GeoFactsheet. The Causes & Consequences of Underpopulation. January 1999 Number 59
|
|
|
- Frank Nichols
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 GeoFactsheet January 1999 Number 9 The Causes & Consequences of Underpopulation Underpopulation is frequently thought of as being a good thing or, at least, much less of a problem then overpopulation. This belief is reinforced by Fig 1, which often appears in GCSE and some A Level texts. However, underpopulation can also be a serious problem. This Factsheet examines the causes and consequences of underpopulation. Fig 1. Relationship between population and resources in areas with varying populations Lack Balance Surplus overpopulation optimum population underpopulation The three terms overpopulation, optimum population and underpopulation, all refer to relationships between an area s total population and its natural resources i.e. climate, soils, mineral deposits, water supplies etc. Any geographical area has what is known as a carrying capacity (C.C.) which is the maximum number of people it can sustainably support with the available natural resources. This C.C. will vary through time with changes in technology and economic and social development. For example an area in a LEDC may have a C.C. of 0 per km before tractors and tube wells are introduced but a C.C. of 80 per km afterwards. The C.C. can vary widely e.g. Bangladesh with its fertile, low-lying, delta plains has a C.C. of 00 per km. Semi-arid West Africa, on the other hand, with its poor soils, unreliable rainfall etc. has a C.C. of 10 per km. Overpopulation occurs where the size of population is too big for a country s resources. i.e. Population Density/km > C.C./km Optimum population is a theoretical situation that would exist if the population total was ideal for the available resources. i.e. Population Density/km = C.C./km Underpopulation exists when the population numbers are too small to fully exploit an area s resources or conversely where the resources could support a much bigger population than they do, without lowering the standard of living. Exam Hint - This figure implies that underpopulation is a good thing. any economic geographers would disagree. essage: Do not blindly accept everything you read in textbooks. Think critically. If it doesn't make sense, don't try to remember it. Exam Hint - Before we look in detail at the causes of underpopulation it is important to point out two common misunderstandings about underpopulation: Underpopulation in an area does not necessarily mean that there is a low population density. This may be the case e.g. Canada which is underpopulated and has an overall population density of only 8 per square mile. However, California is also underpopulated but has a density of just over 300 per square mile. Underpopulation does not necessarily mean that a country is poor, undeveloped or under-developed. If we take Gross National Product (GNP) as a measure of development/wealth, Canada and Brazil, both regarded as underpopulated, have GNPs of $1970 and $3370 respectively. Do watch these points and when writing exam answers remind yourself constantly of exactly what you are writing about. It is easy to get carried away and forget halfway through an answer. i.e. Population Density/km < C.C./km 1
2 Causes of underpopulation 1. Environmental disadvantages: The majority of underpopulated countries have certain physical disadvantages e.g. climate, vegetation, soils, etc. which discourage people from living there and without enough people, economic development is restricted. (a) Climate: Very extreme climates i.e. too hot, too cold, too wet, or too dry are usually unfavourable for concentrations of population. Canada and Siberia have extremely severe winters with many months when temperatures are below freezing-point. The equatorial climate of the Amazon Basin with its high humidities, and the hot desert conditions of the Central Australian Desert also discourage people from settling there. All these areas have vast mineral resources but unless the companies involved can make substantial profits and afford to pay workers very high wages for working in such physical conditions, settlement and development will not occur. (b) Vegetation: The natural vegetation of an area can prove an obstacle to settlement and economic development if it is costly and difficult to clear for building houses, roads etc. e.g. the northern coniferous forests of Canada and Siberia (taiga) or the tropical rainforests (TRF) of Brazil. (c) Soils: Both of the forest types mentioned above, taiga and tropical rainforest (see Factsheet #3 - Forest and Soils), have infertile soils once the natural vegetation has been removed which can again deter settlers. Soil conditions can also limit development such as in the Canadian tundra where the ground is permanently frozen in winter and in a marshy condition for most of the rest of the year. Both states limit the construction of houses, roads etc. and make them more costly. Thus, many underpopulated areas suffer from physical disadvantages which makes it unfavourable for settlement and economic development even if there are abundant supplies such as natural resources e.g. minerals present.. Accessibility: Physical drawbacks often restrict the development of communications, which result in underpopulation. If people and companies find it difficult or costly to travel to an area, they are reluctant to make the journey. The actual size or area of a country is relevant here. any underpopulated countries have large areas (Table 1) so the development of a successful network of communications is obviously far more expensive than in a small one. New Zealand is the exception to the rule here; it is small and yet underpopulated. Table 1. Size, population density and economic development 3. Communications: Establishing a basic communications network is often a major problem in an underpopulated area. (a) Roads: These can be difficult to construct in tundra (ground frozen or marshy), tropical rainforest and taiga (tree-felling needed). The cost per head of population likely to use the routes is also often prohibitive in the initial stages. However, without a basic road system little can be done to increase the population numbers. (b) Railways: These are usually a much quicker means of travel but again the cost of an extensive system to be developed is usually far too great, much higher than for roads. (c) Air: If the ground conditions are suitable i.e. if it is feasible to clear the land for landing strips, this is a very fast, efficient and flexible system. Forests and tundra ground conditions can again be a problem. (d) Water: River transport is often highly developed in underpopulated areas as there is little actual initial cost involved e.g. Amazon Basin and Northern Canada, and can be very convenient, especially for bulky goods. However, in the northern areas of Canada and Siberia the rivers can be frozen for many months in the winter, which is limiting. 4. Remoteness: This is very closely linked to accessibility. any underpopulated areas are a long way from large centres of population. On a world scale this is shown by New Zealand which is a considerable distance from its nearest sizeable neighbour. Such isolation can have social drawbacks, discouraging large present-day population concentrations or past migrations. It can also cause economic and trading difficulties when competing in world markets. On a continental scale the most underpopulated areas in Canada are those which are furthest from the more settled southern parts. These peripheral areas have the problems common to any such region. Roads, railways etc. do not pass through the area; they terminate there: there is nowhere to go to beyond that point. This remoteness is an important cause of underpopulation, as workers and their families want access to varied shopping, educational, recreational facilities etc. which these areas do not have. Potential workers are reluctant to move from a well-serviced urban environment to live in a relatively backward frontier settlement.. Historical: any underpopulated areas have been linked in the past with a European nation in a colonial relationship, such as Canada and Australia with Britain or Brazil with Portugal. They became producers of primary goods for the Europeans - wheat from Canada, wool and meat from Australia and coffee from Brazil. Country Area (000s sq. miles) Population (to nearest million) Density (per square mile) Urban G.N.P. (U.S. Dollars) Farming Workforce Industry Inflation Unemployment Canada 3, , Australia, , New Zealand , Brazil 3, , Bangladesh 0 10, USA 3, , U.K ,
3 6. Type of Economy: The Prairies of Canada and the urray-darling Basin of south east Australia both developed commercial, extensive farming systems which were highly mechanised and could function economically with few workers. The volume of goods that they produce today could support far more people than actually live there. People in such areas are usually members of prosperous farming communities with a good standard of living. The tropical rainforest area of Brazil has a traditional subsistence shifting cultivation economy practised by the Amerindians, the indigenous population (original inhabitants). Such a farming type can only support fairly small numbers of people. The vast timber resources and mineral deposits were largely untapped by the immigrants into the country until this century. 7. Population composition: ost underpopulated areas are ones where the indigenous population were only fairly small in number and when they did undergo colonisation were largely left to carry on with their traditional lifestyle whilst the newcomers developed the country s economy. In Brazil the Amerindians now only number about 0. million out of the total population of 16 millions! These groups now live in the areas that are classed as underpopulated. The causes of underpopulation are summarised in Fig. Fig. Causes of underpopulation Remoteness Climate Environmental Soils Inaccessibility Underpopulation Vegetation Poor communications Consequences of underpopulation Countries that are underpopulated exhibit certain characteristics both economically and socially. 1. High rate of immigration: Underpopulated countries tend to be ones which encourage immigration as they need more people to achieve their full economic potential. Foreign workers can help to develop the economy but if they are more qualified than the locals or are prepared to accept lower rates of pay, or take their earnings out of the country, they can create problems even if they are needed to help the economy develop.. Foreign economic involvement: any underpopulated countries have foreign companies involved in their economic activities as they lack the population to support a large number of major corporations themselves, e.g. in Canada 40 of businesses are foreign-owned, especially by the USA. These companies are perceived to be using Canada s resources and taking the profits back to their own countries. In Brazil, many of the beef cattle ranches of Amazonia are owned by European multinationals. Such large amounts of foreign investment can be useful for an underpopulated country s economy especially if it is a LEDC but involvement needs to be carefully controlled. 