Spain s Conflicts King Philip II championed Catholic causes throughout his lands, while England became the leader of Protestant nations of Europe.
|
|
|
- Alison Barnett
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Spain s Conflicts King Philip II championed Catholic causes throughout his lands, while England became the leader of Protestant nations of Europe. 1
2 Spain s Conflicts (cont.) In the sixteenth century, religious wars broke out in Europe as Calvinists and Catholics became more militant. King Philip II of Spain wanted to consolidate the lands of his empire Spain, the Netherlands, and possessions in the Americas and Italy under Catholicism. Height of Spanish Power Under Philip II, c Spain s Conflicts (cont.) Philip II attempted to strengthen his control in the Netherlands by crushing Calvinism, but was resisted by a rebellion led by William the Silent. In 1558, Elizabeth Tudor came to power in England. The Church of England began to follow a moderate form of Protestantism and England became the leader of the Protestant nations of Europe. Spain s Conflicts (cont.) Philip II tried to invade England to restore Catholicism to the island nation. In 1588, the Spanish armada was defeated by the faster English ships. Upon its return to Spain, the fleet was battered by storms en route around Scotland and Ireland. Route of the Spanish Fleet,
3 Spain s Conflicts (cont.) By the end of Philip s reign in 1598, Spain was not the great power that it appeared to be, and England began to create a world empire. Route of the Spanish Fleet, 1588 The French Wars of Religion Conflict between Catholics and Protestants was at the heart of the French Wars of Religion. The French Wars of Religion (cont.) During the 1500s, France encountered a series of civil wars, known as the French Wars of Religion ( ). Huguenots were French Protestants influenced by John Calvin. About half the nobility were Huguenots, a political threat to the Crown. The ultra-catholics opposed the Huguenots and recruited large armies to fight them. 3
4 The French Wars of Religion (cont.) In 1589 a Huguenot political leader named Henry of Navarre succeeded to the throne as Henry IV, bringing the French Wars of Religion to an end. Henry IV converted to Catholicism, but issued the Edict of Nantes, recognizing Catholicism as the state religion and giving Huguenots religious and political rights. France Crises in Europe Population decline in Europe and the hysteria of witchcraft trials contributed to economic and social problems in seventeenth-century Europe. Crises in Europe (cont.) During the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, Europe witnessed severe economic and social problems. Economic problems were caused by the loss of Jewish and Muslim artisans and merchants, economic problems in Italy, and currency policies in Spain. One major economic problem was inflation, or rising prices. 4
5 Crises in Europe (cont.) Europe s population growth during the sixteenth century increased the demand for food and land, while driving up prices. Europe s population had leveled off by War, famine, and plague led to declining population numbers. Religious zeal and hunts for heretics were extended to witchcraft. Crises in Europe (cont.) Fear of witchcraft led to the accusations and trials of over 100,000 people, mostly single or widowed women. The Thirty Years War Started over religious conflicts, the Thirty Years War was sustained by political conflicts. 5
6 The Thirty Years War (cont.) The Thirty Years War was fought primarily in the Holy Roman Empire. It began between Catholics, led by the Hapsburg dynasty, and Protestant forces in Bohemia. All of the major powers in Europe (except England) were involved in the war. Europe After the Peace of Westphalia, 1648 The Thirty Years War (cont.) In 1648 the Peace of Westphalia ended the war and divided the Holy Roman Empire into independent states that could determine their own religion and foreign policy. This brought an end to the Holy Roman Empire as a political entity. Revolutions in England Civil war raged over what roles the king and Parliament should have in governing England. 6
7 Revolutions in England (cont.) James I, the king of Scotland, came to power with the death of Queen Elizabeth. The Stuart line of rulers began in James I believed in the divine right of kings. This contradicted the beliefs of most Englishmen, who accepted that the king and Parliament ruled England together. Revolutions in England (cont.) When Charles I came to the throne, many Puritans were upset that he attempted to put more rituals into the Church of England. This led thousands of Puritans to leave for America. In 1642 England was faced with a civil war between the king s soldiers, known as Cavaliers, and the Roundheads under Oliver Cromwell. Revolutions in England (cont.) Cromwell s forces were victorious, and Charles II was executed. In 1649 England was declared a commonwealth. After Cromwell s death in 1658, England restored the Stuart line of rulers with Charles II. Charles II ruled until his death in 1685, when James II ascended the throne. 7
8 Revolutions in England (cont.) James II was a devout Catholic. Parliament objected to his policies of appointing Catholics because its members were afraid a Catholic dynasty might be possible. In 1688 English nobles invited William and Mary of Orange, who were Protestants, to invade England. William and Mary were offered the throne and accepted the English Bill of Rights. Revolutions in England (cont.) Bill of Rights: Parliament could make laws and levy taxes. Armies could not be raised without the consent of Parliament. Citizens could keep arms and have a jury trial. Revolutions in England (cont.) The Bill of Rights ensured that Parliament would be part of the English government and laid the foundation for a constitutional monarchy. Parliament also enacted the Tolerance Act of 1689, which granted Puritans, but not Catholics, the right of free public worship. 8
9 France under Louis XIV Louis XIV was an absolute monarch whose rule was admired and imitated throughout Europe. France under Louis XIV (cont.) Louis XIV is regarded as the best example of absolutism in the seventeenth century. Louis XIV strengthened control of the government and stabilized France politically, economically, and socially. Prior to Louis XIV becoming king, Cardinals Richelieu and Mazarin weakened Protestant power and strengthened royal power. 9
10 France under Louis XIV (cont.) Louis ruled without the assistance of a royal council, and had complete control of foreign policy, the Church, and taxes. Jean-Baptiste Colbert helped to make France more powerful economically by improving trade, communications, transportation, and by creating a merchant marine. France under Louis XIV (cont.) To ensure that his Bourbon dynasty dominated Europe, Louis developed a standing army and waged four wars between 1667 and Louis left the legacy of an absolute ruler who strengthened France. Louis s political policies and lavish lifestyle left France with great debts and surrounded by enemies. Absolutism in Central and Eastern Europe Prussia and Austria emerged as great European powers in the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. 10
11 Absolutism in Central and Eastern Europe (cont.) Following the Thirty Years War, there were more than three hundred independent German states. Prussia and Austria rose to become European powers. Frederick William the Great Elector laid the foundation for Prussia by creating the fourth-largest military force in Europe. Expansion of Prussia and Austria to 1720 Absolutism in Central and Eastern Europe (cont.) Frederick William centralized power by setting up the General War Commissariat to levy taxes for the army and govern the state. The new Austrian Empire was established by the Hapsburg family, who had previously provided emperors for the Holy Roman Empire. Absolutism in Central and Eastern Europe (cont.) The Hapsburgs created a new empire, including present-day Austria, the Czech Republic, and Hungary. The Austrian monarchy never became a centralized, absolutist state, but remained a collection of territories held together by the Hapsburg emperor. 11
12 Peter The Great Russia emerged as a great power under Peter the Great. Peter The Great (cont.) In sixteenth-century Russia, Ivan IV became the first ruler to take the title of czar. Ivan expanded Russian territory and crushed the power of the boyars. He became known as Ivan the Terrible. Following the end of Ivan s dynasty in 1598, the national assembly selected Michael Romanov as the new czar in Expansion of Russia, Peter The Great (cont.) In 1689 Peter the Great became czar. He modernized the military and made Russia a power in European affairs. Peter introduced Russians to the culture of Western Europe, and built the new capital city of St. Petersburg on the Baltic Sea to open a window to the West. 12
