Building a Better America One Wealth Quintile at a Time. Forthcoming in Perspectives on Psychological Science
|
|
|
- Carmella Hicks
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 Building a Better America 1 Building a Better America One Wealth Quintile at a Time Michael I. Norton Harvard Business School Dan Ariely Duke University Forthcoming in Perspectives on Psychological Science Address correspondence to: Michael I. Norton, Harvard Business School, Soldiers Field Road, Boston, MA 02163, mnorton@hbs.edu; or Dan Ariely, Duke University, One Towerview Road, Durham, NC 27708, dandan@duke.edu. We thank Jordanna Schutz for her many contributions, George Akerlof, Lalin Anik, Ryan Buell, Zoë Chance, Anita Elberse, Ilyana Kuziemko, Jeff Lee, Jolie Martin, Mary Carol Mazza, David Nickerson, John Silva, and Eric Werker for their comments, and surveysampling.com for their assistance administering the survey.
2 Building a Better America 2 Abstract Disagreements about the optimal level of wealth inequality underlie policy debates ranging from taxation to welfare. We attempt to insert the desires of regular Americans into these debates, by asking a nationally representative online panel to estimate the current distribution of wealth in the United States and to build a better America by constructing distributions with their ideal level of inequality. First, respondents dramatically underestimated the current level of wealth inequality. Second, respondents constructed ideal wealth distributions that were far more equitable than even their erroneously low estimates of the actual distribution. Most important from a policy perspective, we observed a surprising level of consensus: All demographic groups even those not usually associated with wealth redistribution such as Republicans and the wealthy desired a more equal distribution of wealth than the status quo.
3 Building a Better America 3 Most scholars agree that wealth inequality in the United States is at historic highs, with some estimates suggesting that the top 1% of Americans hold nearly 50% of the wealth, topping even the levels seen just before the Great Depression in the 1920 s (Davies, Sandstrom, Shorrocks, & Wolff, 2009; Keister, 2000; Wolff, 2002). While it is clear that wealth inequality is high, determining the ideal distribution of wealth in a society has proven to be an intractable question, in part because differing beliefs about the ideal distribution of wealth are the source of friction between policymakers who shape that distribution: Proponents of the estate tax, for example, argue that the wealth that parents bequeath to their children should be taxed more heavily than those who refer to this policy as a burdensome death tax. We take a different approach to determining the ideal level of wealth inequality: Following the philosopher John Rawls (1971), we ask Americans to construct distributions of wealth they deem just. Of course, this approach may simply add to the confusion if Americans disagree about the ideal wealth distribution in the same way that policymakers do. Thus, we have two primary goals. First, we explore whether there is general consensus among Americans about the ideal level of wealth inequality, or whether differences driven by factors such as political beliefs and income outweigh any consensus (McCarty, Poole, & Rosenthal, 2006). Second, assuming sufficient agreement, we hope to insert the preferences of regular Americans regarding wealth inequality into policy debates. A nationally representative online sample of respondents (N = 5,522, 51% female, M age = 44.1), randomly drawn from a panel of over one million Americans, completed the
4 Building a Better America 4 survey in December, Respondents household income (Median = $45,000) was similar to that reported in the 2006 United States census (Median = $48,000), and their voting pattern in the 2004 election (50.6% Bush, 46.0% Kerry) was also similar to the actual outcome (50.8% Bush, 48.3% Kerry). In addition, the sample contained respondents from 47 states. We ensured that all respondents had the same working definition of wealth by requiring them to read the following before beginning the survey: Wealth, also known as net worth, is defined as the total value of everything someone owns minus any debt that he or she owes. A person's net worth includes his or her bank account savings plus the value of other things such as property, stocks, bonds, art, collections, etc., minus the value of things like loans and mortgages. Americans Prefer Sweden For the first task, we created three unlabeled pie charts of wealth distributions, one of which depicted a perfectly equal distribution of wealth. Unbeknownst to respondents, a second distribution reflected the wealth distribution in the United States; in order to create a distribution with a level of inequality that clearly fell in between these two charts, we constructed a third pie chart from the income distribution of Sweden (Figure 1). 2 We presented respondents with the three pair-wise combinations of these pie charts (in random order) and asked them to choose which nation they would rather join given a Rawls constraint for determining a just society (Rawls, 1971): In considering 1 We used the survey organization Survey Sampling International (surveysampling.com) to conduct this survey. As a result, we do not have direct access to panelist response rates. 2 We used Sweden s income rather than wealth distribution because it provided a clearer contrast to the equal and United States wealth distributions; while more equal than the United States wealth distribution, Sweden s wealth distribution is still extremely top heavy.
5 Building a Better America 5 this question, imagine that if you joined this nation, you would be randomly assigned to a place in the distribution, so you could end up anywhere in this distribution, from the very richest to the very poorest. As can be seen in Figure 1, the (unlabeled) United States distribution was far less desirable than both the (unlabeled) Sweden distribution and the equal distribution, with some 92% of Americans preferring the Sweden distribution to the United States. In addition, this overwhelming preference for the Sweden distribution over the United States distribution was robust across gender (Females: 92.7%; Males: 90.6%), preferred candidate in the 2004 election (Bush Voters: 90.2%; Kerry Voters: 93.5%) and income (less than $50,000: 92.1%; $50, ,000: 91.7%; more than $100,000: 89.1%). In addition, there was a slight preference for the distribution that resembled Sweden relative to the equal distribution, suggesting that Americans prefer some inequality to perfect equality, but not to the degree currently present in the United States. Building a Better America While the choices among the three distributions shed some light into preferences for distributions of wealth in the abstract, we wanted to explore respondents specific beliefs about their own society. In the next task, we therefore removed Rawls veil of ignorance and assessed both respondents estimates of the actual distribution of wealth and their preferences for the ideal distribution of wealth in the United States. For their estimates of the actual distribution, we asked respondents to indicate what percent of wealth they thought was owned by each of the five quintiles in the United States, in order starting with the top 20% and ending with the bottom 20%. For their ideal distributions,
6 Building a Better America 6 we asked them to indicate what percent of wealth they thought each of the quintiles ideally should hold, again starting with the top 20% and ending with the bottom 20%. To help them with this task, we provided them with the two most extreme examples, instructing them to assign 20% of the wealth to each quintile if they thought that each quintile should have the same level of wealth, or to assign 100% of the wealth to one quintile if they thought that one quintile should hold all of the wealth. Figure 2 shows the actual wealth distribution in the United States at the time of the survey, respondents overall estimate of that distribution, and finally respondents ideal distribution. These results demonstrate two clear messages. First, respondents vastly underestimated the actual level of wealth inequality in the United States, believing that the wealthiest quintile held about 59% of the wealth when the actual number is closer to 84%. More interesting, respondents constructed ideal wealth distributions that were far more equitable than even their erroneously low estimates of the actual distribution, reporting a desire for the top quintile to own just 32% of the wealth. These desires for more equal distributions of wealth took the form of moving money from the top quintile to the bottom three quintiles, while leaving the second quintile unchanged, evidencing a greater concern for the less fortunate than the more fortunate (Charness & Rabin, 2002). We next explored how demographic characteristics of our respondents affected these estimates. Figure 3 shows these estimates broken down by three levels of income, by whether respondents voted for George W. Bush (Republican) or John Kerry (Democrat) for United States president in 2004, and by gender. Males, Kerry voters, and wealthier individuals estimated that the distribution of wealth was relatively more unequal than did women, Bush voters, and poorer individuals. For estimates of the ideal
7 Building a Better America 7 distribution, women, Kerry voters, and the poor desired relatively more equal distributions than their counterparts. What is most striking about Figure 3, however, is its demonstration of much more consensus than disagreement among these different demographic groups. All groups even the wealthiest respondents desired a more equal distribution of wealth than what they estimated the current United States level to be, while all groups also desired some inequality even the poorest respondents. In addition, all groups agreed that such redistribution should take the form of moving wealth from the top quintile to the bottom three quintiles. In short, while Americans tend to be relatively more favorable toward economic inequality than members of other countries (Osberg & Smeeding, 2006), Americans consensus about the ideal distribution of wealth within the United States appears to dwarf their disagreements across gender, political orientation, and income. Overall, these results demonstrate two primary messages. First, a large nationally representative sample of Americans seem to prefer to live in a country more like Sweden than like the United States. Americans also construct ideal distributions that are far more equal than they estimated the United States to be estimates which themselves were far more equal than the actual level of inequality. Second, across groups from different sides of the political spectrum, there was much more consensus than disagreement about this desire for a more equal distribution of wealth, suggesting that Americans may possess a commonly held normative standard for the distribution of wealth despite the many disagreements about policies that affect that distribution, such as taxation and welfare (Kluegel & Smith, 1986). We hasten to add, however, that our use of normative is in a descriptive sense reflecting the fact that Americans agree on the ideal distribution but
8 Building a Better America 8 not necessarily in a prescriptive sense. While some evidence suggests that economic inequality is associated with decreased well-being and health (Napier & Jost, 2008; Wilkinson & Pickett, 2009), creating a society with the precise level of inequality that our respondents report as ideal may not be optimal from an economic or public policy perspective (Krueger, 2004). Given the consensus among disparate groups on the gap between an ideal distribution of wealth and the actual level of wealth inequality, why don t more Americans especially those with low income advocate for greater redistribution of wealth? First, our results demonstrate that Americans appear to drastically underestimate the current level of wealth inequality, suggesting they may simply be unaware of the gap. Second, just as people have erroneous beliefs about the actual level of wealth inequality, they may also hold overly optimistic beliefs about opportunities for social mobility in the United States (Benabou & Ok, 2001; Charles & Hurst, 2003; Keister, 2005), beliefs which in turn may drive support for unequal distributions of wealth. Third, despite the fact that conservatives and liberals in our sample agree that the current level of inequality far from ideal, public disagreements about the causes of that inequality may drown out this consensus (Alesina & Angeletos, 2005; Piketty, 1995). Finally, and more broadly, Americans exhibit a general disconnect between their attitudes towards economic inequality and their self-interest and public policy preferences (Bartels, 2005; Fong, 2001), suggesting that even given increased awareness of the gap between ideal and actual wealth distributions, Americans may remain unlikely to advocate for policies that would narrow this gap.
