1869 Wyoming Territory gave women the right to vote Comstock Law passed illegal to use the U.S. post office to mail obscene material
|
|
|
- Dennis Harmon
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Unit 6 (Period 7 Part 1) Timeline Review.Important Dates and Chronological Review Keep in mind that memorizing dates is not required, however sometimes significant years do pop up on tests. Those dates in bold are years that have popped up in the past. Far more important is reviewing general chronology. You are expected to understand chronology, so use this list to help you review sequencing. Add notes/comments on major themes as you review to make the timeline complete, and highlight any information that you do not yet have in long term memory. THIS TIMELINE HAS TWO COLUMNS THE SPACES DO NOT MEAN THERE IS MISSING INFORMATION TREAT IT AS TWO TIMELINES IN ONE. Empire Building (LEFT COLUMN) (RIGHT COLUMN) 1866 Transatlantic cable completed 1867 Seward s Folly purchased Alaska Midway Islands annexed 1868 Burlingame Treaty signed with China 1869 Wyoming Territory gave women the right to vote 1870 Annexing Dominican Republic is discussed but rejected 1873 Comstock Law passed illegal to use the U.S. post office to mail obscene material 1874 Woman s Christian Temperance Union formed 1877-Compromise of 1877 ends the Civil War Reconstruction Era Chautauqua education movement began educating adults through lectures, seminars, gatherings 1878 U.S. products appeared at the Paris World s Fair 1879 Henry George Progress and Poverty explained the cyclical nature of the economy Dumbbell tenements built 1881 Booker T. Washington became head of the Tuskegee Institute 1882 First immigration restriction laws passed 1883 The new navy emerged 1885 Louis Sullivan built the first skyscraper in NYC 1886 Statue of Liberty erected; gift from France Jane Addams opened Hull House 1887 U.S. acquired the rights to Pearl Harbor, Hawaii Hatch Act passed to supplement Morrill Act (naval rights/naval base) money given to states for education and 1889 Pan-American Conference held in D.C. agricultural experiments/innovation 1890 Alfred T. Mahan The Influence of Sea Power upon History Sherman Anti-Trust Act gave the government some power over trusts, but it is mainly used to weaken labor 1886-Hull House/Jane Addams begins the Progressive Era Other dates often used to define the beginning of Progressivism include 1890 Sherman Anti-Trust Act, 1892 election (People s Party), and 1901 Theodore Roosevelt becomes president.)
2 1892 Grover Cleveland elected Populist Party united several groups including the Farmers Alliance and the Greenbacks and made an unsuccessful run for the presidency by 1896 most Populist platform ideas are absorbed into the democrat party 1893 America enters a serious, economic depression and Anti-Saloon League founded Frederick Jackson Turner s Frontier Thesis stated that the which later joined with the Women s Christian U.S. needs a new Frontier because expansion is the Temperance Union to limit then abolish alcohol essential building block of American character U.S. entered a depression that lasted until Pullman Strike 1895 Cuban Revolution began Booker T. Washington s Atlanta Compromise accepted Separate but Equal but wanted blackwhite cooperation to focus on vocational training Venezuelan boundary dispute with Britain (he founded the Tuskegee Institute) and economic independence for blacks as a first step toward equality 1896 McKinley elected Plessy vs Ferguson: Separate But Equal; segregation upheld as Constitutional 1896-Election marks the end o the Gilded Age / Era 1898 U.S.S. Maine is sunk and led America to war; Spanish-American War, the 16-week splendid little war Theodore Roosevelt participates as Rough Rider Dewey led victory in Manila Bay U.S. annexed Hawaii 1899 Treaty of Paris (and secondary treaty for Phil.) ratified U.S. gained Philippines, Guam, Puerto Rico from Spain Open Door Note sent to Europe 1900 mass immigration from eastern and southern Europe hit peak in this decade ( ) Forraker Act for Puerto Rico Hawaii became U.S. territory Boxer Rebellion in China Second Open Door Note sent McKinley beats Bryan again William Jennings Bryan ran for president Cross of Gold Speech 1898-Spanish American War begins America s Rise to Power Era 1901 McKinley assassinated, Teddy took over Commission system established in Galveston Aguinaldo is captured, ended war in Philippines which began after Spanish-American War when Filipinos rebelled against their new Robert La Follette elected governor of American mother Wisconsin became leading Progressive reformer the Wisconsin experiment increased government regulation of city services and returning power to people (from trusts)
3 Hay-Pauncefote Treaty: Britain stepped aside from canal plans Oh yeah U.S. power Who s your Daddy? Insular Cases Supreme Court ruled that peoples in empire are not subject to Constitution Does the Constitution follow the flag? No Colombian senate rejects Canal Treaty they want more $$ Lincoln Steffens Shame of the Cities 1903 Panama broke from Colombia with help from Teddy and his big stick Hay-Bunau-Varilla Treaty U.S. takes over Canal Zone from Panama Platt Amendment forbade Cuba from making treaties without U.S. approval and forced to accept new Constitution Ida Tarbell exposed Standard Oil T.R. sides with workers and forced arbitration in Anthracite Coal Strike of 1902 Newlands Reclamation Act (conservation) 1904 Teddy elected president Northern Securities Case: ruled that J.P. Morgan s Northern Securities Company must cease restraining freedom of commerce. Roosevelt Corollary: a latter-day addendum to the Monroe Doctrine that gave the U.S. the right to step into any fray that threatened its sovereignty made America an international police power. Construction of canal began Russo-Japanese War began 1905 Taft-Katsura Agreement U.S. granted Japan hegemony Niagara Falls Convention to protest Atlanta over Korea and Japan agreed to leave the Philippines alone Compromise and pledged staunch militancy against racism/segregation Niagara Movement Portsmouth Conference: Teddy Roosevelt served as mediator in the Russo-Japanese War U.S. and the Dominican Republic signed an agreement that the U.S. would handle their finances attempt to keep European powers out of hemisphere Heavy Japanese immigration into California lead to San Francisco segregating its schools T.R. arranges diplomatic talks Lochner vs New York struck down 10 work day Upton Sinclair The Jungle exposed meat packing industry 1906 U.S. invaded Cuba to stop a revolution stayed for 3 years Hepburn Act imposed stricter controls on many other occupations followed and Guantanamo Bay established railroads ICC expanded Pure Food and Drug Act and the Meat Inspection Act Marked the beginning of government regulations to protect the public/consumers
4 1907 T.R. sent the Great White Fleet on the naval world tour to U.S. experienced an economic panic impress other countries with its power Japan responded by building up its navy Gentlemen s Agreement with Japan U.S. to reduce prejudice against Japanese (remember San Francisco Schools) and Japan agrees to stop flow temporary agreement, never officially ratified more like a gentlemen s agreement or handshake 1908 Root-Takahira Agreement U.S. and Japan respect each Muller vs Oregon Supreme Court upheld other s territories and the Open Door in China Oregon law that limited working hours for women because the negative impact of exhausted women on society (bad for women s movement) William Howard Taft is elected Teddy Roosevelt s hand-picked Successor 1909 Taft sent troops to Nicaragua financial supervision NAACP formed (National Association for (Wilson later sends them back off and on U.S. intervenes here) the Advancement of Colored People) Payne-Aldrich Act a compromise tariff in the battle to lower them 1910 Mexican Revolution began Mann-Elkins Act strengthened ICC with new regulations on railroad (can t charge more for short trip than long trip) and new powers over telephone and other wires Mann Act (aka White Slave Traffic Act) prohibited intestate/international transportation of women for immoral purposes Ballinger-Pinchot Controversy Secretary of the Interior, Richard Ballinger, allowed private use of Arkansas land that had been set aside for conservation Taft fired Pinchot for questioning Ballinger s connection to Arkansas coal interests (Ballinger was Pinchot s boss Taft didn t like the insubordination) 1911 Standard Oil case Supreme Court ruled the company be broken up into 34 companies U.S. Steel antitrust case even though bigger than Standard Oil court ruled in its favor this is the act that drove Teddy back into politics as he was furious with Taft for going after Morgan who had bought the company from Carnegie Teddy saw it as a good trust Triangle Shirtwaist Fire led to more local and state regulations to protect workers 1912 election of 1912 Teddy-Taft-Wilson Woodrow Wilson elected President Bull-Moose (Progressive Party) nominate T.R., Taft as Republican, and Wilson the Democrat (largest 3 rd party vote until Ross Perot in 1992) Socialist Eugene V. Debs also runs.
