4.2 United States: Early Development and Globalization
|
|
|
- Lee Strickland
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
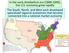
1 4.2 United States: Early Development and Globalization LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Explain how the United States acquired its geographic boundaries. 2. Examine patterns of immigration to and migration within the United States through the period of westward settlement. 3. Examine urban growth and its connection to development of new forms of transportation. 4. Explain which economic patterns helped the United States become the world s largest economy. 5. Consider how the concept of the American Dream has been exported globally. Early Development Patterns 1. The colonies of Britain in North America that fought the American Revolution and became the United States. With abundant resources and opportunity, the original thirteen colonies 1 prospered and expanded into what became the fifty US states. The political geography of this nation was a product of various treaties and acquisitions that eventually resulted in the country extending from the Atlantic to the Pacific Ocean. Fueling the expansion was the concept of Manifest Destiny 2 : the belief of some Americans that the new nation was divinely predestined to expand across the continent. The United States negotiated with France for the Louisiana Purchase in 1803, acquiring millions of acres in the central United States (see Figure 4.5 "Geopolitical Map of the Creation of the United States from the Atlantic to the Pacific"). Florida was acquired from Spain in 1819, and Texas was annexed in The British sold portions of the Pacific Northwest to the United States, and the exact northern boundary between the United States and Canada was settled in Through conflicts with Mexico, large portions of the West were ceded to the United States in the mid-nineteenth century. Alaska was purchased from the Russians in 1867 for only $7.2 million. Alaska and Hawaii were the last two possessions to enter into statehood, which they did in The belief that it was the duty and destiny of Americans to continue to move westward and conquer all the land between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. 206
2 Figure 4.4 The Thirteen Original Colonies Figure 4.5 Geopolitical Map of the Creation of the United States from the Atlantic to the Pacific 4.2 United States: Early Development and Globalization 207
3 Source: Map courtesy of National Atlas of the United States, File:U.S._Territorial_Acquisitions.png. Manifest Destiny The concept of Manifest Destiny came from the works of John O Sullivan in O Sullivan wrote, The far-reaching, the boundless future will be the era of American greatness. In its magnificent domain of space and time, the nation of many nations is destined to manifest to mankind the excellence of divine principles; to establish on earth the noblest temple ever dedicated to the worship of the Most High the Sacred and the True. Its floor shall be a hemisphere its roof the firmament of the star-studded heavens, and its congregation an Union of many Republics, comprising hundreds of happy millions, calling, owning no man master, but governed by God s natural and moral law of equality, the law of brotherhood of peace and good will amongst men. John L. O'Sullivan on Manifest Destiny, 1839, As the United States developed, it acquired external colonial possessions. With victory over Spain in the Spanish-American War of 1898, the US government gained control of the Philippines, Cuba, Puerto Rico, Guam, and various Pacific islands. Cuba and the Philippines later became independent countries, but Puerto Rico and Guam continue to be part of the United States. The US Virgin Islands were purchased from Denmark in 1918 after World War I as a location to provide strategic military support to protect the shipping lanes through the Caribbean and the Panama Canal. Westward Settlement Patterns and European Immigration 3. The place where a new culture forms and from which it spreads. The thirteen original colonies are often grouped into three regions, each with its own economic and cultural patterns. These three areas New England, the Mid- Atlantic, and the South are considered culture hearths 3, or places where culture formed and from which it spread. The three regions were source areas for westward migration, and migrants from these regions carried with them the cultural traditions of their culture hearths. New England was characterized by poor soils, subsistence agriculture, and fishing communities and was the birthplace of North America s Industrial Revolution. Its largest city was Boston. Settlers from New 4.2 United States: Early Development and Globalization 208
4 England traveled west across New York State and into the upper Midwest and the Great Lakes region. The Mid-Atlantic region, focused on Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, was known for its fertile soils, prosperous small-scale agriculture, and multinational population. Prosperous farming led to a vibrant economy and a robust network of towns and cities. People who wanted to migrate west from this region traveled down the Great Valley into the Appalachian Mountains and across the Cumberland Gap into Kentucky, or they crossed Pennsylvania and traveled west via the Ohio River valley. The heart of the South was Virginia, a region oriented around plantation agriculture. The South was overwhelmingly rural, and in time the bulk of its agricultural workforce consisted of slaves brought to the United States from Subsaharan Africa. Westward migration was spurred along by the gold boom in California (1849) and by the completion of the transcontinental railroad (1869). The settlement frontier pushed westward during the course of the nineteenth century and was declared closed by the Bureau of the Census in This did not mean that settlers were spread uniformly across the continent by 1890; indeed, vast areas of the Great Plains and the mountain west remained sparsely populated by Europeans at that time. The Homestead Act of 1862 also encouraged westward migration by offering 160 acres of free land to households willing to move west. The continental United States had been organized into official states by the end of the nineteenth century, except Oklahoma (1907), Arizona (1912), and New Mexico (1912). Most US residents at its founding in 1776 had roots in Great Britain, with large numbers from other northern and western European countries and many others from Africa (most of whom were slaves in the South). During the nineteenth century, migrants continued to immigrate to the United States as its economy grew, especially after the 1830s. Germans and Irish began arriving in large numbers, joining others from Britain and other countries, predominantly those in western Europe. As the century progressed, others from southern and eastern Europe, from countries such as Italy, Russia, and Austria, became the most significant stream of immigrants to the United States. The new arrivals were different from the early British immigrants: they practiced Roman Catholic or Eastern Orthodox Christianity (not Protestantism), they primarily moved to urban areas, and they found work in the new manufacturing sector growing rapidly in the Figure 4.6 The Holy Trinity Serb Orthodox Church in Butte, Montana This church gives testimony to the impact that European immigration has had on the North American continent and the freedom of religion that the US Constitution provides. 4.2 United States: Early Development and Globalization 209
5 Northeast and around the Great Lakes. Very few immigrants came from Latin America or Asia at that time. Source: Photo by R. Berglee. Industrial Development and Urbanization The Industrial Revolution that began in Great Britain in the late eighteenth century eventually moved across the Atlantic and took hold in the United States. Rapid industrial growth emerged in the nineteenth century and was focused in the northeastern United States around the Great Lakes in an area called the Manufacturing Belt 4 (Figure 4.7 "Manufacturing Belt Turned Rust Belt"). Mechanized manufacturing began with textiles (New England), moved to steel and other metals (Pennsylvania and Indiana), and later was dominated by the manufacture of automobiles (Michigan). Of course, manufacturing would not have been possible without an abundant supply of power. Coal mining became an important industry in western Pennsylvania and in Appalachia. Manufacturing took place in the cities and towns of the Manufacturing Belt. Not until the second half of the twentieth century did manufacturing move to rural areas; until then, it was almost entirely an urban activity. As the United States went through its Industrial Revolution, its population shifted from being almost entirely rural to being mostly urban. In 1790, only about 5 percent of the US population lived in urban areas; by 1920, about 50 percent lived in cities. As the rural to urban shift took place, the function and form of US cities also changed. 4. The upper Midwest and the northeastern United States; the heart of the early manufacturing sector. 4.2 United States: Early Development and Globalization 210
6 Figure 4.7 Manufacturing Belt Turned Rust Belt Table 4.1 US Population and Percentage Urban Year Percentage Urban Population in Millions United States: Early Development and Globalization 211
