SS6 Unit 1: Latin America. Summative Assessment Review
|
|
|
- Hubert Day
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SS6 Unit 1: Latin America Summative Assessment Review
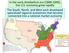
2 1. Which is found near the 1 on the map? a. Panama Canal b. Atacama Desert c. Andes Mountains d. Sierra Madre Mountains
3 2. Which number on the map marks the country of Cuba? Map at the right: a. 2 b. 3 c. 5 d. 6
4 3. What are the main sources of air pollution in Mexico City? a. intense sunlight b. the high altitude c. factories and cars d. cars that produce little or no air pollution
5 4. Which is a problem associated with deforestation? a. More oxygen is available on the planet. b. Poor people earn money from selling trees. c. Native people have too much forest for their needs. d. There is less forest to produce goods that humans need.
6 5. What trend is there in deforestation after 2004? a. The amount of deforestation is going up. b. The amount of deforestation is going down. c. Deforestation levels have stayed about the same. d. Deforestation levels are lower than they were in the 1980s.
7 6. What problem has been caused by oil production in Venezuela? a. About 15 percent of U.S. oil comes from Venezuela. b. The coast along the Caribbean Sea has been polluted with oil. c. Lake Maracaibo has become the largest lake in South America. d. Venezuela is more polluted than other South American countries.
8 7. Which region of Mexico has the most people? a. Central Plateau b. northern deserts c. tropical beaches d. Sierra Madre Mountains
9 8. Which is a negative result of Venezuela s oil business? a. Health care services have improved. b. Pollution has damaged the air and land. c. Education for poor children has improved. d. Road and telephone networks have been expanded.
10 9. Where do most Brazilians live in their country? a. in the interior b. along the Amazon River c. in the Amazon rain forest d. along the eastern coastal area
11 10. What has been the major export for Cuba for the past two hundred years? a. fish b. fruits c. sugar d. coffee
12 11. Which country supported Cuba until 1991? a. Canada b. Venezuela c. Soviet Union d. United States
13 12. Who is Brazil s largest trading partner? a. Cuba b. Guyana c. Venezuela d. United States
14 13. In which industries do Cuba and Brazil compete with each other for trade with other countries? a. coffee, sugar, tourism b. Brazil nuts, tobacco, nickel c. iron ore, soybeans, footwear d. tobacco, autos, medical products
15 14. What are the three main sources of the cultural groups of Latin America and the Caribbean? a. Africans, Mulattoes, Catholics b. Africans, Europeans, Native Americans c. Mestizos, Native Americans, Europeans d. Native Americans, Mulattoes, Europeans
16 15. How is the Day of the Dead an example of blended culture? a. It is celebrated by traditional African cultures. b. A Roman Catholic holiday is given a new name in Mexico. c. The Roman Catholic holiday is celebrated in a way which includes Native American traditions. d. The traditional Native American belief is celebrated in the same way that it has been for thousands of years.
17 16. What are the two primary language of Latin America? a. English and French b. French and Spanish c. Portuguese and English d. Spanish and Portuguese
18 17. On what common language are the languages of Spain and Portugal based? a. Spanish b. Portuguese c. ancient Latin d. ancient German
19 18. Why does the term Latin America fit as a description for the regions of Central and South America and the Caribbean? a. The people in these countries speak Latin. b. The countries share similar histories and culture. c. The people in these countries speak languages that come from Latin. d. The countries share similar histories and culture, and they mostly speak languages based on Latin.
20 19. Why do some countries have higher literacy rates for boys than for girls? a. Boys enjoy learning to read and write more than girls do. b. Girls enjoy learning to read and write more than boys do. c. Some cultures believe that it is not as important for girls to learn to read and write as it is for boys. d. Some cultures believe that it is not as important for boys to learn to read and write as it is for girls.
21 20. If a businesswoman wanted to build a factory and have educated workers, which country would be the best choice? a. Brazil b. Bolivia c. Mexico d. Guatemala
22 21. What type of government exists in Mexico? a. monarchy b. communist c. parliamentary democracy d. presidential democracy
23 22. What type of government exists in Cuba? a. monarch b. dictatorship c. presidential democracy d. parliamentary democracy
24 23. Which term describes how political power is distributed in Cuba? a. federal government b. unitary government c. aristocratic government
25 Use timeline above to answer question 24: 24. Which statement describes the economy of Brazil? a. Brazil has a pure market economy. b. Brazil has a pure command economy. c. Brazil is mostly a market economy, but the government does control some businesses. d. Brazil is mostly a command economy, but the government allows some farmers to sell some of their goods on their own.
26 25. What is an advantage of specialization? a. Factories cannot produce goods as quickly. b. Workers do not become experts in their jobs. c. A factory can produce more goods in less time and for less money. d. Businesses cannot sell as many types of goods when they specialize.
27 26. A main purpose of NAFTA was to a. increase trade by creating a large free-trade zone. b. create tariffs between Canada, Mexico, and the United States. c. decrease the standard of living for some people while raising it for others. d. keep people in one country from buying goods from the other two countries.
28 27. Which issues did some people think would be a problem related to NAFTA? a. increases in immigrants from Mexico to the United States. b. decreases in income to governments because of lower tariffs. c. increases in pollution in Mexico and the southwest United States. d. decreases in the standard of living for the people of the three countries.
29 28. Which problem did many Americans believe would result from NAFTA? a. American factory workers would lose jobs. b. The countries would not have a strong central government. c. More immigrants would come to the United States from Mexico. d. Rules about trading fairly between different countries would be removed.
30 29. Which is an example of investment in human capital? a. trucks b. factories c. education d. highways
31 30. How does investment in capital by companies help a country increase its GDP? a. The GDP of a country goes down when companies make more money. b. Companies that invest in capital are able to provide a better place for their workers to work. c. Highly trained workers help the company be more profitable by finding ways to help the company work better. d. When a company invests in capital, it can produce more goods at a better price and increase the profit that it makes
32 31. Which natural resources are the greatest help to the economies of some countries in Latin America? a. forests, oil, water b. steel, natural gas, fertile soil c. fertile soil, forests, mountains d. forests, hydroelectric power, oil
33 32. Which statement explains what items in box have in common? a. They are ways to invest extra money. b. They are things that wealthy people purchase. c. Banks sell them as a way to improve their profits. d. They are bought by people as a way to save money.
34 33. Which modern country includes land that was part of the Inca Empire? a. Peru b. Brazil c. Panama d. Venezuela
35 34. The king of Spain rewarded Pizarro for his plan to conquer the Incas by a. making him viceroy. b. allowing him to travel with Balboa. c. building him a palace in Lima, Peru. d. letting him keep all the gold he found.