5 th Amendment legalized federal income tax Underwood Tariff Act drastically reduces tariffs (some are completely illuminated) and created income tax 17 th Amendment direct election of senators (instead of state legislatures voters choose) Federal Reserve Act new banking system that set up our current districts and Federal Reserve reduced Wall Street s control of economy 1914 Panama Canal opened Federal Trade Commission Act enforced fair trade practices and suppressed unlawful competition WWI began in Europe; USA neutral Clayton Anti-Trust Act legalized peaceful U.S. troops occupy Vera Cruz, Mexico strikes, picketing, and boycotting protecting workers where the Sherman Anti-Trust Act had targeted them and extended Sherman as far as government power to break up monopolies (trusts) Margaret Sanger was indicted for distributing obscene literature (advice on birth control) and fled to Europe she later returned in 1916 and founded an organization that later became Planned Parenthood 1915 meanwhile in Europe Germany using La Follett s Seaman Act decent treatment and unrestricted submarine warfare Lusitania sunk wages for sailors U.S. marines sent to Haiti for financial supervision 1916 Jones Act U.S. Constitution for the Philippines Federal Farm Loan Act provided loans to In place until Japan took over the islands farmers for up to 50% of the value of their land (promised independence as soon as they were stable) Philippines didn t become independent until after WWII Workingman s Compensation Act help to federal employees who lost job Wilson sent troops to Dominican Republic financial supervision Wilson sent Sussex Pledge (ultimatum) to Germany Child Labor Law struck down by Supreme Court (Keating Owen Act) Warehouse Act loans to secure staple crops 1917 Puerto Ricans granted U.S. citizenship U.S. bought Virgin Islands from Denmark Zimmerman Note Russian Revolution U.S. entered WWI American Expeditionary Force commanded by John J. Pershing Adamson Act 8-hour workday for train and interstate commerce employees & over-time pay Wilson nominate the first Jewish Supreme Court Justice, Louis D. Brandeis 1918 Wilson issued Fourteen Points Battle of Argonne Forest (U.S. breaks through German lines) th Amendment prohibited production, transportation, and sale of alcohol 1920 United States rejected Treaty of Versailles and refused to 19 th Amendment gave women the vote join League of Nations (worked out their own deal with Germany & returned to isolationism/protectionist/neutral foreign policy) 1918 End of WWI marks the end of America s Rise to Power Era th Amendment marks the end of the Progressive Era Eugene V. Debs runs for president (from jail) as socialist and gets 900,000 votes (in jail for sedition)
6 The rest of the timeline is a single column. World War I 1914 World War begins in Europe following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand and entangling alliances among several nations 1915 German declared the seas around the British Isles a war zone and subs sank luxury liner Lusitania killing more than 1,000 people (128 were American). Woodrow Wilson rejected the suggestion that U.S. end neutrality. Instead he sent a warning to Germany to stop its unrestricted submarine warfare. Yeah that worked. William Jennings Bryan (Wilson s Secretary of State and former candidate) was a pacifist who favored U.S. neutrality and he resigned after Wilson took steps toward war preparations Wilson runs for re-election with the slogan, He kept us out of war. He is reelected. U.S. troops invaded Mexico again. The Gore-McLemore Resolution prohibited Americans from travelling on armed or contraband-carrying ships. It fails when Wilson doesn t support it. The French ship (luxury liner), Sussex, is attacked by German U-boats. Wilson threatened to cut off all ties with Germany, so Germany changed its policy (Sussex Pledge) until later in 1917 when they felt confident victory required unrestricted warfare. National Defense Act increased the size of the Army and National Guard, and authorized $500 million investment for Navy Germany returned to unrestricted submarine warfare against merchant ships The Zimmerman Telegram was intercepted by British intelligence. Sent Germany to Mexico asking for Mexico to join in the war effort with promises of regaining lands lost in the Mexican-American War and Texas War for Independence. This is the event that finally pushes America into the war officially. The Russian Revolution caused Russia to back out of war. Bolshevik Revolution led to communism and soon after the formation of the Soviet Union under Vladimir Lenin. The communists side with Germany. Selective Service Act created a military draft, the Espionage Act made it illegal to interfere with the draft or encourage treason, the War Industries Board was created to set prices and discourage use of unnecessary products during wartime (this would continue after the war), and the War Revenue Act graduated the personal income tax, corporate income tax, excess profits tax, and increased excise taxes on alcohol, tobacco, and luxury items Wilson wrote his Fourteen Points which outlined plan for peace after the war, including the creation of the League of Nations. The Sedition Act made it illegal to criticize war efforts. Troops entered France and fought with the Allies. An Armistice is declared for the 11 th hour of the 11 th day of the 11 th month later became Veterans Day The Paris Peace Conference at Versailles led to the Treaty of Versailles in which Germany accepted the blame for the war. Germany is also forced to give up territory, Alsace-Lorraine, and all other colonies. They were forced to accept war reparations in excess of 35 billion dollars (which crippled Germany along with loss of land and resources). Adolf Hitler, who fought in WWI, declared the Treaty of Versailles was a betrayal, not a treaty and definitely not a defeat. The Treaty went against much of Wilson s Fourteen Points, as Europe was focused on punishing Germany not setting up future peace. This set the stage for WWII The American Legion was founded to promote veterans benefits and to hunt communists in the Red Scare. The U.S. Communist Party was founded. Wilson suffered a stroke after tirelessly traveling the country trying to raise support for the League and Treaty. His last months in office are spent in bed with his wife communicating for him and running things (the first female president?). Vice President refuses to take over. Schenk v. U.S. upheld the 1 st Amendment restrictions during war. 18 th Amendment and Volstead Act outlawed alcohol. The Seattle General Strike struck fear into the heart of America. Not a good time to be involved in organized labor since labor movements = communist revolution red scare. Chicago race riot 1920 A. Mitchell Palmer (Attorney General) led raids (Palmer Raids) to protect America from communists. Thousands are arrested, some held without bail or counsel. 249 were deported to the USSR. Other were released. The Senate rejected the Treaty of Versailles as Wilson s rival, Henry Cabot Lodge, lobbied to keep America out of entangling alliances (European affairs). The Roaring Twenties/The Jazz Age th Amendment (Women s Suffrage) Republican Warren G. Harding elected president under the slogan Return to Normalcy The first commercial radio broadcast aired. It was now official the U.S. was an urban nation as more people lived in cities than rural communities. Fitzgerald published This Side of Paradise which inspired the youth (including flappers) to bewildered and sometimes reckless abandon to life all gods dead, all wars fought, all faiths in man shaken.
