and military competition from world powers convinced the United States it must be a world power. The United States
Chapter 17 Becoming a World Power (1872 1912) 1 Chapter Overview: During this era, economic and military competition from world powers convinced the United States it must be a world power. The United States
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e. Chapter Nineteen: From Crisis to Empire
 Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e The Politics of Equilibrium Electoral Stability High Turnout for Elections Cultural Basis of Party Identification Catholics Tended to Vote Democrat 2 The Politics of
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e The Politics of Equilibrium Electoral Stability High Turnout for Elections Cultural Basis of Party Identification Catholics Tended to Vote Democrat 2 The Politics of
Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War
 Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War 1 Imperialism & Expansion CH 14-1 Imperialism & War Name Reasons why the United States becomes an imperialist nation. 1-New Markets 2-Anglo-Saxonism 3-Modern Navy 4-Into
Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War 1 Imperialism & Expansion CH 14-1 Imperialism & War Name Reasons why the United States becomes an imperialist nation. 1-New Markets 2-Anglo-Saxonism 3-Modern Navy 4-Into
Guided Reading & Analysis: Becoming a World Power, Chapter 20- Spanish American War, American Imperialism pp
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Guided Reading & Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1898-1917 Chapter 20- Spanish American War, American Imperialism pp 380-391 Reading Assignment: Ch. 20 AMSCO; If you
Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Guided Reading & Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1898-1917 Chapter 20- Spanish American War, American Imperialism pp 380-391 Reading Assignment: Ch. 20 AMSCO; If you
Unit 4: Imperialism. Name: Word Definition Analysis
 Name: Unit 4: Imperialism Word Definition Analysis 1. Imperialism (191) Policy by which strong nations Did America practice imperialism? extend their political, military, If so where? and economic control
Name: Unit 4: Imperialism Word Definition Analysis 1. Imperialism (191) Policy by which strong nations Did America practice imperialism? extend their political, military, If so where? and economic control
Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea
 Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea In the last half of the 1800s, the United States joined the race for control of overseas territories.
Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea In the last half of the 1800s, the United States joined the race for control of overseas territories.
8 TH GRADE UNITS OF INSTRUCTION
 Name Date Per. Social Studies 8 1/3 Review Packet Mrs. Myles McAnally 8 TH GRADE UNITS OF INSTRUCTION Reconstruction: Economic Expansion: a. Immigration b. Industrialization c. US Expansion and Imperialism
Name Date Per. Social Studies 8 1/3 Review Packet Mrs. Myles McAnally 8 TH GRADE UNITS OF INSTRUCTION Reconstruction: Economic Expansion: a. Immigration b. Industrialization c. US Expansion and Imperialism
Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism ( )
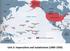 Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism (1890-1930) What is an empire? Is imperialism the same as colonization? Why would the U.S. get involved in this practice? What is the difference between acquiring and
Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism (1890-1930) What is an empire? Is imperialism the same as colonization? Why would the U.S. get involved in this practice? What is the difference between acquiring and
CHAPTER 24 The Industrial Age,
 CHAPTER 24 The Industrial Age, 1865 1900 1. Railroad Expansion (pp. 528-536) a. The government gave away land bigger than the state of to various railroad companies. What benefits did the government get
CHAPTER 24 The Industrial Age, 1865 1900 1. Railroad Expansion (pp. 528-536) a. The government gave away land bigger than the state of to various railroad companies. What benefits did the government get