7 Year Percentage Urban Population in Millions Source: The World Factbook, Central Intelligence Agency, From the colonial era until the late nineteenth century, US cities were walking cities 5. Because most Americans lived on farms, cities were small, compact, and centrally oriented: everything was located within walking distance. Only wealthy people had access to transportation by horse, and city dwellers needed to live within a short distance of where they worked, shopped, and carried out all their activities. The invention of the electric streetcar (1888) allowed cities to increase in size. People could live farther from their place of employment as long as they lived within walking distance of a streetcar line. Streetcar suburbs grew up along streetcar lines, and these neighborhoods were often segregated by ethnicity and race. Fewer people lived in downtowns, which became dedicated to retail and manufacturing. Cities remained oriented around a central business district (CBD) 6, which was often located near the railway station. Factories needed to be near modes of transportation for both shipping in parts and shipping out completed products and so that workers could easily get to work. 5. A city developed before the automobile or mass transportation, designed for accessing everything on foot. 6. The location in a city that is considered the downtown, characterized by high rents and high density of buildings and commerce. 7. A residential area outside the city center to which people commute by automobile. 8. Sometimes called a suburban downtown, a high-density business district that forms outside the limits of a traditional city, often at the intersection of major highways. Edge cities may contain shopping malls, hotels, office parks, and entertainment venues. Large numbers of middle class Americans began acquiring automobiles after about 1920; this eventually led to a complete rethinking of the spatial layout of the city. Automobile suburbs 7 sprang up outside the traditional city limits as people were able to buy homes far from streetcar lines or railway stations. Cities became increasingly decentralized: people could go shopping in suburban malls instead of downtown department stores, factories could spring up at highway interchanges and not only near rivers and the railroad, and people could live in one suburb and work in another instead of living in the suburbs and working downtown. Neighborhoods became even more racially and economically segregated than they had in the past as middle-class whites moved into the new automobile suburbs and left the poorer African Americans behind in the cities. By the late twentieth century, the automobile had led to a new urban form: the edge city 8. Edge cities are areas of dense urban development outside the boundaries of the traditional city. They often form at the intersection of major interstate highways and contain shopping malls, office complexes, high-rise apartment buildings, industrial parks, restaurants, and hotels. Sometimes edge cities are called suburban downtowns. Edge cities have supplanted the CBD as the destination of choice for Americans, whether they are heading to work or to play. 4.2 United States: Early Development and Globalization 212
8 Economic Changes For the purpose of understanding economic geography, all economic activities can be grouped into one of four categories, each with its respective terms, depending on the nature of what is being produced: 1. Primary economic sector 9 activities include everything that pertains to the collection of raw materials, such as agriculture, forestry, fishing, and mining in other words, growing and extracting activities. 2. Secondary economic sector 10 activities involve the processing of those raw materials through manufacturing, which has been the mainstay of economic growth for most developed countries. 3. Tertiary economic sector 11 activities are those that produce services, not physical products. 4. Quaternary economic sector 12 activities are those that deal with information collecting and processing, as well as management. The tertiary and quaternary economic sectors are often thought of together as the service sector. In the explanation of how countries gain national income (Section 1.4 "Globalization and Development"), only primary and secondary activities produce actual physical products, and manufacturing traditionally earns the highest value-added profits. Tertiary activities are selective in gaining national wealth. For example, service activities such as tourism can bring in national wealth if the visitors are from outside the country. Tourism within a country can also influence economic conditions by increasing the amount of consumer spending. 9. Division of the economy including everything that pertains to the collection of raw materials, such as agriculture, forestry, fishing, and mining (i.e., growing and extracting activities). 10. Division of the economy involving the processing of raw materials through manufacturing. 11. Division of the economy that produce services, not physical products. 12. Division of the economy that deals with information collecting and processing, as well as management. During the colonial era and into the nineteenth century, when the majority of Americans lived on farms and worked in agriculture, most economic activity in the United States took place within the primary economic sector. Today, the primary sector is still an important component of the US economy, but far fewer people are employed in it. For example, less than 1 percent of Americans make their living by farming, but agricultural output has continued to grow because of advancements in mechanization and the development of high-tech seeds, fertilizers, and pesticides. The United States has been able to export surplus agricultural output to other parts of the world. Fewer people work in coal mines than in the past, but because of new mining technologies and methods such as mountaintop removal, coal production remains high. The geographic distribution of primary activities depends both on the location of natural features such as physical geography and climate and on the location of the market for a particular crop or resource. The nineteenth-century German economist Johann von Thünen created a model that predicted land use around a 4.2 United States: Early Development and Globalization 213
9 central market. In his theory, land closest to the market would be used to produce crops that were expensive to transport, such as dairy. Land far from the market would be used for the production of crops that were less expensive to transport and less perishable, such as grain. The von Thünen model 13 predicts a series of concentric rings surrounding a central market, with each ring producing a different kind of crop. If the von Thünen model is applied at a much larger scale to the United States as a whole, with the densely populated urban zone from Boston to Washington, DC (called a megalopolis), used as the central market, the model does a fairly good job predicting the United States agricultural land use. Dairy farms are found close to the market, grain farms are farther away, and ranch lands used for livestock production are even farther away. Figure 4.8 The von Thünen Model The von Thünen model as it relates to the development west of the East Coast megalopolis. For example, New Jersey is called the Garden State, Appalachia has its forests, the Midwest has its agricultural production, and the Great Plains has its large cattle ranching operations. This model was more applicable in past centuries for local communities when modern transportation technology was not available. 13. A model that seeks to predict agricultural land use in a closed economic system, with only one market surrounded by land of uniform quality. 4.2 United States: Early Development and Globalization 214
10 Chapter 4 North America Figure 4.9 Farm Resource Regions Source: Map courtesy of the US Department of Agriculture, Anything that involves the processing of raw materials manufacturing is a secondary activity. As the United States moved into the Industrial Revolution and into the mid-twentieth century, the percentage of the US workforce involved in manufacturing grew from almost nothing until it peaked in the late 1970s. It was the main area of economic growth for decades. Although manufacturing was present in most areas of the country, it was focused in the northeastern United States and along the Great Lakes. Factories were close both to the reserves of labor and to the markets for manufactured products found in the densely populated Northeast. The steel industry was located in Pittsburgh and its environs because of the area s access to iron ore (mined in Minnesota and transported via the Great Lakes) and to coal (mined in Pennsylvania, West Virginia, and other parts of Appalachia). As manufacturing has grown in other parts of the world, the secondary economic sector has declined in the United States. US labor statistics indicate that the United States lost about five million manufacturing jobs between 2000 and 2010.Sheryl Nance-Nash, Made in America Leaders That Really Make a Difference, Daily Finance, United States: Early Development and Globalization 215
11 really-make-a-difference/. Many of these jobs were lost to countries with lower labor costs, such as Mexico or China. The third group of economic activities takes place in the tertiary and quaternary sectors, commonly known as the service sector. Tertiary and quaternary activities create services, not physical products. Service jobs include everything from engineering to finance, restaurants to sports, and childcare to medicine. The tertiary sector makes up more than three quarters of the US economy, as measured by its share of the gross domestic product (GDP), which is the total value of all goods and services produced in a country in a given year. The GDP is then divided by the country s population to provide a GDP per capita 14 statistic. The 2010 estimated GDP composition by sector for the United States is shown in Table 4.2 "US GDP by Sector (2010 Data)". Table 4.2 US GDP by Sector (2010 Data) Economic Sector GDP (%) Agriculture 1.2 Industry and mining 22.2 Services 76.7 Source: The World Factbook, Central Intelligence Agency, library/publications/the-world-factbook/geos/us.html. 14. The total value of goods and services produced by a country, divided by the population. 15. Jobs that are not tied to a specific location because of access to raw materials or manufacturing infrastructure. These jobs can be carried out in any location. 16. The region extending through the American South, Southwest, and into California. These figures show that the United States has shifted to a postindustrial service economy. The rise of the information age in the latter part of the twentieth century shifted the workforce into the information sector. By the start of the twenty-first century, less than 2 percent of the US workforce was employed in agriculture, 15 percent in industry, and the rest in services (18 percent) and information activities (65 percent). The locations of service-sector jobs are much more flexible than are jobs in the primary or secondary sectors. They are called footloose jobs 15 : an accountant can live in New York or in Denver, whereas it is much more difficult for factories to move from one place to another and it is impossible for farms to relocate. Many of the information-technology jobs are emerging in the southern regions of the United States called the Sun Belt 16. Southern cities such as Atlanta, Dallas, and Phoenix are centers of innovation and population growth. The warmer climate, combined with a lower cost of living and less congestion, makes the Sun Belt an attractive location for emerging information-based companies. Note that the popularity of the South 4.2 United States: Early Development and Globalization 216
