curriculum scavenger hunt
|
|
|
- Leslie Little
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 scavenger hunt curriculum Introduction and Objective This activity is inspired by and adapted from Rethinking School s The U.S.-Mexico War Tea Party found in The Line Between Us (Wisconsin: Rethinking Schools, 2006). Spanning more than ten years, the Mexican Revolution is a complex historical event that involved numerous individuals. The scavenger hunt activity will introduce students to many of these individuals, and the various motivations of those individuals participating in or resisting the Revolution. Each student will take on the role of one individual involved in the Mexican Revolution. Then, using the provided questionnaire hand-out, students will move around the room interviewing classmates in order to appropriately answer all of the questions on the hand-out. Image: Provided by Fototeca-INAH. Núm Palacio Nacional, mural del arco central realizado por Diego Rivera This activity can be used after a brief introduction to the Mexican Revolution. It does not require a great deal of background knowledge on the Revolution. Its purpose is to solidify knowledge and understanding of the individuals involved in the Mexican Revolution. An Educator s Guide to the Mexican Revolution 24
2 Materials Scavenger hunt roles, cut up (one for each student in the class) Blank nametags (enough for every student in the class) Copies of The Mexican Revolution Scavenger Hunt hand-out for every student Procedure 4. Explain to students that they are going to do an activity about the Mexican Revolution. Distribute one nametag and one scavenger hunt role to each student in the class. There are only 16, so depending upon the number of students in the class, some students will be assigned the same historical character. 5. Have students fill out their nametags using the name of the individual they are assigned. Tell students that in this activity you would like each of them to attempt to become these people from history. Ask students to read their roles several times and to memorize as much of the information as possible. Encourage them to underline key points. 6. Distribute a copy of The Mexican Revolution Scavenger Hunt hand-out to each student. Explain their assignment: Students should circulate through the classroom, meeting other individuals from the Mexican Revolution. They should use the questions on the sheet as a guide to talk with others about the war and complete the questions as fully as possible. They must use a different individual to answer each of the 11 questions. Tell them that it s not a race; the aim is for students to spend time hearing each other s stories, not just hurriedly scribbling down answers to the different questions. It may be helpful to ask for a student volunteer to demonstrate with the teacher an encounter between two of the individuals, so that the rest of the class can sense the kind of interaction that is expected 7. Afterwards ask students to share some of their finding with the whole class. This needn t be exhaustive, as students will learn a lot more about these issues throughout the rest of the unit. Possible Questions What surprised you about this activity? Who found someone with an opinion very different from your character s opinion? What were some of the different opinions you encountered on why individuals were fighting in the Revolution? What were the results of the Revolution? What questions does this activity leave you with? An Educator s Guide to the Mexican Revolution 25
3 Extension: Timeline/Flowchart of the Mexican Revolution Save the cards used during the Scavenger Hunt. As students learn more about the events of Revolution, use the pictures to create a timeline or flowchart of the Revolution on a large piece of butcher paper or bulletin board. You may need to print out extra copies of some of the cards in order to mark all of the important events that particular figure was involved in. Various information can be displayed on the timeline: important events, changing alliances, and deaths of major leaders are a few examples. An Educator s Guide to the Mexican Revolution 26
4 The Mexican Revolution Scavenger Hunt 1. Find someone who was affected by the war. Who is this person? How was this person affected? 2. Find someone who supports the Mexican Revolution. Who is this person? Why do they support the revolution? 3. Find someone who is in opposition to the Mexican Revolution. Who is this person? Why do they support the revolution? 4. Find someone from Southern Mexico. What is their experience with the Revolution? 5. Find someone from Northern Mexico. What is their experience with the Revolution? 6. Find someone who saw things in the war that he or she found shocking. Who is this person? What shocked this person? 7. Find someone who fought in the revolution. Who did they fight for? Why did they join the Revolution? 8. Find one of the major leaders of the revolution. Why did they join the Revolution? What did they hope to accomplish through the Revolution? 9. Find someone from outside Mexico who has an opinion about the Revolution. Where are they from? Why are they in Mexico? What do they think about the Revolution? 10. Find someone who was a dictator of Mexico. Why did they take control of the country? What did they hope to accomplish? 11. Find someone who was killed fighting for the Revolution. How did they die?
5 An Educator s Guide to the Mexican Revolution 28
6 wealthy landowner from sonora Location: Sonora born - died: 19th - 20th centuries social class: Aristocrat / Haciendado allegiance: Porfiriato peasant from morelos Location: Morelos born - died: 19th - 20th centuries social class: Indigenous / Peasantry allegiance: Zapatistas I fully support Díaz in this war against the traitor, Madero. The state of Sonora has grown rich during the Porfiriato. Our mining industry thrives. We have eliminated the Yaqui problem, making excellent use of land that had too long sat stagnant. I hear dangerous talk from the small landholders that they will join Madero. Election clubs are forming all around me in support of the traitor. This is a mistake. I will personally take up arms to aid my government, which has blessed us with stability and order. My father s land now belongs to the hacendado. It is part of a massive sugar plantation more land than any one man could ever need. I work this land as a slave, spending my entire wage on food at the company store. I am told that I am constantly in debt and must pay my debt by working long days in the fields. But how can this be? I buy nothing except what I need to survive. When Madero became president, we expected that our families lands would be returned. That is apparently a lie. I am ready to join Emiliano Zapata and his army which is preparing to move north against the traitor Madero. u.s. ambassador henry lane wilson Location: Mexico City / Washington, D.C. born - died: social class: Privileged allegiance: U.S. Department of State laborer from veracruz Location: Veracruz born - died: 19th - 20th centuries social class: Laborer allegiance: Unknown / Multiple I have done much work in Mexico in furtherance of U.S. interests. After enormous difficulties, I got General Huerta and Félix Díaz to agree that Huerta should be the Provisional President of the Republic I expect no further trouble in the city, and I congratulate the Department of State upon the happy outcome of events, which have been directly or indirectly the result of its instructions. I work twelve hour days, seven days per week. I make a pittance for a wage. My two youngest sons were worked to death in the textile mills. Recently, workers lashed out, setting the tienda de raya aflame. The local jefe called in federal troops to punish all of us. Federales fired pointblank into crowds, killing women and children without distinction. The dictator, Díaz, always supports the oppressive mill owners. If the workers strike again, I am afraid that my wife and remaining children will be killed. An Educator s Guide to the Mexican Revolution 29
7 An Educator s Guide to the Mexican Revolution 30
