How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism?
|
|
|
- Blanche Green
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? IGCSE Cambridge International Relations since 1919
2 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? Events in Korea Korean War Background Japanese ruled Korea from Why was the USA involved? Why was the USSR involved? After WWII Japan had lost and left Korea, with the Russian army in the North and USA army in the South. Country divided along 38th parallel. In the North - communists ruled with Kim Il Sung as leader. Before 1950 USA was not very interested in Korea. BUT in 1950: USA policy of Containment: stop communism V Before 1950 USSR was not very interested in Korea. BUT in 1949: NATO was formed and Stalin was worried, plus USA was helping Japan. Stalin thought USA was being aggressive In the South - elections were held & anti-communist Syngman Rhee was leader. USA ideas in NSC 68 which said USA needed more arms & it should roll back communism. USA believed in Domino Theory. If South Korea were to become communist it would spread to other countries for example Japan. When Kim Il Sung leader of North Korea told Stalin he wanted to invade the South, Stalin thought it a good idea as it would cause the USA problems USSR gave North Korea weapons and advice, but never sent Russian soldiers 5.4 Impact of the Korean War Both sides claimed to be the rulers of all Korea. Sometimes there was fighting (clashes) on the border between North & South.. made the Cold War worse. spread the Cold War from Europe to Asia. SEATO - South Asian Treaty Organization formed (similar to NATO). USSR set up the Warsaw Pact. Korea was ruined by the war, one in ten Koreans died. USA thought the war was a success because South Korea did not become communist (Truman Doctrine). United Nations showed it could be strong
3 Phase One: June - Sept 1950 Phase Two: Sept - Nov 1950 Phase Three: Nov Feb 1951 Phase Four: Feb March 1951 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? Events in Korea Korean War: events On 25 June 1950, the North Koreans attacked. They were very successful. The North Korean People's Army (NKPA) easily defeated the Republic of Korea's army (the ROKs). They captured most of South Korea. The USA was shocked and alarmed. On 27 June they persuaded the United Nations to pass a resolution supporting South Korea. The USA sent troops to Korea as part of the UN force to help the South Korean Army at Pusan. On 15 September, the US General MacArthur led a UN amphibious landing at Inchon (near Seoul) behind the NKPA. Out of the 300,000 UN troops, 260,000 were Americans. In danger of being cut off, the NKPA had to retreat. The Americans drove them back and recaptured South Korea. 125,000 NKPA prisoners were taken. On 7 October 1950 MacArthur invaded North Korea. He advanced as far as the Chinese border. He boasted that the Americans would be 'home by Christmas'. The Americans landed more troops. They used bombers. The Chinese admitted to losing 390,000 men dead - UN sources put the figure at up to a million Chinese and half a million North Koreans dead.the US drove the Chinese back, but 54,000 American soldiers died doing so. MacArthur reached the 38 th parallel in March He threatened to invade China. Now the Chinese were alarmed. On 25 November, 200,000 Chinese troops ('People's Volunteers') attacked MacArthur. They had modern weapons supplied by Russia, and a fanatical hatred of the Americans. Then, on 31 December, half a million more Chinese troops entered the war and attacked the Americans. They drove the Americans back (using 'human wave tactics'). They recaptured North Korea, and advanced into South Korea. 5.9 Phase Five: March Truman told MacArthur to stop. MacArthur was sacked when he publicly criticised Truman s order. In 1953, Eisenhower became American president. The Americans threatened to use the atomic bomb if China did not stop fighting. The Chinese & Koreans agreed to a truce, which was signed on 27 July It is estimated that 10 million people died in the war - as many as died in the First World War.
4 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? Events in Cuba Background Before 1959 Dictator Batista was the ruler but was unpopular with many Cubans. Many USA businesses benefitted under Batista including sugar plantations & casinos. Cuba leased Guantanamo Bay to the USA. Fidel Castro wanted to improve the lives of the peasants & end corruption. USA was opposed to Castro. He was friends with communists & was a threat to US business interests. Cuban Revolution 1959 Castro seized power & appointed communists to his government. Castro turns to the USSR after USA opposed his rule. Many Cubans fled to the USA. Nationalisation: Castro seized much of the land & many companies USA response:. refused to buy Cuban sugar. end all trade with Cuba. refused to supply arms. ended diplomatic relations. supported Cuban exiles in overthrowing Castro USSR response: (after 1961). bought Cuban sugar. supplied Cuba with arms. offered support to Cuba 5.10 USA response: (to USSR). feared USSR supported the country on the USA's doorstep. USA warns USSR not to put nuclear missiles on Cuba 5.11 Plan. President Eisenhower supported Cuban exiles in overthrowing Castro. JFK continued with the plan, with the exiles invading Cuba with the support of the CIA 5.12 Cuban Missile Crisis Bay of Pigs Operation 1961 Invasion. CIA trained 1,400 exiles. invaded with support of bombers flown by Cubans. invasion easily stopped & 1,200 exiles were captured by Castro's forces Consequences. USA: JFK hugely embarrassed - seen as a bully. Cuba: moved Castro closer to the USSR. USSR: supports Cuba, gains an ally (friend) in Central America Central America. Supporting Cuba was seen as important in establishing an ally (friend) in Central America & try to limit or stop US influence Soviet Missiles in Cuba Why did Khrushchev put missiles in Cuba? Kennedy weak Some saw Kennedy as a young inexperienced President who could be pushed around. He was seen as being weak after the unsuccessful Bay of Pigs operation Missiles in Turkey. US missiles in Turkey gave the US a strategic military advantage. Khrushchev hoped that his missiles in Cuba could be used to negotiate the removal of the Turkish missiles plus US position in Berlin
5 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? Events in Cuba a test your knowledge True or False Read each statement and decide if it is TRUE or FALSE Statement T F 1 Batista was a Cuban leader 2 Cuba leased Guantanamo Bay to the USA. 3 USA supported Castro to take over in Cuba 4 Castro had friends who were communists 5 Everyone in Cuba was happy when Castro took over as leader 6 Castro introduced nationalisation 7 The USA remained trading partners with Cuba 8 The USA supported Cubans exiles in overthrowing Castro 9 The CIA trained 10,400 exiles to invade Cuba - Bay of Pigs 10 The exiles invasion was a disaster & JFK was embarrassed as a result 11 Cuba became friendlier with the USSR after the attempted exile invasion 12 Khrushchev wanted a friendly country in central America 13 Khrushchev thought JFK was weak & could be pushed around 14 USSR hoped to get the US missiles in Greece removed 15 The USA warned the USSR not to place missiles on Cuba
6 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? Events in Cuba Cuban Missile Crisis Events 1962 August: USA spy planes observe Soviet personnel & weapons in Cuba. September: JFK warned the USSR that he would prevent them from putting missiles on Cuba 'by whatever means necessary. 14 October: USA U2 spy plane takes photographs of the construction of nuclear missile launch site in Cuba. USSR ships seen in the Atlantic Ocean heading to Cuba, with what looked like missiles on board. 16 October: was opposed to Castro. He was friends with communists & was a threat to US business interests. By 16 October it had become clear that the Cubans were allowing the USSR to assemble missile sites. JFK was advised that the missiles could be ready to be fired before the end of October. JFK had announced he would not allow the Soviets to place missiles on Cuba, but how could he get Khrushchev to remove them without risking a nuclear war? 5.14 Attack the missile sites by air to destroy the missile launch sites But no guarantee that all the sites would be hit & risk the Soviets striking back. Invasion of Cuba Destroy the missile sites & remove Castro But invasion lead to killing Soviet personnel & likely result in war against USSR Kennedy s Choices Do nothing and avoid a possible nuclear war with the USSR But make JFK look weak & risk Soviet action elsewhere e.g. Berlin. Blockade of Cuba naval blockade of Cuba to stop missiles arriving & give JFK time to negotiate But no guarantee that the Soviet ships would stop & not necessarily get missiles removed from Cuba. Choice: naval blockade JFK announced all Soviet ships would be searched & those carrying missiles turned back. At the same time US armed forces were put on red alert & the USSR warned any missile launch would be met with full retaliation Situation: missiles close to the USA Nuclear deterrence was based on MAD: Mutually Assured Destruction. Neither superpower would attack the other as retaliation from the other would mean both countries would be destroyed - potentially many times over. However, missiles based in Cuba, could in theory mean the USSR could attack and destroy nuclear bases in the USA before they could retaliate. Thus the USSR could win a nuclear war.
7 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? Events in Cuba b test your knowledge Explain the advantages & disadvantages for each of the choices that Kennedy faced Cuban Missile Crisis - Kennedy s Choices Kennedy s Choice Advantages Disadvantages Diplomacy Blockade of Cuba Attack missile sites from the air Invasion of Cuba
8 1962 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? Events in Cuba Timeline of events 23 October Cuban Missile Crisis: events & consequences Khrushchev's response was to ignore the blockade & did not admit to having missiles on Cuba. It said it was merely helping Cuba defend itself & the USA was taking the world to war. 24 October Soviet ships stop and turn around at the blockade line, except one carrying oil 25 October Missile sites construction continued in Cuba 26 October Khrushchev sent a letter saying that the USSR would remove the missiles if: USA stopped the blockade & USA promise not to invade Cuba in the future 27 October Khrushchev second letter adds a demand that US missiles should be removed from Turkey. A U2 spy plane is shot down & JFK is pushed to retaliate. USA agree to first letter demands then JFK sends a secret message to Khrushchev agreeing to remove Turkey missiles. 28 October Removal of missiles from Cuba agreed by Khrushchev 5.18 USA. Cuban Missile Crisis showed the need to look at all options and not always use the military one. Kennedy looked strong in the USA, making Khrushchev back down. Kennedy was respected around the world for avoiding war. A communist Cuba was still embarrassing. US missiles removed from Turkey Superpower Relations. Cold War thaw after CMC, as both leaders realised there was nearly a war. Hot line established so leaders could talk directly to each other to avoid misunderstandings. Nuclear Test Ban Treaty was signed in 1963 helped improve relations Consequences of the Cuban Missile Crisis Cuba. Missiles removed. Stayed Communist. Kept Soviet support. Acted as a centre for communism in central America USSR. Stopped US invasion of Cuba. China criticised Soviets for backing down to USA. Khrushchev seen as backing down to Kennedy. Khrushchev removed from power two years later - partly due to CMC
9 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? Events in Cuba c Answer: test your knowledge Question: Answers & Questions:You have the answer, but what is the question? Cuban Revolution Answer: Blockade of Cuba Question: Answer: Batista Question: Answer: Nuclear Test Ban Treaty Question: Answer: Cuban missile sites Question: Answer: Question: Hot line Answer: Agreed by Khrushchev Question: Answer: US spy planes Question: Answer: Fidel Castro Question:
10 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? Events in Cuba d Events & consequences test your knowledge Decide for each statement if it is a: a. reason for Khrushchev to put missiles in Cuba b. a choice for Kennedy to make c. an event of the Cuban Missile Crisis d. a consequence of the Cuban Misslie Crisis Circle the correct answer. Kennedy. Khrushchev. Event. Consequence. Do nothing and avoid a possible nuclear war with the USSR. But make JFK look weak & risk Soviet action elsewhere e.g. Berlin.. Kennedy. Khrushchev. Event. Consequence. Cuba stayed Communist.and continued to receive Soviet support.. Kennedy. Khrushchev. Event. Consequence.. Kennedy. Khrushchev. Event. Consequence Some saw Kennedy as a young inexperienced President who could be pushed around. He was seen as being weak after the unsuccessful Bay of Pigs operation. Destroy the missile sites & remove Castro, but an invasion lead to killing Soviet personnel & likely result in war against USSR.. Kennedy. Khrushchev. Event. Consequence.. Kennedy. Khrushchev. Event. Consequence. Hot line established so leaders could talk directly to each other to avoid misunderstandings. Naval blockade of Cuba to stop missiles arriving & give JFK time to negotiate, but no guarantee that the Soviet ships would stop & not necessarily get missiles removed from Cuba. Kennedy. Khrushchev. Event. Consequence.. Kennedy. Khrushchev. Event. Consequence. US missiles in Turkey gave the US a strategic military advantage. Khrushchev hoped that his missiles in Cuba could be used to negotiate the removal of the Turkish missiles. Khrushchev seen as backing down to Kennedy. Khrushchev removed from power two years later - partly due to CMC.. Kennedy. Khrushchev. Event. Consequence.. Kennedy. Khrushchev. Event. Consequence. Khrushchev's response was to ignore the blockade & did not admit to having missiles on Cuba. It said it was merely helping Cuba defend itself & the USA was taking the world to war. Cuban Missile Crisis showed the need to explore the all options and not always go the direct military one.. Kennedy. Khrushchev. Event. Consequence.. Kennedy. Khrushchev. Event. Consequence. Khrushchev sent a letter outlining that the USSR would remove the missiles if: USA stopped the blockade & USA promise not to invade Cuba in the future. Kennedy looked strong in the USA, making Khrushchev back down and was respected around the world for avoiding war.