1. How did the Dawes Act aid in destroying the way of life of Native American s?
 Name Period Chapter 4 Reconstruction **List and discuss the failures and successes of Reconstruction concerning political and social rights of African Americans. Make sure and include the Amendments 13,
Name Period Chapter 4 Reconstruction **List and discuss the failures and successes of Reconstruction concerning political and social rights of African Americans. Make sure and include the Amendments 13,
Chapter 18. American Claims an Empire
 Chapter 18 American Claims an Empire Section 1: Imperialism and American Imperialism 1880s U.S. interest in building an Empire builds Imperialism = Stronger : Economic, political, or military control Europeans
Chapter 18 American Claims an Empire Section 1: Imperialism and American Imperialism 1880s U.S. interest in building an Empire builds Imperialism = Stronger : Economic, political, or military control Europeans
The United States Looks Overseas
 The United States Looks Overseas 1853-1915 Interact with History In 1893, American sugar planters in the Kingdom of Hawaii thought they could make more money if Hawaii were an American state. So they staged
The United States Looks Overseas 1853-1915 Interact with History In 1893, American sugar planters in the Kingdom of Hawaii thought they could make more money if Hawaii were an American state. So they staged
Imperalism.notebook March 03, 2015
 Agenda Bell ringer Notability 1 Objective: I can discuss and explain why the United States Foreign Policy changed during the late 19th century. Bell Ringer Notability HW: Due Thursday 2 1 A B C D 3 2 A
Agenda Bell ringer Notability 1 Objective: I can discuss and explain why the United States Foreign Policy changed during the late 19th century. Bell Ringer Notability HW: Due Thursday 2 1 A B C D 3 2 A
Industry Comes of Age Chapter 24
 Industry Comes of Age 1865-1900 Chapter 24 The Iron Colt Becomes an Iron Horse Is there more power in BUSINESS or POLITICS? Surge in railroad development 1865 35,000 miles of track 1900 over 192,000 miles
Industry Comes of Age 1865-1900 Chapter 24 The Iron Colt Becomes an Iron Horse Is there more power in BUSINESS or POLITICS? Surge in railroad development 1865 35,000 miles of track 1900 over 192,000 miles
Unit 8: Imperialism. February 15th & 16th
 Unit 8: Imperialism February 15th & 16th WarmUp - February 15th & 16th Pick up papers from front table Jot down anything that comes to mind when you see the word IMPERIALISM (this is our next topic Unit
Unit 8: Imperialism February 15th & 16th WarmUp - February 15th & 16th Pick up papers from front table Jot down anything that comes to mind when you see the word IMPERIALISM (this is our next topic Unit
INDUSTRY COMES OF AGE CHAPTER 24
 INDUSTRY COMES OF AGE CHAPTER 24 Railroad Boom By 1900 the U.S. had more track than all of Europe combined 1890 Govt. Help for Railroads The U.S. govt encouraged railroad building in a # of ways Gave RR
INDUSTRY COMES OF AGE CHAPTER 24 Railroad Boom By 1900 the U.S. had more track than all of Europe combined 1890 Govt. Help for Railroads The U.S. govt encouraged railroad building in a # of ways Gave RR
BELLRINGER. Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies?
 BELLRINGER Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies? U.S. INTERVENTION ABROAD Ms. Luco IB Hist Americas LEARNING
BELLRINGER Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies? U.S. INTERVENTION ABROAD Ms. Luco IB Hist Americas LEARNING
Progressive Era, Imperialism, and World War 1
 Progressive Era, Imperialism, and World War 1 Section 7.1 Imperialism- a nation desires to gain more territory outside it s borders Reasons for US Imperialism: Economic growth- new people to sell to National
Progressive Era, Imperialism, and World War 1 Section 7.1 Imperialism- a nation desires to gain more territory outside it s borders Reasons for US Imperialism: Economic growth- new people to sell to National
America s Path to Empire. APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 2
 America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 2 Major Events 1890-1892 McKinley Tariff October 1, 1890 Raised the average duty on imports to almost fifty percent Intended to protect domestic industries
America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 2 Major Events 1890-1892 McKinley Tariff October 1, 1890 Raised the average duty on imports to almost fifty percent Intended to protect domestic industries
Imperialism. Creation of the U.S. Empire
 Imperialism Creation of the U.S. Empire Please Note: The images included in this presentation, some of which are copyrighted, are being used under the fair use provision (for educational purposes) of the
Imperialism Creation of the U.S. Empire Please Note: The images included in this presentation, some of which are copyrighted, are being used under the fair use provision (for educational purposes) of the
Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power
 Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power Objective: Why did the United States become imperialistic and what were the outcomes? Goal: Students will be able to understand the causes and effects of imperialism
Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power Objective: Why did the United States become imperialistic and what were the outcomes? Goal: Students will be able to understand the causes and effects of imperialism
American Upon the Global Stage Was America Imperialist? Or Was America Exceptional?
 APUSH Kind American Imperialism American Upon the Global Stage Was America Imperialist? Or Was America Exceptional? History of American Foreign Policy Neutrality & Isolationism Neutrality Proclamation
APUSH Kind American Imperialism American Upon the Global Stage Was America Imperialist? Or Was America Exceptional? History of American Foreign Policy Neutrality & Isolationism Neutrality Proclamation
Becoming a World Power Chapter 17
 Becoming a World Power 1872-1912 Chapter 17 imperialism Imperialism Why? New Markets Sen. Beverage Anglo-Saxon World Kipling Christianity Josiah Strong The work which the English race began when it
Becoming a World Power 1872-1912 Chapter 17 imperialism Imperialism Why? New Markets Sen. Beverage Anglo-Saxon World Kipling Christianity Josiah Strong The work which the English race began when it
(Think in reverse for America s products)
 Foreign countries put tariffs on incoming American goods. This made American goods more expensive in those countries and less desirable. Having more control over other countries and their economies would
Foreign countries put tariffs on incoming American goods. This made American goods more expensive in those countries and less desirable. Having more control over other countries and their economies would
Chapter 17, Section 1 I. Building Support for Imperialism (pages ) A. Beginning in the 1880s, Americans wanted the United States to become a
 Chapter 17, Section 1 I. Building Support for Imperialism (pages 520 522) A. Beginning in the 1880s, Americans wanted the United States to become a world power. Their change in attitude was a result of
Chapter 17, Section 1 I. Building Support for Imperialism (pages 520 522) A. Beginning in the 1880s, Americans wanted the United States to become a world power. Their change in attitude was a result of
Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914?
 Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914? From 1890 to 1914, the United States expanded its role in world affairs and gained new overseas colonies Class Activity:
Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914? From 1890 to 1914, the United States expanded its role in world affairs and gained new overseas colonies Class Activity:
Unit 7: America Comes of Age FRQ Outlines
 Prompt: 2. Analyze the extent to which the Spanish-American War was a turning point in American foreign policy. Re-written as a Question: What was the extent to which the Spanish American war a turning
Prompt: 2. Analyze the extent to which the Spanish-American War was a turning point in American foreign policy. Re-written as a Question: What was the extent to which the Spanish American war a turning
CHAPTER 22. The Quest for Empire, Learning Objectives. Thematic Guide
 CHAPTER 22 The Quest for Empire, 1865 1914 Learning Objectives After you have studied Chapter 22 in your textbook and worked through this study guide chapter, you should be able to: 1. Examine the late-nineteenth-century
CHAPTER 22 The Quest for Empire, 1865 1914 Learning Objectives After you have studied Chapter 22 in your textbook and worked through this study guide chapter, you should be able to: 1. Examine the late-nineteenth-century
Letter from President Fillmore asking Japan. American ships to stop for supplies safety reasons
 Chapter 19-21 Introduction Japan 1853 Not open to trading with other countries Commodore Matthew Perry went to Japan with a small fleet of warships (Gunboat Diplomacy) Letter from President Fillmore asking
Chapter 19-21 Introduction Japan 1853 Not open to trading with other countries Commodore Matthew Perry went to Japan with a small fleet of warships (Gunboat Diplomacy) Letter from President Fillmore asking
Imperialism and America
 CHAPTER 10 Section 1 ( pages 342 345) Imperialism and America BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about Woodrow Wilson. In this section, you will learn how economic activity led to political
CHAPTER 10 Section 1 ( pages 342 345) Imperialism and America BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about Woodrow Wilson. In this section, you will learn how economic activity led to political
BECOMING A WORLD POWER
 BECOMING A WORLD POWER CHAPTER 10 IMPERIALISM THE PRESSURE TO EXPAND Americans had always sought to expand the size of their nation, and throughout the 19th century they extended their control toward the
BECOMING A WORLD POWER CHAPTER 10 IMPERIALISM THE PRESSURE TO EXPAND Americans had always sought to expand the size of their nation, and throughout the 19th century they extended their control toward the
Imperialism and America
 Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire CHAPTER 10 Section 1 (pages 342-345) Imperialism and America American Expansionism (pages 342-344) Why did Americans support imperialism? In 1893, Queen Liliuokalani
Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire CHAPTER 10 Section 1 (pages 342-345) Imperialism and America American Expansionism (pages 342-344) Why did Americans support imperialism? In 1893, Queen Liliuokalani
Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of???
 Need to know What was President Roosevelt s Gentlemen s Agreement with Japan? Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of??? imperialism Stronger nations dominating
Need to know What was President Roosevelt s Gentlemen s Agreement with Japan? Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of??? imperialism Stronger nations dominating
Becoming A World Power,
 Becoming A World Power, 1890-1915 United States History Week of April 27, 2015 What Factors Caused Imperialism? Economic factors: need for natural resources, new markets for manufactured goods Nationalistic
Becoming A World Power, 1890-1915 United States History Week of April 27, 2015 What Factors Caused Imperialism? Economic factors: need for natural resources, new markets for manufactured goods Nationalistic
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved.
 Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. US History Immigration and Foreign policy Blizzard Bag 2014-2015 1. In a 1904 address to Congress, President Theodore Roosevelt stated that the United States
Copyright 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. US History Immigration and Foreign policy Blizzard Bag 2014-2015 1. In a 1904 address to Congress, President Theodore Roosevelt stated that the United States
SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR VOCAB
 SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR VOCAB 1. War of 1812 2. Monroe Doctrine 3. Mexican War 4. Yellow journalism 5. USS Maine 6. Rough Riders 7. San Juan Hill 8. Anti-Imperialist League 9. Platt Amendment 10.Diplomacy
SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR VOCAB 1. War of 1812 2. Monroe Doctrine 3. Mexican War 4. Yellow journalism 5. USS Maine 6. Rough Riders 7. San Juan Hill 8. Anti-Imperialist League 9. Platt Amendment 10.Diplomacy
Lesson 9: An Emerging World Power Imperialist = Expansionist (Chapter 9 in Textbook)
 Lesson 9: An Emerging World Power Imperialist = Expansionist (Chapter 9 in Textbook) Time Period: Late 1800s- 1914 Presidents William Mckinley 1897-1901 Theodore Roosevelt 1901-1909 William Howard Taft
Lesson 9: An Emerging World Power Imperialist = Expansionist (Chapter 9 in Textbook) Time Period: Late 1800s- 1914 Presidents William Mckinley 1897-1901 Theodore Roosevelt 1901-1909 William Howard Taft
Semester Exam Review: US History
 Name Class Period Semester Exam Review: US History Identify the major eras in U.S. history and describe their defining characteristics (US2C). Label each of the following eras on the timeline that follows.
