Useful for Union and State Civil Services, Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand Judicial Services etc. By Abhinav Misra UPKAR PRAKASHAN, AGRA-2
|
|
|
- Amice Sparks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2 Useful for Union and State Civil Services, Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand Judicial Services etc. By Abhinav Misra UPKAR PRAKASHAN, AGRA-2
3 Publishers Publishers UPKAR PRAKASHAN (An ISO 9001 : 2000 Company) 2/11A, Swadeshi Bima Nagar, AGRA Phone : , , Fax : (0562) , care@upkar.in Website : Branch Offices 4845, Ansari Road, Daryaganj, 1-8-1/B, R.R. Complex (Near Sundaraiah Park, New Delhi Adjacent to Manasa Enclave Gate), Bagh Lingampally, Phone : /66 Hyderabad (A.P.), Phone : The publishers have taken all possible precautions in publishing this book, yet if any mistake has crept in, the publishers shall not be responsible for the same. This book or any part thereof may not be reproduced in any form by Photographic, Mechanical, or any other method, for any use, without written permission from the Publishers. Only the courts at Agra shall have the jurisdiction for any legal dispute. ISBN : Price : (Rs. Forty Two Only) Code No Printed at : Upkar Prakashan (Printing Unit) Bye-pass, AGRA
4 Contents Chapter-1 : Nature and Concept 3 4 Chapter-2 : Schools of Jurisprudence 5 17 Chapter-3 : Definition of Law Chapter-4 : Administration of Justice Chapter-5 : Sources of Law Chapter-6 : Legal Concepts Chapter-7 : Legal Persons Miscellaneous 47 56
5 Jurisprudence
6 CHAPTER 1 Nature and Concept The word Jurisprudence is made from two words or it is a combination of two latin words Juris and prudentia. Meaning of Juris is law and meaning of prudentia is knowledge. Clearly meaning of Jurisprudence is knowledge of law. The Study of Jurisprudence started among Romans at first. Definition 1. Ulpian Ulpian was a Roman Jurist, according to him Jurisprudence is the knowledge of things, divine and human, the science of right and wrong. This definition is similar to the definition of Dharma of Hindu philosophy. According to Jaimini Dharma is that which is signified by a command and leads to man s matarial and spiritual salvation. Yajnavalkya has defined that Vyavahara, means those rules which determine the Judicial Proceeding. 2. According to Holland, Jurisprudence is the formal science of positive law. According to him formal science is a science which deals with the various relations which are regulated by legal rules. Definition by Salmond According to Salmond, Jurisprudence is the Science of law, and law means civil law. In this sense Jurisprudence has three kinds (i) Expository or Systematic (ii) Legal history (iii) Science of legislation Samond makes a difference between General and Specific Jurisprudence. According to him General Jurisprudence includes the General group of principles of law. Branches of Jurisprudence Jurisprudence can be classified into three groups (a) Analytical (b) Historical (c) Ethical (i) Definition by Gray According to Gray, it is the systematic arrangement of rules followed by Courts and principles underlying them. Criticism of Gray According to Stone, Gray has failed to determine any province of Jurisprudence rather he has reduced Jurisprudence to merely a matter of arrangement of rules. According to Keeton, Jurisprudence is the Study and systematic arrangement of General principals of laws. Definition by E.M. Patterson Jurisprudence means a body of ordered knowledge, which deals wih a particular species of law. Use of Jurisprudence Jurisprudence is supposed as a theoretical topic and it is also that this has no practical importance but according to Salmond it has its own intrinsic importance and interest. Practical ability Jurisprudence serves to render the complexities of law more manageable and rationable and in this way this can help to improve practice in law. According to Holland The Jurisprudence is the ever reviewed complexity of human relations calls for an increasing complexity of legal details, till a merely empirical knowledge of law becomes impossible. According to Dias The study of Jurisprudence provides an opportunity for the layer to bring theory and life into focus, for it concerns human thought in relation to social existence. Other Basic Uses of Jurisprudence are (i) Jurisprudence provides scientific development law. (ii) Jurisprudence provides help to judges and lawyers in ascertaining the meaning of words and expressions in statutes. (iii) It provides an epistemology of law. (iv) Jurisprudence gives an idea of the nature of law.
7 4 Jurisprudence 1. According to whom Jurist Jurisprudence is the knowledge of just and unjust? (A) Ulpian (B) Gray (C) Salmond (D) Hobbes 2. According to whom Jurist Jurisprudence is a science? (A) Ulpian (B) Gray (C) Salmond (D) None 3. According to whom Jurisprudence is science of the principles of the civil law? (A) Ulpian (B) Gray (C) Salmond (D) None 4. Who calls the Jurisprudence as philosophy of positive law? (A) Ulpian (B) Gray (C) Austin (D) Holland 5. Who defines Jurisprudence as the formal science of positive law? (A) Ulpian (B) Austin (C) Holland (D) Allen 6. Who defines Jurisprudence as study of, and systematic arrangement of the general principle of law? (A) Holland (B) Allen (C) Keeton (D) Pound 7. According to whom Jurisprudence is the science of law using the term law? (A) Pound (B) Keeton (C) Allen (D) Holland 8. According to whom jurisprudence is a part of history, a part of economics and sociology, a part of ethics and a philosophy of life? (A) Pound (B) Keeton (C) Radclifle (D) None 9. According to whom Jurisprudence is a complete scientific treatment of any body of law involves the study of these categories mentioned above? (A) Holland (B) Keeton (C) Salmond (D) None 10. According to Ulpian Jurisprudence is Which are correct? 1. The Knowledge of things, divine and human 2. Science of right and wrong Objective Questions 3. Scientific synthesis of the essential principles of law (A) 1 (B) 1 and 2 (C) 1 and 3 (D) 1, 2 and According to whom Jurisprudence means a body of ordered knolwedge. Which deals with a particular species of law? (A) Dias (B) Keeton (C) Patterson (D) Pound 12. According to whom Jurisprudence means a body of ordered knowledge. Which deals with a particular species of law? (A) Patterson (B) Pound (C) Keeton (D) Holland 13. According to Salmond, the types of Jurisprudence are (A) One (B) Two (C) Six (D) Three 14. According to Salmond, the kinds of Jurisprudence are (A) Expository, legal history, science of legislation (B) Civil, Expository, Science of Legislation (C) Both (A) and (B) (D) None 15. The uses of study of Jurisprudence are (A) It throws light on the basic ideas and fundamental principles of law in a given society (B) Supplies an epistemology of law, a theory as to the possibility of genuine knolwedge in the legal sphere (C) Both (A) and (B) (D) None of these 16. Three branches of Jurisprudence are 1. Analytical 2. Historical 3. Economic 4. Ethical (A) 1, 2, 3 (B) 1, 2, 4 (C) 2, 3, 4 (D) 1, 2, 3, 4 Answers 1. (A) 2. (B) 3. (C) 4. (C) 5. (C) 6. (C) 7. (A) 8. (C) 9. (C) 10. (B) 11. (A) 12. (A) 13. (D) 14. (A) 15. (C) 16. (A)
8 CHAPTER 2 Schools of Jurisprudence Schools of Jurisprudence are (i) Natural Law School (ii) Analytical School (iii) Historical School (iv) Philosophical School (v) Sociological School (vi) Realist School Natural Law School The rules which have came from God or nature are known as natural law. These are also named as Divine law, Law of God, universal law, unwritten law and law of Nature. It is an appeal to absolute justice. The natural law philosophy dominated in Greece and by it, it was believed that there is something external to man and it is universal source. Definitions of Natural Law (i) According to Friedmann, the history of natural law is a tale of the search of mankind for absolute justice and its failure. (ii) According to Black Stone, the natural law being coexistent with mankind emanating from God himself is superior to all other laws. It is binding over all the countries at all the times and no man made law will be valid if it is contrary to the law of nature. (iii) According to Cohen, it is not a body of actual enacted interpreted law enforced by courts. It is in fact a way of looking at things and a humanistic approach of Judges and Jurists. Main Points of Natural Law 1. The Principle Rule of Law (in India and England) and due process (in USA) are based on natural law. 2. It has been used to maintain status quo. 3. These are moral ideals having universal applicability everywhere. Classification of Natural Law Natural law may be classified into four groups (i) Ancient, (ii) Medieval, (iii) Renaissance, (iv) Modern. Ancient Natural Law The fundamental concept of Natural law is invented in Greek. It was invented by philosophers not by Jurists. Main philosopers were (i) Heraclitus Heraclitus provided the fundamental features of natural law at first time. He pointed that the main characteristic of law are reason density and order. According to Heraclitus, reason is an essential of Natural law. (ii) Socrates Socrates was one of stoic philosophers. According to Socrates, there is a natural moral law also similar to natural physical law. According to him each and every human personalities possesses in sight and this in sight provides him a capacity to distinguish between goodness and badness. His principle is a plea for Stability and Security. (iii) Plato Plato was pupil of Socrates. According to him only those persons who are worthy and intelligent person should be the king. The book of Plato is Republic. (iv) Aristotle According to Aristotle, a man is a part of nature in two ways (1) he is a part of God creation. (2) he possesses in sight. According to his principle reason unaffected by desires are known as natural laws. Observations of Rescoe Pound about natural law are 1. Natural law was the result of views and ideas expressed by philosophers not of Jurists.