3. Regional disparities: Underpopulation is usually relative rather than absolute within a country i.e. it affects certain areas rather than all of it. There are therefore often quite large regional differences in wealth and development within such countries due to settlement and economic activity being concentrated in the most favourable areas. This can cause problems of unrest in the less fortunate areas and also exaggerate the situation of underpopulation if people migrate from the more remote regions to the wealthier ones in search of an improved lifestyle. This has occurred in Brazil and increased housing and other social problems in, for example, Sao Paulo. 4. Service provision: Due to an overall lack of demand many underpopulated countries have a lower than average service provision for their inhabitants. The threshold population necessary for certain services may not be met.. Urban population: Underpopulated countries tend to exhibit a high degree of urbanisation because the people tend to live in the more settled urban areas rather than in the less favourable remote areas. Also, many such countries have many physical drawbacks and people are less likely to be involved in rural occupations. 6. High standard of living: The majority of underpopulated countries are EDCs. (Brazil is the exception here).they tend to have high levels of technology, (if population resource ratios are low this is vital), high income levels, (if workers are in demand they can obtain higher wages) and a good standard of living. It is likely that the standard of living would rise even further if the population rose due to an increase in production and exploitation of resources. History Type of economy The majority of underpopulated areas are what we could class as economically developed. Brazil is an exception for a variety of reasons, size, environment, etc. We will look at three main case-studies - Brazil, Canada and Western Australia. Population composition Exam Hint - Stronger candidates understood the causes of underpopulation and were able to illustrate these causes by reference to actual examples on different scales. 3
4 Brazil Canada Equator A Carajas Project Alaska Rockies NWT 0-1 person/sq.km. Brasilia P Political boundary Prairies P USA densely populated SE coastal belt Political Boundary Amazon River Rio de Janeiro Sao Paulo Tundra Forest Great Lakes A NWT North-West Territories Brazil has a total population of nearly 16 million, 90 of whom live in the south east coastal belt. uch of the rest of the country is underpopulated with considerable resource potential that is virtually untouched. It is not, however, merely a lack of people that is the problem. Brazil is an LEDC and there is: A lack of capital to develop the area A shortage of scientific and technological know-how within the country itself. There have been attempts to attract people to the interior by various government schemes. Brasilia, a new capital, was created in the 1960s, nearly 1000km from the coast. A network of highways was built linking the interior with the coastal area using the new city as its focus. It was hoped that these roads would act as a basic infrastructure framework and encourage the spread of further development and settlement into the interior. However, only the area immediately around the city has shown any substantial development. In fact the city has acted like a magnet on its immediate surroundings causing ruralurban migration as people move in hope to find employment and an improved way of life there. Brazil has recently adopted a more comprehensive regional development programme for the interior, especially the plateau region and Amazonia. This will involve further road building as well as the establishment of secondary growth points to encourage rural development. An important development scheme has been The Great Carajas Project. The main features of this scheme are: Large-scale, covering an area the size of the UK and France together, including mining, ranching, forestry, industry etc. World s largest known deposits of iron are being developed. Foreign finance (USA, Japan, World Bank, EC) is being used to help to fund the project. These countries will benefit from their investment by having access to iron-ore supplies etc. Environmental side-effects: unfortunately forest destruction, flooding of large areas of land for HEP etc. forced relocation of indigenous people. Canada has a total population of 7 million. It is very different to Brazil and yet is also underpopulated. Canada s economy is based on its natural resources of fish, timber and wood products (pulp, paper etc.) minerals, natural gas, oil and HEP. Only of its land is arable (mainly cereal-growing in the Prairies) but wheat and barley are important exports. The average income and employment levels have both fallen over the past 10 years and it is becoming increasingly difficult for the country to maintain its previous wealth and high standards of living. One of the most underpopulated parts of Canada is the North West Territories (NWT) occupying one third of Canada s total area. This province is the size of India but has a population of less than, 000! (India s population is nearly 940 million!). NWT has vast deposits of zinc, tin, gold, lead, silver, oil and gas. One of its problems, apart from the environmental disadvantages, is that 60 of the population of the NWT are indigenous tribes such as Eskimos, who still practise traditional ways of life to a large extent. In the last 30 years various attempts have been made to develop the area. The road network has been expanded, but even now there are only 30km of paved roads and 430km of all-weather ones. 90 of the area is more than 100km. from the nearest road and half the population depend on air transport for year-round access. Even air transport is dated with old planes and runways that are unpaved or too short. In summer, river transport is used, although that again is out-moded and limited. ining operations have been increased, although some of the private ones have had to be discouraged, they were using outside labour and merely exploiting the resources, giving very little in return and not investing locally. ost of the resources are what are termed as frontier resources i.e. hard to get at, expensive to develop, and subject to world market price fluctuations which again limits development. Canada has great potential wealth in NWT but a major problem as to how to realise it. Exam Hint - Case-studies enable examiners to see how you can apply your theoretical knowledge to an actual situation. It is not necessary to be able to regurgitate lots of data, it has been used here simply to illustrate the points. Concentrate on familiarising yourself with the general geography of the 3 countries concerned. 4
5 Western Australia Long distance commuting - solving a problem? Underpopulation as a result of depopulation Underpopulation can also be found in some of the areas in the rural periphery of Western Europe and other fringe regions. ore and more younger people are leaving these rural areas to work in the cities and leaving the country to migrate to the more prosperous south. It must be mentioned here that the development of North Sea oil and gas has helped Scotland s economic position considerably, although here again workers have often been imported from elsewhere. Perth Bush Hot Desert -D elbourne Peripheral Britain e.g. South West England; Central Wales; Highlands of Scotland. These areas have suffered from rural depopulation due to: Agricultural changes such as a decline in hill-sheep-farming, which has become more difficult due to foreign competition, EU reform etc. Decline in traditional industries such as textile crafts due to increased mechanisation and mass-production as well as cheaper imports from abroad. embership of the EU and the recent building of the Channel Tunnel has also meant that these areas are becoming more economically isolated from the centre of economic activity. -D urray-darling River System ining Areas In Western Australia, (and in a few parts of Canada), a solution to developing some of the more remote underpopulated areas has been found by the use of long distance commuting similar to that used by the North Sea oil and gas Industry. i.e. the work is so isolated from the workers homes that food and accommodation are provided at the work site and the workers schedule involves a fixed number of work days followed by a number of days home leave. This is widely used in Western Australia, (over 40 mining operations), and has several advantages: Lower costs as fewer facilities are needed for workers families e.g. schools etc. Air transport is cheaper than building roads and more flexible, if mining locations change as deposits become exhausted Easier to attract workers with less family upheaval. Disadvantages include: Local communities do not benefit from these developments as labour is imported as well as supplies etc. In fact local teenagers move 1000km to cities for work. any of the mining companies are also multi-nationals which have been accused of merely using Australia as a source of raw materials for their many overseas plants and not contributing to Australia s economy. Conclusion You should now have some ideas as to what causes underpopulation and what the consequences are for the areas that experience it. Two very different countries, Canada, one of the wealthiest EDCs, and Brazil, a poor LEDC, have been used to illustrate our study. Underpopulation is a problem. It may not be as obvious or as immediate as overpopulation but nevertheless it is there and in some ways it is more difficult and challenging to overcome. Practice Questions 1. Explain what is meant by the terms overpopulation and underpopulation. ( marks). Name a country that is underpopulated. Outline why it is underpopulated and describe how it has attempted to deal with the problem. (10 marks) Answer Hints 1. Explain the relationships between numbers of people and the resources of a country. Say what the consequences of both over and underpopulation are. e.g. Overpopulation - starvation, malnutrition, health problems, lack of jobs, slow economic development, financial problems for government in supporting its people etc. e.g. Underpopulation - High rate of immigration, foreign economic involvement, regional disparities, service provision, high levels of urbanisation and standards of living.. Take one of the Case Studies from this Factsheet e.g. Brazil or Canada. Describe what the problems are and why the country is underpopulated. ention any schemes that there are to reduce underpopulation. e.g. Immigration schemes, settlement/decentralisation plans, communication improvements, independence from foreign influences, national development, regional development etc. Acknowledgements; This was researched and written by Barbara elbourne Curriculum Press, Unit 30B, The Big Peg, 10 Vyse Street,Birmingham, B18 6NF Geopress Factsheets may be copied free of charge by teaching staff or students, provided that their school is a registered subscriber. No part of these Factsheets may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system, or transmitted, in any other form or by any other means, without the prior permission of the publisher. ISSN
Demography. Demography is the study of human population. Population is a dynamic open systems with inputs, processes and outputs.