11 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? Events in Cuba e Consequences of the Cuban Missile Crisis Place each consequence as a short, medium or long term consequence test your knowledge Then rank each consequence according to its importance by highlighting each consequence: most important = RED important = BLUE least important = GREEN Short Term (immediate) Medium Term (soon after the event) Long Term (over the next year or more)
12 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? US involvement in Vietnam 5 Background. French colony since C19th called Indochina.. Rebellion in 1930s crushed by the French army.. WWII, 1940 French surrender to Germans.. Japan (Germany s allies) take over Vietnam from French.. WWII, anti-japan resistance movement (Viet Minh) led by Ho Chi Minh, who wanted an end to colonial rule.. WWII, 1945 Allies victory meant France wanted Vietnam back, even though Ho Chi Minh had declared an independent Vietnam war broke out between Viet Minh & the French. Ho Chi Minh was a communist but kept quiet so not to upset USA. The USA was against colonialism , Mao s communist takeover in China meant support for the Viet Minh USA now saw Ho Chi Minh as a communist enemy & friends with China. They gave $500 million pa to the French as part of their policy of containment.. French controlled the cities & the Viet Minh the countryside.. Viet Minh guerrilla tactics meant the French pulled out after defeat at Dien Bien Phu Peace Conference, Geneva Settlement saw Vietnam divided into North & South (along 17th parallel) until elections were held which the USA did not want as they feared a communist victory Already involved USA had supported France since the end WWII. Given $500 million per year to help France inc. equipment After 1954, helped South Vietnam with money, equipment & military advisors. USA counter the support that North Vietnam was getting from USSR & China. Committed to supporting the South Vietnam government at Geneva Settlement. Backed unpopular leader Ngo Diem with $1.6 billion in 1950s. Vietcong = South Vietnamese communists + North Vietnamese 5.21 Vietnam War Steps to War for the USA Reasons why the USA became involved in Vietnam Truman Doctrine Policy of containment said USA to support anticommunists. Presidents Eisenhower in the 1950s and Kennedy after 1960 believed in the Domino Theory. If Vietnam became communist then other countries would follow: Cambodia, Laos, Thailand, Burma, India etc : Kennedy increased military advisors from 900 to 11, : Vietcong take over 40% of S.Vietnamese countryside. 1963: President Johnson sends more help to stop Vietcong Johnson not a war monger but not want to be seen as soft on communism Defence Sec. McNamara believed war was winnable 2. Aug. 1964: Gulf of Tonkin Resolution (still debate about circumstances of incident) US ships attacked by North Vietnamese torpedo boats Johnson attacked North Vietnamese naval bases 3. March 1965: US Marines arrive No longer called advisors but troops US bombers start bombing North Vietnam called Rolling Thunder 4. After 1966: Total war Over 500,000 US soldiers in Vietnam on 12 month tours Draft of young men in the US army : Nixon elected President - withdraw from Vietnam Peace with honour - took 4 years
13 5f How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? Events in Cuba test your knowledge Vietnam War Rank Reasons why USA became involved in the Vietnam & explanation of ranking Mark /10 Steps to war: how far did each step take USA closer to war (mark out of 10) Explain how it took the USA closer to war in Vietnam : Kennedy increased military advisors 1963: Johnson sent more help to South Vietnam & McNamara believed war was winnable 1964: Gulf of Tonkin resolution 1965: US marines arrive in South Vietnam & Rolling Thunder begins
14 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? US involvement in Vietnam 5 Events Trail through Laos & Cambodia kept Vietcong supplied. Bombing of trail was very controversial as countries not involved in the war. Bombing did little to disrupt supply lines as 35,000 + Vietnamese kept it open. Turning points: My Lai Massacre Charlie Company on search & destroy mission killed villagers, mainly women, children & old men. No Vietcong were found. It was considered a success. One year later a letter was sent to politicians & Life magazine printed photos. An investigation ended in mass murder charges for Lt. Calley & others. Calley was blamed & got 20 years hard labour. USA people were shocked & protests increased. Tet Offensive 1968 On Tet religious holiday, Vietcong launched over 100 attacks across South Vietnam. Scale of offensive shocked USA. Vietcong suffered huge causalities, but USA morale badly affected. Americans thought the war was unwinnable Bombing Operation Rolling Thunder (Feb ). Targets:. industrial & military targets initially approved by President. then town & cities. then in Laos & Cambodia Ho Chi Minh Trail Result:. reduced number of soldiers needed. dropped more bombs than on Germany & Japan in WWII. damaged NV ability to fight the war. attacked Vietcong targets in South. 14,000 US bombers shot down. failed to stop the communists. Killing civilians (women & children) turned many in USA against the war 5.24 General Giap (AP photo) Guerilla tactics. Less soldiers & outgunned by US & South Viet forces. Ho Chi Minh used guerilla tactics like Mao in China. Attack & disappear into jungle. Retreat if out numbered. Not always wear uniforms. Got peasant support - sometimes through terror Result:. Very motivated fighters. Lower morale of US soldiers. Had peasant support. Network of informants. Over 1 million died Vietnam War US tactics in Vietnam Vietcong tactics Chemical Weapons Agent Orange & Napalm. It was a sort of weedkiller. Used to destroy the jungles, so the Vietcong had no hiding place Result:. Destroyed thousands of sq km of jungle. Burned & killed thousands of guerrilla fighters & civilians. Shocking pictures of women & children burned by chemical weapons turned many people in the USA against the war Search & destroy. Bombing was not winning the war. USA built strong bases in the south & launched attacks via helicopters. Result:. Some successes against Vietcong. Pointless attacks based on poor information. Vietcong often vanished before attacks. Many civilians killed during attacks. Turned many peasants against the USA/South Vietnamese. My Lai Massacre turned US public opinion against the war After a napalm attack Supply lines & tunnels. The Vietcong in the South were supplied via trails in Laos & Cambodia. USA failed to stop the flow of supplies, often carried on bicycles, despite heavy bombing. Underground bases & tunnels kept Vietcong safe from bombing Result:. Vietcong constantly supplied. Tunnel network destroyed US morale
15 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? Events in Cuba g Vietnam War test your knowledge Vietcong Success /10 Explanation Guerilla Tactics Supply Lines USA Success /10 Explanation Bombing Chemical weapons Search & Destroy
16 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? US involvement in Vietnam 5 Why was the USA unable to win the Vietnam War? Communists Military situation U.S.A. Harsh lifestyle Vietcong use to hard peasant lifestyle At home in jungle environment & communal living Win the hearts & minds Communits worked hard to win over the peasants BUT treated peasants harshly if they did not support them Serve their country Patriotic soldiers fighting for their homeland Against colonial rule - French then USA 5.25 Attitude to war US soldiers used to a comfortable life Join up for different reasons: hero; patriotism; learn to fly etc Life in Vietnam was harsh & uncomfortable Many conscripts did not want to be there Killing civilians Bombing & chemical weapons killed civilians & turned Vietnamese against the USA Tour of duty Soldiers were in Vietnam for 365 days The priority was to survive & go home, rather than win the war Unity Soldiers & Vietnamese people very motivated to defeat the colonial invading army & worked together Communists controlled & motivated in a variety of ways People made huge personal sacrifices inc. women & children to help the soldiers: Shock brigades repaired bomb damage after air raids Information Communists had informants in South Vietnam - in all areas inc.army, US Army and CIA They often knew of planned attacks in advance Guerilla warfare Guerilla warfare was central to VC tactics though Tet offensive showed it was capable of traditional warfare which shocked US generals and US public alike US troops always scared of VC ambushes Supplies VC supplied through network of tunnels + Ho Chi Minh trails in Laos & Cambodia People repaired trials after US bombing 5.26 Quality of soldiers Disunity in the Army US forces distrust South Vietnamese, as communists had infiltrated the South Viet. army & government Drugs & R & R Soldiers were in Vietnam for 365 days Priority was to survive & go home, rather than win the war Many resorted to drugs to overcome the shock of war Conflicts within the US army Officers often lacked experience & authority - soldiers mutinied Over 100 officers were killed by their own men Grunts (infantrymen) were on average 19 years old, had low morale & going on patrols was very unpopular with booby traps and ambushes common Many army units experienced racial problems 5.27 Military tactics 5.28 High tech weapons Up to 1964 US military advisors had good relationsnip with Vietnamese After 1965 US Marines very aggressive & came to hate Vietnamese After 1965 US relied on bombing inc. chemical weapons which killed civilians US forces could not tell friend or enemy apart because of Vietcong tactics Support in Vietnam + China & Russia Full support of Vietnamese people - working together USSR & China supplied military hardware + advice Support Reaction in USA Anti-war movement showed soldiers to be baby killers Many soldiers were anti-war before they even went to Vietnam Upon returning home not treated as heroes In fact soldiers became anti-war protesters!
17 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? US involvement in Vietnam 5h Why was the test USA unable your to win the Vietnam knowledge War? Write in whether the statement applies to either the USA or communists USA or Communists Statement At home in the jungle environment & with communal living Priority was to survive & go home Supported & supplied by the USSR & China Motivated to defeat the invading colonial armies Grunts were on average 19 years old After 1965 they relied on bombing & the use of chemical weapons Had informants in the South Vietnamese govt., US army & CIA Shock brigades repaired bomb damage after air raids Soldiers were in Vietnam for 365 day tour of duty Supplied through a network of tunnels & trails through laos & Cambodia Patriotic soldiers fighting for their homeland Worked hard to win the hearts & minds of the peasants Often knew, in adavnce, of planned attacks Found life in Vietnam harsh & uncomfortable Many soldiers took drugs to overcome the shock & horror of war At home soldiers were often known as child killers Officers often lacked authority & there were mutinies
18 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? US involvement in Vietnam 5i Why was the USA unable to win a military victory in Vietnam? Rank with an explanation the military strengths of the North Vietnamese communists and the military weaknesses of the USA Communists strengths USA weaknesses Rank Strengths Explanation Rank Weakness Explanation
19 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? US involvement in Vietnam 5 Why was the USA unable to win the Vietnam War? Situation in the USA President Johnson s aims Public aim: defeat communism (containment) support democracy (S.Vietnam) Private aims: save face for USA not be first President to lose a war BUT: many in US not care about democracy in Vietnam US supporting a corrupt S. Vietnam government President Johnson s methods Political: Support democracy but alien to Vietnamese Support educational, medical & social programmes Military: Use bombing to win the war Destroy VC supply routes BUT: bombing made Vietnamese more determined Chemical attacks turned US people against the war Public opinion Students protests e.g. teach-ins - against conscription Anti-war debates & demonstrations 5.30 Public opinion Members of Congress start criticising Johnson s policies Buddhist nun sets herself on fire in protest in Vietnam Martin Luther King & other church leaders join anti-war protests Tax increases to pay for war, leads to more demonstrations Media turn against the war Loss of McNamara 1967 McNamara (Defence Sec.) with JFK then Johnson McNamara responsible for military policy & tactics McNamara changed from saying easily winnable, to the war being unwinnable Replaced by Clark (advisor & friend of Johnson) Problems in South Vietnam Government was corrupt & unpopular Many South Vietnamese supported Ho Chi Minh Tet Offensive North Vietnamese VC attacked multiple targets in the South Attacked during Tet holiday surprising everyone Attacks were unsuccessful & the VC lost 60,000 soldiers BUT: US shocked by size of attack, confidence shaken US intelligence failed & 10,000 US/South troops killed People in USA shocked by what their saw US media showed it as a failure for the USA Defence Secretary Clark Realised USA did not have a plan to win in Vietnam (policy of not losing to save face) By March 1968 Clark was telling President Johnson the war was unwinnable President Johnson Johnson s health suffered Advisors started looking at peace options Bombing stopped whilst peace talks held Financial costs Great Society spending cut as military spending increased Deficit: from $1.6 billion (1963) to $25.3 billion (1968) Inflation increased + people not want to pay increase in tax to pay for war Public opinion TV coverage: bombing & chemical attacks turned people against war Mai Lai incident shocked people around the world Opinion: win the war or get out BUT: Peace difficult as North Vietnamese not want to compromise Johnson in a weak negotiating position Divided US society USA torn apart by the war - totally divided Civil unrest - some feared civil war
20 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? US involvement in Vietnam 5 The end of war in Vietnam The My Lai Massacre Event: Unit of soldiers (Charlie Company) on a search & destroy mission. Attacked what they thought was a Vietcong stronghold. After 3 / 4 hours civilians were dead inc. women & children. There were no Vietcong & only 3 weapons found. Official report: only 20 civilians killed, the rest were Vietcong. The soldiers were praised for their actions. The letter: Soldier Ridenhour who knew many soldiers at My Lai wrote a letter to politicians & officials in Washington saying what really happened there. Life Magazine: published photos of the massacre. Investigation: Lieutenant Calley was charged with murder and others were also charged, but the army made Calley solely responsible & said he was not acting on orders. Calley was sentenced to 20 years hard labour. (He was released after 3 years). The events of My Lai shocked the US people The Peace Movement Peace movement: no longer hippies & students but ordinary middle class people who wanted an end to the pointless war. My Lai Massacre: after the incident came to light over 500,000 people protested against in the war in Washington DC. The largest protest ever in the USA. Politics: to be pro-war was political suicide for most politicians. Nixon was very anti-communist but had to be against the war or at least pro peace to get elected in 1968 Loss of faith in the military leadership Realisation that the USA could not win a military victory after the Tet Offensive People lost faith in the US army Bombing Nixon ordered bombing to be increased. He hoped this would put pressure on the communists as peace negotiations continued. When talks broke down in Dec 1972, Nixon ordered a massive bombing campaign. In 11 days more bombs were dropped than in the previous 2 years. US invasion of Cambodia The US was unable to cut off the supply lines as the communists used trials & bases in Laos & Cambodia. Nixon ordered the invasion of Viet Cong bases in Cambodia Negotiations: Peace with Honour May 1968: USA wanted a South Vietnam, the communists wanted a united Vietnam. USA wanted free elections in the south but North Vietnam did not trust the elections would be fair. Kissinger (USA) & Le Duc Tho (North Vietnam) agreed:. US troops withdraw after ceasefire. Prisoners of war released. Elections in the south Paris Peace Agreement - 27 January Nixon s strategy Vietnamization Nixon started replacing US soldiers with Vietnamese soldiers AVRN. Between ,000 troops were withdrawn from Vietnam. AVRN were no match for communist fighters. USSR & China relations USSR & China relations in 1969 were so bad some feared there would be a war between the two. As a result both countries tried to improve their relations with the USA. 1970: Nixon & USSR began talks about limiting nuclear arms (SALT) & asked USSR to pressure North Vietnam to end the war. 1972: Nixon was invited to visit China & he asked China to pressure North Vietnam to end the war. The end.. Fighting restarted in 1973, AVRN held for a while but low morale & poor leadership meant that by April 1975, communist forces entered Saigon - hundreds of thousands of S. Vietnamese were executed. People watched on TV as 6000 Americans fled, helicopters lifting people off the Embassy roof.