9 6 Jurisprudence 2. In fact enacted laws were the declared customs, it was not effected by natural laws. 3. Natural law was influenced by politically declared laws and tribal customs which were not differentiated in social order. (v) Roman System Stoics philosophy had a great influence on the contemporary Roman philosophy. Natural law found an expression in Roman law philosophy through division of Roman law into three, namely (1) Jus Naturale (2) Jus Gentium (3) Jus Civile Jus Naturale are laws for all persons but Jus Gentium are laws for foreigners and Jus civile are laws only for citizens. Cicero Cicero was a Roman Jurist, his famous book is De Legibus. According to Cicero, True law is a right reason in agreement with nature, it is of universal application, unchanging and everlasting. Hindu System, New era of Natural Law Hindu Judicial System is the most ancient Judicial System. It was given by Hindu Sages. The anicient sources was Shruti and Smritis. Reason and Justice also have been considered as Sources. According to this law is provided by and organised by the God, so it was law of nature. According to Brahaspati, Decision should be given according to Shastras and reason. According to Manu, Vedas, Smritis, usages and good conscience are declared sources of Hindu Law. Dark Ages (Christian ages) St. Augustine and some other fathers expressed views on the natural law. Medieval Naural Law The period of medieval natural law is from 12th century to fourteenth century. This is propagated by Christian fathers to establish superiority of church over the state. By using the theory of natural law they establish a new political and legal order and Christianity. St. Augustine, Ambrose and Gregory and other Christian saints establish a new era that Devine law is superior to all other laws. According to Gierke, the medieval natural law theory centred round two fundamental principles, these are (i) Unity derived from God, involving one chruch, and one empire. (ii) Supremacy of God made and manmade law, as a part of unity of universe. Main Philosophers of Medieval Period Thomas Aquinas Thomas Aquinas was the main philosopher and theologicians of medieval ages. Aquinas provided a new theory of natural law. The views of Christian fathers are more logical and systematic. The views of Aquinas are similar to views of Aristotle. According to him, there are four categories of law, these are (i) Law of Devine (ii) Law of Nature, revealed through the reason of man (iii) Law of God (iv) Human laws (Now positive law). Renaissance Natural Law Theory The development history of natural law is renaissance. The period of renaissance marks a general awakening of new ideas in all fields of knowledge. This period is marked by rationalism and emergence of new ideas in various fields. In other hand the development in the field of trade and commerce created new groups in society, which required more protection from state, and nationalism had developed, due to this concept the state must have sovereign power or due to commulative effect of these trade. Social, commerce developments were created due to this sovereignity of state and supremacy of positive law overthrows the dominance of the Church and new theories was developed. These new theories were propounded by rationalist thinkers such as Machiavelli. Some theories about natural law was propounded by Grotius, Locke, so a social contract forms between concepts. What is Social Contract This principle is basically provided by Italian Marsilius. According to this concept, in beginning man lived in the natural state. They had no structure means had neither any government nor any law. There was no certain structure about society. After a certain time, men entered into an agreement for protection of property and lives, this agreement was a social
10 Jurisprudence 7 contract and known as pactum unionis. And due to this, society came into existence. Now men entered in a other agreement, which is pactum subjectionis, according to this, sovereign power or government came into existence. Hugo Grotius (1583 to 1645) The reason of Grotius is not similar to the reason of Thomas, in other words Grotius provided a new legal theory on Social Contract, according to this, it is a duty of the sovereign to safeguard the citizens further Grotius says that king should be obeyed in all possible conditions. On this concept Grotius laid the foundations of International law. Thomas Hobbes ( ) Hobbes theory is also based upon social contract, he made use of natural law to justify the absolute authority. According to Hobbes, man s life in a state of nature was one of fear and selfishness, it was solitary, poor, brutish and short. According to him the idea of self-preservation and pain are inherent in his nature. A man desires society also. These inclinations induced him to enter into a contract and surrender power and freedom to authority. Natural law can be discovered by reason which decides what a man should do and what he should not do so confirmly he make ideas that sovereign must be bound by morality. John Lock ( ) During the middle ages the church remained supreme, then Renaissance came and new political theories started, which favoured absolute sovereignty of the state. The state emerged very powerful. It provided to undetermine the importance of the individual. Now a new definition of natural law was compulsory in order to support the individual against power of sovereign. John Lock had given the Revolution of 1688 and the wave of individualism. Lock provided new definitions of social contract and natural law. John Lock emphasised on the protection of three main rights (i) Right to life (ii) Right to liberty (iii) Right to property It is also that Lock s idea about social contract was founded on secular approach to natural law. The laissez faire theory in economics was derived from his views. Jean Rousseau ( ) Rousseau provided a new interpretation to social contract and natural law. He explained that social contract is a hypothetical construction of reason not a historical fact. His natural law belongs for the freedom and equality of men. Modern Law School (a) Hostility During nineteenth century, theories became hostile to natural law. In this various social, economic and political changes had taken place in Europe. (b) Revival At the last of nineteenth century, natural law theories revives. The basic causes of it was (i) Reaction against legal theories developed in nineteenth century. (ii) It was realised that abstract thinking or a priori assumptions were not completely futile. This theory is known as natural law with a variable content. Stammler ( ) Stammler was a professor in Germany. According to him law may be defined as species of will others regarding, self authoritative and inviolable. According to Stammler all positive law is an attempt at just law. His concept is known as natural law with a variable content. Rawis Rawis propounded two basic principles of natural justice (i) Social and economic inequalities These should be are arranged to provide maximum benefit to the community as whole. (ii) Equality of right to secure opportunities, liberties and power. Kohalar He is a new Hegalian. According to him law is the standard of conduct which is consequence of the inner impulse that urges upon men towards a reasonable form of life, emanates from the whole and is forced upon the individual. According to him legal interpretation should not be materialistic.