 Population Demography Demography is the study of human population. Population is a dynamic open systems with inputs, processes and outputs. This means that change constantly occurs in population numbers,
Population Demography Demography is the study of human population. Population is a dynamic open systems with inputs, processes and outputs. This means that change constantly occurs in population numbers,
Geo Factsheet September 2000 Number 97
 September 2000 Number 97 Rural and Urban Structures - How and why they vary in LEDCs and MEDs Introduction structure is the percentage distribution of males and females by age group within an area and
September 2000 Number 97 Rural and Urban Structures - How and why they vary in LEDCs and MEDs Introduction structure is the percentage distribution of males and females by age group within an area and
Some important terms and Concepts in population dynamics
 By Dr. Sengupta, CJD International School, Braunschweig Some important terms and Concepts in population dynamics DEMOGRAPHY- is the study of population Population Density Population per unit of land area;
By Dr. Sengupta, CJD International School, Braunschweig Some important terms and Concepts in population dynamics DEMOGRAPHY- is the study of population Population Density Population per unit of land area;
What is Human Resource?
 Human Resources What is resource? What is Human Resource? Human Resource Human resources are the people who make up the workforce of an organization, business sector, or economy. People are a nation s
Human Resources What is resource? What is Human Resource? Human Resource Human resources are the people who make up the workforce of an organization, business sector, or economy. People are a nation s
Australia and Canada Unit Test-DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST
 Australia and Canada Unit Test-DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST 1. Which U-shaped rocky land covering is mineral rich and covers eastern and central Canada? A. Canadian Shield B. Rocky Mountains C. Lake Huron
Australia and Canada Unit Test-DO NOT WRITE ON THIS TEST 1. Which U-shaped rocky land covering is mineral rich and covers eastern and central Canada? A. Canadian Shield B. Rocky Mountains C. Lake Huron
Human Resources. There are 500 children in my How many. My village has 1,000 people. school. people do you think, there are in the whole world?
 Human Resources Do you know? The Government of India has a Ministry of Human Resource Development. The Ministry was created in 1985 with an aim to improve people s skills. This just shows how important
Human Resources Do you know? The Government of India has a Ministry of Human Resource Development. The Ministry was created in 1985 with an aim to improve people s skills. This just shows how important
Chapter 4 North America
 Chapter 4 North America Identifying the Boundaries Figure 4.1 The geographic center of North America is located near Rugby, North Dakota. Notice the flags of Mexico, Canada, and the United States. Source:
Chapter 4 North America Identifying the Boundaries Figure 4.1 The geographic center of North America is located near Rugby, North Dakota. Notice the flags of Mexico, Canada, and the United States. Source:
London Examinations IGCSE
 G144738_M23045A.qxd 22/03/2005 08:51 Page 1 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4370/1F London Examinations IGCSE Geography Foundation Tier Paper 1F Tuesday 17 May 2005 Morning Time: 1 hour 45
G144738_M23045A.qxd 22/03/2005 08:51 Page 1 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4370/1F London Examinations IGCSE Geography Foundation Tier Paper 1F Tuesday 17 May 2005 Morning Time: 1 hour 45
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 www.xtremepapers.com Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education * 6 2 2 3 4 1 6 0 1 5 * GEOGRAPHY 0460/13 Paper 1 October/November 2014 Candidates
www.xtremepapers.com Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education * 6 2 2 3 4 1 6 0 1 5 * GEOGRAPHY 0460/13 Paper 1 October/November 2014 Candidates
Chapter 12. The study of population numbers, distribution, trends, and issues.
 Chapter 12 Population Challenges Demography: The study of population numbers, distribution, trends, and issues. Population Statistics for October, 2004, Land Area (Square Km.) And Population Density Canada
Chapter 12 Population Challenges Demography: The study of population numbers, distribution, trends, and issues. Population Statistics for October, 2004, Land Area (Square Km.) And Population Density Canada
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *7762547120* GEOGRAPHY 0460/11 Paper 1 May/June 2016 Candidates answer on the Question Paper. Additional
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *7762547120* GEOGRAPHY 0460/11 Paper 1 May/June 2016 Candidates answer on the Question Paper. Additional
Population Composition
 Unit-II Chapter-3 People of any country are diverse in many respects. Each person is unique in her/his own way. People can be distinguished by their age, sex and their place of residence. Some of the other
Unit-II Chapter-3 People of any country are diverse in many respects. Each person is unique in her/his own way. People can be distinguished by their age, sex and their place of residence. Some of the other
London Examinations IGCSE
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4370/2H London Examinations IGCSE Geography Higher Tier Paper 2H Tuesday 17 May 2005 Morning Time: 2 hours 30 minutes Materials required for examination Ruler,
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4370/2H London Examinations IGCSE Geography Higher Tier Paper 2H Tuesday 17 May 2005 Morning Time: 2 hours 30 minutes Materials required for examination Ruler,
Paper Reference. Paper Reference(s) 4370/1F London Examinations IGCSE Geography Foundation Tier Paper 1F
 Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4370/1F London Examinations IGCSE Geography Foundation Tier Paper 1F Monday 30 October 2006 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials required for examination
Centre No. Candidate No. Paper Reference(s) 4370/1F London Examinations IGCSE Geography Foundation Tier Paper 1F Monday 30 October 2006 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials required for examination
birth control birth control brain drain birth rate coastal plain commuting Consciously preventing unwanted pregnancies.