13 Art after the Renaissance The artistic movements of Mannerism and the baroque began in Italy and reflected the spiritual perceptions of the time. Art after the Renaissance (cont.) Mannerism was an art form that emerged in Italy before spreading throughout Europe. Mannerism broke away from the Renaissance principles of balance, harmony, and moderation and represented people as elongated, to show suffering and heightened emotion. The characteristics of Mannerism are reflected in the work of El Greco, whose figures are elongated and contorted. Art after the Renaissance (cont.) A new movement known as baroque replaced Mannerism. It was embraced by Catholic architecture, especially in the Hapsburg courts of Madrid, Prague, Vienna, and Brussels. Baroque churches and palaces were magnificent and reflected a search for power. 13
14 Art after the Renaissance (cont.) The baroque artist Gian Lorenzo Bernini captured these ideas with his work on Saint Peter s Basilica in Rome. Golden Age of Literature Shakespeare and Lope de Vega were prolific writers of dramas and comedies that reflected the human condition. Golden Age of Literature (cont.) William Shakespeare was a famous playwright and actor whose understanding of human psychology enabled him to write comedies and tragedies that are still studied today. In Spain, Miguel de Cervantes wrote one of the greatest literary works of all time, Don Quixote. 14
15 Golden Age of Literature (cont.) The story of Don Quixote elicits the idea that hard work and visionary dreams are requisite of the human condition. As in England, Spanish plays became very popular, and touring companies of actors brought current productions to all parts of the empire. Lope de Vega is the most famous Spanish playwright, writing nearly 1,500 plays that are considered witty, charming, realistic, and action-packed. Political Thought Hobbes and Locke wrote very different books about political thought in response to the English revolutions. Political Thought (cont.) Seventeenth-century political thinkers Thomas Hobbes and John Locke wrote about political power and influenced future philosophies of government. Thomas Hobbes wrote Leviathan to deal with the problem of disorder. Hobbes asserted that people made a social contract to form a state in exchange for protection and peace. Absolute power was needed to preserve order in society, and rebellions must be suppressed. 15
16 Political Thought (cont.) John Locke believed that man in his natural state enjoyed freedom and had certain natural rights. In Locke s Two Treatises of Government, Locke argued against the absolute rule of one person. He stated that the government and the people have mutual obligations to protect each other, and if the government usurps its power, then man has the right to abolish the government. Political Thought (cont.) Locke s ideas were used by American and French revolutionaries in the eighteenth century, and his influence can be found in the American Declaration of Independence and the U.S. Constitution. 16
17 RELIGIOUS CONFLICTS in Europe Religious conflicts between Protestants and Catholics were widespread. French kings persecuted Protestants. Philip II of Spain was a great supporter of militant Catholicism. The Thirty Years War was triggered by religious and political conflicts. POLITICAL, ECONOMIC, AND SOCIAL CRISES in Europe Civil war arose in England from power struggles between King Charles I and Parliament. English Protestant forces triumphed in the civil war and tried and executed King Charles I. Population growth, famine, and plague contributed to social tensions throughout Europe. The conflicts in seventeenth-century Europe were reflected in art, literature, and political works. ABSOLUTISM as a Response to Crises Frederick William of Prussia used the General War Commissariat to maintain his power. The Austrian monarchy tried but failed to achieve a centralized, absolutist state. The absolute rule of Louis XIV of France influenced monarchs throughout Europe. Russia emerged as a great power under the absolute rule of Peter the Great. 17
18 18
19 19
20 Chapter Transparencies Menu Chapter Transparency Unit Time Line Transparency Cause-and-Effect Transparency Select a transparency to view. 20
21 21
22 22
23 militant combative armada a fleet of warships conflict opposition; a fight, battle, or war 23
24 policy an overall plan embracing the general goals and acceptable procedures of a governmental body inflation a rapid increase in prices witchcraft magic 24
25 divine right of kings the belief that kings receive their power from God and are responsible only to God commonwealth a republic restoration a bringing back to a former position or condition 25
26 convert to change over from one belief to another absolutism a political system in which a ruler holds total power boyar a Russian noble 26
27 czar Russian for caesar, the title used by Russian emperors stability the state of being stable; strong enough to endure authority power; person in command 27
28 Mannerism an artistic movement that emerged in Italy in the 1520s and 1530s; it marked the end of the Renaissance by breaking down the principles of balance, harmony, and moderation natural rights rights with which all humans are born, including the rights to life, liberty, and property baroque an artistic style of the seventeenth century characterized by complex forms, bold ornamentation, and contrasting elements 28
29 drama a composition that tells a story usually involving conflicts and emotions through action and dialogue and typically designed for the theater creative imaginative To use this Presentation Plus! product: Click the Forward button to go to the next slide. Click the Previous button to return to the previous slide. Click the Home button to return to the Chapter Menu. Click the Transparency button from the Chapter Menu, Chapter Introduction slides, or Visual Summary slides to access the transparencies that are relevant to this chapter. From within a section, click on this button to access the relevant Daily Focus Skills Transparency. Click the Return button in a feature to return to the main presentation. Click the History Online button to access online textbook features. Click the Reference Atlas button to access the Interactive Reference Atlas. Click the Exit button or press the Escape key [Esc] to end the slide show. Click the Help button to access this screen. Links to Presentation Plus! features such as Maps in Motion, Graphs in Motion, Charts in Motion, Concepts in Motion, and figures from your textbook are located at the bottom of relevant screens. 29
30 This slide is intentionally blank. 30
I. Western Europe s Monarchs A. France and the Age of Absolutism 1. Henry IV (The first of the Bourbon line) a) Huguenot (Protestant) converts to
 I. Western Europe s Monarchs A. France and the Age of Absolutism 1. Henry IV (The first of the Bourbon line) a) Huguenot (Protestant) converts to Catholicism to unite country (1) Paris is well worth a
I. Western Europe s Monarchs A. France and the Age of Absolutism 1. Henry IV (The first of the Bourbon line) a) Huguenot (Protestant) converts to Catholicism to unite country (1) Paris is well worth a
ABSOLUTE RULERS EUROPE: S HELPFUL TO UNDERSTANDING OUR PRESENT WORLD
 ABSOLUTE RULERS EUROPE: 1500-1600 S HELPFUL TO UNDERSTANDING OUR PRESENT WORLD Questions to consider How did the Absolute Monarchs get their power? What might citizens gain from having an Absolute Monarch?
ABSOLUTE RULERS EUROPE: 1500-1600 S HELPFUL TO UNDERSTANDING OUR PRESENT WORLD Questions to consider How did the Absolute Monarchs get their power? What might citizens gain from having an Absolute Monarch?
The Age of Absolutism and Limited Government. Name: World History I Mr. Horas
 The Age of Absolutism and Limited Government Name: World History I Mr. Horas www.chshistory.net 1 World History I Mr. Horas Absolutism and Limited Government Reading #1 Reading #1: Europe in Crisis: The
The Age of Absolutism and Limited Government Name: World History I Mr. Horas www.chshistory.net 1 World History I Mr. Horas Absolutism and Limited Government Reading #1 Reading #1: Europe in Crisis: The
I. SPANISH POWER GROWS pg 504 A. Charles V* Inherits Two Crowns 1. Ruling the Hapsburg Empire* a. Charles=grandson of Ferdinand & Isabella b.
