Congress. J. Alexander Branham Fall 2016
|
|
|
- Jayson Murphy
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Congress J. Alexander Branham Fall 2016
2 Representation
3 Who elects representatives? Constituency the people in the district that an MC represents 1
4 Principal - Agent Principal constituency 2
5 Principal - Agent Principal constituency Agent elected representative 2
6 Representational styles Delegate represents preferences of the constituency 3
7 Representational styles Delegate represents preferences of the constituency Trustee represents based on what the MC thinks is best 3
8 Descriptive representation House Senate US population Age Women 20% 20% 50% Black 10% 2% 12% Hispanic 8% 4% 16% LGBT 1.3% 1%???? 1 1 Probably somewhere between 1 and 10% 4
9 House and senate - differences Bicameral legislature 5
10 House and senate - differences Bicameral legislature House is closer to the people 5
11 House and senate - differences Bicameral legislature House is closer to the people Money bills in House 5
12 House and senate - differences Bicameral legislature House is closer to the people Money bills in House 435 members, of House, 100 in Senate 5
13 House and Senate: differences House Senate Minimum age 25 years 30 years Length of citizenship 7 years 9 years Term length 2 years 6 years (rotates) Represents how many? ~700,000 today max: CA 39 million ~30,000 in 1789 min: WY 500,000 6
14 House and senate - differences 7
15 House and senate - differences 7
16 House and senate - differences House of Representatives 7
17 House and senate - differences House of Representatives Organized 7
18 House and senate - differences House of Representatives Organized Centralized 7
19 House and senate - differences House of Representatives Organized Centralized Strong leadership 7
20 House and senate - differences House of Representatives Organized Centralized Strong leadership Members specialized 7
21 House and senate - differences House of Representatives Organized Centralized Strong leadership Members specialized 7
22 House and senate - differences House of Representatives Organized Centralized Strong leadership Members specialized Senate 7
23 House and senate - differences House of Representatives Organized Centralized Strong leadership Members specialized Senate Senate more deliberative (historically) 7
24 House and senate - differences House of Representatives Organized Centralized Strong leadership Members specialized Senate Senate more deliberative (historically) Leadership weaker 7
25 House and senate - differences House of Representatives Organized Centralized Strong leadership Members specialized Senate Senate more deliberative (historically) Leadership weaker Less specialization 7
26 The electoral system Who runs? 8
27 The electoral system Who runs? Don t really know. The ambitious? 8
28 The electoral system Who runs? Don t really know. The ambitious? Incumbency - provides an advantage through 8
29 The electoral system Who runs? Don t really know. The ambitious? Incumbency - provides an advantage through Casework - constituency services 8
30 The electoral system Who runs? Don t really know. The ambitious? Incumbency - provides an advantage through Casework - constituency services Patronage - pork-barrel legislation 8
31 The electoral system Who runs? Don t really know. The ambitious? Incumbency - provides an advantage through Casework - constituency services Patronage - pork-barrel legislation Franking privilege 8
32 The electoral system House districts redrawn every 10 years 9
33 The electoral system House districts redrawn every 10 years House fixed at 435 members since 1929 law 9
34 The electoral system House districts redrawn every 10 years House fixed at 435 members since 1929 law West and South generally gain seats, NE and Midwest generally lose 9
35 The electoral system House districts redrawn every 10 years House fixed at 435 members since 1929 law West and South generally gain seats, NE and Midwest generally lose TX gained 4 seats post
36 The electoral system Gerrymandering - drawing districts to (dis)favor a party or incumbents 2 Supreme Court later orders TX to redraw lines as the plan violated rights of Latino voters 10
37 The electoral system Gerrymandering - drawing districts to (dis)favor a party or incumbents 2003: TX Republicans redraw districts 2 Supreme Court later orders TX to redraw lines as the plan violated rights of Latino voters 10
38 The electoral system Gerrymandering - drawing districts to (dis)favor a party or incumbents 2003: TX Republicans redraw districts Democrats fled to Oklahoma to delay vote 2 Supreme Court later orders TX to redraw lines as the plan violated rights of Latino voters 10
39 The electoral system Gerrymandering - drawing districts to (dis)favor a party or incumbents 2003: TX Republicans redraw districts Democrats fled to Oklahoma to delay vote 2004: Republicans gain five seats, defeating 4 Democratic incumbents 2 2 Supreme Court later orders TX to redraw lines as the plan violated rights of Latino voters 10
40 What kinds of bills pass Congress?
41 How does Congress decide? Constituency 11
42 How does Congress decide? Constituency Interest groups 11
43 How does Congress decide? Constituency Interest groups Party discipline 11
44 How does Congress decide? Constituency Interest groups Party discipline Committee assignments 11
45 How does Congress decide? Constituency Interest groups Party discipline Committee assignments Access to the floor 11
46 How does Congress decide? Constituency Interest groups Party discipline Committee assignments Access to the floor Whips 11
47 How does Congress decide? Constituency Interest groups Party discipline Committee assignments Access to the floor Whips Logrolling 11
48 How does Congress decide? Constituency Interest groups Party discipline Committee assignments Access to the floor Whips Logrolling President 11
49 Increased polarization - House 12
50 Increased polarization - Senate 13
51 Increased polarization 14
52 Congressional organization
53 Leadership in the House Party caucus/conference at the beginning of each Congressional session to select nomination for Speaker 15
54 Leadership in the House Party caucus/conference at the beginning of each Congressional session to select nomination for Speaker Speaker of the House chosen at the beginning of each Congress 15
55 Leadership in the House Party caucus/conference at the beginning of each Congressional session to select nomination for Speaker Speaker of the House chosen at the beginning of each Congress Presides over House meetings 15
56 Leadership in the House Party caucus/conference at the beginning of each Congressional session to select nomination for Speaker Speaker of the House chosen at the beginning of each Congress Presides over House meetings Most important leader of House and party 15
57 Leadership in the House Party caucus/conference at the beginning of each Congressional session to select nomination for Speaker Speaker of the House chosen at the beginning of each Congress Presides over House meetings Most important leader of House and party Majority leader, minority leader, whips 15
58 Leadership in the House and Senate - current Republicans have held the House since
59 Leadership in the House and Senate - current Republicans have held the House since 2010 Republicans have held the Senate since
60 Leadership in the House and Senate - current Republicans have held the House since 2010 Republicans have held the Senate since
61 Leadership in the House and Senate - current Republicans have held the House since 2010 Republicans have held the Senate since
62 Leadership in the House and Senate - current Republicans have held the House since 2010 Republicans have held the Senate since 2014 Republicans 16
63 Leadership in the House and Senate - current Republicans have held the House since 2010 Republicans have held the Senate since 2014 Republicans Speaker: Paul Ryan (WI) 16
64 Leadership in the House and Senate - current Republicans have held the House since 2010 Republicans have held the Senate since 2014 Republicans Speaker: Paul Ryan (WI) Majority leader: 16
65 Leadership in the House and Senate - current Republicans have held the House since 2010 Republicans have held the Senate since 2014 Republicans Speaker: Paul Ryan (WI) Majority leader: House: Kevin McCarthy (CA) 16
66 Leadership in the House and Senate - current Republicans have held the House since 2010 Republicans have held the Senate since 2014 Republicans Speaker: Paul Ryan (WI) Majority leader: House: Kevin McCarthy (CA) Senate: Mitch McConnell (KY) 16
67 Leadership in the House and Senate - current Republicans have held the House since 2010 Republicans have held the Senate since 2014 Republicans Speaker: Paul Ryan (WI) Majority leader: House: Kevin McCarthy (CA) Senate: Mitch McConnell (KY) 16
68 Leadership in the House and Senate - current Republicans have held the House since 2010 Republicans have held the Senate since 2014 Republicans Speaker: Paul Ryan (WI) Majority leader: House: Kevin McCarthy (CA) Senate: Mitch McConnell (KY) Democrats 16
69 Leadership in the House and Senate - current Republicans have held the House since 2010 Republicans have held the Senate since 2014 Republicans Speaker: Paul Ryan (WI) Majority leader: House: Kevin McCarthy (CA) Senate: Mitch McConnell (KY) Democrats Minority leader: 16
