Essential Question. Industrialization increased the standard of living and the opportunities of most Americans, but at what cost?
|
|
|
- Jemimah Byrd
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Essential Questions: 1) What industries and inventions drove the 2 nd Industrial Revolution? 2) How did the Industrial Revolution create social class divisions and labor conflict? What drove the labor movement? 3) What were the political, economic, social, and intellectual consequences of the Industrial Revolution? Essential Question Industrialization increased the standard of living and the opportunities of most Americans, but at what cost? 1
2 Timeline Using your notes and textbook, Review! complete the timeline of inventions. Cause: Complete the Cause/Effect Chart on the Industrial Revolution Effect: Cause: Effect: Cause: Effect: Cause: Effect: Cause: Effect: 2
3 Causes of Rapid Industrialization 1. Steam Revolution of the 1830s-1850s. 2. The Railroad fueled the growing US economy: First big business in the US. A magnet for financial investment. The key to opening the West. Aided the development of other industries. Causes of Rapid Industrialization 3. Unskilled & semi-skilled labor in abundance. 4. Abundant capital. 5. New, talented group of businessmen [entrepreneurs] and advisors. 6. Market growing as US population increased. 7. Government willing to help at all levels to stimulate economic growth. 8. Abundant natural resources. 3
4 Causes of Rapid Industrialization 9. Technological innovations. Bessemer and open hearth process Refrigerated cars Edison o Wizard of Menlo Park o light bulb, phonograph, motion pictures. Video: The American Industrial Revolution (27:22 m) Video Introduction: In the decades following the Civil War, America was transformed from a rural republic to an urban state. Frontiers vanished in the face of westward expansion. Floods of immigrants streamed through the great eastern seaports, fueling the need for industrial labor. And transcontinental railroad lines linked the country together like never before. The film explores the people behind the changes, the birth of organized labor, The Homestead Act of 1862, and the birth of the environmental movement. Pay attention! Your assignments follow! 4
5 5
6 Copy This! Upper Class Owners of big business and capital Middle Class or Bourgeoisie How does this show life during the Industrial Revolution? Why did I use a pyramid shape here? Working Class and Poor Stereotype of the Factory Owner 6
7 Upstairs / Downstairs Life 7
8 19 c Bourgeoisie: The Industrial Nouveau Riche How does this cartoon Criticize the New Bourgeoisie? 8
9 Middle Class and Politics: Liberalism Little Gov t Involvement No Help for Poor Middle Class and Politics 9
10 The Factory System ) Factory System: )Concentrates production in one place [materials, labor]. )Located near sources of power [rather than labor or markets]. )Requires a lot of capital investment [factory, machines, etc.] more than skilled labor. 10
11 The Factory System Rigid schedule hour day. Dangerous conditions. Mind-numbing monotony. Young Bobbin-Doffers 11
12 Textile Factory Workers in England 12
13 Working Class Culture: Factory Life 13
14 Poverty of the Working Class Life in the Industrial City 14
15 Working Class Accommodations Factory Workers at Home 15
16 The New Urban Poor: A Dickensian Nightmare! Private Charities: Soup Kitchens 16
17 Working Class Leisure 17
18 Yes, for real! Let me prove it! 18
19 Child Labor Child Labor! 19
20 Galley Labor Young Coal Miners 20
21 Child Labor in the Mines Child hurriers 21
22 22
23 Welcome to the Flugenhoggen Factory, My Teenage Slaves! Ha! Ha! I only have time to be interviewed for twenty minutes because spent time is money wasted! So, hurry it up! Then, I dare you to publish a newspaper report on the abuses at my factory! I dare you! You ll have to finish for tomorrow s morning edition! 23
24 24
25 Thomas Malthus Population growth will outpace the food supply. War, disease, or famine could control population. The poor should have less children. Food supply will then keep up with population. The Utilitarians: Jeremy Bentham & John Stuart Mill The goal of society is the greatest good for the greatest number. There is a role to play for government intervention to provide some social safety net. 25
26 The Socialists: Utopians & Marxists People as a society would operate and own the means of production, not individuals. Their goal was a society that benefited everyone, not just a rich, well-connected few. Tried to build perfect communities [utopias]. The Legacy of Marx Karl Marx wrote the Communist Manifesto, an indictment of the capitalist system. He predicted that angry workers would overthrow the capitalist system and establish a socialist state-- workers shared equally in the wealth from the product of their labors. His work later formed the basis for many communist countries. 26
27 Literary Response Romanticism Charles Dickens Christmas Carole, 1843 Charles Dickens Complete: Karl Marx: A Failed Vision of History reading. Complete the questions For Discussion and Writing. Then, we will complete the activity What Is a Just Society? 27
28 By: Mr. Cegielski Labor Force Distribution
29 The Changing American Labor Force Labor Unrest:
30 The Molly Maguires (1875) James McParland The Molly Maguires were members of a secret Irish organization. Many historians believe the "Mollies" were present in the anthracite coal fields of Pennsylvania in the United States from approximately the time of the American Civil War until a series of sensational arrests and trials in the years Evidence that the Molly Maguires were responsible for coalfield crimes and kidnapping in the U.S. rests largely upon allegations of one powerful industrialist, James McParland, and the testimony of one Pinkerton detective. Fellow prisoners also testified against the alleged Molly Maguires, but some believe these witnesses may have been coerced or bribed. The Corporate Bully-Boys : Pinkerton Agents The Pinkerton National Detective Agency, usually shortened to the Pinkertons, was a private U.S. security guard and detective agency established by Allan Pinkerton in During the labor unrest of the late 19th century, businessmen hired Pinkerton agents to infiltrate unions, and as guards to keep strikers and suspected unionists out of factories. 30
31 Management vs. Labor Tools of Management Tools of Labor scabs P. R. campaign Pinkertons lockout blacklisting yellow-dog contracts court injunctions open shop boycotts sympathy demonstrations informational picketing closed shops organized strikes wildcat strikes Why form Trade Unions? 31
32 Unions and Strikes A Striker Confronts a SCAB! 32
33 Knights of Labor Terence V. Powderly An injury to one is the concern of all! 33
34 Knights of Labor The Knights of Labor, also known as Noble and Holy Order of the Knights of Labor, was one of the most important American labor organizations of the 19th century. Founded by nine Philadelphia tailors in 1869 and led by Uriah Stephens, its ideology may be described as producerist, demanding an end to child and convict labor, equal pay for women, a progressive income tax, and the cooperative employer-employee ownership of mines and factories. Knights of Labor trade card Goals of the Knights of ù Eight-hour workday. Labor ù Workers cooperatives. ù Worker-owned factories. ù Abolition of child and prison labor. ù Increased circulation of greenbacks. ù Equal pay for men and women. ù Safety codes in the workplace. ù Prohibition of contract foreign labor. ù Abolition of the National Bank. 34
35 The Great Railroad Strike of 1877 The Great Railroad Strike of
36 The Tournament of Today: A Set-to Between Labor and Monopoly Anarchists Meet on the Lake Front in
37 Haymarket Riot (1886) McCormick Harvesting Machine Co. Haymarket Martyrs 37
38 Governor John Peter Altgeld The American Federation of Labor: 1886 Samuel Gompers 38
39 How the AF of L Would Help the Workers ù Catered to the skilled worker. ù Represented workers in matters of national legislation. ù Maintained a national strike fund. ù Evangelized the cause of unionism. ù Prevented disputes among the many craft unions. ù Mediated disputes between management and labor. ù Pushed for closed shops. Homestead Steel Strike (1892) The Amalgamated Association of Iron & Steel Workers Homestead Steel Works 39
40 Big Corporate Profits! Attempted Assassination! Henry Clay Frick Alexander Berkman 40