11 Jurisprudence 31% OFF Publisher : Upkar Prakashan ISBN : Author : Abhinav Misra Type the URL : Get this ebook
(USEFUL FOR JUDICIAL SERVICES EXAMINATIONS) By Abhinav Misra UPKAR PRAKASHAN, AGRA 2
 (USEFUL FOR JUDICIAL SERVICES EXAMINATIONS) By Abhinav Misra UPKAR PRAKASHAN, AGRA 2 Publishers Publishers UPKAR PRAKASHAN (An ISO 9001 : 2000 Company) 2/11A, Swadeshi Bima Nagar, AGRA 282 002 Phone :
(USEFUL FOR JUDICIAL SERVICES EXAMINATIONS) By Abhinav Misra UPKAR PRAKASHAN, AGRA 2 Publishers Publishers UPKAR PRAKASHAN (An ISO 9001 : 2000 Company) 2/11A, Swadeshi Bima Nagar, AGRA 282 002 Phone :
UPKAR PRAKASHAN, AGRA 2
 (USEFUL FOR UNION AND STATE CIVIL SERVICES, JUDICIAL SERVICES AND OTHER EQUIVALENT EXAMS.) Including Objective Questions with Explanations By Abhinav Misra UPKAR PRAKASHAN, AGRA 2 Publishers Publishers
(USEFUL FOR UNION AND STATE CIVIL SERVICES, JUDICIAL SERVICES AND OTHER EQUIVALENT EXAMS.) Including Objective Questions with Explanations By Abhinav Misra UPKAR PRAKASHAN, AGRA 2 Publishers Publishers
JURISPRUDENCE: PHILOSOPHY ABOUT STUDY OF LAW
 390 JURISPRUDENCE: PHILOSOPHY ABOUT STUDY OF LAW Abstract Shivangi 1 Jurisprudence has had controversial definitions since classical times. The history of evolution of jurisprudence is based upon two main
390 JURISPRUDENCE: PHILOSOPHY ABOUT STUDY OF LAW Abstract Shivangi 1 Jurisprudence has had controversial definitions since classical times. The history of evolution of jurisprudence is based upon two main
TOPIC: - THE PLACE OF KELSONS PURE THEORY OF LAW IN
 1 LEGAL THEORY SEMINAR TOPIC: - THE PLACE OF KELSONS PURE THEORY OF LAW IN FUNCTIONAL JURISPRUDENCE NAME: SANKALP BHANGUI CLASS: FIRST YEAR L.L.M 2 INDEX SR.NO. TOPIC PG.NO. THE PLACE OF KELSON S PURE
1 LEGAL THEORY SEMINAR TOPIC: - THE PLACE OF KELSONS PURE THEORY OF LAW IN FUNCTIONAL JURISPRUDENCE NAME: SANKALP BHANGUI CLASS: FIRST YEAR L.L.M 2 INDEX SR.NO. TOPIC PG.NO. THE PLACE OF KELSON S PURE
PERSPECTIVE OF NATURAL LAW IN TODAY S GLOBALIZED SCENARIO
 281 PERSPECTIVE OF NATURAL LAW IN TODAY S GLOBALIZED SCENARIO Author:- Chaitali Sadayet 1 ABSTRACT The natural law philosophy occupies an important place in the realm of politics, law, religion and ethics
281 PERSPECTIVE OF NATURAL LAW IN TODAY S GLOBALIZED SCENARIO Author:- Chaitali Sadayet 1 ABSTRACT The natural law philosophy occupies an important place in the realm of politics, law, religion and ethics
Name: Global 10 Section. Global Regents Pack #10. Turning Points
 Name: Global 10 Section Global Regents Pack #10 Turning Points Theme : Turning Points Most events in history are turning points! Ancient Greece Athens City-States (because of geography) Democracy Theatre
Name: Global 10 Section Global Regents Pack #10 Turning Points Theme : Turning Points Most events in history are turning points! Ancient Greece Athens City-States (because of geography) Democracy Theatre
Summary of Social Contract Theory by Hobbes, Locke and Rousseau
 Summary of Social Contract Theory by Hobbes, Locke and Rousseau Manzoor Elahi Laskar LL.M Symbiosis Law School, Pune Electronic copy available at: http://ssrn.com/abstract=2410525 Abstract: This paper
Summary of Social Contract Theory by Hobbes, Locke and Rousseau Manzoor Elahi Laskar LL.M Symbiosis Law School, Pune Electronic copy available at: http://ssrn.com/abstract=2410525 Abstract: This paper
CONTENTS PART ONE INTRODUCTORY REFLECTIONS
 CONTENTS Preface Table of Cases Table of Statutes xiii XV xix PART ONE INTRODUCTORY REFLECTIONS 1. THE PLACE AND FUNCTION OF LEGAL THEORY 3 2. GREEK PHILOSOPHY AND THE BASIC PROBLEMS OF LAW 5 From Homer
CONTENTS Preface Table of Cases Table of Statutes xiii XV xix PART ONE INTRODUCTORY REFLECTIONS 1. THE PLACE AND FUNCTION OF LEGAL THEORY 3 2. GREEK PHILOSOPHY AND THE BASIC PROBLEMS OF LAW 5 From Homer
Political Theory From Antiquity to the 18 th Century. CPW4U Lesson 2 Roots of Modern Political Thought
 Political Theory From Antiquity to the 18 th Century CPW4U Lesson 2 Roots of Modern Political Thought Aristotle (384-322 B.C.) One of the first empiricists knowledge comes from experience and evidence
Political Theory From Antiquity to the 18 th Century CPW4U Lesson 2 Roots of Modern Political Thought Aristotle (384-322 B.C.) One of the first empiricists knowledge comes from experience and evidence
Warm-Up: Read the following document and answer the comprehension questions below.
 Lowenhaupt 1 Enlightenment Objective: What were some major ideas to come out of the Enlightenment? How did the thinkers of the Enlightenment change or impact society? Warm-Up: Read the following document
Lowenhaupt 1 Enlightenment Objective: What were some major ideas to come out of the Enlightenment? How did the thinkers of the Enlightenment change or impact society? Warm-Up: Read the following document
The Enlightenment & Democratic Revolutions. Enlightenment Ideas help bring about the American & French Revolutions
 The Enlightenment & Democratic Revolutions Enlightenment Ideas help bring about the American & French Revolutions Before 1500, scholars generally decided what was true or false by referring to an ancient
The Enlightenment & Democratic Revolutions Enlightenment Ideas help bring about the American & French Revolutions Before 1500, scholars generally decided what was true or false by referring to an ancient
The Enlightenment. European thinkers developed new ideas about government and society during the Enlightenment.
 Main Idea The Enlightenment European thinkers developed new ideas about government and society during the Enlightenment. Content Statement 5 /Learning Goal Describe how the Scientific Revolution s impact
Main Idea The Enlightenment European thinkers developed new ideas about government and society during the Enlightenment. Content Statement 5 /Learning Goal Describe how the Scientific Revolution s impact
Absolutism. Absolutism, political system in which there is no legal, customary, or moral limit on the government s
 Absolutism I INTRODUCTION Absolutism, political system in which there is no legal, customary, or moral limit on the government s power. The term is generally applied to political systems ruled by a single
Absolutism I INTRODUCTION Absolutism, political system in which there is no legal, customary, or moral limit on the government s power. The term is generally applied to political systems ruled by a single
John Locke (29 August, October, 1704)
 John Locke (29 August, 1632 28 October, 1704) John Locke was English philosopher and politician. He was born in Somerset in the UK in 1632. His father had enlisted in the parliamentary army during the
John Locke (29 August, 1632 28 October, 1704) John Locke was English philosopher and politician. He was born in Somerset in the UK in 1632. His father had enlisted in the parliamentary army during the
The Enlightenment. The Age of Reason
 The Enlightenment The Age of Reason Social Contract Theory is the view that persons' moral and/or political obligations are dependent upon a contract or agreement among them to form the society in which
The Enlightenment The Age of Reason Social Contract Theory is the view that persons' moral and/or political obligations are dependent upon a contract or agreement among them to form the society in which
Political Theory. Political theorist Hannah Arendt, born in Germany in 1906, fled to France in 1933 when the Nazis came to power.
 Political Theory I INTRODUCTION Hannah Arendt Political theorist Hannah Arendt, born in Germany in 1906, fled to France in 1933 when the Nazis came to power. In 1941, following the German invasion of France,
Political Theory I INTRODUCTION Hannah Arendt Political theorist Hannah Arendt, born in Germany in 1906, fled to France in 1933 when the Nazis came to power. In 1941, following the German invasion of France,
JURISPRUDENCE - I. (Legal Theory)
 JURISPRUDENCE - I (Legal Theory) 1. Introduction: Definition, Nature and Scope of Jurisprudence, Importance of the Study of Jurisprudence. Pg. 2 2. Natural Law School: Classical Natural Law, Revival of
JURISPRUDENCE - I (Legal Theory) 1. Introduction: Definition, Nature and Scope of Jurisprudence, Importance of the Study of Jurisprudence. Pg. 2 2. Natural Law School: Classical Natural Law, Revival of
POLITICAL SCIENCE. PS 0200 AMERICAN POLITICAL PROCESS 3 cr. PS 0211 AMERICAN SYSTEM OF CRIMINAL JUSTICE 3 cr. PS 0300 COMPARATIVE POLITICS 3 cr.