12 and West for service-sector jobs only came about after the invention and adoption of air-conditioning. Air-conditioning was not widespread until after the Second World War in the 1950s. While the population of the Southern states has increased, the population of some Northern states has decreased. The Sun Belt has always been a destination for people escaping the harsh winters of the Northern states. This has usually been only a seasonal transition. However, the new trend is one of permanent growth because of the increase in information technologies and in the service industry. Emerging companies looking to establish their businesses have targeted major cities from the Carolinas to the Southwest. Migration Patterns The United States has not only undergone a massive rural-to-urban shift in its population; intermigration within the United States from one region to another has also been prevalent. Each of the US regions has witnessed changes in demographics because of migration patterns. In the agricultural regions of the United States, such as the Midwest, the migration pattern has been caused by changes in farm technology. Portions of the United States were opened up for agriculture because of the Homestead Act of 1862, where each person could receive 160 acres from the government to start a farm. They could keep the acres if they lived on them and farmed them for a period of years. In the 1800s, 160 acres was enough land to support a family if conditions were appropriate. The Industrial Revolution brought about improved farm equipment and technology. Larger and more expensive tractors and improved farming methods pushed the small farmers to sell out. Farms increased in size and fewer people were required to operate them. Since fewer farm workers are needed in rural areas, there has been a major rural-to-urban shift in the population. Central cities are increasing in population, while small towns and rural areas in the Midwest and across the nation are decreasing in population. Americanism and Globalization The freedom of personal expression in the United States has supported individual ingenuity and creative ambition to create the largest economy in the world. US citizens have pushed American corporations to become a major force in the world markets. Products and franchises from the United States are being distributed throughout the world. Items such as fast food, computers, news networks, and Hollywood movies have become the products of choice in countries across the globe. The English language dominates the Internet, which has been heavily 4.2 United States: Early Development and Globalization 217
13 influenced by US corporations. The power of the American Dream 17 the idea that through hard work anyone can achieve upward mobility and financial success as it is portrayed in the US media holds sway in the minds of people both in the United States and abroad. US news networks, such as CNN, are so dominant that small countries, having no resources to create networks, rely on the US networks to deliver their world news. US fast food franchises, of which McDonald s is the largest, exist in over one hundred countries. Despite humble beginnings in Arkansas, Walmart grew to become the world s largest corporation. It has become the buyer and seller of retail trade that shapes and molds cultural attitudes and fashions internationally. Figure 4.10 US Corporate McDonald s Franchise in Israel The size of the US population (more than 310 million strong as of 2010) and the country s vast resource base have allowed it to become a world military superpower. After the fall of the Soviet Union, the United States became the most powerful military force in the world. Source: Photo by R. Berglee. The United States has also dominated the world s economy and its communications networks. The advancements of multinational corporations have in essence enabled the sale of America to the rest of the world. The selling of American products and the large consumer market in the United States have provided the profits that have fueled global economic markets. The United States has become a worldwide franchise of its own. Corporate colonialism has advanced the American brand to a level that is now synonymous with consumerism, success, and power worldwide. Media advancements have promoted the concept of the American Dream across the seven seas. The reaction of the global community includes both admiration and disdain. Many view Americanism as interchangeable with globalization. Some welcome it; others reject it. The country of Iran is an example of this dichotomy. Young people in Iran wearing blue jeans gather in secret to watch American television programming from a hidden illegal satellite dish, while at the same time the anti-american forces in their government condemn America as decadent, immoral, and imperialistic. 17. The belief that through hard work a person can achieve upward mobility and financial success, no matter his or her background. Corporate colonialism has become a dominant force impacting the global cultural fabric. Supporters appreciate access to American goods and services, while opponents claim that the English language and the American corporate franchise 4.2 United States: Early Development and Globalization 218
14 system are destroying the culture and heritage of untold millions who see their unique traditional ways of life being overshadowed and destroyed. Some argue that American television advertisements exemplify a trend that supports conformity and uniformity in American culture. They contend that America s unique cultural diversity, which historically has provided ingenuity and creativity, is being eroded by the franchising of similar retail products, fast food, professional sports, and Hollywood entertainment that stifle the creative will of the American people. Others continue to see opportunities to pursue the American Dream and believe that innovation and ideas continue to emerge in spite of these trends. Many people worry about the future of the American Dream. American culture continues to evolve as people face changing economic and social conditions. Over the course of their history, Americans have faced both difficult and prosperous times, and now the future of this vibrant country is in the hands of the current generation. The United States has developed into one of the most powerful countries on the planet. Will the American Dream continue to motivate people in the future? Only time will tell. Figure 4.11 Walmart is one of the greatest success stories of the American Dream. It started in Arkansas with one store and grew to become the largest corporation in the world. Now it is one of the most aggressive forces of corporate colonialism across the globe. Source: Photo by R. Berglee. 4.2 United States: Early Development and Globalization 219
15 KEY TAKEAWAYS The United States territory expanded gradually through various treaties and land acquisitions and was influenced by the concept of Manifest Destiny. The three main colonial regions in the United States New England, the Mid-Atlantic, and the South had their own distinct economic foundations, settlement patterns, and social structures. People from these regions moved westward in particular migration patterns. In the beginning of the nineteenth century, most immigrants were from western and northern Europe. By the end of the nineteenth century and the beginning of the twentieth century, immigrants were coming in large numbers from southern and Eastern Europe and moving to industrial cities of the Northeast. City structure changed from the walking cities of colonial America, to the railroad and streetcar cities of the late nineteenth century, to the automobile cities of the mid- and late-twentieth century. The US economy was initially based in the primary economic sector (particularly farming), then was based in the secondary economic sector (manufacturing), and is now oriented around the tertiary and quaternary economic sectors (services and information). The diverse immigrants who have created American society have been unified by common aspirations and common ideals that created the concept of the American Dream. The concept indicates that regardless of one s station in life, by working hard, applying oneself, and following the rules, one can obtain upward economic mobility. 4.2 United States: Early Development and Globalization 220
16 DISCUSSION AND STUDY QUESTIONS 1. What did Manifest Destiny mean for the United States? 2. What European region did most early nineteenth-century immigrants come from? How did that change by the end of the nineteenth century? 3. How did modes of transportation affect the layout of American cities? 4. What is an edge city, and how did edge cities form? 5. How does the von Thünen model relate to the spatial pattern of land use in the United States? 6. How have economic sectors shifted in the United States in the past two hundred years? 7. What is the American Dream, and how has it been expanded globally? 8. What has been the major migration pattern in the Midwest region of the United States? Why is this occurring? 9. What part of the United States has been a target for the location of information age based businesses? What was the role of airconditioning technology in making this possible? 10. Outline some examples of how US culture influences the rest of the world. GEOGRAPHY EXERCISE Identify the following key places on a map: Cumberland Gap Great Valley Manufacturing Belt Midwest Original thirteen colonies Sun Belt 4.2 United States: Early Development and Globalization 221
Chapter 6 Shaping an Abundant Land. Page 135
 Chapter 6 Shaping an Abundant Land Page 135 Waves of immigrants came to the U.S. in order to find a better life. Push-pull factors were at play. Immigration is not the only movement of people in the U.S.
Chapter 6 Shaping an Abundant Land Page 135 Waves of immigrants came to the U.S. in order to find a better life. Push-pull factors were at play. Immigration is not the only movement of people in the U.S.