 birth control birth control Consciously preventing unwanted pregnancies. Consciously preventing unwanted pregnancies. birth rate brain drain Scientists from Britain to America The number of live births
birth control birth control Consciously preventing unwanted pregnancies. Consciously preventing unwanted pregnancies. birth rate brain drain Scientists from Britain to America The number of live births
GCE. Edexcel GCE. Geography A (8214 / 9214) Summer Edexcel GCE. Mark Scheme (Results) Geography A (8214 / 9214)
 GCE Edexcel GCE Geography A (8214 / 9214) 6462 Summer 2005 Mark Scheme (Results) Edexcel GCE Geography A (8214 / 9214) 6462 6462 Summer 2005 Mark Scheme SECTION A 1 Study Figure 1 which shows global variations
GCE Edexcel GCE Geography A (8214 / 9214) 6462 Summer 2005 Mark Scheme (Results) Edexcel GCE Geography A (8214 / 9214) 6462 6462 Summer 2005 Mark Scheme SECTION A 1 Study Figure 1 which shows global variations
Global Immigration Consultancy Services. Immigration, Study and Work temporarily in Canada
 1 GICS Global Immigration Consultancy Services A quality professional Immigration, Education & Recruitment Service provider to our clients for Canada Immigration, Study and Work temporarily in Canada A
1 GICS Global Immigration Consultancy Services A quality professional Immigration, Education & Recruitment Service provider to our clients for Canada Immigration, Study and Work temporarily in Canada A
STRENGTHENING RURAL CANADA: Fewer & Older: The Coming Population and Demographic Challenges in Rural Newfoundland & Labrador
 STRENGTHENING RURAL CANADA: Fewer & Older: The Coming Population and Demographic Challenges in Rural Newfoundland & Labrador An Executive Summary 1 This paper has been prepared for the Strengthening Rural
STRENGTHENING RURAL CANADA: Fewer & Older: The Coming Population and Demographic Challenges in Rural Newfoundland & Labrador An Executive Summary 1 This paper has been prepared for the Strengthening Rural
Canadian History 1201 Unit 6. Canada Matures: Growth in the Post-War Period ( )
 Canadian History 1201 Unit 6 Canada Matures: Growth in the Post-War Period (1945-1970) Student Workbook 6.1 Student Name: SCO 2.0: The student will be expected to demonstrate an understanding of the economic,
Canadian History 1201 Unit 6 Canada Matures: Growth in the Post-War Period (1945-1970) Student Workbook 6.1 Student Name: SCO 2.0: The student will be expected to demonstrate an understanding of the economic,
Brazil, Cuba & Mexico
 Brazil, Cuba & Mexico Standards SS6E1 Analyze different economic systems. a. Compare how traditional, command, and market economies answer the economic questions of 1-what to produce, 2- how to produce,
Brazil, Cuba & Mexico Standards SS6E1 Analyze different economic systems. a. Compare how traditional, command, and market economies answer the economic questions of 1-what to produce, 2- how to produce,
module1 ANSWERS TO Unit 1 Development ACTIVITIES ACTIVITY 1 ACTIVITY 2 ACTIVITY 3 Hint
 ANSWERS TO ACTIVITIES module1 Unit 1 Development ACTIVITY 1 1 Development is a process of change in a society, which should improve people s living conditions. (This is the simplest definition of development.
ANSWERS TO ACTIVITIES module1 Unit 1 Development ACTIVITY 1 1 Development is a process of change in a society, which should improve people s living conditions. (This is the simplest definition of development.
Paper Reference. Paper Reference(s) 4370/1F London Examinations IGCSE Geography Foundation Tier
 Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 4370/1F London Examinations IGCSE Geography Foundation Tier Paper 1F Thursday 15 November 2007 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials required
Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 4370/1F London Examinations IGCSE Geography Foundation Tier Paper 1F Thursday 15 November 2007 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials required
Household income in present day Vietnam
 2011 2nd International Conference on Humanities, Historical and Social Sciences IPEDR vol.17 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Household income in present day Vietnam Nguyen, Thanh Binh 1 Free University
2011 2nd International Conference on Humanities, Historical and Social Sciences IPEDR vol.17 (2011) (2011) IACSIT Press, Singapore Household income in present day Vietnam Nguyen, Thanh Binh 1 Free University
Internal migration within China
 Core units: Exemplars Year 8 Illustration 4: Migration within China Internal migration within China In China, there is a clear pattern of internal migration from the rural areas to the urban areas and,
Core units: Exemplars Year 8 Illustration 4: Migration within China Internal migration within China In China, there is a clear pattern of internal migration from the rural areas to the urban areas and,
STRENGTHENING RURAL CANADA: Fewer & Older: Population and Demographic Crossroads in Rural Saskatchewan. An Executive Summary
 STRENGTHENING RURAL CANADA: Fewer & Older: Population and Demographic Crossroads in Rural Saskatchewan An Executive Summary This paper has been prepared for the Strengthening Rural Canada initiative by:
STRENGTHENING RURAL CANADA: Fewer & Older: Population and Demographic Crossroads in Rural Saskatchewan An Executive Summary This paper has been prepared for the Strengthening Rural Canada initiative by:
Violation of Refugee Rights and Migration in India
 International Journal of Research in Social Sciences Vol. 7 Issue 5, May 2017, ISSN: 2249-2496 Impact Factor: 7.081 Journal Homepage: Double-Blind Peer Reviewed Refereed Open Access International Journal
International Journal of Research in Social Sciences Vol. 7 Issue 5, May 2017, ISSN: 2249-2496 Impact Factor: 7.081 Journal Homepage: Double-Blind Peer Reviewed Refereed Open Access International Journal
Key Terminology. in 1990, Ireland was overpopulated only had population of 3.5 million but 70,000 emigrated due to unemployment.
 Key Terminology Overpopulation = when there are too many people in an area for the resources of that area to maintain an adequate standard of living. in 1990, Ireland was overpopulated only had population
Key Terminology Overpopulation = when there are too many people in an area for the resources of that area to maintain an adequate standard of living. in 1990, Ireland was overpopulated only had population
Unit Six: Canada Matures: Growth in the Post-War Period ( )
 Unit Six: Canada Matures: Growth in the Post-War Period (1945-1970) 6.1 Economic changes: growth of primary and secondary industries, infrastructure, Cold War economy, labour relations Veterans Come Home
Unit Six: Canada Matures: Growth in the Post-War Period (1945-1970) 6.1 Economic changes: growth of primary and secondary industries, infrastructure, Cold War economy, labour relations Veterans Come Home
Russia. Chapter 20. Chapter 20, Section
 Chapter 20, Section World Geography Chapter 20 Russia Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 20, Section World Geography
Chapter 20, Section World Geography Chapter 20 Russia Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter 20, Section World Geography
STRENGTHENING RURAL CANADA: Fewer & Older: The Coming Demographic Crisis in Rural Ontario
 STRENGTHENING RURAL CANADA: Fewer & Older: The Coming Demographic Crisis in Rural Ontario An Executive Summary 1 This paper has been prepared for the Strengthening Rural Canada initiative by: Dr. Bakhtiar
STRENGTHENING RURAL CANADA: Fewer & Older: The Coming Demographic Crisis in Rural Ontario An Executive Summary 1 This paper has been prepared for the Strengthening Rural Canada initiative by: Dr. Bakhtiar
3.1 How does the economy of the globalised world function in different places?
 3.1 How does the economy of the globalised world function in different places? a. The balance between employment sectors (primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary) varies spatially and is changing.