9 Building a Better America 9 References Alesina, A. & Angeletos, G.M. (2005). Fairness and redistribution. American Economic Review, 95, Bartels, L.M. (2005). Homer gets a tax cut: Inequality and public policy in the American mind. Perspectives on Politics, 3, Benabou, R. & Ok, E.A. (2001). Social mobility and the demand for redistribution: The POUM hypothesis. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 116, Charles, K.K. & Hurst, E. (2003). The correlation of wealth across generations. Journal of Political Economy, 111, Charness, G. & Rabin, M. (2002). Understanding social preferences with simple tests. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 117, Davies, J.B., Sandstrom, S., Shorrocks, A., & Wolff, E.N. (2009). The global pattern of household wealth. Journal of International Development, 21, Fong, C. (2001). Social preferences, self-interest, and the demand for redistribution. Journal of Public Economics, 82, Keister, L.A. (2000). Wealth in America. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. Keister, L.A. (2005). Getting rich: America s new rich and how they got that way. Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press. Kluegel, J.R. & Smith, E.R. (1986). Beliefs about inequality: Americans views of what is and what ought to be. New York: Aldine de Gruyter. Krueger, A.B. (2004). Inequality, too much of a good thing. In J.J. Heckman & A.B. Krueger (Eds.), Inequality in America: What role for human capital policies (pp. 1-75).Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
10 Building a Better America 10 McCarty, N., Poole, K.T., & Rosenthal, H. (2006). Polarized America: The dance of ideology and unequal riches. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. Napier, J.L. & Jost, J.T. (2008). Why are conservatives happier than liberals? Psychological Science, 19, Osberg, L. & Smeeding, T. (2006). 'Fair' inequality? Attitudes to pay differentials: The United States in comparative perspective. American Sociological Review, 71, Piketty, T. (1995). Social mobility and redistributive politics. Quarterly Journal of Economics, 110, Rawls, J. (1971). A theory of justice. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press. Wilkinson, R. & Pickett, K. (2009). The spirit level: Why greater equality makes societies stronger. New York: Bloomsbury. Wolff, E.N. (2002). Top heavy: The increasing inequality of wealth in America and what can be done about it. New York, NY: The New Press.
11 Building a Better America 11 Figure 1: Relative preference among all respondents for three distributions: Sweden (upper left), an equal distribution (upper right), and the United States (bottom). Note. Pie charts depict the percentage of wealth possessed by each quintile; for instance, in the United States, the top wealth quintile owns 84% of the total wealth, the second highest 11%, and so on.
12 Building a Better America 12 Figure 2. The actual United States wealth distribution plotted against the estimated and ideal distributions across all respondents. Top 20% 2nd 20% Middle 20% 4th 20% Bottom 20% Actual Estimated Ideal 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% Percent Wealth Owned Note: Because of their small percentage share of total wealth, both the 4 th 20% value (0.2%) and the Bottom 20% value (0.1%) are not visible in the Actual distribution.
13 Building a Better America 13 Figure 3. The actual United States wealth distribution plotted against the estimated and ideal distributions of respondents of different income levels, political affiliations, and genders. Top 20% 2nd 20% Middle 20% 4th 20% Bottom 20% Actual Estimated (< $50K) Estimated ($50-100K) Estimated (> $100K) Estimated (Bush Voters) Estimated (Kerry Voters) Estimated (Women) Estimated (Men) Ideal (< $50K) Ideal ($50-100K) Ideal (> $100K) Ideal (Bush Voters) Ideal (Kerry Voters) Ideal (Women) Ideal (Men) 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 100% Percent Wealth Owned Note: Because of their small percentage share of total wealth, both the 4 th 20% value (0.2%) and the Bottom 20% value (0.1%) are not visible in the Actual distribution.
U.S. Family Income Growth
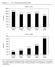 Figure 1.1 U.S. Family Income Growth Growth 140% 120% 100% 80% 60% 115.3% 1947 to 1973 97.1% 97.7% 102.9% 84.0% 40% 20% 0% Lowest Fifth Second Fifth Middle Fifth Fourth Fifth Top Fifth 70% 60% 1973 to
Figure 1.1 U.S. Family Income Growth Growth 140% 120% 100% 80% 60% 115.3% 1947 to 1973 97.1% 97.7% 102.9% 84.0% 40% 20% 0% Lowest Fifth Second Fifth Middle Fifth Fourth Fifth Top Fifth 70% 60% 1973 to
Income Inequality in the United States Through the Lens of Other Advanced Economies
 Mia DeSanzo Wealth & Power Major Writing Assignment 3/3/16 Income Inequality in the United States Through the Lens of Other Advanced Economies Income inequality in the United States has become a political
Mia DeSanzo Wealth & Power Major Writing Assignment 3/3/16 Income Inequality in the United States Through the Lens of Other Advanced Economies Income inequality in the United States has become a political
19 ECONOMIC INEQUALITY. Chapt er. Key Concepts. Economic Inequality in the United States
 Chapt er 19 ECONOMIC INEQUALITY Key Concepts Economic Inequality in the United States Money income equals market income plus cash payments to households by the government. Market income equals wages, interest,
Chapt er 19 ECONOMIC INEQUALITY Key Concepts Economic Inequality in the United States Money income equals market income plus cash payments to households by the government. Market income equals wages, interest,
Why are relatively poor people not more supportive of redistribution? Evidence from a Survey Experiment across 10 countries
 Why are relatively poor people not more supportive of redistribution? Evidence from a Survey Experiment across 10 countries Christopher Hoy 1 Franziska Mager 2 First Draft (November 2018) Abstract. Using
Why are relatively poor people not more supportive of redistribution? Evidence from a Survey Experiment across 10 countries Christopher Hoy 1 Franziska Mager 2 First Draft (November 2018) Abstract. Using
Consumer Expectations: Politics Trumps Economics. Richard Curtin University of Michigan
 June 1, 21 Consumer Expectations: Politics Trumps Economics Richard Curtin University of Michigan An unprecedented partisan divide in economic expectations occurred following President Trump s election.