 POLITICAL SCIENCE PS 0200 AMERICAN POLITICAL PROCESS 3 cr. Designed to provide students with a basic working knowledge of the basic goals of the constitutional framers, giving students an understanding
POLITICAL SCIENCE PS 0200 AMERICAN POLITICAL PROCESS 3 cr. Designed to provide students with a basic working knowledge of the basic goals of the constitutional framers, giving students an understanding
POLITICAL SCIENCE. PS 0200 AMERICAN POLITICS 3 cr. PS 0211 AMERICAN SYSTEM OF CRIMINAL JUSTICE 3 cr. PS 0300 COMPARATIVE POLITICS 3 cr.
 POLITICAL SCIENCE PS 0200 AMERICAN POLITICS 3 cr. Designed to provide students with a basic working knowledge of the basic goals of the constitutional framers, giving students an understanding of the purposes
POLITICAL SCIENCE PS 0200 AMERICAN POLITICS 3 cr. Designed to provide students with a basic working knowledge of the basic goals of the constitutional framers, giving students an understanding of the purposes
Evolution of the Human Rights Issue
 Evolution of the Human Rights Issue DRAGNE LUMINIŢA Associate Professor PhD. Faculty of Legal and Administrative Sciences Dimitrie Cantemir Christian University E-mail: luminita_ucdc@yahoo.com ABSTRACT
Evolution of the Human Rights Issue DRAGNE LUMINIŢA Associate Professor PhD. Faculty of Legal and Administrative Sciences Dimitrie Cantemir Christian University E-mail: luminita_ucdc@yahoo.com ABSTRACT
MLL110 LEGAL PRINCIPLES & SKILLS EXAM NOTES. problems
 WHAT DOES IT MEAN TO BE A LAWYER MLL110 LEGAL PRINCIPLES & SKILLS EXAM NOTES MYTH All lawyers earn a lot of money There is a right side and wrong side in a dispute A lawyer needs only to be good at arguing
WHAT DOES IT MEAN TO BE A LAWYER MLL110 LEGAL PRINCIPLES & SKILLS EXAM NOTES MYTH All lawyers earn a lot of money There is a right side and wrong side in a dispute A lawyer needs only to be good at arguing
Unit Portfolio: DBQ-Political Cartoons 15. What is happening in this cartoon? 16. What point is the cartoonist trying to make?
 Unit Portfolio: DBQ-Political Cartoons 15. What is happening in this cartoon? 16. What point is the cartoonist trying to make? Unit 2: Age of Reason Lesson 3: Enlightenment Textbook Correlation: Chapter
Unit Portfolio: DBQ-Political Cartoons 15. What is happening in this cartoon? 16. What point is the cartoonist trying to make? Unit 2: Age of Reason Lesson 3: Enlightenment Textbook Correlation: Chapter
World History Test Review. Western Civilizations to the American Revolution
 World History Test Review Western Civilizations to the American Revolution Rules of the Game 1.Each group will begin the game with 10 x s 2.A question will be asked and to a team. 3.If the team gets the
World History Test Review Western Civilizations to the American Revolution Rules of the Game 1.Each group will begin the game with 10 x s 2.A question will be asked and to a team. 3.If the team gets the
Mastering the TEKS in World History Ch. 13
 Name: Class: _ Date: _ Mastering the TEKS in World History Ch. 13 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which sources of knowledge were most
Name: Class: _ Date: _ Mastering the TEKS in World History Ch. 13 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. Which sources of knowledge were most
Bellringer: Who do you think gives people who run the government the authority or power to rule us?
 Bellringer: Who do you think gives people who run the government the authority or power to rule us? Bellringer What is a contract? Give an example of a Contract. How would you feel about living when people
Bellringer: Who do you think gives people who run the government the authority or power to rule us? Bellringer What is a contract? Give an example of a Contract. How would you feel about living when people
Essential Question: What were the key ideas of the Enlightenment?
 Essential Question: What were the key ideas of the Enlightenment? Warm-Up Question: What do you not like about Duluth High? What suggestions do you have to make this school better? From 1650 to 1800, European
Essential Question: What were the key ideas of the Enlightenment? Warm-Up Question: What do you not like about Duluth High? What suggestions do you have to make this school better? From 1650 to 1800, European
1.1 Foundations and Constitution. Mr. Desjarlais Allatoona High School
 1.1 Foundations and Constitution Mr. Desjarlais Allatoona High School Standards SSCG1: Compare and contrast various systems of government. SSCG1a: Determine how governments differ in geographic distribution
1.1 Foundations and Constitution Mr. Desjarlais Allatoona High School Standards SSCG1: Compare and contrast various systems of government. SSCG1a: Determine how governments differ in geographic distribution
The Enlightenment. Global History & Geography 2
 The Enlightenment Global History & Geography 2 What was it? A time period when philosophers examined the relationship between humans and their government Key ideas: 17 th & 18 th centuries Extension of
The Enlightenment Global History & Geography 2 What was it? A time period when philosophers examined the relationship between humans and their government Key ideas: 17 th & 18 th centuries Extension of
The Enlightenment. Age of Reason
 The Enlightenment Age of Reason Students will be able to define the Enlightenment and key vocabulary, and identify the historical roots of this time period. Learning Objective Today State Standards of
The Enlightenment Age of Reason Students will be able to define the Enlightenment and key vocabulary, and identify the historical roots of this time period. Learning Objective Today State Standards of
COURSE OUTLINES AND TEACHING AIDS BY JOHN GUEGUEN,
 COURSE OUTLINES AND TEACHING AIDS BY JOHN GUEGUEN, 1958-2000 The archive housed at the Lincoln Green Foundation in Urbana, Illinois, contains for each of the following courses a detailed syllabus, and
COURSE OUTLINES AND TEACHING AIDS BY JOHN GUEGUEN, 1958-2000 The archive housed at the Lincoln Green Foundation in Urbana, Illinois, contains for each of the following courses a detailed syllabus, and
[ITEM NO.:07] Important Questions for the final Examination For B.A. First Year (Honours) (Part - I) Students:
![[ITEM NO.:07] Important Questions for the final Examination For B.A. First Year (Honours) (Part - I) Students: [ITEM NO.:07] Important Questions for the final Examination For B.A. First Year (Honours) (Part - I) Students:](/thumbs/94/120376021.jpg) [ITEM NO.:07] Important Questions for the final Examination For B.A. First Year (Honours) (Part - I) Students: Principles of Political Theory Paper: I; Half: I Questions containing 15 Marks: 01. What is
[ITEM NO.:07] Important Questions for the final Examination For B.A. First Year (Honours) (Part - I) Students: Principles of Political Theory Paper: I; Half: I Questions containing 15 Marks: 01. What is
SENIOR 4: WESTERN CIVILIZATION HISTORICAL REVIEW OF ITS DEVELOPMENT (OPTIONAL)
 SENIOR 4: WESTERN CIVILIZATION HISTORICAL REVIEW OF ITS DEVELOPMENT (OPTIONAL) The Senior 4 Western Civilization curriculum is designed to help students understand that Canadian society and other Western
SENIOR 4: WESTERN CIVILIZATION HISTORICAL REVIEW OF ITS DEVELOPMENT (OPTIONAL) The Senior 4 Western Civilization curriculum is designed to help students understand that Canadian society and other Western
II. NUMBER OF TIMES THE COURSE MAY BE TAKEN FOR CREDIT: One
 San Bernardino Valley College Curriculum Approved: February 10, 2003 Last Updated: January 2003 I. COURSE DESCRIPTION: A. Department Information: Division: Social Science Department: Political Science
San Bernardino Valley College Curriculum Approved: February 10, 2003 Last Updated: January 2003 I. COURSE DESCRIPTION: A. Department Information: Division: Social Science Department: Political Science
The Enlightenment. Transition from the Scientific Revolution to new ideas in Philosophy, Art, Economics,& Government
 The Enlightenment Transition from the Scientific Revolution to new ideas in Philosophy, Art, Economics,& Government Effects of the Scientific Revolution nduring the Scientific Revolution, people began
The Enlightenment Transition from the Scientific Revolution to new ideas in Philosophy, Art, Economics,& Government Effects of the Scientific Revolution nduring the Scientific Revolution, people began
Jurisprudence- Latin word Jurisprudentia - Knowledge of Law or Skill in Law.
