The Last Day of Oppression, and the First Day of the Same
|
|
|
- Victoria Burke
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1
2
3 The Last Day of Oppression, and the First Day of the Same The Politics and Economics of the New Latin American Left Jeffery R. Webber
4
5 First published 2016 by Haymarket This edition published 2017 by Pluto Press 345 Archway Road, London N6 5AA Copyright Jeffery Webber 2016 The right of Jeffery Webber to be identified as the author of this work has been asserted by him in accordance with the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act British Library Cataloguing in Publication Data A catalogue record for this book is available from the British Library ISBN Paperback ISBN PDF ebook ISBN Kindle ebook ISBN EPUB ebook Printed in Canada by union labor
6
7 Contents One Latin America s Second Independence 1 Two Three four Global Crisis and Latin American Tendencies: The Political Economy of the New Latin American Left 9 Contemporary Latin American Inequality: Class Struggle, Decolonization, and the Limits of Liberal Citizenship 73 The Indigenous Community as Living Organism : José Carlos Mariátegui, Romantic Marxism, and Extractive Capitalism in the Andes 105 five Chile s New Left: More Than a Student Movement 135 six seven eight Evo Morales and the Political Economy of Passive Revolution in Bolivia, The Long March East: Evo Morales and the Consolidation of Agrarian Capitalism in Bolivia 189 Dual Powers, Class Compositions, and the Venezuelan People: Reflections on We Created Chávez 239 nine Conclusion: From Hegemony to Impasse 273 Acknowledgments 301 Index 305
8 One Latin America s Second Independence Ecuador s independence from Spain in the early nineteenth century did not bring with it a social revolution. The racist and unequal pyramidal hierarchy of colonial society was not turned on its head. Instead, the elite descendants of Spanish conquistadores now ruled on their own behalf, rather than in the service of the Spanish crown. For those beneath them, much remained as it had been. Thus a popular slogan of the postindependence period emerged: the last day of oppression, and the first day of the same. 1 The expression, if in a novel form, captures something essential of the first decade and a half of twenty-first-century Latin American politics. The early 2000s saw a remarkable political and economic crisis of neoliberalism facilitate an explosive reawakening of extraparliamentary social movements throughout Latin America, but particularly in South America strikes, land occupations, unemployed workers roadblocks and factory takeovers, and indigenous uprisings. By the mid-2000s, this effervescence translated in a muted style into the parliamentary halls and presidential palaces of many South American countries as center-left and left parties were elected to office. Parallel to these political dynamics, the economic crisis of neoliberalism 1 Oppression in this phrase is translated as despotism in Agustín Cueva s famous text El proceso de dominación política del Ecuador (Quito: Ediciones Crítica, 1972). I prefer oppression in this book, following common use of the slogan today, as described to me in a 2010 interview by indigenous activist Luis Macas in Quito, Ecuador. 1
9 2 The Last Day of Oppression, and the First Day of the Same in the region was eclipsed by the rising tide of a China-driven boom in international commodity prices. With minimal changes to the tax regimes and royalty rates on resource commodities mining minerals, natural gas and oil, and agro-industrial products left governments witnessed massive revenue increases in the state treasuries, even as multinational and domestic capitalists enjoyed soaring net profits. Targeted distribution through cash-transfer programs and other social welfare initiatives, along with higher employment rates, led to falling poverty rates, and even some falls in income inequality in parts of Latin America ruled by the various shades of the left. Still, even taking into account variability across cases, the new Latin American left did not challenge the underlying class structures of its societies or the systems of capitalist accumulation that fundamentally reproduce the basic patterns of simultaneous wealth and poverty, of luxury alongside misery. The facility with which center-left and left governments were able to skim a portion of the rent generated by the commodities boom and redirect it to the popular classes helped for a time to conceal underlying structures of continuity. Politically, social movements were channeled into the labyrinth of state apparatuses and significantly disarmed in the process. Then global capitalism entered its latest severe crisis in The impact on Latin America was not immediate. Indeed, after a dip in growth in 2009, the next two years seemed to suggest the region had somehow escaped world dynamics. By 2012, however, China had dramatically slowed down, the Eurozone and the United States were sputtering, and the commodity prices that had done much to hold South America aloft started their swift descent. The politics of austerity already introduced with such rabidity in North America and Europe (especially southern Europe and particularly Greece) were now dictating the winds of Latin American political economies once again. This time, however, it was center-left and left governments that began to make the class decisions of austerity politics. With declining state revenues, they began again with variation across cases to socialize the costs of declines in state treasuries onto the vast majority, rather than turning on the rich. They sided with the surplus appropriators rather than the direct producers of Latin American wealth. These class decisions often took the form of cuts to social programs that had been primed during the era of commodity booms. As opposed to radicalizing the left turn in the context of the emerging crisis, center-left and left governments increasingly adapted to the imperatives of capital. But while capital had flourished under many of these governments, the new left had never been the first choice of private investors. They have sensed
10 Latin America s Second Independence 3 blood, and are now going for the kill new right politics are on the ascent in extraparliamentary and parliamentary forms throughout the region. Thus, while left governments bend over backward to capitulate to capital and ensure market confidence, capital has left them to flounder in the political darkness, preferring a return to traditional and new rights, or sometimes a novel symbiosis of the two. Meanwhile, the austerity drives of left governments have alienated much of their popular bases, who show up in meager numbers when they are finally called upon to defend left administrations against right-wing belligerence in the streets, as in Congress. The last day of oppression, and the first day of the same. But this phrase should not be understood in fatalistic terms of predestined outcomes. The end of the cycle of progressive governments should not be equated straightforwardly with the end of the Latin American left. The latter s social movement and trade union modalities are unlikely to suffer quietly the counteroffensive of the right. The future is still in play. The outcome is undecided. And we will need to turn our eyes below and to the left to register the pulse of political developments in the years ahead to the evolving ideological, organizational, and political balance of forces outside the institutional halls of formal professional politics and leaderships, as much as to what is happening inside those visible corridors of power. This book raises some of the questions that are important to keep in mind and provides some preliminary outlines of responses to these questions. The Architecture of the Book Chapter 2 examines the political and economic dynamics of the Latin American left from the early 1990s to the present. It measures the shifting balance of forces ideological, social, economic, and military between the rural and urban popular classes and oppressed groups, the domestic ruling classes, and imperialism across the different phases of the period in question. It maps the 1990s as a period of neoliberal hegemony and left-wing disarticulation before shifting to the economic crisis of neoliberalism between 1998 and It shows how this economic crisis transformed into a political crisis through the rise of extraparliamentary social movements and left-wing rearticulation in the early 2000s. From here it charts the movement of the left from the extraparliamentary terrain to the corridors of state power through the election of center-left and left governments in the mid-2000s in the context of a
11 4 The Last Day of Oppression, and the First Day of the Same commodities boom. In this context, it explores the rise of compensatory states as the dominant left form of rule during the boom period. Next, the chapter maps the delayed reverberation of the global economic crisis of into the region and its political consequences. It provides in-depth case studies of the present conjuncture in Argentina, Venezuela, Brazil, and Ecuador. The predominant themes in the case studies are declining forms of left hegemony and the various modalities of right-wing rearticulation. Chapter 3 interrogates contemporary theoretical debates around enduring patterns of inequality in contemporary Latin America. It argues that the dominant streams of academic and policy writing on the topic are limited by their acknowledged or unacknowledged adherence to Weberian historical sociology and/or neostructuralist economics. These theoretical limitations mean that most writing on inequality in contemporary Latin America is flawed by a thin conception of democracy and a misconceptualization of capitalism, class, and other social relations of oppression. Much of this scholarship and policy literature is underpinned by a liberal ideology incapable of conceiving the constitutive coercive features of the capitalist market. Instead, the market is understood to require regulation at the margins, but it is ultimately understood to be a sphere of opportunities either to be seized or missed. Starting with the axiom of the market as the preeminent domain of freedom itself, liberal ideology cannot grasp struggles for freedom from the market. It thus misses most of what has been important about popular struggles in recent decades in Latin America. The chapter suggests as an alternative a combined Marxist and decolonial theoretical framework to approach inequality, one that attempts to encompass the totalizing power of capital and the complexity of class relations and other internally related social oppressions gender, sexuality, race, and nation in contemporary Latin American capitalism. The chapter grounds these theoretical discussions in concrete investigations of extractive capitalism and the militant biography of Luis Macas, an indigenous-marxist dissident in contemporary Ecuador. Chapter 4 explores the complex relationship between Marxism and Romanticism in the work of early twentieth-century Peruvian Marxist José Carlos Mariátegui. Following Michael Löwy, it argues that there is a utopian-revolutionary dialectic of the precapitalist past and socialist future running through Mariátegui s core works. The romantic thread of Mariátegui s thought was in many ways a response to the prevalent evolutionist and economistic Marxist orthodoxies of his time. An argument is made that the fruitful heresy embedded in the Mariáteguist framework might suggest