June 1, 21 Consumer Expectations: Politics Trumps Economics Richard Curtin University of Michigan An unprecedented partisan divide in economic expectations occurred following President Trump s election.
One. After every presidential election, commentators lament the low voter. Introduction ...
 One... Introduction After every presidential election, commentators lament the low voter turnout rate in the United States, suggesting that there is something wrong with a democracy in which only about
One... Introduction After every presidential election, commentators lament the low voter turnout rate in the United States, suggesting that there is something wrong with a democracy in which only about
Rising Share of Americans See Conflict Between Rich and Poor
 Social & Demographic Trends Wednesday, Jan 11, 2012 Rising Share of Americans See Conflict Between Rich and Poor Paul Taylor, Director Kim Parker, Associate Director Rich Morin, Senior Editor Seth Motel,
Social & Demographic Trends Wednesday, Jan 11, 2012 Rising Share of Americans See Conflict Between Rich and Poor Paul Taylor, Director Kim Parker, Associate Director Rich Morin, Senior Editor Seth Motel,
Europe and the US: Preferences for Redistribution
 Europe and the US: Preferences for Redistribution Peter Haan J. W. Goethe Universität Summer term, 2010 Peter Haan (J. W. Goethe Universität) Europe and the US: Preferences for Redistribution Summer term,
Europe and the US: Preferences for Redistribution Peter Haan J. W. Goethe Universität Summer term, 2010 Peter Haan (J. W. Goethe Universität) Europe and the US: Preferences for Redistribution Summer term,
Misinformed in an Unequal World: How Accurate Information about Inequality and Income Affects Public Support for Redistributive Policies
 Misinformed in an Unequal World: How Accurate Information about Inequality and Income Affects Public Support for Redistributive Policies Cheryl Boudreau & Scott A. MacKenzie University of California, Davis
Misinformed in an Unequal World: How Accurate Information about Inequality and Income Affects Public Support for Redistributive Policies Cheryl Boudreau & Scott A. MacKenzie University of California, Davis
INEQUALITY: POVERTY AND WEALTH CHAPTER 2
 INEQUALITY: POVERTY AND WEALTH CHAPTER 2 Defining Economic Inequality Social Stratification- rank individuals based on objective criteria, often wealth, power and/or prestige. Human beings have a tendency
INEQUALITY: POVERTY AND WEALTH CHAPTER 2 Defining Economic Inequality Social Stratification- rank individuals based on objective criteria, often wealth, power and/or prestige. Human beings have a tendency
Does Knowledge of Inequality Affect Beliefs about Inequality?
 Does Knowledge of Inequality Affect Beliefs about Inequality? Leslie McCall Departments of Sociology and Political Science Faculty Fellow, Institute for Policy Research Northwestern University Fiona Chin
Does Knowledge of Inequality Affect Beliefs about Inequality? Leslie McCall Departments of Sociology and Political Science Faculty Fellow, Institute for Policy Research Northwestern University Fiona Chin
In Relative Policy Support and Coincidental Representation,
 Reflections Symposium The Insufficiency of Democracy by Coincidence : A Response to Peter K. Enns Martin Gilens In Relative Policy Support and Coincidental Representation, Peter Enns (2015) focuses on
Reflections Symposium The Insufficiency of Democracy by Coincidence : A Response to Peter K. Enns Martin Gilens In Relative Policy Support and Coincidental Representation, Peter Enns (2015) focuses on
Coyote Economist. The Political Economy of the Occupy Movement. News from the Department of Economics, CSUSB Volume 18, Issue 1..
 Coyote Economist News from the Department of Economics, CSUSB Volume 18, Issue 1.. Fall 2011 The Political Economy of the Occupy Movement Inside this Issue: Staying Informed...2 We re on Facebook...5 Tentative
Coyote Economist News from the Department of Economics, CSUSB Volume 18, Issue 1.. Fall 2011 The Political Economy of the Occupy Movement Inside this Issue: Staying Informed...2 We re on Facebook...5 Tentative
Political Inequality Worsens Economic Inequality
 Political Inequality Worsens Economic Inequality Ruy Teixeira is a senior fellow at the Center for American Progress and co-director of a new joint project between the Center and the American Enterprise
Political Inequality Worsens Economic Inequality Ruy Teixeira is a senior fellow at the Center for American Progress and co-director of a new joint project between the Center and the American Enterprise
WHEN IS INEQUALITY FAIR? AN EXPERIMENT ON THE EFFECT OF PROCEDURAL JUSTICE AND AGENCY 1. Merve Akbaş Dan Ariely Sevgi Yüksel. July 24, 2014.
 WHEN IS INEQUALITY FAIR? AN EXPERIMENT ON THE EFFECT OF PROCEDURAL JUSTICE AND AGENCY 1 Merve Akbaş Dan Ariely Sevgi Yüksel July 24, 2014 Abstract We investigate how the perceived fairness of income distributions
WHEN IS INEQUALITY FAIR? AN EXPERIMENT ON THE EFFECT OF PROCEDURAL JUSTICE AND AGENCY 1 Merve Akbaş Dan Ariely Sevgi Yüksel July 24, 2014 Abstract We investigate how the perceived fairness of income distributions
Income Distributions and the Relative Representation of Rich and Poor Citizens
 Income Distributions and the Relative Representation of Rich and Poor Citizens Eric Guntermann Mikael Persson University of Gothenburg April 1, 2017 Abstract In this paper, we consider the impact of the
Income Distributions and the Relative Representation of Rich and Poor Citizens Eric Guntermann Mikael Persson University of Gothenburg April 1, 2017 Abstract In this paper, we consider the impact of the
Poverty and Inequality
 Chapter 4 Poverty and Inequality Problems and Policies: Domestic After completing this chapter, you will be able to 1. Measure poverty across countries using different approaches and explain how poverty
Chapter 4 Poverty and Inequality Problems and Policies: Domestic After completing this chapter, you will be able to 1. Measure poverty across countries using different approaches and explain how poverty
American Inequality in Six Charts
 Page 1 of 8 «Six Reasons the Affordable Care Act Isn t Hurricane Katrina Main Americans Like Obamacare Where They Can Get It» November 18, 2013 American Inequality in Six Charts Posted by John Cassidy
Page 1 of 8 «Six Reasons the Affordable Care Act Isn t Hurricane Katrina Main Americans Like Obamacare Where They Can Get It» November 18, 2013 American Inequality in Six Charts Posted by John Cassidy
Income Inequality as a Political Issue: Does it Matter?
 University of Colorado, Boulder CU Scholar Undergraduate Honors Theses Honors Program Spring 2015 Income Inequality as a Political Issue: Does it Matter? Jacqueline Grimsley Jacqueline.Grimsley@Colorado.EDU
University of Colorado, Boulder CU Scholar Undergraduate Honors Theses Honors Program Spring 2015 Income Inequality as a Political Issue: Does it Matter? Jacqueline Grimsley Jacqueline.Grimsley@Colorado.EDU
Perceptions of inequality: perspectives of national policy makers
 6 Perceptions of inequality: perspectives of national policy makers A large amount of research shows that, besides material interests, cognitive and normative factors, i.e. perceptions and values, greatly
6 Perceptions of inequality: perspectives of national policy makers A large amount of research shows that, besides material interests, cognitive and normative factors, i.e. perceptions and values, greatly
How Much (More) Should CEOs Make? A Universal Desire for More Equal Pay
 How Much (More) Should CEOs Make? A Universal Desire for More Equal Pay The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
How Much (More) Should CEOs Make? A Universal Desire for More Equal Pay The Harvard community has made this article openly available. Please share how this access benefits you. Your story matters. Citation
CH 19. Name: Class: Date: Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question.