36 35. What did Atahualpa hope to keep when he gave away 24 tons of gold and silver to Pizarro? a. his life b. his family c. his palace d. his empire
37 36. Which animal helped native people hunt and trade over a larger area? a. pig b. goat c. horse d. sheep
38 37. What was the Columbian Exchange? a. sending food and people from the Old World to the New World b. sending animals and plants from the Old World to the New World c. the moving of animals, plants, people, and diseases from Central and South America to North America d. the moving of animals, plants, people, and diseases from the Old World to the New World and from the New World to the Old
39 38. Which foods came to Europe from Central and South America? a. peaches, coffee, corn, wheat b. coffee, peaches, sugar, wheat c. coffee, sugar, cocoa, peaches d. corn, peppers, potatoes, tomatoes
40 39. Where did Europeans in the sixteenth century find a cheap labor source for work in the New World? a. slaves from Africa b. settlers that came from Europe c. peasants from Spain and Portugal d. indigenous people of Central and South America
41 40. Which is one reason Europeans chose slaves from Africa as a labor source in the New World? a. The New World had diseases that did not affect African workers. b. European workers did not know how to do farm and mining work. c. Indigenous people were in short supply due to warfare and disease. d. Settlers from Europe did not know how to operate large plantations.
42 41. When did slavery end for most parts of Latin America? a. after the slaves revolted b. as countries got independence from Europe c. after the kings of Spain and Portugal outlawed slavery d. when the people of the country voted to free the slaves
43 42. Which two European countries contributed most to the languages of Latin America? a. England and Spain b. Spain and Portugal c. France and Portugal d. England and Portugal
44 43. What is the most common religion of Latin America? a. Creole b. Aymara c. Quechua d. Roman Catholic
45 44. How did the Spanish government have an influence on the spread of the Roman Catholic Church in the New World? a. The Catholic Church controlled Spain. b. Spanish royalty did not support the Catholic Church. c. It paid to build missions to bring Christianity to the native population. d. Churches from other parts of the world did not send missionaries to the New World.
46 45. What was the main job of the priests, friars, and monks sent by Spain to the New World? a. find food and shelter for the poor b. convert the Indians to Christianity c. build missions to serve the settlers d. minister to the armies of the Spanish king
47 46. Which important goal did Toussaint L Ouverture want to achieve? a. freedom for the slaves in Saint Dominique b. improved production on sugar cane plantations c. control of the French, Spanish, and British armies in the Caribbean d. a meeting with the French government in France to get better working conditions
48 47. Simon Bolivar was known as the liberator for which people? a. Mexicans b. Spanish soldiers c. South Americans d. Indigenous people
49 48. Which country got its independence because of Simon Bolivar s efforts? a. Canada b. Mexico c. Venezuela d. United States
50 49. Miguel Hidalgo was known as the father of independence for which country? a. Peru b. Bolivia c. Mexico d. Venezuela
51 50. Who took over as dictator of Cuba in 1959? a. Fidel Castro b. Raul Castro c. John F. Kennedy d. Fulgencio Batista
52 51. What was one reaction the United States had to Cuba taking over property owned by Americans? a. The United States threatened a nuclear attach. b. The United States put an embargo of Cuban goods c. the United States wanted Cuba to trade with other countries. d. An agreement was reached to limit the number of Cubans entering the United States.
53 52. Which country helped Castro build Cuba into a communist country? a. Mexico b. Venezuela c. Soviet Union d. United States
54 53. The Zapatistas did not like NAFTA because they believed it would a. mean U.S. factories would move to Mexico. b. force Mexicans to move to the United States. c. hurt businesses in Canada and the United States. d. cause poor Mexican farmers to go out of business.
55 54. Which group do the Zapatistas support? a. Canadian farmers b. U.S. factory workers c. indigenous people of Mexico d. poor farmers in North America
56 55. What did Zapatistas do to show they were against NAFTA? a. attacked government troops in Mexico City b. took over several towns in southern Mexico c. formed friendships with groups in other countries with similar goals d. worked with the government on agreements to improve the rights of poor Mexicans
57 Answer key 1- D 2- C 3- C 4- D 5- B 6- B 7- A 8- B 9- D 10- C 11- C 12- D 13- A 14- B 15- C 16- D 17- C 18- D 19- C 20- C 21- D 22- B 23- B 24- C 25- C 26- A 27- C 28- A 29- C 30- D 31- A 32- A 33- A 34- A 35- A 36- C 37- D 38- D 39- A 40- C 41- B 42- B 43- D 44- C 45- B 46- A 47- C 48- C 49- C 50- A 51- B 52- C 53- D 54- C 55- B
Teachers. Ideas for Use:
 Ideas for Use: Teachers Begin each class period with 1 (or more questions). Have students keep a section of their Interactive Notebooks reserved specifically for Warm-ups. (My students flip their notebooks
Ideas for Use: Teachers Begin each class period with 1 (or more questions). Have students keep a section of their Interactive Notebooks reserved specifically for Warm-ups. (My students flip their notebooks
Curriculum Map and Pacing Guide: 6 th Grade World Area Studies
 : The focus of this first unit is on the concepts & enduring understandings rather than specific standards SS6G8a, b SS6G9a SS6G10a, b SS6G11a, b, c MARKING PERIOD 1 SS6CG4a, b, c SS6CG5a SS6CG5b SS6E5a,
: The focus of this first unit is on the concepts & enduring understandings rather than specific standards SS6G8a, b SS6G9a SS6G10a, b SS6G11a, b, c MARKING PERIOD 1 SS6CG4a, b, c SS6CG5a SS6CG5b SS6E5a,
MAPS. Environmental Issues. Economics Government History Pictures
 MAPS Environmental Issues Economics Government History Pictures 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Q: 100 Which letter
MAPS Environmental Issues Economics Government History Pictures 100 100 100 100 100 100 200 200 200 200 200 200 300 300 300 300 300 300 400 400 400 400 400 400 500 500 500 500 500 500 Q: 100 Which letter
Australia and Canada Unit Test-DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST
 Australia and Canada Unit Test-DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST 1. Which U-shaped rocky land covering is mineral rich and covers eastern and central Canada? A. Canadian Shield B. Rocky Mountains C. Lake Huron
Australia and Canada Unit Test-DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST 1. Which U-shaped rocky land covering is mineral rich and covers eastern and central Canada? A. Canadian Shield B. Rocky Mountains C. Lake Huron
Latin America s Independence Movement
 Latin America s Independence Movement Unit 7 Notes Bennett Spain Builds An Empire Spain conquered most of the lands in the Americas (Portugal = Brazil). Divided empire into provinces 2 most important provinces
Latin America s Independence Movement Unit 7 Notes Bennett Spain Builds An Empire Spain conquered most of the lands in the Americas (Portugal = Brazil). Divided empire into provinces 2 most important provinces
The History of Latin America. European Conquest Present Day. Name: KEY Section:
 The History of Latin America European Conquest Present Day Name: KEY Section: Key Terms 1. conquistador: one of the conquerors who claimed and ruled land in America for the Spanish. 2. Moctezuma: ruler
The History of Latin America European Conquest Present Day Name: KEY Section: Key Terms 1. conquistador: one of the conquerors who claimed and ruled land in America for the Spanish. 2. Moctezuma: ruler
Toussaint L Ouverture, Simon Bolivar, & Miguel Hidalgo
 Toussaint L Ouverture, Simon Bolivar, & Miguel Hidalgo Spain conquered most of the lands in the Americas (while Portugal conquered Brazil0. It divided its empire into provinces. The two most important
Toussaint L Ouverture, Simon Bolivar, & Miguel Hidalgo Spain conquered most of the lands in the Americas (while Portugal conquered Brazil0. It divided its empire into provinces. The two most important
Henry6SS5 (H6SSALL) 4. In which economic system are the production and distribution of goods owned by private individuals or corporations?
