Texas Elections Part II
|
|
|
- Lynn Aubrey Lyons
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Texas Elections Part II In a society governed passively by free markets and free elections, organized greed always defeats disorganized democracy. Matt Taibbi
2 Regulation of Campaign Finance in Texas 1955: new provision for campaign expenditure reports reduced the number required to one before and one after an election 1973: Texas Campaign Reporting and Disclosure Act passed with primary purpose of publicizing names of large donors, no enforcement provision Legislature subsequently refused to make any significant changes in campaign-finance laws... still no limits on the amount any individual or political action committee (PAC) may give any candidate except for someone running for a national office (covered by national law)
3 Regulation of Campaign Finance in Texas 1976: Buckley v. Valeo struck down limits on various types of expenditures by or on behalf of candidates for national office 1991: Texas Ethics Law created Texas Ethics Commission... hasn t been particularly effective, clouded by scandals hard money (political donations that are regulated by law through the FEC) vs. soft money (donated to political parties in a way that leaves the contribution unregulated) Nifty or Shifty: A Campaign Finance Quiz
4 National and Texas Campaign Contribution Limits
5 Media in Texas Campaigns Television exposure increases name recognition. Television increases the costs of campaigning. Television is now fundamental for campaigns TV ad spending in Texas races by non-candidate organizations (PACs, super PACs, labor unions, trade associations, social welfare nonprofits, dark money groups not required to disclose donors) governor $40.4 million lieutenant governor $19.3 million attorney general $10.5 million comptroller $3.1 million state senator $3.1 million state representative $1.8 million agriculture commissioner $586,200 supreme court judge $187,900
6 Negative Campaigning corrosive effect on democracy elections affected by inaccurate or irrelevant charges limits discussion on public policy dissuades candidates: may choose not to run to avoid being a target disheartens citizens: may choose not to vote contributes to voter apathy and alienation but does increase voter turnout
7 Why do Texans vote? civic duty... despite the fact that one vote rarely matters elect candidates decreases alienation affects public policy helps prevent corruption
8 Why don t Texans vote? Texas is a poor and minority state. 17.5%+ in poverty poor and less educated tend not to vote Minorities tend to vote at lower rates than Anglos, and Latinos in Texas vote at even lower rates than Latinos elsewhere. Of Texas 8400 precincts, over 1400 white, wealthy precincts often have turnouts of 80% or more, while over 1000 precincts composed largely of the working class and minorities seldom have 25% turnout. low social capital: the variety of social ties between individuals, and the differing connections that arise between individuals as a result of participating in various activities
9 Why don t Texans vote? Texas political culture: women, the poor and minorities historically have enjoyed only low levels of political participation... places the responsibility for access on the individual, not on institutions or governmental processes... political institutions tend to reinforce patterns of political behavior, which in turn reinforce existing habits and ways of thinking about politics... interprets social change as a threat to established practices and beliefs... respects traditional authority figures Texas has a historically low level of competition, leading to a lack of interest in elections. Minimal competition in minority-dominated districts has induced voter apathy. lack of political efficacy: lack faith that their vote will make a difference in their lives disengaged: very cynical that the system won't respond to them and won't address their needs
10 Why don t Texans vote? have no faith in the integrity of the process barriers to voting: voter intimidation, location of polling places coupled with lack of transportation, registration and voting requirements, workday elections barriers to political influence: congressional districts are drawn so that Hispanic population is packed into isolated districts or so diluted in other districts that their needs are ignored by representatives... creates an overall sense of political helplessness even though Hispanics are the majority population in some regions Candidates don t talk about the issues that matter to minorities. Leads to lack of interest in candidates.
11 Why don t Texans vote? information disconnect: aren t informed about the issues, don t know how to register/vote voter fatigue weak political parties dissatisfaction with elected officials Voting is a decision with costs and consequences, costs that fall most heavily on those in the lowest strata of society. self-fulfilling prophecy: put little to nothing in low-income minority neighborhoods, get little back in return, and so spend time in more reliably high-turnout communities lack of sustained investment in voter registration and get out the vote (GOTV) drives Why Does Texas Have Such a Low Voter Turnout?
12 Inequalities in Electoral Participation racial distortion: After the Voting Rights Act of 1965, African American turnout increased sharply, and the gaps in registration rates between blacks and whites in the South closed to less than 10 points. Currently, African Americans tend to vote and donate to campaigns at rates just below whites and tend to be more likely to participate in other ways. Latino and Asian-American voters tend to participate at lower rates than black and white citizens... might be due to language and cultural differences, as well as to lower levels of income and education in those groups. age distortion: Among eligible citizens, historically and currently, younger citizens are much less likely to participate and vote in elections than those in older age groups. This could be because younger citizens move around more and are undergoing transitions in life, such as leaving school or having children.
13 Inequalities in Electoral Participation gender distortion: Currently, women vote at a slightly higher rate than men, with unmarried women voting at an even more pronounced rate than unmarried men. However, men are more likely to donate to a campaign, discuss politics with others or run for elected office, which may in part be because of the perception that politics is a man s world. Evidence shows that when women do hold high-profile offices, women as a group become more interested in politics. income distortion: A large inequality in participation exists between citizens in different income brackets, with those making more money turning out to the polls, donating and participating in other ways in much larger numbers than those with lower income. This may be caused both by the resources at the disposal of those with higher income as well as disparities in education between income groups.
14 Reasons Given for Not Voting
15 How Texans Did (or Did Not) Vote, 2014 and 2016
16 Turnout as a Percentage of Voting Age Population in Texas and Nationally,
17 The Consequences of Nonvoting in Texas White elites tend to determine election results policy Because minority citizens tend to be more liberal than Anglos, their low voter turnout rates contribute to the conservative character of public policy in Texas. Winners don t have a positive mandate for their policies. The power structure assumes citizens are satisfied. no weapon against corruption
18 The Consequences of Nonvoting in Texas affects the level of vitriol in the political debate Primaries have become increasingly activist-driven, reducing the influence of moderates. more ideologically rigid candidates elected allows for greater influence by moneyed outside groups greater influence by smaller groups Disparities in ethnic voter turnout rates compel a modification in the portrait of the state so that partisanship of population is not reflected in government. Republicans will continue to dominate Texas as long as its minority citizens continue to stay away from the voting booth.
19 The Consequences of Nonvoting in Texas the jury theorem: (1) there is a choice to be made with only two options (one right and one wrong) and (2) each person has at least a slightly better chance of choosing correctly instead of incorrectly... therefore the majority will more often than not choose the correct choice and the greater the majority, the greater the probability that the majority has made the correct choice lack of accountability: the participating electorate is not representative of the entire population so government is no longer responsive to the views of the populace as a whole, but instead only responds to the groups of citizens who are most likely to vote
20 Texas Voters Decide Political scientists identify a number of factors influencing voter choice. Incumbents (current officeholders) enjoy a distinct advantage over challengers due to greater name recognition. voting choice focuses on: party ID, issues, candidate characteristics Political party identification is closely related to voter choice. Party ID makes how people vote more predictable. party in the electorate: voters affiliated with the party declining partisanship: There are more independent voters and voters with no party ID. (Partisanship appears to be stabilizing recently.) Issues continue to remain important for influencing voter choice.
