The Kinds of Promises Legally Enforced
|
|
|
- Henry McDaniel
- 5 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 The Kinds of Promises Legally Enforced Offers There can be serious consequences if an offer is found to be legally binding. In Denton a railway schedule was found to be a unilateral contract, and thus the company was liable for publishing trains in the schedule that they knew would not run. Intent to be bound Generally there must be an intent to be bound and price quotes are merely invitations to negotiate not an offer to sell (Johnson Bros.). An exception to this is when the offer is clear, explicit and definite. The offeror may impose any conditions they please upon the initial offer but may not add arbitrary conditions following acceptance (Lefkowitz). When items are displayed in a store, this is only an invitation to treat. The offer occurs when a customer takes an item to the cashier and the shopkeeper must then accept the offer (Boots). Withdrawal of Offers An offer that is not accepted within a reasonable amount of time is viewed as withdrawn or refused (Manchester Diocesan Council). Offers may be withdrawn at any time so long as the offer has not been accepted and it has been communicated (which may be indirectly) to the other party (Dickson v. Dodds). Acceptance Acceptance of an offer must be communicated to the other party to have a binding contract (Larken v. Gardiner). Both parties must agree on the exact terms of a contract for it to be binding, and acceptance on different terms is really a counter offer (Eliason v Henshaw). In battle of the forms it is the last form that is seen to lay out the terms of he contract (Butler Machine Tool Co.). This is generally seen to favour sellers. Tendering In Ron Engineering the SCC adopted the two-contract approach for tendering.
2 o Contract A (unilateral) The call for tenders. It s terms governs the tendering process. If a bid is successful the bidder is bound to enter in to contract B. Now seen as a bilateral contract, exchange of promises for future performance. o Contract B The construction contract. A privilege clause in a call for tenders may allow for a bid that is not the lowest to be accepted but does not give the right to accept non-compliant tenders (MJB Enterprises). Contract A is now seen to have two implicit terms: that all bids be treated equally and that only compliant offers may be accepted (Double N Earthmovers). Formalization and Certainty An agreement to agree does not give rise to a contract. Here the missing terms were price, quantity and delivery (May and Butch Ltd.) Alternately, documents should be read broadly and a contract will not fail due to some ambiguity if the parties clearly intended to be bound and had a working relationship (Hillas v Arcos). Contracts can be enforced even when price is not agreed upon. In Foley v. Classique Coaches the price was to be agreed upon time to time in writing. Here the price had to be reasonable and the sales contract for petrol was a part of a sale of land contract. There can be an implied term to negotiate in good faith by a landlord and not refuse the renewal of a rental contract where offer was market rent (Empress Towers). Not used in precedent. Even if the parties believe they have a contract it may only be illusionary if no clear bargain ever occurred (Scammell). Correspondence Postal Acceptance Rule The Postal Acceptance Rule is the exception to the rule that acceptance must be communicated to the other party to form a contract. Here acceptance occurs when the offeree puts their acceptance into the mail, not when it is received. This rule only applies to acceptances, not revocation of offers (Henthorn v Fraser and Byrne v Van Tienhoven). Today this rule is only used when the parties clearly intend to use mail for communications. An exception to the post acceptance rule is when a letter is lost in the mail and never received even if it was properly addressed (Holwell Securities Ltd.).
3 Instantaneous Communication The post acceptance rule does not apply to faxed documents. They are received when they arrive at the other fax machine. There will be little time between these two occurrences, but it can effect who has jurisdiction over a dispute (Eastern Power). The rule for electronic transactions is similar to that for fax. An acceptance is received when it arrives in the offerors server / inbox s. 18(2). Here the location acceptance is seen to be sent / received is the parties places of business s. 18(3) (BC Electronic Transactions Act) Consideration Consideration is formally required to have a contract. Formalities in contracts serve three functions: evidentiary, cautionary, channelling. Policy framework for enforcement of promises: o Evidence always important o Deliberation did the parties try to make a contract? o Unjust Enrichment important but still only a policy factor o Reliance desire to protect reasonable reliance on a promise o Facilitate Private Ordering what sort of arrangements do we want to enforce for the betterment of society. Enforcement of Gift Promises The adequacy of consideration is not a factor in determining if there was a contract (Thomas). Here payment of 1 pound per year was sufficient consideration as it formalized the contract. Agreement to give up something you had no right to in the first place is not good consideration (White). Here there was also the policy factor of not wanting to reward whining. An agreement to give up things you are legally entitled to (forbearance on legal rights) can be consideration (Hamer). Here there was also clear intention to form a contract. Can only be distinguished from White on policy factors. Mutuality There must be an obligation on both parties in order for a contract to be formed (GNR v Witham). This obligation can take the form of minimum purchase amounts or exclusivity for example. o However, framework contracts such as this are enforced in some jurisdictions. o In Tobias v Dick a one-sided promise was not enforced both due to lack of mutuality and to prevent one party from taking advantage of the other.
4 Court may imply in a promise to use reasonable efforts as consideration when the agreement had been functioning in that way (Wood v Lucy, Lady Duff Gordon). Here profits were also split which gave benefit to the defendant who tried to claim there was no contract. Going Transaction Modifications An agreement to complete a pre-existing contract or duty is not consideration and therefore not enforceable and any extra money promised is an unenforceable gift (Harris v Watson 1791 and Stilk v Myrik 1809). These cases were both seamen already on the ship they had agreed to serve on. In sale of goods contracts agreeing to a price increase is not enforceable as it lacks consideration (Gilbert Steel). o Plaintiff claims that it was a new contract not a modification which was rejected. o Estoppel was used by the plaintiff but was rejected as it cannot be used to create obligations. o Plaintiff also tried to argue increased credit and promise to give good prices in the future but these are good examples poor arguments for consideration. o This goes against the International Sale of Goods Act. Canada has no modern sale of goods laws. In England courts have accepted that receiving a practical benefit from agreeing to a price increase may serve as consideration (Roffey Bros. 1991). Here extra money was required for the job to be completed on time, which was offered by the initial offeror. In New Brunswick it has been established that GTAs do not require fresh consideration as long as the modification did not occur under duress (NAV Canada 2008). In British Columbia the doctrine from NAV Canada has been accepted with the additional term that there was detrimental reliance (River Wind Ventures 2009). Debt settlement is a special case in GTAs. Formerly it followed traditional rules and an agreement to accept less was not enforceable (Foakes v Beer 1894); however the Mercantile Law Amendment Act and the Law and Equity Act (BC) now enforce and agreement to collect less money by creditors. Settlements Forbearance on the right to make a legal claim is good consideration even if that claim would have failed (Fairgrief v Ellis). What you are giving up here is a chance of succeeding, even if it is unlikely. However if the settlement is based on misleading facts it may not be enforceable (B.(D.C.) v Arkin). This decision was based on mistake, not lack of consideration. Stott v Merit sets out criteria for a valid settlement: reasonable claim, good faith in making the claim, no concealment of the fact.
5 Charitable Subscription Charitable subscriptions are gift promises not enforced by common law even if there was reliance on a donation (Dalhousie College). Intention and Non-Bargain Promises There must always be an intent to be bound, which would lead a reasonable person to believe that there was a contract. Natural love and affection may not serve as consideration (Balfour in Jones v Padavatton) However family situations may result in a legal relationship in special circumstances where there was a clear intent to be bound and consideration is found in a party giving up many things (Jones v Padvatton). Here there were also communications via lawyers. Parties may also purposefully enter non-binding agreements so long as it is clear this was the intention (Rose v JR Crompton) Promises Under Seal A seal is not equivalent to consideration. Sealed documents are a transfer of property. Requirements: in writing, sealed, signed, and delivered. A sealed document cannot be obtained by fraud as it is the intentions of the parties that give rise to legal obligations. Purposes of using a seal o Evidentiary show there was a contract o Cautionary formalization encourages thought about rights that are being given up o Channelling declares parties intend to be bound Past Consideration Past consideration is not good consideration. Policy factors for this: o Lack of deliberation o Lack of reliance o No unjust enrichment o Distinguish moral from legal obligations o Concerns regarding fraud on creditors could give a relative creditor status by claiming you owed them for what was a gift.