Name Class Period Semester Exam Review: US History Identify the major eras in U.S. history and describe their defining characteristics (US2C). Label each of the following eras on the timeline that follows.
AP UNITED STATES HISTORY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES
 AP UNITED STATES HISTORY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 To what extent did the role of the federal government change under President Theodore Roosevelt in regard to TWO of the following: Labor Trusts
AP UNITED STATES HISTORY 2007 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 To what extent did the role of the federal government change under President Theodore Roosevelt in regard to TWO of the following: Labor Trusts
America s Path to Empire. APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 5
 America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 5 Mariam Haider, Emma Tresch, 5th Period America s Path to Empire 1892-1894 Feb 29, 1892: Britain and US sign treaty on seal hunting in the Bering
America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 5 Mariam Haider, Emma Tresch, 5th Period America s Path to Empire 1892-1894 Feb 29, 1892: Britain and US sign treaty on seal hunting in the Bering
Welcome to History 12 Political and Social History of the U.S. II From 1876 to the present Prof. Valadez
 Welcome to History 12 Political and Social History of the U.S. II From 1876 to the present Prof. Valadez 1 Topics The U.S. as a World Power Progressive Era 2 Becoming a World Power The New Imperialism
Welcome to History 12 Political and Social History of the U.S. II From 1876 to the present Prof. Valadez 1 Topics The U.S. as a World Power Progressive Era 2 Becoming a World Power The New Imperialism
IMPERIALISM. Policing the Western Hemisphere
 Alaska William Seward Sec. of State purchased from Russia for $7 million. Twice the size of Texas Nicknamed Seward s Folly or Seward s Icebox 1890 gold found there Hawaii IMPERIALISM Grew sugar that was
Alaska William Seward Sec. of State purchased from Russia for $7 million. Twice the size of Texas Nicknamed Seward s Folly or Seward s Icebox 1890 gold found there Hawaii IMPERIALISM Grew sugar that was
Difficult choice. Republican ideals? Imperial power?
 Difficult choice Republican ideals? Imperial power? Anti-Imperialist League Founded in 1899. Mark Twain, Andrew Carnegie, William James, and William Jennings Bryan among the leaders. Campaigned against
Difficult choice Republican ideals? Imperial power? Anti-Imperialist League Founded in 1899. Mark Twain, Andrew Carnegie, William James, and William Jennings Bryan among the leaders. Campaigned against
Becoming a World Power
 20 Becoming a World Power (1) CHAPTER OUTLINE As the United States Senate debates whether to annex the Philippine Isls, tension mounts near Manila as Filipinos Americans confront each other across an uneasy
20 Becoming a World Power (1) CHAPTER OUTLINE As the United States Senate debates whether to annex the Philippine Isls, tension mounts near Manila as Filipinos Americans confront each other across an uneasy
1 U.S. Expansion Pacific to Caribbean 2 Imperialism & Manifest Destiny Imperialism: The quest for colonial empires Manifest Destiny: US was destined
 1 U.S. Expansion Pacific to Caribbean 2 Imperialism & Manifest Destiny Imperialism: The quest for colonial empires Manifest Destiny: US was destined by God to expand from Atlantic coast into Pacific Ocean
1 U.S. Expansion Pacific to Caribbean 2 Imperialism & Manifest Destiny Imperialism: The quest for colonial empires Manifest Destiny: US was destined by God to expand from Atlantic coast into Pacific Ocean
America s Path to Empire. APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8
 America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8 1890-1892 Foreign Policy The Influence of Sea Power upon History (1890): Alfred Thayer Mahan Sea power throughout history gives advantages US lies
America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8 1890-1892 Foreign Policy The Influence of Sea Power upon History (1890): Alfred Thayer Mahan Sea power throughout history gives advantages US lies
Standards US History 10-25
 Standards US History 10-25 Progressivism Progressivism A reform movement focused on improving living conditions, education, working conditions, stopping political corruption, and gain women the right to
Standards US History 10-25 Progressivism Progressivism A reform movement focused on improving living conditions, education, working conditions, stopping political corruption, and gain women the right to
Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power ( )
 Name: Period Page# Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power (1890 1915) Section 1: The Pressure to Expand What factors led to the growth of imperialism around the world? In what ways did the United States begin
Name: Period Page# Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power (1890 1915) Section 1: The Pressure to Expand What factors led to the growth of imperialism around the world? In what ways did the United States begin
A. True or False Where the statement is true, mark T. Where it is false, mark F, and correct it in the space immediately below.