70 Leadership in the House and Senate - current Republicans have held the House since 2010 Republicans have held the Senate since 2014 Republicans Speaker: Paul Ryan (WI) Majority leader: House: Kevin McCarthy (CA) Senate: Mitch McConnell (KY) Democrats Minority leader: House: Nancy Pelosi (CA) 16
71 Leadership in the House and Senate - current Republicans have held the House since 2010 Republicans have held the Senate since 2014 Republicans Speaker: Paul Ryan (WI) Majority leader: House: Kevin McCarthy (CA) Senate: Mitch McConnell (KY) Democrats Minority leader: House: Nancy Pelosi (CA) Senate: Harry Reid (NV) 16
72 The committee system Congress has to deal with a huge number of issues, so created the committee system to allow for specialization 17
73 The committee system Congress has to deal with a huge number of issues, so created the committee system to allow for specialization Standing committee - permanent committee with formal rules 17
74 Standing committees - House 18
75 Standing committees - House 18
76 Standing committees - House Agriculture 18
77 Standing committees - House Agriculture Appropriations 18
78 Standing committees - House Agriculture Appropriations Armed services 18
79 Standing committees - House Agriculture Appropriations Armed services Budget 18
80 Standing committees - House Agriculture Appropriations Armed services Budget Education & workforce 18
81 Standing committees - House Agriculture Appropriations Armed services Budget Education & workforce Energy & commerce 18
82 Standing committees - House Agriculture Appropriations Armed services Budget Education & workforce Energy & commerce Ethics 18
83 Standing committees - House Agriculture Appropriations Armed services Budget Education & workforce Energy & commerce Ethics Financial services 18
84 Standing committees - House Agriculture Appropriations Armed services Budget Education & workforce Energy & commerce Ethics Financial services Foreign affairs 18
85 Standing committees - House Agriculture Appropriations Armed services Budget Education & workforce Energy & commerce Ethics Financial services Foreign affairs Homeland security 18
86 Standing committees - House Agriculture Appropriations Armed services Budget Education & workforce Energy & commerce Ethics Financial services Foreign affairs Homeland security 18
87 Standing committees - House Agriculture Appropriations Armed services Budget Education & workforce Energy & commerce Ethics Financial services Foreign affairs Homeland security House administration 18
88 Standing committees - House Agriculture Appropriations Armed services Budget Education & workforce Energy & commerce Ethics Financial services Foreign affairs Homeland security House administration Judiciary 18
89 Standing committees - House Agriculture Appropriations Armed services Budget Education & workforce Energy & commerce Ethics Financial services Foreign affairs Homeland security House administration Judiciary Natural resources 18
90 Standing committees - House Agriculture Appropriations Armed services Budget Education & workforce Energy & commerce Ethics Financial services Foreign affairs Homeland security House administration Judiciary Natural resources Oversight & gvt reform 18
91 Standing committees - House Agriculture Appropriations Armed services Budget Education & workforce Energy & commerce Ethics Financial services Foreign affairs Homeland security House administration Judiciary Natural resources Oversight & gvt reform Rules 18
92 Standing committees - House Agriculture Appropriations Armed services Budget Education & workforce Energy & commerce Ethics Financial services Foreign affairs Homeland security House administration Judiciary Natural resources Oversight & gvt reform Rules Science, space, & tech 18
93 Standing committees - House Agriculture Appropriations Armed services Budget Education & workforce Energy & commerce Ethics Financial services Foreign affairs Homeland security House administration Judiciary Natural resources Oversight & gvt reform Rules Science, space, & tech Small business 18
94 Standing committees - House Agriculture Appropriations Armed services Budget Education & workforce Energy & commerce Ethics Financial services Foreign affairs Homeland security House administration Judiciary Natural resources Oversight & gvt reform Rules Science, space, & tech Small business Transport & Infrastructure 18
95 Standing committees - House Agriculture Appropriations Armed services Budget Education & workforce Energy & commerce Ethics Financial services Foreign affairs Homeland security House administration Judiciary Natural resources Oversight & gvt reform Rules Science, space, & tech Small business Transport & Infrastructure Veteran s affairs 18
96 Standing committees - House Agriculture Appropriations Armed services Budget Education & workforce Energy & commerce Ethics Financial services Foreign affairs Homeland security House administration Judiciary Natural resources Oversight & gvt reform Rules Science, space, & tech Small business Transport & Infrastructure Veteran s affairs Ways & Means 18
97 Standing committees - Senate 19
98 Standing committees - Senate 19
99 Standing committees - Senate Agriculture, nutrition, & forestry 19
100 Standing committees - Senate Agriculture, nutrition, & forestry Appropriations 19
101 Standing committees - Senate Agriculture, nutrition, & forestry Appropriations Armed services 19
102 Standing committees - Senate Agriculture, nutrition, & forestry Appropriations Armed services Banking, housing, & urban affairs 19
103 Standing committees - Senate Agriculture, nutrition, & forestry Appropriations Armed services Banking, housing, & urban affairs Budget 19
104 Standing committees - Senate Agriculture, nutrition, & forestry Appropriations Armed services Banking, housing, & urban affairs Budget Commerce, science, & transportation 19
105 Standing committees - Senate Agriculture, nutrition, & forestry Appropriations Armed services Banking, housing, & urban affairs Budget Commerce, science, & transportation Energy & natural resources 19
106 Standing committees - Senate Agriculture, nutrition, & forestry Appropriations Armed services Banking, housing, & urban affairs Budget Commerce, science, & transportation Energy & natural resources Environment & public works 19
107 Standing committees - Senate Agriculture, nutrition, & forestry Appropriations Armed services Banking, housing, & urban affairs Budget Commerce, science, & transportation Energy & natural resources Environment & public works 19
108 Standing committees - Senate Agriculture, nutrition, & forestry Appropriations Armed services Banking, housing, & urban affairs Budget Commerce, science, & transportation Energy & natural resources Environment & public works Finance 19
109 Standing committees - Senate Agriculture, nutrition, & forestry Appropriations Armed services Banking, housing, & urban affairs Budget Commerce, science, & transportation Energy & natural resources Environment & public works Finance Foreign relations 19
110 Standing committees - Senate Agriculture, nutrition, & forestry Appropriations Armed services Banking, housing, & urban affairs Budget Commerce, science, & transportation Energy & natural resources Environment & public works Finance Foreign relations Health, education, labor, & pensions 19
111 Standing committees - Senate Agriculture, nutrition, & forestry Appropriations Armed services Banking, housing, & urban affairs Budget Commerce, science, & transportation Energy & natural resources Environment & public works Finance Foreign relations Health, education, labor, & pensions Homeland security & governmental affairs 19
112 Standing committees - Senate Agriculture, nutrition, & forestry Appropriations Armed services Banking, housing, & urban affairs Budget Commerce, science, & transportation Energy & natural resources Environment & public works Finance Foreign relations Health, education, labor, & pensions Homeland security & governmental affairs Judiciary 19
113 Standing committees - Senate Agriculture, nutrition, & forestry Appropriations Armed services Banking, housing, & urban affairs Budget Commerce, science, & transportation Energy & natural resources Environment & public works Finance Foreign relations Health, education, labor, & pensions Homeland security & governmental affairs Judiciary Rules & administration 19
114 Standing committees - Senate Agriculture, nutrition, & forestry Appropriations Armed services Banking, housing, & urban affairs Budget Commerce, science, & transportation Energy & natural resources Environment & public works Finance Foreign relations Health, education, labor, & pensions Homeland security & governmental affairs Judiciary Rules & administration Small business & entrepreneurship 19
115 Standing committees - Senate Agriculture, nutrition, & forestry Appropriations Armed services Banking, housing, & urban affairs Budget Commerce, science, & transportation Energy & natural resources Environment & public works Finance Foreign relations Health, education, labor, & pensions Homeland security & governmental affairs Judiciary Rules & administration Small business & entrepreneurship Veterans affairs 19
116 The committee system Jurisdiction is important in determining which committee has power over an issue 20