 I. SPANISH POWER GROWS pg 504 A. Charles V* Inherits Two Crowns 1. Ruling the Hapsburg Empire* a. Charles=grandson of Ferdinand & Isabella b.=ruler of Spain + Holy Roman Empire A Kingdom Too Spread Out
I. SPANISH POWER GROWS pg 504 A. Charles V* Inherits Two Crowns 1. Ruling the Hapsburg Empire* a. Charles=grandson of Ferdinand & Isabella b.=ruler of Spain + Holy Roman Empire A Kingdom Too Spread Out
Absolutism Test Review
 Absolutism Test Review 1. Spain- Philip II- son Charles V Religious persecution wars (1588) Rise and Decline of Spain Rise- Gold and Silver Decline- Fought wars, lost Navy to England, instead of investing
Absolutism Test Review 1. Spain- Philip II- son Charles V Religious persecution wars (1588) Rise and Decline of Spain Rise- Gold and Silver Decline- Fought wars, lost Navy to England, instead of investing
SOCIAL STUDIES SAMPLE
 Chapter 16 Terms to Look for in this Section: Age of Discovery Absolute Monarchs SOCIAL STUDIES SAMPLE What Have You Learned About World History So Far? Section 1: What Do You Remember About Early Civilizations?
Chapter 16 Terms to Look for in this Section: Age of Discovery Absolute Monarchs SOCIAL STUDIES SAMPLE What Have You Learned About World History So Far? Section 1: What Do You Remember About Early Civilizations?
AP Euro Free Response Questions
 AP Euro Free Response Questions Late Middle Ages to the Renaissance 2004 (#5): Analyze the influence of humanism on the visual arts in the Italian Renaissance. Use at least THREE specific works to support
AP Euro Free Response Questions Late Middle Ages to the Renaissance 2004 (#5): Analyze the influence of humanism on the visual arts in the Italian Renaissance. Use at least THREE specific works to support
Honors World History Harkness Seminars and Homework for Unit 4 Chapters 16 and and Documents
 Honors World History Harkness Seminars and Homework for Unit 4 Chapters 16 and 17- - 1 and 17- - - 2 + Documents Day of Presentation: Chapter- - Section Homework Guiding Questions: Define all key terms
Honors World History Harkness Seminars and Homework for Unit 4 Chapters 16 and 17- - 1 and 17- - - 2 + Documents Day of Presentation: Chapter- - Section Homework Guiding Questions: Define all key terms
Unit 4: Age of isms Rise of European Dominance
 Unit 4: 1450-1750 Age of isms Rise of European Dominance Renaissance the word renaissance means rebirth this is Europe s rebirth of culture and thought begins ~ 1400 in Italy, and spreads northward resurgence
Unit 4: 1450-1750 Age of isms Rise of European Dominance Renaissance the word renaissance means rebirth this is Europe s rebirth of culture and thought begins ~ 1400 in Italy, and spreads northward resurgence
9/17 Political and Religious Conflict: Introduction to Religious Wars of the 16 th and 17 th Century
 One Law, One King, One Faith: The Rise of Absolutism in Europe Guiding Questions: (Themes for LEQ prompts) What factors give rise to Absolutist governments and what challenges do they face in their attempts
One Law, One King, One Faith: The Rise of Absolutism in Europe Guiding Questions: (Themes for LEQ prompts) What factors give rise to Absolutist governments and what challenges do they face in their attempts
Absolutism Activity 1
 Absolutism Activity 1 Who is in the painting? What do you think is going on in the painting? Take note of the background. What is the message of the painting? For example, why did the author paint this?
Absolutism Activity 1 Who is in the painting? What do you think is going on in the painting? Take note of the background. What is the message of the painting? For example, why did the author paint this?
Britain vs. France by 1715
 Absolutism Britain vs. France by 1715 English Monarchy Limited monarchy Free trade Strong parliament Stable government down to the present Seeds of American Revolution French Monarchy Absolute monarchy
Absolutism Britain vs. France by 1715 English Monarchy Limited monarchy Free trade Strong parliament Stable government down to the present Seeds of American Revolution French Monarchy Absolute monarchy
Absolute Monarchs Activity
 Absolute Monarchs Activity Feudalism King Aristocracy Knights Serfs Medieval Monarchs Power Feudalism was the basis of European governments Kings maintained power & control through the support of their
Absolute Monarchs Activity Feudalism King Aristocracy Knights Serfs Medieval Monarchs Power Feudalism was the basis of European governments Kings maintained power & control through the support of their
(What would you buy if you won the lottery?) What will move Kings and Queens from Monarchy to Absolute Monarchy?
 Predictions Predict how the Empires in the Americas, Africa and Asia, built by Europeans rulers during the Age of Exploration, will affect Europe s monarchs. Predict what they might do with their increased
Predictions Predict how the Empires in the Americas, Africa and Asia, built by Europeans rulers during the Age of Exploration, will affect Europe s monarchs. Predict what they might do with their increased
Part Read about the regions of great Britain and Northern Ireland. Briefly describe its two regions:
 Social Studies 9 Unit 3 Worksheet Chapter 2, Part 1. 1. Democracy and have only been won after much. Many Canadian democratic traditions come originally from. The was signed in 1215 and recognized individual
Social Studies 9 Unit 3 Worksheet Chapter 2, Part 1. 1. Democracy and have only been won after much. Many Canadian democratic traditions come originally from. The was signed in 1215 and recognized individual
Absolutism and Enlightenment
 Absolutism and Enlightenment The Commercial Revolution Most of Europe remained agricultural between 1600-1770 The Commercial Revolution marked an important step in the transition from the local economies
Absolutism and Enlightenment The Commercial Revolution Most of Europe remained agricultural between 1600-1770 The Commercial Revolution marked an important step in the transition from the local economies
Notes: Chapter 13 The Old Regime: Absolutism and Enlightenment
 Name Notes: Chapter 13 The Old Regime: Absolutism and Enlightenment Introduction In this chapter, you will learn about important changes that took place in Europe between. The Old Regime refers to Europe
Name Notes: Chapter 13 The Old Regime: Absolutism and Enlightenment Introduction In this chapter, you will learn about important changes that took place in Europe between. The Old Regime refers to Europe
STANDARD WHII.6e The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth,
 STANDARD WHII.6e The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth, and eighteenth centuries by e) describing the French
STANDARD WHII.6e The student will demonstrate knowledge of scientific, political, economic, and religious changes during the sixteenth, seventeenth, and eighteenth centuries by e) describing the French
Vocabulary Ch
 Vocabulary Ch 17-1818 Absolute monarch Divine right Armada Intendant Balance of Power Dissenter Habeas corpus Limited monarchy Elector Mercenary Depopulation Westernization Boyar Warm-water port Natural
Vocabulary Ch 17-1818 Absolute monarch Divine right Armada Intendant Balance of Power Dissenter Habeas corpus Limited monarchy Elector Mercenary Depopulation Westernization Boyar Warm-water port Natural
Absolute, Catholic, Wars and bad economic decisions
 Absolute, Catholic, Wars and bad economic decisions Palace of Versailles / new power and status From Tudors to Stuarts To Parliament or not to Parliament Cavaliers / Roundheads Oliver Cromwell and theocracy
Absolute, Catholic, Wars and bad economic decisions Palace of Versailles / new power and status From Tudors to Stuarts To Parliament or not to Parliament Cavaliers / Roundheads Oliver Cromwell and theocracy
The History of the Huguenots. Western Civilization II Marshall High School Mr. Cline Unit ThreeDA
 The History of the Huguenots Western Civilization II Marshall High School Mr. Cline Unit ThreeDA Reformation Comes to France When the Reformation came to France, its message spread quickly. By 1534, there
The History of the Huguenots Western Civilization II Marshall High School Mr. Cline Unit ThreeDA Reformation Comes to France When the Reformation came to France, its message spread quickly. By 1534, there
Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman Perspectives
 STANDARD 10.1.1 Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman Perspectives Specific Objective: Analyze the similarities and differences in Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman views of law, reason and faith, and duties of
STANDARD 10.1.1 Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman Perspectives Specific Objective: Analyze the similarities and differences in Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman views of law, reason and faith, and duties of
How did the basic structure of society in eastern Europe become different from that of western Europe in the early modern period? How and why did the
 How did the basic structure of society in eastern Europe become different from that of western Europe in the early modern period? How and why did the rulers of Austria, Prussia, and Russia manage to build
How did the basic structure of society in eastern Europe become different from that of western Europe in the early modern period? How and why did the rulers of Austria, Prussia, and Russia manage to build
Unit 5 Chapter Test. World History: Patterns of Interaction Grade 10 McDougal Littell NAME. Main Ideas Choose the letter of the best answer.
