READ Explain how political system organization (federal or unitary presidential or parliamentary) impacts political party strength.
|
|
|
- Nancy Martin
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 READ NAME PERIOD 1. Define political party. What three functions do parties perform? 2. Explain how political system organization (federal or unitary presidential or parliamentary) impacts political party strength. 3. Compare American and most European (parliamentary) systems in the following categories. candidate selection chief executive selection cabinet selection 4. Describe the founding and development to the mid-19 th century of American political parties. Include outstanding personalities.
2 5. What are critical (realigning) elections? List three historic such elections and state the issues involved. 6. What regional realignment seems to have been occurring in recent decades? 7. Why did split ticket voting not occur until the arrival of progressive reforms?
3 READ NAME PERIOD 1. How are American National parties organized? 2. What was the organizational difference between Republicans and Democrats from the late 1960 s to the early 1980 s? 3. What is party money spent for? 4. Why are delegate selection formulas important to national nominating conventions? 5. Define super-delegates. 6. Describe traditional political machines.
4 READ NAME PERIOD 1. Compare America s two-party system with the system found in most European countries. 2. Identify and discuss at least two reasons for the long endurance of the American biparty system. 3. What impact have 3 rd parties had on American politics? 4. How representative are convention delegates opinions of those of party voters? Why? 5. See Table 9.3. How do both parties delegates compare to voters in terms of: Income Being African American Gender Abortion- Government solving national problems Same Sex Relationships-
5 READ NAME PERIOD 1. In what 3 ways are modern elections different from those of the 19 th century? 2. Which voters are most influenced by emotional ads? 3. When does fund raising begin after an election to congress is won? 4. Compare presidential and congressional campaigns in at least three ways. 5. What seems to be have happened to the coattail effect in recent elections? 6. What legal restrictions are placed on campaign money? 7. List the four strategic questions of campaigns. 8. What is the difference between malapportionment and gerrymandering? 9. What is the difference between delegate and trustee?
6 READ NAME PERIOD 1. What are the constitutional qualifications for being a member of either house of Congress? Who judges whether those qualifications and elections have been met? 2. What special constitutional privilege do members of Congress enjoy? What defines when this privilege is available and when it is not? 3. Why must Democratic candidates for their party s nomination for the presidency be more liberal than in the general election and Republican candidates for their party s nomination for the presidency be more conservative than in the general election? 4. What is the difference between a presidential primary election and a caucus? 5. What is a clothespin vote? 6. Distinguish between position issues and valence issues. Modern campaigns have tended to emphasize which more? Why? 7. What impacts do political science studies say the following have on election outcomes? Be complete.
7 TV news coverage of campaigns and TV spots TV debates 8. Characterize safe presidential campaign speeches. What pitfalls are they designed to avoid? 9. What impact have computers had on presidential campaigning? 10. How do modern technology dominated campaigns differ from campaigns of the past?
8 READ PAGES NAME PERIOD 1. What requirements are placed on presidential campaign funding if the candidates take federal money? 2. Comment on the source of most money for congressional campaigns and on the difference between incumbent and challenger campaign funding. 3. How did the Federal Election Campaign Act change funding after Watergate? 4. Read The 2008 Election on page 243. Refer to figure 10.3 on page 244. Considering the pre-election circumstances, what was unusual about the outcome of the 2008 presidential election. Which groups voted for Obama and which voted for McCain? What role did Obama s race play in the outcome? 5. What were the negative impacts of the campaign reform laws of the 1970 s? 6. List and describe the three changes in congressional finance law passed in 2002.
9 7. Describe the impact of the following on presidential races. Pay attention to detail. Independent voters pocket-book vote character vice presidential nominee political reporting religion abortion new voting groups money 8. What advantages do congressional incumbents have over challengers other than money? 9. What are 527 s?
10 READ NAME PERIOD 1. Compare Democrats and Republicans in terms of size and strength of support. 2. Define and discuss the relative importance of prospective voting and retrospective voting. 3. What are the best predictors of presidential election outcomes? 4. List and describe three ways that campaigns influence election outcomes.
11 5. According to Table 10.6 on page 253, briefly match up the preference of party (Republican or Democrat) per each demographic. Race Gender Education Level Age- Religion Geographic Location (regions/urban/rural, etc.)-
12 READ NAME PERIOD 1. Cite and explain three reasons for the multitude of American interest groups. 2. What factors cause the formation of interest groups? 3. Explain the difference between institutional and membership interest groups. 4. List and describe three incentives for joining membership interest groups. 5. What type of purposive interest group is most controversial? 6. What makes a public-interest group public?
13 READ NAME PERIOD 1. Social movements spawn many interest groups. Label and describe solidarity, purposive and material incentive interest groups formed by the environmental, feminist and union movements. 2. What types of interest groups heavily depend on foundation grants? Name three such foundations. 3. How do federal grants help interest groups? 4. What direct mailing techniques are described here? How costly is direct mailing? What percent of mail-outs must respond in order to make money? 5. Cite four reasons for an upper class bias in active Washington, D.C. interest groups. 6. If there is an interest group upper class bias, why do those interest groups remain relevant to middle class Americans?
14 READ NAME PERIOD 1. What is the single most important commodity that interest groups supply? When is that commodity most valuable? 2. What are earmarks? Why did they increase in number since the 1970 s? Why do some people want them stopped? 3. What were two changes in financing campaigns that occurred as a result of the 1973 reform law? 4. What outsider techniques do lobbyists use to pressure politicians? 5. Why aren t PAC contributions of money an effective lobbying tool? 6. How have members of Congress used the PAC technique to their own advantage? 7. Describe the Revolving Door?
15 8. Cite three ways that some interest groups hope to further their causes by using trouble causing tactics. 9. How is the activity of interest groups protected by the constitution? 10. What was required under the 1946 Federal Regulation of Lobbying Act and why didn t it work?
16 READ NAME PERIOD 1. Compare American press freedom to that of the British and French. Cite laws to back up your position. 2. Describe the development of the American media by answering the following questions. - How were late 18 th and early 19 th century newspapers supported and who was their audience? Why? - How did instruction of the telegraph in the 1840 s change newspapers? - What other techniques boosted the popular press by the turn of the 20 th Century? - What impact did radio have on politics? - What issues were often topics of late 19 th century magazine articles? - How has electronic media changed of the past 40 years? - See Table 12.1 (p. 292). Which decade was worst for the big three? 3. How has the internet changed the relationship between voters and political types?