21 Texas Voters Decide Voter perceptions of the personal images of candidates influence candidate choice. The choices for voters are defined by the type of campaigns developed. Citizens make voting decisions based on their evaluations of the past and expectations for the future. retrospective voting: concept that voters choose candidates based on perceptions of an incumbent s past performance in office or the past performance of the incumbent party prospective voting: concept that voters evaluate the incumbent officeholder and the incumbent s party based on expectations of future developments National factors can effect decisions in Texas.
22 Texas Voting Patterns, % 55% 92% 84% 72% 62% 96% 49% 87% 54% 58% 64% 58% 66% 54% 69% 53% 88% 82% 49% 55% 53% 48% 58% 54% 51% 52% 57% 68% 69% 51% 60% 63% 70% 47% 55% 59% 64% 52% 50% 49%
23 Redistricting in Texas Every ten years, after the national census, election districts must be redrawn to adjust for changes in population distribution. redistricting: process of redrawing the boundaries of political districts... applies to Texas house and senate districts, US congressional districts in Texas, state board of education districts and the districts of local governing bodies (county commissioners, JPs, etc) Michael Li runs an excellent blog about Texas redistricting and election law if you re interested in the issue.
24 Redistricting in Texas: Doctrine of One Person, One Vote The failure of legislatures in a number of states, including Texas, to redistrict despite dramatic population shifts, led the US Supreme Court to address the issue in a series of cases in which the court established the doctrine of one person, one vote....judicial ruling that the equal protection clause of the 14th amendment requires that legislative districts be apportioned on the basis of population had a significant impact on policymaking in Texas... caused urban areas to gain in representation and rural areas to lose representation Davis v. Bandemer (1986): Supreme Court held that partisan redistricting violated the equal protection clause, but the court could not agree on the appropriate constitutional standard against which legal claims of partisan redistricting should be evaluated
25 Redistricting in Texas: Voting Rights Act (VRA)...national law designed to protect the voting rights of racial and ethnic minorities makes it illegal for state and local governments to enact and enforce election rules and procedures that diminish African American and Latino voting power pre-clearance provision of the VRA: Requires state and local governments in areas with a history of voting discrimination to submit redistricting plans to the US Department of Justice for approval before they can go into effect. Shaw v. Reno (Shaw I) (1993): relying on race in redistricting "reinforces racial stereotypes and threatens to undermine our system of representative democracy by signaling to elected officials that they represent a particular racial group rather than their constituency as a whole"
26 Redistricting in Texas: Voting Rights Act (VRA) In the late 1980s and early 1990s, interpretations of the VRA led to the drawing of majority-minority districts in order to maximize minority representation by maximizing the number of legislative districts with populations that were more than 50% minority. In the mid-1990s, the US Supreme Court overruled the Justice Department s interpretation of the VRA. The court ruled that the goal of maximizing the number of minority districts was not sufficient to justify race-based redistricting.
27 The Politics of Redistricting in Texas Redistricting is a highly political process. gerrymandering: drawing legislative districts to give advantage to one political party, one candidate, one ethnic/racial group, etc Gerrymandering frequently affects election outcomes. On the average, a political party with complete control of the redistricting process can gerrymander legislative districts to allow that party s candidates to win 54% of legislative districts while capturing 50% of the total vote. Partisan Gerrymandering: The Efficiency Gap
28 How to Gerrymander 5 Districts
29 The Politics of Redistricting in Texas After the 2000 census, the political landscape was considerably different than ten years earlier, and neither party enjoyed clear control of the redistricting process. Redistricting in Texas, thereafter, became a highly charged and contentious political process. The 2001 session of the Texas legislature ended without passage of redistricting plans for either of the two houses of the state legislature or for Congress. if chess allowed gerrymandering The failure of the legislature and governor to adopt a redistricting plan placed the responsibility for drawing new district lines on the Legislative Redistricting Board (LRB), an agency composed of the speaker, lieutenant governor, comptroller, land commissioner and attorney general.
30 The Politics of Redistricting in Texas A new redistricting plan, approved by the LRB, was officially adopted with some modifications imposed by a federal court for the election of members to the Texas House and Senate in After the November elections of 2002, the Republicans captured a majority of the seats in the Texas House for the first time in more than a century and kept a majority of the seats in the Texas Senate. Republicans, however, failed to capture a majority in the state s congressional delegation, prompting a revisiting of the issue of redistricting.
31 The Politics of Redistricting in Texas In 2003, Congressman Tom Delay proposed to the GOP leadership in the Texas House a congressional redistricting plan that could increase the number of Republicans in Congress and lead to a Republican majority in the state s congressional delegation. The redistricting proposal was highly controversial and bitterly opposed by Texas Democrats. Democratic house members made history by leaving the state (for Ardmore, Oklahoma) during the 2003 regular session of the legislature in order to prevent a quorum and prevent the House from passing Delay s redistricting bill.
32 The Politics of Redistricting in Texas Republican Governor Rick Perry called the legislature into a 30-day special session to consider redistricting. The first special session failed. 11 senate Democrats left the state (for Albuquerque, New Mexico) to block a quorum and passage of the redistricting bill in the second session. Eventually the Senate Democrats returned and the legislature passed a redistricting bill in a third session. The battle over congressional redistricting was intense because the shape of legislative districts determines the outcomes of elections, which in turn affect public policy. It illustrates the importance of election rules and procedures.
33 The Politics of Redistricting in Texas The plan proved highly successful for the GOP in Texas. After the 2004 elections, Republicans gained six seats in the state s congressional delegation, which included 21 Republicans and 11 Democrats. In late 2005, the US Supreme Court agreed to hear a legal challenge to the Texas mid-cycle redistricting. The case presented to the court several intriguing legal issues: violation of VRA, constitutionality of mid-cycle redistricting, violation of the one person one vote doctrine, unconstitutional gerrymandering. In June of 2006, the Supreme Court upheld the basic Republican Congressional redistricting plan, but ruled that the Texas legislature violated the VRA in redrawing Congressional District #23, requiring the boundaries of that district to be redrawn.
34 Reforming the Redistricting Process Critics believe that the modern redistricting process undermines the quality of democracy in the US. They contend that the redistricting process typically produces legislative districts that are safe for one party or the other, depriving voters of the opportunity to participate in competitive elections for Congress or state legislatures. Critics also believe that it produces legislators who represent the extremes of the political spectrum. Reformers want to change the redistricting process to make it less political. The 2017 Texas gerrymandering trial could change all of America.
35 Elections and Policymaking in Texas Elections, particularly those in which only a small number of the voting age population participates, as well as who gets elected, have a significant impact on the policymaking process. agenda building: typically includes only those issues of importance to a small group of elites, ignoring issues of importance to the larger population and reinforcing the larger population s perception that the government doesn t care about them policy formulation and adoption: policies of importance to the larger population are ignored and policies harmful to the larger population are often adopted policy implementation and evaluation: implementation often occurs in such a way as to benefit elite groups... evaluation seldom occurs at all
36 Partisan Differences in Ranking Voting Issues
37 The Changing Face Of The Lone Star State The End
Texas Elections Part I
 Texas Elections Part I In a society governed passively by free markets and free elections, organized greed always defeats disorganized democracy. Matt Taibbi Elections...a formal decision-making process
Texas Elections Part I In a society governed passively by free markets and free elections, organized greed always defeats disorganized democracy. Matt Taibbi Elections...a formal decision-making process
Texas Voting & Elections (Chapter 04) Dr. Michael Sullivan. Texas State Government GOVT 2306 Houston Community College
 Texas Voting & Elections (Chapter 04) Dr. Michael Sullivan Texas State Government GOVT 2306 Houston Community College AGENDA 1. Current Events 2. Political Participation in Texas 3. Voting Trends 4. Summary
Texas Voting & Elections (Chapter 04) Dr. Michael Sullivan Texas State Government GOVT 2306 Houston Community College AGENDA 1. Current Events 2. Political Participation in Texas 3. Voting Trends 4. Summary
EDW Chapter 9 Campaigns and Voting Behavior: Nominations, Caucuses
 EDW Chapter 9 Campaigns and Voting Behavior: Nominations, Caucuses 1. Which of the following statements most accurately compares elections in the United States with those in most other Western democracies?