117 The committee system Jurisdiction is important in determining which committee has power over an issue Does tobacco regulation go to the health committee or the agriculture committee? 20
118 The committee system Jurisdiction is important in determining which committee has power over an issue Does tobacco regulation go to the health committee or the agriculture committee? Gatekeepers - decides if a bill will make it out of committee 20
119 The committee system Jurisdiction is important in determining which committee has power over an issue Does tobacco regulation go to the health committee or the agriculture committee? Gatekeepers - decides if a bill will make it out of committee Can also amend 20
120 The committee system Jurisdiction is important in determining which committee has power over an issue Does tobacco regulation go to the health committee or the agriculture committee? Gatekeepers - decides if a bill will make it out of committee Can also amend Responsible for oversight 20
121 The committee system Jurisdiction is important in determining which committee has power over an issue Does tobacco regulation go to the health committee or the agriculture committee? Gatekeepers - decides if a bill will make it out of committee Can also amend Responsible for oversight Subcommittees 20
122 Committee chairs Decides on a committees agenda 21
123 Committee chairs Decides on a committees agenda Usually (though not always) the senior member of the majority party 21
124 How do committees decide? By vote! 22
125 How do committees decide? By vote! Median voter examples 22
126 How a bill becomes a law
127 Schoolhouse Rock a little simplified 23
128 Regular procedure Bill received by Speaker/president of Senate 24
129 Regular procedure Bill received by Speaker/president of Senate Assigned to a committee, and/or subcommittee 24
130 Regular procedure Bill received by Speaker/president of Senate Assigned to a committee, and/or subcommittee (Sub)committee markup 24
131 Regular procedure Bill received by Speaker/president of Senate Assigned to a committee, and/or subcommittee (Sub)committee markup (House) Rules committee 24
132 Regular procedure Bill received by Speaker/president of Senate Assigned to a committee, and/or subcommittee (Sub)committee markup (House) Rules committee closed rule versus open rule 24
133 Regular procedure Bill received by Speaker/president of Senate Assigned to a committee, and/or subcommittee (Sub)committee markup (House) Rules committee closed rule versus open rule Floor debate 24
134 Regular procedure Bill received by Speaker/president of Senate Assigned to a committee, and/or subcommittee (Sub)committee markup (House) Rules committee closed rule versus open rule Floor debate Senate: filibuster, cloture, and 60-vote Senate 24
135 Regular procedure Bill received by Speaker/president of Senate Assigned to a committee, and/or subcommittee (Sub)committee markup (House) Rules committee closed rule versus open rule Floor debate Senate: filibuster, cloture, and 60-vote Senate Senate: holds and amendments 24
136 Regular procedure Bill received by Speaker/president of Senate Assigned to a committee, and/or subcommittee (Sub)committee markup (House) Rules committee closed rule versus open rule Floor debate Senate: filibuster, cloture, and 60-vote Senate Senate: holds and amendments Floor vote (possible conference committee) 24
137 Regular procedure Bill received by Speaker/president of Senate Assigned to a committee, and/or subcommittee (Sub)committee markup (House) Rules committee closed rule versus open rule Floor debate Senate: filibuster, cloture, and 60-vote Senate Senate: holds and amendments Floor vote (possible conference committee) Presidential action (sign or veto) 24
138 Regular procedure Bill received by Speaker/president of Senate Assigned to a committee, and/or subcommittee (Sub)committee markup (House) Rules committee closed rule versus open rule Floor debate Senate: filibuster, cloture, and 60-vote Senate Senate: holds and amendments Floor vote (possible conference committee) Presidential action (sign or veto) If veto, return for another vote, two-thirds of both houses needed to override 24
139 Unorthodox procedure 25
140 Unorthodox procedure 25
141 Unorthodox procedure Example (Obamacare) 25
142 Unorthodox procedure Example (Obamacare) House passes 25
143 Unorthodox procedure Example (Obamacare) House passes Scott Walker 25
144 Unorthodox procedure Example (Obamacare) House passes Scott Walker House passes Senate (as amended) 25
145 Unorthodox procedure Example (Obamacare) House passes Scott Walker House passes Senate (as amended) Reconciliation 25
146 Unorthodox procedure Example (Obamacare) House passes Scott Walker House passes Senate (as amended) Reconciliation 25
147 Unorthodox procedure Example (Obamacare) Example (Omnibus bills) House passes Scott Walker House passes Senate (as amended) Reconciliation 25
148 Unorthodox procedure Example (Obamacare) House passes Scott Walker House passes Senate (as amended) Reconciliation Example (Omnibus bills) Usually pass 13 separate appropriations 25
149 Unorthodox procedure Example (Obamacare) House passes Scott Walker House passes Senate (as amended) Reconciliation Example (Omnibus bills) Usually pass 13 separate appropriations More common to package them all together as one omnibus bill 25
150 Unorthodox procedure Example (Obamacare) House passes Scott Walker House passes Senate (as amended) Reconciliation Example (Omnibus bills) Usually pass 13 separate appropriations More common to package them all together as one omnibus bill Omnibus bill not great, but gvt shutdown otherwise 25
Basic Government Processes. Heather Sachs, National Down Syndrome Congress Chris Masey, Coalition for Texans with Disabilities
 Basic Government Processes Heather Sachs, National Down Syndrome Congress Chris Masey, Coalition for Texans with Disabilities Branches of government The legislative branch Leadership & Committees How a
Basic Government Processes Heather Sachs, National Down Syndrome Congress Chris Masey, Coalition for Texans with Disabilities Branches of government The legislative branch Leadership & Committees How a
How Congress Works Part I
 How Congress Works Part I House-Senate Differences House 435 members; 2 yr. terms 25 Years Old Low turnover Decisions hard to challenge Scheduling/rules controlled by majority party (controls time of debate,
How Congress Works Part I House-Senate Differences House 435 members; 2 yr. terms 25 Years Old Low turnover Decisions hard to challenge Scheduling/rules controlled by majority party (controls time of debate,
Objectives. ! Compare the Constitutional requirements of the House and Senate.
 Congress Objectives! Compare the Constitutional requirements of the House and Senate.! List the roles of Congressmen.! Describe the compensation of Congressmen. Background! The Constitution created a bicameral
Congress Objectives! Compare the Constitutional requirements of the House and Senate.! List the roles of Congressmen.! Describe the compensation of Congressmen. Background! The Constitution created a bicameral
Unit 3 Learning Objectives
 AP AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Unit Three Part 3 Political Parties, Congress, and Special Interests 2 1 Unit 3 Learning Objectives The Structure and Powers of Congress 3.5 Differentiate the powers of Congress,
AP AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Unit Three Part 3 Political Parties, Congress, and Special Interests 2 1 Unit 3 Learning Objectives The Structure and Powers of Congress 3.5 Differentiate the powers of Congress,
Congress: Structure & Powers
 Congress: Structure & Powers Role of Political Parties In each chamber of Congress, the party breakdown determines the leadership positions Chairpersons of committees ~ majority party always leads the
Congress: Structure & Powers Role of Political Parties In each chamber of Congress, the party breakdown determines the leadership positions Chairpersons of committees ~ majority party always leads the
CIS Political Science Chapter 11. Legislative Branch: Congress. Mr. Makela. St. Clair High School. University of Minnesota
 CIS Political Science Chapter 11 Legislative Branch: Congress Mr. Makela St. Clair High School University of Minnesota The Origin and Powers of Congress Bicameral problems w/ Representation (Great Compromise)
CIS Political Science Chapter 11 Legislative Branch: Congress Mr. Makela St. Clair High School University of Minnesota The Origin and Powers of Congress Bicameral problems w/ Representation (Great Compromise)
Chapter 12: Congress. American Democracy Now, 4/e
 Chapter 12: Congress American Democracy Now, 4/e Congress Where Do You Stand? How would you rate the overall performance of Congress today? a. Favorably b. Unfavorably c. Neither favorably nor unfavorably
Chapter 12: Congress American Democracy Now, 4/e Congress Where Do You Stand? How would you rate the overall performance of Congress today? a. Favorably b. Unfavorably c. Neither favorably nor unfavorably
Name: Date: 1. Like most other national legislatures, Congress is (comprising two houses ). A) bicameral B) bilateral C) binary D) bicentenary
 Name: Date: 1. Like most other national legislatures, Congress is (comprising two houses ). A) bicameral B) bilateral C) binary D) bicentenary 2. A House member represents a district of about people. A)