8 emiliano zapata Location: Morelos / The South born - died: social class: Indigenous / Peasantry allegiance: Zapatistas pancho villa Location: Durango / The North born - died: social class: Peasantry allegiance: Villistas It never occurred to Carranza that the Revolution was fought for the benefit of the great masses, for the legions of the oppressed whom he motivated with his harangues. He has given or rented our haciendas to his favorites. The old landholdings have been taken over by new landlords, and the people are mocked in their hopes. I am the leader of the Southern armies that fight for agrarian reform. My nickname is Attila of the South. My nickname is Centaur of the North. I will never be president of Mexico. I was born without wealth, in Durango. I never went to school a day in my life, and I am not educated enough for the post. My alphabet has been the sight and trigger of my rifle; my books have been the movements of the enemy. I can fight only for the liberation of my people. If the federales win they will have to fight us again, but if we win we will leave them in such shape that they will not be able to recuperate. My defeat at Ceyala was the beginning of the end. álvaro obregón Location: Sonora / The North / Mexico City born - died: social class: Indigenous / Peasantry allegiance: Obregónistas gildardo magaña Location: Michoacán / Morelos born - died: social class: Merchant/Educated allegiance: Zapatistas/Obregónistas I view land ownership as important to the dignity of the people. This is one thing I learned from the Zapatistas. Since I have become president of Mexico, I have begun distributing land, and in the process, buying future support against potential opponents. The goals of my presidency will include land reform, modernization, and expanded access to education. With these goals, I should be able to easily gain the support of the Zapatistas and bring stability back to Mexico. I am a Mexican, through and through, but I have been trained in economics in the U.S. With this background, I travelled south to join the Zapatistas. While other intellectuals were villainizing Zapata without reason, I recognized that his cause land reform was for the good of Mexico. When Zapata was assassinated by cowards, I was elected to lead his army. Though I will never fill his massive shoes with my tiny feet, I will do my best to try. In the interest of Mexico, I plan to pledge allegiance to Obregón, who has promised to return indigenous lands in exchange. The land we seek was nourished by the blood of those who died fighting for a liberated Mexico. An Educator s Guide to the Mexican Revolution 31
9 An Educator s Guide to the Mexican Revolution 32
10 porfirio díaz Location: Oaxaca / Mexico City / Europe born - died: social class: Working Class allegiance: Porfiriato I have learned much from the great cities of Europe. I am using Paris and London as examples to modernize our economy and our transportation systems. I am building an international railroad from Texas to Durango! My cientificos have brought Order, Liberty, and Progress to Mexico. It is true that the lower classes complain of brutal working conditions, poor diet and debilitating disease, but their lives too would improve if they would just stop drinking pulque and apply themselves to our great national project. Besides, if one complains too loudly, I will have him thrown in prison! My system of enforced peace is flawless. venustiano carranza Location: Coahuila / The North born - died: social class: Privileged / Ranching allegiance: Carrancistas I have restored the constitution of 1857 and ended the Huerta dictatorship. The revolution is over and the people of Mexico must begin rebuilding. I have heard that workers in Veracruz are striking again. I will not respond kindly to this. I have also heard that Zapata has called me a traitor to the revolution. I am devising a daring plot to kill this peasant from Morelos. One of my colonels will gain his trust, feign defection to his cause, accompany him to the Hacienda de Chinameca and assassinate him where he stands. With the labor movement and the Zapatistas finally quieted, Mexico will be rebuilt. american journalist Location: U.S. / Veracruz born - died: 19th - 20th centuries social class: Privileged / Educated allegiance: None / Multiple I am here during the American naval occupation of Veracruz. The occupation has given Veracruz a bull market in health, order, and business. Mexican paper money appreciated. Prices rose. Profits soared. Verily, the Veracruzans will long remember this being conquered by the Americans and yearn for the blissful day when the Americans will conquer them again. They would not mind thus being conquered to the end of time. victoriano huerta Location: Jalisco / Mexico City born - died: social class: Privileged / Military allegiance: Huerta I am sick of these men of inaction. I have spent my life fighting against the Yaqui and Maya, and recently against the Zapatistas in Morelos. My president, Madero, could never do what I have done. He is weak. Let me tell you a secret: I have been working with the U.S. Ambassador to devise a plan for Mexico. He has reported to me that the soldiers are unhappy and that Don Porfirio s nephew, Félix, is staging a coup against Madero. I am seriously considering this opportunity to join these men and purge Mexico of its weakness. An Educator s Guide to the Mexican Revolution 33
11 An Educator s Guide to the Mexican Revolution 34
12 pascual orozco Location: Chihuahua / The North born - died: social class: Middle Class allegiance: Huerta Who am I, you ask? I am an experienced businessman, investor, and importer of U.S. weapons. I supplied and commanded Madero s forces against the tyranny of Diáz. When I defeated federal troops in battle after battle, I stripped their corpses of their uniforms and sent those rags to the dictator with a note that read: Here are the wrappers, send me more tamales! Thousands celebrated when my colonel, Villa, and I took Ciudad Juárez against all odds and guided Madero to the presidency. But Madero is not suited to rebuild Mexico. General Huerta and I will dispose of him shortly. francisco i. madero Location: Coahuila / Europe / The North / Mexico City born - died: social class: Extremely Privileged allegiance: Maderistas Diáz s perpetual tyranny is intolerable. This violent and illegal system can no longer exist. The people designated me as their candidate in the 1910 election because I have the vigor of a patriot, ready to sacrifice myself, if necessary, to obtain liberty and to help the people free themselves! I declare the 1910 election illegal and I assume the provisional presidency of the republic. On Sunday, November 20, 1910, all the towns in the republic will rise in arms at 6 o clock p.m. Viva la Revolucion! soldadera Location: Durango / The North born - died: 19th - 20th Centuries social class: Indigenous / Peasantry allegiance: Villa john j. pershing Location: Sonora / The North born - died: social class: Privileged / Military allegiance: U.S. Many don t realize that women were an important part of the Mexican Revolution. We fought alongside our fathers, brothers, and husbands. We traveled on the tops of trains with our armies. I am one of those women, a coronela in Villa s army. I joined the army because Díaz had my father assassinated. While many say I could have been one of the most famous women of I am a fighter at heart. As a young man I was wounded fighting the Lakota at Wounded Knee. Pancho Villa, then, is nothing to me. I treated this man with respect when he met with me in And now he dares to invade U.S. territory and kill U.S. citizens? My troops will hunt down and rid the world of this common bandit. the Revolution, I left the fighting and returned home to Catarinas. I was too disillusioned with corruption of the Revolution. An Educator s Guide to the Mexican Revolution 35
13 References for Images 1. Peasant from Morelos. Image provided by Fototeca-INAH. Núm 4930 Revolucionario zapatista al parecer frente a un parque, reprografía 2. Wealthy landowner from Sonora. Image provided by Fototeca-INAH. Núm Filiberto Villareal con ferrocarrileros durante la revolucion Delahuertista 3. Laborer from Veracruz. Image provided by Fototeca-INAH. Núm 5070 Revolucionario zapatista al parecer frente a un parque, reprografía 4. U.S. Ambassador Henry Lane Wilson. Image retrieved from com/2013/03/ambwilson-hires.jpg 5. Pancho Villa. Image provided by Fototeca-INAH. Núm 5770 Francisco Villa en San Pedro de las Colonias, retrato 6. Emiliano Zapata. Image provided by Fototeca-INAH. Núm 6341 Emiliano Zapata, general, retrato de tres cuartos de perfil 7. Gildardo Magaña. Image provided by Fototeca-INAH. Núm Gildardo Magaña, general, vestido de traje, retrato 8. Alvaro Obregón. Image provided by Fototeca-INAH. Núm Alvaro Obregon, general, retrato 9. Venustiano Carranza. Image provided by Fototeca-INAH. Núm 6356 Venustiano Carranza, retrato 10. Porfirio Díaz. Image retrieved from // Victoriano Huerta. Image retrieved from American Journalist [Jack London]. Image retrieved from wp-content/uploads/2013/02/7-7-10_jack3.jpg 13. Francisco I. Madero. Image retrieved from Madero.jpg 14. Pascual Orozco. Image retrieved from cb / althistory/es/images/4/47/pascual_orozco.png. 15. John J. Pershing. Image retrieved from John_Joseph_Pershing_head_on_shoulders.jpg 16. Soldadera. Image provided by Fototeca-INAH. Núm Herculano de la Rodia y Clara Rodia de Peña, familia minera de Durango que se alzó en contra de la dictadura An Educator s Guide to the Mexican Revolution 36
Pre-Revolutionary & Revolutionary Mexico
 Pre-Revolutionary & Revolutionary Mexico Colonial Mexico For millenia (since 1200 B.C.E. at the latest) Mesoamerica, and what we now call Mexico, was populated by a mix of Mayan peoples, Toltecs, and Aztecs
Pre-Revolutionary & Revolutionary Mexico Colonial Mexico For millenia (since 1200 B.C.E. at the latest) Mesoamerica, and what we now call Mexico, was populated by a mix of Mayan peoples, Toltecs, and Aztecs
The Mexican Revolution TOWARD A GLOBAL COMMUNITY (1900 PRESENT)
 The Mexican Revolution TOWARD A GLOBAL COMMUNITY (1900 PRESENT) Unlike much of Africa & India that had to wait until after WWII for independence, most of Latin America became independent in the early 1800s.
