SS 11: COUNTERPOINTS CH. 13: POPULATION: CANADA AND THE WORLD NOTES the UN declared the world s population had reached 6 billion.
|
|
|
- Elfrieda McCarthy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 SS 11: COUNTERPOINTS CH. 13: POPULATION: CANADA AND THE WORLD NOTES 1 INTRODUCTION the UN declared the world s population had reached 6 billion. 2. Forecasters are sure that at least another billion will be added by the year Some people see the growth in population as a contributor to shortages in energy, housing, and food, and an increase in pollution, unemployment, and the destruction of the environment. 4. According to optimists, world population will increase to 9 billion in 2054 and level off at 10 billion after By then, they predict, technology will have found ways to provide for the increased numbers of people years ago there were about 300 million people on Earth. In 1804, there were 1 billion. 6. The 20 th century began with world population under 2 billion and ended with triple that number BCE AD 1750 about people each year were added to the Earth s population. Today that number is added in less than 7 hours. DEMOGRAPHY 1. Demography is the statistical study of human population. 2. It helps us to understand the causes and consequences of population change. The Census: Counting People 1. Today, according to the UN, a census of population is the total process of collecting, compiling, and publishing demographic, economic, and social data pertaining to a particular time, to all persons in a particular country.
2 2. Since Confederation in 1867, Canada has had a major census every 10 years in the first year after the end of each decade and a less detailed one every 5 years Statistics Canada collects detailed information on population numbers and population characteristics such as age and education. 4. All Canadians are required by law to be counted in the census. 5. A selection of people has to give more detailed information about their accommodations, household contents, income, buying habits, etc. 6. Surveys on market trends, television viewing patterns, and voting preferences, together with health, scholastic, and job-related statistics, amounts to a major demographic file on every Canadian. 7. A developed country like Canada has the resources to keep its data current, yet its figures still have a margin for error. 8. In developing countries, the census data are usually much less accurate because the registration of births and deaths is not as complete as in developed countries. Population Rates Go Figure! 1. Demographers are most interested in statistics that help them predict and explain changes in society. E.g. the number of working women will have an effect on the birth rate. 2. The components of population change are: how many people are born, how many die, and how many move in or out of an area. Equation: Births deaths + immigrants emigrants = increase or decrease of population 3. Demographers use rates per thousand when figuring population change.
3 4. Crude birth rate is calculated by dividing the number of births in one year by the population and then multiplying the result by The same method is used to calculate crude death rate. 5. Subtracting deaths from births gives the rate of natural increase. 6. Canada s annual crude birth rate is about eleven per thousand, and the crude death rate is about seven per thousand. 7. The natural increase of the Canadian population for a given year is six per thousand. This is usually expressed as 0.6% and does not include immigrants. 8. The Rule of Seventy = doubling time is approximately equal to 70 divided by the growth rate (in per cent) per year. E.g. Gabon at the present rate of natural increase has a doubling time of approximately 47 years: 70 divided by 1.5 (% growth per year) = 46.7 years. 9. Exponential rate of increase = e.g. a couple has 4 children, and each of these grows up to produce 4 children. By the 3 rd generation the couple will have 16 descendants. The Effects of Migrations 1. The immigration rates and emigration rates are calculated in a similar manner to birth and death rates. The difference between the two gives the net migration rate. 2. Net migration rate is given as a rate per thousand. 3. A combination of the birth rate, the death rate, and the net migration rate gives a complete picture of the annual change in the Canadian population: Birth Rate (BR) Death Rate (DR) + Net Migration Rate (NMR) = Population Growth Rate THE DEMOGRAPHIC REVOLUTION 1. Before the 1700s people had a life expectancy the average number of years that an individual is expected to live of little more than 30 years. (Today in Canada life expectancy is over 75 years.) 3
4 Disease, poor medical care, poor nutrition, and unsanitary conditions contributed to the high death rate. Families needed to have many children to ensure a few survived. Large families were needed to help farm the land, from which most people made a living, and to provide security for parents in old age. This is still common today in many developing countries. 2. The rapid increases in population growth after 1750 were mainly due to falling death rates. The agricultural revolution increased food production, so that people had better diets. Hygiene and medical knowledge improved. 3. The falling death rate was finally matched by a decline in the birth rate. 3 likely reasons: economic development, the move to cities, and rising standards of living. 4. After WW II, the World Health Organization (WHO) and aid programs made improved health measures available to all countries. Death rates fell, but birth rates are still high in many developing countries. The Demographic Transition Model 1. shows changes over a period of time in 3 elements: birth rates, death rates, and trends in overall population numbers. 2. assumes that in any country high birth rates and high death rates will gradually fall. 3. Because the model is based on what has happened in developed countries, it assumes that countries will pass through periods of industrialization and urbanization on the way to reduced birth and death rates. 4. is useful in showing how the population growth rates of countries that are industrializing are in a state of transition. THE AGE STRUCTURE OF POPULATIONS 1. Demographers divide populations into 3 age groups: children up to age 15; working adults from 16 to 64; and adults 65 and older. 4
5 2. This gives the dependency ratio = the proportion of the population that is being supported by the working age group census Canada s population included 21% children and 12% adults 65 years and older = dependency load of 33%. Bangladesh has a dependency rate of 53% = 47% children and 6% adults aged 65 years and older. Population Pyramids 1. graphs that show the age and sex structure of a population. 2. A series of horizontal bar graphs for the male and female populations are placed back to back at age intervals of five years, called cohorts. 3. Useful in comparing the population structures of different countries. 4. Countries with high birth rates have many children and an expanding population. A stable population will have birth rates and death rates in balance. A contracting population will have a growth rate below replacement level. 5. In general, the expanding pyramids are representative of developing countries, while the stable and contracting pyramids represent developed countries. Canada s Population: The Past and the Future 1. Canada s birth rate and death rate have been dropping steadily in the past 30 years. This means the population is getting older. 2. In 1951, 1 in 10 Canadians was over 65 years of age. In 2020, 1 in 5 will be over that age. 3. Life expectancy in Canada increased from an average of 45 years in 1900 to 65 by 1950 and to 79 by the year This trend is the same for most developed countries. 4. The increasing numbers of elderly people put immense strains on social and medical services. There are fewer children to look after aging parents. 5
6 5. The age structure of Canada s population is one of the main factors the federal government considers when deciding on the number of immigrants Canada should accept each year Without immigration between 1991 and 1996, our population would have shrunk by almost instead of increasing by more than The average age of the Canadian population would have increased rapidly. 7. The number of immigrants entering Canada fluctuates above or below the level. This is far from the federal government s goal, which is to have annual immigration equal 1% of the population. 8. Immigration numbers have never come near the record level of immigrants in 1913, which represented 5.5% of a population of 7.3 million. 9. The number of refugees accepted into Canada in 1999 was close to the projected number of The single largest group of refugees came from China. Dependency: Too Young or Too Old 1. There has been a major change in the age structure of the world s population as the numbers of people have increased. There have never been so many people in the dependent category. 2. E.g. Japan the life expectancy is 81 years for males and 84 for females, the highest in the world. If present trends continue, ¼ of the Japanese population will be over 65 by the year At the other end of the scale, some developing countries have young dependents under the age of 15 making up ½ their population. Any fall in birth rates in these areas has been offset by a greater number of women who can bear children, even if families are smaller. These countries remain in a cycle of poverty, as their limited resources and attempts to improve development are swallowed up by young populations.