21 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? US involvement in Vietnam 5j The Vietnam War test your Match the knowledge event to the correct year McNamara changed from saying easily winnable, to the war being unwinnable Members of Congress start criticising Johnson s policies North Vietnamese VC attacked multiple targets in South Vietnam Peace movement: no longer hippies & students but ordinary middle class people who wanted an end to the pointless war. The invasion of Viet Cong bases in Cambodia Over 500,000 people protested against in th war in Washington DC. The largest peace protest ever in the USA. Both the USSR & China tried to improve their relations with the USA. Nixon was very anti-communist, but had to be against the war or at least pro peace to get elected Nixon s strategy Johnson s aims: defeat communism (containment) & support democracy (S.Vietnam) When talks broke down ordered a massive bombing campaign. Military spending increased to $25.3 billion Realisation that the USA could not win a military victory after the Tet Offensive and people lost faith in the US arm North Vietnamese VC attacked multiple targets in the South Attacked during Tet holiday surprising everyone In 11 days more bombs were dropped than in the previous 2 years Students start protests e.g. teach-ins - against conscription Nixon started replacing US soldiers with Vietnamese soldiers AVRN. 400,000 US troops were withdrawn from Vietnam
22 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? US involvement in Vietnam 5k What were the turning points that contributed to the situation in the USA becoming increasingly anti-war? test your knowledge Score each event out of 10, in terms of it being a turning point that influenced the American public into becoming more anti-war - explain your score. Event Score out of /10 Explanantion Johnson s aims Johnson s methods: bombing & chemical weapons McNamara resigns: war unwinnable Tet Offensive Clark: there is no plan to win the war My Lai massacre Invasion of Cambodia & Laos Nixon s increase in bombing
23 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? US involvement in Vietnam 5 Consequences of the Vietnam War Society Many peasants left the countryside & lived in shanty towns: poverty, prostitution & drugs Refugees = 5 million Corruption in the South was rife Black market in US goods 5.34 Vietnam Environment Chemical warfare: Huge areas of forest & agricultural land destroyed Food shortages as a result Water supply poisoned Mines & unexploded bombs were everywhere and continued to kill people t=years after the war Economic USA banned trade with Vietnam Food shortages were common Boat people : 1970s saw 1 million Vietnamese try to leave the country Took 20 years to recover to pre-war levels Political Vietnam unified under communism Communism spread to Cambodia & Laos South Vietnamese victimised after the war, thousands executed & re-educated US foreign policy: end of containment Propaganda disaster for the USA Use of bombing, chemical warfare lost US support Nixon ended the Truman Doctrine US abandoned policy of containment Military intervention less likely after Vietnam Looked to talk with USSR & China: Detente Economic Military industrial production increased, consumer goods decreased USA had budget deficits which caused inflation Interest rates rose Value of the dollar fell Govt. spending was reduced on social programmes in Johnson s Great Society 5.35 USA Political President Johnson destroyed by the war - even though vast majority supported the war at the start Pro-war became political liability Nixon anti-communist but had to pursue peace Politicians more isolationist Society 58,000 died in the war Divided the nation: Student demonstrations Draft dodgers Many veterans became anti-war protestors drug addicts & suffered post traumatic stress (est. at 800,000) Others who handled Agent Orange suffered cancer TV war: pictures of the horrors of war on the news every evening USA lost confidence in their country
24 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? US involvement in Vietnam 5l test your knowledge List the consequences for both sides as Consequences of the Vietnam War Communists positive + positive & negative on a scale of = very positive/negative U.S.A Many peasants left the countryside & lived in shanty towns: poverty, prostitution & drugs negative US abandoned policy of containment South Vietnamese victimised after the war, thousands executed & re-educated Took 20 years to recover to pre-war levels USA banned trade with Vietnam Food shortages were common Boat people : 1970s saw 1 million people try to leave the country Communism spread to Cambodia & Laos Interest rates rose and the value of the dollar fell Vietnam unified under communism Looked to talk with USSR & China: Detente Nixon ended the Truman Doctrine Food shortages were common Govt. spending was reduced on social programmes in Johnson s Great Society Many veterans became anti-war protestors drug addicts & suffered post traumatic stress
25 Cambridge IGCSE History : International Relations since 1919 How effectively did the USA stop the spread of communism? US involvement in Vietnam
26 How secure was the USSR s control over Eastern Europe, c.1989? IGCSE Cambridge International Relations since 1919
27 How secure was the USSR s control over Eastern Europe, c.1989? Opposition to Soviet rule in Hungary Hungary Background 6.2 Yugoslavia had gained some independence from the Soviet Union Poland had seen demonstrations which had seen them gain more freedoms. Hungary was established at the end of WWI, after the collapse of the Austro- Hungarian empire. At the end of WWII, the USSR's Red Army occupied Hungary & continued to do so with a 'mutual assistance treaty'. A coalition government was elected in The Hungarian communist party got 17% of the vote. Over the next 4 years Communists took over key positions & set up the secret police, who intimidated, arrested & imprisoned non communists. Patriotism Hungary had a long history & a rich culture. They disliked the fact that Russian soldiers were in their country and the Russian language was being used. Reasons why Hungarians opposed Soviet control Freedom of Speech The Hungarians were not able to speak freely. The communist government controlled the newspapers, radio, arts, theatre and music. The Hungarians were scared of the secret police - State Protection Group (AVO) - who arrested people for criticising the government, or communism or the Soviets. People's Republic of Hungary (communist) was declared in 1949, under the leadership of Rakos. Hungary had to pay $300 million in reparations to the Soviet Union. The Soviet system was quickly established e.g.: collectivisation, nationalisation of industry etc. Education Children in schools were taught the communist version of history, ignoring much of Hungary's history, especially its empire & links with Austria & Germany. Religion The communists were against religion which upset Christians. The Catholic leader, Cardinal Minszenty, was arrested & sent to prison. Quality of life In addition, to censorship & the secret police, the Hungarians standard of living declined as pay decreased for many workers. Food shortages were common under the communists. Some of the best industrial equipment was shipped to the Soviet Union. The period after Stalin's death 'Peaceful Co-existence', under Khrushchev brought some changes to many communist countries in Eastern Europe. Many countries wanted to 'reform' some of the communist policies & systems. Hungary brought in a more reformist leader - Imre Nagy
28 How secure was the USSR s control over Eastern Europe, c.1989? Opposition to Soviet rule in Hungary Hungary 1956 Events: 23 October Demonstrations in Budapest including pulling down a statue of Stalin. Demonstrators want Emo Gero out & Imre Nagy in. 24 October Nagy becomes Prime Minister with Khrushchev's approval. 27 October Nagy forms new government including non communists. Religious leader Cardinal Minszenty freed from prison. 29 October Soviet troops withdrawn after battles with the Hungarian army & militia. Nagy announces:. end of collectivisation (farms to return to private ownership). end of one party rule. Hungary to be neutral. withdrawal from Warsaw Pact 4 November Red Army (200,000) + 2,500 tanks invades Hungary Nagy appeals to President Eisenhower for help Janos Kadar becomes Prime Minister USSR. Domino effect Khrushchev was worried that other communist countries would want more freedoms & independence if they let Hungary have reforms.. China China advised Khrushchev to be strong with Hungary & not give in.. Khrushchev's leadership Khrushchev could not afford to look weak in the USSR & Eastern Europe.. United Nations The USSR used its veto to block action & stopped the UN Secretary General from visiting Hungary 6.5 Short term Hungarians killed: 3,000 Red Army killed: 7-8, ,000 Hungarians left the country Nagy arrested, sent to Moscow & shot. Responses to the Hungarian uprising Consequences of the Hungarian uprising The West. Voice of America USA's radio station 'Voice of America' encouraged the uprising & suggested the USA would help Hungary. Suez Crisis Many Western countries were distracted by the Suez Crisis. Protests President Eisenhower & other leaders protested to Khrushchev. United Nations The Western countries tried to get a resolution (Soviet troops to leave Hungary) but the USSR vetoed it Medium term New leader Kadar crushed further resistance: arrested 35,000 & killed 300+ Khrushchev established himself as Soviet leader & showed he could be strong like Stalin if he needed to be - giving a warning to other communist countries Long term Many Hungarians lost faith in the West - after their false promises & realised the policy of 'containment' did not include Eastern European countries. United Nations proved to be ineffective against an agressor East - West relations deteriorated. USA was unable to influence events in Eastern Europe but were more determined to stop communist expansion elsewhere in the world.
29 How secure was the USSR s control over Eastern Europe, c.1989? Opposition to Soviet rule in Hungary a Hungary 1956 test List your the reasons why the Hungarians knowledge opposed Soviet control & explain why you gave it that ranking Rank Reason why Hungarians opposed Communist/Soviet control Explanation
30 test your knowledge Hungary The Hungarian secret police: Group 2. The Hungarians were proud of their country and its long history: 3. The name given when the government controls newspapers, radio, TV etc 4. Name of new Hungarian leader: 5 Capital of Hungary: 6. Name of religious leader: 7. Leader of USSR in 1956: 8. Name of leader appointed on 4th November : 9. USSR blocked action in the United Nations by using its : 10. Month when the demonstrations started in Hungary: 11. Western Countries were distracted by the: 12. Hungary withdrew from this organisation in October 1956: W P 13. USSR s first satellite in space: S S T A T B K A R A T F D E O A P R R R E B T B X E O V C T R I C E M O S T H D E F T E V E O R C E R G A G C M E Y E S O P U R Y N A R T O W U P R S A T B P C O I G E A O H E N C W Y E L T Z C T C T E V A U R B S C T E H Y Z N S O U M E R S C E N S O R S H I P I U T V L N K A P S M A S N I A I I L W A T R D I A O F H M L O C I E U S G N T R E Y K T N N B E U T D F I C I O P A G J O A N I H C T F I G E D P P L K A P O L P Y T R E WORDSEARCH Answer the questions & find the word(s) in the wordsearch 6b How secure was the USSR s control over Eastern Europe, c.1989? Opposition to Soviet rule in Hungary 1956
31 How secure was the USSR s control over Eastern Europe, c.1989? Opposition to Soviet rule in Czechoslovakia Czechoslovakia: The Prague Spring 1968 Background The attempt to win more political & economic freedoms & be more independent of Soviet control. The Red Army & Czech fighters defeated the Nazi German forces. After WWII a coalition government was formed, including Communists who held key posts. Communist policies of nationalisation were introduced for industry & banks, plus land reforms elections: Communists 38% PM Gottwald accepted Marshall Aid until Stalin blocked it. Coalition parties were kicked out of government by the communists. Czechoslovakia became a one-party state in Dubcek became leader in Jan. 1968, with the approval of the Soviets. Political Parties People wanted alternatives to the Communist Party. They wanted other political parties, to vote & choose their own leaders. The economy People s standard of living was very poor. Soviet style control of industry & agriculture did not work well. The country was already well industrialised & not suited to the Soviet plans. Reasons why Czechs opposed Soviet control Freedom of Speech The Czechs were not able to speak freely. The communist government controlled the newspapers, radio, arts, theatre and music. People were arrested for criticising the government, or communism or the Soviets. Worker democracy Factory workers wanted a greater say in how their factories were managed. Unrealistic targets & poor working conditions left the workers wanting reforms. Consumer goods were ignored for heavy industrial goods. Secret Police The STB were both feared & hated. These plain clothed police watched & listened to all activities, via telephone taps, reading mail etc. Anti communists were arrested & show trials were common in the 1950s In Feb the Czech communist party introduced an economic reform programme to try to improve the economy. Dubcek spoke of the need for change now that socialism had triumphed. 6.8 Ducek s Action Programme Socialism with a Human Face 1. Improve people s standard of living (more consumer goods made) 2. More freedoms (let workers have more say, public discussions, free speech & media, political parties) 3. Federal Czechoslovakia (more power to the regions) + keep links with the USSR stay in the Warsaw Pact
32 How secure was the USSR s control over Eastern Europe, c.1989? Opposition to Soviet rule in Czechoslovakia Czechoslovakia: The Prague Spring 1968 Background 6.9 April 1968 Dubcek launches the Action Programme May 1968 On May Day people executed during 1952 show rials were honoured. Workers Councils were proposed. June 1968 Censorship was abolished & political prisoners freed. People demanded more than Dubcek s Action Programme. Soviet forces stay in Czech after Warsaw Pact exercises July 1968 Soviet troops at the Czech border. Warsaw Pact meets to discuss situation in Czech. & warn leaders August 1968 Dubcek speech said there was no going back. Warsaw Pact agreed to stop anti-socialist forces & backed the Brezhnev Doctrine 20 Soviet & Warsaw Pact forces invade Czech 6.10 Dubcek s ideas Dubcek s Action Programme & then the ideas & reforms that followed scared the Soviet Union & other Warsaw pact communists. The USSR & other countries were scared that their people would demand similar freedoms. USSR not want to lose control East-West relations Soviet invasion condemned by the West but no more. US President Johnson wanted better relations with the USSR rather than oppose the Soviet s actions. Why did the USSR invade Czechoslovakia? Reactions Protests across the West. Some protests in Moscow & East Germany. Communists reaction around the world was mixed. Many western communists were shocked by the Soviet action, others were against the revolutionary actions of the reformers. Warsaw Pact Yugoslavia was communist but free from Soviet control. Romania was not going to Warsaw Pact meetings. Soviets & others not want the break up of the Warsaw Pact. USSR not want to lose control. Political cartoon showing the different reactions to Soviet troops in 1945 & 1968 Eastern Europe Reformers in other Eastern European countries were reminded that reforms had limits. 21 Dubcek* arrested & flown to Moscow & signed Moscow Protocol (Soviet troops to stay in Czech) Workers & students confronted invading troops Czechs were killed September/October 70,000 plus fled from Czech New govt formed headed by Husak. * after release from solitary confinement Dubcek became a forestry official & remained under police surveillance Brezhnev Doctrine Brezhnev showed that no Eastern European country would be allowed to pursue its own reforms. Countries: China, Yugoslavia & Romania spoke out against this. Consequences of the Prague Spring Gorbachev Gorbachev said that his reforms in the USSR in the 1980s were influenced by the Prague Spring. He, like Dubcek wanted an end to totalitarianism. Czechoslovakia Under Husak s leadership thousands of communist members were expelled & lived as outcasts doing menial jobs. Most of the Czech communist party had supported Dubcek s reforms. Strict rule followed for the next 20 years. Reformers remained silent.
