REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER)
|
|
|
- Johnathan Wells
- 6 years ago
- Views:
Transcription
1 REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER) 1. T F The pre-offer phase of a transaction is also known as preliminary negotiation. 2. T F Preliminary negotiation takes place after an offer has been made. 3. T F The Restatement (Second) of Contracts 24 defines an offer as: the manifestation of willingness to enter into a bargain, so made as to justify another person in understanding that his assent to that bargain is invited and will conclude it. 4. T F Offer, as defined in the Restatement (Second) of Contracts 24, is based on an objective standard rather than on a subjective standard. 5. T F The offeror, to create the power of acceptance in the offeree, must state the terms of the contract so nothing remains for the offeror to negotiate once the offeree assents to these terms. 6. T F An offer is a promise made by one party to another in exchange for the other s promise or performance. 7. T F An offeror must make a promise for there to be an 8. T F The consideration for the offeror s promise is also called the price for the offeror s promise and is part of a bargainedfor exchange. 9. T F Consideration for the offeror s promise may be either the offeree s promise or performance, depending on which the offeror prefers. 10. T F An offer which is a promise for a promise is an offer for a unilateral contract. 11. T F A manifestation of willingness or a demonstration of willingness refers to the outward actions of the negotiating parties as understood by an impartial third person watching the parties. 12. T F The third person who is evaluating the outward actions of the negotiating parties is referred to as the reasonable person. 13. T F The reasonable person s standard is a subjective standard. 14. T F Early contracts cases used an objective standard. 15. T F Both the Restatement (First) and the Restatement (Second) of Contracts use an objective standard for the law of contracts. 16. T F An advertisement made to the general public may be an
2 17. T F An advertisement may never be an 18. T F An offer must always be made to a specific party. 19. T F In an auction with reserve, the auctioneer is the offeror. 20. T F In an auction with reserve, the auctioneer may withdraw the property at any time until he or she announces the completion of the sale. 21. T F Once a bidder had made a bid in an auction, he or she may not retract this bid. 22. T F A statement in an advertisement for an auction that says the property will be offered to the highest bidder means that the auction will be conducted without reserve. 23. T F An auction is with reserve unless a contrary intention is apparent from a statute, court order, or advertisement or by an announcement at the beginning of the auction. 24. T F Sam Brown, the auctioneer, presented a Louis XV ormolu clock to the potential bidders at an auction. Susan Sanchez, the owner of this valuable antique clock, had told Sam not to sell it for less than $5,000. In spite of Sam s best efforts, the highest bid was $2,500. Sam could withdraw the clock from the auction. 25. T F A person with a secret (subjective) intent to make a joke while outwardly expressing (objective) intent to make an offer will be judged on his or her subjective intent. 26. T F Contract formation occurs upon acceptance of the 27. T F If the offeror proposes a unilateral contract, the offeree must fully perform to accept the 28. T F An illusory promise is an unequivocal assurance that something will or will not be done. 29. T F An indefinite promise contains all essential terms to allow the court, in the event of breach, to fashion a remedy. 30. T F Consideration is the price that the offeror demands in return for his or her promise. 31. T F Every contract has not one but two considerations: one for the offeror s promise and one for the offeree s promise or performance. 32. T F The consideration for the offeror s promise in the offer is the same as the offeree s promise or performance in the acceptance. 33. T F The consideration for the offeree s promise or performance in the acceptance is the same as the offeror s promise in the 34. T F The promisor s promise to make a future gift lacks consideration and therefore cannot be an 35. T F If a donor of a gift changes his or her mind, a gift that has already been made must be returned.
3 36. T F For an offer to exist, the consideration for the promisor s promise must be adequate. 37. T F A peppercorn cannot be consideration for the promisor s promise. 38. T F I promise to pay you $1,000 for your love and affection is an 39. T F I promise to paint your barn for $10 is an 40. T F Motive can be consideration for a promise. 41. T F Moral obligation may be consideration for a promise. 42. T F An obligation already owed to the promisor (a preexisting duty) may be consideration for the promisor s promise. 43. T F If the promisee has already promised or performed (past consideration), the promisor would not be making his or her promise to induce a promise or performance and there would be no bargained-for exchange. 44. T F Modern contract law allows a less rigid adherence to the classical consideration doctrine. 45. T F Reliance can never be an alternative to consideration. 46. T F Gloria VanFleet had a five-year contract to coach the Springfield Volunteers, a professional football team. During Gloria s second year as coach, her team won its league championship. The owners were so delighted that they offered to replace Gloria s contract with a new five-year contract at a 50 percent increase in salary. Gloria s promise to coach for five years would be consideration for the owner s promise to pay 50 percent more. 47. T F The restitution cause of action is based on the policy of preventing unjust enrichment. 48. T F The restitution cause of action is based on the fact that the promisee relied on the promisor s promise to his or her detriment. 49. T F A restitution cause of action is based on a contract. 50. T F A restitution remedy in a breach of contract action is the same as a restitution cause of action. 51. T F Quantum meruit means as much as it is worth. 52. T F Under the Restatement of Restitution 2 (1937), an officious person is one who is entitled to receive compensation for a benefit conferred upon another while serving in an official capacity. 53. T F An officious person is a meddler. 54. T F Restitution actions are often called contracts implied by law. 55. T F When negotiations end without one party making an offer, the parties are always free to walk away from each other without any obligation. 56. T F Restitution may be both a cause of action and a remedy.
4 57. T F Reliance may be both a cause of action and a remedy. 58. T F The elements for the reliance cause of action come from Restatement of Contracts T F An express contract and an implied in fact contract are real contracts and may form the basis for a breach of contract action. A contract implied by law is not a real contract but rather a judicial construct and may form the basis for a restitution cause of action. 60. T F A person who is officious can recover in a restitution action for a benefit that he or she has conferred on another party. 61. T F When business was slow for the Quality Paving Company, employees would cruise neighborhoods in search of vacant houses with For Sale signs. If the driveway was in a state of disrepair, Quality would repave the drive and send a bill to the owner. Quality could not successfully maintain a restitution cause of action for compensation for the new driveway because Quality was officious. FILL-IN-THE-BLANK QUESTIONS 1.. A third person who is evaluating the outward actions of the negotiating parties. 2.. The reasonable person s standard. 3.. Standard used in early contracts cases. 4.. An auction in which the auctioneer is the offeror. 5.. An auction in which the bidder is the offeror. 6.. A contract that results from a promise for a performance. 7.. A contract that results from a promise for a promise. 8.. The price that the promisor expects to receive for his or her promise. 9.. May sometimes be an alternative to consideration under modern contract law An unequivocal assurance that something will or will not be done An equivocal assurance that something will or will not be done I promise to sell you my car if I feel like it A promise that omits terms essential for the court to determine an appropriate remedy in the event the promise is breached Feigned or pretended consideration An obligation already owed to the promisor by the promisee.