 Class: Date: CH 19 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In the United States, the poorest 20 percent of the household receive approximately
Class: Date: CH 19 Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. 1. In the United States, the poorest 20 percent of the household receive approximately
Crawford School of Public Policy TTPI Tax and Transfer Policy Institute TTPI - Working Paper 1/2018 January 2018 Chris Hoy Franziska Mager Abstract
 Crawford School of Public Policy TTPI Tax and Transfer Policy Institute TTPI - Working Paper 1/2018 January 2018 Chris Hoy The Australian National University PhD Candidate Franziska Mager Oxfam, Great
Crawford School of Public Policy TTPI Tax and Transfer Policy Institute TTPI - Working Paper 1/2018 January 2018 Chris Hoy The Australian National University PhD Candidate Franziska Mager Oxfam, Great
Non-Voted Ballots and Discrimination in Florida
 Non-Voted Ballots and Discrimination in Florida John R. Lott, Jr. School of Law Yale University 127 Wall Street New Haven, CT 06511 (203) 432-2366 john.lott@yale.edu revised July 15, 2001 * This paper
Non-Voted Ballots and Discrimination in Florida John R. Lott, Jr. School of Law Yale University 127 Wall Street New Haven, CT 06511 (203) 432-2366 john.lott@yale.edu revised July 15, 2001 * This paper
CAUSES AND CONSEQUENCES OF GROWING INEQUALITY and what can be done about it
 THE FOURTH ANNUAL OXFORD FULBRIGHT DISTINGUISHED LECTURE ON INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS CAUSES AND CONSEQUENCES OF GROWING INEQUALITY and what can be done about it Professor Joseph E. Stiglitz Friday 23 May
THE FOURTH ANNUAL OXFORD FULBRIGHT DISTINGUISHED LECTURE ON INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS CAUSES AND CONSEQUENCES OF GROWING INEQUALITY and what can be done about it Professor Joseph E. Stiglitz Friday 23 May
A Statistical Abstract Analysis of the Gelman Paradox: Why correlation does not denote. causation in voting outcomes based on regional average incomes
 A Statistical Abstract Analysis of the Gelman Paradox: Why correlation does not denote causation in voting outcomes based on regional average incomes John W, PhD Peru State College Dr. Andrew Gelman Ph.D.
A Statistical Abstract Analysis of the Gelman Paradox: Why correlation does not denote causation in voting outcomes based on regional average incomes John W, PhD Peru State College Dr. Andrew Gelman Ph.D.
CHAPTER 10: ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL INEQUALITY
 Microeconomics in Context, Fourth Edition CHAPTER 10: ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL INEQUALITY As the United States economy began recovering from the Great Recession of 2007-2009, economic data indicated that the
Microeconomics in Context, Fourth Edition CHAPTER 10: ECONOMIC AND SOCIAL INEQUALITY As the United States economy began recovering from the Great Recession of 2007-2009, economic data indicated that the
The 2005 Ohio Ballot Initiatives: Public Opinion on Issues 1-5. Ray C. Bliss Institute of Applied Politics University of Akron.
 The 2005 Ohio Ballot Initiatives: Public Opinion on Issues 1-5 Ray C. Bliss Institute of Applied Politics University of Akron Executive Summary A survey of Ohio citizens finds mixed results for the 2005
The 2005 Ohio Ballot Initiatives: Public Opinion on Issues 1-5 Ray C. Bliss Institute of Applied Politics University of Akron Executive Summary A survey of Ohio citizens finds mixed results for the 2005
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES INTERGENERATIONAL MOBILITY AND SUPPORT FOR REDISTRIBUTION. Alberto Alesina Stefanie Stantcheva Edoardo Teso
 NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES INTERGENERATIONAL MOBILITY AND SUPPORT FOR REDISTRIBUTION Alberto Alesina Stefanie Stantcheva Edoardo Teso Working Paper 23027 http://www.nber.org/papers/w23027 NATIONAL BUREAU
NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES INTERGENERATIONAL MOBILITY AND SUPPORT FOR REDISTRIBUTION Alberto Alesina Stefanie Stantcheva Edoardo Teso Working Paper 23027 http://www.nber.org/papers/w23027 NATIONAL BUREAU
Poverty & Inequality
 Sociology 125 Lecture 12/13 Poverty & Inequality October 18 & 23, 2006 Film #2: Bread & Roses 7:00 p.m. Tuesday and Wednesday, October 17 & 18 125 Ag Hall 1450 Linden Drive U.S. Household Income Distribution
Sociology 125 Lecture 12/13 Poverty & Inequality October 18 & 23, 2006 Film #2: Bread & Roses 7:00 p.m. Tuesday and Wednesday, October 17 & 18 125 Ag Hall 1450 Linden Drive U.S. Household Income Distribution
CASE 12: INCOME INEQUALITY, POVERTY, AND JUSTICE
 CASE 12: INCOME INEQUALITY, POVERTY, AND JUSTICE The Big Picture The headline in the financial section of the January 20, 2015 edition of USA Today read, By 2016 1% will have 50% of total global wealth.
CASE 12: INCOME INEQUALITY, POVERTY, AND JUSTICE The Big Picture The headline in the financial section of the January 20, 2015 edition of USA Today read, By 2016 1% will have 50% of total global wealth.
Most Say Immigration Policy Needs Big Changes
 MAY 9, 2013 But Little Agreement on Specific Approaches Most Say Immigration Policy Needs Big Changes FOR FURTHER INFORMATION CONTACT THE PEW RESEARCH CENTER FOR THE PEOPLE & THE PRESS Michael Dimock Director
MAY 9, 2013 But Little Agreement on Specific Approaches Most Say Immigration Policy Needs Big Changes FOR FURTHER INFORMATION CONTACT THE PEW RESEARCH CENTER FOR THE PEOPLE & THE PRESS Michael Dimock Director
Oxfam Education
 Background notes on inequality for teachers Oxfam Education What do we mean by inequality? In this resource inequality refers to wide differences in a population in terms of their wealth, their income
Background notes on inequality for teachers Oxfam Education What do we mean by inequality? In this resource inequality refers to wide differences in a population in terms of their wealth, their income
Persistent Economic Discontent Casts a Continuing Political Pall
 ABC NEWS/WASHINGTON POST POLL: POST-ELECTION POLITICS EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE AFTER 5 p.m. Tuesday, Dec. 14, 2010 Persistent Economic Discontent Casts a Continuing Political Pall Congressional Republicans
ABC NEWS/WASHINGTON POST POLL: POST-ELECTION POLITICS EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE AFTER 5 p.m. Tuesday, Dec. 14, 2010 Persistent Economic Discontent Casts a Continuing Political Pall Congressional Republicans
WISCONSIN ECONOMIC SCORECARD
 RESEARCH BRIEF Q4 2013 Joseph Cera, PhD CUIR Survey Center University of Wisconsin Milwaukee WISCONSIN ECONOMIC SCORECARD The Wisconsin Economic Scorecard is a quarterly poll of Wisconsin residents conducted
RESEARCH BRIEF Q4 2013 Joseph Cera, PhD CUIR Survey Center University of Wisconsin Milwaukee WISCONSIN ECONOMIC SCORECARD The Wisconsin Economic Scorecard is a quarterly poll of Wisconsin residents conducted
IDEOLOGY, THE AFFORDABLE CARE ACT RULING, AND SUPREME COURT LEGITIMACY
 Public Opinion Quarterly, Vol. 78, No. 4, Winter 2014, pp. 963 973 IDEOLOGY, THE AFFORDABLE CARE ACT RULING, AND SUPREME COURT LEGITIMACY Christopher D. Johnston* D. Sunshine Hillygus Brandon L. Bartels