33 How secure was the USSR s control over Eastern Europe, c.1989? Opposition to Soviet rule in Czechoslovakia c Czechoslovakia: The Prague Spring 1968 For each statement decide if it was: a reason for Czechs opposed the Soviets a reason for the Soviets to invade Czechoslovakia Soviets or invade or consequence Statement Reformers in other Eastern European countries were reminded that refoms had limits. Gorbachev said that his reforms in the USSR in the 1980s were influenced by the Prague Spring. USSR not want to lose control. People were arrested for criticising the government, or communism or the Soviets. The USSR & other countries were scared that their people would demand similar freedoms. People wanted alternatives to the Communist Party Anti communists were arrested & show trials were common in the 1950s People s standard of living was very poor. Under Husak s leadership thousands of communist members were expelled & lived as outcasts doing menial jobs. Consumer goods were ignored for heavy industrial goods. Strict rule followed for the next 20 years. Reformers remained silent. Duncek s Action Programme & then the ideas & reforms that followed scared the Soviet Union & other Warsaw pact communists Brezhnev showed that no Eastern European country would be allowed to persue its own reforms. Soviets & others not want the break up of the Warsaw Pact. The Czechs were not able to speak freely. The communist government controlled the newspapers, radio, arts, theatre and music.
34 How secure was the USSR s control over Eastern Europe, c.1989? Opposition to Soviet rule in Czechoslovakia d test your knowledge The Prague Spring 1968 Rank Reasons why Czechs opposed Soviet control Explanation Rank Reasons for the Soviet invasion Explanation Rank Consequences of the Prague Spring Explanation
35 How secure was the USSR s control over Eastern Europe, c.1989? Opposition to Soviet rule in Hungary & Czechoslovakia 6e test your knowledge Make bullet points for: background; cause; events & consequences Highlight similarities between the two Hungary Czechoslovakia Background Causes Events Consequences
36 How secure was the USSR s control over Eastern Europe, c.1989? Why was the Berlin Wall built in 1961? Aims Berlin Wall 1961 Background Potsdam agreement 1945: Berlin divided between: Allies (USA/FRANCE/UK) Soviet Union until all parties agree on a suitable government Assumed that this would be a temporary situation. USSR:. stop migration from East to West Berlin. keep control of East Germany. get the West to recognise East Germany 6.14 Events 1953: East Germans need permission to travel to West Berlin Allies:. keep West Berlin under their control. unite a democratic Germany. reduce influence of the USSR in Berlin In 1960 Berlin was still divided: East Berlin: communist part of East Germany West Berlin: capitalist part of West Germany 1957: Leaving East Germany without permission = 3 years in prison 1958: Soviet demands - Khrushchev demanded:. the West to recognise east Germany. the West to take soldiers out of West Berlin. all routes into Berlin to be controlled by East Germany - The West refused the demands & Khrushchev backed 1960: West Germany is bad for East German economy & it must be corrected according to East German leader 1961: June Summit - Khrushchev tries to pressure the new US president, Kennedy, by insisting the Western powers leave Berlin Kennedy pledges to support West Berlin Berlin a focus for all leaders since Stalin was planning to build a wall before his death. Khrushchev often threatened West Berlin. By 1961 about 2.5 million East Germans left for West Berlin, including many skilled workers. 1961: 15th June - East German leader Walter Ulbricht said he no intention of erecting a wall 1961: 25th July - US President J.F. Kennedy spoke about the need to hold onto West Berlin. That NATO should react to any threat from the Soviets. 1961: 12th August - East German leader orders a barricade to separate Berlin Barbed wire used followed by concrete wall. The 'brain drain' was a cause for concern for East Germany & they wanted to find a way to stop it.
37 How secure was the USSR s control over Eastern Europe, c.1989? Consequences of the Berlin Wall Berlin Wall Berlin Wall Facts Wall was feet high Total length of the border to West Berlin 155km Inner city border between East & West Berlin 43km 6.16 East - West Relations. Soviet & US tanks faced each other for 18 hours at Checkpoint Charlie. JFK had to accept the Wall or risk war. USA stayed in West Berlin despite Khrushchev's statement. Tensions between USSR & USA increased. Berlin remain a potential flashpoint. In a 1963 speech JFK said" Ich bin ein Berliner" (I am a Berliner), giving his support to West Berlin Border crossings between East & West Berlin 8 Observation tower 302 Escapes. Constant embarrassment Bunkers 20 Dog runs 259 Anti vehicle trenches 105km Contact/signal fences 127km to USSR as people attempted to go over & under the wall (100,000+). Over 200 people killed whilst attempting to escape Consequences Divided Berlin. Access from East to West since 1945 ended. Families split, unable to see each other. People unable to get to work Border patrol roads 124km Number of mines unknown Attempted escapes 100,000+ Successful escapes 5-10,000 Killed while attempting to escape 200+ Most famous checkpoint Checkpoint Charlie USA / the West. JFK appointed General Clay to Berlin as an ambassador. Army presence in Berlin was increased. Propaganda victory for the West as East Berlin residents continued to find ways to escape USSR/East Germany. Called the wall a necessary anti-facist rampart. Gained control of East Berlin. Ended black market & economy began to grow. Communism embarrassed by shooting would-be escapees over next 25 years +
38 How secure was the USSR s control over Eastern Europe, c.1989? Berlin Wall f Berlin Wall test your knowledge Read each statement and decide whether it is: an aim of USSR, an aim of the USA, an event or a consequence USSR aim. USA aim Event. Consequences Statement Tensions between USSR & USA increased Reduce influence of the USSR in Berlin JFK had to accept the Wall or risk war East Germans need permission to travel to West Berlin Stop migration from East to West Berlin Families split, unable to see each other East German leader Walter Ulbricht said he no intention of erecting a wall USA stayed in West Berlin despite Khrushchev's statement Constant embarrassment to USSR as people attempted to go over & under the wall (100,000+) Khrushchev demanded that the West to recognise east Germany, the West to take soldiers out of West Berlin and all routes into Berlin to be controlled by East Germany US President J.F. Kennedy spoke about the need to hold onto West Berlin. Khrushchev tries to pressure the new US president, Kennedy, by insisting the Western powers leave Berlin Berlin remain a potential flashpoint
39 6 Background 6.17 How secure was the USSR s control over Eastern Europe, c.1989? 6.18 Detente Detente USSR Chinese - Soviet relations were not good, so the USSR looked for better relations with the USA. Detente is French for relaxation or known as a thawing in relations between the USSR & USA. During the Cold War there were periods when relations between the superpowers improved, when tensions were reduced. Arms Race USA & USSR concerned over cost & risk of arms race. Missiles now had multiple nuclear warheads & submarines could launch nuclear missiles. Reasons for Detente in the 1970s Peace Movement People across the world but especially in Europe were increasingly against nuclear weapons. They questioned the morality of weapons that killed women & children. Detente Nixon & Brezhnev Summits x 5:. SALT I (1972): limit nuclear missiles & bombers. SALT II (1975): further limits but stopped because of Afghanistan. joint space mission: shook hands in space. trade links: more trade between West & East BUT. conventional forces: no agreement to reduce forces, USSR wanted larger army. SALT II: never really happened 2. Helsinki Conference (European Security Conference) Signed Helsinki Accords:. security: European borders agreed inc. West/East Germany. human rights: respect human rights & right to travel between countries. co-operation: better links through trade & cultural visits BUT. human rights: no improvement in USSR & E.Europe. Brezhnev said it was not others business.critics of communism were still harshly treated.. rivalry: rivalry continued around the world as the superpowers looked to extend their influence 6.19 USA USA s failure in Vietnam forced Nixon to look for a new approach, as containment did not work. People in the US wanted an alternative to war to solve the problems. Brezhnev did not see detente as an end to the rivalry. Ronald Reagan Became in US President. He was very anti communist & pro containment. Started Star Wars programme for lasers to hit missiles from space. Some in the West said Critics detente was a waste of time as USSR would not change. Conflicts USA & USSR continued to fund allies with conflicts in: Angola, Nicaragua, El Salvador & Arab-Israeli war. End of Detente in the 1980s said detente made little difference to the superpower rivalry. Nuclear Weapons Both sides were replacing old weapons with new missiles. Afghanistan Soviet forces invaded to support the communist govt. against the Mujahideen fighters. The USA was very worried that the Soviets were so close to the oil in the Middle East. The USA supported the Mujahideen with money & supplies. Moscow Olympics In protest the USA boycotted the 1980 Olympic Games in Moscow. Communist countries then boycotted the LA Games in 1984
40 How secure was the USSR s control over Eastern Europe, c.1989? Solidarity movement in Poland and its effects 6 Background Nationalism Polish people wanted to make their own decisions about their own country. Quality of life Life was hard in communist Poland. There was often a shortage of food & other goods. People wanted more freedoms. Role of the catholic church The catholic church was very influential in Poland, despite the communists trying to reduce its role. People looked to the church for leadership. Pope John Paul II In 1978 a Polish cardinal, became Pope. This gave the people a sense of pride & made them more nationalist. The catholic church in Poland felt more able to stand up to communism. Leader: Gierek Introduced economic reforms that helped living standards rise BUT: food shortages continued prices rose police attacked protesters Gdansk shipworkers Ship workers in the port of Gdansk started a movement called solidarity. (Aug 1980) It s leader was Lech Walesa It had three main demands:. the right to form a trade union. improve the living standards of working people. more freedoms of expression It soon became linked with the catholic church Govt. agreed:. right to form trade unions. workers have the right to protest & strike. to improve conditions for the workers. some freedoms & less control of the newspapers 6.22 Solidarity in Poland 1980 Solidarity formed. First year nearly 10 million members 1981 Solidarity demands free elections USSR imposes military rule under Jaruzelski Martial law imposed Walesa & other union leaders arrested 1982 Solidarity banned Demonstrations across the country but Walesa released from prison Martial law ended 31/12/ Lech Walesa awarded the Nobel Peace prize Results of Solidarity strikes & protests in 1980 Long term consequences:. Communist party undermined by workers. showed the power of non violent protests. communists less willing to use force Workers agreed:. communist party rule in Poland. socialist form of government. Poland s links with USSR & other communist countries & membership of Warsaw pact etc. highlighted failings of communist economic policies Poland: from communism to democracy 1991 Red army leaves Poland First full free elections since WW Lech Walesa elected President 1989 Free elections for lower house of parliament Solidarity does well, communists do badly in elections Solidarity refuses to join with communists in govt Jaruzelski appoints non communist as Prime Minister 1988 More strikes & demonstrations Talks between Walesa & govt 1984 Preist for Solidarity murdered by govt. agents 1985 Solidarity prisoners (225) released
41 How secure was the USSR s control over Eastern Europe, c.1989? Solidarity movement in Poland and its effects 6g test your knowledge Results of the Solidarity protests in 1980 Rank Results Explanation h Solidarity events For each event give its date: 1980, 1981, 1982, 1983, 1984, 1985, 1988, 1989, 1990, 1991 Free elections for lower house of parliament Solidarity does well, communists do badly in elections Solidarity refuses to join with communists in govt Jaruzelski appoints non communist as Prime Minister Solidarity demands free elections USSR imposes military rule under Jaruzelski Martial law imposed Walesa & other union leaders arrested More strikes & demonstrations Talks between Walesa & govt Lech Walesa elected President Red army leaves Poland First full free elections since WW2 Preist for Solidarity murdered by govt. agents Solidarity banned Demonstrations across the country but Walesa released from prison Martial law ended 31/12/82 Solidarity prisoners (225) released Lech Walesa awarded the Nobel Peace prize Solidarity formed First year nearly 10 million members
42 How secure was the USSR s control over Eastern Europe, c.1989? Gorbachev s effect on the collapse of Soviet control of Eastern Europe Communist Party. only communists could stand in elections.. communism more important than national identity Censorship & Propoganda. communists controlled radio, TV & newspapers. criticism of the government or communism was rare. people were given a diet of propaganda about the good of communism & the evil of capitalism & the West Life under communism Police state. police were feared by everyone. people were scared of being arrested if they criticised the govt or communism. the police could do as they wish Religion. communists did not believe in God. religion was discouraged. many religious leaders were arrested Economy. the state controlled the economy. people were often forced to pray in private. heavy industry was often preferred to consumer goods. the quality of goods was often poor. there were often shortages of food. in the 1980s inflation rose 6.24 Background. became leader in USSR in relations between USSR & Eastern Europe had changed:. USSR no longer use force. some communist countries wanted more control over their affairs. food shortages in USSR. poor quality of USSR goods. need imports from USA. quality of life was poor Perestroika.restructuring of the economic & political system. less control of economy by communists. have more investment form the West. wanted economy to be more efficient Changes under Mikhail Gorbachev Gorbachev s new attitude. Marxism had failed. communist party had to listen to the people. USSR no longer use force. military spending was too high. USSR not keep supporting other countries Glasnost. translates to openness. more justice less corruption. open to more debate about economy & management of industry. open to more freedoms of speech. multi candidates (communists) in elections