5 16.. A cause of action based on the policy of preventing unjust enrichment Preclusion of an assertion by the promisor that is inconsistent with a previously made promise upon which the promisee has relied A figment of the court s imagination A Latin expression meaning as much as it is worth A term used to describe what takes place when the plaintiff has conferred a benefit on the defendant and it would be unfair to permit the defendant to retain this benefit without compensating the plaintiff A promise that is neither express nor implied in fact but is a legal fiction which represents the court s label attached to a set of facts to reach a desired result A promise that is inferred from conduct rather than expressed orally or in writing. MULTIPLE-CHOICE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE ALL THE CORRECT ANSWERS) 1. The following statements are preliminary negotiation: (a) What will you take for your car? (b) I will give you $1,500 for your car. (c) Will you take $1,500 for your car? (d) Quote me a price for your car. (e) I will pay you no more than $1,500 for your car. 2. Identify the offer in the following sequence of events. (a) Please advise us of the lowest price you can make on our order for 10 car loads of Mason green jars, complete, with caps, packed one dozen in a case, either delivered here, or f.o.b. cars your place, as you prefer. State terms and cash discount. (b) Replying to your letter, we quote you Mason fruit jars, complete, in one-dozen boxes, delivered to your place: pints $4.50, quarts $5.00, half gallons $6.50, per gross, for immediate acceptance. Credit 60 days trade acceptance or 2 percent off if cash in 10 days. Your order subject to the approval of our executive officer. (c) Your letter received. Enter order for 10 car loads as per your quotation. (d) Replying to your letter, price now pints $5.00, quarts $5.50, half gallon $6.50, per gross, for immediate acceptance. (e) Seller ships 10 car loads to the Buyer. 3. Identify which of the following are offers for a unilateral contract. (a) I promise to pay $500 for your promise to sell me your gold watch. (b) I promise to pay $500 for your selling me your gold watch. (c) I promise to sell you my gold watch for your promise to pay $500. (d) I promise to sell you my gold watch for your paying me $500. (e) I promise to pay you $500 for your refraining from smoking for five years.
6 4.Identify which of the following is an (a) I may sell you my car for $5,000. (b) I will sell you my car for $5,000. (c) I will sell you one of my cars for $5,000. (d) I might sell you my car for $5,000. (e) I will consider selling you my car for $5, Identify which of the following is an (a) I promise to sell you my car. (b) I will sell you my car for your promise to pay $5. (c) I promise to give you my car if you roof my house. (d) (e) I will give you my car for your having roofed my house. I will give you $1,000 for your having taken care of me while I was ill. 6. Under classical contract law, the court will investigate the following: (a) Whether there is consideration for the promisor s promise (b) Whether what appears to be consideration is really a sham (c) Whether there is mutuality of obligation (d) Whether the promisor s motive is appropriate (e) Whether the consideration is adequate 7. A restitution cause of action has also been known as a cause of action based upon which of the following? (a) A contract implied by law (b) A constructive contract (c) An express contract (d) Quasi-contract (e) An implied contract 8. When may a cause of action for reliance occur? (a) When the parties have not negotiated (b) When the parties have negotiated, but no offer has been made (c) After an offer has been revoked (d) After an offer has been rejected (e) After an offer has been accepted 9. A restitution cause of action requires: (a) a promise by the promisor. (b) a benefit being conferred by one party on another. (c) that the promisor reasonably expected to induce action or forbearance on the part of the other party. (d) that the retention of the benefit without compensating the party conferring the benefit would be unjust. (e) that injustice could be avoided only by enforcement of the promise.
7 10. Anderson s car skidded off the highway during an ice storm and hit a tree. Anderson was knocked unconscious by the impact. McGill, a doctor of internal medicine, came upon the accident scene on her way home from making rounds at the local hospital. Dr. McGill rendered first aid at the scene and later sent Anderson a bill for her services. Anderson refused to pay, claiming that he did not request her services. (a) Dr. McGill could not successfully maintain either a breach of contract or a restitution cause of action against Anderson. (b) Dr. McGill could successfully maintain a breach of contract action against Anderson but not a restitution cause. (c) Dr. McGill could successfully maintain a restitution cause of action against Anderson but not a breach of contract cause of action. (d) Dr. McGill could successfully maintain both a breach of contract cause of action and a restitution cause of action against Anderson. SHORT-ANSWER QUESTIONS 1. Describe the difference between evaluating a communication using an objective standard rather than a subjective standard. 2. Discuss the practical significance between an offer for a unilateral contract and an offer for a bilateral contract. 3. Discuss why past services cannot be consideration for the promisor s promise. 4. A father told his son that if the son would move back to town, the father would start him in business. Is the son s moving back to town consideration for the father s promise or only a condition? 5. Discuss several ways legislatures have tinkered with the classical consideration doctrine. 6. Discuss several ways courts have tinkered with the classical consideration doctrine. 7. List the four elements of the reliance doctrine necessary to enable it to be used as an alternative to consideration. 8. List the four elements for a cause of action for reliance. 9. Grandpa Jones sent his 18-year-old granddaughter, Katie, a letter in which he promised to give her $10,000 when she became 25. In the meantime, he would pay her 6 percent interest annually on the $10,000 so she could stop working. Upon receiving this letter, Katie quit her job. Could Katie successfully sue Grandpa Jones s estate if after he died his estate discontinued paying her the annual interest? 10. Describe the role of expectation when negotiations fail to produce an 11. Describe the role of reliance when negotiations fail to produce an 12. Describe the role of restitution when negotiations fail to produce an 13. Are implied by law, implied in fact and implied contracts really contracts? 14. When is a person officious?
Contract Law for Paralegals: Chapter 2 Chapter 2
 Contract Law for Paralegals: Chapter 2 Chapter 2 Tab Text CHAPTER 2 The Offer Phase Chapter 2 is in three parts: (1) the classical offer-the promisor s promise and consideration for that promise; (2) alternatives
Contract Law for Paralegals: Chapter 2 Chapter 2 Tab Text CHAPTER 2 The Offer Phase Chapter 2 is in three parts: (1) the classical offer-the promisor s promise and consideration for that promise; (2) alternatives
Chapter 11 Consideration and Promissory Estoppel 25-1
 Chapter 11 Consideration and Promissory Estoppel 25-1 Consideration Consideration: something of legal value given in exchange for a promise Necessary for the existence of a contract Elements: Something
Chapter 11 Consideration and Promissory Estoppel 25-1 Consideration Consideration: something of legal value given in exchange for a promise Necessary for the existence of a contract Elements: Something
Termination of an Offer
 Termination of an Offer Lapse! If the offer contains a time limit, then it lapses according to the explicit provisions! Offer must be accepted by midnight tonight.! If the offer does not contain a time
Termination of an Offer Lapse! If the offer contains a time limit, then it lapses according to the explicit provisions! Offer must be accepted by midnight tonight.! If the offer does not contain a time
CONTRACTS AND SALES QUESTION 1
 CONTRACTS AND SALES QUESTION Peter responded to an advertisement placed by Della, a dentist, seeking a dental hygienist. After an interview, Della offered Peter the job and said she would either: () pay
CONTRACTS AND SALES QUESTION Peter responded to an advertisement placed by Della, a dentist, seeking a dental hygienist. After an interview, Della offered Peter the job and said she would either: () pay
Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Spring Contract Formation
 Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Contract Formation I. Foundations A. Mutual Assent: Each party to a contract manifests its assent to the
Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Contract Formation I. Foundations A. Mutual Assent: Each party to a contract manifests its assent to the
REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER)
 REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER) 1. T F The first step in the contract analysis is to determine the applicable law. 2. T F The second step in the contract analysis is to
REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER) 1. T F The first step in the contract analysis is to determine the applicable law. 2. T F The second step in the contract analysis is to
Contract Law Final Exam Version C
 Contract Law Final Exam Version C True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Compliance and excuse are valid defenses to a breach of contract action. 2. To have a constructive or implied
Contract Law Final Exam Version C True/False Indicate whether the statement is true or false. 1. Compliance and excuse are valid defenses to a breach of contract action. 2. To have a constructive or implied
FAQ: Elements of Establishing A Contract
 Question 1: What is the procedure for analyzing a set of facts to establish the existence of a contract? Answer 1: The procedure involves an examination of the facts to determine whether each element of
Question 1: What is the procedure for analyzing a set of facts to establish the existence of a contract? Answer 1: The procedure involves an examination of the facts to determine whether each element of
Contracts II Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Spring 2004
 Contracts II Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Sample Exam Question #5 - Model Answer In the words of renowned contracts scholar Pete Townshend, A promise
Contracts II Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Sample Exam Question #5 - Model Answer In the words of renowned contracts scholar Pete Townshend, A promise
Beginning Law Essay Writing Part 2 Professor Mary Schofield
 Beginning Law Essay Writing Part 2 Professor Mary Schofield The following pages provide hard copies of the hypothetical used during this session, as well as a copy of the sample answer discussed. I suggest
Beginning Law Essay Writing Part 2 Professor Mary Schofield The following pages provide hard copies of the hypothetical used during this session, as well as a copy of the sample answer discussed. I suggest
CONTRACTS MID-TERM EXAMINATION December 2006 Santa Barbara/Ventura Colleges of Law Instructor: Craig Smith QUESTION 1
 CONTRACTS MID-TERM EXAMINATION December 2006 Santa Barbara/Ventura Colleges of Law Instructor: Craig Smith QUESTION 1 Moe was a collector of exotic cars. One day he saw an ad in the classified section
CONTRACTS MID-TERM EXAMINATION December 2006 Santa Barbara/Ventura Colleges of Law Instructor: Craig Smith QUESTION 1 Moe was a collector of exotic cars. One day he saw an ad in the classified section
CONTRACT VS. PROMISE
 CONTRACT VS. PROMISE Promise: A person s declaration that he will perform or refrain from performing some present or future act. Promisor: The person making the promise. Promisee: The person to whom the
CONTRACT VS. PROMISE Promise: A person s declaration that he will perform or refrain from performing some present or future act. Promisor: The person making the promise. Promisee: The person to whom the
Chapter 9: Contract Formation. Copyright 2009 South-Western Legal Studies in Business, a part of South-Western Cengage Learning.