Name: Date: 1. Like most other national legislatures, Congress is (comprising two houses ). A) bicameral B) bilateral C) binary D) bicentenary 2. A House member represents a district of about people. A)
Functions of Congress
 Functions of Congress Make laws Represent people Perform oversight Help constituents Educate the public Powers of Congress 1 Congressional Powers Legislative Powers Power to Tax Power to Borrow Regulate
Functions of Congress Make laws Represent people Perform oversight Help constituents Educate the public Powers of Congress 1 Congressional Powers Legislative Powers Power to Tax Power to Borrow Regulate
Congressional Elections
 Name: Government In America, Chapter 12 Big Idea Questions Guided Notes The Representatives and Senators The Members: in total - 100 Senators and 435 members of the House Requirements to be a member of
Name: Government In America, Chapter 12 Big Idea Questions Guided Notes The Representatives and Senators The Members: in total - 100 Senators and 435 members of the House Requirements to be a member of
Chapter 13 Congress. Congress. Know the terms/names (especially with FRQs) House of Representatives. Senate
 Chapter 13 Congress Know the terms/names (especially with FRQs) Congress House of Representatives Senate Almost always referred to as Congress A term of Congress is 2 years Term begins on January 3 rd
Chapter 13 Congress Know the terms/names (especially with FRQs) Congress House of Representatives Senate Almost always referred to as Congress A term of Congress is 2 years Term begins on January 3 rd
CONGRESSIONAL ELECTIONS
 CONGRESS CONGRESSIONAL ELECTIONS Who Wins Elections? Incumbent: Those already holding office. Figure 12.1 CONGRESSIONAL ELECTIONS The Role of Party Identification Most members represent the majority party
CONGRESS CONGRESSIONAL ELECTIONS Who Wins Elections? Incumbent: Those already holding office. Figure 12.1 CONGRESSIONAL ELECTIONS The Role of Party Identification Most members represent the majority party
Congress. Congress, the Presidency, and the Legislative Process (a refresher lecture) Congress
 Congress, the Presidency, and the Legislative Process (a refresher lecture) Congress Congress Legislative supremacy Bicameralism Two different chambers House Senate Term: 2 6 Size: 435 100 District Size:
Congress, the Presidency, and the Legislative Process (a refresher lecture) Congress Congress Legislative supremacy Bicameralism Two different chambers House Senate Term: 2 6 Size: 435 100 District Size:
Article I: Legislative Branch
 Article I: Legislative Branch Jobs of Congress Legislate- make the laws Lay and collect taxes Pass appropriations- authorizes the government to spend money Oversight- investigate how money is spent, how
Article I: Legislative Branch Jobs of Congress Legislate- make the laws Lay and collect taxes Pass appropriations- authorizes the government to spend money Oversight- investigate how money is spent, how
Video: The Big Picture IA_1/polisci/presidency/Edwards_Ch11_Congress_Seg1_v 2.
 Congress 11 Video: The Big Picture 11 http://media.pearsoncmg.com/ph/hss/ssa_shared_med IA_1/polisci/presidency/Edwards_Ch11_Congress_Seg1_v 2.html Learning Objectives 11 11.1 11.2 Characterize the backgrounds
Congress 11 Video: The Big Picture 11 http://media.pearsoncmg.com/ph/hss/ssa_shared_med IA_1/polisci/presidency/Edwards_Ch11_Congress_Seg1_v 2.html Learning Objectives 11 11.1 11.2 Characterize the backgrounds
Congress. AP US Government Spring 2017
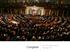 Congress AP US Government Spring 2017 Congressional Elections: House vs Senate Constituent: citizen who is represented by a member of Congress House is closer to constitutents House members come from individual
Congress AP US Government Spring 2017 Congressional Elections: House vs Senate Constituent: citizen who is represented by a member of Congress House is closer to constitutents House members come from individual
Exceptions to Symmetry. Congress: The Legislative Branch. In comparative perspective, Congress is unusual.
 Congress: The Legislative Branch In comparative perspective, Congress is unusual. Most legislatures, particularly in parliamentary systems, are relatively weak. Congress exhibits symmetric bicameralism:
Congress: The Legislative Branch In comparative perspective, Congress is unusual. Most legislatures, particularly in parliamentary systems, are relatively weak. Congress exhibits symmetric bicameralism:
How Congress Works Part 1:
 How Congress Works Part 1: Who s in Congress? Demographic Profile of Congress Age Groups Party Gender Ethnicity Source: http://www.congress.org/congressorg/directory/demographics.tt House-Senate Differences
How Congress Works Part 1: Who s in Congress? Demographic Profile of Congress Age Groups Party Gender Ethnicity Source: http://www.congress.org/congressorg/directory/demographics.tt House-Senate Differences
[ 4.1 ] National Legislature Overview
![[ 4.1 ] National Legislature Overview [ 4.1 ] National Legislature Overview](/thumbs/81/84208472.jpg) [ 4.1 ] National Legislature Overview [ 4.1 ] National Legislature Overview Key Terms bills, floor consideration oversight function term session convenes adjourns recess prorogue special session franking
[ 4.1 ] National Legislature Overview [ 4.1 ] National Legislature Overview Key Terms bills, floor consideration oversight function term session convenes adjourns recess prorogue special session franking
Chapter 12 Congress Guided Reading and Study Notes
 Chapter 12 Congress Guided Reading and Study Notes 1. What is the most important fact about congressional elections? Name Date Period 2. List (and describe) five advantages incumbents have over their opponents
Chapter 12 Congress Guided Reading and Study Notes 1. What is the most important fact about congressional elections? Name Date Period 2. List (and describe) five advantages incumbents have over their opponents
Two separate chambers in Congress (BICAMERAL)
 CONGRESS Origins of Congress Great Compromise Two separate chambers in Congress (BICAMERAL) Senate Each state receives two senators; 6 year terms Originally selected by state legislatures, but 17th amendment
CONGRESS Origins of Congress Great Compromise Two separate chambers in Congress (BICAMERAL) Senate Each state receives two senators; 6 year terms Originally selected by state legislatures, but 17th amendment
Congress. Chapter 13
 Congress Chapter 13 Introduction Congress is the first branch of the government It is also seen as the most broken and distrusted Surprisingly, incumbents still win re-election (more so in the House, less
Congress Chapter 13 Introduction Congress is the first branch of the government It is also seen as the most broken and distrusted Surprisingly, incumbents still win re-election (more so in the House, less
Chapter 6 Congress 9/28/2015. Roots of the U.S. Congress 6.1. Bicameral legislature. TABLE 6.1 What are the powers of Congress? 6.
 Chapter 6 Congress Roots of the U.S. Congress 6.1 Bicameral legislature House Representatives based on population Two-year term Senate Two from each state Six-year term TABLE 6.1 What are the powers of
Chapter 6 Congress Roots of the U.S. Congress 6.1 Bicameral legislature House Representatives based on population Two-year term Senate Two from each state Six-year term TABLE 6.1 What are the powers of
Unit V Test Congress and the President Practice Test
 Unit V Test Congress and the President Practice Test 1. The "revolving door" involves: (A) members of Congress who travel extensively between Washington D.C. and their home states (B) diplomats who engage
Unit V Test Congress and the President Practice Test 1. The "revolving door" involves: (A) members of Congress who travel extensively between Washington D.C. and their home states (B) diplomats who engage
Legislative Branch Unit Day Section Standard(s) Focus
 Day Section Standard(s) Focus 1 Congressional Membership LWBBAT understand a rough outline of Congress. LWBBAT describe the similarities and differences of the House and Senate. on historical background
Day Section Standard(s) Focus 1 Congressional Membership LWBBAT understand a rough outline of Congress. LWBBAT describe the similarities and differences of the House and Senate. on historical background
Chapter Ten: The Congress
 Chapter Ten: The Congress Learning Outcomes 1. Describe the various roles played by Congress and the constitutional basis of its powers. 2. Explain some of the differences between the House and the Senate
Chapter Ten: The Congress Learning Outcomes 1. Describe the various roles played by Congress and the constitutional basis of its powers. 2. Explain some of the differences between the House and the Senate
Ch. 4 The Congress. Ch. 4 The Congress. Ch. 4 The Congress. Ch. 4 The Congress. The National Legislature
 The National Legislature The National Legislature is known as Congress and is made up of two chambers the House of Representatives & the Term - The length of time elected officials serve in office before
The National Legislature The National Legislature is known as Congress and is made up of two chambers the House of Representatives & the Term - The length of time elected officials serve in office before
Chapter 11. Congress. What is Congress main job?