Public Opinion Quarterly, Vol. 78, No. 4, Winter 2014, pp. 963 973 IDEOLOGY, THE AFFORDABLE CARE ACT RULING, AND SUPREME COURT LEGITIMACY Christopher D. Johnston* D. Sunshine Hillygus Brandon L. Bartels
ATTITUDES TOWARDS INCOME AND WEALTH INEQUALITY AND SUPPORT FOR SCOTTISH INDEPENDENCE OVER TIME AND THE INTERACTION WITH NATIONAL IDENTITY
 Scottish Affairs 23.1 (2014): 27 54 DOI: 10.3366/scot.2014.0004 # Edinburgh University Press www.euppublishing.com/scot ATTITUDES TOWARDS INCOME AND WEALTH INEQUALITY AND SUPPORT FOR SCOTTISH INDEPENDENCE
Scottish Affairs 23.1 (2014): 27 54 DOI: 10.3366/scot.2014.0004 # Edinburgh University Press www.euppublishing.com/scot ATTITUDES TOWARDS INCOME AND WEALTH INEQUALITY AND SUPPORT FOR SCOTTISH INDEPENDENCE
Michael Förster. OECD Social Policy Division. November 3 rd 2015
 Michael Förster OECD Social Policy Division November 3 rd 2015 Rózsavölgyi Szalon Budapest 4 November 2015 Three major OECD studies since 2008 2008 2011 2015 2/16 Results from recent OECD study on inequality:
Michael Förster OECD Social Policy Division November 3 rd 2015 Rózsavölgyi Szalon Budapest 4 November 2015 Three major OECD studies since 2008 2008 2011 2015 2/16 Results from recent OECD study on inequality:
UTS:IPPG Project Team. Project Director: Associate Professor Roberta Ryan, Director IPPG. Project Manager: Catherine Hastings, Research Officer
 IPPG Project Team Project Director: Associate Professor Roberta Ryan, Director IPPG Project Manager: Catherine Hastings, Research Officer Research Assistance: Theresa Alvarez, Research Assistant Acknowledgements
IPPG Project Team Project Director: Associate Professor Roberta Ryan, Director IPPG Project Manager: Catherine Hastings, Research Officer Research Assistance: Theresa Alvarez, Research Assistant Acknowledgements
Research Statement. Jeffrey J. Harden. 2 Dissertation Research: The Dimensions of Representation
 Research Statement Jeffrey J. Harden 1 Introduction My research agenda includes work in both quantitative methodology and American politics. In methodology I am broadly interested in developing and evaluating
Research Statement Jeffrey J. Harden 1 Introduction My research agenda includes work in both quantitative methodology and American politics. In methodology I am broadly interested in developing and evaluating
University of California Institute for Labor and Employment
 University of California Institute for Labor and Employment The State of California Labor, 2002 (University of California, Multi-Campus Research Unit) Year 2002 Paper Weir Income Polarization and California
University of California Institute for Labor and Employment The State of California Labor, 2002 (University of California, Multi-Campus Research Unit) Year 2002 Paper Weir Income Polarization and California
MEMORANDUM. The pregnancy endangers the life of the woman 75% 18% The pregnancy poses a threat to the physical health 70% 21% of the woman
 MEMORANDUM TO: FROM: Ed Whelan, Ethics and Public Policy Center Wendy Long, Judicial Confirmation Network Whit Ayres DATE: May 14, 2007 RE: Public Opinion on Overturning Roe v. Wade A national survey our
MEMORANDUM TO: FROM: Ed Whelan, Ethics and Public Policy Center Wendy Long, Judicial Confirmation Network Whit Ayres DATE: May 14, 2007 RE: Public Opinion on Overturning Roe v. Wade A national survey our
download slides at: Politics Inequality in the United States 1
 Inequality in the United States 1 Political Participation and Income Percent Active 90.0 67.5 45.0 22.5 0 Voting Campaign Work Campaign Contribution under $15,000 $75,000 and over Contact Protest Affiliated
Inequality in the United States 1 Political Participation and Income Percent Active 90.0 67.5 45.0 22.5 0 Voting Campaign Work Campaign Contribution under $15,000 $75,000 and over Contact Protest Affiliated
PRESS RELEASE October 15, 2008
 PRESS RELEASE October 15, 2008 Americans Confidence in Their Leaders Declines Sharply Most agree on basic aspects of presidential leadership, but candidate preferences reveal divisions Cambridge, MA 80%
PRESS RELEASE October 15, 2008 Americans Confidence in Their Leaders Declines Sharply Most agree on basic aspects of presidential leadership, but candidate preferences reveal divisions Cambridge, MA 80%
Europe s Hidden Inequality i
 Focus on Europe London Office October 2010 Europe s Hidden Inequality i Income distribution in the European Union (EU) is much more unequal than the EU itself avows: indeed, it is more unequal than in,
Focus on Europe London Office October 2010 Europe s Hidden Inequality i Income distribution in the European Union (EU) is much more unequal than the EU itself avows: indeed, it is more unequal than in,
Asking for More: Support for Redistribution in the Age of Inequality
 Asking for More: Support for Redistribution in the Age of Inequality Charlotte Cavaille Institute for Advanced Study in Toulouse (until December 2016) Georgetown University (starting in January 2017) The
Asking for More: Support for Redistribution in the Age of Inequality Charlotte Cavaille Institute for Advanced Study in Toulouse (until December 2016) Georgetown University (starting in January 2017) The
Globalization and Inequality. An International Comparison between Sweden and the US
 ISBN: 978-84-695-8923-6 Documento de trabajo: Globalization and Inequality An International Comparison between Sweden and the US Luis P. Pérez-Megino and Sergio A. Berumen Universidad Rey Juan Carlos de
ISBN: 978-84-695-8923-6 Documento de trabajo: Globalization and Inequality An International Comparison between Sweden and the US Luis P. Pérez-Megino and Sergio A. Berumen Universidad Rey Juan Carlos de
The Racial Dimension of New York s Income Inequality
 The Racial Dimension of New York s Income Inequality Data Brief, March 2017 It is well-known that New York State has one of the highest degrees of income inequality among all fifty states, and that the
The Racial Dimension of New York s Income Inequality Data Brief, March 2017 It is well-known that New York State has one of the highest degrees of income inequality among all fifty states, and that the
THE WORKMEN S CIRCLE SURVEY OF AMERICAN JEWS. Jews, Economic Justice & the Vote in Steven M. Cohen and Samuel Abrams
 THE WORKMEN S CIRCLE SURVEY OF AMERICAN JEWS Jews, Economic Justice & the Vote in 2012 Steven M. Cohen and Samuel Abrams 1/4/2013 2 Overview Economic justice concerns were the critical consideration dividing
THE WORKMEN S CIRCLE SURVEY OF AMERICAN JEWS Jews, Economic Justice & the Vote in 2012 Steven M. Cohen and Samuel Abrams 1/4/2013 2 Overview Economic justice concerns were the critical consideration dividing
Claire L. Adida, UC San Diego Adeline Lo, Princeton University Melina Platas Izama, New York University Abu Dhabi
 The American Syrian Refugee Consensus* Claire L. Adida, UC San Diego Adeline Lo, Princeton University elina Platas Izama, New York University Abu Dhabi Working Paper 198 January 2019 The American Syrian
The American Syrian Refugee Consensus* Claire L. Adida, UC San Diego Adeline Lo, Princeton University elina Platas Izama, New York University Abu Dhabi Working Paper 198 January 2019 The American Syrian
In What s the Matter with Kansas?