 AP U.S. History Chapter 24 Industry Comes of Age, 1865-1900 Name A. True or False Where the statement is true, mark T. Where it is false, mark F, and correct it in the space immediately below. 1. 2. 3.
AP U.S. History Chapter 24 Industry Comes of Age, 1865-1900 Name A. True or False Where the statement is true, mark T. Where it is false, mark F, and correct it in the space immediately below. 1. 2. 3.
Let's discuss: to stop human rights abuses under no circumstances
 Let's discuss: When do you think it is appropriate for the US to send soldiers to fight and face death on foreign soil? (Choose up to 3 of the following and briefly explain your choices) to assist an ally
Let's discuss: When do you think it is appropriate for the US to send soldiers to fight and face death on foreign soil? (Choose up to 3 of the following and briefly explain your choices) to assist an ally
throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not.
 1. Tell what at least three of the symbols you see on this flag represent. 2. Do you think these three symbols would be recognized throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not. 3. Why would this
1. Tell what at least three of the symbols you see on this flag represent. 2. Do you think these three symbols would be recognized throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not. 3. Why would this
Imperialism. Policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker territories
 Imperialism Policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker territories Global Competition European nations had been establishing colonies for years Asia
Imperialism Policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker territories Global Competition European nations had been establishing colonies for years Asia
affairs of other countries
 Competency Goal 6: The Emergence of the United States in World Affairs (1890-1914), analyze causes and effects of the United States emergence as a world power 6.01: Examine the factors that led to the
Competency Goal 6: The Emergence of the United States in World Affairs (1890-1914), analyze causes and effects of the United States emergence as a world power 6.01: Examine the factors that led to the
Unit 6: A New Role in the World
 Unit 6: A New Role in the World Study online at quizlet.com/_1fnvlz 1. alliances 5. conscription An agreement between nations to aid and protect each other. 2. Allies A military draft 6. dollar diplomacy
Unit 6: A New Role in the World Study online at quizlet.com/_1fnvlz 1. alliances 5. conscription An agreement between nations to aid and protect each other. 2. Allies A military draft 6. dollar diplomacy
Industry Comes of Age. Chapter 24
 Industry Comes of Age Chapter 24 Chapter 24 theme: America s Second Industrial Revolution in the Gilded Age (1865-1900) was spurred initially by the transcontinental rail network, and saw large businesses
Industry Comes of Age Chapter 24 Chapter 24 theme: America s Second Industrial Revolution in the Gilded Age (1865-1900) was spurred initially by the transcontinental rail network, and saw large businesses
ID- Captured Filipino Insurrectionists (642) Summary 1-How many Filipinos died in the three year insurrection against the US? 600,000 Summary 2- How
 Ch 27 P2 Insights 1) Define and explain why the US issued the Open Door Policy 2) Explain how the Open Door Policy changed the United States role in the world. 3) Was the US a good neighbor to Latin America?
Ch 27 P2 Insights 1) Define and explain why the US issued the Open Door Policy 2) Explain how the Open Door Policy changed the United States role in the world. 3) Was the US a good neighbor to Latin America?