17 4. How has newspaper competition in major American markets changed in recent decades? 5. Cite two ways in which the national press in America differs from the local American press. 6. How do the national media fulfill the following roles? Gatekeeper- Scorekeeper- Watchdog-
18 READ NAME PERIOD 1. Under what circumstances may the American government censor newspapers? 2. Define libel. How are standards different for common people and a public figure? 3. Under what circumstances may reporters keep sources confidential? 4. Compare competition and regulation in printed and electronic media. 5. Why does a greater portion of candidates for Senate seats spend campaign money on TV ads than do candidates for House seats? 6. See How to read a newspaper on page 300. What questions should readers of newspaper stories be asking concerning the following topics? - stories covered - sources of information - language used 7. What evidence can you cite that might be useful in labeling a news medium as liberal or conservative?
19 READ NAME PERIOD 1. How did the White House press corps come to be? 2. How have the House and Senate dealt with the need to be before the media? 3. Which secret becomes public knowledge first? Which stories are inaccurate? Which stories are rosiest? When is bad news released? Who should one never argue with? 4. Cite four reasons for so many leaks in the American political system. 5. It has been established that there is an adversarial relationship between government and media reporters. What economic reason is there for the shift around 1980 to sensational stories like sex scandals involving prominent politicians?
20 6. What is the difference between off the record and background story? 7. In a conflict between a politician (like a president) and the media, who wins?
Reading Questions - Chapter Seven
 Reading Questions - Chapter Seven 1. What are the three political arenas within which a party may be found? 2. In what ways are American political parties weak? (This is an extremely important point so
Reading Questions - Chapter Seven 1. What are the three political arenas within which a party may be found? 2. In what ways are American political parties weak? (This is an extremely important point so
Role of Political and Legal Systems. Unit 5
 Role of Political and Legal Systems Unit 5 Political Labels Liberal call for peaceful and gradual change of the nations political system, would like to see the government involved in the promotion of the
Role of Political and Legal Systems Unit 5 Political Labels Liberal call for peaceful and gradual change of the nations political system, would like to see the government involved in the promotion of the
Campaigns & Elections. US Government POS 2041
 Campaigns & Elections US Government POS 2041 Votes for Women, inspired by Katja Von Garner. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lvqnjwk W7gA For Discussion Do you think that democracy is endangered by the
Campaigns & Elections US Government POS 2041 Votes for Women, inspired by Katja Von Garner. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lvqnjwk W7gA For Discussion Do you think that democracy is endangered by the
Unit 7 Political Process
 -Study Guide- Unit 7 Political Process Explain or define the following: 1) Public Opinion 2) Public Affairs 3) How they influence our political opinions: a) Family b) Schools peer groups c) Historical
-Study Guide- Unit 7 Political Process Explain or define the following: 1) Public Opinion 2) Public Affairs 3) How they influence our political opinions: a) Family b) Schools peer groups c) Historical
American political campaigns
 American political campaigns William L. Benoit OHIO UNIVERSITY, USA ABSTRACT: This essay provides a perspective on political campaigns in the United States. First, the historical background is discussed.
American political campaigns William L. Benoit OHIO UNIVERSITY, USA ABSTRACT: This essay provides a perspective on political campaigns in the United States. First, the historical background is discussed.
Unit 7 - Personal Involvement
 Unit 7 - Personal Involvement Getting Interested -Personal Involvement- Of the people, by the people, for the people Abraham Lincoln used these words in a famous speech the Gettysburg Address. He was talking
Unit 7 - Personal Involvement Getting Interested -Personal Involvement- Of the people, by the people, for the people Abraham Lincoln used these words in a famous speech the Gettysburg Address. He was talking
Purposes of Elections
 Purposes of Elections o Regular free elections n guarantee mass political action n enable citizens to influence the actions of their government o Popular election confers on a government the legitimacy
Purposes of Elections o Regular free elections n guarantee mass political action n enable citizens to influence the actions of their government o Popular election confers on a government the legitimacy
CHAPTER 5: POLITICAL PARTIES
 CHAPTER 5: POLITICAL PARTIES I. Development of Political Parties Political Party Group with similar ideology with the goal of winning control of government Who was the first Democrat president? Who was
CHAPTER 5: POLITICAL PARTIES I. Development of Political Parties Political Party Group with similar ideology with the goal of winning control of government Who was the first Democrat president? Who was
INTEREST GROUPS/POLITICAL PARTIES/MEDIA: PRACTICE TEST
 INTEREST GROUPS/POLITICAL PARTIES/MEDIA: PRACTICE TEST 1) Ticket-splitting can result in: A) difficulties in enacting public policy. B) increased party discipline. C) more votes for a minor party. D) switching
INTEREST GROUPS/POLITICAL PARTIES/MEDIA: PRACTICE TEST 1) Ticket-splitting can result in: A) difficulties in enacting public policy. B) increased party discipline. C) more votes for a minor party. D) switching
Unit IV Test Political Parties, Media & Interest Groups Practice Test
 Unit IV Test Political Parties, Media & Interest Groups Practice Test 1. Ticket-splitting refers to: (A) the procedure used to conduct computerized, automated vote counting. (B) voting for one party for
Unit IV Test Political Parties, Media & Interest Groups Practice Test 1. Ticket-splitting refers to: (A) the procedure used to conduct computerized, automated vote counting. (B) voting for one party for
Bellwork. Explain the purpose of a political party.
 Bellwork Explain the purpose of a political party. Unit 4: Linkage Institutions APGOPO Questions 1. What are the 4 linkage institutions? Political Parties 1. Linkage Institutions are groups / organizations
Bellwork Explain the purpose of a political party. Unit 4: Linkage Institutions APGOPO Questions 1. What are the 4 linkage institutions? Political Parties 1. Linkage Institutions are groups / organizations
Chapter 6: Public Opinion and Political Action Topics Key Questions Key Terms. on American politics.