Chapter 4: North America
 Chapter 4: North America Identifying the Boundaries Figure 4.1 The geographic center of North America is located near Rugby, North Dakota. Notice the flags of Mexico, Canada, and the United States. Photo
Chapter 4: North America Identifying the Boundaries Figure 4.1 The geographic center of North America is located near Rugby, North Dakota. Notice the flags of Mexico, Canada, and the United States. Photo
Chapter 4 North America
 Chapter 4 North America Identifying the Boundaries Figure 4.1 The geographic center of North America is located near Rugby, North Dakota. Notice the flags of Mexico, Canada, and the United States. Source:
Chapter 4 North America Identifying the Boundaries Figure 4.1 The geographic center of North America is located near Rugby, North Dakota. Notice the flags of Mexico, Canada, and the United States. Source:
Imperialism by the US
 Imperialism by the US Quick Class Discussion: Based on this image, what important changes took place in the United States from 1783 to 1900? 115 years after gaining independence from Britain, the United
Imperialism by the US Quick Class Discussion: Based on this image, what important changes took place in the United States from 1783 to 1900? 115 years after gaining independence from Britain, the United
Tuesday, September 12, 2017 United States Human Geography
 Tuesday, September 12, 2017 United States Human Geography Objective: Explain how the United States acquired its geographic boundaries. Examine patterns of immigration to and migration within the United
Tuesday, September 12, 2017 United States Human Geography Objective: Explain how the United States acquired its geographic boundaries. Examine patterns of immigration to and migration within the United
Countries Of The World: The United States
 Countries Of The World: The United States By National Geographic Kids, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.26.18 Word Count 859 Level MAX Image 1: U.S. Route 101 in Oregon. This highway runs along the entire
Countries Of The World: The United States By National Geographic Kids, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.26.18 Word Count 859 Level MAX Image 1: U.S. Route 101 in Oregon. This highway runs along the entire
National History National Standards: Grades K-4. National Standards in World History: Grades 5-12
 The Henry Ford American Industrial Revolution National History National Standards: Grades K-4 Standard 3D: The student understands the interactions among all these groups throughout the history of his
The Henry Ford American Industrial Revolution National History National Standards: Grades K-4 Standard 3D: The student understands the interactions among all these groups throughout the history of his
The Statue of Liberty has long been a symbol of the American ideals that welcome immigrants to
 4.3 United States: Population and Religion Figure 4.12 The Statue of Liberty has long been a symbol of the American ideals that welcome immigrants to America. Source: Photo courtesy of the US Government,http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Freiheitsstatue_NYC_full.jpg.
4.3 United States: Population and Religion Figure 4.12 The Statue of Liberty has long been a symbol of the American ideals that welcome immigrants to America. Source: Photo courtesy of the US Government,http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Freiheitsstatue_NYC_full.jpg.
Emergence of Modern America: 1877 to 1930s
 VUS.8a Emergence of Modern America: 1877 to 1930s What factors influenced American growth and expansion in the late nineteenth and early twentieth century? In the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries,
VUS.8a Emergence of Modern America: 1877 to 1930s What factors influenced American growth and expansion in the late nineteenth and early twentieth century? In the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries,
Locating Places. 7. G Hudson Bay 8. D Great Bear Lake 9. B Pacific Ranges 10. I Mackenzie River 11. H Rio Grande 12. E Great Slave Lake
 Locating Places Match the letters on the map with the physical features of the United States and Canada. Write your answers on a sheet of paper. 7. G Hudson Bay 8. D Great Bear Lake 9. B Pacific Ranges
Locating Places Match the letters on the map with the physical features of the United States and Canada. Write your answers on a sheet of paper. 7. G Hudson Bay 8. D Great Bear Lake 9. B Pacific Ranges
The United States Lesson 2: History of the United States
 Lesson 2: History of the United States ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is history important? Terms to Know indigenous living or occurring naturally in a particular place nomadic describes a way of life in which
Lesson 2: History of the United States ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is history important? Terms to Know indigenous living or occurring naturally in a particular place nomadic describes a way of life in which
EXAM INFORMATION. Human Geography II of the United States and Canada. European Exploration. Europe in North America. Age of Discovery 2/28/2013
 Human Geography II of the United States and Canada Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 13 EXAM INFORMATION Exam One is Tuesday, March 5. Bring a # pencil, eraser and a pen. Multiple choice short answer plus choice
Human Geography II of the United States and Canada Prof. Anthony Grande AFG 13 EXAM INFORMATION Exam One is Tuesday, March 5. Bring a # pencil, eraser and a pen. Multiple choice short answer plus choice
Migration and Settlement (MIG)
 Migration and Settlement (MIG) This theme focuses on why and how the various people who moved to and within the United States both adapted to and transformed their new social and physical environments.
Migration and Settlement (MIG) This theme focuses on why and how the various people who moved to and within the United States both adapted to and transformed their new social and physical environments.
Essential Question: & Latin America? Clicker Review. What role did the United States play as an imperial power in Asia. CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.
 Essential Question: What role did the United States play as an imperial power in Asia & Latin America? CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.8: Clicker Review Imperialism by the USA notes Today s HW: 28.3 Unit 10 Test:
Essential Question: What role did the United States play as an imperial power in Asia & Latin America? CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.8: Clicker Review Imperialism by the USA notes Today s HW: 28.3 Unit 10 Test:
White Pages Copymasters Blue Pages Answer Keys. Introduction... v Class Record...ix. Student Activities
 The Nystrom Atlas of United States Histor y Student Activities Contents White Pages Copymasters Blue Pages Answer Keys Introduction......................................................... v Class Record........................................................ix
The Nystrom Atlas of United States Histor y Student Activities Contents White Pages Copymasters Blue Pages Answer Keys Introduction......................................................... v Class Record........................................................ix
PRESENT TRENDS IN POPULATION DISTRIBUTION
 PRESENT TRENDS IN POPULATION DISTRIBUTION Conrad Taeuber Associate Director, Bureau of the Census U.S. Department of Commerce Our population has recently crossed the 200 million mark, and we are currently
PRESENT TRENDS IN POPULATION DISTRIBUTION Conrad Taeuber Associate Director, Bureau of the Census U.S. Department of Commerce Our population has recently crossed the 200 million mark, and we are currently
Unit 8. Innovation Brings Change 1800 s-1850 s
 Unit 8 Innovation Brings Change 1800 s-1850 s Unit Overview: Industrialization Era This unit addresses the development of the economies in the North and the South, innovations in technology and the application
Unit 8 Innovation Brings Change 1800 s-1850 s Unit Overview: Industrialization Era This unit addresses the development of the economies in the North and the South, innovations in technology and the application
Unit III Outline Organizing Principles
 Unit III Outline Organizing Principles British imperial attempts to reassert control over its colonies and the colonial reaction to these attempts produced a new American republic, along with struggles
Unit III Outline Organizing Principles British imperial attempts to reassert control over its colonies and the colonial reaction to these attempts produced a new American republic, along with struggles
The most densely populated and industrialized region in the United States is the what?
 Chapter 5 The United States pg. 120 153 5 1 From Coast to Coast pg. 123 127 Northeast What states are included in the Northeast? A continent is what? Landforms, Climate, and Vegetation What are the two
Chapter 5 The United States pg. 120 153 5 1 From Coast to Coast pg. 123 127 Northeast What states are included in the Northeast? A continent is what? Landforms, Climate, and Vegetation What are the two
3/21/ Global Migration Patterns. 3.1 Global Migration Patterns. Distance of Migration. 3.1 Global Migration Patterns
 3.1 Global Migration Patterns Emigration is migration from a location; immigration is migration to a location. Net migration is the difference between the number of immigrants and emigrants. Geography
3.1 Global Migration Patterns Emigration is migration from a location; immigration is migration to a location. Net migration is the difference between the number of immigrants and emigrants. Geography
Unit 1 Test (Version B)
 Unit 1 Test (Version B) 1. The city of Lewisville has a population of 1,000 people living in 100 square miles. What is the population density of Lewisville? a. 10 people per square mile b. 50 people per
Unit 1 Test (Version B) 1. The city of Lewisville has a population of 1,000 people living in 100 square miles. What is the population density of Lewisville? a. 10 people per square mile b. 50 people per
Map of the Foreign Born Population of the United States, 1900
 Introduction According to the 1900 census, the population of the United States was then 76.3 million. Nearly 14 percent of the population approximately 10.4 million people was born outside of the United
Introduction According to the 1900 census, the population of the United States was then 76.3 million. Nearly 14 percent of the population approximately 10.4 million people was born outside of the United
CHAPTER 11 KEY ISSUE TWO: WHERE IS INDUSTRY DISTRIBUTED?
