ABSOLUTE RULERS EUROPE: S HELPFUL TO UNDERSTANDING OUR PRESENT WORLD
|
|
|
- Augustine Walker
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 ABSOLUTE RULERS EUROPE: S HELPFUL TO UNDERSTANDING OUR PRESENT WORLD
2 Questions to consider How did the Absolute Monarchs get their power? What might citizens gain from having an Absolute Monarch? What might citizens lose? What factors might weaken an Absolute Monarch s power?
3 POLITICAL BELIEF THAT A MONARCH (ie. KING/QUEEN) SHOULD: HOLD ALL OF THE POWER IN A COUNTRY (BE UNLIMITED) CONTROL ALL PARTS OF SOCIETY AS MUCH AS POSSIBLE ABSOLUTISM: DEFINITION
4 POLITICAL BELIEF TIED IN W/ ABSOLUTISM: GOD CREATED MONARCHS MONARCHS ARE GOD S SPOKESPERSON ON EARTH MONARCHS ANSWER ONLY TO GOD, NOT THEIR SUBJECTS DIVINE RIGHT: DEFINITION
5 TURN AND TALK TOPIC POINT: DO THE HEAVENS/GOD CHOOSE LEADERS LIKE EUROPEANS AND ASIANS BELIEVED (and some leaders still do)? AND IF SO, SHOULD PEOPLE FOLLOW THEIR LAWS AND COMMANDS?
6 MOST COUNTRIES GET ABSOLUTE RULERS BY S WESTERN EUROPEAN ABSOLUTISM (ENGLAND, FRANCE, & SPAIN) EASTERN EUROPEAN ABSOLUTISM (AUSTRIA, PRUSSIA, RUSSIA) BIG DIFFERENCES BTWN THESE REGIONS (AFFECTS WORLD TODAY!) GEOGRAPHY: AFFECTS ABSOLUTISM
7 DYNASTY: SERIES OF RULERS FROM A SINGLE FAMILY ( HOUSE OF ) ENGLAND: TUDOR ~120 YRS FRANCE/SPAIN: BOURBON 200 YRS AUSTRIA/SPAIN:HAPSBURG 500+YRS PRUSSIA: HOHENZOLLERN 500+ YRS RUSSIA: ROMANOV 300 YRS EUROPEAN DYNASTIES: CENTURIES OF RULE HELP ESTABLISH ABSOLUTISM
8 ABSOLUTE RULERS FACE CHALLENGES TO THEIR POWER: NOBILITY RELIGION LEGISLATURES MONEY AGE OF RULERS ROAD BLOCKS TO ABSOLUTISM
9 NOBILITY: THEY RE ALL RELATED! NOBLES CONSIDER THEMSELVES = TO MONARCHS BELIEVE THEY ALSO COULD BE KING/QUEEN (if only...) ARISTOCRACY: THEN & NOW
10 RELIGION: CATHOLICS & PROTESTANTS FIGHT EACH OTHER SO... RULERS USUALLY WANT THEIR COUNTRY JUST 1 RELIGION 30 YEARS WAR, ST. BARTHOLOMEW S MASSACRE
11 TURN AND TALK TOPIC POINT: IF YOU WERE A RULER 350 YEARS AGO, WOULD YOU WANT ALL YOUR SUBJECTS ONE RELIGION? WHY OR WHY NOT?
12 LEGISLATURES: MAKE LAWS AND HAND OUT MONEY WANT A BIT OF POWER IN RETURN FROM KING WANT TO LIMIT, NOT DESTROY, KING S POWER ENG. PARLIAMENT & FRENCH ESTATES-GENERAL
13 MONEY: NOBILITY NOT TAXED CHURCH NOT TAXED SO MONEY HAS TO COME FROM... PEASANTS AND MIDDLE CLASS TAXING TOO MUCH --OR TOO OFTEN-- CAUSES PROBLEMS: REVOLTS LEGISLATIVE PAYBACKS ISSUES W/ ECONOMY ROAD BLOCKS TO ABSOLUTISM
14 MANY MONARCHS START RULING AT A YOUNG AGE! LITTLE EXPERIENCE; JUDGMENT LACKING NEED ADULTS TO HELP THEM RULE: USUALLY NOBLES! IVAN (TERRIBLE) 3;LOUIS XIV 4;PETER THE GREAT 10; FREDERICK (THE GREAT ELECTOR) 20;PHILIP II 27; MARIA THERESA 28; FREDERICK THE GREAT 28
15 PHILIP II INHERITS AND RULES: SPAIN, NETHERLANDS, NAPLES, SICILY, AND ALL OF SPANISH AMERICAS! ABSOLUTISM: SPAIN
16 GOLD & SILVER FROM AMERICAS MAKE SPAIN RICH BUT... FEW FARMERS, SO must BUY FOREIGN FOOD FEW FACTORIES, SO must BUY FOREIGN GOODS FEW BANKS, SO must USE FOREIGN ONES = s INFLATION! HURTS SPANISH ECONOMY ABSOLUTISM: SPAIN
17 GOLD & SILVER BUY HUGE ARMY AND NAVY SPANISH ARMADA AGAINST ENGLAND 1588 (THEY LOSE) SUPPRESS DUTCH; THEY REVOLT; NORTH WINS FREEDOM ABSOLUTISM: Phillip II s Policies
18 1) KEEP SPAIN ALL ONE RELIGION: No religious conflict-- but hurts Spain b/c lose Jews and Moors 2) MERCANTILISM: expand colonies to bring in raw materials--boosts economy 3) WAR & WAR ABSOLUTISM: Phillip II s Policies
19 BACKGROUND: FRENCH PROTESTANTS & CATHOLICS FIGHT 8 WARS ST. BARTHOLOMEW S DAY MASSACRE: 1,000 S HUGUENOTS KILLED FRENCH PROTESTANTS KNOWN AS HUGUENOTS FRANCE: ABSOLUTISM
20 HENRY OF NAVARRE (STARTS BOURBON LINE) EDICT OF NANTES 1598: OK S FR. PROTESTANTS (& HENRY TURNS CATHOLIC) HENRY STABLIZES FRANCE LOVED BY FRENCH: ONLY STATUE NOT PULLED DOWN DURING FR. REV. FRANCE: ABSOLUTISM
21 WEAK LOUIS XIII BECOMES KING HELPED BY CARDINAL RICHELIEU (#1 MINISTER) INCREASES KING S POWER BY ATTACKING NOBLES FRANCE: ABSOLUTISM
22 LOUIS XIV TAKES OVER CARDINAL MAZARIN HELPS HIM TO BECOME MOST POWERFUL RULER IN FR. HISTORY HAS ANTI-NOBLE POLICIES FRANCE: ABSOLUTISM
23 TWO EVENTS SHAPE LOUIS XIV S EARLY LIFE: 30 YEARS WAR FRENCH CIVIL WAR LOUIS DISTRUSTS NOBLES AFTER THIS THE FRONDE means SLINGSHOT (weapon of choice at 1 st in Paris) FRANCE: ABSOLUTISM
24 BUILDS VERSAILLES MAKES NOBLES LIVE THERE TO CONTROL THEM PALACE SHOWS ABSOLUTE POWER TO FOREIGNERS OTHER RULERS COPY HIS LIFESTYLE FRANCE: LOUIS XIV S POLICIES
25 I AM THE STATE LIVED SUCH A POWERFUL, SHOWY LIFE KNOWN AS: THE SUN KING EXACT DAILY ROUTINE, PATRON OF THE ARTS, FINE FOOD, CLOTHES, WIGS, HUNTS. LOUIS XIV
26 SENDS ROYAL OFFICERS OUT TO COLLECT TAXES, RUN LAW COURTS (INSTEAD OF NOBLES) MERCANTILISM: COLONIES (take raw products) & LUXURY MANUFACTURING MAKE FRANCE SELF- SUFFICENT ($) ONE RELIGION removes Edict of Nantes=France Catholic FRENCH FUR TRADE FRANCE: LOUIS XIV S POLICIES
27 WAR, WAR, WAR LOUIS BUILDS UP-& USES- BIGGEST ARMY IN EUROPE = 400,000! WEAKENS FRANCE A LOT CAUSES SUFFERING, FAMINE, INFLATION WAR OF SPANISH SUCCESSION: 6+ COUNTRIES ATTACK FRANCE STOPS FRANCE & SPAIN UNITING FRANCE: LOUIS XIV S POLICIES
28 30 YEARS WAR STAGES (NOT FULL 30 YEARS) FOUGHT OVER RELIGION: DEFENESTRATION OF PRAGUE CHANGES HISTORY OF EUROPE HISTORY HINT: IF YOU WANT TO KNOW WHAT A WAR WAS FOUGHT OVER, EXAMINE THE PEACE TREATY HISTORY HINT: POLITICAL CHANGES ALWAYS BRING ON OTHER CHANGES: STAY TUNED FOR SCIENTIFIC REVOLUTION & ENLIGHTENMENT! EASTERN ABSOLUTISM (BRIEFLY)
29 DEVASTATES GERMANY, HURTS H.R.E HELPS SETTLE RELIGIOUS ISSUES (LAST RELIGIOUS WAR IN EUROPE) STARTS MODERN STATE SYSTEM & AND WAY WE DO PEACE TALKS OUTCOMES OF 30 YEARS WAR: TREATY OF WESTPHALIA 1648
30 BASICALLY THIS IS GERMANY broken into 300 SEPARATE PARTS HAS HAPSBURG EMPEROR RULING W/ PRESTIGE BUT LITTLE POWER HOLY ROMAN EMPIRE: BRIEFLY Hard to rule such big, diverse area.