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Government Government Identify the key functions of government and explain why they matter. political participation Politics The Policymaking System Democracy in America Define
Chapter 1: Introduction to Government Government Identify the key functions of government and explain why they matter. political participation Politics The Policymaking System Democracy in America Define
US Government Module 3 Study Guide
 US Government Module 3 Study Guide There are 3 branches of government. Module 3 will cover the legislative and execute and module 4 will cover the judicial. 3.01 The Legislative Branch aka Congress Established
US Government Module 3 Study Guide There are 3 branches of government. Module 3 will cover the legislative and execute and module 4 will cover the judicial. 3.01 The Legislative Branch aka Congress Established
AP US GOVERNMENT & POLITICS GUIDED READINGS UNIT 3: POLITICAL PARTIES, INTERST GROUPS, & MASS MEDIA
 AP US GOVERNMENT & POLITICS GUIDED READINGS UNIT 3: POLITICAL PARTIES, INTERST GROUPS, & MASS MEDIA As you read each chapter, answer the core questions within this packet. You should also define vocabulary
AP US GOVERNMENT & POLITICS GUIDED READINGS UNIT 3: POLITICAL PARTIES, INTERST GROUPS, & MASS MEDIA As you read each chapter, answer the core questions within this packet. You should also define vocabulary
Practice Test Unit The Kennedy-Nixon presidential debate of 1960 showed
 Practice Test Unit 3 1. All of the following typically apply to American interest groups EXCEPT A) They run candidates for office. B) They frequently look to the bureaucracy or the judiciary to achieve
Practice Test Unit 3 1. All of the following typically apply to American interest groups EXCEPT A) They run candidates for office. B) They frequently look to the bureaucracy or the judiciary to achieve
The Electoral Process. Learning Objectives Students will be able to: STEP BY STEP. reading pages (double-sided ok) to the students.
 Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One Class Period The Electoral Process Learning Objectives Students will be able to: Materials Needed: Student worksheets Copy Instructions: All student pages can be copied
Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One Class Period The Electoral Process Learning Objectives Students will be able to: Materials Needed: Student worksheets Copy Instructions: All student pages can be copied
AIM: Does the election process guarantee that the most qualified person wins the presidency?
 Election Process Core Curriculum Reading-Social Studies (RH) 1. Use relevant information and ideas from documents to support analysis 2. Determine the main idea of a document 3. Use information/ideas to
Election Process Core Curriculum Reading-Social Studies (RH) 1. Use relevant information and ideas from documents to support analysis 2. Determine the main idea of a document 3. Use information/ideas to
Unit #2: Political Beliefs/Political Behaviors AP US Government & Politics Mr. Coia
 Unit #2: Political Beliefs/Political Behaviors AP US Government & Politics Mr. Coia Name: Date: Period: Thurs 10/10 (Tues 10/15) Grading FRQs Conservative and liberal views of the Affordable Care Act Video:
Unit #2: Political Beliefs/Political Behaviors AP US Government & Politics Mr. Coia Name: Date: Period: Thurs 10/10 (Tues 10/15) Grading FRQs Conservative and liberal views of the Affordable Care Act Video:
Reading Questions for Chapter Two: The Constitution
 Reading Questions for Chapter Two: The Constitution 1. Make a list of the points that the text makes on what the Colonial Mind was thinking at the time of the Revolution. 2. Make a detailed list of the
Reading Questions for Chapter Two: The Constitution 1. Make a list of the points that the text makes on what the Colonial Mind was thinking at the time of the Revolution. 2. Make a detailed list of the
CH. 9 ELECTIONS AND CAMPAIGNS
 APGoPo - Unit 3 CH. 9 ELECTIONS AND CAMPAIGNS Elections form the foundation of a modern democracy, and more elections are scheduled every year in the United States than in any other country in the world.
APGoPo - Unit 3 CH. 9 ELECTIONS AND CAMPAIGNS Elections form the foundation of a modern democracy, and more elections are scheduled every year in the United States than in any other country in the world.
AP U.S. Government & Politics Exam Must Know Vocabulary
 AP U.S. Government & Politics Exam Must Know Vocabulary Amicus curiae brief: friend of the court brief filed by an interest group to influence a Supreme Court decision. Appellate jurisdiction: authority
AP U.S. Government & Politics Exam Must Know Vocabulary Amicus curiae brief: friend of the court brief filed by an interest group to influence a Supreme Court decision. Appellate jurisdiction: authority
Unit 1 Review (Chapters 1, 2, 3)
 Unit 1 Review (Chapters 1, 2, 3) New Deal Policies (cooperative federalism) Interstate Relations (Full Faith & Credit Clause) Supremacy Clause Federalists Papers #10 & #51 Direct/Indirect Democracy Initiatives/Referendums/Recall
Unit 1 Review (Chapters 1, 2, 3) New Deal Policies (cooperative federalism) Interstate Relations (Full Faith & Credit Clause) Supremacy Clause Federalists Papers #10 & #51 Direct/Indirect Democracy Initiatives/Referendums/Recall
Unit #2: Political Beliefs/Political Behaviors AP US Government & Politics Mr. Coia
 Unit #2: Political Beliefs/Political Behaviors AP US Government & Politics Mr. Coia Name: Date: Period: Mon 10/6 AP Gov course evaluation Grading FRQs Conservative and liberal views Explain Election Interview
Unit #2: Political Beliefs/Political Behaviors AP US Government & Politics Mr. Coia Name: Date: Period: Mon 10/6 AP Gov course evaluation Grading FRQs Conservative and liberal views Explain Election Interview
ORGANIZING TOPIC: NATIONAL GOVERNMENT: SHAPING PUBLIC POLICY STANDARD(S) OF LEARNING
 ORGANIZING TOPIC: NATIONAL GOVERNMENT: SHAPING PUBLIC POLICY STANDARD(S) OF LEARNING GOVT.9 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the process by which public policy is made by a) examining different
ORGANIZING TOPIC: NATIONAL GOVERNMENT: SHAPING PUBLIC POLICY STANDARD(S) OF LEARNING GOVT.9 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the process by which public policy is made by a) examining different
PARTISANSHIP AND WINNER-TAKE-ALL ELECTIONS
 Number of Representatives October 2012 PARTISANSHIP AND WINNER-TAKE-ALL ELECTIONS ANALYZING THE 2010 ELECTIONS TO THE U.S. HOUSE FairVote grounds its analysis of congressional elections in district partisanship.
Number of Representatives October 2012 PARTISANSHIP AND WINNER-TAKE-ALL ELECTIONS ANALYZING THE 2010 ELECTIONS TO THE U.S. HOUSE FairVote grounds its analysis of congressional elections in district partisanship.