Unit 5. US Foreign Policy, Friday, December 9, 11
 Unit 5 US Foreign Policy, 1890-1920 I. American Imperialism A. What is Imperialism? B. Stated motivations (how we were helping others) Helping free countries from foreign domination Spreading Christianity
Unit 5 US Foreign Policy, 1890-1920 I. American Imperialism A. What is Imperialism? B. Stated motivations (how we were helping others) Helping free countries from foreign domination Spreading Christianity
U.S. INDUSTRIALISM. Chap 9
 U.S. INDUSTRIALISM Chap 9 How did the US industrialize? Plenty of raw materials needed for industry: water, wood, coal, iron, copper Large workforce: population tripled between 1860-1910 Technology and
U.S. INDUSTRIALISM Chap 9 How did the US industrialize? Plenty of raw materials needed for industry: water, wood, coal, iron, copper Large workforce: population tripled between 1860-1910 Technology and
Unit Four: The Gilded Age and a Maturing Industrial Society AP US History Unit 4 Overview
 Unit Four: The Gilded Age and a Maturing Industrial Society 1877-1914 AP US History Unit 4 Overview OVERVIEW OF TIME SPAN: Few topics have triggered as much intellectual warfare as the twenty-five years
Unit Four: The Gilded Age and a Maturing Industrial Society 1877-1914 AP US History Unit 4 Overview OVERVIEW OF TIME SPAN: Few topics have triggered as much intellectual warfare as the twenty-five years
Calvin Coolidge The last 3 decades of the 1800s was more productive than all of America s history before it By 1900 America was the unquestioned
 Calvin Coolidge The last 3 decades of the 1800s was more productive than all of America s history before it By 1900 America was the unquestioned economic powerhouse of the world 1. Abundant raw materials
Calvin Coolidge The last 3 decades of the 1800s was more productive than all of America s history before it By 1900 America was the unquestioned economic powerhouse of the world 1. Abundant raw materials
Imperial America The United States in the World
 Imperial America The United States in the World 1890-1914 Gilded Age: A Tale of Today 1873 Novel by Mark Twain and Charles Warner: fictional account of political and economic corruption in the USA gild
Imperial America The United States in the World 1890-1914 Gilded Age: A Tale of Today 1873 Novel by Mark Twain and Charles Warner: fictional account of political and economic corruption in the USA gild
STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015
 STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015 AGE OF IMPERIALISM! (1900s- 1914) MILITARY Alfred T. Mahan argued for a strong NAVY in his book Influence of Sea Power Upon History Easier
STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015 AGE OF IMPERIALISM! (1900s- 1914) MILITARY Alfred T. Mahan argued for a strong NAVY in his book Influence of Sea Power Upon History Easier
In the early 1900's the United States engaged in conflicts with Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines.
 Ch 18-Section 3 - Acquiring New Lands In the early 1900's the United States engaged in conflicts with Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines. Puerto Rico Fearful of losing autonomy that they had won under
Ch 18-Section 3 - Acquiring New Lands In the early 1900's the United States engaged in conflicts with Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines. Puerto Rico Fearful of losing autonomy that they had won under
don t just GITMO, get SAMOA
 Presented by David C. Burton, February 6, 2010 Oklahoma State Social Studies & Fine Arts Conference davidburton@mooreschools.com don t just GITMO, get SAMOA IMPERIALISM The act of extending one country
Presented by David C. Burton, February 6, 2010 Oklahoma State Social Studies & Fine Arts Conference davidburton@mooreschools.com don t just GITMO, get SAMOA IMPERIALISM The act of extending one country
Today s Topics. Quiz 1 Populism & The Segregated South The U.S. as a World Power
 Today s Topics Quiz 1 Populism & The Segregated South The U.S. as a World Power 1 The Transformation of the West 2 The Transformation of the West Remaking Indian Life Forced assimilation The Dawes Act
Today s Topics Quiz 1 Populism & The Segregated South The U.S. as a World Power 1 The Transformation of the West 2 The Transformation of the West Remaking Indian Life Forced assimilation The Dawes Act
APUSH REVIEWED! INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION: INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
 APUSH 1865-1900 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION: REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 24 American History (Brinkley) Chapters 17, 18 America s History (Henretta) Chapters 17, 19 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION By 1900
APUSH 1865-1900 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION: REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 24 American History (Brinkley) Chapters 17, 18 America s History (Henretta) Chapters 17, 19 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION By 1900
APUSH REVIEWED! INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION:
 APUSH 1865-1900 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION: REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 24 American History (Brinkley) Chapters 17, 18 America s History (Henretta) Chapters 17, 19 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION By 1900
APUSH 1865-1900 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION: REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 24 American History (Brinkley) Chapters 17, 18 America s History (Henretta) Chapters 17, 19 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION By 1900
God Bless the USA! (4) Mr. Cegielski
 God Bless the USA! (4) Mr. Cegielski 1 IMPERIALISM Imperialism is the quest for colonial empires and it often involves the use of economic, political, or military power 2 The Main Idea The United States
God Bless the USA! (4) Mr. Cegielski 1 IMPERIALISM Imperialism is the quest for colonial empires and it often involves the use of economic, political, or military power 2 The Main Idea The United States
STANDARD VUS.8a. Essential Questions What factors influenced American growth and expansion in the late nineteenth and early twentieth century?