43 How secure was the USSR s control over Eastern Europe, c.1989? Gorbachev s effect on the collapse of Soviet control of Eastern Europe 6i test your knowledge Decide whether the statement for life in the USSR is either TRUE (T) or FALSE (F) Statement T F 1 Only selected communists could stand in elections 2 Communist newspapers were critical of the government 3 Gorbachev said that the Red Army would not be used in other countries 4 Gorbachev said people should believe in Marxist ideas 5 Gorbachev wanted to increase military spending 6 The USSR was producing quality goods in their factories 7 The government controlled the TV, radio and newspapers 8 The USSR suffered from food shortages 9 Gorbachev wanted more openess and less corruption 10 Gorbachev wanted investment money from the West 11 Religion was encouraged in the USSR 12 The quality of life in the USSR was similar to that in the USA 13 The police were feared in the USSR 14 Gorbachev introduced Glasnost & Peretrokia 15 The communist party listened to the people s concerns
44 How secure was the USSR s control over Eastern Europe, c.1989? Gorbachev s effect on the collapse of Soviet control of Eastern Europe 6 Background A new Cold War US foreign policy Reagan (Republican) became President in He did not support detente, he thought the USA should be strong with the USSR. Reagan was more aggressive towards the USSR e.g.. increased defence spending. Pershing & cruise missiles in Europe. started Strategic Defence Initiative (Star Wars) - which could in theory shoot down Soviet missiles in space. Tried to get arms reduction but relationship with USSR was tense from (see above). Reagan hoped that being more aggressive would force the USSR into reducing arms as the cost was rising. Afghanistan USSR s invasion of Afghanistan & the USA s support for the Mujaheddin continued to be a problem between the two superpowers. Iranian Revolution 1979 The USA supported the Shah but he was overthrown in an Islamic revolution. The new govt was both anti US and anti communist. Both the superpowers were worried the revolution might spread across the Middle East. Olympic Games 6.25 The USA boycotted the Moscow Games in 1980, and then the USSR + Eastern European countries boycotted the Los Angeles Games in New Detente after 1985 Gorbachev s need for change. wanted to end the Cold war. reduce military spending. arms race unsustainable. needed Western money to overhaul industry Europeans. W.German, UK & French govts pushing for detente. European Economic Community looking to end Cold War. needed imported food Reasons for new Detente Arms Reduction. Intermediate Nuclear Forces Treaty 1987 both sides to remove all intermediate range missiles in Europe in 3 years. Conventional Forces 1990 talks to reduce NATO & Warsaw Pact forces. Strategic Arms Reduction Talks (START) 1991 agreed to reduce weapons USA 20% & USSR 30% Consequences of new Detente End of the Cold War. US President George Bush took over from Reagan more cautious, but Soviet control in E. Europe already collapsing. Malta Summit Dec 1989 Personalities. Reagan & Gorbachev got on very well. Reagan thought Gorbachev to be genuine. Reagan less aggressive after both willing to negotiate Reagan s approach. saw an opportunity to reduce arms. bargain hard with Gorbachev, knowing that USSR could not afford to continue with military spending. knew USSR weak after Afghanistan. Star Wars development worried the USSR 6.27 Collapse of Soviet Empire in Eastern Europe. Gorbachev s reforms in the USSR had a domino effect in Eastern Europe admission that Marxism had failed & communism party not always right, leaders confused without Red Army support E.European leaders not control their populations. collapse an unintended consequence not part of Gorbachev s plans & took the West by surprise as well
45 How secure was the USSR s control over Eastern Europe, c.1989? Gorbachev s effect on the collapse of Soviet control of Eastern Europe 6j New Detente after 1985 test your knowledge Rank the reasons for Detente: explain your decision Rank Reason for New Detente Explanation k Consequences: For each consequence decide if it is a consequence of Arms reduction, the collapse of the Soviet Empire or the end of the Cold war. Write in Arms / Collapse or Cold War as your answer. Arms reduction Collapse of Soviet Empire End of Cold War Consequence Intermediate Nuclear Forces Treaty 1987 Talks to reduce NATO & Warsaw Pact forces Malta Summit Dec 1989 Admission that Marxism had failed & communism party not always right, leaders confused US President George Bush more cautious, but Soviet control already collapsing Agreed to reduce weapons USA 20% & USSR 30% Without Red Army support E.European leaders not control their populations
46 How secure was the USSR s control over Eastern Europe, c.1989? Gorbachev s effect on the collapse of Soviet control of Eastern Europe Collapse of Soviet control in Eastern Europe Events leading to collapse Geneva summit Nov 1985 Reagan & Gorbachev discussed a variety of issues, from SDI to human rights. No agreements but laid the foundation for further talks. Reykjavik summit Oct 1986 Gorbachev & Reagan discussed getting rid of all ballistic missiles. Agreement was close, but the USA would not give up research & development on SDI. Without that there was no agreement form the USSR. But it showed that both leaders were willing to discuss serious arms reduction. Hungary May: border with Austria opened. Dec: free elections announced Nationalists & Catholics won election Czechoslovakia Nov: large demonstrations inc. Dubcek. Dec: communist govt. resigned. 1990: free elections, communists only 14% 6.29 Poland June: free elections, Solidarity won easily. Dec 1990: Lech Walesa became first non Washington summit Dec 1987 Discussed a range of issues including Afghanistan, Central America, South Africa & chemical weapons. Agreement on limiting intermediate range nuclear missiles. Gorbachev s UN speech Dec 1988 Announced huge military reductions in Europe & on the Chinese border. Decision was unilateral and inc. 500,000 soldiers. Soviet troops were withdrawn from E. European countries. Soviet withdrawal from Afghanistan 1989 Soviet power was shown to be limited. It become to USSR what Vietnam was to the USA. Soviets worried that anti Soviet feeling would spread across Muslim population in USSR. Solidarity movement in Poland Throughout the 1980s the Solidarity movement in Poland had been gaining ground and winning concessions from the communist government. Other Eastern European countries were watching what was happening in Poland. Leaders were concerned by events and Gorbachev s new attitude. Many people in E. Europe wanted changes to their lives: less Soviet interference, freedoms, better standard of living etc. Romania Dec: short & violent revolution where communist leader Ceausescu is executed. 1990: Former Communists win free elections East Germany Sept: East Germans escape to West Germany via Hungary Break-up of the USSR. Communist leader resigns, after no support from army. Guards at the wall join the protests. 10 Nov: Berlin Wall pulled down. March 1990: free elections. Oct 1990: East & West Germany reunited Bulgaria Nov: large demonstrations Zhikov leader since 1954 resigns. Communist party becomes Socialist Party elections won by Socialist Party. The Baltic states, Latvia, Estonia & Lithuania & Azerbaijan wanted independence from the USSR, Gorbachev refused & sent in troops. In Russia Boris Yeltsin became the leader & called for the end of the USSR & for the republics to become independent. Hard-line communists in Russia were shocked at events, they led a coup & imprisoned Gorbachev in his holiday home in the Crimea. Yeltsin led demonstrations against the coup & for the reforms. Yeltsin ended the Soviet Communist Party & the USSR in Dec Gorbachev resigned as President of the USSR (there was no USSR)
Chapter 17 Lesson 1: Two Superpowers Face Off. Essential Question: Why did tension between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R increase after WWII?
 Chapter 17 Lesson 1: Two Superpowers Face Off Essential Question: Why did tension between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R increase after WWII? Post WWII Big Three meet in Yalta Divide Germany into 4 zones (U.S.,
Chapter 17 Lesson 1: Two Superpowers Face Off Essential Question: Why did tension between the U.S. and the U.S.S.R increase after WWII? Post WWII Big Three meet in Yalta Divide Germany into 4 zones (U.S.,
World History (Survey) Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present
 World History (Survey) Chapter 33: Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present Section 1: Two Superpowers Face Off The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February
World History (Survey) Chapter 33: Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945 Present Section 1: Two Superpowers Face Off The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February
THE IRON CURTAIN. From Stettin in the Baltic to Trieste in the Adriatic an iron curtain has descended across the continent. - Winston Churchill
 COLD WAR 1945-1991 1. The Soviet Union drove the Germans back across Eastern Europe. 2. They occupied several countries along it s western border and considered them a necessary buffer or wall of protection
COLD WAR 1945-1991 1. The Soviet Union drove the Germans back across Eastern Europe. 2. They occupied several countries along it s western border and considered them a necessary buffer or wall of protection
Ch 29-1 The War Develops
 Ch 29-1 The War Develops The Main Idea Concern about the spread of communism led the United States to become increasingly violent in Vietnam. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze how the Cold war and
Ch 29-1 The War Develops The Main Idea Concern about the spread of communism led the United States to become increasingly violent in Vietnam. Content Statement/Learning Goal Analyze how the Cold war and
The War in Vietnam. Chapter 30
 The War in Vietnam Chapter 30 Vietnam A colony of France until after World War II 1954- War for Independence led by Ho Chi Minh Ho Chi Minh The Geneva Accords The Geneva Accords divided the country into
The War in Vietnam Chapter 30 Vietnam A colony of France until after World War II 1954- War for Independence led by Ho Chi Minh Ho Chi Minh The Geneva Accords The Geneva Accords divided the country into
Write 3 words you think of when you hear Cold War? THE COLD WAR ( )
 THE Write 3 words you think of when you hear Cold War? COLD WAR (1948-1989) ORIGINS of the Cold War: (1945-1948) Tension or rivalry but NO FIGHTING between the United States and the Soviet Union This rivalry
THE Write 3 words you think of when you hear Cold War? COLD WAR (1948-1989) ORIGINS of the Cold War: (1945-1948) Tension or rivalry but NO FIGHTING between the United States and the Soviet Union This rivalry
THE COLD WAR ( )
 THE COLD WAR (1948-1989) ORIGINS of the Cold War: (1945-1948) Tension or rivalry but NO FIGHTING between the United States and the Soviet Union This rivalry divided the world into two teams (capitalism
THE COLD WAR (1948-1989) ORIGINS of the Cold War: (1945-1948) Tension or rivalry but NO FIGHTING between the United States and the Soviet Union This rivalry divided the world into two teams (capitalism
The Cold War Finally Thaws Out. Korean War ( ) Vietnam War ( ) Afghan War ( )
 The Cold War Finally Thaws Out Korean War (1950-1953) Vietnam War (1963-1973) Afghan War (1979-1989) Korean war Split after WWII between US and USSR Temporary gov ts created in images of their major allies
The Cold War Finally Thaws Out Korean War (1950-1953) Vietnam War (1963-1973) Afghan War (1979-1989) Korean war Split after WWII between US and USSR Temporary gov ts created in images of their major allies
TEKS 8C: Calculate percent composition and empirical and molecular formulas. Cold War Tensions (Chapter 30 Quiz)
 Cold War Tensions (Chapter 30 Quiz) What were the military and political consequences of the Cold War in the Soviet Union, Europe, and the United States? After World War II ended, the United States and
Cold War Tensions (Chapter 30 Quiz) What were the military and political consequences of the Cold War in the Soviet Union, Europe, and the United States? After World War II ended, the United States and
Ended French rule in Indo-China
 Vietnam Review Dien Bien Phu in 1954 the main French forces were surrounded at this location in the north of Vietnam and forced to surrender. This was a turning point in that it ended the French control
Vietnam Review Dien Bien Phu in 1954 the main French forces were surrounded at this location in the north of Vietnam and forced to surrender. This was a turning point in that it ended the French control
Unit 7: The Cold War
 Unit 7: The Cold War Standard 7-5 Goal: The student will demonstrate an understanding of international developments during the Cold War era. Vocabulary 7-5.1 OCCUPIED 7-5.2 UNITED NATIONS NORTH ATLANTIC
Unit 7: The Cold War Standard 7-5 Goal: The student will demonstrate an understanding of international developments during the Cold War era. Vocabulary 7-5.1 OCCUPIED 7-5.2 UNITED NATIONS NORTH ATLANTIC
The Cold War. Chapter 30
 The Cold War Chapter 30 Two Side Face Off in Europe Each superpower formed its own military alliance NATO USA and western Europe Warsaw Pact USSR and eastern Europe Berlin Wall 1961 Anti-Soviet revolts
The Cold War Chapter 30 Two Side Face Off in Europe Each superpower formed its own military alliance NATO USA and western Europe Warsaw Pact USSR and eastern Europe Berlin Wall 1961 Anti-Soviet revolts
UNIT Y222 THE COLD WAR IN ASIA
 UNIT Y222 THE COLD WAR IN ASIA 1945-1993 NOTE: BASED ON 2 X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources Western Policies
UNIT Y222 THE COLD WAR IN ASIA 1945-1993 NOTE: BASED ON 2 X 50 MINUTE LESSONS PER WEEK TERMS BASED ON 6 TERM YEAR. Key Topic Term Week Number Indicative Content Extended Content Resources Western Policies
Chapter 19: Going To war in Vietnam
 Heading Towards War Vietnam during WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the. returned to Vietnam
Heading Towards War Vietnam during WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the. returned to Vietnam
ANSWER KEY..REVIEW FOR Friday s QUIZ #15 Chapter: 29 -Vietnam
 ANSWER KEY..REVIEW FOR Friday s QUIZ #15 Chapter: 29 -Vietnam Ch. 29 sec. 1 - skim and scan pages 908-913 and then answer the questions. French Indochina: French ruled colony made up of Vietnam, Laos,
ANSWER KEY..REVIEW FOR Friday s QUIZ #15 Chapter: 29 -Vietnam Ch. 29 sec. 1 - skim and scan pages 908-913 and then answer the questions. French Indochina: French ruled colony made up of Vietnam, Laos,
The Cold War Begins. After WWII
 The Cold War Begins After WWII After WWII the US and the USSR emerged as the world s two. Although allies during WWII distrust between the communist USSR and the democratic US led to the. Cold War tension
The Cold War Begins After WWII After WWII the US and the USSR emerged as the world s two. Although allies during WWII distrust between the communist USSR and the democratic US led to the. Cold War tension
World History Chapter 23 Page Reading Outline
 World History Chapter 23 Page 601-632 Reading Outline The Cold War Era: Iron Curtain: a phrased coined by Winston Churchill at the end of World War I when her foresaw of the impending danger Russia would
World History Chapter 23 Page 601-632 Reading Outline The Cold War Era: Iron Curtain: a phrased coined by Winston Churchill at the end of World War I when her foresaw of the impending danger Russia would
Vietnam Introduction. Answer the following questions on a sticky note...
