Was America Imperialist? Or Was America Exceptional?
|
|
|
- Bruce Bradley
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 American upon the Global Stage Was America Imperialist? Or Was America Exceptional? 1994 DBQ To what extent was late nineteenth-century and early twentieth-century expansionism a continuation of past United States expansionism and to what extent was it a departure? History of American Foreign Policy Neutrality & Isolationism Neutrality Proclamation (1793) & Washington s Farewell Address (1796) Failure of Diplomacy--Jay s Treaty (1794) & XYZ Affair (1797) Setting Boundaries & Continental Expansion Louisiana Purchase (1803) War of 1812 as Second American Revolution Monroe Doctrine (1823) Manifest Destiny Participation in the Imperial Scramble Was it imperialism? Colonialism Sphere of Influence Open Door Policy Gunboat Diplomacy Dollar Diplomacy Cultural Imperialism Definition of New Imperialism: The extension of a nation s authority by territorial acquisition -OR- by the establishment of economic & political hegemony over other nations. Factors to Consider Intent or Purpose of Initial Involvement Religious Mission Economic Markets, Resources & Investment Diplomatic Ties Military & Strategic Need Method of Takeover & Control Duration of Involvement & Exit Strategy Liberation & Independence Protectorate
2 Annexation Basis for Imperialism Economic Basis--Growing importance of foreign trade as domestic markets were saturated. Military or Strategic Basis--Connected to Economic Basis, spurred by Mahan Thesis in The Influence of Sea Power upon History Exacerbated by International Competition--Perceived carving up of the globe, America s primary competition was Germany, another New Imperialist power. Imperialism Justifications & Influences Social Darwinism Right of Conquest Social Gospel Duty of Civilization Pan-Americanism Regional Responsibility Nationalism & Jingoism Everything filtered through the yellow press Sensationalism sold better than fact; Politicians sought out the Pulitzer & Hearst papers to publicize their proposals (Modern Navy) Spanish-American War America s Splendid Little War or the First Imperialist Quagmire Spanish Misrule in Cuba One of the last colonies of Spain; Stalemate of the Ten Year s War followed by emancipation & Hispanization in 1880s; Jose Marti (Washington & Jefferson rolled into one) mobilizes mixed-race forces & begins attacks in 1894; Spain sends more than 200,000 troops to suppress rebellion & General Weyler institutes policy of Reconcentration Camps that leads to ~100,000 deaths due to inadequate food & sanitation; Spain granted limited autonomy in American Concerns in Cuba Cuban Sugar Industry Estates transferred to American ownership in 1880s; 90% of Cuban sugar exports were to US; Wilson-Gorman Tariff (1894) took sugar of the Duty-free List placing American producers in Cuba at a disadvantage. Policies of the McKinley Administration
3 McKinley elected on a more aggressive, Imperialist platform; Replaced Cleveland who had stressed neutrality. Competition among Hearst & Pulitzer Cuba was the front-page story for months; You furnish the pictures & I ll furnish the war. De Lomé Letter Besides the natural and inevitable coarseness with which he repeats all that the press and public opinion of Spain has said of Weyler, it shows once more what McKinley is: weak and catering to the rabble, and, besides, a low politician, who desires to leave a door open to me and to stand well with the jingoes of his party. February 9, Military History Spain agreed to US demands End Reconcentration Camps & sign armistice with Cuban rebels; Giving in to media & public pressure, McKinley declared that this was not enough. Combat in Cuba Spanish fleet blockaded in Santiago Harbor; Outgunned by USS Oregon which steamed in from Pacific; US army forces took high ground with little opposition; 379 American battle deaths but 5,000 deaths due to disease US combat in the Philippines Largely a fluke, as Roosevelt ordered the attack though he had no authority to do so; Dewey s fleet saw no opposition from the Spanish fleet; Land forces assisted by Filipino exile Emilio Aguinaldo & the Katipunan. US Combat in Puerto Rico Invaded as an afterthought, possibly an attempt to lay claim to the island before the war officially ended; American troops met no opposition, welcomed as liberators. Cuba as Spoils of War? Cuba on the Road to Independence Teller Amendment declared that American intent in war against Spain was not territorial acquisition; Military Government until 1902 improves financial, medical & educational facilities until withdrawal of troops; Platt Amendment introduced into Cuban Constitution Ostensibly to protect Cuba while it was vulnerable to foreign interference; Restricted Cuban treaties with other nations;
4 Allowed the US to intervene to restore order or in cases of mutual protection; Promised to lease facilities to US (Guantanamo Bay) Puerto Rico as Spoils of War Made into a US Protectorate by Treaty of Paris (1898) Foraker Act (1900)--Appointment of civilian government Insular Cases ( ) deal with questions of: Right of US to acquire territories Yes. Whether all Constitutional protections applied to people of those territories No, only the fundamental ones, because some populations were not fit enough. Overall question of whether the Constitution followed the flag Not necessarily. Jones Act (1917) US Citizenship for Puerto Ricans. Puerto Rico made a Commonwealth in The Philippines as Spoils of War? Engendered the most debate Most complex in terms of negotiations with Spanish; US took Manila after Spain sued for peace; Largest land mass & populations of Spanish possessions (7 million Filipinos); Major arguments made by the Military, Businessmen & Missionaries to keep the islands; Philippines seen as most foreign acquisition: Need for standing army for occupation; Competition for labor, relocation of factories; Fears of mogrelization of white race. McKinley s calls for Benevolent Assimilation Believed that an inner voice told him to take the Philippines to Christianize & civilize them; Fit with argument that Filipinos were not ready for independence, would be preyed upon by other Imperial powers; US did a great deal to advance infrastructure, sanitation & public health with little profit to US. Filipinos under Aguinaldo had expected independence Defeat of Spanish was not possible without; Wanted less sanitation & more liberty; Insurrection did not survive the capture of Aguinaldo. Philippine Insurrection Filipinos early on switched to Guerilla tactics Infuriated American soldiers, led to atrocities;
5 Nearly 5,000 American soldiers killed (primarily from disease); more than 50,000 Filipino soldiers killed in combat; More Filipinos killed in captivity after US Military applied General Order 100 denying POW status allowing torture such as Water Cure Civilian casualties grew as war dragged on US Military relocated civilians into protected zones around towns & villages, similar to Spanish Reconcentration camps; In Batangas nearly 300,000 civilians died as malaria & dysentery spread through the zones. Legacy of Philippine Insurrection Most Filipinos accepted the paternalistic policies of the Philippine Commission led by William H. Taft, who referred to Filipinos as is little brown brothers. Final legacy came with Senate Investigation & War Trials that publicized the combat tactics High-ranking officers defended their Kill & Burn policy; General Hell Roaring Jake Smith court-martialed for Samar campaign where he issued the order to kill everyone over the age of ten and turn the region into a howling wilderness. Philippines gained official independence in 1946; US maintained lease on Subic Bay & other military bases. The Progressive Movement Domestic American Imperialism? Origins of Progressivism Definition: Gradual, sometimes middle-class movement focused on improving, quieting & leveling--not radical--reform. Origins Cyclical trends--reform decades of 1840s & 1870s; Building on the Populist Movement, especially the Omaha Platform that called for Income Tax & Government ownership of infrastructure; Early reformers such as Henry George, Edward Bellamy, Thorstein Veblen & Charles Seldon. Progressivism as a Middle-class Movement Rose in response to more radical Socialist challenge Eugene V. Debs (Presidential candidate in 1904, 1908 & 1912) & Victor Berger (Socialist mayor of Milwaukee, WI); Fear of growing immigrant influence; Intellectuals such as Jack London, Helen Keller & Charlotte Perkins Gilman.