CHAPTER 9: THE POLITICAL PROCESS. Section 1: Public Opinion Section 2: Interest Groups Section 3: Political Parties Section 4: The Electoral Process
 CHAPTER 9: THE POLITICAL PROCESS 1 Section 1: Public Opinion Section 2: Interest Groups Section 3: Political Parties Section 4: The Electoral Process SECTION 1: PUBLIC OPINION What is Public Opinion? The
CHAPTER 9: THE POLITICAL PROCESS 1 Section 1: Public Opinion Section 2: Interest Groups Section 3: Political Parties Section 4: The Electoral Process SECTION 1: PUBLIC OPINION What is Public Opinion? The
CHAPTER 12: UNDERSTANDING ELECTIONS
 CHAPTER 12: UNDERSTANDING ELECTIONS 1 Section 1: Election Campaigns Section 2: Campaign Funding and Political Action Committees Section 3: Election Day and the Voters SECTION 1: ELECTION CAMPAIGNS 2 SECTION
CHAPTER 12: UNDERSTANDING ELECTIONS 1 Section 1: Election Campaigns Section 2: Campaign Funding and Political Action Committees Section 3: Election Day and the Voters SECTION 1: ELECTION CAMPAIGNS 2 SECTION
Chapter Nine. Political Parties
 Chapter Nine Political Parties Political Parties A party is a group that seeks to by supplying them with a label (party identification), by which they are known to the electorate United States parties
Chapter Nine Political Parties Political Parties A party is a group that seeks to by supplying them with a label (party identification), by which they are known to the electorate United States parties
9. Some industries like oil and gas companies largely support candidates. A) Democrats B) Republicans C) Libertarians D) Independent candidates
 Name: Date: 1. is the constitutional clause that delegates control of elections to the state governments. A) Time, place, and manner clause B) Time and place clause C) Time clause D) Election clause 2.
Name: Date: 1. is the constitutional clause that delegates control of elections to the state governments. A) Time, place, and manner clause B) Time and place clause C) Time clause D) Election clause 2.
Chapter 9: The Political Process
 Chapter 9: The Political Process Section 1: Public Opinion Section 2: Interest Groups Section 3: Political Parties Section 4: The Electoral Process Public Opinion Section 1 at a Glance Public opinion is
Chapter 9: The Political Process Section 1: Public Opinion Section 2: Interest Groups Section 3: Political Parties Section 4: The Electoral Process Public Opinion Section 1 at a Glance Public opinion is
Analyzing American Democracy
 SUB Hamburg Analyzing American Democracy Politics and Political Science Jon R. Bond Texas A&M University Kevin B. Smith University of Nebraska-Lincoln O Routledge Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON
SUB Hamburg Analyzing American Democracy Politics and Political Science Jon R. Bond Texas A&M University Kevin B. Smith University of Nebraska-Lincoln O Routledge Taylor & Francis Group NEW YORK AND LONDON
Name Class Period. MAIN IDEA PACKET: Political Behavior AMERICAN GOVERNMENT CHAPTERS 5, 6, 7, 8 & 9
 Name Class Period UNIT 3 MAIN IDEA PACKET: Political Behavior AMERICAN GOVERNMENT CHAPTERS 5, 6, 7, 8 & 9 CHAPTER 5 POLITICAL PARTIES Chapter 5 Section 1: Parties and What They Do Political Parties, essential
Name Class Period UNIT 3 MAIN IDEA PACKET: Political Behavior AMERICAN GOVERNMENT CHAPTERS 5, 6, 7, 8 & 9 CHAPTER 5 POLITICAL PARTIES Chapter 5 Section 1: Parties and What They Do Political Parties, essential
8. The Bill of Rights was originally intended to limit the power of.
 Adv Gov/Ms. Strong Name US GOVERNMENT 1 ST SEMESTER EXAM REVIEW Directions: You will turn this packet in the day of the exam and will receive a quiz grade. Compete this packet using your class notes, handouts,
Adv Gov/Ms. Strong Name US GOVERNMENT 1 ST SEMESTER EXAM REVIEW Directions: You will turn this packet in the day of the exam and will receive a quiz grade. Compete this packet using your class notes, handouts,
Chapter 6: Public Opinion and Political Action Topics Key Questions Key Terms. on American politics.
 Chapter 1: Introduction to Government Government Identify the key functions of government and explain why they matter. political participation Politics The Policymaking System Democracy in America Define
Chapter 1: Introduction to Government Government Identify the key functions of government and explain why they matter. political participation Politics The Policymaking System Democracy in America Define
Exception to incumbency advantage: scandal or unpopular president
 The Incumbency Advantage Incumbency tradition is high in both Senate (generally above 50%) and House (generally above 80%, incumbent rate more stable than Senate) Media coverage is higher for incumbents
The Incumbency Advantage Incumbency tradition is high in both Senate (generally above 50%) and House (generally above 80%, incumbent rate more stable than Senate) Media coverage is higher for incumbents
The Electoral Process STEP BY STEP. the worksheet activity to the class. the answers with the class. (The PowerPoint works well for this.
 Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector Copy Instructions: Reading (2 pages; class set) Activity (3 pages; class set) The Electoral Process Learning
Teacher s Guide Time Needed: One class period Materials Needed: Student worksheets Projector Copy Instructions: Reading (2 pages; class set) Activity (3 pages; class set) The Electoral Process Learning
Unit II: Public Opinion and Political Action
 AP American Government S15 Mrs. Wiens Essential Questions: Unit II: Public Opinion and Political Action! What is public opinion and how is it measured?! What role did the Framers think public opinion should
AP American Government S15 Mrs. Wiens Essential Questions: Unit II: Public Opinion and Political Action! What is public opinion and how is it measured?! What role did the Framers think public opinion should
Unit 3 Take-Home Test (AP GaP)
 Unit 3 Take-Home Test (AP GaP) Please complete these test items on the GradeCam form provided by your teacher. These are designed to be practice test items in preparation for the Midterm exam and for the
Unit 3 Take-Home Test (AP GaP) Please complete these test items on the GradeCam form provided by your teacher. These are designed to be practice test items in preparation for the Midterm exam and for the
Laws and the Electoral Process
 Government 12 Laws and the Electoral Process Constitution gives Congress certain conditions and requirements for elections Passed a number of laws and regulations Rules vary a great deal because states
Government 12 Laws and the Electoral Process Constitution gives Congress certain conditions and requirements for elections Passed a number of laws and regulations Rules vary a great deal because states
CHAPTER 9: Political Parties
 CHAPTER 9: Political Parties Reading Questions 1. The Founders and George Washington in particular thought of political parties as a. the primary means of communication between voters and representatives.