 STANDARD VUS.8a through the early twentieth century by explaining the relationship among territorial expansion, westward movement of the population, new immigration, growth of cities, and the admission
STANDARD VUS.8a through the early twentieth century by explaining the relationship among territorial expansion, westward movement of the population, new immigration, growth of cities, and the admission
-King Kalahaua: Queen Liliuokalani (Sandford B. Dole)
 Imperialism Causes of Imperialism If it were necessary to give the briefest possible definition of imperialism, we should have to say that imperialism is the monopoly stage of capitalism. --Vladimir Lenin
Imperialism Causes of Imperialism If it were necessary to give the briefest possible definition of imperialism, we should have to say that imperialism is the monopoly stage of capitalism. --Vladimir Lenin
Imperialism. U.S. Foreign Policy. U.S. Foreign Policy 10/30/13. Chapter 10. Monroe Doctrine. Many Spanish colonies revolting
 Imperialism Chapter 10 U.S. Foreign Policy Monroe Doctrine No new colonization by Europe in western hemisphere U.S. stays out of European affairs If Europe attempts to colonize in the west, U.S. would
Imperialism Chapter 10 U.S. Foreign Policy Monroe Doctrine No new colonization by Europe in western hemisphere U.S. stays out of European affairs If Europe attempts to colonize in the west, U.S. would
French on the Mexican-American border Expansion. Intervention confined to Latin America Europe
 French on the Mexican-American border Expansion Alaska Midway Islands left alone to pursue interests Reducing army and navy No longer interested in Caribbean Intervention confined to Latin America Europe
French on the Mexican-American border Expansion Alaska Midway Islands left alone to pursue interests Reducing army and navy No longer interested in Caribbean Intervention confined to Latin America Europe
Imperialism Practice Test
 Imperialism Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What did Liliuokalani propose after she became Queen of the Hawaiian Islands?
Imperialism Practice Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. What did Liliuokalani propose after she became Queen of the Hawaiian Islands?
Essential Question: & Latin America? Clicker Review. What role did the United States play as an imperial power in Asia. CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.
 Essential Question: What role did the United States play as an imperial power in Asia & Latin America? CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.8: Clicker Review Imperialism by the USA notes Today s HW: 28.3 Unit 10 Test:
Essential Question: What role did the United States play as an imperial power in Asia & Latin America? CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.8: Clicker Review Imperialism by the USA notes Today s HW: 28.3 Unit 10 Test:
2. Social Darwinism in America New Business Culture: The American Dream? 3. Protestant (Puritan) Work Ethic Horatio Alger [100+ novels] The Gospel of
![2. Social Darwinism in America New Business Culture: The American Dream? 3. Protestant (Puritan) Work Ethic Horatio Alger [100+ novels] The Gospel of 2. Social Darwinism in America New Business Culture: The American Dream? 3. Protestant (Puritan) Work Ethic Horatio Alger [100+ novels] The Gospel of](/thumbs/79/79175911.jpg) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Unit 7: The Gilded Age AP United States History AP Note This time period is sometimes difficult to study, yet it is important for U.S. History and the AP exam. Read carefully and before
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Unit 7: The Gilded Age AP United States History AP Note This time period is sometimes difficult to study, yet it is important for U.S. History and the AP exam. Read carefully and before
Between 1870 and 1900, Europeans had taken over 1/5 of land and 1/10 of population of the world Germany became America s biggest imperialist foe and
 U.S. Imperialism Between 1870 and 1900, Europeans had taken over 1/5 of land and 1/10 of population of the world Germany became America s biggest imperialist foe and largely spurred U.S. into imperialism;
U.S. Imperialism Between 1870 and 1900, Europeans had taken over 1/5 of land and 1/10 of population of the world Germany became America s biggest imperialist foe and largely spurred U.S. into imperialism;
Section 1 Introduction to Period 6, page 318
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Ch. 16 AMSCO or other source for Period 6 Directions: 1. Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before you read the chapter. 2. Skim:
Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Ch. 16 AMSCO or other source for Period 6 Directions: 1. Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before you read the chapter. 2. Skim:
Warm Up. Complete the Captains of Industry vs. Robber Barons DBQ
 Warm Up 1 Complete the Captains of Industry vs. Robber Barons DBQ 2 Be prepared to argue whether the industrial entrepreneurs of the Gilded Age are CI or RB 3 Read the intro to help you answer the questions
Warm Up 1 Complete the Captains of Industry vs. Robber Barons DBQ 2 Be prepared to argue whether the industrial entrepreneurs of the Gilded Age are CI or RB 3 Read the intro to help you answer the questions
Acquiring and Managing Global Power
 1890 1917 Chapter 21 Acquiring and Managing Global Power Were U.S. interventions abroad between 1890 and 1917 motivated more by realism or idealism? 21.1 Introduction On May 1, 1901, the Pan-American Exposition
1890 1917 Chapter 21 Acquiring and Managing Global Power Were U.S. interventions abroad between 1890 and 1917 motivated more by realism or idealism? 21.1 Introduction On May 1, 1901, the Pan-American Exposition
American Foreign Policy, : The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly.