6 Rise of Muckrakers in major magazines McClure s, Cosmopolitan, Collier s, Everybody s Lincoln Steffens (Machine politics in Shame of the City), Ida Tarbell (Standard Oil), Ray Stannard Baker (Race in Following the Color Line) Central role of women reformers Women s Christian Temperance Union, Anti-Saloon League; Settlement House movement--jane Addams & Hull House; Florence Kelly & National Consumer League often joined forces with Women s Trade Union League. Major, Mobilizing, Solidifying Events Triangle Shirtwaist Factory Fire--Following a successful International Ladies Garment Workers Strike; Publication of Upton Sinclair s The Jungle followed by passage of Pure Food & Drug Act. Correcting Abuses & Injustices of Urban Industrialization Trust-Busting Elkins Act addressed abuses of railroad rebates; Hepburn Act expanded power of the Interstate Commerce Commission to deal with Bad Trusts Regulation & Consumer Protection Meat Inspection Act provided for safety of meat shipped across state borders; Pure Food & Drug Act provided for true product labeling. Early Environmentalism Preservation accomplished with National Park System; Conservation more popular, especially forestry management. Restoring Control of Gov t to the People Electoral Reform Secret Ballot ended public & recorded voting that often led to coercion & intimidation; Direct Primary took selection of candidates away from the smoke-filled backrooms of thee political parties; 17th Amendment allowed for direct election of Senators. Legislating at the Ballot Box Initiative--Voters could propose laws for consideration; Referendum--Voters could vote on passage of laws directly; Recall--Immediate removal of public officials by vote of the people. Pragmatism, Scientific Principles & Efficient Management
7 Replaced of elected mayors & city councils with City Managers & County Commissions; Instituted Civil Service reform to end spoils system & cronyism; Municipal ownership & operation of utilities; Wisconsin Idea --Incorporating the expertise of university professionals in public policy; Complicated Nature of Progressivism: Drive for efficiency often led to centralization of government policy that were often less than democratic. Emphasizing Social Justice, Humane Treatment & Morality Development of Social Work to formalize charity & welfare; Institutions such as the settlement houses provided direct services to the community; Belief that education for a greater portion of the population would solve problems of the present & future; 18th Amendment finally brought about Prohibition of alcohol. Election of Flood Tide of Progressivism Incumbent Taft the practical Progressive Return of Roosevelt & the Square Deal Control of Corporations, Consumer Protection & Conservation of Natural Resources; Displaces Robert La Follette as the candidate of the Progressive Party. Democrat Woodrow Wilson & the New Freedom Attacked the Triple Wall of Privilege with antitrust legislation, monetary changes & tariff reductions. Eugene V. Debs (Socialist not Marxist) polled nearly a 6%, a million votes. America & the Great War American Neutrality Economic Benefits Private US industry served as arsenal ($2.4 billion) & bank ($3 billion) for Allies; Trade with Central Powers was open, but difficult--no great loss ($169 million) Isolationism Neutrality Re-established cultural & economic ties with England
8 Spread of British propaganda to US 11 million Americans w/parent from Central Power nation; Large urban Irish & Jewish populations did not favor Allies; Division exacerbated natural isolation of Americans. End of Neutrality Progressive Idealism Response to German Actions & Atrocities Final Straw? Zimmerman Telegram Military Mobilization--Volunteerism National Defense Act (1916) Increased the enlistment of Army & National Guard Called for training of Citizen Soldiers Naval Act (1916)--Largest expansion of Navy in US history. Selective Service Act (1917)--Required registration of all males (later 18-45) Specifically intended to prepare the nation for battle; Also meant to instill patriotism & aid in assimilation of ethnic Americans-- Heat up the melting pot Economic Mobilization--Voluntary Compliance It is not the army that we must shape & train for war; it is the nation. -- Woodrow Wilson. Cost of the War $760 million each month; $33.5 billion total, but more than three times that when veterans benefits & interest on loans paid after war. Greatest Need: Mobilizing all resources toward war effort Americans accepted that the war would require sacrifice; But would they accept formal control & regulation? Mobilization & the Food Administration Herbert Hoover s agency relied on Voluntary Compliance to production & consumption Prohibition & 18th Amendment were part of this strategy--restrictions on using grain to produce alcohol Pushed people to grow Victory Gardens & follow wheatless Wednesdays & meatless Tuesdays; Never implemented a system of rations. Voluntary Compliance was a success Farm production increased 25% Food exports to Allies tripled; Policy was used by Fuel Administration & bond drives. Mobilization & War Industries Board
9 Bernard Baruch s agency worked with trade associations to regulate production & costs Late in war after conflicts between military & industry; Some attempts to mobilize labor without recognizing the rights of labor. Most policies were clearly pro-industry Antitrust laws abandoned for duration Competitive bidding was abandoned during war & Cost-Plus contracts guaranteed companies a profit no matter costs cost; Despite pro-industry stance, arguments that arms merchants & bankers brought about--myth Opposition to Mobilization Labor Unrest Over 6,000 strikes during the war, especially those by the Wobblies; Government was forced to form National War Labor Board, prohibiting strikes but also encouraging reform & further recognizing rights of labor. Henry Ford s Unrest Refused to accept War Industry Board s limit on automobile production; Baruch threatened to send troops & seize Ford s plants; These types of threats were used repeatedly but never came to anything. The 14 Points & Treaty of Versailles From Progressive Idealism to Imperialist Reality Wilson s 14 Points--January 8, 1918 Abolish Secret Treaties; Freedom of the Seas; Remove Economic Barriers; Reductions in Armaments; Adjustments in Colonial Claims; Self-Determination, especially in Austria-Hungary; Realignments & Readjustments for Italy, Russia, Belgium, Balkans, Turkey, Poland & France; Formation of League of Nations From 14 Points to Treaty of Versailles Clemenceau, Lloyd George & Orlando were not as idealistic as Wilson & politically more savvy; Political Self-Determination limited to European colonies & denied to those in Africa & Asia. Article 231--War-Guilt Clause Placed sole blame for war on Germany; Obliged Germany to pay $31 billion in reparations;
10 Forced Germany to accept restrictions on military & loss of Sudetenland & Rhineland. German bitterness arose out expectations that Treaty of Versailles would more closely mirror 14 Points. Senate Undermines Wilsonian Idealism Constitution gives the Senate role of advice & consent over treaties negotiated by the Executive Branch. Opposition to League of Nations in Senate Henry Cabot Lodge bogs down Treaty of Versailles; Major fears of US giving up American sovereignty to an international body; Irreconcilables (Borah & Johnson) opposed the League on any terms; Lodge Reservations--Reserved rights of US to have an independent foreign policy. Wilson Overestimates US Idealism Wilson attempted an end-run around the Senate, going directly to the people Went on a whistle-stop tour to drum up support; Fairly successful, but ability to mobilize popular support hindered by a stroke. Wilson s Political Blunder Attempted to win support without the Lodge Reservation; Ordered Democrats to vote w/irreconcilables against treaty; 80% of Senators supported the treaty but was never ratified. US signed separate peace w/germany on July 25, Mobilization gone too far? Opposition to Difference & Dissent during & after the Great War Creel s Committee on Public Information Propaganda seen as necessary for Volunteerism & Voluntary Compliance Established voluntary censorship in press; Supported newsreels, documentaries & anti-german movies including The Kaiser: Beast of Berlin; Sent out Four-Minute Men to directly drum up support. Supported several controversial measures 100% Americanism movement whipped anti-german sentiment against recent immigrants; Creation of Liberty Leagues in communities across the country, advocated spying on neighbors, especially those with foreign-sounding names. Restrictions on Dissent & Speech Espionage Act (1917)--Fines & prison for those making statements that impeded draft or promoted insubordination in the military.