 Chapter 9: Contract Formation a Copyright part of South-Western 2009 South-Western Cengage Legal Learning. Studies Business, Introduction is a declaration that something will or will not happen in the
Chapter 9: Contract Formation a Copyright part of South-Western 2009 South-Western Cengage Legal Learning. Studies Business, Introduction is a declaration that something will or will not happen in the
Question If CapCo files a lawsuit against the Bears seeking damages for breach of contract, who is likely to prevail? Discuss.
 Question 2 CapCo sells baseball caps to youth leagues and recently approached two new teams, the Bears and the Lions. Uncertain how many caps the team would require, the Bears team manager signed a written
Question 2 CapCo sells baseball caps to youth leagues and recently approached two new teams, the Bears and the Lions. Uncertain how many caps the team would require, the Bears team manager signed a written
Contract Law. 2. Contract formation: a) mutual assent: offer & acceptance b) consideration: need to have an exchange of something.
 Contract Law Jan 18th, 2012: 1. Sources of law: -statutory law: United Commercial Code, uniformed state law; (only for sales of goods, does not require parties to be merchants) -common law; -restatement:
Contract Law Jan 18th, 2012: 1. Sources of law: -statutory law: United Commercial Code, uniformed state law; (only for sales of goods, does not require parties to be merchants) -common law; -restatement:
CONTRACT LAW SUMMARY
 CONTRACT LAW SUMMARY LAWSKOOL UK CONTENTS INTRODUCTION TO CONTRACT LAW 6 DEFINITION OF CONTRACT LAW 6 1) The Classical Model of Contract Law 6 INTENTION TO CREATE LEGAL RELATIONS 8 INTRODUCTION TO INTENTION
CONTRACT LAW SUMMARY LAWSKOOL UK CONTENTS INTRODUCTION TO CONTRACT LAW 6 DEFINITION OF CONTRACT LAW 6 1) The Classical Model of Contract Law 6 INTENTION TO CREATE LEGAL RELATIONS 8 INTRODUCTION TO INTENTION
California Bar Examination
 California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question On May 1, Owner asked Builder
California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question On May 1, Owner asked Builder
CONTRACTS. Midterm Examination Santa Barbara College of Law Fall 2001 Instructor: Craig Smith. Time Allotted - Two Hours
 Santa Barbara College of Law Fall 2001 Instructor: Craig Smith Time Allotted - Two Hours An answer should demonstrate your ability to analyze the facts presented by the question, to select the material
Santa Barbara College of Law Fall 2001 Instructor: Craig Smith Time Allotted - Two Hours An answer should demonstrate your ability to analyze the facts presented by the question, to select the material
Question 3. Sam hereby agrees that he will not perform interior design services in Town for a period of two years.
 Question 3 Sam decided to sell his interior design business in Town to Betty. While reviewing a purchase agreement drafted by Sam, Betty insisted on a covenant by Sam not to compete with her in the interior
Question 3 Sam decided to sell his interior design business in Town to Betty. While reviewing a purchase agreement drafted by Sam, Betty insisted on a covenant by Sam not to compete with her in the interior
CONTRACTS Ponoroff 2016
 A. Contract Law (Overview) a. Contract The promise or set of promises that the law recognizes by way of enforcement. i. Promise The liability involved in contract law is undertaken intentionally by the
A. Contract Law (Overview) a. Contract The promise or set of promises that the law recognizes by way of enforcement. i. Promise The liability involved in contract law is undertaken intentionally by the
MBE WORKSHOP: CONTRACTS PROFESSOR LISA MCELROY DREXEL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF LAW
 MBE WORKSHOP: CONTRACTS PROFESSOR LISA MCELROY DREXEL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF LAW CHAPTER 1: CONTRACTS Editor's Note 1: The below outline is taken from the National Conference of Bar Examiners' website. NOTE:
MBE WORKSHOP: CONTRACTS PROFESSOR LISA MCELROY DREXEL UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF LAW CHAPTER 1: CONTRACTS Editor's Note 1: The below outline is taken from the National Conference of Bar Examiners' website. NOTE:
California Bar Examination
 California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question Betty is a physician. One of her
California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question Betty is a physician. One of her
California Bar Examination
 California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question PC manufactures computers. Mart
California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question PC manufactures computers. Mart
CONTRACTS TOPIC OUTLINE1
 CONTRACTS TOPIC OUTLINE1 1. OFFER AND ACCEPTANCE a. offer defined b. preliminary negotiations c. advertisements d. unilateral offer e. who may accept an offer f. irrevocable offer g. material terms h.
CONTRACTS TOPIC OUTLINE1 1. OFFER AND ACCEPTANCE a. offer defined b. preliminary negotiations c. advertisements d. unilateral offer e. who may accept an offer f. irrevocable offer g. material terms h.
CONTRACT LAW. Elements of a Contract
 CONTRACT LAW Contracts: Types and Sources in Australia CONTRACT: An agreement concerning promises made between two or more parties with the intention of creating certain legal rights and obligations upon
CONTRACT LAW Contracts: Types and Sources in Australia CONTRACT: An agreement concerning promises made between two or more parties with the intention of creating certain legal rights and obligations upon
THIS IS A SAMPLE EXAM. QUESTIONS ARE FOR LEARNING PURPOSES ONLY. THE FINAL EXAM MAY SUBSTANTIALLY DIFFER FROM THIS SAME. EXAM #
 EXAM # FALL 2018 CONTRACTS I (ORANBURG) SAMPLE EXAM INSTRUCTIONS 1. This exam contains one (1) essay question. You will have two (2) hours to write this exam. Do not turn over this instruction page until
EXAM # FALL 2018 CONTRACTS I (ORANBURG) SAMPLE EXAM INSTRUCTIONS 1. This exam contains one (1) essay question. You will have two (2) hours to write this exam. Do not turn over this instruction page until
QUESTION 1. Carl said, Let me think a moment.