CHAPTER 9: Political Parties Reading Questions 1. The Founders and George Washington in particular thought of political parties as a. the primary means of communication between voters and representatives.
Chapter 10: Elections and Campaigns
 Chapter 10: Elections and Campaigns Who Wants to Be a Candidate? There are two categories of individuals who run for office the self-starters and those who are recruited by the party The nomination process
Chapter 10: Elections and Campaigns Who Wants to Be a Candidate? There are two categories of individuals who run for office the self-starters and those who are recruited by the party The nomination process
UNIT 4 INTEREST GROUPS, POLITICAL PARTIES, MASS MEDIA
 UNIT 4 INTEREST GROUPS, POLITICAL PARTIES, MASS MEDIA INTEREST GROUPS Historical Background of Interest Groups Interest groups have often been viewed with suspicion. In Federalist #10, James Madison warned
UNIT 4 INTEREST GROUPS, POLITICAL PARTIES, MASS MEDIA INTEREST GROUPS Historical Background of Interest Groups Interest groups have often been viewed with suspicion. In Federalist #10, James Madison warned
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 12, you should be able to: 1. Describe the characteristics of our senators and representatives, and the nature of their jobs. 2. Explain what factors have the
LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 12, you should be able to: 1. Describe the characteristics of our senators and representatives, and the nature of their jobs. 2. Explain what factors have the
The Electoral Process
 Barack Obama speaks at the Democratic National Convention in 2012. Narrowing the Field It s Election Time! Candidates for the larger political parties are chosen at party meetings called conventions. The
Barack Obama speaks at the Democratic National Convention in 2012. Narrowing the Field It s Election Time! Candidates for the larger political parties are chosen at party meetings called conventions. The
STUDY GUIDE: 1 ST SEMESTER EXAM ADV GOV
 STUDY GUIDE: 1 ST SEMESTER EXAM ADV GOV ANSWER KEY Directions: You will turn this packet in the day of the exam and will receive a quiz grade. Compete this packet using your class notes, handouts, Magruder
STUDY GUIDE: 1 ST SEMESTER EXAM ADV GOV ANSWER KEY Directions: You will turn this packet in the day of the exam and will receive a quiz grade. Compete this packet using your class notes, handouts, Magruder
Unit #2: Political Beliefs/Political Behaviors AP US Government & Politics Mr. Coia
 Unit #2: Political Beliefs/Political Behaviors AP US Government & Politics Mr. Coia Name: Date: Period: Fri 10/7 Unit 1 Constitutional Underpinnings Test Writing Gov FRQs Explain Election Interview sheet
Unit #2: Political Beliefs/Political Behaviors AP US Government & Politics Mr. Coia Name: Date: Period: Fri 10/7 Unit 1 Constitutional Underpinnings Test Writing Gov FRQs Explain Election Interview sheet
Chapter 9: Elections, Campaigns, and Voting. American Democracy Now, 4/e
 Chapter 9: Elections, Campaigns, and Voting American Democracy Now, 4/e Political Participation: Engaging Individuals, Shaping Politics Elections, campaigns, and voting are fundamental aspects of civic
Chapter 9: Elections, Campaigns, and Voting American Democracy Now, 4/e Political Participation: Engaging Individuals, Shaping Politics Elections, campaigns, and voting are fundamental aspects of civic
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 10, you should be able to: 1. Explain the functions and unique features of American elections. 2. Describe how American elections have evolved using the presidential
LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 10, you should be able to: 1. Explain the functions and unique features of American elections. 2. Describe how American elections have evolved using the presidential
Political Attitudes &Participation: Campaigns & Elections. State & Local Government POS 2112 Ch 5
 Political Attitudes &Participation: Campaigns & Elections State & Local Government POS 2112 Ch 5 Votes for Women, inspired by Katja Von Garner. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lvqnjwkw7ga We will examine:
Political Attitudes &Participation: Campaigns & Elections State & Local Government POS 2112 Ch 5 Votes for Women, inspired by Katja Von Garner. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lvqnjwkw7ga We will examine:
The Road To The White House
 The Road To The White House Decision Exploratory Committee file with FEC Theme Can I win? Name Recognition $$ Do I have presidential competencies/qualities? Presidential qualities/competencies Official
The Road To The White House Decision Exploratory Committee file with FEC Theme Can I win? Name Recognition $$ Do I have presidential competencies/qualities? Presidential qualities/competencies Official
- 1 - Second Exam American Government PSCI Fall, 2001
 Second Exam American Government PSCI 1201-001 Fall, 2001 Instructions: This is a multiple choice exam with 40 questions. Select the one response that best answers the question. True false questions should
Second Exam American Government PSCI 1201-001 Fall, 2001 Instructions: This is a multiple choice exam with 40 questions. Select the one response that best answers the question. True false questions should
Watch the video and take the pre-test for Be sure you are working on getting your collaboration and service learning project completed.
 Module 3 Note Taking Guide Module 3 Policy and Elections Module 3 Lessons 3.00 Introduction Watch the video and take the pre-test for 3.00. Be sure you are working on getting your collaboration and service
Module 3 Note Taking Guide Module 3 Policy and Elections Module 3 Lessons 3.00 Introduction Watch the video and take the pre-test for 3.00. Be sure you are working on getting your collaboration and service
The Constitution and the Legislative Branch of the Government
 Chapter 7 Congress The Constitution and the Legislative Branch of the Government o Article I describes structure of Congress n Bicameral legislature o Divided into two houses o Each state sends two Senators
Chapter 7 Congress The Constitution and the Legislative Branch of the Government o Article I describes structure of Congress n Bicameral legislature o Divided into two houses o Each state sends two Senators
Chpt 1: Foundations Key Terms to Know: Authority. Bureaucratic theory. Democracy. Direct democracy. Initiative. Legitimacy Marxist theory
 Chpt 1: Foundations Authority Bureaucratic theory Democracy Direct democracy Initiative Legitimacy Marxist theory Nongovernmental elitist theory Pluralist theory Political elite Power Referendum Representative
Chpt 1: Foundations Authority Bureaucratic theory Democracy Direct democracy Initiative Legitimacy Marxist theory Nongovernmental elitist theory Pluralist theory Political elite Power Referendum Representative
Rabalais AP Government Review Vocabulary List
 Rabalais AP Government Review Vocabulary List Chapter 2 The Constitution Democracy Government by the people, both directly or indirectly, with free and frequent elections. Direct democracy Government in
Rabalais AP Government Review Vocabulary List Chapter 2 The Constitution Democracy Government by the people, both directly or indirectly, with free and frequent elections. Direct democracy Government in
Part 1 Role of Mass Media
 Part 1 Role of Mass Media Questions to Ask What is Mass Media? How does the mass media fulfill its role to provide the public with political information? How does the mass media influence politics? What
Part 1 Role of Mass Media Questions to Ask What is Mass Media? How does the mass media fulfill its role to provide the public with political information? How does the mass media influence politics? What
12. The electronic surveillance of suspected terrorists by federal agencies is most likely to be opposed by a A) civil libertarian B) consumer advocat
 1. If the most liberal wing of the Democratic Party takes control of the party platform and focuses on social reforms, it would be most likely to alienate A) graduate students B) Northeastern suburban
1. If the most liberal wing of the Democratic Party takes control of the party platform and focuses on social reforms, it would be most likely to alienate A) graduate students B) Northeastern suburban
EDW Chapter 9 Campaigns and Voting Behavior: Nominations, Caucuses
 EDW Chapter 9 Campaigns and Voting Behavior: Nominations, Caucuses 1. Which of the following statements most accurately compares elections in the United States with those in most other Western democracies?