 Name: Date: 1. Which word has the same meaning as the economic term "tariff"? A. tax B. savings C. debt D. money 2. Which of these factors best helps to explain why a strong navy and a large fleet of trading
Name: Date: 1. Which word has the same meaning as the economic term "tariff"? A. tax B. savings C. debt D. money 2. Which of these factors best helps to explain why a strong navy and a large fleet of trading
Which number on the map represents the country of Cuba? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4. Nair 1
 Which number on the map represents the country of Cuba? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Nair 1 In the Soviet Union, Joseph Stalin governed through a single party dictatorship, using methods such as secret police,
Which number on the map represents the country of Cuba? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 Nair 1 In the Soviet Union, Joseph Stalin governed through a single party dictatorship, using methods such as secret police,
Dooly County Middle School. Social Studies Georgia Standards of Excellent. 6 th Grade (July 31, 2017-Oct. 2, 2017) First 9 Weeks
 Unit 1: Connecting Themes Dooly County Middle School Social Studies Georgia Standards of Excellent 6 th Grade Social Studies GSE Pacing Guide 2017-2018 6 th Grade (July 31, 2017-Oct. 2, 2017) First 9 Weeks
Unit 1: Connecting Themes Dooly County Middle School Social Studies Georgia Standards of Excellent 6 th Grade Social Studies GSE Pacing Guide 2017-2018 6 th Grade (July 31, 2017-Oct. 2, 2017) First 9 Weeks
Geography- Physical and Political Locations
 CRCT Social Studies Review- 6th Grade Physical Features: Geography- Physical and Political Locations 1. The mountain range that separates Europe from Asia. It is located in Russia. 2. The mountain range
CRCT Social Studies Review- 6th Grade Physical Features: Geography- Physical and Political Locations 1. The mountain range that separates Europe from Asia. It is located in Russia. 2. The mountain range
Which number on the map represents the country of Cuba? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 AN 1
 Which number on the map represents the country of Cuba? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 AN 1 In the Soviet Union, Joseph Stalin governed through a single party dictatorship, using methods such as secret police, terror,
Which number on the map represents the country of Cuba? A. 1 B. 2 C. 3 D. 4 AN 1 In the Soviet Union, Joseph Stalin governed through a single party dictatorship, using methods such as secret police, terror,
Brazil, Cuba & Mexico
 Brazil, Cuba & Mexico Standards SS6E1 Analyze different economic systems. a. Compare how traditional, command, and market economies answer the economic questions of 1-what to produce, 2- how to produce,
Brazil, Cuba & Mexico Standards SS6E1 Analyze different economic systems. a. Compare how traditional, command, and market economies answer the economic questions of 1-what to produce, 2- how to produce,
LATIN AMERICAN REVOLUTIONS
 LATIN AMERICAN REVOLUTIONS It takes a revolution. to make a solution. - Bob Marley WHAT WERE THE PROBLEMS? LATIN AMERICAN REVOLUTIONS: MENU CAUSES LEADERS EFFECTS PROBLEMS OF THE SPANISH EMPIRE THE ENLIGHTENMENT
LATIN AMERICAN REVOLUTIONS It takes a revolution. to make a solution. - Bob Marley WHAT WERE THE PROBLEMS? LATIN AMERICAN REVOLUTIONS: MENU CAUSES LEADERS EFFECTS PROBLEMS OF THE SPANISH EMPIRE THE ENLIGHTENMENT
A Place of Three Cultures
 A Place of Three Cultures A Place of Three Cultures A broad square in Mexico City stands as a symbol of the complexity of Mexican culture. The Plaza de lastresculturas The Three Cultures is located on
A Place of Three Cultures A Place of Three Cultures A broad square in Mexico City stands as a symbol of the complexity of Mexican culture. The Plaza de lastresculturas The Three Cultures is located on
Nation Building and economic transformation in the americas,
 Chapter 23 Nation Building and economic transformation in the americas, 1800-1890 BEFORE YOU BEGIN Most students have significantly more knowledge of U.S. history than other regions in the Americas. This
Chapter 23 Nation Building and economic transformation in the americas, 1800-1890 BEFORE YOU BEGIN Most students have significantly more knowledge of U.S. history than other regions in the Americas. This
Chapter 25. Revolution and Independence in Latin America
 Chapter 25 Revolution and Independence in Latin America Goals of Revolutionary Movements Develop representative governments Gain economic freedom (individual and National) Establish individual rights
Chapter 25 Revolution and Independence in Latin America Goals of Revolutionary Movements Develop representative governments Gain economic freedom (individual and National) Establish individual rights
The Latin American Wars of Independence were the revolutions that took place during the late 18th and early 19th centuries and resulted in the
 The Latin American Wars of Independence were the revolutions that took place during the late 18th and early 19th centuries and resulted in the creation of a number of independent countries in Latin America.
The Latin American Wars of Independence were the revolutions that took place during the late 18th and early 19th centuries and resulted in the creation of a number of independent countries in Latin America.
European Empires: 1660s
 European Empires: 1660s 16c-18c: New Ideas Brewing in Europe Causes of Latin American Revolutions 1. Enlightenment Ideas writings of John Locke, Voltaire, & Jean Rousseau; Thomas Jefferson and Thomas Paine.
European Empires: 1660s 16c-18c: New Ideas Brewing in Europe Causes of Latin American Revolutions 1. Enlightenment Ideas writings of John Locke, Voltaire, & Jean Rousseau; Thomas Jefferson and Thomas Paine.
Growing Pains in the Americas THE EUROPEAN MOMENT ( )
 Growing Pains in the Americas THE EUROPEAN MOMENT (1750 1900) Or we could call today s notes: The history of the Western Hemisphere in the 19 th century as they face problems keeping order and confront
Growing Pains in the Americas THE EUROPEAN MOMENT (1750 1900) Or we could call today s notes: The history of the Western Hemisphere in the 19 th century as they face problems keeping order and confront
CANADA. Our big neighbor to the north.