31 SERFS IN WESTERN EUROPE BECAME FREE AT END OF MIDDLE AGES ( TOWN AIR MAKES A MAN FREE ) MADE $$$$$ CHOSE OWN JOBS MARRY WHO THEY WANTED EASTERN SERFS WERE TIED TO THE LAND (SOLD ALONG W/ IT) COULDN T ESCAPE TO TOWNS (TOO FEW) WORKED FOR LITTLE REWARD TREATED VERY POORLY FORCED INTO LIFELONG JOBS (SOLDIERS, MINES, FARMING, FACTORIES) WESTERN ABSOLUTISM VS EASTERN ABSOLUTISM
32 IVAN THE TERRIBLE RULED AT AGE 3 MISTREATED BY NOBLES GOOD RULER AT 1 ST, BECAME TERRIBLE AFTER HIS WIFE DIED (BLAMED NOBLES) RUSSIAN ABSOLUTISM LAID DOWN BASE FOR ABSOLUTISM SECRET POLICE SEIZED NOBLE S LANDS KILLED OLDEST SON, LEAVING RUSSIA IN TIME OF TROUBLES Civil War ended with a ROMANOV RULER
33 Austria:Home to the Hapsburg Dynasty (where the Holy Roman Emperor comes from) As HRE starts to decline, rulers try to keep Austria strong Emperor worked hard to get HRE accept his daughter after his death Maria Theresa: Attacked by Prussia, lost land but fought back Two Eastern Absolutism Countries
34 Tried to bring the Church under the control of the State Reduced the power of the nobles by Taxing them Giving serfs more rights Created bureaucracies Policies of Maria Theresa
35 War War, War!!! continued to build up army Took Silesia from Austria 2X Prussia Allowed freedom of worship: to keep Calvinists/Huguenots INCREASED NOBLES POWER OVER ESTATES --but still kept only nobles as Army officers Prussia: Frederick the Great
36 yeducation.com/lea rn/videos/47ae226 E-219B-481C-A072-90ECDB04254C?has LocalHost=true Frederick the Great
37 Prussia
38 Prussia
39 Prussia--WWI
40 PETER THE GREAT RULES FEET, 7 INCHES UNBELIEVABLY STRONG WILD TEMPER/ SENSE OF HUMOR INTELLIGENT, CURIOUS, STRONG-WILLED RUSSIAN ABSOLUTISM
41 1600 S RUSSIA LIKE GERMANY IN S PETER WANTS TO CHANGE THIS VISITS WEST, BRINGS BACK TECHNOLOGY AND EXPERTS WESTERNIZATION: BRINGING WESTERN: SOCIAL POLITICAL ECONOMIC SCIENTIFIC IDEAS & GOODS INTO ONE S COUNTRY WHILE KEEPING COUNTRY S OWN CULTURE IN PLACE WHAT PETER DOES FOR RUSSIA
42 WINDOW ON THE WEST : BUILDS ST. PETERSBURG FORCES NOBLES TO LIVE THERE & LEAVE TO GO TO SCHOOL IN WEST PUTS ORTHODOX CHURCH UNDER GOV T CONTROL WHAT PETER DOES FOR RUSSIA
43 WAR, WAR, WAR BUILDS, & USES, HUGE ARMY EXPANDS RUSSIA TO BOTH SEAS WHAT PETER DOES FOR RUSSIA
44 BACKGROUND: ENG. KINGS COULDN T TAX LIKE IN OTHER COUNTRIES HAD TO ASK PARLIAMENT FOR MONEY WHICH GOT PARLIAMENT SOME POWER IN RETURN ELIZABETH I ( VIRGIN QUEEN ) DIES (NO HEIR) JAMES I (KING OF SCOTLAND & CATHOLIC) TAKES OVER PROTESTANT ENGLAND STARTS STUART RULE:1OO+ YEARS ABSOLUTISM ENGLAND: A A DIFFERENT STORY
45 JAME S SON CHARLES I IN POWER STRUGGLE W/ PARLIAMENT CIVIL WAR starts! PURITANS (think Pilgrims) vs ANGLICANS/royalists KING CAPTURED, TRIED, & BEHEADED ENGLISH CIVIL WAR: (FRENCH CIVIL WAR )
46 EXECUTION SENDS A MESSAGE TO FUTURE RULERS O. CROMWELL: STARTS SUPER STRICT, UNPOPULAR MILITARY RULE ENGLISH GET TIRED OF: NO DRINKING DARK CLOTHES NO DANCING NO THEATER NO SPORTING EVENTS CROMWELL DIES ENGLISH INVITE KING BACK TO RULE RESULTS OF ENG. CIVIL WAR
47 e.com/watch?v=3fc 6R0pv5vE English Civil War
48 SO HE CAN TAKE THE PLACE OF CROMWELL, CHARLES II FORCED TO GIVE: HABEAS CORPUS NO JAIL W/O CHARGES MUST HAVE TRIALS (NOT THROWN IN JAIL W/O A KEY) CHARLES CATHOLIC BROTHER JAMES II TAKES OVER PARLIAMENT WORRIED ABOUT CATHOLIC JAMES II, INVITE HIS PROTESTANT RELATIVE FROM HOLLAND TO RULE RESTORATION & GLORIOUS REV.