EDW Chapter 9 Campaigns and Voting Behavior: Nominations, Caucuses 1. Which of the following statements most accurately compares elections in the United States with those in most other Western democracies?
Magruder s American Government
 Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 8 Mass Media and Public Opinion 200 by Prentice Hall, Inc. S E C T I O N The Formation of Public Opinion 2 3 Chapter 8, Section What is Public
Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 8 Mass Media and Public Opinion 200 by Prentice Hall, Inc. S E C T I O N The Formation of Public Opinion 2 3 Chapter 8, Section What is Public
Elections and Voting Behavior
 Elections and Voting Behavior Running for Office: 4 step process Presidential election process: Nomination caucus/primary national convention general election slate of candidates election held with in
Elections and Voting Behavior Running for Office: 4 step process Presidential election process: Nomination caucus/primary national convention general election slate of candidates election held with in
Chapter 13: The Presidency Section 4
 Chapter 13: The Presidency Section 4 Objectives 1. Describe the role of conventions in the presidential nominating process. 2. Evaluate the importance of presidential primaries. 3. Understand the caucus-convention
Chapter 13: The Presidency Section 4 Objectives 1. Describe the role of conventions in the presidential nominating process. 2. Evaluate the importance of presidential primaries. 3. Understand the caucus-convention
ELECTIONS AND VOTING BEHAVIOR CHAPTER 10, Government in America
 ELECTIONS AND VOTING BEHAVIOR CHAPTER 10, Government in America Page 1 of 6 I. HOW AMERICAN ELECTIONS WORK A. Elections serve many important functions in American society, including legitimizing the actions
ELECTIONS AND VOTING BEHAVIOR CHAPTER 10, Government in America Page 1 of 6 I. HOW AMERICAN ELECTIONS WORK A. Elections serve many important functions in American society, including legitimizing the actions
SAMPLE EXAMINATION ONE
 SAMPLE EXAMINATION ONE SECTION I Time 45 minutes 60 Multiple-Choice Questions Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by either four suggested answers or completions.
SAMPLE EXAMINATION ONE SECTION I Time 45 minutes 60 Multiple-Choice Questions Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by either four suggested answers or completions.
4) Once every decade, the Constitution requires that the population be counted. This is called the 4)
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The Founders intended that the House of Representatives be 1) A) professional. B) electorally insulated.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The Founders intended that the House of Representatives be 1) A) professional. B) electorally insulated.
Unit 4 Active Citizenship
 Unit 4 Active Citizenship Objective 1 Explain the process of naturalization, as well as the rights and responsibilities of American citizens. Objective 2 Analyze the role of political parties, the media,
Unit 4 Active Citizenship Objective 1 Explain the process of naturalization, as well as the rights and responsibilities of American citizens. Objective 2 Analyze the role of political parties, the media,
Chapter 14: THE CAMPAIGN PROCESS. Chapter 14.1: Trace the evolution of political campaigns in the United States.
 Chapter 14: THE CAMPAIGN PROCESS Chapter 14.1: Trace the evolution of political campaigns in the United States. Jer_4:15 For a voice declareth from Dan, and publisheth affliction from mount Ephraim. Introduction:
Chapter 14: THE CAMPAIGN PROCESS Chapter 14.1: Trace the evolution of political campaigns in the United States. Jer_4:15 For a voice declareth from Dan, and publisheth affliction from mount Ephraim. Introduction:
What is Public Opinion?
 What is Public Opinion? Citizens opinions about politics and government actions Why does public opinion matter? Explains the behavior of citizens and public officials Motivates both citizens and public
What is Public Opinion? Citizens opinions about politics and government actions Why does public opinion matter? Explains the behavior of citizens and public officials Motivates both citizens and public
Magruder s American Government
 Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 7 The Electoral Process 200 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 7 The Electoral Process SECTION The Nominating Process SECTION 2 Elections
Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 7 The Electoral Process 200 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 7 The Electoral Process SECTION The Nominating Process SECTION 2 Elections
Chapter 10 Elections and Campaigns
 Chapter 10 Elections and Campaigns WHO GOVERNS? 1. How do American elections determine the kind of people who govern us? 2. What matters most in deciding who wins presidential and congressional elections?
Chapter 10 Elections and Campaigns WHO GOVERNS? 1. How do American elections determine the kind of people who govern us? 2. What matters most in deciding who wins presidential and congressional elections?
1. One of the various ways in which parties contribute to democratic governance is by.
 11 Political Parties Multiple-Choice Questions 1. One of the various ways in which parties contribute to democratic governance is by. a. dividing the electorate b. narrowing voter choice c. running candidates
11 Political Parties Multiple-Choice Questions 1. One of the various ways in which parties contribute to democratic governance is by. a. dividing the electorate b. narrowing voter choice c. running candidates
Chapter 11. Congress. What is Congress main job?
 Chapter 11 Congress What is Congress main job? The Constitution and the Legislative Branch of the Government o Article I describes structure of Congress n Bicameral legislature o Divided into two houses
Chapter 11 Congress What is Congress main job? The Constitution and the Legislative Branch of the Government o Article I describes structure of Congress n Bicameral legislature o Divided into two houses
IN THE KNOW: The Supreme Court s Decision on Corporate Spending: Now What?