 CHAPTER 11 KEY ISSUE TWO: WHERE IS INDUSTRY DISTRIBUTED? WORLD INDUSTRIAL REGIONS North America Industrialized areas in North America Changing distribution of U.S. manufacturing Europe Western Europe Eastern
CHAPTER 11 KEY ISSUE TWO: WHERE IS INDUSTRY DISTRIBUTED? WORLD INDUSTRIAL REGIONS North America Industrialized areas in North America Changing distribution of U.S. manufacturing Europe Western Europe Eastern
Immigration and the Peopling of the United States
 Immigration and the Peopling of the United States Theme: American and National Identity Analyze relationships among different regional, social, ethnic, and racial groups, and explain how these groups experiences
Immigration and the Peopling of the United States Theme: American and National Identity Analyze relationships among different regional, social, ethnic, and racial groups, and explain how these groups experiences
World Industrial Regions
 World Industrial Regions North America Industrialized areas in North America Changing distribution of U.S. manufacturing Europe Western Europe Eastern Europe East Asia Manufacturing Regions Fig. 11-3:
World Industrial Regions North America Industrialized areas in North America Changing distribution of U.S. manufacturing Europe Western Europe Eastern Europe East Asia Manufacturing Regions Fig. 11-3:
Migration PPT by Abe Goldman
 Chapter 3 Migration PPT by Abe Goldman Key Issue 1 / EQ / Purpose Why do people migrate? Migration Terms Migration Form of relocation diffusion involving permanent move to a new location. Example: Family
Chapter 3 Migration PPT by Abe Goldman Key Issue 1 / EQ / Purpose Why do people migrate? Migration Terms Migration Form of relocation diffusion involving permanent move to a new location. Example: Family
Summary The Beginnings of Industrialization KEY IDEA The Industrial Revolution started in Great Britain and soon spread elsewhere.
 Summary The Beginnings of Industrialization KEY IDEA The Industrial Revolution started in Great Britain and soon spread elsewhere. In the early 1700s, large landowners in Britain bought much of the land
Summary The Beginnings of Industrialization KEY IDEA The Industrial Revolution started in Great Britain and soon spread elsewhere. In the early 1700s, large landowners in Britain bought much of the land
AP EXAM REVIEW: UNIT 6 Chapters 11-13
 AP EXAM REVIEW: UNIT 6 Chapters 11-13 1 Mexico s system of maquiladoras is located A. Along the coast of the Pacific Ocean B. On the Baja Peninsula C. On the Yucatan Peninsula D. Along the Mexico-US border
AP EXAM REVIEW: UNIT 6 Chapters 11-13 1 Mexico s system of maquiladoras is located A. Along the coast of the Pacific Ocean B. On the Baja Peninsula C. On the Yucatan Peninsula D. Along the Mexico-US border
Name Chapter 4 TEKS. Subsistence Agriculture VS Market-Oriented (Commercial) Agriculture. by selling their products and then buy what they need
 Name Chapter 4 TEKS Sequence Subsistence Agriculture VS Market-Oriented (Commercial) Agriculture Farming is done to meet the immediate family needs Labor force consists of a family or small group Family
Name Chapter 4 TEKS Sequence Subsistence Agriculture VS Market-Oriented (Commercial) Agriculture Farming is done to meet the immediate family needs Labor force consists of a family or small group Family
Migration. Introducing
 Introducing Migration Diffusion was defined in Chapter 1 as a process by which a characteristic spreads from one area to another, and relocation diffusion was the spread of a characteristic through the
Introducing Migration Diffusion was defined in Chapter 1 as a process by which a characteristic spreads from one area to another, and relocation diffusion was the spread of a characteristic through the
American Political Culture
 American Political Culture Defining the label American can be complicated. What makes someone an American? Citizenship status? Residency? Paying taxes, playing baseball, speaking English, eating apple
American Political Culture Defining the label American can be complicated. What makes someone an American? Citizenship status? Residency? Paying taxes, playing baseball, speaking English, eating apple
In the first half of the nineteenth century, economic changes called by historians the market revolution transformed the United States.
 1 2 In the first half of the nineteenth century, economic changes called by historians the market revolution transformed the United States. Innovations in transportation and communication sparked these
1 2 In the first half of the nineteenth century, economic changes called by historians the market revolution transformed the United States. Innovations in transportation and communication sparked these
2010 CENSUS POPULATION REAPPORTIONMENT DATA
 Southern Tier East Census Monograph Series Report 11-1 January 2011 2010 CENSUS POPULATION REAPPORTIONMENT DATA The United States Constitution, Article 1, Section 2, requires a decennial census for the
Southern Tier East Census Monograph Series Report 11-1 January 2011 2010 CENSUS POPULATION REAPPORTIONMENT DATA The United States Constitution, Article 1, Section 2, requires a decennial census for the
DRAWING FROM EXPERIENCEII
 Chapter 10, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 306 311 ECONOMIC GROWTH KEY TERMS Industrial Revolution A new way of working and producing goods (page 307) capital Money invested to start new businesses
Chapter 10, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 306 311 ECONOMIC GROWTH KEY TERMS Industrial Revolution A new way of working and producing goods (page 307) capital Money invested to start new businesses
Economic History of the US
 Economic History of the US Revolution to Civil War, 1776-1860 Lecture #2 Peter Allen Econ 120 Map 8.1 US Land Expansion Early Western Migrations Population at independence (in thousands) Total White African
Economic History of the US Revolution to Civil War, 1776-1860 Lecture #2 Peter Allen Econ 120 Map 8.1 US Land Expansion Early Western Migrations Population at independence (in thousands) Total White African
Political Geography Unit Test (Version B)
 Political Geography Unit Test (Version B) Figure 1 1. What shape BEST describes the country shown in Figure 1 above? a. elongated b. perforated c. prorupted d. compact e. fragmented Figure 2 2. What shape
Political Geography Unit Test (Version B) Figure 1 1. What shape BEST describes the country shown in Figure 1 above? a. elongated b. perforated c. prorupted d. compact e. fragmented Figure 2 2. What shape
INDUSTRY AND MIGRATION/THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH. pp
 INDUSTRY AND MIGRATION/THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH pp 382-405 What drives history? Table Talk: Brainstorm some things that have driven history forward What do these things have in common? What changes have
INDUSTRY AND MIGRATION/THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH pp 382-405 What drives history? Table Talk: Brainstorm some things that have driven history forward What do these things have in common? What changes have
The Beginnings of Industrialization
 Name CHAPTER 25 Section 1 (pages 717 722) The Beginnings of BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about romanticism and realism in the arts. In this section, you will read about the beginning of
Name CHAPTER 25 Section 1 (pages 717 722) The Beginnings of BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about romanticism and realism in the arts. In this section, you will read about the beginning of
Grade Level, Course Fifth Grade Social Studies PLSD Balanced Assessment Practices. Type* DOK
 Unit Guides Assessment Items Indic ator s Concept Standard Curricular Indicator DOK Type* SR CR PB Assessment Questions # DOK Level 1E 1M 1H 2E 2M 2H 3E 3M 3H Civics Students will develop and apply the
Unit Guides Assessment Items Indic ator s Concept Standard Curricular Indicator DOK Type* SR CR PB Assessment Questions # DOK Level 1E 1M 1H 2E 2M 2H 3E 3M 3H Civics Students will develop and apply the
3.1 How does the economy of the globalised world function in different places?
 3.1 How does the economy of the globalised world function in different places? a. The balance between employment sectors (primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary) varies spatially and is changing.
3.1 How does the economy of the globalised world function in different places? a. The balance between employment sectors (primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary) varies spatially and is changing.