49 ONE OF THE ONLY BLOODLESS REVOLUTIONS IN WORLD HISTORY NEW MONARCHS FORCED TO SIGN ENG. BILL OF RIGHTS IN ORDER TO RULE ENG. BECOMES A CONSTITUTIONAL MONARCHY NO TAXATION W/O REPRESENTATION FREEDOM OF SPEECH RIGHT TO PETITION NO CRUEL/UNUSUAL PUNISHMENT RIGHT TO BEAR ARMS NO STANDING ARMY GLORIOUS REVOLUTION!
50 CHANGES IN ENGLAND PASSED ON TO AMERICA, CHANGING WORLD HISTORY LEADS TO FRENCH REVOLUTION CHANGING WORLD HISTORY GERMAN, AUSTRIAN, PRUSSIAN, & RUSSIAN ABSOLUTISM LEADS TO WWI (& WWII) EASTERN ABSOLUTISM LEADS TO RUSSIAN ISOLATION AND POST-WWII COLD WAR EFFECTS OF ABSOLUTISM
I. Western Europe s Monarchs A. France and the Age of Absolutism 1. Henry IV (The first of the Bourbon line) a) Huguenot (Protestant) converts to
 I. Western Europe s Monarchs A. France and the Age of Absolutism 1. Henry IV (The first of the Bourbon line) a) Huguenot (Protestant) converts to Catholicism to unite country (1) Paris is well worth a
I. Western Europe s Monarchs A. France and the Age of Absolutism 1. Henry IV (The first of the Bourbon line) a) Huguenot (Protestant) converts to Catholicism to unite country (1) Paris is well worth a
I. SPANISH POWER GROWS pg 504 A. Charles V* Inherits Two Crowns 1. Ruling the Hapsburg Empire* a. Charles=grandson of Ferdinand & Isabella b.
 I. SPANISH POWER GROWS pg 504 A. Charles V* Inherits Two Crowns 1. Ruling the Hapsburg Empire* a. Charles=grandson of Ferdinand & Isabella b.=ruler of Spain + Holy Roman Empire A Kingdom Too Spread Out
I. SPANISH POWER GROWS pg 504 A. Charles V* Inherits Two Crowns 1. Ruling the Hapsburg Empire* a. Charles=grandson of Ferdinand & Isabella b.=ruler of Spain + Holy Roman Empire A Kingdom Too Spread Out
Absolutism Test Review
 Absolutism Test Review 1. Spain- Philip II- son Charles V Religious persecution wars (1588) Rise and Decline of Spain Rise- Gold and Silver Decline- Fought wars, lost Navy to England, instead of investing
Absolutism Test Review 1. Spain- Philip II- son Charles V Religious persecution wars (1588) Rise and Decline of Spain Rise- Gold and Silver Decline- Fought wars, lost Navy to England, instead of investing
Spain s Conflicts King Philip II championed Catholic causes throughout his lands, while England became the leader of Protestant nations of Europe.
 Spain s Conflicts King Philip II championed Catholic causes throughout his lands, while England became the leader of Protestant nations of Europe. 1 Spain s Conflicts (cont.) In the sixteenth century,
Spain s Conflicts King Philip II championed Catholic causes throughout his lands, while England became the leader of Protestant nations of Europe. 1 Spain s Conflicts (cont.) In the sixteenth century,
Eastern European and Russian Absolutism. Ivan IV Ivan the Terrible ( )
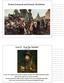 Eastern European and Russian Absolutism Ivan IV Ivan the Terrible (1547-1584) became Tsar at age of 3 and watched rival groups of nobles who sought to control the country when he took charge, he saw treason
Eastern European and Russian Absolutism Ivan IV Ivan the Terrible (1547-1584) became Tsar at age of 3 and watched rival groups of nobles who sought to control the country when he took charge, he saw treason
9/17 Political and Religious Conflict: Introduction to Religious Wars of the 16 th and 17 th Century
 One Law, One King, One Faith: The Rise of Absolutism in Europe Guiding Questions: (Themes for LEQ prompts) What factors give rise to Absolutist governments and what challenges do they face in their attempts
One Law, One King, One Faith: The Rise of Absolutism in Europe Guiding Questions: (Themes for LEQ prompts) What factors give rise to Absolutist governments and what challenges do they face in their attempts
Absolutism and Enlightenment
 Absolutism and Enlightenment The Commercial Revolution Most of Europe remained agricultural between 1600-1770 The Commercial Revolution marked an important step in the transition from the local economies
Absolutism and Enlightenment The Commercial Revolution Most of Europe remained agricultural between 1600-1770 The Commercial Revolution marked an important step in the transition from the local economies
Unit 4: Age of isms Rise of European Dominance
 Unit 4: 1450-1750 Age of isms Rise of European Dominance Renaissance the word renaissance means rebirth this is Europe s rebirth of culture and thought begins ~ 1400 in Italy, and spreads northward resurgence
Unit 4: 1450-1750 Age of isms Rise of European Dominance Renaissance the word renaissance means rebirth this is Europe s rebirth of culture and thought begins ~ 1400 in Italy, and spreads northward resurgence
Enlightened Absolutism. Prussian, Russian, and Austrian Politics in the Enlightenment
 Enlightened Absolutism Prussian, Russian, and Austrian Politics in the Enlightenment Politics Before Enlightenment Absolutism: traditional assumption of power (hereditary throne) and belief in divine right
Enlightened Absolutism Prussian, Russian, and Austrian Politics in the Enlightenment Politics Before Enlightenment Absolutism: traditional assumption of power (hereditary throne) and belief in divine right
Absolutism Activity 1
 Absolutism Activity 1 Who is in the painting? What do you think is going on in the painting? Take note of the background. What is the message of the painting? For example, why did the author paint this?
Absolutism Activity 1 Who is in the painting? What do you think is going on in the painting? Take note of the background. What is the message of the painting? For example, why did the author paint this?
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions.
 SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. EQ: What is characteristics
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. EQ: What is characteristics
SOCIAL STUDIES SAMPLE
 Chapter 16 Terms to Look for in this Section: Age of Discovery Absolute Monarchs SOCIAL STUDIES SAMPLE What Have You Learned About World History So Far? Section 1: What Do You Remember About Early Civilizations?
Chapter 16 Terms to Look for in this Section: Age of Discovery Absolute Monarchs SOCIAL STUDIES SAMPLE What Have You Learned About World History So Far? Section 1: What Do You Remember About Early Civilizations?
Britain vs. France by 1715
 Absolutism Britain vs. France by 1715 English Monarchy Limited monarchy Free trade Strong parliament Stable government down to the present Seeds of American Revolution French Monarchy Absolute monarchy
Absolutism Britain vs. France by 1715 English Monarchy Limited monarchy Free trade Strong parliament Stable government down to the present Seeds of American Revolution French Monarchy Absolute monarchy
Wars of the 18 th Century
 Wars of the 18 th Century Major Conflicts 1. War of Spanish Succession (1701-1714) Ends with the Treaty of Utrecht 2. War of Austrian Succession (1740-1748) Ends with the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle 3. Seven
Wars of the 18 th Century Major Conflicts 1. War of Spanish Succession (1701-1714) Ends with the Treaty of Utrecht 2. War of Austrian Succession (1740-1748) Ends with the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle 3. Seven
Eastern Absolutism Serfdom In the west peasants gained rights as a labor shortage swept eastern Europe workers became a necessity In eastern Europe
 Eastern Absolutism Serfdom In the west peasants gained rights as a labor shortage swept eastern Europe workers became a necessity In eastern Europe during the seventeenth century the rights of the peasants
Eastern Absolutism Serfdom In the west peasants gained rights as a labor shortage swept eastern Europe workers became a necessity In eastern Europe during the seventeenth century the rights of the peasants
Elizabeth I. Though the sex to which I belong is considered weak, you will nevertheless find me a rock that bends to no wind. - Queen Elizabeth I
 King Louis XIV L etat, c est moi, I am the state, said King Louis XIV of France. Louis believed that he was the only one responsible for governing France when he ruled from 1643 to 1715. A tutor to his
King Louis XIV L etat, c est moi, I am the state, said King Louis XIV of France. Louis believed that he was the only one responsible for governing France when he ruled from 1643 to 1715. A tutor to his
Vocabulary Ch
 Vocabulary Ch 17-1818 Absolute monarch Divine right Armada Intendant Balance of Power Dissenter Habeas corpus Limited monarchy Elector Mercenary Depopulation Westernization Boyar Warm-water port Natural
Vocabulary Ch 17-1818 Absolute monarch Divine right Armada Intendant Balance of Power Dissenter Habeas corpus Limited monarchy Elector Mercenary Depopulation Westernization Boyar Warm-water port Natural
Absolute, Catholic, Wars and bad economic decisions
 Absolute, Catholic, Wars and bad economic decisions Palace of Versailles / new power and status From Tudors to Stuarts To Parliament or not to Parliament Cavaliers / Roundheads Oliver Cromwell and theocracy
Absolute, Catholic, Wars and bad economic decisions Palace of Versailles / new power and status From Tudors to Stuarts To Parliament or not to Parliament Cavaliers / Roundheads Oliver Cromwell and theocracy
Notes: Chapter 13 The Old Regime: Absolutism and Enlightenment
 Name Notes: Chapter 13 The Old Regime: Absolutism and Enlightenment Introduction In this chapter, you will learn about important changes that took place in Europe between. The Old Regime refers to Europe
Name Notes: Chapter 13 The Old Regime: Absolutism and Enlightenment Introduction In this chapter, you will learn about important changes that took place in Europe between. The Old Regime refers to Europe
The 18 th Century. European States, International Wars and Social Change
 The 18 th Century European States, International Wars and Social Change Enlightened Absolutism The Enlightenment also had an effect upon the political development of Europe Concept of Natural Rights A
The 18 th Century European States, International Wars and Social Change Enlightened Absolutism The Enlightenment also had an effect upon the political development of Europe Concept of Natural Rights A
Pre-Enlightenment Europe. Unit 3: Revolution
 Pre-Enlightenment Europe Unit 3: Revolution Central Questions In order to understand the significance of the Enlightenment, we need to answer the following: What was European society like prior to the
Pre-Enlightenment Europe Unit 3: Revolution Central Questions In order to understand the significance of the Enlightenment, we need to answer the following: What was European society like prior to the
Eastern European and Russian Absolutism. Ivan IV Ivan the Terrible ( )
 Eastern European and Russian Absolutism Ivan IV Ivan the Terrible (1547-1584) became Tsar at age of 3 and watched rival groups of nobles who sought to control the country when he took charge, he saw treason
Eastern European and Russian Absolutism Ivan IV Ivan the Terrible (1547-1584) became Tsar at age of 3 and watched rival groups of nobles who sought to control the country when he took charge, he saw treason
(What would you buy if you won the lottery?) What will move Kings and Queens from Monarchy to Absolute Monarchy?
 Predictions Predict how the Empires in the Americas, Africa and Asia, built by Europeans rulers during the Age of Exploration, will affect Europe s monarchs. Predict what they might do with their increased
Predictions Predict how the Empires in the Americas, Africa and Asia, built by Europeans rulers during the Age of Exploration, will affect Europe s monarchs. Predict what they might do with their increased
ERA 7 - Revolutions & Empire
 ERA 7 - Revolutions & Empire ERA 7 Exam Jeopardy Review Game The Age of Absolutism Enlightenment & Revolutions The Industrial Revolution Economic Systems The Age of Imperialism $100 $200 $300 $400 $500
ERA 7 - Revolutions & Empire ERA 7 Exam Jeopardy Review Game The Age of Absolutism Enlightenment & Revolutions The Industrial Revolution Economic Systems The Age of Imperialism $100 $200 $300 $400 $500
Politics of the 18th Century
 Politics of the 18th Century Enlightened Absolutism The Enlightenment also had an effect upon the political development of Europe Concept of Natural Rights A corollary to the idea of natural laws were
Politics of the 18th Century Enlightened Absolutism The Enlightenment also had an effect upon the political development of Europe Concept of Natural Rights A corollary to the idea of natural laws were
SSWH14: ANALYZE THE AGE OF REVOLUTIONS ELEMENT A: EXAMINE ABSOLUTISM THROUGH A COMPARISON OF THE REIGNS OF LOUIS XIV & TSAR PETER THE GREAT.
 SSWH14: ANALYZE THE AGE OF REVOLUTIONS ELEMENT A: EXAMINE ABSOLUTISM THROUGH A COMPARISON OF THE REIGNS OF LOUIS XIV & TSAR PETER THE GREAT. LOUIS XIV v Medieval European feudalism had placed the majority
SSWH14: ANALYZE THE AGE OF REVOLUTIONS ELEMENT A: EXAMINE ABSOLUTISM THROUGH A COMPARISON OF THE REIGNS OF LOUIS XIV & TSAR PETER THE GREAT. LOUIS XIV v Medieval European feudalism had placed the majority
Unit 5 Chapter Test. World History: Patterns of Interaction Grade 10 McDougal Littell NAME. Main Ideas Choose the letter of the best answer.
 World History: Patterns of Interaction Grade 10 McDougal Littell NAME Unit 5 Chapter Test Main Ideas 1) What was the significance of the English Bill of Rights? (a) It established the group of government
World History: Patterns of Interaction Grade 10 McDougal Littell NAME Unit 5 Chapter Test Main Ideas 1) What was the significance of the English Bill of Rights? (a) It established the group of government
How did the basic structure of society in eastern Europe become different from that of western Europe in the early modern period? How and why did the
 How did the basic structure of society in eastern Europe become different from that of western Europe in the early modern period? How and why did the rulers of Austria, Prussia, and Russia manage to build
How did the basic structure of society in eastern Europe become different from that of western Europe in the early modern period? How and why did the rulers of Austria, Prussia, and Russia manage to build
Part Read about the regions of great Britain and Northern Ireland. Briefly describe its two regions:
 Social Studies 9 Unit 3 Worksheet Chapter 2, Part 1. 1. Democracy and have only been won after much. Many Canadian democratic traditions come originally from. The was signed in 1215 and recognized individual
Social Studies 9 Unit 3 Worksheet Chapter 2, Part 1. 1. Democracy and have only been won after much. Many Canadian democratic traditions come originally from. The was signed in 1215 and recognized individual
The French Revolution THE EUROPEAN MOMENT ( )
 The French Revolution THE EUROPEAN MOMENT (1750 1900) Quick Video 1 The French Revolution In a Nutshell Below is a YouTube link to a very short, but very helpful introduction to the French Revolution.
The French Revolution THE EUROPEAN MOMENT (1750 1900) Quick Video 1 The French Revolution In a Nutshell Below is a YouTube link to a very short, but very helpful introduction to the French Revolution.