 IN THE KNOW: The Supreme Court s Decision on Corporate Spending: Now What? On January 21, 2010, the United States Supreme Court issued a 5 4 decision to allow corporations and unions unprecedented freedom
IN THE KNOW: The Supreme Court s Decision on Corporate Spending: Now What? On January 21, 2010, the United States Supreme Court issued a 5 4 decision to allow corporations and unions unprecedented freedom
Texas. SUPER DISTRICT A - FIVE SEATS % 2000 Presidential Vote
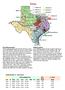 Texas Racial Representation Of the voting population of 6,232,350, 28.7 are Latino and 11.0 are black. Under the current 32-district system, black voters do not make up the majority in any district and
Texas Racial Representation Of the voting population of 6,232,350, 28.7 are Latino and 11.0 are black. Under the current 32-district system, black voters do not make up the majority in any district and
C) It elects candidates from its party to public office. C) Code of Hammurabi B) During wartime, limitations on civil rights have been upheld
 Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by four suggested answers or completions. Select the one that is best in each case and fill in the corresponding oval on the
Directions: Each of the questions or incomplete statements below is followed by four suggested answers or completions. Select the one that is best in each case and fill in the corresponding oval on the
SUMMARY We the People Democracy Reform Act of 2017 Sponsored by Senator Udall and Representative Price
 SUMMARY We the People Democracy Reform Act of 2017 Sponsored by Senator Udall and Representative Price September 27, 2017 The We the People Democracy Reform Act of 2017 S. 1880 in the Senate and H.R. 3848
SUMMARY We the People Democracy Reform Act of 2017 Sponsored by Senator Udall and Representative Price September 27, 2017 The We the People Democracy Reform Act of 2017 S. 1880 in the Senate and H.R. 3848
Mass Media and Public Opinion Chapter 8
 Mass Media and Public Opinion Chapter 8 Public Opinion/Mood What issues are the public interested in at the moment? What do you think the general mood of the population is on those issues? How do we decide
Mass Media and Public Opinion Chapter 8 Public Opinion/Mood What issues are the public interested in at the moment? What do you think the general mood of the population is on those issues? How do we decide
State Legislatures. State & Local Government. Ch. 7
 State Legislatures State & Local Government Ch. 7 Legislature in some states is the dominant branch of govt. Highlights State Legislatures have 4 clear functions: 1. Making laws 2. Represent their constituents
State Legislatures State & Local Government Ch. 7 Legislature in some states is the dominant branch of govt. Highlights State Legislatures have 4 clear functions: 1. Making laws 2. Represent their constituents
Chapter 8: Mass Media and Public Opinion Section 1 Objectives Key Terms public affairs: public opinion: mass media: peer group: opinion leader:
 Chapter 8: Mass Media and Public Opinion Section 1 Objectives Examine the term public opinion and understand why it is so difficult to define. Analyze how family and education help shape public opinion.
Chapter 8: Mass Media and Public Opinion Section 1 Objectives Examine the term public opinion and understand why it is so difficult to define. Analyze how family and education help shape public opinion.
What early 1900s movement fought the political bosses making all the decisions regarding the nomination process?
 What makes an effective campaign ad? Emotion Persuasion Truth Style Three top entities that make campaign ads: Candidates Super Pac Political Party Red State Blue State Democrat State Republican State
What makes an effective campaign ad? Emotion Persuasion Truth Style Three top entities that make campaign ads: Candidates Super Pac Political Party Red State Blue State Democrat State Republican State
Dealignment Argument. Feeding frenzy
 Amicus curiae brief Fairness doctrine Dealignment Argument Feeding frenzy Divided government Free rider problem Elite theory Horse race coverage factions Iron triangle FCC rule (no longer in Effect) that
Amicus curiae brief Fairness doctrine Dealignment Argument Feeding frenzy Divided government Free rider problem Elite theory Horse race coverage factions Iron triangle FCC rule (no longer in Effect) that
Unit 3 Review: Political Beliefs & the Mass Media
 Unit 3 Review: Political Beliefs & the Mass Media American Political Culture Despite our diversity, a common political culture exists in the U.S à common set of beliefs & attitudes about gov t & politics
Unit 3 Review: Political Beliefs & the Mass Media American Political Culture Despite our diversity, a common political culture exists in the U.S à common set of beliefs & attitudes about gov t & politics
UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS Practice Exam #10 Time 45 minutes 60 Questions
 UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS Practice Exam #10 Time 45 minutes 60 Questions 1. All of the following were weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation EXCEPT (A) nine of the thirteen states had
UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS Practice Exam #10 Time 45 minutes 60 Questions 1. All of the following were weaknesses of the Articles of Confederation EXCEPT (A) nine of the thirteen states had
1. Amendments impacting Voting. 15th - No Racial Discrimination. 17th - Direct election of senators by citizens, not state legislature appointment
 Exam 6A Notes 1. Amendments impacting Voting 15th - No Racial Discrimination 17th - Direct election of senators by citizens, not state legislature appointment 19th - no sex/gender discrimination (Female
Exam 6A Notes 1. Amendments impacting Voting 15th - No Racial Discrimination 17th - Direct election of senators by citizens, not state legislature appointment 19th - no sex/gender discrimination (Female
Instructor: Merrilynn Giles Course Title: Advanced Government Time Allotment: 16_ Topic/Concept: The American System (Chapter 1) Unit Sequence: 1.