 Voting on Values or Bread-and-Butter? Effects of Union Membership on the Politics of the White Working Class PETER L. FRANCIA the focus because, in the political arena, they typically endorse Democratic
Voting on Values or Bread-and-Butter? Effects of Union Membership on the Politics of the White Working Class PETER L. FRANCIA the focus because, in the political arena, they typically endorse Democratic
DATE: October 7, 2004 CONTACT: Adam Clymer at or (cell) VISIT:
 DATE: October 7, 2004 CONTACT: Adam Clymer at 202-879-6757 or 202 549-7161 (cell) VISIT: www.naes04.org Kerry Gained Favorability after Debate but Bush Is Still Preferred As Commander-In-Chief, Annenberg
DATE: October 7, 2004 CONTACT: Adam Clymer at 202-879-6757 or 202 549-7161 (cell) VISIT: www.naes04.org Kerry Gained Favorability after Debate but Bush Is Still Preferred As Commander-In-Chief, Annenberg
About the Broadbent Institute. Get Involved
 EQUALITY PROJECT About the Broadbent Institute Founded in 2011, with the endorsement of Jack Layton, the Broadbent Institute is Canada s newest resource for social democrats seeking change. The Institute
EQUALITY PROJECT About the Broadbent Institute Founded in 2011, with the endorsement of Jack Layton, the Broadbent Institute is Canada s newest resource for social democrats seeking change. The Institute
Economic Context and Americans Perceptions of Income Inequality n
 Economic Context and Americans Perceptions of Income Inequality n Ping Xu, Louisiana State University James C. Garand, Louisiana State University Objectives. The increase in income inequality in the United
Economic Context and Americans Perceptions of Income Inequality n Ping Xu, Louisiana State University James C. Garand, Louisiana State University Objectives. The increase in income inequality in the United
Reducing income inequality by economics growth in Georgia
 Reducing income inequality by economics growth in Georgia Batumi Shota Rustaveli State University Faculty of Economics and Business PhD student in Economics Nino Kontselidze Abstract Nowadays Georgia has
Reducing income inequality by economics growth in Georgia Batumi Shota Rustaveli State University Faculty of Economics and Business PhD student in Economics Nino Kontselidze Abstract Nowadays Georgia has
Jeffrey M. Stonecash Maxwell Professor
 Campbell Public Affairs Institute Inequality and the American Public Results of the Fourth Annual Maxwell School Survey Conducted September, 2007 Jeffrey M. Stonecash Maxwell Professor Campbell Public
Campbell Public Affairs Institute Inequality and the American Public Results of the Fourth Annual Maxwell School Survey Conducted September, 2007 Jeffrey M. Stonecash Maxwell Professor Campbell Public
Openness and Poverty Reduction in the Long and Short Run. Mark R. Rosenzweig. Harvard University. October 2003
 Openness and Poverty Reduction in the Long and Short Run Mark R. Rosenzweig Harvard University October 2003 Prepared for the Conference on The Future of Globalization Yale University. October 10-11, 2003
Openness and Poverty Reduction in the Long and Short Run Mark R. Rosenzweig Harvard University October 2003 Prepared for the Conference on The Future of Globalization Yale University. October 10-11, 2003
Chapter 5. Attitudes toward the Income Gap: Japan-U.S. Comparison *
 Chapter 5 Attitudes toward the Income Gap: Japan-U.S. Comparison * Fumio Ohtake, Osaka University Shinji Takenaka, Osaka University Abstract Employing the Japan-U.S. international survey, this study analyzed
Chapter 5 Attitudes toward the Income Gap: Japan-U.S. Comparison * Fumio Ohtake, Osaka University Shinji Takenaka, Osaka University Abstract Employing the Japan-U.S. international survey, this study analyzed
Framing the 2010 election
 September 20, 2010 Page 1 September 20, 2010 Framing the 2010 election Message test using a web-panel experiment September 20, 2010 Page 2 Republican message frameworks The following is a statement by
September 20, 2010 Page 1 September 20, 2010 Framing the 2010 election Message test using a web-panel experiment September 20, 2010 Page 2 Republican message frameworks The following is a statement by
Attitudes toward Immigration: Iowa Republican Caucus-Goers
 November 0 Survey Attitudes toward Immigration: Iowa Republican Caucus-Goers Partnership for a New American Economy Methodology: Survey Sample frame: Sample size: Weighting: Margin of error: Method/length:
November 0 Survey Attitudes toward Immigration: Iowa Republican Caucus-Goers Partnership for a New American Economy Methodology: Survey Sample frame: Sample size: Weighting: Margin of error: Method/length:
Prof. Bryan Caplan Econ 854
 Prof. Bryan Caplan bcaplan@gmu.edu http://www.bcaplan.com Econ 854 Week 6: Voter Motivation, III: Miscellaneous I. Religion, Party, and Ideology A. Many observers of modern American politics think that
Prof. Bryan Caplan bcaplan@gmu.edu http://www.bcaplan.com Econ 854 Week 6: Voter Motivation, III: Miscellaneous I. Religion, Party, and Ideology A. Many observers of modern American politics think that
Income Inequality and the Effects on Government Responsiveness
 Political Analysis Volume 19 Article 6 2018 Income Inequality and the Effects on Government Responsiveness Marina Kaghado Seton Hall University, marina.kaghado@student.shu.edu Follow this and additional
Political Analysis Volume 19 Article 6 2018 Income Inequality and the Effects on Government Responsiveness Marina Kaghado Seton Hall University, marina.kaghado@student.shu.edu Follow this and additional
Does Information about Income Inequality Shape Demand for Redistribution? Evidence from an On-line Experiment
 Does Information about Income Inequality Shape Demand for Redistribution? Evidence from an On-line Experiment Jan Zilinsky University of Chicago Booth School of Business February 28, 2013 Preliminary and
Does Information about Income Inequality Shape Demand for Redistribution? Evidence from an On-line Experiment Jan Zilinsky University of Chicago Booth School of Business February 28, 2013 Preliminary and
Intergenerational Mobility and Preferences for Redistribution
 American Economic Review 2018, 108(2): 521 554 https://doi.org/10.1257/aer.20162015 Intergenerational Mobility and Preferences for Redistribution By Alberto Alesina, Stefanie Stantcheva, and Edoardo Teso*
American Economic Review 2018, 108(2): 521 554 https://doi.org/10.1257/aer.20162015 Intergenerational Mobility and Preferences for Redistribution By Alberto Alesina, Stefanie Stantcheva, and Edoardo Teso*
Voter Turnout, Income Inequality, and Redistribution. Henning Finseraas PhD student Norwegian Social Research
 Voter Turnout, Income Inequality, and Redistribution Henning Finseraas PhD student Norwegian Social Research hfi@nova.no Introduction Motivation Robin Hood paradox No robust effect of voter turnout on
Voter Turnout, Income Inequality, and Redistribution Henning Finseraas PhD student Norwegian Social Research hfi@nova.no Introduction Motivation Robin Hood paradox No robust effect of voter turnout on
There is a seemingly widespread view that inequality should not be a concern
 Chapter 11 Economic Growth and Poverty Reduction: Do Poor Countries Need to Worry about Inequality? Martin Ravallion There is a seemingly widespread view that inequality should not be a concern in countries
Chapter 11 Economic Growth and Poverty Reduction: Do Poor Countries Need to Worry about Inequality? Martin Ravallion There is a seemingly widespread view that inequality should not be a concern in countries
From the veil of ignorance to the overlapping consensus: John Rawls as a theorist of communication
 From the veil of ignorance to the overlapping consensus: John Rawls as a theorist of communication Klaus Bruhn Jensen Professor, dr.phil. Department of Media, Cognition, and Communication University of
From the veil of ignorance to the overlapping consensus: John Rawls as a theorist of communication Klaus Bruhn Jensen Professor, dr.phil. Department of Media, Cognition, and Communication University of
Is the American Electorate Increasingly Polarized Because of Growing Income Inequality?
 Is the American Electorate Increasingly Polarized Because of Growing Income Inequality? James E. Campbell Department of Political Science University at Buffalo, SUNY Buffalo, NY 14260 jcampbel@buffalo.edu
Is the American Electorate Increasingly Polarized Because of Growing Income Inequality? James E. Campbell Department of Political Science University at Buffalo, SUNY Buffalo, NY 14260 jcampbel@buffalo.edu
At a time when political philosophy seemed nearly stagnant, John Rawls
 Bronwyn Edwards 17.01 Justice 1. Evaluate Rawls' arguments for his conception of Democratic Equality. You may focus either on the informal argument (and the contrasts with Natural Liberty and Liberal Equality)
Bronwyn Edwards 17.01 Justice 1. Evaluate Rawls' arguments for his conception of Democratic Equality. You may focus either on the informal argument (and the contrasts with Natural Liberty and Liberal Equality)
FOR RELEASE SEPTEMBER 13, 2018
 FOR RELEASE SEPTEMBER 13, 2018 FOR MEDIA OR OTHER INQUIRIES: Carroll Doherty, Director of Political Research Jocelyn Kiley, Associate Director, Research Bridget Johnson, Communications Manager 202.419.4372
FOR RELEASE SEPTEMBER 13, 2018 FOR MEDIA OR OTHER INQUIRIES: Carroll Doherty, Director of Political Research Jocelyn Kiley, Associate Director, Research Bridget Johnson, Communications Manager 202.419.4372
Iceland and the European Union Wave 2. Analytical report
 Flash Eurobarometer European Commission Iceland and the European Union Wave 2 Analytical report Fieldwork: August 2011 Report: October 2011 Flash Eurobarometer 327 The Gallup Organization This survey was
Flash Eurobarometer European Commission Iceland and the European Union Wave 2 Analytical report Fieldwork: August 2011 Report: October 2011 Flash Eurobarometer 327 The Gallup Organization This survey was
Who Cares About Income Inequality?
 Philip S. Morrison Who Cares About Income Inequality? On the eve of the lecture by the authors of The Spirit Level at the University of Auckland in May 2014, Tim Hazledine pointed to a 2006 international
Philip S. Morrison Who Cares About Income Inequality? On the eve of the lecture by the authors of The Spirit Level at the University of Auckland in May 2014, Tim Hazledine pointed to a 2006 international
Edexcel (A) Economics A-level
 Edexcel (A) Economics A-level Theme 4: A Global Perspective 4.2 Poverty and Inequality 4.2.2 Inequality Notes Distinction between wealth and income inequality Wealth is defined as a stock of assets, such
Edexcel (A) Economics A-level Theme 4: A Global Perspective 4.2 Poverty and Inequality 4.2.2 Inequality Notes Distinction between wealth and income inequality Wealth is defined as a stock of assets, such
THE COLOR OF ENTREPRENEURSHIP Why the Racial Gap among Firms Costs the U.S. Billions
 APRIL 2016 Why the Racial Gap among Firms Costs the U.S. Billions BY ALGERNON AUSTIN Businesses owned by people of color are playing an important part in restoring the health of the American economy after
APRIL 2016 Why the Racial Gap among Firms Costs the U.S. Billions BY ALGERNON AUSTIN Businesses owned by people of color are playing an important part in restoring the health of the American economy after
The Rich, The Poor, and The Changing Gap: An Investigation of the Determinants of Income Inequality from
 The Rich, The Poor, and The Changing Gap: An Investigation of the Determinants of Income Inequality from 1996-2002 Thomas Clark The College of New Jersey April 2004 1 I. Introduction The gap between the
The Rich, The Poor, and The Changing Gap: An Investigation of the Determinants of Income Inequality from 1996-2002 Thomas Clark The College of New Jersey April 2004 1 I. Introduction The gap between the
The Black-White Wage Gap Among Young Women in 1990 vs. 2011: The Role of Selection and Educational Attainment
 The Black-White Wage Gap Among Young Women in 1990 vs. 2011: The Role of Selection and Educational Attainment James Albrecht, Georgetown University Aico van Vuuren, Free University of Amsterdam (VU) Susan
The Black-White Wage Gap Among Young Women in 1990 vs. 2011: The Role of Selection and Educational Attainment James Albrecht, Georgetown University Aico van Vuuren, Free University of Amsterdam (VU) Susan
Expert group meeting. New research on inequality and its impacts World Social Situation 2019
 Expert group meeting New research on inequality and its impacts World Social Situation 2019 New York, 12-13 September 2018 Introduction In 2017, the General Assembly encouraged the Secretary-General to
Expert group meeting New research on inequality and its impacts World Social Situation 2019 New York, 12-13 September 2018 Introduction In 2017, the General Assembly encouraged the Secretary-General to
Should the Democrats move to the left on economic policy?
 Should the Democrats move to the left on economic policy? Andrew Gelman Cexun Jeffrey Cai November 9, 2007 Abstract Could John Kerry have gained votes in the recent Presidential election by more clearly
Should the Democrats move to the left on economic policy? Andrew Gelman Cexun Jeffrey Cai November 9, 2007 Abstract Could John Kerry have gained votes in the recent Presidential election by more clearly
THE GRANITE STATE POLL THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW HAMPSHIRE
 THE GRANITE STATE POLL THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW HAMPSHIRE NH WANTS NEW JUSTICE TO UPHOLD ROE v.wade By: Andrew E. Smith, Ph.D. 603/862-2226 FOR RELEASE UNH Survey Center July 20, 2005 www.unh.edu/survey-center
THE GRANITE STATE POLL THE UNIVERSITY OF NEW HAMPSHIRE NH WANTS NEW JUSTICE TO UPHOLD ROE v.wade By: Andrew E. Smith, Ph.D. 603/862-2226 FOR RELEASE UNH Survey Center July 20, 2005 www.unh.edu/survey-center
WISCONSIN ECONOMIC SCORECARD
 RESEARCH BRIEF Q1 2014 Joseph Cera, PhD CUIR Survey Center University of Wisconsin Milwaukee WISCONSIN ECONOMIC SCORECARD The Wisconsin Economic Scorecard is a quarterly poll of Wisconsin residents conducted
RESEARCH BRIEF Q1 2014 Joseph Cera, PhD CUIR Survey Center University of Wisconsin Milwaukee WISCONSIN ECONOMIC SCORECARD The Wisconsin Economic Scorecard is a quarterly poll of Wisconsin residents conducted
Iowa Voting Series, Paper 6: An Examination of Iowa Absentee Voting Since 2000
 Department of Political Science Publications 5-1-2014 Iowa Voting Series, Paper 6: An Examination of Iowa Absentee Voting Since 2000 Timothy M. Hagle University of Iowa 2014 Timothy M. Hagle Comments This
Department of Political Science Publications 5-1-2014 Iowa Voting Series, Paper 6: An Examination of Iowa Absentee Voting Since 2000 Timothy M. Hagle University of Iowa 2014 Timothy M. Hagle Comments This
THERE ARE NO RICH PEOPLE IN THE WORLD
 THERE ARE NO RICH PEOPLE IN THE WORLD There are no rich people in the world, and there are no poor people. There are just people. The rich may have lots of pieces of green paper that many pretend are worth
THERE ARE NO RICH PEOPLE IN THE WORLD There are no rich people in the world, and there are no poor people. There are just people. The rich may have lots of pieces of green paper that many pretend are worth
GPP 501 Microeconomic Analysis for Public Policy Fall 2017
 GPP 501 Microeconomic Analysis for Public Policy Fall 2017 Given by Kevin Milligan Vancouver School of Economics University of British Columbia Lecture Sept 20th: Inequality and Justice MPPG 501: Sept
GPP 501 Microeconomic Analysis for Public Policy Fall 2017 Given by Kevin Milligan Vancouver School of Economics University of British Columbia Lecture Sept 20th: Inequality and Justice MPPG 501: Sept
In Defense of Liberal Equality
 Public Reason 9 (1-2): 99-108 M. E. Newhouse University of Surrey 2017 by Public Reason Abstract: In A Theory of Justice, Rawls concludes that individuals in the original position would choose to adopt
Public Reason 9 (1-2): 99-108 M. E. Newhouse University of Surrey 2017 by Public Reason Abstract: In A Theory of Justice, Rawls concludes that individuals in the original position would choose to adopt
PEW RESEARCH CENTER. FOR RELEASE January 16, 2019 FOR MEDIA OR OTHER INQUIRIES:
 FOR RELEASE January 16, 2019 FOR MEDIA OR OTHER INQUIRIES: Carroll Doherty, Director of Political Research Jocelyn Kiley, Associate Director, Research Bridget Johnson, Communications Manager 202.419.4372
FOR RELEASE January 16, 2019 FOR MEDIA OR OTHER INQUIRIES: Carroll Doherty, Director of Political Research Jocelyn Kiley, Associate Director, Research Bridget Johnson, Communications Manager 202.419.4372
Povery and Income among African Americans
 Povery and Income among African Americans Black Median Household income: $35,481 (all races $53,657) All Black Workers 2015 weekly earnings:$624 (all races $803) Black Men weekly earnings: $652 (All men
Povery and Income among African Americans Black Median Household income: $35,481 (all races $53,657) All Black Workers 2015 weekly earnings:$624 (all races $803) Black Men weekly earnings: $652 (All men
Immigration and Multiculturalism: Views from a Multicultural Prairie City
 Immigration and Multiculturalism: Views from a Multicultural Prairie City Paul Gingrich Department of Sociology and Social Studies University of Regina Paper presented at the annual meeting of the Canadian
Immigration and Multiculturalism: Views from a Multicultural Prairie City Paul Gingrich Department of Sociology and Social Studies University of Regina Paper presented at the annual meeting of the Canadian
RUSSELL SAGE FOUNDATION
 RUSSELL SAGE FOUNDATION Working Paper #201 POLITICAL POLARIZATION AND INCOME INEQUALITY Nolan McCarty Keith T. Poole Howard Rosenthal February 2003 Russell Sage Working Papers have not been reviewed by
RUSSELL SAGE FOUNDATION Working Paper #201 POLITICAL POLARIZATION AND INCOME INEQUALITY Nolan McCarty Keith T. Poole Howard Rosenthal February 2003 Russell Sage Working Papers have not been reviewed by
Do you think you are a Democrat, Republican or Independent? Conservative, Moderate, or Liberal? Why do you think this?