3.1 How does the economy of the globalised world function in different places? a. The balance between employment sectors (primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary) varies spatially and is changing.
Population density is a measure of how crowded a population is. It looks at land area as well as population.
 Population Population density is a measure of how crowded a population is. It looks at land area as well as population. Population Density = population per unit area (unit area is usually measured in Km
Population Population density is a measure of how crowded a population is. It looks at land area as well as population. Population Density = population per unit area (unit area is usually measured in Km
In small groups work together to create lists of places you can think of that have highest populations. What continents are these countries located
 In small groups work together to create lists of places you can think of that have highest populations. What continents are these countries located on? What about most populated cities? DO NOT USE A PHONE!!!!!
In small groups work together to create lists of places you can think of that have highest populations. What continents are these countries located on? What about most populated cities? DO NOT USE A PHONE!!!!!
CANADA. Our big neighbor to the north.
 CANADA Our big neighbor to the north. CANADA VIDEO Geography made us neighbors, history made us friends, economics made us partners, and necessity made us allies. -JF Kennedy WELCOME TO CANADA Welcome
CANADA Our big neighbor to the north. CANADA VIDEO Geography made us neighbors, history made us friends, economics made us partners, and necessity made us allies. -JF Kennedy WELCOME TO CANADA Welcome
ECONOMY AND DEVELOPMENT FROM THEN TO NOW TAKEN FROM
 ECONOMY AND DEVELOPMENT FROM THEN TO NOW TAKEN FROM HTTP://MISSVHISTORY.BLOGSPOT.CA/ FIRST OCCUPANTS 1. TRADE NETWORKS BARTER BETWEEN NATIVES; NOMADIC GROUPS EXCHANGED GOODS WITH OTHERS, LIKE SEDENTARY
ECONOMY AND DEVELOPMENT FROM THEN TO NOW TAKEN FROM HTTP://MISSVHISTORY.BLOGSPOT.CA/ FIRST OCCUPANTS 1. TRADE NETWORKS BARTER BETWEEN NATIVES; NOMADIC GROUPS EXCHANGED GOODS WITH OTHERS, LIKE SEDENTARY
The EU-Brazil Relations
 The EU-Brazil Relations Introduction Brazil: Background Information The Current Economic and Political Situation The European Union EU-Brazil Relations: First Steps Strategic Partnership: Contextualization.
The EU-Brazil Relations Introduction Brazil: Background Information The Current Economic and Political Situation The European Union EU-Brazil Relations: First Steps Strategic Partnership: Contextualization.
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6693166312* GEOGRAPHY 0460/23 Paper 2 October/November 2013 Candidates answer on the Question
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6693166312* GEOGRAPHY 0460/23 Paper 2 October/November 2013 Candidates answer on the Question
A STUDY ON THE SOCIO-ECONOMIC AND DEMOGRAPHIC SIGNIFICANCE OF FIRE IN THE DEVELOPED AND THE DEVELOPING COUNTRIES
 , Volume 7, Number 2, p.57-64, 25 A STUDY ON THE SOCIO-ECONOMIC AND DEMOGRAPHIC SIGNIFICANCE OF FIRE IN THE DEVELOPED AND THE DEVELOPING COUNTRIES G. Boustras* and J.X. Wen School of Engineering, Kingston
, Volume 7, Number 2, p.57-64, 25 A STUDY ON THE SOCIO-ECONOMIC AND DEMOGRAPHIC SIGNIFICANCE OF FIRE IN THE DEVELOPED AND THE DEVELOPING COUNTRIES G. Boustras* and J.X. Wen School of Engineering, Kingston
World Industrial Regions
 World Industrial Regions North America Industrialized areas in North America Changing distribution of U.S. manufacturing Europe Western Europe Eastern Europe East Asia Manufacturing Regions Fig. 11-3:
World Industrial Regions North America Industrialized areas in North America Changing distribution of U.S. manufacturing Europe Western Europe Eastern Europe East Asia Manufacturing Regions Fig. 11-3:
4 Rebuilding a World Economy: The Post-war Era
 4 Rebuilding a World Economy: The Post-war Era The Second World War broke out a mere two decades after the end of the First World War. It was fought between the Axis powers (mainly Nazi Germany, Japan
4 Rebuilding a World Economy: The Post-war Era The Second World War broke out a mere two decades after the end of the First World War. It was fought between the Axis powers (mainly Nazi Germany, Japan
What are Treaties? The PLEA Vol. 30 No.
 The PLEA Vol. 30 No. No.11 What are Treaties? A treaty is a negotiated agreement between two or more nations. Nations all over the world have a long history of using treaties, often for land disputes and
The PLEA Vol. 30 No. No.11 What are Treaties? A treaty is a negotiated agreement between two or more nations. Nations all over the world have a long history of using treaties, often for land disputes and
NFU Seasonal Labour Survey: Results & Analysis
 NFU Seasonal Labour Survey: Results & Analysis Report contributors: Author, Hayley Campbell-Gibbons, NFU Chief Horticulture & Potatoes Adviser Data collection and analysis, David Clifford, NFU Research
NFU Seasonal Labour Survey: Results & Analysis Report contributors: Author, Hayley Campbell-Gibbons, NFU Chief Horticulture & Potatoes Adviser Data collection and analysis, David Clifford, NFU Research
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *4335501261* PAKISTAN STUDIES 2059/02 Paper 2 The Environment of Pakistan May/June 2015 Candidates answer on the Question Paper. READ THESE
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge Ordinary Level *4335501261* PAKISTAN STUDIES 2059/02 Paper 2 The Environment of Pakistan May/June 2015 Candidates answer on the Question Paper. READ THESE
History of Trade and Globalization
 History of Trade and Globalization Pre 1800 East Asian Economy Rice, textiles, metals Atlantic Economy Agricultural Products Silver Luxuries Small distance trade in necessities Rice in S-E asia, grain
History of Trade and Globalization Pre 1800 East Asian Economy Rice, textiles, metals Atlantic Economy Agricultural Products Silver Luxuries Small distance trade in necessities Rice in S-E asia, grain
Factors affecting Distribution of Population
 Factors affecting Distribution of Population 1.1 Introduction Population distribution is the spatial pattern of the dispersal of populations, formation of agglomerations, linear spreads of population,
Factors affecting Distribution of Population 1.1 Introduction Population distribution is the spatial pattern of the dispersal of populations, formation of agglomerations, linear spreads of population,
DEVELOPMENT AID IN NORTHEAST ASIA
 DEVELOPMENT AID IN NORTHEAST ASIA Sahiya Lhagva An Oven iew of Development Aid in Northeast Asia It is well known that Northeast Asia covers different economies which vary considerably in terms of economic
DEVELOPMENT AID IN NORTHEAST ASIA Sahiya Lhagva An Oven iew of Development Aid in Northeast Asia It is well known that Northeast Asia covers different economies which vary considerably in terms of economic
SMALL TOWNS: GOVERNANCE AND MIGRATION
 SMALL TOWNS: GOVERNANCE AND MIGRATION The Case of Pakistan IIED Workshop, London 06 07 January 2007 This case study is an exploration. Much of what is in it is already presented in the following documents:
SMALL TOWNS: GOVERNANCE AND MIGRATION The Case of Pakistan IIED Workshop, London 06 07 January 2007 This case study is an exploration. Much of what is in it is already presented in the following documents:
STRENGTHENING RURAL CANADA: Fewer & Older: Population and Demographic Challenges Across Rural Canada A Pan-Canadian Report
 STRENGTHENING RURAL CANADA: Fewer & Older: Population and Demographic Challenges Across Rural Canada A Pan-Canadian Report This paper has been prepared for the Strengthening Rural Canada initiative by:
STRENGTHENING RURAL CANADA: Fewer & Older: Population and Demographic Challenges Across Rural Canada A Pan-Canadian Report This paper has been prepared for the Strengthening Rural Canada initiative by:
Bringing the Census to schools
 Bringing the Census to schools 6 th Year Course In preparation for: 1 Table of Contents Introduction to Population Studies... 3 Lesson 1... 4 You will need... 4 Objectives... 4 Calculating Population Density...