41 41
42 A Company Town : Pullman, IL Pullman Cars A Pullman porter 42
43 The Pullman Strike of 1894 President Grover Cleveland If it takes the entire army and navy to deliver a postal card in Chicago, that card will be delivered! 43
44 The Pullman Strike of 1894 Government by injunction! 44
45 The Socialists Eugene V. Debs International Workers of the World ( Wobblies ) 45
46 Big Bill Haywood of the IWW Violence was justified to overthrow capitalism. I W W & the Internationale 46
47 The Hand That Will Rule the World One Big Union Mother Jones: The Miner s Angel Mary Harris. Organizer for the United Mine Workers. Founded the Social Democratic Party in One of the founding members of the I. W. W. in
48 Lawrence, MA Strike: 1912 The Bread & Roses Strike DEMANDS: ù 15 /hr. wage increase. ù Double pay for overtime. ù No discrimination against strikers. ù An end to speed-up on the assembly line. ù An end to discrimination against foreign immigrant workers. 48
49 Lawrence, MA Strike: 1912 The Formula unions + violence + strikes + socialists + immigrants = anarchists 49
50 Labor Union Membership Solidarity Forever! by Ralph Chapin (1915) When the union's inspiration through the workers blood shall run, There can be no power greater anywhere beneath the sun; Yet what force on earth is weaker than the feeble strength of one, But the union makes us strong! CHORUS: Solidarity forever, Solidarity forever, Solidarity forever, For the union makes us strong! 50
51 Come On and Sing Along!! Solidarity Forever! Is there aught we hold in common with the greedy parasite, Who would lash us into serfdom and would crush us with his might? Is there anything left to us but to organize and fight? For the union makes us strong! CHORUS: Solidarity forever, Solidarity forever, Solidarity forever, For the union makes us strong! 51
52 Solidarity Forever! * * * * Through our sisters and our brothers we can make our union strong, For respect and equal value, we have done without too long. We no longer have to tolerate injustices and wrongs, Yes, the union makes us strong! CHORUS: Solidarity forever, Solidarity forever, Solidarity forever, For the union makes us strong! Workers Benefits Today 52
53 The Rise & Decline of Organized Labor Right-to-Work States Today 53
54 Unionism & Globalization? ACTIVITY: STOP CRUEL LABOR! Task As a newly elected U.S. Senator, you have been asked to analyze the effects of the "Industrial Revolution." As with most revolutions, it brings benefits to some and problems for others. In groups (committees) of 3-4, you are asked to: I. Write a bill. It must be very specific. Conditions addressed in your bill must accurately represent the U.S. at the time. The bill, to be passed, should be realistic for the period around For example, if you believe people work too many hours, be very specific about how many hours they will be allowed to work. As an MP, you are developing law, so bills should not say "should", but rather "will" or "must". Your bill should be organized as a numbered list of three to four major points in complete sentences. II. Write a speech which you will deliver in front of our upcoming mock Congress. While a bill must be specific, your speech can supply reasons and arguments for passage of your bill. You should answer questions such as: What conditions in England specifically caused you to write the bill? What pieces of evidence can be referred to in your speech to persuade other Senators to vote for your bill? How will the bill benefit the people of the U.S.? How is your bill realistic given the time and economy of the U.S.? How is the bill in line with your party beliefs? III. Design a political/union poster in support of your cause! IV. Participate in debates: In addition, a good Senator participates in debating the merits of bills both in committee and the general sessions. 54
55 Your bill, speech and debate preparation should answer the following concerns: 1) What do we know about the U.S., our position, and our task? 2) What are important things we need to know to accomplish our tasks? 3) What are some places we can search for information? 4) What sorts of homes and furnishings did people of the time have? 5) What kind of meals did factory workers eat? 6) How much money did various kinds of workers make? 7) What were working conditions (hours, days, safety) like, and how did they compare to working conditions for agricultural workers or people in other countries at that time? VI. Participate in Groups (Committees). The speaker (leader of the group) will appoint tasks to each group member in order to divide up the work responsibility. The ultimate goal is to complete all requirements of this assignment and to unanimously agree upon a bill. This bill must be written down! VII. Participate in a Mock Congress Pass your bill into law! When all of the committees have finished preparing, the President (your teacher) will convene a session of Congress. Each group will: 1) Read their speech 2) Read their bill 3) Waive their poster/sign around and convince Congress to pass the bill. 3) Defend their bill against questions from myself and the other committees 4) Request that their bill be passed into law. The whole class will vote. Twothirds majority vote plus the President s signature is needed for passage! 55
Labor Unrest:
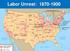 Labor Unrest: 1870-1900 The Railroad Strike of 1877 Haymarket Riot of 1886 The Homestead Strike of 1892 The Pullman Strike of 1894 Major economic downturn Overexpansion and stock market crash Decrease
Labor Unrest: 1870-1900 The Railroad Strike of 1877 Haymarket Riot of 1886 The Homestead Strike of 1892 The Pullman Strike of 1894 Major economic downturn Overexpansion and stock market crash Decrease
Big Business, Railroads, and Labor in the Late 1800 s. American History 11R
 Big Business, Railroads, and Labor in the Late 1800 s American History 11R Causes of Rapid Industrialization Unskilled & semi-skilled labor in abundance. Abundant capital. New, talented group of businessmen
Big Business, Railroads, and Labor in the Late 1800 s American History 11R Causes of Rapid Industrialization Unskilled & semi-skilled labor in abundance. Abundant capital. New, talented group of businessmen
Questions to answer today:
 US History, Feb 19 Entry Task: Read the small slip of paper with your table and try to come up with a group answer (write on white board). Announcements: BAND students I could use a few more quotes for
US History, Feb 19 Entry Task: Read the small slip of paper with your table and try to come up with a group answer (write on white board). Announcements: BAND students I could use a few more quotes for
Labor Unrest Unionization and the Populist Party. The Changing American Labor Force 1/6/15. Chapters 23-24
 Labor Unrest Unionization and the Populist Party Chapters 23-24 The Changing American Labor Force By 1880, 5 million people worked in factories. What were the working conditions like? Unsafe: 1882-675
Labor Unrest Unionization and the Populist Party Chapters 23-24 The Changing American Labor Force By 1880, 5 million people worked in factories. What were the working conditions like? Unsafe: 1882-675
Chapter 13 Section 4 T H E G R E A T S T R I K E S
 Chapter 13 Section 4 T H E G R E A T S T R I K E S Gulf Between Rich and Poor In 1890, the richest 9% of Americans held nearly 75% of the nation s wealth The average worker could earn only a few hundred
Chapter 13 Section 4 T H E G R E A T S T R I K E S Gulf Between Rich and Poor In 1890, the richest 9% of Americans held nearly 75% of the nation s wealth The average worker could earn only a few hundred
Labor Unrest Unionization and the Populist Party. The Changing American Labor Force 12/17/12. Chapters 23-24
 Labor Unrest Unionization and the Populist Party Chapters 23-24 The Changing American Labor Force By 1880, 5 million people worked in factories. What were the working conditions like? Unsafe: 1882-675
Labor Unrest Unionization and the Populist Party Chapters 23-24 The Changing American Labor Force By 1880, 5 million people worked in factories. What were the working conditions like? Unsafe: 1882-675
UNIONS CHAPTER 3 US HISTORY (EOC)
 UNIONS CHAPTER 3 US HISTORY (EOC) ESSENTIAL QUESTION: WHAT IMPACT DID SCIENTIFIC DISCOVERIES AND MANUFACTURING PROCESSES HAVE ON THE NATURE OF WORK, THE AMERICAN LABOR MOVEMENT, AND AMERICAN BUSINESSES?