12 Latin America s Second Independence 5 the outlines for a theoretical research agenda to counter a novel orthodoxy emerging out of the state ideologies of the Andean new left in an era of intensifying extractive capitalism. Deploying a certain Marxist idiom, figures such as Bolivian vice president Álvaro García Linera defend as progressive the extension of large-scale mining, natural gas and oil extraction, and agro-industrial mono-cropping in alliance with multinational capital. Left and indigenous critics of this latest iteration of extractive capitalism in Latin America are condemned in this worldview as naive romantics, or worse, the useful idiots of imperialism. A creative return to Mariátegui allows us to read the opposition of left and indigenous critique and activism in a different light. What is more, we can see in the biographies of activists such as Felipe Quispe in Bolivia a concrete realization of the Romantic Marxist critique of evolutionism and economism being discussed theoretically in our exploration of Mariátegui. Chapter 5 investigates the origins and outcomes of the student-worker rebellions of in Chile. It argues that these remarkable mobilizations marked a before-and-after break in contemporary Chilean history. They introduced new elements into the common sense of Chilean society that broke with the neoliberal paradigm introduced under the dictatorship of Augusto Pinochet and consolidated under the post-authoritarian governments of the center-left Concertación coalitions. The revolts were not reducible to student rebellion, although this obviously played a key part in the events. There were also various interconnections established in this period between the student movement and the revitalization of parts of the labor movement, Mapuche indigenous struggles, and socio-ecological resistance. Although the rebellions as a whole introduced a significant rupture in Chilean politics, the model of accumulation and political domination persisted in many respects. While the conservative government of Sebastián Piñera ( ) provided a common enemy around which popular forces could easily cohere, the new center-left administration of Michelle Bachelet and her Nueva Mayoría (New Majority, NM) coalition, in office since 2014, has proved a more complicated antagonist. Bachelet ran on a platform to the left of her earlier presidency ( ), absorbing key elements of the popular demands coming from below, even while consolidating relations with the dominant sections of capital in the country. The NM government has incorporated the Partido Comunista de Chile (Chilean Communist Party, PCC) and, crucially, many of its leading youth, who played such an important role in the rebellions of In office, the overarching logic of the administration has been to introduce
13 6 The Last Day of Oppression, and the First Day of the Same reforms at the margins, stabilizing political life and protecting the underlying fundamentals of the system of accumulation and the mode of political domination consolidated in the 1990s under the Concertación governments. It has sought to channel and disarm pressures from below, while surviving economic and political pressures from the hard right. Bachelet appeared to be eminently capable of such a dance for the first year in office, but 2015 has seen renewed instability, with charges of corruption coming from the right and a rebirth of the student-worker movement in the streets. Chapter 6 examines the dynamics of the urban labor markets of Bolivia under Evo Morales ( ) as a prism through which to characterize the class character of that administration. While the government of Morales rules in the name of indigenous workers and peasants, the chapter shows how in fact the country s political economy since 2006 has witnessed the ongoing subjugation of these classes. If the logic of large capital persists, it is legitimated in and through petty indigenous capitalists. The chapter argues that Antonio Gramsci s conceptualization of passive revolution offers a superior analytical point of departure for understanding contemporary Bolivian politics than Álvaro García Linera s more widely accepted theory of creative tensions. However, the dominant manner in which passive revolution has been employed in contemporary Latin American debates has treated the sociopolitical and the ideological as relatively autonomous from the process of capital accumulation. What is necessary, instead, is a sharper appreciation of the base/superstructure metaphor as expressing a dialectical unity of internal relations between the economic and the political, thus avoiding one determinism or another. Through a reading of Gramsci that emphasizes such unity, chapter 6 interrogates the dynamics of extractive distribution, class contradictions of the plural economy, and transformations in the urban labor market that have characterized Bolivia s passive revolution under Evo Morales between 2006 and Chapter 7 also deals with Bolivia, but this time from the vantage point of the countryside. It begins with a survey of Bolivia s rural sociospatial dynamics. From this point of departure it then explores the historical development of agrarian capitalism across three historical phases: 1) the period of nationalist import-substitution industrialization; 2) the period of orthodox neoliberal restructuring between 1985 and 2000; and 3) the period of contested neodevelopmentalism under Evo Morales between 2006 and The chapter challenges the notion that there has been extensive, egalitarian reform in Bolivia since Morales assumed the presidency in Its argument hinges on the changing balance of agrarian class forces in Bolivian society and
14 Latin America s Second Independence 7 the related changes in the class composition of the ruling MAS (Movimiento al Socialismo) bloc over time. Initially, there was a period under Morales s rule, between 2006 and 2009, in which the indigenous peasant social movement alliance, the Unity Pact, fought from below for a genuine transformation of the Bolivian rural class structure, and in which the agro-industrial elite fought openly against the central government through an autonomist and regionalist destabilization campaign, headquartered in Santa Cruz and radiating outward through the rest of the lowland departments of the country. The main institutional terrain of struggle in these opening years of the Morales regime was the Constituent Assembly process, and there was a possibility during this period of deep structural reform to the countryside. However, by 2010 the Morales government had defeated the political project of autonomy in the lowlands, and this laid the basis for a class realignment in the ruling bloc. Between 2010 and 2016, a novel agro-capital-state alliance emerged, with subordinate support from rich peasants in the coca, soy, and quinoa commercial export sectors, among others. The Unity Pact fragmented, and the lowland indigenous movements were expelled from their earlier participation in the governing alliance. Chapter 8 shifts our attention to Venezuela. It offers an analysis of the Bolivarian process under Hugo Chávez ( ) through an extended interrogation of George Ciccariello-Maher s influential We Created Chávez. The chapter argues that We Created Chávez is the most important book available in English proposing an anticapitalist framework for understanding the Bolivarian process in contemporary Venezuela, as well as its historical backdrop dating back to The book contains within it a laudable critique of Eurocentrism and a masterful combination of oral history, ethnography, and theoretical sophistication. It reveals with unusual clarity and insight the multiplicity of popular movements that allowed for Hugo Chávez s eventual ascension to presidential office in the late 1990s. We Created Chávez has set a new scholarly bar for social histories of the Bolivarian process and demands serious engagement by Marxists. As a first attempt at such engagement, this chapter reveals some critical theoretical and sociological flaws in the text and other areas of analytical imprecision. Divided into theoretical and historical parts, it unpacks some of the strengths and weaknesses by moving from the abstract to the concrete. The intervention begins with concepts the mutually determining dialectic between Chávez and social movements; the people ; and dual power. From here, it grounds these concepts, and Ciccariello-Maher s use of them, in various themes and movements across specific historical periods of Venezuelan political development the rural guerrillas of the 1960s, the
15 8 The Last Day of Oppression, and the First Day of the Same urban guerrillas of the 1970s, the new urban sociopolitical formations of the 1980s, Afro-indigenous struggles in the Bolivarian process, and formal and informal working-class transformations since the onset of neoliberalism and its present contestation in the Venezuelan context.