 Vietnam Introduction Answer the following questions on a sticky note... https://www.youtube.c om/watch?v=epfnsk5l 26U Burning Monk 1. Why was the burning monk event significant? How did people in the U.S.
Vietnam Introduction Answer the following questions on a sticky note... https://www.youtube.c om/watch?v=epfnsk5l 26U Burning Monk 1. Why was the burning monk event significant? How did people in the U.S.
EOC Test Preparation: The Cold War Era
 EOC Test Preparation: The Cold War Era Conflict in Europe Following WWII, tensions were running high between western Allies and USSR US and Great Britain: Allies should not occupy territories they conquered
EOC Test Preparation: The Cold War Era Conflict in Europe Following WWII, tensions were running high between western Allies and USSR US and Great Britain: Allies should not occupy territories they conquered
THE EARLY COLD WAR YEARS. US HISTORY Chapter 15 Section 2
 THE EARLY COLD WAR YEARS US HISTORY Chapter 15 Section 2 THE EARLY COLD WAR YEARS CONTAINING COMMUNISM MAIN IDEA The Truman Doctrine offered aid to any nation resisting communism; The Marshal Plan aided
THE EARLY COLD WAR YEARS US HISTORY Chapter 15 Section 2 THE EARLY COLD WAR YEARS CONTAINING COMMUNISM MAIN IDEA The Truman Doctrine offered aid to any nation resisting communism; The Marshal Plan aided
Notes: LG: Analyze how the 1960s changed America.
 Notes: LG: Analyze how the 1960s changed America. USSR Nikita Khrushchev 1953-1964 1. Cold War Abroad in the 1960s a. 1961, Bay of Pigs Invasion (Cuba) i. President Eisenhower and CIA train Cuban
Notes: LG: Analyze how the 1960s changed America. USSR Nikita Khrushchev 1953-1964 1. Cold War Abroad in the 1960s a. 1961, Bay of Pigs Invasion (Cuba) i. President Eisenhower and CIA train Cuban
Modern American History Unit 8: The 1960s The Vietnam War Notes and Questions
 Modern American History Unit 8: The 1960s The Vietnam War Notes and Questions The Vietnam War A. Vietnam: A Painful War U.S. involvement in conflicts in Vietnam lasted from mid-1940s to 1975 Only war the
Modern American History Unit 8: The 1960s The Vietnam War Notes and Questions The Vietnam War A. Vietnam: A Painful War U.S. involvement in conflicts in Vietnam lasted from mid-1940s to 1975 Only war the
Chapter 33 Summary/Notes
 Chapter 33 Summary/Notes Unit 8 Perspectives on the Present Chapter 33 Section 1. The Cold War Superpowers Face off We learned about the end of WWII. Now we learn about tensions that followed the war.
Chapter 33 Summary/Notes Unit 8 Perspectives on the Present Chapter 33 Section 1. The Cold War Superpowers Face off We learned about the end of WWII. Now we learn about tensions that followed the war.
Communism. Soviet Union government State (government) controls everything Opposite of democracy and capitalism (USA)
 Cold War VS Communism Soviet Union government State (government) controls everything Opposite of democracy and capitalism (USA) United Nations (UN) Started with 50 member countries Created to promote peace
Cold War VS Communism Soviet Union government State (government) controls everything Opposite of democracy and capitalism (USA) United Nations (UN) Started with 50 member countries Created to promote peace
Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs. non Communist South Organized by Ho Chi Minh
 1956 Elections are cancelled (1 of Geneva Accords) 1957 The Vietcong attack in South Vietnam Vietcong are South Vietnamese communists Guerrilla fighters Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs.
1956 Elections are cancelled (1 of Geneva Accords) 1957 The Vietcong attack in South Vietnam Vietcong are South Vietnamese communists Guerrilla fighters Civil War erupts in Vietnam Communist North vs.
Standard 8.0- Demonstrate an understanding of social, economic and political issues in contemporary America. Closing: Quiz
 Standard 8.0- Demonstrate an understanding of social, economic and political issues in contemporary America. Opening: Great Society Chart Work Period: Vietnam War Notes Political Cartoon Double Flow Map
Standard 8.0- Demonstrate an understanding of social, economic and political issues in contemporary America. Opening: Great Society Chart Work Period: Vietnam War Notes Political Cartoon Double Flow Map
General Certificate of Secondary Education History Unit 2: The Cold War Foundation Tier [GHY21] TUESDAY 12 JUNE, AFTERNOON
![General Certificate of Secondary Education History Unit 2: The Cold War Foundation Tier [GHY21] TUESDAY 12 JUNE, AFTERNOON General Certificate of Secondary Education History Unit 2: The Cold War Foundation Tier [GHY21] TUESDAY 12 JUNE, AFTERNOON](/thumbs/87/95530393.jpg) General Certificate of Secondary Education 2012 History Unit 2: The Cold War 1945 1991 Foundation Tier [GHY21] TUESDAY 12 JUNE, AFTERNOON MARK SCHEME 7487.01 Foundation Tier Mark Scheme The detail given
General Certificate of Secondary Education 2012 History Unit 2: The Cold War 1945 1991 Foundation Tier [GHY21] TUESDAY 12 JUNE, AFTERNOON MARK SCHEME 7487.01 Foundation Tier Mark Scheme The detail given
The Vietnam War,
 The Vietnam War, 1954 1975 Who was Ho Chi Minh? Vietnamese Communist who wanted self rule for Vietnam. Why did the United States aid the French? The French returned to Vietnam in 1946. As the Vietminh
The Vietnam War, 1954 1975 Who was Ho Chi Minh? Vietnamese Communist who wanted self rule for Vietnam. Why did the United States aid the French? The French returned to Vietnam in 1946. As the Vietminh
VUS.13b. The Vietnam War. U. S. government s anti- Communist strategy of containment in Asia
 VUS.13b The Vietnam War U. S. government s anti- Communist strategy of containment in Asia Help the French and send some advisors- Increase advisors, send some troops- Escalate- we can not lose a war Peace
VUS.13b The Vietnam War U. S. government s anti- Communist strategy of containment in Asia Help the French and send some advisors- Increase advisors, send some troops- Escalate- we can not lose a war Peace
OBJECTIVES. Describe and evaluate the events that led to the war between North Vietnam and South Vietnam.
 OBJECTIVES Describe and evaluate the events that led to the war between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. Identify and explain the foreign policy of the United States at this time, and how it relates to
OBJECTIVES Describe and evaluate the events that led to the war between North Vietnam and South Vietnam. Identify and explain the foreign policy of the United States at this time, and how it relates to
Modern World History Spring Final Exam 09
 1. What was the goal of the Marshall Plan? A. to provide aid to European countries damaged by World War II B. to protect member nations against Soviet Union aggression C. to protect the United States economically
1. What was the goal of the Marshall Plan? A. to provide aid to European countries damaged by World War II B. to protect member nations against Soviet Union aggression C. to protect the United States economically
Conflict U.S. War
 Conflict - 1945-1975 U.S. War 1964-1973 Overview of the Vietnam War Why is Vietnam still a painful war to remember? Longest war in U.S. history and only war we lost It showed Americans that our power is
Conflict - 1945-1975 U.S. War 1964-1973 Overview of the Vietnam War Why is Vietnam still a painful war to remember? Longest war in U.S. history and only war we lost It showed Americans that our power is
VIETNAM WAR
 VIETNAM WAR 1955-1975 #30 http://www.military.com/video/offduty/movies/classic-forrest-gump-invietnam-war/1069387728001 PRESIDENTS DURING THE VIETNAM WAR Dwight D. Eisenhower. John F. Kennedy. Lyndon B.
VIETNAM WAR 1955-1975 #30 http://www.military.com/video/offduty/movies/classic-forrest-gump-invietnam-war/1069387728001 PRESIDENTS DURING THE VIETNAM WAR Dwight D. Eisenhower. John F. Kennedy. Lyndon B.