Bringing the Census to schools 6 th Year Course In preparation for: 1 Table of Contents Introduction to Population Studies... 3 Lesson 1... 4 You will need... 4 Objectives... 4 Calculating Population Density...
1. Global Disparities Overview
 1. Global Disparities Overview The world is not an equal place, and throughout history there have always been inequalities between people, between countries and between regions. Today the world s population
1. Global Disparities Overview The world is not an equal place, and throughout history there have always been inequalities between people, between countries and between regions. Today the world s population
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *3079117882* GEOGRAPHY 0460/12 Paper 1 May/June 2016 Candidates answer on the Question Paper. Additional
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *3079117882* GEOGRAPHY 0460/12 Paper 1 May/June 2016 Candidates answer on the Question Paper. Additional
Modern America Assessment Settling the West and Industrialization
 Modern America Assessment Settling the West and Industrialization NAME: 1. During the 1870s, the principal agricultural product of the shaded region on this map was A. poultry B. rice C. cattle D. cotton
Modern America Assessment Settling the West and Industrialization NAME: 1. During the 1870s, the principal agricultural product of the shaded region on this map was A. poultry B. rice C. cattle D. cotton
Development Dynamics. GCSE Geography Edexcel B Practice Exam Questions and Answers
 Development Dynamics GCSE Geography Edexcel B Practice Exam Questions and Answers 2.1 Measuring Development Describe two indicators that show a country s level of development. [4 marks] This question is
Development Dynamics GCSE Geography Edexcel B Practice Exam Questions and Answers 2.1 Measuring Development Describe two indicators that show a country s level of development. [4 marks] This question is
General Certificate of Secondary Education Foundation Tier June 2014
 Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Geography (Specification A) Unit 2 Human Geography Thursday 22 May 2014 9.00
Centre Number Surname Candidate Number For Examiner s Use Other Names Candidate Signature Examiner s Initials Question Mark Geography (Specification A) Unit 2 Human Geography Thursday 22 May 2014 9.00
Atlantic Provinces. Deciduous forests. Smallest region-5% of Canada s land and 8% of its people.
 Canada Chapter 8 Canada s Regions Canada s 10 provinces and 3 territories are divided into 5 regions based on physical features, culture, and economy. Regions are more distinct than those in the US. -Smaller
Canada Chapter 8 Canada s Regions Canada s 10 provinces and 3 territories are divided into 5 regions based on physical features, culture, and economy. Regions are more distinct than those in the US. -Smaller
Analysis of Global Migration Patterns Part I: Push and Pull factors Adapted from Farhan
 Name: Analysis of Global Migration Patterns 1750-1900 - Part I: Push and Pull factors Adapted from Farhan Exercise: This exercise is designed to help you visualize areas which recommended themselves to
Name: Analysis of Global Migration Patterns 1750-1900 - Part I: Push and Pull factors Adapted from Farhan Exercise: This exercise is designed to help you visualize areas which recommended themselves to
Europe s. Natural Resources, Capital Goods, Human Capital, & Entrepreneurship. Ame. Brain Wrinkles
 Europe s Ame Natural Resources, Capital Goods, Human Capital, & Entrepreneurship STANDARDS: SS6E9 Describe factors that influence economic growth and examine their presence or absence in the United Kingdom,
Europe s Ame Natural Resources, Capital Goods, Human Capital, & Entrepreneurship STANDARDS: SS6E9 Describe factors that influence economic growth and examine their presence or absence in the United Kingdom,
Railway, Growth of Cities, Mass Production
 Railway, Growth of Cities, Mass Production New technologies appeared in a relatively short time that helped improve the lives of many Canadians. It was the beginnings of a consumer society. As we discussed
Railway, Growth of Cities, Mass Production New technologies appeared in a relatively short time that helped improve the lives of many Canadians. It was the beginnings of a consumer society. As we discussed
To be opened on receipt
 Oxford Cambridge and RSA To be opened on receipt A2 GCE ECONOMICS F585/01/SM The Global Economy STIMULUS MATERIAL *6373303001* JUNE 2016 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES This copy must not be taken into the
Oxford Cambridge and RSA To be opened on receipt A2 GCE ECONOMICS F585/01/SM The Global Economy STIMULUS MATERIAL *6373303001* JUNE 2016 INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES This copy must not be taken into the
POPULATION: DISTRIBUTION
 POPULATION: DISTRIBUTION FACTS Best to concentrate on one country NEW ZEALAND Percentage of population living in: North Island? Northern half of North Island? Auckland? Lowland areas? Urban areas? Areas/regions
POPULATION: DISTRIBUTION FACTS Best to concentrate on one country NEW ZEALAND Percentage of population living in: North Island? Northern half of North Island? Auckland? Lowland areas? Urban areas? Areas/regions
GEOGRAPHY SPECIFICATION A 1986/2
 OXFORD CAMBRIDGE AND RSA EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Secondary Education GEOGRAPHY SPECIFICATION A 1986/2 PAPER 2 HIGHER TIER Monday 5 JUNE 2006 Morning 2 hours Candidates answer on separate answer
OXFORD CAMBRIDGE AND RSA EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Secondary Education GEOGRAPHY SPECIFICATION A 1986/2 PAPER 2 HIGHER TIER Monday 5 JUNE 2006 Morning 2 hours Candidates answer on separate answer
Setting up in Denmark
 Setting up in Denmark 1. Denmark and the Danes Denmark is an attractive northern European country that offers many advantages to foreign investors. It is one of the 25 member states of the European Union
Setting up in Denmark 1. Denmark and the Danes Denmark is an attractive northern European country that offers many advantages to foreign investors. It is one of the 25 member states of the European Union
CHAPTER 11 KEY ISSUE TWO: WHERE IS INDUSTRY DISTRIBUTED?