Dinerstein makes two major contributions to which I will draw attention and around which I will continue this review: (1) systematising autonomy and
 Ana C. Dinerstein, The Politics of Autonomy in Latin America: The Art of Organising Hope, London: Palgrave Macmillan, 2015. ISBN: 978-0-230-27208-8 (cloth); ISBN: 978-1-349-32298-5 (paper); ISBN: 978-1-137-31601-1
Ana C. Dinerstein, The Politics of Autonomy in Latin America: The Art of Organising Hope, London: Palgrave Macmillan, 2015. ISBN: 978-0-230-27208-8 (cloth); ISBN: 978-1-349-32298-5 (paper); ISBN: 978-1-137-31601-1
Diversity and Democratization in Bolivia:
 : SOURCES OF INCLUSION IN AN INDIGENOUS MAJORITY SOCIETY May 2017 As in many other Latin American countries, the process of democratization in Bolivia has been accompanied by constitutional reforms that
: SOURCES OF INCLUSION IN AN INDIGENOUS MAJORITY SOCIETY May 2017 As in many other Latin American countries, the process of democratization in Bolivia has been accompanied by constitutional reforms that
early twentieth century Peru, but also for revolutionaries desiring to flexibly apply Marxism to
 José Carlos Mariátegui s uniquely diverse Marxist thought spans a wide array of topics and offers invaluable insight not only for historians seeking to better understand the reality of early twentieth
José Carlos Mariátegui s uniquely diverse Marxist thought spans a wide array of topics and offers invaluable insight not only for historians seeking to better understand the reality of early twentieth
The Left in Latin America Today
 The Left in Latin America Today Midge Quandt Much to the dismay of the U.S. Government which fears losing its grip on its own back yard, left and center-left governments in Latin America have in recent
The Left in Latin America Today Midge Quandt Much to the dismay of the U.S. Government which fears losing its grip on its own back yard, left and center-left governments in Latin America have in recent
The Politics of Market Discipline in Latin America: Globalization and Democracy *
 Globalization and Democracy * by Flávio Pinheiro Centro de Estudos das Negociações Internacionais, Brazil (Campello, Daniela. The Politics of Market Discipline in Latin America: Globalization and Democracy.
Globalization and Democracy * by Flávio Pinheiro Centro de Estudos das Negociações Internacionais, Brazil (Campello, Daniela. The Politics of Market Discipline in Latin America: Globalization and Democracy.
Latin America Goes Global. Midge Quandt. Latin America Goes Global
 Latin America Goes Global Midge Quandt Latin America Goes Global Latin America in the New Global Capitalism, by William I. Robinson, from NACLA: Report on the Americas 45, No. 2 (Summer 2012): 3-18. In
Latin America Goes Global Midge Quandt Latin America Goes Global Latin America in the New Global Capitalism, by William I. Robinson, from NACLA: Report on the Americas 45, No. 2 (Summer 2012): 3-18. In
Leandro Vergara-Camus
 Leandro Vergara-Camus, Land and Freedom: The MST, the Zapatistas and Peasant Alternatives to Neoliberalism, London: Zed Books, 2014. ISBN: 978-1-78032-743-3 (cloth); ISBN: 978-1- 78032-742-6 (paper); ISBN:
Leandro Vergara-Camus, Land and Freedom: The MST, the Zapatistas and Peasant Alternatives to Neoliberalism, London: Zed Books, 2014. ISBN: 978-1-78032-743-3 (cloth); ISBN: 978-1- 78032-742-6 (paper); ISBN:
Old wine, new bottles: In search of dialectics
 Dialect Anthropol (2011) 35:243 247 DOI 10.1007/s10624-011-9250-x Old wine, new bottles: In search of dialectics Forrest Hylton Published online: 3 September 2011 Ó Springer Science+Business Media B.V.
Dialect Anthropol (2011) 35:243 247 DOI 10.1007/s10624-011-9250-x Old wine, new bottles: In search of dialectics Forrest Hylton Published online: 3 September 2011 Ó Springer Science+Business Media B.V.
overproduction and underemployment are temporally offset. He cites the crisis of 1848, the great depression of the 1930s, the post-wwii era, and the
 David Harvey, Rebel Cities: From the Right to the City to the Urban Revolution, New York: Verso, 2012. ISBN: 9781781680742 (paper); ISBN: 9781844679041 (ebook); ISBN: 9781844678822 (cloth) The recent wave
David Harvey, Rebel Cities: From the Right to the City to the Urban Revolution, New York: Verso, 2012. ISBN: 9781781680742 (paper); ISBN: 9781844679041 (ebook); ISBN: 9781844678822 (cloth) The recent wave
Sociological Marxism Volume I: Analytical Foundations. Table of Contents & Outline of topics/arguments/themes
 Sociological Marxism Volume I: Analytical Foundations Table of Contents & Outline of topics/arguments/themes Chapter 1. Why Sociological Marxism? Chapter 2. Taking the social in socialism seriously Agenda
Sociological Marxism Volume I: Analytical Foundations Table of Contents & Outline of topics/arguments/themes Chapter 1. Why Sociological Marxism? Chapter 2. Taking the social in socialism seriously Agenda
Chile and the Neoliberal Trap
 Chile and the Neoliberal Trap The Post-Pinochet Era ANDRES SOLIMANO International Center for Globalization and Development, Santiago, Chile CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List of Figures List of Tables
Chile and the Neoliberal Trap The Post-Pinochet Era ANDRES SOLIMANO International Center for Globalization and Development, Santiago, Chile CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY PRESS Contents List of Figures List of Tables
Contemporary Latin American Politics Jonathan Hartlyn UNC-Chapel Hill. World View and others March 2010
 Contemporary Latin American Politics Jonathan Hartlyn UNC-Chapel Hill World View and others March 2010 Outline I. Broad regional trends and challenges: Democracy, Development, Drugs and violence. II. U.S.-Latin
Contemporary Latin American Politics Jonathan Hartlyn UNC-Chapel Hill World View and others March 2010 Outline I. Broad regional trends and challenges: Democracy, Development, Drugs and violence. II. U.S.-Latin
Democracy's ten-year rut Oct 27th 2005 From The Economist print edition
 The Latinobarómetro poll Democracy's ten-year rut Oct 27th 2005 From The Economist print edition Latin Americans do not want to go back to dictatorship but they are still unimpressed with their democracies.
The Latinobarómetro poll Democracy's ten-year rut Oct 27th 2005 From The Economist print edition Latin Americans do not want to go back to dictatorship but they are still unimpressed with their democracies.