 Do you think you are a Democrat, Republican or Independent? Conservative, Moderate, or Liberal? Why do you think this? Reactionary Moderately Conservative Conservative Moderately Liberal Moderate Radical
Do you think you are a Democrat, Republican or Independent? Conservative, Moderate, or Liberal? Why do you think this? Reactionary Moderately Conservative Conservative Moderately Liberal Moderate Radical
Election Day Voter Registration in
 Election Day Voter Registration in Massachusetts Executive Summary We have analyzed the likely impact of adoption of Election Day Registration (EDR) by the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. 1 Consistent with
Election Day Voter Registration in Massachusetts Executive Summary We have analyzed the likely impact of adoption of Election Day Registration (EDR) by the Commonwealth of Massachusetts. 1 Consistent with
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE DATE: August 3, 2004 CONTACT: Adam Clymer at or (cell) VISIT:
 FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE DATE: August 3, 2004 CONTACT: Adam Clymer at 202-879-6757 or 202 549-7161 (cell) VISIT: www.naes04.org Fahrenheit 9/11 Viewers and Limbaugh Listeners About Equal in Size Even Though
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE DATE: August 3, 2004 CONTACT: Adam Clymer at 202-879-6757 or 202 549-7161 (cell) VISIT: www.naes04.org Fahrenheit 9/11 Viewers and Limbaugh Listeners About Equal in Size Even Though
Princeton University Spring 2012 T. Romer. Politics 584/Economics 576 Foundations of Political Economy. Reading List
 Princeton University Spring 2012 T. Romer The main readings are indicated by *. Politics 584/Economics 576 Foundations of Political Economy Reading List References denoted by PT are to Political Economics
Princeton University Spring 2012 T. Romer The main readings are indicated by *. Politics 584/Economics 576 Foundations of Political Economy Reading List References denoted by PT are to Political Economics
Gettysburg Social Sciences Review Fall 2018
 Gettysburg Social Sciences Review Volume 2 Issue 2 Article 1 2018 Gettysburg Social Sciences Review Fall 2018 Follow this and additional works at: https://cupola.gettysburg.edu/gssr Part of the American
Gettysburg Social Sciences Review Volume 2 Issue 2 Article 1 2018 Gettysburg Social Sciences Review Fall 2018 Follow this and additional works at: https://cupola.gettysburg.edu/gssr Part of the American
Handout 1: Empirics of Economic Growth
 14.451: Macroeconomic Theory I Suman S. Basu, MIT Handout 1: Empirics of Economic Growth Welcome to 14.451, the introductory course of the macro sequence. The aim of this course is to familiarize you with
14.451: Macroeconomic Theory I Suman S. Basu, MIT Handout 1: Empirics of Economic Growth Welcome to 14.451, the introductory course of the macro sequence. The aim of this course is to familiarize you with
An Equity Assessment of the. St. Louis Region
 An Equity Assessment of the A Snapshot of the Greater St. Louis 15 counties 2.8 million population 19th largest metropolitan region 1.1 million households 1.4 million workforce $132.07 billion economy
An Equity Assessment of the A Snapshot of the Greater St. Louis 15 counties 2.8 million population 19th largest metropolitan region 1.1 million households 1.4 million workforce $132.07 billion economy
RECOMMENDED CITATION: Pew Research Center, July, 2015, Negative Views of Supreme Court at Record High, Driven by Republican Dissatisfaction
 NUMBERS, FACTS AND TRENDS SHAPING THE WORLD FOR RELEASE JULY 29, 2015 FOR FURTHER INFORMATION ON THIS REPORT: Carroll Doherty, Director of Political Research Bridget Jameson, Communications Associate 202.419.4372
NUMBERS, FACTS AND TRENDS SHAPING THE WORLD FOR RELEASE JULY 29, 2015 FOR FURTHER INFORMATION ON THIS REPORT: Carroll Doherty, Director of Political Research Bridget Jameson, Communications Associate 202.419.4372
Where are the Middle Class in OECD Countries? Nathaniel Johnson (CUNY and LIS) David Johnson (University of Michigan)
 Where are the Middle Class in OECD Countries? Nathaniel Johnson (CUNY and LIS) David Johnson (University of Michigan) The Middle Class is all over the US Headlines A strong middle class equals a strong
Where are the Middle Class in OECD Countries? Nathaniel Johnson (CUNY and LIS) David Johnson (University of Michigan) The Middle Class is all over the US Headlines A strong middle class equals a strong
POSC 4931 Topics in Political Science: The Politics of Inequality Spring, 2016
 POSC 4931 Topics in Political Science: The Politics of Inequality Spring, 2016 Office 450 William Wehr Physics Office Hours: Tuesday/Thursday 12:30-1:30; 3:30-5:30 Phone: 8-6842/3418 Email: duane.swank@marquette.edu
POSC 4931 Topics in Political Science: The Politics of Inequality Spring, 2016 Office 450 William Wehr Physics Office Hours: Tuesday/Thursday 12:30-1:30; 3:30-5:30 Phone: 8-6842/3418 Email: duane.swank@marquette.edu
September 2017 Toplines
 The first of its kind bi-monthly survey of racially and ethnically diverse young adults Field Period: 08/31-09/16/2017 Total N: 1,816 adults Age Range: 18-34 NOTE: All results indicate percentages unless
The first of its kind bi-monthly survey of racially and ethnically diverse young adults Field Period: 08/31-09/16/2017 Total N: 1,816 adults Age Range: 18-34 NOTE: All results indicate percentages unless
Budget 2018 & foreign aid: Two-thirds see moral obligation to help abroad and half that many say Canada should raise spending
 Budget 2018 & foreign aid: Two-thirds see moral obligation to help abroad and half that many say Canada should raise spending Comprehensive study looks at perspectives on international aid at governmental
Budget 2018 & foreign aid: Two-thirds see moral obligation to help abroad and half that many say Canada should raise spending Comprehensive study looks at perspectives on international aid at governmental