EDW Chapter 9 Campaigns and Voting Behavior: Nominations, Caucuses 1. Which of the following statements most accurately compares elections in the United States with those in most other Western democracies?
Purposes of Elections
 Purposes of Elections o Regular free elections n guarantee mass political action n enable citizens to influence the actions of their government o Popular election confers on a government the legitimacy
Purposes of Elections o Regular free elections n guarantee mass political action n enable citizens to influence the actions of their government o Popular election confers on a government the legitimacy
Partisan Advantage and Competitiveness in Illinois Redistricting
 Partisan Advantage and Competitiveness in Illinois Redistricting An Updated and Expanded Look By: Cynthia Canary & Kent Redfield June 2015 Using data from the 2014 legislative elections and digging deeper
Partisan Advantage and Competitiveness in Illinois Redistricting An Updated and Expanded Look By: Cynthia Canary & Kent Redfield June 2015 Using data from the 2014 legislative elections and digging deeper
Chapter 9: Elections, Campaigns, and Voting. American Democracy Now, 4/e
 Chapter 9: Elections, Campaigns, and Voting American Democracy Now, 4/e Political Participation: Engaging Individuals, Shaping Politics Elections, campaigns, and voting are fundamental aspects of civic
Chapter 9: Elections, Campaigns, and Voting American Democracy Now, 4/e Political Participation: Engaging Individuals, Shaping Politics Elections, campaigns, and voting are fundamental aspects of civic
COSSA Colloquium on Social and Behavioral Science and Public Policy
 COSSA Colloquium on Social and Behavioral Science and Public Policy Changes Regarding Race in America : The Voting Rights Act and Minority communities John A. Garcia Director, Resource Center for Minority
COSSA Colloquium on Social and Behavioral Science and Public Policy Changes Regarding Race in America : The Voting Rights Act and Minority communities John A. Garcia Director, Resource Center for Minority
Political Attitudes &Participation: Campaigns & Elections. State & Local Government POS 2112 Ch 5
 Political Attitudes &Participation: Campaigns & Elections State & Local Government POS 2112 Ch 5 Votes for Women, inspired by Katja Von Garner. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lvqnjwkw7ga We will examine:
Political Attitudes &Participation: Campaigns & Elections State & Local Government POS 2112 Ch 5 Votes for Women, inspired by Katja Von Garner. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lvqnjwkw7ga We will examine:
ORGANIZING TOPIC: NATIONAL GOVERNMENT: SHAPING PUBLIC POLICY STANDARD(S) OF LEARNING
 ORGANIZING TOPIC: NATIONAL GOVERNMENT: SHAPING PUBLIC POLICY STANDARD(S) OF LEARNING GOVT.9 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the process by which public policy is made by a) examining different
ORGANIZING TOPIC: NATIONAL GOVERNMENT: SHAPING PUBLIC POLICY STANDARD(S) OF LEARNING GOVT.9 The student will demonstrate knowledge of the process by which public policy is made by a) examining different
Campaigns & Elections. US Government POS 2041
 Campaigns & Elections US Government POS 2041 Votes for Women, inspired by Katja Von Garner. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lvqnjwk W7gA For Discussion Do you think that democracy is endangered by the
Campaigns & Elections US Government POS 2041 Votes for Women, inspired by Katja Von Garner. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lvqnjwk W7gA For Discussion Do you think that democracy is endangered by the
LESSON Money and Politics
 LESSON 22 157-168 Money and Politics 1 EFFORTS TO REFORM Strategies to prevent abuse in political contributions Imposing limitations on giving, receiving, and spending political money Requiring public
LESSON 22 157-168 Money and Politics 1 EFFORTS TO REFORM Strategies to prevent abuse in political contributions Imposing limitations on giving, receiving, and spending political money Requiring public
TX RACIAL GERRYMANDERING
 TX RACIAL GERRYMANDERING https://www.texastribune.org/2018/04/23/texas-redistricting-fight-returns-us-supreme-court/ TX RACIAL GERRYMANDERING https://www.texastribune.org/2018/04/23/texas-redistricting-fight-returns-us-supreme-court/
TX RACIAL GERRYMANDERING https://www.texastribune.org/2018/04/23/texas-redistricting-fight-returns-us-supreme-court/ TX RACIAL GERRYMANDERING https://www.texastribune.org/2018/04/23/texas-redistricting-fight-returns-us-supreme-court/
Growth Leads to Transformation
 Growth Leads to Transformation Florida attracted newcomers for a variety of reasons. Some wanted to escape cold weather (retirees). Others, primarily from abroad, came in search of political freedom or
Growth Leads to Transformation Florida attracted newcomers for a variety of reasons. Some wanted to escape cold weather (retirees). Others, primarily from abroad, came in search of political freedom or
Testimony of FairVote The Center for Voting and Democracy Jack Santucci, Program for Representative Government. October 16, 2006
 Testimony of FairVote The Center for Voting and Democracy Jack Santucci, Program for Representative Government Given in writing to the Assembly Standing Committee on Governmental Operations and Assembly
Testimony of FairVote The Center for Voting and Democracy Jack Santucci, Program for Representative Government Given in writing to the Assembly Standing Committee on Governmental Operations and Assembly
POLITICAL LEADERSHIP AND THE LATINO VOTE By NALEO Educational Fund
 POLITICAL LEADERSHIP AND THE LATINO VOTE By NALEO Educational Fund Already the second largest population group in the United States, the American Latino community continues to grow rapidly. Latino voting,
POLITICAL LEADERSHIP AND THE LATINO VOTE By NALEO Educational Fund Already the second largest population group in the United States, the American Latino community continues to grow rapidly. Latino voting,
APPORTIONMENT Statement of Position As announced by the State Board, 1966
 APPORTIONMENT The League of Women Voters of the United States believes that congressional districts and government legislative bodies should be apportioned substantially on population. The League is convinced
APPORTIONMENT The League of Women Voters of the United States believes that congressional districts and government legislative bodies should be apportioned substantially on population. The League is convinced
Cooper v. Harris, 581 U.S. (2017).