 CHAPTER 11 KEY ISSUE TWO: WHERE IS INDUSTRY DISTRIBUTED? WORLD INDUSTRIAL REGIONS North America Industrialized areas in North America Changing distribution of U.S. manufacturing Europe Western Europe Eastern
CHAPTER 11 KEY ISSUE TWO: WHERE IS INDUSTRY DISTRIBUTED? WORLD INDUSTRIAL REGIONS North America Industrialized areas in North America Changing distribution of U.S. manufacturing Europe Western Europe Eastern
Logging Road, Transportation and Outward Migration in Sarawak: The Local Perspective of Marudi Town
 Logging Road, Transportation and Outward Migration in Sarawak: The Local Perspective of Marudi Town Bemen Win Keong Wong Faculty of Social Sciences, Department of Development Studies Universiti Malaysia
Logging Road, Transportation and Outward Migration in Sarawak: The Local Perspective of Marudi Town Bemen Win Keong Wong Faculty of Social Sciences, Department of Development Studies Universiti Malaysia
World Population A.D World Population from the Beginnings to the Present. Words
 1 Today, about 6 billion people live on our earth. Each year, the world s population grows by about 80 million. If it continues to grow at such a rate the world s population will reach 9 billion by the
1 Today, about 6 billion people live on our earth. Each year, the world s population grows by about 80 million. If it continues to grow at such a rate the world s population will reach 9 billion by the
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level *6971435557* GEOGRAPHY 2217/12 Paper 1 October/November 2010 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level *6971435557* GEOGRAPHY 2217/12 Paper 1 October/November 2010 Additional Materials: Answer Booklet/Paper
Growing Pains in the Americas THE EUROPEAN MOMENT ( )
 Growing Pains in the Americas THE EUROPEAN MOMENT (1750 1900) Or we could call today s notes: The history of the Western Hemisphere in the 19 th century as they face problems keeping order and confront
Growing Pains in the Americas THE EUROPEAN MOMENT (1750 1900) Or we could call today s notes: The history of the Western Hemisphere in the 19 th century as they face problems keeping order and confront
Newfoundland and Labrador Studies 2205
 1 Newfoundland and Labrador Studies 2205 Text Book: Newfoundland & Labrador Studies Selected Topics, NL Dept. of Education http://www.ed.gov.nl.ca/edu/k12/curriculum/documents/socialstudies/ Go directly
1 Newfoundland and Labrador Studies 2205 Text Book: Newfoundland & Labrador Studies Selected Topics, NL Dept. of Education http://www.ed.gov.nl.ca/edu/k12/curriculum/documents/socialstudies/ Go directly
M.K. Ammosov Yakut State University Faculty of Foreign Languages Department of Interpretation
 M.K. Ammosov Yakut State University Faculty of Foreign Languages Department of Interpretation Project on the general economics: «The North-East Economic Region of the Russian Federation. The main directions
M.K. Ammosov Yakut State University Faculty of Foreign Languages Department of Interpretation Project on the general economics: «The North-East Economic Region of the Russian Federation. The main directions
Industry. Tale of Two Cities
 Industry Tale of Two Cities Write these on your article! 1. Connect to Agriculture, how does NAFTA put Mexican corn farmers out of business? 2. Why does Juarez virtually transform overnight as opposed
Industry Tale of Two Cities Write these on your article! 1. Connect to Agriculture, how does NAFTA put Mexican corn farmers out of business? 2. Why does Juarez virtually transform overnight as opposed
IX Geography CHEPTER 6 : POPULATION
 IX Geography CHEPTER 6 : POPULATION Introduction: The people are important to develop the economy and society. The people make and use resources and are themselves resources with varying quality. Resources,
IX Geography CHEPTER 6 : POPULATION Introduction: The people are important to develop the economy and society. The people make and use resources and are themselves resources with varying quality. Resources,
Understanding institutions
 by Daron Acemoglu Understanding institutions Daron Acemoglu delivered the 2004 Lionel Robbins Memorial Lectures at the LSE in February. His theme was that understanding the differences in the formal and
by Daron Acemoglu Understanding institutions Daron Acemoglu delivered the 2004 Lionel Robbins Memorial Lectures at the LSE in February. His theme was that understanding the differences in the formal and
Paper Reference. Paper Reference(s) 4370/1F London Examinations IGCSE Geography Foundation Tier
 Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 4370/1F London Examinations IGCSE Geography Foundation Tier Paper 1F Tuesday 11 November 2008 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials required
Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 4370/1F London Examinations IGCSE Geography Foundation Tier Paper 1F Tuesday 11 November 2008 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials required
FECCA Submission to the Inquiry into regional skills relocation
 FECCA Submission to the Inquiry into regional skills relocation About FECCA The Federation of Ethnic Communities Councils of Australia (FECCA) is the national peak body representing the interests of Culturally
FECCA Submission to the Inquiry into regional skills relocation About FECCA The Federation of Ethnic Communities Councils of Australia (FECCA) is the national peak body representing the interests of Culturally
IGCSE Geography Unit 1: Population Dynamics
 IGCSE Geography Unit 1: Population Dynamics www.xtremepapers.com Recommended Prior Knowledge An understanding of population distribution, population change and the interrelationship of population and resources.
IGCSE Geography Unit 1: Population Dynamics www.xtremepapers.com Recommended Prior Knowledge An understanding of population distribution, population change and the interrelationship of population and resources.
The US Government Policy towards the Plains Indians
 The US Government Policy towards the Plains Indians Learning Objective To know the US Government policy towards the Plains Indians in the 1830s 1850s and assess the reasons for the changes in policy that
The US Government Policy towards the Plains Indians Learning Objective To know the US Government policy towards the Plains Indians in the 1830s 1850s and assess the reasons for the changes in policy that
Locating Places. 7. G Hudson Bay 8. D Great Bear Lake 9. B Pacific Ranges 10. I Mackenzie River 11. H Rio Grande 12. E Great Slave Lake
 Locating Places Match the letters on the map with the physical features of the United States and Canada. Write your answers on a sheet of paper. 7. G Hudson Bay 8. D Great Bear Lake 9. B Pacific Ranges
Locating Places Match the letters on the map with the physical features of the United States and Canada. Write your answers on a sheet of paper. 7. G Hudson Bay 8. D Great Bear Lake 9. B Pacific Ranges
TASC Social Studies Sample Test Items
 TASC Sample Test Items This chart is the stimulus for Items 1 and 2. The chart lists some examples of international organizations and their functions. The use of charts in social studies allows students
TASC Sample Test Items This chart is the stimulus for Items 1 and 2. The chart lists some examples of international organizations and their functions. The use of charts in social studies allows students
NATIONAL POPULATION PLAN FOR REGIONAL AUSTRALIA
 NATIONAL POPULATION PLAN FOR REGIONAL AUSTRALIA February 2019 KNOWLEDGE POLICY PRACTICE KEY POINTS People vote with their feet and many are showing strong preferences for living in regions. Enhancing liveability
NATIONAL POPULATION PLAN FOR REGIONAL AUSTRALIA February 2019 KNOWLEDGE POLICY PRACTICE KEY POINTS People vote with their feet and many are showing strong preferences for living in regions. Enhancing liveability
FECCA Regional Migration Policy. February 2010
 FECCA Regional Migration Policy February 2010 Aims of FECCA FECCA is the national peak body representing Australians from diverse multicultural backgrounds. We provide advocacy, develop policy and promote
FECCA Regional Migration Policy February 2010 Aims of FECCA FECCA is the national peak body representing Australians from diverse multicultural backgrounds. We provide advocacy, develop policy and promote
SS 11: COUNTERPOINTS CH. 13: POPULATION: CANADA AND THE WORLD NOTES the UN declared the world s population had reached 6 billion.
 SS 11: COUNTERPOINTS CH. 13: POPULATION: CANADA AND THE WORLD NOTES 1 INTRODUCTION 1. 1999 the UN declared the world s population had reached 6 billion. 2. Forecasters are sure that at least another billion
SS 11: COUNTERPOINTS CH. 13: POPULATION: CANADA AND THE WORLD NOTES 1 INTRODUCTION 1. 1999 the UN declared the world s population had reached 6 billion. 2. Forecasters are sure that at least another billion
SS6 Unit 1: Latin America. Summative Assessment Review
 SS6 Unit 1: Latin America Summative Assessment Review 1. Which is found near the 1 on the map? a. Panama Canal b. Atacama Desert c. Andes Mountains d. Sierra Madre Mountains 2. Which number on the map
SS6 Unit 1: Latin America Summative Assessment Review 1. Which is found near the 1 on the map? a. Panama Canal b. Atacama Desert c. Andes Mountains d. Sierra Madre Mountains 2. Which number on the map
CFE HIGHER GEOGRAPHY: POPULATION MIGRATION
 CFE HIGHER GEOGRAPHY: POPULATION MIGRATION A controversial issue! What are your thoughts? WHAT IS MIGRATION? Migration is a movement of people from one place to another Emigrant is a person who leaves
CFE HIGHER GEOGRAPHY: POPULATION MIGRATION A controversial issue! What are your thoughts? WHAT IS MIGRATION? Migration is a movement of people from one place to another Emigrant is a person who leaves
! Elements of Worldview
 Geography Identifying Through The Actions and Decisions Of Canadians Climate (weather, seasons, temperature): Geography - How do these factors impact the actions and decisions of Canadians? Canada is quite
Geography Identifying Through The Actions and Decisions Of Canadians Climate (weather, seasons, temperature): Geography - How do these factors impact the actions and decisions of Canadians? Canada is quite
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6205074481* GEOGRAPHY 0460/11 Paper 1 October/November 2015 Candidates answer on the Question Paper.