A spectre has arisen, one of anti-american nationalism, pronounced The
 Third Quarter, 2006 Vol. 29, No. 3 Latin American Populism Between Left and Right by Harry der Nederlanden A spectre has arisen, one of anti-american nationalism, pronounced The Economist portentously
Third Quarter, 2006 Vol. 29, No. 3 Latin American Populism Between Left and Right by Harry der Nederlanden A spectre has arisen, one of anti-american nationalism, pronounced The Economist portentously
LSE Global South Unit Policy Brief Series
 ISSN 2396-765X LSE Policy Brief Series Policy Brief No.1/2018. The discrete role of Latin America in the globalization process. By Iliana Olivié and Manuel Gracia. INTRODUCTION. The global presence of
ISSN 2396-765X LSE Policy Brief Series Policy Brief No.1/2018. The discrete role of Latin America in the globalization process. By Iliana Olivié and Manuel Gracia. INTRODUCTION. The global presence of
Developing the Periphery & Theorising the Specificity of Peripheral Development
 Developing the Periphery & Theorising the Specificity of Peripheral Development From modernisation theory to the different theories of the dependency school ADRIANA CERDENA CALDERON LAURA MALAJOVICH SHAHANA
Developing the Periphery & Theorising the Specificity of Peripheral Development From modernisation theory to the different theories of the dependency school ADRIANA CERDENA CALDERON LAURA MALAJOVICH SHAHANA
New Economical, Political and Social Trends in Latin America, and the Demands for Participation
 New Economical, Political and Social Trends in Latin America, and the Demands for Participation Bernardo Kliksberg DPADM/DESA/ONU 21 April, 2006 AGENDA 1. POLITICAL CHANGES 2. THE STRUCTURAL ROOTS OF THE
New Economical, Political and Social Trends in Latin America, and the Demands for Participation Bernardo Kliksberg DPADM/DESA/ONU 21 April, 2006 AGENDA 1. POLITICAL CHANGES 2. THE STRUCTURAL ROOTS OF THE
Perspectives on the Americas
 Perspectives on the Americas A Series of Opinion Pieces by Leading Commentators on the Region Trade is not a Development Strategy: Time to Change the U.S. Policy Focus by JOY OLSON Executive Director Washington
Perspectives on the Americas A Series of Opinion Pieces by Leading Commentators on the Region Trade is not a Development Strategy: Time to Change the U.S. Policy Focus by JOY OLSON Executive Director Washington
Perspectives on the Americas. A Series of Opinion Pieces by Leading Commentators on the Region. Trade is not a Development Strategy:
 Perspectives on the Americas A Series of Opinion Pieces by Leading Commentators on the Region Trade is not a Development Strategy: Time to Change the U.S. Policy Focus by JOY OLSON Executive Director Washington
Perspectives on the Americas A Series of Opinion Pieces by Leading Commentators on the Region Trade is not a Development Strategy: Time to Change the U.S. Policy Focus by JOY OLSON Executive Director Washington
Imperial China Collapses Close Read
 Imperial China Collapses Close Read Standards Alignment Text with Close Read instructions for students Intended to be the initial read in which students annotate the text as they read. Students may want
Imperial China Collapses Close Read Standards Alignment Text with Close Read instructions for students Intended to be the initial read in which students annotate the text as they read. Students may want
After several decades of neoliberal dominance, during. Power to the Left, Autonomy for the Right? by Kent Eaton
 19 Photo by Charlie Perez. TRENDS Pro-autonomy marchers demonstrate in Guayaquil, January 2008. Power to the Left, Autonomy for the Right? by Kent Eaton After several decades of neoliberal dominance, during
19 Photo by Charlie Perez. TRENDS Pro-autonomy marchers demonstrate in Guayaquil, January 2008. Power to the Left, Autonomy for the Right? by Kent Eaton After several decades of neoliberal dominance, during
Imperialism and War. Capitalist imperialism produces 3 kinds of wars: 1. War of conquest to establish imperialist relations.
 Imperialism and War Capitalist imperialism produces 3 kinds of wars: 1. War of conquest to establish imperialist relations. 2. War of national liberation to force out the imperial master. 3. War of inter-imperial
Imperialism and War Capitalist imperialism produces 3 kinds of wars: 1. War of conquest to establish imperialist relations. 2. War of national liberation to force out the imperial master. 3. War of inter-imperial
US Regime Changes : The Historical Record. James Petras. As the US strives to overthrow the democratic and independent Venezuelan
 US Regime Changes : The Historical Record James Petras As the US strives to overthrow the democratic and independent Venezuelan government, the historical record regarding the short, middle and long-term
US Regime Changes : The Historical Record James Petras As the US strives to overthrow the democratic and independent Venezuelan government, the historical record regarding the short, middle and long-term
Living in our Globalized World: Notes 18 Antisystemic protest Copyright Bruce Owen 2009 Robbins: most protest is ultimately against the capitalist
 Living in our Globalized World: Notes 18 Antisystemic protest Copyright Bruce Owen 2009 Robbins: most protest is ultimately against the capitalist system that is, it opposes the system: it is antisystemic
Living in our Globalized World: Notes 18 Antisystemic protest Copyright Bruce Owen 2009 Robbins: most protest is ultimately against the capitalist system that is, it opposes the system: it is antisystemic
Zapatista Women. And the mobilization of women s guerrilla forces in Latin America during the 20 th century
 Zapatista Women And the mobilization of women s guerrilla forces in Latin America during the 20 th century Twentieth Century Latin America The Guerrilla Hero Over the course of the century, new revolutionary
Zapatista Women And the mobilization of women s guerrilla forces in Latin America during the 20 th century Twentieth Century Latin America The Guerrilla Hero Over the course of the century, new revolutionary
Dependency theorists, or dependentistas, are a group of thinkers in the neo-marxist tradition mostly
 Dependency theorists and their view that development in the North takes place at the expense of development in the South. Dependency theorists, or dependentistas, are a group of thinkers in the neo-marxist
Dependency theorists and their view that development in the North takes place at the expense of development in the South. Dependency theorists, or dependentistas, are a group of thinkers in the neo-marxist
FIGHTING FOR POLITICAL FREEDOM: COMPARATIVE STUDIES OF THE LEGAL COMPLEX AND POLITICAL LIBERALISM, TERENCE C. HALLIDAY, LUCIEN KARPIK
 FIGHTING FOR POLITICAL FREEDOM 291 FIGHTING FOR POLITICAL FREEDOM: COMPARATIVE STUDIES OF THE LEGAL COMPLEX AND POLITICAL LIBERALISM, TERENCE C. HALLIDAY, LUCIEN KARPIK AND MALCOLM M. FEELEY, EDS. (OXFORD:
FIGHTING FOR POLITICAL FREEDOM 291 FIGHTING FOR POLITICAL FREEDOM: COMPARATIVE STUDIES OF THE LEGAL COMPLEX AND POLITICAL LIBERALISM, TERENCE C. HALLIDAY, LUCIEN KARPIK AND MALCOLM M. FEELEY, EDS. (OXFORD:
Potential and Limits of Social and Solidarity Economy 6-8 May 2013 GB Room and Room II, ILO, UNRISD Geneva, Switzerland
 Potential and Limits of Social and Solidarity Economy 6-8 May 2013 GB Room and Room II, ILO, UNRISD Geneva, Switzerland 1 Conceptual framework 2 The economy 3 What is the true meaning of economy? A system
Potential and Limits of Social and Solidarity Economy 6-8 May 2013 GB Room and Room II, ILO, UNRISD Geneva, Switzerland 1 Conceptual framework 2 The economy 3 What is the true meaning of economy? A system
Course Schedule Spring 2009
 SPRING 2009 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS Ph.D. Program in Political Science Course Schedule Spring 2009 Decemberr 12, 2008 American Politics :: Comparative Politics International Relations :: Political Theory ::
SPRING 2009 COURSE DESCRIPTIONS Ph.D. Program in Political Science Course Schedule Spring 2009 Decemberr 12, 2008 American Politics :: Comparative Politics International Relations :: Political Theory ::
The Common Program of The Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference, 1949
 The Common Program of The Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference, 1949 Adopted by the First Plenary Session of the Chinese People's PCC on September 29th, 1949 in Peking PREAMBLE The Chinese
The Common Program of The Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference, 1949 Adopted by the First Plenary Session of the Chinese People's PCC on September 29th, 1949 in Peking PREAMBLE The Chinese
Chapter Test. Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Chapter 22-23 Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In contrast to the first decolonization of the Americas in the eighteenth and early
Chapter 22-23 Test Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In contrast to the first decolonization of the Americas in the eighteenth and early
Latin American and North Carolina
 Latin American and North Carolina World View and The Consortium in L. American and Caribbean Studies (UNC-CH and Duke University) Concurrent Session (Chile) - March 27, 2007 Inés Valdez - PhD Student Department
Latin American and North Carolina World View and The Consortium in L. American and Caribbean Studies (UNC-CH and Duke University) Concurrent Session (Chile) - March 27, 2007 Inés Valdez - PhD Student Department
ICOR Founding Conference
 Statute of the ICOR 6 October 2010 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 I. Preamble "Workers of all countries, unite!" this urgent call of Karl Marx and Frederick Engels at the end of the Communist Manifesto was formulated
Statute of the ICOR 6 October 2010 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 I. Preamble "Workers of all countries, unite!" this urgent call of Karl Marx and Frederick Engels at the end of the Communist Manifesto was formulated
CHAPTER 4: Theories of International Relations: Economic Structuralism, Constructivism, and Feminism
 1. Which three Latin American countries recently called for Twenty-first Century Socialism? a. Cuba, Mexico, and Chile b. Brazil, Costa Rica, and Peru c. Venezuela, Bolivia, and Ecuador d. Argentina, Chile,
1. Which three Latin American countries recently called for Twenty-first Century Socialism? a. Cuba, Mexico, and Chile b. Brazil, Costa Rica, and Peru c. Venezuela, Bolivia, and Ecuador d. Argentina, Chile,
island Cuba: Reformulation of the Economic Model and External Insertion I. Economic Growth and Development in Cuba: some conceptual challenges.