 Cooper v. Harris, 581 U.S. (2017). ELECTIONS AND REDISTRICTING TOP 8 REDISTRICTING CASES SINCE 2010 Plaintiffs alleged that the North Carolina legislature violated the Equal Protection Clause when it increased
Cooper v. Harris, 581 U.S. (2017). ELECTIONS AND REDISTRICTING TOP 8 REDISTRICTING CASES SINCE 2010 Plaintiffs alleged that the North Carolina legislature violated the Equal Protection Clause when it increased
Political Beliefs and Behaviors
 Political Beliefs and Behaviors Political Beliefs and Behaviors; How did literacy tests, poll taxes, and the grandfather clauses effectively prevent newly freed slaves from voting? A literacy test was
Political Beliefs and Behaviors Political Beliefs and Behaviors; How did literacy tests, poll taxes, and the grandfather clauses effectively prevent newly freed slaves from voting? A literacy test was
2017 CAMPAIGN FINANCE REPORT
 2017 CAMPAIGN FINANCE REPORT PRINCIPAL AUTHORS: LONNA RAE ATKESON PROFESSOR OF POLITICAL SCIENCE, DIRECTOR CENTER FOR THE STUDY OF VOTING, ELECTIONS AND DEMOCRACY, AND DIRECTOR INSTITUTE FOR SOCIAL RESEARCH,
2017 CAMPAIGN FINANCE REPORT PRINCIPAL AUTHORS: LONNA RAE ATKESON PROFESSOR OF POLITICAL SCIENCE, DIRECTOR CENTER FOR THE STUDY OF VOTING, ELECTIONS AND DEMOCRACY, AND DIRECTOR INSTITUTE FOR SOCIAL RESEARCH,
Chapter 5 - The Organization of Congress
 Congressional Membership - Section 1 Chapter 5 - The Organization of Congress Introduction The Founders did not intend to make Congress a privileged group. They did intend to make the legislative branch
Congressional Membership - Section 1 Chapter 5 - The Organization of Congress Introduction The Founders did not intend to make Congress a privileged group. They did intend to make the legislative branch
McCutcheon v Federal Election Commission:
 McCutcheon v Federal Election Commission: Q and A on Supreme Court case that challenges the constitutionality of the overall limits on the total amount an individual can contribute to federal candidates
McCutcheon v Federal Election Commission: Q and A on Supreme Court case that challenges the constitutionality of the overall limits on the total amount an individual can contribute to federal candidates
CITIZEN ADVOCACY CENTER
 CITIZEN ADVOCACY CENTER Congressional Redistricting: Understanding How the Lines are Drawn LESSON PLAN AND ACTIVITIES All rights reserved. No part of this lesson plan may be reproduced in any form or by
CITIZEN ADVOCACY CENTER Congressional Redistricting: Understanding How the Lines are Drawn LESSON PLAN AND ACTIVITIES All rights reserved. No part of this lesson plan may be reproduced in any form or by
AP US GOVERNMENT & POLITICS UNIT 2 REVIEW
 AP US GOVERNMENT & POLITICS UNIT 2 REVIEW POLITICAL BELIEFS & BEHAVIORS Public Opinion vs. Political Ideology Public opinion: the distribution of the population s beliefs about politics and policy issues.
AP US GOVERNMENT & POLITICS UNIT 2 REVIEW POLITICAL BELIEFS & BEHAVIORS Public Opinion vs. Political Ideology Public opinion: the distribution of the population s beliefs about politics and policy issues.
Shifting Political Landscape Impacts San Diego City Mayoral Election
 Shifting Political Landscape Impacts San Diego City Mayoral Election Executive Summary The November 2012 election brought a sea change to San Diego City Hall, as the first Democratic mayor in more than
Shifting Political Landscape Impacts San Diego City Mayoral Election Executive Summary The November 2012 election brought a sea change to San Diego City Hall, as the first Democratic mayor in more than
Chapter Ten: Campaigning for Office
 1 Chapter Ten: Campaigning for Office Learning Objectives 2 Identify the reasons people have for seeking public office. Compare and contrast a primary and a caucus in relation to the party nominating function.
1 Chapter Ten: Campaigning for Office Learning Objectives 2 Identify the reasons people have for seeking public office. Compare and contrast a primary and a caucus in relation to the party nominating function.
Guide to 2011 Redistricting
 Guide to 2011 Redistricting Texas Legislative Council July 2010 1 Guide to 2011 Redistricting Prepared by the Research Division of the Texas Legislative Council Published by the Texas Legislative Council
Guide to 2011 Redistricting Texas Legislative Council July 2010 1 Guide to 2011 Redistricting Prepared by the Research Division of the Texas Legislative Council Published by the Texas Legislative Council
Chapter 10: Elections and Campaigns
 Chapter 10: Elections and Campaigns Who Wants to Be a Candidate? There are two categories of individuals who run for office the self-starters and those who are recruited by the party The nomination process
Chapter 10: Elections and Campaigns Who Wants to Be a Candidate? There are two categories of individuals who run for office the self-starters and those who are recruited by the party The nomination process
Elections and Voting Behavior
 Edwards, Wattenberg, and Lineberry Government in America: People, Politics, and Policy Fourteenth Edition Chapter 10 Elections and Voting Behavior How American Elections Work Three types of elections:
Edwards, Wattenberg, and Lineberry Government in America: People, Politics, and Policy Fourteenth Edition Chapter 10 Elections and Voting Behavior How American Elections Work Three types of elections:
Chapter 6: Voters and Voter Behavior Section 4
 Chapter 6: Voters and Voter Behavior Section 4 Objectives 1. Examine the problem of nonvoting in this country. 2. Identify those people who typically do not vote. 3. Examine the behavior of those who vote
Chapter 6: Voters and Voter Behavior Section 4 Objectives 1. Examine the problem of nonvoting in this country. 2. Identify those people who typically do not vote. 3. Examine the behavior of those who vote
- 1 - Second Exam American Government PSCI Fall, 2001
 Second Exam American Government PSCI 1201-001 Fall, 2001 Instructions: This is a multiple choice exam with 40 questions. Select the one response that best answers the question. True false questions should
Second Exam American Government PSCI 1201-001 Fall, 2001 Instructions: This is a multiple choice exam with 40 questions. Select the one response that best answers the question. True false questions should
Unit 2: Political Beliefs and Behaviors Session 2: Political Participation
 Unit 2: Political Beliefs and Behaviors Session 2: Political Participation Learning Targets How do Americans participate politically? How have voting rights been suppressed within the United States How
Unit 2: Political Beliefs and Behaviors Session 2: Political Participation Learning Targets How do Americans participate politically? How have voting rights been suppressed within the United States How
Guided Reading & Analysis: Voting and Voting Behavior - Chapter 12, pp
 Guided Reading & Analysis: Voting and Voting Behavior - Chapter 12, pp 424-451 Purpose: This guide is not only a place to record notes as you read but also to provide a place and structure for reflections
Guided Reading & Analysis: Voting and Voting Behavior - Chapter 12, pp 424-451 Purpose: This guide is not only a place to record notes as you read but also to provide a place and structure for reflections
What is Public Opinion?
 What is Public Opinion? Citizens opinions about politics and government actions Why does public opinion matter? Explains the behavior of citizens and public officials Motivates both citizens and public
What is Public Opinion? Citizens opinions about politics and government actions Why does public opinion matter? Explains the behavior of citizens and public officials Motivates both citizens and public
Fighting Big Money, Empowering People: A 21st Century Democracy Agenda
 : A 21st Century Democracy Agenda Like every generation before us, Americans are coming together to preserve a democracy of the people, by the people, and for the people. American democracy is premised
: A 21st Century Democracy Agenda Like every generation before us, Americans are coming together to preserve a democracy of the people, by the people, and for the people. American democracy is premised
16 Ohio U.S. Congressional Districts: What s wrong with this picture?
 Gerrymandering Gerrymandering happens when the party in power draws district lines to rig elections to favor one political party over another. Both Republicans and Democrats have done it. Gerrymandering
Gerrymandering Gerrymandering happens when the party in power draws district lines to rig elections to favor one political party over another. Both Republicans and Democrats have done it. Gerrymandering
REDISTRICTING commissions
 independent REDISTRICTING commissions REFORMING REDISTRICTING WITHOUT REVERSING PROGRESS TOWARD RACIAL EQUALITY a report by THE POLITICAL PARTICIPATION GROUP NAACP LEGAL DEFENSE AND EDUCATIONAL FUND, INC.
independent REDISTRICTING commissions REFORMING REDISTRICTING WITHOUT REVERSING PROGRESS TOWARD RACIAL EQUALITY a report by THE POLITICAL PARTICIPATION GROUP NAACP LEGAL DEFENSE AND EDUCATIONAL FUND, INC.