 World History: Patterns of Interaction Grade 10 McDougal Littell NAME Unit 5 Chapter Test Main Ideas 1) What was the significance of the English Bill of Rights? (a) It established the group of government
World History: Patterns of Interaction Grade 10 McDougal Littell NAME Unit 5 Chapter Test Main Ideas 1) What was the significance of the English Bill of Rights? (a) It established the group of government
Ch. 6.3 Radical Period of the French Revolution. leader of the Committee of Public Safety; chief architect of the Reign of Terror
 the right to vote Ch. 6.3 Radical Period of the French Revolution leader of the Committee of Public Safety; chief architect of the Reign of Terror period from September 1793 to July 1794 when those who
the right to vote Ch. 6.3 Radical Period of the French Revolution leader of the Committee of Public Safety; chief architect of the Reign of Terror period from September 1793 to July 1794 when those who
World History I (Master) Content Skills Learning Targets Assessment Resources & Technology CEQ: features of early. civilizations.
 St. Michael Albertville High School Teacher: Derek Johnson World History I (Master) September 2014 Content Skills Learning Targets Assessment Resources & Technology CEQ: Early Civilizations 1. I can explain
St. Michael Albertville High School Teacher: Derek Johnson World History I (Master) September 2014 Content Skills Learning Targets Assessment Resources & Technology CEQ: Early Civilizations 1. I can explain
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Chapter 12, Section 2 For use with textbook pages 371 376 REACTION AND REVOLUTION KEY TERMS conservatism a political philosophy based on tradition and social stability (page 372) principle of intervention
Chapter 12, Section 2 For use with textbook pages 371 376 REACTION AND REVOLUTION KEY TERMS conservatism a political philosophy based on tradition and social stability (page 372) principle of intervention
SSWH14: ANALYZE THE AGE OF REVOLUTIONS ELEMENT A: EXAMINE ABSOLUTISM THROUGH A COMPARISON OF THE REIGNS OF LOUIS XIV & TSAR PETER THE GREAT.
 SSWH14: ANALYZE THE AGE OF REVOLUTIONS ELEMENT A: EXAMINE ABSOLUTISM THROUGH A COMPARISON OF THE REIGNS OF LOUIS XIV & TSAR PETER THE GREAT. LOUIS XIV v Medieval European feudalism had placed the majority
SSWH14: ANALYZE THE AGE OF REVOLUTIONS ELEMENT A: EXAMINE ABSOLUTISM THROUGH A COMPARISON OF THE REIGNS OF LOUIS XIV & TSAR PETER THE GREAT. LOUIS XIV v Medieval European feudalism had placed the majority
Name Class Date. The French Revolution and Napoleon Section 3
 Name Class Date Section 3 MAIN IDEA Napoleon Bonaparte rose through military ranks to become emperor over France and much of Europe. Key Terms and People Napoleon Bonaparte ambitious military leader who
Name Class Date Section 3 MAIN IDEA Napoleon Bonaparte rose through military ranks to become emperor over France and much of Europe. Key Terms and People Napoleon Bonaparte ambitious military leader who
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions.
 SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. EQ: What is characteristics
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. EQ: What is characteristics
CHAPTER 13 THE OLD REGIME: ABSOLUTISM AND ENLIGHTENMENT
 CHAPTER 13 THE OLD REGIME: ABSOLUTISM AND ENLIGHTENMENT INTRODUCTION In this chapter, you will learn about important changes that took place in Old Regime Europe between 1600 and 1770. The Old Regime refers
CHAPTER 13 THE OLD REGIME: ABSOLUTISM AND ENLIGHTENMENT INTRODUCTION In this chapter, you will learn about important changes that took place in Old Regime Europe between 1600 and 1770. The Old Regime refers
Elizabeth I. Though the sex to which I belong is considered weak, you will nevertheless find me a rock that bends to no wind. - Queen Elizabeth I
 King Louis XIV L etat, c est moi, I am the state, said King Louis XIV of France. Louis believed that he was the only one responsible for governing France when he ruled from 1643 to 1715. A tutor to his
King Louis XIV L etat, c est moi, I am the state, said King Louis XIV of France. Louis believed that he was the only one responsible for governing France when he ruled from 1643 to 1715. A tutor to his
Causes of the French Revolu2on
 1789-1815 Causes of the French Revolu2on Social and economic injustices American Revolution Economic troubles High taxes and bread prices, debt, crop failures in the 1780s A weak, inept leadership Old
1789-1815 Causes of the French Revolu2on Social and economic injustices American Revolution Economic troubles High taxes and bread prices, debt, crop failures in the 1780s A weak, inept leadership Old
The Enlightenment and the scientific revolution changed people s concepts of the universe and their place within it Enlightenment ideas affected
 The Enlightenment and the scientific revolution changed people s concepts of the universe and their place within it Enlightenment ideas affected politics, music, art, architecture, and literature of Europe
The Enlightenment and the scientific revolution changed people s concepts of the universe and their place within it Enlightenment ideas affected politics, music, art, architecture, and literature of Europe
AP Euro: Past Free Response Questions
 AP Euro: Past Free Response Questions 1. To what extent is the term "Renaissance" a valid concept for s distinct period in early modern European history? 2. Explain the ways in which Italian Renaissance
AP Euro: Past Free Response Questions 1. To what extent is the term "Renaissance" a valid concept for s distinct period in early modern European history? 2. Explain the ways in which Italian Renaissance
1. Topic 3 Lesson 1 Interactive Reading Notepad. 2. Topic 3 Lesson 1 Quiz. 3. Topic 3 Lesson 2 Interactive Reading Notepad. 4. Topic 3 Lesson 2 Quiz
 Topic 3: Absolutism and Revolution Assignments to do: 1. Topic 3 Lesson 1 Interactive Reading Notepad 2. Topic 3 Lesson 1 Quiz 3. Topic 3 Lesson 2 Interactive Reading Notepad 4. Topic 3 Lesson 2 Quiz 5.
Topic 3: Absolutism and Revolution Assignments to do: 1. Topic 3 Lesson 1 Interactive Reading Notepad 2. Topic 3 Lesson 1 Quiz 3. Topic 3 Lesson 2 Interactive Reading Notepad 4. Topic 3 Lesson 2 Quiz 5.
Ancient World Timelines World History Through the Renaissance Middle Ages Timelines Before the Renaissance Empires in Africa such as Ghana, Mali, and
 Ancient World Timelines World History Through the Renaissance Middle Ages Timelines Empires in Africa such as Ghana, Mali, and Songhai came to power. Muhammad was told by the angel Gabriel to be a prophet
Ancient World Timelines World History Through the Renaissance Middle Ages Timelines Empires in Africa such as Ghana, Mali, and Songhai came to power. Muhammad was told by the angel Gabriel to be a prophet
The French Revolution and Napoleon,
 The French Revolution and Napoleon, 1789 1815 Why was it so hard for the French to establish a republic than it was for the Americans? How was Napoleon able to take power twice? The French Revolution and
The French Revolution and Napoleon, 1789 1815 Why was it so hard for the French to establish a republic than it was for the Americans? How was Napoleon able to take power twice? The French Revolution and
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. The Age of Napoleon
 The Age of Napoleon Objectives Understand Napoleon s rise to power and why the French strongly supported him. Explain how Napoleon built an empire and what challenges the empire faced. Analyze the events
The Age of Napoleon Objectives Understand Napoleon s rise to power and why the French strongly supported him. Explain how Napoleon built an empire and what challenges the empire faced. Analyze the events
John Locke Natural Rights- Life, Liberty, and Property Two Treaties of Government
 Enlightenment Enlightenment 1500s Enlightenment was the idea that man could use logic and reason to solve the social problems of the day. Philosophers spread this idea of logic and reason to the people
Enlightenment Enlightenment 1500s Enlightenment was the idea that man could use logic and reason to solve the social problems of the day. Philosophers spread this idea of logic and reason to the people
The French Revolution and Napoleon, The French Revolution and Napoleon, The French Revolution Begins.
 The French Revolution and Napoleon, 789 8 The French Revolution establishes a new political order, Napoleon Bonaparte gains and loses an empire, and European states forge a balance of power. The French
The French Revolution and Napoleon, 789 8 The French Revolution establishes a new political order, Napoleon Bonaparte gains and loses an empire, and European states forge a balance of power. The French
The French Revolution and Napoleon. ( ) Chapter 11
 The French Revolution and Napoleon (1789-1815) Chapter 11 Main Ideas Social inequality & economic problems contributed to the French Revolution Radical groups controlled the Revolution Revolution allowed
The French Revolution and Napoleon (1789-1815) Chapter 11 Main Ideas Social inequality & economic problems contributed to the French Revolution Radical groups controlled the Revolution Revolution allowed
Essential Question Section 1: The Colonial Period Section 2: Uniting for Independence Section 3: The Articles of Confederation Section 4: The
 Essential Question Section 1: The Colonial Period Section 2: Uniting for Independence Section 3: The Articles of Confederation Section 4: The Constitutional Convention Chapter Summary Content Vocabulary
Essential Question Section 1: The Colonial Period Section 2: Uniting for Independence Section 3: The Articles of Confederation Section 4: The Constitutional Convention Chapter Summary Content Vocabulary
Eastern European and Russian Absolutism. Ivan IV Ivan the Terrible ( )
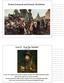 Eastern European and Russian Absolutism Ivan IV Ivan the Terrible (1547-1584) became Tsar at age of 3 and watched rival groups of nobles who sought to control the country when he took charge, he saw treason
Eastern European and Russian Absolutism Ivan IV Ivan the Terrible (1547-1584) became Tsar at age of 3 and watched rival groups of nobles who sought to control the country when he took charge, he saw treason
French Revolution. II. Louis XVI A. Supported the American Revolution 1. This caused hardship on the economy
 1 French Revolution I. 3 estates A. 1 st estate 1. Clergy 5-10% of the land B. 2 nd estate 1. Nobles 25% of the land C. 3 rd estate 1. Peasants 40-60% of the land 2. Artisans 3. Bourgeoisie (Middle Class)
1 French Revolution I. 3 estates A. 1 st estate 1. Clergy 5-10% of the land B. 2 nd estate 1. Nobles 25% of the land C. 3 rd estate 1. Peasants 40-60% of the land 2. Artisans 3. Bourgeoisie (Middle Class)
CAUSES OF THE FRENCH REVOLUTION
 REVOLUTIONS CAUSES OF THE FRENCH REVOLUTION During the reign of Louis XIV. A political system known as the Old Regime Divided France into 3 social classes- Estates First Estate Catholic clergy own 10 percent
REVOLUTIONS CAUSES OF THE FRENCH REVOLUTION During the reign of Louis XIV. A political system known as the Old Regime Divided France into 3 social classes- Estates First Estate Catholic clergy own 10 percent
(3) parliamentary democracy (2) ethnic rivalries
 1) In the Soviet Union, Joseph Stalin governed by means of secret police, censorship, and purges. This type of government is called (1) democracy (2) totalitarian 2) The Ancient Athenians are credited
1) In the Soviet Union, Joseph Stalin governed by means of secret police, censorship, and purges. This type of government is called (1) democracy (2) totalitarian 2) The Ancient Athenians are credited
Eastern Absolutism Serfdom In the west peasants gained rights as a labor shortage swept eastern Europe workers became a necessity In eastern Europe
 Eastern Absolutism Serfdom In the west peasants gained rights as a labor shortage swept eastern Europe workers became a necessity In eastern Europe during the seventeenth century the rights of the peasants
Eastern Absolutism Serfdom In the west peasants gained rights as a labor shortage swept eastern Europe workers became a necessity In eastern Europe during the seventeenth century the rights of the peasants
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 3 The Rise of Napoleon and the Napoleonic Wars ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What causes revolution? How does revolution change society? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary capable having or showing ability
Lesson 3 The Rise of Napoleon and the Napoleonic Wars ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What causes revolution? How does revolution change society? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary capable having or showing ability
EUROPEAN HISTORY. 5. The Enlightenment. Form 3
 EUROPEAN HISTORY 5. The Enlightenment Form 3 Europe at the time of the Enlightenment and on the eve of the French Revolution 1 Unit 5.1 - The Origins of the Enlightenment Source A: Philosophers debating
EUROPEAN HISTORY 5. The Enlightenment Form 3 Europe at the time of the Enlightenment and on the eve of the French Revolution 1 Unit 5.1 - The Origins of the Enlightenment Source A: Philosophers debating
Pre-Enlightenment Europe. Unit 3: Revolution
 Pre-Enlightenment Europe Unit 3: Revolution Central Questions In order to understand the significance of the Enlightenment, we need to answer the following: What was European society like prior to the
Pre-Enlightenment Europe Unit 3: Revolution Central Questions In order to understand the significance of the Enlightenment, we need to answer the following: What was European society like prior to the
LESSON OBJECTIVE(S) 1.) DEFINE the Enlightenment. 2.) EXPLAIN the development of the English Enlightenment
 NAME: - WORLD HISTORY II UNIT TWO: AN AGE OF REASON LESSON 8 CW & HW BLOCK: - CENTRAL HISTORICAL QUESTION - WHAT CAUSED THE ENGLISH ENLIGHTENMENT? PICTURED BELOW: 768 oil-on-canvas painting by Joseph Wright
NAME: - WORLD HISTORY II UNIT TWO: AN AGE OF REASON LESSON 8 CW & HW BLOCK: - CENTRAL HISTORICAL QUESTION - WHAT CAUSED THE ENGLISH ENLIGHTENMENT? PICTURED BELOW: 768 oil-on-canvas painting by Joseph Wright
The French Revolution establishes a new political order, Napoleon Bonaparte gains and loses an empire, and European states forge a balance of power.