UNIONS CHAPTER 3 US HISTORY (EOC) ESSENTIAL QUESTION: WHAT IMPACT DID SCIENTIFIC DISCOVERIES AND MANUFACTURING PROCESSES HAVE ON THE NATURE OF WORK, THE AMERICAN LABOR MOVEMENT, AND AMERICAN BUSINESSES?
Industrial Development
 Industrial Development Rapid growth 1865 1914 Abundance of cheap natural resources Large pools of labor immigrants Largest free trade market in the world Capital, no government regulation New technological
Industrial Development Rapid growth 1865 1914 Abundance of cheap natural resources Large pools of labor immigrants Largest free trade market in the world Capital, no government regulation New technological
Working conditions Monotonous same job day after day hour shifts, 6 days a week Dangerous machinery with no safety precautions Workers frequentl
 Labor Unions Working conditions Monotonous same job day after day 12 16 hour shifts, 6 days a week Dangerous machinery with no safety precautions Workers frequently lost fingers, limbs, eyesight, & hearing
Labor Unions Working conditions Monotonous same job day after day 12 16 hour shifts, 6 days a week Dangerous machinery with no safety precautions Workers frequently lost fingers, limbs, eyesight, & hearing
The Birth of Unions SE: US 3B. By Brad Harris, Grand Prairie HS
 The Birth of Unions SE: US 3B By Brad Harris, Grand Prairie HS What is a Labor Union? A labor union is an organization of workers who unite to protect the rights of the workers from abusive practices of
The Birth of Unions SE: US 3B By Brad Harris, Grand Prairie HS What is a Labor Union? A labor union is an organization of workers who unite to protect the rights of the workers from abusive practices of
Labor Response to. Industrialism
 Labor Response to Industrialism Was the rise of industry good for American workers? 1. Introduction Rose Schneiderman Organized Uprising of 20,000 1000 s of women in shirtwaist industry strike Higher wages,
Labor Response to Industrialism Was the rise of industry good for American workers? 1. Introduction Rose Schneiderman Organized Uprising of 20,000 1000 s of women in shirtwaist industry strike Higher wages,
Calvin Coolidge The last 3 decades of the 1800s was more productive than all of America s history before it By 1900 America was the unquestioned
 Calvin Coolidge The last 3 decades of the 1800s was more productive than all of America s history before it By 1900 America was the unquestioned economic powerhouse of the world 1. Abundant raw materials
Calvin Coolidge The last 3 decades of the 1800s was more productive than all of America s history before it By 1900 America was the unquestioned economic powerhouse of the world 1. Abundant raw materials
Industrial Revolution: Reform. Key Concept 5.1 Industrialization and Global Capitalism Tuesday March 27, 2018
 Industrial Revolution: Reform Key Concept 5.1 Industrialization and Global Capitalism Tuesday March 27, 2018 Capitalism An economic idea that promoted maximum profit through competition and investment
Industrial Revolution: Reform Key Concept 5.1 Industrialization and Global Capitalism Tuesday March 27, 2018 Capitalism An economic idea that promoted maximum profit through competition and investment
Chapter 17: THE GREAT RAILROAD STRIKES:
 Chapter 17: THE GREAT RAILROAD STRIKES: Objectives: o We will study the growing conflict between labor and ownership during this era. o We will examine the rise of organized labor in attempting to address
Chapter 17: THE GREAT RAILROAD STRIKES: Objectives: o We will study the growing conflict between labor and ownership during this era. o We will examine the rise of organized labor in attempting to address
Industry Comes of Age Chapter 24
 Industry Comes of Age 1865-1900 Chapter 24 The Iron Colt Becomes an Iron Horse Is there more power in BUSINESS or POLITICS? Surge in railroad development 1865 35,000 miles of track 1900 over 192,000 miles
Industry Comes of Age 1865-1900 Chapter 24 The Iron Colt Becomes an Iron Horse Is there more power in BUSINESS or POLITICS? Surge in railroad development 1865 35,000 miles of track 1900 over 192,000 miles
The Industrial Revolution. Europe s
 The Industrial Revolution Europe 1780-1840s Another Ism Effects Europe: Industrialism Spurs of Industrial Revolution Why Did Industrialization Begin in England First? Industrial Revolution was largely
The Industrial Revolution Europe 1780-1840s Another Ism Effects Europe: Industrialism Spurs of Industrial Revolution Why Did Industrialization Begin in England First? Industrial Revolution was largely
Chapter 18 Lecture Outline
 Chapter 18 Lecture Outline Big Business and Organized Labor 2013 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Chapter 18 Lecture Outline Big Business and Organized Labor 2013 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Robber Barons
Chapter 18 Lecture Outline Big Business and Organized Labor 2013 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Chapter 18 Lecture Outline Big Business and Organized Labor 2013 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. Robber Barons
Chapter 14. A New Industrial Age
 Chapter 14 A New Industrial Age Section 1: A New Industrial Age Industry Expands Period between Civil War and 1920s Industrial Boom Natural Resources Government Support Urban Population: Exploiting Natural
Chapter 14 A New Industrial Age Section 1: A New Industrial Age Industry Expands Period between Civil War and 1920s Industrial Boom Natural Resources Government Support Urban Population: Exploiting Natural
America: Pathways to the Present. Chapter 6. The Expansion of American Industry ( )
 America: Pathways to the Present Chapter 6 The Expansion of American Industry (1850 1900) Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey. All rights
America: Pathways to the Present Chapter 6 The Expansion of American Industry (1850 1900) Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey. All rights
The Industrialization of America:
 The Industrialization of America: 1865-1900 1 Learning Objectives 2 Explain how the transcontinental railroad network provided the basis for the great post- Civil War industrial transformation. Identify
The Industrialization of America: 1865-1900 1 Learning Objectives 2 Explain how the transcontinental railroad network provided the basis for the great post- Civil War industrial transformation. Identify
Chapter 13: The Expansion of American Industry ( )
 Name: Period Page# Chapter 13: The Expansion of American Industry (1850 1900) Section 1: A Technological Revolution Why did people s daily lives change in the decades following the Civil War? How did advances
Name: Period Page# Chapter 13: The Expansion of American Industry (1850 1900) Section 1: A Technological Revolution Why did people s daily lives change in the decades following the Civil War? How did advances