11 Sedition Act (1918)--Went further to include anything that impeded sale of war bonds or any disloyal, profane, scurrilous, or abusive language used to describe the US government, Constitution, flag or allies. Schenck v. US (1919)--Constitutionality of Espionage Act Supreme Court argued that certain speech did not deserve protection on its very face (Shouting fire in a crowded theater); Determined wartime represented special circumstances; speech representing a Clear & Present Danger could be restricted. Red Summer & Red Scare Red Summer (1919)--Limits of Mobilization Great Migration part of wartime industrial mobilization; Race riots in 2 dozen cities, worst in Chicago. Red Scare ( )--Mobilization Out of Control Anti-Immigrant sentiment turns from Germans to Socialists/Anarchists Real fears of bombings--38 mailed to prominent Americans, one exploded on Wall Street, anarchist blown up outside home of Attorney General A. Mitchell Palmer; Major strikes continued across the nation; Led to Palmer Raids & deportations of radicals & leftists (4000 alleged communists arrested, 556 aliens deported, most w/out trials) No major violence developed, support for Palmer Raids waned.
American Upon the Global Stage Was America Imperialist? Or Was America Exceptional?
 APUSH Kind American Imperialism American Upon the Global Stage Was America Imperialist? Or Was America Exceptional? History of American Foreign Policy Neutrality & Isolationism Neutrality Proclamation
APUSH Kind American Imperialism American Upon the Global Stage Was America Imperialist? Or Was America Exceptional? History of American Foreign Policy Neutrality & Isolationism Neutrality Proclamation
Unit 5. US Foreign Policy, Friday, December 9, 11
 Unit 5 US Foreign Policy, 1890-1920 I. American Imperialism A. What is Imperialism? B. Stated motivations (how we were helping others) Helping free countries from foreign domination Spreading Christianity
Unit 5 US Foreign Policy, 1890-1920 I. American Imperialism A. What is Imperialism? B. Stated motivations (how we were helping others) Helping free countries from foreign domination Spreading Christianity
Unit 7: America Comes of Age FRQ Outlines
 Prompt: 2. Analyze the extent to which the Spanish-American War was a turning point in American foreign policy. Re-written as a Question: What was the extent to which the Spanish American war a turning
Prompt: 2. Analyze the extent to which the Spanish-American War was a turning point in American foreign policy. Re-written as a Question: What was the extent to which the Spanish American war a turning
Empire and Expansion. Chapter 27
 Empire and Expansion Chapter 27 Imperialism Stronger nations attempt to create empires by dominating weaker nations. The late 1800s marked the peak of European imperialism, with much of Africa and Asia
Empire and Expansion Chapter 27 Imperialism Stronger nations attempt to create empires by dominating weaker nations. The late 1800s marked the peak of European imperialism, with much of Africa and Asia
Expanding Horizons: Imperialism
 Expanding Horizons: Imperialism In August 1914, World War I broke out in Europe, which drowned out the Progressive Era. Leading up to this, U.S. foreign policy had been drastically changing. IMPERIALISM
Expanding Horizons: Imperialism In August 1914, World War I broke out in Europe, which drowned out the Progressive Era. Leading up to this, U.S. foreign policy had been drastically changing. IMPERIALISM
Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism ( )
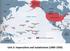 Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism (1890-1930) What is an empire? Is imperialism the same as colonization? Why would the U.S. get involved in this practice? What is the difference between acquiring and
Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism (1890-1930) What is an empire? Is imperialism the same as colonization? Why would the U.S. get involved in this practice? What is the difference between acquiring and
Imperialism. Policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker territories
 Imperialism Policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker territories Global Competition European nations had been establishing colonies for years Asia
Imperialism Policy in which stronger nations extend their economic, political, or military control over weaker territories Global Competition European nations had been establishing colonies for years Asia
World War I: America s Home Front
 World War I: America s Home Front 1. The U.S. and WWI! US neutral until 1917; favors Allies! Protect loans to Allies! US shares Allies culture and democratic government! Allied propaganda! German Unrestricted
World War I: America s Home Front 1. The U.S. and WWI! US neutral until 1917; favors Allies! Protect loans to Allies! US shares Allies culture and democratic government! Allied propaganda! German Unrestricted
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e. Chapter Nineteen: From Crisis to Empire
 Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e The Politics of Equilibrium Electoral Stability High Turnout for Elections Cultural Basis of Party Identification Catholics Tended to Vote Democrat 2 The Politics of
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e The Politics of Equilibrium Electoral Stability High Turnout for Elections Cultural Basis of Party Identification Catholics Tended to Vote Democrat 2 The Politics of
Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War
 Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War 1 Imperialism & Expansion CH 14-1 Imperialism & War Name Reasons why the United States becomes an imperialist nation. 1-New Markets 2-Anglo-Saxonism 3-Modern Navy 4-Into
Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War 1 Imperialism & Expansion CH 14-1 Imperialism & War Name Reasons why the United States becomes an imperialist nation. 1-New Markets 2-Anglo-Saxonism 3-Modern Navy 4-Into
Midwest still opposes war Wilson
 Chapter 30 Germany seeks to force U.S. to enter WWI Zimmermann note, submarine warfare Midwest still opposes war Wilson Make the world safe for democracy Rallies country behind altruistic appeals 1. Abolish
Chapter 30 Germany seeks to force U.S. to enter WWI Zimmermann note, submarine warfare Midwest still opposes war Wilson Make the world safe for democracy Rallies country behind altruistic appeals 1. Abolish
Progressive Era, Imperialism, and World War 1
 Progressive Era, Imperialism, and World War 1 Section 7.1 Imperialism- a nation desires to gain more territory outside it s borders Reasons for US Imperialism: Economic growth- new people to sell to National
Progressive Era, Imperialism, and World War 1 Section 7.1 Imperialism- a nation desires to gain more territory outside it s borders Reasons for US Imperialism: Economic growth- new people to sell to National
Letter from President Fillmore asking Japan. American ships to stop for supplies safety reasons
 Chapter 19-21 Introduction Japan 1853 Not open to trading with other countries Commodore Matthew Perry went to Japan with a small fleet of warships (Gunboat Diplomacy) Letter from President Fillmore asking
Chapter 19-21 Introduction Japan 1853 Not open to trading with other countries Commodore Matthew Perry went to Japan with a small fleet of warships (Gunboat Diplomacy) Letter from President Fillmore asking
Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea
 Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea In the last half of the 1800s, the United States joined the race for control of overseas territories.
Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea In the last half of the 1800s, the United States joined the race for control of overseas territories.
8 TH GRADE UNITS OF INSTRUCTION
 Name Date Per. Social Studies 8 1/3 Review Packet Mrs. Myles McAnally 8 TH GRADE UNITS OF INSTRUCTION Reconstruction: Economic Expansion: a. Immigration b. Industrialization c. US Expansion and Imperialism
Name Date Per. Social Studies 8 1/3 Review Packet Mrs. Myles McAnally 8 TH GRADE UNITS OF INSTRUCTION Reconstruction: Economic Expansion: a. Immigration b. Industrialization c. US Expansion and Imperialism
STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015
 STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015 AGE OF IMPERIALISM! (1900s- 1914) MILITARY Alfred T. Mahan argued for a strong NAVY in his book Influence of Sea Power Upon History Easier
STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015 AGE OF IMPERIALISM! (1900s- 1914) MILITARY Alfred T. Mahan argued for a strong NAVY in his book Influence of Sea Power Upon History Easier
Chapter 17. Becoming a World Power ( )
 Chapter 17 Becoming a World Power (1872 1912) 1 Chapter Overview: During this era, economic and military competition from world powers convinced the United States it must be a world power. The United States
Chapter 17 Becoming a World Power (1872 1912) 1 Chapter Overview: During this era, economic and military competition from world powers convinced the United States it must be a world power. The United States
APUSH. U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! EMPIRE & EXPANSION
 APUSH 1890-1909 EMPIRE & EXPANSION U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 27 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 19 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 21 Important Ideas Since the
APUSH 1890-1909 EMPIRE & EXPANSION U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 27 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 19 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 21 Important Ideas Since the
Title Student Check Notebook Check Class Notes The West 1890s /15 Class Notes Imperialism (2 days = Double
 In your notebook Title Student Check Notebook Check Class Notes The West 1890s /15 Class Notes Imperialism (2 days = Double /30 Points) Class Notes Philippines Cartoons /15 Class Notes Progressive Era
In your notebook Title Student Check Notebook Check Class Notes The West 1890s /15 Class Notes Imperialism (2 days = Double /30 Points) Class Notes Philippines Cartoons /15 Class Notes Progressive Era
Unit 6: A New Role in the World
 Unit 6: A New Role in the World Study online at quizlet.com/_1fnvlz 1. alliances 5. conscription An agreement between nations to aid and protect each other. 2. Allies A military draft 6. dollar diplomacy
Unit 6: A New Role in the World Study online at quizlet.com/_1fnvlz 1. alliances 5. conscription An agreement between nations to aid and protect each other. 2. Allies A military draft 6. dollar diplomacy
U.S. History PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT REVIEWED! THE PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT
 9/28/17 U.S. History 1890-1912 PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT REVIEWED! THE PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT WHY: Industrialization, urbanization, and immigration created significant changes and challenges for the United States.
9/28/17 U.S. History 1890-1912 PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT REVIEWED! THE PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT WHY: Industrialization, urbanization, and immigration created significant changes and challenges for the United States.
Standards US History 10-25
 Standards US History 10-25 Progressivism Progressivism A reform movement focused on improving living conditions, education, working conditions, stopping political corruption, and gain women the right to
Standards US History 10-25 Progressivism Progressivism A reform movement focused on improving living conditions, education, working conditions, stopping political corruption, and gain women the right to
The Progressive Era. Political, Social, and Economic Reform ( )
 The Progressive Era Political, Social, and Economic Reform (1901-1917) POLITICAL SOCIAL ECONOMIC Expanded Suffrage Decline of Political Machines Increased Party Influence Expanded Workers Rights Assimilation
The Progressive Era Political, Social, and Economic Reform (1901-1917) POLITICAL SOCIAL ECONOMIC Expanded Suffrage Decline of Political Machines Increased Party Influence Expanded Workers Rights Assimilation
18 America Claims an Empire QUIT
 18 America Claims an Empire QUIT CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE SECTION 1 Imperialism and America GRAPH MAP SECTION 2 The Spanish-American War SECTION 3 Acquiring New Lands SECTION 4
18 America Claims an Empire QUIT CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE SECTION 1 Imperialism and America GRAPH MAP SECTION 2 The Spanish-American War SECTION 3 Acquiring New Lands SECTION 4
The Spanish American-War 4 Causes of the War: Important Events 1/7/2018. Effects of the Spanish American War
 The Spanish American-War 4 Causes of the War: Sugar (Economic) Spanish Cruelties (Humanitarian) The Sinking of the USS Maine (Self-Defense/National Pride) Spanish Brutalities and Yellow Journalism (Political
The Spanish American-War 4 Causes of the War: Sugar (Economic) Spanish Cruelties (Humanitarian) The Sinking of the USS Maine (Self-Defense/National Pride) Spanish Brutalities and Yellow Journalism (Political
APUSH REVIEWED! PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT
 APUSH 1890-1912 PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 28 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 20 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 19-20 THE PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT WHY: Industrialization,
APUSH 1890-1912 PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 28 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 20 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 19-20 THE PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT WHY: Industrialization,
Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism
 Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism 1. List the ideas that fueled American Imperialism. 2. How were yellow journalists able to influence Americans opinions on foreign policy? 3. The person who urged
Unit VII Study Guide- American Imperialism 1. List the ideas that fueled American Imperialism. 2. How were yellow journalists able to influence Americans opinions on foreign policy? 3. The person who urged
Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power,
 Name: Class Period: Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1865-1917 Amsco Chapter 20 Reading Assignment: Ch. 21 AMSCO Purpose: This guide is intended to provide a space for you to record
Name: Class Period: Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1865-1917 Amsco Chapter 20 Reading Assignment: Ch. 21 AMSCO Purpose: This guide is intended to provide a space for you to record
War Industry Board. Encouraged use of Massproduction
 World War I Home Front Encouraged use of Massproduction War Industry Board Standardized similar products (in 1917 there were 150 different types of typewriter ribbons, they suggested 5 types ) Set production
World War I Home Front Encouraged use of Massproduction War Industry Board Standardized similar products (in 1917 there were 150 different types of typewriter ribbons, they suggested 5 types ) Set production
Name: Date: Class: TEST: World War I. Part A: Multiple Choice: Instructions: Choose the option that answers the question or completes the sentence.
 Name: Date: Class: TEST: World War I Part A: Multiple Choice: Instructions: Choose the option that answers the question or completes the sentence. 1. Who helped pioneer the efforts to use electricity in
Name: Date: Class: TEST: World War I Part A: Multiple Choice: Instructions: Choose the option that answers the question or completes the sentence. 1. Who helped pioneer the efforts to use electricity in
15 November Turn in #19 War to End all Wars Test Friday: Review and Notebook Due
 15 November 2016 Turn in #19 War to End all Wars Test Friday: Review and Notebook Due Congress Rejects League of Nations The Treaty of Versailles did include a charter or covenant for the League of Nations,
15 November 2016 Turn in #19 War to End all Wars Test Friday: Review and Notebook Due Congress Rejects League of Nations The Treaty of Versailles did include a charter or covenant for the League of Nations,
Imperialism and WWI US History Unit 4. Name:
 Imperialism and WWI US History Unit 4 Name: 2 Imperialism and WWI [all homework assignments must be turned in prior to taking your assessment] 4.1: Due Pages 187-207 1. Imperialism 2. Annexing Hawaii 3.