 Instructor: Merrilynn Giles Course Title: Advanced Government Time Allotment: 16_ Topic/Concept: The American System (Chapter 1) Unit Sequence: 1. 1. Understand the impact of the demographic profile in
Instructor: Merrilynn Giles Course Title: Advanced Government Time Allotment: 16_ Topic/Concept: The American System (Chapter 1) Unit Sequence: 1. 1. Understand the impact of the demographic profile in
Civics Quarter Assignment. Mr. Primeaux
 Civics Quarter Assignment Mr. Primeaux 12.4.4 Article II of the Constitution talks about the President, Vice President and the powers they hold in the Executive branch. The President has the power to enforce
Civics Quarter Assignment Mr. Primeaux 12.4.4 Article II of the Constitution talks about the President, Vice President and the powers they hold in the Executive branch. The President has the power to enforce
Unit V Test Congress and the President Practice Test
 Unit V Test Congress and the President Practice Test 1. The "revolving door" involves: (A) members of Congress who travel extensively between Washington D.C. and their home states (B) diplomats who engage
Unit V Test Congress and the President Practice Test 1. The "revolving door" involves: (A) members of Congress who travel extensively between Washington D.C. and their home states (B) diplomats who engage
Electoral Dynamics: The Role of Campaign Context in Voting Choice
 Electoral Dynamics: The Role of Campaign Context in Voting Choice Carlos Algara calgara@ucdavis.edu October 19, 2017 Agenda 1 Incumbency 2 Partisanship 3 Campaign Resources 4 Collective Responsibility
Electoral Dynamics: The Role of Campaign Context in Voting Choice Carlos Algara calgara@ucdavis.edu October 19, 2017 Agenda 1 Incumbency 2 Partisanship 3 Campaign Resources 4 Collective Responsibility
Chapter 10: Congress
 Chapter 10: Congress Congress with all of its faults is the most representative body in the land. It reflects however imperfectly the bigness and diversity of America. It responds however imperfectly to
Chapter 10: Congress Congress with all of its faults is the most representative body in the land. It reflects however imperfectly the bigness and diversity of America. It responds however imperfectly to
MATERIAL ON THE TEST Edwards Chapters 6, 9, 8, 10, 11 Sides ( Science of Trump ) chapters 4, 5, 6, 15, 24, 12 CHAPTER 6
 Study Guide for Exam 2: October 25 in class 47 multiple choice questions worth 1 point each and probably a couple of extra credit problems. Bring a pencil with you to the exam. As with the last exam, there
Study Guide for Exam 2: October 25 in class 47 multiple choice questions worth 1 point each and probably a couple of extra credit problems. Bring a pencil with you to the exam. As with the last exam, there
Bits and Pieces to Master the Exam Random Thoughts, Trivia, and Other Facts (that may help you be successful AP EXAM)
 Bits and Pieces to Master the Exam Random Thoughts, Trivia, and Other Facts (that may help you be successful AP EXAM) but what is government itself but the greatest of all reflections on human nature?
Bits and Pieces to Master the Exam Random Thoughts, Trivia, and Other Facts (that may help you be successful AP EXAM) but what is government itself but the greatest of all reflections on human nature?
Elections and Voting and The Campaign Process
 12 & 13 Elections and Voting and The Campaign Process Multiple-Choice Questions 1. A command, indicated by an electorate s votes, for the elected officials to carry out a party platform or policy agenda
12 & 13 Elections and Voting and The Campaign Process Multiple-Choice Questions 1. A command, indicated by an electorate s votes, for the elected officials to carry out a party platform or policy agenda
Campaigning in General Elections (HAA)
 Campaigning in General Elections (HAA) Once the primary season ends, the candidates who have won their party s nomination shift gears to campaign in the general election. Although the Constitution calls
Campaigning in General Elections (HAA) Once the primary season ends, the candidates who have won their party s nomination shift gears to campaign in the general election. Although the Constitution calls
What have been the main consequences of the graying of America?
 AP* US Government and Politics/Arnold Unit II Guided Reading Questions Chapter 6 Public Opinion and Political Action The American People: Pgs. 168-172 In what ways is the U.S. an immigrant society? What
AP* US Government and Politics/Arnold Unit II Guided Reading Questions Chapter 6 Public Opinion and Political Action The American People: Pgs. 168-172 In what ways is the U.S. an immigrant society? What
Campaigns & Elections November 6, 2017 Dr. Michael Sullivan. FEDERAL GOVERNMENT GOVT 2305 MoWe 5:30 6:50 MoWe 7 8:30
 Campaigns & Elections November 6, 2017 Dr. Michael Sullivan FEDERAL GOVERNMENT GOVT 2305 MoWe 5:30 6:50 MoWe 7 8:30 Current Events, Recent Polls, & Review Background influences on campaigns Presidential
Campaigns & Elections November 6, 2017 Dr. Michael Sullivan FEDERAL GOVERNMENT GOVT 2305 MoWe 5:30 6:50 MoWe 7 8:30 Current Events, Recent Polls, & Review Background influences on campaigns Presidential
Magruder s American Government
 Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 9 Interest Groups 200 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 9 Interest Groups SECTION The Nature of Interest Groups SECTION 2 Types of Interest
Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 9 Interest Groups 200 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 9 Interest Groups SECTION The Nature of Interest Groups SECTION 2 Types of Interest
The Campaign Process. The Nature of Modern Political Campaigns. The National Campaign. The General Election Campaign
 The Campaign Process Campaigns start long before most of us notice them. Trial balloons are floated years before the active campaign begins. Often, political candidates make special efforts to work hard
The Campaign Process Campaigns start long before most of us notice them. Trial balloons are floated years before the active campaign begins. Often, political candidates make special efforts to work hard
LESSON Money and Politics
 LESSON 22 157-168 Money and Politics 1 EFFORTS TO REFORM Strategies to prevent abuse in political contributions Imposing limitations on giving, receiving, and spending political money Requiring public
LESSON 22 157-168 Money and Politics 1 EFFORTS TO REFORM Strategies to prevent abuse in political contributions Imposing limitations on giving, receiving, and spending political money Requiring public
UNIT THREE POLITICAL PARTIES. Jessup 16
 UNIT THREE ITEM ELECTIONS INTEREST GROUPS MASS MEDIA OF LINKAGE A group which tries to win elections so they can control the government. A process in which one person is selected for a governmental job.
UNIT THREE ITEM ELECTIONS INTEREST GROUPS MASS MEDIA OF LINKAGE A group which tries to win elections so they can control the government. A process in which one person is selected for a governmental job.
EXAM: Parties & Elections
 AP Government EXAM: Parties & Elections Mr. Messinger INSTRUCTIONS: Mark all answers on your Scantron. Do not write on the test. Good luck!! 1. All of the following are true of the Electoral College system
AP Government EXAM: Parties & Elections Mr. Messinger INSTRUCTIONS: Mark all answers on your Scantron. Do not write on the test. Good luck!! 1. All of the following are true of the Electoral College system
Political Polit Parties Parti
 Political Parties Chapter 5 S E C T I O N 1 What Is a Party? A political party is a group of persons who seek to control government by winning elections and holding office. The two major parties in American
Political Parties Chapter 5 S E C T I O N 1 What Is a Party? A political party is a group of persons who seek to control government by winning elections and holding office. The two major parties in American