U.S. INDUSTRIALISM. Chap 9
 U.S. INDUSTRIALISM Chap 9 How did the US industrialize? Plenty of raw materials needed for industry: water, wood, coal, iron, copper Large workforce: population tripled between 1860-1910 Technology and
U.S. INDUSTRIALISM Chap 9 How did the US industrialize? Plenty of raw materials needed for industry: water, wood, coal, iron, copper Large workforce: population tripled between 1860-1910 Technology and
Organized Labor DBQ Scoring Guidelines
 Organized Labor DBQ Scoring Guidelines How successful was organized labor in improving the position of workers in the period from 1875 to 1900? Analyze the factors that contributed to the level of success
Organized Labor DBQ Scoring Guidelines How successful was organized labor in improving the position of workers in the period from 1875 to 1900? Analyze the factors that contributed to the level of success
APUSH REVIEWED! INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION: INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
 APUSH 1865-1900 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION: REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 24 American History (Brinkley) Chapters 17, 18 America s History (Henretta) Chapters 17, 19 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION By 1900
APUSH 1865-1900 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION: REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 24 American History (Brinkley) Chapters 17, 18 America s History (Henretta) Chapters 17, 19 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION By 1900
APUSH REVIEWED! INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION:
 APUSH 1865-1900 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION: REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 24 American History (Brinkley) Chapters 17, 18 America s History (Henretta) Chapters 17, 19 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION By 1900
APUSH 1865-1900 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION: REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 24 American History (Brinkley) Chapters 17, 18 America s History (Henretta) Chapters 17, 19 INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION By 1900
Unit #6. Chapter 20 Big Business & Organized Labor
 Unit #6 Chapter 20 Big Business & Organized Labor APUSH PowerPoint #6.1 (Part 1 of 2) Unit #6 Chapter 16 BFW Textbook TOPIC Big Business & Organized Labor [1865-1900] I. The Rise of Big Business A. Causes
Unit #6 Chapter 20 Big Business & Organized Labor APUSH PowerPoint #6.1 (Part 1 of 2) Unit #6 Chapter 16 BFW Textbook TOPIC Big Business & Organized Labor [1865-1900] I. The Rise of Big Business A. Causes
UNIT 2. Industrialization, Immigration, and the Gilded Age
 UNIT 2 Industrialization, Immigration, and the Gilded Age -Switch from manpower to machine power - Great Britain leads the way; US catches up in latter 19 th century - factors of production needed for
UNIT 2 Industrialization, Immigration, and the Gilded Age -Switch from manpower to machine power - Great Britain leads the way; US catches up in latter 19 th century - factors of production needed for
I-The Age of Industry
 STRIKE ONE! { Learning Target: I can describe the working conditions that an individual faced when working in factories and why Unions were created to help workers. I-The Age of Industry A-People began
STRIKE ONE! { Learning Target: I can describe the working conditions that an individual faced when working in factories and why Unions were created to help workers. I-The Age of Industry A-People began
Chapter 13: The Expansion of American Industry ( )
 Name: Period Page# Chapter 13: The Expansion of American Industry (1850 1900) Section 1: A Technological Revolution Why did people s daily lives change in the decades following the Civil War? How did advances
Name: Period Page# Chapter 13: The Expansion of American Industry (1850 1900) Section 1: A Technological Revolution Why did people s daily lives change in the decades following the Civil War? How did advances
SSUSH11A thru E and 12B & D Industrialization
 SSUSH11A thru E and 12B & D Industrialization Causes of U.S. Industrialization The earliest forms of industrialization in the U.S. began in the late 1700 s with the development of the transportation and
SSUSH11A thru E and 12B & D Industrialization Causes of U.S. Industrialization The earliest forms of industrialization in the U.S. began in the late 1700 s with the development of the transportation and
The Industrial Revolution. The Start of Mass Production
 The Industrial Revolution The Start of Mass Production Section 1 Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
The Industrial Revolution The Start of Mass Production Section 1 Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
S apt ect er ion 25 1 Section 1 hnology nd Industrial Growth
 Chapter 13 Objectives Analyze the factors that led to the industrialization of the United States in the late 1800s. Explain how new inventions and innovations changed Americans lives. Describe the impact
Chapter 13 Objectives Analyze the factors that led to the industrialization of the United States in the late 1800s. Explain how new inventions and innovations changed Americans lives. Describe the impact
Ch. 15: The Industrial Revolution
 Ch. 15: The Industrial Revolution I. Understanding Economics a. The Three Economic Questions i. People have unlimited wants, but limited resources. ii. 3 basic questions: 1. What should be produced? 2.
Ch. 15: The Industrial Revolution I. Understanding Economics a. The Three Economic Questions i. People have unlimited wants, but limited resources. ii. 3 basic questions: 1. What should be produced? 2.
The Rise of Smokestack America
 18 The Rise of Smokestack America (1) CHAPTER OUTLINE Thomas O'Donnell's testimony highlights the marginal existence of many workingclass Americans in the late nineteenth century. The responses of congressional
18 The Rise of Smokestack America (1) CHAPTER OUTLINE Thomas O'Donnell's testimony highlights the marginal existence of many workingclass Americans in the late nineteenth century. The responses of congressional
68 Response to Industrial Revolution Presentation Notes notebookMarch 20, 2018
 68 Response to Industrial Revolution Presentation Notes 2017 2018.notebookMarch 20, 2018 1 Group Tasks Spirit 89 91 & 91 92 How do the Knights of Labor plan to reform the working conditions for workers?
68 Response to Industrial Revolution Presentation Notes 2017 2018.notebookMarch 20, 2018 1 Group Tasks Spirit 89 91 & 91 92 How do the Knights of Labor plan to reform the working conditions for workers?