6 A promise about a contract that has already been executed is without consideration (Riscorla v Thomas) An exception to this is an initial request for service can imply a payment; however this is categorized as a unilateral contract, not as allowing past consideration (Lampleigh v Brathwait). Promissory Estoppel Reliance is not consideration. Common law estoppel barred a party from denying facts that had been previously agreed upon. Promissory Estoppel addresses future conduct, which had been agreed upon. It is only available as a defence not as a cause of action (Combe v Combe). Equitable doctrine articulated in Hughes. Promissory estoppel is only available when there is an underlying assumption of legal relationships (NM V ATA). Here the contract was based on a romantic relationship. May be used to defend the belief that strict rights under contract are suspended during negotiations (Hughes). A promise can be binding so long as it was indented to be and there was an existing legal relationship; however this may only be used as a defence to damages not as an independent cause of action, which results in promises to pay less being enforced but not promises to pay more (High Trees). However in Australia the courts have allowed estoppel to be used to enforce a pre-contractual promise (Waltons v Maher). As estoppel is an equitable doctrine fairness is sometimes considered in its application (Combe v Combe). Indulgences in allowing late payments do not give rise to estoppel unless there was clear intention to alter legal relationships (John Burrows). Intent to change legal relationship may be implied through the conduct of the parties (Owen Sound). This is seen as at odds with the John Burrows case. As estoppel is an equitable doctrine and agreement to accept less is not enforced when there is undue pressure or intimidation (D&C Builders). Unilateral Contracts Unilateral contracts are open ended and accepted through performance A unilateral contract is formed with anyone who fulfills the conditions regardless of whether the offer motivated them or not (Williams v Carwardine). An exception to this is when the party who fulfills the offer did not know it existed (R v Clarke). This is contrary to the Quebec Civil Code, which state that fulfilling all conditions is sufficient for the formation of a unilateral contract.
7 It is not necessary to notify the offeror of acceptance; the offeree only needs to perform to result in contract formation (Carbolic Smoke Ball Company). A common current form of unilateral contracts is government subsidy programs. o An affirmative action program which offered funding for disadvantaged students to attend university was not allowed to be cut half way as the offer was for full degrees (Dale v Manitoba) o In a potato subsidy program, it was found that everyone who met the conditions was entitled to subsidy (Grant v New Brunswick) Courts can also imply in a second contract to not break the first one in the middle of performance (Errington v Errington), which lines up with the modern rule that once performance has commenced the contract may not be revoked (Ayerswood Development Corp v Hydro One Network). o As a result of this government subsidy programs now have very specific wording with regards to eligibility. Courts may also choose to view something as mutual promises instead of a unilateral contract if it is favoured by the situation and by policy factors (Dawson v Helicopter Exploraction). Contracts and Third Parties Third-party beneficiaries The common law rule of privity of contract states that only someone party to a contract may enforce it, even if the contract was made for the benefit of a third party (Tweedle v. Atkinson) Privity of contract exists both vertically and horizontally o Vertical privity is seen in retail settings: consumer retailer distributer manufacturer. Here one may only sue the person next to them in the chain. This can cause problems as the chain may be broken such as by bankruptcy. o Horizontal privity is seen when it is a person who is not the buyer affected by a product. Privity of contract can be avoided using trust, assignment or agency. o Under trust law a beneficiary may sue o Assignment is a transfer of rights but not of obligations o Agency results in the principle granting rights to contract to the agent on their behalf. In Beswick v. Beswick a contract between uncle and nephew that included that the nephew support the widow was able to be enforced by the widow but only because she was the administratrix of the will. o The remedy granted was specific performance. o There were strong policy reasons to enforce the contract here
8 Privity of contract also comes up in the case of employee liability. When an employee damages something are the protected via their employers contract with the customer? o In London Drugs the issue was whether the employees would be covered by a limited liability clause that was in the storage contract. Here the court read in an intent to cover the 3 rd party when they were acting in the course of their employment performing action laid out in the contract. o In London Drugs the SCC relaxes privity of contract from the approach in Greenwood using a modified agency test. o It is important to note that London Drugs only gives coverage to employees when their employers have insurance. The employer may also expressly exclude employees from coverage. In Fraser River Pile, the approach in London Drugs is applied in a general commercial setting. Here the court establishes that third parties are to be covered when their actions are that which was expected to fall under the contract. In Canadian Tire, the action fails in contract for a boy damaged by a bicycle purchased by his father as he was not privy to the sale of goods contract and was not a buyer for the purpose of the Sale of Goods Act. Note that British Columbia does not have any legislation on third-party rights to contracts. Mistaken Identity In mistaken identity cases there are two victims: the initial seller and the good faith purchaser. Because the rouge is rarely still around, contract law must allocate the risk between these two victims Nemo dat principle: You cannot sell what you do not have. Codified in the Sale of Goods Act s26(1) o In mistaken identity this principle goes against the policy reasons which state that the final good faith purchaser deserves protection. In Philips v. Brooks the seller was unable to claim against the final purchaser, because the rogue s false identity was not brought up until after the terms of sale had been established. o The contract was clearly with the person there not with Sir George In Ingram v. Little the contract was void as the court found the offer was made to PGM Hutchinson and only he was legally able to accept it. o The dissent found that you contract with the person in front of you. Also wanted to apportion the loss which isn t usually allowed for in Canadian Law
9 In Avery v. Lewis the court finds that the initial sales contract based on mistaken identity is voidable until the goods are re-sold to a good faith purchaser. Here the car was sold and the initially seller cannot reclaim it. o General presumption that you contract with the person in front of you o Puts the risk on the seller who allows the rogue to leave with the goods before there has been full payment. Non est factum Historically non est factum was available in cases of fraud/forgery or when the party was blind/illiterate and did not know what they were signing. o It is not available to a person of full capacity who mistakenly signs a document, because generally the person who signed the document was in the best position to prevent the loss. In Saunders v. Anglia, even though the old lady did not know exactly what the document said because her glasses were broken, she was aware of the fundamental nature of the document which prevented the claim of non est factum. o This contract would have been voidable before the mortgage to Anglia Building. In Marvco v. Harris, non est factum was not available because the Harris signed the documents trusting their son in-law. They could have easily read them.
LAW 108A private law: contracts
 LAW 108A private law: contracts midterm outline 2012-2013 John Bullock TABLE OF CONTENTS Interests Protected & Consequences of Contract... 4 Remedies... 4 Damages... 4 Kinds of Promises Legally Enforced...
LAW 108A private law: contracts midterm outline 2012-2013 John Bullock TABLE OF CONTENTS Interests Protected & Consequences of Contract... 4 Remedies... 4 Damages... 4 Kinds of Promises Legally Enforced...
Privity: Third party to K can t enforce its obligations b/c they haven t contributed consideration for its promises ( Tweddle ); Principal not named
 Privity: Third party to K can t enforce its obligations b/c they haven t contributed consideration for its promises ( Tweddle ); Principal not named in K can sue if promisee was contracted as principal
Privity: Third party to K can t enforce its obligations b/c they haven t contributed consideration for its promises ( Tweddle ); Principal not named in K can sue if promisee was contracted as principal
Was there a counter offer? Was there silence? Is it by mail or an instantaneous mode?