 CANADA Our big neighbor to the north. CANADA VIDEO Geography made us neighbors, history made us friends, economics made us partners, and necessity made us allies. -JF Kennedy WELCOME TO CANADA Welcome
CANADA Our big neighbor to the north. CANADA VIDEO Geography made us neighbors, history made us friends, economics made us partners, and necessity made us allies. -JF Kennedy WELCOME TO CANADA Welcome
Taking the Lead. By: Toussaint L Ouverture
 Taking the Lead By: Toussaint L Ouverture I was born Toussaint Breda in 1743 in the French colony called Saint Domingue. My father was captured in Africa and my mother was an American-born slave. I was
Taking the Lead By: Toussaint L Ouverture I was born Toussaint Breda in 1743 in the French colony called Saint Domingue. My father was captured in Africa and my mother was an American-born slave. I was
1. Base your answer to question on the partial outline below and on your knowledge of social studies.
 Frederick Douglass Academy Global Studies 1. Base your answer to question on the partial outline below and on your knowledge of social studies. I. A. Ideas from the American Revolution spread. B. Enslaved
Frederick Douglass Academy Global Studies 1. Base your answer to question on the partial outline below and on your knowledge of social studies. I. A. Ideas from the American Revolution spread. B. Enslaved
SOCIAL STUDIES DESCRIPTION OF TEST FORMAT AND ORGANIZATION. Georgia Milestones Grade 6 EOG Study/Resource Guide for Students and Parents
 SOCIAL STUDIES DESCRIPTION OF TEST FORMAT AND ORGANIZATION The Grade 6 Social Studies EOG assessment has a total of 75 selected-response (multiple-choice) items. The test will be given in two sections.
SOCIAL STUDIES DESCRIPTION OF TEST FORMAT AND ORGANIZATION The Grade 6 Social Studies EOG assessment has a total of 75 selected-response (multiple-choice) items. The test will be given in two sections.
Unit 5, SSWH 14 b Parliament & the English Monarchy
 Unit 5, SSWH 14 b Parliament & the English Monarchy What effect did the Age of Revolution have on Global Society? SSWH 14 b Identify the causes and results of the revolutions in England (1689), United
Unit 5, SSWH 14 b Parliament & the English Monarchy What effect did the Age of Revolution have on Global Society? SSWH 14 b Identify the causes and results of the revolutions in England (1689), United
Imperialism by the US
 Imperialism by the US Quick Class Discussion: Based on this image, what important changes took place in the United States from 1783 to 1900? 115 years after gaining independence from Britain, the United
Imperialism by the US Quick Class Discussion: Based on this image, what important changes took place in the United States from 1783 to 1900? 115 years after gaining independence from Britain, the United
OAS is formed. Castro wins Cuba. Argentina gets democracy
 Chapter 37 Latin America. (1945-Present). (1) Forces Shaping Modern Latin America. (2) Latin America: the United States, and the World. (3) Mexico, Central America, and the Caribbean. (4) Focus on Argentina
Chapter 37 Latin America. (1945-Present). (1) Forces Shaping Modern Latin America. (2) Latin America: the United States, and the World. (3) Mexico, Central America, and the Caribbean. (4) Focus on Argentina
SS6E1 The student will analyze different economic systems.
 Brazil & Cuba Standards SS6E1 The student will analyze different economic systems. a. Compare how traditional, command, and market, economies answer the economic questions of 1-what to produce, 2- how
Brazil & Cuba Standards SS6E1 The student will analyze different economic systems. a. Compare how traditional, command, and market, economies answer the economic questions of 1-what to produce, 2- how
Characteristics of the Colonial System. Influence of French and American Revolutions. Rigid Class Structure VICEROYS (Colonial Leader)
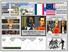 Characteristics of the Colonial System Influence of French and American Revolutions SPAIN PERU Catholic Influence in South America Colonial Governments mirrored Home Governments Unjust Agricultural & Mining
Characteristics of the Colonial System Influence of French and American Revolutions SPAIN PERU Catholic Influence in South America Colonial Governments mirrored Home Governments Unjust Agricultural & Mining
Impact & Political Outcomes in Mexico
 Impact & Political Outcomes in Mexico Standards SS6H3 The student will analyze important 20th century issues in Latin America and the Caribbean. b. Explain the impact and political outcomes of the Zapatista
Impact & Political Outcomes in Mexico Standards SS6H3 The student will analyze important 20th century issues in Latin America and the Caribbean. b. Explain the impact and political outcomes of the Zapatista
INDEPENDENCE MOVEMENTS IN LATIN AMERICA
 INDEPENDENCE MOVEMENTS IN LATIN AMERICA Essential Question: Why and how did the independence movement occur in Latin America? Standard: SS6H2c: Explain the Latin American independence movement: include
INDEPENDENCE MOVEMENTS IN LATIN AMERICA Essential Question: Why and how did the independence movement occur in Latin America? Standard: SS6H2c: Explain the Latin American independence movement: include
Mexican History and Systems of Empire
 Mexican History and Systems of Empire Day 1: The Conquest of Mexico 1. I can explain the systems the Spaniards put in place in New Spain and how they impacted Mexico over the long term. 2. I can use OPVL
Mexican History and Systems of Empire Day 1: The Conquest of Mexico 1. I can explain the systems the Spaniards put in place in New Spain and how they impacted Mexico over the long term. 2. I can use OPVL
The Industrial Revolution and Latin America
 The Industrial Revolution and Latin America AP WORLD HISTORY NOTES CHAPTER 17 (1750-1914) After Independence in Latin America Decimated populations Flooded or closed silver mines Diminished herds of livestock
The Industrial Revolution and Latin America AP WORLD HISTORY NOTES CHAPTER 17 (1750-1914) After Independence in Latin America Decimated populations Flooded or closed silver mines Diminished herds of livestock
Revolutions in Latin America (19c - Early 20c) Ms. Susan M. Pojer & Ms. Lisbeth Rath Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NY
 Revolutions in Latin America (19c - Early 20c) Ms. Susan M. Pojer & Ms. Lisbeth Rath Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NY European Empires: 1660s 16c-18c: New Ideas Brewing in Europe 4. Preoccupation of Spain
Revolutions in Latin America (19c - Early 20c) Ms. Susan M. Pojer & Ms. Lisbeth Rath Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NY European Empires: 1660s 16c-18c: New Ideas Brewing in Europe 4. Preoccupation of Spain
Latin America Since 1750
 Latin America Since 1750 Christ the Redeemer, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil Global History & Geography J.F. Walters 1 Latin America by the 18th Century: Essential Questions What was the nature of European colonialism
Latin America Since 1750 Christ the Redeemer, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil Global History & Geography J.F. Walters 1 Latin America by the 18th Century: Essential Questions What was the nature of European colonialism
SOCIAL STUDIES CURRICULUM GRADE 5
 VALLEY CENTRAL SCHOOL DISTRICT 944 STATE ROUTE 17K MONTGOMERY, NY 12549 Telephone Number: (845) 457-2400 ext. 8121 Fax Number: (845) 457-4254 SOCIAL STUDIES CURRICULUM GRADE 5 JULY 2008 Approved by the
VALLEY CENTRAL SCHOOL DISTRICT 944 STATE ROUTE 17K MONTGOMERY, NY 12549 Telephone Number: (845) 457-2400 ext. 8121 Fax Number: (845) 457-4254 SOCIAL STUDIES CURRICULUM GRADE 5 JULY 2008 Approved by the
Name: 8 th Grade U.S. History. STAAR Review. Colonization
 Name: _ 8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Colonization FORT BURROWS 2018 Name: _ VOCABULARY Agriculture - Farming, raising crops and livestock. Assembly a group of people who make and change laws for
Name: _ 8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Colonization FORT BURROWS 2018 Name: _ VOCABULARY Agriculture - Farming, raising crops and livestock. Assembly a group of people who make and change laws for
Test Booklet. Subject: SS, Grade: 08 Grade 8 Social Studies Practice Test Student name:
 Test Booklet Subject: SS, Grade: 08 Grade 8 Social Studies Practice Test 2006 Student name: Author: Ohio District: Ohio Released Tests Printed: Sunday September 02, 2012 1 According to Article I of the
Test Booklet Subject: SS, Grade: 08 Grade 8 Social Studies Practice Test 2006 Student name: Author: Ohio District: Ohio Released Tests Printed: Sunday September 02, 2012 1 According to Article I of the
Copyright 2016 Edmentum - All rights reserved. 1. Which of these physical regions is labeled number 5 on the map above?