Name 1. Why were the League of Nations and the United Nations created? A.
 Name 1. Why were the League of Nations and the United Nations created? A. to end world hunger B. to prevent future wars C. to unify the world economy D. to spread democracy in the world 2. How did the
Name 1. Why were the League of Nations and the United Nations created? A. to end world hunger B. to prevent future wars C. to unify the world economy D. to spread democracy in the world 2. How did the
Chapter 3: Migration. most people migrate in search of three objectives: economic opportunity, cultural freedom, and environmental comfort
 Chapter 3: Migration most people migrate in search of three objectives: economic opportunity, cultural freedom, and environmental comfort emigrant vs. immigration Key issue 1 Why do people migrate? push
Chapter 3: Migration most people migrate in search of three objectives: economic opportunity, cultural freedom, and environmental comfort emigrant vs. immigration Key issue 1 Why do people migrate? push
BECOMING A WORLD POWER
 BECOMING A WORLD POWER CHAPTER 10 IMPERIALISM THE PRESSURE TO EXPAND Americans had always sought to expand the size of their nation, and throughout the 19th century they extended their control toward the
BECOMING A WORLD POWER CHAPTER 10 IMPERIALISM THE PRESSURE TO EXPAND Americans had always sought to expand the size of their nation, and throughout the 19th century they extended their control toward the
The Cultural Landscape Eleventh Edition
 Chapter 3 Lecture The Cultural Landscape Eleventh Edition Migration Matthew Cartlidge University of Nebraska-Lincoln Key Issues Where are migrants distributed? Where do people migrate within a country?
Chapter 3 Lecture The Cultural Landscape Eleventh Edition Migration Matthew Cartlidge University of Nebraska-Lincoln Key Issues Where are migrants distributed? Where do people migrate within a country?
Beyond cities: How Airbnb supports rural America s revitalization
 Beyond cities: How Airbnb supports rural America s revitalization Table of contents Overview 03 Our growth in rural areas 04 Creating opportunity 05 Helping seniors and women 07 State leaders in key categories
Beyond cities: How Airbnb supports rural America s revitalization Table of contents Overview 03 Our growth in rural areas 04 Creating opportunity 05 Helping seniors and women 07 State leaders in key categories
Settling the Western Frontier
 Settling the Western Frontier 1860-1890 Library of Congress America Moves West America s desire to expand meant that thousands would migrate to western lands (Manifest Destiny). What are some pull factors?
Settling the Western Frontier 1860-1890 Library of Congress America Moves West America s desire to expand meant that thousands would migrate to western lands (Manifest Destiny). What are some pull factors?
United States Migration Patterns (Internal)
 United States Migration Patterns (Internal) Internal US Migration (interregional) U.S. settlement patterns Movement is East to West Colonial settlement clustered on the East Coast Limited to coastal areas
United States Migration Patterns (Internal) Internal US Migration (interregional) U.S. settlement patterns Movement is East to West Colonial settlement clustered on the East Coast Limited to coastal areas
This Land Is Your Land
 Fifty United States Where in the world is the United States? (Can you spot it on this map? Is all of it on this map?) Most of the U.S. is part of the continent called North America. It is in the northern
Fifty United States Where in the world is the United States? (Can you spot it on this map? Is all of it on this map?) Most of the U.S. is part of the continent called North America. It is in the northern
Practice for the TOEFL & other Reading Tests
 Practice for the TOEFL & other Reading Tests Practice for important reading tests by reading this six-paragraph passage on early industry and mechanized agriculture in the U.S. and answering the questions
Practice for the TOEFL & other Reading Tests Practice for important reading tests by reading this six-paragraph passage on early industry and mechanized agriculture in the U.S. and answering the questions
Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change
 Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change 1800-1860 Nationalism and Economic Growth By 1815, following the end of The War of 1812, America had shown: That it could defend its sovereignty against
Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change 1800-1860 Nationalism and Economic Growth By 1815, following the end of The War of 1812, America had shown: That it could defend its sovereignty against
EXAM INFORMATION. Human Geography II of the United States and Canada. L Anse aux Meadows World Heritage Site, NFD. Early European Exploration
 /4/017 EXAM INFORMATION Exam One is Tues, Mar 7th. Format. Multiple choice questions on material covered through Human Geog III; some aimed at maps/diagrams and essay topics from a choice. See Study Guide.
/4/017 EXAM INFORMATION Exam One is Tues, Mar 7th. Format. Multiple choice questions on material covered through Human Geog III; some aimed at maps/diagrams and essay topics from a choice. See Study Guide.
the Philadelphia region became more diverse and cosmopolitan as it was energized by immigrants
 The Encyclopedia of Greater Philadelphia 1 Immigration in Philadelphia, 1870-1930 (Extract) By Barbara Klaczynska Source: The Encyclopedia of Greater Philadelphia http://philadelphiaencyclopedia.org/archive/immigration-1870-1930/
The Encyclopedia of Greater Philadelphia 1 Immigration in Philadelphia, 1870-1930 (Extract) By Barbara Klaczynska Source: The Encyclopedia of Greater Philadelphia http://philadelphiaencyclopedia.org/archive/immigration-1870-1930/
Population & Migration
 Population & Migration Population Distribution Humans are not distributed evenly across the earth. Geographers identify regions of Earth s surface where population is clustered and regions where it is
Population & Migration Population Distribution Humans are not distributed evenly across the earth. Geographers identify regions of Earth s surface where population is clustered and regions where it is
Chapter 3 Notes Earth s Human and Cultural Geography
 Chapter 3 Notes Earth s Human and Cultural Geography Section 1: World Population Geographers study how people and physical features are distributed on Earth s surface. Although the world s population is
Chapter 3 Notes Earth s Human and Cultural Geography Section 1: World Population Geographers study how people and physical features are distributed on Earth s surface. Although the world s population is
Chapter 3. Migration
 Chapter 3 Migration Terms Migration a permanent move to a new location. Emigration movement from a location (Exit) Immigration movement to a location (In) Net Migration Total number of migrants. Immigration
Chapter 3 Migration Terms Migration a permanent move to a new location. Emigration movement from a location (Exit) Immigration movement to a location (In) Net Migration Total number of migrants. Immigration
Industry. Tale of Two Cities
 Industry Tale of Two Cities Write these on your article! 1. Connect to Agriculture, how does NAFTA put Mexican corn farmers out of business? 2. Why does Juarez virtually transform overnight as opposed
Industry Tale of Two Cities Write these on your article! 1. Connect to Agriculture, how does NAFTA put Mexican corn farmers out of business? 2. Why does Juarez virtually transform overnight as opposed
STANDARD VUS.8a. Essential Questions What factors influenced American growth and expansion in the late nineteenth and early twentieth century?