 FORMATION OF A VALID CONTRACT 1 Is there intent to create legal obligations? 2 Is there communication of the offer? 3 Is there acceptance of the offer? 4 Is there a certainty of terms? Is there a social
FORMATION OF A VALID CONTRACT 1 Is there intent to create legal obligations? 2 Is there communication of the offer? 3 Is there acceptance of the offer? 4 Is there a certainty of terms? Is there a social
the parties had dealt with each other before and were well acquainted with the timber industry
 Formation of a Contract To start with it needs to be identified whether and which party is alleging a contract. For a contract to be valid it must be: 1.! An agreement 2.! Contractual intention 3.! Consideration
Formation of a Contract To start with it needs to be identified whether and which party is alleging a contract. For a contract to be valid it must be: 1.! An agreement 2.! Contractual intention 3.! Consideration
CHAPTER 1. The question requires a discussion of the law with regard to offer an acceptance. For a contract to be valid it must be:
 CHAPTER 1 property of 1stclasslawnotes lawstoreuk Formation Formation of Contract The question requires a discussion of the law with regard to offer an acceptance. For a contract to be valid it must be:
CHAPTER 1 property of 1stclasslawnotes lawstoreuk Formation Formation of Contract The question requires a discussion of the law with regard to offer an acceptance. For a contract to be valid it must be:
CONTRACT LAW. Elements of a Contract
 CONTRACT LAW Contracts: Types and Sources in Australia CONTRACT: An agreement concerning promises made between two or more parties with the intention of creating certain legal rights and obligations upon
CONTRACT LAW Contracts: Types and Sources in Australia CONTRACT: An agreement concerning promises made between two or more parties with the intention of creating certain legal rights and obligations upon
Offer: Has a valid offer been made?
 Agreement Offer and acceptance based can exist between 2 or more (Clarke v Dunraven) May be necessary to look at whole agreement rather than isolate offer and acceptance (Empirnall Holdings v Machon Paul
Agreement Offer and acceptance based can exist between 2 or more (Clarke v Dunraven) May be necessary to look at whole agreement rather than isolate offer and acceptance (Empirnall Holdings v Machon Paul
Business Law - Contract Law Study Notes
 Business Law - Contract Law Study Notes Comprehensive unit study notes as per Victoria University. 1 Table of Contents Note topic Content page Full semester notes 3-49 How to write IRAC 50-51 response
Business Law - Contract Law Study Notes Comprehensive unit study notes as per Victoria University. 1 Table of Contents Note topic Content page Full semester notes 3-49 How to write IRAC 50-51 response
Chapter 9: Contract Formation. Copyright 2009 South-Western Legal Studies in Business, a part of South-Western Cengage Learning.
 Chapter 9: Contract Formation a Copyright part of South-Western 2009 South-Western Cengage Legal Learning. Studies Business, Introduction is a declaration that something will or will not happen in the
Chapter 9: Contract Formation a Copyright part of South-Western 2009 South-Western Cengage Legal Learning. Studies Business, Introduction is a declaration that something will or will not happen in the
The Objective Principle of a Promise... 2 Intention to Create Legal Relations... 4 Offer and Acceptance... 5
 1 Contents The Objective Principle of a Promise... 2 Intention to Create Legal Relations... 4 Offer and Acceptance... 5 Offer vs. Invitation to Treat... 5 Termination/Lapse of Offer... 6 Acceptance of
1 Contents The Objective Principle of a Promise... 2 Intention to Create Legal Relations... 4 Offer and Acceptance... 5 Offer vs. Invitation to Treat... 5 Termination/Lapse of Offer... 6 Acceptance of
Business Law & Ethics notes Lec Lecture topic Topic s covered Text book refs. constitution expansion of power interpreting power
 Business Law & Ethics notes Lec Lecture topic Topic s covered Text book refs 1 law, morality and philosophical views of ch 1 meaning of eithics law 2 the source of laws governing constitution expansion
Business Law & Ethics notes Lec Lecture topic Topic s covered Text book refs 1 law, morality and philosophical views of ch 1 meaning of eithics law 2 the source of laws governing constitution expansion
CONTRACTS LAW. Fall 2015 CAN IQRA AZHAR
 CONTRACTS LAW Fall 2015 CAN IQRA AZHAR Contracts CANs Fall 2015 Iqra Azhar 1 1. Table of Contents 1. FORMATION OF A VALID CONTRACT... 5 Offer and Invitation to Treat... 5 Canadian Dryers Association v
CONTRACTS LAW Fall 2015 CAN IQRA AZHAR Contracts CANs Fall 2015 Iqra Azhar 1 1. Table of Contents 1. FORMATION OF A VALID CONTRACT... 5 Offer and Invitation to Treat... 5 Canadian Dryers Association v
PRINCIPLES OF CONTRACTUAL LIABILITY 1.1. AGREEMENT TEMPLATE: CERTAINTY TEMPLATE:... Error! Bookmark not defined.
 PRINCIPLES OF CONTRACTUAL LIABILITY 1. FORMATION OF CONTRACT:... 2 1.1. AGREEMENT TEMPLATE:... 2 1.2. CAPACITY TEMPLATE:... = Error! Bookmark not defined. 1.3. INTENTION TEMPLATE: (objective test)... Error!
PRINCIPLES OF CONTRACTUAL LIABILITY 1. FORMATION OF CONTRACT:... 2 1.1. AGREEMENT TEMPLATE:... 2 1.2. CAPACITY TEMPLATE:... = Error! Bookmark not defined. 1.3. INTENTION TEMPLATE: (objective test)... Error!
Table of Content - Commercial Law. Year End Examination Notes
 Table of Content - Commercial Law Year End Examination Notes Chapter 4: Contract: Offer & Acceptance... 2 Chapter 5: Intention & Consideration... 7 Chapter 6: Express Terms of the Contract... 12 Chapter
Table of Content - Commercial Law Year End Examination Notes Chapter 4: Contract: Offer & Acceptance... 2 Chapter 5: Intention & Consideration... 7 Chapter 6: Express Terms of the Contract... 12 Chapter
MLL111- Exam Notes Contract Law (All Topics + Cases)
 1 MLL111- Exam Notes Contract Law (All Topics + Cases) 2 Contents Page Page 8: Formation of Contracts Offer and Acceptance Page 9: Acceptance Communication of Acceptance: Waiver Silence Page 10: Acceptance
1 MLL111- Exam Notes Contract Law (All Topics + Cases) 2 Contents Page Page 8: Formation of Contracts Offer and Acceptance Page 9: Acceptance Communication of Acceptance: Waiver Silence Page 10: Acceptance
CONTRACT LAW. What is a contract? A promise or set of promises that is legally binding. Why is contract so important? Contract forms the basis for
 CONTRACT LAW What is a contract? A promise or set of promises that is legally binding Why is contract so important? Contract forms the basis for - Commercial transactions - Consumer transactions; and o
CONTRACT LAW What is a contract? A promise or set of promises that is legally binding Why is contract so important? Contract forms the basis for - Commercial transactions - Consumer transactions; and o
Consideration sits alongside, offer and acceptance to form a legally binding contract.
 CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG Consideration and Estoppel Refer to Richards Law of Contract Chapter 3 A Introduction Background and function Consideration sits alongside, offer and acceptance to form a legally
CITY UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG Consideration and Estoppel Refer to Richards Law of Contract Chapter 3 A Introduction Background and function Consideration sits alongside, offer and acceptance to form a legally
CONTRACTS. Fall 2015 JENNA DAVIS THOMPSON RIVERS UNIVERSITY LAW 3030
 CONTRACTS Fall 2015 JENNA DAVIS THOMPSON RIVERS UNIVERSITY LAW 3030 1 1 Is there an intention to create legal obligations? 2 Is there communication of an offer? 3 Is there acceptance of the offer? 4 Is
CONTRACTS Fall 2015 JENNA DAVIS THOMPSON RIVERS UNIVERSITY LAW 3030 1 1 Is there an intention to create legal obligations? 2 Is there communication of an offer? 3 Is there acceptance of the offer? 4 Is
Law of Contracts. Determining Contractual Intent. Offer. 6 Elements of Legally Enforceable Contracts
 6 Elements of Legally Enforceable Contracts Law of Contracts 1. Offer and Acceptance 2. Genuine Assent 3. Legal Purpose Business Law Chapters 6-11 4. Consideration (Exchange of value) 5. Capacity to Contract
6 Elements of Legally Enforceable Contracts Law of Contracts 1. Offer and Acceptance 2. Genuine Assent 3. Legal Purpose Business Law Chapters 6-11 4. Consideration (Exchange of value) 5. Capacity to Contract
Emily M. Weitzenboeck, 2012 Norwegian Research Center for Computers & Law
 What is acceptance? i. The final and unconditional expression of consent to offer ii. made in response to offer iii. exactly matching terms of offer iv. communicated to offeror. Element (i): final and
What is acceptance? i. The final and unconditional expression of consent to offer ii. made in response to offer iii. exactly matching terms of offer iv. communicated to offeror. Element (i): final and
FORMATION OF A VALID CONTRACT 4 1. Offer and Invitations to Treat 4 Canadian Dyers Assn v. Burton (1920, H.L.) 4 Pharmaceutical Society v.
 FORMATION OF A VALID CONTRACT 4 1. Offer and Invitations to Treat 4 Canadian Dyers Assn v. Burton (1920, H.L.) 4 Pharmaceutical Society v. Boots Cash Chemists (1953, C.A.) 4 Carlill v. Carbolic Smoke Ball
FORMATION OF A VALID CONTRACT 4 1. Offer and Invitations to Treat 4 Canadian Dyers Assn v. Burton (1920, H.L.) 4 Pharmaceutical Society v. Boots Cash Chemists (1953, C.A.) 4 Carlill v. Carbolic Smoke Ball
CONTRACT LAW SUMMARY
 CONTRACT LAW SUMMARY LAWSKOOL UK CONTENTS INTRODUCTION TO CONTRACT LAW 6 DEFINITION OF CONTRACT LAW 6 1) The Classical Model of Contract Law 6 INTENTION TO CREATE LEGAL RELATIONS 8 INTRODUCTION TO INTENTION
CONTRACT LAW SUMMARY LAWSKOOL UK CONTENTS INTRODUCTION TO CONTRACT LAW 6 DEFINITION OF CONTRACT LAW 6 1) The Classical Model of Contract Law 6 INTENTION TO CREATE LEGAL RELATIONS 8 INTRODUCTION TO INTENTION
Is there a contract?
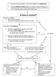 1. te whether this transaction is governed by UCC or the Restatement. 2. Does the Statute of Frauds apply? The contract must be in writing if it is in regard to land, if by its nature it takes more than
1. te whether this transaction is governed by UCC or the Restatement. 2. Does the Statute of Frauds apply? The contract must be in writing if it is in regard to land, if by its nature it takes more than
MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 9084 LAW
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 9084 LAW 9084/31 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the October/November 2013 series 9084 LAW 9084/31 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers
TOPIC 1: AGREEMENT Lucy v Zehmer (1954) 84 SE 2d 516). ACCC v CG Berbatis Holdings Pty Ltd (2003) 214 CLR 51) However: Smith v Hughes
 1 TOPIC 1: AGREEMENT An agreement is an understanding between two parties that one of them will do something, or will promise to do, in return for the other doing something, or promising to do so Requires
1 TOPIC 1: AGREEMENT An agreement is an understanding between two parties that one of them will do something, or will promise to do, in return for the other doing something, or promising to do so Requires
Termination of an Offer
 Termination of an Offer Lapse! If the offer contains a time limit, then it lapses according to the explicit provisions! Offer must be accepted by midnight tonight.! If the offer does not contain a time
Termination of an Offer Lapse! If the offer contains a time limit, then it lapses according to the explicit provisions! Offer must be accepted by midnight tonight.! If the offer does not contain a time
CONTRACTS TOPIC OUTLINE1
 CONTRACTS TOPIC OUTLINE1 1. OFFER AND ACCEPTANCE a. offer defined b. preliminary negotiations c. advertisements d. unilateral offer e. who may accept an offer f. irrevocable offer g. material terms h.
CONTRACTS TOPIC OUTLINE1 1. OFFER AND ACCEPTANCE a. offer defined b. preliminary negotiations c. advertisements d. unilateral offer e. who may accept an offer f. irrevocable offer g. material terms h.
OVERVIEW OF CONTRACT LAW
 OVERVIEW OF CONTRACT LAW Liability is generally the key issue in regards to contractual disputes. Purpose of K law is to provide the rules which determine when one party is liable to another under or in
OVERVIEW OF CONTRACT LAW Liability is generally the key issue in regards to contractual disputes. Purpose of K law is to provide the rules which determine when one party is liable to another under or in
Contracts Summary Notes
 Contracts Summary Notes TOPIC ONE: AGREEMENT- OFFER AND ACCEPTANCE There are 4 elements of a contract: Agreement, consideration, intention to create legal relations and certainty The above are all required
Contracts Summary Notes TOPIC ONE: AGREEMENT- OFFER AND ACCEPTANCE There are 4 elements of a contract: Agreement, consideration, intention to create legal relations and certainty The above are all required
Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Spring Contract Formation
 Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Contract Formation I. Foundations A. Mutual Assent: Each party to a contract manifests its assent to the
Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Contract Formation I. Foundations A. Mutual Assent: Each party to a contract manifests its assent to the
Law 410 CONTRACTS BUCKWOLD
 Law 410 CONTRACTS BUCKWOLD 1 FORMATION: Is there a contract? In order to have a contract, you must have: o Capacity to contract: Note that minors can enforce a contract against adults, but adults cannot
Law 410 CONTRACTS BUCKWOLD 1 FORMATION: Is there a contract? In order to have a contract, you must have: o Capacity to contract: Note that minors can enforce a contract against adults, but adults cannot
Sample. 2.1 Introduction. 2.2 Types of consideration
 Chapter 2: Consideration Outline 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Types of consideration 2.3 Consideration must move from the promisee 2.4 Consideration must be of some value 2.5 Summary 2.1 Introduction As noted
Chapter 2: Consideration Outline 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Types of consideration 2.3 Consideration must move from the promisee 2.4 Consideration must be of some value 2.5 Summary 2.1 Introduction As noted
LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JUNE 2011
 Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JUNE 2011 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JUNE 2011 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
Torts & Contracts II
 LAWS5006 Torts & Contracts II Problem question scaffold Issue: some sort of error/mistake can the contract be set aside? CONTRACT SOLUTION When you think a mistake is present, first assess whether there
LAWS5006 Torts & Contracts II Problem question scaffold Issue: some sort of error/mistake can the contract be set aside? CONTRACT SOLUTION When you think a mistake is present, first assess whether there
Chapter 3: The Bargain Context
 Chapter 3: The Bargain Context A. Introduction: Contracting parties, no matter how hard they try, cannot negotiate every rule. For example, suppose I agree to sell and you agree to buy my tractor. We agree
Chapter 3: The Bargain Context A. Introduction: Contracting parties, no matter how hard they try, cannot negotiate every rule. For example, suppose I agree to sell and you agree to buy my tractor. We agree
Define genuine agreement and rescission. Identify when duress occurs. Describe how someone may exercise undue influence.