SECTION 1: MOVING TOWARD CONFLICT PAGE 730
 CHAPTER 22 SECTION 1: MOVING TOWARD CONFLICT PAGE 730 Main Idea: America gets involved in Vietnam to stop the spread of communism TERMS AND NAMES: Ho Chi Minh Ngo Dinh Diem Vietcong Vietminh domino theory
CHAPTER 22 SECTION 1: MOVING TOWARD CONFLICT PAGE 730 Main Idea: America gets involved in Vietnam to stop the spread of communism TERMS AND NAMES: Ho Chi Minh Ngo Dinh Diem Vietcong Vietminh domino theory
4.2.2 Korea, Cuba, Vietnam. Causes, Events and Results
 4.2.2 Korea, Cuba, Vietnam Causes, Events and Results This section will illustrate the extent of the Cold War outside of Europe & its impact on international affairs Our focus will be to analyze the causes
4.2.2 Korea, Cuba, Vietnam Causes, Events and Results This section will illustrate the extent of the Cold War outside of Europe & its impact on international affairs Our focus will be to analyze the causes
2014 Brain Wrinkles. Origins and Consequences
 Origins and Consequences Standards SS5H7 The student will discuss the origins and consequences of the Cold War. a. Explain the origin and meaning of the term Iron Curtain. b. Explain how the United States
Origins and Consequences Standards SS5H7 The student will discuss the origins and consequences of the Cold War. a. Explain the origin and meaning of the term Iron Curtain. b. Explain how the United States
the Cold War The Cold War would dominate global affairs from 1945 until the breakup of the USSR in 1991
 U.S vs. U.S.S.R. ORIGINS OF THE COLD WAR After being Allies during WWII, the U.S. and U.S.S.R. soon viewed each other with increasing suspicion Their political differences created a climate of icy tension
U.S vs. U.S.S.R. ORIGINS OF THE COLD WAR After being Allies during WWII, the U.S. and U.S.S.R. soon viewed each other with increasing suspicion Their political differences created a climate of icy tension
Chapter 20. The Vietnam War Era
 Chapter 20 The Vietnam War Era 1954-1975 Ho Chi Minh The most important voice who demanded independence for Vietnam. Communist leader of the Vietminh. Vietminh The term initially used to describe all Vietnamese
Chapter 20 The Vietnam War Era 1954-1975 Ho Chi Minh The most important voice who demanded independence for Vietnam. Communist leader of the Vietminh. Vietminh The term initially used to describe all Vietnamese
The Cold War. Origins - Korean War
 The Cold War Origins - Korean War What is a Cold War? WW II left two nations of almost equal strength but differing goals Cold War A struggle over political differences carried on by means short of direct
The Cold War Origins - Korean War What is a Cold War? WW II left two nations of almost equal strength but differing goals Cold War A struggle over political differences carried on by means short of direct
Introduction to the Cold War
 Introduction to the Cold War What is the Cold War? The Cold War is the conflict that existed between the United States and Soviet Union from 1945 to 1991. It is called cold because the two sides never
Introduction to the Cold War What is the Cold War? The Cold War is the conflict that existed between the United States and Soviet Union from 1945 to 1991. It is called cold because the two sides never
ALLIES BECOME ENEMIES
 Cold War: Super Powers Face Off ALLIES BECOME ENEMIES What caused the Cold War? The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February 1945, they agreed to divide Germany into
Cold War: Super Powers Face Off ALLIES BECOME ENEMIES What caused the Cold War? The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February 1945, they agreed to divide Germany into
Vietnam Before WWII During the early 1900s, nationalism was strong in. As the Vietnamese sought or reform of the colonial government, several
 Name Date Per Vietnam Before WWII During the early 1900s, nationalism was strong in. As the Vietnamese sought or reform of the colonial government, several political parties formed. One of the leaders
Name Date Per Vietnam Before WWII During the early 1900s, nationalism was strong in. As the Vietnamese sought or reform of the colonial government, several political parties formed. One of the leaders
Europe and North America Section 1
 Europe and North America Section 1 Europe and North America Section 1 Click the icon to play Listen to History audio. Click the icon below to connect to the Interactive Maps. Europe and North America Section
Europe and North America Section 1 Europe and North America Section 1 Click the icon to play Listen to History audio. Click the icon below to connect to the Interactive Maps. Europe and North America Section
THE COLD WAR Part Two Teachers Notes by Paul Latham
 THE COLD WAR Part Two Teachers Notes by Paul Latham Notes also available on DVD disc as either a Word document or PDF file. Also available on the website 1 2 The Cold War (Part 2) Teachers Notes CUBA AND
THE COLD WAR Part Two Teachers Notes by Paul Latham Notes also available on DVD disc as either a Word document or PDF file. Also available on the website 1 2 The Cold War (Part 2) Teachers Notes CUBA AND
Russian History. Lecture #1 Ancient History The Romanov s
 Russian History Lecture #1 Ancient History The Romanov s Outline Russia Lecture #1 Ancient Russia Settlement of Russia Yaroslav the Wise Mongol Invasion of Russia Retaking Russia Ivan the Great Ivan the
Russian History Lecture #1 Ancient History The Romanov s Outline Russia Lecture #1 Ancient Russia Settlement of Russia Yaroslav the Wise Mongol Invasion of Russia Retaking Russia Ivan the Great Ivan the
The Cold War
 The Cold War 1945-1989 What is the Cold War It was an intense rivalry between the United States and Russia between West and East and between capitalism and communism that dominated the years following
The Cold War 1945-1989 What is the Cold War It was an intense rivalry between the United States and Russia between West and East and between capitalism and communism that dominated the years following
Section 4: How did the Cold War develop?
 Section 4: How did the Cold War develop? 1943-56 4 (a) Describe one reason why the Allies met at Yalta in February 1945. 1 1 Simple statement(s) e.g. To discuss what to do with Germany. 2 2 Developed statements
Section 4: How did the Cold War develop? 1943-56 4 (a) Describe one reason why the Allies met at Yalta in February 1945. 1 1 Simple statement(s) e.g. To discuss what to do with Germany. 2 2 Developed statements
2. The State Department asked the American Embassy in Moscow to explain Soviet behavior.
 1. The Americans become increasingly impatient with the Soviets. 2. The State Department asked the American Embassy in Moscow to explain Soviet behavior. 3. On February 22, 1946, George Kennan an American
1. The Americans become increasingly impatient with the Soviets. 2. The State Department asked the American Embassy in Moscow to explain Soviet behavior. 3. On February 22, 1946, George Kennan an American
Cold War Conflicts Chapter 26
 Cold War Conflicts Chapter 26 Former Allies Clash After World War II the US and the Soviets had very different goals for the future. Under Soviet communism the state controlled all property and economic
Cold War Conflicts Chapter 26 Former Allies Clash After World War II the US and the Soviets had very different goals for the future. Under Soviet communism the state controlled all property and economic
VIETNAM WAR
 VIETNAM WAR 1965-1972 FRENCH CONTROL French controlled Vietnam until World War II Vietnam taken by Japan Ho Chi Minh called for an independence of Vietnam Eight Year war between France and Ho Chi Minh
VIETNAM WAR 1965-1972 FRENCH CONTROL French controlled Vietnam until World War II Vietnam taken by Japan Ho Chi Minh called for an independence of Vietnam Eight Year war between France and Ho Chi Minh
Cold War: Superpowers Face Off
 Cold War: Superpowers Face Off ALLIES BECOME ENEMIES What caused the Cold War? The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February 1945, they agreed to divide Germany into
Cold War: Superpowers Face Off ALLIES BECOME ENEMIES What caused the Cold War? The United States and the Soviet Union were allies during World War II. In February 1945, they agreed to divide Germany into
Chapter 30-1 CN I. Early American Involvement in Vietnam (pages ) A. Although little was known about Vietnam in the late 1940s and early
 Chapter 30-1 CN I. Early American Involvement in Vietnam (pages 892 894) A. Although little was known about Vietnam in the late 1940s and early 1950s, American officials felt Vietnam was important in their
Chapter 30-1 CN I. Early American Involvement in Vietnam (pages 892 894) A. Although little was known about Vietnam in the late 1940s and early 1950s, American officials felt Vietnam was important in their
TRUMAN S ROLE IN VIETNAM. = America is busy!!!!!
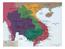 TRUMAN S ROLE IN VIETNAM Saw Vietnam as extension of Cold War - democracy v. communism! France fighting to re-gain Vietnam Truman supported France with money supplies because didn t want Something going
TRUMAN S ROLE IN VIETNAM Saw Vietnam as extension of Cold War - democracy v. communism! France fighting to re-gain Vietnam Truman supported France with money supplies because didn t want Something going
Chapter 25 Cold War America, APUSH Mr. Muller
 Chapter 25 Cold War America, 1945-1963 APUSH Mr. Muller Aim: How does the U.S. and U.S.S.R. go from allies to rivals? Do Now: Communism holds that the world is so deeply divided into opposing classes that
Chapter 25 Cold War America, 1945-1963 APUSH Mr. Muller Aim: How does the U.S. and U.S.S.R. go from allies to rivals? Do Now: Communism holds that the world is so deeply divided into opposing classes that
The Cold War TOWARD A GLOBAL COMMUNITY (1900 PRESENT)
 The Cold War TOWARD A GLOBAL COMMUNITY (1900 PRESENT) Throughout WWII the U.S. and the Soviet Union began to view each other with increasing suspicion. He s a commie, and once made an alliance with Hitler...
The Cold War TOWARD A GLOBAL COMMUNITY (1900 PRESENT) Throughout WWII the U.S. and the Soviet Union began to view each other with increasing suspicion. He s a commie, and once made an alliance with Hitler...
 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 The reason the French did not want to give up Vietnam.
$100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $100 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $200 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $300 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $400 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 $500 The reason the French did not want to give up Vietnam.
The end of WWII caused major changes:
 The Cold War The end of WWII caused major changes: 1. Europe is no longer the world s dominant power The USA and the USSR have become superpowers. 2. The world has entered...the nuclear age Tension was
The Cold War The end of WWII caused major changes: 1. Europe is no longer the world s dominant power The USA and the USSR have become superpowers. 2. The world has entered...the nuclear age Tension was
Lyndon Johnson and Vietnam. A Case Study
 Lyndon Johnson and Vietnam A Case Study Who was Lyndon B Johnson? Which US President won an election with the largest ever popular majority? Lyndon Baines Johnson, who took 61% of the vote in 1964. He
Lyndon Johnson and Vietnam A Case Study Who was Lyndon B Johnson? Which US President won an election with the largest ever popular majority? Lyndon Baines Johnson, who took 61% of the vote in 1964. He
Challenges to Soviet Control and the End of the Cold War I. Early Cold War A. Eastern European Soviet Control 1. In the early years of the Cold War,
 Challenges to Soviet Control and the End of the Cold War I. Early Cold War A. Eastern European Soviet Control 1. In the early years of the Cold War, Eastern European nations (Hungary, Czechoslovakia, Romania,
Challenges to Soviet Control and the End of the Cold War I. Early Cold War A. Eastern European Soviet Control 1. In the early years of the Cold War, Eastern European nations (Hungary, Czechoslovakia, Romania,
Chapter 19 GOING TO WAR IN VIETNAM
 Chapter 19 GOING TO WAR IN VIETNAM VIETNAM DURING WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the Japanese.
Chapter 19 GOING TO WAR IN VIETNAM VIETNAM DURING WWII After the French were conquered by the Germans, the Nazi controlled government turned the Indochina Peninsula over to their Axis allies, the Japanese.
Cold War: Superpowers Face Off
 Section 1 Cold War: Superpowers Face Off Reading Comprehension Find the name or term in the second column that best matches the description in the first column. Then write the letter of your answer in
Section 1 Cold War: Superpowers Face Off Reading Comprehension Find the name or term in the second column that best matches the description in the first column. Then write the letter of your answer in
Chapter 17: Restructuring the Postwar World: 1945-Present I. Cold War: Superpowers Face Off (Section 1) a. Allies Become Enemies i.
 Chapter 17: Restructuring the Postwar World: 1945-Present I. Cold War: Superpowers Face Off (Section 1) a. Allies Become Enemies i. Yalta Conference: A Postwar Plan 1. In February 1945, British, American
Chapter 17: Restructuring the Postwar World: 1945-Present I. Cold War: Superpowers Face Off (Section 1) a. Allies Become Enemies i. Yalta Conference: A Postwar Plan 1. In February 1945, British, American
1) Read the article on American involvement in Vietnam
 Warm Up 1) Read the article on American involvement in Vietnam 1) Circle in the causes of the Vietnam War 2) Put a star next to the key people/ countries 3) Box in key events, battles, treaties 4) Put
Warm Up 1) Read the article on American involvement in Vietnam 1) Circle in the causes of the Vietnam War 2) Put a star next to the key people/ countries 3) Box in key events, battles, treaties 4) Put
Unit 4 Notes - The Cold War
 Unit 4 Notes - The Cold War 4.1.1 Cold War: The period following WWII, 1945 to 1990, when increasing diplomatic and political tension between the West / United States and the East /Soviet Union created
Unit 4 Notes - The Cold War 4.1.1 Cold War: The period following WWII, 1945 to 1990, when increasing diplomatic and political tension between the West / United States and the East /Soviet Union created
THEMES. 1) EXPANDING DEMOCRACY: America s mission in Vietnam was to halt the spread of communism-a threat to democracy.
 THEMES 1) EXPANDING DEMOCRACY: America s mission in Vietnam was to halt the spread of communism-a threat to democracy. 2) CONSTITUTIONAL CONCERNS: Among the constitutional issues of the Vietnam War era
THEMES 1) EXPANDING DEMOCRACY: America s mission in Vietnam was to halt the spread of communism-a threat to democracy. 2) CONSTITUTIONAL CONCERNS: Among the constitutional issues of the Vietnam War era
The Vietnam War. Summary
 The Vietnam War Summary The Vietnam War grew out of the American commitment to the containment of communism during the Cold War. For approximately fifteen years, the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (North
The Vietnam War Summary The Vietnam War grew out of the American commitment to the containment of communism during the Cold War. For approximately fifteen years, the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (North
BACKGROUND: why did the USA and USSR start to mistrust each other? What was the Soviet View? What was the Western view? What is a Cold War?
 BACKGROUND: why did the USA and USSR start to mistrust each other? The 2 sides were enemies long before they were allies in WWII. Relations had been bad since 1917 as Russia had become communist and the
BACKGROUND: why did the USA and USSR start to mistrust each other? The 2 sides were enemies long before they were allies in WWII. Relations had been bad since 1917 as Russia had become communist and the
netw rks Where in the world? When did it happen? The Vietnam Era Lesson 1 Kennedy s Foreign Policy ESSENTIAL QUESTION Terms to Know GUIDING QUESTIONS
 Lesson 1 Kennedy s Foreign Policy ESSENTIAL QUESTION What motivates people to act? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. Why did President Kennedy seek new ways to deal with the challenges and fears of the Cold War? 2.
Lesson 1 Kennedy s Foreign Policy ESSENTIAL QUESTION What motivates people to act? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. Why did President Kennedy seek new ways to deal with the challenges and fears of the Cold War? 2.