 SLIDE 1 Chapter 23 The French Revolution and Napoleon, 1789 1815 The French Revolution establishes a new political order, Napoleon Bonaparte gains and loses an empire, and European states forge a balance
SLIDE 1 Chapter 23 The French Revolution and Napoleon, 1789 1815 The French Revolution establishes a new political order, Napoleon Bonaparte gains and loses an empire, and European states forge a balance
AP European History Outline Period 2,
 AP European History Outline Period 2, 1648-1815 Key Concept 1. Different models of political sovereignty affected the relationship among states and between states and individuals. 1. In much of Europe,
AP European History Outline Period 2, 1648-1815 Key Concept 1. Different models of political sovereignty affected the relationship among states and between states and individuals. 1. In much of Europe,
The French Revolution Absolutism monarchs didn t share power with a counsel or parliament--
 The French Revolution Absolutism monarchs didn t share power with a counsel or parliament-- The Seigneurial System method of land ownership and organization Peasant labor Louis XIV Ruled from 1643 1715
The French Revolution Absolutism monarchs didn t share power with a counsel or parliament-- The Seigneurial System method of land ownership and organization Peasant labor Louis XIV Ruled from 1643 1715
French Revolution 1789 and Age of Napoleon. Background to Revolution. American Revolution
 French Revolution 1789 and Age of Napoleon Background to Revolution Scientific Revolution and Enlightenment Enlightenment validated human beings ability to think for themselves and govern themselves. Rousseau
French Revolution 1789 and Age of Napoleon Background to Revolution Scientific Revolution and Enlightenment Enlightenment validated human beings ability to think for themselves and govern themselves. Rousseau
AP European History Chapter 16 Notes v Two models of European political development in the 17 th century Ø Political absolutism strong centralized
 AP European History Chapter 16 Notes v Two models of European political development in the 17 th century Ø Political absolutism strong centralized monarchies where the royal power is dominant Ø Parliamentary
AP European History Chapter 16 Notes v Two models of European political development in the 17 th century Ø Political absolutism strong centralized monarchies where the royal power is dominant Ø Parliamentary
An Unequal French Society. Reading #1: The French Revolution (Page ) Topic: Long term problems: Inequality in France
 Reading #1: Problem (Old Regime) Phase Experiencing World History An Unequal French Society Reading #1: The French Revolution (Page 476 478) Topic: Long term problems: Inequality in France 1. Who made
Reading #1: Problem (Old Regime) Phase Experiencing World History An Unequal French Society Reading #1: The French Revolution (Page 476 478) Topic: Long term problems: Inequality in France 1. Who made
Essential Question: What were the important causes & effects of the French Revolution?
 Essential Question: What were the important causes & effects of the French Revolution? Do Now On your ipad or blank piece of paper write down one example on what is needed to consider a revolution as successful.
Essential Question: What were the important causes & effects of the French Revolution? Do Now On your ipad or blank piece of paper write down one example on what is needed to consider a revolution as successful.
The French Revolution A Concise Overview
 The French Revolution A Concise Overview The Philosophy of the Enlightenment and the success of the American Revolution were causing unrest within France. People were taxed heavily and had little or no
The French Revolution A Concise Overview The Philosophy of the Enlightenment and the success of the American Revolution were causing unrest within France. People were taxed heavily and had little or no
ECON Financial History John Lovett
 Study Questions for Neal, Larry (2000). How it all began: the monetary and financial architecture of Europe during the first global financial capital markets. Financial History Review. 117-140. 1. When
Study Questions for Neal, Larry (2000). How it all began: the monetary and financial architecture of Europe during the first global financial capital markets. Financial History Review. 117-140. 1. When
Background Information
 Background Information 1791 The seating of these representatives gives us our modern political terms of Right Wing or Left Wing Legislative Assembly rules France Members with similar political views sat
Background Information 1791 The seating of these representatives gives us our modern political terms of Right Wing or Left Wing Legislative Assembly rules France Members with similar political views sat
From 1789 to 1804, France experienced revolutionary changes that transformed France from an absolute monarchy to a republic to an empire
 From 1789 to 1804, France experienced revolutionary changes that transformed France from an absolute monarchy to a republic to an empire The success of the American Revolution & Enlightenment ideas such
From 1789 to 1804, France experienced revolutionary changes that transformed France from an absolute monarchy to a republic to an empire The success of the American Revolution & Enlightenment ideas such
Chapter 16: Attempts at Liberty
 Chapter 16: Attempts at Liberty 18 th Century Few people enjoyed such rights as, and the pursuit of ; and absolutism was the order of the day. The desire for personal and political liberty prompted a series
Chapter 16: Attempts at Liberty 18 th Century Few people enjoyed such rights as, and the pursuit of ; and absolutism was the order of the day. The desire for personal and political liberty prompted a series
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 4 The Fall of Napoleon and the European Reaction ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What causes revolution? How does revolution change society? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary civil involving the general
Lesson 4 The Fall of Napoleon and the European Reaction ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS What causes revolution? How does revolution change society? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary civil involving the general
Enlightenment with answers Which statement represents a key idea directly associated with John Locke s Two Treatises of
 Enlightenment with answers 1. 2 Supported reforms Believed in natural rights and religious toleration Viewed themselves as servants of their state In the 18th century, European leaders that fit these characteristics
Enlightenment with answers 1. 2 Supported reforms Believed in natural rights and religious toleration Viewed themselves as servants of their state In the 18th century, European leaders that fit these characteristics
World History Alpha Lenze Final Exam Study Guide. Answer the questions as best you can include Who, What, When, Where, Why, How and So What.
 World History Alpha Lenze 2013-14 Final Exam Study Guide Answer the questions as best you can include Who, What, When, Where, Why, How and So What. 1. What was a result of the Treaty of Verdun in 843?
World History Alpha Lenze 2013-14 Final Exam Study Guide Answer the questions as best you can include Who, What, When, Where, Why, How and So What. 1. What was a result of the Treaty of Verdun in 843?
History (Exam Board: AQA) Linear September 2016
 History (Exam Board: AQA) Linear September 2016 Subject Leader: Miss E. Dickey What do I need? This course does not require a GCSE in history. If you have studied History at GCSE, you should have achieved
History (Exam Board: AQA) Linear September 2016 Subject Leader: Miss E. Dickey What do I need? This course does not require a GCSE in history. If you have studied History at GCSE, you should have achieved
The French Revolution THE EUROPEAN MOMENT ( )
 The French Revolution THE EUROPEAN MOMENT (1750 1900) Quick Video 1 The French Revolution In a Nutshell Below is a YouTube link to a very short, but very helpful introduction to the French Revolution.
The French Revolution THE EUROPEAN MOMENT (1750 1900) Quick Video 1 The French Revolution In a Nutshell Below is a YouTube link to a very short, but very helpful introduction to the French Revolution.
AP European History. -Russian politics and the liberalist movement -parallel developments in. Thursday, August 21, 2003 Page 1 of 21
 Instructional Unit Consolidation of Large Nation States -concept of a nation-state The students will be -define the concept of a -class discussion 8.1.2.A,B,C,D -Mazzini, Garibaldi and Cavour able to define
Instructional Unit Consolidation of Large Nation States -concept of a nation-state The students will be -define the concept of a -class discussion 8.1.2.A,B,C,D -Mazzini, Garibaldi and Cavour able to define
Wars of the 18 th Century
 Wars of the 18 th Century Major Conflicts 1. War of Spanish Succession (1701-1714) Ends with the Treaty of Utrecht 2. War of Austrian Succession (1740-1748) Ends with the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle 3. Seven
Wars of the 18 th Century Major Conflicts 1. War of Spanish Succession (1701-1714) Ends with the Treaty of Utrecht 2. War of Austrian Succession (1740-1748) Ends with the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle 3. Seven
Chapter 23. The Transformation of Europe. 2011, The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All Rights Reserved.
 Chapter 23 The Transformation of Europe 1 The Protestant Reformation n Martin Luther (1483-1546) attacks Roman Catholic church practices, 1517 q Indulgences: preferential pardons for charitable donors
Chapter 23 The Transformation of Europe 1 The Protestant Reformation n Martin Luther (1483-1546) attacks Roman Catholic church practices, 1517 q Indulgences: preferential pardons for charitable donors
A. True or False Where the statement is true, mark T. Where it is false, mark F, and correct it in the space immediately below.
 AP European History Mr. Mercado (Rev. 09) Chapter 23 Ideologies and Upheavals, 1815-1850 Name A. True or False Where the statement is true, mark T. Where it is false, mark F, and correct it in the space
AP European History Mr. Mercado (Rev. 09) Chapter 23 Ideologies and Upheavals, 1815-1850 Name A. True or False Where the statement is true, mark T. Where it is false, mark F, and correct it in the space
Nationalism movement wanted to: UNIFICATION: peoples of common culture from different states were joined together
 7-3.2 Analyze the effects of the Napoleonic Wars on the development and spread of nationalism in Europe, including the Congress of Vienna, the revolutionary movements of 1830 and 1848, and the unification
7-3.2 Analyze the effects of the Napoleonic Wars on the development and spread of nationalism in Europe, including the Congress of Vienna, the revolutionary movements of 1830 and 1848, and the unification
World Civilizations. The Global Experience. Chapter. The Rise of Russia. AP Seventh Edition
 World Civilizations The Global Experience AP Seventh Edition Chapter 21 The Rise of Russia Figure 21.1 Early Russian tsar Ivan V, 1682 1696. Ivan was actually sickly and ineffective and soon gave way to
World Civilizations The Global Experience AP Seventh Edition Chapter 21 The Rise of Russia Figure 21.1 Early Russian tsar Ivan V, 1682 1696. Ivan was actually sickly and ineffective and soon gave way to
THE AGE OF ENLIGHTENMENT. Time of Great Change in Thought
 THE AGE OF ENLIGHTENMENT Time of Great Change in Thought 1 OBJECTIVES Students will examine ideas of natural law in the Age of Reason Students will describe how the Enlightenment affected the arts and
THE AGE OF ENLIGHTENMENT Time of Great Change in Thought 1 OBJECTIVES Students will examine ideas of natural law in the Age of Reason Students will describe how the Enlightenment affected the arts and
Paris, France, the heart of the Enlightenment, drew many intellectuals and others eager to debate new ideas.
 Enlightenment Ideas Spread Paris, France, the heart of the Enlightenment, drew many intellectuals and others eager to debate new ideas. Enlightenment ideas flowed from France, across Europe, and beyond.
Enlightenment Ideas Spread Paris, France, the heart of the Enlightenment, drew many intellectuals and others eager to debate new ideas. Enlightenment ideas flowed from France, across Europe, and beyond.
Chapter 23 Test- The French Revolution & Napoleon
 Name Date Period Chapter 23 Test- The French Revolution & Napoleon Part 1- Main Ideas Write the letter of the best answer (2 points each) 1. What is the name of the social and political system in France
Name Date Period Chapter 23 Test- The French Revolution & Napoleon Part 1- Main Ideas Write the letter of the best answer (2 points each) 1. What is the name of the social and political system in France
The Enlightenment and the American Revolution. Philosophy in the Age of Reason
 The Enlightenment and the American Revolution Philosophy in the Age of Reason The Enlightenment and the American Revolution A. By the early 1700s, European thinkers ( was out of reach for the human mind.
The Enlightenment and the American Revolution Philosophy in the Age of Reason The Enlightenment and the American Revolution A. By the early 1700s, European thinkers ( was out of reach for the human mind.
The French Revolution and Napoleon Section 4. Napoleon s Fall
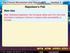 Main Idea Napoleon s Fall After defeating Napoleon, the European allies sent him into exile and held a meeting in Vienna to restore order and stability to Europe. 1) Disaster and Defeat /The Russian Campaign
Main Idea Napoleon s Fall After defeating Napoleon, the European allies sent him into exile and held a meeting in Vienna to restore order and stability to Europe. 1) Disaster and Defeat /The Russian Campaign
Unit 2: Age of Revolutions Review. 1st Semester Final Exam Review
 Unit 2: Age of Revolutions Review 1st Semester Final Exam Review The Enlightenment The Enlightenment was an age of reason in which philosophes shared ideas about reason, government, and human nature. Major
Unit 2: Age of Revolutions Review 1st Semester Final Exam Review The Enlightenment The Enlightenment was an age of reason in which philosophes shared ideas about reason, government, and human nature. Major
The French Revolution
 The French Revolution The Old Regime or Old Order France was ruled by Louis XVI and his wife Queen Marie Antoinette France was an advanced and prosperous nation Beneath this was unrest caused by bad harvests,
The French Revolution The Old Regime or Old Order France was ruled by Louis XVI and his wife Queen Marie Antoinette France was an advanced and prosperous nation Beneath this was unrest caused by bad harvests,
Absolutism Concept Formation
 Absolutism Concept Formation You will be participating in a concept formation lesson designed to teach you the understanding of absolutism. You will uncover the critical attributes of absolutism by reading
Absolutism Concept Formation You will be participating in a concept formation lesson designed to teach you the understanding of absolutism. You will uncover the critical attributes of absolutism by reading
The Old Regime. The Old Regime The Traditional, Political and Social System of France People were Divided into Social Classes called Estates
 (1789-1815) The Old Regime The Old Regime The Traditional, Political and Social System of France People were Divided into Social Classes called Estates Estate Population Land 1 st - Clergy 0.5% 10% 2 nd
(1789-1815) The Old Regime The Old Regime The Traditional, Political and Social System of France People were Divided into Social Classes called Estates Estate Population Land 1 st - Clergy 0.5% 10% 2 nd
PETERS TOWNSHIP HIGH SCHOOL
 PETERS TOWNSHIP HIGH SCHOOL COURSE SYLLABUS: ACADEMIC HISTORY OF WESTERN CIVILIZATION Course Overview and Essential Skills The purpose of this overview course is to provide students with an understanding
PETERS TOWNSHIP HIGH SCHOOL COURSE SYLLABUS: ACADEMIC HISTORY OF WESTERN CIVILIZATION Course Overview and Essential Skills The purpose of this overview course is to provide students with an understanding
French Revolution. Revolution in France (Cause) Estates (Cont) 1/23/ s Feudalist Government. 1 st & 2 nd Estate are Privileged
 French Revolution 1789-1815 Revolution in France (Cause) 1770s Feudalist Government System of the wealthy in power Poor works the land in return for food & protection 3 Estates (Classes of People) 1 st
French Revolution 1789-1815 Revolution in France (Cause) 1770s Feudalist Government System of the wealthy in power Poor works the land in return for food & protection 3 Estates (Classes of People) 1 st
CHAPTER SEVENTEEN The Transformation of the West:
 CHAPTER SEVENTEEN The Transformation of the West: 1450-1750 World Civilizations, The Global Experience AP* Edition, 5th Edition Stearns/Adas/Schwartz/Gilbert *AP and Advanced Placement are registered trademarks
CHAPTER SEVENTEEN The Transformation of the West: 1450-1750 World Civilizations, The Global Experience AP* Edition, 5th Edition Stearns/Adas/Schwartz/Gilbert *AP and Advanced Placement are registered trademarks
SAUCY KINGS, SIMMERING TENSIONS REVOLUTION IN ENGLAND
 REVOLUTION IN ENGLAND CRANE BRINTON S ANATOMY OF A REVOLUTION Brinton s Thesis: Revolutions follow a pattern encompassed by five distinct phases, which usually occur in sequential order CRANE BRINTON S
REVOLUTION IN ENGLAND CRANE BRINTON S ANATOMY OF A REVOLUTION Brinton s Thesis: Revolutions follow a pattern encompassed by five distinct phases, which usually occur in sequential order CRANE BRINTON S
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions.
 SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. Known as the Sun
SSWH14 The student will analyze the Age of Revolutions and Rebellions. a. Examine absolutism through a comparison of the rules of Louis XIV, Tsar Peter the Great, and Tokugawa Ieyasu. Known as the Sun
Chapter Introduction Section 1: Section 2: Section 3: Visual Summary
 Chapter Introduction Section 1: The French Revolution Begins Section 2: Radical Revolution and Reaction Section 3: The Age of Napoleon Visual Summary 1 What makes a nation? The Arc de Triomphe is one of
Chapter Introduction Section 1: The French Revolution Begins Section 2: Radical Revolution and Reaction Section 3: The Age of Napoleon Visual Summary 1 What makes a nation? The Arc de Triomphe is one of
1. Explain how science led to the Enlightenment. 2. Compare the ideas of Hobbes and Locke.
 Introduction to the Enlightenment 1. Explain how science led to the Enlightenment. 2. Compare the ideas of Hobbes and Locke. 3. Identify the beliefs and contributions of the philosophes. 4. Summarize how
Introduction to the Enlightenment 1. Explain how science led to the Enlightenment. 2. Compare the ideas of Hobbes and Locke. 3. Identify the beliefs and contributions of the philosophes. 4. Summarize how
Exam 3 - Fall 2014 Code Name:
 Exam 3 - Fall 2014 Code Name: Part 1: The details (70.5 points. Each question is worth 2 pts each unless noted.) # s 1 4: You are transported to the alien world of Gerbilstan. The inhabitants, intelligent
Exam 3 - Fall 2014 Code Name: Part 1: The details (70.5 points. Each question is worth 2 pts each unless noted.) # s 1 4: You are transported to the alien world of Gerbilstan. The inhabitants, intelligent
Enlightened Absolutism. Prussian, Russian, and Austrian Politics in the Enlightenment
 Enlightened Absolutism Prussian, Russian, and Austrian Politics in the Enlightenment Politics Before Enlightenment Absolutism: traditional assumption of power (hereditary throne) and belief in divine right
Enlightened Absolutism Prussian, Russian, and Austrian Politics in the Enlightenment Politics Before Enlightenment Absolutism: traditional assumption of power (hereditary throne) and belief in divine right
Previous AP FRQ Questions by Unit. Unit II: Chapter 14-Renaissance Europe, ( ) AP FRQ Essays: Other Potential Essays:
 Previous AP FRQ Questions by Unit Unit II: Chapter 14-Renaissance Europe, 1400-1500 (505-544) Analyze the influence of humanism on the visual arts in the Italian Renaissance. Use at least THREE specific
Previous AP FRQ Questions by Unit Unit II: Chapter 14-Renaissance Europe, 1400-1500 (505-544) Analyze the influence of humanism on the visual arts in the Italian Renaissance. Use at least THREE specific
Teddington School Sixth Form
 Teddington School Sixth Form A-Level AQA Advanced GCE in History Key Course Materials September 2018 Advanced Level History Exam Board - AQA Course Title / Size & Structure /Summary Purpose Pearson Edexcel
Teddington School Sixth Form A-Level AQA Advanced GCE in History Key Course Materials September 2018 Advanced Level History Exam Board - AQA Course Title / Size & Structure /Summary Purpose Pearson Edexcel
Unit 5, SSWH 14 b Parliament & the English Monarchy
 Unit 5, SSWH 14 b Parliament & the English Monarchy What effect did the Age of Revolution have on Global Society? SSWH 14 b Identify the causes and results of the revolutions in England (1689), United
Unit 5, SSWH 14 b Parliament & the English Monarchy What effect did the Age of Revolution have on Global Society? SSWH 14 b Identify the causes and results of the revolutions in England (1689), United
ERA 7 - Revolutions & Empire
 ERA 7 - Revolutions & Empire ERA 7 Exam Jeopardy Review Game The Age of Absolutism Enlightenment & Revolutions The Industrial Revolution Economic Systems The Age of Imperialism $100 $200 $300 $400 $500
ERA 7 - Revolutions & Empire ERA 7 Exam Jeopardy Review Game The Age of Absolutism Enlightenment & Revolutions The Industrial Revolution Economic Systems The Age of Imperialism $100 $200 $300 $400 $500
Chapter 19. The French Revolution
 Chapter 19 The French Revolution Old/Ancien Regime First Estate - Clergy Second Estate - Nobility Third Estate - Everyone else - Traditionally the peasantry, but by now had come to include merchants and
Chapter 19 The French Revolution Old/Ancien Regime First Estate - Clergy Second Estate - Nobility Third Estate - Everyone else - Traditionally the peasantry, but by now had come to include merchants and
Warm-Up: Read the following document and answer the comprehension questions below.
 Lowenhaupt 1 Enlightenment Objective: What were some major ideas to come out of the Enlightenment? How did the thinkers of the Enlightenment change or impact society? Warm-Up: Read the following document
Lowenhaupt 1 Enlightenment Objective: What were some major ideas to come out of the Enlightenment? How did the thinkers of the Enlightenment change or impact society? Warm-Up: Read the following document
Clash of Philosophies: 11/10/2010
 1. Notebook Entry: Nationalism Vocabulary 2. What does nationalism look like? EQ: What role did Nationalism play in 19 th century political development? Common Language, Romanticism, We vs. They, Irrational
1. Notebook Entry: Nationalism Vocabulary 2. What does nationalism look like? EQ: What role did Nationalism play in 19 th century political development? Common Language, Romanticism, We vs. They, Irrational