INDUSTRY COMES OF AGE CHAPTER 24
 INDUSTRY COMES OF AGE CHAPTER 24 Railroad Boom By 1900 the U.S. had more track than all of Europe combined 1890 Govt. Help for Railroads The U.S. govt encouraged railroad building in a # of ways Gave RR
INDUSTRY COMES OF AGE CHAPTER 24 Railroad Boom By 1900 the U.S. had more track than all of Europe combined 1890 Govt. Help for Railroads The U.S. govt encouraged railroad building in a # of ways Gave RR
68 Response to Industrial Revolution Presentation Notes notebook. March 20, 2017
 68 Response to Industrial Revolution Presentation Notes 2016 17.notebook 1 Group Tasks Spirit 89 91 & 91 92 How do the Knights of Labor plan to reform the working conditions for workers? Explain why Samuel
68 Response to Industrial Revolution Presentation Notes 2016 17.notebook 1 Group Tasks Spirit 89 91 & 91 92 How do the Knights of Labor plan to reform the working conditions for workers? Explain why Samuel
3. Evaluate the impact of industrialization on the transformation of American society, economy, and politics.
 3. Evaluate the impact of industrialization on the transformation of American society, economy, and politics. A. Analyze the impact of leading industrialists as robber barons and as philanthropists including
3. Evaluate the impact of industrialization on the transformation of American society, economy, and politics. A. Analyze the impact of leading industrialists as robber barons and as philanthropists including
Section 3: The Organized Labor Movement
 Chapter 13: The Triumph of Industry (1865-1914) Section 3: The Organized Labor Movement Objectives Assess the problems that workers faced in the late 1800s. Compare the goals and strategies of different
Chapter 13: The Triumph of Industry (1865-1914) Section 3: The Organized Labor Movement Objectives Assess the problems that workers faced in the late 1800s. Compare the goals and strategies of different
SOCIAL IMPACT OF THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION
 SOCIAL IMPACT OF THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION I REPLACED THE TRADITION HIERACHRY WITH A NEW SOCIAL ORDER II THE GOLDEN AGE OF THE MIDDLE CLASS. 1. A new class of factory owners emerged in this period: the
SOCIAL IMPACT OF THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION I REPLACED THE TRADITION HIERACHRY WITH A NEW SOCIAL ORDER II THE GOLDEN AGE OF THE MIDDLE CLASS. 1. A new class of factory owners emerged in this period: the
Assess the problems that workers faced in the late 1800s. Compare the goals and strategies of different labor organizations.
 Objectives Assess the problems that workers faced in the late 1800s. Compare the goals and strategies of different labor organizations. Analyze the causes and effects of strikes. Terms and People sweatshop
Objectives Assess the problems that workers faced in the late 1800s. Compare the goals and strategies of different labor organizations. Analyze the causes and effects of strikes. Terms and People sweatshop
The Early Industrial Revolution Chapter 22 AP World History
 The Early Industrial Revolution 1760-1851 Chapter 22 AP World History Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
The Early Industrial Revolution 1760-1851 Chapter 22 AP World History Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
Economic Theory: How has industrial development changed living and working conditions?
 Economic Theory: How has industrial development changed living and working conditions? Adam Smith Karl Marx Friedrich Engels Thomas Malthus BACK David Ricardo Jeremy Bentham Robert Owen Classical Economics:
Economic Theory: How has industrial development changed living and working conditions? Adam Smith Karl Marx Friedrich Engels Thomas Malthus BACK David Ricardo Jeremy Bentham Robert Owen Classical Economics:
5-3: Industry and Unions
 5-3: Industry and Unions Overview Rise of industrial capitalism Technological advances Large-scale production methods Opening of new markets Pro-growth government policies Business consolidation Variety
5-3: Industry and Unions Overview Rise of industrial capitalism Technological advances Large-scale production methods Opening of new markets Pro-growth government policies Business consolidation Variety
BIG BUSINESS AND LABOR A NEW INDUSTRIAL AGE
 BIG BUSINESS AND LABOR A NEW INDUSTRIAL AGE CARNEGIE S INNOVATIONS CARNEGIE MAKES A FORTUNE Andrew Carnagie: one of first moguls to make own fortune Carnegie searches for ways to make better products more
BIG BUSINESS AND LABOR A NEW INDUSTRIAL AGE CARNEGIE S INNOVATIONS CARNEGIE MAKES A FORTUNE Andrew Carnagie: one of first moguls to make own fortune Carnegie searches for ways to make better products more
Aim: What actions could workers have taken to improve their conditions during the late 19 th century?
 December 7, 2018 Aim: What actions could workers have taken to improve their conditions during the late 19 th century? Tuesday 12/11: Review Sheet Due Wednesday 12/12: Exam DECEMBER 7, 1941 A DATE WHICH
December 7, 2018 Aim: What actions could workers have taken to improve their conditions during the late 19 th century? Tuesday 12/11: Review Sheet Due Wednesday 12/12: Exam DECEMBER 7, 1941 A DATE WHICH
CHAPTER 24 The Industrial Age,
 CHAPTER 24 The Industrial Age, 1865 1900 1. Railroad Expansion (pp. 528-536) a. The government gave away land bigger than the state of to various railroad companies. What benefits did the government get
CHAPTER 24 The Industrial Age, 1865 1900 1. Railroad Expansion (pp. 528-536) a. The government gave away land bigger than the state of to various railroad companies. What benefits did the government get
American Labor Timeline: 1860s to Modern Times
 American Labor Timeline: 1860s to Modern Times Origins of Today's Union Movement Pullman Strike began on May 11, 1894. 1866 National Labor Union founded 1867 Congress begins reconstruction policy in former
American Labor Timeline: 1860s to Modern Times Origins of Today's Union Movement Pullman Strike began on May 11, 1894. 1866 National Labor Union founded 1867 Congress begins reconstruction policy in former
Phrase penned by Mark Twain as satire for the way America had become. It revealed the best and worst of America.
 Phrase penned by Mark Twain as satire for the way America had become. It revealed the best and worst of America. The Gilded Agesuggests that there was a glittering layer of prosperity that covered the
Phrase penned by Mark Twain as satire for the way America had become. It revealed the best and worst of America. The Gilded Agesuggests that there was a glittering layer of prosperity that covered the
Ch. 4 Industrialization, 5.4 Populism, 6.1 Politics of the Gilded Age Quiz 2011
 Ch. 4 Industrialization, 5.4 Populism, 6.1 Politics of the Gilded Age Quiz 2011 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. IDENTIFYING MAIN IDEAS 1.
Ch. 4 Industrialization, 5.4 Populism, 6.1 Politics of the Gilded Age Quiz 2011 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. IDENTIFYING MAIN IDEAS 1.