 American Foreign Policy, 1880-1920: The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly. Each group will become experts on their assigned country. Create poster showing how U.S. policy toward your respective country was good,
American Foreign Policy, 1880-1920: The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly. Each group will become experts on their assigned country. Create poster showing how U.S. policy toward your respective country was good,
Work Period: Latin America and China Foreign policies Notes President Chart Activity
 USHC 5.0 DEMONSTRATE AN UNDERSTANDING OF DOMESTIC AND FOREIGN DEVELOPMENTS THAT CONTRIBUTED TO THE EMERGENCE OF THE UNITED STATES AS A WORLD POWER IN THE 20 TH CENTURY Opening: Complete pages 185-188 in
USHC 5.0 DEMONSTRATE AN UNDERSTANDING OF DOMESTIC AND FOREIGN DEVELOPMENTS THAT CONTRIBUTED TO THE EMERGENCE OF THE UNITED STATES AS A WORLD POWER IN THE 20 TH CENTURY Opening: Complete pages 185-188 in
THE EMERGENCE OF THE AMERICAS IN GLOBAL AFFAIRS,
 THE EMERGENCE OF THE AMERICAS IN GLOBAL AFFAIRS, 1880-1929 INTRODUCTION END OF 19 TH C. MARKED BY GLOBAL INTEGRATION 2 ND HALF OF 19 TH C. U.S. MOVES INTO A PERIOD OF ECONOMIC EXPANSION AND IMPERIALIZATION
THE EMERGENCE OF THE AMERICAS IN GLOBAL AFFAIRS, 1880-1929 INTRODUCTION END OF 19 TH C. MARKED BY GLOBAL INTEGRATION 2 ND HALF OF 19 TH C. U.S. MOVES INTO A PERIOD OF ECONOMIC EXPANSION AND IMPERIALIZATION
Chapter 18 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 18 Lecture Outline Big Business and Organized Labor 2013 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Chapter 18 Lecture Outline Big Business and Organized Labor 2013 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Robber Barons
Chapter 18 Lecture Outline Big Business and Organized Labor 2013 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Chapter 18 Lecture Outline Big Business and Organized Labor 2013 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Robber Barons
Chapters 18 Review American History
 Chapters 18 Review American History I. Policy of Imperialism: a. Imperialism is a countries policy and practice of creating an empire and maintaining control to expand their control of raw materials, and
Chapters 18 Review American History I. Policy of Imperialism: a. Imperialism is a countries policy and practice of creating an empire and maintaining control to expand their control of raw materials, and
America as a World Power
 CHAPTER22 1867 1920 America as a World Power Essential Question How did America s growing power affect its relationships with other nations? What You Will Learn... In this chapter you will learn about
CHAPTER22 1867 1920 America as a World Power Essential Question How did America s growing power affect its relationships with other nations? What You Will Learn... In this chapter you will learn about
Imperialism by the US
 Imperialism by the US Quick Class Discussion: Based on this image, what important changes took place in the United States from 1783 to 1900? 115 years after gaining independence from Britain, the United
Imperialism by the US Quick Class Discussion: Based on this image, what important changes took place in the United States from 1783 to 1900? 115 years after gaining independence from Britain, the United
Unit Plan: 11 th Grade US History
 Unit Plan: 11 th Grade US History Unit #4: The Great Depression and the New Deal 20 Instructional Days Unit Overview Big Idea: After Years of Postwar economic boom the world economy collapses which forces
Unit Plan: 11 th Grade US History Unit #4: The Great Depression and the New Deal 20 Instructional Days Unit Overview Big Idea: After Years of Postwar economic boom the world economy collapses which forces
Unit 2: The Rise of Big Government
 Unit 2: The Rise of Big Government Imperialism, the Progressive Era, and the First World War 1898-1920 Unit Overview: By 1896, American industry had caught up with the rest of the world. Since the nation
Unit 2: The Rise of Big Government Imperialism, the Progressive Era, and the First World War 1898-1920 Unit Overview: By 1896, American industry had caught up with the rest of the world. Since the nation
US History Mr. Martin Unit 7: The Birth of Modern America Chapters 13-16
 US History Mr. Martin Unit 7: The Birth of Modern America Chapters 13-16 This unit explores the transformation of the US from a rural nation into an industrial, urban nation during the period from 1865
US History Mr. Martin Unit 7: The Birth of Modern America Chapters 13-16 This unit explores the transformation of the US from a rural nation into an industrial, urban nation during the period from 1865
The Rise of Smokestack America
 18 The Rise of Smokestack America (1) CHAPTER OUTLINE Thomas O'Donnell's testimony highlights the marginal existence of many workingclass Americans in the late nineteenth century. The responses of congressional
18 The Rise of Smokestack America (1) CHAPTER OUTLINE Thomas O'Donnell's testimony highlights the marginal existence of many workingclass Americans in the late nineteenth century. The responses of congressional
The Progressive Presidents
 The Progressive Presidents Main Ideas o The federal government responded to grassroots reform efforts by enacting progressive policies. o Progressive reforms sought to established a greater degree of democratic
The Progressive Presidents Main Ideas o The federal government responded to grassroots reform efforts by enacting progressive policies. o Progressive reforms sought to established a greater degree of democratic