7 1921 Federal Highway Act provided aid for state roads Immigration quotas were established Emergency Quota Act of 1921 Maternity and Infancy Protection Act passed in order to help women and children (healthcare/welfare) Sacco & Vanzetti trial 1922 The economy recovered and post-war prosperity began ending in Washington Naval Conference produced several treaties including the 4-Power Treaty (U.S., G.B., France, and Japan to respect Pacific holdings) and 5-Power Treaty (naval ratios 5:5:3; U.S.:G.B.:Japan) and 9-Power Treaty (9 nations recognized open door in China) Meanwhile Benito Mussolini and the Fascists came to power in Italy while Americans celebrate the victories of disarmament and diplomacy 1922 Sinclair Lewis published Babbit (slave to consumerism) and T.S. Eliot published The Waste Land Fordney-McCumber Tariff Law increased tariffs almost as high as the Payne-Aldrich Tariff of 1909 (Taft) 1923 Harding died and VP Calvin Coolidge took over. KKK surges reached all-time high membership. Lucretia Mott Amendment (named after 19 th century leader for suffrage equal rights for women becomes the Equal Rights Amendment aka ERA) is demanded by women s movement. Alice Paul led the way to write it. It was never ratified. Adkins vs Children s Hospital declared federal minimum wage legislation for women was an unconstitutional infringement of liberty of contract, as protected by the due process clause of the Fifth Amendment. (later overturned in 1937) 1924 Teapot Dome scandal was exposed Harding s Secretary of the Interior, Albert B. Fall, leased Navy petroleum reserves at Teapot Dome and two other locations to private oil companies at low rates without competitive bidding. (and received bribe/kickback from them for doing so). Up until the Watergate scandal in the early 1970s, this was seen as the worst government scandal in history. National Origins Act set strict quotas on immigration of Eastern and Southern Europeans and all Asians. Calvin Coolidge elected President. Charles Dawes German Reparation Plan established a schedule for German reparation payments with American banks loaning the money. (U.S. loans money to Germany so Germany can pay reparation to allies so allies can repay their loans to the U.S.) 1925 Scopes Trial (aka the Monkey trial) Clarence Darrow for the defense of John Scopes (teacher who taught evolution despite state law forbidding it) and William Jennings Bryan (former candidate numerous times and Wilson s VP until he resigned because he was a pacifist) for the prosecution. This case illustrated the conflict of modernism vs fundamentalism science vs religion. Scopes was found guilty and fined $100 Florida real estate boomed. (too bad a lot of it was swampland) F. Scott Fitzgerald published The Great Gatsby (glamour and cruelty of an achievement oriented society) Theodore Dreiser published An American Tragedy (pregnant girl murdered by her socially ambitious lover... similar theme to Gatsby) Al Capone built a large gang in Chicago. Gang wars killed hundreds, controlled cities, and kept the booze flowing during the era of Prohibition. Prohibition = Crime U.S. troops occupy Nicaragua (it s a financial thing age of Imperialism not exactly over) Ernest Hemingway published The Sun Also Rises disillusionment was high in much of the 20s literature, but none as much as Hemingway who actually fought in WWI. Langston Hughes published The Weary Blues Harlem Renaissance produced numerous talents 1927 Nicola Sacco and Bartolomeo Vanzetti were executed amid protest convicted for a murder they probably didn t commit targeted because they were undesirable immigrants who were also anarchists. Charles Lindbergh flew solo across the Atlantic in The Spirit of St. Louis from New York to France the first to do so became instant superstar. (The Wright Brothers flew the first airplane in 1903) Babe Ruth hit 60 home runs in one season. The Jazz Singer, the first talking movie, was released. (the first story-sequence motion picture aired in.. began silent movie era) Ford stopped producing the Model T the car that revolutionized America during the 1920s. Marcus Garvey was deported following conviction of mail fraud but before he left the country, his Black Star Line Co. (he founded the United Negro Improvement Association to promote resettlement of Blacks to Africa) and Black pride movement inspired many and helped inspire the Nation of Islam decades later The Stock Market hit an all-time high. Herbert Hoover elected President. Kellogg-Briand Pact was signed by 62 nations which condemned the use of war tried to outlaw war. Yup dumb Stock Market crashed after a plummeting fall this marked the end of the Roaring Twenties and the Jazz Age and marked the beginning of the world s worst economic depression. Ernest Hemingway published A Farewell To Arms which is one of the best wartime novels ever.
1869 Wyoming Territory gave women the right to vote Comstock Law passed illegal to use the U.S. post office to mail obscene material
 Unit 6 (Period 7 Part 1) Timeline Review.Important Dates and Chronological Review Keep in mind that memorizing dates is not required, however sometimes significant years do pop up on tests. Those dates
Unit 6 (Period 7 Part 1) Timeline Review.Important Dates and Chronological Review Keep in mind that memorizing dates is not required, however sometimes significant years do pop up on tests. Those dates
The Progressive Presidents
 The Progressive Presidents Main Ideas o The federal government responded to grassroots reform efforts by enacting progressive policies. o Progressive reforms sought to established a greater degree of democratic
The Progressive Presidents Main Ideas o The federal government responded to grassroots reform efforts by enacting progressive policies. o Progressive reforms sought to established a greater degree of democratic
Post-War America. Section 1
 Twenties Unit 6 Post-War America Section 1 Outline Red Scare Details: Labor Relations: Details: Immigration Changes Limits: Assembly Line Who and What: Suburbs Details: Consumers Details: Economic Weaknesses
Twenties Unit 6 Post-War America Section 1 Outline Red Scare Details: Labor Relations: Details: Immigration Changes Limits: Assembly Line Who and What: Suburbs Details: Consumers Details: Economic Weaknesses
Chapter 28: Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt,
 APUSH CH 28+29 Lecture Name: Hour: Chapter 28: Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt, 1901-1912 I. The Progressive Era A. What Was It? 1. A time period that focused on correcting political, economic,
APUSH CH 28+29 Lecture Name: Hour: Chapter 28: Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt, 1901-1912 I. The Progressive Era A. What Was It? 1. A time period that focused on correcting political, economic,
STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015
 STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015 AGE OF IMPERIALISM! (1900s- 1914) MILITARY Alfred T. Mahan argued for a strong NAVY in his book Influence of Sea Power Upon History Easier
STAAR BLITZ: IMPERIALISM, SPANISH-AMERICAN WAR, WWI APRIL 22, 2015 AGE OF IMPERIALISM! (1900s- 1914) MILITARY Alfred T. Mahan argued for a strong NAVY in his book Influence of Sea Power Upon History Easier
Expanding Horizons: Imperialism
 Expanding Horizons: Imperialism In August 1914, World War I broke out in Europe, which drowned out the Progressive Era. Leading up to this, U.S. foreign policy had been drastically changing. IMPERIALISM
Expanding Horizons: Imperialism In August 1914, World War I broke out in Europe, which drowned out the Progressive Era. Leading up to this, U.S. foreign policy had been drastically changing. IMPERIALISM
ROARING TWENTIES Fear following World War I 1/15/16
 1/15/16 U.S. History 1919-1929 ROARING TWENTIES REVIEWED! Watch the video American Pageant Chapter 31 & annotate the slides. Read pages 412-459 The Americans and add additional notes. Fear following World
1/15/16 U.S. History 1919-1929 ROARING TWENTIES REVIEWED! Watch the video American Pageant Chapter 31 & annotate the slides. Read pages 412-459 The Americans and add additional notes. Fear following World
Unit 5. US Foreign Policy, Friday, December 9, 11
 Unit 5 US Foreign Policy, 1890-1920 I. American Imperialism A. What is Imperialism? B. Stated motivations (how we were helping others) Helping free countries from foreign domination Spreading Christianity
Unit 5 US Foreign Policy, 1890-1920 I. American Imperialism A. What is Imperialism? B. Stated motivations (how we were helping others) Helping free countries from foreign domination Spreading Christianity
Title Student Check Notebook Check Class Notes The West 1890s /15 Class Notes Imperialism (2 days = Double
 In your notebook Title Student Check Notebook Check Class Notes The West 1890s /15 Class Notes Imperialism (2 days = Double /30 Points) Class Notes Philippines Cartoons /15 Class Notes Progressive Era
In your notebook Title Student Check Notebook Check Class Notes The West 1890s /15 Class Notes Imperialism (2 days = Double /30 Points) Class Notes Philippines Cartoons /15 Class Notes Progressive Era
APUSH. U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! EMPIRE & EXPANSION
 APUSH 1890-1909 EMPIRE & EXPANSION U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 27 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 19 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 21 Important Ideas Since the
APUSH 1890-1909 EMPIRE & EXPANSION U.S. Imperialism REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 27 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 19 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 21 Important Ideas Since the
How did conditions in eastern Europe in the late 1800s lead to an increase in Jewish immigration?