 Jurisprudence Class Notes 04.01.2011 Module I- Introduction to Jurisprudence 1. Nature and Scope of Jurisprudence 2. The Nature of Law Nature and Scope of Jurisprudence What is Jurisprudence? There is
Jurisprudence Class Notes 04.01.2011 Module I- Introduction to Jurisprudence 1. Nature and Scope of Jurisprudence 2. The Nature of Law Nature and Scope of Jurisprudence What is Jurisprudence? There is
Choose one question from each section to answer in the time allotted.
 Theory Comp May 2014 Choose one question from each section to answer in the time allotted. Ancient: 1. Compare and contrast the accounts Plato and Aristotle give of political change, respectively, in Book
Theory Comp May 2014 Choose one question from each section to answer in the time allotted. Ancient: 1. Compare and contrast the accounts Plato and Aristotle give of political change, respectively, in Book
UNIT 1: POLITICAL SCIENCE: MEANING, NATURE AND SCOPE
 UNIT 1: POLITICAL SCIENCE: MEANING, NATURE AND SCOPE UNIT STRUCTURE 1.1 Learning Objectives 1.2 Introduction 1.3 Meaning of Political Science and Politics 1.4 Nature of Political Science 1.4.1 Political
UNIT 1: POLITICAL SCIENCE: MEANING, NATURE AND SCOPE UNIT STRUCTURE 1.1 Learning Objectives 1.2 Introduction 1.3 Meaning of Political Science and Politics 1.4 Nature of Political Science 1.4.1 Political
Business Law - Complete Notes
 1. Introduction 1 1.1 Meaning and Nature of Law An ancient time people were free. They ruled by themselves. When people lived with group then they made rule to manage their behavior and conduct. Then after
1. Introduction 1 1.1 Meaning and Nature of Law An ancient time people were free. They ruled by themselves. When people lived with group then they made rule to manage their behavior and conduct. Then after
Essential Question: What were the key ideas of the Enlightenment?
 Essential Question: What were the key ideas of the Enlightenment? Warm-Up Question: What do you not like about South Cobb High? What suggestions do you have to make this school better? From 1650 to 1800,
Essential Question: What were the key ideas of the Enlightenment? Warm-Up Question: What do you not like about South Cobb High? What suggestions do you have to make this school better? From 1650 to 1800,
School of Law, Governance & Citizenship. Ambedkar University Delhi. Course Outline
 School of Law, Governance & Citizenship Ambedkar University Delhi Course Outline Time Slot- Course Code: Title: Western Political Philosophy Type of Course: Major (Politics) Cohort for which it is compulsory:
School of Law, Governance & Citizenship Ambedkar University Delhi Course Outline Time Slot- Course Code: Title: Western Political Philosophy Type of Course: Major (Politics) Cohort for which it is compulsory:
Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman Perspectives
 STANDARD 10.1.1 Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman Perspectives Specific Objective: Analyze the similarities and differences in Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman views of law, reason and faith, and duties of
STANDARD 10.1.1 Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman Perspectives Specific Objective: Analyze the similarities and differences in Judeo-Christian and Greco-Roman views of law, reason and faith, and duties of
S Y L L A B U S M.A. POLITICS: II SEMESTER Paper I: COMPARATIVE POLITICS I. Introduction: 1. Meaning, Nature, Scope of Comparative Politics. 2.
 S Y L L A B U S M.A. POLITICS: II SEMESTER Paper I: COMPARATIVE POLITICS I. Introduction: 1. Meaning, Nature, Scope of Comparative Politics. 2. Growth of the study of Comparative Politics 3. New Approaches
S Y L L A B U S M.A. POLITICS: II SEMESTER Paper I: COMPARATIVE POLITICS I. Introduction: 1. Meaning, Nature, Scope of Comparative Politics. 2. Growth of the study of Comparative Politics 3. New Approaches
Philosophers that Influenced American Government
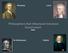 Rousseau Locke Philosophers that Influenced American Government De Montesquieu Hobbes Basic Ideals and Principles of Democracy Consent of the Governed Government gets its power from the people they govern
Rousseau Locke Philosophers that Influenced American Government De Montesquieu Hobbes Basic Ideals and Principles of Democracy Consent of the Governed Government gets its power from the people they govern
POL 343 Democratic Theory and Globalization February 11, "The history of democratic theory II" Introduction
 POL 343 Democratic Theory and Globalization February 11, 2005 "The history of democratic theory II" Introduction Why, and how, does democratic theory revive at the beginning of the nineteenth century?
POL 343 Democratic Theory and Globalization February 11, 2005 "The history of democratic theory II" Introduction Why, and how, does democratic theory revive at the beginning of the nineteenth century?
Determining the Sovereignty on the Ground of State-Citizen Relations in Cicero and Bodin s Works
 Review of History and Political Science December 2014, Vol. 2, No. 3 & 4, pp. 43-67 ISSN: 2333-5718 (Print), 2333-5726 (Online) Copyright The Author(s). 2014. All Rights Reserved. Published by American
Review of History and Political Science December 2014, Vol. 2, No. 3 & 4, pp. 43-67 ISSN: 2333-5718 (Print), 2333-5726 (Online) Copyright The Author(s). 2014. All Rights Reserved. Published by American
Lesson 7 Enlightenment Ideas / Lesson 8 Founding Documents Views of Government. Topic 1 Enlightenment Movement
 Lesson 7 Enlightenment Ideas / Lesson 8 Founding Documents Views of Government Main Topic Topic 1 Enlightenment Movement Topic 2 Thomas Hobbes (1588 1679) Topic 3 John Locke (1632 1704) Topic 4 Charles
Lesson 7 Enlightenment Ideas / Lesson 8 Founding Documents Views of Government Main Topic Topic 1 Enlightenment Movement Topic 2 Thomas Hobbes (1588 1679) Topic 3 John Locke (1632 1704) Topic 4 Charles
Choose one question from each section to answer in the time allotted.
 Choose one question from each section to answer in the time allotted. Ancient: 1. How did Thucydides, Plato, and Aristotle describe and evaluate the regimes of the two most powerful Greek cities at their
Choose one question from each section to answer in the time allotted. Ancient: 1. How did Thucydides, Plato, and Aristotle describe and evaluate the regimes of the two most powerful Greek cities at their
Great Awakening & Enlightenment
 Great Awakening & Enlightenment American Revolu8on British colonists in America revolt against their political system (monarchy/king), declaring independence from Great Britain. Objec&ve: Explain how these
Great Awakening & Enlightenment American Revolu8on British colonists in America revolt against their political system (monarchy/king), declaring independence from Great Britain. Objec&ve: Explain how these
REVIEW of BOOKS. A Journal of Faith, Law & Public Policy. Nadine L. Jackson, Editor-in-Chief. Orestes Brownson LIBERTY, ORDER, AND JUSTICE
 The TELLER REVIEW of BOOKS A Journal of Faith, Law & Public Policy Nadine L. Jackson, Editor-in-Chief VOL. II POLITICAL SCIENCE & PUBLIC POLICY JUNE 2015 THE AMERICAN REPUBLIC Orestes Brownson LIBERTY,
The TELLER REVIEW of BOOKS A Journal of Faith, Law & Public Policy Nadine L. Jackson, Editor-in-Chief VOL. II POLITICAL SCIENCE & PUBLIC POLICY JUNE 2015 THE AMERICAN REPUBLIC Orestes Brownson LIBERTY,
No part of this work may be copied or reproduced in any form without prior permission of the Author.