 Study Island Copyright 2016 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Generation Date: 02/29/2016 Generated By: Jenni Long Title: SS Grade 3 TNReady Part II_North & South America 1. Which of these physical regions
Study Island Copyright 2016 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Generation Date: 02/29/2016 Generated By: Jenni Long Title: SS Grade 3 TNReady Part II_North & South America 1. Which of these physical regions
Chapter 20. By: The AP Euro Class
 Chapter 20 By: The AP Euro Class Spanish Revolution The drive for independence was inspired by both the Age of Enlightenment and the French Revolutions A priest, Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla started gatherings
Chapter 20 By: The AP Euro Class Spanish Revolution The drive for independence was inspired by both the Age of Enlightenment and the French Revolutions A priest, Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla started gatherings
1. It disappeared after President James Monroe s landslide election victory in 1816.
 Chapter 10: A Changing Nation 1815-1840 Section 1: Building National Identity 1. It disappeared after President James Monroe s landslide election victory in 1816. 2. You were to put an X on the chart next
Chapter 10: A Changing Nation 1815-1840 Section 1: Building National Identity 1. It disappeared after President James Monroe s landslide election victory in 1816. 2. You were to put an X on the chart next
The Latin Community in London. The Hispanic Community in London
 The Latin Community in London The Hispanic Community in London Introduction LATIN AMERICA 20 Latin countries Territories: Mexico Central America The islands of the Caribbean South America Colonized by
The Latin Community in London The Hispanic Community in London Introduction LATIN AMERICA 20 Latin countries Territories: Mexico Central America The islands of the Caribbean South America Colonized by
January 31, CM Book Chapter 2-10.notebook. Chapter 2. Issue Cause Effect. Jan 14-2:16 PM
 CM Book Chapter 2-10.notebook Jan 8-9:07 AM 1 Chapter 2 Issue Cause Effect Jan 14-2:16 PM 2 Chapter 3 Jan 15-2:20 PM 3 Chapter 4 1. Muslim women don't have to wear the hijab in this culture. (Bantu) 2.
CM Book Chapter 2-10.notebook Jan 8-9:07 AM 1 Chapter 2 Issue Cause Effect Jan 14-2:16 PM 2 Chapter 3 Jan 15-2:20 PM 3 Chapter 4 1. Muslim women don't have to wear the hijab in this culture. (Bantu) 2.
Chapter Summary. Section 1: An Age of Ideologies. Section 2: Revolutions of 1830 and 1848
 Chapter Review Chapter Summary Section 1: An Age of Ideologies Conservatives such as Prince Metternich battled liberal ideas such as freedom of speech and natural rights as well as nationalistic revolts
Chapter Review Chapter Summary Section 1: An Age of Ideologies Conservatives such as Prince Metternich battled liberal ideas such as freedom of speech and natural rights as well as nationalistic revolts
Curriculum Map. Essential Questions (Questions for students that reflect the skills we want them to learn) Where are things located?
 Map August - September Geography -World *different maps(population, pop. Density) -Physical *landforms and what makes them -Cultural *Why people live where they do, how that relates to geography want the
Map August - September Geography -World *different maps(population, pop. Density) -Physical *landforms and what makes them -Cultural *Why people live where they do, how that relates to geography want the
Paper 03 Essays In Chronological Order
 Paper 03 Essays 1985-2012 In Chronological Order 1. Examine the view that the role of the mestizo during and after the Wars for Independence brought about significant changes in cultural, social and political
Paper 03 Essays 1985-2012 In Chronological Order 1. Examine the view that the role of the mestizo during and after the Wars for Independence brought about significant changes in cultural, social and political
COUNTRY DATA: Guatemala: Information from the CIA World Factbook INTRODUCTION GEOGRAPHY
 COUNTRY DATA: Guatemala: Information from the CIA World Factbook INTRODUCTION The Mayan civilization flourished in Guatemala and surrounding regions during the first millennium A.D. After almost three
COUNTRY DATA: Guatemala: Information from the CIA World Factbook INTRODUCTION The Mayan civilization flourished in Guatemala and surrounding regions during the first millennium A.D. After almost three
A Trip Through Latin America. The Age of Independence
 A Trip Through Latin America The Age of Independence Classroom Directions As students visit each loca5on, they will read the informa5on cards, view the images, and iden5fy the dates significant for the
A Trip Through Latin America The Age of Independence Classroom Directions As students visit each loca5on, they will read the informa5on cards, view the images, and iden5fy the dates significant for the
C8S3: Latin Americans Wins Independence
 C8S3: Latin Americans Wins Independence 1 IV. Life in Colonial America: 1492 1800 s A. Portugal colonized Brazil B. Spain colonized majority of the Americas C. Mercantilist Economy colonies existed to
C8S3: Latin Americans Wins Independence 1 IV. Life in Colonial America: 1492 1800 s A. Portugal colonized Brazil B. Spain colonized majority of the Americas C. Mercantilist Economy colonies existed to
NAME: DATE: PER: Unit 5 Section 2: POLITICAL REVOLUTIONS
 Unit 5 Section 2: POLITICAL REVOLUTIONS SUMMARY: The term political means government. A political revolution is an event in which the people of a country overthrow an existing government and create a new
Unit 5 Section 2: POLITICAL REVOLUTIONS SUMMARY: The term political means government. A political revolution is an event in which the people of a country overthrow an existing government and create a new
Unit Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution
 Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
2. If something happened to the president, who would take his or her place? 1. The U.S. Congress is a group of people who
 1. The U.S. Congress is a group of people who A. run the city. B. are soldiers. C. are lawyers. D. make laws 2. If something happened to the president, who would take his or her place? A. Vice president
1. The U.S. Congress is a group of people who A. run the city. B. are soldiers. C. are lawyers. D. make laws 2. If something happened to the president, who would take his or her place? A. Vice president
World History Chapter 6.4 Vocabulary Student Materials
 World History Chapter 6.4 Vocabulary Student Materials Standards Alignment Reading Vocabulary List Thematic Organization Visual Vocabulary Teacher Materials Standards Alignment California State Standards
World History Chapter 6.4 Vocabulary Student Materials Standards Alignment Reading Vocabulary List Thematic Organization Visual Vocabulary Teacher Materials Standards Alignment California State Standards
Demographic and Environmental Changes
 Demographic and Environmental Changes 1750-1914 Key changes -- overview End of Atlantic slave trade and slavery Large scale migration to the Americas Dropping birth rates in the west due to industrialization