 STANDARD VUS.8a through the early twentieth century by explaining the relationship among territorial expansion, westward movement of the population, new immigration, growth of cities, and the admission
STANDARD VUS.8a through the early twentieth century by explaining the relationship among territorial expansion, westward movement of the population, new immigration, growth of cities, and the admission
Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages ) Economic Growth
 Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages 304 309) Economic Growth Essential Question What effects did the Industrial Revolution have on the U. S. economy? Directions: As you read, complete a graphic organizer like
Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages 304 309) Economic Growth Essential Question What effects did the Industrial Revolution have on the U. S. economy? Directions: As you read, complete a graphic organizer like
Chapter 12. Services
 Chapter 12 Services Services The regular distribution (of settlements) observed over North America and over other more developed countries is not seen in less developed countries. The regular pattern of
Chapter 12 Services Services The regular distribution (of settlements) observed over North America and over other more developed countries is not seen in less developed countries. The regular pattern of
HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON
 CHAPTER 8 The United States Section 1: History and Culture Section 2: Regions of the United States Section 3: Geographic Issues 1, RINEHART AND WINSTON Section 1 History and Culture Objectives: What are
CHAPTER 8 The United States Section 1: History and Culture Section 2: Regions of the United States Section 3: Geographic Issues 1, RINEHART AND WINSTON Section 1 History and Culture Objectives: What are
8th Grade Social Studies Continued All Areas (8thgradesocials)
 Name: Date: 1. A federal system divides the power to make laws. Which body has the power to enact laws concerning marriage and divorce? A. national government B. city councils C. church leaders D. state
Name: Date: 1. A federal system divides the power to make laws. Which body has the power to enact laws concerning marriage and divorce? A. national government B. city councils C. church leaders D. state
Agenda for Monday/Tuesday. CNN 10 Westward Expansion Notes Manifest Destiny Map Assignment
 Agenda for Monday/Tuesday CNN 10 Westward Expansion Notes Manifest Destiny Map Assignment Learning Objectives I can describe the treaties such as the Adams-Onis treaty and/or the Treaty of Guadelupe-Hidalgo
Agenda for Monday/Tuesday CNN 10 Westward Expansion Notes Manifest Destiny Map Assignment Learning Objectives I can describe the treaties such as the Adams-Onis treaty and/or the Treaty of Guadelupe-Hidalgo
Unit 4 Changing America at the Turn of the Century Study Guide Name:
 Unit 4 Changing America at the Turn of the Century Study Guide SS5H3 The student will describe how life changed in America at the turn of the century a Describe the role of the cattle trails in the late
Unit 4 Changing America at the Turn of the Century Study Guide SS5H3 The student will describe how life changed in America at the turn of the century a Describe the role of the cattle trails in the late
In the early Antebellum era ( ), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that
 In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
AP Human Geography Pacing Guide
 1 st Semester August 5 August 8 Day 1 Day 2 AP Human Geography Pacing Guide 1 st Day of School Attendance/Seating Chart Syllabus Parent Signature Format of the AP Exam Movie Nights Seven Major Curriculum
1 st Semester August 5 August 8 Day 1 Day 2 AP Human Geography Pacing Guide 1 st Day of School Attendance/Seating Chart Syllabus Parent Signature Format of the AP Exam Movie Nights Seven Major Curriculum
Geographers generally divide the reasons for migration into push and pull factors.
 Migration What reasons cause people to migrate to different areas? Important Vocabulary Migration Push and Pull Factors Social Factors Ethnic Persecution Religious Persecution Environmental Factors Forced
Migration What reasons cause people to migrate to different areas? Important Vocabulary Migration Push and Pull Factors Social Factors Ethnic Persecution Religious Persecution Environmental Factors Forced
Adapted to the Physical Environment
 Adapted to the Physical Environment People change their ways of doing things in response to physical characteristics of places like building a house of logs, stone, or sod. Belief Systems Include the beliefs
Adapted to the Physical Environment People change their ways of doing things in response to physical characteristics of places like building a house of logs, stone, or sod. Belief Systems Include the beliefs
Beyond cities: How Airbnb supports rural America s revitalization
 Beyond cities: How Airbnb supports rural America s revitalization Table of contents Overview 03 Our growth in rural areas 04 Creating opportunity 05 Helping seniors and women 07 State leaders in key categories
Beyond cities: How Airbnb supports rural America s revitalization Table of contents Overview 03 Our growth in rural areas 04 Creating opportunity 05 Helping seniors and women 07 State leaders in key categories
A. Panama B. Canada C. India D. Cameroon
 1 Which country has the highest rate of natural population increase? A. Panama B. Canada C. India D. Cameroon 2 Which statement best explains why a country may have a zero natural population increase?
1 Which country has the highest rate of natural population increase? A. Panama B. Canada C. India D. Cameroon 2 Which statement best explains why a country may have a zero natural population increase?
Subject: U.S. History Calendar: Aug., Sept. Timeframe: 2 wks Level/Grade: 5
 Subject: U.S. History Calendar: Aug., Sept. Timeframe: 2 wks Level/Grade: 5 Our Country s Geography Apply critical thinking skills to organize and analyze information Use primary sources to acquire information
Subject: U.S. History Calendar: Aug., Sept. Timeframe: 2 wks Level/Grade: 5 Our Country s Geography Apply critical thinking skills to organize and analyze information Use primary sources to acquire information
Geography and the Environment (GEO)
 Geography and the Environment (GEO) This theme focuses on the role of geography and both the natural and human-made environments on social and political developments in what would become the United States.
Geography and the Environment (GEO) This theme focuses on the role of geography and both the natural and human-made environments on social and political developments in what would become the United States.
Chapter 7. Migration
 Chapter 7 Migration Chapter 7 Migration Americans have traditionally been highly higher levels of educational attainment than Figure 7-1. mobile, with nearly 1 in 7 people changing residence each year.
Chapter 7 Migration Chapter 7 Migration Americans have traditionally been highly higher levels of educational attainment than Figure 7-1. mobile, with nearly 1 in 7 people changing residence each year.
Unit Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution
 Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
THE RECONSTRUCTION ERA
 THE RECONSTRUCTION ERA 1865-1877 ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS I. What problems faced the nation during Reconstruction? II. How well did Reconstruction governments in the South succeed? III. What factors promoted
THE RECONSTRUCTION ERA 1865-1877 ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS I. What problems faced the nation during Reconstruction? II. How well did Reconstruction governments in the South succeed? III. What factors promoted
This era corresponds to information in Unit 5 ( ), Unit 6 ( ) and Unit 7 ( )
 PERIOD 4: 1800 1848 The content for APUSH is divided into 9 periods. The outline below contains the required course content for Period 4. The Thematic Learning Objectives (historical themes) are included
PERIOD 4: 1800 1848 The content for APUSH is divided into 9 periods. The outline below contains the required course content for Period 4. The Thematic Learning Objectives (historical themes) are included
Social Studies Content Expectations
 The fifth grade social studies content expectations mark a departure from the social studies approach taken in previous grades. Building upon the geography, civics and government, and economics concepts
The fifth grade social studies content expectations mark a departure from the social studies approach taken in previous grades. Building upon the geography, civics and government, and economics concepts
CANADA. Our big neighbor to the north.
 CANADA Our big neighbor to the north. CANADA VIDEO Geography made us neighbors, history made us friends, economics made us partners, and necessity made us allies. -JF Kennedy WELCOME TO CANADA Welcome
CANADA Our big neighbor to the north. CANADA VIDEO Geography made us neighbors, history made us friends, economics made us partners, and necessity made us allies. -JF Kennedy WELCOME TO CANADA Welcome
U.S. History Chapter Millionaire Review
 U.S. History Chapter 14-15 Millionaire Review #1 Which of the following best describes the cotton gin s contribution to industrialization? Created jobs for A: B: immigrants Lowered price of cotton in South
U.S. History Chapter 14-15 Millionaire Review #1 Which of the following best describes the cotton gin s contribution to industrialization? Created jobs for A: B: immigrants Lowered price of cotton in South
Unit 6 - Chapters 11 & 12 INDUSTRY & SERVICES Test Review
 Name Date Period Unit 6 - Chapters 11 & 12 INDUSTRY & SERVICES Test Review 1) Approximately 75% of the world's industrial production is concentrated in which four regions? 2) The Industrial Revolution
Name Date Period Unit 6 - Chapters 11 & 12 INDUSTRY & SERVICES Test Review 1) Approximately 75% of the world's industrial production is concentrated in which four regions? 2) The Industrial Revolution
Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914?
 Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914? From 1890 to 1914, the United States expanded its role in world affairs and gained new overseas colonies Class Activity:
Essential Question: How did America s role in the world change from 1890 to 1914? From 1890 to 1914, the United States expanded its role in world affairs and gained new overseas colonies Class Activity:
Fifth Grade History/Social Science Pacing Guide Trimester One
 History/Social Science Pacing Guide Trimester One Date: -Weeks 1-6 Nature s Fury History Standard 5.1: Students describe the major pre-columbian settlements, including the cliff dwellers and pueblo people
History/Social Science Pacing Guide Trimester One Date: -Weeks 1-6 Nature s Fury History Standard 5.1: Students describe the major pre-columbian settlements, including the cliff dwellers and pueblo people
SS6 Unit 1: Latin America. Summative Assessment Review
 SS6 Unit 1: Latin America Summative Assessment Review 1. Which is found near the 1 on the map? a. Panama Canal b. Atacama Desert c. Andes Mountains d. Sierra Madre Mountains 2. Which number on the map
SS6 Unit 1: Latin America Summative Assessment Review 1. Which is found near the 1 on the map? a. Panama Canal b. Atacama Desert c. Andes Mountains d. Sierra Madre Mountains 2. Which number on the map
7.1.3.a.1: Identify that trade facilitates the exchange of culture and resources.