 Chapter 22 Rise of American Cities 1865-1900 Section 1 Growing Immigration from Europe Ellis Island nationality Thinking Map- Describe Immigration during this time period Who were the new immigrants of
Chapter 22 Rise of American Cities 1865-1900 Section 1 Growing Immigration from Europe Ellis Island nationality Thinking Map- Describe Immigration during this time period Who were the new immigrants of
The Progressive Era. Political, Social, and Economic Reform ( )
 The Progressive Era Political, Social, and Economic Reform (1901-1917) POLITICAL SOCIAL ECONOMIC Expanded Suffrage Decline of Political Machines Increased Party Influence Expanded Workers Rights Assimilation
The Progressive Era Political, Social, and Economic Reform (1901-1917) POLITICAL SOCIAL ECONOMIC Expanded Suffrage Decline of Political Machines Increased Party Influence Expanded Workers Rights Assimilation
Letter from President Fillmore asking Japan. American ships to stop for supplies safety reasons
 Chapter 19-21 Introduction Japan 1853 Not open to trading with other countries Commodore Matthew Perry went to Japan with a small fleet of warships (Gunboat Diplomacy) Letter from President Fillmore asking
Chapter 19-21 Introduction Japan 1853 Not open to trading with other countries Commodore Matthew Perry went to Japan with a small fleet of warships (Gunboat Diplomacy) Letter from President Fillmore asking
Unit 6: A New Role in the World
 Unit 6: A New Role in the World Study online at quizlet.com/_1fnvlz 1. alliances 5. conscription An agreement between nations to aid and protect each other. 2. Allies A military draft 6. dollar diplomacy
Unit 6: A New Role in the World Study online at quizlet.com/_1fnvlz 1. alliances 5. conscription An agreement between nations to aid and protect each other. 2. Allies A military draft 6. dollar diplomacy
U.S. TAKS Review. 11th
 11th U.S. TAKS Review Add a background color or design template to the following slides and use as a Power Point presentation. Print as slides in black and white on colored paper to use as placards for
11th U.S. TAKS Review Add a background color or design template to the following slides and use as a Power Point presentation. Print as slides in black and white on colored paper to use as placards for
Unit 6 Study Guide. Period 7.1:
 Unit 6 Study Guide Period 7.1: 1890 1920 In a Nutshell An increasingly pluralistic United States faced profound domestic and global challenges, debated the proper degree of government activism, and sought
Unit 6 Study Guide Period 7.1: 1890 1920 In a Nutshell An increasingly pluralistic United States faced profound domestic and global challenges, debated the proper degree of government activism, and sought
U.S. History PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT REVIEWED! THE PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT
 9/28/17 U.S. History 1890-1912 PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT REVIEWED! THE PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT WHY: Industrialization, urbanization, and immigration created significant changes and challenges for the United States.
9/28/17 U.S. History 1890-1912 PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT REVIEWED! THE PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT WHY: Industrialization, urbanization, and immigration created significant changes and challenges for the United States.
Wilsonian Progressivism at Home and Abroad. Chapter 29
 Wilsonian Progressivism at Home and Abroad Chapter 29 Election of 1912 Taft was elected President in 1908 as Republican with the support of Teddy Roosevelt Roosevelt did not think Taft s presidency was
Wilsonian Progressivism at Home and Abroad Chapter 29 Election of 1912 Taft was elected President in 1908 as Republican with the support of Teddy Roosevelt Roosevelt did not think Taft s presidency was
Conflicted Legacies of World War I
 Name: America s History: Chapter 22 Video Guide Big Idea Questions What journalist in the South wrote about the horrors of lynching? Guided Notes Conflicted Legacies of World War I The Red Scare Great
Name: America s History: Chapter 22 Video Guide Big Idea Questions What journalist in the South wrote about the horrors of lynching? Guided Notes Conflicted Legacies of World War I The Red Scare Great
Unit 7: America Comes of Age FRQ Outlines
 Prompt: 2. Analyze the extent to which the Spanish-American War was a turning point in American foreign policy. Re-written as a Question: What was the extent to which the Spanish American war a turning
Prompt: 2. Analyze the extent to which the Spanish-American War was a turning point in American foreign policy. Re-written as a Question: What was the extent to which the Spanish American war a turning
American History 11R
 American History 11R Progressive Movement Goals Protecting Social Welfare Promoting Moral Improvement Creating Economic Reform Fostering Efficiency Reform Political System Protecting Social Welfare Tried
American History 11R Progressive Movement Goals Protecting Social Welfare Promoting Moral Improvement Creating Economic Reform Fostering Efficiency Reform Political System Protecting Social Welfare Tried
Chapter 13 The 1920s
 Chapter 13 The 1920s 1. Red Scare A nationwide fear that Communists might seize power in the Untied States. 2. Palmer Raids A. Mitchell Palmer, the Attorney General of the US organized a series of raids
Chapter 13 The 1920s 1. Red Scare A nationwide fear that Communists might seize power in the Untied States. 2. Palmer Raids A. Mitchell Palmer, the Attorney General of the US organized a series of raids
Power Point Credit: Johnny Burkowski
 Power Point Credit: Johnny Burkowski Fundamental Questions Did the Roaring Twenties continue the Progressive Era reforms? Warren G. Harding (R) A Return to Normalcy James M. Cox (D) Eugene V. Debs (Socialist)
Power Point Credit: Johnny Burkowski Fundamental Questions Did the Roaring Twenties continue the Progressive Era reforms? Warren G. Harding (R) A Return to Normalcy James M. Cox (D) Eugene V. Debs (Socialist)
APUSH REVIEWED! PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT
 APUSH 1890-1912 PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 28 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 20 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 19-20 THE PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT WHY: Industrialization,
APUSH 1890-1912 PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT REVIEWED! American Pageant (Kennedy)Chapter 28 American History (Brinkley) Chapter 20 America s History (Henretta) Chapter 19-20 THE PROGRESSIVE MOVEMENT WHY: Industrialization,
Section 1: From Neutrality to War
 Section 1: From Neutrality to War 1. What Caused World War I? a. Militarism: I m bigger than you b. Alliances: Who s my friend? c. Imperialism: I want this too d. Nationalism: Everyone wants to be their
Section 1: From Neutrality to War 1. What Caused World War I? a. Militarism: I m bigger than you b. Alliances: Who s my friend? c. Imperialism: I want this too d. Nationalism: Everyone wants to be their
Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea
 Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea In the last half of the 1800s, the United States joined the race for control of overseas territories.
Chapter 7 America as a World Power Notes 7.1 The United States Gains Overseas Territories The Big Idea In the last half of the 1800s, the United States joined the race for control of overseas territories.
PROGRESSIVE ERA. 1890s A21w
 PROGRESSIVE ERA 1890s-1920 A21w 9.2.13 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Who were the Progressives, and in what ways did they seek to reform US society form 1890-1920? Consider: political change, social change (industrial
PROGRESSIVE ERA 1890s-1920 A21w 9.2.13 ESSENTIAL QUESTION Who were the Progressives, and in what ways did they seek to reform US society form 1890-1920? Consider: political change, social change (industrial
Progressivism. Definition of Progressivism A movement of the people to curb the powers of the special interests When did it occur?
 Progressivism Definition of Progressivism A movement of the people to curb the powers of the special interests When did it occur? Where did Progressivism originate? Who were the Progressives? Middle Class
Progressivism Definition of Progressivism A movement of the people to curb the powers of the special interests When did it occur? Where did Progressivism originate? Who were the Progressives? Middle Class
Socorro Independent School District US History MP2: 2 nd 9 Weeks
 Unit Essential Questions SE Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Unit 4-- Emergence as a World Power, 1898-1920 How did the economic growth of the U.S. contribute to its emergence as a world power?