Imperialism and WWI US History Unit 4 Name: 2 Imperialism and WWI [all homework assignments must be turned in prior to taking your assessment] 4.1: Due Pages 187-207 1. Imperialism 2. Annexing Hawaii 3.
Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of???
 Need to know What was President Roosevelt s Gentlemen s Agreement with Japan? Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of??? imperialism Stronger nations dominating
Need to know What was President Roosevelt s Gentlemen s Agreement with Japan? Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of??? imperialism Stronger nations dominating
5. Base your answer on the map below and on your knowledge of social studies.
 Name: 1. To help pay for World War II, the United States government relied heavily on the 1) money borrowed from foreign governments 2) sale of war bonds 3) sale of United States manufactured goods to
Name: 1. To help pay for World War II, the United States government relied heavily on the 1) money borrowed from foreign governments 2) sale of war bonds 3) sale of United States manufactured goods to
Chapter 28: Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt,
 APUSH CH 28+29 Lecture Name: Hour: Chapter 28: Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt, 1901-1912 I. The Progressive Era A. What Was It? 1. A time period that focused on correcting political, economic,
APUSH CH 28+29 Lecture Name: Hour: Chapter 28: Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt, 1901-1912 I. The Progressive Era A. What Was It? 1. A time period that focused on correcting political, economic,
Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power
 Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power Objective: Why did the United States become imperialistic and what were the outcomes? Goal: Students will be able to understand the causes and effects of imperialism
Chapter 22: America Becomes a World Power Objective: Why did the United States become imperialistic and what were the outcomes? Goal: Students will be able to understand the causes and effects of imperialism
American Foreign Policy, : The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly.
 American Foreign Policy, 1880-1920: The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly. Each group will become experts on their assigned country. Create poster showing how U.S. policy toward your respective country was good,
American Foreign Policy, 1880-1920: The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly. Each group will become experts on their assigned country. Create poster showing how U.S. policy toward your respective country was good,
Warm-up. List the causes of WWI. Describe how the US got involved.
 Warm-up List the causes of WWI. Describe how the US got involved. Causes M- Militarism A- Alliance N- Nationalism I- Imperialism A- Assassination Objectives US on the Home front Terms: Selective Service
Warm-up List the causes of WWI. Describe how the US got involved. Causes M- Militarism A- Alliance N- Nationalism I- Imperialism A- Assassination Objectives US on the Home front Terms: Selective Service
WORLD WAR 1. Causes of WWI
 WORLD WAR 1 1914-1918 Causes of WWI 1. Imperialism: Germany, France, & Great Britain Scramble for power and claim to lands in Africa, Asia, and the Pacific 2. Militarism Aggressive build up of a nation
WORLD WAR 1 1914-1918 Causes of WWI 1. Imperialism: Germany, France, & Great Britain Scramble for power and claim to lands in Africa, Asia, and the Pacific 2. Militarism Aggressive build up of a nation
throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not.
 1. Tell what at least three of the symbols you see on this flag represent. 2. Do you think these three symbols would be recognized throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not. 3. Why would this
1. Tell what at least three of the symbols you see on this flag represent. 2. Do you think these three symbols would be recognized throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not. 3. Why would this
THE EMERGENCE OF THE AMERICAS IN GLOBAL AFFAIRS,
 THE EMERGENCE OF THE AMERICAS IN GLOBAL AFFAIRS, 1880-1929 INTRODUCTION END OF 19 TH C. MARKED BY GLOBAL INTEGRATION 2 ND HALF OF 19 TH C. U.S. MOVES INTO A PERIOD OF ECONOMIC EXPANSION AND IMPERIALIZATION
THE EMERGENCE OF THE AMERICAS IN GLOBAL AFFAIRS, 1880-1929 INTRODUCTION END OF 19 TH C. MARKED BY GLOBAL INTEGRATION 2 ND HALF OF 19 TH C. U.S. MOVES INTO A PERIOD OF ECONOMIC EXPANSION AND IMPERIALIZATION
Chapter 18. American Claims an Empire
 Chapter 18 American Claims an Empire Section 1: Imperialism and American Imperialism 1880s U.S. interest in building an Empire builds Imperialism = Stronger : Economic, political, or military control Europeans
Chapter 18 American Claims an Empire Section 1: Imperialism and American Imperialism 1880s U.S. interest in building an Empire builds Imperialism = Stronger : Economic, political, or military control Europeans
PROGRESSIVE ERA. 1890s A21w
 PROGRESSIVE ERA 1890s-1920 A21w 9.2.13 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Who were the Progressives, and in what ways did they seek to reform US society form 1890-1920? Consider: political change, social change (industrial
PROGRESSIVE ERA 1890s-1920 A21w 9.2.13 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Who were the Progressives, and in what ways did they seek to reform US society form 1890-1920? Consider: political change, social change (industrial
Standards 5.1 and 5.2 Expansionism and the Spanish-American War
 EXPANSIONISM Standards 5.1 and 5.2 Expansionism and the Spanish-American War Westward expansion was motivated by o Led to the establishment of Expansionism in the late 19 th century reached beyond the
EXPANSIONISM Standards 5.1 and 5.2 Expansionism and the Spanish-American War Westward expansion was motivated by o Led to the establishment of Expansionism in the late 19 th century reached beyond the
America and World War I Notes
 Woodrow Wilson Won the Election in 1912 Progressive New Freedom Platform Promised significant: America and World War I Notes Attacks the Triple Wall of Privilege Underwood Act: Federal Reserve Act: Clayton
Woodrow Wilson Won the Election in 1912 Progressive New Freedom Platform Promised significant: America and World War I Notes Attacks the Triple Wall of Privilege Underwood Act: Federal Reserve Act: Clayton
The US faced profound domestic and global challenges as the country battled through the Great Depression and world wars.
 1890 1945 The US faced profound domestic and global challenges as the country battled through the Great Depression and world wars. 1. Continued growth of large corporations a. Dominated the US economy
1890 1945 The US faced profound domestic and global challenges as the country battled through the Great Depression and world wars. 1. Continued growth of large corporations a. Dominated the US economy
PROGRESSIVE ERA. 1890s A21w
 PROGRESSIVE ERA 1890s-1920 A21w 9.2.13 ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Who were the Progressives? What reforms did they seek? How successful were Progressive Era reforms in the period 1890-1920? Consider: political
PROGRESSIVE ERA 1890s-1920 A21w 9.2.13 ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Who were the Progressives? What reforms did they seek? How successful were Progressive Era reforms in the period 1890-1920? Consider: political
BECOMING A WORLD POWER
 BECOMING A WORLD POWER CHAPTER 10 IMPERIALISM THE PRESSURE TO EXPAND Americans had always sought to expand the size of their nation, and throughout the 19th century they extended their control toward the
BECOMING A WORLD POWER CHAPTER 10 IMPERIALISM THE PRESSURE TO EXPAND Americans had always sought to expand the size of their nation, and throughout the 19th century they extended their control toward the
 The Most Famous Recruitment Poster Uncle Sam He the Man! Don t Mess with the U. S. Huns Kill Women and Children! The Little Soldier World War I American Anthem The Spirit of 76 1917 Selective Service
The Most Famous Recruitment Poster Uncle Sam He the Man! Don t Mess with the U. S. Huns Kill Women and Children! The Little Soldier World War I American Anthem The Spirit of 76 1917 Selective Service
The First World War NEXT
 The First World War Domestic life is greatly affected as the U.S. helps the Allies achieve victory in World War I. The Treaty of Versailles punishes Germany, but is never ratified by the U.S. Senate. Section
The First World War Domestic life is greatly affected as the U.S. helps the Allies achieve victory in World War I. The Treaty of Versailles punishes Germany, but is never ratified by the U.S. Senate. Section
God Bless the USA! (4) Mr. Cegielski
 God Bless the USA! (4) Mr. Cegielski 1 IMPERIALISM Imperialism is the quest for colonial empires and it often involves the use of economic, political, or military power 2 The Main Idea The United States
God Bless the USA! (4) Mr. Cegielski 1 IMPERIALISM Imperialism is the quest for colonial empires and it often involves the use of economic, political, or military power 2 The Main Idea The United States
BELLRINGER. Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies?