The Industrial Revolution. A new era in human history
 The Industrial Revolution A new era in human history definition The Industrial Revolution is the replacement of human and animal power by other sources Agricultural Revolution Improved farming techniques
The Industrial Revolution A new era in human history definition The Industrial Revolution is the replacement of human and animal power by other sources Agricultural Revolution Improved farming techniques
Industrialization. Module 3
 Industrialization Module 3 Lesson 1 Natural Resources Fuel Industrialization Machines begin to replace workers By 1920, U.S. is leading industrial power Black Gold Pre-European arrival, Native Americans
Industrialization Module 3 Lesson 1 Natural Resources Fuel Industrialization Machines begin to replace workers By 1920, U.S. is leading industrial power Black Gold Pre-European arrival, Native Americans
Chapter 16. Wonder and Woe The Rise of Industrial America
 Chapter 16 Wonder and Woe The Rise of Industrial America 1865-1900 The Emergence of Big Business Sources of the Industrial Revolution Enormous quantities of two essential items for industrialization 1.
Chapter 16 Wonder and Woe The Rise of Industrial America 1865-1900 The Emergence of Big Business Sources of the Industrial Revolution Enormous quantities of two essential items for industrialization 1.
Warm Up. Complete the Captains of Industry vs. Robber Barons DBQ
 Warm Up 1 Complete the Captains of Industry vs. Robber Barons DBQ 2 Be prepared to argue whether the industrial entrepreneurs of the Gilded Age are CI or RB 3 Read the intro to help you answer the questions
Warm Up 1 Complete the Captains of Industry vs. Robber Barons DBQ 2 Be prepared to argue whether the industrial entrepreneurs of the Gilded Age are CI or RB 3 Read the intro to help you answer the questions
A Giant Brotherhood of Toil Knights of Labor
 A Giant Brotherhood of Toil Knights of Labor Storm the fort, ye Knights of Labor Battle for your cause; Equal rights for every neighbor Down with tyrant laws. Toiling millions now are waking see them marching
A Giant Brotherhood of Toil Knights of Labor Storm the fort, ye Knights of Labor Battle for your cause; Equal rights for every neighbor Down with tyrant laws. Toiling millions now are waking see them marching
Industrialization Module 3. CRASH COURSE: Industrial Age
 Industrialization Module 3 CRASH COURSE: Industrial Age Section 1:The Expansion of Industry: Main Idea: At the end of the 19 th century, natural resources, creative ideas, and growing markets fueled an
Industrialization Module 3 CRASH COURSE: Industrial Age Section 1:The Expansion of Industry: Main Idea: At the end of the 19 th century, natural resources, creative ideas, and growing markets fueled an
Deflation deflation,
 Unions Deflation Between 1865 and 1897, the United States experienced deflation, or a rise in the value of money Deflation caused prices to fall and companies to cut wages To the workers, it seemed their
Unions Deflation Between 1865 and 1897, the United States experienced deflation, or a rise in the value of money Deflation caused prices to fall and companies to cut wages To the workers, it seemed their
U. S. History Topic 9 Reading Guides Industry and Immigration
 1 U. S. History Topic 9 Reading Guides Industry and Immigration Lesson 1: Innovation Boosts Growth Key Terms: Use the textbook or quizlet.com to define the following term entrepreneur free enterprise laissez
1 U. S. History Topic 9 Reading Guides Industry and Immigration Lesson 1: Innovation Boosts Growth Key Terms: Use the textbook or quizlet.com to define the following term entrepreneur free enterprise laissez
Wonder and Woe The Rise of Industrial America CHAPTER 18
 Wonder and Woe The Rise of Industrial America 1865-1900 CHAPTER 18 World s Fair Chicago 1892 Results of American industrial, culture, and commerce dominance. AC/DC debate Chicago World s Fair: display
Wonder and Woe The Rise of Industrial America 1865-1900 CHAPTER 18 World s Fair Chicago 1892 Results of American industrial, culture, and commerce dominance. AC/DC debate Chicago World s Fair: display
America at the turn of the Century
 America at the turn of the Century Gilding is the process of covering something in a thin layer of Gold, making it seem more valuable than it is. This time period was one of rapid Industrialization and
America at the turn of the Century Gilding is the process of covering something in a thin layer of Gold, making it seem more valuable than it is. This time period was one of rapid Industrialization and
Chapter 14, Section 1 I. The United States Industrializes (pages ) A. With the end of the Civil War, American industry expanded and millions
 Chapter 14, Section 1 I. The United States Industrializes (pages 436 437) A. With the end of the Civil War, American industry expanded and millions of people left their farms to work in mines and factories.
Chapter 14, Section 1 I. The United States Industrializes (pages 436 437) A. With the end of the Civil War, American industry expanded and millions of people left their farms to work in mines and factories.
Note Taking Study Guide DAWN OF THE INDUSTRIAL AGE
 SECTION 1 DAWN OF THE INDUSTRIAL AGE Focus Question: What events helped bring about the Industrial Revolution? As you read this section in your textbook, complete the following flowchart to list multiple
SECTION 1 DAWN OF THE INDUSTRIAL AGE Focus Question: What events helped bring about the Industrial Revolution? As you read this section in your textbook, complete the following flowchart to list multiple
Industrialization! &! the Gilded Age. *** Go to Mrs. Lang s teacher page for the recorded lecture!!!
 Industrialization! &! the Gilded Age *** Go to Mrs. Lang s teacher page for the recorded lecture!!! Essential Question How did industrialization bring both positive and negative changes? Technological
Industrialization! &! the Gilded Age *** Go to Mrs. Lang s teacher page for the recorded lecture!!! Essential Question How did industrialization bring both positive and negative changes? Technological
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century)
 The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 6: TELESCOPING THE TIMES A New Industrial Age CHAPTER OVERVIEW Technological innovations and the growth of the railroad industry help fuel an
The Americans (Reconstruction to the 21st Century) Chapter 6: TELESCOPING THE TIMES A New Industrial Age CHAPTER OVERVIEW Technological innovations and the growth of the railroad industry help fuel an
Chapter 9 Section 1 & 2. Origins of Progressivism
 Chapter 9 Section 1 & 2 Origins of Progressivism Progressive Movement 4 goals of the movement Promote social welfare Promote moral improvement Create economic reform Foster efficiency Prohibition Banning
Chapter 9 Section 1 & 2 Origins of Progressivism Progressive Movement 4 goals of the movement Promote social welfare Promote moral improvement Create economic reform Foster efficiency Prohibition Banning
Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain????
 Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain???? Read textbook pages 612-615. Write a paragraph explaining why the industrial revolution began in Great Britain. Please include something about
Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in Great Britain???? Read textbook pages 612-615. Write a paragraph explaining why the industrial revolution began in Great Britain. Please include something about
World History Chapter 25
 World History Chapter 25 Renaissance Reformation Age of Exploration Scientific Revolution Enlightenment The Industrial Revolution starts in England and soon spreads to other countries. Plentiful natural
World History Chapter 25 Renaissance Reformation Age of Exploration Scientific Revolution Enlightenment The Industrial Revolution starts in England and soon spreads to other countries. Plentiful natural
Vocabulary: protective tariff laissez faire capitalism mass production corporation monopoly trust social darwinism Insterate Commerce Act
 Lesson 4: Industrialization Time Period: Late 1800s (Chapter 4 in Textbook) Late 1800s = Late 19 th Century Vocabulary: protective tariff laissez faire capitalism mass production corporation monopoly trust
Lesson 4: Industrialization Time Period: Late 1800s (Chapter 4 in Textbook) Late 1800s = Late 19 th Century Vocabulary: protective tariff laissez faire capitalism mass production corporation monopoly trust
World History Chapter 25
 World History Chapter 25 Renaissance Reformation Age of Exploration Scientific Revolution Enlightenment The Industrial Revolution starts in England and soon spreads to other countries. Plentiful natural
World History Chapter 25 Renaissance Reformation Age of Exploration Scientific Revolution Enlightenment The Industrial Revolution starts in England and soon spreads to other countries. Plentiful natural
The Industrial Revolution began in Britain in the 1700s. It soon spread to America.