 Issue N o 13 from the Providing Unique Perspectives of Events in Cuba island Cuba: Reformulation of the Economic Model and External Insertion Antonio Romero, Universidad de la Habana November 5, 2012 I.
Issue N o 13 from the Providing Unique Perspectives of Events in Cuba island Cuba: Reformulation of the Economic Model and External Insertion Antonio Romero, Universidad de la Habana November 5, 2012 I.
MODERN WORLD
 B/60470 The Birth of the MODERN WORLD 1780-1914 Global Connections and Comparisons C. A. Bayly Blackwell Publishing CONTENTS List of Illustrations List of Maps and Tables Series Editor's Preface Acknowledgments
B/60470 The Birth of the MODERN WORLD 1780-1914 Global Connections and Comparisons C. A. Bayly Blackwell Publishing CONTENTS List of Illustrations List of Maps and Tables Series Editor's Preface Acknowledgments
Sociological Marxism Erik Olin Wright and Michael Burawoy. Chapter 1. Why Sociological Marxism? draft 2.1
 Sociological Marxism Erik Olin Wright and Michael Burawoy Chapter 1. Why Sociological Marxism? draft 2.1 From the middle of the 19 th century until the last decade of the 20 th, the Marxist tradition provided
Sociological Marxism Erik Olin Wright and Michael Burawoy Chapter 1. Why Sociological Marxism? draft 2.1 From the middle of the 19 th century until the last decade of the 20 th, the Marxist tradition provided
Decentralization and Local Governance: Comparing US and Global Perspectives
 Allan Rosenbaum. 2013. Decentralization and Local Governance: Comparing US and Global Perspectives. Haldus kultuur Administrative Culture 14 (1), 11-17. Decentralization and Local Governance: Comparing
Allan Rosenbaum. 2013. Decentralization and Local Governance: Comparing US and Global Perspectives. Haldus kultuur Administrative Culture 14 (1), 11-17. Decentralization and Local Governance: Comparing
Pablo Noyola February 22, 2016 Comparison of the Mexican War of Independence and the Mexican Revolution Hutson 1st Period Comparative Revolutions
 Pablo Noyola February 22, 2016 Comparison of the Mexican War of Independence and the Mexican Revolution Hutson 1st Period Comparative Revolutions Research Paper Noyola 1 Though these two revolutions took
Pablo Noyola February 22, 2016 Comparison of the Mexican War of Independence and the Mexican Revolution Hutson 1st Period Comparative Revolutions Research Paper Noyola 1 Though these two revolutions took
Master of Arts in Social Science (International Program) Faculty of Social Sciences, Chiang Mai University. Course Descriptions
 Master of Arts in Social Science (International Program) Faculty of Social Sciences, Chiang Mai University Course Descriptions Core Courses SS 169701 Social Sciences Theories This course studies how various
Master of Arts in Social Science (International Program) Faculty of Social Sciences, Chiang Mai University Course Descriptions Core Courses SS 169701 Social Sciences Theories This course studies how various
Natural Resources and Democracy in Latin America
 Natural Resources and Democracy in Latin America Thad Dunning Department of Political Science Yale University Does Oil Promote Authoritarianism? The prevailing consensus: yes Seminal work by Ross (2001),
Natural Resources and Democracy in Latin America Thad Dunning Department of Political Science Yale University Does Oil Promote Authoritarianism? The prevailing consensus: yes Seminal work by Ross (2001),
MARXISM AND INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS ELİF UZGÖREN AYSELİN YILDIZ
 MARXISM AND INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS ELİF UZGÖREN AYSELİN YILDIZ Outline Key terms and propositions within Marxism Marxism and IR: What is the relevance of Marxism today? Is Marxism helpful to explain current
MARXISM AND INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS ELİF UZGÖREN AYSELİN YILDIZ Outline Key terms and propositions within Marxism Marxism and IR: What is the relevance of Marxism today? Is Marxism helpful to explain current
Political Science (PSCI)
 Political Science (PSCI) Political Science (PSCI) Courses PSCI 5003 [0.5 credit] Political Parties in Canada A seminar on political parties and party systems in Canadian federal politics, including an
Political Science (PSCI) Political Science (PSCI) Courses PSCI 5003 [0.5 credit] Political Parties in Canada A seminar on political parties and party systems in Canadian federal politics, including an
Lecture 25 Sociology 621 HEGEMONY & LEGITIMATION December 12, 2011
 Lecture 25 Sociology 621 HEGEMONY & LEGITIMATION December 12, 2011 I. HEGEMONY Hegemony is one of the most elusive concepts in Marxist discussions of ideology. Sometimes it is used as almost the equivalent
Lecture 25 Sociology 621 HEGEMONY & LEGITIMATION December 12, 2011 I. HEGEMONY Hegemony is one of the most elusive concepts in Marxist discussions of ideology. Sometimes it is used as almost the equivalent
Roosevelts Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine Monroe Doctrine Clayton- Bulwer Treaty Westward Expansion.
 Origins Westward Expansion Monroe Doctrine 1820 Clayton- Bulwer Treaty 1850 Roosevelts Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine 1904 Manifest Destiny U.S. Independence & Westward Expansion Monroe Doctrine 1820
Origins Westward Expansion Monroe Doctrine 1820 Clayton- Bulwer Treaty 1850 Roosevelts Corollary to the Monroe Doctrine 1904 Manifest Destiny U.S. Independence & Westward Expansion Monroe Doctrine 1820
Latin America: Class Struggle from Above and Below. James Petras. Class struggle is the motor-force of History. Karl Marx
 Latin America: Class Struggle from Above and Below James Petras Class struggle is the motor-force of History Karl Marx Introduction One looks in vain among the writings of historians and social scientists
Latin America: Class Struggle from Above and Below James Petras Class struggle is the motor-force of History Karl Marx Introduction One looks in vain among the writings of historians and social scientists
7. The Informal Empire of London
 7. The Informal Empire of London Andy Higginbottom Associate Professor of Politics and Human Rights, Kingston University By Maria Dyveke Styve I meet Andy Higginbottom at a café at the South Bank Centre
7. The Informal Empire of London Andy Higginbottom Associate Professor of Politics and Human Rights, Kingston University By Maria Dyveke Styve I meet Andy Higginbottom at a café at the South Bank Centre
The Way Forward: Pathways toward Transformative Change
 CHAPTER 8 We will need to see beyond disciplinary and policy silos to achieve the integrated 2030 Agenda. The Way Forward: Pathways toward Transformative Change The research in this report points to one
CHAPTER 8 We will need to see beyond disciplinary and policy silos to achieve the integrated 2030 Agenda. The Way Forward: Pathways toward Transformative Change The research in this report points to one
Beyond the Zeitgeist of Post-neoliberal Theory in Latin America: The Politics of Anti-colonial Struggles in Bolivia
 Beyond the Zeitgeist of Post-neoliberal Theory in Latin America: The Politics of Anti-colonial Struggles in Bolivia Anna Frances Laing School of Geographical and Earth Sciences, University of Glasgow,
Beyond the Zeitgeist of Post-neoliberal Theory in Latin America: The Politics of Anti-colonial Struggles in Bolivia Anna Frances Laing School of Geographical and Earth Sciences, University of Glasgow,
The order in which the fivefollowing themes are presented here does not imply an order of priority.