 Define genuine agreement and rescission Identify when duress occurs Describe how someone may exercise undue influence. Genuine Agreement/Assent: meeting of the minds Must be willful and voluntary Must
Define genuine agreement and rescission Identify when duress occurs Describe how someone may exercise undue influence. Genuine Agreement/Assent: meeting of the minds Must be willful and voluntary Must
LAW OF CONTRACT (PART I) Shanila H. Gunawardena LL.B. (Hons.) (Colombo) Attorney-at-Law, CTA (CASL)
 LAW OF CONTRACT (PART I) Shanila H. Gunawardena LL.B. (Hons.) (Colombo) Attorney-at-Law, CTA (CASL) 30-07-2017 MAIN COMPONENTS OF A CONTRACT 1. Intention to create legal relations 2. Agreement between
LAW OF CONTRACT (PART I) Shanila H. Gunawardena LL.B. (Hons.) (Colombo) Attorney-at-Law, CTA (CASL) 30-07-2017 MAIN COMPONENTS OF A CONTRACT 1. Intention to create legal relations 2. Agreement between
a) The body of law as made by judges through the determination of cases. d) The system of law that emerged following the Norman Conquest in 1066.
 1. Who of the following was NOT a proponent of natural law? a) Aristotle b) Jeremy Bentham c) St Augustine d) St Thomas Aquinas 2. The term 'common law' has three different meanings. Which of the following
1. Who of the following was NOT a proponent of natural law? a) Aristotle b) Jeremy Bentham c) St Augustine d) St Thomas Aquinas 2. The term 'common law' has three different meanings. Which of the following
AGREEMENT = OFFER + ACCEPTANCE + CERTAINTY Clarke v Duncan
 CONTRACTS A AGREEMENT = OFFER + ACCEPTANCE + CERTAINTY Clarke v Duncan Offeror: Person who makes the offer (Promisor) Offeree: Person who receives the offer (Promisee) (accepts) 1. Was (insert method of
CONTRACTS A AGREEMENT = OFFER + ACCEPTANCE + CERTAINTY Clarke v Duncan Offeror: Person who makes the offer (Promisor) Offeree: Person who receives the offer (Promisee) (accepts) 1. Was (insert method of
Question If CapCo files a lawsuit against the Bears seeking damages for breach of contract, who is likely to prevail? Discuss.
 Question 2 CapCo sells baseball caps to youth leagues and recently approached two new teams, the Bears and the Lions. Uncertain how many caps the team would require, the Bears team manager signed a written
Question 2 CapCo sells baseball caps to youth leagues and recently approached two new teams, the Bears and the Lions. Uncertain how many caps the team would require, the Bears team manager signed a written
LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JANUARY 2013
 Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JANUARY 2013 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 3 - UNIT 2 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS - JANUARY 2013 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
Chinese Contract Law: A Brief Introduction. ZHANG Xuezhong. Assistant Professor of Law.
 Chinese Contract Law: A Brief Introduction ZHANG Xuezhong Assistant Professor of Law zhangxuezhong@ecupl.edu.cn East China University of Politics and Law Overview 1. In General 2. Principles of Chinese
Chinese Contract Law: A Brief Introduction ZHANG Xuezhong Assistant Professor of Law zhangxuezhong@ecupl.edu.cn East China University of Politics and Law Overview 1. In General 2. Principles of Chinese
7/23/2010. The. Contract. Sources of contractual obligations
 Law for Spatial Designers Introduction to the Law of Contract Module 3 Topic 1 Sources of contractual obligations Obligations imposed by law and equity The Contract Statutory obligations The obligations
Law for Spatial Designers Introduction to the Law of Contract Module 3 Topic 1 Sources of contractual obligations Obligations imposed by law and equity The Contract Statutory obligations The obligations
Creation of the K a. Statute of Frauds land part performance one year debt 500 b. Offer master of the offer revoke mailbox rule absence of terms
 Contracts outline I. Creation of the K a. Statute of Frauds requires that a sufficient writing, signed by the party to be charged be in existence for the following subject-matter (doesn t apply to restitution
Contracts outline I. Creation of the K a. Statute of Frauds requires that a sufficient writing, signed by the party to be charged be in existence for the following subject-matter (doesn t apply to restitution
9084 LAW. 9084/32 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75
 CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2014 series 9084 LAW 9084/32 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and candidates,
CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2014 series 9084 LAW 9084/32 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme is published as an aid to teachers and candidates,
BARRY ALLAN CONTACT PART II. Introduction 1. OBJECTIVE THEORY OF CONTRACT 2. A MODEL OF CONTRACT
 BARRY ALLAN CONTACT PART II Introduction 1. OBJECTIVE THEORY OF CONTRACT We use the objective principle to decide whether there has been an agreement, consideration and intention to be bound between the
BARRY ALLAN CONTACT PART II Introduction 1. OBJECTIVE THEORY OF CONTRACT We use the objective principle to decide whether there has been an agreement, consideration and intention to be bound between the
Contract Law Final Exam Version C
 Contract Law Final Exam Version C True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Compliance and excuse are valid defenses to a breach of contract action. 2. To have a constructive or implied
Contract Law Final Exam Version C True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Compliance and excuse are valid defenses to a breach of contract action. 2. To have a constructive or implied
Genuineness of Assent
 Genuineness of Assent A party who demonstrates that she did not genuinely assent to the terms of a contract may avoid an otherwise valid contract. Genuine assent may be lacking due to mistake, fraudulent
Genuineness of Assent A party who demonstrates that she did not genuinely assent to the terms of a contract may avoid an otherwise valid contract. Genuine assent may be lacking due to mistake, fraudulent
California Bar Examination
 California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question PC manufactures computers. Mart
California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question PC manufactures computers. Mart
Chapter 11 Consideration and Promissory Estoppel 25-1
 Chapter 11 Consideration and Promissory Estoppel 25-1 Consideration Consideration: something of legal value given in exchange for a promise Necessary for the existence of a contract Elements: Something
Chapter 11 Consideration and Promissory Estoppel 25-1 Consideration Consideration: something of legal value given in exchange for a promise Necessary for the existence of a contract Elements: Something
Sources of Australian Contract Law Common law (Judge-made law found in UK and Australian Legal cases) Statutory Law (i.e ACL, Sale of Goods Act)
 Week 7 Introduction to Contract Law CONTRACT: o An AGREEMENT between TWO OR MORE PARTIES giving rise to LEGAL OBLIGATIONS which are enforced or recognised by law CONTRACT vary in complexity and size: o
Week 7 Introduction to Contract Law CONTRACT: o An AGREEMENT between TWO OR MORE PARTIES giving rise to LEGAL OBLIGATIONS which are enforced or recognised by law CONTRACT vary in complexity and size: o
University of Miami School of Law. CONTRACTS PROFESSOR ROBERT ROSEN Fall Syllabus 1
 University of Miami School of Law CONTRACTS PROFESSOR ROBERT ROSEN Fall 2007 Syllabus 1 [Unless otherwise indicated, all page # s refer to MACAULEY, ET.AL. CONTRACTS: LAW IN ACTION (2 ND ED., 2003)]. YOU
University of Miami School of Law CONTRACTS PROFESSOR ROBERT ROSEN Fall 2007 Syllabus 1 [Unless otherwise indicated, all page # s refer to MACAULEY, ET.AL. CONTRACTS: LAW IN ACTION (2 ND ED., 2003)]. YOU
Question 2. Delta has not yet paid for any of the three Model 100 presses despite repeated demands by Press.