GOVERNMENT INTEGRITY 14
 GOVERNMENT INTEGRITY 14 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION...14-1 CAMPAIGN FINANCE REFORM...14-1 LOBBY REFORM...14-3 ETHICS AND ACCOUNTABILITY...14-4 VOTING RIGHTS...14-5 VOTER EDUCATION...14-7 REDISTRICTING...14-8
GOVERNMENT INTEGRITY 14 Table of Contents INTRODUCTION...14-1 CAMPAIGN FINANCE REFORM...14-1 LOBBY REFORM...14-3 ETHICS AND ACCOUNTABILITY...14-4 VOTING RIGHTS...14-5 VOTER EDUCATION...14-7 REDISTRICTING...14-8
The worst illiterate is the political illiterate. He hears nothing, sees nothing, takes no part in political life. He doesn't seem to know that the
 The worst illiterate is the political illiterate. He hears nothing, sees nothing, takes no part in political life. He doesn't seem to know that the cost of living, the price of beans, of flour, of rent,
The worst illiterate is the political illiterate. He hears nothing, sees nothing, takes no part in political life. He doesn't seem to know that the cost of living, the price of beans, of flour, of rent,
9. Some industries like oil and gas companies largely support candidates. A) Democrats B) Republicans C) Libertarians D) Independent candidates
 Name: Date: 1. is the constitutional clause that delegates control of elections to the state governments. A) Time, place, and manner clause B) Time and place clause C) Time clause D) Election clause 2.
Name: Date: 1. is the constitutional clause that delegates control of elections to the state governments. A) Time, place, and manner clause B) Time and place clause C) Time clause D) Election clause 2.
Lecture Outline: Chapter 7
 Lecture Outline: Chapter 7 Campaigns and Elections I. An examination of the campaign tactics used in the presidential race of 1896 suggests that the process of running for political office in the twenty-first
Lecture Outline: Chapter 7 Campaigns and Elections I. An examination of the campaign tactics used in the presidential race of 1896 suggests that the process of running for political office in the twenty-first
Redrawing the Map: Redistricting Issues in Michigan. Jordon Newton Research Associate Citizens Research Council of Michigan
 Redrawing the Map: Redistricting Issues in Michigan Jordon Newton Research Associate Citizens Research Council of Michigan 2 Why Does Redistricting Matter? 3 Importance of Redistricting District maps have
Redrawing the Map: Redistricting Issues in Michigan Jordon Newton Research Associate Citizens Research Council of Michigan 2 Why Does Redistricting Matter? 3 Importance of Redistricting District maps have
1. Amendments impacting Voting. 15th - No Racial Discrimination. 17th - Direct election of senators by citizens, not state legislature appointment
 Exam 6A Notes 1. Amendments impacting Voting 15th - No Racial Discrimination 17th - Direct election of senators by citizens, not state legislature appointment 19th - no sex/gender discrimination (Female
Exam 6A Notes 1. Amendments impacting Voting 15th - No Racial Discrimination 17th - Direct election of senators by citizens, not state legislature appointment 19th - no sex/gender discrimination (Female
Gerrymandering: t he serpentine art VCW State & Local
 Gerrymandering: the serpentine art VCW State & Local What is gerrymandering? Each state elects a certain number of congressional Reps. Process is controlled by the party in power in the state legislature
Gerrymandering: the serpentine art VCW State & Local What is gerrymandering? Each state elects a certain number of congressional Reps. Process is controlled by the party in power in the state legislature
This presentation is designed to focus our attention on New York s broken campaign finance system and discuss what can be done to fix it All the
 This presentation is designed to focus our attention on New York s broken campaign finance system and discuss what can be done to fix it All the issues you are concerned with on a day to day basis have
This presentation is designed to focus our attention on New York s broken campaign finance system and discuss what can be done to fix it All the issues you are concerned with on a day to day basis have
A.P. United States Government Review Topic #1 Constitutional Underpinnings. Sources: Text Wilson; Reader - Roche and Beard, Federalist #51
 A.P. United States Government Review Topic #1 Constitutional Underpinnings Sources: Text Wilson; Reader - Roche and Beard, Federalist #51 I. Articles of Confederation A. Shay s Rebellion II. Constitutional
A.P. United States Government Review Topic #1 Constitutional Underpinnings Sources: Text Wilson; Reader - Roche and Beard, Federalist #51 I. Articles of Confederation A. Shay s Rebellion II. Constitutional
Below are examples of how public financing policies have increased opportunities for candidates of color.
 MEMO To: Larry Parham, Citizen Action of New York From: Chloe Tribich, Center for Working Families Date: February 16, 2012 Re: Public financing of elections and communities of color At your request, we
MEMO To: Larry Parham, Citizen Action of New York From: Chloe Tribich, Center for Working Families Date: February 16, 2012 Re: Public financing of elections and communities of color At your request, we
The Midterm Elections (And a Peek Toward 2016) Andrew H. Friedman The Washington Update
 The Midterm Elections (And a Peek Toward 2016) Andrew H. Friedman The Washington Update With fiscal deadlines out of the way for 2014, attention is now turning toward the 2014 midterm elections. This white
The Midterm Elections (And a Peek Toward 2016) Andrew H. Friedman The Washington Update With fiscal deadlines out of the way for 2014, attention is now turning toward the 2014 midterm elections. This white
Congress has three major functions: lawmaking, representation, and oversight.
 Unit 5: Congress A legislature is the law-making body of a government. The United States Congress is a bicameral legislature that is, one consisting of two chambers: the House of Representatives and the
Unit 5: Congress A legislature is the law-making body of a government. The United States Congress is a bicameral legislature that is, one consisting of two chambers: the House of Representatives and the
FOR RELEASE APRIL 26, 2018
 FOR RELEASE APRIL 26, 2018 FOR MEDIA OR OTHER INQUIRIES: Carroll Doherty, Director of Political Research Jocelyn Kiley, Associate Director, Research Bridget Johnson, Communications Associate 202.419.4372
FOR RELEASE APRIL 26, 2018 FOR MEDIA OR OTHER INQUIRIES: Carroll Doherty, Director of Political Research Jocelyn Kiley, Associate Director, Research Bridget Johnson, Communications Associate 202.419.4372
CH. 9 ELECTIONS AND CAMPAIGNS
 APGoPo - Unit 3 CH. 9 ELECTIONS AND CAMPAIGNS Elections form the foundation of a modern democracy, and more elections are scheduled every year in the United States than in any other country in the world.
APGoPo - Unit 3 CH. 9 ELECTIONS AND CAMPAIGNS Elections form the foundation of a modern democracy, and more elections are scheduled every year in the United States than in any other country in the world.
UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT WESTERN DISTRICT OF TEXAS SAN ANTONIO DIVISION
 Case 5:11-cv-00360-OLG-JES-XR Document 6 Filed 06/07/11 Page 1 of 5 UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT WESTERN DISTRICT OF TEXAS SAN ANTONIO DIVISION SHANNON PEREZ, HAROLD DUTTON, JR, AND GREGORY TAMEZ V. Plaintiffs
Case 5:11-cv-00360-OLG-JES-XR Document 6 Filed 06/07/11 Page 1 of 5 UNITED STATES DISTRICT COURT WESTERN DISTRICT OF TEXAS SAN ANTONIO DIVISION SHANNON PEREZ, HAROLD DUTTON, JR, AND GREGORY TAMEZ V. Plaintiffs
Applying Ranked Choice Voting to Congressional Elections. The Case for RCV with the Top Four Primary and Multi-Member Districts. Rob Richie, FairVote
 Applying Ranked Choice Voting to Congressional Elections The Case for RCV with the Top Four Primary and Multi-Member Districts Rob Richie, FairVote American Exceptionalism: Inescapable Realities for Reformers
Applying Ranked Choice Voting to Congressional Elections The Case for RCV with the Top Four Primary and Multi-Member Districts Rob Richie, FairVote American Exceptionalism: Inescapable Realities for Reformers
Public Opinion and Political Participation
 CHAPTER 5 Public Opinion and Political Participation CHAPTER OUTLINE I. What Is Public Opinion? II. How We Develop Our Beliefs and Opinions A. Agents of Political Socialization B. Adult Socialization III.
CHAPTER 5 Public Opinion and Political Participation CHAPTER OUTLINE I. What Is Public Opinion? II. How We Develop Our Beliefs and Opinions A. Agents of Political Socialization B. Adult Socialization III.
U.S. Senate Committee on Rules and Administration
 Executive Summary of Testimony of Professor Daniel P. Tokaji Robert M. Duncan/Jones Day Designated Professor of Law The Ohio State University, Moritz College of Law U.S. Senate Committee on Rules and Administration
Executive Summary of Testimony of Professor Daniel P. Tokaji Robert M. Duncan/Jones Day Designated Professor of Law The Ohio State University, Moritz College of Law U.S. Senate Committee on Rules and Administration
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 9, you should be able to: 1. Explain the nomination process and the role of the national party conventions. 2. Discuss the role of campaign organizations and
LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 9, you should be able to: 1. Explain the nomination process and the role of the national party conventions. 2. Discuss the role of campaign organizations and
Illinois Redistricting Collaborative Talking Points Feb. Update
 Goals: Illinois Redistricting Collaborative Talking Points Feb. Update Raise public awareness of gerrymandering as a key electionyear issue Create press opportunities on gerrymandering to engage the public
Goals: Illinois Redistricting Collaborative Talking Points Feb. Update Raise public awareness of gerrymandering as a key electionyear issue Create press opportunities on gerrymandering to engage the public
AP GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS: UNITED STATES 1999 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1! 8 total points possible on this question.
 AP GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS: UNITED STATES 1999 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1! 8 total points possible on this question. Two ways MEDIA have contributed to candidate-centered presidential campaigns: 1 point
AP GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS: UNITED STATES 1999 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 1! 8 total points possible on this question. Two ways MEDIA have contributed to candidate-centered presidential campaigns: 1 point
PARTISAN GERRYMANDERING
 10 TH ANNUAL COMMON CAUSE INDIANA CLE SEMINAR DECEMBER 2, 2016 PARTISAN GERRYMANDERING NORTH CAROLINA -MARYLAND Emmet J. Bondurant Bondurant Mixson & Elmore LLP 1201 W Peachtree Street NW Suite 3900 Atlanta,
10 TH ANNUAL COMMON CAUSE INDIANA CLE SEMINAR DECEMBER 2, 2016 PARTISAN GERRYMANDERING NORTH CAROLINA -MARYLAND Emmet J. Bondurant Bondurant Mixson & Elmore LLP 1201 W Peachtree Street NW Suite 3900 Atlanta,
Putting an end to Gerrymandering in Ohio: A new citizens initiative
 Putting an end to Gerrymandering in Ohio: A new citizens initiative Gerrymandering is the practice of stacking the deck in favor of the candidates of one party and underrepresenting its opponents by drawing
Putting an end to Gerrymandering in Ohio: A new citizens initiative Gerrymandering is the practice of stacking the deck in favor of the candidates of one party and underrepresenting its opponents by drawing
Congressional Apportionment
 Congress-II Congressional Apportionment House seats are apportioned among the states every ten years, following the census. Reapportionment the allocation of seats in the House of Representatives to each
Congress-II Congressional Apportionment House seats are apportioned among the states every ten years, following the census. Reapportionment the allocation of seats in the House of Representatives to each
Standard &
 Standard 12.3.1 & 12.6.4 12.3.1 Explain how civil society provides opportunities for individuals to associate for social, cultural, religious, economic and political purposes. 12.6.4 Describe the means
Standard 12.3.1 & 12.6.4 12.3.1 Explain how civil society provides opportunities for individuals to associate for social, cultural, religious, economic and political purposes. 12.6.4 Describe the means
Campaigns and Elections
 Campaigns and Elections Congressional Elections For the House of Representatives, every state elects a representative from each congressional district in the state. The number of congressional districts
Campaigns and Elections Congressional Elections For the House of Representatives, every state elects a representative from each congressional district in the state. The number of congressional districts
Political Parties. Chapter 9
 Political Parties Chapter 9 Political Parties What Are Political Parties? Political parties: organized groups that attempt to influence the government by electing their members to local, state, and national
Political Parties Chapter 9 Political Parties What Are Political Parties? Political parties: organized groups that attempt to influence the government by electing their members to local, state, and national
Fair Maps=Fair Elections
 Fair Maps=Fair Elections Gerrymandering: A Primer 1812 2012 There is no issue that is more sensitive to politicians of all colors and ideological persuasions than redistricting. It will determine who wins
Fair Maps=Fair Elections Gerrymandering: A Primer 1812 2012 There is no issue that is more sensitive to politicians of all colors and ideological persuasions than redistricting. It will determine who wins
Transcript: Election Law Symposium February 19, Panel 3
 University of Miami Law School Institutional Repository University of Miami Law Review 1-1-2006 Transcript: Election Law Symposium February 19, 2005 -- Panel 3 Paul Smith Follow this and additional works
University of Miami Law School Institutional Repository University of Miami Law Review 1-1-2006 Transcript: Election Law Symposium February 19, 2005 -- Panel 3 Paul Smith Follow this and additional works
Primary Election Systems. An LWVO Study
 Primary Election Systems An LWVO Study CONSENSUS QUESTIONS with pros and cons Question #1. What do you believe is the MORE important purpose of primary elections? a. A way for political party members alone
Primary Election Systems An LWVO Study CONSENSUS QUESTIONS with pros and cons Question #1. What do you believe is the MORE important purpose of primary elections? a. A way for political party members alone
STATEMENT OF WADE HENDERSON, PRESIDENT & CEO THE LEADERSHIP CONFERENCE ON CIVIL AND HUMAN RIGHTS
 STATEMENT OF WADE HENDERSON, PRESIDENT & CEO THE LEADERSHIP CONFERENCE ON CIVIL AND HUMAN RIGHTS FROM SELMA TO SHELBY COUNTY: WORKING TOGETHER TO RESTORE THE PROTECTIONS OF THE VOTING RIGHTS ACT SENATE
STATEMENT OF WADE HENDERSON, PRESIDENT & CEO THE LEADERSHIP CONFERENCE ON CIVIL AND HUMAN RIGHTS FROM SELMA TO SHELBY COUNTY: WORKING TOGETHER TO RESTORE THE PROTECTIONS OF THE VOTING RIGHTS ACT SENATE
Become a Delegate.