 Chapter 11 Congress What is Congress main job? The Constitution and the Legislative Branch of the Government o Article I describes structure of Congress n Bicameral legislature o Divided into two houses
Chapter 11 Congress What is Congress main job? The Constitution and the Legislative Branch of the Government o Article I describes structure of Congress n Bicameral legislature o Divided into two houses
The Congress 113th Congress (ISTOCKPHOTO)
 The Congress 113th Congress (ISTOCKPHOTO) Get it right!! Congress = House + Senate House Senate Total Number 435 100 representatives A. Congress by the numbers! Pop-based! Equal - 2 per state Elected Period
The Congress 113th Congress (ISTOCKPHOTO) Get it right!! Congress = House + Senate House Senate Total Number 435 100 representatives A. Congress by the numbers! Pop-based! Equal - 2 per state Elected Period
State Legislatures. State & Local Government. Ch. 7
 State Legislatures State & Local Government Ch. 7 Legislature in some states is the dominant branch of govt. Highlights State Legislatures have 4 clear functions: 1. Making laws 2. Represent their constituents
State Legislatures State & Local Government Ch. 7 Legislature in some states is the dominant branch of govt. Highlights State Legislatures have 4 clear functions: 1. Making laws 2. Represent their constituents
The Legislative Branch How Congress is Organized
 The Legislative Branch How Congress is Organized The First Branch of this Government The U.S. Congress The Legislative Branch of the U.S. Government Consists of 535 members in a two house ( bicameral )
The Legislative Branch How Congress is Organized The First Branch of this Government The U.S. Congress The Legislative Branch of the U.S. Government Consists of 535 members in a two house ( bicameral )
AP U.S. Government & Politics Unit 3: Institutions of National Government: The Congress
 AP U.S. Government & Politics 2017-18 Unit 3: Institutions of National Government: The Congress Textbook: Chapter 11; Congress: Balancing National Goals and Local Interests ; pp. 286-321 Web sites to use:
AP U.S. Government & Politics 2017-18 Unit 3: Institutions of National Government: The Congress Textbook: Chapter 11; Congress: Balancing National Goals and Local Interests ; pp. 286-321 Web sites to use:
AP GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS, STUDY GUIDE. Unit 7 - CONGRESS
 AP GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS, STUDY GUIDE Unit 7 - CONGRESS Study Guide - Congress AP US Government and Politics Reading / Resources: Presentation Reviews Herzog Ch.10 Quizzes: Targets 1-3 Targets 4-6 Target
AP GOVERNMENT AND POLITICS, STUDY GUIDE Unit 7 - CONGRESS Study Guide - Congress AP US Government and Politics Reading / Resources: Presentation Reviews Herzog Ch.10 Quizzes: Targets 1-3 Targets 4-6 Target
What do we think of Congress?
 What do we think of Congress? Discuss each quotation: What does it mean? (your interpretation) What does the author think of Congress? (bias) What does/can the quote tell us about how Congress works? Founders
What do we think of Congress? Discuss each quotation: What does it mean? (your interpretation) What does the author think of Congress? (bias) What does/can the quote tell us about how Congress works? Founders
4.3: ORGANIZATION & MEMBERSHIP OF CONGRESS. AP U. S. Government
 4.3: ORGANIZATION & MEMBERSHIP OF CONGRESS AP U. S. Government DEMOGRAPHICS OF THOSE IN 113 TH CONGRESS DEMOGRAPHICS Mostly male Well educated Middle and upper incomes Law is most common occupation Recently,
4.3: ORGANIZATION & MEMBERSHIP OF CONGRESS AP U. S. Government DEMOGRAPHICS OF THOSE IN 113 TH CONGRESS DEMOGRAPHICS Mostly male Well educated Middle and upper incomes Law is most common occupation Recently,
AP Govt. Day 53. Objectives: The Learner will examine and understand the institutions of national government: Congress
 Objectives: 4.00 - The Learner will examine and understand the institutions of national government: Congress 4.01 - Examine the Constitutional framework for this institution 4.02 - Explain the legislative
Objectives: 4.00 - The Learner will examine and understand the institutions of national government: Congress 4.01 - Examine the Constitutional framework for this institution 4.02 - Explain the legislative
Congress general info
 Congress Congress general info Founders believed Congress served their local constituents, but more importantly, the nation Article I-structure, powers, and operation Bicameral- House & Senate (reflected
Congress Congress general info Founders believed Congress served their local constituents, but more importantly, the nation Article I-structure, powers, and operation Bicameral- House & Senate (reflected
The Legislative Branch C H A P T E R S 2 A N D 7 E S S E N T I A L S O F A M E R I C A N G O V E R N M E N T R O O T S A N D R E F O R M
 The Legislative Branch C H A P T E R S 2 A N D 7 E S S E N T I A L S O F A M E R I C A N G O V E R N M E N T R O O T S A N D R E F O R M M S. CAMPBELL A P GOVERNMENT EDGREN HIGH SCHOOL Imagine for a moment
The Legislative Branch C H A P T E R S 2 A N D 7 E S S E N T I A L S O F A M E R I C A N G O V E R N M E N T R O O T S A N D R E F O R M M S. CAMPBELL A P GOVERNMENT EDGREN HIGH SCHOOL Imagine for a moment
Congress: Structure & Powers
 Congress: Structure & Powers Role of Political Parties In each chamber of Congress, the party breakdown determines the leadership positions Seating in the House & Senate done by political parties Committee
Congress: Structure & Powers Role of Political Parties In each chamber of Congress, the party breakdown determines the leadership positions Seating in the House & Senate done by political parties Committee
One useless man is a shame, two is a law firm, three or more is congress. -John Adams
 One useless man is a shame, two is a law firm, three or more is congress. -John Adams Legislate: turn public will into public policy (laws) Help their constituents deal with the federal bureaucracy (Veterans
One useless man is a shame, two is a law firm, three or more is congress. -John Adams Legislate: turn public will into public policy (laws) Help their constituents deal with the federal bureaucracy (Veterans
AP Government & Politics CH. 11 & 13 Unit Exam b. Joint d. pork barrel
 AP Government & Politics CH. 11 & 13 Unit Exam 1. committees exist in both the House and Senate, may be temporary or permanent, and usually have a focused responsibility. a. Conference d. Standing b. Joint
AP Government & Politics CH. 11 & 13 Unit Exam 1. committees exist in both the House and Senate, may be temporary or permanent, and usually have a focused responsibility. a. Conference d. Standing b. Joint
Unit 3 Learning Objectives Part 1 Political Parties
 AP AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Unit Three Political Parties, Congress, and Special Interests 2 1 Unit 3 Learning Objectives Part 1 Political Parties What are Political Parties? 3.1 Identify the functions and characteristics
AP AMERICAN GOVERNMENT Unit Three Political Parties, Congress, and Special Interests 2 1 Unit 3 Learning Objectives Part 1 Political Parties What are Political Parties? 3.1 Identify the functions and characteristics
(ISTOCKPHOTO) Exam 6B Notes
 (ISTOCKPHOTO) Exam 6B Notes Get it right!! Congress = House + Senate House Senate Total Number 435 100 representatives A. Congress by the numbers! Pop-based! Equal - 2 per state Elected Period 2 6 years
(ISTOCKPHOTO) Exam 6B Notes Get it right!! Congress = House + Senate House Senate Total Number 435 100 representatives A. Congress by the numbers! Pop-based! Equal - 2 per state Elected Period 2 6 years
Congress: Balancing National Goals and Local Interests. Chapter 11
 Congress: Balancing National Goals and Local Interests Chapter 11 Original intent Leading branch of government Parts of executive and judicial branches cannot exist without congressional approval Branch
Congress: Balancing National Goals and Local Interests Chapter 11 Original intent Leading branch of government Parts of executive and judicial branches cannot exist without congressional approval Branch
How Congress Is Organized
 SECTION How Congress Is Organized GUIDE TO READING Main Idea In Congress, members of each party select their own leaders and work mainly in committees to carry out their duties. Key Terms bicameral, census,
SECTION How Congress Is Organized GUIDE TO READING Main Idea In Congress, members of each party select their own leaders and work mainly in committees to carry out their duties. Key Terms bicameral, census,
Congress has three major functions: lawmaking, representation, and oversight.