 Samir Amin PROGRAMME FOR WFA/TWF FOR 2014-2015 FROM THE ALGIERS CONFERENCE (September 2013) This symposium resulted in rich discussions that revolved around a central axis: the question of the sovereign
Samir Amin PROGRAMME FOR WFA/TWF FOR 2014-2015 FROM THE ALGIERS CONFERENCE (September 2013) This symposium resulted in rich discussions that revolved around a central axis: the question of the sovereign
Sunday s Presidential Election: Where Will Chile Go? Anders Beal, Latin American Program Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars
 Sunday s Presidential Election: Where Will Chile Go? Anders Beal, Latin American Program Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars November 17, 2017 A SECOND TERM LIKELY FOR SEBASTIÁN PIÑERA Chileans
Sunday s Presidential Election: Where Will Chile Go? Anders Beal, Latin American Program Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars November 17, 2017 A SECOND TERM LIKELY FOR SEBASTIÁN PIÑERA Chileans
Japan Imperialism, Party Government, and Fascism. February 24, 2015
 Japan 1900--1937 Imperialism, Party Government, and Fascism February 24, 2015 Review Can we find capitalism in Asia before 1900? Was there much social mobility in pre-modern China, India, or Japan? Outsiders
Japan 1900--1937 Imperialism, Party Government, and Fascism February 24, 2015 Review Can we find capitalism in Asia before 1900? Was there much social mobility in pre-modern China, India, or Japan? Outsiders
The Landslide in Bolivia
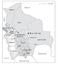 0 100 miles PANDO B R A Z I L P E R U BENI Lake Titicaca Yungas El Alto La Paz LA PAZ Oruro Chapare COCHABAMBA Cochabamba B O L I V I A Santa Cruz SANTA CRUZ ORURO Potosí Sucre Chaco POTOSÍ CHUQUISACA
0 100 miles PANDO B R A Z I L P E R U BENI Lake Titicaca Yungas El Alto La Paz LA PAZ Oruro Chapare COCHABAMBA Cochabamba B O L I V I A Santa Cruz SANTA CRUZ ORURO Potosí Sucre Chaco POTOSÍ CHUQUISACA
Anti-Populism: Ideology of the Ruling Class. James Petras. The media s anti-populism campaign has been used and abused by ruling elites and their
 Anti-Populism: Ideology of the Ruling Class James Petras Introduction Throughout the US and European corporate and state media, right and left, we are told that populism has become the overarching threat
Anti-Populism: Ideology of the Ruling Class James Petras Introduction Throughout the US and European corporate and state media, right and left, we are told that populism has become the overarching threat
Women of Color Critiques of Capitalism and the State. WMST 60 Professor Miller-Young Week 2
 Women of Color Critiques of Capitalism and the State WMST 60 Professor Miller-Young Week 2 Questions to Consider Why are WOCF writers critical of capitalism and the state? How do economic, political or
Women of Color Critiques of Capitalism and the State WMST 60 Professor Miller-Young Week 2 Questions to Consider Why are WOCF writers critical of capitalism and the state? How do economic, political or
Cemal Burak Tansel (ed)
 Cemal Burak Tansel (ed), States of Discipline: Authoritarian Neoliberalism and the Contested Reproduction of Capitalist Order, London: Rowman & Littlefield, 2017. ISBN: 9781783486182 (cloth); ISBN: 9781783486199
Cemal Burak Tansel (ed), States of Discipline: Authoritarian Neoliberalism and the Contested Reproduction of Capitalist Order, London: Rowman & Littlefield, 2017. ISBN: 9781783486182 (cloth); ISBN: 9781783486199
Understanding Social Equity 1 (Caste, Class and Gender Axis) Lakshmi Lingam
 Understanding Social Equity 1 (Caste, Class and Gender Axis) Lakshmi Lingam This session attempts to familiarize the participants the significance of understanding the framework of social equity. In order
Understanding Social Equity 1 (Caste, Class and Gender Axis) Lakshmi Lingam This session attempts to familiarize the participants the significance of understanding the framework of social equity. In order
The Economics, Culture, and Politics of Oil in Venezuela. By Gregory Wilpert.
 The Economics, Culture, and Politics of Oil in Venezuela By Gregory Wilpert www.venezuelanalysis.com Perhaps the most important thing to know about Venezuela is that it is an oil exporting country, the
The Economics, Culture, and Politics of Oil in Venezuela By Gregory Wilpert www.venezuelanalysis.com Perhaps the most important thing to know about Venezuela is that it is an oil exporting country, the
Socialist Rhetoric and Increasing Inequality
 BOIKE REHBEIN Laos in 2017 Socialist Rhetoric and Increasing Inequality ABSTRACT While the economy, and socioeconomic inequality, continue to grow rapidly, the leadership of Laos has returned to a rhetoric
BOIKE REHBEIN Laos in 2017 Socialist Rhetoric and Increasing Inequality ABSTRACT While the economy, and socioeconomic inequality, continue to grow rapidly, the leadership of Laos has returned to a rhetoric
Ghent University UGent Ghent Centre for Global Studies Erasmus Mundus Global Studies Master Programme
 Ghent University UGent Ghent Centre for Global Studies Erasmus Mundus Global Studies Master Programme Responsibility Dept. of History Module number 1 Module title Introduction to Global History and Global
Ghent University UGent Ghent Centre for Global Studies Erasmus Mundus Global Studies Master Programme Responsibility Dept. of History Module number 1 Module title Introduction to Global History and Global
Empire and Multitude: Shaping Our Century
 June 2018 Empire and Multitude: Shaping Our Century An Interview with Michael Hardt Twenty-first-century crises demand twenty-first-century social movements. What would such movements look like, and how
June 2018 Empire and Multitude: Shaping Our Century An Interview with Michael Hardt Twenty-first-century crises demand twenty-first-century social movements. What would such movements look like, and how
Introduction to Latin American Politics POLS 2570
 Introduction to Latin American Politics POLS 2570 Fall 2015 Professor- J.D. Bowen Tues/Thurs 9:30-10:45 Office- McGannon #149 McGannon Hall #121 Email- jbowen5@slu.edu Phone- 314.977.4239 Office hours-
Introduction to Latin American Politics POLS 2570 Fall 2015 Professor- J.D. Bowen Tues/Thurs 9:30-10:45 Office- McGannon #149 McGannon Hall #121 Email- jbowen5@slu.edu Phone- 314.977.4239 Office hours-
Constructing a Socially Just System of Social Welfare in a Multicultural Society: The U.S. Experience
 Constructing a Socially Just System of Social Welfare in a Multicultural Society: The U.S. Experience Michael Reisch, Ph.D., U. of Michigan Korean Academy of Social Welfare 50 th Anniversary Conference
Constructing a Socially Just System of Social Welfare in a Multicultural Society: The U.S. Experience Michael Reisch, Ph.D., U. of Michigan Korean Academy of Social Welfare 50 th Anniversary Conference
Introduction to Cultural Anthropology: Class 14 An exploitative theory of inequality: Marxian theory Copyright Bruce Owen 2010 Example of an
 Introduction to Cultural Anthropology: Class 14 An exploitative theory of inequality: Marxian theory Copyright Bruce Owen 2010 Example of an exploitative theory of inequality: Marxian theory the Marxian
Introduction to Cultural Anthropology: Class 14 An exploitative theory of inequality: Marxian theory Copyright Bruce Owen 2010 Example of an exploitative theory of inequality: Marxian theory the Marxian
The Alternative to Capitalism? Wayne Price
 The Alternative to Capitalism? Wayne Price November 2013 Contents Hegelianism?......................................... 4 Marxism and Anarchism.................................. 4 State Capitalism.......................................
The Alternative to Capitalism? Wayne Price November 2013 Contents Hegelianism?......................................... 4 Marxism and Anarchism.................................. 4 State Capitalism.......................................