 1 Become a Delegate www.utahnsforpublicschools.org 2 What is the Process? Neighbors gather in March of an election year in caucus meetings (sometimes also called mass meetings or precinct meetings) to
1 Become a Delegate www.utahnsforpublicschools.org 2 What is the Process? Neighbors gather in March of an election year in caucus meetings (sometimes also called mass meetings or precinct meetings) to
CIRCLE The Center for Information & Research on Civic Learning & Engagement 70% 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10%
 FACT SHEET CIRCLE The Center for Information & Research on Civic Learning & Engagement Youth Voter Increases in 2006 By Mark Hugo Lopez, Karlo Barrios Marcelo, and Emily Hoban Kirby 1 June 2007 For the
FACT SHEET CIRCLE The Center for Information & Research on Civic Learning & Engagement Youth Voter Increases in 2006 By Mark Hugo Lopez, Karlo Barrios Marcelo, and Emily Hoban Kirby 1 June 2007 For the
Chapter 7: Legislatures
 Chapter 7: Legislatures Objectives Explain the role and activities of the legislature. Discuss how the legislatures are organized and how they operate. Identify the characteristics of the state legislators.
Chapter 7: Legislatures Objectives Explain the role and activities of the legislature. Discuss how the legislatures are organized and how they operate. Identify the characteristics of the state legislators.
RUBRICS FOR FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS
 RUBRICS FOR FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS 1. Using the chart above answer the following: a) Describe an electoral swing state and explain one reason why the U. S. electoral system magnifies the importance of
RUBRICS FOR FREE-RESPONSE QUESTIONS 1. Using the chart above answer the following: a) Describe an electoral swing state and explain one reason why the U. S. electoral system magnifies the importance of
Chapter 8. Political Participation and Voting
 Chapter 8 Political Participation and Voting Forms of Political Participation Forms of Political Participation Forms of Political Participation Traditional political participation: various activities designed
Chapter 8 Political Participation and Voting Forms of Political Participation Forms of Political Participation Forms of Political Participation Traditional political participation: various activities designed
Texas. SUPER DISTRICT A - FIVE SEATS % 2000 Presidential Vote
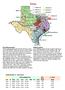 Texas Racial Representation Of the voting population of 6,232,350, 28.7 are Latino and 11.0 are black. Under the current 32-district system, black voters do not make up the majority in any district and
Texas Racial Representation Of the voting population of 6,232,350, 28.7 are Latino and 11.0 are black. Under the current 32-district system, black voters do not make up the majority in any district and
What Is A Political Party?
 What Is A Political Party? A group of office holders, candidates, activists, and voters who identify with a group label and seek to elect to public office individuals who run under that label. Consist
What Is A Political Party? A group of office holders, candidates, activists, and voters who identify with a group label and seek to elect to public office individuals who run under that label. Consist
Where Have All the Voters Gone?
 Where Have All the Voters Gone? A Discussion Guide Many Americans express frustration and concern about poor and decreasing voter turnout rates in local and national elections. Discussion about why citizens
Where Have All the Voters Gone? A Discussion Guide Many Americans express frustration and concern about poor and decreasing voter turnout rates in local and national elections. Discussion about why citizens
Should Politicians Choose Their Voters? League of Women Voters of MI Education Fund
 Should Politicians Choose Their Voters? 1 Politicians are drawing their own voting maps to manipulate elections and keep themselves and their party in power. 2 3 -The U.S. Constitution requires that the
Should Politicians Choose Their Voters? 1 Politicians are drawing their own voting maps to manipulate elections and keep themselves and their party in power. 2 3 -The U.S. Constitution requires that the
Campaign Finance Fall 2016
 Campaign Finance 17.251 Fall 2016 1 Problems Thinking about Campaign Finance Anti incumbency/politician hysteria Problem of strategic behavior Why the no effects finding of $$ What we want to know: Why
Campaign Finance 17.251 Fall 2016 1 Problems Thinking about Campaign Finance Anti incumbency/politician hysteria Problem of strategic behavior Why the no effects finding of $$ What we want to know: Why
5/5/2015. AP GOPO Late Start Review Session. Top 21 Most Tested Concepts. 1. The Articles of Confederation. 2. The Federalist Papers
 AP GOPO Late Start Review Session May 5, 2015 Top 21 Most Tested Concepts 1. The Articles of Confederation Established a decentralized system of government with a weak central government that had limited
AP GOPO Late Start Review Session May 5, 2015 Top 21 Most Tested Concepts 1. The Articles of Confederation Established a decentralized system of government with a weak central government that had limited
Redistricting Matters
 Redistricting Matters Protect Your Vote Common Cause Minnesota (CCMN) is a nonpartisan, grassroots organization dedicated to restoring the core values of American democracy, reinventing an open, honest
Redistricting Matters Protect Your Vote Common Cause Minnesota (CCMN) is a nonpartisan, grassroots organization dedicated to restoring the core values of American democracy, reinventing an open, honest
Paul Smith, Attorney at Law Jenner and Block Washington, DC. Gerry Hebert, Attorney at Law Washington, DC
 Paul Smith, Attorney at Law Jenner and Block Washington, DC Gerry Hebert, Attorney at Law Washington, DC The 63rd Annual Meeting of the Southern Legislative Conference August 15, 2009 First the basics:
Paul Smith, Attorney at Law Jenner and Block Washington, DC Gerry Hebert, Attorney at Law Washington, DC The 63rd Annual Meeting of the Southern Legislative Conference August 15, 2009 First the basics:
POLI 201 / Chapter 10 Fall 2007
 CHAPTER 10 Elections POLI 201: American National Government The Paradox of Voting in America Americans believe voting is important. They see it as: a civic duty; key to maintaining popular control of government;
CHAPTER 10 Elections POLI 201: American National Government The Paradox of Voting in America Americans believe voting is important. They see it as: a civic duty; key to maintaining popular control of government;
Every&Voice& Free&Speech&for&People& People&for&the&American&Way& Public&Citizen
 BrennanCenterforJustice!CommonCause!Democracy21!DemosAction!DemocracyMatters EveryVoice!FreeSpeechforPeople!PeoplefortheAmericanWay!PublicCitizen June10,2016 PlatformDraftingCommittee DemocraticNationalConvention
BrennanCenterforJustice!CommonCause!Democracy21!DemosAction!DemocracyMatters EveryVoice!FreeSpeechforPeople!PeoplefortheAmericanWay!PublicCitizen June10,2016 PlatformDraftingCommittee DemocraticNationalConvention
Chapter 9: The Political Process
 Chapter 9: The Political Process Section 1: Public Opinion Section 2: Interest Groups Section 3: Political Parties Section 4: The Electoral Process Public Opinion Section 1 at a Glance Public opinion is
Chapter 9: The Political Process Section 1: Public Opinion Section 2: Interest Groups Section 3: Political Parties Section 4: The Electoral Process Public Opinion Section 1 at a Glance Public opinion is
4) Once every decade, the Constitution requires that the population be counted. This is called the 4)
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The Founders intended that the House of Representatives be 1) A) professional. B) electorally insulated.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The Founders intended that the House of Representatives be 1) A) professional. B) electorally insulated.