 BELLRINGER Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies? U.S. INTERVENTION ABROAD Ms. Luco IB Hist Americas LEARNING
BELLRINGER Read the abridged platform of the American Anti- Imperialist League. What is the main argument presented against imperialist policies? U.S. INTERVENTION ABROAD Ms. Luco IB Hist Americas LEARNING
ID- Captured Filipino Insurrectionists (642) Summary 1-How many Filipinos died in the three year insurrection against the US? 600,000 Summary 2- How
 Ch 27 P2 Insights 1) Define and explain why the US issued the Open Door Policy 2) Explain how the Open Door Policy changed the United States role in the world. 3) Was the US a good neighbor to Latin America?
Ch 27 P2 Insights 1) Define and explain why the US issued the Open Door Policy 2) Explain how the Open Door Policy changed the United States role in the world. 3) Was the US a good neighbor to Latin America?
Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914?
 Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914? From 1890 to 1914, the United States expanded its role in world affairs and gained new overseas colonies Class Activity:
Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914? From 1890 to 1914, the United States expanded its role in world affairs and gained new overseas colonies Class Activity:
Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power ( )
 Name: Period Page# Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power (1890 1915) Section 1: The Pressure to Expand What factors led to the growth of imperialism around the world? In what ways did the United States begin
Name: Period Page# Chapter 17: Becoming a World Power (1890 1915) Section 1: The Pressure to Expand What factors led to the growth of imperialism around the world? In what ways did the United States begin
1. Commercial/Business Interests. U. S. Foreign Investments:
 1. Commercial/Business Interests U. S. Foreign Investments: 1869-1908 1. Commercial/Business Interests American Foreign Trade: 1870-1914 2. Military/Strategic Interests Alfred T. Mahan The Influence of
1. Commercial/Business Interests U. S. Foreign Investments: 1869-1908 1. Commercial/Business Interests American Foreign Trade: 1870-1914 2. Military/Strategic Interests Alfred T. Mahan The Influence of
Period 7: World War I
 Period 7: 1890 1945 World War I Neutrality to War In 1914 war breaks out among European nations after Archduke Franz Ferdinand and his wife are assassinated by Gavrilo Princip President Woodrow Wilson
Period 7: 1890 1945 World War I Neutrality to War In 1914 war breaks out among European nations after Archduke Franz Ferdinand and his wife are assassinated by Gavrilo Princip President Woodrow Wilson
Imperialism and America
 Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire CHAPTER 10 Section 1 (pages 342-345) Imperialism and America American Expansionism (pages 342-344) Why did Americans support imperialism? In 1893, Queen Liliuokalani
Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire CHAPTER 10 Section 1 (pages 342-345) Imperialism and America American Expansionism (pages 342-344) Why did Americans support imperialism? In 1893, Queen Liliuokalani
Becoming A World Power,
 Becoming A World Power, 1890-1915 United States History Week of April 27, 2015 What Factors Caused Imperialism? Economic factors: need for natural resources, new markets for manufactured goods Nationalistic
Becoming A World Power, 1890-1915 United States History Week of April 27, 2015 What Factors Caused Imperialism? Economic factors: need for natural resources, new markets for manufactured goods Nationalistic
Do Now Open to page 9 and identify and categorize the countries labeled with a number. World War I. US History & Government
 Do Now Open to page 9 and identify and categorize the countries labeled with a number. World War I US History & Government Causes of World War I M Militarism A Alliance System I Imperialism N Nationalism
Do Now Open to page 9 and identify and categorize the countries labeled with a number. World War I US History & Government Causes of World War I M Militarism A Alliance System I Imperialism N Nationalism
Unit 8: Imperialism. February 15th & 16th
 Unit 8: Imperialism February 15th & 16th WarmUp - February 15th & 16th Pick up papers from front table Jot down anything that comes to mind when you see the word IMPERIALISM (this is our next topic Unit
Unit 8: Imperialism February 15th & 16th WarmUp - February 15th & 16th Pick up papers from front table Jot down anything that comes to mind when you see the word IMPERIALISM (this is our next topic Unit
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e. Chapter Twenty-one: America and the Great War
 Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e America and the Great War Introduction Total War The Big Stick : America and the World, 1901-1917 Roosevelt and Civilization Racial and Economic Basis of Roosevelt
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e America and the Great War Introduction Total War The Big Stick : America and the World, 1901-1917 Roosevelt and Civilization Racial and Economic Basis of Roosevelt
President William McKinley
 President William McKinley William McKinley was born in Niles, Ohio on January 29, 1843 to a large family where he was the seventh of eight children. His family moved to Poland, Ohio when he was ten years
President William McKinley William McKinley was born in Niles, Ohio on January 29, 1843 to a large family where he was the seventh of eight children. His family moved to Poland, Ohio when he was ten years
Define the following: a. Neutrality Policy. b. Louisiana Purchase. c. War of d. Monroe Doctrine. e. Mexican-American War
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Chapter 20 in AMSCO or other resource covering the Spanish American War. Directions: 1. Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before
Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Chapter 20 in AMSCO or other resource covering the Spanish American War. Directions: 1. Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before
Imperialism. U.S. Foreign Policy. U.S. Foreign Policy 10/30/13. Chapter 10. Monroe Doctrine. Many Spanish colonies revolting
 Imperialism Chapter 10 U.S. Foreign Policy Monroe Doctrine No new colonization by Europe in western hemisphere U.S. stays out of European affairs If Europe attempts to colonize in the west, U.S. would
Imperialism Chapter 10 U.S. Foreign Policy Monroe Doctrine No new colonization by Europe in western hemisphere U.S. stays out of European affairs If Europe attempts to colonize in the west, U.S. would
Imperalism.notebook March 03, 2015
 Agenda Bell ringer Notability 1 Objective: I can discuss and explain why the United States Foreign Policy changed during the late 19th century. Bell Ringer Notability HW: Due Thursday 2 1 A B C D 3 2 A
Agenda Bell ringer Notability 1 Objective: I can discuss and explain why the United States Foreign Policy changed during the late 19th century. Bell Ringer Notability HW: Due Thursday 2 1 A B C D 3 2 A
Chapter 19: Republic To Empire
 Chapter 19: Republic To Empire Objectives: o We will examine the policies America implemented in their newly conquered territories after the Spanish American War. o We will examine the various changes
Chapter 19: Republic To Empire Objectives: o We will examine the policies America implemented in their newly conquered territories after the Spanish American War. o We will examine the various changes
MUCKRAKERS. social, economic, and political injustices. corruption, scandal and injustice to the public view
 THE PROGRESSIVE ERA MUCKRAKERS Journalists focusing on social, economic, and political injustices Known for exposing corruption, scandal and injustice to the public view They investigated governments,
THE PROGRESSIVE ERA MUCKRAKERS Journalists focusing on social, economic, and political injustices Known for exposing corruption, scandal and injustice to the public view They investigated governments,
The Progressive Era,
 The Progressive Era, 1880-1920 FROM: www.faculty.utep.edu/linkclick.aspx?link=progressivism1.ppt Revised: R Ryland, 2013 The progressive impulse took many forms so many, in fact, that even today scholars
The Progressive Era, 1880-1920 FROM: www.faculty.utep.edu/linkclick.aspx?link=progressivism1.ppt Revised: R Ryland, 2013 The progressive impulse took many forms so many, in fact, that even today scholars
Section 1: From Neutrality to War
 Section 1: From Neutrality to War 1. What Caused World War I? a. Militarism: I m bigger than you b. Alliances: Who s my friend? c. Imperialism: I want this too d. Nationalism: Everyone wants to be their