Unit Four: Historical Materialism & IPE. Dr. Russell Williams
 Unit Four: Historical Materialism & IPE Dr. Russell Williams Essay Proposal due in class, October 8!!!!!! Required Reading: Cohn, Ch. 5. Class Discussion Reading: Robert W. Cox, Civil Society at the Turn
Unit Four: Historical Materialism & IPE Dr. Russell Williams Essay Proposal due in class, October 8!!!!!! Required Reading: Cohn, Ch. 5. Class Discussion Reading: Robert W. Cox, Civil Society at the Turn
Competing Theories of Economic Development
 http://www.uiowa.edu/ifdebook/ebook2/contents/part1-iii.shtml Competing Theories of Economic Development By Ricardo Contreras In this section we are going to introduce you to four schools of economic thought
http://www.uiowa.edu/ifdebook/ebook2/contents/part1-iii.shtml Competing Theories of Economic Development By Ricardo Contreras In this section we are going to introduce you to four schools of economic thought
2 Article Title. Plaza de Armas, Santiago, Chile. Photo by Roberto Stelling. BERKELEY REVIEW OF LATIN AMERICAN STUDIES
 2 Article Title Plaza de Armas, Santiago, Chile. Photo by Roberto Stelling. Fall 2007 3 CHILE by Bryce Breslin How can Latin American countries articulate economic growth, social development and democracy
2 Article Title Plaza de Armas, Santiago, Chile. Photo by Roberto Stelling. Fall 2007 3 CHILE by Bryce Breslin How can Latin American countries articulate economic growth, social development and democracy
Define, significance, source [author & title of book/article], example
![Define, significance, source [author & title of book/article], example Define, significance, source [author & title of book/article], example](/thumbs/82/86049494.jpg) SOSC 1000 Midterm Study Define, significance, source [author & title of book/article], example 1) Thomas Hobbes [taken from Shusky s History of Social Science philosopher key to origin of social science.
SOSC 1000 Midterm Study Define, significance, source [author & title of book/article], example 1) Thomas Hobbes [taken from Shusky s History of Social Science philosopher key to origin of social science.
Was the Falange fascist?
 Was the Falange fascist? In order to determine whether or not the Falange was fascist, it is first necessary to determine what fascism is and what is meant by the term. The historiography concerning the
Was the Falange fascist? In order to determine whether or not the Falange was fascist, it is first necessary to determine what fascism is and what is meant by the term. The historiography concerning the
Information for the 2017 Open Consultation of the ITU CWG-Internet Association for Proper Internet Governance 1, 6 December 2016
 Summary Information for the 2017 Open Consultation of the ITU CWG-Internet Association for Proper Internet Governance 1, 6 December 2016 The Internet and the electronic networking revolution, like previous
Summary Information for the 2017 Open Consultation of the ITU CWG-Internet Association for Proper Internet Governance 1, 6 December 2016 The Internet and the electronic networking revolution, like previous
Emory University States at Regional Risk (SARR) Professor Bruce M. Knauft, PI. Northern Andes Component: Off Centered States Executive Summary
 Emory University States at Regional Risk (SARR) Professor Bruce M. Knauft, PI Northern Andes Component: Off Centered States Executive Summary Submitted to The Carnegie Corporation of New York August 16,
Emory University States at Regional Risk (SARR) Professor Bruce M. Knauft, PI Northern Andes Component: Off Centered States Executive Summary Submitted to The Carnegie Corporation of New York August 16,
ECONOMICS CHAPTER 11 AND POLITICS. Chapter 11
 CHAPTER 11 ECONOMICS AND POLITICS I. Why Focus on India? A. India is one of two rising powers (the other being China) expected to challenge the global power and influence of the United States. B. India,
CHAPTER 11 ECONOMICS AND POLITICS I. Why Focus on India? A. India is one of two rising powers (the other being China) expected to challenge the global power and influence of the United States. B. India,
Professor Robert F. Alegre, Ph.D. Department of History University of New England
 Professor Robert F. Alegre, Ph.D. Department of History University of New England e-mail: ralegre_2000@une.edu Rebellion and Revolution in Twentieth-Century Latin America This course examines the major
Professor Robert F. Alegre, Ph.D. Department of History University of New England e-mail: ralegre_2000@une.edu Rebellion and Revolution in Twentieth-Century Latin America This course examines the major
COMMUNISTS AND NATIONAL SOCIALISTS
 COMMUNISTS AND NATIONAL SOCIALISTS Also by Ken Post ARISE YE STARVELINGS: The Jamaica Labour Rebellion of 1938 and its Aftermath REGAINING MARXISM REVOLUTION, SOCIALISM AND NATIONALISM IN VIET NAM Volume
COMMUNISTS AND NATIONAL SOCIALISTS Also by Ken Post ARISE YE STARVELINGS: The Jamaica Labour Rebellion of 1938 and its Aftermath REGAINING MARXISM REVOLUTION, SOCIALISM AND NATIONALISM IN VIET NAM Volume
SUB Hamburg A/ Talons of the Eagle. Latin America, the United States, and the World. PETER H.^MITH University of California, San Diego
 SUB Hamburg A/591327 Talons of the Eagle Latin America, the United States, and the World PETER H.^MITH University of California, San Diego FOURTH EDITION New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS BRIEF CONTENTS
SUB Hamburg A/591327 Talons of the Eagle Latin America, the United States, and the World PETER H.^MITH University of California, San Diego FOURTH EDITION New York Oxford OXFORD UNIVERSITY PRESS BRIEF CONTENTS
The character of the crisis: Seeking a way-out for the social majority
 The character of the crisis: Seeking a way-out for the social majority 1. On the character of the crisis Dear comrades and friends, In order to answer the question stated by the organizers of this very
The character of the crisis: Seeking a way-out for the social majority 1. On the character of the crisis Dear comrades and friends, In order to answer the question stated by the organizers of this very
UNITED NATIONS COMMISSION ON SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY FOR DEVELOPMENT. Working Group on Enhanced Cooperation
 UNITED NATIONS COMMISSION ON SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY FOR DEVELOPMENT Working Group on Enhanced Cooperation Contribution to the guiding questions agreed during first meeting of the WGEC Submitted by Association
UNITED NATIONS COMMISSION ON SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY FOR DEVELOPMENT Working Group on Enhanced Cooperation Contribution to the guiding questions agreed during first meeting of the WGEC Submitted by Association
how is proudhon s understanding of property tied to Marx s (surplus
 Anarchy and anarchism What is anarchy? Anarchy is the absence of centralized authority or government. The term was first formulated negatively by early modern political theorists such as Thomas Hobbes
Anarchy and anarchism What is anarchy? Anarchy is the absence of centralized authority or government. The term was first formulated negatively by early modern political theorists such as Thomas Hobbes
Marcelo Lopes de Souza, Richard J. White and Simon Springer (eds)
 Marcelo Lopes de Souza, Richard J. White and Simon Springer (eds), Theories of Resistance: Anarchism, Geography, and the Spirit of Revolt, London: Rowman & Littlefield, 2016. ISBN: 9781783486663 (cloth);
Marcelo Lopes de Souza, Richard J. White and Simon Springer (eds), Theories of Resistance: Anarchism, Geography, and the Spirit of Revolt, London: Rowman & Littlefield, 2016. ISBN: 9781783486663 (cloth);
MEXICO. Part 1: The Making of the Modern State
 MEXICO Part 1: The Making of the Modern State Why Study Mexico? History of Revolution, One-Party Dominance, Authoritarianism But has ended one-party rule, democratized, and is now considered a newly industrializing
MEXICO Part 1: The Making of the Modern State Why Study Mexico? History of Revolution, One-Party Dominance, Authoritarianism But has ended one-party rule, democratized, and is now considered a newly industrializing
John Rawls, Socialist?
 John Rawls, Socialist? BY ED QUISH John Rawls is remembered as one of the twentieth century s preeminent liberal philosophers. But by the end of his life, he was sharply critical of capitalism. Review
John Rawls, Socialist? BY ED QUISH John Rawls is remembered as one of the twentieth century s preeminent liberal philosophers. But by the end of his life, he was sharply critical of capitalism. Review
Lecture Outline, The French Revolution,
 Lecture Outline, The French Revolution, 1789-1799 A) Causes growth of "liberal" public opinion the spread of Enlightenment ideas re. rights, liberty, limited state power, need for rational administrative
Lecture Outline, The French Revolution, 1789-1799 A) Causes growth of "liberal" public opinion the spread of Enlightenment ideas re. rights, liberty, limited state power, need for rational administrative
Available through a partnership with
 The African e-journals Project has digitized full text of articles of eleven social science and humanities journals. This item is from the digital archive maintained by Michigan State University Library.