 History: 6.1.1.a.1: Identify the cultural achievements of ancient civilizations in Europe and Mesoamerica. Examples: Greek, Roman, Mayan, Inca, and Aztec civilizations. 6.1.2.a.1: Describe and compare
History: 6.1.1.a.1: Identify the cultural achievements of ancient civilizations in Europe and Mesoamerica. Examples: Greek, Roman, Mayan, Inca, and Aztec civilizations. 6.1.2.a.1: Describe and compare
MARKING PERIOD 1. Shamokin Area 7 th Grade American History I Common Core I. UNIT 1: THREE WORLDS MEET. Assessments Formative/Performan ce
 Shamokin Area 7 th Grade American History I Common Core Marking Period Content Targets Common Core Standards Objectives Assessments Formative/Performan ce MARKING PERIOD 1 I. UNIT 1: THREE WORLDS MEET
Shamokin Area 7 th Grade American History I Common Core Marking Period Content Targets Common Core Standards Objectives Assessments Formative/Performan ce MARKING PERIOD 1 I. UNIT 1: THREE WORLDS MEET
Grades 2-7. American Government and the Election Process Unit Study SAMPLE PAGE. A Journey Through Learning
 A J T L Grades 2-7 American Government and the Election Process Unit Study A Journey Through Learning www.ajourneythroughlearning.com Copyright 2008 A Journey Through Learning 1 Authors: Paula Winget and
A J T L Grades 2-7 American Government and the Election Process Unit Study A Journey Through Learning www.ajourneythroughlearning.com Copyright 2008 A Journey Through Learning 1 Authors: Paula Winget and
2. If something happened to the president, who would take his or her place? 1. The U.S. Congress is a group of people who
 1. The U.S. Congress is a group of people who A. run the city. B. are soldiers. C. are lawyers. D. make laws 2. If something happened to the president, who would take his or her place? A. Vice president
1. The U.S. Congress is a group of people who A. run the city. B. are soldiers. C. are lawyers. D. make laws 2. If something happened to the president, who would take his or her place? A. Vice president
National Population Growth Declines as Domestic Migration Flows Rise
 National Population Growth Declines as Domestic Migration Flows Rise By William H. Frey U.S. population trends are showing something of a dual personality when viewed from the perspective of the nation
National Population Growth Declines as Domestic Migration Flows Rise By William H. Frey U.S. population trends are showing something of a dual personality when viewed from the perspective of the nation
Unit II Migration. Unit II Population and Migration 21
 Unit II Migration 91. The type of migration in which a person chooses to migrate is called A) chain migration. B) step migration. C) forced migration. D) voluntary migration. E. channelized migration.
Unit II Migration 91. The type of migration in which a person chooses to migrate is called A) chain migration. B) step migration. C) forced migration. D) voluntary migration. E. channelized migration.
Name: 8 th Grade U.S. History. STAAR Review. Colonization
 Name: _ 8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Colonization FORT BURROWS 2018 Name: _ VOCABULARY Agriculture - Farming, raising crops and livestock. Assembly a group of people who make and change laws for
Name: _ 8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Colonization FORT BURROWS 2018 Name: _ VOCABULARY Agriculture - Farming, raising crops and livestock. Assembly a group of people who make and change laws for
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Geographers define overpopulation as A) too many people compared to resources. B) too
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Geographers define overpopulation as A) too many people compared to resources. B) too
Chapter 10: America s Economic Revolution
 Chapter 10: America s Economic Revolution Lev_19:34 But the stranger that dwelleth with you shall be unto you as one born among you, and thou shalt love him as thyself; for ye were strangers in the land
Chapter 10: America s Economic Revolution Lev_19:34 But the stranger that dwelleth with you shall be unto you as one born among you, and thou shalt love him as thyself; for ye were strangers in the land
SSWH 15 Presentation. Describe the impact of industrialization and urbanization.
 SSWH 15 Presentation Describe the impact of industrialization and urbanization. Vocabulary Industrial Revolution Industrialization Adam Smith Capitalism Laissiez-Faire Wealth of Nations Karl Marx Communism
SSWH 15 Presentation Describe the impact of industrialization and urbanization. Vocabulary Industrial Revolution Industrialization Adam Smith Capitalism Laissiez-Faire Wealth of Nations Karl Marx Communism
Cultures of the World
 Chapter 4, Section World Explorer Chapter 4 Cultures of the World Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 4, Section
Chapter 4, Section World Explorer Chapter 4 Cultures of the World Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 4, Section
Period V ( ): Industrialization and Global Integration
 Period V (1750-1900): Industrialization and Global Integration 5.1 Industrialization and Global Capitalism I. I can describe and explain how industrialism fundamentally changed how goods were produced.
Period V (1750-1900): Industrialization and Global Integration 5.1 Industrialization and Global Capitalism I. I can describe and explain how industrialism fundamentally changed how goods were produced.
PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS EXAM BOOKLET
 Unit 2b Exam - Migration PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS EXAM BOOKLET MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The most prominent type of intraregional
Unit 2b Exam - Migration PLEASE DO NOT WRITE ON THIS EXAM BOOKLET MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The most prominent type of intraregional
Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation
 Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation Explain how the states new constitutions reflected republican ideals. Describe the structure and powers of the national government under the Articles of Confederation.
Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation Explain how the states new constitutions reflected republican ideals. Describe the structure and powers of the national government under the Articles of Confederation.
Review. Geographic Change Essay. Essay Blocking. Possible Thematic Essays 6/7/2013
 Review Essay Blocking Possible Thematic Essays Study 2 of the following: 5 W s- Who, What, When, Why - Reform Movements (Women, Civil Rights, Progressive Era) - Manifest Destiny ( Louisiana Purchase, Homestead
Review Essay Blocking Possible Thematic Essays Study 2 of the following: 5 W s- Who, What, When, Why - Reform Movements (Women, Civil Rights, Progressive Era) - Manifest Destiny ( Louisiana Purchase, Homestead
Growing Pains in the Americas THE EUROPEAN MOMENT ( )
 Growing Pains in the Americas THE EUROPEAN MOMENT (1750 1900) Or we could call today s notes: The history of the Western Hemisphere in the 19 th century as they face problems keeping order and confront
Growing Pains in the Americas THE EUROPEAN MOMENT (1750 1900) Or we could call today s notes: The history of the Western Hemisphere in the 19 th century as they face problems keeping order and confront
REVIEWED! APUSH PERIOD 5: Irish Immigrants KEY CONCEPT 5.1
 4/9/18 APUSH PERIOD 5: KEY CONCEPT 5.1 1844-1877 REVIEWED! Key Concept 5.1: The idea of Manifest Destiny and the movement west will have a variety of economic, political, and social consequences. Irish
4/9/18 APUSH PERIOD 5: KEY CONCEPT 5.1 1844-1877 REVIEWED! Key Concept 5.1: The idea of Manifest Destiny and the movement west will have a variety of economic, political, and social consequences. Irish
HUMAN GEOGRAPHY. By Brett Lucas
 HUMAN GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas MIGRATION Migration Push and pull factors Types of migration Determining destinations Why do people migrate? Push Factors Pull Factors Emigration and immigration Change in
HUMAN GEOGRAPHY By Brett Lucas MIGRATION Migration Push and pull factors Types of migration Determining destinations Why do people migrate? Push Factors Pull Factors Emigration and immigration Change in