7 THE ONE-CHILD POLICY: CHINA S SOLUTION 7 1. Nearly 1/5 of the world s population lives in China. Even with growth rates below the world average, China adds 20 million children to its population each year. 2. These are 20 million more mouths to feed in a country that depends on agriculture, yet where less than 15% of the land is suitable for cultivation. Although it is one of the largest countries in the world, ½ of China s area is mountains, hills, and deserts. 3. The leader of the newly established Communist government in 1949, Mao Zedong, encouraged increases in the population of 540 million He saw this as a way to make China into a great power. When challenged to explain how China would feed the growing population, Mao pointed out that every stomach comes with two hands attached. 4. By 1972,the population had swelled to 852 million. Dealing with growth rates reaching 2.85% was using up over ½ the output of China s economy s the government reacted with a publicity campaign encouraging people to limit their family to 2 children. This had the effect of reducing the growth rate to 1.57%, still too high for a population approaching 900 million (Mao Zedong had died in1976) the Chinese government launched a policy of one child per family, a challenge for a culture that valued large families. 7. Cash rewards, free medical care, and improved educational and housing opportunities were offered as incentives for those who had one child. 8. People who did not cooperate were fined for each child after the firstborn, and lost many medical and educational privileges. Pressure to be sterilized and have abortions was common at the height of the program in the mid-1980s. 9. By 1980, China s birth rate had been halved. The success of the onechild policy was greater in urban than in rural areas, which could not be as tightly controlled. Sons were valued as labourers on the farms, and
8 they were expected to look after their parents in their old age. This, and reports of forced abortions and infanticide if the first-born was a girl, led the government to relax the policy in the late 1980s. A second child was allowed in rural areas if the first-born was a girl or was born with a disability. 10. Today, China s one-child policy is firmly established in the cities. Still, China began to face a baby boom in the 1990s, with hundreds of millions of rural peasants apparently ignoring the policy. 11. The results of the one-child policy on Chinese society are now beginning to be felt. The growth in the rural population is putting more pressure on farmland. This may lead to a migration of massive proportions by the younger rural population to cities. 12. Little Emperor Syndrome children who have been raised in singlechild families and feel no sense of obligation to their families or society 13. Canadians particularly have felt the immediate effects of population pressure in southern China with the arrival of smuggled Chinese migrants on Canada s West Coast. 14. And if a controlled society like China has such difficulty in limiting population increase, what hope is there for India, which will eventually outstrip China to have the world s largest population? WHERE DO SIX BILLION PEOPLE LIVE? 1. Population distribution = the way people are spaced over the Earth s surface. 2. ecumene (from Greek) = permanently inhabited places 3. Approximately 35% of the world s land area is not good for settlement. 4. Over ½ the population lives on only 5% of the land, and 90% of people live on 20% of the land. 5. 2/3 of people live within 500 km of the ocean. 6. population density = number of people in a given area 8
9 7. crude densities = calculated by dividing the population of a country by its area. 8. See the web in Figure that shows some of the major physical and human factors that affect population density. What are the Limits of Population Growth? 1. British economist, Thomas Malthus, published Essays on the Principles of Population in 1798, at the beginning of the Industrial Revolution. He predicted that the numbers of people would be checked by diseases and famine at under 14 million as the population outstripped the food supply. 2. Malthus was not able to foresee the improvements in agriculture, transportation, hygiene, and medicine that would make larger populations possible. Also, in the 19 th century, migrations of millions opened up new farmlands in North and South America, Asiatic Russia, and Australia. 3. Some thinkers, called neo-malthusians, predict that in the long term, Malthus was right. Disaster will overtake populations in the world s poorest developing countries in the next 50 years. They predict increasing shortages of arable (used for farming) land to grow enough food, conflicts over fresh water, declining fish stocks, and the spread of AIDS or other diseases. Africa will be most vulnerable to these threats. 4. Neo-Malthusians claim that migrations, technology, and new farming lands cannot solve the problems of the poorest developing countries. Studies from UBC point out that if everyone were to live at the North American standard of living, the resources of 3 Earths would be required. 5. carrying capacity = the idea that land can produce only so much in the way of food or goods given the technology of the time. As population outstrips food supplies, it is reduced by checks such as famine and disease until it stabilizes close to the land s carrying capacity. 6. The UN, the World Bank, and most international aid societies are more positive. 9
10 They claim technological developments, increased trade, and more efficient ways of sharing the Earth s resources will ease the problems of developing nations. They point to the rapid increases in population in the 20 th century that were always matched by increased food production. Food production has increased by 25% since the 1960s. New developments in genetic engineering of crops and animals could repeat this success. 7. Those with a positive outlook claim that educational programs will increase awareness of the benefits of population control. that enough food is produced to feed everyone adequately, and it is the distribution system that causes malnutrition in some countries. that increased globalization will help to create a more equal distribution of food and resources. that raising the standard of living of people around the world will cause population growth to level off. Nutritional Density 1. There are great differences in the productivity of farmlands in different parts of the world. e.g. Fraser Valley in southern B.C. has exceptionally rich agricultural soils, but its output is restricted by a short growing season. Canadian farms cannot match the output of areas like southern China, where rich soils and ideal climate produce 3 crops a year. This means that a square km of farmland in southern China can produce far more food for people than a similar area in the Fraser Valley. 2. Nutritional density of land is a measure of how much nutrition in calories can be produced from the land. EARTH S CROWDED FUTURE 1. Age structure is an important factor in determining how fast a population will increase. 2. Developing countries with high numbers of young dependents will likely experience greater population growth than developed countries. 10
11 3. Birth rates will continue to decline worldwide, but the large base in countries like India means increases will continue to be too high for the population to be sustained without environmental damage The future will be determined by the youth of developing nations. The age at which they choose to marry, and the number of children they have, may be the most important decisions of the 21 st century.
Population Trends and Issues
 11 Population Trends and Issues GUIDING QUESTIONS Economy & Human Geography What are the components of population change. What is the formula used to calculate population growth in a country? Explain the
11 Population Trends and Issues GUIDING QUESTIONS Economy & Human Geography What are the components of population change. What is the formula used to calculate population growth in a country? Explain the
Chapter 11 - Population
 Chapter 11 - Population Social Studies 11 Mrs Mactavish Images and notes graciously borrowed and adapted from Thielmann s Web River (http://dpts.sd57.bc.ca/~gthielmann/ss11/index.html) Part A - Population
Chapter 11 - Population Social Studies 11 Mrs Mactavish Images and notes graciously borrowed and adapted from Thielmann s Web River (http://dpts.sd57.bc.ca/~gthielmann/ss11/index.html) Part A - Population
CHAPTER 11 POPULATION TRENDS AND ISSUES
 CHAPTER 11 POPULATION TRENDS AND ISSUES DEMOGRAPHY From the Greek Demo = people Graphy = writing/field of study AMERICAN MUSEUM OF NATURAL HISTORY - HUMAN POPULATION THROUGH TIME OVERPOPULATION Overpopulation
CHAPTER 11 POPULATION TRENDS AND ISSUES DEMOGRAPHY From the Greek Demo = people Graphy = writing/field of study AMERICAN MUSEUM OF NATURAL HISTORY - HUMAN POPULATION THROUGH TIME OVERPOPULATION Overpopulation
What is Human Resource?
 Human Resources What is resource? What is Human Resource? Human Resource Human resources are the people who make up the workforce of an organization, business sector, or economy. People are a nation s
Human Resources What is resource? What is Human Resource? Human Resource Human resources are the people who make up the workforce of an organization, business sector, or economy. People are a nation s
Demography. Demography is the study of human population. Population is a dynamic open systems with inputs, processes and outputs.
 Population Demography Demography is the study of human population. Population is a dynamic open systems with inputs, processes and outputs. This means that change constantly occurs in population numbers,
Population Demography Demography is the study of human population. Population is a dynamic open systems with inputs, processes and outputs. This means that change constantly occurs in population numbers,
Population & Migration
 Population & Migration Population Distribution Humans are not distributed evenly across the earth. Geographers identify regions of Earth s surface where population is clustered and regions where it is
Population & Migration Population Distribution Humans are not distributed evenly across the earth. Geographers identify regions of Earth s surface where population is clustered and regions where it is
Unit 2 People and the Planet Population Dynamics
 Unit 2 People and the Planet Population Dynamics 1. Use the glossary and chapter 9 in your text book to define the words below. A. Demographer = A person who studies population B. Population= The total
Unit 2 People and the Planet Population Dynamics 1. Use the glossary and chapter 9 in your text book to define the words below. A. Demographer = A person who studies population B. Population= The total
Human Population Growth Through Time
 Human Population Growth Through Time Current world population: 7.35 Billion (Nov. 2016) http://www.worldometers.info/world-population/ 2012 7 billion 1999 13 years 12 years 1974 1927 1804 13 years 14 years
Human Population Growth Through Time Current world population: 7.35 Billion (Nov. 2016) http://www.worldometers.info/world-population/ 2012 7 billion 1999 13 years 12 years 1974 1927 1804 13 years 14 years
Human Resources. There are 500 children in my How many. My village has 1,000 people. school. people do you think, there are in the whole world?
 Human Resources Do you know? The Government of India has a Ministry of Human Resource Development. The Ministry was created in 1985 with an aim to improve people s skills. This just shows how important
Human Resources Do you know? The Government of India has a Ministry of Human Resource Development. The Ministry was created in 1985 with an aim to improve people s skills. This just shows how important
Chapter 6: Human Population & Its Impact How many is too many? 7 billion currently; 1.6 mill. more each week ~2.4 bill. more by 2050 Developing 82%
 Chapter 6: Human Population & Its Impact How many is too many? 7 billion currently; 1.6 mill. more each week ~2.4 bill. more by 2050 Developing 82% of population Developed high resource use; (more coming
Chapter 6: Human Population & Its Impact How many is too many? 7 billion currently; 1.6 mill. more each week ~2.4 bill. more by 2050 Developing 82% of population Developed high resource use; (more coming
10/24/2017. China. Labor Shortage in China?! Outline. Population Pattern. Population from Censuses
 China Population and Family Planning (chapter 6) Labor Shortage in China?! 1.4 Billion vs. 325 million (U.S.) Made in China, China as the factory of the world V.S. Chinese Labor, Cheap No More In Coastal
China Population and Family Planning (chapter 6) Labor Shortage in China?! 1.4 Billion vs. 325 million (U.S.) Made in China, China as the factory of the world V.S. Chinese Labor, Cheap No More In Coastal
 http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ymwwrgv_aie Demographics Demography is the scientific study of population. Demographers look statistically as to how people are distributed spatially by age, gender, occupation,
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ymwwrgv_aie Demographics Demography is the scientific study of population. Demographers look statistically as to how people are distributed spatially by age, gender, occupation,
Pages What is cultural diffusion? 2. What is diversity?
 10.24.16 Pages 96-97 1. What is cultural diffusion? 2. What is diversity? POPULATION & MOVEMENT Core Concept 6 Population Growth World Population = ~7 Billion Demographers are people who study human populations
10.24.16 Pages 96-97 1. What is cultural diffusion? 2. What is diversity? POPULATION & MOVEMENT Core Concept 6 Population Growth World Population = ~7 Billion Demographers are people who study human populations
The Human Population and Its Impact. Chapter 6
 The Human Population and Its Impact Chapter 6 Core Case Study: Are There Too Many of Us? (1) Estimated 2.4 billion more people by 2050 Are there too many people already? Will technological advances overcome
The Human Population and Its Impact Chapter 6 Core Case Study: Are There Too Many of Us? (1) Estimated 2.4 billion more people by 2050 Are there too many people already? Will technological advances overcome
A population with a rising average age, with a growing proportion of people aged over 65yrs. Ageing population
 Ageing population Age structure Agricultural change A population with a rising average age, with a growing proportion of people aged over 65yrs Percentage of the population (or number of people of each
Ageing population Age structure Agricultural change A population with a rising average age, with a growing proportion of people aged over 65yrs Percentage of the population (or number of people of each
In small groups work together to create lists of places you can think of that have highest populations. What continents are these countries located
 In small groups work together to create lists of places you can think of that have highest populations. What continents are these countries located on? What about most populated cities? DO NOT USE A PHONE!!!!!
In small groups work together to create lists of places you can think of that have highest populations. What continents are these countries located on? What about most populated cities? DO NOT USE A PHONE!!!!!
Supplementary Notes: (PJ Shlachtman, Miller book) Human Population: Growth, Demography, and Carrying Capacity
 Supplementary Notes: (PJ Shlachtman, Miller book) Human Population:, Demography, and Carrying Capacity Factors Affecting Human Population Size Pop. size is affected by birth s, death s, emigration and
Supplementary Notes: (PJ Shlachtman, Miller book) Human Population:, Demography, and Carrying Capacity Factors Affecting Human Population Size Pop. size is affected by birth s, death s, emigration and
Population density is a measure of how crowded a population is. It looks at land area as well as population.
 Population Population density is a measure of how crowded a population is. It looks at land area as well as population. Population Density = population per unit area (unit area is usually measured in Km
Population Population density is a measure of how crowded a population is. It looks at land area as well as population. Population Density = population per unit area (unit area is usually measured in Km
Case study: China s one-child policy
 Human Population Case study: China s one-child policy In 1970, China s 790 million people faced starvation The government instituted a onechild policy China s growth rate plummeted In 1984, the policy
Human Population Case study: China s one-child policy In 1970, China s 790 million people faced starvation The government instituted a onechild policy China s growth rate plummeted In 1984, the policy
Some important terms and Concepts in population dynamics
 By Dr. Sengupta, CJD International School, Braunschweig Some important terms and Concepts in population dynamics DEMOGRAPHY- is the study of population Population Density Population per unit of land area;
By Dr. Sengupta, CJD International School, Braunschweig Some important terms and Concepts in population dynamics DEMOGRAPHY- is the study of population Population Density Population per unit of land area;
Chapter 12. The study of population numbers, distribution, trends, and issues.
 Chapter 12 Population Challenges Demography: The study of population numbers, distribution, trends, and issues. Population Statistics for October, 2004, Land Area (Square Km.) And Population Density Canada
Chapter 12 Population Challenges Demography: The study of population numbers, distribution, trends, and issues. Population Statistics for October, 2004, Land Area (Square Km.) And Population Density Canada
Chapter 5. World Population. Population. Population Geography. Population geography. Emigration Immigration Demography. What s the world population?
 CO.6 Chapter 5 Population Geography Population Population geography Distribution of humankind Emigration Immigration Demography Specific group characteristics World Population What s the world population?
CO.6 Chapter 5 Population Geography Population Population geography Distribution of humankind Emigration Immigration Demography Specific group characteristics World Population What s the world population?
The myth of an optimal number
 Published on N-IUSSP.ORG February 29, 2016 Do we need a population policy? Jacques Vallin From the writings of Plato (4th century BCE) on the population of the ideal Greek city, to the famous precept of
Published on N-IUSSP.ORG February 29, 2016 Do we need a population policy? Jacques Vallin From the writings of Plato (4th century BCE) on the population of the ideal Greek city, to the famous precept of
Population & Migration
 Population & Migration Population Distribution Humans are not distributed evenly across the earth. Geographers identify regions of Earth s surface where population is clustered and regions where it is
Population & Migration Population Distribution Humans are not distributed evenly across the earth. Geographers identify regions of Earth s surface where population is clustered and regions where it is
FRQ 1 Population growth rates vary around the world. Given this fact, answer the following:
 AP Human Geography Unit II. Population and Migration Free Response Questions FRQ 1 Population growth rates vary around the world. Given this fact, answer the following: A) Explain the difference between
AP Human Geography Unit II. Population and Migration Free Response Questions FRQ 1 Population growth rates vary around the world. Given this fact, answer the following: A) Explain the difference between
2. In what stage of the demographic transition model are most LDC? a. First b. Second c. Third d. Fourth e. Fifth
 1. The three largest population clusters in the world are in a. East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia b. East Asia, South Asia, South America c. Africa, South Asia, East Asia d. Australia, South Asia,
1. The three largest population clusters in the world are in a. East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia b. East Asia, South Asia, South America c. Africa, South Asia, East Asia d. Australia, South Asia,
World Population A.D World Population from the Beginnings to the Present. Words
 1 Today, about 6 billion people live on our earth. Each year, the world s population grows by about 80 million. If it continues to grow at such a rate the world s population will reach 9 billion by the
1 Today, about 6 billion people live on our earth. Each year, the world s population grows by about 80 million. If it continues to grow at such a rate the world s population will reach 9 billion by the
Changing Times, Changing Enrollments: How Recent Demographic Trends are Affecting Enrollments in Portland Public Schools
 Portland State University PDXScholar School District Enrollment Forecast Reports Population Research Center 7-1-2000 Changing Times, Changing Enrollments: How Recent Demographic Trends are Affecting Enrollments
Portland State University PDXScholar School District Enrollment Forecast Reports Population Research Center 7-1-2000 Changing Times, Changing Enrollments: How Recent Demographic Trends are Affecting Enrollments
Population. Thursday, March 19, Geography 05: Population and Migration. Population geography. Emigration: Immigration:
 Thursday, March 19, 2015 Geography 05: Population and Migration Population Population geography Distribution of humankind Emigration: The flow of people out of a place Immigration: The flow of people into
Thursday, March 19, 2015 Geography 05: Population and Migration Population Population geography Distribution of humankind Emigration: The flow of people out of a place Immigration: The flow of people into
1. GEOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF POPULATION Population & Migration
 1. GEOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF POPULATION Population & Migration BASICS OF DEMOGRAPHY Demography - study of: POPULATION DISTRIBUTION Distribution: (Distribution is ) Living space of humans on earth s surface:
1. GEOGRAPHIC ANALYSIS OF POPULATION Population & Migration BASICS OF DEMOGRAPHY Demography - study of: POPULATION DISTRIBUTION Distribution: (Distribution is ) Living space of humans on earth s surface:
TOPICS INCLUDE: Population Growth Demographic Data Rule of 70 Age-Structure Pyramids Impact of Growth UNIT 3: POPULATION
 TOPICS INCLUDE: Population Growth Demographic Data Rule of 70 Age-Structure Pyramids Impact of Growth UNIT 3: POPULATION # of individuals in a given area Uniform equally spaced Clumped/Clustered individuals
TOPICS INCLUDE: Population Growth Demographic Data Rule of 70 Age-Structure Pyramids Impact of Growth UNIT 3: POPULATION # of individuals in a given area Uniform equally spaced Clumped/Clustered individuals
Module 2.1: Population (ch. 2) 1. Using the population pyramid below, identify which stage of growth the country is in?
 1. Using the population pyramid below, identify which stage of growth the country is in? a. Low Growth b. High Growth c. Moderate Growth d. Stationary Growth 2. What type of population density is measured
1. Using the population pyramid below, identify which stage of growth the country is in? a. Low Growth b. High Growth c. Moderate Growth d. Stationary Growth 2. What type of population density is measured
Age Cohort A group of people who share the same age. age distribution The age structure of a population.
 Anti- Natalist A government policy concerned with limiting population growth. Agriculture Revolution The time when human begins first domesticated plants and animals and no longer relied entirely on hunting
Anti- Natalist A government policy concerned with limiting population growth. Agriculture Revolution The time when human begins first domesticated plants and animals and no longer relied entirely on hunting
The Human Population 8
 8 The Human Population Overview of Chapter 8 The Science of Demography Demographics of Countries Demographic Stages Age Structure Population and Quality of Life Reducing the Total Fertility Rate Government
8 The Human Population Overview of Chapter 8 The Science of Demography Demographics of Countries Demographic Stages Age Structure Population and Quality of Life Reducing the Total Fertility Rate Government
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Geographers define overpopulation as A) too many people compared to resources. B) too
Exam Name MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) Geographers define overpopulation as A) too many people compared to resources. B) too
First, some key facts. * Population growth rates are much higher in most low- and middle-income countries than in most high-income countries.
 VERY IMPORTANT READING ABOUT POPULATION GROWTH. You must have a good understanding of this in order to complete the analysis of the Population Pyramid Assignment. Population Growth: Positives and Negatives
VERY IMPORTANT READING ABOUT POPULATION GROWTH. You must have a good understanding of this in order to complete the analysis of the Population Pyramid Assignment. Population Growth: Positives and Negatives
Chapter 3 Notes Earth s Human and Cultural Geography
 Chapter 3 Notes Earth s Human and Cultural Geography Section 1: World Population Geographers study how people and physical features are distributed on Earth s surface. Although the world s population is
Chapter 3 Notes Earth s Human and Cultural Geography Section 1: World Population Geographers study how people and physical features are distributed on Earth s surface. Although the world s population is
birth control birth control brain drain birth rate coastal plain commuting Consciously preventing unwanted pregnancies.
 birth control birth control Consciously preventing unwanted pregnancies. Consciously preventing unwanted pregnancies. birth rate brain drain Scientists from Britain to America The number of live births
birth control birth control Consciously preventing unwanted pregnancies. Consciously preventing unwanted pregnancies. birth rate brain drain Scientists from Britain to America The number of live births
Population and Migration. Chapters 2 and 3 Test Review
 Population and Migration Chapters 2 and 3 Test Review 1. What is land suited for agriculture? 1. Farm Land 2. Brain Drain 3. Arable Land 4. Crop Land 1. What is land suited for agriculture? 1. Farm Land
Population and Migration Chapters 2 and 3 Test Review 1. What is land suited for agriculture? 1. Farm Land 2. Brain Drain 3. Arable Land 4. Crop Land 1. What is land suited for agriculture? 1. Farm Land
ndtv.com POPULATION Ann Maureen Samm-Regis
 ndtv.com POPULATION Ann Maureen Samm-Regis Definitions Population is the total number of people living in a specific area at a particular time. Demography: is the study of the population to determine its
ndtv.com POPULATION Ann Maureen Samm-Regis Definitions Population is the total number of people living in a specific area at a particular time. Demography: is the study of the population to determine its
Chapter One: people & demographics
 Chapter One: people & demographics The composition of Alberta s population is the foundation for its post-secondary enrolment growth. The population s demographic profile determines the pressure points
Chapter One: people & demographics The composition of Alberta s population is the foundation for its post-secondary enrolment growth. The population s demographic profile determines the pressure points
Social Studies 11 First Assignment: Welcome!
 First Assignment: Welcome! Welcome to The Link! Choosing to complete courses through Distributed Learning is an exciting choice! You have the opportunity to complete work at your own pace, at times of
First Assignment: Welcome! Welcome to The Link! Choosing to complete courses through Distributed Learning is an exciting choice! You have the opportunity to complete work at your own pace, at times of
Unit 1 Population dynamics
 Unit 1 Population dynamics Dynamics continually changing Population is the centre around which human geography revolves. Because populations change constantly over time it is necessary for geographers
Unit 1 Population dynamics Dynamics continually changing Population is the centre around which human geography revolves. Because populations change constantly over time it is necessary for geographers
Population Pressures. Analyzing Global Population, Migration Patterns and Trends
 Population Pressures Analyzing Global Population, Migration Patterns and Trends 100 People: A World Portrait If the World were 100 PEOPLE: 50 would be female 50 would be male 26 would be children There
Population Pressures Analyzing Global Population, Migration Patterns and Trends 100 People: A World Portrait If the World were 100 PEOPLE: 50 would be female 50 would be male 26 would be children There
Grade 9 Geography Chapter 15 - Population. 1. What are the four general ways in which the population of Canada increases and decreases?
 Grade 9 Geography Chapter 15 - Population 1. What are the four general ways in which the population of Canada increases and decreases? 2. What term is used to describe the difference between the level
Grade 9 Geography Chapter 15 - Population 1. What are the four general ways in which the population of Canada increases and decreases? 2. What term is used to describe the difference between the level
THE DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITION MODEL
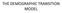 THE DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITION MODEL What are the stages of the Demographic Transition Model? In Stage 1, which applied to most of the world before the Industrial Revolution, both birth rates and death rates
THE DEMOGRAPHIC TRANSITION MODEL What are the stages of the Demographic Transition Model? In Stage 1, which applied to most of the world before the Industrial Revolution, both birth rates and death rates
brownd Monday, May 9, :05:58 AM CT 58:b0:35:ac:27:98 Popula'on
 Popula'on Basic Terms Demography Immigra'on Emigra'on Ecumene Non- Ecumene Basic Terms Demography- Study of human popula'on Immigra'on- people coming into a country Emigra'on- people leaving a country
Popula'on Basic Terms Demography Immigra'on Emigra'on Ecumene Non- Ecumene Basic Terms Demography- Study of human popula'on Immigra'on- people coming into a country Emigra'on- people leaving a country
APES Chapter 10 Study Guide. 1. How can the population change in a particular year be calculated?
 APES Chapter 10 Study Guide 1. How can the population change in a particular year be calculated? 2. Define the term crude birth rate. 3. Name the continent that has the highest crude birth rate and crude
APES Chapter 10 Study Guide 1. How can the population change in a particular year be calculated? 2. Define the term crude birth rate. 3. Name the continent that has the highest crude birth rate and crude
NAME DATE CLASS. Directions: Answer each of the following questions. Include in your answers the vocabulary words in parentheses.
 Vocabulary Activity Content Vocabulary Directions: Answer each of the following questions. Include in your answers the vocabulary words in parentheses. 1. What does the term crude birthrate have to do
Vocabulary Activity Content Vocabulary Directions: Answer each of the following questions. Include in your answers the vocabulary words in parentheses. 1. What does the term crude birthrate have to do
Chapter 18 Development and Globalization
 Chapter 18 Development and Globalization 1. Levels of Development 2. Issues in Development 3. Economies in Transition 4. Challenges of Globalization Do the benefits of economic development outweigh the
Chapter 18 Development and Globalization 1. Levels of Development 2. Issues in Development 3. Economies in Transition 4. Challenges of Globalization Do the benefits of economic development outweigh the
STATISTICAL REFLECTIONS
 World Population Day, 11 July 217 STATISTICAL REFLECTIONS 18 July 217 Contents Introduction...1 World population trends...1 Rearrangement among continents...2 Change in the age structure, ageing world
World Population Day, 11 July 217 STATISTICAL REFLECTIONS 18 July 217 Contents Introduction...1 World population trends...1 Rearrangement among continents...2 Change in the age structure, ageing world
Key Terminology. in 1990, Ireland was overpopulated only had population of 3.5 million but 70,000 emigrated due to unemployment.
 Key Terminology Overpopulation = when there are too many people in an area for the resources of that area to maintain an adequate standard of living. in 1990, Ireland was overpopulated only had population
Key Terminology Overpopulation = when there are too many people in an area for the resources of that area to maintain an adequate standard of living. in 1990, Ireland was overpopulated only had population
Unit 2 Test Population and Migration
 Unit 2 Test Population and Migration 1. Geographers might characterize as overpopulated a country where a. There are too many people according to a standard economic measure of poverty. b. The population
Unit 2 Test Population and Migration 1. Geographers might characterize as overpopulated a country where a. There are too many people according to a standard economic measure of poverty. b. The population
PREPARING TO DO THE MATH
 DO The Math PREPARING TO DO THE MATH Four math topics that have shown up on multiple-choice released exams are 1. Calculating global growth rate (including CBR, CDR & etc) 2. National population growth
DO The Math PREPARING TO DO THE MATH Four math topics that have shown up on multiple-choice released exams are 1. Calculating global growth rate (including CBR, CDR & etc) 2. National population growth
FERTILITY RATE average number of children a woman will have between 15 and 44 (reproductive age)
 HUMAN GEOGRAPHY: Population Change INDICATORS OF DEVELOPMENT KEY TERMS BIRTH RATE live births per 1000 people per year DEATH RATE deaths per 1000 people per year FERTILITY RATE average number of children
HUMAN GEOGRAPHY: Population Change INDICATORS OF DEVELOPMENT KEY TERMS BIRTH RATE live births per 1000 people per year DEATH RATE deaths per 1000 people per year FERTILITY RATE average number of children
Population Problems in LEDCs
 Exam Practice When you sit your exams it is important that you understand exactly what the question wants and know what the examiner will be looking for Exam Practice Exam Practice Population Problems
Exam Practice When you sit your exams it is important that you understand exactly what the question wants and know what the examiner will be looking for Exam Practice Exam Practice Population Problems
Poverty Profile. Executive Summary. Kingdom of Thailand
 Poverty Profile Executive Summary Kingdom of Thailand February 2001 Japan Bank for International Cooperation Chapter 1 Poverty in Thailand 1-1 Poverty Line The definition of poverty and methods for calculating
Poverty Profile Executive Summary Kingdom of Thailand February 2001 Japan Bank for International Cooperation Chapter 1 Poverty in Thailand 1-1 Poverty Line The definition of poverty and methods for calculating
The Demography of the Labor Force in Sub- Saharan Africa
 The Demography of the Labor Force in Sub- Saharan Africa David Lam Department of Economics and Population Studies Center University of Michigan Conference on Labor Markets in Western Africa: Evidence and
The Demography of the Labor Force in Sub- Saharan Africa David Lam Department of Economics and Population Studies Center University of Michigan Conference on Labor Markets in Western Africa: Evidence and
Summary of the Results
 Summary of the Results CHAPTER I: SIZE AND GEOGRAPHICAL DISTRIBUTION OF THE POPULATION 1. Trends in the Population of Japan The population of Japan is 127.77 million. It increased by 0.7% over the five-year
Summary of the Results CHAPTER I: SIZE AND GEOGRAPHICAL DISTRIBUTION OF THE POPULATION 1. Trends in the Population of Japan The population of Japan is 127.77 million. It increased by 0.7% over the five-year
People. Population size and growth. Components of population change
 The social report monitors outcomes for the New Zealand population. This section contains background information on the size and characteristics of the population to provide a context for the indicators
The social report monitors outcomes for the New Zealand population. This section contains background information on the size and characteristics of the population to provide a context for the indicators
Economic Development and Transition
 Economic Development and Transition Developed Nations and Less Developed Countries Developed Nations Developed nations are nations with higher average levels of material well-being. Less Developed Countries
Economic Development and Transition Developed Nations and Less Developed Countries Developed Nations Developed nations are nations with higher average levels of material well-being. Less Developed Countries
4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS- SOCIAL SCIENCE UNIT 6: POPULATION AND TERRITORY
 4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS- SOCIAL SCIENCE UNIT 6: POPULATION AND TERRITORY POPULATION AND ITS DISTRIBUTION The population is the total number of people who live in a town, a country, a continent or on
4th GRADE MINIMUM CONTENTS- SOCIAL SCIENCE UNIT 6: POPULATION AND TERRITORY POPULATION AND ITS DISTRIBUTION The population is the total number of people who live in a town, a country, a continent or on
Executive summary. Strong records of economic growth in the Asia-Pacific region have benefited many workers.
 Executive summary Strong records of economic growth in the Asia-Pacific region have benefited many workers. In many ways, these are exciting times for Asia and the Pacific as a region. Dynamic growth and
Executive summary Strong records of economic growth in the Asia-Pacific region have benefited many workers. In many ways, these are exciting times for Asia and the Pacific as a region. Dynamic growth and
Environmental Studies ENVR 30: Intro to Science of the Environment. Chapter 2 HUMAN POPULATION GROWTH. Introduction. Question. Population History
 Exponential growth: If graph curves upward Watch out! Aug 1992: GOES-7 satellite; notice hurricane Andrew Environmental Studies ENVR 30: Intro to Science of the Environment Question If a large piece of
Exponential growth: If graph curves upward Watch out! Aug 1992: GOES-7 satellite; notice hurricane Andrew Environmental Studies ENVR 30: Intro to Science of the Environment Question If a large piece of
Gender, migration and well-being of the elderly in rural China
 Gender, migration and well-being of the elderly in rural China Shuzhuo Li 1 Marcus W. Feldman 2 Xiaoyi Jin 1 Dongmei Zuo 1 1. Institute for Population and Development Studies, Xi an Jiaotong University
Gender, migration and well-being of the elderly in rural China Shuzhuo Li 1 Marcus W. Feldman 2 Xiaoyi Jin 1 Dongmei Zuo 1 1. Institute for Population and Development Studies, Xi an Jiaotong University
Human Population Growth. {Human Population
 Human Population Growth {Human Population This lecture will help you understand: Human population growth Demography Affluence, technology, the status of women, and the environment Population control programs
Human Population Growth {Human Population This lecture will help you understand: Human population growth Demography Affluence, technology, the status of women, and the environment Population control programs
Unit 3 - Geography of Population: Demography, Migration
 Unit 3 - Geography of Population: Demography, Migration 38:180 Human Geography 2.1 Demography Demography is the study of the size and composition of population, including the dynamics of population change,
Unit 3 - Geography of Population: Demography, Migration 38:180 Human Geography 2.1 Demography Demography is the study of the size and composition of population, including the dynamics of population change,
Britain s Population Exceptionalism within the European Union
 Britain s Population Exceptionalism within the European Union Introduction The United Kingdom s rate of population growth far exceeds that of most other European countries. This is particularly problematic
Britain s Population Exceptionalism within the European Union Introduction The United Kingdom s rate of population growth far exceeds that of most other European countries. This is particularly problematic
WORLD VIEWS & HUMAN POPULATION
 WORLD VIEWS & HUMAN POPULATION WORLD VIEW HOW AN INDIVIDUAL THINKS EARTH S NATURAL RESOURCES SHOULD BE USED BY HUMANS. THERE ARE 2 TYPES: CORNUCOPIANISM & ENVIRONMENTALISM NATURAL RESOURCES ANY MATERIALS
WORLD VIEWS & HUMAN POPULATION WORLD VIEW HOW AN INDIVIDUAL THINKS EARTH S NATURAL RESOURCES SHOULD BE USED BY HUMANS. THERE ARE 2 TYPES: CORNUCOPIANISM & ENVIRONMENTALISM NATURAL RESOURCES ANY MATERIALS
Population Change and Economic Development in Albania
 Population Change and Economic Development in Albania Alma Meta Dr. Abdulmenaf Sejdini Abstract This paper studies, to what extent have population changes and economic growth have affected each other in
Population Change and Economic Development in Albania Alma Meta Dr. Abdulmenaf Sejdini Abstract This paper studies, to what extent have population changes and economic growth have affected each other in
Human Population Growth
 Human Population Growth Clarifying Objective 2.1.4 Explain how ecosystems can be relatively stable over hundreds or thousands of years, even though populations may fluctuate due to availability of food
Human Population Growth Clarifying Objective 2.1.4 Explain how ecosystems can be relatively stable over hundreds or thousands of years, even though populations may fluctuate due to availability of food
Unit 3: Migration and Urbanization (Lessons 5-7)
 Unit 3: Migration and Urbanization (Lessons 5-7) Introduction Have you ever moved to a new place? If you have, there was probably a very strong reason that motivated your family to pack up everything you
Unit 3: Migration and Urbanization (Lessons 5-7) Introduction Have you ever moved to a new place? If you have, there was probably a very strong reason that motivated your family to pack up everything you
Population Projection Alberta
 Population Projection Alberta 215 241 Solid long term growth expected Alberta s population is expected to expand by about 2.1 million people by the end of the projection period, reaching just over 6.2
Population Projection Alberta 215 241 Solid long term growth expected Alberta s population is expected to expand by about 2.1 million people by the end of the projection period, reaching just over 6.2
Human development in China. Dr Zhao Baige
 Human development in China Dr Zhao Baige 19 Environment Twenty years ago I began my academic life as a researcher in Cambridge, and it is as an academic that I shall describe the progress China has made
Human development in China Dr Zhao Baige 19 Environment Twenty years ago I began my academic life as a researcher in Cambridge, and it is as an academic that I shall describe the progress China has made
The Implications of New Brunswick s Population Forecasts
 The Implications of New Brunswick s Post-Secondary Education, Training and Labour September 2017 In spring 2017, two papers (i) New Brunswick Population Snapshot and (ii) Small Area Population Forecasts
The Implications of New Brunswick s Post-Secondary Education, Training and Labour September 2017 In spring 2017, two papers (i) New Brunswick Population Snapshot and (ii) Small Area Population Forecasts
People. Population size and growth
 The social report monitors outcomes for the New Zealand population. This section provides background information on who those people are, and provides a context for the indicators that follow. People Population
The social report monitors outcomes for the New Zealand population. This section provides background information on who those people are, and provides a context for the indicators that follow. People Population
Working paper 20. Distr.: General. 8 April English
 Distr.: General 8 April 2016 Working paper 20 English Economic Commission for Europe Conference of European Statisticians Work Session on Migration Statistics Geneva, Switzerland 18-20 May 2016 Item 8
Distr.: General 8 April 2016 Working paper 20 English Economic Commission for Europe Conference of European Statisticians Work Session on Migration Statistics Geneva, Switzerland 18-20 May 2016 Item 8
CHAPTER I: SIZE AND GEOGRAPHICAL DISTRIBUTION OF THE POPULATION
 CHAPTER I: SIZE AND GEOGRAPHICAL DISTRIBUTION OF THE POPULATION 1. Trends in the Population of Japan The population of Japan is 127.77 million. It increased by 0.7% over the five-year period, the lowest
CHAPTER I: SIZE AND GEOGRAPHICAL DISTRIBUTION OF THE POPULATION 1. Trends in the Population of Japan The population of Japan is 127.77 million. It increased by 0.7% over the five-year period, the lowest
Population Composition
 Unit-II Chapter-3 People of any country are diverse in many respects. Each person is unique in her/his own way. People can be distinguished by their age, sex and their place of residence. Some of the other
Unit-II Chapter-3 People of any country are diverse in many respects. Each person is unique in her/his own way. People can be distinguished by their age, sex and their place of residence. Some of the other
Demographic Transition in Japan and Rural Development
 "Population and Development" Series No. 1 Demographic Transition in Japan and Rural Development FEBRUARY 1985 The Asian Population and Development Association (foundation) CHAPTER 1 CHARACTERISTICS OF
"Population and Development" Series No. 1 Demographic Transition in Japan and Rural Development FEBRUARY 1985 The Asian Population and Development Association (foundation) CHAPTER 1 CHARACTERISTICS OF
Alberta Population Projection
 Alberta Population Projection 213 241 August 16, 213 1. Highlights Population growth to continue, but at a moderating pace Alberta s population is expected to expand by 2 million people through 241, from
Alberta Population Projection 213 241 August 16, 213 1. Highlights Population growth to continue, but at a moderating pace Alberta s population is expected to expand by 2 million people through 241, from
c4hxpxnrz0
 Update Jan 2010 HUMAN RACE In the 6 seconds it takes you to read this sentence, 24 13 people will be added to the Earth s population. o Before you ve finished this letter, that number will reach 1000.
Update Jan 2010 HUMAN RACE In the 6 seconds it takes you to read this sentence, 24 13 people will be added to the Earth s population. o Before you ve finished this letter, that number will reach 1000.
Trends in Labour Supply
 Trends in Labour Supply Ellis Connolly, Kathryn Davis and Gareth Spence* The labour force has grown strongly since the mid s due to both a rising participation rate and faster population growth. The increase
Trends in Labour Supply Ellis Connolly, Kathryn Davis and Gareth Spence* The labour force has grown strongly since the mid s due to both a rising participation rate and faster population growth. The increase
Introduction CHRISTCHURCH CITY UPDATE 2000
 CHRISTCHURCH CITY UPDATE 2000 Introduction Christchurch City experienced significant population growth during the first half of the 1990s. This trend was fuelled by high levels of international migration,
CHRISTCHURCH CITY UPDATE 2000 Introduction Christchurch City experienced significant population growth during the first half of the 1990s. This trend was fuelled by high levels of international migration,
3/12/2015. Global Issues 621 WORLD POPULATION. 1.6 Billion. 6 Billion (approximately) 2.3 Billion
 Global Issues 621 WORLD POPULATION 1.6 Billion 1 2 2.3 Billion 6 Billion (approximately) 3 4 1 7.10 Billion (and growing) Population Notes While populations in many parts of the world are expanding, those
Global Issues 621 WORLD POPULATION 1.6 Billion 1 2 2.3 Billion 6 Billion (approximately) 3 4 1 7.10 Billion (and growing) Population Notes While populations in many parts of the world are expanding, those
WORLD POPULATION 3/24/2013. Global Issues Billion. 6 Billion (approximately) 2.3 Billion. Population Notes Billion (and growing)
 Global Issues 621 WORLD POPULATION 1.6 Billion 1 2 2.3 Billion 6 Billion (approximately) 3 4 7.10 Billion (and growing) Population Notes While populations in many parts of the world are expanding, those
Global Issues 621 WORLD POPULATION 1.6 Billion 1 2 2.3 Billion 6 Billion (approximately) 3 4 7.10 Billion (and growing) Population Notes While populations in many parts of the world are expanding, those
Studying Populations II
 GEOG 247 Cultural Geography Studying Populations II Projected Population Change 2010-2100 Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College CUNY AFG 2015 From US News and World Report article using UN data, Oct., 2014
GEOG 247 Cultural Geography Studying Populations II Projected Population Change 2010-2100 Prof. Anthony Grande Hunter College CUNY AFG 2015 From US News and World Report article using UN data, Oct., 2014
FARMWORKERS IN MEXICO AGUSTÍN ESCOBAR OMAR STABRIDIS
 FARMWORKERS IN MEXICO AGUSTÍN ESCOBAR OMAR STABRIDIS Mexican farm workers play a central role in the production of fruits and vegetables for the U.S. market in both countries. Recently,Taylor, Charlton
FARMWORKERS IN MEXICO AGUSTÍN ESCOBAR OMAR STABRIDIS Mexican farm workers play a central role in the production of fruits and vegetables for the U.S. market in both countries. Recently,Taylor, Charlton
Population Projection Methodology and Assumptions
 Population Projection Methodology and Assumptions Introduction Population projections for Alberta and each of its 19 census divisions are available for the period 217 to 241 by sex and single year of age.
Population Projection Methodology and Assumptions Introduction Population projections for Alberta and each of its 19 census divisions are available for the period 217 to 241 by sex and single year of age.
Levels and trends in international migration
 Levels and trends in international migration The number of international migrants worldwide has continued to grow rapidly over the past fifteen years reaching million in 1, up from million in 1, 191 million
Levels and trends in international migration The number of international migrants worldwide has continued to grow rapidly over the past fifteen years reaching million in 1, up from million in 1, 191 million
Population and sustainable development in the context of the post-2015 UN development agenda
 Population and sustainable development in the context of the post-2015 UN development agenda United Nations Commission on Population and Development 8 April 2014 David Lam Department of Economics and Population
Population and sustainable development in the context of the post-2015 UN development agenda United Nations Commission on Population and Development 8 April 2014 David Lam Department of Economics and Population
POPULATION STUDIES RESEARCH BRIEF ISSUE Number
 POPULATION STUDIES RESEARCH BRIEF ISSUE Number 2008021 School for Social and Policy Research 2008 Population Studies Group School for Social and Policy Research Charles Darwin University Northern Territory
POPULATION STUDIES RESEARCH BRIEF ISSUE Number 2008021 School for Social and Policy Research 2008 Population Studies Group School for Social and Policy Research Charles Darwin University Northern Territory
Jens Thomsen: The global economy in the years ahead
 Jens Thomsen: The global economy in the years ahead Statement by Mr Jens Thomsen, Governor of the National Bank of Denmark, at the Indo- Danish Business Association, Delhi, 9 October 2007. Introduction
Jens Thomsen: The global economy in the years ahead Statement by Mr Jens Thomsen, Governor of the National Bank of Denmark, at the Indo- Danish Business Association, Delhi, 9 October 2007. Introduction
GROWTH OF SCHEDULED CASTE POPULATION
 CHAPTER NO. 4 GROWTH OF SCHEDULED CASTE POPULATION 4.1 INTRODUCTION 4.2 TREND IN GROWTH OF SCHEDULED CASTE POPULATION 4.2.1 TAHSIL WISE GROWTH RATE OF SCHEDULED CASTE POPULATION 4.2.2 TAHSIL WISE MALE
CHAPTER NO. 4 GROWTH OF SCHEDULED CASTE POPULATION 4.1 INTRODUCTION 4.2 TREND IN GROWTH OF SCHEDULED CASTE POPULATION 4.2.1 TAHSIL WISE GROWTH RATE OF SCHEDULED CASTE POPULATION 4.2.2 TAHSIL WISE MALE
Population Aging, Immigration and Future Labor Shortage : Myths and Virtual Reality
 Population Aging, Immigration and Future Labor Shortage : Myths and Virtual Reality Alain Bélanger Speakers Series of the Social Statistics Program McGill University, Montreal, January 23, 2013 Montréal,
Population Aging, Immigration and Future Labor Shortage : Myths and Virtual Reality Alain Bélanger Speakers Series of the Social Statistics Program McGill University, Montreal, January 23, 2013 Montréal,
Introduction: The State of Europe s Population, 2003
 Introduction: The State of Europe s Population, 2003 Changes in the size, growth and composition of the population are of key importance to policy-makers in practically all domains of life. To provide
Introduction: The State of Europe s Population, 2003 Changes in the size, growth and composition of the population are of key importance to policy-makers in practically all domains of life. To provide
CHINA S ONE-CHILD POLICY
 Sinology by Andy Rothman 5 December 1 a Last year s decision to relax China s onechild policy effectively ended one of the most draconian examples of government social engineering ever seen. a But, contrary
Sinology by Andy Rothman 5 December 1 a Last year s decision to relax China s onechild policy effectively ended one of the most draconian examples of government social engineering ever seen. a But, contrary
DOWNLOAD PDF SEX AND POPULATION
 Chapter 1 : World Population by Gender, Age, Fertility Rate, Immigration - Worldometers Focusing on a population's age and sex composition is one of the most basic ways to understand population change
Chapter 1 : World Population by Gender, Age, Fertility Rate, Immigration - Worldometers Focusing on a population's age and sex composition is one of the most basic ways to understand population change
Population, Migration and Urbanization
 Population, Migration and Urbanization Contemporary National Development (CONADEV) Alellie B. Sobreviñas, Ph.D. alellie.sobrevinas@dlsu.edu.ph Estimated World Population 2017: 7.6 billion people first
Population, Migration and Urbanization Contemporary National Development (CONADEV) Alellie B. Sobreviñas, Ph.D. alellie.sobrevinas@dlsu.edu.ph Estimated World Population 2017: 7.6 billion people first
6.1 Population Density & Global Patterns "Population Density" on pages of your text book. Page 2
 Unit 6 Notes Population Geography Word Geo 3202 This review document contains: 1. The notes 2. the active learning lessons we completed in class during this unit. 3. Page references for reading about each
Unit 6 Notes Population Geography Word Geo 3202 This review document contains: 1. The notes 2. the active learning lessons we completed in class during this unit. 3. Page references for reading about each