 Chapter 13 The Triumph of Industry Section 1 The Industrial Revolution began in Britain in the 1700s. It soon spread to America. The first Industrial Revolution was marked by the introduction of steam
Chapter 13 The Triumph of Industry Section 1 The Industrial Revolution began in Britain in the 1700s. It soon spread to America. The first Industrial Revolution was marked by the introduction of steam
I. The Agricultural Revolution
 I. The Agricultural Revolution A. The Agricultural Revolution Paves the Way 1. Wealthy farmers cultivated large fields called enclosures. 2. The enclosure movement caused landowners to try new methods.
I. The Agricultural Revolution A. The Agricultural Revolution Paves the Way 1. Wealthy farmers cultivated large fields called enclosures. 2. The enclosure movement caused landowners to try new methods.
Key Concepts Chart (The Progressive Era)
 Unit 3, Activity 1, Key Concepts Chart Key Concepts Chart (The Progressive Era) Key Concept +? - Explanation Extra Information Knights of Labor American Federation of Labor Industrial Workers of the World
Unit 3, Activity 1, Key Concepts Chart Key Concepts Chart (The Progressive Era) Key Concept +? - Explanation Extra Information Knights of Labor American Federation of Labor Industrial Workers of the World
Name: Date: Period: VUS. 8 a&b: Westward Expansion and Industrialization. Filled In. Notes VUS. 8a&b: Westward Expansion and Industrialization 1
 Name: Date: Period: VUS 8 a&b: Westward Expansion and Industrialization Filled In Notes VUS 8a&b: Westward Expansion and Industrialization 1 Objectives about Westward Expansion and Industrialization VUS8
Name: Date: Period: VUS 8 a&b: Westward Expansion and Industrialization Filled In Notes VUS 8a&b: Westward Expansion and Industrialization 1 Objectives about Westward Expansion and Industrialization VUS8
Welcome back to WHAP! Thursday 2/15/18
 Welcome back to WHAP! Thursday 2/15/18 Turn your Ch. 17 Skills Activity into the tray- make sure your name is on it You need to have your notes out and something to write with- be ready to take some notes
Welcome back to WHAP! Thursday 2/15/18 Turn your Ch. 17 Skills Activity into the tray- make sure your name is on it You need to have your notes out and something to write with- be ready to take some notes
The Start of the Industrial Revolution
 The Start of the Industrial Revolution I. Agricultural Revolution A. Industrial Revolution changed Europe from a mostly agricultural economy to industrialization- work driven by machinery B. Improved Farm
The Start of the Industrial Revolution I. Agricultural Revolution A. Industrial Revolution changed Europe from a mostly agricultural economy to industrialization- work driven by machinery B. Improved Farm
The Industrial Revolution Begins ( )
 Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 20, Section World History: Connection to Today Chapter 20 The Industrial Revolution
Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 20, Section World History: Connection to Today Chapter 20 The Industrial Revolution
25.4 Reforming the Industrial World. The Industrial Revolution leads to economic, social, and political reforms.
 25.4 Reforming the Industrial World The Industrial Revolution leads to economic, social, and political reforms. The Philosophers of Industrialization Laissez-faire Economics Laissez faire economic policy
25.4 Reforming the Industrial World The Industrial Revolution leads to economic, social, and political reforms. The Philosophers of Industrialization Laissez-faire Economics Laissez faire economic policy
Captains of Industry or Robber Barons
 1. Growth of Industrialization----1865 to 1900 Why? Factors in place Railroad industry Distribution System Symbol of growth Government assists industry ---- 1860 to 1880 laissez faire economy Laws to promote
1. Growth of Industrialization----1865 to 1900 Why? Factors in place Railroad industry Distribution System Symbol of growth Government assists industry ---- 1860 to 1880 laissez faire economy Laws to promote
The Industrial Revolution Beginnings. Ways of the World Strayer Chapter 18
 The Industrial Revolution Beginnings Ways of the World Strayer Chapter 18 Explaining the Industrial Revolution The global context for the Industrial Revolution lies in a very substantial increase in human
The Industrial Revolution Beginnings Ways of the World Strayer Chapter 18 Explaining the Industrial Revolution The global context for the Industrial Revolution lies in a very substantial increase in human
Section 1 Introduction to Period 6, page 318
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Ch. 16 AMSCO or other source for Period 6 Directions: 1. Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before you read the chapter. 2. Skim:
Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Ch. 16 AMSCO or other source for Period 6 Directions: 1. Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before you read the chapter. 2. Skim:
The Industrialization of the United States s 1910 s
 The Industrialization of the United States 1860 s 1910 s O O O O O O O O O O O O O O SSUSH11 The student will describe the growth of big business and technological innovations after Reconstruction. a.
The Industrialization of the United States 1860 s 1910 s O O O O O O O O O O O O O O SSUSH11 The student will describe the growth of big business and technological innovations after Reconstruction. a.
Section 4 Notes Window panes
 Term Picture 10 word max summary Answer questions at the end of the section. Section 4 Notes Window panes Laissez-faire Capitalism Utilitarianism Socialism Karl Marx Communism Unions Factory Act of 1883
Term Picture 10 word max summary Answer questions at the end of the section. Section 4 Notes Window panes Laissez-faire Capitalism Utilitarianism Socialism Karl Marx Communism Unions Factory Act of 1883
As settlement continued in the West, the nation
 Name Date CHAPTER 14 Summary TELESCOPING THE TIMES A New Industrial Age CHAPTER OVERVIEW Technological innovations and the growth of the railroad industry help fuel an industrial boom. Some business leaders
Name Date CHAPTER 14 Summary TELESCOPING THE TIMES A New Industrial Age CHAPTER OVERVIEW Technological innovations and the growth of the railroad industry help fuel an industrial boom. Some business leaders
CH 17: The European Moment in World History, Revolutions in Industry,
 CH 17: The European Moment in World History, 1750-1914 Revolutions in Industry, 1750-1914 Explore the causes & consequences of the Industrial Revolution Root Europe s Industrial Revolution in a global
CH 17: The European Moment in World History, 1750-1914 Revolutions in Industry, 1750-1914 Explore the causes & consequences of the Industrial Revolution Root Europe s Industrial Revolution in a global
3. Predatory unionism occurs when the union's prime goal is to enhance itself at the expense of the workers it represents.