Unit Essential Questions SE Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Unit 4-- Emergence as a World Power, 1898-1920 How did the economic growth of the U.S. contribute to its emergence as a world power?
All Possible Questions You Will Find in Reading Quiz D
 All Possible Questions You Will Find in Reading Quiz D These questions are used as quizzes. These questions are also 1/3 of the questions for the objective part of the Exam that ends Unit 2, with the other
All Possible Questions You Will Find in Reading Quiz D These questions are used as quizzes. These questions are also 1/3 of the questions for the objective part of the Exam that ends Unit 2, with the other
1. How did the Dawes Act aid in destroying the way of life of Native American s?
 Name Period Chapter 4 Reconstruction **List and discuss the failures and successes of Reconstruction concerning political and social rights of African Americans. Make sure and include the Amendments 13,
Name Period Chapter 4 Reconstruction **List and discuss the failures and successes of Reconstruction concerning political and social rights of African Americans. Make sure and include the Amendments 13,
I. A Brief History of American Foreign Policy
 I. A Brief History of American Foreign Policy A. Isolationism 1. In his Farewell Address in 1796, President George Washington urged Americans to avoid entangling alliances and maintain neutrality. 2. Since
I. A Brief History of American Foreign Policy A. Isolationism 1. In his Farewell Address in 1796, President George Washington urged Americans to avoid entangling alliances and maintain neutrality. 2. Since
Empire and Expansion. Chapter 27
 Empire and Expansion Chapter 27 Imperialism Stronger nations attempt to create empires by dominating weaker nations. The late 1800s marked the peak of European imperialism, with much of Africa and Asia
Empire and Expansion Chapter 27 Imperialism Stronger nations attempt to create empires by dominating weaker nations. The late 1800s marked the peak of European imperialism, with much of Africa and Asia
Progressive Era, Imperialism, and World War 1
 Progressive Era, Imperialism, and World War 1 Section 7.1 Imperialism- a nation desires to gain more territory outside it s borders Reasons for US Imperialism: Economic growth- new people to sell to National
Progressive Era, Imperialism, and World War 1 Section 7.1 Imperialism- a nation desires to gain more territory outside it s borders Reasons for US Imperialism: Economic growth- new people to sell to National
Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War
 Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War 1 Imperialism & Expansion CH 14-1 Imperialism & War Name Reasons why the United States becomes an imperialist nation. 1-New Markets 2-Anglo-Saxonism 3-Modern Navy 4-Into
Unit 11 Part 1-Spanish American War 1 Imperialism & Expansion CH 14-1 Imperialism & War Name Reasons why the United States becomes an imperialist nation. 1-New Markets 2-Anglo-Saxonism 3-Modern Navy 4-Into
Semester Exam Review: US History
 Name Class Period Semester Exam Review: US History Identify the major eras in U.S. history and describe their defining characteristics (US2C). Label each of the following eras on the timeline that follows.
Name Class Period Semester Exam Review: US History Identify the major eras in U.S. history and describe their defining characteristics (US2C). Label each of the following eras on the timeline that follows.
Presidents in general are not lovable. They ve had to do too much to get where they are. But there was one president who was lovable Teddy Roosevelt
 Presidents in general are not lovable. They ve had to do too much to get where they are. But there was one president who was lovable Teddy Roosevelt and I loved him Walter Lippmann Theodore Roosevelt brought
Presidents in general are not lovable. They ve had to do too much to get where they are. But there was one president who was lovable Teddy Roosevelt and I loved him Walter Lippmann Theodore Roosevelt brought
The 1920s see three GOP presidents Warren Harding was elected in 1920
 CHAPTER 33 REPUBLICANS GALORE The 1920s see three GOP presidents Warren Harding was elected in 1920 Scandal, scandal, scandal Sec. of State - Charles Evans Hughes Sec. of Treasury - Andrew Mellon Sec.
CHAPTER 33 REPUBLICANS GALORE The 1920s see three GOP presidents Warren Harding was elected in 1920 Scandal, scandal, scandal Sec. of State - Charles Evans Hughes Sec. of Treasury - Andrew Mellon Sec.
Period 7: World War I
 Period 7: 1890 1945 World War I Neutrality to War In 1914 war breaks out among European nations after Archduke Franz Ferdinand and his wife are assassinated by Gavrilo Princip President Woodrow Wilson
Period 7: 1890 1945 World War I Neutrality to War In 1914 war breaks out among European nations after Archduke Franz Ferdinand and his wife are assassinated by Gavrilo Princip President Woodrow Wilson
8 TH GRADE UNITS OF INSTRUCTION
 Name Date Per. Social Studies 8 1/3 Review Packet Mrs. Myles McAnally 8 TH GRADE UNITS OF INSTRUCTION Reconstruction: Economic Expansion: a. Immigration b. Industrialization c. US Expansion and Imperialism
Name Date Per. Social Studies 8 1/3 Review Packet Mrs. Myles McAnally 8 TH GRADE UNITS OF INSTRUCTION Reconstruction: Economic Expansion: a. Immigration b. Industrialization c. US Expansion and Imperialism
Standards US History 10-25
 Standards US History 10-25 Progressivism Progressivism A reform movement focused on improving living conditions, education, working conditions, stopping political corruption, and gain women the right to
Standards US History 10-25 Progressivism Progressivism A reform movement focused on improving living conditions, education, working conditions, stopping political corruption, and gain women the right to
AP Exam Review C. Ms. Ramos Alta Loma High School
 AP Exam Review C Ms. Ramos Alta Loma High School Gilded Age Industrialism Politics Urbanization 1875 1925 Largely rural No electricity, telephones, etc. Immigration largely German, Irish and English Railroads
AP Exam Review C Ms. Ramos Alta Loma High School Gilded Age Industrialism Politics Urbanization 1875 1925 Largely rural No electricity, telephones, etc. Immigration largely German, Irish and English Railroads
PROGRESSIVE ERA. 1890s A21w
 PROGRESSIVE ERA 1890s-1920 A21w 9.2.13 ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Who were the Progressives? What reforms did they seek? How successful were Progressive Era reforms in the period 1890-1920? Consider: political
PROGRESSIVE ERA 1890s-1920 A21w 9.2.13 ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Who were the Progressives? What reforms did they seek? How successful were Progressive Era reforms in the period 1890-1920? Consider: political
OUTLINE 7-3: THE PROGRESSIVE ERA, II
 OUTLINE 7-3: THE PROGRESSIVE ERA, II Growth expanded opportunity, while economic instability led to new efforts to reform U.S. society and its economic system. In the Progressive Era of the early 20 th
OUTLINE 7-3: THE PROGRESSIVE ERA, II Growth expanded opportunity, while economic instability led to new efforts to reform U.S. society and its economic system. In the Progressive Era of the early 20 th
World War I: America s Home Front
 World War I: America s Home Front 1. The U.S. and WWI! US neutral until 1917; favors Allies! Protect loans to Allies! US shares Allies culture and democratic government! Allied propaganda! German Unrestricted
World War I: America s Home Front 1. The U.S. and WWI! US neutral until 1917; favors Allies! Protect loans to Allies! US shares Allies culture and democratic government! Allied propaganda! German Unrestricted
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e. Chapter Nineteen: From Crisis to Empire
 Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e The Politics of Equilibrium Electoral Stability High Turnout for Elections Cultural Basis of Party Identification Catholics Tended to Vote Democrat 2 The Politics of
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e The Politics of Equilibrium Electoral Stability High Turnout for Elections Cultural Basis of Party Identification Catholics Tended to Vote Democrat 2 The Politics of
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e. Chapter Twenty-one: America and the Great War
 Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e America and the Great War Introduction Total War The Big Stick : America and the World, 1901-1917 Roosevelt and Civilization Racial and Economic Basis of Roosevelt
Alan Brinkley, AMERICAN HISTORY 13/e America and the Great War Introduction Total War The Big Stick : America and the World, 1901-1917 Roosevelt and Civilization Racial and Economic Basis of Roosevelt
Chapter 27: The Path of Empire, (Pages )
 Chapter 27: The Path of Empire, 1890 1899 (Pages 626 653) I. America Turns Outward A. Motives for overseas expansion 1. Farmers and industrialists Name Per. Date Row 2. The yellow press 3. Role of religion
Chapter 27: The Path of Empire, 1890 1899 (Pages 626 653) I. America Turns Outward A. Motives for overseas expansion 1. Farmers and industrialists Name Per. Date Row 2. The yellow press 3. Role of religion
Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of???