 Unit 5: Congress A legislature is the law-making body of a government. The United States Congress is a bicameral legislature that is, one consisting of two chambers: the House of Representatives and the
Unit 5: Congress A legislature is the law-making body of a government. The United States Congress is a bicameral legislature that is, one consisting of two chambers: the House of Representatives and the
Unit 3: Structure and Functions of the Federal Government
 Unit 3: Structure and Functions of the Federal Government Three branches compose the basic structure of the federal government. Public policy is created through the making of laws, the execution of the
Unit 3: Structure and Functions of the Federal Government Three branches compose the basic structure of the federal government. Public policy is created through the making of laws, the execution of the
1. States must meet certain requirements in drawing district boundaries. Identify one of these requirements.
 Multiple Choice 1. States must meet certain requirements in drawing district boundaries. Identify one of these requirements. a. A person's vote in the largest district of a state must have only half the
Multiple Choice 1. States must meet certain requirements in drawing district boundaries. Identify one of these requirements. a. A person's vote in the largest district of a state must have only half the
Demographic Profile of the 111th Congress
 How Congress Works Who s in Congress? Demographic Profile of the 111th Congress Age Groups Party Gender Ethnicity Source: http://www.congress.org/congressorg/directory/demographics.tt House-Senate Differences
How Congress Works Who s in Congress? Demographic Profile of the 111th Congress Age Groups Party Gender Ethnicity Source: http://www.congress.org/congressorg/directory/demographics.tt House-Senate Differences
Political Science 10 American Politics: Congress
 Political Science 10 American Politics: Congress Loren Collingwood, Political Science May 27, 2014 1 / 23 Current Events: Jim Messina 2 / 23 Current Events: SCOTUS Raises Bar on low-iq Executions 3 / 23
Political Science 10 American Politics: Congress Loren Collingwood, Political Science May 27, 2014 1 / 23 Current Events: Jim Messina 2 / 23 Current Events: SCOTUS Raises Bar on low-iq Executions 3 / 23
THE LEGISLATIVE BRANCH
 2004 By Default! THE LEGISLATIVE BRANCH Mr. P s Class Yellow on the left, RED on the right Slide 1 2004 By Default! KEY QUESTION You have a great idea for a new bill. Describe the process, in detail, of
2004 By Default! THE LEGISLATIVE BRANCH Mr. P s Class Yellow on the left, RED on the right Slide 1 2004 By Default! KEY QUESTION You have a great idea for a new bill. Describe the process, in detail, of
Shelley Fuld Nasso Lindsay Houff
 Shelley Fuld Nasso Lindsay Houff Staging Your Impact Overview of Congress Advocate Perspective Congressional Staff Member Perspective The Meeting The Ask Practice & Make a Plan Role Play Exercise House
Shelley Fuld Nasso Lindsay Houff Staging Your Impact Overview of Congress Advocate Perspective Congressional Staff Member Perspective The Meeting The Ask Practice & Make a Plan Role Play Exercise House
Opener: Monday, April 11 th. The Almost Painless Guide to the Legislature Legislative Branch U.S. Government Structure in 5 Minutes
 Opener: Monday, April 11 th The Almost Painless Guide to the Legislature Legislative Branch U.S. Government Structure in 5 Minutes Legislative Branch Congressional Structure The Constitution & the Legislative
Opener: Monday, April 11 th The Almost Painless Guide to the Legislature Legislative Branch U.S. Government Structure in 5 Minutes Legislative Branch Congressional Structure The Constitution & the Legislative
ARTICLE 1 - THE LEGISLATIVE BRANCH DAY 2
 ARTICLE 1 - THE LEGISLATIVE BRANCH DAY 2 THE U.S. CONGRESS Article I, Section 1: Creates Congress Bicameral (Great Compromise) Senate - Upper 100 members 6 years House - Lower 435 2 years Reapportioned
ARTICLE 1 - THE LEGISLATIVE BRANCH DAY 2 THE U.S. CONGRESS Article I, Section 1: Creates Congress Bicameral (Great Compromise) Senate - Upper 100 members 6 years House - Lower 435 2 years Reapportioned
The Constitution and the Legislative Branch of the Government
 Chapter 7 Congress The Constitution and the Legislative Branch of the Government o Article I describes structure of Congress n Bicameral legislature o Divided into two houses o Each state sends two Senators
Chapter 7 Congress The Constitution and the Legislative Branch of the Government o Article I describes structure of Congress n Bicameral legislature o Divided into two houses o Each state sends two Senators
The Legislative Branch (Makes Laws) 114th Congress 131st Ohio General Assembly Portage County Commissioners City Council Kent, Ohio
 The Legislative Branch (Makes Laws) 114th Congress 131st Ohio General Assembly Portage County Commissioners City Council Kent, Ohio 1 U.S. Congress Washington, D.C. 2 3 U.S. Capitol Building Holds the
The Legislative Branch (Makes Laws) 114th Congress 131st Ohio General Assembly Portage County Commissioners City Council Kent, Ohio 1 U.S. Congress Washington, D.C. 2 3 U.S. Capitol Building Holds the
Chapter 7. Congress. American Government 2006 Edition To accompany Comprehensive, Alternate, Texas, and Essentials Editions O Connor and Sabato
 Chapter 7 Congress American Government 2006 Edition To accompany Comprehensive, Alternate, Texas, and Essentials Editions O Connor and Sabato The Constitution and the Legislative Branch of the Government
Chapter 7 Congress American Government 2006 Edition To accompany Comprehensive, Alternate, Texas, and Essentials Editions O Connor and Sabato The Constitution and the Legislative Branch of the Government
Name: Class: Date: 5., a self-governing possession of the United States, is represented by a nonvoting resident commissioner.
 1. A refers to a Congress consisting of two chambers. a. bicameral judiciary b. bicameral legislature c. bicameral cabinet d. bipartisan filibuster e. bipartisan caucus 2. In the context of the bicameral
1. A refers to a Congress consisting of two chambers. a. bicameral judiciary b. bicameral legislature c. bicameral cabinet d. bipartisan filibuster e. bipartisan caucus 2. In the context of the bicameral
Legislative Branch Notes
 Legislative Branch Notes Characteristics of Congress Senate: members year terms Qualifications: years old, citizen for years members year terms Qualifications: years old; citizen for years How are they
Legislative Branch Notes Characteristics of Congress Senate: members year terms Qualifications: years old, citizen for years members year terms Qualifications: years old; citizen for years How are they
DUE 2/1. Name: Date: Directions: Simply identify and describe the important terms, places, events, and people listed below.
 Name: Date: AP United States Government & Politics Directions: Simply identify and describe the important terms, places, events, and people listed below. Then & Now DUE 2/1 the first branch power of the
Name: Date: AP United States Government & Politics Directions: Simply identify and describe the important terms, places, events, and people listed below. Then & Now DUE 2/1 the first branch power of the
Topic 4: Congress Section 1
 Topic 4: Congress Section 1 Introduction Why does the Constitution establish a bicameral legislature? Historically, it is modeled on the two houses of the British Parliament and colonial legislatures.
Topic 4: Congress Section 1 Introduction Why does the Constitution establish a bicameral legislature? Historically, it is modeled on the two houses of the British Parliament and colonial legislatures.