Demographic and Environmental Changes 1750-1914 Key changes -- overview End of Atlantic slave trade and slavery Large scale migration to the Americas Dropping birth rates in the west due to industrialization
which is slightly smaller than Maryland. It is commonly known as The Heart of Africa. The
 Burundi Location The Republic of Burundi is located in Central Africa and covers 10,740 square miles which is slightly smaller than Maryland. It is commonly known as The Heart of Africa. The capital is
Burundi Location The Republic of Burundi is located in Central Africa and covers 10,740 square miles which is slightly smaller than Maryland. It is commonly known as The Heart of Africa. The capital is
C. Regions of Mexico
 C. Regions of Mexico 1. Mountains a. Sierra Madre Occidental on west coast b. Sierra Madre Oriental on east coast c. Sierra Madre Del Sur on southern Pacific Coast 2. Coastal Regions a. Northern Pacific
C. Regions of Mexico 1. Mountains a. Sierra Madre Occidental on west coast b. Sierra Madre Oriental on east coast c. Sierra Madre Del Sur on southern Pacific Coast 2. Coastal Regions a. Northern Pacific
Chapter 8- Empresarios and Colonization
 Chapter 8- Empresarios and Colonization Empresario *In 1789 George Morgan became the first empresario for the Spanish government as he brought U.S. settlers into New Madrid, Missouri. His example would
Chapter 8- Empresarios and Colonization Empresario *In 1789 George Morgan became the first empresario for the Spanish government as he brought U.S. settlers into New Madrid, Missouri. His example would
Test Booklet. Subject: SS, Grade: 05 MCAS th Grade History and Social Science. Student name:
 Test Booklet Subject: SS, Grade: 05 MCAS 2008 5th Grade History and Social Science Student name: Author: Massachusetts District: Massachusetts Released Tests Printed: Wednesday February 27, 2013 1 Which
Test Booklet Subject: SS, Grade: 05 MCAS 2008 5th Grade History and Social Science Student name: Author: Massachusetts District: Massachusetts Released Tests Printed: Wednesday February 27, 2013 1 Which
Essential Question: & Latin America? Clicker Review. What role did the United States play as an imperial power in Asia. CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.
 Essential Question: What role did the United States play as an imperial power in Asia & Latin America? CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.8: Clicker Review Imperialism by the USA notes Today s HW: 28.3 Unit 10 Test:
Essential Question: What role did the United States play as an imperial power in Asia & Latin America? CPWH Agenda for Unit 10.8: Clicker Review Imperialism by the USA notes Today s HW: 28.3 Unit 10 Test:
Central America and the Caribbean
 Chapter 11, Section World Geography Chapter 11 Central America and the Caribbean Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter
Chapter 11, Section World Geography Chapter 11 Central America and the Caribbean Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter
Title Notes: The Rise and Fall of Napoleon Answer these questions in your notes...
 Title Notes: The Rise and Fall of Napoleon Answer these questions in your notes... Would you have executed King Louis? Does this violate Enlightenment principles? Why or why not? Is the guillotine an example
Title Notes: The Rise and Fall of Napoleon Answer these questions in your notes... Would you have executed King Louis? Does this violate Enlightenment principles? Why or why not? Is the guillotine an example
WHY DO ECONOMIES GROW?
 UNIT TWO: COLONIZATION AND SETTLEMENT LESSON 3 WHY DO ECONOMIES GROW? FOCUS: UNDERSTANDING ECONOMICS IN UNITED STATES HISTORY NATIONAL COUNCIL ON ECONOMIC EDUCATION, NEW YORK, NY 29 LESSON 3 WHY DO ECONOMIES
UNIT TWO: COLONIZATION AND SETTLEMENT LESSON 3 WHY DO ECONOMIES GROW? FOCUS: UNDERSTANDING ECONOMICS IN UNITED STATES HISTORY NATIONAL COUNCIL ON ECONOMIC EDUCATION, NEW YORK, NY 29 LESSON 3 WHY DO ECONOMIES
Cherokee County School District Student Performance Standards Unit Guides - Social Studies: Seventh Grade
 Unit The Modern Middle East SS7H2. SS7G5. SS7G7. SS7G8. The student will analyze continuity and change in Southwest Asia (Middle East) leading to the 21st century. b) Explain the historical reasons for
Unit The Modern Middle East SS7H2. SS7G5. SS7G7. SS7G8. The student will analyze continuity and change in Southwest Asia (Middle East) leading to the 21st century. b) Explain the historical reasons for
Chapter 3 Notes Earth s Human and Cultural Geography
 Chapter 3 Notes Earth s Human and Cultural Geography Section 1: World Population Geographers study how people and physical features are distributed on Earth s surface. Although the world s population is
Chapter 3 Notes Earth s Human and Cultural Geography Section 1: World Population Geographers study how people and physical features are distributed on Earth s surface. Although the world s population is
Name Date Period. Quarter 3 Study Guide: Europe
 Name Date Period Quarter 3 Study Guide: Europe (1) SS6G8 The student will locate selected features of Europe. a. Locate on a world and regional political- physical map: the Danube River, Rhine River, English
Name Date Period Quarter 3 Study Guide: Europe (1) SS6G8 The student will locate selected features of Europe. a. Locate on a world and regional political- physical map: the Danube River, Rhine River, English
MEXICO. Part 1: The Making of the Modern State
 MEXICO Part 1: The Making of the Modern State Why Study Mexico? History of Revolution, One-Party Dominance, Authoritarianism But has ended one-party rule, democratized, and is now considered a newly industrializing
MEXICO Part 1: The Making of the Modern State Why Study Mexico? History of Revolution, One-Party Dominance, Authoritarianism But has ended one-party rule, democratized, and is now considered a newly industrializing
European Economic Growth Factors
 European Economic Growth Factors European Economic Growth Factors Essential Question: What factors influence a country's economic growth? Economic Check Point Economics is the study of how a market makes,
European Economic Growth Factors European Economic Growth Factors Essential Question: What factors influence a country's economic growth? Economic Check Point Economics is the study of how a market makes,
Chapter 23. Nation Building and Economic Transformation in the Americas,
 Chapter 23 Nation Building and Economic Transformation in the Americas, 1800-1890 24 1 Essential Question: What forces drove the revolutions of the 1700s, 1800s, and early 1900s? what were the causes of
Chapter 23 Nation Building and Economic Transformation in the Americas, 1800-1890 24 1 Essential Question: What forces drove the revolutions of the 1700s, 1800s, and early 1900s? what were the causes of
Chapter 32 Latin America: Revolution and Reaction Into the 21 st Century
 Chapter 32 Latin America: Revolution and Reaction Into the 21 st Century I. Introduction a. General Augusto Pinochet 1. Former commander of Chilean army brought up on crimes against humanity a. Seized