 QUESTION 1 Zena placed an advertisement in a local newspaper: Wanted: Someone to clean my four-bedroom, four-bath house (2500 square feet) once a week for the next month; pay $35 per hour. No interview
QUESTION 1 Zena placed an advertisement in a local newspaper: Wanted: Someone to clean my four-bedroom, four-bath house (2500 square feet) once a week for the next month; pay $35 per hour. No interview
OVERVIEW OF CONTRACT LAW
 OVERVIEW OF CONTRACT LAW Liability is generally the key issue in regards to contractual disputes. Purpose of K law is to provide the rules which determine when one party is liable to another under or in
OVERVIEW OF CONTRACT LAW Liability is generally the key issue in regards to contractual disputes. Purpose of K law is to provide the rules which determine when one party is liable to another under or in
Contract Law for Paralegals: Chapter 13 Chapter 13
 Contract Law for Paralegals: Chapter 13 Chapter 13 Tab Text CHAPTER 13 The Defendant s No Breach- Justification Response to the Plaintiff s Allegation of Breach Chapter 13 deals exclusively with the no
Contract Law for Paralegals: Chapter 13 Chapter 13 Tab Text CHAPTER 13 The Defendant s No Breach- Justification Response to the Plaintiff s Allegation of Breach Chapter 13 deals exclusively with the no
Introduction to Contracts
 Chapter 9 Introduction to Contracts 1 Exhibit 9.1 (page 225) 2 In Chronological Order 3 1 Second 4 Third 5 Fourth 6 2 Exhibit 9.1 (page 225) 7 The Four Essential Elements of a (Valid) Contract 1. Agreement
Chapter 9 Introduction to Contracts 1 Exhibit 9.1 (page 225) 2 In Chronological Order 3 1 Second 4 Third 5 Fourth 6 2 Exhibit 9.1 (page 225) 7 The Four Essential Elements of a (Valid) Contract 1. Agreement
Contracts Final Exam Notes Formation of a contract What is a contract MUST Offer REASONABLE PERSON Acceptance
 Contracts Final Exam Notes Formation of a contract What is a contract - Binding promise between two or more parties, reliant upon several important factors - Offer - Acceptance - Consideration - Certainty
Contracts Final Exam Notes Formation of a contract What is a contract - Binding promise between two or more parties, reliant upon several important factors - Offer - Acceptance - Consideration - Certainty
Creation of the K a. Statute of Frauds land part performance one year debt 500 b. Offer master of the offer revoke mailbox rule absence of terms
 Contracts outline I. Creation of the K a. Statute of Frauds requires that a sufficient writing, signed by the party to be charged be in existence for the following subject-matter (doesn t apply to restitution
Contracts outline I. Creation of the K a. Statute of Frauds requires that a sufficient writing, signed by the party to be charged be in existence for the following subject-matter (doesn t apply to restitution
Wald v Graev 2014 NY Slip Op 32433(U) September 15, 2014 Supreme Court, New York County Docket Number: /2013 Judge: Saliann Scarpulla Cases
 Wald v Graev 2014 NY Slip Op 32433(U) September 15, 2014 Supreme Court, New York County Docket Number: 652461/2013 Judge: Saliann Scarpulla Cases posted with a "30000" identifier, i.e., 2013 NY Slip Op
Wald v Graev 2014 NY Slip Op 32433(U) September 15, 2014 Supreme Court, New York County Docket Number: 652461/2013 Judge: Saliann Scarpulla Cases posted with a "30000" identifier, i.e., 2013 NY Slip Op
CONTRACTS Bartlett Spring 2010
 Generally... 2 Slide: Components of course... 3 Contract existed (Formation)... 3 Slide: Contract formation... 3 Offer... 4 Interim period: Revocation... 5 Acceptance... 6 Acceptance: Bilateral v. Unilateral...
Generally... 2 Slide: Components of course... 3 Contract existed (Formation)... 3 Slide: Contract formation... 3 Offer... 4 Interim period: Revocation... 5 Acceptance... 6 Acceptance: Bilateral v. Unilateral...
A) Preliminaries B) Formation
 Contracts Page 1 of 12 A) Preliminaries 1) Governing law The Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) governs transactions that are predominantly for goods (movable property, identifiable to the contract at formation),
Contracts Page 1 of 12 A) Preliminaries 1) Governing law The Uniform Commercial Code (UCC) governs transactions that are predominantly for goods (movable property, identifiable to the contract at formation),
Chapter 1. Bases for Enforcing Promises 1. What is a K? a promise (or set of promises) the law will enforce. The norm in contract law how much money
 Chapter 1. Bases for Enforcing Promises 1. What is a K? a promise (or set of promises) the law will enforce. The norm in contract law how much money will it take to make the injured party WHOLE again.
Chapter 1. Bases for Enforcing Promises 1. What is a K? a promise (or set of promises) the law will enforce. The norm in contract law how much money will it take to make the injured party WHOLE again.
Thomson Learning TM. Consideration. Chapter
 Chapter 12 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Consideration inducement to make a promise enforceable Gratuitous promise promise made without consideration Legal sufficiency benefit to the promisor or detriment to the
Chapter 12 LEARNING OBJECTIVES Consideration inducement to make a promise enforceable Gratuitous promise promise made without consideration Legal sufficiency benefit to the promisor or detriment to the
CHAPTER 2 CONTRACT LAWS INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, A contract is an agreement made between two or more parties which the law will enforce.
 CHAPTER 2 CONTRACT LAWS INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, 1872 Definition of Contract A contract is an agreement made between two or more parties which the law will enforce. Sec 2(h) defines contract as an agreement
CHAPTER 2 CONTRACT LAWS INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, 1872 Definition of Contract A contract is an agreement made between two or more parties which the law will enforce. Sec 2(h) defines contract as an agreement
Chapter 3: The Bargain Context
 Chapter 3: The Bargain Context A. Introduction: Contracting parties, no matter how hard they try, cannot negotiate every rule. For example, suppose I agree to sell and you agree to buy my tractor. We agree
Chapter 3: The Bargain Context A. Introduction: Contracting parties, no matter how hard they try, cannot negotiate every rule. For example, suppose I agree to sell and you agree to buy my tractor. We agree
A
 Contracts with Vincent Rougeau in Spring 2008 1. Basic Theories 1.1. Classical Theory - Neutral principles can be instilled from cases 1.1.1. Characteristics 1.1.1.1. Preference for clear rules over general
Contracts with Vincent Rougeau in Spring 2008 1. Basic Theories 1.1. Classical Theory - Neutral principles can be instilled from cases 1.1.1. Characteristics 1.1.1.1. Preference for clear rules over general
Answer A to Question 1
 Answer A to Question 1 The issue is whether Pat has a valid contract with Danco and whether Danco has breached such contract, and what damages Pat is entitled to as a result. Service Contract Contracts
Answer A to Question 1 The issue is whether Pat has a valid contract with Danco and whether Danco has breached such contract, and what damages Pat is entitled to as a result. Service Contract Contracts
Simple. CONTRACTS & UCC Outline. NINETY PERCENT of the LAW in NINETY PAGES. Tim Tyler, Ph.D., Attorney at Law
 NAILING THE BAR Simple CONTRACTS & UCC Outline Tim Tyler, Ph.D., Attorney at Law NINETY PERCENT of the LAW in NINETY PAGES NAILING THE BAR Simple CONTRACTS & UCC Outline Table of Contents CHAPTER 1: CONTRACT
NAILING THE BAR Simple CONTRACTS & UCC Outline Tim Tyler, Ph.D., Attorney at Law NINETY PERCENT of the LAW in NINETY PAGES NAILING THE BAR Simple CONTRACTS & UCC Outline Table of Contents CHAPTER 1: CONTRACT
Law of Contracts. Determining Contractual Intent. Offer. 6 Elements of Legally Enforceable Contracts
 6 Elements of Legally Enforceable Contracts Law of Contracts 1. Offer and Acceptance 2. Genuine Assent 3. Legal Purpose Business Law Chapters 6-11 4. Consideration (Exchange of value) 5. Capacity to Contract
6 Elements of Legally Enforceable Contracts Law of Contracts 1. Offer and Acceptance 2. Genuine Assent 3. Legal Purpose Business Law Chapters 6-11 4. Consideration (Exchange of value) 5. Capacity to Contract
Foundation Level LAW PRACTICE MANUAL
 Part: - 1 The Indian Contract Act, 1872 Chapter 1:- Nature and Kinds of Contracts 5. The general principles of law of contract applied to all kinds of contract irrespective of their nature. (a) True, as
Part: - 1 The Indian Contract Act, 1872 Chapter 1:- Nature and Kinds of Contracts 5. The general principles of law of contract applied to all kinds of contract irrespective of their nature. (a) True, as
Foundation Level LAW PRACTICE MANUAL
 Chapter 2:- Offer and Acceptance 2.1 Definition And Essential Elements Of A VALID OFFER 1. The term 'offer or proposal' in legal terms, is defined in (a) Section 2 (a) (b) Section 2 (b) (c) Section 2 (i)
Chapter 2:- Offer and Acceptance 2.1 Definition And Essential Elements Of A VALID OFFER 1. The term 'offer or proposal' in legal terms, is defined in (a) Section 2 (a) (b) Section 2 (b) (c) Section 2 (i)
Opening Assignment. The Bargain. Contracts. Elements of Contract. Ending an Offer. What is an Offer 10/31/2017
 Opening Assignment Should the shopkeeper have been allowed to continue increasing the price of the vase? Explain. The Bargain Contracts What is a contract? Legally binding agreement Who may enter into
Opening Assignment Should the shopkeeper have been allowed to continue increasing the price of the vase? Explain. The Bargain Contracts What is a contract? Legally binding agreement Who may enter into
Question 2. Delta has not yet paid for any of the three Model 100 presses despite repeated demands by Press.
 Question 2 Delta Print Co. ( Delta ) ordered three identical Model 100 printing presses from Press Manufacturer Co. ( Press ). Delta s written order form described the items ordered by model number. Delta
Question 2 Delta Print Co. ( Delta ) ordered three identical Model 100 printing presses from Press Manufacturer Co. ( Press ). Delta s written order form described the items ordered by model number. Delta
Contracts II Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Spring 2003
 Contracts II Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Sample Exam Question #9 - Model Answer Jenny Beasley wants to sue her former employer, The Owl s Nest,
Contracts II Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Sample Exam Question #9 - Model Answer Jenny Beasley wants to sue her former employer, The Owl s Nest,
PRINCIPLES OF CONTRACTUAL LIABILITY 1.1. AGREEMENT TEMPLATE: CERTAINTY TEMPLATE:... Error! Bookmark not defined.
 PRINCIPLES OF CONTRACTUAL LIABILITY 1. FORMATION OF CONTRACT:... 2 1.1. AGREEMENT TEMPLATE:... 2 1.2. CAPACITY TEMPLATE:... = Error! Bookmark not defined. 1.3. INTENTION TEMPLATE: (objective test)... Error!
PRINCIPLES OF CONTRACTUAL LIABILITY 1. FORMATION OF CONTRACT:... 2 1.1. AGREEMENT TEMPLATE:... 2 1.2. CAPACITY TEMPLATE:... = Error! Bookmark not defined. 1.3. INTENTION TEMPLATE: (objective test)... Error!
BUSINESS LAW Chapter 5 PowerPoint Notes & Assignment How Contracts Arise
 BUSINESS LAW Chapter 5 PowerPoint Notes & Assignment How Contracts Arise SECTION 5.1 CONTRACTS The Nature of a Contract A ** is any agreement enforceable by law. Not all agreements are contracts, however.
BUSINESS LAW Chapter 5 PowerPoint Notes & Assignment How Contracts Arise SECTION 5.1 CONTRACTS The Nature of a Contract A ** is any agreement enforceable by law. Not all agreements are contracts, however.
California First-Year Law Students Examination. Essay Questions and Selected Answers
 California First-Year Law Students Examination Essay Questions and Selected Answers October 2005 ESSAY QUESTIONS AND SELECTED ANSWERS OCTOBER 2005 FIRST-YEAR LAW STUDENTS EXAMINATION This publication contains
California First-Year Law Students Examination Essay Questions and Selected Answers October 2005 ESSAY QUESTIONS AND SELECTED ANSWERS OCTOBER 2005 FIRST-YEAR LAW STUDENTS EXAMINATION This publication contains
SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR LEVEL 4 DIPLOMA IN PARALEGAL STUDIES
 SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR LEVEL 4 DIPLOMA IN PARALEGAL STUDIES UNIT 1 ENGLISH LEGAL SYSTEM Explain how laws are made in the UK and the role that the Crown plays in this process (10 marks) This question relates
SAMPLE QUESTIONS FOR LEVEL 4 DIPLOMA IN PARALEGAL STUDIES UNIT 1 ENGLISH LEGAL SYSTEM Explain how laws are made in the UK and the role that the Crown plays in this process (10 marks) This question relates
Question 1. Is there adequate consideration for Chip Co s agreements above-described with Pam, Dave, Bob and Silicon, Inc.? Discuss.