Redistricting 101 Why Redistrict?
 Redistricting 101 Why Redistrict? Supreme Court interpretation of the U.S. Constitution, specifically: - for Congress, Article 1, Sec. 2. and Section 2 of the 14 th Amendment - for all others, the equal
Redistricting 101 Why Redistrict? Supreme Court interpretation of the U.S. Constitution, specifically: - for Congress, Article 1, Sec. 2. and Section 2 of the 14 th Amendment - for all others, the equal
Presidential Race Nip and Tuck in Michigan
 SOSS Bulletin Preliminary Draft 1.1 Presidential Race Nip and Tuck in Michigan Darren W. Davis Professor of Political Science Brian D. Silver Director of the State of the State Survey (SOSS) and Professor
SOSS Bulletin Preliminary Draft 1.1 Presidential Race Nip and Tuck in Michigan Darren W. Davis Professor of Political Science Brian D. Silver Director of the State of the State Survey (SOSS) and Professor
A Fair Division Solution to the Problem of Redistricting
 A Fair ivision Solution to the Problem of edistricting Z. Landau, O. eid, I. Yershov March 23, 2006 Abstract edistricting is the political practice of dividing states into electoral districts of equal
A Fair ivision Solution to the Problem of edistricting Z. Landau, O. eid, I. Yershov March 23, 2006 Abstract edistricting is the political practice of dividing states into electoral districts of equal
Chapter 6: Voters and Voter Behavior Section 1: The Constitution and the Right to Vote
 Section 1: The Constitution and the Right to Vote Key Terms: suffrage; franchise; electorate A. The History of Voting Rights 1. In the early 1800s religious, property-ownership, and tax-payment qualifications
Section 1: The Constitution and the Right to Vote Key Terms: suffrage; franchise; electorate A. The History of Voting Rights 1. In the early 1800s religious, property-ownership, and tax-payment qualifications
Chapter 12: Congress. American Democracy Now, 4/e
 Chapter 12: Congress American Democracy Now, 4/e Congress Where Do You Stand? How would you rate the overall performance of Congress today? a. Favorably b. Unfavorably c. Neither favorably nor unfavorably
Chapter 12: Congress American Democracy Now, 4/e Congress Where Do You Stand? How would you rate the overall performance of Congress today? a. Favorably b. Unfavorably c. Neither favorably nor unfavorably
CIS Political Science Chapter 11. Legislative Branch: Congress. Mr. Makela. St. Clair High School. University of Minnesota
 CIS Political Science Chapter 11 Legislative Branch: Congress Mr. Makela St. Clair High School University of Minnesota The Origin and Powers of Congress Bicameral problems w/ Representation (Great Compromise)
CIS Political Science Chapter 11 Legislative Branch: Congress Mr. Makela St. Clair High School University of Minnesota The Origin and Powers of Congress Bicameral problems w/ Representation (Great Compromise)
Redistricting: Nuts & Bolts. By Kimball Brace Election Data Services, Inc.
 Redistricting: Nuts & Bolts By Kimball Brace Election Data Services, Inc. Reapportionment vs Redistricting What s the difference Reapportionment Allocation of districts to an area US Congressional Districts
Redistricting: Nuts & Bolts By Kimball Brace Election Data Services, Inc. Reapportionment vs Redistricting What s the difference Reapportionment Allocation of districts to an area US Congressional Districts
Who Votes for America s Mayors?
 Who Votes for America s Mayors? A Pilot study to determine who casts ballots and who doesn t in 4 U.S. Cities: Charlotte, Detroit, Portland, and St. Paul Jason R. Jurjevich, PhD 1 Phil Keisling 1 Kevin
Who Votes for America s Mayors? A Pilot study to determine who casts ballots and who doesn t in 4 U.S. Cities: Charlotte, Detroit, Portland, and St. Paul Jason R. Jurjevich, PhD 1 Phil Keisling 1 Kevin
Census Bureau ships North Carolina's local census data to the governor and legislative leaders.
 2011 March 1 June 17 July 27 July 28 July 28 Census Bureau ships North Carolina's local census data to the governor and legislative leaders. Republicans release redistricting proposal for Voting Rights
2011 March 1 June 17 July 27 July 28 July 28 Census Bureau ships North Carolina's local census data to the governor and legislative leaders. Republicans release redistricting proposal for Voting Rights
Chapter 8: Campaigns and Voting Behavior
 Chapter 8: Campaigns and Voting Behavior 1. American presidential campaigns are best described as (A) inexpensive (B) tightly regulated. (C) easygoing. (D) long and arduous. 2. A party s official endorsement
Chapter 8: Campaigns and Voting Behavior 1. American presidential campaigns are best described as (A) inexpensive (B) tightly regulated. (C) easygoing. (D) long and arduous. 2. A party s official endorsement
Voting Rights League of Women Voters of Mason County May Pat Carpenter-The ALEC Study Group
 Voting Rights League of Women Voters of Mason County May 2016 Pat Carpenter-The ALEC Study Group Essential to the League s Mission Protection of Voting Rights Promotion of Voting Rights Expansion of Voting
Voting Rights League of Women Voters of Mason County May 2016 Pat Carpenter-The ALEC Study Group Essential to the League s Mission Protection of Voting Rights Promotion of Voting Rights Expansion of Voting
Political Participation
 Political Participation Objective: SWBAT describe how American turnout compares to other democracies, the expansion of suffrage in the U.S., and what factors explain who participates in politics. Who can
Political Participation Objective: SWBAT describe how American turnout compares to other democracies, the expansion of suffrage in the U.S., and what factors explain who participates in politics. Who can
Chapter 7 Political Parties: Essential to Democracy
 Key Chapter Questions Chapter 7 Political Parties: Essential to Democracy 1. What do political parties do for American democracy? 2. How has the nomination of candidates changed throughout history? Also,
Key Chapter Questions Chapter 7 Political Parties: Essential to Democracy 1. What do political parties do for American democracy? 2. How has the nomination of candidates changed throughout history? Also,
The Effect of North Carolina s New Electoral Reforms on Young People of Color
 A Series on Black Youth Political Engagement The Effect of North Carolina s New Electoral Reforms on Young People of Color In August 2013, North Carolina enacted one of the nation s most comprehensive
A Series on Black Youth Political Engagement The Effect of North Carolina s New Electoral Reforms on Young People of Color In August 2013, North Carolina enacted one of the nation s most comprehensive
Americans of all political backgrounds agree: there is way too much corporate money in politics. Nine
 DĒMOS.org BRIEF Citizens Actually United The Overwhelming, Bi-Partisan Opposition to Corporate Political Spending And Support for Achievable Reforms by: Liz Kennedy Americans of all political backgrounds
DĒMOS.org BRIEF Citizens Actually United The Overwhelming, Bi-Partisan Opposition to Corporate Political Spending And Support for Achievable Reforms by: Liz Kennedy Americans of all political backgrounds
State Legislative Redistricting in : Emerging Trends and Issues in Reapportionment By Ronald E. Weber
 State Legislative Redistricting in 2001-2002: Emerging Trends and Issues in Reapportionment By Ronald E. Weber This article assesses the progress of the states in redrawing state legislative-district lines
State Legislative Redistricting in 2001-2002: Emerging Trends and Issues in Reapportionment By Ronald E. Weber This article assesses the progress of the states in redrawing state legislative-district lines