 All Rights Reserved No part of this work may be copied or reproduced in any form without prior permission of the Author. Disclaimer While all care has been taken in drafting this material, no responsibility
All Rights Reserved No part of this work may be copied or reproduced in any form without prior permission of the Author. Disclaimer While all care has been taken in drafting this material, no responsibility
Part 1 INTRODUCTION TO LAW. 1 The nature of law
 Part 1 INTRODUCTION TO LAW 1 The nature of law Chapter 1 The nature of law Learning objectives After studying this chapter you will understand the following main points: nature of law; object of law; functions
Part 1 INTRODUCTION TO LAW 1 The nature of law Chapter 1 The nature of law Learning objectives After studying this chapter you will understand the following main points: nature of law; object of law; functions
Section 1 What ideas gave birth to the world s first democratic nation?
 After reading answer the questions that follow The Roots of American Democracy Section 1 What ideas gave birth to the world s first democratic nation? Bicentennial celebrations, 1976 On July 4, 1976, Americans
After reading answer the questions that follow The Roots of American Democracy Section 1 What ideas gave birth to the world s first democratic nation? Bicentennial celebrations, 1976 On July 4, 1976, Americans
Jean-Jacques Rousseau ( )
 Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712-1778) Jean-Jacques Rousseau was born in Geneva, Switzerland. He moved to Paris as a young man to pursue a career as a musician. Instead, he became famous as one of the greatest
Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712-1778) Jean-Jacques Rousseau was born in Geneva, Switzerland. He moved to Paris as a young man to pursue a career as a musician. Instead, he became famous as one of the greatest
Four ENLIGHTENMENT THINKERS
 Four ENLIGHTENMENT THINKERS 1. Thomas Hobbes (1588 1679) 2. John Locke (1632 1704) 3. Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712 1778) 4. Baron de Montesquieu (1689 1755) State of Nature- Nature is governed by laws such
Four ENLIGHTENMENT THINKERS 1. Thomas Hobbes (1588 1679) 2. John Locke (1632 1704) 3. Jean-Jacques Rousseau (1712 1778) 4. Baron de Montesquieu (1689 1755) State of Nature- Nature is governed by laws such
Required Texts. Course Requirements
 Introduction to Political Philosophy Nicholas Tampio Fall 2017 Fordham University POSC 2401 R01 Class: MR Dealy 105, 8:30-9:45 am Office: Faber 665, MR 2-4 pm Email: tampio@fordham.edu Plato and Aristotle
Introduction to Political Philosophy Nicholas Tampio Fall 2017 Fordham University POSC 2401 R01 Class: MR Dealy 105, 8:30-9:45 am Office: Faber 665, MR 2-4 pm Email: tampio@fordham.edu Plato and Aristotle
Why. Government? What are the pros & cons of a government? Why do we need one? What is it for? Could we do without?
 Why do we need one? Why What is it for? What are the pros & cons of a government? Could we do without? Government? How did we setup a government? What happens if we don t have one? Why Government? HOBBES,
Why do we need one? Why What is it for? What are the pros & cons of a government? Could we do without? Government? How did we setup a government? What happens if we don t have one? Why Government? HOBBES,
The Enlightenment. Standard 7-2.3
 The Enlightenment Standard 7-2.3 Vocabulary 1.Reason- the use of scientific and logical thinking. 2.Enlightenment- period of time when faith is replaced by reason. 3.Natural Rights rights belonging to
The Enlightenment Standard 7-2.3 Vocabulary 1.Reason- the use of scientific and logical thinking. 2.Enlightenment- period of time when faith is replaced by reason. 3.Natural Rights rights belonging to
Understanding the Enlightenment Reading & Questions
 Understanding the Enlightenment Reading & Questions The word Enlightenment refers to a change in outlook among many educated Europeans that began during the 1600s. The new outlook put great trust in reason
Understanding the Enlightenment Reading & Questions The word Enlightenment refers to a change in outlook among many educated Europeans that began during the 1600s. The new outlook put great trust in reason
C H A P T E R THEORETICAL BACKGROUND. certain theories, which have been developed by persons of legal authorities
 C H A P T E R III THEORETICAL BACKGROUND Theoretical background shows how a research is based on or contributing to the existing theory. The present study is also based on certain theories, which have
C H A P T E R III THEORETICAL BACKGROUND Theoretical background shows how a research is based on or contributing to the existing theory. The present study is also based on certain theories, which have
Nature and Scope of Jurisprudence
 Nature and Scope of Jurisprudence What is Jurisprudence? There is no universal or uniform definition of Jurisprudence since people have different ideologies and notions throughout the world. It is a very
Nature and Scope of Jurisprudence What is Jurisprudence? There is no universal or uniform definition of Jurisprudence since people have different ideologies and notions throughout the world. It is a very
Warm Up Review: Mr. Cegielski s Presentation of Origins of American Government
 Mr. Cegielski s Presentation of Origins of American Government Essential Questions: What political events helped shaped our American government? Why did the Founding Fathers fear a direct democracy? How
Mr. Cegielski s Presentation of Origins of American Government Essential Questions: What political events helped shaped our American government? Why did the Founding Fathers fear a direct democracy? How
Topic: - Meaning, Nature and Functions of Law
 1. Introduction Topic: - Meaning, Nature and Functions of Law The term Law denotes different kinds of rules and Principles. Law is an instrument which regulates human conduct/behavior. Law means Justice,
1. Introduction Topic: - Meaning, Nature and Functions of Law The term Law denotes different kinds of rules and Principles. Law is an instrument which regulates human conduct/behavior. Law means Justice,
DR. BERNARD J. MAUSER DR. RICHARD LAND
 DR. RICHARD LAND DR. BERNARD J. MAUSER Dr. Richard Land is president of Southern Evangelical Seminary. In addition to his presidency, Dr. Land also teaches courses at the seminary. Previously, Dr. Land
DR. RICHARD LAND DR. BERNARD J. MAUSER Dr. Richard Land is president of Southern Evangelical Seminary. In addition to his presidency, Dr. Land also teaches courses at the seminary. Previously, Dr. Land
The Enlightenment and Democratic Revolutions MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW TERMS & NAMES
 4 The Enlightenment and Democratic Revolutions MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW TERMS & NAMES REVOLUTION Enlightenment ideas helped bring about the American and French revolutions. These revolutions and the
4 The Enlightenment and Democratic Revolutions MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW TERMS & NAMES REVOLUTION Enlightenment ideas helped bring about the American and French revolutions. These revolutions and the
John Locke Natural Rights- Life, Liberty, and Property Two Treaties of Government
 Enlightenment Enlightenment 1500s Enlightenment was the idea that man could use logic and reason to solve the social problems of the day. Philosophers spread this idea of logic and reason to the people
Enlightenment Enlightenment 1500s Enlightenment was the idea that man could use logic and reason to solve the social problems of the day. Philosophers spread this idea of logic and reason to the people
Rousseau, On the Social Contract
 Rousseau, On the Social Contract Introductory Notes The social contract is Rousseau's argument for how it is possible for a state to ground its authority on a moral and rational foundation. 1. Moral authority
Rousseau, On the Social Contract Introductory Notes The social contract is Rousseau's argument for how it is possible for a state to ground its authority on a moral and rational foundation. 1. Moral authority
Hobbes, Locke, Montesquieu, and Rousseau on Government
 Handout A Hobbes, Locke, Montesquieu, and Rousseau on Government Starting in the 1600s, European philosophers began debating the question of who should govern a nation. As the absolute rule of kings weakened,
Handout A Hobbes, Locke, Montesquieu, and Rousseau on Government Starting in the 1600s, European philosophers began debating the question of who should govern a nation. As the absolute rule of kings weakened,
Social Inequality in a Global Age, Fifth Edition. CHAPTER 2 The Great Debate
 Social Inequality in a Global Age, Fifth Edition CHAPTER 2 The Great Debate TEST ITEMS Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions 1. According to Lenski, early radical social reformers included a. the Hebrew prophets
Social Inequality in a Global Age, Fifth Edition CHAPTER 2 The Great Debate TEST ITEMS Part I. Multiple-Choice Questions 1. According to Lenski, early radical social reformers included a. the Hebrew prophets
Second Edition. Political Theory. Ideas and Concepts. Sushila Ramaswamy
 Second Edition Political Theory Ideas and Concepts Sushila Ramaswamy POLITICAL THEORY Ideas and Concepts Second Edition SUSHILA RAMASWAMY Associate Professor Department of Political Science Jesus and Mary
Second Edition Political Theory Ideas and Concepts Sushila Ramaswamy POLITICAL THEORY Ideas and Concepts Second Edition SUSHILA RAMASWAMY Associate Professor Department of Political Science Jesus and Mary
Great Political Theories V.2: A Comprehensive Selection Of The Crucial Ideas In Political Philosophy From The French Revolution To Modern Times
 Great Political Theories V.2: A Comprehensive Selection Of The Crucial Ideas In Political Philosophy From The French Revolution To Modern Times (Harper Perennial Modern Thought) By Michael Curtis, M Curtis
Great Political Theories V.2: A Comprehensive Selection Of The Crucial Ideas In Political Philosophy From The French Revolution To Modern Times (Harper Perennial Modern Thought) By Michael Curtis, M Curtis
BACHELOR OF ARTS (B.A.)
