HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK. 11th Grade Unit 5
|
|
|
- Lesley Bridges
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK 11th Grade Unit 5
2 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 1105 A NATION DIVIDED AND UNITED Unit 5 A NATION DIVIDED AND UNITED INTRODUCTION 3 1. REGIONAL LIFESTYLES 5 REGIONAL LIFESTYLES: THE EAST AND WEST 6 REGIONAL LIFESTYLES: THE SOUTH 15 SELF TEST CIVIL WAR 22 CIVIL WAR: DIVISION AND ANTAGONISM 23 THE ANTAGONISTS 28 CIVIL WAR: UNION BLOCKADE AND HOSTILITIES 31 THE CIVIL WAR: FINAL PHASE 37 SELF TEST RECONSTRUCTION 46 NORTHERN INFLUENCES 47 SOUTHERN REACTIONS 51 SELF TEST 3 55 LIFEPAC Test is located in the center of the booklet. Please remove before starting the unit. 1
3 A NATION DIVIDED AND UNITED Unit 5 Author: Alpha Omega Staff Editor: Alan Christopherson, M.S. Media Credits: Page 22: cmfotoworks, istock, Thinkstock; 24, 50: Photos.com, Thinkstock; 25: Thinkstock, Stockbyte, Thinkstock; 25, 34, 48: wynnter, istock,thinkstock; 29, 35: fotosmania, istock, Thinkstock; 32: Jupiterimages, liquidlibrary, Thinkstock; 35, 39, 49: denisk0, istock, Thinkstock; 47: TonyBaggett, istock, Thinkstock; 51: herlordship, istock, Thinkstock. 804 N. 2nd Ave. E. Rock Rapids, IA MM by Alpha Omega Publications, Inc. All rights reserved. LIFEPAC is a registered trademark of Alpha Omega Publications, Inc. All trademarks and/or service marks referenced in this material are the property of their respective owners. Alpha Omega Publications, Inc. makes no claim of ownership to any trademarks and/or service marks other than their own and their affiliates, and makes no claim of affiliation to any companies whose trademarks may be listed in this material, other than their own. 2
4 Unit 5 A NATION DIVIDED AND UNITED A Nation Divided and United Introduction During the years after the War of 1812, the population of the United States increased rapidly. Industry expanded, agricultural production boomed, settlers began to move into new territories, roads and canals were constructed over mountains and through dense forests, and the cry of Manifest Destiny could be heard across the nation. Manifest Destiny was the idea that the citizens of the United States had a God-given right to extend their way of life from the Atlantic to the Pacific and that no physical barrier or human force could stop the settlement of these lands. This idea became a prevalent thought in the minds of many United States citizens. The expansion into new territories across the continent was a direct link in the chain of events leading to the Civil War. Each time new territory was acquired by the United States, the troublesome question of slavery was raised. Many people in the anti-slavery faction of the North and West persisted in thinking that slavery in the territories would result in the economic superiority of the South and the demise of free enterprise. The proslavery faction, in contrast, feared the destruction of the Southern lifestyle unless the balance between free states and slave states could be maintained. The increase in universal white male suffrage was another factor that helped create the sectionalism that paved the way for the war. After the Declaration of Independence, state laws in the thirteen states stipulated that only white men with considerable property or those who paid high taxes were allowed to vote. These laws were still in effect after the War of Between 1816 and 1821 six new states were admitted to the Union that allowed all white men to vote without regard for property qualifications. With the addition of these new states, the eastern and southern states began to relax their voting restrictions; many men who had never shown an interest in politics began to participate in the elective process. For the first time the common man had the opportunity of electing people to office who would encourage the federal government to adopt policies primarily beneficial to his sectional needs. In the years following the War of 1812, the United States extended its boundaries from the Atlantic coast to the Pacific coast. With this expansion came issues that divided one section of the nation from another. As the United States grew, the way of life changed from one section to another. Southern living, for example, was entirely different from that of the West or Northeast. In this unit you will study the conditions of life in the East, the West, and the South. You will also study the Civil War and the reconstruction efforts after the war. Introduction 3
5 A NATION DIVIDED AND UNITED Unit 5 Objectives Read these objectives. The objectives tell you what you will be able to do when you have successfully completed this LIFEPAC. When you have finished this LIFEPAC, you should be able to: 1. Describe the physical and sociological features of the South, the West, and the Northeast. 2. Define issues which caused the polarization of the nation prior to the Civil War. 3. Review both the Northern and the Southern views of these issues. 4. Identify the leading personalities of the Civil War era and explain the consequences of their actions. 5. Identify generalizations about the effect of slavery on owners and slaves. 6. Define the strengths and weaknesses each side possessed in facing the Civil War. 7. Identify major battles of the war and how each victory or defeat contributed to the outcome of the war. 8. Outline effects of the war on the North and the South. 9. Examine the reconstruction efforts made after the Civil War. 10. Recognize that God is no respecter of persons and that we are all equal in his sight. Survey the LIFEPAC. Ask yourself some questions about this study and write your questions here. 4 Introduction
6 Unit 5 A NATION DIVIDED AND UNITED 1. REGIONAL LIFESTYLES In this section and the next you will examine the prewar lifestyles of three regions and see how these differences in lifestyle contributed to sectionalism and the problems that followed. Section Objectives Review these objectives. When you have completed this section, you should be able to: 1. Describe the physical and sociological features of the South, the West, and the Northeast. 2. Define issues which caused the polarization of the nation prior to the Civil War. 3. Review both the Northern and the Southern views of these issues. Vocabulary Study these words to enhance your learning success in this section. agrarian Organized or designed to promote agricultural interests. artisan One trained in some mechanical art or trade. drainage basin A land drained by a river and its tributaries. fall line Place where rivers descend in falls or rivers from a piedmont to a plain. growing season The period between the last killing frost in the spring and the first killing frost in the fall. piedmont Hilly land at the foot of mountains. sod Soil filled with the roots of grass, herbs, and so forth. Note: All vocabulary words in this LIFEPAC appear in boldface print the first time they are used. If you are not sure of the meaning when you are reading, study the definitions given. Section 1 5