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *6205074481* GEOGRAPHY 0460/11 Paper 1 October/November 2015 Candidates answer on the Question Paper.
A. Panama B. Canada C. India D. Cameroon
 1 Which country has the highest rate of natural population increase? A. Panama B. Canada C. India D. Cameroon 2 Which statement best explains why a country may have a zero natural population increase?
1 Which country has the highest rate of natural population increase? A. Panama B. Canada C. India D. Cameroon 2 Which statement best explains why a country may have a zero natural population increase?
THE DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITION MODEL
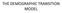 THE DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITION MODEL What are the stages of the Demographic Transition Model? In Stage 1, which applied to most of the world before the Industrial Revolution, both birth rates and death rates
THE DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITION MODEL What are the stages of the Demographic Transition Model? In Stage 1, which applied to most of the world before the Industrial Revolution, both birth rates and death rates
Dimensions of rural urban migration
 CHAPTER-6 Dimensions of rural urban migration In the preceding chapter, trends in various streams of migration have been discussed. This chapter examines the various socio-economic and demographic aspects
CHAPTER-6 Dimensions of rural urban migration In the preceding chapter, trends in various streams of migration have been discussed. This chapter examines the various socio-economic and demographic aspects
Unit 1 Test (Version B)
 Unit 1 Test (Version B) 1. The city of Lewisville has a population of 1,000 people living in 100 square miles. What is the population density of Lewisville? a. 10 people per square mile b. 50 people per
Unit 1 Test (Version B) 1. The city of Lewisville has a population of 1,000 people living in 100 square miles. What is the population density of Lewisville? a. 10 people per square mile b. 50 people per
Manufacturing in queretaro. everything you need to know
 Manufacturing in queretaro everything you need to know Table of Contents INTRODUCTION AUTOMOTIVE AND AEROSPACE INDUSTRIES LOCATION 1 2 NEARBY MANUFACTURING AND MATERIALS SOURCING LABOR AND WORKFORCE ECONOMY
Manufacturing in queretaro everything you need to know Table of Contents INTRODUCTION AUTOMOTIVE AND AEROSPACE INDUSTRIES LOCATION 1 2 NEARBY MANUFACTURING AND MATERIALS SOURCING LABOR AND WORKFORCE ECONOMY
Paper Reference. Paper Reference(s) 4370/1F London Examinations IGCSE Geography Foundation Tier. Thursday 8 May 2008 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes
 Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 4370/1F London Examinations IGCSE Geography Foundation Tier Paper 1F Thursday 8 May 2008 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials required
Centre No. Candidate No. Surname Signature Paper Reference(s) 4370/1F London Examinations IGCSE Geography Foundation Tier Paper 1F Thursday 8 May 2008 Morning Time: 1 hour 45 minutes Materials required
National Farmers Federation
 National Farmers Federation Submission to the 457 Programme Temporary Skilled Migration Income Threshold (TSMIT) 8 March 2016 Page 1 NFF Member Organisations Page 2 The National Farmers Federation (NFF)
National Farmers Federation Submission to the 457 Programme Temporary Skilled Migration Income Threshold (TSMIT) 8 March 2016 Page 1 NFF Member Organisations Page 2 The National Farmers Federation (NFF)
Central America and the Caribbean
 Chapter 11, Section World Geography Chapter 11 Central America and the Caribbean Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter
Chapter 11, Section World Geography Chapter 11 Central America and the Caribbean Copyright 2003 by Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ. All rights reserved. Chapter
Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission
 2009. S28 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission JUNIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2009 GEOGRAPHY - HIGHER LEVEL FRIDAY, 5 JUNE - AFTERNOON, 2.00 to 4.00 SECTION 2 (90 MARKS) Answer
2009. S28 Coimisiún na Scrúduithe Stáit State Examinations Commission JUNIOR CERTIFICATE EXAMINATION, 2009 GEOGRAPHY - HIGHER LEVEL FRIDAY, 5 JUNE - AFTERNOON, 2.00 to 4.00 SECTION 2 (90 MARKS) Answer
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *1305303660* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/23 Paper 2 October/November 2016 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *1305303660* ENVIRONMENTAL MANAGEMENT 0680/23 Paper 2 October/November 2016 1 hour 45 minutes Candidates
Globalization and the North: Impacts of Trade Treaties On Canada s Northern Governments
 Globalization and the North: Impacts of Trade Treaties On Canada s Northern Governments By Noel Schacter, Jim Beebe and Luigi Zanasi Copyright 2004 Canadian Centre for Policy Alternatives and the authors.
Globalization and the North: Impacts of Trade Treaties On Canada s Northern Governments By Noel Schacter, Jim Beebe and Luigi Zanasi Copyright 2004 Canadian Centre for Policy Alternatives and the authors.
January 2018 Special Preview Edition
 January 2018 Special Preview Edition What s inside this booklet? The contents you ll explore 2 Americas 4 Europe 6 Far East & Oceania 8 Central & South Asia 10 Africa & Middle East 12 International 14
January 2018 Special Preview Edition What s inside this booklet? The contents you ll explore 2 Americas 4 Europe 6 Far East & Oceania 8 Central & South Asia 10 Africa & Middle East 12 International 14
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *4468786993* GEOGRAPHY 0460/13 Paper 1 May/June 2016 Candidates answer on the Question Paper. Additional
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International General Certificate of Secondary Education *4468786993* GEOGRAPHY 0460/13 Paper 1 May/June 2016 Candidates answer on the Question Paper. Additional
OECD Rural Development Policy: Scotland. Betty-Ann Bryce Administrator OECD Regional and Rural Unit
 OECD Rural Development Policy: Scotland Betty-Ann Bryce Administrator OECD Regional and Rural Unit Roadmap 1. About OECD Rural Programme 2. New Rural Paradigm 3. Common threads in OECD Countries 4. Placing
OECD Rural Development Policy: Scotland Betty-Ann Bryce Administrator OECD Regional and Rural Unit Roadmap 1. About OECD Rural Programme 2. New Rural Paradigm 3. Common threads in OECD Countries 4. Placing
Table A2-1. Civilian Labor Force, Sanford/Springvale Labor Force Unemployed Unemployment Rate 5.8% 5.
 APPENDIX A2 THE LOCAL ECONOMY (September 10, 2002) From the mid 19 th Century, the Town of Sanford s economic importance in the region has been as a manufacturing community. In the late 19 th Century,
APPENDIX A2 THE LOCAL ECONOMY (September 10, 2002) From the mid 19 th Century, the Town of Sanford s economic importance in the region has been as a manufacturing community. In the late 19 th Century,