 BACHELOR OF ARTS (B.A.) (THREE YEAR DEGREE COURSE) SUBJECT POLITICAL SCIENCE PAGE 1 COURSE STRUCTURE FIRST YEAR PAPER 101 : POLITICAL THEORY 50 MARKS PAPER 102 : NATIONAL MOVEMNT and CONSTITUTION OF INDIA
BACHELOR OF ARTS (B.A.) (THREE YEAR DEGREE COURSE) SUBJECT POLITICAL SCIENCE PAGE 1 COURSE STRUCTURE FIRST YEAR PAPER 101 : POLITICAL THEORY 50 MARKS PAPER 102 : NATIONAL MOVEMNT and CONSTITUTION OF INDIA
Theory Comprehensive January 2015
 Theory Comprehensive January 2015 This is a closed book exam. You have six hours to complete the exam. Please send your answers to Sue Collins and Geoff Layman within six hours of beginning the exam. Choose
Theory Comprehensive January 2015 This is a closed book exam. You have six hours to complete the exam. Please send your answers to Sue Collins and Geoff Layman within six hours of beginning the exam. Choose
Standard USG 1: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the United States government its origins and its functions.
 Standard USG 1: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the United States government its origins and its functions. USG 1.1 Summarize arguments for the necessity and purpose of government and
Standard USG 1: The student will demonstrate an understanding of the United States government its origins and its functions. USG 1.1 Summarize arguments for the necessity and purpose of government and
Running head: MOST SCRIPTURALLY CORRECT THEORY OF GOVERNMENT 1. Name of Student. Institutional Affiliation
 Running head: MOST SCRIPTURALLY CORRECT THEORY OF GOVERNMENT 1 Hobbes, Locke, and Rousseau: Who Has the Most Scripturally Correct Theory of Government? Name of Student Institutional Affiliation MOST SCRIPTURALLY
Running head: MOST SCRIPTURALLY CORRECT THEORY OF GOVERNMENT 1 Hobbes, Locke, and Rousseau: Who Has the Most Scripturally Correct Theory of Government? Name of Student Institutional Affiliation MOST SCRIPTURALLY
UNIT 11: POWER, AUTHORITY AND LEGITIMACY
 UNIT 11: POWER, AUTHORITY AND LEGITIMACY UNIT STRUCTURE 11.1 Learning Objectives 11.2 Introduction 11.3 Power 11.3.1 Meaning of Power 11.3.2 Characteristics of Power 11.3.3 Sources of Power 11.3.4 Forms
UNIT 11: POWER, AUTHORITY AND LEGITIMACY UNIT STRUCTURE 11.1 Learning Objectives 11.2 Introduction 11.3 Power 11.3.1 Meaning of Power 11.3.2 Characteristics of Power 11.3.3 Sources of Power 11.3.4 Forms
The Birth of Territory
 Stuart Elden The Birth of Territory 2013. Chicago and London: The University of Chicago Press. Pages: 512. Language: English. ISBN 9780226202570. Stuart Elden s new book The Birth of Territory is a magisterial
Stuart Elden The Birth of Territory 2013. Chicago and London: The University of Chicago Press. Pages: 512. Language: English. ISBN 9780226202570. Stuart Elden s new book The Birth of Territory is a magisterial
Political Science (BA, Minor) Course Descriptions
 Political Science (BA, Minor) Course Descriptions Note: This program includes course requirements from more than one discipline. For complete course descriptions for this major, refer to each discipline
Political Science (BA, Minor) Course Descriptions Note: This program includes course requirements from more than one discipline. For complete course descriptions for this major, refer to each discipline
Thomas Hobbes. Station 1. Where is he from? What is his view of people (quote examples from Leviathan)?
 Station 1 Thomas Hobbes Where is he from? What is his view of people (quote examples from Leviathan)? What is his view of government (quote examples from Leviathan)? Who would be most likely to like Hobbes
Station 1 Thomas Hobbes Where is he from? What is his view of people (quote examples from Leviathan)? What is his view of government (quote examples from Leviathan)? Who would be most likely to like Hobbes
DOWNLOAD PDF THE OXFORD HANDBOOK OF THE HISTORY OF POLITICAL PHILOSOPHY
 Chapter 1 : the oxford handbook of political philosophy Download ebook pdf, epub, tuebl, mobi This book presents fifty original articles, each covering the entire subject in the history of political philosophy.
Chapter 1 : the oxford handbook of political philosophy Download ebook pdf, epub, tuebl, mobi This book presents fifty original articles, each covering the entire subject in the history of political philosophy.
Why Government? STEP BY STEP
 Teacher s Guide Why Government? This lesson combines two readings from the icivics Influence Library and adds activities that bridge the two topics: Thomas Hobbes and John Locke. Time Needed: One class
Teacher s Guide Why Government? This lesson combines two readings from the icivics Influence Library and adds activities that bridge the two topics: Thomas Hobbes and John Locke. Time Needed: One class
Fall Ø Course materials p p User name: p Password: panlaoshi. Chapter 1
 International Politics and Theories PAN Zhongqi 潘忠岐 Professor, SIRPA, Fudan R625, Wenke Building Tel: 65642320; 13917273597; Email: zqpan@fudan.edu.cn Fall 2015 Syllabus and Course Overview Ø Course materials
International Politics and Theories PAN Zhongqi 潘忠岐 Professor, SIRPA, Fudan R625, Wenke Building Tel: 65642320; 13917273597; Email: zqpan@fudan.edu.cn Fall 2015 Syllabus and Course Overview Ø Course materials
Multiple Choice Questions. Principles of law as they currently exist are studied under which of the following?
 MGT611-Business and Labor Laws- Solved MCQs and Subjective for With Reference For Midterm Examination Prepared and Solved by Sparkle Fairy 100% Accurate File Which of the following is not true about Law?
MGT611-Business and Labor Laws- Solved MCQs and Subjective for With Reference For Midterm Examination Prepared and Solved by Sparkle Fairy 100% Accurate File Which of the following is not true about Law?