 Question 2 Delta Print Co. ( Delta ) ordered three identical Model 100 printing presses from Press Manufacturer Co. ( Press ). Delta s written order form described the items ordered by model number. Delta
Question 2 Delta Print Co. ( Delta ) ordered three identical Model 100 printing presses from Press Manufacturer Co. ( Press ). Delta s written order form described the items ordered by model number. Delta
California Bar Examination
 California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question On May 1, Owner asked Builder
California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question On May 1, Owner asked Builder
CONTRACT LAW IN THE SOUTH PACIFIC
 CONTRACT LAW IN THE SOUTH PACIFIC Jennifer Corrin Care Senior Lecturer TC Beirne School of Law University of Queensland Cavendish Publishing Limited London Sydney CONTENTS Preface Table of Cases Table
CONTRACT LAW IN THE SOUTH PACIFIC Jennifer Corrin Care Senior Lecturer TC Beirne School of Law University of Queensland Cavendish Publishing Limited London Sydney CONTENTS Preface Table of Cases Table
Construction Law: Recent Developments of Importance
 Construction Law: Recent Developments of Importance Bruce Reynolds and James MacLellan Published in the Guide to the Leading 500 Lawyers in Canada (2002 Lexpert/American Lawyer Media) During the past year
Construction Law: Recent Developments of Importance Bruce Reynolds and James MacLellan Published in the Guide to the Leading 500 Lawyers in Canada (2002 Lexpert/American Lawyer Media) During the past year
MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2008 question paper 9084 LAW. 9084/03 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2008 question paper 9084 LAW 9084/03 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level www.xtremepapers.com MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2008 question paper 9084 LAW 9084/03 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark scheme
Foundation Level LAW PRACTICE MANUAL
 Part: - 1 The Indian Contract Act, 1872 Chapter 1:- Nature and Kinds of Contracts 5. The general principles of law of contract applied to all kinds of contract irrespective of their nature. (a) True, as
Part: - 1 The Indian Contract Act, 1872 Chapter 1:- Nature and Kinds of Contracts 5. The general principles of law of contract applied to all kinds of contract irrespective of their nature. (a) True, as
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level. Published
 Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level LAW 9084/31 Paper 3 October/November 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 75 Published This mark scheme is
Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level LAW 9084/31 Paper 3 October/November 2016 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 75 Published This mark scheme is
Unilateral Contracts vs. Bilateral Contracts
 Unilateral Contracts vs. Bilateral Contracts A unilateral contract is a promise in exchange for a performance. A bilateral contract is a promise in exchange for a promise. Note: An implied-in-fact contract
Unilateral Contracts vs. Bilateral Contracts A unilateral contract is a promise in exchange for a performance. A bilateral contract is a promise in exchange for a promise. Note: An implied-in-fact contract
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level. Published
 Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level LAW 9084/32 Paper 3 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 75 Published This mark scheme is published as an
Cambridge Assessment International Education Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced Level LAW 9084/32 Paper 3 MARK SCHEME Maximum Mark: 75 Published This mark scheme is published as an
Contracts Final Exam Notes Formation of a contract What is a contract MUST Offer REASONABLE PERSON Acceptance
 Contracts Final Exam Notes Formation of a contract What is a contract - Binding promise between two or more parties, reliant upon several important factors - Offer - Acceptance - Consideration - Certainty
Contracts Final Exam Notes Formation of a contract What is a contract - Binding promise between two or more parties, reliant upon several important factors - Offer - Acceptance - Consideration - Certainty
The United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (CISG)
 Rechtswissenschaftliche Fakultät Institut für Zivilrecht Wintersemester 2017 KU UN-Kaufrecht Uniform Sales Law The United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (CISG) José
Rechtswissenschaftliche Fakultät Institut für Zivilrecht Wintersemester 2017 KU UN-Kaufrecht Uniform Sales Law The United Nations Convention on Contracts for the International Sale of Goods (CISG) José
Sample. Aims of this Chapter. 2.1 Introduction
 Chapter 2: Consideration Outline 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Types of consideration 2.3 Consideration must move from the promisee 2.4 Consideration must be of some value 2.5 Insufficiency of consideration 2.6
Chapter 2: Consideration Outline 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Types of consideration 2.3 Consideration must move from the promisee 2.4 Consideration must be of some value 2.5 Insufficiency of consideration 2.6
QUESTION What contract rights and remedies, if any, does Olivia have against Juan? Discuss.
 QUESTION 1 Olivia is a florist who specializes in roses. She has a five-year written contract with Juan to sell him as many roses as he needs for his wedding chapel. Over the past three years, Olivia sold
QUESTION 1 Olivia is a florist who specializes in roses. She has a five-year written contract with Juan to sell him as many roses as he needs for his wedding chapel. Over the past three years, Olivia sold
MBE WORKSHOP: CONTRACTS PROFESSOR LISA MCELROY DREXEL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF LAW
 MBE WORKSHOP: CONTRACTS PROFESSOR LISA MCELROY DREXEL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF LAW CHAPTER 1: CONTRACTS Editor's Note 1: The below outline is taken from the National Conference of Bar Examiners' website. NOTE:
MBE WORKSHOP: CONTRACTS PROFESSOR LISA MCELROY DREXEL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF LAW CHAPTER 1: CONTRACTS Editor's Note 1: The below outline is taken from the National Conference of Bar Examiners' website. NOTE:
UNIT 2 : CONSIDERATION
 1.28 BUSINESS LAWS UNIT 2 : CONSIDERATION LEARNING OUTCOMES After studying this unit, you would be able to: Understand the concept of consideration, its importance for a contract and its double aspect.
1.28 BUSINESS LAWS UNIT 2 : CONSIDERATION LEARNING OUTCOMES After studying this unit, you would be able to: Understand the concept of consideration, its importance for a contract and its double aspect.
Contracts I Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas. Fall 2004
 Contracts I Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Optional HW Assignment #1 - Model Answers 1. Read the attached version of Coakley & Williams, Inc. v.
Contracts I Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Optional HW Assignment #1 - Model Answers 1. Read the attached version of Coakley & Williams, Inc. v.
CONTRACTS. Miscellaneous applications of ACL for Contracts:! 6 PROMISSORY ESTOPPEL! Assumption! Detrimental Reliance!...
 CONTRACTS Miscellaneous applications of ACL for Contracts:! 6 PROMISSORY ESTOPPEL! 7 1. Assumption!... 7 2. Detrimental Reliance!... 7 3. Unconscionability!... 8 Remedy of Promissory Estoppel!... 8 PRIVITY!
CONTRACTS Miscellaneous applications of ACL for Contracts:! 6 PROMISSORY ESTOPPEL! 7 1. Assumption!... 7 2. Detrimental Reliance!... 7 3. Unconscionability!... 8 Remedy of Promissory Estoppel!... 8 PRIVITY!
requires a + = WHAT IS IN A CONTRACT? by to another to create.