WINNING the WAR / PLANNING the PEACE The Allies: US, England, USSR, and China Feb 1945 Yalta Conference: US-USSR-England GERMANY must agree to
 WINNING the WAR / PLANNING the PEACE The Allies: US, England, USSR, and China Feb 1945 Yalta Conference: US-USSR-England GERMANY must agree to UNCONDITIONAL SURRENDER Germany will be divided into 4 parts
WINNING the WAR / PLANNING the PEACE The Allies: US, England, USSR, and China Feb 1945 Yalta Conference: US-USSR-England GERMANY must agree to UNCONDITIONAL SURRENDER Germany will be divided into 4 parts
VIETNAM 04/14/15 ORIGINS OF THE VIETNAM WAR s French establish control over Indochina - Southeast Asia
 VIETNAM Have you seen Charlie? 04/12/15 2 ORIGINS OF THE VIETNAM WAR 1800 s French establish control over Indochina - Southeast Asia Modern countries: Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos Transplanted French laws
VIETNAM Have you seen Charlie? 04/12/15 2 ORIGINS OF THE VIETNAM WAR 1800 s French establish control over Indochina - Southeast Asia Modern countries: Vietnam, Cambodia, and Laos Transplanted French laws
Bell Ringers - April 21
 WWII: Bell Ringers - April 21 What were the Nuremburg Trials? Trials set up by the Allies (International Military Tribunal) to make sure the NAZIs were punished for their crimes for waging a war of aggression
WWII: Bell Ringers - April 21 What were the Nuremburg Trials? Trials set up by the Allies (International Military Tribunal) to make sure the NAZIs were punished for their crimes for waging a war of aggression
THE EASTERN EUROPE AND THE USSR
 THE EASTERN EUROPE AND THE USSR After the defeat of Germany in World War Two Eastern European countries were left without government. Some countries had their governments in exile. If not, it was obvious
THE EASTERN EUROPE AND THE USSR After the defeat of Germany in World War Two Eastern European countries were left without government. Some countries had their governments in exile. If not, it was obvious
The Cold War A bitter rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union, the two superpowers after WWII, that lasted for almost 50 years.
 The Cold War A bitter rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union, the two superpowers after WWII, that lasted for almost 50 years. Satellite Nation: One that is dominated politically and economically
The Cold War A bitter rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union, the two superpowers after WWII, that lasted for almost 50 years. Satellite Nation: One that is dominated politically and economically
America after WWII. The 1946 through the 1950 s
 America after WWII The 1946 through the 1950 s The United Nations In 1944 President Roosevelt began to think about what the world would be like after WWII He especially wanted to be sure that there would
America after WWII The 1946 through the 1950 s The United Nations In 1944 President Roosevelt began to think about what the world would be like after WWII He especially wanted to be sure that there would
The Cold War. Chap. 18, 19
 The Cold War Chap. 18, 19 Cold War 1945-1991 Political and economic conflict between U.S. and USSR Not fought on battlefield U.S. Vs. USSR Democracy- free elections private ownership Free market former
The Cold War Chap. 18, 19 Cold War 1945-1991 Political and economic conflict between U.S. and USSR Not fought on battlefield U.S. Vs. USSR Democracy- free elections private ownership Free market former
Unit 15 Cold War-Present
 Unit 15 Cold War-Present Section 1: Introduction Cold War Definition A cold war in general is a state of political hostility between countries characterized by threats, propaganda, and other measures short
Unit 15 Cold War-Present Section 1: Introduction Cold War Definition A cold war in general is a state of political hostility between countries characterized by threats, propaganda, and other measures short
Chapter 29. Section 3 and 4
 Chapter 29 Section 3 and 4 The War Divides America Section 3 Objectives Describe the divisions within American society over the Vietnam War. Analyze the Tet Offensive and the American reaction to it. Summarize
Chapter 29 Section 3 and 4 The War Divides America Section 3 Objectives Describe the divisions within American society over the Vietnam War. Analyze the Tet Offensive and the American reaction to it. Summarize
Early Cold War
 Early Cold War 1945-1972 Capitalism vs. Communism Capitalism Communism Free-Market Economy Upper, Middle and Working Class North Atlantic Treaty Organization Government Controlled Economy Classless Society
Early Cold War 1945-1972 Capitalism vs. Communism Capitalism Communism Free-Market Economy Upper, Middle and Working Class North Atlantic Treaty Organization Government Controlled Economy Classless Society
Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos Annotation
 Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos Annotation Name Directions: A. Read the entire article, CIRCLE words you don t know, mark a + in the margin next to paragraphs you understand and a next to paragraphs you don t
Vietnam, Cambodia, Laos Annotation Name Directions: A. Read the entire article, CIRCLE words you don t know, mark a + in the margin next to paragraphs you understand and a next to paragraphs you don t
THE ELECTION OF 1960
 THE ELECTION OF 1960 THE RACE FOR OFFICE Both were: young, military veterans, lawyers and cold warriors However, many historians believe there were (2) important factors that decided the race.. 1. TELEVISED
THE ELECTION OF 1960 THE RACE FOR OFFICE Both were: young, military veterans, lawyers and cold warriors However, many historians believe there were (2) important factors that decided the race.. 1. TELEVISED
The Cold War ( )
 The Cold War (1945-1991) Timeline USSR dissolves WWII Cold War 1939 1945 1989 1991 Revolutions of 1989 What is it US vs. USSR state of tension nuclear arms race Space Race propaganda war fighting through
The Cold War (1945-1991) Timeline USSR dissolves WWII Cold War 1939 1945 1989 1991 Revolutions of 1989 What is it US vs. USSR state of tension nuclear arms race Space Race propaganda war fighting through
unit 4: The Cold War
 unit 4: The Cold War Vocabulary & Important People 1. Cold War: the state of political hostility that existed between the Soviet bloc countries and the US-led Western powers from 1945 to 1990. 2. Harry
unit 4: The Cold War Vocabulary & Important People 1. Cold War: the state of political hostility that existed between the Soviet bloc countries and the US-led Western powers from 1945 to 1990. 2. Harry
COLD WAR ORIGINS. U.S vs. U.S.S.R. Democ./Cap vs Comm.
 COLD WAR ORIGINS U.S vs. U.S.S.R. Democ./Cap vs Comm. Section One: Objectives By the end, I will be able to: 1. Explain the breakdown in relations between the United States and the Soviet Union after World
COLD WAR ORIGINS U.S vs. U.S.S.R. Democ./Cap vs Comm. Section One: Objectives By the end, I will be able to: 1. Explain the breakdown in relations between the United States and the Soviet Union after World
THE COLD WAR Part One Teachers Notes by Paul Latham
 THE COLD WAR Part One Teachers Notes by Paul Latham Notes also available on DVD disc as either a Word document or PDF file. Also available on the website. 1 2 The Cold War (Part 1) Teachers Notes ORIGINS
THE COLD WAR Part One Teachers Notes by Paul Latham Notes also available on DVD disc as either a Word document or PDF file. Also available on the website. 1 2 The Cold War (Part 1) Teachers Notes ORIGINS
Kennedy & Johnson. Chapters 38 & 39
 Kennedy & Johnson Chapters 38 & 39 Kennedy s Presidency Young, inspirational, refreshing Young Cabinet Sec. of Defense - Robert McNamara Attorney General - Robert Kennedy Wanted to target organized crime
Kennedy & Johnson Chapters 38 & 39 Kennedy s Presidency Young, inspirational, refreshing Young Cabinet Sec. of Defense - Robert McNamara Attorney General - Robert Kennedy Wanted to target organized crime
Topic 5: The Cold War (Compiled from 10 Topic and 6 Topic Format) Revised 2014
 Topic 5: The Cold War (Compiled from 10 Topic and 6 Topic Format) Revised 2014 [Since 1998, the pattern is: two subject specific questions, two questions allowing a choice of examples, and one question
Topic 5: The Cold War (Compiled from 10 Topic and 6 Topic Format) Revised 2014 [Since 1998, the pattern is: two subject specific questions, two questions allowing a choice of examples, and one question
The Americans (Survey)
 The Americans (Survey) Chapter 26: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Cold War Conflicts CHAPTER OVERVIEW After World War II, tensions between the United States and the Soviet Union lead to a war without direct military
The Americans (Survey) Chapter 26: TELESCOPING THE TIMES Cold War Conflicts CHAPTER OVERVIEW After World War II, tensions between the United States and the Soviet Union lead to a war without direct military
C. Continuing protests Doves wanted an immediate withdrawal that was complete, unconditional, and irreversible.
 I. VIETNAM WAR spread across 5 presidencies and spanned 25 years Direct U.S involvement from 1963-1973 A. France lost control of Vietnam after the battle of Dien Bien Phu in 1954 1. U.S. by 1954 had financed
I. VIETNAM WAR spread across 5 presidencies and spanned 25 years Direct U.S involvement from 1963-1973 A. France lost control of Vietnam after the battle of Dien Bien Phu in 1954 1. U.S. by 1954 had financed
Communism. Communism is a form of economy. Everyone gets the same resources. Gov t owns the means of production -so no individuals own the businesses
 The Cold War Communism Communism is a form of economy Everyone gets the same resources Gov t owns the means of production -so no individuals own the businesses Idea of Communism Gov t will work in the
The Cold War Communism Communism is a form of economy Everyone gets the same resources Gov t owns the means of production -so no individuals own the businesses Idea of Communism Gov t will work in the
Topic 5: The Cold War (Compiled from 10 Topic and 6 Topic Format) Revised 2012
 Topic 5: The Cold War (Compiled from 10 Topic and 6 Topic Format) Revised 2012 [Since 1998, the pattern is: two subject specific questions, two questions allowing a choice of examples, and one question
Topic 5: The Cold War (Compiled from 10 Topic and 6 Topic Format) Revised 2012 [Since 1998, the pattern is: two subject specific questions, two questions allowing a choice of examples, and one question
National Nightmare Begins: Origins of Vietnam War
 National Nightmare Begins: Origins of Vietnam War From late 1800 s until WWII (When Japan took over) France ruled Indochina (Vietnam, Laos & Cambodia). French took land from peasants & built large plantations,
National Nightmare Begins: Origins of Vietnam War From late 1800 s until WWII (When Japan took over) France ruled Indochina (Vietnam, Laos & Cambodia). French took land from peasants & built large plantations,
One war ends, another begins
 One war ends, another begins Communism comes from the word common, meaning to belong equally to more than one individual. The related word, commune is a place where people live together and share property
One war ends, another begins Communism comes from the word common, meaning to belong equally to more than one individual. The related word, commune is a place where people live together and share property
Politics of the Cold War
 Politics of the Cold War Standards SSUSH20 The student will analyze the domestic and international impact of the Cold War on the United States. c. Describe the Cuban Revolution, the Bay of Pigs, and the
Politics of the Cold War Standards SSUSH20 The student will analyze the domestic and international impact of the Cold War on the United States. c. Describe the Cuban Revolution, the Bay of Pigs, and the
Cold War Containment Policies
 VUS.13b Cold War Containment Policies How did the U.S. respond to the threat of communist expansion? "Flags courtesy of www.theodora.com/flags used with permission" Origins of the Cold War The Cold War
VUS.13b Cold War Containment Policies How did the U.S. respond to the threat of communist expansion? "Flags courtesy of www.theodora.com/flags used with permission" Origins of the Cold War The Cold War
[GHT22] TUESDAY 14 JUNE, AFTERNOON MARK SCHEME
![[GHT22] TUESDAY 14 JUNE, AFTERNOON MARK SCHEME [GHT22] TUESDAY 14 JUNE, AFTERNOON MARK SCHEME](/thumbs/89/98741510.jpg) New Specification General Certificate of Secondary Education 2016 History Unit 2: The Cold War 1945 1991 Higher Tier [GHT22] TUESDAY 14 JUNE, AFTERNOON MARK SCHEME General Marking Instructions Introduction
New Specification General Certificate of Secondary Education 2016 History Unit 2: The Cold War 1945 1991 Higher Tier [GHT22] TUESDAY 14 JUNE, AFTERNOON MARK SCHEME General Marking Instructions Introduction
Domestic policy WWI. Foreign Policy. Balance of Power
 Domestic policy WWI The decisions made by a government regarding issues that occur within the country. Healthcare, education, Social Security are examples of domestic policy issues. Foreign Policy Caused
Domestic policy WWI The decisions made by a government regarding issues that occur within the country. Healthcare, education, Social Security are examples of domestic policy issues. Foreign Policy Caused
Former Allies Diverge
 Chapter 17-1 Two Superpowers Face Off Former Allies Diverge The Soviet Union Corrals Eastern Europe United States Counters Soviet Expansion The Cold War and a Divided World Former Allies Diverge Before
Chapter 17-1 Two Superpowers Face Off Former Allies Diverge The Soviet Union Corrals Eastern Europe United States Counters Soviet Expansion The Cold War and a Divided World Former Allies Diverge Before
World History: Patterns of Interaction
 Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945-Present The United States and the Soviet Union vie for superiority, and both countries extend their control over other nations. Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945-Present
Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945-Present The United States and the Soviet Union vie for superiority, and both countries extend their control over other nations. Restructuring the Postwar World, 1945-Present
Beginnings of the Cold War
 Beginnings of the Cold War Chapter 15 Section 1 Problems of Peace At the end of World War II, Germany was in ruins and had no government. Much of Europe was also in ruins. Problems of Peace Occupied Germany
Beginnings of the Cold War Chapter 15 Section 1 Problems of Peace At the end of World War II, Germany was in ruins and had no government. Much of Europe was also in ruins. Problems of Peace Occupied Germany
Note Taking Study Guide THE COLD WAR UNFOLDS
 SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide THE COLD WAR UNFOLDS Focus Question: What were the military and political consequences of the Cold War in the Soviet Union, Europe, and the United States? As you read
SECTION 1 Note Taking Study Guide THE COLD WAR UNFOLDS Focus Question: What were the military and political consequences of the Cold War in the Soviet Union, Europe, and the United States? As you read