 Labor Relations Development Structure Process 12th Edition Fossum Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/labor-relations-development-structure-process-12th-edition-fossum-test-bank/
Labor Relations Development Structure Process 12th Edition Fossum Test Bank Full Download: http://testbanklive.com/download/labor-relations-development-structure-process-12th-edition-fossum-test-bank/
Age of Growth and Disorder, s
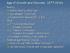 Age of Growth and Disorder, 1877-1910s Naming Robber Barons, Gilded Age Industrialism Triumphant Examine from several POV: G & D What 2 nd Industrial Revolution Increase in production 2 nd Wave of Immigration
Age of Growth and Disorder, 1877-1910s Naming Robber Barons, Gilded Age Industrialism Triumphant Examine from several POV: G & D What 2 nd Industrial Revolution Increase in production 2 nd Wave of Immigration
The Industrial Revolution Last Third of 19 th Century
 The Industrial Revolution Last Third of 19 th Century Advertisement for Chicago & Alton Railroad. 1 The Expansion of Industry Natural Resources Fuel Industrialization The Growth of Industry (concentrated
The Industrial Revolution Last Third of 19 th Century Advertisement for Chicago & Alton Railroad. 1 The Expansion of Industry Natural Resources Fuel Industrialization The Growth of Industry (concentrated
The Beginnings of Industrialization
 Name CHAPTER 25 Section 1 (pages 717 722) The Beginnings of BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about romanticism and realism in the arts. In this section, you will read about the beginning of
Name CHAPTER 25 Section 1 (pages 717 722) The Beginnings of BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about romanticism and realism in the arts. In this section, you will read about the beginning of
SSUSH11 Examine connections between the rise of big business, the growth of labor unions, and technological innovations. a. Explain the effects of
 SSUSH11 Examine connections between the rise of big business, the growth of labor unions, and technological innovations. a. Explain the effects of railroads on other industries, including steel and oil.
SSUSH11 Examine connections between the rise of big business, the growth of labor unions, and technological innovations. a. Explain the effects of railroads on other industries, including steel and oil.
The Gilded Age
 The Gilded Age 1865-1900 Gilded Age 1870-1900 Post-Reconstruction America Phrase coined by Mark Twain; used to represent America during this time Also, think of a beautiful, shiny, red apple that is rotten
The Gilded Age 1865-1900 Gilded Age 1870-1900 Post-Reconstruction America Phrase coined by Mark Twain; used to represent America during this time Also, think of a beautiful, shiny, red apple that is rotten
PPT: Power to the People
 PPT: Power to the People The Rise and Fall of the Populist Party 1867-1896 new machines = overproduction = lower prices = loss of $ for farmers Farmers Problems Crop prices fell. A bushel of wheat that
PPT: Power to the People The Rise and Fall of the Populist Party 1867-1896 new machines = overproduction = lower prices = loss of $ for farmers Farmers Problems Crop prices fell. A bushel of wheat that
The Americans: Reconstruction to the 21 st Century
 A New Industrial Age Natural resources and new ideas create a boom for industry and railroads. Government addresses corruption in business, and laborers organize for better working conditions. A New Industrial
A New Industrial Age Natural resources and new ideas create a boom for industry and railroads. Government addresses corruption in business, and laborers organize for better working conditions. A New Industrial
Working Conditions, Unions and Strikes
 Working Conditions, Unions and Strikes Working conditions in American Factories at the turn of the century Long hours: 12-14 hours and 6-7 days a week. Employees were not entitled to vacation, sick leave,
Working Conditions, Unions and Strikes Working conditions in American Factories at the turn of the century Long hours: 12-14 hours and 6-7 days a week. Employees were not entitled to vacation, sick leave,
Unit 9 Industrial Revolution
 Unit 9 Industrial Revolution Section 1: Beginnings of Industrialization The Industrial Revolution c. 1750/60-1850/60 The Industrial Revolution begins in Britain/England, spreads to other countries, and
Unit 9 Industrial Revolution Section 1: Beginnings of Industrialization The Industrial Revolution c. 1750/60-1850/60 The Industrial Revolution begins in Britain/England, spreads to other countries, and
United States History 11R
 United States History 11R After Civil War United States - Agricultural Nation Would become leading Industrial Power in 60 years Why? Wealth of Natural Resources Government support for business Growing
United States History 11R After Civil War United States - Agricultural Nation Would become leading Industrial Power in 60 years Why? Wealth of Natural Resources Government support for business Growing
Guided Reading & Analysis: The Rise of Industrial America, Chapter 16- The Second Industrial Revolution pp
 Name: Due Date: APUSH Mrs. Pate Guided Reading & Analysis: The Rise of Industrial America, 1865-11900 Chapter 16- The Second Industrial Revolution pp 318-332 Reading Assignment: Ch. 16 AMSCO or other source
Name: Due Date: APUSH Mrs. Pate Guided Reading & Analysis: The Rise of Industrial America, 1865-11900 Chapter 16- The Second Industrial Revolution pp 318-332 Reading Assignment: Ch. 16 AMSCO or other source
Workers in the Gilded Age and Progressive Era
 T H E G I L D E D AG E A N D P RO G R E S S I V E E R A UNIT 1: BUILDING A NEW ECONOMY LESSON 2 Workers in the Gilded Age and Progressive Era OVERVIEW During the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries,
T H E G I L D E D AG E A N D P RO G R E S S I V E E R A UNIT 1: BUILDING A NEW ECONOMY LESSON 2 Workers in the Gilded Age and Progressive Era OVERVIEW During the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries,
Big Business. Native Americans. Rise of the City. Organized Labor. Political Corruption. Cultural Developments
 THIS IS With Your Host... Big Business Native Americans Political Corruption Rise of the City Organized Labor Cultural Developments 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300
THIS IS With Your Host... Big Business Native Americans Political Corruption Rise of the City Organized Labor Cultural Developments 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300
U.S. History Final, ch 16-18
 U.S. History Final, ch 16-18 Chapter 16 1. President Lincoln was determined to make the South suffer for many years even after the war had ended. (T/F) 2. Louisiana was the first southern state to rejoin
U.S. History Final, ch 16-18 Chapter 16 1. President Lincoln was determined to make the South suffer for many years even after the war had ended. (T/F) 2. Louisiana was the first southern state to rejoin
Chapter 9 Section 1. The Beginnings of Industrialization
 Chapter 9 Section 1 The Beginnings of Industrialization Industrialization begins in Great Britain Took place between 1760 1840 Before the I.R. hands did most of the work By the mid 1700 s, began using
Chapter 9 Section 1 The Beginnings of Industrialization Industrialization begins in Great Britain Took place between 1760 1840 Before the I.R. hands did most of the work By the mid 1700 s, began using