 Question 1 Ted is the President of Chip Co, a small company that makes computer chips for the secondary personal computer market. In the regular course of Chip Co s business Ted did the following: Ted
Question 1 Ted is the President of Chip Co, a small company that makes computer chips for the secondary personal computer market. In the regular course of Chip Co s business Ted did the following: Ted
TITLE 7 CONTRACTS TABLE OF CONTENTS
 TITLE 7 CONTRACTS TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 7.01 General Provisions 7.0101 Definition 1 7.0102 Essential elements of a contract 1 7.0103 Law of place applied to contracts 1 7.0104 Time of performance 1
TITLE 7 CONTRACTS TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 7.01 General Provisions 7.0101 Definition 1 7.0102 Essential elements of a contract 1 7.0103 Law of place applied to contracts 1 7.0104 Time of performance 1
Contracts Summary Notes
 Contracts Summary Notes TOPIC ONE: AGREEMENT- OFFER AND ACCEPTANCE There are 4 elements of a contract: Agreement, consideration, intention to create legal relations and certainty The above are all required
Contracts Summary Notes TOPIC ONE: AGREEMENT- OFFER AND ACCEPTANCE There are 4 elements of a contract: Agreement, consideration, intention to create legal relations and certainty The above are all required
10/29/2007 7:36:00 PM
 10/29/2007 7:36:00 PM I. Article 2 Sales of Goods II. Contractual Assent/Intent & Objective Test A. Contracts are formed by mutual consent. Both parties must intend to enter the contract and agree on its
10/29/2007 7:36:00 PM I. Article 2 Sales of Goods II. Contractual Assent/Intent & Objective Test A. Contracts are formed by mutual consent. Both parties must intend to enter the contract and agree on its
Contract Law for Paralegals: Chapter 5 Chapter 5
 Contract Law for Paralegals: Chapter 5 Chapter 5 Tab Text CHAPTER 5 The Post-Acceptance Phase Chapter 5, the post-acceptance phase, discusses modifying a contract and terminating a contract before it has
Contract Law for Paralegals: Chapter 5 Chapter 5 Tab Text CHAPTER 5 The Post-Acceptance Phase Chapter 5, the post-acceptance phase, discusses modifying a contract and terminating a contract before it has
LAW OF CONTRACT (PART I) Shanila H. Gunawardena LL.B. (Hons.) (Colombo) Attorney-at-Law, CTA (CASL)
 LAW OF CONTRACT (PART I) Shanila H. Gunawardena LL.B. (Hons.) (Colombo) Attorney-at-Law, CTA (CASL) 30-07-2017 MAIN COMPONENTS OF A CONTRACT 1. Intention to create legal relations 2. Agreement between
LAW OF CONTRACT (PART I) Shanila H. Gunawardena LL.B. (Hons.) (Colombo) Attorney-at-Law, CTA (CASL) 30-07-2017 MAIN COMPONENTS OF A CONTRACT 1. Intention to create legal relations 2. Agreement between
Sample. 2.1 Introduction. 2.2 Types of consideration
 Chapter 2: Consideration Outline 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Types of consideration 2.3 Consideration must move from the promisee 2.4 Consideration must be of some value 2.5 Summary 2.1 Introduction As noted
Chapter 2: Consideration Outline 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Types of consideration 2.3 Consideration must move from the promisee 2.4 Consideration must be of some value 2.5 Summary 2.1 Introduction As noted
IN THE SUPERIOR COURT OF THE COMMONWEALTH OF THE NORTHERN MARIANA ISLANDS
 IN THE SUPERIOR COURT OF THE COMMONWEALTH OF THE NORTHERN MARIANA ISLANDS In the Matter of the Estate of ) CIVIL ACTION NO. 97-1257 ) FIDELIA RANGAMAR MERUR, ) DECISION AND ORDER ) AS TO CLAIMANTS SHAKIR
IN THE SUPERIOR COURT OF THE COMMONWEALTH OF THE NORTHERN MARIANA ISLANDS In the Matter of the Estate of ) CIVIL ACTION NO. 97-1257 ) FIDELIA RANGAMAR MERUR, ) DECISION AND ORDER ) AS TO CLAIMANTS SHAKIR
Contracts I Office: Room 1115 Professor Meyerson Phone: (410)
 Contracts I Office: Room 1115 Professor Meyerson Phone: (410) 837-4550 Fall 2014 E-mail: mmeyerson@ubalt.edu The course packet [available at the Bookstore] contains most of the cases we will be reading
Contracts I Office: Room 1115 Professor Meyerson Phone: (410) 837-4550 Fall 2014 E-mail: mmeyerson@ubalt.edu The course packet [available at the Bookstore] contains most of the cases we will be reading
UNIT 2 : CONSIDERATION
 1.28 BUSINESS LAWS UNIT 2 : CONSIDERATION LEARNING OUTCOMES After studying this unit, you would be able to: Understand the concept of consideration, its importance for a contract and its double aspect.
1.28 BUSINESS LAWS UNIT 2 : CONSIDERATION LEARNING OUTCOMES After studying this unit, you would be able to: Understand the concept of consideration, its importance for a contract and its double aspect.
California Bar Examination
 California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question On April 1, Pat, a computer software
California Bar Examination Essay Question: Contracts And Selected Answers The Orahte Group is NOT affiliated with The State Bar of California PRACTICE PACKET p.1 Question On April 1, Pat, a computer software
In the Court of Appeals of Georgia
 SECOND DIVISION BARNES, P. J., DOYLE, P. J. and MILLER, J. NOTICE: Motions for reconsideration must be physically received in our clerk s office within ten days of the date of decision to be deemed timely
SECOND DIVISION BARNES, P. J., DOYLE, P. J. and MILLER, J. NOTICE: Motions for reconsideration must be physically received in our clerk s office within ten days of the date of decision to be deemed timely
Business Law Contract Law Unit Textbook
 Business Law Contract Law Unit Textbook Contract Law 1 UNIT OUTLINE 1. Introduction 2. Elements of a Contract A. Capacity B. Offer C. Acceptance D. Consideration E. Legality F. Writing 3. Types of Contracts
Business Law Contract Law Unit Textbook Contract Law 1 UNIT OUTLINE 1. Introduction 2. Elements of a Contract A. Capacity B. Offer C. Acceptance D. Consideration E. Legality F. Writing 3. Types of Contracts
MISTAKE. (1) the other party to the contract knew or should have known of the mistake; or
 MISTAKE Mistake of Fact: The parties entered into a contract with different understandings of one or more material facts relating to the contract s performance. Mutual Mistake: A mistake by both contracting
MISTAKE Mistake of Fact: The parties entered into a contract with different understandings of one or more material facts relating to the contract s performance. Mutual Mistake: A mistake by both contracting
Acceptance of Unilateral Contract Offer Requiring Time in Performance
 SMU Law Review Volume 5 1951 Acceptance of Unilateral Contract Offer Requiring Time in Performance Charles B. Redman Follow this and additional works at: http://scholar.smu.edu/smulr Recommended Citation
SMU Law Review Volume 5 1951 Acceptance of Unilateral Contract Offer Requiring Time in Performance Charles B. Redman Follow this and additional works at: http://scholar.smu.edu/smulr Recommended Citation
Exam Approach: I. CONTRACT FORMATION
 Exam Approach: 1. On scrap paper, write out all main topics (the purple enumerated topics in this outline) look back at them after reading through the fact pattern to MAKE SURE I haven t missed spotting
Exam Approach: 1. On scrap paper, write out all main topics (the purple enumerated topics in this outline) look back at them after reading through the fact pattern to MAKE SURE I haven t missed spotting
Principles of European Contract Law
 Article 1:101: Application of the Principles Principles of European Contract Law CHAPTER 1: GENERAL PROVISIONS Section 1: Scope of the Principles (1) These Principles are intended to be applied as general
Article 1:101: Application of the Principles Principles of European Contract Law CHAPTER 1: GENERAL PROVISIONS Section 1: Scope of the Principles (1) These Principles are intended to be applied as general
MUST THE REJECTION OF AN OFFER BE COMMUNICATED TO THE OFFEROR?
 Yale Law Journal Volume 12 Issue 7 Yale Law Journal Article 2 1903 MUST THE REJECTION OF AN OFFER BE COMMUNICATED TO THE OFFEROR? Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.law.yale.edu/ylj
Yale Law Journal Volume 12 Issue 7 Yale Law Journal Article 2 1903 MUST THE REJECTION OF AN OFFER BE COMMUNICATED TO THE OFFEROR? Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.law.yale.edu/ylj
THE TRUE CONCEPTION OF UNILATERAL CONTRACTS
 Yale Law Journal Volume 26 Issue 2 Yale Law Journal Article 4 1916 THE TRUE CONCEPTION OF UNILATERAL CONTRACTS I. MAURICE WORMSER Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.law.yale.edu/ylj
Yale Law Journal Volume 26 Issue 2 Yale Law Journal Article 4 1916 THE TRUE CONCEPTION OF UNILATERAL CONTRACTS I. MAURICE WORMSER Follow this and additional works at: http://digitalcommons.law.yale.edu/ylj
CONTRACTS Mid-Term Examination Santa Barbara College of Law Fall 2000 Instructor: Craig Smith. Time Allotted - Two Hours
 CONTRACTS Mid-Term Examination Santa Barbara College of Law Fall 2000 Instructor: Craig Smith Time Allotted - Two Hours An answer should demonstrate your ability to analyze the facts presented by the question,
CONTRACTS Mid-Term Examination Santa Barbara College of Law Fall 2000 Instructor: Craig Smith Time Allotted - Two Hours An answer should demonstrate your ability to analyze the facts presented by the question,
REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER)
 REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER) 1. T F When a court or legislature protects a class, this protection extends to all members of that class in every contractual transaction.
REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER) 1. T F When a court or legislature protects a class, this protection extends to all members of that class in every contractual transaction.
QUESTION What contract rights and remedies, if any, does Olivia have against Juan? Discuss.
 QUESTION 1 Olivia is a florist who specializes in roses. She has a five-year written contract with Juan to sell him as many roses as he needs for his wedding chapel. Over the past three years, Olivia sold
QUESTION 1 Olivia is a florist who specializes in roses. She has a five-year written contract with Juan to sell him as many roses as he needs for his wedding chapel. Over the past three years, Olivia sold
Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Spring Course Introduction
 Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Course Introduction I. What is a Contract? A. Epstein, Markell & Ponoroff (p. 1): [A] promise or set of
Contracts Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Course Introduction I. What is a Contract? A. Epstein, Markell & Ponoroff (p. 1): [A] promise or set of
FULL OUTLINE. Bar Exam Doctor BAREXAMDOCTOR.COM. CONTRACTS
 FULL OUTLINE www.barexamdoctor.com CONTRACTS I. VOCABULARY a. K = legally enforceable agreement (or legally enforceable promise) b. Quasi-K = equitable remedy. NOT K law. i. Elements: 1. P has conferred
FULL OUTLINE www.barexamdoctor.com CONTRACTS I. VOCABULARY a. K = legally enforceable agreement (or legally enforceable promise) b. Quasi-K = equitable remedy. NOT K law. i. Elements: 1. P has conferred
Sample. Aims of this Chapter. 2.1 Introduction
 Chapter 2: Consideration Outline 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Types of consideration 2.3 Consideration must move from the promisee 2.4 Consideration must be of some value 2.5 Insufficiency of consideration 2.6
Chapter 2: Consideration Outline 2.1 Introduction 2.2 Types of consideration 2.3 Consideration must move from the promisee 2.4 Consideration must be of some value 2.5 Insufficiency of consideration 2.6
--- N.E.2d ---- FOR EDUCATIONAL USE ONLY Page N.E.2d ----, 2007 WL (Ill.App. 1 Dist.) (Cite as: --- N.E.2d ----) Nov. 13, 2007.
 --- N.E.2d ---- FOR EDUCATIONAL USE ONLY Page 1 Ross v. May Co. Ill.App. 1 Dist.,2007. Only the Westlaw citation is currently available. Appellate Court of Illinois,First District, Second Division. Gary
--- N.E.2d ---- FOR EDUCATIONAL USE ONLY Page 1 Ross v. May Co. Ill.App. 1 Dist.,2007. Only the Westlaw citation is currently available. Appellate Court of Illinois,First District, Second Division. Gary
IN THE COURT OF COMMON PLEAS CUYAHOGA COUNTY, OHIO 201B jul q P 12 5^
 104500613 RODGER SAFFOLD, II Plaintiff 104500613. f' c IN THE COURT OF COMMON PLEAS CUYAHOGA COUNTY, OHIO 201B jul q P 12 5^ Case No: CV-17-878065 CLERK OF COURTS CUYAHOGA COUNTY Judge: JOHN P O'DONNELL
104500613 RODGER SAFFOLD, II Plaintiff 104500613. f' c IN THE COURT OF COMMON PLEAS CUYAHOGA COUNTY, OHIO 201B jul q P 12 5^ Case No: CV-17-878065 CLERK OF COURTS CUYAHOGA COUNTY Judge: JOHN P O'DONNELL
Memorandum. To: Remedies Class Fall Date: December 2004
 To: Remedies Class Fall 2004 Memorandum From: Mike Allen Date: December 2004 Subject: Final Exam I have set out in this memorandum my thoughts about the essay questions on the final examination. To be
To: Remedies Class Fall 2004 Memorandum From: Mike Allen Date: December 2004 Subject: Final Exam I have set out in this memorandum my thoughts about the essay questions on the final examination. To be
IN THE COURT OF APPEALS OF THE STATE OF WASHINGTON
 IN THE COURT OF APPEALS OF THE STATE OF WASHINGTON SYDNEY ALLRUD, Administrator of ) the Estate of Tracey Kirsten Allrud, ) No. 66061-6-I ) Appellant, ) DIVISION ONE ) v. ) ) CITY OF EDMONDS, a municipal
IN THE COURT OF APPEALS OF THE STATE OF WASHINGTON SYDNEY ALLRUD, Administrator of ) the Estate of Tracey Kirsten Allrud, ) No. 66061-6-I ) Appellant, ) DIVISION ONE ) v. ) ) CITY OF EDMONDS, a municipal
Define genuine agreement and rescission. Identify when duress occurs. Describe how someone may exercise undue influence.
 Define genuine agreement and rescission Identify when duress occurs Describe how someone may exercise undue influence. Genuine Agreement/Assent: meeting of the minds Must be willful and voluntary Must
Define genuine agreement and rescission Identify when duress occurs Describe how someone may exercise undue influence. Genuine Agreement/Assent: meeting of the minds Must be willful and voluntary Must
a) test the strength of the opposing positions and encourage the parties to reach a compromise b) ensure that all documents are in order before trial
 Question 1 The purpose of discovery is to a) test the strength of the opposing positions and encourage the parties to reach a compromise b) ensure that all documents are in order before trial c) ensure
Question 1 The purpose of discovery is to a) test the strength of the opposing positions and encourage the parties to reach a compromise b) ensure that all documents are in order before trial c) ensure
PENNSY SUPPLY, INC. v. AMERICAN ASH RECYCLING CORP. OF PENNSYLVANIA Pennsylvania Superior Court 2006 Pa. Super. 54, 895 A.
 PENNSY SUPPLY, INC. v. AMERICAN ASH RECYCLING CORP. OF PENNSYLVANIA Pennsylvania Superior Court 2006 Pa. Super. 54, 895 A.2d 595 (2006) JOYCE, ORIE MELVIN and TAMILIA, JJ. ORIE MELVIN, J. Appellant, Pennsy
PENNSY SUPPLY, INC. v. AMERICAN ASH RECYCLING CORP. OF PENNSYLVANIA Pennsylvania Superior Court 2006 Pa. Super. 54, 895 A.2d 595 (2006) JOYCE, ORIE MELVIN and TAMILIA, JJ. ORIE MELVIN, J. Appellant, Pennsy
Is there a contract?
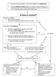 1. te whether this transaction is governed by UCC or the Restatement. 2. Does the Statute of Frauds apply? The contract must be in writing if it is in regard to land, if by its nature it takes more than
1. te whether this transaction is governed by UCC or the Restatement. 2. Does the Statute of Frauds apply? The contract must be in writing if it is in regard to land, if by its nature it takes more than
v No Wayne Circuit Court
 S T A T E O F M I C H I G A N C O U R T O F A P P E A L S JOWHARA ZINDANI and GAMEEL ZINDANI, Plaintiff-Appellees, UNPUBLISHED March 20, 2018 v No. 337042 Wayne Circuit Court NAGI ZINDANI and ANTESAR ZINDANI,
S T A T E O F M I C H I G A N C O U R T O F A P P E A L S JOWHARA ZINDANI and GAMEEL ZINDANI, Plaintiff-Appellees, UNPUBLISHED March 20, 2018 v No. 337042 Wayne Circuit Court NAGI ZINDANI and ANTESAR ZINDANI,
Contracts: Offer, Acceptance, and Mutual Assent
 Chapter 7 Contracts: Offer, Acceptance, and Mutual Assent 1 The Purposes of Contract Enforcement When people keep their business promises to one another, good things happen: buildings get built on time
Chapter 7 Contracts: Offer, Acceptance, and Mutual Assent 1 The Purposes of Contract Enforcement When people keep their business promises to one another, good things happen: buildings get built on time
Chinese Contract Law: A Brief Introduction. ZHANG Xuezhong. Assistant Professor of Law.
 Chinese Contract Law: A Brief Introduction ZHANG Xuezhong Assistant Professor of Law zhangxuezhong@ecupl.edu.cn East China University of Politics and Law Overview 1. In General 2. Principles of Chinese
Chinese Contract Law: A Brief Introduction ZHANG Xuezhong Assistant Professor of Law zhangxuezhong@ecupl.edu.cn East China University of Politics and Law Overview 1. In General 2. Principles of Chinese
Contracts. Introduction. Introductions Seth C. Oranburg 1. Professor Seth C. Oranburg
 Contracts Professor Seth C. Oranburg Introduction 1. Introductions 2. Overview of Contract Law 3. Which Contract Law Applies? 4. How to Use the IRAC Writing Paradigm? 5. What Is a Contract, Anyway? 6.
Contracts Professor Seth C. Oranburg Introduction 1. Introductions 2. Overview of Contract Law 3. Which Contract Law Applies? 4. How to Use the IRAC Writing Paradigm? 5. What Is a Contract, Anyway? 6.
Contracts II Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Spring Optional Homework #1 - Model Answers
 Contracts II Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Optional Homework #1 - Model Answers 1. Read King v. Trustees of Boston University, 647 N.E.2d 1196 (Mass.
Contracts II Professor Keith A. Rowley William S. Boyd School of Law University of Nevada Las Vegas Optional Homework #1 - Model Answers 1. Read King v. Trustees of Boston University, 647 N.E.2d 1196 (Mass.
REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER)
 REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER) 1. T F The nonbreaching party is entitled to a remedy for the breach of an enforceable contract. 2. T F A remedy for breach of contract
REVIEW QUESTIONS TRUE/FALSE QUESTIONS (CIRCLE THE CORRECT ANSWER) 1. T F The nonbreaching party is entitled to a remedy for the breach of an enforceable contract. 2. T F A remedy for breach of contract
PART 2 FORMATION, TERMS, AND READJUSTMENT OF CONTRACT. (a) A contract or modification thereof is enforceable,
 1 PART 2 FORMATION, TERMS, AND READJUSTMENT OF CONTRACT SECTION 2-201. NO FORMAL REQUIREMENTS. (a) A contract or modification thereof is enforceable, whether or not there is a record signed by a party
1 PART 2 FORMATION, TERMS, AND READJUSTMENT OF CONTRACT SECTION 2-201. NO FORMAL REQUIREMENTS. (a) A contract or modification thereof is enforceable, whether or not there is a record signed by a party
Table of Content - Commercial Law. Year End Examination Notes
 Table of Content - Commercial Law Year End Examination Notes Chapter 4: Contract: Offer & Acceptance... 2 Chapter 5: Intention & Consideration... 7 Chapter 6: Express Terms of the Contract... 12 Chapter
Table of Content - Commercial Law Year End Examination Notes Chapter 4: Contract: Offer & Acceptance... 2 Chapter 5: Intention & Consideration... 7 Chapter 6: Express Terms of the Contract... 12 Chapter
A REVIEW OF PROMISSORY ESTOPPEL LAW IN MICHIGAN. Lee Hornberger. This article reviews Michigan promissory estoppel law, including the development of
 A REVIEW OF PROMISSORY ESTOPPEL LAW IN MICHIGAN by Lee Hornberger This article reviews Michigan promissory estoppel law, including the development of promissory estoppel, the present law, and specific
A REVIEW OF PROMISSORY ESTOPPEL LAW IN MICHIGAN by Lee Hornberger This article reviews Michigan promissory estoppel law, including the development of promissory estoppel, the present law, and specific
Business Law. Business Law
 M N Business Law IM S Business Law Business Law COURSE DESIGN COMMITTEE TOC Reviewer Mr. Mario Sequeira Visiting Faculty, Global Access - School for Continuing Education Specialization: Intellectual Property
M N Business Law IM S Business Law Business Law COURSE DESIGN COMMITTEE TOC Reviewer Mr. Mario Sequeira Visiting Faculty, Global Access - School for Continuing Education Specialization: Intellectual Property
THE INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, 1872 CHAPTER 1 INTRODUCTION
 CHAPTER 1 THE INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, 1872 INTRODUCTION The term contract means, in ordinary sense, any agreement between any two persons. For business persons, making of contracts with others is a very important
CHAPTER 1 THE INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, 1872 INTRODUCTION The term contract means, in ordinary sense, any agreement between any two persons. For business persons, making of contracts with others is a very important
Genuineness of Assent
 Genuineness of Assent A party who demonstrates that she did not genuinely assent to the terms of a contract may avoid an otherwise valid contract. Genuine assent may be lacking due to mistake, fraudulent
Genuineness of Assent A party who demonstrates that she did not genuinely assent to the terms of a contract may avoid an otherwise valid contract. Genuine assent may be lacking due to mistake, fraudulent
Spring 2018 Business Law Fundamentals O'Hara 2018 D
 Page 1 of 7 as your signature PRINT your name EXAM #2 Business Law Fundamentals LAWS 3930 sections -001, -002-003 Chapters 1-4, 24, 6, 7, 9-19 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Affix your printed name as your signature
Page 1 of 7 as your signature PRINT your name EXAM #2 Business Law Fundamentals LAWS 3930 sections -001, -002-003 Chapters 1-4, 24, 6, 7, 9-19 INSTRUCTIONS: 1. Affix your printed name as your signature
UNITED NATIONS CONVENTION ON CONTRACTS FOR THE INTERNATIONAL SALE OF GOODS (1980) [CISG]
![UNITED NATIONS CONVENTION ON CONTRACTS FOR THE INTERNATIONAL SALE OF GOODS (1980) [CISG] UNITED NATIONS CONVENTION ON CONTRACTS FOR THE INTERNATIONAL SALE OF GOODS (1980) [CISG]](/thumbs/73/69200382.jpg) Go to CISG Table of Contents Go to Database Directory UNITED NATIONS CONVENTION ON CONTRACTS FOR THE INTERNATIONAL SALE OF GOODS (1980) [CISG] For U.S. citation purposes, the UN-certified English text
Go to CISG Table of Contents Go to Database Directory UNITED NATIONS CONVENTION ON CONTRACTS FOR THE INTERNATIONAL SALE OF GOODS (1980) [CISG] For U.S. citation purposes, the UN-certified English text
IN THE COURT OF APPEALS OF TENNESSEE AT NASHVILLE January 7, 2003 Session
 IN THE COURT OF APPEALS OF TENNESSEE AT NASHVILLE January 7, 2003 Session LEROY McBEE v. DAVID ELLIOTT, ET AL. Appeal from the Chancery Court for Franklin County No. 15,854 Jeffrey F. Stewart, Chancellor
IN THE COURT OF APPEALS OF TENNESSEE AT NASHVILLE January 7, 2003 Session LEROY McBEE v. DAVID ELLIOTT, ET AL. Appeal from the Chancery Court for Franklin County No. 15,854 Jeffrey F. Stewart, Chancellor