Section 1: From Neutrality to War 1. What Caused World War I? a. Militarism: I m bigger than you b. Alliances: Who s my friend? c. Imperialism: I want this too d. Nationalism: Everyone wants to be their
Unit 9 Imperialism and WWI. New US Power and Diplomacy
 Unit 9 Imperialism and WWI New US Power and Diplomacy Attitudes Toward an International Role Arguments for Expansion Economics: new markets/investment opportunities/raw materials Culture: Social Darwinism/Protestant
Unit 9 Imperialism and WWI New US Power and Diplomacy Attitudes Toward an International Role Arguments for Expansion Economics: new markets/investment opportunities/raw materials Culture: Social Darwinism/Protestant
1 U.S. Expansion Pacific to Caribbean 2 Imperialism & Manifest Destiny Imperialism: The quest for colonial empires Manifest Destiny: US was destined
 1 U.S. Expansion Pacific to Caribbean 2 Imperialism & Manifest Destiny Imperialism: The quest for colonial empires Manifest Destiny: US was destined by God to expand from Atlantic coast into Pacific Ocean
1 U.S. Expansion Pacific to Caribbean 2 Imperialism & Manifest Destiny Imperialism: The quest for colonial empires Manifest Destiny: US was destined by God to expand from Atlantic coast into Pacific Ocean
Problems Brought About By
 Progressivism Industrialization: Problems Brought About By Industrialization and Urbanization Big Business dominates the economy and monopolies destroy competition; Big Business, with all its wealth and
Progressivism Industrialization: Problems Brought About By Industrialization and Urbanization Big Business dominates the economy and monopolies destroy competition; Big Business, with all its wealth and
Objective To explain how the progressive movement managed to increase the power of government to regulate business and to protect society from the
 Objective To explain how the progressive movement managed to increase the power of government to regulate business and to protect society from the injustices fostered by big business. What was Progressivism?
Objective To explain how the progressive movement managed to increase the power of government to regulate business and to protect society from the injustices fostered by big business. What was Progressivism?
American History 11R
 American History 11R Progressive Movement Goals Protecting Social Welfare Promoting Moral Improvement Creating Economic Reform Fostering Efficiency Reform Political System Protecting Social Welfare Tried
American History 11R Progressive Movement Goals Protecting Social Welfare Promoting Moral Improvement Creating Economic Reform Fostering Efficiency Reform Political System Protecting Social Welfare Tried
Between 1870 and 1900, Europeans had taken over 1/5 of land and 1/10 of population of the world Germany became America s biggest imperialist foe and
 U.S. Imperialism Between 1870 and 1900, Europeans had taken over 1/5 of land and 1/10 of population of the world Germany became America s biggest imperialist foe and largely spurred U.S. into imperialism;
U.S. Imperialism Between 1870 and 1900, Europeans had taken over 1/5 of land and 1/10 of population of the world Germany became America s biggest imperialist foe and largely spurred U.S. into imperialism;
SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR VOCAB
 SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR VOCAB 1. War of 1812 2. Monroe Doctrine 3. Mexican War 4. Yellow journalism 5. USS Maine 6. Rough Riders 7. San Juan Hill 8. Anti-Imperialist League 9. Platt Amendment 10.Diplomacy
SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR VOCAB 1. War of 1812 2. Monroe Doctrine 3. Mexican War 4. Yellow journalism 5. USS Maine 6. Rough Riders 7. San Juan Hill 8. Anti-Imperialist League 9. Platt Amendment 10.Diplomacy
1. In 1914, combined to drag Europe into a world war. 1. Among the powers of Europe, nationalism caused a desire to.
 Name Class Period Chapter 11: World War I (The Great War) and Beyond 1914-1920 Lecture Notes Section 1: From Neutrality to War (pages 282-291) I What Caused World War I? A What caused World War I, and
Name Class Period Chapter 11: World War I (The Great War) and Beyond 1914-1920 Lecture Notes Section 1: From Neutrality to War (pages 282-291) I What Caused World War I? A What caused World War I, and
Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt. Chapter 28
 Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt Chapter 28 Progressive Reformers Progressives wanted government actively involved protecting poor and needy Attacked monopolies, corruption, inefficiency and
Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt Chapter 28 Progressive Reformers Progressives wanted government actively involved protecting poor and needy Attacked monopolies, corruption, inefficiency and
IMPERIALISM. Policing the Western Hemisphere
 Alaska William Seward Sec. of State purchased from Russia for $7 million. Twice the size of Texas Nicknamed Seward s Folly or Seward s Icebox 1890 gold found there Hawaii IMPERIALISM Grew sugar that was
Alaska William Seward Sec. of State purchased from Russia for $7 million. Twice the size of Texas Nicknamed Seward s Folly or Seward s Icebox 1890 gold found there Hawaii IMPERIALISM Grew sugar that was
A great democracy must be progressive or it will soon cease to be a great democracy Theodore Roosevelt
 A great democracy must be progressive or it will soon cease to be a great democracy Theodore Roosevelt The Progressive Impulse Rapid industrialization and urbanization had created many problems for many
A great democracy must be progressive or it will soon cease to be a great democracy Theodore Roosevelt The Progressive Impulse Rapid industrialization and urbanization had created many problems for many
Imperialism and America
 CHAPTER 10 Section 1 ( pages 342 345) Imperialism and America BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about Woodrow Wilson. In this section, you will learn how economic activity led to political
CHAPTER 10 Section 1 ( pages 342 345) Imperialism and America BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about Woodrow Wilson. In this section, you will learn how economic activity led to political
The United States Looks Overseas
 The United States Looks Overseas 1853-1915 Interact with History In 1893, American sugar planters in the Kingdom of Hawaii thought they could make more money if Hawaii were an American state. So they staged
The United States Looks Overseas 1853-1915 Interact with History In 1893, American sugar planters in the Kingdom of Hawaii thought they could make more money if Hawaii were an American state. So they staged
10. Settlement houses were most closely associated with what Progressive Era personality? A) Frank Norris B) Upton Sinclair C) Jane Addams D) Carrie N
 1. One difference between the Progressives of the early twentieth century and the Populists from the 1880s and 1890s is A) Progressives never gained the political power that the Populists possessed. B)
1. One difference between the Progressives of the early twentieth century and the Populists from the 1880s and 1890s is A) Progressives never gained the political power that the Populists possessed. B)
The Progressive Era. The Drive For Reform
 The Progressive Era The Drive For Reform 1890 to 1917 Progressives were reformers who attempted to solve problems caused by industry, growth of cities and laissez faire. Progressives were: White Protestants
The Progressive Era The Drive For Reform 1890 to 1917 Progressives were reformers who attempted to solve problems caused by industry, growth of cities and laissez faire. Progressives were: White Protestants
Unit 4: Imperialism. Name: Word Definition Analysis
 Name: Unit 4: Imperialism Word Definition Analysis 1. Imperialism (191) Policy by which strong nations Did America practice imperialism? extend their political, military, If so where? and economic control
Name: Unit 4: Imperialism Word Definition Analysis 1. Imperialism (191) Policy by which strong nations Did America practice imperialism? extend their political, military, If so where? and economic control
2. COMPARISON -- TWO PHILOSOPHIES:
 THE PROGRESSIVE ERA 1. PROGRESSIVE ERA: Definition = a period of widespread social activism and political reform (1890s-1920s) Also called the Progressive Movement A Progressive = an activist; usually
THE PROGRESSIVE ERA 1. PROGRESSIVE ERA: Definition = a period of widespread social activism and political reform (1890s-1920s) Also called the Progressive Movement A Progressive = an activist; usually
In the early 1900's the United States engaged in conflicts with Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines.