Congress A. Carafiello
 Congress A. Carafiello Essential Questions Why does the Constitution divide power between the two houses of Congress? What is a term of Congress? What are Congressional sessions? What benefits to members
Congress A. Carafiello Essential Questions Why does the Constitution divide power between the two houses of Congress? What is a term of Congress? What are Congressional sessions? What benefits to members
Andrew Johnson 1868 Bill Clinton Executive Powers
 Nonlegislative Powers of Congress Constitutional amendments: propose by 2/3 agreements of both houses Electoral duties o if no President, the House decides if no one receive a majority of the electoral
Nonlegislative Powers of Congress Constitutional amendments: propose by 2/3 agreements of both houses Electoral duties o if no President, the House decides if no one receive a majority of the electoral
Ch Congress. AP Government Mr. Zach
 Ch. 11 - Congress AP Government Mr. Zach Purpose of Congress: Resolve disputes in public policy Center of policymaking Source of power in govt (controls $$) Members have to be in 2 places at same time
Ch. 11 - Congress AP Government Mr. Zach Purpose of Congress: Resolve disputes in public policy Center of policymaking Source of power in govt (controls $$) Members have to be in 2 places at same time
A POST-ELECTION VIEW FROM WASHINGTON: IMPACT OF THE 2016 PRESIDENTIAL AND CONGRESSIONAL CONTESTS
 2015 Morgan, 2016 Morgan, Lewis Lewis & Bockius & Bockius LLP LLP A POST-ELECTION VIEW FROM WASHINGTON: IMPACT OF THE 2016 PRESIDENTIAL AND CONGRESSIONAL CONTESTS Matthew Miner, Partner, Washington D.C.
2015 Morgan, 2016 Morgan, Lewis Lewis & Bockius & Bockius LLP LLP A POST-ELECTION VIEW FROM WASHINGTON: IMPACT OF THE 2016 PRESIDENTIAL AND CONGRESSIONAL CONTESTS Matthew Miner, Partner, Washington D.C.
Chapter 10: Congress
 Chapter 10: Congress 1. Which of the following is not one of the reasons why a number of congressional members have stepped down from office? (A) constant fundraising (B) to take more prestigious positions
Chapter 10: Congress 1. Which of the following is not one of the reasons why a number of congressional members have stepped down from office? (A) constant fundraising (B) to take more prestigious positions
Organization. -Great Compromise of branches of government Bicameral legislature. -House. -Senate Upper house
 Organization -Great Compromise of 1787 3 branches of government Bicameral legislature -House Lower house -Senate Upper house The House of Representatives is based on population The Senate is based on equal
Organization -Great Compromise of 1787 3 branches of government Bicameral legislature -House Lower house -Senate Upper house The House of Representatives is based on population The Senate is based on equal
Congress. Chapter 11
 Congress Chapter 11 Warm-Up Crash Course Video: Bicameral Congress Notes Sheet Fill in as many aspects of each chamber of Congress as you can. Video The Purposes/Jobs of Congress 1. Lawmaking 2. Representation
Congress Chapter 11 Warm-Up Crash Course Video: Bicameral Congress Notes Sheet Fill in as many aspects of each chamber of Congress as you can. Video The Purposes/Jobs of Congress 1. Lawmaking 2. Representation
The Federalist, No. 51
 The Legislative Branch Fall, 2015 In republican government, the legislative authority necessarily predominates. The remedy for this inconveniency is to divide the legislature into different branches; and
The Legislative Branch Fall, 2015 In republican government, the legislative authority necessarily predominates. The remedy for this inconveniency is to divide the legislature into different branches; and
The Legislative Branch. How does the legislature work to represent the citizens?
 The Legislative Branch How does the legislature work to represent the citizens? Congress Senate House of Representatives How Congress is Organized House and Senate Terms of Congress Congress- the national
The Legislative Branch How does the legislature work to represent the citizens? Congress Senate House of Representatives How Congress is Organized House and Senate Terms of Congress Congress- the national
Chapter 4: The Legislative Branch
 Chapter 4: The Legislative Branch United States Government Fall, 2017 In republican government, the legislative authority necessarily predominates. The remedy for this inconveniency is to divide the legislature
Chapter 4: The Legislative Branch United States Government Fall, 2017 In republican government, the legislative authority necessarily predominates. The remedy for this inconveniency is to divide the legislature
4) Once every decade, the Constitution requires that the population be counted. This is called the 4)
 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The Founders intended that the House of Representatives be 1) A) professional. B) electorally insulated.
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) The Founders intended that the House of Representatives be 1) A) professional. B) electorally insulated.
UNIT 5-1 CONGRESS AND THE PRESIDENCY
 UNIT 5-1 CONGRESS AND THE PRESIDENCY STRUCTURE OF CONGRESS House of Representatives Senate Membership 435 members (apportioned by population) 100 members (two from each state) Term of office 2 years; entire
UNIT 5-1 CONGRESS AND THE PRESIDENCY STRUCTURE OF CONGRESS House of Representatives Senate Membership 435 members (apportioned by population) 100 members (two from each state) Term of office 2 years; entire
AP United States Government & Politics EXAM: Congress and the Presidency, Ch. 12 & 13
 AP United States Government & Politics EXAM: Congress and the Presidency, Ch. 12 & 13 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) privileges
AP United States Government & Politics EXAM: Congress and the Presidency, Ch. 12 & 13 MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1) privileges
CHAPTER 5: CONGRESS: THE LEGISLATIVE BRANCH
 CHAPTER 5: CONGRESS: THE LEGISLATIVE BRANCH 1 Section 1: Congress Section 2: The Powers of Congress Section 3: The House of Representative Section 4: The Senate Section 5: Congress At Work SECTION 1: CONGRESS
CHAPTER 5: CONGRESS: THE LEGISLATIVE BRANCH 1 Section 1: Congress Section 2: The Powers of Congress Section 3: The House of Representative Section 4: The Senate Section 5: Congress At Work SECTION 1: CONGRESS
Key House Committees
 115 th Congress Jan. 3 62 new House Members and 473 incumbents Rep. Paul D. Ryan (R-WI) -- Speaker of the House Rep. Nancy Pelosi (D-CA) -- House Minority Leader Key House Committees Appropriations o Subcommittee
115 th Congress Jan. 3 62 new House Members and 473 incumbents Rep. Paul D. Ryan (R-WI) -- Speaker of the House Rep. Nancy Pelosi (D-CA) -- House Minority Leader Key House Committees Appropriations o Subcommittee
Unit 4 Test Bank Congress
 Unit 4 Test Bank Congress 2) Which of the following did the framers of the Constitution conceive of as the center of policymaking in America? A) the President B) the people C) Congress D) the courts E)
Unit 4 Test Bank Congress 2) Which of the following did the framers of the Constitution conceive of as the center of policymaking in America? A) the President B) the people C) Congress D) the courts E)
The Legislative Branch and Domestic Policy. POLS 103 Unit 2 Week 7-8
 The Legislative Branch and Domestic Policy POLS 103 Unit 2 Week 7-8 The Institutional Design of Congress Unit 2 BICAMERAL Legislature! The House of Representatives Elected Via Popular vote. 2 year term
The Legislative Branch and Domestic Policy POLS 103 Unit 2 Week 7-8 The Institutional Design of Congress Unit 2 BICAMERAL Legislature! The House of Representatives Elected Via Popular vote. 2 year term
Chapter 5: Congress: The Legislative Branch
 Chapter 5: Congress: The Legislative Branch Section 1: Congress Section 2: The Powers of Congress Section 3: The House of Representatives Section 4: The Senate Section 5: Congress at Work Congress Main
Chapter 5: Congress: The Legislative Branch Section 1: Congress Section 2: The Powers of Congress Section 3: The House of Representatives Section 4: The Senate Section 5: Congress at Work Congress Main
Unit 4 The Legislative Branch Study Guide Explain all the following: 1. Bi-Cameral 2. Congress: - Office - term - Number of members - Selection -
 Unit 4 The Legislative Branch Study Guide Explain all the following: 1. Bi-Cameral 2. Congress: - Office - term - Number of members - Selection - Requirements 3. 17 th Amendment 4. 20 th amendment 5. 27
Unit 4 The Legislative Branch Study Guide Explain all the following: 1. Bi-Cameral 2. Congress: - Office - term - Number of members - Selection - Requirements 3. 17 th Amendment 4. 20 th amendment 5. 27
The Legislative Branch: The United States of America in Congress Assembled
 The Legislative Branch: The United States of America in Congress Assembled Basic Structure Bicameral Legislature House: Terms and qualifications Reapportionment, Redistricting Senate Election of Senators
The Legislative Branch: The United States of America in Congress Assembled Basic Structure Bicameral Legislature House: Terms and qualifications Reapportionment, Redistricting Senate Election of Senators
 LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 12, you should be able to: 1. Describe the characteristics of our senators and representatives, and the nature of their jobs. 2. Explain what factors have the
LEARNING OBJECTIVES After studying Chapter 12, you should be able to: 1. Describe the characteristics of our senators and representatives, and the nature of their jobs. 2. Explain what factors have the
Ch. 5 Test Legislative Branch Government
 Name: Date: 1. In 1998, California had forty-five representatives in the U.S. House of Representatives while Louisiana had seven. What accounts for the difference in these numbers? A. area of the states
Name: Date: 1. In 1998, California had forty-five representatives in the U.S. House of Representatives while Louisiana had seven. What accounts for the difference in these numbers? A. area of the states
Federal Legislative Process Overview
 Federal Legislative Process Overview Prof. Tracy Hester University of Houston Law Center Jan. 25, 2018 I m just a bill Let s take a deeper look House Introduction of Bill Referral to Committee Referral
Federal Legislative Process Overview Prof. Tracy Hester University of Houston Law Center Jan. 25, 2018 I m just a bill Let s take a deeper look House Introduction of Bill Referral to Committee Referral
Congress Outline Notes
 Congress Outline Notes I. INTRODUCTION A. Congress as the center of policymaking in America. 1. Although the prominence of Congress has fluctuated over time. 2. Some critics charge Congress with being
Congress Outline Notes I. INTRODUCTION A. Congress as the center of policymaking in America. 1. Although the prominence of Congress has fluctuated over time. 2. Some critics charge Congress with being
Unit 5 Reading Guide
 Unit 5 Reading Guide Chapter Seven Congress 1. Outline the major differences between the House and Senate. CHARACTERISTIC HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES SENATE Number of members Length of term Qualifications
Unit 5 Reading Guide Chapter Seven Congress 1. Outline the major differences between the House and Senate. CHARACTERISTIC HOUSE OF REPRESENTATIVES SENATE Number of members Length of term Qualifications
Chapter 13 Congress 3/6/2014 WHO GOVERNS? TO WHAT ENDS?