 Need to know What was President Roosevelt s Gentlemen s Agreement with Japan? Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of??? imperialism Stronger nations dominating
Need to know What was President Roosevelt s Gentlemen s Agreement with Japan? Female progressives often justified their reformist political activities on the basis of??? imperialism Stronger nations dominating
Unit 5 Preview Sheet: Becoming A World Power
 Unit 5 Preview Sheet: Becoming A World Power 1. What factors led the US to follow a policy of imperialism in the late 1800 s? 2. How does a policy of imperialism differ from those foreign policies of earlier
Unit 5 Preview Sheet: Becoming A World Power 1. What factors led the US to follow a policy of imperialism in the late 1800 s? 2. How does a policy of imperialism differ from those foreign policies of earlier
The Spanish American-War 4 Causes of the War: Important Events 1/7/2018. Effects of the Spanish American War
 The Spanish American-War 4 Causes of the War: Sugar (Economic) Spanish Cruelties (Humanitarian) The Sinking of the USS Maine (Self-Defense/National Pride) Spanish Brutalities and Yellow Journalism (Political
The Spanish American-War 4 Causes of the War: Sugar (Economic) Spanish Cruelties (Humanitarian) The Sinking of the USS Maine (Self-Defense/National Pride) Spanish Brutalities and Yellow Journalism (Political
The Progressive Era AP US History
 The Progressive Era 1900-1920 AP US History Presidents of the Progressive Era Theodore Roosevelt 1901-1909 William H. Taft 1909-1913 Woodrow Wilson 1913-1921 The Progressive Era Defined: Reform movement
The Progressive Era 1900-1920 AP US History Presidents of the Progressive Era Theodore Roosevelt 1901-1909 William H. Taft 1909-1913 Woodrow Wilson 1913-1921 The Progressive Era Defined: Reform movement
U.S. Imperialism s Impact on Other Nations
 U.S. Imperialism s Impact on Other Nations U.S.-Japanese Relations Japan had closed itself to outsiders in the late 1400s; held a strong mistrust of Western cultures In mid-1800s, US businesses began to
U.S. Imperialism s Impact on Other Nations U.S.-Japanese Relations Japan had closed itself to outsiders in the late 1400s; held a strong mistrust of Western cultures In mid-1800s, US businesses began to
1. Complete the graphic below by identifying major characteristics for each era and identify significant turning points.
 Name: Class Period: Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills Correlation to APUSH Unit 6 1890-1929 (Partial Period 7 of Framework) Essential TEKS 1 Objective: Directions: Analyze main events from the Progressive
Name: Class Period: Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills Correlation to APUSH Unit 6 1890-1929 (Partial Period 7 of Framework) Essential TEKS 1 Objective: Directions: Analyze main events from the Progressive
18 America Claims an Empire QUIT
 18 America Claims an Empire QUIT CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE SECTION 1 Imperialism and America GRAPH MAP SECTION 2 The Spanish-American War SECTION 3 Acquiring New Lands SECTION 4
18 America Claims an Empire QUIT CHAPTER OBJECTIVE INTERACT WITH HISTORY TIME LINE SECTION 1 Imperialism and America GRAPH MAP SECTION 2 The Spanish-American War SECTION 3 Acquiring New Lands SECTION 4
AP United States Unit Six Study Guide Mr. Hansen The Progressive Era, WWI and the 1920 s
 AP United States Unit Six Study Guide Mr. Hansen The Progressive Era, WWI and the 1920 s Text chapters: Chapter 21: The Rise of Progressivism Chapter 22: The Battle for National Reform Chapter 23: America
AP United States Unit Six Study Guide Mr. Hansen The Progressive Era, WWI and the 1920 s Text chapters: Chapter 21: The Rise of Progressivism Chapter 22: The Battle for National Reform Chapter 23: America
Quick Class Discussion: What problems existed within the city, state, and national gov ts?
 During the Gilded Age, city, state, and national governments were in need of reform Corrupt political machines controlled city gov ts Political positions were gained based on patronage not merit Corruption
During the Gilded Age, city, state, and national governments were in need of reform Corrupt political machines controlled city gov ts Political positions were gained based on patronage not merit Corruption
Second area = state constitutions Direct primaries Initiative Referendum Recall. Progressives P. 1
 Progressivism Movement overlaps decline of Populist Movement Main causes = social & political evils of time Goal = eliminating abuses Progressives mobilized middle class Method = disclosing social & political
Progressivism Movement overlaps decline of Populist Movement Main causes = social & political evils of time Goal = eliminating abuses Progressives mobilized middle class Method = disclosing social & political
9/28/2007. The Progressive Era, The Progressive Era, The Progressive Era, Topics of Discussion
 Topics of Discussion I. Shift from Gilded Age to Progressive Era Reform II. Four Goals of the Progressive Era Reform Movement III. Theodore Roosevelt and Republican Progressivism IV. William H. Taft, Roosevelt
Topics of Discussion I. Shift from Gilded Age to Progressive Era Reform II. Four Goals of the Progressive Era Reform Movement III. Theodore Roosevelt and Republican Progressivism IV. William H. Taft, Roosevelt
The Progressive Era,
 The Progressive Era, 1900-1920 The Progressive Era, 1900-1920 Topics of Discussion I. Shift from Gilded Age to Progressive Era Reform II. Four Goals of the Progressive Era Reform Movement III. Theodore
The Progressive Era, 1900-1920 The Progressive Era, 1900-1920 Topics of Discussion I. Shift from Gilded Age to Progressive Era Reform II. Four Goals of the Progressive Era Reform Movement III. Theodore
America s Path to Empire. APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8
 America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8 1890-1892 Foreign Policy The Influence of Sea Power upon History (1890): Alfred Thayer Mahan Sea power throughout history gives advantages US lies
America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 8 1890-1892 Foreign Policy The Influence of Sea Power upon History (1890): Alfred Thayer Mahan Sea power throughout history gives advantages US lies
Define the following: a. Neutrality Policy. b. Louisiana Purchase. c. War of d. Monroe Doctrine. e. Mexican-American War
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Chapter 20 in AMSCO or other resource covering the Spanish American War. Directions: 1. Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before
Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Chapter 20 in AMSCO or other resource covering the Spanish American War. Directions: 1. Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before
End of the war November, Germany signs armistice ending conflict
 World War I Origins of WWI nationalism Germany and Italy imperialism competition over colonies militarism war is glorious and beneficial alliances Triple Alliance - Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy Triple
World War I Origins of WWI nationalism Germany and Italy imperialism competition over colonies militarism war is glorious and beneficial alliances Triple Alliance - Germany, Austria-Hungary, Italy Triple
3. Theodore Roosevelt expanded the Monroe Doctrine as a way to prevent. European involvement in the affairs of Latin American countries.