Chapter 32 Latin America: Revolution and Reaction Into the 21 st Century I. Introduction a. General Augusto Pinochet 1. Former commander of Chilean army brought up on crimes against humanity a. Seized
Nationalism. Chapter 8
 Nationalism Chapter 8 Latin American Revolutions Haiti Slave revolt 1791 Toussaint L Ouverture Dessalines 1804 Independence Latin American Revolutions Rigid Social Structure Peninsular Creole Mestizo Indian
Nationalism Chapter 8 Latin American Revolutions Haiti Slave revolt 1791 Toussaint L Ouverture Dessalines 1804 Independence Latin American Revolutions Rigid Social Structure Peninsular Creole Mestizo Indian
Washington County School District Social Studies Pacing Guide
 Grade: Course: Date(s) # of Days Unit Themes / Selections Priority Standards July 4 Days Pre Planning 30-August 2 August 3 1 Day Introduction to the Class, Rules, Books, Other Information August 4 Days
Grade: Course: Date(s) # of Days Unit Themes / Selections Priority Standards July 4 Days Pre Planning 30-August 2 August 3 1 Day Introduction to the Class, Rules, Books, Other Information August 4 Days
10/18/2017. Globalization and Diversity 4 th Edition
 Chapter X 4 Lecture Globalization and Diversity 4 th Edition Latin America Latin America Multiethnic - Colonial landscape - Indigenous peoples - Language - Religion - Urbanized 4 Megacities - Growing pop
Chapter X 4 Lecture Globalization and Diversity 4 th Edition Latin America Latin America Multiethnic - Colonial landscape - Indigenous peoples - Language - Religion - Urbanized 4 Megacities - Growing pop
Life in France in 1789
 Life in France in 1789 Roughly 90% of France s population were poor peasants Peasants had to produce food for the entire country The king had a lavish lifestyle The king ruled as an absolute monarch The
Life in France in 1789 Roughly 90% of France s population were poor peasants Peasants had to produce food for the entire country The king had a lavish lifestyle The king ruled as an absolute monarch The
The United States Lesson 2: History of the United States
 Lesson 2: History of the United States ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is history important? Terms to Know indigenous living or occurring naturally in a particular place nomadic describes a way of life in which
Lesson 2: History of the United States ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is history important? Terms to Know indigenous living or occurring naturally in a particular place nomadic describes a way of life in which
Latin America in the 19th and 20th Centuries
 Latin America in the 19th and 20th Centuries Prior to the 20th Century In the 1700s Spanish power was starting to decline. Creoles(criollos) began to question the policies of Spain and Portugal. However,
Latin America in the 19th and 20th Centuries Prior to the 20th Century In the 1700s Spanish power was starting to decline. Creoles(criollos) began to question the policies of Spain and Portugal. However,
New Global Patterns. Imperialism II
 New Global Patterns Imperialism II 1800-1914 本は近代化 Japan Modernizes Japan isolated itself from the world from 1600-1853 Japan s reaction to western imperialism was to become imperialist herself. Japan
New Global Patterns Imperialism II 1800-1914 本は近代化 Japan Modernizes Japan isolated itself from the world from 1600-1853 Japan s reaction to western imperialism was to become imperialist herself. Japan
ERA 4 REVIEW
 APWH Massey ERA 4 REVIEW 1750-1914 Name Date Block OMH 1. Compare the similarities and differences between the French Revolution, American Revolution, Haitian Revolution and the Latin American Independence
APWH Massey ERA 4 REVIEW 1750-1914 Name Date Block OMH 1. Compare the similarities and differences between the French Revolution, American Revolution, Haitian Revolution and the Latin American Independence
IB HL History Paper 03 History of the Americas Essays Organized by HL History Details Revised 2007
 Paper 03 History of the Americas Essays Organized by HL History Details Revised 2007 Topic 1 The Colonial Period political and economic relationship with the colonial lpowers: Britain, France, Spain, Portugal
Paper 03 History of the Americas Essays Organized by HL History Details Revised 2007 Topic 1 The Colonial Period political and economic relationship with the colonial lpowers: Britain, France, Spain, Portugal
Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy?
 Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.4: Clickers Questions Market Revolution inquiry activity
Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.4: Clickers Questions Market Revolution inquiry activity
Originates in France during the French Revolution, after Louis XVI is executed. Spreads across Europe as Napoleon builds his empire by conquering
 Originates in France during the French Revolution, after Louis XVI is executed. Spreads across Europe as Napoleon builds his empire by conquering neighboring nations. Characteristics: Historical Origins:
Originates in France during the French Revolution, after Louis XVI is executed. Spreads across Europe as Napoleon builds his empire by conquering neighboring nations. Characteristics: Historical Origins:
Eagle s Landing Middle School 7 th Grade Social Studies Pacing Guide
 Getting to Know You/ Establishing Procedures July 30 th August 3rd Fundamentals of Economics and Government August 6 th -August 20 th SS7E1a-b, SS7E4a-b, SS6E7a-b Analyze different economic systems. Terminology
Getting to Know You/ Establishing Procedures July 30 th August 3rd Fundamentals of Economics and Government August 6 th -August 20 th SS7E1a-b, SS7E4a-b, SS6E7a-b Analyze different economic systems. Terminology
CMS Lesson Plan Template Teacher: Carter, Wright, Robinson Course/Level: SS/6th
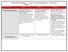 CMS Lesson Plan Template Teacher: Carter, Wright, Robinson Course/Level: SS/6th Week of: March 9-13 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Focused Standard/Element(s) SS6CG2 The student will explain the structures of
CMS Lesson Plan Template Teacher: Carter, Wright, Robinson Course/Level: SS/6th Week of: March 9-13 Monday Tuesday Wednesday Focused Standard/Element(s) SS6CG2 The student will explain the structures of
AP World History: Coercive (Forced) Labor Systems in the Early Modern Period
 Date: Name: AP World History: Coercive (Forced) Labor Systems in the Early Modern Period Overview: Although slavery had existed in human societies since the emergence of early complex societies in Mesopotamia
Date: Name: AP World History: Coercive (Forced) Labor Systems in the Early Modern Period Overview: Although slavery had existed in human societies since the emergence of early complex societies in Mesopotamia
Chapter 4 North America
 Chapter 4 North America Identifying the Boundaries Figure 4.1 The geographic center of North America is located near Rugby, North Dakota. Notice the flags of Mexico, Canada, and the United States. Source:
Chapter 4 North America Identifying the Boundaries Figure 4.1 The geographic center of North America is located near Rugby, North Dakota. Notice the flags of Mexico, Canada, and the United States. Source:
Nation Building & Economic Transformation in the Americas
 Nation Building & Economic Transformation in the Americas 1800-1890 Independence in Latin America, 1800 1830 Roots of Revolution to 1810 Wealthy colonial residents of Latin America were frustrated by the
Nation Building & Economic Transformation in the Americas 1800-1890 Independence in Latin America, 1800 1830 Roots of Revolution to 1810 Wealthy colonial residents of Latin America were frustrated by the
After the French Revolution
 Warm Up In your spiral (page ), answer the following prompt. After the French Revolution (think of the video from last class), what would the people of France be looking for? Napoleon, the Napoleonic Wars,
Warm Up In your spiral (page ), answer the following prompt. After the French Revolution (think of the video from last class), what would the people of France be looking for? Napoleon, the Napoleonic Wars,
SOCIAL STUDIES. Specimen Papers and Mark Scheme/Key
 CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL Caribbean Primary Exit Assessment TM CPEA TM SOCIAL STUDIES Specimen Papers and Mark Scheme/Key C B SPEC 2017/06243011 TEST CODE 06243011 C A R I B B E A N E X A M I N A
CARIBBEAN EXAMINATIONS COUNCIL Caribbean Primary Exit Assessment TM CPEA TM SOCIAL STUDIES Specimen Papers and Mark Scheme/Key C B SPEC 2017/06243011 TEST CODE 06243011 C A R I B B E A N E X A M I N A
Revolutions in Europe and Latin America Chapter 8 World History A
 Revolutions in Europe and Latin America Chapter 8 World History A Section 1 1. Know what ideology means. 2. Know what autonomy is. 3. Be able to describe what the Concert of Europe was. 4. Know what was
Revolutions in Europe and Latin America Chapter 8 World History A Section 1 1. Know what ideology means. 2. Know what autonomy is. 3. Be able to describe what the Concert of Europe was. 4. Know what was
HOLT, RINEHART AND WINSTON
 CHAPTER 8 The United States Section 1: History and Culture Section 2: Regions of the United States Section 3: Geographic Issues 1, RINEHART AND WINSTON Section 1 History and Culture Objectives: What are
CHAPTER 8 The United States Section 1: History and Culture Section 2: Regions of the United States Section 3: Geographic Issues 1, RINEHART AND WINSTON Section 1 History and Culture Objectives: What are
Locating Places. 7. G Hudson Bay 8. D Great Bear Lake 9. B Pacific Ranges 10. I Mackenzie River 11. H Rio Grande 12. E Great Slave Lake
 Locating Places Match the letters on the map with the physical features of the United States and Canada. Write your answers on a sheet of paper. 7. G Hudson Bay 8. D Great Bear Lake 9. B Pacific Ranges
Locating Places Match the letters on the map with the physical features of the United States and Canada. Write your answers on a sheet of paper. 7. G Hudson Bay 8. D Great Bear Lake 9. B Pacific Ranges
World History (Survey) Chapter 28: Transformations Around the Globe,
 World History (Survey) Chapter 28: Transformations Around the Globe, 1800 1914 Section 1: China Responds to Pressure from the West In the late 1700s, China was self-sufficient. It had a strong farming
World History (Survey) Chapter 28: Transformations Around the Globe, 1800 1914 Section 1: China Responds to Pressure from the West In the late 1700s, China was self-sufficient. It had a strong farming
Test Instructions. Three ways to use Which Word Does Not Belong?
 Test Instructions Four Ways to Use the Cloze Tests for Easy English NEWS Print out the tests and make copies for every student. Choose the most appropriate way to use the tests: 1. After reading the article,
Test Instructions Four Ways to Use the Cloze Tests for Easy English NEWS Print out the tests and make copies for every student. Choose the most appropriate way to use the tests: 1. After reading the article,
World Interactions to 1450 and Beyond: The Age of Exploration
 World Interactions to 1450 and Beyond: The Age of Exploration 1. Effects of Muslim trade on Indian Ocean a. How did Muslim trade affect the populations of the trading cities in the Indian Ocean? b. Why
World Interactions to 1450 and Beyond: The Age of Exploration 1. Effects of Muslim trade on Indian Ocean a. How did Muslim trade affect the populations of the trading cities in the Indian Ocean? b. Why
Unit 4 Mexican Colonization and the Empresario System
 Unit 4 Mexican Colonization and the Empresario System 1821-1836 For these notes you write the slides with the red titles!!! Unit 4 Vocab empresario an agent who makes all the arrangements to bring settlers
Unit 4 Mexican Colonization and the Empresario System 1821-1836 For these notes you write the slides with the red titles!!! Unit 4 Vocab empresario an agent who makes all the arrangements to bring settlers
Latin America s Political Pendulum. March 30, 2017
 Latin America s Political Pendulum March 30, 2017 Because Mexico, Central and South America were dominated by languages derived from Latin, people began to refer to the area as "Latin America." Latin America
Latin America s Political Pendulum March 30, 2017 Because Mexico, Central and South America were dominated by languages derived from Latin, people began to refer to the area as "Latin America." Latin America
Final Review. Global Studies
 Final Review Global Studies Major Belief Systems Judaism Confucianism Christianity Buddhism Hinduism Islam Middle East China Middle East India, China India Middle East Monotheism, 10 Commandments, Torah,
Final Review Global Studies Major Belief Systems Judaism Confucianism Christianity Buddhism Hinduism Islam Middle East China Middle East India, China India Middle East Monotheism, 10 Commandments, Torah,
ANCIENT GREECE & ROME
 ANCIENT GREECE & ROME 3.1 The student will explain how the contributions of ancient Greece and Rome have influenced the present world in terms of architecture, government (direct and representative democracy),
ANCIENT GREECE & ROME 3.1 The student will explain how the contributions of ancient Greece and Rome have influenced the present world in terms of architecture, government (direct and representative democracy),
In the early Antebellum era ( ), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that
 In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
Welcome to History 06 History of the Americas II Prof. Valadez
 Welcome to History 06 History of the Americas II Prof. Valadez 1 Topics Review: Positivism Participation Assignment #3 U.S. Foreign Policy In Latin America Early 20 th Century Revolutions in Latin America
Welcome to History 06 History of the Americas II Prof. Valadez 1 Topics Review: Positivism Participation Assignment #3 U.S. Foreign Policy In Latin America Early 20 th Century Revolutions in Latin America
REGIONS OF THE WORLD
 REGIONS OF THE WORLD NORTH AMERICA Some countries: 3 Nations: USA, Mexico, Canada Population: Power: Main Languages: English, Spanish, French Religion: Mostly Christian, but many other groups Number of
REGIONS OF THE WORLD NORTH AMERICA Some countries: 3 Nations: USA, Mexico, Canada Population: Power: Main Languages: English, Spanish, French Religion: Mostly Christian, but many other groups Number of