7 A NATION DIVIDED AND UNITED Unit 5 REGIONAL LIFESTYLES: THE EAST AND WEST Life in the East. In 1850 more than half of the factories in the United States were located in the Northeast with two-thirds of the nation s production value centered in that region. The Northeast was unsuitable for large-scale farming because of the mountainous terrain and the short growing season only three months in some places. However, the rough, rocky mountains with rivers coursing down their sides were an ideal source for the power necessary to run the machinery in the new mills and factories of the budding Northeastern textile industry. They also had a ready source of cotton in the South. Pennsylvania 2,258,160 53,626/ Northeastern Statistics Maine 581,813 1,356/ Rhode Island 143,875 3,670/ New Hampshire 317, / Because the growing season was short and the hard, rocky ground kept agricultural production near the subsistence level, more people lived in the cities of the Northeast to find work than in either the West or the South. New York 3,048,325 49,069/ Massachusetts 985,450 9,064/ New Jersey 465,509 23,810/ Vermont 313, / Connecticut 363,099 7,693/ In the years preceding the Civil War, a new wave of immigrants came to the United States, fleeing the potato famine of 1845 and 1846 in Ireland. A few of the immigrants remained in the southern entry White Population Free Black Population/Slave Population Number of People Who Lived in 1 Square Mile From Idea and Action in American History, M. Brady & H. Brady; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ; Used by Permission. Ireland 2.9 M Germany 1.5 M 1840s and 1850s England 420,000 France 180,000 Scotland 40,000 Immigration Switzerland 30,000 Netherlands 20,000 Belgium 20,000 Italy 15,000 Wales 15,000 Poland 5,000 6 Section 1
8 Unit 5 A NATION DIVIDED AND UNITED ports of Charleston and New Orleans. However, the majority swelled the numbers in the northern cities where they found work in the factories. By 1857 the number of factory workers had risen to 1.2 million, and the industrial labor force to almost 1 million people working an average of sixty-eight to seventytwo hours a week. Northeastern Statistics Workers in the Northeast 1840 City workers developed machines and products to make their lives easier. Charles Goodyear s vulcanized rubber was patented in 1844 and was used for boots and shoes. Elias Howe s sewing machine was patented in The telegraph was patented by Samuel Morse in 1862 and increased intercontinental communications. These inventions are examples of some of the machines and products of the period. The major cities of the Northeast Philadelphia, Trenton, New York, Buffalo, Hartford, Providence, and Boston had cobblestone streets, gas lanterns posted on brick or flagstone sidewalks, and gutters that ran down the middle or sides of the streets carrying the sewage. The more enlightened cities had street cleaners, watchmen who handled thieves and looters, and chief engineers who coordinated the efforts of volunteer firemen. The shops of small artisans, merchants, cabinetmakers, silversmiths, candle makers, blacksmiths, clock makers, milliners, printers, and grocers lined the streets. Horse-drawn carriages rumbled across the cobblestones while hawkers called out, selling water, milk, wood for fuel, fruit, and hot foods such as boiled corn and gingerbread. Other peddlers bought rags, old metal, and rope. Agriculture 64.2% Manufacturing 27.3% Commerce 4.2% Navigation 2.1% Learned professions 1.9% Mining 0.3% From Idea and Action in American History, M. Brady & H. Brady; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ; Used by Permission Northeastern Statistics The Percent of Land Being Farmed in the Northeast 1850 Brick or board houses lined the streets of the residential areas, and a few public and religious schools and academies were available for those who were able to pay tuition. Tenement houses became home for some factory workers; other factories provided small houses near the plant for their laborers. Black freedmen and Indians lived in the cities of the North. They ran small businesses, were service workers in homes and inns, and worked in the factories like other common people of the time. PERCENT % Wealthy merchants and industrial capitalists wielded vast political power because of their great wealth. The general public tended to agree with their political and industrial leaders, whatever their own social or economic class. During that period, the people of the Northeast became more concerned about the needs of those around them. Most of the great reform movements flowered in this region of the country. The demand for public education, prison Maine Vermont New Hampshire Rhode Island Massachusetts Connecticut New York New Jersey Pennsylvania Used by Permission. Section 1 7
9 A NATION DIVIDED AND UNITED Unit 5 reform, assistance for the physically handicapped, care for the insane, women s rights, temperance, ideal societies, and abolition all found support in that region. The Northeast favored governmental aid to business, the protective tariff, and controlled bank credit. It did not, however, favor westward expansion, especially if it included slavery. Study the statistics of the Northeastern states from the charts and fill in the blanks. 1.1_ The largest Northeastern state was with a white population of _ people. The smallest Northeastern state was with a white population of people. The most densely populated state was with people per square mile. 1.4_ The state with the highest percentage of land being farmed was. 1.5_ In Maine only percent of the land was used for farming. Match the countries with the number of immigrants. 1.6 Ireland 1.7 Germany 1.8 Poland 1.9 France 1.10 Belgium 1.11 England 1.12 Italy a. 420,000 b. 180,000 c. 15,000 d. 2,900,000 e. 5,000 f. 20,000 g. 1,500,000 8 Section 1
10 Unit 5 A NATION DIVIDED AND UNITED Complete this map activity. 1.13_ Write the numbers of the cities listed below at their correct location on the map. 1. Charleston 2. New Orleans 3. Philadelphia 4. Trenton 5. New York 6. Hartford 7. Boston 8. Providence 9. Buffalo Choose the best answer(s). 1.14_ Two emerging factors after the War of 1812 that contributed to development of sectionalism were: a. the stricter voting laws b. the demise of free enterprise c. an increase in the number of men voting d. a rapid decrease in the population of the United States e. the concept of Manifest Destiny Section 1 9
11 HIS1105 Sept 17 Printing 804 N. 2nd Ave. E. Rock Rapids, IA ISBN
INDUSTRY AND MIGRATION/THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH. pp
 INDUSTRY AND MIGRATION/THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH pp 382-405 What drives history? Table Talk: Brainstorm some things that have driven history forward What do these things have in common? What changes have
INDUSTRY AND MIGRATION/THE NORTH AND THE SOUTH pp 382-405 What drives history? Table Talk: Brainstorm some things that have driven history forward What do these things have in common? What changes have
Unit 8. Innovation Brings Change 1800 s-1850 s
 Unit 8 Innovation Brings Change 1800 s-1850 s Unit Overview: Industrialization Era This unit addresses the development of the economies in the North and the South, innovations in technology and the application
Unit 8 Innovation Brings Change 1800 s-1850 s Unit Overview: Industrialization Era This unit addresses the development of the economies in the North and the South, innovations in technology and the application
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK. 11th Grade Unit 2
 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK 11th Grade Unit 2 Unit 2 DEVELOPMENT OF CONSTITUTIONAL GOVERNMENT HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 1102 DEVELOPMENT OF CONSTITUTIONAL GOVERNMENT INTRODUCTION 3 1. RELATIONS WITH ENGLAND
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK 11th Grade Unit 2 Unit 2 DEVELOPMENT OF CONSTITUTIONAL GOVERNMENT HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 1102 DEVELOPMENT OF CONSTITUTIONAL GOVERNMENT INTRODUCTION 3 1. RELATIONS WITH ENGLAND
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 1102 DEVELOPMENT OF CONSTITUTIONAL GOVERNMENT
 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 1102 DEVELOPMENT OF CONSTITUTIONAL GOVERNMENT CONTENTS I. RELATIONS WITH ENGLAND... 2 Trade Regulations... 3 French and Indian War... 6 Colonial Resistance... 12 II. THE REVOLUTIONARY
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 1102 DEVELOPMENT OF CONSTITUTIONAL GOVERNMENT CONTENTS I. RELATIONS WITH ENGLAND... 2 Trade Regulations... 3 French and Indian War... 6 Colonial Resistance... 12 II. THE REVOLUTIONARY
UNIT 4: EXPANSION & REFORM LESSON 4.1: EFFECTS OF MANIFEST DESTINY & INDUSTRIALIZATION
 UNIT 4: EXPANSION & REFORM LESSON 4.1: EFFECTS OF MANIFEST DESTINY & INDUSTRIALIZATION ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does expansion and industrialization contribute to growing sectionalism within the United States
UNIT 4: EXPANSION & REFORM LESSON 4.1: EFFECTS OF MANIFEST DESTINY & INDUSTRIALIZATION ESSENTIAL QUESTION How does expansion and industrialization contribute to growing sectionalism within the United States
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK. 12th Grade Unit 2
 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 2 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 1202 UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT Unit 2 UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT INTRODUCTION 3 1. U.S. CONSTITUTION AND RIGHTS 5 UNITED STATES CONSTITUTION
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 2 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 1202 UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT Unit 2 UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT INTRODUCTION 3 1. U.S. CONSTITUTION AND RIGHTS 5 UNITED STATES CONSTITUTION
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK. 11th Grade Unit 3
 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK 11th Grade Unit 3 Unit 3 NATIONAL EXPANSION HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 1103 NATIONAL EXPANSION INTRODUCTION 3 1. SHIP OF STATE 5 FEDERAL GOVERNMENT 7 FIRST POLITICAL PARTIES 11
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK 11th Grade Unit 3 Unit 3 NATIONAL EXPANSION HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 1103 NATIONAL EXPANSION INTRODUCTION 3 1. SHIP OF STATE 5 FEDERAL GOVERNMENT 7 FIRST POLITICAL PARTIES 11
Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change
 Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change 1800-1860 Nationalism and Economic Growth By 1815, following the end of The War of 1812, America had shown: That it could defend its sovereignty against
Nationalism, Economic Revolution, and Social Change 1800-1860 Nationalism and Economic Growth By 1815, following the end of The War of 1812, America had shown: That it could defend its sovereignty against
Emergence of Modern America: 1877 to 1930s
 VUS.8a Emergence of Modern America: 1877 to 1930s What factors influenced American growth and expansion in the late nineteenth and early twentieth century? In the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries,
VUS.8a Emergence of Modern America: 1877 to 1930s What factors influenced American growth and expansion in the late nineteenth and early twentieth century? In the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries,
DRAWING FROM EXPERIENCEII
 Chapter 10, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 306 311 ECONOMIC GROWTH KEY TERMS Industrial Revolution A new way of working and producing goods (page 307) capital Money invested to start new businesses
Chapter 10, Section 1 For use with textbook pages 306 311 ECONOMIC GROWTH KEY TERMS Industrial Revolution A new way of working and producing goods (page 307) capital Money invested to start new businesses
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK. 12th Grade Unit 10
 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 10 Unit 10 GEOGRAPHY HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 1210 GEOGRAPHY INTRODUCTION 3 1. EURO AND INTERNATIONAL FINANCE 4 THE WORLD OF THE EURO 5 CITIES OF INTERNATIONAL
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK 12th Grade Unit 10 Unit 10 GEOGRAPHY HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 1210 GEOGRAPHY INTRODUCTION 3 1. EURO AND INTERNATIONAL FINANCE 4 THE WORLD OF THE EURO 5 CITIES OF INTERNATIONAL
Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages ) Economic Growth
 Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages 304 309) Economic Growth Essential Question What effects did the Industrial Revolution have on the U. S. economy? Directions: As you read, complete a graphic organizer like
Chapter 10, Section 1 (Pages 304 309) Economic Growth Essential Question What effects did the Industrial Revolution have on the U. S. economy? Directions: As you read, complete a graphic organizer like
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY TEACHER S GUIDE. 12th Grade
 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY TEACHER S GUIDE 12th Grade HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 1200 Teacher s Guide LIFEPAC Overview 5 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY SCOPE & SEQUENCE 6 STRUCTURE OF THE LIFEPAC CURRICULUM 10 TEACHING SUPPLEMENTS
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY TEACHER S GUIDE 12th Grade HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 1200 Teacher s Guide LIFEPAC Overview 5 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY SCOPE & SEQUENCE 6 STRUCTURE OF THE LIFEPAC CURRICULUM 10 TEACHING SUPPLEMENTS
STANDARD VUS.8a. Essential Questions What factors influenced American growth and expansion in the late nineteenth and early twentieth century?
 STANDARD VUS.8a through the early twentieth century by explaining the relationship among territorial expansion, westward movement of the population, new immigration, growth of cities, and the admission
STANDARD VUS.8a through the early twentieth century by explaining the relationship among territorial expansion, westward movement of the population, new immigration, growth of cities, and the admission
Inventor Invention Impact
 Industrialization and Reform Test Review Test Date: Name 1. Fill in the missing boxes Inventor Invention Impact Eli Whitney Cotton Gin Robert Fulton Decreased the amount of time needed for travel. Decreased
Industrialization and Reform Test Review Test Date: Name 1. Fill in the missing boxes Inventor Invention Impact Eli Whitney Cotton Gin Robert Fulton Decreased the amount of time needed for travel. Decreased
Settling the Western Frontier
 Settling the Western Frontier 1860-1890 Library of Congress America Moves West America s desire to expand meant that thousands would migrate to western lands (Manifest Destiny). What are some pull factors?
Settling the Western Frontier 1860-1890 Library of Congress America Moves West America s desire to expand meant that thousands would migrate to western lands (Manifest Destiny). What are some pull factors?
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY TEACHER S GUIDE. 9th Grade
 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY TEACHER S GUIDE 9th Grade Author: Alpha Omega Publications Editor: Alan Christopherson, M.S. 2 25 History & Geography 900 Teacher Notes INSTRUCTIONS FOR HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY The LIFEPAC
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY TEACHER S GUIDE 9th Grade Author: Alpha Omega Publications Editor: Alan Christopherson, M.S. 2 25 History & Geography 900 Teacher Notes INSTRUCTIONS FOR HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY The LIFEPAC
In the early Antebellum era ( ), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that
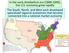 In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The South, North, and West each developed specialized regional economies that became connected into a national market economy The
Transformation. Society
 Transformation of the Economy & Society in Antebellum America 1820-1860 A09W 10.11.01 Guiding Question Analyze the causes of the transformation of the American economy in the first half of the nineteenth
Transformation of the Economy & Society in Antebellum America 1820-1860 A09W 10.11.01 Guiding Question Analyze the causes of the transformation of the American economy in the first half of the nineteenth
The North s People. Guide to Reading
 The North s People Guide to Reading Main Idea Many cities grew tremendously during this period. Key Terms trade union, strike, prejudice, discrimination, famine, nativist Reading Strategy Determining Cause
The North s People Guide to Reading Main Idea Many cities grew tremendously during this period. Key Terms trade union, strike, prejudice, discrimination, famine, nativist Reading Strategy Determining Cause
Unit Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution
 Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
Unit 4 1800-1848 Module 2: Transportation, Market, and Industrial Revolution Antebellum America: The Market and Transportation In the early Antebellum era (1800-1840), the U.S. economy grew rapidly The
Industrial Revolution
 Chapter 9 Economic Transformation Industrial Revolution Division of Labor Industry in America 1790 1820 aided by transportation Industrial Revolution outwork system work done outside of shop modern factory
Chapter 9 Economic Transformation Industrial Revolution Division of Labor Industry in America 1790 1820 aided by transportation Industrial Revolution outwork system work done outside of shop modern factory
Chapter 6 Shaping an Abundant Land. Page 135
 Chapter 6 Shaping an Abundant Land Page 135 Waves of immigrants came to the U.S. in order to find a better life. Push-pull factors were at play. Immigration is not the only movement of people in the U.S.
Chapter 6 Shaping an Abundant Land Page 135 Waves of immigrants came to the U.S. in order to find a better life. Push-pull factors were at play. Immigration is not the only movement of people in the U.S.
netw rks Reading Essentials and Study Guide Growth and Division, Lesson 2 Early Industry ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS Reading HELPDESK
 and Study Guide Lesson 2 Early Industry ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How did the nation s economy help shape its politics? How did the economic differences between the North and the South cause tension? Reading
and Study Guide Lesson 2 Early Industry ESSENTIAL QUESTIONS How did the nation s economy help shape its politics? How did the economic differences between the North and the South cause tension? Reading
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK. 9th Grade Unit 2
 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK 9th Grade Unit 2 Unit 2 Our National Government HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 902 Our National Government INTRODUCTION 3 1. THE IDEALS OF OUR NATIONAL GOVERNMENT 5 PURPOSE OF OUR
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY STUDENT BOOK 9th Grade Unit 2 Unit 2 Our National Government HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 902 Our National Government INTRODUCTION 3 1. THE IDEALS OF OUR NATIONAL GOVERNMENT 5 PURPOSE OF OUR
Chapter 14, Section 1 Immigrants and Urban Challenges
 Chapter 14, Section 1 Immigrants and Urban Challenges Pages 438-442 The revolutions in industry, transportation, and technology were not the only major changes in the United States in the mid-1800s. Millions
Chapter 14, Section 1 Immigrants and Urban Challenges Pages 438-442 The revolutions in industry, transportation, and technology were not the only major changes in the United States in the mid-1800s. Millions
Economic Growth. Guided Reading Activity. Growth and Expansion. Answering Questions DIRECTIONS: As you read the section, answer the questions below.
 Guided Reading Activity Growth and Expansion Section Economic Growth Give yourself enough time to read and understand the text. Don t rush through it. Take your time and pause to reread sections or to
Guided Reading Activity Growth and Expansion Section Economic Growth Give yourself enough time to read and understand the text. Don t rush through it. Take your time and pause to reread sections or to
ID-Irish and German Immigration by Decade (291) Summary 1- What decade brought the greatest number of Irish immigrants? Summary 2- What
 Ch 14 Insights Goals Questions Part 1 Identify the two largest immigrant groups to the US in the first half of the 1800 s and explain how their experiences were different Explain how those different experiences
Ch 14 Insights Goals Questions Part 1 Identify the two largest immigrant groups to the US in the first half of the 1800 s and explain how their experiences were different Explain how those different experiences
Q3/Q4 Sectionalism Vocab
 Q3/Q4 Sectionalism Vocab North: Industrial Revolution Sectionalism: loyalty to one region (section) of the country rather than the whole country Industrial Revolution: period of rapid growth in the use
Q3/Q4 Sectionalism Vocab North: Industrial Revolution Sectionalism: loyalty to one region (section) of the country rather than the whole country Industrial Revolution: period of rapid growth in the use
Inventor Invention Impact
 Industrialization and Reform Test Review Test Date: Name 1. Fill in the missing boxes Inventor Invention Impact Eli Whitney Cotton Gin -Increased slavery -Made cleaning cotton faster and more efficient
Industrialization and Reform Test Review Test Date: Name 1. Fill in the missing boxes Inventor Invention Impact Eli Whitney Cotton Gin -Increased slavery -Made cleaning cotton faster and more efficient
Several early American leaders believed that Tariffs were the best way for the government to generate funds that could be used to improve the country
 Several early American leaders believed that Tariffs were the best way for the government to generate funds that could be used to improve the country s transportation network as well as other government
Several early American leaders believed that Tariffs were the best way for the government to generate funds that could be used to improve the country s transportation network as well as other government
Unit III Outline Organizing Principles
 Unit III Outline Organizing Principles British imperial attempts to reassert control over its colonies and the colonial reaction to these attempts produced a new American republic, along with struggles
Unit III Outline Organizing Principles British imperial attempts to reassert control over its colonies and the colonial reaction to these attempts produced a new American republic, along with struggles
Warm Up. I. Create an episode map on the Market Revolution
 Warm Up I. Create an episode map on the Market Revolution The Rise of Industry I. The Market Revolution led to increased industrialization in the United States A. More products are made by machines than
Warm Up I. Create an episode map on the Market Revolution The Rise of Industry I. The Market Revolution led to increased industrialization in the United States A. More products are made by machines than
In the first half of the nineteenth century, economic changes called by historians the market revolution transformed the United States.
 1 2 In the first half of the nineteenth century, economic changes called by historians the market revolution transformed the United States. Innovations in transportation and communication sparked these
1 2 In the first half of the nineteenth century, economic changes called by historians the market revolution transformed the United States. Innovations in transportation and communication sparked these
Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy?
 Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.4: Clickers Questions Market Revolution inquiry activity
Essential Question: How did the development of regional economies & Clay s American System led to a national market economy? CPUSH Agenda for Unit 4.4: Clickers Questions Market Revolution inquiry activity
Eighth Grade Social Studies United States History Course Outline
 Crossings Christian School Academic Guide Middle School Division Grades 5-8 Eighth Grade Social Studies Chapter : Early Exploration of the Americas How do new ideas change the way people live? Why do people
Crossings Christian School Academic Guide Middle School Division Grades 5-8 Eighth Grade Social Studies Chapter : Early Exploration of the Americas How do new ideas change the way people live? Why do people
The most densely populated and industrialized region in the United States is the what?
 Chapter 5 The United States pg. 120 153 5 1 From Coast to Coast pg. 123 127 Northeast What states are included in the Northeast? A continent is what? Landforms, Climate, and Vegetation What are the two
Chapter 5 The United States pg. 120 153 5 1 From Coast to Coast pg. 123 127 Northeast What states are included in the Northeast? A continent is what? Landforms, Climate, and Vegetation What are the two
#1 INDUSTRIALIZATION
 #1 INDUSTRIALIZATION Industrialization the shift from an agricultural economy to one based on production and manufacturing completely changed the northern and western economy between 1820 and 1860. For
#1 INDUSTRIALIZATION Industrialization the shift from an agricultural economy to one based on production and manufacturing completely changed the northern and western economy between 1820 and 1860. For
The Market Revolution:
 The Market Revolution: By midcentury (1850s), capital and technology were converting enough central workshops into mechanized factories to convert the market revolution into a staggeringly productive industrial
The Market Revolution: By midcentury (1850s), capital and technology were converting enough central workshops into mechanized factories to convert the market revolution into a staggeringly productive industrial
FORGING THE NATIONAL ECONOMY, Chapter 14
 FORGING THE NATIONAL ECONOMY, 1790 1860 Chapter 14 WESTWARD MOVEMENT & SHAPING THE WESTERN LANDSCAPE America West of the Alleghenies Population center shifts Life is brutal, primitive, isolated Land becomes
FORGING THE NATIONAL ECONOMY, 1790 1860 Chapter 14 WESTWARD MOVEMENT & SHAPING THE WESTERN LANDSCAPE America West of the Alleghenies Population center shifts Life is brutal, primitive, isolated Land becomes
Mr. Saccullo 8 th Grade Social Studies Review Sheet IV
 Mr. Saccullo 8 th Grade Social Studies Review Sheet IV Key Points of the Time Period Word Bank mass production poorly northern wages machines working western unions rural urban southern Europe eastern
Mr. Saccullo 8 th Grade Social Studies Review Sheet IV Key Points of the Time Period Word Bank mass production poorly northern wages machines working western unions rural urban southern Europe eastern
AMERICA S ECONOMIC REVOLUTION. HIST 103 Chapter 10
 AMERICA S ECONOMIC REVOLUTION HIST 103 Chapter 10 The Changing American Population Population increased rapidly between 1820-1840 - improvements in public health - high birth rate - decreasing child mortality
AMERICA S ECONOMIC REVOLUTION HIST 103 Chapter 10 The Changing American Population Population increased rapidly between 1820-1840 - improvements in public health - high birth rate - decreasing child mortality
Chapter 10: America s Economic Revolution
 Chapter 10: America s Economic Revolution Lev_19:34 But the stranger that dwelleth with you shall be unto you as one born among you, and thou shalt love him as thyself; for ye were strangers in the land
Chapter 10: America s Economic Revolution Lev_19:34 But the stranger that dwelleth with you shall be unto you as one born among you, and thou shalt love him as thyself; for ye were strangers in the land
The Beginnings of Industrialization
 Name CHAPTER 25 Section 1 (pages 717 722) The Beginnings of BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about romanticism and realism in the arts. In this section, you will read about the beginning of
Name CHAPTER 25 Section 1 (pages 717 722) The Beginnings of BEFORE YOU READ In the last section, you read about romanticism and realism in the arts. In this section, you will read about the beginning of
This era corresponds to information in Unit 5 ( ), Unit 6 ( ) and Unit 7 ( )
 PERIOD 4: 1800 1848 The content for APUSH is divided into 9 periods. The outline below contains the required course content for Period 4. The Thematic Learning Objectives (historical themes) are included
PERIOD 4: 1800 1848 The content for APUSH is divided into 9 periods. The outline below contains the required course content for Period 4. The Thematic Learning Objectives (historical themes) are included
Chapter 9 and part of Chapter 8: Transforming the Economy,
 Chapter 9 and part of Chapter 8: Transforming the Economy, 1790-1860 The Big Questions: What were the causes and consequences of the industrial and market revolutions, and how did they change the way ordinary
Chapter 9 and part of Chapter 8: Transforming the Economy, 1790-1860 The Big Questions: What were the causes and consequences of the industrial and market revolutions, and how did they change the way ordinary
Immigration. Emigrants Leaving Ireland, a 19th-century painting
 Immigration German immigration: Rising land costs, overcrowding, and political instability Settled in Midwest to farm Irish immigration: Great Hunger (potato famine) Settled on East Coast for industrial
Immigration German immigration: Rising land costs, overcrowding, and political instability Settled in Midwest to farm Irish immigration: Great Hunger (potato famine) Settled on East Coast for industrial
Commerce and Industry Men and Women at Work. Adait Mou, Dewey Dugger, and Juliane Ponce
 Commerce and Industry Men and Women at Work Adait Mou, Dewey Dugger, and Juliane Ponce Nationalism and Economic Growth (1) (2) Juliane Ponce New wave of nationalism + growing geographic size = democratic
Commerce and Industry Men and Women at Work Adait Mou, Dewey Dugger, and Juliane Ponce Nationalism and Economic Growth (1) (2) Juliane Ponce New wave of nationalism + growing geographic size = democratic
-rocky soil. -forests. -clean water. -rivers. -forests. -good soil for farming. -harsh winters. -summer rain
 John Winthrop lead Puritans here to freely practice their religion. -rocky soil -forests -clean water -lumbering -fishing -democratic -decisions were made at town meetings; majority rules -cold winters
John Winthrop lead Puritans here to freely practice their religion. -rocky soil -forests -clean water -lumbering -fishing -democratic -decisions were made at town meetings; majority rules -cold winters
Benchmark 1 Review Read and Complete the following review questions below
 KEY Benchmark 1 Review Read and Complete the following review questions below Colonization Era This era can be described as the beginning of American roots. Many different groups of people immigrated from
KEY Benchmark 1 Review Read and Complete the following review questions below Colonization Era This era can be described as the beginning of American roots. Many different groups of people immigrated from
Economic Issues and Growth
 Economic Issues and Growth 1800-1848 Tariff of 1816 Passed to protect American industries after War of 1812 What would be advantages and disadvantages of high tariffs? Would different regions of the country
Economic Issues and Growth 1800-1848 Tariff of 1816 Passed to protect American industries after War of 1812 What would be advantages and disadvantages of high tariffs? Would different regions of the country
CH. 8: GROWTH OF A NATIONAL ECONOMY
 1 2 3 4 CH. 8: GROWTH OF A NATIONAL ECONOMY 1790-1850 Mr. Anderson, M.Ed., J.D. Review Who was John Marshall? Which president appointed him? What is he best remembered for? The Industrial Revolution Section
1 2 3 4 CH. 8: GROWTH OF A NATIONAL ECONOMY 1790-1850 Mr. Anderson, M.Ed., J.D. Review Who was John Marshall? Which president appointed him? What is he best remembered for? The Industrial Revolution Section
We re Free Let s Grow!
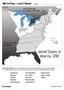 Atlantic Ocean Find Those States! The United States started out with just thirteen states. Use the list below to correctly identify each one on the map. Watch out: Things were a little different back then!
Atlantic Ocean Find Those States! The United States started out with just thirteen states. Use the list below to correctly identify each one on the map. Watch out: Things were a little different back then!
( ) WORKERS... 9 WILD WEST GARFIELD TO FIRST CLEVELAND AMERICA BECOMES A WORLD POWER ROOSEVELT TAFT...
 HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 807 GILDED AGE TO PROGRESSIVE ERA (1880 1915) CONTENTS I. THE GILDED AGE....................... 3 RISE OF INDUSTRY.................................. 5 WORKERS........................................
HISTORY & GEOGRAPHY 807 GILDED AGE TO PROGRESSIVE ERA (1880 1915) CONTENTS I. THE GILDED AGE....................... 3 RISE OF INDUSTRY.................................. 5 WORKERS........................................
The Start of the Industrial Revolution
 The Start of the Industrial Revolution I. Agricultural Revolution A. Industrial Revolution changed Europe from a mostly agricultural economy to industrialization- work driven by machinery B. Improved Farm
The Start of the Industrial Revolution I. Agricultural Revolution A. Industrial Revolution changed Europe from a mostly agricultural economy to industrialization- work driven by machinery B. Improved Farm
The Westward Movement
 The Westward Movement The American West- the most typically American part of America Young America- half of all Americans were under the age of 30 Life in the West was grim for American families Poorly
The Westward Movement The American West- the most typically American part of America Young America- half of all Americans were under the age of 30 Life in the West was grim for American families Poorly
Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation
 Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation Explain how the states new constitutions reflected republican ideals. Describe the structure and powers of the national government under the Articles of Confederation.
Unit 2 Part 2 Articles of Confederation Explain how the states new constitutions reflected republican ideals. Describe the structure and powers of the national government under the Articles of Confederation.
HISTORY AND GEOGRAPHY 1108 A NATION AT WAR
 HISTORY AND GEOGRAPHY 1108 A NATION AT WAR CONTENTS I. WORLD WAR II... 2 World War II: Causes of the War... 3 World War II: Theaters of Operation... 9 II. KOREAN CONFLICT... 23 Communist Threat: World
HISTORY AND GEOGRAPHY 1108 A NATION AT WAR CONTENTS I. WORLD WAR II... 2 World War II: Causes of the War... 3 World War II: Theaters of Operation... 9 II. KOREAN CONFLICT... 23 Communist Threat: World
Industrial Revolution
 The student will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and the different responses to it. a. Explain the impact of the Industrial
The student will explain the process of economic growth, its regional and national impact in the first half of the 19th century, and the different responses to it. a. Explain the impact of the Industrial
Chapter 9 1/14/2019. Alabama Standard. Ch.9 Section 1 (page #283)
 Chapter 9 THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION Alabama Standard Describe the impact of technological inventions, conditions of labor and economic theories of capitalism, liberalism, socialism, and Marxism during
Chapter 9 THE INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION Alabama Standard Describe the impact of technological inventions, conditions of labor and economic theories of capitalism, liberalism, socialism, and Marxism during
Prentice Hall US History: Reconstruction to the Present 2010 Correlated to: Minnesota Academic Standards in History and Social Studies, (Grades 9-12)
 Minnesota Academic in History and Social Studies, (Grades 9-12) GRADES 9-12 I. U.S. HISTORY A. Indigenous People of North America The student will demonstrate knowledge of indigenous cultures in North
Minnesota Academic in History and Social Studies, (Grades 9-12) GRADES 9-12 I. U.S. HISTORY A. Indigenous People of North America The student will demonstrate knowledge of indigenous cultures in North
The Early Industrial and Transportation Revolution Chapter 14
 The Early Industrial and Transportation Revolution Chapter 14 1. Population growth 1800 = 5.5 million to 33 million by 1861 13 states to 33 states by 1861 Expansion of cities 2. Flow of Immigration 1830
The Early Industrial and Transportation Revolution Chapter 14 1. Population growth 1800 = 5.5 million to 33 million by 1861 13 states to 33 states by 1861 Expansion of cities 2. Flow of Immigration 1830
8 th grade American Studies sample test questions
 8 th grade American Studies sample test questions PASS 1.2 Standard 1. The student will develop and practice process skills in social studies. PASS OBJECTIVE 1.2: Identify, analyze, and interpret primary
8 th grade American Studies sample test questions PASS 1.2 Standard 1. The student will develop and practice process skills in social studies. PASS OBJECTIVE 1.2: Identify, analyze, and interpret primary
Grades 2-7. American Government and the Election Process Unit Study SAMPLE PAGE. A Journey Through Learning
 A J T L Grades 2-7 American Government and the Election Process Unit Study A Journey Through Learning www.ajourneythroughlearning.com Copyright 2008 A Journey Through Learning 1 Authors: Paula Winget and
A J T L Grades 2-7 American Government and the Election Process Unit Study A Journey Through Learning www.ajourneythroughlearning.com Copyright 2008 A Journey Through Learning 1 Authors: Paula Winget and
Name: 8 th Grade U.S. History. STAAR Review. Colonization
 Name: _ 8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Colonization FORT BURROWS 2018 Name: _ VOCABULARY Agriculture - Farming, raising crops and livestock. Assembly a group of people who make and change laws for
Name: _ 8 th Grade U.S. History STAAR Review Colonization FORT BURROWS 2018 Name: _ VOCABULARY Agriculture - Farming, raising crops and livestock. Assembly a group of people who make and change laws for
The Industrial Revolution: England s Cities. The factory system changes the way people live and work, introducing a variety of problems.
 The Industrial Revolution: England s Cities The factory system changes the way people live and work, introducing a variety of problems. Last class: Industrial Revolution Industrialization The Industrial
The Industrial Revolution: England s Cities The factory system changes the way people live and work, introducing a variety of problems. Last class: Industrial Revolution Industrialization The Industrial
Countries Of The World: The United States
 Countries Of The World: The United States By National Geographic Kids, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.26.18 Word Count 859 Level MAX Image 1: U.S. Route 101 in Oregon. This highway runs along the entire
Countries Of The World: The United States By National Geographic Kids, adapted by Newsela staff on 06.26.18 Word Count 859 Level MAX Image 1: U.S. Route 101 in Oregon. This highway runs along the entire
People Come and People Go
 The Northeast: America s Gateway to the World People Come and People Go a lesson on Population INTRODUCTION: In this lesson we are going to investigate population growth in the northeastern part of the
The Northeast: America s Gateway to the World People Come and People Go a lesson on Population INTRODUCTION: In this lesson we are going to investigate population growth in the northeastern part of the
Locating Places. 7. G Hudson Bay 8. D Great Bear Lake 9. B Pacific Ranges 10. I Mackenzie River 11. H Rio Grande 12. E Great Slave Lake
 Locating Places Match the letters on the map with the physical features of the United States and Canada. Write your answers on a sheet of paper. 7. G Hudson Bay 8. D Great Bear Lake 9. B Pacific Ranges
Locating Places Match the letters on the map with the physical features of the United States and Canada. Write your answers on a sheet of paper. 7. G Hudson Bay 8. D Great Bear Lake 9. B Pacific Ranges
Imperialism by the US
 Imperialism by the US Quick Class Discussion: Based on this image, what important changes took place in the United States from 1783 to 1900? 115 years after gaining independence from Britain, the United
Imperialism by the US Quick Class Discussion: Based on this image, what important changes took place in the United States from 1783 to 1900? 115 years after gaining independence from Britain, the United
HISTORY AND GEOGRAPHY 1203 THE AMERICAN PARTY SYSTEM
 HISTORY AND GEOGRAPHY 1203 THE AMERICAN PARTY SYSTEM CONTENTS I. POLITICAL PARTIES... 2 The American Party System... 2 Development of American Political Parties... 9 Republican and Third Parties... 14
HISTORY AND GEOGRAPHY 1203 THE AMERICAN PARTY SYSTEM CONTENTS I. POLITICAL PARTIES... 2 The American Party System... 2 Development of American Political Parties... 9 Republican and Third Parties... 14
MARKING PERIOD 1. Shamokin Area 7 th Grade American History I Common Core I. UNIT 1: THREE WORLDS MEET. Assessments Formative/Performan ce
 Shamokin Area 7 th Grade American History I Common Core Marking Period Content Targets Common Core Standards Objectives Assessments Formative/Performan ce MARKING PERIOD 1 I. UNIT 1: THREE WORLDS MEET
Shamokin Area 7 th Grade American History I Common Core Marking Period Content Targets Common Core Standards Objectives Assessments Formative/Performan ce MARKING PERIOD 1 I. UNIT 1: THREE WORLDS MEET
Industrialization Spreads. Section 9.3
 Industrialization Spreads Section 9.3 England First country to industrialize on huge scale Inspired other countries to industrialize Copy the British miracle Class structure becomes more rigid Raises the
Industrialization Spreads Section 9.3 England First country to industrialize on huge scale Inspired other countries to industrialize Copy the British miracle Class structure becomes more rigid Raises the
WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer
 WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer Subject(s) Social Studies Conceptual Lenses Grade/Course 8 th Grade Leadership Unit of Study Expansion and Reform (1801-1861) Innovation Unit Title Unit 4 Growing Up: Expanding
WS/FCS Unit Planning Organizer Subject(s) Social Studies Conceptual Lenses Grade/Course 8 th Grade Leadership Unit of Study Expansion and Reform (1801-1861) Innovation Unit Title Unit 4 Growing Up: Expanding
A FIRM FOUNDATION ( )
 HISTORY AND GEOGRAPHY 804 A FIRM FOUNDATION (1789 1820) CONTENTS I. FEDERALIST ERA....................... 3 WASHINGTON S FIRST TERM.......................... 4 THE GREAT SEAL..................................
HISTORY AND GEOGRAPHY 804 A FIRM FOUNDATION (1789 1820) CONTENTS I. FEDERALIST ERA....................... 3 WASHINGTON S FIRST TERM.......................... 4 THE GREAT SEAL..................................
The Origins of the Constitution
 The Origins of the Constitution Before the colonies signed the Treaty of Paris ending the Revolutionary War in 1783, they ratified the Articles of Confederation in 1781, The Articles provided a weak union
The Origins of the Constitution Before the colonies signed the Treaty of Paris ending the Revolutionary War in 1783, they ratified the Articles of Confederation in 1781, The Articles provided a weak union
U.S. History Chapter Millionaire Review
 U.S. History Chapter 14-15 Millionaire Review #1 Which of the following best describes the cotton gin s contribution to industrialization? Created jobs for A: B: immigrants Lowered price of cotton in South
U.S. History Chapter 14-15 Millionaire Review #1 Which of the following best describes the cotton gin s contribution to industrialization? Created jobs for A: B: immigrants Lowered price of cotton in South
The Early Industrial Revolution Chapter 22 AP World History
 The Early Industrial Revolution 1760-1851 Chapter 22 AP World History Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
The Early Industrial Revolution 1760-1851 Chapter 22 AP World History Beginnings of Industrialization Main Idea The Industrial Revolution started in England and soon spread to other countries Why It Matters
7th Grade Social Studies GLEs
 7th Grade Social Studies GLEs Geography The World in Spatial Terms. Analyze various types of maps, charts, graphs, and diagrams related to U.S. history (G-A-M2) Places and Regions 2. Explain how physical
7th Grade Social Studies GLEs Geography The World in Spatial Terms. Analyze various types of maps, charts, graphs, and diagrams related to U.S. history (G-A-M2) Places and Regions 2. Explain how physical
X On record with the USOE.
 Textbook Alignment to the Utah Core 8 th Grade Social Studies U.S. History This alignment has been completed using an Independent Alignment Vendor from the USOE approved list (www.schools.utah.gov/curr/imc/indvendor.html.)
Textbook Alignment to the Utah Core 8 th Grade Social Studies U.S. History This alignment has been completed using an Independent Alignment Vendor from the USOE approved list (www.schools.utah.gov/curr/imc/indvendor.html.)
X On record with the USOE.
 Textbook Alignment to the Utah Core 8 th Grade Social Studies U.S. History This alignment has been completed using an Independent Alignment Vendor from the USOE approved list (www.schools.utah.gov/curr/imc/indvendor.html.)
Textbook Alignment to the Utah Core 8 th Grade Social Studies U.S. History This alignment has been completed using an Independent Alignment Vendor from the USOE approved list (www.schools.utah.gov/curr/imc/indvendor.html.)
X On record with the USOE.
 Textbook Alignment to the Utah Core 8 th Grade Social Studies U.S. History This alignment has been completed using an Independent Alignment Vendor from the USOE approved list (www.schools.utah.gov/curr/imc/indvendor.html.)
Textbook Alignment to the Utah Core 8 th Grade Social Studies U.S. History This alignment has been completed using an Independent Alignment Vendor from the USOE approved list (www.schools.utah.gov/curr/imc/indvendor.html.)
Industrialization Spreads
 3 Industrialization Spreads MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW TERMS & NAMES EMPIRE BUILDING The industrialization that began in Great Britain spread to other parts of the world. The Industrial Revolution set
3 Industrialization Spreads MAIN IDEA WHY IT MATTERS NOW TERMS & NAMES EMPIRE BUILDING The industrialization that began in Great Britain spread to other parts of the world. The Industrial Revolution set
Tuesday, September 12, 2017 United States Human Geography
 Tuesday, September 12, 2017 United States Human Geography Objective: Explain how the United States acquired its geographic boundaries. Examine patterns of immigration to and migration within the United
Tuesday, September 12, 2017 United States Human Geography Objective: Explain how the United States acquired its geographic boundaries. Examine patterns of immigration to and migration within the United
Indiana Academic Standards Social Studies
 A Correlation of To the Introduction This document demonstrates how,, meets the for,. Correlation page references are to the Student Edition and Teacher Edition. The all new myworld Interactive encourages
A Correlation of To the Introduction This document demonstrates how,, meets the for,. Correlation page references are to the Student Edition and Teacher Edition. The all new myworld Interactive encourages
Era of Good Feelings:
 Era of Good Feelings: 1815-1825 After the War of 1812 Americans finally have international respect The Republicans are the only political party James Monroe, the third member of the Virginia Dynasty, is
Era of Good Feelings: 1815-1825 After the War of 1812 Americans finally have international respect The Republicans are the only political party James Monroe, the third member of the Virginia Dynasty, is
CHAPTER 11 KEY ISSUE TWO: WHERE IS INDUSTRY DISTRIBUTED?
 CHAPTER 11 KEY ISSUE TWO: WHERE IS INDUSTRY DISTRIBUTED? WORLD INDUSTRIAL REGIONS North America Industrialized areas in North America Changing distribution of U.S. manufacturing Europe Western Europe Eastern
CHAPTER 11 KEY ISSUE TWO: WHERE IS INDUSTRY DISTRIBUTED? WORLD INDUSTRIAL REGIONS North America Industrialized areas in North America Changing distribution of U.S. manufacturing Europe Western Europe Eastern
THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN THE U.S. How the War of 1812 & Technological Progress Change the Country
 THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN THE U.S. How the War of 1812 & Technological Progress Change the Country TECHNOLOGY MEANS PROGRESS Developments in technology begin to transform life in the U.S. in the
THE FIRST INDUSTRIAL REVOLUTION IN THE U.S. How the War of 1812 & Technological Progress Change the Country TECHNOLOGY MEANS PROGRESS Developments in technology begin to transform life in the U.S. in the
I. The Agricultural Revolution
 I. The Agricultural Revolution A. The Agricultural Revolution Paves the Way 1. Wealthy farmers cultivated large fields called enclosures. 2. The enclosure movement caused landowners to try new methods.
I. The Agricultural Revolution A. The Agricultural Revolution Paves the Way 1. Wealthy farmers cultivated large fields called enclosures. 2. The enclosure movement caused landowners to try new methods.
World Industrial Regions
 World Industrial Regions North America Industrialized areas in North America Changing distribution of U.S. manufacturing Europe Western Europe Eastern Europe East Asia Manufacturing Regions Fig. 11-3:
World Industrial Regions North America Industrialized areas in North America Changing distribution of U.S. manufacturing Europe Western Europe Eastern Europe East Asia Manufacturing Regions Fig. 11-3:
Industrialization & Reform Learning Targets
 Industrialization & Reform Learning Targets Topic: History I can identify major eras and events in U.S. History and explain: Industrial Revolution Age of Reform Topic: Economics I can understand the origins
Industrialization & Reform Learning Targets Topic: History I can identify major eras and events in U.S. History and explain: Industrial Revolution Age of Reform Topic: Economics I can understand the origins
1: Population* and urbanisation for want of more hands
 1: Population* and urbanisation for want of more hands *Remember that the study of population is called Demographics By 1900 there were nearly five times as many people in Britain as there were in 1750.
1: Population* and urbanisation for want of more hands *Remember that the study of population is called Demographics By 1900 there were nearly five times as many people in Britain as there were in 1750.
The United States Lesson 2: History of the United States
 Lesson 2: History of the United States ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is history important? Terms to Know indigenous living or occurring naturally in a particular place nomadic describes a way of life in which
Lesson 2: History of the United States ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why is history important? Terms to Know indigenous living or occurring naturally in a particular place nomadic describes a way of life in which
Geography 8th Grade Social Studies Standard 1
 Geography Standard 1 1. I can determine how geography affected the development of the United States. 8. 1. a I can identify the 5 aspects of geography including location, place, human-environmental interaction,
Geography Standard 1 1. I can determine how geography affected the development of the United States. 8. 1. a I can identify the 5 aspects of geography including location, place, human-environmental interaction,
Map of the Foreign Born Population of the United States, 1900
 Introduction According to the 1900 census, the population of the United States was then 76.3 million. Nearly 14 percent of the population approximately 10.4 million people was born outside of the United
Introduction According to the 1900 census, the population of the United States was then 76.3 million. Nearly 14 percent of the population approximately 10.4 million people was born outside of the United
The Market Revolution
 The Market Revolution Expansion of Industry Both Alexander Hamilton and Thomas Jefferson had quite different visions of what they hoped the United States would become. Each had taken steps to put policies
The Market Revolution Expansion of Industry Both Alexander Hamilton and Thomas Jefferson had quite different visions of what they hoped the United States would become. Each had taken steps to put policies
National History National Standards: Grades K-4. National Standards in World History: Grades 5-12
 The Henry Ford American Industrial Revolution National History National Standards: Grades K-4 Standard 3D: The student understands the interactions among all these groups throughout the history of his
The Henry Ford American Industrial Revolution National History National Standards: Grades K-4 Standard 3D: The student understands the interactions among all these groups throughout the history of his
Forging the National Economy
 Forging the National Economy 1790-1860 Western Demographics By 1840: demographic center of American population had crossed over the Alleghenies 1850: half of Americans under age 30 Pioneer Americans: ill-informed,
Forging the National Economy 1790-1860 Western Demographics By 1840: demographic center of American population had crossed over the Alleghenies 1850: half of Americans under age 30 Pioneer Americans: ill-informed,
Forging a National Economy. Chapter 14
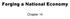 Forging a National Economy Chapter 14 Westward Movement Original Areas of settlement Oregon Territory California Territory Texas Northwest Territories Great Plains were not settled because it was hard
Forging a National Economy Chapter 14 Westward Movement Original Areas of settlement Oregon Territory California Territory Texas Northwest Territories Great Plains were not settled because it was hard
Mohawk Local Schools Grade 8 Social Studies Quarter 1 Curriculum Guide
 Mohawk Local Schools Grade 8 Social Studies Quarter 1 Curriculum Guide Historical Thinking and Skills, Spatial Thinking and Skills, Civic Participation and Skills, Economic Decision Making and Skills,
Mohawk Local Schools Grade 8 Social Studies Quarter 1 Curriculum Guide Historical Thinking and Skills, Spatial Thinking and Skills, Civic Participation and Skills, Economic Decision Making and Skills,