 Block Name Date USII.5a-6c Post Test Review USII.5a: The Spanish American War 1. What were the causes/reasons for the Spanish American War? (complete answers!) American Business interests in Cuba (sugar)
Block Name Date USII.5a-6c Post Test Review USII.5a: The Spanish American War 1. What were the causes/reasons for the Spanish American War? (complete answers!) American Business interests in Cuba (sugar)
Background. 0 PASSIONATE HUNTER 0 Remarried & had six kids. 0 abandoned politics
 Background 0 Born Oct 27, 1858 into wealthy family 0 Asthma as a child 0 Harvard at 18 excelled in school and athletics (marksmanship and horseback riding) 0 Wife and mother died 1884 from illness 0 abandoned
Background 0 Born Oct 27, 1858 into wealthy family 0 Asthma as a child 0 Harvard at 18 excelled in school and athletics (marksmanship and horseback riding) 0 Wife and mother died 1884 from illness 0 abandoned
US History Fall 2013 Final Exam Review
 US History Fall 2013 Final Exam Review Unit 1 - Foundations of Government 1. Define individual rights. Rights, freedom of speech, BILL OF RIGHTS Turn in the Review Sheet on the Day of the Final. 5pts.
US History Fall 2013 Final Exam Review Unit 1 - Foundations of Government 1. Define individual rights. Rights, freedom of speech, BILL OF RIGHTS Turn in the Review Sheet on the Day of the Final. 5pts.
Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt. Chapter 28
 Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt Chapter 28 Progressive Reformers Progressives wanted government actively involved protecting poor and needy Attacked monopolies, corruption, inefficiency and
Progressivism and the Republican Roosevelt Chapter 28 Progressive Reformers Progressives wanted government actively involved protecting poor and needy Attacked monopolies, corruption, inefficiency and
The Progressive Era
 The Progressive Era 1895 1915 Growing Division Affluence flaunted by the wealthy Progressives Social Darwinism Philosophical approach Big business running small shops out 2% controlled most of the wealth
The Progressive Era 1895 1915 Growing Division Affluence flaunted by the wealthy Progressives Social Darwinism Philosophical approach Big business running small shops out 2% controlled most of the wealth
Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power,
 Name: Class Period: Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1865-1917 Amsco Chapter 20 Reading Assignment: Ch. 21 AMSCO Purpose: This guide is intended to provide a space for you to record
Name: Class Period: Guided Reading and Analysis: Becoming a World Power, 1865-1917 Amsco Chapter 20 Reading Assignment: Ch. 21 AMSCO Purpose: This guide is intended to provide a space for you to record
CHAPTER 22 CONCEPT CARDS
 CHAPTER 22 CONCEPT CARDS Section 1 CIVIL SERVICE COMMISSION - ORANGE Government agency created by the Pendleton Act of 1863 to fill federal jobs on the basis of merit. - People who scored highest on civil
CHAPTER 22 CONCEPT CARDS Section 1 CIVIL SERVICE COMMISSION - ORANGE Government agency created by the Pendleton Act of 1863 to fill federal jobs on the basis of merit. - People who scored highest on civil
The Progressive Era. America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century
 The Progressive Era America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century Origins of Progressivism As America entered the 20 th century, middle class reformers at the municipal, state, and national levels addressed
The Progressive Era America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century Origins of Progressivism As America entered the 20 th century, middle class reformers at the municipal, state, and national levels addressed
Jeopardy. Luck of the Draw. People Places Dates Events Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200
 Jeopardy People Places Dates Events Luck of the Draw Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q
Jeopardy People Places Dates Events Luck of the Draw Q $100 Q $200 Q $300 Q $400 Q $500 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $100 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $200 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $300 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q $400 Q
The Progressive Era,
 The Progressive Era, 1900-1920 Topics of Discussion I. Shift from Gilded Age to Progressive Era Reform III. Theodore Roosevelt and Republican Progressivism IV. William H. Taft, Roosevelt s protégé outdoes
The Progressive Era, 1900-1920 Topics of Discussion I. Shift from Gilded Age to Progressive Era Reform III. Theodore Roosevelt and Republican Progressivism IV. William H. Taft, Roosevelt s protégé outdoes
Progressivism Takes Hold. American History Chapter 9
 Progressivism Takes Hold American History Chapter 9 Theodore Roosevelt & the Modern Presidency Early Political Career 1880 Graduate of Harvard 1881 Elected to the N.Y. State Assembly 1884 Moved to Dakota
Progressivism Takes Hold American History Chapter 9 Theodore Roosevelt & the Modern Presidency Early Political Career 1880 Graduate of Harvard 1881 Elected to the N.Y. State Assembly 1884 Moved to Dakota
Economic Overview. Post-war recession Unemployment = 10% Trade cut in half Prices for products dropped 20%
 Post-war recession Economic Overview Unemployment = 10% Trade cut in half Prices for products dropped 20% 1922-29 Unemployment 3%-4% Gross National Product (GNP) increased from $74.1 billion to $103.1
Post-war recession Economic Overview Unemployment = 10% Trade cut in half Prices for products dropped 20% 1922-29 Unemployment 3%-4% Gross National Product (GNP) increased from $74.1 billion to $103.1
Chap. 33: Wilsonian Progressivism at Home and Abroad, Woodrow Wilson, Domestic Progressivism, and Foreign Relations
 Chap. 33: Wilsonian Progressivism at Home and Abroad, 1912-1916 1 Woodrow Wilson, Domestic Progressivism, and Foreign Relations Learning Objectives 2 Discuss the key issues of the 1912 election and the
Chap. 33: Wilsonian Progressivism at Home and Abroad, 1912-1916 1 Woodrow Wilson, Domestic Progressivism, and Foreign Relations Learning Objectives 2 Discuss the key issues of the 1912 election and the
Essential U.S. History
 EOY Revision Sheet Social Studies, Level K Page 1 of 10 Mount Auburn International Academy SABIS School Network Social Studies Level K / Grade 9 EOY Grade 9 Social Studies Revision guide For Essential
EOY Revision Sheet Social Studies, Level K Page 1 of 10 Mount Auburn International Academy SABIS School Network Social Studies Level K / Grade 9 EOY Grade 9 Social Studies Revision guide For Essential
2. How does the Transcontinental Railroad help with the rapid settlement of the West? (p.124)
 U.S. History Fall Semester Exam Review 2015 December 15 th 3 rd and 4 th periods December 16 th 7 th and 8 th periods December 17 th 1 st and 2 nd periods December 18 th 5 th and 6 th periods Westward
U.S. History Fall Semester Exam Review 2015 December 15 th 3 rd and 4 th periods December 16 th 7 th and 8 th periods December 17 th 1 st and 2 nd periods December 18 th 5 th and 6 th periods Westward
1920s: American Culture and Disillusionment
 1920s: American Culture and Disillusionment 1 Learning Objectives and Thematic Questions 1. Analyze the movement toward social conservatism and the cultural conflicts over the issues of race, religion,
1920s: American Culture and Disillusionment 1 Learning Objectives and Thematic Questions 1. Analyze the movement toward social conservatism and the cultural conflicts over the issues of race, religion,
Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism ( )
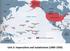 Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism (1890-1930) What is an empire? Is imperialism the same as colonization? Why would the U.S. get involved in this practice? What is the difference between acquiring and
Unit 2: Imperialism and Isolationism (1890-1930) What is an empire? Is imperialism the same as colonization? Why would the U.S. get involved in this practice? What is the difference between acquiring and
An era of prosperity, Republican power, and conflict
 The Roaring 20 s An era of prosperity, Republican power, and conflict 1920's collectively known as the "Roaring 20's", or the "Jazz Age" in sum, a period of great change in American Society - modern America
The Roaring 20 s An era of prosperity, Republican power, and conflict 1920's collectively known as the "Roaring 20's", or the "Jazz Age" in sum, a period of great change in American Society - modern America
Unit 9 Imperialism and WWI. New US Power and Diplomacy
 Unit 9 Imperialism and WWI New US Power and Diplomacy Attitudes Toward an International Role Arguments for Expansion Economics: new markets/investment opportunities/raw materials Culture: Social Darwinism/Protestant