 Ch 18-Section 3 - Acquiring New Lands In the early 1900's the United States engaged in conflicts with Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines. Puerto Rico Fearful of losing autonomy that they had won under
Ch 18-Section 3 - Acquiring New Lands In the early 1900's the United States engaged in conflicts with Cuba, Puerto Rico, and the Philippines. Puerto Rico Fearful of losing autonomy that they had won under
Chapter 27: The Path of Empire, (Pages )
 Chapter 27: The Path of Empire, 1890 1899 (Pages 626 653) I. America Turns Outward A. Motives for overseas expansion 1. Farmers and industrialists Name Per. Date Row 2. The yellow press 3. Role of religion
Chapter 27: The Path of Empire, 1890 1899 (Pages 626 653) I. America Turns Outward A. Motives for overseas expansion 1. Farmers and industrialists Name Per. Date Row 2. The yellow press 3. Role of religion
Defense agreements that could pull countries into battles. Competition to prove dominance and power. Loyalty and devotion to one s country of origin
 Chapters 22-25 Militarism Build-up of weapons and navies Alliances Defense agreements that could pull countries into battles Imperialism Competition to prove dominance and power Nationalism Loyalty and
Chapters 22-25 Militarism Build-up of weapons and navies Alliances Defense agreements that could pull countries into battles Imperialism Competition to prove dominance and power Nationalism Loyalty and
The Progressive Era
 The Progressive Era 1890-1920 Bell Work: 10/13/14 (Monday) Now, it is very necessary that we should not flinch from seeing what is vile and debasing. There is filth on the floor, and it must be scraped
The Progressive Era 1890-1920 Bell Work: 10/13/14 (Monday) Now, it is very necessary that we should not flinch from seeing what is vile and debasing. There is filth on the floor, and it must be scraped
UNITED STATES HISTORY. Unit 3 THE PROGRESSIVE ERA Aka Power to the People
 UNITED STATES HISTORY Unit 3 THE PROGRESSIVE ERA Aka Power to the People THE ORIGINS OF PROGRESSIVISM Progressivism- reform movement in the U.S. in early 1900s aimed at returning control of the government
UNITED STATES HISTORY Unit 3 THE PROGRESSIVE ERA Aka Power to the People THE ORIGINS OF PROGRESSIVISM Progressivism- reform movement in the U.S. in early 1900s aimed at returning control of the government
Unit 6 Study Guide. Period 7.1:
 Unit 6 Study Guide Period 7.1: 1890 1920 In a Nutshell An increasingly pluralistic United States faced profound domestic and global challenges, debated the proper degree of government activism, and sought
Unit 6 Study Guide Period 7.1: 1890 1920 In a Nutshell An increasingly pluralistic United States faced profound domestic and global challenges, debated the proper degree of government activism, and sought
The Progressive Era. America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century
 The Progressive Era America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century Origins of Progressivism As America entered the 20 th century, middle class reformers at the municipal, state, and national levels addressed
The Progressive Era America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century Origins of Progressivism As America entered the 20 th century, middle class reformers at the municipal, state, and national levels addressed
Progressivism and the Age of Reform
 Progressivism and the Age of Reform This political cartoon shows President Theodore Roosevelt as a hunter who s captured two bears: the good trusts bear he s put on a leash labeled restraint, and the bad
Progressivism and the Age of Reform This political cartoon shows President Theodore Roosevelt as a hunter who s captured two bears: the good trusts bear he s put on a leash labeled restraint, and the bad
Chapter 17, Section 1 I. Building Support for Imperialism (pages ) A. Beginning in the 1880s, Americans wanted the United States to become a
 Chapter 17, Section 1 I. Building Support for Imperialism (pages 520 522) A. Beginning in the 1880s, Americans wanted the United States to become a world power. Their change in attitude was a result of
Chapter 17, Section 1 I. Building Support for Imperialism (pages 520 522) A. Beginning in the 1880s, Americans wanted the United States to become a world power. Their change in attitude was a result of
The Progressive Era. America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century
 The Progressive Era America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century Origins of Progressivism As America entered the 20 th century, middle class reformers at the municipal, state, and national levels addressed
The Progressive Era America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century Origins of Progressivism As America entered the 20 th century, middle class reformers at the municipal, state, and national levels addressed
Review. 1. During which years did the Gilded Age take place? 2. What were some of the problems of the Gilded Age?
 The Progressive Era Review 1. During which years did the Gilded Age take place? 1877-1900 2. What were some of the problems of the Gilded Age? Political corruption Crime, violence, unsanitary living conditions
The Progressive Era Review 1. During which years did the Gilded Age take place? 1877-1900 2. What were some of the problems of the Gilded Age? Political corruption Crime, violence, unsanitary living conditions
Populism-agrarian revolt that swept through the Midwest in the late 19 th C.
 The Progressive Era Progressivism Not one single unified movement A wide range of economic, political, social, and moral reforms. Progress to occur through human intervention to solve problems. Origins
The Progressive Era Progressivism Not one single unified movement A wide range of economic, political, social, and moral reforms. Progress to occur through human intervention to solve problems. Origins
America s Path to Empire. APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8
 America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8 1890-1892 Foreign Policy The Influence of Sea Power upon History (1890): Alfred Thayer Mahan Sea power throughout history gives advantages US lies
America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8 1890-1892 Foreign Policy The Influence of Sea Power upon History (1890): Alfred Thayer Mahan Sea power throughout history gives advantages US lies