The African e-journals Project has digitized full text of articles of eleven social science and humanities journals. This item is from the digital archive maintained by Michigan State University Library.
I. Normative foundations
 Sociology 621 Week 2 September 8, 2014 The Overall Agenda Four tasks of any emancipatory theory: (1) moral foundations for evaluating existing social structures and institutions; (2) diagnosis and critique
Sociology 621 Week 2 September 8, 2014 The Overall Agenda Four tasks of any emancipatory theory: (1) moral foundations for evaluating existing social structures and institutions; (2) diagnosis and critique
long term goal for the Chinese people to achieve, which involves all round construction of social development. It includes the Five in One overall lay
 SOCIOLOGICAL STUDIES (Bimonthly) 2017 6 Vol. 32 November, 2017 MARXIST SOCIOLOGY Be Open to Be Scientific: Engels Thought on Socialism and Its Social Context He Rong 1 Abstract: Socialism from the very
SOCIOLOGICAL STUDIES (Bimonthly) 2017 6 Vol. 32 November, 2017 MARXIST SOCIOLOGY Be Open to Be Scientific: Engels Thought on Socialism and Its Social Context He Rong 1 Abstract: Socialism from the very
3. Which region had not yet industrialized in any significant way by the end of the nineteenth century? a. b) Japan Incorrect. The answer is c. By c.
 1. Although social inequality was common throughout Latin America in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, a nationwide revolution only broke out in which country? a. b) Guatemala Incorrect.
1. Although social inequality was common throughout Latin America in the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries, a nationwide revolution only broke out in which country? a. b) Guatemala Incorrect.
Memory of Salvador Allende Celebrated in Toronto. With Salvador Allende in our Memory, We Stand with the Honduran People
 Memory of Salvador Allende Celebrated in Toronto On September 11, the Salvador Allende Festival opened a two-week-long commemoration of the thirty-sixth anniversary of the military coup in Chile. The activities
Memory of Salvador Allende Celebrated in Toronto On September 11, the Salvador Allende Festival opened a two-week-long commemoration of the thirty-sixth anniversary of the military coup in Chile. The activities
Chapter 36: Nationalism and Political Identities in Asia, Africa, and Latin America Due: Thursday, April 2, 2015
 Chapter 36: Nationalism and Political Identities in Asia, Africa, and Latin America Due: Thursday, April 2, 2015 Overview During the 1920s and 1930s, after the Great War and during the Great Depression,
Chapter 36: Nationalism and Political Identities in Asia, Africa, and Latin America Due: Thursday, April 2, 2015 Overview During the 1920s and 1930s, after the Great War and during the Great Depression,
DRAWING TOGETHER A SOCIOLOGY OF LAW IN AUSTRALIA: LAW, CAPITALISM AND DEMOCRACY
 84 Australian Journal of Law & Society Vol. 2 No. 2, 1985 DRAWING TOGETHER A SOCIOLOGY OF LAW IN AUSTRALIA: LAW, CAPITALISM AND DEMOCRACY by Pat O Malley Sydney : Allen & Unwin, 1983 viii +204 pp $11.95
84 Australian Journal of Law & Society Vol. 2 No. 2, 1985 DRAWING TOGETHER A SOCIOLOGY OF LAW IN AUSTRALIA: LAW, CAPITALISM AND DEMOCRACY by Pat O Malley Sydney : Allen & Unwin, 1983 viii +204 pp $11.95
Why the United Socialist Party of Venezuela (PSUV) Won the Election. James Petras
 Why the United Socialist Party of Venezuela (PSUV) Won the Election James Petras Introduction Every major newspaper, television channel and US government official has spent the past two years claiming
Why the United Socialist Party of Venezuela (PSUV) Won the Election James Petras Introduction Every major newspaper, television channel and US government official has spent the past two years claiming
The Politics of Emotional Confrontation in New Democracies: The Impact of Economic
 Paper prepared for presentation at the panel A Return of Class Conflict? Political Polarization among Party Leaders and Followers in the Wake of the Sovereign Debt Crisis The 24 th IPSA Congress Poznan,
Paper prepared for presentation at the panel A Return of Class Conflict? Political Polarization among Party Leaders and Followers in the Wake of the Sovereign Debt Crisis The 24 th IPSA Congress Poznan,
A-Level POLITICS PAPER 3
 A-Level POLITICS PAPER 3 Political ideas Mark scheme Version 1.0 Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of subject teachers.
A-Level POLITICS PAPER 3 Political ideas Mark scheme Version 1.0 Mark schemes are prepared by the Lead Assessment Writer and considered, together with the relevant questions, by a panel of subject teachers.
Prof. Ljupco Kevereski, PhD. Faculty of Education, Bitola UDK: ISBN , 16 (2011), p Original scientific paper
 Prof. Ljupco Kevereski, PhD. Faculty of Education, Bitola UDK: 371.95 ISBN 978-86-7372-131-6, 16 (2011), p.323-328 Original scientific paper GLOBALIZATION-ADVANTAGE OR DISADVANTAGE FOR THE GIFTED Abstract:
Prof. Ljupco Kevereski, PhD. Faculty of Education, Bitola UDK: 371.95 ISBN 978-86-7372-131-6, 16 (2011), p.323-328 Original scientific paper GLOBALIZATION-ADVANTAGE OR DISADVANTAGE FOR THE GIFTED Abstract:
President Trump s Losing Strategy: Embracing Brazil. And Confronting China
 President Trump s Losing Strategy: Embracing Brazil And Confronting China Introduction The US embraces a regime doomed to failure and threatens the world s most dynamic economy. President Trump has lauded
President Trump s Losing Strategy: Embracing Brazil And Confronting China Introduction The US embraces a regime doomed to failure and threatens the world s most dynamic economy. President Trump has lauded
Notes from discussion in Erik Olin Wright Lecture #2: Diagnosis & Critique Middle East Technical University Tuesday, November 13, 2007
 Notes from discussion in Erik Olin Wright Lecture #2: Diagnosis & Critique Middle East Technical University Tuesday, November 13, 2007 Question: In your conception of social justice, does exploitation
Notes from discussion in Erik Olin Wright Lecture #2: Diagnosis & Critique Middle East Technical University Tuesday, November 13, 2007 Question: In your conception of social justice, does exploitation
BOOK REVIEW: Human Rights in Latin America A Politics of Terror and Hope
 Volume 4, Issue 2 December 2014 Special Issue Senior Overview BOOK REVIEW: Human Rights in Latin America A Politics of Terror and Hope Javier Cardenas, Webster University Saint Louis Latin America has
Volume 4, Issue 2 December 2014 Special Issue Senior Overview BOOK REVIEW: Human Rights in Latin America A Politics of Terror and Hope Javier Cardenas, Webster University Saint Louis Latin America has
The Latin American Wars of Independence were the revolutions that took place during the late 18th and early 19th centuries and resulted in the
 The Latin American Wars of Independence were the revolutions that took place during the late 18th and early 19th centuries and resulted in the creation of a number of independent countries in Latin America.
The Latin American Wars of Independence were the revolutions that took place during the late 18th and early 19th centuries and resulted in the creation of a number of independent countries in Latin America.
CHANTAL MOUFFE GLOSSARY
 CHANTAL MOUFFE GLOSSARY This is intended to introduce some key concepts and definitions belonging to Mouffe s work starting with her categories of the political and politics, antagonism and agonism, and
CHANTAL MOUFFE GLOSSARY This is intended to introduce some key concepts and definitions belonging to Mouffe s work starting with her categories of the political and politics, antagonism and agonism, and
Political Risk Analysis -I- Michel Henry Bouchet
 SKEMA BUSINESS SCHOOL Political Risk Analysis -I- Michel Henry Bouchet COUNTRY RISK AND POLITICAL RISK ASSESSMENT A reminder: Sovereign Risk is the possibility that a foreign country may be unable or unwilling
SKEMA BUSINESS SCHOOL Political Risk Analysis -I- Michel Henry Bouchet COUNTRY RISK AND POLITICAL RISK ASSESSMENT A reminder: Sovereign Risk is the possibility that a foreign country may be unable or unwilling