The Ancien Régime and the Age of Enlightement
 The Ancien Régime and the Age of Enlightement 1.- The Ancien Régime. At the beginning of the 18th Century most of european countries were under the Ancien régime. The Ancien régime (French for the Old
The Ancien Régime and the Age of Enlightement 1.- The Ancien Régime. At the beginning of the 18th Century most of european countries were under the Ancien régime. The Ancien régime (French for the Old
The Rise of Russia. AP World History
 The Rise of Russia AP World History A Newly Independent Russia 1380: Battle of Kulikova (alliance of Russian feudal princes) led to Golden Horde defeat Mongol attempts to subjugate Russians continued for
The Rise of Russia AP World History A Newly Independent Russia 1380: Battle of Kulikova (alliance of Russian feudal princes) led to Golden Horde defeat Mongol attempts to subjugate Russians continued for
French Revolution. II. Louis XVI A. Supported the American Revolution 1. This caused hardship on the economy
 1 French Revolution I. 3 estates A. 1 st estate 1. Clergy 5-10% of the land B. 2 nd estate 1. Nobles 25% of the land C. 3 rd estate 1. Peasants 40-60% of the land 2. Artisans 3. Bourgeoisie (Middle Class)
1 French Revolution I. 3 estates A. 1 st estate 1. Clergy 5-10% of the land B. 2 nd estate 1. Nobles 25% of the land C. 3 rd estate 1. Peasants 40-60% of the land 2. Artisans 3. Bourgeoisie (Middle Class)
The French Revolution Liberty, Equality and Fraternity!!!! Chapter 22
 The French Revolution Liberty, Equality and Fraternity!!!! Chapter 22 What was going on in Europe? Remember absolutism The Enlightenment Scientific Revolution Colonialism England in America, which starts
The French Revolution Liberty, Equality and Fraternity!!!! Chapter 22 What was going on in Europe? Remember absolutism The Enlightenment Scientific Revolution Colonialism England in America, which starts
The French Revolution and Napoleon. ( ) Chapter 11
 The French Revolution and Napoleon (1789-1815) Chapter 11 Main Ideas Social inequality & economic problems contributed to the French Revolution Radical groups controlled the Revolution Revolution allowed
The French Revolution and Napoleon (1789-1815) Chapter 11 Main Ideas Social inequality & economic problems contributed to the French Revolution Radical groups controlled the Revolution Revolution allowed
The French Revolution and Napoleon,
 The French Revolution and Napoleon, 1789 1815 Why was it so hard for the French to establish a republic than it was for the Americans? How was Napoleon able to take power twice? The French Revolution and
The French Revolution and Napoleon, 1789 1815 Why was it so hard for the French to establish a republic than it was for the Americans? How was Napoleon able to take power twice? The French Revolution and
Russia During the Early- Modern Period
 Russia During the Early- Modern Period Review of Russian History Kievan Rus Dominated by Kiev, but various other principalities throughout Ties with Byzantine Empire Adopted Orthodox Christianity in 900
Russia During the Early- Modern Period Review of Russian History Kievan Rus Dominated by Kiev, but various other principalities throughout Ties with Byzantine Empire Adopted Orthodox Christianity in 900
Dates and Periods in European History
 Dates and Periods in European History Students often have difficulty keeping track of the parallel timelines of politics, culture, and economics. Give them a guide like this to help keep them from getting
Dates and Periods in European History Students often have difficulty keeping track of the parallel timelines of politics, culture, and economics. Give them a guide like this to help keep them from getting
CHAPTER 13 THE OLD REGIME: ABSOLUTISM AND ENLIGHTENMENT
 CHAPTER 13 THE OLD REGIME: ABSOLUTISM AND ENLIGHTENMENT INTRODUCTION In this chapter, you will learn about important changes that took place in Old Regime Europe between 1600 and 1770. The Old Regime refers
CHAPTER 13 THE OLD REGIME: ABSOLUTISM AND ENLIGHTENMENT INTRODUCTION In this chapter, you will learn about important changes that took place in Old Regime Europe between 1600 and 1770. The Old Regime refers
Absolute Monarchs Activity
 Absolute Monarchs Activity Feudalism King Aristocracy Knights Serfs Medieval Monarchs Power Feudalism was the basis of European governments Kings maintained power & control through the support of their
Absolute Monarchs Activity Feudalism King Aristocracy Knights Serfs Medieval Monarchs Power Feudalism was the basis of European governments Kings maintained power & control through the support of their
The French Revolution establishes a new political order, Napoleon Bonaparte gains and loses an empire, and European states forge a balance of power.
 SLIDE 1 Chapter 23 The French Revolution and Napoleon, 1789 1815 The French Revolution establishes a new political order, Napoleon Bonaparte gains and loses an empire, and European states forge a balance
SLIDE 1 Chapter 23 The French Revolution and Napoleon, 1789 1815 The French Revolution establishes a new political order, Napoleon Bonaparte gains and loses an empire, and European states forge a balance
AP Euro Free Response Questions
 AP Euro Free Response Questions Late Middle Ages to the Renaissance 2004 (#5): Analyze the influence of humanism on the visual arts in the Italian Renaissance. Use at least THREE specific works to support
AP Euro Free Response Questions Late Middle Ages to the Renaissance 2004 (#5): Analyze the influence of humanism on the visual arts in the Italian Renaissance. Use at least THREE specific works to support
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions.
 SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. Known as the Sun
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. Known as the Sun
STANDARD WHII.6e The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth,
 STANDARD WHII.6e The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth, and eighteenth centuries by e) describing the French
STANDARD WHII.6e The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth, and eighteenth centuries by e) describing the French
The History of the Huguenots. Western Civilization II Marshall High School Mr. Cline Unit ThreeDA
 The History of the Huguenots Western Civilization II Marshall High School Mr. Cline Unit ThreeDA Reformation Comes to France When the Reformation came to France, its message spread quickly. By 1534, there
The History of the Huguenots Western Civilization II Marshall High School Mr. Cline Unit ThreeDA Reformation Comes to France When the Reformation came to France, its message spread quickly. By 1534, there
CAUSES OF THE FRENCH REVOLUTION
 REVOLUTIONS CAUSES OF THE FRENCH REVOLUTION During the reign of Louis XIV. A political system known as the Old Regime Divided France into 3 social classes- Estates First Estate Catholic clergy own 10 percent
REVOLUTIONS CAUSES OF THE FRENCH REVOLUTION During the reign of Louis XIV. A political system known as the Old Regime Divided France into 3 social classes- Estates First Estate Catholic clergy own 10 percent
Absolutism Concept Formation
 Absolutism Concept Formation You will be participating in a concept formation lesson designed to teach you the understanding of absolutism. You will uncover the critical attributes of absolutism by reading
Absolutism Concept Formation You will be participating in a concept formation lesson designed to teach you the understanding of absolutism. You will uncover the critical attributes of absolutism by reading
Honors World History Harkness Seminars and Homework for Unit 4 Chapters 16 and and Documents
 Honors World History Harkness Seminars and Homework for Unit 4 Chapters 16 and 17- - 1 and 17- - - 2 + Documents Day of Presentation: Chapter- - Section Homework Guiding Questions: Define all key terms
Honors World History Harkness Seminars and Homework for Unit 4 Chapters 16 and 17- - 1 and 17- - - 2 + Documents Day of Presentation: Chapter- - Section Homework Guiding Questions: Define all key terms
17 th C Growth of French Absolutism. 17 th Century politics French Domination, Wars
 17 th C Growth of French Absolutism 17 th Century politics French Domination, Wars Absolutism develops in France Henry IV: curtailed privileges of French nobility issued Edict of Nantes without nobility
17 th C Growth of French Absolutism 17 th Century politics French Domination, Wars Absolutism develops in France Henry IV: curtailed privileges of French nobility issued Edict of Nantes without nobility
Chapter 16: Attempts at Liberty
 Chapter 16: Attempts at Liberty 18 th Century Few people enjoyed such rights as, and the pursuit of ; and absolutism was the order of the day. The desire for personal and political liberty prompted a series
Chapter 16: Attempts at Liberty 18 th Century Few people enjoyed such rights as, and the pursuit of ; and absolutism was the order of the day. The desire for personal and political liberty prompted a series
Enlightenment and Prussia. The Story of Fredrick I and Fredrick II
 Enlightenment and Prussia The Story of Fredrick I and Fredrick II Have you ever ignored good advice? If yes, tell me about a time when you wish you would have taken someone else's advice? If no, tell me
Enlightenment and Prussia The Story of Fredrick I and Fredrick II Have you ever ignored good advice? If yes, tell me about a time when you wish you would have taken someone else's advice? If no, tell me
ABSOLUTISM TO REVOLUTION REVIEW GAME
 ABSOLUTISM TO REVOLUTION REVIEW GAME Monarchs Peter the Great William & Mary Louis XIV Philip II of Spain Explain the difference between an absolute monarchy and a constitutional monarchy. Name that monarch!
ABSOLUTISM TO REVOLUTION REVIEW GAME Monarchs Peter the Great William & Mary Louis XIV Philip II of Spain Explain the difference between an absolute monarchy and a constitutional monarchy. Name that monarch!
AP European History Chapter 16 Notes v Two models of European political development in the 17 th century Ø Political absolutism strong centralized
 AP European History Chapter 16 Notes v Two models of European political development in the 17 th century Ø Political absolutism strong centralized monarchies where the royal power is dominant Ø Parliamentary
AP European History Chapter 16 Notes v Two models of European political development in the 17 th century Ø Political absolutism strong centralized monarchies where the royal power is dominant Ø Parliamentary
The French Revolution A Concise Overview
 The French Revolution A Concise Overview The Philosophy of the Enlightenment and the success of the American Revolution were causing unrest within France. People were taxed heavily and had little or no
The French Revolution A Concise Overview The Philosophy of the Enlightenment and the success of the American Revolution were causing unrest within France. People were taxed heavily and had little or no
French Revolution. Revolution in France (Cause) Estates (Cont) 1/23/ s Feudalist Government. 1 st & 2 nd Estate are Privileged
 French Revolution 1789-1815 Revolution in France (Cause) 1770s Feudalist Government System of the wealthy in power Poor works the land in return for food & protection 3 Estates (Classes of People) 1 st
French Revolution 1789-1815 Revolution in France (Cause) 1770s Feudalist Government System of the wealthy in power Poor works the land in return for food & protection 3 Estates (Classes of People) 1 st
(3) parliamentary democracy (2) ethnic rivalries
 1) In the Soviet Union, Joseph Stalin governed by means of secret police, censorship, and purges. This type of government is called (1) democracy (2) totalitarian 2) The Ancient Athenians are credited
1) In the Soviet Union, Joseph Stalin governed by means of secret police, censorship, and purges. This type of government is called (1) democracy (2) totalitarian 2) The Ancient Athenians are credited
The Age of Absolutism and Limited Government. Name: World History I Mr. Horas
 The Age of Absolutism and Limited Government Name: World History I Mr. Horas www.chshistory.net 1 World History I Mr. Horas Absolutism and Limited Government Reading #1 Reading #1: Europe in Crisis: The
The Age of Absolutism and Limited Government Name: World History I Mr. Horas www.chshistory.net 1 World History I Mr. Horas Absolutism and Limited Government Reading #1 Reading #1: Europe in Crisis: The
ERA 7 Revolutions & Empire
 ERA 7 Revolutions & Empire ERA 7 Exam Jeopardy Review Game The Age of Absolutism Enlightenment The Industrial & Revolutions Revolution Economic Systems The Age of Imperialism $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200
ERA 7 Revolutions & Empire ERA 7 Exam Jeopardy Review Game The Age of Absolutism Enlightenment The Industrial & Revolutions Revolution Economic Systems The Age of Imperialism $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200
The Enlightenment and the scientific revolution changed people s concepts of the universe and their place within it Enlightenment ideas affected
 The Enlightenment and the scientific revolution changed people s concepts of the universe and their place within it Enlightenment ideas affected politics, music, art, architecture, and literature of Europe
The Enlightenment and the scientific revolution changed people s concepts of the universe and their place within it Enlightenment ideas affected politics, music, art, architecture, and literature of Europe
Causes of the French Revolu2on
 1789-1815 Causes of the French Revolu2on Social and economic injustices American Revolution Economic troubles High taxes and bread prices, debt, crop failures in the 1780s A weak, inept leadership Old
1789-1815 Causes of the French Revolu2on Social and economic injustices American Revolution Economic troubles High taxes and bread prices, debt, crop failures in the 1780s A weak, inept leadership Old
Unit 5, SSWH 14 b Parliament & the English Monarchy
 Unit 5, SSWH 14 b Parliament & the English Monarchy What effect did the Age of Revolution have on Global Society? SSWH 14 b Identify the causes and results of the revolutions in England (1689), United
Unit 5, SSWH 14 b Parliament & the English Monarchy What effect did the Age of Revolution have on Global Society? SSWH 14 b Identify the causes and results of the revolutions in England (1689), United
Essential Question: What were the important causes & effects of the French Revolution?
 Essential Question: What were the important causes & effects of the French Revolution? Do Now On your ipad or blank piece of paper write down one example on what is needed to consider a revolution as successful.
Essential Question: What were the important causes & effects of the French Revolution? Do Now On your ipad or blank piece of paper write down one example on what is needed to consider a revolution as successful.
Causes of French Revolution. 3 Causes
 Causes of French Revolution 3 Causes Contextualization 1. Burdens of absolutism 2. Enlightenment present solutions to absolutism 1. Burdens of Absolutism Louis XIV: gold standard of absolute monarchs When
Causes of French Revolution 3 Causes Contextualization 1. Burdens of absolutism 2. Enlightenment present solutions to absolutism 1. Burdens of Absolutism Louis XIV: gold standard of absolute monarchs When
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 3 The Rise of Napoleon and the Napoleonic Wars ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What causes revolution? How does revolution change society? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary capable having or showing ability
Lesson 3 The Rise of Napoleon and the Napoleonic Wars ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What causes revolution? How does revolution change society? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary capable having or showing ability
From Absolutism to Revolution
 5 From Absolutism to Revolution 448 1500 1815 CHAPTER 19 Monarchs of Europe 1500 1800 CHAPTER 20 Enlightenment and Revolution in England and America 1550 1789 CHAPTER 21 The French Revolution and Napoléon
5 From Absolutism to Revolution 448 1500 1815 CHAPTER 19 Monarchs of Europe 1500 1800 CHAPTER 20 Enlightenment and Revolution in England and America 1550 1789 CHAPTER 21 The French Revolution and Napoléon
The French Revolution
 The French Revolution The Old Regime or Old Order France was ruled by Louis XVI and his wife Queen Marie Antoinette France was an advanced and prosperous nation Beneath this was unrest caused by bad harvests,
The French Revolution The Old Regime or Old Order France was ruled by Louis XVI and his wife Queen Marie Antoinette France was an advanced and prosperous nation Beneath this was unrest caused by bad harvests,
The French Revolution Absolutism monarchs didn t share power with a counsel or parliament--
 The French Revolution Absolutism monarchs didn t share power with a counsel or parliament-- The Seigneurial System method of land ownership and organization Peasant labor Louis XIV Ruled from 1643 1715
The French Revolution Absolutism monarchs didn t share power with a counsel or parliament-- The Seigneurial System method of land ownership and organization Peasant labor Louis XIV Ruled from 1643 1715
Page 1 of 9 AP European History Topic 5 The Absolutist State Multiple Choice (Weight 2) Points Possible: 200 pts
 Page 1 of 9 AP European History Topic 5 The Absolutist State Multiple Choice (Weight 2) Points Possible: 200 pts Directions: Read the statement and choose the most correct answer. Page 2 of 9 1. Louis
Page 1 of 9 AP European History Topic 5 The Absolutist State Multiple Choice (Weight 2) Points Possible: 200 pts Directions: Read the statement and choose the most correct answer. Page 2 of 9 1. Louis
World History Unit 12 Lesson 1 The Congress of Vienna
 Unit 12 Lesson 1 The Congress of Vienna After the Napoleonic Wars, Europe faced many problems: 1) Many countries leaders had been replaced by Napoleon. 2) Some countries had been eliminated. 3) The liberalism
Unit 12 Lesson 1 The Congress of Vienna After the Napoleonic Wars, Europe faced many problems: 1) Many countries leaders had been replaced by Napoleon. 2) Some countries had been eliminated. 3) The liberalism
The French Revolution Timeline
 Michael Plasmeier Smith Western Civ 9H 12 December 2005 The French Revolution Timeline May 10, 1774 - Louis XVI made King King Louis the 16 th became king in 1774. He was a weak leader and had trouble
Michael Plasmeier Smith Western Civ 9H 12 December 2005 The French Revolution Timeline May 10, 1774 - Louis XVI made King King Louis the 16 th became king in 1774. He was a weak leader and had trouble
THE AGE OF ENLIGHTENMENT
 THE AGE OF ENLIGHTENMENT THE OLD REGIME/ THE ANCIEN REGIME Name used by the revolutionaries to refer the times before the French revolution Later adopted by historians to refer to characteristics of the
THE AGE OF ENLIGHTENMENT THE OLD REGIME/ THE ANCIEN REGIME Name used by the revolutionaries to refer the times before the French revolution Later adopted by historians to refer to characteristics of the
Modern Europe- Cooke French Revolution Notes (Powerpoint)
 Modern Europe- Cooke Name: French Revolution Notes (Powerpoint) I. Background: The French Revolution occurred in 1789 over 100 years after the English Revolution. Why then? o France in the late 18 th century
Modern Europe- Cooke Name: French Revolution Notes (Powerpoint) I. Background: The French Revolution occurred in 1789 over 100 years after the English Revolution. Why then? o France in the late 18 th century
The Enlightenment. Global History & Geography 2
 The Enlightenment Global History & Geography 2 What was it? A time period when philosophers examined the relationship between humans and their government Key ideas: 17 th & 18 th centuries Extension of
The Enlightenment Global History & Geography 2 What was it? A time period when philosophers examined the relationship between humans and their government Key ideas: 17 th & 18 th centuries Extension of
Adapted from: ubpage= Absolutism
 Adapted from: http://www.buffaloschools.org/socialstudiesdept.cfm?s ubpage=27738 Absolutism TERMS Divine Right: the European belief that God chose who could be King or Queen (similar to Chinese Mandate
Adapted from: http://www.buffaloschools.org/socialstudiesdept.cfm?s ubpage=27738 Absolutism TERMS Divine Right: the European belief that God chose who could be King or Queen (similar to Chinese Mandate
EUROPEAN HISTORY. 5. The Enlightenment. Form 3
 EUROPEAN HISTORY 5. The Enlightenment Form 3 Europe at the time of the Enlightenment and on the eve of the French Revolution 1 Unit 5.1 - The Origins of the Enlightenment Source A: Philosophers debating
EUROPEAN HISTORY 5. The Enlightenment Form 3 Europe at the time of the Enlightenment and on the eve of the French Revolution 1 Unit 5.1 - The Origins of the Enlightenment Source A: Philosophers debating
The French Revolution -Mr. Leon s Class Liberty, Equality, Fraternity
 The French Revolution -Mr. Leon s Class 1789-1815 Liberty, Equality, Fraternity European Monarchies 1750-1789 What are some current issues facing the American people that cause great divisiveness and anger?
The French Revolution -Mr. Leon s Class 1789-1815 Liberty, Equality, Fraternity European Monarchies 1750-1789 What are some current issues facing the American people that cause great divisiveness and anger?
GHSGT. Social Studies Review: World Geography World History United States History American Government
 GHSGT Social Studies Review: World Geography World History United States History American Government What to Expect From: World History World History Content Area Covered: New World Explorations Scientific
GHSGT Social Studies Review: World Geography World History United States History American Government What to Expect From: World History World History Content Area Covered: New World Explorations Scientific
Nationalism. Chapter 8
 Nationalism Chapter 8 Latin American Revolutions Haiti Slave revolt 1791 Toussaint L Ouverture Dessalines 1804 Independence Latin American Revolutions Rigid Social Structure Peninsular Creole Mestizo Indian
Nationalism Chapter 8 Latin American Revolutions Haiti Slave revolt 1791 Toussaint L Ouverture Dessalines 1804 Independence Latin American Revolutions Rigid Social Structure Peninsular Creole Mestizo Indian
The French Revolution and Napoleon, The French Revolution and Napoleon, The French Revolution Begins.
 The French Revolution and Napoleon, 789 8 The French Revolution establishes a new political order, Napoleon Bonaparte gains and loses an empire, and European states forge a balance of power. The French
The French Revolution and Napoleon, 789 8 The French Revolution establishes a new political order, Napoleon Bonaparte gains and loses an empire, and European states forge a balance of power. The French
From 1789 to 1804, France experienced revolutionary changes that transformed France from an absolute monarchy to a republic to an empire
 From 1789 to 1804, France experienced revolutionary changes that transformed France from an absolute monarchy to a republic to an empire The success of the American Revolution & Enlightenment ideas such
From 1789 to 1804, France experienced revolutionary changes that transformed France from an absolute monarchy to a republic to an empire The success of the American Revolution & Enlightenment ideas such
CAUSES OF REVOLUTION
 CAUSES OF REVOLUTION The reasons for revolution can be complex and varied, but we can narrow the causes of revolution into 4 general categories. Revolutions happen due to: New Ideas Social Conflict Political
CAUSES OF REVOLUTION The reasons for revolution can be complex and varied, but we can narrow the causes of revolution into 4 general categories. Revolutions happen due to: New Ideas Social Conflict Political
MODERN EUROPEAN HISTORY CURRICULUM MAP
 ESSENTIAL THEMES TIME FRAME UNITS OF STUDY SKILLS ASSESSMENT *1, 10, 11, 12, 13, 1 19, 21 Aug/Sept Middle Ages * See attached appe with Essentia listed 1. VASSALAGE Students will: a. Explain and compare
ESSENTIAL THEMES TIME FRAME UNITS OF STUDY SKILLS ASSESSMENT *1, 10, 11, 12, 13, 1 19, 21 Aug/Sept Middle Ages * See attached appe with Essentia listed 1. VASSALAGE Students will: a. Explain and compare
History through art: Fine art. see p.575
 History through art: Fine art see p.575 The French Revolution was a major transformation of the society and the political system of France, lasting from 1789 to 1799. During the course of the Revolution,
History through art: Fine art see p.575 The French Revolution was a major transformation of the society and the political system of France, lasting from 1789 to 1799. During the course of the Revolution,
The Napoleonic Era
 The Napoleonic Era 1799-1815 1796-1799 Gained popularity during the French Revolution as a military hero November 1799 Napoleon overthrows Directory in 1799 which is called the Brumaire Coup Directory
The Napoleonic Era 1799-1815 1796-1799 Gained popularity during the French Revolution as a military hero November 1799 Napoleon overthrows Directory in 1799 which is called the Brumaire Coup Directory
Bell Activity. What does it feel like to be in a group where one person insists on always getting his or her own way? How might other members respond?
 History of Russia Objectives Know important events and people from the history of tsarist Russia. Know the reason for the rise and fall of the Soviet Union. Explain the cause and effects of the Russian
History of Russia Objectives Know important events and people from the history of tsarist Russia. Know the reason for the rise and fall of the Soviet Union. Explain the cause and effects of the Russian
World History Alpha Lenze Final Exam Study Guide. Answer the questions as best you can include Who, What, When, Where, Why, How and So What.
 World History Alpha Lenze 2013-14 Final Exam Study Guide Answer the questions as best you can include Who, What, When, Where, Why, How and So What. 1. What was a result of the Treaty of Verdun in 843?
World History Alpha Lenze 2013-14 Final Exam Study Guide Answer the questions as best you can include Who, What, When, Where, Why, How and So What. 1. What was a result of the Treaty of Verdun in 843?
Napoleon & the French Revolution. Napoleon & the French Revolution v 1700 s France is the most
 u Palace in Versailles focal point of anger.! u Example of the American Revolution and the Enlightenment ideas the people of France are not happy.! u Louis XVI is in trouble..!!! v 1700 s France is the
u Palace in Versailles focal point of anger.! u Example of the American Revolution and the Enlightenment ideas the people of France are not happy.! u Louis XVI is in trouble..!!! v 1700 s France is the
The French Revolution Begins
 Name CHAPTER 23 Section 1 (pages 651 655) The French Revolution Begins BEFORE YOU READ In the last chapter, you read about the Enlightenment and the American Revolution. In this section, you will learn
Name CHAPTER 23 Section 1 (pages 651 655) The French Revolution Begins BEFORE YOU READ In the last chapter, you read about the Enlightenment and the American Revolution. In this section, you will learn
Name Class Date. The French Revolution and Napoleon Section 3
 Name Class Date Section 3 MAIN IDEA Napoleon Bonaparte rose through military ranks to become emperor over France and much of Europe. Key Terms and People Napoleon Bonaparte ambitious military leader who
Name Class Date Section 3 MAIN IDEA Napoleon Bonaparte rose through military ranks to become emperor over France and much of Europe. Key Terms and People Napoleon Bonaparte ambitious military leader who
The French Revolution Begins
 The French Revolution Begins name: hr: (SOLO) THE OLD ORDER---HOW WAS FRENCH SOCIETY UNEQUAL? In the 1700s, France was the leading country of Europe. It was the center of the new ideas of the Enlightenment.
The French Revolution Begins name: hr: (SOLO) THE OLD ORDER---HOW WAS FRENCH SOCIETY UNEQUAL? In the 1700s, France was the leading country of Europe. It was the center of the new ideas of the Enlightenment.
Background Information
 Background Information 1791 The seating of these representatives gives us our modern political terms of Right Wing or Left Wing Legislative Assembly rules France Members with similar political views sat
Background Information 1791 The seating of these representatives gives us our modern political terms of Right Wing or Left Wing Legislative Assembly rules France Members with similar political views sat
Life in France in 1789
 Life in France in 1789 Roughly 90% of France s population were poor peasants Peasants had to produce food for the entire country The king had a lavish lifestyle The king ruled as an absolute monarch The
Life in France in 1789 Roughly 90% of France s population were poor peasants Peasants had to produce food for the entire country The king had a lavish lifestyle The king ruled as an absolute monarch The
The Rise of Russia and Russia s Interaction with the West
 The Rise of Russia and Russia s Interaction with the West I. Introduction A. Between 1450 and 1750 Russia 1. Land based empire B. Foundation derived from C. Began Selective Westernization WHAT??? 1. Emulated
The Rise of Russia and Russia s Interaction with the West I. Introduction A. Between 1450 and 1750 Russia 1. Land based empire B. Foundation derived from C. Began Selective Westernization WHAT??? 1. Emulated
Modern History 112: Learning Objectives 1.1 Causes of Revolutions
 Modern History 112: Learning Objectives 1.1 Causes of Revolutions Students will: 1.1.1 Identify and understand the general causes of revolutions: new ideas, social conflict, political factors, and economic
Modern History 112: Learning Objectives 1.1 Causes of Revolutions Students will: 1.1.1 Identify and understand the general causes of revolutions: new ideas, social conflict, political factors, and economic
1. Topic 3 Lesson 1 Interactive Reading Notepad. 2. Topic 3 Lesson 1 Quiz. 3. Topic 3 Lesson 2 Interactive Reading Notepad. 4. Topic 3 Lesson 2 Quiz
 Topic 3: Absolutism and Revolution Assignments to do: 1. Topic 3 Lesson 1 Interactive Reading Notepad 2. Topic 3 Lesson 1 Quiz 3. Topic 3 Lesson 2 Interactive Reading Notepad 4. Topic 3 Lesson 2 Quiz 5.
Topic 3: Absolutism and Revolution Assignments to do: 1. Topic 3 Lesson 1 Interactive Reading Notepad 2. Topic 3 Lesson 1 Quiz 3. Topic 3 Lesson 2 Interactive Reading Notepad 4. Topic 3 Lesson 2 Quiz 5.
Chapter 19. The French Revolution
 Chapter 19 The French Revolution Old/Ancien Regime First Estate - Clergy Second Estate - Nobility Third Estate - Everyone else - Traditionally the peasantry, but by now had come to include merchants and
Chapter 19 The French Revolution Old/Ancien Regime First Estate - Clergy Second Estate - Nobility Third Estate - Everyone else - Traditionally the peasantry, but by now had come to include merchants and
Econ Modern European Economic History John Lovett. Part 1: (70 points. Answer on this paper. 2.0 pts each unless noted.)
 Econ 40970 Modern European Economic History John Lovett Exam 3 Code Name: Part 1: (70 points. Answer on this paper. 2.0 pts each unless noted.) # s 1 4: According to our reading (Power to the People by
Econ 40970 Modern European Economic History John Lovett Exam 3 Code Name: Part 1: (70 points. Answer on this paper. 2.0 pts each unless noted.) # s 1 4: According to our reading (Power to the People by
French Revolution 1789 and Age of Napoleon. Background to Revolution. American Revolution
 French Revolution 1789 and Age of Napoleon Background to Revolution Scientific Revolution and Enlightenment Enlightenment validated human beings ability to think for themselves and govern themselves. Rousseau
French Revolution 1789 and Age of Napoleon Background to Revolution Scientific Revolution and Enlightenment Enlightenment validated human beings ability to think for themselves and govern themselves. Rousseau
Extra Credit. 1. What Estate held high offices in army, government & courts? 2. Besides the French Revolution, what other event took place in 1789?
 Extra Credit 1. What Estate held high offices in army, government & courts? 2. Besides the French Revolution, what other event took place in 1789? 3. Identify the three groups of people that made up the
Extra Credit 1. What Estate held high offices in army, government & courts? 2. Besides the French Revolution, what other event took place in 1789? 3. Identify the three groups of people that made up the
AP Euro: Past Free Response Questions
 AP Euro: Past Free Response Questions 1. To what extent is the term "Renaissance" a valid concept for s distinct period in early modern European history? 2. Explain the ways in which Italian Renaissance
AP Euro: Past Free Response Questions 1. To what extent is the term "Renaissance" a valid concept for s distinct period in early modern European history? 2. Explain the ways in which Italian Renaissance