 UNIT 3 CONTRACTS NBEA STANDARD II: Analyze the relationships between contract law, law of sales, and consumer law. OBJECTIVE: Develop an understanding of contracts: distinguish between express and implied
UNIT 3 CONTRACTS NBEA STANDARD II: Analyze the relationships between contract law, law of sales, and consumer law. OBJECTIVE: Develop an understanding of contracts: distinguish between express and implied
BLAW BUSINESS LAW, SECTION B3
 UNIVERSITY OF ALBERTA School of Business Department of Marketing, Business Economics and Law BLAW 301 - BUSINESS LAW, SECTION B3 Professor: Ivan Ivankovich Course Outline Class: TR 9:30-10:50 Term 2, Winter
UNIVERSITY OF ALBERTA School of Business Department of Marketing, Business Economics and Law BLAW 301 - BUSINESS LAW, SECTION B3 Professor: Ivan Ivankovich Course Outline Class: TR 9:30-10:50 Term 2, Winter
LEVEL 4 - UNIT 1 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS JANUARY 2015
 Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 4 - UNIT 1 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS JANUARY 2015 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
Note to Candidates and Tutors: LEVEL 4 - UNIT 1 CONTRACT LAW SUGGESTED ANSWERS JANUARY 2015 The purpose of the suggested answers is to provide students and tutors with guidance as to the key points students
ESSENTIAL CONTRACT LAW SECOND EDITION. London Sydney. Cavendish Publishing Limited
 ESSENTIAL CONTRACT LAW SECOND EDITION CP Cavendish Publishing Limited London Sydney Titles in the series: Company Law Constitutional & Administrative Law Contract Law Criminal Law EC Law English Legal
ESSENTIAL CONTRACT LAW SECOND EDITION CP Cavendish Publishing Limited London Sydney Titles in the series: Company Law Constitutional & Administrative Law Contract Law Criminal Law EC Law English Legal
Contracts: Kinds of Contracts: Offer: Communication of Offer:
 Contracts: Kinds of Contracts: - Executory Contract - Obligations are not enforceable immediately - Executed Contract - Immediately fulfilled upon entry - Partly Executed Contract - Some obligations fulfilled,
Contracts: Kinds of Contracts: - Executory Contract - Obligations are not enforceable immediately - Executed Contract - Immediately fulfilled upon entry - Partly Executed Contract - Some obligations fulfilled,
CONTRACTS AND SALES QUESTION 1
 CONTRACTS AND SALES QUESTION Peter responded to an advertisement placed by Della, a dentist, seeking a dental hygienist. After an interview, Della offered Peter the job and said she would either: () pay
CONTRACTS AND SALES QUESTION Peter responded to an advertisement placed by Della, a dentist, seeking a dental hygienist. After an interview, Della offered Peter the job and said she would either: () pay
Contents. Table of Statutes. Table of Secondary Legislation. Table of Cases. The Agreement to Contract
 Contents Table of Statutes Table of Secondary Legislation Table of Cases Chapter 1: The Agreement to Contract 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Elements required for a valid simple contract 1.3 The phenomenon of agreement
Contents Table of Statutes Table of Secondary Legislation Table of Cases Chapter 1: The Agreement to Contract 1.1 Introduction 1.2 Elements required for a valid simple contract 1.3 The phenomenon of agreement
THE LAW RELATING TO GUARANTEES
 THE LAW RELATING TO GUARANTEES ISBN 978-983-3519-16-3 Author: Nasser Hamid Binding: Softcover / 938 pages Publication Price: MYR 290.00 The law is stated as of March 31, 2009 CONTENTS CHAPTER ONE GUARANTEES
THE LAW RELATING TO GUARANTEES ISBN 978-983-3519-16-3 Author: Nasser Hamid Binding: Softcover / 938 pages Publication Price: MYR 290.00 The law is stated as of March 31, 2009 CONTENTS CHAPTER ONE GUARANTEES
Although the costs of materials and labor are roughly equal, the primary purpose of the
 Claim 1: Acme Flooring Applicable Law: Although the costs of materials and labor are roughly equal, the primary purpose of the contract was for rendering services because the service component of installation
Claim 1: Acme Flooring Applicable Law: Although the costs of materials and labor are roughly equal, the primary purpose of the contract was for rendering services because the service component of installation
THE CYPRUS INSTITUTE OF MARKETING DMM COMMERCIAL LAW
 THE CYPRUS INSTITUTE OF MARKETING DMM COMMERCIAL LAW INTRODUCTION 18 LECTURES CIM BOOKLET + TEXT BOOK ATTENDANCE CONTACT yangos@cima.ac.cy COURSE ASSESSMENT 1. ASSIGNMENT No1. 7.5 % 2. ASSIGNEMENT No2.
THE CYPRUS INSTITUTE OF MARKETING DMM COMMERCIAL LAW INTRODUCTION 18 LECTURES CIM BOOKLET + TEXT BOOK ATTENDANCE CONTACT yangos@cima.ac.cy COURSE ASSESSMENT 1. ASSIGNMENT No1. 7.5 % 2. ASSIGNEMENT No2.
TABLE OF CONTENTS. Preface... iii Preface to the First Edition... v Table of Cases... TC-1 Table of Statutes... TS-1
 TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE Preface... iii Preface to the First Edition... v Table of Cases... TC-1 Table of Statutes... TS-1 PART I. INTRODUCTION... 1-17 CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION... 1 PART II. ENFORCEABILITY...
TABLE OF CONTENTS PAGE Preface... iii Preface to the First Edition... v Table of Cases... TC-1 Table of Statutes... TS-1 PART I. INTRODUCTION... 1-17 CHAPTER 1. INTRODUCTION... 1 PART II. ENFORCEABILITY...
MARKING GUIDE. Subject Name: Commercial Law 1. Exam Date: June Number of pages: 7
 MARKING GUIDE Subject No: 8395F/8672D Subject Name: Commercial Law 1 Exam Date: June 2005 Number of pages: 7 2 MARKING GUIDE Part A 20 multiple choice questions worth 1 mark each: 1. [ d ] 2. [ b ] 3.
MARKING GUIDE Subject No: 8395F/8672D Subject Name: Commercial Law 1 Exam Date: June 2005 Number of pages: 7 2 MARKING GUIDE Part A 20 multiple choice questions worth 1 mark each: 1. [ d ] 2. [ b ] 3.
THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA FACULTY OF LAW DECEMBER 2015 EXAMINATION. LAW 211 Contract Law. Section 2 Professor Biukovh TOTAL MARKS: 100
 r THIS EXAMINATION CONSISTS OF THREE (3) PAGES PLEASE ENSURE THAT YOU HAVE A COMPLETE PAPER THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA FACULTY OF LAW DECEMBER 2015 EXAMINATION LAW 211 Contract Law Section 2 Professor
r THIS EXAMINATION CONSISTS OF THREE (3) PAGES PLEASE ENSURE THAT YOU HAVE A COMPLETE PAPER THE UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA FACULTY OF LAW DECEMBER 2015 EXAMINATION LAW 211 Contract Law Section 2 Professor
CONTRACT LAW EXAM NOTES
 What is a contract? CONTRACT LAW EXAM NOTES Topic 1: The Nature and Importance of Contract Law A contract is a legally binding promise or agreement. A promise of agreement is not legally binding and enforceable
What is a contract? CONTRACT LAW EXAM NOTES Topic 1: The Nature and Importance of Contract Law A contract is a legally binding promise or agreement. A promise of agreement is not legally binding and enforceable
Contract and Tort Law for Engineers
 Contract and Tort Law for Engineers Christian S. Tacit Tel: 613-599-5345 Email: ctacit@tacitlaw.com Canadian Systems of Law There are two systems of law that operate in Canada Common Law and Civil Law
Contract and Tort Law for Engineers Christian S. Tacit Tel: 613-599-5345 Email: ctacit@tacitlaw.com Canadian Systems of Law There are two systems of law that operate in Canada Common Law and Civil Law
REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER)
 REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER) 1. T F The pre-offer phase of a transaction is also known as preliminary negotiation. 2. T F Preliminary negotiation takes place after
REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER) 1. T F The pre-offer phase of a transaction is also known as preliminary negotiation. 2. T F Preliminary negotiation takes place after
!"#$%&'(&)'*+%*+,& /G$+:'($"0B",E$"#'8E,",0"?$+%'9*,$"..."HH" I'('9B0+%*,'09"..."H>" ?E$")*+02"/4'&$9:$"#J2$"..."HK"
 !#$%&'(&)'*+%*+,& #$%$&'$()*+,-...- /(,011$2...3 )+'4',5678$9:5*9&7(('89%$9,(;< +& )*+,'$(=...>?$+%(*9&@9,$+1+$,*,'09...A @9,$+1+$,*,'090BC09,+*:,(...-- )$+B0+%*9:$*9&?$+%'9*,'09...-3?$+%'9*,'09B0+D+$*:E...-F
!#$%&'(&)'*+%*+,& #$%$&'$()*+,-...- /(,011$2...3 )+'4',5678$9:5*9&7(('89%$9,(;< +& )*+,'$(=...>?$+%(*9&@9,$+1+$,*,'09...A @9,$+1+$,*,'090BC09,+*:,(...-- )$+B0+%*9:$*9&?$+%'9*,'09...-3?$+%'9*,'09B0+D+$*:E...-F
Contract Law for Paralegals: Chapter 8 Chapter 8
 Contract Law for Paralegals: Chapter 8 Chapter 8 Tab Text CHAPTER 8 Contract Enforceability: Protecting a Party Against Overreaching Chapter 8 deals with the second group of contract enforcement problems-ad
Contract Law for Paralegals: Chapter 8 Chapter 8 Tab Text CHAPTER 8 Contract Enforceability: Protecting a Party Against Overreaching Chapter 8 deals with the second group of contract enforcement problems-ad
Simple. CONTRACTS & UCC Outline. NINETY PERCENT of the LAW in NINETY PAGES. Tim Tyler, Ph.D., Attorney at Law
 NAILING THE BAR Simple CONTRACTS & UCC Outline Tim Tyler, Ph.D., Attorney at Law NINETY PERCENT of the LAW in NINETY PAGES NAILING THE BAR Simple CONTRACTS & UCC Outline Table of Contents CHAPTER 1: CONTRACT
NAILING THE BAR Simple CONTRACTS & UCC Outline Tim Tyler, Ph.D., Attorney at Law NINETY PERCENT of the LAW in NINETY PAGES NAILING THE BAR Simple CONTRACTS & UCC Outline Table of Contents CHAPTER 1: CONTRACT
Date Revised: 8/12 COURSE SYLLABUS. Syllabus for: BUS 2610 LEGAL ENVIRONMENT OF BUSINESS. Former Quarter Course(s):
 Date last reviewed: Date Approved: COURSE SYLLABUS Syllabus for: Date Revised: 8/12 Former Quarter Course(s): Catalog Description: This course is a study of the legal and regulatory environment of business.
Date last reviewed: Date Approved: COURSE SYLLABUS Syllabus for: Date Revised: 8/12 Former Quarter Course(s): Catalog Description: This course is a study of the legal and regulatory environment of business.
Leoppky v. Meston, 2008 ABQB 45
 Two cases concerning the Statute of Frauds (1677, U.K.) by Jonnette Watson Hamilton Leoppky v. Meston, 2008 ABQB 45 http://www.albertacourts.ab.ca/jdb/2003-/qb/family/2008/2008abqb0045.ed1.pdf Wasylyshyn
Two cases concerning the Statute of Frauds (1677, U.K.) by Jonnette Watson Hamilton Leoppky v. Meston, 2008 ABQB 45 http://www.albertacourts.ab.ca/jdb/2003-/qb/family/2008/2008abqb0045.ed1.pdf Wasylyshyn
Please distribute and reproduce these notes freely
 Course: Law of Contracts Date: Fall/Winter (2000-2001) Professor: Berryman (Fall) & Whiteside (Winter) Textbook: Contract Law in Canada Please distribute and reproduce these notes freely Although great
Course: Law of Contracts Date: Fall/Winter (2000-2001) Professor: Berryman (Fall) & Whiteside (Winter) Textbook: Contract Law in Canada Please distribute and reproduce these notes freely Although great
Foundation Level LAW PRACTICE MANUAL
 Chapter 2:- Offer and Acceptance 2.1 Definition And Essential Elements Of A VALID OFFER 1. The term 'offer or proposal' in legal terms, is defined in (a) Section 2 (a) (b) Section 2 (b) (c) Section 2 (i)
Chapter 2:- Offer and Acceptance 2.1 Definition And Essential Elements Of A VALID OFFER 1. The term 'offer or proposal' in legal terms, is defined in (a) Section 2 (a) (b) Section 2 (b) (c) Section 2 (i)
ASSIGNMENT SOLUTIONS GUIDE ( ) E.C.O.-5
 N 1 ASSIGNMENT SOLUTIONS GUIDE (2015-2016) E.C.O.-5 Mercantile Law Disclaimer/Special Note: These are just the sample of the Answers/Solutions to some of the Questions given in the Assignments. These Sample
N 1 ASSIGNMENT SOLUTIONS GUIDE (2015-2016) E.C.O.-5 Mercantile Law Disclaimer/Special Note: These are just the sample of the Answers/Solutions to some of the Questions given in the Assignments. These Sample
9084 LAW 9084/32 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75
 UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9084 LAW 9084/32 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark
UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE INTERNATIONAL EXAMINATIONS GCE Advanced Level MARK SCHEME for the May/June 2011 question paper for the guidance of teachers 9084 LAW 9084/32 Paper 3, maximum raw mark 75 This mark
failing to get the contract signed (something that never ceases to amaze lawyers!);
 Professionals involved in design-build projects should be aware of the risks they face when they contract with the owner to be solely responsible for both construction and design. In this respect, the
Professionals involved in design-build projects should be aware of the risks they face when they contract with the owner to be solely responsible for both construction and design. In this respect, the
LLB120 NOTES !!!!!!!!!!!!!!
 LLB120 NOTES!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Contents Contract Formation 5 Agreement 5 Offer 6 Willingness to be bound without further negotiation 6 Gibson v Manchester 6 Carlill v Carbolic Smoke Ball Company 7 Pharmaceutical
LLB120 NOTES!!!!!!!!!!!!!! Contents Contract Formation 5 Agreement 5 Offer 6 Willingness to be bound without further negotiation 6 Gibson v Manchester 6 Carlill v Carbolic Smoke Ball Company 7 Pharmaceutical
TITLE 7 CONTRACTS TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TITLE 7 CONTRACTS TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 7.01 General Provisions 7.0101 Definition 1 7.0102 Essential elements of a contract 1 7.0103 Law of place applied to contracts 1 7.0104 Time of performance 1
TITLE 7 CONTRACTS TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 7.01 General Provisions 7.0101 Definition 1 7.0102 Essential elements of a contract 1 7.0103 Law of place applied to contracts 1 7.0104 Time of performance 1
Company Law: Conwest Exploration Company Limited et al. v. Letain, (1964) S.C.R. 20
 Osgoode Hall Law Journal Volume 3, Number 3 (October 1965) Article 3 Company Law: Conwest Exploration Company Limited et al. v. Letain, (1964) S.C.R. 20 Burton B. C. Tait Follow this and additional works
Osgoode Hall Law Journal Volume 3, Number 3 (October 1965) Article 3 Company Law: Conwest Exploration Company Limited et al. v. Letain, (1964) S.C.R. 20 Burton B. C. Tait Follow this and additional works
California Bar Examination
 California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question Betty is a physician. One of her
California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question Betty is a physician. One of her
 1 of 5 8/27/2014 2:11 PM Units: Teacher: LawandJustice, CORE Course: LawandJustice Year: 2012-13 Constitutional Law and Justice process of ethical decision-making and how does this process relate to law?
1 of 5 8/27/2014 2:11 PM Units: Teacher: LawandJustice, CORE Course: LawandJustice Year: 2012-13 Constitutional Law and Justice process of ethical decision-making and how does this process relate to law?