 Chapter 13 Congress WHO GOVERNS? 1. Are members of Congress representative of the American people? 2. Does Congress normally do what most citizens want it to do? TO WHAT ENDS? 1. Should Congress run under
Chapter 13 Congress WHO GOVERNS? 1. Are members of Congress representative of the American people? 2. Does Congress normally do what most citizens want it to do? TO WHAT ENDS? 1. Should Congress run under
WHO GOVERNS? TO WHAT ENDS?
 Chapter 13 Congress WHO GOVERNS? 1. Are members of Congress representative of the American people? 2. Does Congress normally do what most citizens want it to do? TO WHAT ENDS? 1. Should Congress run under
Chapter 13 Congress WHO GOVERNS? 1. Are members of Congress representative of the American people? 2. Does Congress normally do what most citizens want it to do? TO WHAT ENDS? 1. Should Congress run under
Week. DRIVE Act. Authorization Act. rule. The House Rules 22, alternative to the does. years Now debt. process of
 Weekl ly Legislative Update Week of November 2, 2015 Congressional Outlook Week of November 2nd The House and the Senate are in session this week. The House is scheduled to vote on 9 bills and resolutions
Weekl ly Legislative Update Week of November 2, 2015 Congressional Outlook Week of November 2nd The House and the Senate are in session this week. The House is scheduled to vote on 9 bills and resolutions
Members policy specialists
 Institutions of National Government (Congress, Presidency, and Bureaucracy) Congress (435 representatives and 100 senators).house v. Senate (study chart on page 375 Key Differences ) A) Party Leadership.
Institutions of National Government (Congress, Presidency, and Bureaucracy) Congress (435 representatives and 100 senators).house v. Senate (study chart on page 375 Key Differences ) A) Party Leadership.
Effective Communications with Congressional Staff
 Effective Communications with Congressional Staff Nicole Kunko ASTHO Chief of Public Policy Former Professional Staff, House Appropriations Subcommittee On Labor, HHS, and Education (2001-2010) Population
Effective Communications with Congressional Staff Nicole Kunko ASTHO Chief of Public Policy Former Professional Staff, House Appropriations Subcommittee On Labor, HHS, and Education (2001-2010) Population
Lecture Outline: Chapter 10
 Lecture Outline: Chapter 10 Congress I. Most Americans see Congress as paralyzed by partisan bickering and incapable of meaningful action. A. The disdain that many citizens have for Congress is expressed
Lecture Outline: Chapter 10 Congress I. Most Americans see Congress as paralyzed by partisan bickering and incapable of meaningful action. A. The disdain that many citizens have for Congress is expressed
whoo hoo! Congressional leadership House and Senate floor procedure (part 1) For more on floor procedure, see. Pocket floor procedures
 whoo hoo! Congressional leadership House and Senate floor procedure (part 1) For more on floor procedure, see. Pocket floor procedures Have you checked out LegSim resources? Congressional Leadership Constitutional
whoo hoo! Congressional leadership House and Senate floor procedure (part 1) For more on floor procedure, see. Pocket floor procedures Have you checked out LegSim resources? Congressional Leadership Constitutional
Ch. 11 Powers of Congress (Article I) Ch. 11 Powers of Congress (Article I) Ch. 11 Powers of Congress (Article I) Non Legislative Powers
 Non Legislative Powers Congress can propose an Amendment to the Constitution The House of Representatives can elect the President if no candidate gets a majority of electoral votes The Senate can elect
Non Legislative Powers Congress can propose an Amendment to the Constitution The House of Representatives can elect the President if no candidate gets a majority of electoral votes The Senate can elect
Congressional Policy-Making. How does a Bill become a Law?
 Congressional Policy-Making How does a Bill become a Law? Recap: Political Competition! Interest group competition! Distributive politics! Collective action and free riding! Useful for understanding which
Congressional Policy-Making How does a Bill become a Law? Recap: Political Competition! Interest group competition! Distributive politics! Collective action and free riding! Useful for understanding which
That body, worried by the flood of floor amendments, began issuing more restrictive rules. By the mid- 1980s, this had reached the point where
 OVERVIEW Over the last fifty years or so, Congress, especially the House, has evolved through three stages. The Congress is presently an uneasy combination of stages two and three. During the first stage,
OVERVIEW Over the last fifty years or so, Congress, especially the House, has evolved through three stages. The Congress is presently an uneasy combination of stages two and three. During the first stage,
Notes on Congress (a bit outdated but still worthwhile)
 Notes on Congress (a bit outdated but still worthwhile) EVOLUTIONARY POWERS The elastic (or necessary and proper clause) gives Congress the authority to pass laws it deems necessary and proper to carry
Notes on Congress (a bit outdated but still worthwhile) EVOLUTIONARY POWERS The elastic (or necessary and proper clause) gives Congress the authority to pass laws it deems necessary and proper to carry
Government in America: People, Politics, and Policy Thirteenth Edition, and Texas Edition Edwards/Wattenberg/Lineberry. Chapter 12 Congress
 Government in America: People, Politics, and Policy Thirteenth Edition, and Texas Edition Edwards/Wattenberg/Lineberry Chapter 12 Congress The Representatives and The Job Senators Salary of $168,500 with
Government in America: People, Politics, and Policy Thirteenth Edition, and Texas Edition Edwards/Wattenberg/Lineberry Chapter 12 Congress The Representatives and The Job Senators Salary of $168,500 with
Chapter 5 The Organization of Congress. Section 1 Congressional Membership
 Chapter 5 The Organization of Congress Section 1 Congressional Membership Congressional Sessions Each term of Congress has two sessions. Each session lasts until Congress votes to adjourn. Membership of
Chapter 5 The Organization of Congress Section 1 Congressional Membership Congressional Sessions Each term of Congress has two sessions. Each session lasts until Congress votes to adjourn. Membership of
NAME CLASS DATE. 1. What is the historical reason for Americans choosing a bicameral system?
 10 Section 1 Guided Reading and Review The National Legislature The main points of Section 1 are supplied for you below in the form of questions. As you read the section, fill in the answers to the questions.
10 Section 1 Guided Reading and Review The National Legislature The main points of Section 1 are supplied for you below in the form of questions. As you read the section, fill in the answers to the questions.