JURISPRUDENCE: a brief story by. Alexander B R Ö S T L. Košice 2010
 JURISPRUDENCE: a brief story by Alexander B R Ö S T L Košice 2010 The aim of these lessons is to provide the students of Jurisprudence by a basic and clear analysis of the major and most important theories
JURISPRUDENCE: a brief story by Alexander B R Ö S T L Košice 2010 The aim of these lessons is to provide the students of Jurisprudence by a basic and clear analysis of the major and most important theories
POLITICAL SCIENCE. Chair: Nathan Bigelow. Faculty: Audrey Flemming, Frank Rohmer. Visiting Faculty: Marat Akopian
 POLITICAL SCIENCE Chair: Nathan Bigelow Faculty: Audrey Flemming, Frank Rohmer Visiting Faculty: Marat Akopian Emeriti: Kenneth W. Street, Shelton Williams A major in political science or international
POLITICAL SCIENCE Chair: Nathan Bigelow Faculty: Audrey Flemming, Frank Rohmer Visiting Faculty: Marat Akopian Emeriti: Kenneth W. Street, Shelton Williams A major in political science or international
Comparison of Plato s Political Philosophy with Aristotle s. Political Philosophy
 Original Paper Urban Studies and Public Administration Vol. 1, No. 1, 2018 www.scholink.org/ojs/index.php/uspa ISSN 2576-1986 (Print) ISSN 2576-1994 (Online) Comparison of Plato s Political Philosophy
Original Paper Urban Studies and Public Administration Vol. 1, No. 1, 2018 www.scholink.org/ojs/index.php/uspa ISSN 2576-1986 (Print) ISSN 2576-1994 (Online) Comparison of Plato s Political Philosophy
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1
 Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Define government and the basic powers every government holds. 2. Describe the four defining characteristics of a state. 3. Identify four theories
Chapter 1: Principles of Government Section 1 Objectives 1. Define government and the basic powers every government holds. 2. Describe the four defining characteristics of a state. 3. Identify four theories
Why Government? STEP BY STEP
 Teacher s Guide Why Government? This lesson combines two readings from the icivics Influence Library and adds activities that bridge the two topics: Thomas Hobbes and John Locke. Time Needed: One class
Teacher s Guide Why Government? This lesson combines two readings from the icivics Influence Library and adds activities that bridge the two topics: Thomas Hobbes and John Locke. Time Needed: One class
Modern Political Thinkers and Ideas
 B 46401 Modern Political Thinkers and Ideas An historical introduction Tudor Jones ' * Fran cvi London and New York Contents LIST OF BOXED BIOGRAPHIES ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS INTRODUCTION xiii xv xvii 1 Sovereignty
B 46401 Modern Political Thinkers and Ideas An historical introduction Tudor Jones ' * Fran cvi London and New York Contents LIST OF BOXED BIOGRAPHIES ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS INTRODUCTION xiii xv xvii 1 Sovereignty
Appendix D: Standards
 Appendix D: Standards This unit was developed to meet the following standards. National Council for the Social Studies National Curriculum Standards for Social Studies Literacy Skills 13. Locate, analyze,
Appendix D: Standards This unit was developed to meet the following standards. National Council for the Social Studies National Curriculum Standards for Social Studies Literacy Skills 13. Locate, analyze,
3.0: ANALYSIS OF THE THEORY OF SOCIAL CONTRACT 3.1: AN ANALYSIS OF THE THEORY OF SOCIAL CONTRACT AS ESPOUSED BY THOMAS HOBBES:
 The Theoretical Perspective and Strands of the Social Contract as Espoused in the Works of Hobbes, Locke, and Rousseau: It s Effects on the Contemporary Society Augustine Adu Frimpong 1 Chanika R. Jones,
The Theoretical Perspective and Strands of the Social Contract as Espoused in the Works of Hobbes, Locke, and Rousseau: It s Effects on the Contemporary Society Augustine Adu Frimpong 1 Chanika R. Jones,
Enlightenment & America
 Enlightenment & America Our Political Beginnings What is a Government? Defined: The institution through which a society makes and enforces its public policies. It is made up of those people who exercise
Enlightenment & America Our Political Beginnings What is a Government? Defined: The institution through which a society makes and enforces its public policies. It is made up of those people who exercise
Unit 2 Assessment The Development of American Democracy
 Unit 2 Assessment 7 Unit 2 Assessment The Development of American Democracy 1. Which Enlightenment Era thinker stated that everyone is born equal and had certain natural rights of life, liberty, and property
Unit 2 Assessment 7 Unit 2 Assessment The Development of American Democracy 1. Which Enlightenment Era thinker stated that everyone is born equal and had certain natural rights of life, liberty, and property
Unit 1 Guided Notes: Foundations of Government
 Name: Date: Block: Unit 1: 5 Days (08/01 08/07) Unit 1 Quiz: 08/03 Unit 1 Test: 08/07 Standards for Unit 1: SSGSE 1: Compare and contrast various systems of government. a. Determine how governments differ
Name: Date: Block: Unit 1: 5 Days (08/01 08/07) Unit 1 Quiz: 08/03 Unit 1 Test: 08/07 Standards for Unit 1: SSGSE 1: Compare and contrast various systems of government. a. Determine how governments differ
The Enlightenment Origins of the United States Government
 The Enlightenment Origins of the United States Government Origins of Government Force Theory: superior strength Evolutionary Theory: family structure Divine Right Theory: royal birth Social Contract Theory:
The Enlightenment Origins of the United States Government Origins of Government Force Theory: superior strength Evolutionary Theory: family structure Divine Right Theory: royal birth Social Contract Theory:
The Enlightenment: The French Revolution:
 The Enlightenment: How did Enlightenment ideas change intellectual thought, including views about the role of government. Which Enlightenment ideas form the basis for our U.S. government? How did Enlightenment
The Enlightenment: How did Enlightenment ideas change intellectual thought, including views about the role of government. Which Enlightenment ideas form the basis for our U.S. government? How did Enlightenment
MODULE -IV: Abetment and Criminal Conspiracy (Sec.107 to 114; Sec 120-A, B)
 NAME OF SUBJECT: LAW OF CRIME-PAPER- I: PENAL CODE PAPER CODE: LAW 501 MAXIMUM MARKS: 30+70=100 TIME ALLOWED: 3 HRS. INTERNAL ASSESSMENT: 30 MARKS TERM-END EXAMINATION: 70 MARKS OBJECTIVE: Criminal Law
NAME OF SUBJECT: LAW OF CRIME-PAPER- I: PENAL CODE PAPER CODE: LAW 501 MAXIMUM MARKS: 30+70=100 TIME ALLOWED: 3 HRS. INTERNAL ASSESSMENT: 30 MARKS TERM-END EXAMINATION: 70 MARKS OBJECTIVE: Criminal Law
The Forgotten Principles of American Government by Daniel Bonevac
 The Forgotten Principles of American Government by Daniel Bonevac The United States is the only country founded, not on the basis of ethnic identity, territory, or monarchy, but on the basis of a philosophy
The Forgotten Principles of American Government by Daniel Bonevac The United States is the only country founded, not on the basis of ethnic identity, territory, or monarchy, but on the basis of a philosophy
Lecture 11: The Social Contract Theory. Thomas Hobbes Leviathan Mozi Mozi (Chapter 11: Obeying One s Superior)
 Lecture 11: The Social Contract Theory Thomas Hobbes Leviathan Mozi Mozi (Chapter 11: Obeying One s Superior) 1 Agenda 1. Thomas Hobbes 2. Framework for the Social Contract Theory 3. The State of Nature
Lecture 11: The Social Contract Theory Thomas Hobbes Leviathan Mozi Mozi (Chapter 11: Obeying One s Superior) 1 Agenda 1. Thomas Hobbes 2. Framework for the Social Contract Theory 3. The State of Nature
Essentials of International Relations Eight Edition Chapter 1: Approaches to International Relations LECTURE SLIDES
 Essentials of International Relations Eight Edition Chapter 1: Approaches to International Relations LECTURE SLIDES 1 Learning Objectives Understand how international relations affects you in your daily
Essentials of International Relations Eight Edition Chapter 1: Approaches to International Relations LECTURE SLIDES 1 Learning Objectives Understand how international relations affects you in your daily
Please update your table of contents. Unit 9:
 Please update your table of contents. Unit 9: Enlightenment & Revolution World History New rule about grades: students will no longer be given grades on classwork/folders. You will only be assessed by
Please update your table of contents. Unit 9: Enlightenment & Revolution World History New rule about grades: students will no longer be given grades on classwork/folders. You will only be assessed by