Unit 9 Imperialism and WWI New US Power and Diplomacy Attitudes Toward an International Role Arguments for Expansion Economics: new markets/investment opportunities/raw materials Culture: Social Darwinism/Protestant
MUCKRAKERS. social, economic, and political injustices. corruption, scandal and injustice to the public view
 THE PROGRESSIVE ERA MUCKRAKERS Journalists focusing on social, economic, and political injustices Known for exposing corruption, scandal and injustice to the public view They investigated governments,
THE PROGRESSIVE ERA MUCKRAKERS Journalists focusing on social, economic, and political injustices Known for exposing corruption, scandal and injustice to the public view They investigated governments,
AP UNITED STATES HISTORY 2006 SCORING GUIDELINES. Question 4
 AP UNITED STATES HISTORY 2006 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 Historians have argued that Progressive reform lost momentum in the 1920 s. Evaluate this statement with respect to TWO of the following: Regulation
AP UNITED STATES HISTORY 2006 SCORING GUIDELINES Question 4 Historians have argued that Progressive reform lost momentum in the 1920 s. Evaluate this statement with respect to TWO of the following: Regulation
America s Path to Empire. APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 2
 America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 2 Major Events 1890-1892 McKinley Tariff October 1, 1890 Raised the average duty on imports to almost fifty percent Intended to protect domestic industries
America s Path to Empire APUSH/AP-DC Unit 7 - Period 2 Major Events 1890-1892 McKinley Tariff October 1, 1890 Raised the average duty on imports to almost fifty percent Intended to protect domestic industries
PROGRESSIVISM. Hull House. Jane Addams PROGRESSIVES TARGET PROBLEMS
 Chapter 20 THE PROGRESSIVE ERA PROGRESSIVISM 1890 1920 widespread, many-sided effort both parties middle-class efforts Henry George - Progress and Poverty Edward Bellamy - Looking Backward PROGRESSIVES
Chapter 20 THE PROGRESSIVE ERA PROGRESSIVISM 1890 1920 widespread, many-sided effort both parties middle-class efforts Henry George - Progress and Poverty Edward Bellamy - Looking Backward PROGRESSIVES
The Progressive Era. America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century
 The Progressive Era America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century Origins of Progressivism As America entered the 20 th century, middle class reformers at the municipal, state, and national levels addressed
The Progressive Era America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century Origins of Progressivism As America entered the 20 th century, middle class reformers at the municipal, state, and national levels addressed
Theodore Roosevelt -rose steadily through gov t ranks. -Spanish American War. -Gov. of NY reform governor. -Vice President of William McKinley
 Theodore Roosevelt -rose steadily through gov t ranks -Spanish American War -Gov. of NY reform governor -Vice President of William McKinley -Became President with McKinley s assassination Square Deal -
Theodore Roosevelt -rose steadily through gov t ranks -Spanish American War -Gov. of NY reform governor -Vice President of William McKinley -Became President with McKinley s assassination Square Deal -
Imperialism and America
 Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire CHAPTER 10 Section 1 (pages 342-345) Imperialism and America American Expansionism (pages 342-344) Why did Americans support imperialism? In 1893, Queen Liliuokalani
Chapter 10 America Claims an Empire CHAPTER 10 Section 1 (pages 342-345) Imperialism and America American Expansionism (pages 342-344) Why did Americans support imperialism? In 1893, Queen Liliuokalani
Review: fill these in to help you prepare for the first three quizzes.
 Review: fill these in to help you prepare for the first three quizzes. Thursday s quiz: Warren G. Harding promised a return to after the upsets of 1919 and 1920 that included a, or an economic slump. Then
Review: fill these in to help you prepare for the first three quizzes. Thursday s quiz: Warren G. Harding promised a return to after the upsets of 1919 and 1920 that included a, or an economic slump. Then
The Progressive Era. America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century
 The Progressive Era America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century Origins of Progressivism As America entered the 20 th century, middle class reformers at the municipal, state, and national levels addressed
The Progressive Era America Seeks Reforms in the Early 20 th Century Origins of Progressivism As America entered the 20 th century, middle class reformers at the municipal, state, and national levels addressed
WORLD WAR 1. Causes of WWI
 WORLD WAR 1 1914-1918 Causes of WWI 1. Imperialism: Germany, France, & Great Britain Scramble for power and claim to lands in Africa, Asia, and the Pacific 2. Militarism Aggressive build up of a nation
WORLD WAR 1 1914-1918 Causes of WWI 1. Imperialism: Germany, France, & Great Britain Scramble for power and claim to lands in Africa, Asia, and the Pacific 2. Militarism Aggressive build up of a nation
Chapter 18. American Claims an Empire
 Chapter 18 American Claims an Empire Section 1: Imperialism and American Imperialism 1880s U.S. interest in building an Empire builds Imperialism = Stronger : Economic, political, or military control Europeans
Chapter 18 American Claims an Empire Section 1: Imperialism and American Imperialism 1880s U.S. interest in building an Empire builds Imperialism = Stronger : Economic, political, or military control Europeans
AMERICAN HISTORY SEMESTER FINAL STUDY GUIDE
 AMERICAN HISTORY SEMESTER FINAL STUDY GUIDE Reconstruction and the West 13th Amendment 14th Amendment 15th Amendment Dawes Act Homestead Act manifest destiny 2. Be able to explain why the near-extermination
AMERICAN HISTORY SEMESTER FINAL STUDY GUIDE Reconstruction and the West 13th Amendment 14th Amendment 15th Amendment Dawes Act Homestead Act manifest destiny 2. Be able to explain why the near-extermination
Who: Urban middle and upper class (including many women)
 Who: Urban middle and upper class (including many women) Goals: Fight political corruption, social injustice, and economic inequality Effect social change in cities and among immigrant populations. Use
Who: Urban middle and upper class (including many women) Goals: Fight political corruption, social injustice, and economic inequality Effect social change in cities and among immigrant populations. Use
Answer the following questions by reviewing main events, defining terms, and analyzing significance in the spaces provided.
 Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Chapter 23 in AMSCO or other resource covering the 1920s. Directions: 1. Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before you read the
Name: Class Period: Due Date: / / Reading Assignment: Chapter 23 in AMSCO or other resource covering the 1920s. Directions: 1. Pre-Read: Read the prompts/questions within this guide before you read the
AMERICA SEEKS REFORMS IN THE EARLY 20 TH CENTURY
 AMERICA SEEKS REFORMS IN THE EARLY 20 TH CENTURY ORIGINS OF PROGRESSIVISM As America entered into the 20 th century, middle class reformers addressed many social problems Work conditions, rights for women
AMERICA SEEKS REFORMS IN THE EARLY 20 TH CENTURY ORIGINS OF PROGRESSIVISM As America entered into the 20 th century, middle class reformers addressed many social problems Work conditions, rights for women
HCC 1302 Unit I Study Guide Spring 2017
 Topic A: The Nature of History the primary purposes of studying history the forces of history the processes historians use to produce history HCC 1302 Unit I Study Guide Spring 2017 primary source multiple
Topic A: The Nature of History the primary purposes of studying history the forces of history the processes historians use to produce history HCC 1302 Unit I Study Guide Spring 2017 primary source multiple
Chapter 10 Notes: The Jazz Age. Events after World War I made some Americans intolerant of immigrants and foreign ideas.
 Chapter 10 Notes: The Jazz Age Section 1: Time of Turmoil Fear of Radicalism Events after World War I made some Americans intolerant of immigrants and foreign ideas. As the 1920s began, Americans wanted
Chapter 10 Notes: The Jazz Age Section 1: Time of Turmoil Fear of Radicalism Events after World War I made some Americans intolerant of immigrants and foreign ideas. As the 1920s began, Americans wanted
Unit 3: The Progressive Era
 Unit 3: The Progressive Era Essential Questions: 1. Can government fix our problems? 2. How did Americans address the problems caused by the Gilded Age? 3. Is a strong president good for our nation? Vocabulary:
Unit 3: The Progressive Era Essential Questions: 1. Can government fix our problems? 2. How did Americans address the problems caused by the Gilded Age? 3. Is a strong president good for our nation? Vocabulary:
