SUPREME COURT OF THE UNITED STATES
|
|
|
- Baldwin Ramsey
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Cite as: U. S. (1999) 1 SUPREME COURT OF THE UNITED STATES No RITA L. SAENZ, DIRECTOR, CALIFORNIA DEPARTMENT OF SOCIAL SERVICES, ET AL., PETITIONERS v. BRENDA ROE AND ANNA DOE ETC. ON WRIT OF CERTIORARI TO THE UNITED STATES COURT OF APPEALS FOR THE NINTH CIRCUIT [May 17, 1999] JUSTICE THOMAS, with whom the CHIEF JUSTICE joins, dissenting. I join THE CHIEF JUSTICE s dissent. I write separately to address the majority s conclusion that California has violated the right of the newly arrived citizen to the same privileges and immunities enjoyed by other citizens of the same State. Ante, at 12. In my view, the majority attributes a meaning to the Privileges or Immunities Clause that likely was unintended when the Fourteenth Amendment was enacted and ratified. The Privileges or Immunities Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment provides that [n]o State shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States. U. S. Const., Amdt. 14, 1. Unlike the Equal Protection and Due Process Clauses, which have assumed near-talismanic status in modern constitutional law, the Court all but read the Privileges or Immunities Clause out of the Constitution in the Slaughter-House Cases, 16 Wall. 36 (1873). There, the Court held that the State of Louisiana had not abridged the Privileges or Immunities Clause by granting a partial monopoly of the slaughtering business to one company. Id., at 59 63, 66. The Court reasoned that the Privileges
2 2 SAENZ v. ROE or Immunities Clause was not intended as a protection to the citizen of a State against the legislative power of his own State. Id., at 74. Rather the privileges or immunities of citizens guaranteed by the Fourteenth Amendment were limited to those belonging to a citizen of the United States as such. Id., at 75. The Court declined to specify the privileges or immunities that fell into this latter category, but it made clear that few did. See id., at 76 (stating that nearly every civil right for the establishment and protection of which organized government is instituted, including those rights which are fundamental, are not protected by the Clause). Unlike the majority, I would look to history to ascertain the original meaning of the Clause. 1 At least in American law, the phrase (or its close approximation) appears to stem from the 1606 Charter of Virginia, which provided that all and every the Persons being our Subjects, which shall dwell and inhabit within every or any of the said 1 Legal scholars agree on little beyond the conclusion that the Clause does not mean what the Court said it meant in See, e.g., Harrison, Reconstructing the Privileges or Immunities Clause, 101 Yale L. J. 1385, 1418 (1992) (Clause is an antidiscrimination provision); D. Currie, The Constitution in the Supreme Court (1985) (same); 2 W. Crosskey, Politics and the Constitution in the History of the United States (1953) (Clause incorporates first eight Amendments of the Bill of Rights); M. Curtis, No State Shall Abridge 100 (1986) (Clause protects the rights included in the Bill of Rights as well as other fundamental rights); B. Siegan, Supreme Court s Constitution (1987) (Clause guarantees Lockean conception of natural rights); Ackerman, Constitutional Politics/Constitutional Law, 99 Yale L. J. 453, (1989) (same); J. Ely, Democracy and Distrust 28 (1980) (Clause was a delegation to future constitutional decisionmakers to protect certain rights that the document neither lists... or in any specific way gives directions for finding ); R. Berger, Government by Judiciary 30 (2d ed. 1997) (Clause forbids race discrimination with respect to rights listed in the Civil Rights Act of 1866); R. Bork, The Tempting of America 166 (1990) (Clause is inscrutable and should be treated as if it had been obliterated by an ink blot).
3 Cite as: U. S. (1999) 3 several Colonies... shall HAVE and enjoy all Liberties, Franchises, and Immunities... as if they had been abiding and born, within this our Realme of England. 7 Federal and State Constitutions, Colonial Charters and Other Organic Laws 3788 (F. Thorpe ed. 1909). Other colonial charters contained similar guarantees. 2 Years later, as tensions between England and the American Colonies increased, the colonists adopted resolutions reasserting their entitlement to the privileges or immunities of English citizenship. 3 2 See 1620 Charter of New England, in 3 Thorpe, at 1839 (guaranteeing [l]iberties, and ffranchizes, and Immunities of free Denizens and naturall Subjects ); 1622 Charter of Connecticut, reprinted in 1 id., at 553 (guaranteeing [l]iberties and Immunities of free and natural Subjects ); 1629 Charter of the Massachusetts Bay Colony, in 3 id., at 1857 (guaranteeing the liberties and Immunities of free and naturall subjects ); 1632 Charter of Maine, in 3 id., at 1635 (guaranteeing [l]iberties[,] Francheses and Immunityes of or belonging to any of the naturall borne subjects ); 1632 Charter of Maryland, in 3 id., at 1682 (guaranteeing Privileges, Franchises and Liberties ); 1663 Charter of Carolina, in 5 id., at 2747 (holding liberties, franchises, and privileges inviolate); 1663 Charter of the Rhode Island and Providence Plantations, in 6 id., at 3220 (guaranteeing libertyes and immunityes of ffree and naturall subjects ); 1732 Charter of Georgia, in 2 id., at 773 (guaranteeing liberties, franchises and immunities of free denizens and natural born subjects ). 3 See, e.g., The Massachusetts Resolves, in Prologue to Revolution: Sources and Documents on the Stamp Act Crisis 56 (E. Morgan ed. 1959) ( Resolved, That there are certain essential Rights of the British Constitution of Government, which are founded in the Law of God and Nature, and are the common Rights of Mankind Therefore,... Resolved that no Man can justly take the Property of another without his Consent... this inherent Right, together with all other essential Rights, Liberties, Privileges and Immunities of the People of Great Britain have been fully confirmed to them by Magna Charta ); The Virginia Resolves, id., at ( [T]he Colonists aforesaid are declared entitled to all Liberties, Privileges, and Immunities of Denizens and natural Subjects, to all Intents and Purposes, as if they had been abiding and born within the Realm of England ); 1774 Statement of
4 4 SAENZ v. ROE The colonists repeated assertions that they maintained the rights, privileges and immunities of persons born within the realm of England and natural born persons suggests that, at the time of the founding, the terms privileges and immunities (and their counterparts) were understood to refer to those fundamental rights and liberties specifically enjoyed by English citizens, and more broadly, by all persons. Presumably members of the Second Continental Congress so understood these terms when they employed them in the Articles of Confederation, which guaranteed that the free inhabitants of each of these States, paupers, vagabonds and fugitives from justice excepted, shall be entitled to all privileges and immunities of free citizens in the several States. Art. IV. The Constitution, which superceded the Articles of Confederation, similarly guarantees that [t]he Citizens of each State shall be entitled to all Privileges and Immunities of Citizens in the several States. Art. IV, 2, cl. 1. Justice Bushrod Washington s landmark opinion in Corfield v. Coryell, 6 Fed. Cas. 546 (No. 3, 230) (CCED Pa. 1825), reflects this historical understanding. In Corfield, a citizen of Pennsylvania challenged a New Jersey law that prohibited any person who was not an actual inhabitant and resident of New Jersey from harvesting oysters from New Jersey waters. Id., at 550. Justice Washington, sitting as Circuit Justice, rejected the argument that the New Jersey law violated Article IV s Privileges and Immunities Clause. He reasoned, we cannot accede to the proposition... that, under this provision of the constitu- Violation of Rights, 1 Journals of the Continental Congress 68 (1904) ( [O]ur ancestors, who first settled these colonies, were at the time of their emigration from the mother country, entitled to all the rights, liberties, and immunities of free and natural-born subjects, within the realm of England... Resolved... [t]hat by such emigration they by no means forfeited, surrendered or lost any of those rights ).
5 Cite as: U. S. (1999) 5 tion, the citizens of the several states are permitted to participate in all the rights which belong exclusively to the citizens of any other particular state, merely upon the ground that they are enjoyed by those citizens. Id., at 552. Instead, Washington concluded: We feel no hesitation in confining these expressions to those privileges and immunities which are, in their nature, fundamental; which belong, of right, to the citizens of all free governments; and which have, at all times, been enjoyed by the citizens of the several states which compose this Union, from the time of their becoming free, independent, and sovereign. What these fundamental principles are, it would perhaps be more tedious than difficult to enumerate. They may, however, be all comprehended under the following general heads: Protection by the government; the enjoyment of life and liberty, with the right to acquire and possess property of every kind, and to pursue and obtain happiness and safety; subject nevertheless to such restraints as the government may justly prescribe for the general good of the whole. The right of a citizen of one state to pass through, or to reside in any other state, for purposes of trade, agriculture, professional pursuits, or otherwise; to claim the benefit of the writ of habeas corpus; to institute and maintain actions of any kind in the courts of the state;... and an exemption from higher taxes or impositions than are paid by the other citizens of the state;... the elective franchise, as regulated and established by the laws or constitution of the state in which it is to be exercised. These, and many others which might be mentioned, are, strictly speaking, privileges and immunities. Id. at Washington rejected the proposition that the Privileges and Immunities Clause guaranteed equal access to all
6 6 SAENZ v. ROE public benefits (such as the right to harvest oysters in public waters) that a State chooses to make available. Instead, he endorsed the colonial-era conception of the terms privileges and immunities, concluding that Article IV encompassed only fundamental rights that belong to all citizens of the United States. 4 Id., at 552. Justice Washington s opinion in Corfield indisputably influenced the Members of Congress who enacted the Fourteenth Amendment. When Congress gathered to debate the Fourteenth Amendment, members frequently, if not as a matter of course, appealed to Corfield, arguing that the Amendment was necessary to guarantee the fundamental rights that Justice Washington identified in his opinion. See Harrison, Reconstructing the Privileges or Immunities Clause, 101 Yale L. J. 1385, 1418 (1992) (referring to a Member s obligatory quotation from Corfield ). For just one example, in a speech introducing the Amendment to the Senate, Senator Howard explained the Privileges or Immunities Clause by quoting at length from Corfield. 5 Cong. Globe, 39th Cong., 1st Sess., 2765 (1866). Furthermore, it appears that no Member of Congress 4 During the first half of the 19th century, a number of legal scholars and state courts endorsed Washington s conclusion that the Clause protected only fundamental rights. See, e.g., Campbell v. Morris, 3 Harr. & M. 535, 554 (Md. 1797) (Chase, J.) (Clause protects property and personal rights); Douglass v. Stephens, 1 Del. Ch. 465, 470 (1821) (Clause protects the absolute rights that all men by nature have ); 2 J. Kent, Commentaries on American Law (1836) (Clause confined to those [rights] which were, in their nature, fundamental ). See generally Antieau, Paul s Perverted Privileges or the True Meaning of the Privileges and Immunities Clause of Article Four, 9 Wm. & Mary L. Rev. 1, (1967) (collecting sources). 5 He also observed that, while, Supreme Court had not undertaken to define either the nature or extent of the privileges and immunities, Washington s opinion gave some intimation of what probably will be the opinion of the judiciary. Cong. Globe, 39th Cong., 1st Sess., 2765 (1866).
7 Cite as: U. S. (1999) 7 refuted the notion that Washington s analysis in Corfield undergirded the meaning of the Privileges or Immunities Clause. 6 That Members of the 39th Congress appear to have endorsed the wisdom of Justice Washington s opinion does not, standing alone, provide dispositive insight into their understanding of the Fourteenth Amendment s Privileges or Immunities Clause. Nevertheless, their repeated references to the Corfield decision, combined with what appears to be the historical understanding of the Clause s operative terms, supports the inference that, at the time the Fourteenth Amendment was adopted, people understood that privileges or immunities of citizens were fundamental rights, rather than every public benefit established by positive law. Accordingly, the majority s conclusion that a State violates the Privileges or Immunities Clause when it discriminates against citizens who have been domiciled in the State for less than a year in the distribution of welfare benefit appears contrary to the original understanding and is dubious at best. As THE CHIEF JUSTICE points out, ante at 1, it comes as quite a surprise that the majority relies on the Privileges 6 During debates on the Civil Rights Act of 1866, Members of Congress also repeatedly invoked Corfield to support the legislation. See generally, Siegan, Supreme Court s Constitution, at The Act s sponsor, Senator Trumble, quoting from Corfield, explained that the legislation protected the fundamental rights belonging to every man as a free man, and which under the Constitution as it now exists we have a right to protect every man in. Cong. Globe, supra, at 476. The Civil Rights Act is widely regarded as the precursor to the Fourteenth Amendment. See, e.g., J. tenbroek, Equal Under Law 201 (rev. ed. 1965) ( The one point upon which historians of the Fourteenth Amendment agree, and, indeed, which the evidence places beyond cavil, is that the Fourteenth Amendment was designed to place the constitutionality of the Freedmen s Bureau and civil rights bills, particularly the latter, beyond doubt ).
8 8 SAENZ v. ROE or Immunities Clause at all in this case. That is because, as I have explained supra, at 1 2, The Slaughter-House Cases sapped the Clause of any meaning. Although the majority appears to breathe new life into the Clause today, it fails to address its historical underpinnings or its place in our constitutional jurisprudence. Because I believe that the demise of the Privileges or Immunities Clause has contributed in no small part to the current disarray of our Fourteenth Amendment jurisprudence, I would be open to reevaluating its meaning in an appropriate case. Before invoking the Clause, however, we should endeavor to understand what the framers of the Fourteenth Amendment thought that it meant. We should also consider whether the Clause should displace, rather than augment, portions of our equal protection and substantive due process jurisprudence. The majority s failure to consider these important questions raises the specter that the Privileges or Immunities Clause will become yet another convenient tool for inventing new rights, limited solely by the predilections of those who happen at the time to be Members of this Court. Moore v. East Cleveland, 431 U. S. 494, 502 (1977). I respectfully dissent.
citizens under the Constitution, not the Fourteenth Amendment
 Two citizens under the Constitution, citizens under the Constitution, and not the Fourteenth Amendment not the Fourteenth Amendment 2009 Dan Goodman
Two citizens under the Constitution, citizens under the Constitution, and not the Fourteenth Amendment not the Fourteenth Amendment 2009 Dan Goodman
CORFIELD v. CORYELL. [4 Wash. C. C. 371.]
![CORFIELD v. CORYELL. [4 Wash. C. C. 371.] CORFIELD v. CORYELL. [4 Wash. C. C. 371.]](/thumbs/87/95060554.jpg) CORFIELD v. CORYELL CIRCUIT COURT COURT OF THE OF THE UNITED UNITED STATES STATES FOR PENNSYLVANIA. FOR 1825. PENNSYLVANIA. [4 Wash. C. C. 371.] This was an action of trespass for seizing, taking, and
CORFIELD v. CORYELL CIRCUIT COURT COURT OF THE OF THE UNITED UNITED STATES STATES FOR PENNSYLVANIA. FOR 1825. PENNSYLVANIA. [4 Wash. C. C. 371.] This was an action of trespass for seizing, taking, and
Article IV, Section 2, Clause 1 is defined to have both Fundamental as well as Common Privileges and Immunities
 Article IV, Section 2, Clause 1 is defined to have both Fundamental as well as Common Privileges and Immunities 2011 Dan Goodman Article IV, Section 2, Clause 1 has been defined to have both fundamental
Article IV, Section 2, Clause 1 is defined to have both Fundamental as well as Common Privileges and Immunities 2011 Dan Goodman Article IV, Section 2, Clause 1 has been defined to have both fundamental
SUPREME COURT OF THE UNITED STATES
 Cite as: 561 U. S. (2010) 1 SUPREME COURT OF THE UNITED STATES No. 08 1521 OTIS MCDONALD, ET AL., PETITIONERS v. CITY OF CHICAGO, ILLINOIS, ET AL. ON WRIT OF CERTIORARI TO THE UNITED STATES COURT OF APPEALS
Cite as: 561 U. S. (2010) 1 SUPREME COURT OF THE UNITED STATES No. 08 1521 OTIS MCDONALD, ET AL., PETITIONERS v. CITY OF CHICAGO, ILLINOIS, ET AL. ON WRIT OF CERTIORARI TO THE UNITED STATES COURT OF APPEALS
Supreme Court of the United States
 No. 08 1521 In The Supreme Court of the United States --------------------------------- --------------------------------- OTIS MCDONALD, et al., Petitioners, v. CITY OF CHICAGO, ILLINOIS, et al. Respondent.
No. 08 1521 In The Supreme Court of the United States --------------------------------- --------------------------------- OTIS MCDONALD, et al., Petitioners, v. CITY OF CHICAGO, ILLINOIS, et al. Respondent.
Slaughterhouse Cases
 Slaughterhouse Cases Mr. Justice BRADLEY, dissenting: I concur in the opinion which has just been read by Mr. Justice Field; but desire to add a few observations for the purpose of more fully illustrating
Slaughterhouse Cases Mr. Justice BRADLEY, dissenting: I concur in the opinion which has just been read by Mr. Justice Field; but desire to add a few observations for the purpose of more fully illustrating
Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings. Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings. Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings. Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings
 Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings The US government has its roots in English history Limited Government The concept that government is limited in what it can and cannot do Representative Government Government
Ch. 2.1 Our Political Beginnings The US government has its roots in English history Limited Government The concept that government is limited in what it can and cannot do Representative Government Government
DECLARATION OF COLONIAL RIGHTS RESOLUTIONS OF THE FIRST CONTINENTAL CONGRESS
 RESOLUTIONS OF THE FIRST CONTINENTAL CONGRESS Table of Contents DECLARATION OF COLONIAL RIGHTS...1 RESOLUTIONS OF THE FIRST CONTINENTAL CONGRESS...1 i RESOLUTIONS OF THE FIRST CONTINENTAL CONGRESS This
RESOLUTIONS OF THE FIRST CONTINENTAL CONGRESS Table of Contents DECLARATION OF COLONIAL RIGHTS...1 RESOLUTIONS OF THE FIRST CONTINENTAL CONGRESS...1 i RESOLUTIONS OF THE FIRST CONTINENTAL CONGRESS This
Constitutional Corner Fundamental Principles: Constitutionalism
 Constitutional Corner Fundamental Principles: Constitutionalism Constitutionalism: adherence to or government according to constitutional principles; also : a constitutional system of government. 1 The
Constitutional Corner Fundamental Principles: Constitutionalism Constitutionalism: adherence to or government according to constitutional principles; also : a constitutional system of government. 1 The
LAYING PRIVILEGES OR IMMUNITIES TO REST: MCDONALD V. CITY OF CHICAGO
 LAYING PRIVILEGES OR IMMUNITIES TO REST: MCDONALD V. CITY OF CHICAGO B. AUBREY SMITH* I. INTRODUCTION In District of Columbia v. Heller, the Supreme Court held the Second Amendment prohibits the federal
LAYING PRIVILEGES OR IMMUNITIES TO REST: MCDONALD V. CITY OF CHICAGO B. AUBREY SMITH* I. INTRODUCTION In District of Columbia v. Heller, the Supreme Court held the Second Amendment prohibits the federal
Supreme Court of the United States
 No. 08-1521 IN THE Supreme Court of the United States OTIS MCDONALD, ADAM ORLOV, COLLEEN LAWSON, DAVID LAWSON, SECOND AMENDMENT FOUNDATION, INC., AND ILLINOIS STATE RIFLE ASSOCIATION, Petitioners, v. CITY
No. 08-1521 IN THE Supreme Court of the United States OTIS MCDONALD, ADAM ORLOV, COLLEEN LAWSON, DAVID LAWSON, SECOND AMENDMENT FOUNDATION, INC., AND ILLINOIS STATE RIFLE ASSOCIATION, Petitioners, v. CITY
SUPREME COURT OF THE UNITED STATES
 (Bench Opinion) OCTOBER TERM, 2009 1 NOTE: Where it is feasible, a syllabus (headnote) will be released, as is being done in connection with this case, at the time the opinion is issued. The syllabus constitutes
(Bench Opinion) OCTOBER TERM, 2009 1 NOTE: Where it is feasible, a syllabus (headnote) will be released, as is being done in connection with this case, at the time the opinion is issued. The syllabus constitutes
AP American Government
 AP American Government WILSON, CHAPTER 2 The Constitution OVERVIEW The Framers of the Constitution sought to create a government capable of protecting liberty and preserving order. The solution they chose
AP American Government WILSON, CHAPTER 2 The Constitution OVERVIEW The Framers of the Constitution sought to create a government capable of protecting liberty and preserving order. The solution they chose
Free Speech & Election Law
 Free Speech & Election Law Can States Require Proof of Citizenship for Voter Registration Arizona v. Inter Tribal Council of Arizona By Anthony T. Caso* Introduction This term the Court will hear a case
Free Speech & Election Law Can States Require Proof of Citizenship for Voter Registration Arizona v. Inter Tribal Council of Arizona By Anthony T. Caso* Introduction This term the Court will hear a case
OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS
 CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
CHAPTER 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS The colonists brought with them to North America knowledge of the English political system, including three key ideas about government.
The Constitution CHAPTER 2 CHAPTER OUTLINE WITH KEYED-IN RESOURCES
 CHAPTER 2 The Constitution CHAPTER OUTLINE WITH KEYED-IN RESOURCES I. The problem of liberty (THEME A: THE POLITICAL PHILOSOPHY OF THE FOUNDERS) A. Colonists were focused on traditional liberties 1. The
CHAPTER 2 The Constitution CHAPTER OUTLINE WITH KEYED-IN RESOURCES I. The problem of liberty (THEME A: THE POLITICAL PHILOSOPHY OF THE FOUNDERS) A. Colonists were focused on traditional liberties 1. The
Passport Denial and the Freedom to Travel
 William & Mary Law Review Volume 2 Issue 1 Article 10 Passport Denial and the Freedom to Travel Roger M. Johnson Repository Citation Roger M. Johnson, Passport Denial and the Freedom to Travel, 2 Wm. &
William & Mary Law Review Volume 2 Issue 1 Article 10 Passport Denial and the Freedom to Travel Roger M. Johnson Repository Citation Roger M. Johnson, Passport Denial and the Freedom to Travel, 2 Wm. &
Justice Curtis's Dissent in Dred Scott. Excerpts
 Justice Curtis's Dissent in Dred Scott Excerpts Mr. Justice CURTIS dissenting.... So that, under the allegations contained in this plea, and admitted by the demurrer, the question is, whether any person
Justice Curtis's Dissent in Dred Scott Excerpts Mr. Justice CURTIS dissenting.... So that, under the allegations contained in this plea, and admitted by the demurrer, the question is, whether any person
1. VIRGINIA S FREE EXPRESSION HERITAGE
 1. VIRGINIA S FREE EXPRESSION HERITAGE Virginia is sometimes called Mother of Presidents, because eight of the nation s chief executive officers have come from the commonwealth. 1 Virginia might also be
1. VIRGINIA S FREE EXPRESSION HERITAGE Virginia is sometimes called Mother of Presidents, because eight of the nation s chief executive officers have come from the commonwealth. 1 Virginia might also be
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Page TABLE OF CONTENTS...i. TABLE OF AUTHORITIES... iii INTEREST OF AMICI CURIAE...1 SUMMARY OF ARGUMENT...2 ARGUMENT...
 i TABLE OF CONTENTS Page TABLE OF CONTENTS...i TABLE OF AUTHORITIES... iii INTEREST OF AMICI CURIAE...1 SUMMARY OF ARGUMENT...2 ARGUMENT...4 I. THE PRIVILEGES OR IMMUNITIES CLAUSE OF THE FOURTEENTH AMENDMENT
i TABLE OF CONTENTS Page TABLE OF CONTENTS...i TABLE OF AUTHORITIES... iii INTEREST OF AMICI CURIAE...1 SUMMARY OF ARGUMENT...2 ARGUMENT...4 I. THE PRIVILEGES OR IMMUNITIES CLAUSE OF THE FOURTEENTH AMENDMENT
Amuse Their Minds Publishing. Read, Write and Learn Copybooks: Copywork with a Purpose. Historical US Documents Series: The Articles of Confederation
 Amuse Their Minds Publishing Read, Write and Learn Copybooks: Copywork with a Purpose. Historical US Documents Series: The Articles of Confederation The Articles of Confederation National Archives Grades
Amuse Their Minds Publishing Read, Write and Learn Copybooks: Copywork with a Purpose. Historical US Documents Series: The Articles of Confederation The Articles of Confederation National Archives Grades
Investigation Activities. The Constitution Song SAMPLE. Compiled copyright Jon Schwartz
 Investigation Activities The Constitution Song Compiled 2-26-16 copyright Jon Schwartz 2016 www.rockingteacher.com Name Date Reading Comprehension #1 Let s use the Learn About The Constitution Graphic
Investigation Activities The Constitution Song Compiled 2-26-16 copyright Jon Schwartz 2016 www.rockingteacher.com Name Date Reading Comprehension #1 Let s use the Learn About The Constitution Graphic
Yes, there were four citizens before the Fourteenth Amendment
 Yes, there were four citizens before the Fourteenth Amendment 2011 Dan Goodman Before the Fourteenth Amendment, there were two citizens; one was a citizen of a State, born in the United States of America
Yes, there were four citizens before the Fourteenth Amendment 2011 Dan Goodman Before the Fourteenth Amendment, there were two citizens; one was a citizen of a State, born in the United States of America
AM GOV Chapter 2 The Constitution: The Foundation of Citizens' Rights
 AM GOV 2015-2016 Chapter 2 The Constitution: The Foundation of Citizens' Rights Learning Objectives Having read the chapter, the students should be able to do the following: 1. Discuss the historical background
AM GOV 2015-2016 Chapter 2 The Constitution: The Foundation of Citizens' Rights Learning Objectives Having read the chapter, the students should be able to do the following: 1. Discuss the historical background
Full file at
 Test Questions Multiple Choice Chapter Two Constitutional Democracy: Promoting Liberty and Self-Government 1. The idea that government should be restricted in its lawful uses of power and hence in its
Test Questions Multiple Choice Chapter Two Constitutional Democracy: Promoting Liberty and Self-Government 1. The idea that government should be restricted in its lawful uses of power and hence in its
2018 Visiting Day. Law School 101 Room 1E, 1 st Floor Gambrell Hall. Robert A. Schapiro Asa Griggs Candler Professor of Law
 Law School 101 Room 1E, 1 st Floor Gambrell Hall Robert A. Schapiro Asa Griggs Candler Professor of Law Robert Schapiro has been a member of faculty since 1995. He served as dean of Emory Law from 2012-2017.
Law School 101 Room 1E, 1 st Floor Gambrell Hall Robert A. Schapiro Asa Griggs Candler Professor of Law Robert Schapiro has been a member of faculty since 1995. He served as dean of Emory Law from 2012-2017.
A Constitutional Conspiracy Unmasked: Why "No State" Does Not Mean "No State".
 University of Minnesota Law School Scholarship Repository Constitutional Commentary 1993 A Constitutional Conspiracy Unmasked: Why "No State" Does Not Mean "No State". Mark A. Graber Follow this and additional
University of Minnesota Law School Scholarship Repository Constitutional Commentary 1993 A Constitutional Conspiracy Unmasked: Why "No State" Does Not Mean "No State". Mark A. Graber Follow this and additional
NATIONAL HEARING QUESTIONS ACADEMIC YEAR
 Unit One: What Are the Philosophical and Historical Foundations of the American Political System? 1. The great English historian, James Bryce, wrote that The American Constitution is no exception to the
Unit One: What Are the Philosophical and Historical Foundations of the American Political System? 1. The great English historian, James Bryce, wrote that The American Constitution is no exception to the
Basic Concepts of Government The English colonists brought 3 ideas that loom large in the shaping of the government in the United States.
 Civics Honors Chapter Two: Origins of American Government Section One: Our Political Beginnings Limited Government Representative government Magna Carta Petition of Right English Bill of Rights Charter
Civics Honors Chapter Two: Origins of American Government Section One: Our Political Beginnings Limited Government Representative government Magna Carta Petition of Right English Bill of Rights Charter
Slaughter-House Five: Views of the Case
 Slaughter-House Five: Views of the Case DAVID S. BOGEN* Because I believe that the demise of the Privileges or Immunities Clause has contributed in no small part to the current disarray of our Fourteenth
Slaughter-House Five: Views of the Case DAVID S. BOGEN* Because I believe that the demise of the Privileges or Immunities Clause has contributed in no small part to the current disarray of our Fourteenth
DOES THE CONSTITUTION PROTECT ECONOMIC LIBERTY?
 DOES THE CONSTITUTION PROTECT ECONOMIC LIBERTY? RANDY E. BARNETT * It is my job to defend the proposition that the Court in Lochner v. New York 1 was right to protect the liberty of contract under the
DOES THE CONSTITUTION PROTECT ECONOMIC LIBERTY? RANDY E. BARNETT * It is my job to defend the proposition that the Court in Lochner v. New York 1 was right to protect the liberty of contract under the
Of Inkblots and Originalism: Historical Ambiguity and the Case of the Ninth Amendment
 University of Richmond UR Scholarship Repository Law Faculty Publications School of Law 2008 Of Inkblots and Originalism: Historical Ambiguity and the Case of the Ninth Amendment Kurt T. Lash University
University of Richmond UR Scholarship Repository Law Faculty Publications School of Law 2008 Of Inkblots and Originalism: Historical Ambiguity and the Case of the Ninth Amendment Kurt T. Lash University
Enforcing the Rights of Due Process: The Original Relationship Between the Fourteenth Amendment and the 1866 Civil Rights Act
 Enforcing the Rights of Due Process: The Original Relationship Between the Fourteenth Amendment and the 1866 Civil Rights Act KURT T. LASH* For more than a century, legal scholars have looked to the 1866
Enforcing the Rights of Due Process: The Original Relationship Between the Fourteenth Amendment and the 1866 Civil Rights Act KURT T. LASH* For more than a century, legal scholars have looked to the 1866
Natural Resources Journal
 Natural Resources Journal 43 Nat Resources J. 2 (Spring 2003) Spring 2003 Property Rights: From Magna Carta to the Fourteenth Amendment, by Bernard H. Siegan Ian Bezpalko Recommended Citation Ian Bezpalko,
Natural Resources Journal 43 Nat Resources J. 2 (Spring 2003) Spring 2003 Property Rights: From Magna Carta to the Fourteenth Amendment, by Bernard H. Siegan Ian Bezpalko Recommended Citation Ian Bezpalko,
Bill of Rights. 1. Meet the Source (2:58) Interview with Whitman Ridgway (Professor, University of Maryland, College Park)
 Interview with Whitman Ridgway (Professor, University of Maryland, College Park) Bill of Rights 1. Meet the Source (2:58) Well, the Bill of Rights, in my opinion, is a very remarkable document because
Interview with Whitman Ridgway (Professor, University of Maryland, College Park) Bill of Rights 1. Meet the Source (2:58) Well, the Bill of Rights, in my opinion, is a very remarkable document because
BELL RINGER 10/08 Guess the meaning of the word in RED using context clues.
 BELL RINGER 10/08 Guess the meaning of the word in RED using context clues. 1. The revenue that Senator Hansen brought in from his oil company was beyond his wildest dreams. However, he knew it would make
BELL RINGER 10/08 Guess the meaning of the word in RED using context clues. 1. The revenue that Senator Hansen brought in from his oil company was beyond his wildest dreams. However, he knew it would make
From VOA Learning English, welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in Special English. I m Steve Ember.
 From VOA Learning English, welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in Special English. I m Steve Ember. Today, we continue our story of the United States Constitution. In recent weeks, we told
From VOA Learning English, welcome to THE MAKING OF A NATION American history in Special English. I m Steve Ember. Today, we continue our story of the United States Constitution. In recent weeks, we told
THE ORIGIN OF THE UNITED STATES CONSTITUTION
 THE ORIGIN OF THE UNITED STATES CONSTITUTION BY JAMES BALDWIN Edited and revised by Jim Erskine Copyright 2009, Homeway Press, all rights reserved This document is a part of HomeschoolRadioShows.com's
THE ORIGIN OF THE UNITED STATES CONSTITUTION BY JAMES BALDWIN Edited and revised by Jim Erskine Copyright 2009, Homeway Press, all rights reserved This document is a part of HomeschoolRadioShows.com's
Reading the Privileges or Immunities Clause: Textual Irony, Analytical Revisionism, and an Interpretive Truce
 Reading the Privileges or Immunities Clause: Textual Irony, Analytical Revisionism, and an Interpretive Truce Daniel J. Levin* All persons born or naturalized in the United States... are citizens of the
Reading the Privileges or Immunities Clause: Textual Irony, Analytical Revisionism, and an Interpretive Truce Daniel J. Levin* All persons born or naturalized in the United States... are citizens of the
3.1c- Layer Cake Federalism
 3.1c- Layer Cake Federalism Defining Federalism The United States encompasses many governments over 83,000 separate units. These include municipal, county, regional, state, and federal governments as well
3.1c- Layer Cake Federalism Defining Federalism The United States encompasses many governments over 83,000 separate units. These include municipal, county, regional, state, and federal governments as well
The Parameters of Constitutional Reconstruction: Slaughter-House, Cruikshank, and the Fourteenth Amendment
 College of William & Mary Law School William & Mary Law School Scholarship Repository Faculty Publications Faculty and Deans 1984 The Parameters of Constitutional Reconstruction: Slaughter-House, Cruikshank,
College of William & Mary Law School William & Mary Law School Scholarship Repository Faculty Publications Faculty and Deans 1984 The Parameters of Constitutional Reconstruction: Slaughter-House, Cruikshank,
Major Problem. Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government.
 The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
The Constitution Major Problem Could not tax, regulate trade or enforce its laws because the states held more power than the National Government. Why? Feared a government like King George The Constitutional
1. According to Washington, what is needed to prevent an uprising like Shays Rebellion? [1]
![1. According to Washington, what is needed to prevent an uprising like Shays Rebellion? [1] 1. According to Washington, what is needed to prevent an uprising like Shays Rebellion? [1]](/thumbs/83/87708147.jpg) Part A Short-Answer Questions Directions: Analyze the documents and answer the short-answer questions that follow each document in the space provided. Document 1 We are fast verging to anarchy and confusion!
Part A Short-Answer Questions Directions: Analyze the documents and answer the short-answer questions that follow each document in the space provided. Document 1 We are fast verging to anarchy and confusion!
American Democracy Now Chapter 2: The Constitution
 American Democracy Now Chapter 2: The Constitution Multiple-Choice Questions: 1. Which of these countries employs an unwritten constitution? a. the United States b. Great Britain c. Venezuela d. Kenya
American Democracy Now Chapter 2: The Constitution Multiple-Choice Questions: 1. Which of these countries employs an unwritten constitution? a. the United States b. Great Britain c. Venezuela d. Kenya
Antifederalist No. 84. On the Lack of a Bill of Rights
 Antifederalist No. 84 On the Lack of a Bill of Rights By "Brutus." When a building is to be erected which is intended to stand for ages, the foundation should be firmly laid. The Constitution proposed
Antifederalist No. 84 On the Lack of a Bill of Rights By "Brutus." When a building is to be erected which is intended to stand for ages, the foundation should be firmly laid. The Constitution proposed
US History, Ms. Brown Website: dph7history.weebly.com
 Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #70 Aims: SWBAT understand and explain the debate over representation SWBAT identify and explain the Virginia Plan and
Course: US History/Ms. Brown Homeroom: 7th Grade US History Standard # Do Now Day #70 Aims: SWBAT understand and explain the debate over representation SWBAT identify and explain the Virginia Plan and
Ratifying the Constitution
 Ratifying the Constitution Signing the Constitution Once the debate ended, Governor Morris of New Jersey put the Constitution in its final form. He competed the task of hand-writing 4,300 words in two
Ratifying the Constitution Signing the Constitution Once the debate ended, Governor Morris of New Jersey put the Constitution in its final form. He competed the task of hand-writing 4,300 words in two
CHAPTER 2 ORIGINS OF AMERICAN GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS
 CHAPTER 2 ORIGINS OF AMERICAN GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS Basic Concepts of Government Early settlers brought ideas of government or political systems with them.
CHAPTER 2 ORIGINS OF AMERICAN GOVERNMENT SECTION 1: OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS OUR POLITICAL BEGINNINGS Basic Concepts of Government Early settlers brought ideas of government or political systems with them.
2. Which of the following was not one of the rights granted in the Magna Carta?
 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 Our Political Beginnings SECTION 2 The Coming of Independence
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 Our Political Beginnings SECTION 2 The Coming of Independence
Chapter 02 The Constitution
 Chapter 02 The Constitution Multiple Choice Questions 1. (p. 34) Which of these countries employs an unwritten constitution? A. the United States B. Great Britain C. France D. Sweden E. Germany Difficulty:
Chapter 02 The Constitution Multiple Choice Questions 1. (p. 34) Which of these countries employs an unwritten constitution? A. the United States B. Great Britain C. France D. Sweden E. Germany Difficulty:
Chapter 2. Government
 Chapter 2 Government The way the United States government is organized, its powers, and its limitations, are based on ideas about government that were brought to these shores by the English colonist. Three
Chapter 2 Government The way the United States government is organized, its powers, and its limitations, are based on ideas about government that were brought to these shores by the English colonist. Three
Creating a Nation Test Review
 Creating a Nation Test Review Question #1: Multiple Choice The Northwest ordinance of 1787 is important because. A. It sent troops to the Northwest to protect the colonies from Native Americans. B. It
Creating a Nation Test Review Question #1: Multiple Choice The Northwest ordinance of 1787 is important because. A. It sent troops to the Northwest to protect the colonies from Native Americans. B. It
Constitutional Foundations
 CHAPTER 2 Constitutional Foundations CHAPTER OUTLINE I. The Setting for Constitutional Change II. The Framers III. The Roots of the Constitution A. The British Constitutional Heritage B. The Colonial Heritage
CHAPTER 2 Constitutional Foundations CHAPTER OUTLINE I. The Setting for Constitutional Change II. The Framers III. The Roots of the Constitution A. The British Constitutional Heritage B. The Colonial Heritage
Gov t was needed to maintain peace. Gov t is not all powerful Power is limited to what the people give to it
 Ordered Government Gov t was needed to maintain peace Limited Government*********** Gov t is not all powerful Power is limited to what the people give to it Representative Government Gov t should serve
Ordered Government Gov t was needed to maintain peace Limited Government*********** Gov t is not all powerful Power is limited to what the people give to it Representative Government Gov t should serve
During the, the majority of delegates voted to declare independence from Britain. What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution?
 What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution? A. The Stamp Act B. Boston Tea Party C. Quartering Act D. Battle of Lexington and Concord During the, the majority of delegates voted
What is known as the official beginning of the America Revolution? A. The Stamp Act B. Boston Tea Party C. Quartering Act D. Battle of Lexington and Concord During the, the majority of delegates voted
U.S. Government Unit 1 Notes
 Name Period Date / / U.S. Government Unit 1 Notes C H A P T E R 1 Principles of Government, p. 1-24 1 Government and the State What Is Government? Government is the through which a makes and enforces its
Name Period Date / / U.S. Government Unit 1 Notes C H A P T E R 1 Principles of Government, p. 1-24 1 Government and the State What Is Government? Government is the through which a makes and enforces its
Constitution Scavenger Hunt Use the Constitution in your text to complete this. Article I- Branch writ of habeas corpus Article II- Branch
 Name Constitution Scavenger Hunt Use the Constitution in your text to complete this. DIRECTIONS: Using your copy of the Constitution in your textbook, and the annotations on the side, answer the following
Name Constitution Scavenger Hunt Use the Constitution in your text to complete this. DIRECTIONS: Using your copy of the Constitution in your textbook, and the annotations on the side, answer the following
INDIANA MIDDLE SCHOOL HEARING QUESTIONS Congressional District / Region / State Levels
 Unit One: What Were The Founders Basic Ideas About Government? 1. John Locke was an English philosopher who thought about why it was necessary to have a government. What did Locke think would happen without
Unit One: What Were The Founders Basic Ideas About Government? 1. John Locke was an English philosopher who thought about why it was necessary to have a government. What did Locke think would happen without
CONGRESS S POWER TO DEFINE THE PRIVILEGES AND IMMUNITIES OF CITIZENSHIP
 CONGRESS S POWER TO DEFINE THE PRIVILEGES AND IMMUNITIES OF CITIZENSHIP In 1866, months after the end of the Civil War and the ratification of the Thirteenth Amendment, Congressman John Bingham introduced
CONGRESS S POWER TO DEFINE THE PRIVILEGES AND IMMUNITIES OF CITIZENSHIP In 1866, months after the end of the Civil War and the ratification of the Thirteenth Amendment, Congressman John Bingham introduced
How Does the Constitution Guard Against Having a Ruler that is too
 Constitution MiniQ How Does the Constitution Guard Against Having a Ruler that is too Powerful? Overview: In the summer of 1787, fiftyfive delegates representing twelve of the thirteen states met in Philadelphia
Constitution MiniQ How Does the Constitution Guard Against Having a Ruler that is too Powerful? Overview: In the summer of 1787, fiftyfive delegates representing twelve of the thirteen states met in Philadelphia
Quiz # 2 Chapter 2 The United States Constitution
 Quiz # 2 Chapter 2 The United States Constitution 1. Equality was the goal of the a. French Revolution. b. American Revolution. c. both the French and the American Revolutions. d. neither the French nor
Quiz # 2 Chapter 2 The United States Constitution 1. Equality was the goal of the a. French Revolution. b. American Revolution. c. both the French and the American Revolutions. d. neither the French nor
Name Per. 2. Identify the important principles and issues debated at the Constitutional Convention and describe how they were resolved.
 Name Per CHAPTER 2 THE CONSTITUTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 2, you should be able to: 1. Discuss the importance of the English philosophical heritage, the colonial experience, the Articles
Name Per CHAPTER 2 THE CONSTITUTION LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 2, you should be able to: 1. Discuss the importance of the English philosophical heritage, the colonial experience, the Articles
Ratification of the Constitution. Issues
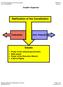 Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
Graphic Organizer Ratification of the Constitution Federalists Anti- Federalists Issues Power of the national government State power Power of the Executive Branch A Bill of Rights Michigan Citizenship
The Coming of Independence. Ratifying the Constitution
 C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 1 SECTION 1 SECTION 2 SECTION 3 SECTION 4 SECTION 5 Our Political Beginnings The Coming of Independence The Critical Period Creating the Constitution Ratifying
C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 1 SECTION 1 SECTION 2 SECTION 3 SECTION 4 SECTION 5 Our Political Beginnings The Coming of Independence The Critical Period Creating the Constitution Ratifying
Supreme Court of the United States
 No. 10-1320 In The Supreme Court of the United States ALEX BLUEFORD, Petitioner, v. STATE OF ARKANSAS, Respondent. On Writ of Certiorari to the Arkansas Supreme Court BRIEF OF CONSTITUTIONAL ACCOUNTABILITY
No. 10-1320 In The Supreme Court of the United States ALEX BLUEFORD, Petitioner, v. STATE OF ARKANSAS, Respondent. On Writ of Certiorari to the Arkansas Supreme Court BRIEF OF CONSTITUTIONAL ACCOUNTABILITY
Spotlight on America:
 Editor Gisela Lee, M.A. Managing Editor Karen J. Goldfluss, M.S. Ed. Spotlight on America: The Constitution Editor-in-Chief Sharon Coan, M.S. Ed. Illustrator Kevin McCarthy Cover Artist Brenda DiAntonis
Editor Gisela Lee, M.A. Managing Editor Karen J. Goldfluss, M.S. Ed. Spotlight on America: The Constitution Editor-in-Chief Sharon Coan, M.S. Ed. Illustrator Kevin McCarthy Cover Artist Brenda DiAntonis
Debating the Constitution
 SECTION 3 A Bill of Rights A bill of rights is what the people are entitled to against every government on earth, general or particular; and what no just government should refuse or rest on inference.
SECTION 3 A Bill of Rights A bill of rights is what the people are entitled to against every government on earth, general or particular; and what no just government should refuse or rest on inference.
In The Supreme Court of the United States
 No. 08-1521 ================================================================ In The Supreme Court of the United States --------------------------------- --------------------------------- OTIS MCDONALD,
No. 08-1521 ================================================================ In The Supreme Court of the United States --------------------------------- --------------------------------- OTIS MCDONALD,
Goal 1 Values and Principles of American Democracy
 Practice Test of Goal 1 Values and Principles of American Democracy Note to teachers: These unofficial sample questions were created to help students review Goal 1 content, as well as practice for the
Practice Test of Goal 1 Values and Principles of American Democracy Note to teachers: These unofficial sample questions were created to help students review Goal 1 content, as well as practice for the
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton
 Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
Grade 7 History Mr. Norton Section 1: A Loose Confederation Section 2: The Constitutional Convention Section 3: Ideas Behind the Constitution Section 4: Ratification and the Bill of Rights Grade 7 History
Articles of Confederation [first printing, first edition] Lancaster, Pennsylvania, 1777 Book, 26 pages. ARTICLES. OF [Illegible] 1777 CONFEDERATION
![Articles of Confederation [first printing, first edition] Lancaster, Pennsylvania, 1777 Book, 26 pages. ARTICLES. OF [Illegible] 1777 CONFEDERATION Articles of Confederation [first printing, first edition] Lancaster, Pennsylvania, 1777 Book, 26 pages. ARTICLES. OF [Illegible] 1777 CONFEDERATION](/thumbs/79/78892399.jpg) Articles of Confederation [first printing, first edition] Lancaster, Pennsylvania, 1777 Book, 26 pages. [2] ARTICLES OF [Illegible] 1777 CONFEDERATION AND Perpetual Union BETWEEN THE S T A T E S OF NEW-HAMPSHIRE,
Articles of Confederation [first printing, first edition] Lancaster, Pennsylvania, 1777 Book, 26 pages. [2] ARTICLES OF [Illegible] 1777 CONFEDERATION AND Perpetual Union BETWEEN THE S T A T E S OF NEW-HAMPSHIRE,
-- The search text of this PDF is generated from uncorrected OCR text.
 Citation: 62 N.C. L. Rev 517 1983-1984 Content downloaded/printed from HeinOnline (http://heinonline.org) Wed Jun 2 23:22:07 2010 -- Your use of this HeinOnline PDF indicates your acceptance of HeinOnline's
Citation: 62 N.C. L. Rev 517 1983-1984 Content downloaded/printed from HeinOnline (http://heinonline.org) Wed Jun 2 23:22:07 2010 -- Your use of this HeinOnline PDF indicates your acceptance of HeinOnline's
INSTRUCTIONS C 4 SIMULATED CONGRESSIONAL HEARING STUDENTS UNIT QUESTIONS
 INSTRUCTIONS As you know from studying your We the People: The Citizen & the Constitution textbook, members of Congress make laws. These laws should protect our rights and promote our welfare. To make
INSTRUCTIONS As you know from studying your We the People: The Citizen & the Constitution textbook, members of Congress make laws. These laws should protect our rights and promote our welfare. To make
Magruder s American Government
 Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 Our Political Beginnings
Presentation Pro Magruder s American Government C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government 2001 by Prentice Hall, Inc. C H A P T E R 2 Origins of American Government SECTION 1 Our Political Beginnings
Ch. 1 Principles of Government
 Ch. 1 Principles of Government Objectives: 1. Identify the four main purposes of government. 2. Identify and explain the four theories that explain the origin of government. I. What is government? A. Government-
Ch. 1 Principles of Government Objectives: 1. Identify the four main purposes of government. 2. Identify and explain the four theories that explain the origin of government. I. What is government? A. Government-
The Constitution. Multiple-Choice Questions
 2 The Constitution Multiple-Choice Questions 1. At the Constitutional Convention, the delegates agreed that slaves would be counted as of a person for determining population for representation in the House
2 The Constitution Multiple-Choice Questions 1. At the Constitutional Convention, the delegates agreed that slaves would be counted as of a person for determining population for representation in the House
In The Supreme Court of the United States
 Nos. 08-1497 & 08-1521 ================================================================ In The Supreme Court of the United States --------------------------------- --------------------------------- NATIONAL
Nos. 08-1497 & 08-1521 ================================================================ In The Supreme Court of the United States --------------------------------- --------------------------------- NATIONAL
Transcript of Articles of Confederation (1777)
 www.ourdocuments.gov October 21, 2010 Transcript of Articles of Confederation (1777) To all to whom these Presents shall come, we, the undersigned, Delegates of the States affixed to our Names, send greeting:
www.ourdocuments.gov October 21, 2010 Transcript of Articles of Confederation (1777) To all to whom these Presents shall come, we, the undersigned, Delegates of the States affixed to our Names, send greeting:
The Declaration of Independence and Its Signers
 The Declaration of Independence and Its Signers Objectives Students will be able to explain the events that led up to the colonies severing ties with Great Britain Students will understand the main grievances
The Declaration of Independence and Its Signers Objectives Students will be able to explain the events that led up to the colonies severing ties with Great Britain Students will understand the main grievances
STATE HEARING QUESTIONS
 Unit One: What Are the Philosophical and Historical Foundations of the American Political System? 1. John Locke wrote that there is a common distinction between an express and a tacit consent. Nobody doubts
Unit One: What Are the Philosophical and Historical Foundations of the American Political System? 1. John Locke wrote that there is a common distinction between an express and a tacit consent. Nobody doubts
Colonial America Learning Targets
 Colonial America Learning Targets Topic: History I can explain the significance of the following dates: 1607 and 1620 1607 - Jamestown 1620 - Plymouth Hunger for resources I can compare the reasons for
Colonial America Learning Targets Topic: History I can explain the significance of the following dates: 1607 and 1620 1607 - Jamestown 1620 - Plymouth Hunger for resources I can compare the reasons for
DOES THE CONSTITUTION EMBODY A PRESUMPTION OF LIBERTY?
 DOES THE CONSTITUTION EMBODY A PRESUMPTION OF LIBERTY? Douglas G. Smith* Review of Restoring the Lost Constitution: The Presumption of Liberty by Randy Barnett, Princeton University Press (2004). The constitutional
DOES THE CONSTITUTION EMBODY A PRESUMPTION OF LIBERTY? Douglas G. Smith* Review of Restoring the Lost Constitution: The Presumption of Liberty by Randy Barnett, Princeton University Press (2004). The constitutional
Establishing A New Government: Creating a Government. Chapter 4 Concept 2
 Establishing A New Government: Creating a Government Chapter 4 Concept 2 4.2 Creating a Government How did the decisions made at the Constitutional Convention affect the balance of power in the new nation?
Establishing A New Government: Creating a Government Chapter 4 Concept 2 4.2 Creating a Government How did the decisions made at the Constitutional Convention affect the balance of power in the new nation?
Supreme Court of the United States
 i No. 12-71 In the Supreme Court of the United States ARIZONA, et al. v. Petitioners, THE INTER TRIBAL COUNCIL OF ARIZONA, INC. et al., Respondents. On Writ of Certiorari to the United States Court of
i No. 12-71 In the Supreme Court of the United States ARIZONA, et al. v. Petitioners, THE INTER TRIBAL COUNCIL OF ARIZONA, INC. et al., Respondents. On Writ of Certiorari to the United States Court of
Copyright 2011 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Longman
 Chapter 2: The Constitution The Origins of the Constitution The Government That Failed: 1776 1787 Making a Constitution: The Philadelphia Convention Critical Issues at the Convention The Madisonian System
Chapter 2: The Constitution The Origins of the Constitution The Government That Failed: 1776 1787 Making a Constitution: The Philadelphia Convention Critical Issues at the Convention The Madisonian System
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes
 Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
Constitutional Convention Unit Notes Civics Textbook: Government and Society - Text p. 5 Cue four reasons why society needs a government Notes 1. Law and Order Government makes laws to protect citizens
Chapters 1-3 Test REVIEW CONSTITUTIONAL FOUNDATIONS PART 1
 Name Date Period Chapters 1-3 Test REVIEW CONSTITUTIONAL FOUNDATIONS PART 1 Chapter 1 AP Government 1. How does government usually protect its national sovereignty? 2. How does our government respond to
Name Date Period Chapters 1-3 Test REVIEW CONSTITUTIONAL FOUNDATIONS PART 1 Chapter 1 AP Government 1. How does government usually protect its national sovereignty? 2. How does our government respond to
Course Outcome Summary American Government/Survey of Government
 American Government/Survey of Government Course Information: Instruction Level: 12th grade Total Credits: 1 (1 semester course) Description: This course is an introduction to the basic concepts of American
American Government/Survey of Government Course Information: Instruction Level: 12th grade Total Credits: 1 (1 semester course) Description: This course is an introduction to the basic concepts of American
American Government. Unit 2 Study Guide
 American Government Unit 2 Study Guide Events leading up the Declaration of Independence: 1) Stamp Act- a tax placed on all printed material a. An attempt to earn money lost in the French and Indian War
American Government Unit 2 Study Guide Events leading up the Declaration of Independence: 1) Stamp Act- a tax placed on all printed material a. An attempt to earn money lost in the French and Indian War
NATIONAL HEARING QUESTIONS ACADEMIC YEAR
 Unit One: What Are the Philosophical and Historical Foundations of the American Political System? 1. In writing the Constitution, the Framers did not start de novo [new or fresh], but drew on their collective
Unit One: What Are the Philosophical and Historical Foundations of the American Political System? 1. In writing the Constitution, the Framers did not start de novo [new or fresh], but drew on their collective
Bill of Rights. Because the Constitution of the United States granted the federal government so much power, as compared with
 Bill of Rights I INTRODUCTION Bill of Rights Because the Constitution of the United States granted the federal government so much power, as compared with the earlier Articles of Confederation, several
Bill of Rights I INTRODUCTION Bill of Rights Because the Constitution of the United States granted the federal government so much power, as compared with the earlier Articles of Confederation, several
DOES THE FOURTEENTH AMENDMENT GUARANTEE EQUAL JUSTICE FOR ALL?
 DOES THE FOURTEENTH AMENDMENT GUARANTEE EQUAL JUSTICE FOR ALL? STEVEN G. CALABRESI * Does the Fourteenth Amendment 1 guarantee equal justice for all? Implicitly, this question asks whether the Supreme
DOES THE FOURTEENTH AMENDMENT GUARANTEE EQUAL JUSTICE FOR ALL? STEVEN G. CALABRESI * Does the Fourteenth Amendment 1 guarantee equal justice for all? Implicitly, this question asks whether the Supreme
Last term the Court heard a case examining a perceived
 Free Speech & Election Law Part II: Can States Require Proof of Citizenship for Voter Registration?: Arizona v. Inter Tribal Council of Arizona By Anthony T. Caso* Note from the Editor: This article discusses
Free Speech & Election Law Part II: Can States Require Proof of Citizenship for Voter Registration?: Arizona v. Inter Tribal Council of Arizona By Anthony T. Caso* Note from the Editor: This article discusses
-- The search text of this PDF is generated from uncorrected OCR text.
 Citation: 43 Ohio St. L.J. 89 1982 Content downloaded/printed from HeinOnline (http://heinonline.org) Wed Jun 2 23:23:29 2010 -- Your use of this HeinOnline PDF indicates your acceptance of HeinOnline's
Citation: 43 Ohio St. L.J. 89 1982 Content downloaded/printed from HeinOnline (http://heinonline.org) Wed Jun 2 23:23:29 2010 -- Your use of this HeinOnline PDF indicates your acceptance of HeinOnline's
US Government Exam Review 2014
 Name: Hour: Date: US Government Exam Review 2014 Chapter 1 Principles of Government 1. is the institution which makes and enforces policy. 2. What are the three basic powers that every government has in
Name: Hour: Date: US Government Exam Review 2014 Chapter 1 Principles of Government 1. is the institution which makes and enforces policy. 2. What are the three basic powers that every government has in
Red, white, and blue. One for each state. Question 1 What are the colors of our flag? Question 2 What do the stars on the flag mean?
 1 What are the colors of our flag? Red, white, and blue 2 What do the stars on the flag mean? One for each state 3 How many stars are there on our flag? There are 50 stars on our flag. 4 What color are
1 What are the colors of our flag? Red, white, and blue 2 What do the stars on the flag mean? One for each state 3 How many stars are there on our flag? There are 50 stars on our flag. 4 What color are
STAAR OBJECTIVE: 3. Government and Citizenship
 STAAR OBJECTIVE: 3 Government and Citizenship 1. What is representative government? A. Government that represents the interests of the king. B. Government in which elected officials represent the interest
STAAR OBJECTIVE: 3 Government and Citizenship 1. What is representative government? A. Government that represents the interests of the king. B. Government in which elected officials represent the interest
netw rks Where in the world? When did it happen? The Constitution Lesson 1 Principles of the Constitution ESSENTIAL QUESTION Terms to Know
 Lesson 1 Principles of the Constitution ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why do people form governments? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. What basic principles of government are set forth by the Constitution? 2. How is the Constitution
Lesson 1 Principles of the Constitution ESSENTIAL QUESTION Why do people form governments? GUIDING QUESTIONS 1. What basic principles of government are set forth by the Constitution? 2. How is the Constitution
Copyright 2014 Organic Laws Institute
 1 The United States In this part of this lesson, we explore the different meanings of the phrases, United States and United States of America used in the Organic Laws of the United States of America. Article
1 The United States In this part of this lesson, we explore the different meanings of the phrases, United States and United States of America used in the Organic Laws of the United States of America. Article
Creating the Constitution 2.2, 2.3, 2.4
 Creating the Constitution 2.2, 2.3, 2.4 Struggle for Government The creation and signing of the Declaration of Independence did not create a government The founding fathers had many problems Declaration
Creating the Constitution 2.2, 2.3, 2.4 Struggle for Government The creation and signing of the Declaration of Independence did not create a government The founding fathers had many problems Declaration