The Mexican Revolution TOWARD A GLOBAL COMMUNITY (1900 PRESENT) Unlike much of Africa & India that had to wait until after WWII for independence, most of Latin America became independent in the early 1800s.
10 year civil war ( ), U.S. concerns owned 20% of the nation s territory. individual rights), and also influenced by the outbreak of WWI
 MEXICAN REVOLUTION 10 year civil war (1910-1920), U.S. concerns owned 20% of the nation s territory. Caused primarily by internal forces (growing nationalist resentment and individual rights), and also
MEXICAN REVOLUTION 10 year civil war (1910-1920), U.S. concerns owned 20% of the nation s territory. Caused primarily by internal forces (growing nationalist resentment and individual rights), and also
Mexican Revolution Notes
 Mexican Revolution Notes Monday, April 23, 2012 11:07 AM Rebellion Against Madera The Zapatista's led revolts calling for restoration of lands to rural villages Revolts spread through Morelos, Guerrero,
Mexican Revolution Notes Monday, April 23, 2012 11:07 AM Rebellion Against Madera The Zapatista's led revolts calling for restoration of lands to rural villages Revolts spread through Morelos, Guerrero,
WASHMUN IX Mexican Revolution of 1910 Joint Crisis Committee: Rebels
 WASHMUN IX Mexican Revolution of 1910 Joint Crisis Committee: Rebels Chaired by: Peter Jacob and Gabriel Sessions Hello Delegates, My name is Peter Jacob and I will be one of your co-chairs for the 2018
WASHMUN IX Mexican Revolution of 1910 Joint Crisis Committee: Rebels Chaired by: Peter Jacob and Gabriel Sessions Hello Delegates, My name is Peter Jacob and I will be one of your co-chairs for the 2018
The Mexican Revolution. Civil War
 The Mexican Revolution Civil War The War of North American Intervention (Mexican-American War) Antonio Lopez Santa Ana was President of 11 different governments Kept central government weak and taxes low
The Mexican Revolution Civil War The War of North American Intervention (Mexican-American War) Antonio Lopez Santa Ana was President of 11 different governments Kept central government weak and taxes low
Between 1821 and 1857, Mexico had about 50
 Land, Liberty, and the Mexican Revolution For more than 100 years after winning independence from Spain in 1821, Mexico suffered a stream of political calamities. These included civil wars, dictatorships,
Land, Liberty, and the Mexican Revolution For more than 100 years after winning independence from Spain in 1821, Mexico suffered a stream of political calamities. These included civil wars, dictatorships,
D70833 D83230 D83232 D83237 D103259
 English I, 3rd Quarter, Week 7 Teacher Key with Answers Ques Answer Level Skill Subskill Item # 1 B Moderate English Language Arts Standards : Writing 2 C Easy English Language Arts 3 B Moderate English
English I, 3rd Quarter, Week 7 Teacher Key with Answers Ques Answer Level Skill Subskill Item # 1 B Moderate English Language Arts Standards : Writing 2 C Easy English Language Arts 3 B Moderate English
Energy Reform in Mexico
 Energy Reform in Mexico From independence in 1821 to current reform May 6, 2014 1 Mexico Eagle Ford Shale 1519 1521 Spanish explorer Hernan Cortes conquers Central Mexico. The war mainly benefited the
Energy Reform in Mexico From independence in 1821 to current reform May 6, 2014 1 Mexico Eagle Ford Shale 1519 1521 Spanish explorer Hernan Cortes conquers Central Mexico. The war mainly benefited the
Revolutions in Latin America (19c - Early 20c) Ms. Susan M. Pojer & Ms. Lisbeth Rath Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NY
 Revolutions in Latin America (19c - Early 20c) Ms. Susan M. Pojer & Ms. Lisbeth Rath Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NY European Empires: 1660s 16c-18c: New Ideas Brewing in Europe 4. Preoccupation of Spain
Revolutions in Latin America (19c - Early 20c) Ms. Susan M. Pojer & Ms. Lisbeth Rath Horace Greeley HS Chappaqua, NY European Empires: 1660s 16c-18c: New Ideas Brewing in Europe 4. Preoccupation of Spain
Difficult choice. Republican ideals? Imperial power?
 Difficult choice Republican ideals? Imperial power? Anti-Imperialist League Founded in 1899. Mark Twain, Andrew Carnegie, William James, and William Jennings Bryan among the leaders. Campaigned against
Difficult choice Republican ideals? Imperial power? Anti-Imperialist League Founded in 1899. Mark Twain, Andrew Carnegie, William James, and William Jennings Bryan among the leaders. Campaigned against
New American Diplomacy. Chapter 5 Section 3 US History (EOC)
 New American Diplomacy Chapter 5 Section 3 US History (EOC) Roxanna Ford 2014 What s the Main Idea? The Russo-Japanese War, the Panama Canal, and the Mexican Revolution added to America s military and
New American Diplomacy Chapter 5 Section 3 US History (EOC) Roxanna Ford 2014 What s the Main Idea? The Russo-Japanese War, the Panama Canal, and the Mexican Revolution added to America s military and
Chapter 12: Transformations Around the Globe,
 Chapter 12: Transformations Around the Globe, 1800 1914 China and Japan respond differently to the European powers. The United States influences Latin America, and Mexico undergoes a revolution. Theodore
Chapter 12: Transformations Around the Globe, 1800 1914 China and Japan respond differently to the European powers. The United States influences Latin America, and Mexico undergoes a revolution. Theodore
Art as Activism Section Panels
 Art as Activism Section Panels Women in Mexico s Revolutionary History Women had significant roles throughout Mexico s revolutionary history. Not only did they care for the soldiers in their family, they
Art as Activism Section Panels Women in Mexico s Revolutionary History Women had significant roles throughout Mexico s revolutionary history. Not only did they care for the soldiers in their family, they
Chapter 7, Section 3. New American Diplomacy
 Chapter 7, Section 3 New American Diplomacy Roosevelt s Diplomacy Big Ideas: Presidents Roosevelt and Taft used a mixture of military and financial tools to expand American hegemony in Asia and Latin America.
Chapter 7, Section 3 New American Diplomacy Roosevelt s Diplomacy Big Ideas: Presidents Roosevelt and Taft used a mixture of military and financial tools to expand American hegemony in Asia and Latin America.
STUDY GUIDE. The Mexican Revolution by Michael J. Gonzales. For IB History HL Paper 3 - OF -
 STUDY GUIDE - OF - The Mexican Revolution by Michael J. Gonzales For IB History HL Paper 3 Chapter 1: General Porfirio Diaz and the Liberal Legacy 1A. Political Consolidation Porfirio Diaz had strong ties
STUDY GUIDE - OF - The Mexican Revolution by Michael J. Gonzales For IB History HL Paper 3 Chapter 1: General Porfirio Diaz and the Liberal Legacy 1A. Political Consolidation Porfirio Diaz had strong ties
STRIVING FOR INDEPENDENCE: MEXICO, ARGENTINA AND BRAZIL A P W O R L D H I S T O R Y C H A P T E R 2 8 C
 STRIVING FOR INDEPENDENCE: MEXICO, ARGENTINA AND BRAZIL 1900-1949 A P W O R L D H I S T O R Y C H A P T E R 2 8 C THE MEXICAN REVOLUTION, 1910 1940 MEXICO IN 1910 Mexico s geographical location made it
STRIVING FOR INDEPENDENCE: MEXICO, ARGENTINA AND BRAZIL 1900-1949 A P W O R L D H I S T O R Y C H A P T E R 2 8 C THE MEXICAN REVOLUTION, 1910 1940 MEXICO IN 1910 Mexico s geographical location made it
The Industrial Revolution and Latin America
 The Industrial Revolution and Latin America AP WORLD HISTORY NOTES CHAPTER 17 (1750-1914) After Independence in Latin America Decimated populations Flooded or closed silver mines Diminished herds of livestock
The Industrial Revolution and Latin America AP WORLD HISTORY NOTES CHAPTER 17 (1750-1914) After Independence in Latin America Decimated populations Flooded or closed silver mines Diminished herds of livestock
Welcome to History 06 History of the Americas II Prof. Valadez
 Welcome to History 06 History of the Americas II Prof. Valadez 1 Topics Review: Positivism Participation Assignment #3 U.S. Foreign Policy In Latin America Early 20 th Century Revolutions in Latin America
Welcome to History 06 History of the Americas II Prof. Valadez 1 Topics Review: Positivism Participation Assignment #3 U.S. Foreign Policy In Latin America Early 20 th Century Revolutions in Latin America
MEXICO. Part 1: The Making of the Modern State
 MEXICO Part 1: The Making of the Modern State Why Study Mexico? History of Revolution, One-Party Dominance, Authoritarianism But has ended one-party rule, democratized, and is now considered a newly industrializing
MEXICO Part 1: The Making of the Modern State Why Study Mexico? History of Revolution, One-Party Dominance, Authoritarianism But has ended one-party rule, democratized, and is now considered a newly industrializing
China Resists Outside Influence
 Name CHAPTER 28 Section 1 (pages 805 809) China Resists Outside Influence BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about imperialism in Asia. In this section, you will see how China dealt with foreign
Name CHAPTER 28 Section 1 (pages 805 809) China Resists Outside Influence BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about imperialism in Asia. In this section, you will see how China dealt with foreign
Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War
 Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War 1 Imperialism & Expansion CH 14-1 Imperialism & War Name Reasons why the United States becomes an imperialist nation. 1-New Markets 2-Anglo-Saxonism 3-Modern Navy 4-Into
Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War 1 Imperialism & Expansion CH 14-1 Imperialism & War Name Reasons why the United States becomes an imperialist nation. 1-New Markets 2-Anglo-Saxonism 3-Modern Navy 4-Into
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e. Chapter Twenty-one: America and the Great War
 Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e America and the Great War Introduction Total War The Big Stick : America and the World, 1901-1917 Roosevelt and Civilization Racial and Economic Basis of Roosevelt
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e America and the Great War Introduction Total War The Big Stick : America and the World, 1901-1917 Roosevelt and Civilization Racial and Economic Basis of Roosevelt
Latin America in the 19th and 20th Centuries
 Latin America in the 19th and 20th Centuries Prior to the 20th Century In the 1700s Spanish power was starting to decline. Creoles(criollos) began to question the policies of Spain and Portugal. However,
Latin America in the 19th and 20th Centuries Prior to the 20th Century In the 1700s Spanish power was starting to decline. Creoles(criollos) began to question the policies of Spain and Portugal. However,
Name Date CHAPTER 28 Section 1 GUIDED READING China Responds to Pressure from the West A. Perceiving Cause and Effect As you read this section, note s
 Name Date CHAPTER 28 Section 1 GUIDED READING China Responds to Pressure from the West A. Perceiving Cause and Effect As you read this section, note some of the causes and effects of events and policies
Name Date CHAPTER 28 Section 1 GUIDED READING China Responds to Pressure from the West A. Perceiving Cause and Effect As you read this section, note some of the causes and effects of events and policies
D51637 D81119 D60043 D73056 D70829 D70831 D70830 D57928 D53569 D81095
 English I, 3rd Quarter, Week 4 Teacher Key with Answers Ques Answer Level Skill Subskill Item # 1 C Moderate English Language Arts 2 C Moderate English Language Arts 3 A Easy English Language Arts 4 C
English I, 3rd Quarter, Week 4 Teacher Key with Answers Ques Answer Level Skill Subskill Item # 1 C Moderate English Language Arts 2 C Moderate English Language Arts 3 A Easy English Language Arts 4 C
Why did the United States oppose the Mexican Revolution, and was it successful in achieving its goals?
 MEXICAN REVOLUTION Why did the United States oppose the Mexican Revolution, and was it successful in achieving its goals? Viewpoint: The United States opposed the Mexican Revolution because American business
MEXICAN REVOLUTION Why did the United States oppose the Mexican Revolution, and was it successful in achieving its goals? Viewpoint: The United States opposed the Mexican Revolution because American business
WASHMUN IX Mexican Revolution of 1910 Joint Crisis Committee: United States Government
 WASHMUN IX Mexican Revolution of 1910 Joint Crisis Committee: United States Government Chaired by: Liam Webster and Cory Dudka Committee Overview The Mexican Revolution committee is a joint crisis committee.
WASHMUN IX Mexican Revolution of 1910 Joint Crisis Committee: United States Government Chaired by: Liam Webster and Cory Dudka Committee Overview The Mexican Revolution committee is a joint crisis committee.
World History (Survey) Chapter 28: Transformations Around the Globe,
 World History (Survey) Chapter 28: Transformations Around the Globe, 1800 1914 Section 1: China Responds to Pressure from the West In the late 1700s, China was self-sufficient. It had a strong farming
World History (Survey) Chapter 28: Transformations Around the Globe, 1800 1914 Section 1: China Responds to Pressure from the West In the late 1700s, China was self-sufficient. It had a strong farming
American Foreign Policy, : The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly.
 American Foreign Policy, 1880-1920: The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly. Each group will become experts on their assigned country. Create poster showing how U.S. policy toward your respective country was good,
American Foreign Policy, 1880-1920: The Good, the Bad, & the Ugly. Each group will become experts on their assigned country. Create poster showing how U.S. policy toward your respective country was good,
U.S. Imperialism s Impact on Other Nations
 U.S. Imperialism s Impact on Other Nations U.S.-Japanese Relations Japan had closed itself to outsiders in the late 1400s; held a strong mistrust of Western cultures In mid-1800s, US businesses began to
U.S. Imperialism s Impact on Other Nations U.S.-Japanese Relations Japan had closed itself to outsiders in the late 1400s; held a strong mistrust of Western cultures In mid-1800s, US businesses began to
Mexican History and Systems of Empire
 Mexican History and Systems of Empire Day 1: The Conquest of Mexico 1. I can explain the systems the Spaniards put in place in New Spain and how they impacted Mexico over the long term. 2. I can use OPVL
Mexican History and Systems of Empire Day 1: The Conquest of Mexico 1. I can explain the systems the Spaniards put in place in New Spain and how they impacted Mexico over the long term. 2. I can use OPVL
Chapter 28 Transformations Around the Globe
 Chapter 28 Transformations Around the Globe 28-1 28-1 China Tea-Opium addiction Opium War 1839 Hong Kong Outlet to the world! Over Population Taiping Rebellion 1850s Heavenly Kingdom of Great Peace Civil
Chapter 28 Transformations Around the Globe 28-1 28-1 China Tea-Opium addiction Opium War 1839 Hong Kong Outlet to the world! Over Population Taiping Rebellion 1850s Heavenly Kingdom of Great Peace Civil
Chapter 3 The Mexican Revolution
 Chapter 3 The Mexican Revolution The Mexican Revolution was the first great political and social revolution of the twentieth century. It was also one of a cluster of revolutions occurring at about the
Chapter 3 The Mexican Revolution The Mexican Revolution was the first great political and social revolution of the twentieth century. It was also one of a cluster of revolutions occurring at about the
Princeton Model United Nations Conference 2017
 Princeton Model United Nations Conference 2017 Mexican Revolution Chair: Ryan Chavez Director: Rohan Shah 1 CONTENTS Letter from the Chair 3 Committee Description. 5 Mexican Revolution:.. 5 Introduction
Princeton Model United Nations Conference 2017 Mexican Revolution Chair: Ryan Chavez Director: Rohan Shah 1 CONTENTS Letter from the Chair 3 Committee Description. 5 Mexican Revolution:.. 5 Introduction
LATIN AMERICA POST-INDEPENDENCE ( )
 LATIN AMERICA POST-INDEPENDENCE (1820-1920) Socially, not much changed w/ independencelarge gap between wealthy landowners & poor laborers Politically unstable- military dictators called caudillos often
LATIN AMERICA POST-INDEPENDENCE (1820-1920) Socially, not much changed w/ independencelarge gap between wealthy landowners & poor laborers Politically unstable- military dictators called caudillos often
MEXICO. Government and Political Culture
 MEXICO Government and Political Culture Historical Background Spanish Colony Hernan Cortes effects on culture, religion, ethnic cleavages, economy, demographics,mestizos Independence Movement led by Father
MEXICO Government and Political Culture Historical Background Spanish Colony Hernan Cortes effects on culture, religion, ethnic cleavages, economy, demographics,mestizos Independence Movement led by Father
COMPREHENSION AND CRITICAL THINKING
 Name Class Date Chapter Summary COMPREHENSION AND CRITICAL THINKING Use information from the graphic organizer to answer the following questions. 1. Recall What caused the sectional controversy that led
Name Class Date Chapter Summary COMPREHENSION AND CRITICAL THINKING Use information from the graphic organizer to answer the following questions. 1. Recall What caused the sectional controversy that led
MEXICO. Government and Political Culture
 MEXICO Government and Political Culture How did Colonialism affect the cultural and political development of Mexico? Hernan Cortes Culture Religion Demographics Mestizos Economics Ethnic cleavages Historical
MEXICO Government and Political Culture How did Colonialism affect the cultural and political development of Mexico? Hernan Cortes Culture Religion Demographics Mestizos Economics Ethnic cleavages Historical
Essential Question: What were the important causes & effects of the French Revolution?
 Essential Question: What were the important causes & effects of the French Revolution? Do Now On your ipad or blank piece of paper write down one example on what is needed to consider a revolution as successful.
Essential Question: What were the important causes & effects of the French Revolution? Do Now On your ipad or blank piece of paper write down one example on what is needed to consider a revolution as successful.
From Marxism to Social History: Adolfo Gilly s Revision of The Mexican Revolution. Luis F. Ruiz University of Oregon
 Vol. 4, No. 2, Winter 2007, 243-253 www.ncsu.edu/project/acontracorriente Review/Reseña Adolfo Gilly. The Mexican Revolution: A People s History. Trans. Patrick Camiller. (New York: The New Press, 2005)
Vol. 4, No. 2, Winter 2007, 243-253 www.ncsu.edu/project/acontracorriente Review/Reseña Adolfo Gilly. The Mexican Revolution: A People s History. Trans. Patrick Camiller. (New York: The New Press, 2005)
Texas Independence
 Texas Independence Introduction WARM UP: Some Canadians are angry that the state of Maine, prominently located between Quebec and New Brunswick, is part of the United States, and should be given up to
Texas Independence Introduction WARM UP: Some Canadians are angry that the state of Maine, prominently located between Quebec and New Brunswick, is part of the United States, and should be given up to
MEXICO. Part 1: The Making of the Modern State
 MEXICO Part 1: The Making of the Modern State Why Study Mexico? History of Revolution, One-Party Dominance, Authoritarianism But has ended one-party rule, democratized, and is now considered a newly industrializing
MEXICO Part 1: The Making of the Modern State Why Study Mexico? History of Revolution, One-Party Dominance, Authoritarianism But has ended one-party rule, democratized, and is now considered a newly industrializing
The Declaration of Independence
 The Declaration of Independence What are the main ideas in the Declaration of Independence? Social Studies Vocabulary Declaration of Independence Founding Fathers militia Minuteman Second Continental Congress
The Declaration of Independence What are the main ideas in the Declaration of Independence? Social Studies Vocabulary Declaration of Independence Founding Fathers militia Minuteman Second Continental Congress
America as a World Power
 Page 1 of 7 America as a World Power WHY IT MATTERS NOW Terms & Names The Russo-Japanese War, the Panama Canal, and the Mexican Revolution added to America s military and economic power. American involvement
Page 1 of 7 America as a World Power WHY IT MATTERS NOW Terms & Names The Russo-Japanese War, the Panama Canal, and the Mexican Revolution added to America s military and economic power. American involvement
Chapter 14 Section 1. Revolutions in Russia
 Chapter 14 Section 1 Revolutions in Russia Revolutionary Movement Grows Industrialization stirred discontent among people Factories brought new problems Grueling working conditions, low wages, child labor
Chapter 14 Section 1 Revolutions in Russia Revolutionary Movement Grows Industrialization stirred discontent among people Factories brought new problems Grueling working conditions, low wages, child labor
Welcome to 7 th Grade Texas History!
 Welcome to 7 th Grade Texas History! Natural Texas and People Age of Contact Spanish Colonial The Battle of San Jacinto & Texas Independence Mexican National 10/16/17 Revolution and Republic Early Statehood
Welcome to 7 th Grade Texas History! Natural Texas and People Age of Contact Spanish Colonial The Battle of San Jacinto & Texas Independence Mexican National 10/16/17 Revolution and Republic Early Statehood
In Your Notebook-- What do you remember about the causes of the Russian Revolution? What were the revolutionaries trying to achieve?
 In Your Notebook-- What do you remember about the causes of the Russian Revolution? What were the revolutionaries trying to achieve? What were some of the major events of the revolution itself? What results
In Your Notebook-- What do you remember about the causes of the Russian Revolution? What were the revolutionaries trying to achieve? What were some of the major events of the revolution itself? What results
Causes of the Mexican Revolution. Section 12-B Talks Back
 Causes of the Mexican Revolution Section 12-B Talks Back Out of the social perspec0ves, poli0cal causes, porfiriato, and economical interests, with much research it is conceivable to say that the economic
Causes of the Mexican Revolution Section 12-B Talks Back Out of the social perspec0ves, poli0cal causes, porfiriato, and economical interests, with much research it is conceivable to say that the economic
Gleeson Arizona. Disorder on the Border. The Mexican Revolution and its effects on the Gleeson area
 Gleeson Arizona Disorder on the Border The Mexican Revolution and its effects on the Gleeson area Glenn Snow November 2009 Copyright 2009 Glenn Snow GSnow@GleesonArizona.com Cover photograph: Mexican Revolutionary
Gleeson Arizona Disorder on the Border The Mexican Revolution and its effects on the Gleeson area Glenn Snow November 2009 Copyright 2009 Glenn Snow GSnow@GleesonArizona.com Cover photograph: Mexican Revolutionary
NOTES: People of the Revolution (Part 1)
 Name: Class Period: NOTES: People of the Revolution (Part 1) George Washington 1. Commander In Chief of Continental Army 2. Led colonies to victory over the English Agreed to lead the Army but refused
Name: Class Period: NOTES: People of the Revolution (Part 1) George Washington 1. Commander In Chief of Continental Army 2. Led colonies to victory over the English Agreed to lead the Army but refused
Cesar Chavez and the Organized Labor Movement
 Cesar Chavez and the Organized Labor Movement The labor movement of earlier generations was reignited in part by the United Farm Workers (UFW), led by a labor union activist Cesar Chavez. He was committed
Cesar Chavez and the Organized Labor Movement The labor movement of earlier generations was reignited in part by the United Farm Workers (UFW), led by a labor union activist Cesar Chavez. He was committed
1. Commercial/Business Interests. U. S. Foreign Investments:
 1. Commercial/Business Interests U. S. Foreign Investments: 1869-1908 1. Commercial/Business Interests American Foreign Trade: 1870-1914 2. Military/Strategic Interests Alfred T. Mahan The Influence of
1. Commercial/Business Interests U. S. Foreign Investments: 1869-1908 1. Commercial/Business Interests American Foreign Trade: 1870-1914 2. Military/Strategic Interests Alfred T. Mahan The Influence of
Saturday, September 30, 2017
 Saturday, September 30, 2017 Human Geography of Mexico Content Objective: WG.15A Identify and give examples of different points of view that influence the development of public policies and decision-making
Saturday, September 30, 2017 Human Geography of Mexico Content Objective: WG.15A Identify and give examples of different points of view that influence the development of public policies and decision-making
Impact & Political Outcomes in Mexico
 Impact & Political Outcomes in Mexico Standards SS6H3 The student will analyze important 20th century issues in Latin America and the Caribbean. b. Explain the impact and political outcomes of the Zapatista
Impact & Political Outcomes in Mexico Standards SS6H3 The student will analyze important 20th century issues in Latin America and the Caribbean. b. Explain the impact and political outcomes of the Zapatista
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Chapter 16, Section 3 For use with textbook pages 514 519 THE RUSSIAN REVOLUTION KEY TERMS soviets councils in Russia composed of representatives from the workers and soldiers (page 516) war communism
Chapter 16, Section 3 For use with textbook pages 514 519 THE RUSSIAN REVOLUTION KEY TERMS soviets councils in Russia composed of representatives from the workers and soldiers (page 516) war communism
throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not.
 1. Tell what at least three of the symbols you see on this flag represent. 2. Do you think these three symbols would be recognized throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not. 3. Why would this
1. Tell what at least three of the symbols you see on this flag represent. 2. Do you think these three symbols would be recognized throughout the US? Around the world? Why or why not. 3. Why would this
British policy of ignoring the colonies. a replacement of a government by the people of that government. No government/chaos mob rule
 1. Define revolution 2. Define tyranny 3. Define anarchy 4. Define salutary neglect a replacement of a government by the people of that government Total loss of freedom/absolute government power No government/chaos
1. Define revolution 2. Define tyranny 3. Define anarchy 4. Define salutary neglect a replacement of a government by the people of that government Total loss of freedom/absolute government power No government/chaos
Welcome to History 06 History of the Americas II Prof. Valadez
 Welcome to History 06 History of the Americas II Prof. Valadez Topics What is Positivism? Why does Latin American adopt positivism? U.S. Foreign Policy In Latin America Early 20 th Century Revolutions
Welcome to History 06 History of the Americas II Prof. Valadez Topics What is Positivism? Why does Latin American adopt positivism? U.S. Foreign Policy In Latin America Early 20 th Century Revolutions
Welcome to History 44 The Mexican-American in the History of the United States II Prof. Valadez
 Welcome to History 44 The Mexican-American in the History of the United States II Prof. Valadez 1 The New Imperialism Becoming a World Power After 1870 European powers scrambled to dominate Africa, Asia,
Welcome to History 44 The Mexican-American in the History of the United States II Prof. Valadez 1 The New Imperialism Becoming a World Power After 1870 European powers scrambled to dominate Africa, Asia,
We re Free Let s Grow!
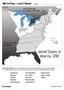 Atlantic Ocean Find Those States! The United States started out with just thirteen states. Use the list below to correctly identify each one on the map. Watch out: Things were a little different back then!
Atlantic Ocean Find Those States! The United States started out with just thirteen states. Use the list below to correctly identify each one on the map. Watch out: Things were a little different back then!
1. What specific activities does Article 3 of the Constitution of 1917 outlawing?
 Global Studies: Unit #2 Mexican Revolution DBQ Name: Document #1: Excerpt of Article 3 of the Constitution of 1917: I. Freedom of religious beliefs being guaranteed by Article 24, the standard which shall
Global Studies: Unit #2 Mexican Revolution DBQ Name: Document #1: Excerpt of Article 3 of the Constitution of 1917: I. Freedom of religious beliefs being guaranteed by Article 24, the standard which shall
El Observador. Dicember 31st, Local News National News
 El Observador Dicember 31st, 1867 Local News National News Back Out of the Stone Age jtrev.htm Nicolas Navarro First the Troops, Now the State. Carlos Moreleon On December the 4th of 1867, José Jerónimo
El Observador Dicember 31st, 1867 Local News National News Back Out of the Stone Age jtrev.htm Nicolas Navarro First the Troops, Now the State. Carlos Moreleon On December the 4th of 1867, José Jerónimo
8th Grade History. American Revolution
 8th Grade History American Revolution BOARD QUESTIONS 1) WHAT DID THE SPANISH WANT IN THE AMERICAS? 2) WHAT DID THE FRENCH WANT IN THE AMERICAS? 3) WHAT DID THE ENGLISH WANT IN THE AMERICAS? 4) HOW DID
8th Grade History American Revolution BOARD QUESTIONS 1) WHAT DID THE SPANISH WANT IN THE AMERICAS? 2) WHAT DID THE FRENCH WANT IN THE AMERICAS? 3) WHAT DID THE ENGLISH WANT IN THE AMERICAS? 4) HOW DID
Welcome to History 06 History of the Americas II Prof. Valadez
 Welcome to History 06 History of the Americas II Prof. Valadez 1 Topics Review: Early 20 th Century Revolutions in Latin America Quiz 3 The Great Depression World War II 2 The Downfall of Diaz 1900 Regeneracion,
Welcome to History 06 History of the Americas II Prof. Valadez 1 Topics Review: Early 20 th Century Revolutions in Latin America Quiz 3 The Great Depression World War II 2 The Downfall of Diaz 1900 Regeneracion,
Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism ( )
 Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism (1890-1930) What is an empire? Is imperialism the same as colonization? Why would the U.S. get involved in this practice? What is the difference between acquiring and
Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism (1890-1930) What is an empire? Is imperialism the same as colonization? Why would the U.S. get involved in this practice? What is the difference between acquiring and
Name Class Date. The French Revolution and Napoleon Section 3
 Name Class Date Section 3 MAIN IDEA Napoleon Bonaparte rose through military ranks to become emperor over France and much of Europe. Key Terms and People Napoleon Bonaparte ambitious military leader who
Name Class Date Section 3 MAIN IDEA Napoleon Bonaparte rose through military ranks to become emperor over France and much of Europe. Key Terms and People Napoleon Bonaparte ambitious military leader who
Toussaint L Ouverture, Simon Bolivar, & Miguel Hidalgo
 Toussaint L Ouverture, Simon Bolivar, & Miguel Hidalgo Spain conquered most of the lands in the Americas (while Portugal conquered Brazil0. It divided its empire into provinces. The two most important
Toussaint L Ouverture, Simon Bolivar, & Miguel Hidalgo Spain conquered most of the lands in the Americas (while Portugal conquered Brazil0. It divided its empire into provinces. The two most important
Florida Notes. had colonized Florida in the late 1500 s By the 1800 s the population of Florida was diverse with and
 Florida Notes Florida had colonized Florida in the late 1500 s By the 1800 s the population of Florida was diverse with and Attempt at Diplomacy Jefferson sent in 1804 to Spain to attempt to buy Florida
Florida Notes Florida had colonized Florida in the late 1500 s By the 1800 s the population of Florida was diverse with and Attempt at Diplomacy Jefferson sent in 1804 to Spain to attempt to buy Florida
America as a World Power
 MAIN IDEA America as a World Power WHY IT MATTERS NOW Terms & Names The Russo-Japanese War, the Panama Canal, and the Mexican Revolution added to America s military and economic power. American involvement
MAIN IDEA America as a World Power WHY IT MATTERS NOW Terms & Names The Russo-Japanese War, the Panama Canal, and the Mexican Revolution added to America s military and economic power. American involvement
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT THE JULY 2018 ELECTIONS IN MEXICO.
 WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT THE JULY 2018 ELECTIONS IN MEXICO. Galicia Abogados, S.C. G a l i c i a A b o g a d o s, S. C. B l v d. M a n u e l Á v i l a C a m a c h o N o. 2 4-7 C o l. L o m a s d e C
WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW ABOUT THE JULY 2018 ELECTIONS IN MEXICO. Galicia Abogados, S.C. G a l i c i a A b o g a d o s, S. C. B l v d. M a n u e l Á v i l a C a m a c h o N o. 2 4-7 C o l. L o m a s d e C
Pablo Noyola February 22, 2016 Comparison of the Mexican War of Independence and the Mexican Revolution Hutson 1st Period Comparative Revolutions
 Pablo Noyola February 22, 2016 Comparison of the Mexican War of Independence and the Mexican Revolution Hutson 1st Period Comparative Revolutions Research Paper Noyola 1 Though these two revolutions took
Pablo Noyola February 22, 2016 Comparison of the Mexican War of Independence and the Mexican Revolution Hutson 1st Period Comparative Revolutions Research Paper Noyola 1 Though these two revolutions took
World War I: Mr. Mattingly U.S. History
 World War I: 1914-1918 Mr. Mattingly U.S. History WWI: The War to End all Wars. 30 Nations on Six Continents Disrupts 40 years of peace Causes of WWI: Powder Keg Nationalism = intense pride in one s homeland
World War I: 1914-1918 Mr. Mattingly U.S. History WWI: The War to End all Wars. 30 Nations on Six Continents Disrupts 40 years of peace Causes of WWI: Powder Keg Nationalism = intense pride in one s homeland
Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea
 Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea In the last half of the 1800s, the United States joined the race for control of overseas territories.
Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea In the last half of the 1800s, the United States joined the race for control of overseas territories.
Revolution and Nationalism
 Revolution and Nationalism 1900-1939 Revolutions in Russia Section 1 Long-term social unrest in Russia exploded in revolution, and ushered in the first Communist government. Czars Resist Change Romanov
Revolution and Nationalism 1900-1939 Revolutions in Russia Section 1 Long-term social unrest in Russia exploded in revolution, and ushered in the first Communist government. Czars Resist Change Romanov
When was Britain closest to revolution in ?
 When was Britain closest to revolution in 1815-1832? Today I will practise Putting dates of when Industrial protest happened into chronological order Explaining the extent of historical change that took
When was Britain closest to revolution in 1815-1832? Today I will practise Putting dates of when Industrial protest happened into chronological order Explaining the extent of historical change that took
New Global Patterns. Imperialism II
 New Global Patterns Imperialism II 1800-1914 本は近代化 Japan Modernizes Japan isolated itself from the world from 1600-1853 Japan s reaction to western imperialism was to become imperialist herself. Japan
New Global Patterns Imperialism II 1800-1914 本は近代化 Japan Modernizes Japan isolated itself from the world from 1600-1853 Japan s reaction to western imperialism was to become imperialist herself. Japan
MANIFEST DESTINY, THE OREGON TRAIL, AND THE MEXICAN AMERICAN WAR
 What do you see? MANIFEST DESTINY, THE OREGON TRAIL, AND THE MEXICAN AMERICAN WAR Manifest Destiny Manifest Destiny was the belief that it was the destiny of the U.S. to expand its territory over the whole
What do you see? MANIFEST DESTINY, THE OREGON TRAIL, AND THE MEXICAN AMERICAN WAR Manifest Destiny Manifest Destiny was the belief that it was the destiny of the U.S. to expand its territory over the whole
CONSTITUTIONAL RIGHTS FOUNDATION Bill of Rights in Action Winter 2004 (20:1) Conflict of Cultures
 CONSTITUTIONAL RIGHTS FOUNDATION Bill of Rights in Action Winter 2004 (20:1) Conflict of Cultures BRIA 20:1 Home President Polk and the Taking of the West Muslim Conquests in Europe The Rise of Islamist
CONSTITUTIONAL RIGHTS FOUNDATION Bill of Rights in Action Winter 2004 (20:1) Conflict of Cultures BRIA 20:1 Home President Polk and the Taking of the West Muslim Conquests in Europe The Rise of Islamist
Why did revolution occur in Russia in March 1917? Why did Lenin and the Bolsheviks launch the November revolution?
 Two Revolutions 1 in Russia Why did revolution occur in Russia in March 1917? Why did Lenin and the Bolsheviks launch the November revolution? How did the Communists defeat their opponents in Russia s
Two Revolutions 1 in Russia Why did revolution occur in Russia in March 1917? Why did Lenin and the Bolsheviks launch the November revolution? How did the Communists defeat their opponents in Russia s
Roosevelts Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine Monroe Doctrine Clayton- Bulwer Treaty Westward Expansion.
 Origins Westward Expansion Monroe Doctrine 1820 Clayton- Bulwer Treaty 1850 Roosevelts Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine 1904 Manifest Destiny U.S. Independence & Westward Expansion Monroe Doctrine 1820
Origins Westward Expansion Monroe Doctrine 1820 Clayton- Bulwer Treaty 1850 Roosevelts Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine 1904 Manifest Destiny U.S. Independence & Westward Expansion Monroe Doctrine 1820
Imperialism and America
 CHAPTER 10 Section 1 ( pages 342 345) Imperialism and America BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about Woodrow Wilson. In this section, you will learn how economic activity led to political
CHAPTER 10 Section 1 ( pages 342 345) Imperialism and America BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about Woodrow Wilson. In this section, you will learn how economic activity led to political
The Federalist Papers
 The Federalist Papers If men were angels, no government would be necessary. James Madison During the Revolutionary War, Americans set up a new national government. They feared a strong central government.
The Federalist Papers If men were angels, no government would be necessary. James Madison During the Revolutionary War, Americans set up a new national government. They feared a strong central government.
Chapters 18 Review American History
 Chapters 18 Review American History I. Policy of Imperialism: a. Imperialism is a countries policy and practice of creating an empire and maintaining control to expand their control of raw materials, and
Chapters 18 Review American History I. Policy of Imperialism: a. Imperialism is a countries policy and practice of creating an empire and maintaining control to expand their control of raw materials, and
The French Revolution A Concise Overview
 The French Revolution A Concise Overview The Philosophy of the Enlightenment and the success of the American Revolution were causing unrest within France. People were taxed heavily and had little or no
The French Revolution A Concise Overview The Philosophy of the Enlightenment and the success of the American Revolution were causing unrest within France. People were taxed heavily and had little or no
Transformations Around the Globe. Ch
 Transformations Around the Globe Ch 28 1800-1914 China + the West China looked down on foreigners China was self-sufficient Strong agricultural economy Extensive mining + industry China wasn t interested
Transformations Around the Globe Ch 28 1800-1914 China + the West China looked down on foreigners China was self-sufficient Strong agricultural economy Extensive mining + industry China wasn t interested
Welcome to History 44 The Mexican-American in the History of the United States II Prof. Valadez
 Welcome to History 44 The Mexican-American in the History of the United States II Prof. Valadez 1 I. 1848-1900 the 1 st Mexican- American Generation II. 1900-1929 Mexico Lindo Generation or Immigrant Gen.
Welcome to History 44 The Mexican-American in the History of the United States II Prof. Valadez 1 I. 1848-1900 the 1 st Mexican- American Generation II. 1900-1929 Mexico Lindo Generation or Immigrant Gen.
Describe the methods the colonists used to protest British taxes. Understand the significance of the First Continental Congress in 1774.
 Objectives Describe the methods the colonists used to protest British taxes. Understand the significance of the First Continental Congress in 1774. Assess why Congress declared independence and the ideas
Objectives Describe the methods the colonists used to protest British taxes. Understand the significance of the First Continental Congress in 1774. Assess why Congress declared independence and the ideas
Click to move forward
 Click to move forward Click on each one of the links below to find out information on each of the different social classes of France. Once you look at each slide describing the different social classes
Click to move forward Click on each one of the links below to find out information on each of the different social classes of France. Once you look at each slide describing the different social classes
Imperialism and America
 Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire CHAPTER 10 Section 1 (pages 342-345) Imperialism and America American Expansionism (pages 342-344) Why did Americans support imperialism? In 1893, Queen Liliuokalani
Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire CHAPTER 10 Section 1 (pages 342-345) Imperialism and America American Expansionism (pages 342-344) Why did Americans support imperialism? In 1893, Queen Liliuokalani
BACKGROUND Historically speaking, . There is NO. * brought to America *Native American depopulated due to
 BACKGROUND Historically speaking,. There is NO. COLONIZATION Impact *Columbus Claims New World for * established * English Colonies Created * brought to America *Native American depopulated due to Motive
BACKGROUND Historically speaking,. There is NO. COLONIZATION Impact *Columbus Claims New World for * established * English Colonies Created * brought to America *Native American depopulated due to Motive
A Place of Three Cultures
 A Place of Three Cultures A Place of Three Cultures A broad square in Mexico City stands as a symbol of the complexity of Mexican culture. The Plaza de lastresculturas The Three Cultures is located on
A Place of Three Cultures A Place of Three Cultures A broad square in Mexico City stands as a symbol of the complexity of Mexican culture. The Plaza de lastresculturas The Three Cultures is located on
Proclamation of French and Indian War. Sugar Act
 Proclamation of 1763 French and Indian War Sugar Act Official announcement made by King George III of England which stopped colonists from settling lands west of the Appalachian Mountains. War fought by
Proclamation of 1763 French and Indian War Sugar Act Official announcement made by King George III of England which stopped colonists from settling lands west of the Appalachian Mountains. War fought by
Sub-SaharanSaharan Africa,
 Chapter 32 Striving for Independence: Africa, India, and Latin America 1900 19491949 Sub-SaharanSaharan Africa, 1900 19451945 Colonial Africa: Economic and Social Changes Outside of Algeria, Kenya, and
Chapter 32 Striving for Independence: Africa, India, and Latin America 1900 19491949 Sub-SaharanSaharan Africa, 1900 19451945 Colonial Africa: Economic and Social Changes Outside of Algeria, Kenya, and
To run away or leave someone in their time of need.
 Desert To run away or leave someone in their time of need. Inflation Rapid rise in prices. Blockade Barrier preventing the movement of troops and supplies. Tributary River or stream that flows into a larger
Desert To run away or leave someone in their time of need. Inflation Rapid rise in prices. Blockade Barrier preventing the movement of troops and supplies. Tributary River or stream that flows into a larger
WORLD WAR 1. Causes of WWI
 WORLD WAR 1 1914-1918 Causes of WWI 1. Imperialism: Germany, France, & Great Britain Scramble for power and claim to lands in Africa, Asia, and the Pacific 2. Militarism Aggressive build up of a nation
WORLD WAR 1 1914-1918 Causes of WWI 1. Imperialism: Germany, France, & Great Britain Scramble for power and claim to lands in Africa, Asia, and the Pacific 2. Militarism Aggressive build up of a nation
NEW GOVERNMENT: CONFEDERATION TO CONSTITUTION FLIP CARD
 NEW GOVERNMENT: CONFEDERATION TO CONSTITUTION FLIP CARD Big Ideas: Imagine trying to make a new country from scratch. You ve just had a war with the only leaders you ve ever known, and now you have to
NEW GOVERNMENT: CONFEDERATION TO CONSTITUTION FLIP CARD Big Ideas: Imagine trying to make a new country from scratch. You ve just had a war with the only leaders you ve ever known, and now you have to
Can your decisions win the Civil War?
 Can your decisions win the Civil War? You are an experienced general trained to fight for the King. However, you are a strict Puritan and do not agree with the way the King is running the country. You
Can your decisions win the Civil War? You are an experienced general trained to fight for the King. However, you are a strict Puritan and do not agree with the way the King is running the country. You
Reading Essentials and Study Guide
 Lesson 2 Uniting for Independence ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why and how did the colonists declare independence? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary draft outline or first copy consent permission or approval
Lesson 2 Uniting for Independence ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why and how did the colonists declare independence? Reading HELPDESK Academic Vocabulary draft outline or first copy consent permission or approval
1. Base your answer to question on the partial outline below and on your knowledge of social studies.
 Frederick Douglass Academy Global Studies 1. Base your answer to question on the partial outline below and on your knowledge of social studies. I. A. Ideas from the American Revolution spread. B. Enslaved
Frederick Douglass Academy Global Studies 1. Base your answer to question on the partial outline below and on your knowledge of social studies. I. A. Ideas from the American Revolution spread. B. Enslaved
